Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller 1 R. Lokeswar Reddy (M.Tech), 2 K. Vasu M. Tech 1 (Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Madanapalle Institute of Science & Technology, Madanapalle Asst. Professors, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Madanapalle Institute of Science & Technology, Madanapalle , Abstract: The growing demand and the aging of networks make it desirable to control the power flow in power-transmission systems fast and reliably. The Load changes the voltage Variation in transmission lines must be limited, other wise the consumer s equipments are damaged at distributed side. For reducing these types of problems to develop this controller. The DPFC (Distributed Power-Flow Controller) is derived from the unified power-flow controller (UPFC). The DPFC (Distribute Power-Flow Controller) modified from UPFC for increasing system reliability and reducing costs. The DPFC independently controlling the active and reactive power flow in transmission line. This paper consists of both active and reactive variations, using MATLAB/SIMULINK is simulated and its effects on the transmission lines observed. The simulated results are analyzed and validated with the real time results for the system considered. Keywords: AC DC power conversion, filters, load flow control, power electronics, power-transmission control, power semiconductor devices, Power system control V-I measurements. 1. Introduction The ability of FACTS controllers to control the interrelated parameters that govern the operation of transmission systems including series impedance, shunt impedance, current, voltage, phase angle, and the damping of oscillations at various frequencies below the rated frequency. These constraints cannot be overcome, whilemaintainingtherequiredsystemreliability, bymechanicalsystems means without lowering the useable transmission capacity. By providing added flexibility, FACTS Controllers can enable a line to carry power closer to its thermal rating. A transmission line can be characterized by four parameters: resistance, inductance, capacitance and conductance. Conductance accounts for the leakage current at the insulators of overhead lines. However, for a short and medium length line (less than 240 km), the capacitance and conductance are so small that they can be neglected with little loss of accuracy. A transmission line can be characterized by four parameters: resistance, inductance, capacitance and conductance. Conductance Accounts for the leakage current at the insulators of overhead lines. However, for a short and medium length line (less than 240 km), the capacitance and conductance are so small that they can be neglected with little loss of accuracy. The DPFC has the same Control capability as the UPFC, which comprises the adjustment of the line impedance, the transmission angle, and the bus voltage. The UPFC is the combination of a static synchronous compensator (STATCOM) and a static synchronous series compensator (SSSC), which are coupled via a common dc link, to allow bidirectional flow of active power between the series output terminals of the SSSC and the shunt output terminals of the STATCOM. 1.1Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) A static, synchronous generator operated without an external electric energy source as a series compensator whose output voltage is in quadrature with and Controllable independently of, the line current for the purpose of increasing or decreasing the overall reactive voltage drop across the line and thereby controlling the transmitted electric power. The SSSC may include transiently rated energy storage or Energy absorbing devices to enhance the dynamic behaviour of the power system by additional temporary real power compensation, to increase or decrease momentarily, the overall real (resistive) voltage drop across the line. An impedance compensation controller can compensate for the transmission line resistance if an SSSC is operated with an energy storage system. An impedance compensation controller, when used with an SSSC and no energy storage system, is essentially a reactance compensation controller. The reactance compensation controller is used to operate the inverter in such a way that the injected alternating voltage in series with the transmission line is proportional to the line current with the emulated reactance being the constant of proportionality. When an SSSC injects an alternating voltage leading the line current, it emulates an inductive reactance in series with the transmission line causing the power flow as well as the line current to decrease as the level of compensation increases and the SSSC is considered to be operating in an inductive mode. When an SSSC injects an alternating voltage lagging the line current, it emulates a capacitive reactance in series with the transmission line causing 1 Page
2 the power flow as well as the line current to increase as the level of compensation increases and the SSSC is considered to be operating in a capacitive mode. An impedance compensation controller can compensate for the transmission line resistance if an SSSC is operated with an energy storage system. An impedance compensation controller, when used with an SSSC and no energy storage system, is essentially a reactance compensation controller. The reactance compensation controller is used to operate the inverter in such a way that the injected alternating voltage in series with the transmission line is proportional to the line current with the emulated reactance being the constant of proportionality. When an SSSC injects an alternating voltage leading the line current, it emulates an inductive reactance in series with the transmission line causing the power flow as well as the line current to decrease as the level of compensation increases and the SSSC is considered to be operating in an inductive mode. When an SSSC injects an alternating voltage lagging the line current, it emulates a capacitive reactance in series with the transmission line causing the power flow as well as the line current to increase as the level of compensation increases and the SSSC is considered to be operating in a capacitive mode. 1.2Static Synchronous Compensator (STATCOM) A static synchronous generator operated as a shunt-connected static var compensator whose capacitive or inductive output current can be controlled independent of the ac system voltage. 1.3 Series Converter The series converter executes the main function of the UPFC by injecting a voltage, with controllable magnitude and phase angle, in series with the transmission line. It is controlled to provide concurrent active and reactive series compensation without an external energy source. By means of the series voltage injection without angular constraint, the UPFC is able to control, concurrently or selectively, the transmission angle, impedance and line voltage or, alternatively, active and reactive power flow through the line. The voltage injected by the series converter results in active and reactive power exchange between the series converter and the transmission line. The reactive power is generated internally by the series converter (SSSC), and the active power is supplied by the shunt converter that is transported through the common DC link. 1.4 Shunt Converter The basic function of the shunt converter is to supply or absorb the active power demanded by the series converter. The shunt converter controls the voltage of the DC capacitor by absorbing or generating active power from the bus, therefore it acts as a synchronous source in parallel with the system. Similar to the STATCOM, the shunt converter can also provide independently controllable reactive compensation for the bus. Considering its control capability, the UPFC can have the functions: Voltage regulation by continuously varying in-phase/anti-phase voltage injection that is similar to a tapchange transformer. Series reactive compensation by injecting a voltage that is in quadrature to the line current. Functionally, this is similar to an SSSC that can provide a controllable inductive and capacitive series compensation. Phase shifting by injecting a voltage with an angular relationship with respect to the bus voltage. By varying the magnitude of this voltage, the phase shift can be controlled. The components of the UPFC handle the voltages and currents with high rating; therefore, the total cost of the system is high. Due to the common dc-link interconnection, a failure that happens at one converter will influence the whole system. To achieve the required reliability for power systems, bypass circuits and redundant backups (backup transformer, etc.) are needed, which on other hand, increase the cost. Accordingly, the UPFC has not been commercially used, even though; it has the most advanced control capabilities. This paper introduces a new concept, called distributed power-flow controller (DPFC) that is derived from the UPFC.The same as the UPFC, the DPFC is able to control all system parameters. The DPFC eliminates the common dc link between the shunt and series converters. The active power exchange between the shunt and the series converter is through the transmission line at the third-harmonic frequency. The series converter of the DPFC employs the distributed FACTS (D-FACTS) concept [6]. Comparing with the UPFC, the DPFC have two major advantages: 1) Low cost because of the low-voltage isolation and the low component rating of the series Converter and 2) High reliability because of the redundancy of the series converters. 2 Page
