Abstract. 1 Introduction
|
|
|
- Lydia Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
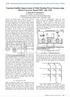
1 Invited Paper Modelling and simulation of electric railway traction, track signalling and power systems R.J. Hill School of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University CWerZom Dotmz, BofA #^42 7,47, Abstract Research at the University of Bath on modelling and simulation of electric traction systems has led to the derivation of an accurate electric circuit model of rail track and traction line. This paper describes the application of that model for the simulation of systems in which the track is the transmission medium. The studies include track signalling system operation, DC and AC traction power line voltage regulation and the prediction of electromagnetic interference between traction power, drives and signalling systems. 1 Introduction Simulation of railway traction systems is necessary to optimise and verify designs in the planning stage, to assist the adjustment of systems during installation and to adapt and further develop existing designs for new situations. To simulate traction power, signalling and propulsion subsystems as electrical circuits, appropriate track and traction line models are required. Work at the University of Bath has resulted in the derivation of accurate, frequencydependent track models, which this paper will review in connection with the simulation of traction power and track signalling systems. A specific difficulty in setting up an electric circuit model of a traction system is in defining the equivalent electric component values of the track and traction line impedance and admittance. The track is laid over and is in contact with the weakly conducting earth, and its impedance is frequency and current dependent from the skin effect in the rails and ground. Moreover, its admittance is highly environmentally dependent. Most prior work in track simulation has relied on simplifications to obtain the track transfer function for specific applications which have been concerned mainly with single-frequency excitation using equivalent single-phase transmission line parameters. This paper describes the application of a comprehensive track simulation model, the development of which has been reviewed in reference [1], to the solution of problems in railway traction and signalling. The applications considered include track signalling operation, power line voltage regulation in both DC and AC
2 384 Railway Design and Management systems including the modelling of rail voltages, and the prediction of electromagnetic interference between traction power, drives and track signalling systems. 2 Coupled track transmission line model The complete rail track and traction line system consists of the running rails, power rails or catenaries, auxiliary conductors and signalling cables laid parallel to the track. A suitable electrical circuit representation must be able to model the current and voltage distribution in all these conductors. As the track is a distributed electrical circuit, it may be modelled as an earth-return transmission line with distributed self and mutual impedance and admittance (Fig. 1). Currents Mutual impedance Mutual admittance t j --' h ^ ' ' ^^1 Phase i ^ Self r voltages impedance I I t h Rail "* t 0 = -; i i Self admittance Remote ground Figure 1. Coupled line rail track impedance and admittance model In the model, the distance-dependent phase voltage and line current vectors are related by the system impedance and admittance matrices through the coupled transmission line equations. The mutual impedances and self admittances are referred to remote ground which is physically inaccessible. The data necessary to utilise the track model is both frequency and current dependent in the case of impedance, and frequency dependent in the case of admittance, because of the variation of the conductivity, permeability and permittivity of the various track components. Work at the University of Bath has led to the derivation of values for this data by practical measurement, finiteelement modelling (FEM) and theoretical modelling. An example of a data set is given in Fig. 2, which was obtained by FEM using a ground conductivity of S/m.. 3 Track circuit modelling A railway track circuit is a failsafe detector used to locate the position of vehicles within a section of track (Fig. 3). A signal transmitter is connected across the rails at one end of the section with a detector at the other end. The receiver deenergises when short circuited by the leading train axle, indicating the presence of a train. If the train is approaching the transmitter, transmission of data for cab signalling and ATC is also possible. In the design of track circuits, it is necessary to choose the operating
3 Railway Design and Management 385 Self capacitance C22-C33 Mutual capacitance -C23 Mutual capacitance -CT2- -C13 Figure 2: Phase impedance and admittance of single track with catenary (]: catenary; 2, 3: running rails) Termination Cab signal receiver Train direction Freq 1 Receiver Freq 3 I Freq 2 Train shunt Transmitter Freq 4 Freq 1 Freq 3 Transmitter Receiver Train direction Figure 3: Vehicle detection and data transmission using track circuits length, carrier & modulation frequencies and the topology of the termination area for target resolution, train shunt sensitivity and broken rail detection performances, given specific variations in track impedance and admittance. Simulation based on a differential-mode transmission line circuit model of the track can be used for the initial setting up and adjustment of track circuits, but the full coupled-line track model is necessary for investigations of asymmetric conditions including broken rail effects and electromagnetic interference. Research at the University of Bath has considered many problems
4 386 Railway Design and Management concerned with track circuits, such as the frequency characteristics of termination areas [2], use of circuit simulation packages for design of audio track circuits [3], and the simulation of parametric effects in the tuned area using a coupled-line track model [4, 5]. The value of the Bath track model for track circuit simulation relates to the structure of the model in separating the effects of the self and mutual impedances and admittances as well as defining their frequency dependency. Present work is aimed at quantifying the effects of current dependency in the track self impedance which is due to saturation and hysteresis effects in the rail iron. 4 Traction power system modelling 4.1 DC traction power system simulation DC traction power supply is the most advantageous for metrorail and urban transportation systems. The standard voltages are 750 V DC third rail and 1.5 kv DC overhead. 3 kv DC was formerly used as the standard main line system in the 1920s and 1930s, but is used now only for existing system extensions. The problems in the design of DC traction power systems solved by simulation are to select the substation spacing and rating for the specified train service to satisfy constraints on permissible catenary or third rail voltage, to maintain rail voltage and earth current below specified levels and to optimise energy flow including power from regenerating vehicles. Whereas static "freeze-frame" pictures can identify particular effects such as worst-case power flow, dynamic simulation, modelling the motion of many trains, can be used to evaluate average conditions over a complete traffic cycle. Simulation in the millisecond timescale is necessary to determine the effects of electromagnetic interference from power-electronic controlled substations and traction drives on sensitive signalling and communications circuits. Figure 4: DC traction power system simulation model
5 Railway Design and Management 387 The DC traction system simulation model shown in Fig. 4 is of a doubletrack light rail system with a track branch. Research at the University of Bath has developed effective solution algorithms to invert the nodal conductance matrix for this circuit [6, 7]. The simulation objectives are to determine the train & rail voltage and the rectifier substation feeding conditions to satisfy the design constraints. The value of the Bath track model in this context is that the determined rail voltage is critically dependent on the value of the track conductance, which has been the subject of extensive investigations via the ground conductivity [1]. Simulation results have been obtained using design data pertinent to the new generation of street-running light rail systems manufactured by companies in Europe, North America and Japan. Further work on DC traction power supply systems at Bath includes the modelling of traction fault currents, as described in references [8, 9]. 4.2 AC traction power system simulation AC traction power supply is used on heavy freight and high speed railways. The standard system is 25 kv at 50/60 Hz although previously established low frequency systems at 16.7 or 25 Hz are in use in Central Europe and North America. Simulation is necessary to assist system design including achievement of the substation rating and spacing necessary to satisfy voltage regulation constraints, and determination of the effects of catenary high-voltage faults on step and touch voltages on the rails and other track components. There are several implementations of AC electrification which include the use of booster transformers or autotransformers. Fig. 5 shows a model of an autotransformer electrified railway. 50 kv is applied between the catenary and return feeder to allow increased substation spacing, greater transmission efficiency and reduced interference to communications systems. Simulation models of this system have been implemented at Bath in order to predict voltage regulation effects [10, 11]. The Bath track model enables the line self impedances and inter-line mutual impedances at the power frequency to be evaluated for use as model data, in addition to harmonic impedances for the determination of higher harmonic resonant conditions in the overhead line. Transformer substation ) Autotransformer Autotransformer Catenary / < Rails ^ Train ^ Return fe»eder / / Transformer substation Earth wire Remote ground I Figure 5: AC traction autotransfortner-fed power system simulation model
6 388 Railway Design and Management 5 Modelling interference between power and signalling systems Electromagnetic interference from traction power systems and power-electronic controlled traction drives appears as noise and can cause in-band interference in the signalling and communications systems. Reference [12], for example, describes some possible interactions between 3 kv DC and 25 kv, 50 Hz traction systems. To produce realistic models of interference, the inclusion of frequency-dependent track data within the simulation models is required. At Bath, research in interference simulation has taken two directions, corresponding to finite-element modelling (FEM) and circuit simulation. 5.1 Crosstalk between parallel tracks Crosstalk occurs when stray electromagnetic fields from one circuit pass through the conductors of an adjacent circuit. The evaluation of crosstalk effects is difficult in traction systems due to nonlinearity in the track component material properties. Although research using the FEM at Bath has been directed mainly at evaluating values for the track impedances and admittances from their known material properties and the track structure, the FEM has also been used to evaluate crosstalk. Fig. 6 gives an example result from one of the Bath models [13]. Currents flowing in the third rail traction power circuit on the right track generate fields which induce crosstalk voltages in the running rails of the left track, which may include the receiver of a track signalling circuit operating at a frequency corresponding to harmonics produced by the transmitter track. The FEM model will produce values for the inter-track coupling and hence help assess the likelihood of crosstalk. Figure 6: Field plot of crosstalk to adjacent track from third rail traction current 5.2 Modal domain modelling Circuit simulation using commercial packages designed for power systems represent transmission lines using a modal domain transformation [14]. This technique has been applied at Bath to model single-frequency interference from chopper traction [15]. Further work has led to a technique for evaluation of the modal characteristics of rail track [16]. To illustrate the problems of using technique, Fig. 7 shows the modal impedance and admittance for overhead catenary electrified track obtained using the phase data of Fig. 2. To apply the method in harmonic studies, models which are accurate over the entire frequency range of interest are required. This is the subject of current work at Bath.
