Sensitivity Analysis of 3D Building Modelassisted Snapshot Positioning
|
|
|
- Joy Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sensitivity Analysis of 3D Building Modelassisted Snapshot Positioning Rakesh Kuar and Mark G. Petovello Position, Location And Navigation (PLAN) Group Departent of Geoatics Engineering Schulich School of Engineering University of Calgary, Calgary, Canada BIOGRAPHIES Rakesh Kuar is a PhD candidate in the Position, Location And Navigation (PLAN) group of the Departent of Geoatics Engineering at the University of Calgary. He received his Bachelor of Engineering in Electronics & Counication Engineering and Master of Technology in Opto-Electronics fro Rajiv Gandhi Technical University, Bhopal India in 2002 and 2004, respectively. His research interests include iproving GNSS based navigation in Urban Canyon. Mark Petovello is a Professor in the Position, Location And Navigation (PLAN) group in the Departent of Geoatics Engineering at the University of Calgary. He has over 19 years of experience with various navigation research areas including software receiver developent, satellite-based navigation, inertial navigation, reliability analysis and dead-reckoning sensor integration. He is also registered as a professional engineer in the province of Alberta, Canada. ABSTRACT Global Navigation Satellite Systes (GNSS) has proven to be a viable and reliable solution in interference-free environent. However, in urban canyons reliable positioning is difficult to achieve in a cost-effective anner using standalone GNSS, due to ultipath probles and Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) signals. In this regard, the authors previously proposed a ethod whereby NLOS signals were used constructively by incorporating the inforation related to nearby reflectors with the help of a 3D building odel (3DBM). Since the proposed 3DBM-assisted algorith incorporates assistance data with the help of a 3DBM, the accuracy of the final estiated position will also depend on the accuracy of the assistance data and processing paraeters. This research investigates the sensitivity of the 3DBMassisted positioning algorith to various algorith paraeters and is tested using data collected in downtown Calgary, Canada. Results confir that errors in the 3DBM increase the error of the final position estiate. For given grid resolution, the size of the position grid does not affect the final solution. Increasing the grid resolution yields slightly better position estiates at the cost of uch higher processing load. The algorith is shown to be weakly sensitive to the accuracy of receiver s tie estiate; even with a tiing error of 10 s, the final estiated position was unchanged. Finally, the coherent integration tie (10 s vs 100 s) was shown to have very little ipact on position accuracy and deonstrates the capability of the algorith to provide good positioning accuracy without external data bit aiding even in dense urban environents. INTRODUCTION Satellite-based navigation and positioning has proven a viable solution in open sky. However, ultipath reains a doinant source of error, especially in urban environents where satellite obscuration (poor geoetry) and signal reflections (errors) fro nearby buildings conflate to produce poor perforance. Reflected or nonlight-of-sight (non-los, or NLOS) signals are delayed with respect to LOS signal; if the signal reaches the antenna via ultiple paths, the result is a ultipath effect that can be hard to detect in standard GNSS receivers. The fact that ultipath cannot be reoved by differential techniques liits positioning accuracy in ultipath prone areas such as urban canyons (Mishra & Enge 2011 and Ward et al 2006). Furtherore, itigation of ultipath errors becoes difficult when the Doppler shift between the direct and secondary propagation paths is very sall (approxiately 1-2 Hz), which is usually the case in urban canyons where the reflectors are often parallel to the direction of otion of the receiver. Aple research has been done towards ultipath itigation in order to iprove GNSS-based navigation in urban environents. Most of the research has been directed towards identifying and eliinating NLOS signals. These ethodologies can be broadly categorized as: ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 1 of 11