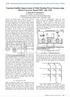
3 Fig.1. DPFC Configuration. Advantages of the DPFC over UPFC: The DPFC can be considered as a UPFC that employs the DFACTS concept and the concept of exchanging power through harmonic. Therefore, the DPFC inherits all the advantages of the UPFC and the D- FACTS, which are as follows. 1) High control capability The DPFC can simultaneously control all the parameters of the power system: the line impedance, the transmission angle, and the bus voltage. The elimination of the common dc link enables separated installation of the DPFC converters. The shunt and series converters can be placed at the most effectively location. Due to the high control capability, the DPFC can also be used to improve the power quality and system stability, such as low-frequency power oscillation damping [8], voltage sag restoration, or balancing asymmetry. 2) High reliability The redundancy of the series converter gives an improved reliability. In addition, the shunt and series converters are independent, and the failure at one place will not influence the other converters. When a failure occurs in the series converter, the converter will be short-circuited by bypass protection, thereby having little influence to the network. In the case of the shunt converter failure, the shunt converter will trip and the series converter will stop providing active compensation and will act as the D-FACTS controller [9]. 3) Low cost There is no phase-to-phase voltage isolation Required by the series converter. Also, the power rating of each converter is small and can be easily produced in Series production lines. II. DPFC Operating Principle 2.1Active power exchange with eliminated DC link Within the DPFC, the transmission line presents a common connection between the AC ports of the shunt and the series converters. Therefore, it is possible to exchange active power through the AC ports. The method is based on power theory of non-sinusoidal components. According to the Fourier analysis, nonsinusoidal voltage and current can be expressed as the sum of sinusoidal functions in different frequencies with different amplitudes. The active power resulting from this non-sinusoidal voltage and current is defined as the mean value of the product of voltage and current. Since the integrals of all the cross product of terms with different frequencies are zero, the active power can be expressed by: P = v I i I cos I By applying this method to the DPFC, the shunt converter can absorb active power from the grid at the fundamental frequency and inject the power back at a harmonic frequency. This harmonic active power flows through a transmission line equipped with series converters. According to the amount of required active power at the fundamental frequency, the DPFC series converters generate a voltage at the harmonic frequency, thereby absorbing the active power from harmonic components. Neglecting losses, the active power generated at the fundamental frequency is equal to the power absorbed at the harmonic frequency. 2.2 Using third harmonic components Due to the unique features of 3rd harmonic frequency components in a three-phase system, the 3rd harmonic is selected for active power exchange in the DPFC. In a three-phase system, the 3rd harmonic in each phase is identical, which means they are zero-sequence Components. Because the zero-sequence harmonic can be naturally blocked by star-delta transformers and these are widely incorporated in power systems (as a means of changing voltage), there is no extra filter required to prevent harmonic leakage. 3 Page
4 Fig. 2. Active power exchange between DPFC converters III. DPFC Control To control multiple converters, a DPFC consists of three types of controllers: central control, shunt control and series control, The shunt and series control are localized controllers and are responsible for maintaining their own converters parameters. The central control takes care of the DPFC functions at the power system level. The function of each controller is listed: Central control The central control generates the reference signals for both the shunt and series converters of the DPFC. Its control function depends on the specifics of the DPFC application at the power system level, such as power flow control, low frequency power oscillation damping and balancing of asymmetrical components. According to the system requirements, the central control gives corresponding voltage reference signals for the series converters and reactive current signal for the shunt converter. All the reference signals generated by the central control concern the fundamental frequency components. Series control Each series converter has its own series control. The controller is used to maintain the capacitor DC voltage of its own converter, by using 3 rd harmonic frequency components, in addition to generating series voltage at the fundamental frequency as required by the central control. Shunt control The objective of the shunt control is to inject a constant 3 rd harmonic current into the line to supply active power for the series converters. At the same time, it maintains the capacitor DC voltage of the shunt converter at a constant value by absorbing active power from the grid at the fundamental frequency and injecting the required reactive current at the fundamental frequency into the grid. Fig. 3. DPFC configuration. The third-harmonic frequency control is the major control loop with the DPFC series converter control. The principle of the vector control is used here for the dc-voltage control [10]. The third-harmonic current through the line is selected as the rotation reference frame for the single-phase park transformation, because it is easy to be captured by the phase-locked loop (PLL) [11] in the series converter. As the line current contains two frequency components, a third high-pass filter is needed to reduce the fundamental current. The d-component of the third harmonic voltage is the parameter that is used to control the dc voltage, and its reference signal is 4 Page
5 generated by the dc-voltage control loop. To minimize the reactive power that is caused by the third harmonic, the series converter is controlled as a resistance at the third-harmonic frequency. The q-component of the thirdharmonic voltage is kept zero during the operation. As the series converter is single phase, there will be voltage ripple at the dc side of each converter. The frequency of the ripple depends on the frequency of the current that flows through the converter. As the current contains the fundamental and third harmonic frequency component, the dc-capacitor voltage will contain 100-, 200-, and 300-Hz frequency component [12], [13]. There are two possible ways to reduce this ripple. One is to increase the turn ratio of the single-phase transformer of the\ series converter to reduce the magnitude of the current that flows into the converter. The other way is to use the dc capacitor with a larger capacitance. Fig. 4. Block diagram of the series converter control. The objective of the shunt control is to inject a constant third harmonic current into the line to provide active power for the series converters. The third-harmonic current is locked with the bus voltage at the fundamental frequency. A PLL is used to capture the bus-voltage frequency, and the output phase signal of the PLL is multiplied by three to create a virtual rotation reference frame for the third-harmonic component. The shunt converter s fundamental frequency control aims to inject a controllable reactive current to grid and to keep the capacitor dc voltage at a constant level. Fig. 5. Block diagram of the shunt converter control. The control for the fundamental frequency components consists of two cascaded controllers. The current control is the inner control loop, which is to modulate the shunt current at the fundamental frequency. The q-component of the reference signal of the shunt converter is obtained from the central Controller and d- component is generated by the dc control. 5 Page
6 TABLE SPECIFICATIONS OF THE DPFC Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller Symbol Description Value Unit Vs Nominal voltage of grid 220 V s Vr Nominal voltage of grid 220 V r Θ transmission angle 1 º between between grid s and r L Line inductance 6 Mн Vsh,ma x Ish,max Vsh,dc Ish,ref,3 Fsω Vse,ma x Ise,max Shunt Converter maximum ac voltage Shunt Converter maximum ac voltage Shunt Converter dc source supply Reference third-ie current injected by the shunt converter Switching frequency for the shunt and series converter maximum ac voltage at line side of series converter maximum ac current at line side of series converter 50 V 9 A 20 V 3 A 6 khz 7 V 15 A One shunt converter and three single-phase series converters are built and tested in a scaled network, as shown in fig.6 Fig.6 Simulated Model for DPFC 6 Page