7 Railway Design and Management 389 5, g X) Figure 7: Modal impedance and admittance of catenary electrified track 5.3 Harmonic interference models in the time domain An alternative approach to model the frequency-dependent behaviour of rail track is to set up component-based models of the phase impedance and admittance that can be used directly in time-domain circuit simulation. This current work is being carried out in association with Universita degli Studi di Genova. 6 Concluding remarks The simulation of railway traction systems is a systems task which must deal with traction power transmission, track signalling and electromagnetic interference. The key to accurate modelling is the representation of the rail track itself, for which sophisticated models have been produced at Bath. Current work will further develop the models to include current dependent effects in track impedance and frequency dependent modal and time domain track models. 1 Acknowledgements i The research reviewed in this paper was funded by sources which include UK SERC through grants GR/E/58816, GR/H/18920 and GR/J/51689 and CASE awards, a British Council/MURST collaborative research grant with Universita degli Studi di Genova, and Royal Society visiting fellowships. 8 References 1. Hill R.J. Modelling frequency-dependent rail track impedance and admittance. Miedzynarodowa Konferencja Naukowa Badania Modelowe i Symulacyjne w Trakcji Elektrycznej, Warsaw, November 1993, vol. 1, pp Hill R.J. & Weedon D.N. Computer-aided design of audio frequency track circuits. International Conference on Electric Railway Systems for a New Century, London, September 1987, pp Hill R.J., Berova ML., Carpenter D.C. & Meecham G.J.W. Using the circuit simulation package EMTDC for audio frequency track circuit design. Institution of Railway Signal Engineers International Conference: ASPECT 91, London, 7-9 October 1991, pp Hill R.J. & Coles P.C. A model for railway track circuit operation using electric power transmission simulation software. 27th Universities Power
8 390 Railway Design and Management Engineering Conference, Bath, September 1992, vol. 1, pp Hill R.J. & Coles P.C. A user-friendly simulator for modelling audio frequency track circuit operation Joint IEEE/ASME Railroad Conference, Pittsburgh PA, 6-8 April 1993, pp Hill R.J. & Cai Y. An efficient computational technique for a DC railway traction power flow simulator incorporating track branches. Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements VI, vol. 2: 6th International Conference on Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements, CMEM 93, Siena, Italy, 3-5 May 1993, pp Hill R.J. & Cai Y. Simulation of rail voltage and earth currents in a PCbased DC traction power simulator. Proceedings ELECTROSOFT 93: Software Applications in Electrical Engineering, Southampton, 6-8 July 1993, pp Hill R.J. & Carpenter D.C. Correspondence: Calculation and measurement of rail impedances applicable to remote short circuit fault currents. IEE Proceedings Part B: Electric Power Applications, vol. 140, no. 6, November 1993, pp Fracchia M., Hill R.J., Pozzobon P. & Sciutto G. Accurate track modeling for fault current studies on third-rail metro railways Joint ASME/IEEE Railroad Conference, Chicago, March 1994, pp Hill R.J. and Cevik I.H. Parallel computer simulation of autotransformerfed AC traction networks ASME/IEEE Joint Railroad Conference, Chicago, April 1990, pp Hill R.J. and Cevik I.H. On-line simulation of voltage regulation in autotransformer-fed AC electric railway traction networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 42, no. 3, August 1993, pp Fracchia M., Hill R.J., Pozzobon P. & Sciutto G.: Modelli per 1'analisi dell'interazione tra sistemi di trazione ferroviaria a 3 kv DC e 25 kv, 50 Hz. 94ma Riunione Annuale Associazione Elettrotecnica ed Elettronica Italiana, Ancona, 3-6 October 1993, vol. 5, pp Carpenter D.C. & Hill R.J. Railroad track electrical impedance and adjacent track crosstalk modelling using the finite-element method of electromagnetic systems analysis. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 42, no. 4, November 1993, pp Hill R.J. & Yu S.L. Computer modelling techniques for railway signalling interference. 15th IASTED International Symposium on Applied Simulation and Modelling: ASM '87, Santa Barbara, May 1987, pp and International Journal of Modelling and Simulation, 1989, vol. 9, no. 1, pp Hill R.J., Yu S.L. & Dunn N.J. Rail transit chopper traction interference modelling using the SPICE circuit simulation package. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 38, no. 4, November 1989, pp Hill R.J. & Carpenter D.C.: Modal propagation characteristics of electrified rail track. International Symposium on Technological Innovation in Guided Transports, Lille, September 1993, vol. 1, pp
Time-domain electric circuit simulation packages designed for power systems
 Evaluation of rail track impedance and capacitance using the electromagnetic transients program R.J. Hill" & S.R. McKay* "School of Electonic and Electrical Engineering, University of Bath, Claverton Down,
Evaluation of rail track impedance and capacitance using the electromagnetic transients program R.J. Hill" & S.R. McKay* "School of Electonic and Electrical Engineering, University of Bath, Claverton Down,
Fail Safe Operation of Audio Frequency Track Circuits for Railway Signalling C. Gautham Ram #1, A. Nithya #2, V. Jayashankar *3, P. R.