2 Traditional ethods of GNSS integration with Inertial Navigation Syste (INS), where the copleentary benefits of both the systes are utilized (Soloviev & Graas 2009, Petovello et al 2008 and Petovello & Lachapelle 2006 etc.) Modified receiver processing strategies, where the receiver architecture is odified for better signal processing aspects (Xie & Petovello 2014 and Van Graas et al 2009) Using ulti-constellation GNSS for increasing the nuber of easureents (Groves et al 2012 and O Driscoll et al 2010 etc ) and paraeter estiation techniques (He & Petovello 2013 and Van Nee 1992) Apart fro ethods entioned above, 3DBMs have been used for identification of NLOS signals towards a constructive use of NLOS signal. At high level, 3DBMs are digital representations of cities which contain the relevant geospatial inforation (Frere 1998). Although 3D odels have been used for non-gnss applications for decades; in urban areas and indoors they have found GNSS related applications, only in the recent past, as described below. Bradbury et al (2007) used a 3D city odel for deterining satellite availability and analysing signal degradation in ultipath environent, based on siulated scenarios. Ben-Moshe et al (2011) have used a 3D odel for iproving perforance in signal degraded areas and also in their work they have tried to use the present position inforation to help in building the surroundings. Suzuki and Kubo (2012) used 3D city odels for positioning in urban canyons using ultipath siulations. Bourdeau (2012) has shown that a 3D odel of the environent can be used to predict the geoetric paths of NLOS signals using 3D city odel. To detect and predict ultipath situations in urban areas without any additional hardware a 3D representation of surrounding was proposed by Obst et al (2012). More recently, 3D city odels have been used for: a portfolio approach-based positioning in urban canyons (Groves et al 2013); ultipath and NLOS delay estiation based on particle filter (Suzuki and Kubo 2013); unique usage of 3DBM for skyline positioning ethod (Petovello and He 2016) and for ultipath paraeter estiation (Kuar and Petovello 2015). Gu et al (2015) have used 3DBM along with onboard sensors for self-localization of a vehicle in urban canyons. Adjrd and Groves (2015) have used real-tie etre-level obile positioning in outdoor urban environents by aking use of spatial data in the for of 3D city odels. Hsu et al (2016, 2016a) have used 3D building odel, for pedestrian positioning using GPS/GLONASS/QZSS in urban canyons and for autonoous driving position applying differential GNSS. Augenting GNSS syste with additional inforation fro 3DBMs has proven to be a viable approach for iproved accuracy in urban canyons; either by using shadow atching algoriths (such as: Groves 2011, Wang et al (2013, 2015), Yozevitch and Ben Moshe 2015) or by using path delay of NLOS signals constructively (Kuar & Petovello 2014 and Bourdeau 2012). Furtherore, Kuar & Petovello (2016) have shown that constructive use of NLOS signals can be used for snapshot-based positioning (using up to a few hundreds of illiseconds of GNSS signal saples), although that work assued the receiver had accurate knowledge of tie and only considered a fixed set of processing paraeters. This work was unique since the ethod was based on providing position solution with a snapshot of GNSS data, without filtering. Moreover, the position estiate was based on a unique atching algorith that differs fro traditional pseudorange-based positioning algoriths. However, as explained in following section, this positioning ethod depends on various algorith paraeters that, in principle, can affect the accuracy and perforance of the positioning ethod. Hence the sensitivity analysis of the positioning algorith with respect to key algorith paraeters needed to be analyzed. The objective of this paper is to expand upon the authors previous work (Kuar & Petovello 2016) in order to better understand the sensitivities of the algorith to various paraeters such as length of the position grid, resolution of the position grid, and error in estiated receiver tie, error in 3DBM and effect of different coherent integration ties. METHODOLOGY The 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning concept is depicted and suarized in Figure 1; for ore detailed inforation refer to Kuar & Petovello (2016). The approach first defines a Position Grid (PG) around the user s approxiate position. Each point in the position grid is called a Candidate Point (CP), one of which will be selected as the final position estiate. For each CP, the 3DBM and a ray-tracer are used to predict the nuber of signal paths and additional delay of each NLOS signal relative to LOS signals ( path delay ). This inforation is then used to fit 1, 2 or 3-path signal odels to the receiver s correlator outputs using least-squares (LSQ) estiation. Intuitively, the LSQ fit will be best as easured by the least-squares residuals for the CP that ost closely atches the user s true position and this CP is selected as the final position estiate. The LSQ fit in Figure 1 is perfored at all CPs and for each satellite and the root-su-of-squared (RSS) of residuals are coputed in each case. For a given position, the RSS of residuals across all satellites are sued together at each CP and the CP with sallest total RSS of residuals value is selected as the final position solution. ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 2 of 11