7 IV. Series Converter SIMULINK Model Within the setup, multiple series converters are controlled by a central controller. The central controller gives the reference voltage signals for all series converters. The voltages and current within the setup are measured by its simulink outputs. Fig.7 Simulated model for series converter 4.1Shunt Converter SIMULINK Model The basic function of the shunt converter is to supply or absorb the active power demanded by the series converter. The shunt converter controls the voltage of the DC capacitor by absorbing or generating active power from the bus, therefore it acts as a synchronous source in parallel with the system. To verify the DPFC principle, two situations are demonstrated: the DPFC behavior in steady state and the step response. In steady state, the series converter is controlled to insert a voltage vector with both d- and q-component, which is Vse,d,ref = 0.3 V and Vse,q,ref = 0.1 V. Figs show one operation point of the DPFC setup. The voltage injected by the series converter, the current through the line, and the voltage and current at the Δ side of the transformer. Fig.8 Simulated model for shunt converter 7 Page
8 V. Results 5.1Reference voltage for the series converters: 5.2 Step response of the DPFC: line current: 5.3Step response of the DPFC: active and reactive power injected by the Series converter: 5.4 Step response of the DPFC: bus voltage and current at the Δ side of the transformer: 8 Page
9 5.5 Step response of the DPFC: series converter voltage. VI. Conclusions The DPFC emerges from the UPFC the common dc link between the shunt and series converters, which is use for exchanging active power in the UPFC, is eliminated. The DPFC reducing the total cost and increasing the reliability comparing with UPFC.The DPFC emerges from the UPFC and inherits the control capability of the UPFC, which is the simultaneous adjustment of the line impedance, the transmission angle, and the bus-voltage magnitude. The common dc link between the shunt and series converters, which is used for exchanging active power in the UPFC, is eliminated. This power is now transmitted through the transmission line at the third-harmonic frequency. The series converter of the DPFC employs the D-FACTS concept, which uses multiple small single-phase converters instead of one large-size converter. The reliability of the DPFC is greatly increased because of the redundancy of the series converters. The total cost of the DPFC is also much lower than the UPFC, because no high-voltage isolation is required at the series-converter part and the rating of the components of is low.it is proved that the shunt and series converters in the DPFC can exchange active power at the third-harmonic frequency, and the series converters are able to inject controllable active and reactive power at the fundamental frequency. References [1] N. G. Hingorani and L. Gyugyi, Understanding FACTS: Concepts and Technology of Flexible AC Transmission Systems. New York: IEEE Press, [2] K.K.Sen., Sssc-static synchronous series compensator: Theory, modeling, and application, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 13, no. 1, pp , Jan [3] N. Mohan, T. M. Undeland, and W. P. Robbins, Power Electronics : Converters, Applications, and Design, 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, [4] M. Mohaddes, A. M. Gole, and S. Elez, Steady state frequency response of statcom, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 16, no. 1, pp , Jan [5] Static Synchronous Series Compensator: A Solid-state Approach to the Series Compensation of Transmission Lines, L. Gyugyi, C. D. Schauder and K. K. Sen, 96 WM PWRD, IEEE PES Winter Meeting, [6] L. Gyugyi, C. D. Schauder, S. L. Williams, T. R. Rietman, D. R. Torgerson, and A. Edris, Unified power flow controller: A new approach to power transmission control, IEEE Trans. Power Delivery, vol. 10, no.2, pp , Apr [7] Y.-H. Song and Y.-H. Song and A. Johns, Flexible ac Transmission Systems (FACTS) (IEE Power and Energy Series), vol. 30. London, U.K.: Institution of Electrical Engineers, A. Johns, Flexible ac Transmission Systems (FACTS) (IEEE Power and Energy Series), vol. 30. London, U.K.: Institution of Electrical Engineers, Page
Performance Of Distributed Power Flow Controller (DPFC) Under Fault Condition
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN CESS Performance Of Distributed Power Flow Controller (DPFC) Under Fault Condition Santosh Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Student, Department of Electrical Engineering National Institute of
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN CESS Performance Of Distributed Power Flow Controller (DPFC) Under Fault Condition Santosh Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Student, Department of Electrical Engineering National Institute of
Improvement of System Reliability & Power Transfer Capability using Distributed Power- Flow Controller (DPFC)
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012 1 Improvement of System Reliability & Power Transfer Capability using Distributed Power- Flow Controller (DPFC) P.RAMESH
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 5, May-2012 1 Improvement of System Reliability & Power Transfer Capability using Distributed Power- Flow Controller (DPFC) P.RAMESH
Power Flow Control by Using DPFC
 Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3977-3988 ISSN: 2249-6645 Power Flow Control by Using DPFC T. Obulesu 1, S. Sarada 2, M. Sudheer babu 3 1,3 M.Tech Student, Department of EEE A.I.T.S Engineering College
Vol.2, Issue.5, Sep-Oct. 2012 pp-3977-3988 ISSN: 2249-6645 Power Flow Control by Using DPFC T. Obulesu 1, S. Sarada 2, M. Sudheer babu 3 1,3 M.Tech Student, Department of EEE A.I.T.S Engineering College
Modeling and Analysis of DPFC to Improve Power Quality
 Modeling and Analysis of DPFC to Improve Power Quality Ishwar K. Charawande 1, S.S. Dhamse 2 P.G. Student, Department of Electrical Engineering, Government College of Engineering, Aurangabad, Maharashtra,
Modeling and Analysis of DPFC to Improve Power Quality Ishwar K. Charawande 1, S.S. Dhamse 2 P.G. Student, Department of Electrical Engineering, Government College of Engineering, Aurangabad, Maharashtra,
Designing and Control of Converters used in DPFC for Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell In Transmission Line
 Designing and of Converters used in DPFC for Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell In Transmission ine Joydeep Sutradhar M. Tech. Student, Electrical Engg. Abha Gaikwad Patil College of Engineering, Nagpur,
Designing and of Converters used in DPFC for Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell In Transmission ine Joydeep Sutradhar M. Tech. Student, Electrical Engg. Abha Gaikwad Patil College of Engineering, Nagpur,
MITIGATION OF VOLTAGE SAG AND SWELL FOR POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT USING DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER
 MITIGATION OF VOLTAGE SAG AND SWELL FOR POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT USING DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER Sai Lakshmi K Department of Electrical and Electronics engineering, G.Narayanamma Institute of
MITIGATION OF VOLTAGE SAG AND SWELL FOR POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT USING DISTRIBUTED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER Sai Lakshmi K Department of Electrical and Electronics engineering, G.Narayanamma Institute of
SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER
 SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER S. Tara Kalyani 1 and G. Tulasiram Das 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad,
SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER S. Tara Kalyani 1 and G. Tulasiram Das 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad,
Power Quality enhancement of a distribution line with DSTATCOM
 ower Quality enhancement of a distribution line with DSTATCOM Divya arashar 1 Department of Electrical Engineering BSACET Mathura INDIA Aseem Chandel 2 SMIEEE,Deepak arashar 3 Department of Electrical
ower Quality enhancement of a distribution line with DSTATCOM Divya arashar 1 Department of Electrical Engineering BSACET Mathura INDIA Aseem Chandel 2 SMIEEE,Deepak arashar 3 Department of Electrical
Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator
 Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator Ishwar Lal Yadav Department of Electrical Engineering Rungta College of Engineering and Technology Bhilai, India
Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator Ishwar Lal Yadav Department of Electrical Engineering Rungta College of Engineering and Technology Bhilai, India
Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell by Ant Colony Optimization Technique using DPFC
 GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 7 June 2016 ISSN: 2455-5703 Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell by Ant Colony Optimization Technique using DPFC B. Gopinath
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 7 June 2016 ISSN: 2455-5703 Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell by Ant Colony Optimization Technique using DPFC B. Gopinath
ENHANCEMENT OF POWER FLOW USING SSSC CONTROLLER
 ENHANCEMENT OF POWER FLOW USING SSSC CONTROLLER 1 PRATIK RAO, 2 OMKAR PAWAR, 3 C. L. BHATTAR, 4 RUSHIKESH KHAMBE, 5 PRITHVIRAJ PATIL, 6 KEDAR KULKARNI 1,2,4,5,6 B. Tech Electrical, 3 M. Tech Electrical
ENHANCEMENT OF POWER FLOW USING SSSC CONTROLLER 1 PRATIK RAO, 2 OMKAR PAWAR, 3 C. L. BHATTAR, 4 RUSHIKESH KHAMBE, 5 PRITHVIRAJ PATIL, 6 KEDAR KULKARNI 1,2,4,5,6 B. Tech Electrical, 3 M. Tech Electrical
Comparison of Dynamic Stability Response of A SMIB with PI and Fuzzy Controlled DPFC
 Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) Vol. 5, No. 3, September 2017, pp. 199~206 ISSN: 2089-3272, DOI: 10.11591/ijeei.v5i3.293 199 Comparison of Dynamic Stability Response
Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) Vol. 5, No. 3, September 2017, pp. 199~206 ISSN: 2089-3272, DOI: 10.11591/ijeei.v5i3.293 199 Comparison of Dynamic Stability Response
Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC
 Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC A.Naveena, M.Venkateswara Rao 2 Department of EEE, GMRIT, Rajam Email id: allumalla.naveena@ gmail.com,
Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC A.Naveena, M.Venkateswara Rao 2 Department of EEE, GMRIT, Rajam Email id: allumalla.naveena@ gmail.com,
VSC Based HVDC Active Power Controller to Damp out Resonance Oscillation in Turbine Generator System
 VSC Based HVDC Active Power Controller to Damp out Resonance Oscillation in Turbine Generator System Rajkumar Pal 1, Rajesh Kumar 2, Abhay Katyayan 3 1, 2, 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical
VSC Based HVDC Active Power Controller to Damp out Resonance Oscillation in Turbine Generator System Rajkumar Pal 1, Rajesh Kumar 2, Abhay Katyayan 3 1, 2, 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical
Investigation of D-Statcom Operation in Electric Distribution System
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., (2)29-297, 2 2, TextRoad Publication ISSN 29-434 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Investigation of D-Statcom Operation in Electric Distribution
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., (2)29-297, 2 2, TextRoad Publication ISSN 29-434 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Investigation of D-Statcom Operation in Electric Distribution
factors that can be affecting the performance of a electrical power transmission system. Main problems which cause instability to a power system is vo
 2011 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing and Applications With workshop of ICEEA 2011 IPCSIT vol.21 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Location of FACTS devices for Real and Reactive
2011 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing and Applications With workshop of ICEEA 2011 IPCSIT vol.21 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Location of FACTS devices for Real and Reactive
Comparison and Simulation of Open Loop System and Closed Loop System Based UPFC used for Power Quality Improvement
 International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-2307, Volume-1, Issue-6, January 2012 Comparison and Simulation of Open Loop System and Closed Loop System Based UPFC used for
International Journal of Soft Computing and Engineering (IJSCE) ISSN: 2231-2307, Volume-1, Issue-6, January 2012 Comparison and Simulation of Open Loop System and Closed Loop System Based UPFC used for
Bhavin Gondaliya 1st Head, Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Subhash Technical Campus, Junagadh, Gujarat (India)
 ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) RESEARCH HUB International Multidisciplinary Research Journal (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com Modeling and Simulation of Distribution STATCOM Bhavin
ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) RESEARCH HUB International Multidisciplinary Research Journal (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com Modeling and Simulation of Distribution STATCOM Bhavin
Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC to Mitigate THD in Power System
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 8 (January 2014), PP. 25-33 Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 8 (January 2014), PP. 25-33 Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC
Performance and Analysis of Reactive Power Compensation by Unified Power Flow Controller
 Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) Vol. 3, No. 3, September 2015, pp. 141~149 ISSN: 2089-3272 141 Performance and Analysis of Reactive Power Compensation by Unified Power
Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) Vol. 3, No. 3, September 2015, pp. 141~149 ISSN: 2089-3272 141 Performance and Analysis of Reactive Power Compensation by Unified Power
Chapter-5 MODELING OF UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER. There are a number of FACTS devices that control power system
 94 Chapter-5 MODELING OF UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER 5.1 Introduction There are a number of FACTS devices that control power system parameters to utilize the existing power system and also to enhance
94 Chapter-5 MODELING OF UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER 5.1 Introduction There are a number of FACTS devices that control power system parameters to utilize the existing power system and also to enhance
[Mahagaonkar*, 4.(8): August, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785
![[Mahagaonkar*, 4.(8): August, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785 [Mahagaonkar*, 4.(8): August, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785](/thumbs/79/80126240.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT OF GRID CONNECTED WIND ENERGY SYSTEM BY USING STATCOM Mr.Mukund S. Mahagaonkar*, Prof.D.S.Chavan * M.Tech
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT OF GRID CONNECTED WIND ENERGY SYSTEM BY USING STATCOM Mr.Mukund S. Mahagaonkar*, Prof.D.S.Chavan * M.Tech
Modeling and Simulation of STATCOM
 Modeling and Simulation of STATCOM Parimal Borse, India Dr. A. G. Thosar Associate Professor, India Samruddhi Shaha, India Abstract:- This paper attempts to model and simulate Flexible Alternating Current
Modeling and Simulation of STATCOM Parimal Borse, India Dr. A. G. Thosar Associate Professor, India Samruddhi Shaha, India Abstract:- This paper attempts to model and simulate Flexible Alternating Current
INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL OF D-STATCOM FOR ENHANCEMENT OF THE STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE
 INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL OF D-STATCOM FOR ENHANCEMENT OF THE STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE Ms. K. Kamaladevi 1, N. Mohan Murali Krishna 2 1 Asst. Professor, Department of EEE, 2 PG Scholar, Department of
INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL OF D-STATCOM FOR ENHANCEMENT OF THE STEADY-STATE PERFORMANCE Ms. K. Kamaladevi 1, N. Mohan Murali Krishna 2 1 Asst. Professor, Department of EEE, 2 PG Scholar, Department of
Real and Reactive Power Coordination for a Unified Power Flow Controller
 Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 20 (11): 1680-1685, 2014 ISSN 1990-9233 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2014.20.11.1939 Real and Reactive Power Coordination for a Unified Power
Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research 20 (11): 1680-1685, 2014 ISSN 1990-9233 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.mejsr.2014.20.11.1939 Real and Reactive Power Coordination for a Unified Power
Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter Based UPFC with ANN
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
PUBLICATIONS OF PROBLEMS & APPLICATION IN ENGINEERING RESEARCH - PAPER CSEA2012 ISSN: ; e-issn:
 POWER FLOW CONTROL BY USING OPTIMAL LOCATION OF STATCOM S.B. ARUNA Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, Tirupati aruna_ee@hotmail.com 305 ABSTRACT In present scenario,
POWER FLOW CONTROL BY USING OPTIMAL LOCATION OF STATCOM S.B. ARUNA Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, Tirupati aruna_ee@hotmail.com 305 ABSTRACT In present scenario,
Analysis of Power System Oscillation Damping & Voltage Stability Improvement Using SSSC in A Multimachine System
 nternational Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (JERT) SSN: 2278-8 Vol. 3 ssue 7, July - 24 Analysis of Power System Oscillation Damping & Voltage Stability mprovement Using SSSC in A Multimachine
nternational Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (JERT) SSN: 2278-8 Vol. 3 ssue 7, July - 24 Analysis of Power System Oscillation Damping & Voltage Stability mprovement Using SSSC in A Multimachine
Power System Stability Enhancement Using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC)
 Vol. 3, Issue. 4, Jul - Aug. 2013 pp-2530-2536 ISSN: 2249-6645 Power System Stability Enhancement Using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) B. M. Naveen Kumar Reddy 1, Mr. G. V. Rajashekar 2,
Vol. 3, Issue. 4, Jul - Aug. 2013 pp-2530-2536 ISSN: 2249-6645 Power System Stability Enhancement Using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) B. M. Naveen Kumar Reddy 1, Mr. G. V. Rajashekar 2,
Enhancement of Power Quality in Multi Feeders by using MC-DPFC
 Enhancement of Power Quality in Multi Feeders by using MC-DPFC B. Manaswini 1, Dr. S. Vathsal 2, Dr. S. Siva Prasad 3 1 M.Tech student, 2 Professor&Dean 3 Professor&HOD J.B. Institute of Engineering and
Enhancement of Power Quality in Multi Feeders by using MC-DPFC B. Manaswini 1, Dr. S. Vathsal 2, Dr. S. Siva Prasad 3 1 M.Tech student, 2 Professor&Dean 3 Professor&HOD J.B. Institute of Engineering and
Improvement of Voltage Profile using D- STATCOM Simulation under sag and swell condition
 ISSN (Online) 232 24 ISSN (Print) 232 5526 Vol. 2, Issue 7, July 24 Improvement of Voltage Profile using D- STATCOM Simulation under sag and swell condition Brijesh Parmar, Prof. Shivani Johri 2, Chetan
ISSN (Online) 232 24 ISSN (Print) 232 5526 Vol. 2, Issue 7, July 24 Improvement of Voltage Profile using D- STATCOM Simulation under sag and swell condition Brijesh Parmar, Prof. Shivani Johri 2, Chetan
Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 9, September 2013 1 Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement Dr.K.Ravichandrudu
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 9, September 2013 1 Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement Dr.K.Ravichandrudu
Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC)
 Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Girish Kumar Prasad 1, Dr. Malaya S Dash 2 1M-Tech Scholar, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Technocrats
Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Girish Kumar Prasad 1, Dr. Malaya S Dash 2 1M-Tech Scholar, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Technocrats
Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper
 Vol. (0) No. 3, pp. 550-554 ISSN 078-365 Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper Akhilesh A. Nimje, Chinmoy Kumar Panigrahi, Ajaya Kumar Mohanty Abstract The Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC)
Vol. (0) No. 3, pp. 550-554 ISSN 078-365 Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper Akhilesh A. Nimje, Chinmoy Kumar Panigrahi, Ajaya Kumar Mohanty Abstract The Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC)
Arvind Pahade and Nitin Saxena Department of Electrical Engineering, Jabalpur Engineering College, Jabalpur, (MP), India
 e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 4(1): 10-16(2013) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Control of Synchronous Generator Excitation and Rotor Angle Stability by
e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 4(1): 10-16(2013) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 Control of Synchronous Generator Excitation and Rotor Angle Stability by
STATCOM WITH POD CONTROLLER FOR REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION Vijai Jairaj 1, Vishnu.J 2 and Sreenath.N.R 3
 STATCOM WITH POD CONTROLLER FOR REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION Vijai Jairaj 1, Vishnu.J 2 and Sreenath.N.R 3 1 PG Student [Electrical Machines], Department of EEE, Sree Buddha College of Engineering Pattoor,
STATCOM WITH POD CONTROLLER FOR REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION Vijai Jairaj 1, Vishnu.J 2 and Sreenath.N.R 3 1 PG Student [Electrical Machines], Department of EEE, Sree Buddha College of Engineering Pattoor,
Design Strategy for Optimum Rating Selection of Interline D-STATCOM
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 3 ǁ March. 2013 ǁ PP.12-17 Design Strategy for Optimum Rating Selection of Interline
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 3 ǁ March. 2013 ǁ PP.12-17 Design Strategy for Optimum Rating Selection of Interline
FACTS devices in Distributed Generation
 FACTS devices in Distributed Generation 1 K. B. MOHD. UMAR ANSARI, 2 SATYENDRA VISHWAKARMA, 3 GOLDY SHARMA 1, 2, 3 M.Tech (Electrical Power & Energy Systems), Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering,
FACTS devices in Distributed Generation 1 K. B. MOHD. UMAR ANSARI, 2 SATYENDRA VISHWAKARMA, 3 GOLDY SHARMA 1, 2, 3 M.Tech (Electrical Power & Energy Systems), Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering,
Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell Using Distributed Power Flow Controller
 Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell Using Distributed Power Flow Controller P.Rajasekhar 1, Ch.Narayana 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE S.V.P.C.E.T Puttur, chittore, Andhra Pradesh India 1 P.G Student,
Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell Using Distributed Power Flow Controller P.Rajasekhar 1, Ch.Narayana 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE S.V.P.C.E.T Puttur, chittore, Andhra Pradesh India 1 P.G Student,
Power Quality Improvement And Mitigation Of Voltage Sag And Current Swell Using Distributed Power Flow Controller
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Power Quality Improvement And Mitigation Of Voltage Sag And Current Swell Using Distributed Power Flow Controller P.NIRMALA 1, SK.SAJIDA 2, SK.JAN BHASHA 3, PG Student [EPS],
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Power Quality Improvement And Mitigation Of Voltage Sag And Current Swell Using Distributed Power Flow Controller P.NIRMALA 1, SK.SAJIDA 2, SK.JAN BHASHA 3, PG Student [EPS],
Enhancement of Power Quality in 14 Bus System using UPFC
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 2(4): 356-361, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted Date: April 07, 2010 Accepted Date: May 21, 2010 Published
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 2(4): 356-361, 2010 ISSN: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2010 Submitted Date: April 07, 2010 Accepted Date: May 21, 2010 Published
STUDY AND SIMULATION OF THE UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER (UPFC) IN POWER SYSTEM
 IETJOURAL ofegieerig &TECHOLOGY Winter 2011 STUDY AD SIMULATIO OF THE UIFIED POWER FLOW COTROLLER (UPFC) I POWER SYSTEM Ragini Malviya' co co L{) I (J) Z (j) (j) The main objectives Abstract of Flexible
IETJOURAL ofegieerig &TECHOLOGY Winter 2011 STUDY AD SIMULATIO OF THE UIFIED POWER FLOW COTROLLER (UPFC) I POWER SYSTEM Ragini Malviya' co co L{) I (J) Z (j) (j) The main objectives Abstract of Flexible
Improving the Electric Power Quality by UPFC Systems in Electrical Networks
 Improving the Electric Power Quality by UPFC Systems in Electrical Networks 1 *DIB Djalel, 1 A.Rezaiguia, 2 Z. Abada Abstract- Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) is used to control the power flow in
Improving the Electric Power Quality by UPFC Systems in Electrical Networks 1 *DIB Djalel, 1 A.Rezaiguia, 2 Z. Abada Abstract- Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) is used to control the power flow in
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online) Volume 3, Issue 1, January- June (2012), pp. 226-234 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijeet.html Journal
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online) Volume 3, Issue 1, January- June (2012), pp. 226-234 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijeet.html Journal
Comparison of FACTS Devices for Power System Stability Enhancement
 Comparison of FACTS Devices for Power System Stability Enhancement D. Murali Research Scholar in EEE Dept., Government College of Engineering, Bargur-635 104, Tamilnadu, India. Dr. M. Rajaram Professor
Comparison of FACTS Devices for Power System Stability Enhancement D. Murali Research Scholar in EEE Dept., Government College of Engineering, Bargur-635 104, Tamilnadu, India. Dr. M. Rajaram Professor
Power flow improvement using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC)
 Page14 Power flow improvement using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Gandla Saraswathi*, Dr.N.Visali ** & B. Narasimha Reddy*** *P.G Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,JNTUACEP,
Page14 Power flow improvement using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Gandla Saraswathi*, Dr.N.Visali ** & B. Narasimha Reddy*** *P.G Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,JNTUACEP,
Power Control Scheme of D-Statcom
 ISSN : 48-96, Vol. 4, Issue 6( Version 3), June 04, pp.37-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Power Control Scheme of D-Statcom A. Sai Krishna, Y. Suri Babu (M. Tech (PS)) Dept of EEE, R.V.R. & J.C. College
ISSN : 48-96, Vol. 4, Issue 6( Version 3), June 04, pp.37-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Power Control Scheme of D-Statcom A. Sai Krishna, Y. Suri Babu (M. Tech (PS)) Dept of EEE, R.V.R. & J.C. College
SIMULATION RESULTS OF EIGHT BUS SYSTEM USING PUSH-PULL INVERTER BASED STATCOM
 SIMULATION RESULTS OF EIGHT BUS SYSTEM USING PUSH-PULL INVERTER BASED STATCOM N. USHA, RESEARCH SCHOLAR, JNTU, ANANTAPUR Prof.M.Vijaya kumar, Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, JNTU, Anantapur
SIMULATION RESULTS OF EIGHT BUS SYSTEM USING PUSH-PULL INVERTER BASED STATCOM N. USHA, RESEARCH SCHOLAR, JNTU, ANANTAPUR Prof.M.Vijaya kumar, Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, JNTU, Anantapur
Comparison of Simulation and Experimental Results of UPFC used for Power Quality Improvement
 Comparison of Simulation and Experimental Results of UPFC used for Power Quality Improvement S. Muthukrishnan and Dr. A. Nirmal Kumar Abstract This paper deals with digital simulation and implementation
Comparison of Simulation and Experimental Results of UPFC used for Power Quality Improvement S. Muthukrishnan and Dr. A. Nirmal Kumar Abstract This paper deals with digital simulation and implementation
Available ONLINE
 Available ONLINE www.ijart.org IJART, Vol. 2 Issue 3, 2012,94-98 ISSN NO: 6602 3127 R E S E A R C H A R T II C L E Enhancement Of Voltage Stability And Power Oscillation Damping Using Static Synchronous
Available ONLINE www.ijart.org IJART, Vol. 2 Issue 3, 2012,94-98 ISSN NO: 6602 3127 R E S E A R C H A R T II C L E Enhancement Of Voltage Stability And Power Oscillation Damping Using Static Synchronous
Design and Simulation of Fuzzy Logic controller for DSTATCOM In Power System
 Design and Simulation of Fuzzy Logic controller for DSTATCOM In Power System Anju Gupta Department of Electrical and Electronics Engg. YMCA University of Science and Technology anjugupta112@gmail.com P.
Design and Simulation of Fuzzy Logic controller for DSTATCOM In Power System Anju Gupta Department of Electrical and Electronics Engg. YMCA University of Science and Technology anjugupta112@gmail.com P.