 Fail Safe Operation of Audio Frequency Track Circuits for Railway Signalling C. Gautham Ram #1, A. Nithya #2, V. Jayashankar *3, P. R. Goundan **4 # Summer Intern, IIT Madras, Chennai, India 1 107107033@nitt.edu
Fail Safe Operation of Audio Frequency Track Circuits for Railway Signalling C. Gautham Ram #1, A. Nithya #2, V. Jayashankar *3, P. R. Goundan **4 # Summer Intern, IIT Madras, Chennai, India 1 107107033@nitt.edu
An Audio Frequency Model of a 2x25 kv Traction Line for High Speed Railway Systems
 An Audio Frequency Model of a 2x25 kv Traction Line for High Speed Railway Systems RICHARD BARTONI Railway Engineer Corso Italia, 83 00100 Rome ITALY bartoni@gtaroma1.191.it REGINA LAMEDICA Full Professor
An Audio Frequency Model of a 2x25 kv Traction Line for High Speed Railway Systems RICHARD BARTONI Railway Engineer Corso Italia, 83 00100 Rome ITALY bartoni@gtaroma1.191.it REGINA LAMEDICA Full Professor
Harmonic Analysis Model Based on 8-port Representation for Korean High Speed Railway
 Harmonic nalysis odel ased on 8-port epresentation for Korean High Speed ailway Kwanghae Oh* Hanmin Lee* Sanghoon hang* * : lectric Power Lab, Korea ailroad esearch nstitute, Woulam-ong, Uiwang-ity, Kyonggi-o,
Harmonic nalysis odel ased on 8-port epresentation for Korean High Speed ailway Kwanghae Oh* Hanmin Lee* Sanghoon hang* * : lectric Power Lab, Korea ailroad esearch nstitute, Woulam-ong, Uiwang-ity, Kyonggi-o,
Ferroresonance Experience in UK: Simulations and Measurements
 Ferroresonance Experience in UK: Simulations and Measurements Zia Emin BSc MSc PhD AMIEE zia.emin@uk.ngrid.com Yu Kwong Tong PhD CEng MIEE kwong.tong@uk.ngrid.com National Grid Company Kelvin Avenue, Surrey
Ferroresonance Experience in UK: Simulations and Measurements Zia Emin BSc MSc PhD AMIEE zia.emin@uk.ngrid.com Yu Kwong Tong PhD CEng MIEE kwong.tong@uk.ngrid.com National Grid Company Kelvin Avenue, Surrey
A new method of DC power supply modelling for rapid transit railway system simulation Z.Y. Shao\ W.S. Chan", J. Allan* & B. Mellitt" Iz'rm'W, ^
 A new method of DC power supply modelling for rapid transit railway system simulation Z.Y. Shao\ W.S. Chan", J. Allan* & B. Mellitt" Iz'rm'W, ^ The University of Birmingham, UK Introduction The Multi-Train
A new method of DC power supply modelling for rapid transit railway system simulation Z.Y. Shao\ W.S. Chan", J. Allan* & B. Mellitt" Iz'rm'W, ^ The University of Birmingham, UK Introduction The Multi-Train
AC INTERFERENCE OF TRANSMISSION LINES ON RAILWAYS: INFLUENCE OF TRACK-CONNECTED EQUIPMENT I. ABSTRACT
 AC INTERFERENCE OF TRANSMISSION LINES ON RAILWAYS: INFLUENCE OF TRACK-CONNECTED EQUIPMENT R. D. Southey, J. Liu, F. P. Dawalibi, Y. Li Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal,
AC INTERFERENCE OF TRANSMISSION LINES ON RAILWAYS: INFLUENCE OF TRACK-CONNECTED EQUIPMENT R. D. Southey, J. Liu, F. P. Dawalibi, Y. Li Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal,
HARMONIC DISTURBANCE COMPENSATING AND MONITORING IN ELECTRIC TRACTION SYSTEM
 HARMONIC DISTURBANCE COMPENSATING AND MONITORING IN ELECTRIC TRACTION SYSTEM A. J. Ghanizadeh, S. H. Hosseinian, G. B. Gharehpetian Electrical Engineering Department, Amirkabir University of Technology,
HARMONIC DISTURBANCE COMPENSATING AND MONITORING IN ELECTRIC TRACTION SYSTEM A. J. Ghanizadeh, S. H. Hosseinian, G. B. Gharehpetian Electrical Engineering Department, Amirkabir University of Technology,
Overvoltage Protection of Light Railway Transportation Systems
 Overvoltage Protection of Light Railway Transportation Systems F. Delfino, R. Procopio, Student Member, IEEE, and M. Rossi, Student Member, IEEE Abstract In this paper the behavior of the power supply
Overvoltage Protection of Light Railway Transportation Systems F. Delfino, R. Procopio, Student Member, IEEE, and M. Rossi, Student Member, IEEE Abstract In this paper the behavior of the power supply
1 Introduction General Background The New Computer Environment Transmission System Developments Theoretical Models and Computer Programs
 Modeling Techniques in Power Systems 1 General Background The New Computer Environment Transmission System Developments Theoretical Models and Computer Programs 2 Transmission Systems Linear Transformation
Modeling Techniques in Power Systems 1 General Background The New Computer Environment Transmission System Developments Theoretical Models and Computer Programs 2 Transmission Systems Linear Transformation
ACCURATE SIMULATION OF AC INTERFERENCE CAUSED BY ELECTRICAL POWER LINES: A PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS
 ACCURATE SIMULATION OF AC INTERFERENCE CAUSED BY ELECTRICAL POWER LINES: A PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS J. Liu and F. P. Dawalibi Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
ACCURATE SIMULATION OF AC INTERFERENCE CAUSED BY ELECTRICAL POWER LINES: A PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS J. Liu and F. P. Dawalibi Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Catenary and autotransformer coupled optimization for 2x25kV systems planning
 Power Supply System Analysis, Design and Planning 113 Catenary and autotransformer coupled optimization for 2x25kV systems planning E. Pilo, L. Rouco & A. Fernández Instituto de Investigación Tecnológica,
Power Supply System Analysis, Design and Planning 113 Catenary and autotransformer coupled optimization for 2x25kV systems planning E. Pilo, L. Rouco & A. Fernández Instituto de Investigación Tecnológica,
Components Track circuits UM71
 Components Track circuits UM71 Track circuits UM71 An essential element of railway safety, the track circuit detects the presence or absence of any vehicle on a given stretch of track. Jointless track
Components Track circuits UM71 Track circuits UM71 An essential element of railway safety, the track circuit detects the presence or absence of any vehicle on a given stretch of track. Jointless track
Distance Protection of Cross-Bonded Transmission Cable-Systems
 Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: April 19, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Distance Protection of Cross-Bonded Transmission Cable-Systems Bak, Claus Leth; F. Jensen, Christian Published in: Proceedings of the 12th
Downloaded from vbn.aau.dk on: April 19, 2019 Aalborg Universitet Distance Protection of Cross-Bonded Transmission Cable-Systems Bak, Claus Leth; F. Jensen, Christian Published in: Proceedings of the 12th
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Analysis and CAD of electric vehicle power electronic converters as a source of electromagnetic disturbances W. Zajac" & A. Szelag^ "Department of Electrical Engineering, Cracow University of Technology,
Analysis and CAD of electric vehicle power electronic converters as a source of electromagnetic disturbances W. Zajac" & A. Szelag^ "Department of Electrical Engineering, Cracow University of Technology,
Power Systems Modelling and Fault Analysis
 Power Systems Modelling and Fault Analysis Theory and Practice Nasser D. Tleis BSc, MSc, PhD, CEng, FIEE AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY
Power Systems Modelling and Fault Analysis Theory and Practice Nasser D. Tleis BSc, MSc, PhD, CEng, FIEE AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE SYDNEY
About the High-Frequency Interferences produced in Systems including PWM and AC Motors
 About the High-Frequency Interferences produced in Systems including PWM and AC Motors ELEONORA DARIE Electrotechnical Department Technical University of Civil Engineering B-dul Pache Protopopescu 66,
About the High-Frequency Interferences produced in Systems including PWM and AC Motors ELEONORA DARIE Electrotechnical Department Technical University of Civil Engineering B-dul Pache Protopopescu 66,
Train Detection Handbook
 Page 1 of 14 Issue and revision record Section/ Issue Date Comments document 1 August 1994 New Document 2 June 1996 Renamed, formerly Track Circuit See CONTENTS for details of other documents. Train Detection
Page 1 of 14 Issue and revision record Section/ Issue Date Comments document 1 August 1994 New Document 2 June 1996 Renamed, formerly Track Circuit See CONTENTS for details of other documents. Train Detection
The Effect of Fault States of the Twelve-pulse Rectifier During the Recuperation
 Transactions on Electrical Engineering, Vol. 3 (04), No. 8 The Effect of Fault States of the Twelve-pulse Rectifier During the Recuperation Ladislav Mlynařík ), Radovan Doleček ), ) University of Pardubice,
Transactions on Electrical Engineering, Vol. 3 (04), No. 8 The Effect of Fault States of the Twelve-pulse Rectifier During the Recuperation Ladislav Mlynařík ), Radovan Doleček ), ) University of Pardubice,
Crosstalk Coupling between Cable Pairs
 Crosstalk Coupling between Cable Pairs By: Mohammed M Al-Asadi and Alistair P. Duffy - De Montfort University, UK and Kenneth G Hodge, and Arthur J Willis - Brand-Rex Ltd, UK Abstract A new approach to
Crosstalk Coupling between Cable Pairs By: Mohammed M Al-Asadi and Alistair P. Duffy - De Montfort University, UK and Kenneth G Hodge, and Arthur J Willis - Brand-Rex Ltd, UK Abstract A new approach to
Research on the modeling of the impedance match bond at station track circuit in Chinese high-speed railway
 Research Article Research on the modeling of the impedance match bond at station track circuit in Chinese high-speed railway Advances in Mechanical Engineering 205, Vol. 7() 7 Ó The Author(s) 205 DOI:
Research Article Research on the modeling of the impedance match bond at station track circuit in Chinese high-speed railway Advances in Mechanical Engineering 205, Vol. 7() 7 Ó The Author(s) 205 DOI:
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Short circuit analysis for traction power supply system of new concept guided busway A. Del Naja, V. Galdi, L. Ippolito & A. Piccolo Diparimento diingegneria dell'informazione ed Ingegneria Elettrica -
Short circuit analysis for traction power supply system of new concept guided busway A. Del Naja, V. Galdi, L. Ippolito & A. Piccolo Diparimento diingegneria dell'informazione ed Ingegneria Elettrica -
Measurements for validation of high voltage underground cable modelling
 Measurements for validation of high voltage underground cable modelling Unnur Stella Gudmundsdottir, Claus Leth Bak, Wojciech T. Wiechowski, Kim Søgaard, Martin Randrup Knardrupgård Abstract-- This paper
Measurements for validation of high voltage underground cable modelling Unnur Stella Gudmundsdottir, Claus Leth Bak, Wojciech T. Wiechowski, Kim Søgaard, Martin Randrup Knardrupgård Abstract-- This paper
p. 1 p. 6 p. 22 p. 46 p. 58
 Comparing power factor and displacement power factor corrections based on IEEE Std. 18-2002 Harmonic problems produced from the use of adjustable speed drives in industrial plants : case study Theory for
Comparing power factor and displacement power factor corrections based on IEEE Std. 18-2002 Harmonic problems produced from the use of adjustable speed drives in industrial plants : case study Theory for
A PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS OF AC INTERFERENCE CAUSED BY HIGH VOLTAGE POWER LINES ON NEIGHBORING RAILROAD TRACKS
 A PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS OF AC INTERFERENCE CAUSED BY HIGH VOLTAGE POWER LINES ON NEIGHBORING RAILROAD TRACKS Yexu Li and Farid Paul Dawalibi Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal,
A PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS OF AC INTERFERENCE CAUSED BY HIGH VOLTAGE POWER LINES ON NEIGHBORING RAILROAD TRACKS Yexu Li and Farid Paul Dawalibi Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal,
Analysis of Multiconductor Quasi-TEM Transmission Lines and Multimode waveguides
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Analysis of Multiconductor Quasi-TEM Transmission Lines and Multimode waveguides S. M. Musa 1, M. N. O. Sadiku 1, and O. D. Momoh 2 Corresponding
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Analysis of Multiconductor Quasi-TEM Transmission Lines and Multimode waveguides S. M. Musa 1, M. N. O. Sadiku 1, and O. D. Momoh 2 Corresponding
Analysis of Indirect Temperature-Rise Tests of Induction Machines Using Time Stepping Finite Element Method
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ENERGY CONVERSION, VOL. 16, NO. 1, MARCH 2001 55 Analysis of Indirect Temperature-Rise Tests of Induction Machines Using Time Stepping Finite Element Method S. L. Ho and W. N. Fu Abstract
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ENERGY CONVERSION, VOL. 16, NO. 1, MARCH 2001 55 Analysis of Indirect Temperature-Rise Tests of Induction Machines Using Time Stepping Finite Element Method S. L. Ho and W. N. Fu Abstract
Harmonic and Unbalance Compensation Based on Direct Power Control for Traction Systems
 Harmonic and Unbalance Compensation Based on Direct Power Control for Traction Systems V.Kotanayak EEE Dept Dhruva Institute of Engineering and Technology (India) ABSTRACT This paper presents a general
Harmonic and Unbalance Compensation Based on Direct Power Control for Traction Systems V.Kotanayak EEE Dept Dhruva Institute of Engineering and Technology (India) ABSTRACT This paper presents a general
ISSN: X Impact factor: (Volume 3, Issue 6) Available online at Modeling and Analysis of Transformer
 ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume 3, Issue 6) Available online at www.ijariit.com Modeling and Analysis of Transformer Divyapradeepa.T Department of Electrical and Electronics, Rajalakshmi Engineering
ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume 3, Issue 6) Available online at www.ijariit.com Modeling and Analysis of Transformer Divyapradeepa.T Department of Electrical and Electronics, Rajalakshmi Engineering
JRC MODIFIED VOLTAGE CONTROL LAW FOR LOW FREQUENCY RAILWAY POWER SYSTEMS
 Proceedings of the 27 IEEE/ASME Joint Rail Conference JRC27 April 4-7, 27, Philadelphia, PA, USA JRC27-2224 MODIFIED VOLTAGE CONTROL LAW FOR LOW FREQUENCY RAILWAY POWER SYSTEMS John Laury Electric Power
Proceedings of the 27 IEEE/ASME Joint Rail Conference JRC27 April 4-7, 27, Philadelphia, PA, USA JRC27-2224 MODIFIED VOLTAGE CONTROL LAW FOR LOW FREQUENCY RAILWAY POWER SYSTEMS John Laury Electric Power
Copenhagen, May 17 th Light Rail and EMC. Dr.-Ing. Lorenz Jung, Siemens AG, Mobility Division. Siemens AG 2016 All rights reserved.