3 Figure 1: Top level ethodology of a 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning using all NLOS signals constructively Using this approach, Kuar and Petovello (2016) showed that the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning algorith provided an RMS error iproveent of 64% across-track and 48% in horizontal plane copared to pseudorangebased receivers when used in downtown Calgary, Canada. More interestingly, the results indicated a relationship between error and sky-visibility; better perforance in poor sky-visibility. However, these results were only obtained for a fixed set of algorith paraeters, naely: a PG size of 30x30, a grid resolution of 1, correct receiver tie (no coarse-tie estiation) and coherent integration tie of 100 s. In order to provide a solid support to above results it is iportant to analyze the results for the sae data set with different sets of processing paraeters. More precisely, the algorith needs to be tested for sensitivity towards: a) Errors in approxiate user position (and thus the size of the PG): Since the algorith s approach is based on initial approxiate user position, the uncertainty in this position would affect the size of position grid. For a larger uncertainty, the size of grid should be large enough to capture the true location. Hence the sensitivity analysis of the algorith with respect to size of positon grid becoes essential. b) Resolution of the PG: As entioned above the final estiated position is one of the candidate points inside the position grid, as deterined fro the output of the atching algorith. That eans the resolution of the grid (distance between two nearest candidate points) will affect the accuracy of the final estiated positon. Thus, the sensitivity analysis of the algorith with respect to resolution of the grid needs to be done. c) Tiing error: The proposed approach uses snapshot positioning algorith where receiver ties are not often known precisely, leading to errors in satellite positions due to incorrect transit tie (i.e., the coarse tie proble). The sensitivity of the proposed algorith to receiver tiing errors is therefore critical to understanding its practicality for real-world application. d) Errors in the 3D building odel: As entioned earlier, the nuber of signal paths and NLOS signal delays are predicted using a 3DBM and ray-tracing, hence any error in 3DBM would affect the quality of predicted paraeters and thus the final estiated position. The effect of error in 3DBM on the algorith s perforance is therefore analyzed here. For sake of siplicity, only the biases in the 3DBM are considered; rando errors (e.g., between buildings) are not considered. e) Coherent integration tie: The power of correlator output depends on coherent integration tie. Since these correlators are used for atching with predicted paraeters, the coherent integration tie will affect the quality of atch and, in turn, the quality of final estiated position. Hence, the sensitivity analysis of the algorith with respect to coherent integration becoes iportant. Considering these factors, this paper s focus is towards accessing the sensitivity of the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning to the size and resolution of the PG, the effect of transit tie, 3DBM errors and coherent integration tie: - Effect of PG size are assessed directly by using different sizes of PG and coparing perforance in ters of horizontal position s RMS error - The grid resolution s effect is assessed in a siilar anner and its effect is considered in ters of processing load and accuracy of the final position estiate - Sensitivity to tiing error is first assessed theoretically and then tested by injecting an intentional tiing error and coparing results corresponding to the true tie - Effect of a translation in the 3DBM coordinates are assessed by adding errors of different agnitudes to the vertices coordinates of the 3DBM and coparing results - Sensitivity to coherent integration tie is assessed by coparing the RMS error of horizontal position for 100 s, 20 s and 10 s coherent integration ties The following section details about the data collection, data processing and results. ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 3 of 11