Optimal Placement of Shunt Connected Facts Device in a Series Compensated Long Transmission Line
 Journal of Agriculture and Life Sciences Vol. 1, No. 1; June 2014 Optimal Placement of Shunt Connected Facts Device in a Series Compensated Long Transmission Line Sudhakar. Muthyala EEE Dept. University
Journal of Agriculture and Life Sciences Vol. 1, No. 1; June 2014 Optimal Placement of Shunt Connected Facts Device in a Series Compensated Long Transmission Line Sudhakar. Muthyala EEE Dept. University
Volume I Issue VI 2012 September-2012 ISSN
 A 24-pulse STATCOM Simulation model to improve voltage sag due to starting of 1 HP Induction-Motor Mr. Ajay Kumar Bansal 1 Mr. Govind Lal Suthar 2 Mr. Rohan Sharma 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of
A 24-pulse STATCOM Simulation model to improve voltage sag due to starting of 1 HP Induction-Motor Mr. Ajay Kumar Bansal 1 Mr. Govind Lal Suthar 2 Mr. Rohan Sharma 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of
DIGITAL SIMULATION OF MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM
 DIGITAL SIMULATION OF MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM G.SUNDAR, S.RAMAREDDY Research Scholar, Bharath University Chenna Professor Jerusalam College of Engg. Chennai ABSTRACT This paper deals with simulation
DIGITAL SIMULATION OF MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM G.SUNDAR, S.RAMAREDDY Research Scholar, Bharath University Chenna Professor Jerusalam College of Engg. Chennai ABSTRACT This paper deals with simulation
Compensation of Distribution Feeder Loading With Power Factor Correction by Using D-STATCOM
 Compensation of Distribution Feeder Loading With Power Factor Correction by Using D-STATCOM N.Shakeela Begum M.Tech Student P.V.K.K Institute of Technology. Abstract This paper presents a modified instantaneous
Compensation of Distribution Feeder Loading With Power Factor Correction by Using D-STATCOM N.Shakeela Begum M.Tech Student P.V.K.K Institute of Technology. Abstract This paper presents a modified instantaneous
Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems
 Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems Introduction The two major problems that the modern power systems are facing are voltage and angle stabilities. There are various approaches to overcome
Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems Introduction The two major problems that the modern power systems are facing are voltage and angle stabilities. There are various approaches to overcome
IJESR/Nov 2012/ Volume-2/Issue-11/Article No-21/ ISSN International Journal of Engineering & Science Research
 International Journal of Engineering & Science Research POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING DSTATCOM DURING FAULT AND NONLINEAR CONDITIONS T. Srinivas* 1, V.Ramakrishna 2, Eedara Aswani Kumar 3 1 M-Tech
International Journal of Engineering & Science Research POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING DSTATCOM DURING FAULT AND NONLINEAR CONDITIONS T. Srinivas* 1, V.Ramakrishna 2, Eedara Aswani Kumar 3 1 M-Tech
Modified Approach for Harmonic Reduction in Transmission System Using 48-pulse UPFC Employing Series Zig-Zag Primary and Y-Y Secondary Transformer
 I.J. Intelligent Systems and Applications, 213, 11, 7-79 Published Online October 213 in MECS (http://www.mecs-press.org/) DOI: 1.5815/ijisa.213.11.8 Modified Approach for Harmonic Reduction in Transmission
I.J. Intelligent Systems and Applications, 213, 11, 7-79 Published Online October 213 in MECS (http://www.mecs-press.org/) DOI: 1.5815/ijisa.213.11.8 Modified Approach for Harmonic Reduction in Transmission
Power Quality Enhancement and Mitigation of Voltage Sag using DPFC
 Power Quality Enhancement and Mitigation of Voltage Sag using DPFC M. Bindu Sahithi 1, Y. Vishnu Murthulu 2 1 (EEE Department, Prasad V Potluri Siddhartha Institute of Technology, A.p, India) 2 (Assistant
Power Quality Enhancement and Mitigation of Voltage Sag using DPFC M. Bindu Sahithi 1, Y. Vishnu Murthulu 2 1 (EEE Department, Prasad V Potluri Siddhartha Institute of Technology, A.p, India) 2 (Assistant
Enhancement of Voltage Stability & reactive Power Control of Distribution System Using Facts Devices
 Enhancement of Voltage Stability & reactive Power Control of Distribution System Using Facts Devices Aarti Rai Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University,
Enhancement of Voltage Stability & reactive Power Control of Distribution System Using Facts Devices Aarti Rai Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekananda Technical University,
EVALUATION OF A NEW MODEL FOR UPFC OPERATING AS IMPEDANCE COMPENSATION APPLIED TO MULTI- MACHINE SYSTEMS WITH NONLINEAR LOAD
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology ol. 9, No. 6 (04) 678-689 School of Engineering, Taylor s University EALUATION OF A NEW MODEL FOR UPFC OPERATING AS IMPEDANCE COMPENSATION APPLIED TO MULTI-
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology ol. 9, No. 6 (04) 678-689 School of Engineering, Taylor s University EALUATION OF A NEW MODEL FOR UPFC OPERATING AS IMPEDANCE COMPENSATION APPLIED TO MULTI-
Brief Study on TSCS, SSSC, SVC Facts Device
 Brief Study on TSCS, SSSC, SVC Facts Device Ramesh Kumari, Parveen M.Tech. Student, Department of EEE, Mata Rajkaur Institute of Engineering & technology, Rewari, Haryana, India Asst. Professor, Department
Brief Study on TSCS, SSSC, SVC Facts Device Ramesh Kumari, Parveen M.Tech. Student, Department of EEE, Mata Rajkaur Institute of Engineering & technology, Rewari, Haryana, India Asst. Professor, Department
Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM) with Reference Voltage Compensation (RVC) control scheme
 I J E E E C International Journal of Electrical, Electronics ISSN No. (Online) : 2277-2626 and Computer Engineering 2(1): 7-12(2013) Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM)
I J E E E C International Journal of Electrical, Electronics ISSN No. (Online) : 2277-2626 and Computer Engineering 2(1): 7-12(2013) Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM)
Transient Stability Enhancement with Application of FACTS Devices
 Transient Stability Enhancement with Application of FACTS Devices Joel.R. Sutter, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, P.O Box 62000-00200, Nairobi, Kenya E-mail: joelruttosutter@gmail.com
Transient Stability Enhancement with Application of FACTS Devices Joel.R. Sutter, Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology, P.O Box 62000-00200, Nairobi, Kenya E-mail: joelruttosutter@gmail.com
Modeling, Simulation and Group Control of Distributed Static Series Compensators
 American J. of Engineering and Applied Sciences 1 (4): 347-357, 2008 ISSN 1941-7020 2008 Science Publications Modeling, Simulation and Group Control of Distributed Static Series Compensators 1 Poria Fajri,
American J. of Engineering and Applied Sciences 1 (4): 347-357, 2008 ISSN 1941-7020 2008 Science Publications Modeling, Simulation and Group Control of Distributed Static Series Compensators 1 Poria Fajri,
A Voltage Controlled D-STATCOM for Power Quality Improvement with DVR
 A Voltage Controlled D-STATCOM for Power Quality Improvement with DVR Rongali. Shiva Kumar P.G Student Scholar, Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Gokul Group Of Institutions Abstract:
A Voltage Controlled D-STATCOM for Power Quality Improvement with DVR Rongali. Shiva Kumar P.G Student Scholar, Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Gokul Group Of Institutions Abstract:
Voltage Control and Power System Stability Enhancement using UPFC
 International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 14) Cordoba (Spain), 8 th to 10 th April, 2014 Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal (RE&PQJ) ISSN 2172-038 X, No.12, April
International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 14) Cordoba (Spain), 8 th to 10 th April, 2014 Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal (RE&PQJ) ISSN 2172-038 X, No.12, April
ELEMENTS OF FACTS CONTROLLERS
 1 ELEMENTS OF FACTS CONTROLLERS Rajiv K. Varma Associate Professor Hydro One Chair in Power Systems Engineering University of Western Ontario London, ON, CANADA rkvarma@uwo.ca POWER SYSTEMS - Where are