 Copenhagen, May 17 th 2016 Light Rail and EMC Dr.-Ing. Lorenz Jung, Siemens AG, siemens.com Contents Light Rail and EMC (Management and special Topics) EMC: Definition and Coupling Model Normative EMC
Copenhagen, May 17 th 2016 Light Rail and EMC Dr.-Ing. Lorenz Jung, Siemens AG, siemens.com Contents Light Rail and EMC (Management and special Topics) EMC: Definition and Coupling Model Normative EMC
SIMULATION of EMC PERFORMANCE of GRID CONNECTED PV INVERTERS
 SIMULATION of EMC PERFORMANCE of GRID CONNECTED PV INVERTERS Qin Jiang School of Communications & Informatics Victoria University P.O. Box 14428, Melbourne City MC 8001 Australia Email: jq@sci.vu.edu.au
SIMULATION of EMC PERFORMANCE of GRID CONNECTED PV INVERTERS Qin Jiang School of Communications & Informatics Victoria University P.O. Box 14428, Melbourne City MC 8001 Australia Email: jq@sci.vu.edu.au
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Invited Paper Models and tools for simulation and analysis of metrorail transit systems R. Minciardi", S. Savio& & G. Scmtto^ e Universitd degli Studi di Genova, Via air Opera Pia, 13-16145 Genova, Italy
Invited Paper Models and tools for simulation and analysis of metrorail transit systems R. Minciardi", S. Savio& & G. Scmtto^ e Universitd degli Studi di Genova, Via air Opera Pia, 13-16145 Genova, Italy
IEEE Power Engineering Society 2001 Winter Meeting Columbus, OH. Panel Session. Data for Modeling System Transients
 IEEE Power Engineering Society 2001 Winter Meeting Columbus, OH Panel Session Data for Modeling System Transients Parameters for Modeling Transmission Lines and Transformers in Transient Studies Bruce
IEEE Power Engineering Society 2001 Winter Meeting Columbus, OH Panel Session Data for Modeling System Transients Parameters for Modeling Transmission Lines and Transformers in Transient Studies Bruce
Harmonic resonances due to transmission-system cables
 International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 14) Cordoba (Spain), 8 th to 1 th April, 214 Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal (RE&PQJ) ISSN 2172-38 X, No.12, April 214
International Conference on Renewable Energies and Power Quality (ICREPQ 14) Cordoba (Spain), 8 th to 1 th April, 214 Renewable Energy and Power Quality Journal (RE&PQJ) ISSN 2172-38 X, No.12, April 214
Influence Of Lightning Strike Location On The Induced Voltage On a Nearby Overhead Line
 NATIONAL POWER SYSTEMS CONFERENCE NPSC22 563 Influence Of Lightning Strike Location On The Induced Voltage On a Nearby Overhead Line P. Durai Kannu and M. Joy Thomas Abstract This paper analyses the voltages
NATIONAL POWER SYSTEMS CONFERENCE NPSC22 563 Influence Of Lightning Strike Location On The Induced Voltage On a Nearby Overhead Line P. Durai Kannu and M. Joy Thomas Abstract This paper analyses the voltages
Validation of a Power Transformer Model for Ferroresonance with System Tests on a 400 kv Circuit
 Validation of a Power Transformer Model for Ferroresonance with System Tests on a 4 kv Circuit Charalambos Charalambous 1, Z.D. Wang 1, Jie Li 1, Mark Osborne 2 and Paul Jarman 2 Abstract-- National Grid
Validation of a Power Transformer Model for Ferroresonance with System Tests on a 4 kv Circuit Charalambos Charalambous 1, Z.D. Wang 1, Jie Li 1, Mark Osborne 2 and Paul Jarman 2 Abstract-- National Grid
ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE Z-SOURCE INVERTER 1
 ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE Z-SOURCE INVERTER 1 K. N. Madakwar, 2 Dr. M. R. Ramteke VNIT-Nagpur Email: 1 kapil.madakwar@gmail.com, 2 mrr_vrce@rediffmail.com Abstract: This paper deals with the analysis of
ANALYSIS OF SINGLE-PHASE Z-SOURCE INVERTER 1 K. N. Madakwar, 2 Dr. M. R. Ramteke VNIT-Nagpur Email: 1 kapil.madakwar@gmail.com, 2 mrr_vrce@rediffmail.com Abstract: This paper deals with the analysis of
Modern Concepts of Energy Control Technology through VVVF Propulsion Drive
 Modern Concepts of Energy Control Technology through VVVF Propulsion Drive Satoru OZAKI, Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd. Ken-ichi URUGA, Toyo Denki Seizo K.K. Dr. D.P. Bhatt, Autometers Alliance Ltd ABSTRACT
Modern Concepts of Energy Control Technology through VVVF Propulsion Drive Satoru OZAKI, Fuji Electric Systems Co., Ltd. Ken-ichi URUGA, Toyo Denki Seizo K.K. Dr. D.P. Bhatt, Autometers Alliance Ltd ABSTRACT
EMI/EMC ASPECTS OF RAIL TRANSIT ELECTRICAL SYSTEM COMPATIBILITY
 EMI/EMC ASPECTS OF RAIL TRANSIT ELECTRICAL SYSTEM COMPATIBILITY L. A. FRASCO FRASCO & ASSOCIATES INC APTA Rail Transit Conference, June 10-14, 2001, Boston Electrical System Compatibility (ESC) System
EMI/EMC ASPECTS OF RAIL TRANSIT ELECTRICAL SYSTEM COMPATIBILITY L. A. FRASCO FRASCO & ASSOCIATES INC APTA Rail Transit Conference, June 10-14, 2001, Boston Electrical System Compatibility (ESC) System
One-day Conference 18 March Power Supply, EMC and Signalling, in Railway Systems
 One-day Conference 18 March 2017 Power Supply, EMC and Signalling, in Railway Systems EMC Management and Related Technical Aspects in Railway Systems By Dr Peter S W LEUNG http://www.ee.cityu.edu.hk/~pswleung/
One-day Conference 18 March 2017 Power Supply, EMC and Signalling, in Railway Systems EMC Management and Related Technical Aspects in Railway Systems By Dr Peter S W LEUNG http://www.ee.cityu.edu.hk/~pswleung/
ELECTRICAL POWER ENGINEERING
 Introduction This trainer has been designed to provide students with a fully comprehensive knowledge in Electrical Power Engineering systems. The trainer is composed of a set of modules for the simulation
Introduction This trainer has been designed to provide students with a fully comprehensive knowledge in Electrical Power Engineering systems. The trainer is composed of a set of modules for the simulation
ABSTRACT 1 INTRODUCTION
 ELECTROMAGNETIC ANALYSIS OF WIND TURBINE GROUNDING SYSTEMS Maria Lorentzou*, Ian Cotton**, Nikos Hatziargyriou*, Nick Jenkins** * National Technical University of Athens, 42 Patission Street, 1682 Athens,
ELECTROMAGNETIC ANALYSIS OF WIND TURBINE GROUNDING SYSTEMS Maria Lorentzou*, Ian Cotton**, Nikos Hatziargyriou*, Nick Jenkins** * National Technical University of Athens, 42 Patission Street, 1682 Athens,
Measurement of Laddering Wave in Lossy Serpentine Delay Line
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2006.4, 3: 291-295 Measurement of Laddering Wave in Lossy Serpentine Delay Line Fang-Lin Chao * Department of industrial Design, Chaoyang University
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2006.4, 3: 291-295 Measurement of Laddering Wave in Lossy Serpentine Delay Line Fang-Lin Chao * Department of industrial Design, Chaoyang University
Analysis of Distance between ATS and ATP Antenna for Normal Operation in Combined On-board Signal System
 IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 5, No. 2 / June 202, pp. 77-83 The Korean Society for Railway Analysis of Distance between ATS and ATP Antenna for Normal peration in Combined n-board Signal System
IJR International Journal of Railway Vol. 5, No. 2 / June 202, pp. 77-83 The Korean Society for Railway Analysis of Distance between ATS and ATP Antenna for Normal peration in Combined n-board Signal System
EMC in the railway environment Hans Bängtsson
 EMC in the railway environment 2018-05-17 Hans Bängtsson Aspects of EMC in the railway environment LEGAL radio-, TV- and tele communications must not be interfered SAFETY The railway signaling ( red and
EMC in the railway environment 2018-05-17 Hans Bängtsson Aspects of EMC in the railway environment LEGAL radio-, TV- and tele communications must not be interfered SAFETY The railway signaling ( red and
Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter Based UPFC with ANN
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
A NEW DIRECTIONAL OVER CURRENT RELAYING SCHEME FOR DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS IN THE PRESENCE OF DG
 A NEW DIRECTIONAL OVER CURRENT RELAYING SCHEME FOR DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS IN THE PRESENCE OF DG CHAPTER 3 3.1 INTRODUCTION In plain radial feeders, the non-directional relays are used as they operate when
A NEW DIRECTIONAL OVER CURRENT RELAYING SCHEME FOR DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS IN THE PRESENCE OF DG CHAPTER 3 3.1 INTRODUCTION In plain radial feeders, the non-directional relays are used as they operate when
Lumped Network Model of a Resistive Type High T c fault current limiter for transient investigations
 Lumped Network Model of a Resistive Type High T c fault current limiter for transient investigations Ricard Petranovic and Amir M. Miri Universität Karlsruhe, Institut für Elektroenergiesysteme und Hochspannungstechnik,
Lumped Network Model of a Resistive Type High T c fault current limiter for transient investigations Ricard Petranovic and Amir M. Miri Universität Karlsruhe, Institut für Elektroenergiesysteme und Hochspannungstechnik,
Power Quality Summary
 Power Quality Summary This article provides an overview of how voltage harmonic distortion is managed on the distribution network and focuses on the current at future issues surround the connection of
Power Quality Summary This article provides an overview of how voltage harmonic distortion is managed on the distribution network and focuses on the current at future issues surround the connection of
ON-LINE PARTIAL DISCHARGE TESTING OF SOME OF THE WORST PERFORMING CIRCUITS ON A UTILITY DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
 ON-LINE PARTIAL DISCHARGE TESTING OF SOME OF THE WORST PERFORMING CIRCUITS ON A UTILITY DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM D. Clark¹ R. Mackinlay² M. Seltzer-Grant² S. Goodfellow² Lee Renforth² Jamie McWilliam³ and Roger
ON-LINE PARTIAL DISCHARGE TESTING OF SOME OF THE WORST PERFORMING CIRCUITS ON A UTILITY DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM D. Clark¹ R. Mackinlay² M. Seltzer-Grant² S. Goodfellow² Lee Renforth² Jamie McWilliam³ and Roger
Alternative Coupling Method for Immunity Testing of Power Grid Protection Equipment
 Alternative Coupling Method for Immunity Testing of Power Grid Protection Equipment Christian Suttner*, Stefan Tenbohlen Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology (IEH), University of
Alternative Coupling Method for Immunity Testing of Power Grid Protection Equipment Christian Suttner*, Stefan Tenbohlen Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology (IEH), University of
MAINS SIGNAL PROPAGATION THROUGH DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS. J. Stones*, S. Perera*, V. Gosbell* and N. Browne**
 ABSTRACT MAINS SIGNAL PROPAGATION THROUGH DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS J. Stones*, S. Perera*, V. Gosbell* and N. Browne** *School of Electrical, Computer and Telecommunications Engineering University of Wollongong
ABSTRACT MAINS SIGNAL PROPAGATION THROUGH DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS J. Stones*, S. Perera*, V. Gosbell* and N. Browne** *School of Electrical, Computer and Telecommunications Engineering University of Wollongong
Analysis of Laddering Wave in Double Layer Serpentine Delay Line
 International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2008. 6, 1: 47-52 Analysis of Laddering Wave in Double Layer Serpentine Delay Line Fang-Lin Chao * Chaoyang University of Technology Taichung, Taiwan
International Journal of Applied Science and Engineering 2008. 6, 1: 47-52 Analysis of Laddering Wave in Double Layer Serpentine Delay Line Fang-Lin Chao * Chaoyang University of Technology Taichung, Taiwan
T + T /13/$ IEEE 236. the inverter s input impedances on the attenuation of a firstorder
 Emulation of Conducted Emissions of an Automotive Inverter for Filter Development in HV Networks M. Reuter *, T. Friedl, S. Tenbohlen, W. Köhler Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology
Emulation of Conducted Emissions of an Automotive Inverter for Filter Development in HV Networks M. Reuter *, T. Friedl, S. Tenbohlen, W. Köhler Institute of Power Transmission and High Voltage Technology
First characteristic harmonic component of output ripple on dc railway rectifiers
 First characteristic harmonic component of output ripple on dc railway rectifiers J. Allan, J. H. Jin & K. Payne ^ The University ofbirmingham, UK. ^London Underground Limited, UK. Abstract A research
First characteristic harmonic component of output ripple on dc railway rectifiers J. Allan, J. H. Jin & K. Payne ^ The University ofbirmingham, UK. ^London Underground Limited, UK. Abstract A research
H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2
 angle VIRTUAL TRANSMISSION LINE OF CONICAL TYPE COAXIALOPEN-ENDED PROBE FOR DIELECTRIC MEASUREMENT H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2 ABSTRACT 1,2 Ecole Polytechnique of Montreal, Canada An improved virtually conical
angle VIRTUAL TRANSMISSION LINE OF CONICAL TYPE COAXIALOPEN-ENDED PROBE FOR DIELECTRIC MEASUREMENT H. Arab 1, C. Akyel 2 ABSTRACT 1,2 Ecole Polytechnique of Montreal, Canada An improved virtually conical
AS the power distribution networks become more and more
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 153 A Unified Three-Phase Transformer Model for Distribution Load Flow Calculations Peng Xiao, Student Member, IEEE, David C. Yu, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 153 A Unified Three-Phase Transformer Model for Distribution Load Flow Calculations Peng Xiao, Student Member, IEEE, David C. Yu, Member,
EE 740 Transmission Lines
 EE 740 Transmission Lines 1 High Voltage Power Lines (overhead) Common voltages in north America: 138, 230, 345, 500, 765 kv Bundled conductors are used in extra-high voltage lines Stranded instead of
EE 740 Transmission Lines 1 High Voltage Power Lines (overhead) Common voltages in north America: 138, 230, 345, 500, 765 kv Bundled conductors are used in extra-high voltage lines Stranded instead of
Mitigation of Electromagnetic Interference in Rolling stock
 I J E E E C International Journal of Electrical, Electronics ISSN No. (Online) : 2277-2626 and Computer Engineering 2(1): 22-27(2013) Mitigation of Electromagnetic Interference in Rolling sck Pranay Soni*,
I J E E E C International Journal of Electrical, Electronics ISSN No. (Online) : 2277-2626 and Computer Engineering 2(1): 22-27(2013) Mitigation of Electromagnetic Interference in Rolling sck Pranay Soni*,
Comparison of Lamination Iron Losses Supplied by PWM Voltages: US and European Experiences
 Comparison of Lamination Iron Losses Supplied by PWM Voltages: US and European Experiences A. Boglietti, IEEE Member, A. Cavagnino, IEEE Member, T. L. Mthombeni, IEEE Student Member, P. Pillay, IEEE Fellow
Comparison of Lamination Iron Losses Supplied by PWM Voltages: US and European Experiences A. Boglietti, IEEE Member, A. Cavagnino, IEEE Member, T. L. Mthombeni, IEEE Student Member, P. Pillay, IEEE Fellow
Ballast Resistance Measurement Theory and Practice
 Ballast Resistance Measurement Theory and Practice Stuart Landau, PE, MIRSE Signal and Train Control Engineer CH2M 119 Cherry Hill Road, Suite 300 Parsippany, NJ 07054 Stuart.Landau@ch2m.com 4,120 words
Ballast Resistance Measurement Theory and Practice Stuart Landau, PE, MIRSE Signal and Train Control Engineer CH2M 119 Cherry Hill Road, Suite 300 Parsippany, NJ 07054 Stuart.Landau@ch2m.com 4,120 words
25kV A.C. Electrified Lines - Traction Bonding
 Date:MAR 94 25kV A.C. Electrified Lines - Traction Page 1 of 6 Part A Synopsis This is issued by the to define the Boards requirements for continuity bonding on railway systems. This will ensure a continuous
Date:MAR 94 25kV A.C. Electrified Lines - Traction Page 1 of 6 Part A Synopsis This is issued by the to define the Boards requirements for continuity bonding on railway systems. This will ensure a continuous
MMC based D-STATCOM for Different Loading Conditions