1 ELEMENTS OF FACTS CONTROLLERS Rajiv K. Varma Associate Professor Hydro One Chair in Power Systems Engineering University of Western Ontario London, ON, CANADA rkvarma@uwo.ca POWER SYSTEMS - Where are
Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different Faults
 Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different s Dr. B. Sure Kumar 1, B. Shravanya 2 1 Assistant Professor, CBIT, HYD 2 M.E (P.S & P.E), CBIT, HYD Abstract: The main
Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different s Dr. B. Sure Kumar 1, B. Shravanya 2 1 Assistant Professor, CBIT, HYD 2 M.E (P.S & P.E), CBIT, HYD Abstract: The main
Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC)
 Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz Kumar Reddy (Associate professor, Electrical and Electronics Department, Sriaditya Engineering College, India)
Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz Kumar Reddy (Associate professor, Electrical and Electronics Department, Sriaditya Engineering College, India)
Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC)
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2012 1 Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2012 1 Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz
Implementation of D-STACTOM for Improvement of Power Quality in Radial Distribution System
 Implementation of D-STACTOM for Improvement of Power Quality in Radial Distribution System Kolli Nageswar Rao 1, C. Hari Krishna 2, Kiran Kumar Kuthadi 3 ABSTRACT: D-STATCOM (Distribution Static Compensator)
Implementation of D-STACTOM for Improvement of Power Quality in Radial Distribution System Kolli Nageswar Rao 1, C. Hari Krishna 2, Kiran Kumar Kuthadi 3 ABSTRACT: D-STATCOM (Distribution Static Compensator)
Power Quality Compensation by using UPFC
 ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume 4, Issue 2) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Power Quality Compensation by using UPFC P. Madhumathi madhumathi9196@gmail.com Vivekanada College of Engineering
ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume 4, Issue 2) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Power Quality Compensation by using UPFC P. Madhumathi madhumathi9196@gmail.com Vivekanada College of Engineering
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 12, December -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 REVIEW
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 12, December -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 REVIEW
Power System Oscillations Damping and Transient Stability Enhancement with Application of SSSC FACTS Devices
 Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 2(11): 73-79 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Power System Oscillations Damping and Transient Stability
Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 2(11): 73-79 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X Power System Oscillations Damping and Transient Stability
POWЕR QUALITY IMPROVEMENT IN POWЕR SYSTЕM BY USING SVPWM BASED STATIC SYNCHRONOUS SЕRIЕS COMPЕNSATOR
 POWЕR QUALITY IMPROVEMENT IN POWЕR SYSTЕM BY USING SVPWM BASED STATIC SYNCHRONOUS SЕRIЕS COMPЕNSATOR Vicky T. Kullarkar 1 and Vinod K. Chandrakar 2 International Journal of Latest Trends in Engineering
POWЕR QUALITY IMPROVEMENT IN POWЕR SYSTЕM BY USING SVPWM BASED STATIC SYNCHRONOUS SЕRIЕS COMPЕNSATOR Vicky T. Kullarkar 1 and Vinod K. Chandrakar 2 International Journal of Latest Trends in Engineering
A NOVEL APPROACH ON INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL OF D-STATCOM WITH CONSIDERATION OF POWER FACTOR CORRECTION
 IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN(E): 2321-8843; ISSN(P): 2347-4599 Vol. 2, Issue 7, Jul 2014, 13-18 Impact Journals A NOVEL APPROACH ON INSTANTANEOUS
IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Engineering & Technology (IMPACT: IJRET) ISSN(E): 2321-8843; ISSN(P): 2347-4599 Vol. 2, Issue 7, Jul 2014, 13-18 Impact Journals A NOVEL APPROACH ON INSTANTANEOUS
The Influence of Thyristor Controlled Phase Shifting Transformer on Balance Fault Analysis
 Vol.2, Issue.4, July-Aug. 2012 pp-2472-2476 ISSN: 2249-6645 The Influence of Thyristor Controlled Phase Shifting Transformer on Balance Fault Analysis Pratik Biswas (Department of Electrical Engineering,
Vol.2, Issue.4, July-Aug. 2012 pp-2472-2476 ISSN: 2249-6645 The Influence of Thyristor Controlled Phase Shifting Transformer on Balance Fault Analysis Pratik Biswas (Department of Electrical Engineering,
SIMULATION OF DSTATCOM FOR POWER FACTOR IMPROVEMENT
 International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research (IJEEER) ISSN(P): 2250-155X; ISSN(E): 2278-943X Vol. 7, Issue 2, Apr 2017, 23-28 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. SIMULATION OF DSTATCOM FOR POWER
International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Research (IJEEER) ISSN(P): 2250-155X; ISSN(E): 2278-943X Vol. 7, Issue 2, Apr 2017, 23-28 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. SIMULATION OF DSTATCOM FOR POWER
Performance of DVR under various Fault conditions in Electrical Distribution System
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 8, Issue 1 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 06-12 Performance of DVR under various Fault conditions
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 8, Issue 1 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 06-12 Performance of DVR under various Fault conditions
Simulation and Comparison of DVR and DSTATCOM Used For Voltage Sag Mitigation at Distribution Side
 Simulation and Comparison of DVR and DSTATCOM Used For Voltage Sag Mitigation at Distribution Side 1 Jaykant Vishwakarma, 2 Dr. Arvind Kumar Sharma 1 PG Student, High voltage and Power system, Jabalpur
Simulation and Comparison of DVR and DSTATCOM Used For Voltage Sag Mitigation at Distribution Side 1 Jaykant Vishwakarma, 2 Dr. Arvind Kumar Sharma 1 PG Student, High voltage and Power system, Jabalpur
CHAPTER 5 DESIGN OF DSTATCOM CONTROLLER FOR COMPENSATING UNBALANCES
 86 CHAPTER 5 DESIGN OF DSTATCOM CONTROLLER FOR COMPENSATING UNBALANCES 5.1 INTRODUCTION Distribution systems face severe power quality problems like current unbalance, current harmonics, and voltage unbalance,
86 CHAPTER 5 DESIGN OF DSTATCOM CONTROLLER FOR COMPENSATING UNBALANCES 5.1 INTRODUCTION Distribution systems face severe power quality problems like current unbalance, current harmonics, and voltage unbalance,
Investigation of negative sequence injection capability in H-bridge Multilevel STATCOM
 Investigation of negative sequence injection capability in H-bridge Multilevel STATCOM Ehsan Behrouzian 1, Massimo Bongiorno 1, Hector Zelaya De La Parra 1,2 1 CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY SE-412
Investigation of negative sequence injection capability in H-bridge Multilevel STATCOM Ehsan Behrouzian 1, Massimo Bongiorno 1, Hector Zelaya De La Parra 1,2 1 CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY SE-412
Compensation of Unbalanced Three Phase Currents in a Transmission line using Distributed Power Flow Controller
 Compensation of Unbalanced Three Phase Currents in a Transmission line using Distributed Power Flow Controller T. Santosh Tej*, M. Ramu**, Ch. Das Prakash***, K. Venkateswara Rao**** *(Department of Electrical
Compensation of Unbalanced Three Phase Currents in a Transmission line using Distributed Power Flow Controller T. Santosh Tej*, M. Ramu**, Ch. Das Prakash***, K. Venkateswara Rao**** *(Department of Electrical
Power Quality and the Need for Compensation
 Power Quality and the Need for Compensation Risha Dastagir 1, Prof. Manish Khemariya 2, Prof. Vivek Rai 3 1 Research Scholar, 2,3 Asst. Professor, Lakshmi Narain College of Technology Bhopal, India Abstract
Power Quality and the Need for Compensation Risha Dastagir 1, Prof. Manish Khemariya 2, Prof. Vivek Rai 3 1 Research Scholar, 2,3 Asst. Professor, Lakshmi Narain College of Technology Bhopal, India Abstract
Improvement in Power Quality of Distribution System Using STATCOM
 Improvement in Power Quality of Distribution System Using STATCOM 1 Pushpa Chakravarty, 2 Dr. A.K. Sharma 1 M.E. Scholar, Depart. of Electrical Engineering, Jabalpur Engineering College, Jabalpur, India.