 International Journal of Engineering Research And Management (IJERM) ISSN : 2349-2058, Volume-02, Issue-12, December 2015 MMC based D-STATCOM for Different Loading Conditions D.Satish Kumar, Geetanjali
International Journal of Engineering Research And Management (IJERM) ISSN : 2349-2058, Volume-02, Issue-12, December 2015 MMC based D-STATCOM for Different Loading Conditions D.Satish Kumar, Geetanjali
Aspects of Network Harmonic Impedance Modelling in High Voltage Distribution Networks
 Aspects of Network Harmonic Impedance Modelling in High Voltage Distribution Networks Diptargha Chakravorty Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (CES) New Delhi, India diptarghachakravorty@gmail.com Jan
Aspects of Network Harmonic Impedance Modelling in High Voltage Distribution Networks Diptargha Chakravorty Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (CES) New Delhi, India diptarghachakravorty@gmail.com Jan
Transformer Engineering
 Transformer Engineering Design, Technology, and Diagnostics Second Edition S.V. Kulkarni S.A. Khaparde / 0 \ CRC Press \Cf*' J Taylor & Francis Group ^ч_^^ Boca Raton London NewYork CRC Press is an imprint
Transformer Engineering Design, Technology, and Diagnostics Second Edition S.V. Kulkarni S.A. Khaparde / 0 \ CRC Press \Cf*' J Taylor & Francis Group ^ч_^^ Boca Raton London NewYork CRC Press is an imprint
Voltage Detectors. Voltage Detectors Voltage Detectors
 Voltage Detectors Voltage Detectors One of the most important operations when working on electrical switchgear is to check that voltage is absent, and this requires voltage detectors that meet the highest
Voltage Detectors Voltage Detectors One of the most important operations when working on electrical switchgear is to check that voltage is absent, and this requires voltage detectors that meet the highest
EE 741. Primary & Secondary Distribution Systems
 EE 741 Primary & Secondary Distribution Systems Radial-Type Primary Feeder Most common, simplest and lowest cost Example of Overhead Primary Feeder Layout Example of Underground Primary Feeder Layout Radial-Type
EE 741 Primary & Secondary Distribution Systems Radial-Type Primary Feeder Most common, simplest and lowest cost Example of Overhead Primary Feeder Layout Example of Underground Primary Feeder Layout Radial-Type
COMMON mode current due to modulation in power
 982 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 14, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 1999 Elimination of Common-Mode Voltage in Three-Phase Sinusoidal Power Converters Alexander L. Julian, Member, IEEE, Giovanna Oriti,
982 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 14, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 1999 Elimination of Common-Mode Voltage in Three-Phase Sinusoidal Power Converters Alexander L. Julian, Member, IEEE, Giovanna Oriti,
Simulation and Design of a Tunable Patch Antenna
 Simulation and Design of a Tunable Patch Antenna Benjamin D. Horwath and Talal Al-Attar Department of Electrical Engineering, Center for Analog Design and Research Santa Clara University, Santa Clara,
Simulation and Design of a Tunable Patch Antenna Benjamin D. Horwath and Talal Al-Attar Department of Electrical Engineering, Center for Analog Design and Research Santa Clara University, Santa Clara,
International Journal of Current Research and Modern Education (IJCRME) ISSN (Online): & Impact Factor: Special Issue, NCFTCCPS -
 GSM TECHNIQUE USED FOR UNDERGROUND CABLE FAULT DETECTOR AND DISTANCE LOCATOR R. Gunasekaren*, J. Pavalam*, T. Sangamithra*, A. Anitha Rani** & K. Chandrasekar*** * Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical
GSM TECHNIQUE USED FOR UNDERGROUND CABLE FAULT DETECTOR AND DISTANCE LOCATOR R. Gunasekaren*, J. Pavalam*, T. Sangamithra*, A. Anitha Rani** & K. Chandrasekar*** * Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical
Article information: Access to this document was granted through an Emerald subscription provided by Emerald Author Access
 COMPEL: The International Journal for Computation and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering Emerald Article: Evaluation of induced AC voltages in underground metallic pipeline Dan D. Micu,
COMPEL: The International Journal for Computation and Mathematics in Electrical and Electronic Engineering Emerald Article: Evaluation of induced AC voltages in underground metallic pipeline Dan D. Micu,
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS. Third Edition JOSEPH EDMINISTER MAHMOOD NAHVI
 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Third Edition JOSEPH EDMINISTER MAHMOOD NAHVI Includes 364 solved problems --fully explained Complete coverage of the fundamental, core concepts of electric circuits All-new chapters
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Third Edition JOSEPH EDMINISTER MAHMOOD NAHVI Includes 364 solved problems --fully explained Complete coverage of the fundamental, core concepts of electric circuits All-new chapters
Control Strategies and Inverter Topologies for Stabilization of DC Grids in Embedded Systems
 Control Strategies and Inverter Topologies for Stabilization of DC Grids in Embedded Systems Nicolas Patin, The Dung Nguyen, Guy Friedrich June 1, 9 Keywords PWM strategies, Converter topologies, Embedded
Control Strategies and Inverter Topologies for Stabilization of DC Grids in Embedded Systems Nicolas Patin, The Dung Nguyen, Guy Friedrich June 1, 9 Keywords PWM strategies, Converter topologies, Embedded
Improving Passive Filter Compensation Performance With Active Techniques
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 50, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2003 161 Improving Passive Filter Compensation Performance With Active Techniques Darwin Rivas, Luis Morán, Senior Member, IEEE, Juan
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 50, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2003 161 Improving Passive Filter Compensation Performance With Active Techniques Darwin Rivas, Luis Morán, Senior Member, IEEE, Juan
Unit 3 Magnetism...21 Introduction The Natural Magnet Magnetic Polarities Magnetic Compass...21
 Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...4 Negative Atomic Charge...4 Positive
Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...4 Negative Atomic Charge...4 Positive
Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals
 Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...5 Negative Atomic Charge...5
Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...5 Negative Atomic Charge...5
Electrification Infrastructure Reducing Whole Life Cost
 Electrification Infrastructure Reducing Whole Life Cost DC Stray Currents Martin Sigrist Thameslink Programme 28-Oct-14 / 1 Overview Objective How are Stray Currents produced Impact of Stray Current Controlling
Electrification Infrastructure Reducing Whole Life Cost DC Stray Currents Martin Sigrist Thameslink Programme 28-Oct-14 / 1 Overview Objective How are Stray Currents produced Impact of Stray Current Controlling
ELECTRICAL POWER TRANSMISSION TRAINER
 ELECTRICAL POWER TRANSMISSION TRAINER ELECTRICAL POWER TRANSMISSION TRAINER This training system has been designed to provide the students with a fully comprehensive knowledge in Electrical Power Engineering
ELECTRICAL POWER TRANSMISSION TRAINER ELECTRICAL POWER TRANSMISSION TRAINER This training system has been designed to provide the students with a fully comprehensive knowledge in Electrical Power Engineering
(2) New Standard IEEE P (3) Core : (4) Windings :
 (d) Electrical characteristics (such as short-circuit withstand, commutating reactance, more number of windings, etc); (e) Longer life expectancy; (f) Energy efficiency; (g) more demanding environment.
(d) Electrical characteristics (such as short-circuit withstand, commutating reactance, more number of windings, etc); (e) Longer life expectancy; (f) Energy efficiency; (g) more demanding environment.
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 18, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 Time domain simulation of variable frequency drive locomotives for electromagnetic compatibility assessment purposes B.M. Steyn, J.D. van Wyk Infrastructure (Signals), Spoornet, South Africa Energy Laboratory,
Time domain simulation of variable frequency drive locomotives for electromagnetic compatibility assessment purposes B.M. Steyn, J.D. van Wyk Infrastructure (Signals), Spoornet, South Africa Energy Laboratory,
Basics of electrical transformer
 Visit: https://engineeringbasic.com Complete basics and theory of Electrical Transformer Electrical Transformer is the most used electrical machine in power system. Both in the power transmission and distribution
Visit: https://engineeringbasic.com Complete basics and theory of Electrical Transformer Electrical Transformer is the most used electrical machine in power system. Both in the power transmission and distribution
NEURO-ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL USING A DECOUPLED LINEAIUNONLINEAR SYSTEM APPROACH
 FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION DECEMBER 15-18, 1997 ADELAIDE, SOUTH AUSTRALIA NEURO-ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL USING A DECOUPLED LINEAIUNONLINEAR SYSTEM APPROACH M. O. Tokhi and R. Wood
FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION DECEMBER 15-18, 1997 ADELAIDE, SOUTH AUSTRALIA NEURO-ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL USING A DECOUPLED LINEAIUNONLINEAR SYSTEM APPROACH M. O. Tokhi and R. Wood
Transient Stability in Low Frequency Railways with Mixed Electronic and Rotational Generation
 LICENTIATE T H E SIS Transient Stability in Low Frequency Railways with Mixed Electronic and Rotational Generation John Laury Electric Power Engineering Transient Stability in Low Frequency Railways with
LICENTIATE T H E SIS Transient Stability in Low Frequency Railways with Mixed Electronic and Rotational Generation John Laury Electric Power Engineering Transient Stability in Low Frequency Railways with
Case Study Survey of Harmonic Pollution Generated by Railway Systems and Filtering Solutions
 Case Study Survey of Harmonic Pollution Generated by Railway Systems and Filtering Solutions MIHAELA POPESCU, ALEXANDRU BITOLEANU, MIRCEA DOBRICEANU Faculty of Electromechanical, Environmental and Industrial
Case Study Survey of Harmonic Pollution Generated by Railway Systems and Filtering Solutions MIHAELA POPESCU, ALEXANDRU BITOLEANU, MIRCEA DOBRICEANU Faculty of Electromechanical, Environmental and Industrial
The design of Ruthroff broadband voltage transformers M. Ehrenfried G8JNJ
 The design of Ruthroff broadband voltage transformers M. Ehrenfried G8JNJ Introduction I started investigating balun construction as a result of various observations I made whilst building HF antennas.
The design of Ruthroff broadband voltage transformers M. Ehrenfried G8JNJ Introduction I started investigating balun construction as a result of various observations I made whilst building HF antennas.
SAFETY ASPECTS AND NOVEL TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS FOR EARTH FAULT MANAGEMENT IN MV ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS
 SAFETY ASPECTS AND NOVEL TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS FOR EARTH FAULT MANAGEMENT IN MV ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS A. Nikander*, P. Järventausta* *Tampere University of Technology, Finland, ari.nikander@tut.fi,
SAFETY ASPECTS AND NOVEL TECHNICAL SOLUTIONS FOR EARTH FAULT MANAGEMENT IN MV ELECTRICITY DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS A. Nikander*, P. Järventausta* *Tampere University of Technology, Finland, ari.nikander@tut.fi,
Voltage Sag and Swell Mitigation Using Dynamic Voltage Restore (DVR)
 Voltage Sag and Swell Mitigation Using Dynamic Voltage Restore (DVR) Mr. A. S. Patil Mr. S. K. Patil Department of Electrical Engg. Department of Electrical Engg. I. C. R. E. Gargoti I. C. R. E. Gargoti
Voltage Sag and Swell Mitigation Using Dynamic Voltage Restore (DVR) Mr. A. S. Patil Mr. S. K. Patil Department of Electrical Engg. Department of Electrical Engg. I. C. R. E. Gargoti I. C. R. E. Gargoti
Accurate Current Measurement Transducer for Relaying Purpose
 Accurate Current Measurement Transducer for Relaying Purpose Ashish S. Paramane 1, Dr.P.K.Katti 2 Department of Electrical Engineering Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, Maharashtra
Accurate Current Measurement Transducer for Relaying Purpose Ashish S. Paramane 1, Dr.P.K.Katti 2 Department of Electrical Engineering Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, Maharashtra
Experimental validation of the electric network model of the Italian 2x25 kv 50 Hz railway
 2th IMEKO TC4 International Symposium and 18th International Workshop on ADC Modelling and Testing Research on Electric and Electronic Measurement for the Economic Upturn Benevento, Italy, September 15-17,
2th IMEKO TC4 International Symposium and 18th International Workshop on ADC Modelling and Testing Research on Electric and Electronic Measurement for the Economic Upturn Benevento, Italy, September 15-17,
A MODEL TO SIMULATE EM SWITCHING TRANSIENTS IN ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION SUBSTATIONS
 A MODEL TO SIMULATE EM SWITCHING TRANSIENTS IN ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION SUBSTATIONS G. Ala, P. Buccheri, M. Inzerillo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica - Universitˆ di Palermo Viale delle Scienze,
A MODEL TO SIMULATE EM SWITCHING TRANSIENTS IN ELECTRIC POWER DISTRIBUTION SUBSTATIONS G. Ala, P. Buccheri, M. Inzerillo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica - Universitˆ di Palermo Viale delle Scienze,
European Railway Agency. Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements. Ireland
 European Railway Agency Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements Ireland Extract of the study on EMC Requirements Lloyd s Register - November 2010 1. Processes The Irish NSA is the Railway Safety Commission
European Railway Agency Electromagnetic Compatibility Requirements Ireland Extract of the study on EMC Requirements Lloyd s Register - November 2010 1. Processes The Irish NSA is the Railway Safety Commission
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR. By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Third Edition by J.
 PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
MODERN COMPUTATIONAL METHODS FOR THE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF POWER SYSTEM GROUNDING
 MODERN COMPUTATIONAL METHODS FOR THE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF POWER SYSTEM GROUNDING J. Ma and F. P. Dawalibi Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, H3M 1G4 Tel.:
MODERN COMPUTATIONAL METHODS FOR THE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF POWER SYSTEM GROUNDING J. Ma and F. P. Dawalibi Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, H3M 1G4 Tel.:
MODELLING & SIMULATION OF ACTIVE SHUNT FILTER FOR COMPENSATION OF SYSTEM HARMONICS
 JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology (JEET) (JEET) ISSN 2347-422X (Print), ISSN JEET I A E M E ISSN 2347-422X (Print) ISSN 2347-4238 (Online) Volume
JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology (JEET) (JEET) ISSN 2347-422X (Print), ISSN JEET I A E M E ISSN 2347-422X (Print) ISSN 2347-4238 (Online) Volume
AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR
 AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR Suraj J. Dhon 1, Sarang V. Bhonde 2 1 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) 2 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) ABSTRACT: Synchronous
AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR Suraj J. Dhon 1, Sarang V. Bhonde 2 1 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) 2 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) ABSTRACT: Synchronous
Accurate Modeling of Core-Type Distribution Transformers for Electromagnetic Transient Studies
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 17, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2002 969 Accurate Modeling of Core-Type Distribution Transformers for Electromagnetic Transient Studies Taku Noda, Member, IEEE, Hiroshi Nakamoto,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 17, NO. 4, OCTOBER 2002 969 Accurate Modeling of Core-Type Distribution Transformers for Electromagnetic Transient Studies Taku Noda, Member, IEEE, Hiroshi Nakamoto,
ISSUES OF SYSTEM AND CONTROL INTERACTIONS IN ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS
 ISSUES OF SYSTEM AND CONTROL INTERACTIONS IN ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS INDO-US Workshop October 2009, I.I.T. Kanpur INTRODUCTION Electric Power Systems are very large, spread over a wide geographical area
ISSUES OF SYSTEM AND CONTROL INTERACTIONS IN ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEMS INDO-US Workshop October 2009, I.I.T. Kanpur INTRODUCTION Electric Power Systems are very large, spread over a wide geographical area
INTEGRATED METHOD IN ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE STUDIES
 INTEGRATED METHOD IN ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE STUDIES Jinxi Ma and Farid P. Dawalibi Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, H3M 1G4 Tel.: (514) 336-2511
INTEGRATED METHOD IN ELECTROMAGNETIC INTERFERENCE STUDIES Jinxi Ma and Farid P. Dawalibi Safe Engineering Services & technologies ltd. 1544 Viel, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, H3M 1G4 Tel.: (514) 336-2511
Resonances in Collection Grids of Offshore Wind Farms
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Resonances in Collection Grids of Offshore Wind Farms Holdyk, Andrzej Publication date: 2013 Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Holdyk, A. (2013). Resonances
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 20, 2017 Resonances in Collection Grids of Offshore Wind Farms Holdyk, Andrzej Publication date: 2013 Link back to DTU Orbit Citation (APA): Holdyk, A. (2013). Resonances