Improvement in Power Quality of Distribution System Using STATCOM 1 Pushpa Chakravarty, 2 Dr. A.K. Sharma 1 M.E. Scholar, Depart. of Electrical Engineering, Jabalpur Engineering College, Jabalpur, India.
Performance Improvement of Power System Using Static Synchronous Compensator (STATCOM) Priya Naikwad, Mayuri Kalmegh, Poonam Bhonge
 2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 235-6011 Online ISSN: 235-602X National Conference on Advances in Engineering and Applied Science (NCAEAS) 16 th February 2017 In association with International
2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 235-6011 Online ISSN: 235-602X National Conference on Advances in Engineering and Applied Science (NCAEAS) 16 th February 2017 In association with International
ENHANCING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING NEURO-FUZZY BASED UPFC
 ENHANCING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING NEURO-FUZZY BASED UPFC R.RAJA NIVEDHA 1, V.BHARATHI 2,P.S.DHIVYABHARATHI 3,V.RAJASUGUNA 4,N.SATHYAPRIYA 5 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EEE,Sri Eshwar college
ENHANCING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING NEURO-FUZZY BASED UPFC R.RAJA NIVEDHA 1, V.BHARATHI 2,P.S.DHIVYABHARATHI 3,V.RAJASUGUNA 4,N.SATHYAPRIYA 5 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EEE,Sri Eshwar college
APPLICATION OF INVERTER BASED SHUNT DEVICE FOR VOLTAGE SAG MITIGATION DUE TO STARTING OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR LOAD
 APPLICATION OF INVERTER BASED SHUNT DEVICE FOR VOLTAGE SAG MITIGATION DUE TO STARTING OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR LOAD A. F. Huweg, S. M. Bashi MIEEE, N. Mariun SMIEEE Universiti Putra Malaysia - Malaysia norman@eng.upm.edu.my
APPLICATION OF INVERTER BASED SHUNT DEVICE FOR VOLTAGE SAG MITIGATION DUE TO STARTING OF AN INDUCTION MOTOR LOAD A. F. Huweg, S. M. Bashi MIEEE, N. Mariun SMIEEE Universiti Putra Malaysia - Malaysia norman@eng.upm.edu.my
OVERVIEW OF SVC AND STATCOM FOR INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL AND POWER FACTOR IMPROVEMENT
 OVERVIEW OF SVC AND STATCOM FOR INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL AND POWER FACTOR IMPROVEMENT Harshkumar Sharma 1, Gajendra Patel 2 1 PG Scholar, Electrical Department, SPCE, Visnagar, Gujarat, India 2 Assistant
OVERVIEW OF SVC AND STATCOM FOR INSTANTANEOUS POWER CONTROL AND POWER FACTOR IMPROVEMENT Harshkumar Sharma 1, Gajendra Patel 2 1 PG Scholar, Electrical Department, SPCE, Visnagar, Gujarat, India 2 Assistant
Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell using Distribution Static Synchronous Compensator (DSTATCOM)
 ABHIYANTRIKI Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell using Distribution Static Synchronous Compensator (DSTATCOM) An International Journal of Engineering & Technology (A Peer Reviewed & Indexed Journal) Vol.
ABHIYANTRIKI Mitigation of Voltage Sag and Swell using Distribution Static Synchronous Compensator (DSTATCOM) An International Journal of Engineering & Technology (A Peer Reviewed & Indexed Journal) Vol.
Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution System using D-STATCOM With PI and PID Controller
 Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution System using D-STATCOM With PI and PID Controller Phanikumar.Ch, M.Tech Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Bapatla Engineering College, Bapatla,
Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution System using D-STATCOM With PI and PID Controller Phanikumar.Ch, M.Tech Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Bapatla Engineering College, Bapatla,
Power System Stability Improvement in Multi-machine 14 Bus System Using STATCOM
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-676,p-ISSN: 232-333, Volume, Issue 3 Ver. II (May Jun. 25), PP 43-47 www.iosrjournals.org Power System Stability Improvement
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-676,p-ISSN: 232-333, Volume, Issue 3 Ver. II (May Jun. 25), PP 43-47 www.iosrjournals.org Power System Stability Improvement
A Novel Approach to Simultaneous Voltage Sag/Swell and Load Reactive Power Compensations Using UPQC
 A Novel Approach to Simultaneous Voltage Sag/Swell and Load Reactive Power Compensations Using UPQC N. Uma Maheshwar, Assistant Professor, EEE, Nalla Narasimha Reddy Group of Institutions. T. Sreekanth,
A Novel Approach to Simultaneous Voltage Sag/Swell and Load Reactive Power Compensations Using UPQC N. Uma Maheshwar, Assistant Professor, EEE, Nalla Narasimha Reddy Group of Institutions. T. Sreekanth,
Size Selection Of Energy Storing Elements For A Cascade Multilevel Inverter STATCOM
 Size Selection Of Energy Storing Elements For A Cascade Multilevel Inverter STATCOM Dr. Jagdish Kumar, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh Abstract the proper selection of values of energy storing
Size Selection Of Energy Storing Elements For A Cascade Multilevel Inverter STATCOM Dr. Jagdish Kumar, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh Abstract the proper selection of values of energy storing
Cascaded Two Level Electrical Converter-Based Multilevel STATCOM for High Power Utilization
 Cascaded Two Level Electrical Converter-Based Multilevel STATCOM for High Power Utilization D.Nagaraju M.Tech-PE, Vidya Bharathi Institute of Technology, T.S, India. L.Ramesh Associate Professor, Vidya
Cascaded Two Level Electrical Converter-Based Multilevel STATCOM for High Power Utilization D.Nagaraju M.Tech-PE, Vidya Bharathi Institute of Technology, T.S, India. L.Ramesh Associate Professor, Vidya
Generation of Voltage Reference Signal in Closed-Loop Control of STATCOM
 Generation of Voltage Reference Signal in Closed-Loop Control of STATCOM M. Tavakoli Bina 1,*, N. Khodabakhshi 1 1 Faculty of Electrical Engineering, K. N. Toosi University of Technology, * Corresponding
Generation of Voltage Reference Signal in Closed-Loop Control of STATCOM M. Tavakoli Bina 1,*, N. Khodabakhshi 1 1 Faculty of Electrical Engineering, K. N. Toosi University of Technology, * Corresponding
Power Quality Improvement in Distribution System Using D-STATCOM
 Power Quality Improvement in Distribution System Using D-STATCOM 1 K.L.Sireesha, 2 K.Bhushana Kumar 1 K L University, AP, India 2 Sasi Institute of Technology, Tadepalligudem, AP, India Abstract This paper
Power Quality Improvement in Distribution System Using D-STATCOM 1 K.L.Sireesha, 2 K.Bhushana Kumar 1 K L University, AP, India 2 Sasi Institute of Technology, Tadepalligudem, AP, India Abstract This paper
Analysis of FACTS Devices in Transmission System
 Volume 02 - Issue 02 February 2017 PP. 22-27 Analysis of FACTS Devices in Transmission System Anand K. Singh, Harshad M. Mummadwar PG Scholar-Electrical Engineering (IPS)-DMIETR-Wardha, PG Scholar-Electrical
Volume 02 - Issue 02 February 2017 PP. 22-27 Analysis of FACTS Devices in Transmission System Anand K. Singh, Harshad M. Mummadwar PG Scholar-Electrical Engineering (IPS)-DMIETR-Wardha, PG Scholar-Electrical
Analysis and Performance of PID Based STATCOM for Voltage Variations
 Analysis and Performance of PID Based STATCOM for Voltage Variations Gangapure Tanuja B. 1, Kulkarni Sameer S. 2, Thorat Sachin D. 3, Vedpathak Onkar B. 4, Prof. Prajakta Jadhav 5 1,2,3,4(Department of
Analysis and Performance of PID Based STATCOM for Voltage Variations Gangapure Tanuja B. 1, Kulkarni Sameer S. 2, Thorat Sachin D. 3, Vedpathak Onkar B. 4, Prof. Prajakta Jadhav 5 1,2,3,4(Department of