4 DATA COLLECTION AND PROCESSING In order to analyse the sensitivity of the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning algorith, live data was collected in downtown Calgary. The data collection setup consisted of a NovAtel SPAN-LCI reference syste, a front-end for interediate frequency (IF) saple collection, a NovAtel antenna and a base station. The reference trajectory was obtained with NovAtel s Inertial-Explorer software using a tightly coupled forward and backward soothing configuration along with differential corrections fro the base station. All of the equipent were ounted on a test van (except for the base station) and the vehicle was driven through downtown Calgary with a axiu speed of about 15 /s. The IF data was processed using the University of Calgary s GSNRx software receiver (Petovello et al 2009) to generate the correlators outputs for input into the LSQ algorith. The default processing paraeters are shown in Table 1 (these will vary depending on the paraeters being evaluated). Table 1: Default Processing Paraeters Search Space Search Step Integration Tie Position solution rate PG size PG resolution Doppler Doain Code Phase Doain Doppler Doain Code Phase Doain 100 s 1 Hz 30x30 1 ±150 Hz ±300 2 Hz 10 Figure 2 shows the trajectory, which is approxiately 2.5 k in length. Although the analysis considers ultiple points along the trajectory, a detailed analysis is perfored at the location indicated by the yellow star in Figure 2. The selected point has sky visibility of approxiately 55% and has reflectors to the north and south and is otherwise representative of any other points in the data set. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS AND ANALYSIS This section provides results and assessent of the sensitivity of the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning to different paraeters. Sensitivity To The Size of Position Grid Figure 3 shows the RSS of residuals across a 30x30 position grid for PRN 1 at the location under consideration. In this case, the true position is located at the centre of the grid and, as expected, the residuals are sallest around this point. The RSS of residuals for the sae PRN for a 200x200 grid is shown in Figure 4, where the shaded regions depict the surrounding buildings (all CPs falling inside a building are excluded fro the position deterination). Ideally, it is expected that the RSS of residuals should increase for CPs farther fro the true location. In general, this is the case in Figures 3 and 4, especially in the northsouth direction (although the values appear to be approxiately binary in nature). However, in the east-west direction the 200x200 grid shows several ore CPs with low RSS of residuals east of the true location. Generally the position is not coputed fro a single satellite; hence this is not a ajor concern. Nevertheless, if only this particular satellite is used, the coputed position has an error of 20 in the east and 5 in the south. This also shows how the proposed algorith can be used to deterine location using only one satellite. The error in case of 200x200 position grid apparently sees to be larger ; however, it is worth entioning that the resolution of the position grid is 5 in this case as opposed to 1 in case of 30x30 grid. Figure 2: Reference trajectory and epoch considered for detailed sensitivity analysis. The user at the epoch considered for the sensitivity analysis is highlighted in yellow star (towards west side) on the trajectory. Figure 3: RSS of residuals for PRN 1 (Az: 297, Elve: 42 ); size of position grid is 30x30 etres ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 4 of 11
5 Figure 4: RSS of residuals for PRN 1(Az: 297, Elev: 42 ); size of position grid 200x200 etres; shaded regions are buildings and are excluded fro position grid for RSS of residuals calculation Figure 6: RSS of residuals due to all PRNs present at this epoch; size of position grid is 200x200 etres; shaded regions are buildings and are excluded fro position grid for RSS of residuals calculation. The white star represents the final estiated position. To explain the results in Figure 4, we consider that PRN 1 has an aziuth of 297 and so its signals will ostly likely reflect fro building south and/or east of the user. In this case, since there are no significant reflectors to the east, the signal is ost likely being reflected fro a building towards south of the user. However, for a reflector whose noral vector points towards north, a change in the eastwest position of the user will not have uch effect on the predicted path length (this is indirectly explained by equation (1) below) and hence the LSQ RSS of residuals should be nearly constant eaning the algorith is not as sensitive in this direction. Figures 5 and 6 show the RSS values sued across all satellites for the 30x30 grid and the 200x200, respectively. Coparing these figures with the results in Figures 3 and 4 (PRN 1 only), adding inforation fro ore satellites gives fewer regions with sall RSS residuals, which is expected. In this case, the final position estiate in the 200x200 case has an error of 5 toward the west and 5 toward the south. The iproveent in east-west error (with respect to using only PRN 1) is obvious due to the inclusion of RSS of residuals fro other satellites. Results presented here indicate that increasing the size of the position grid does not change the final estiated position. The process of estiating the final position for an increased grid size of 200x200 was repeated for the entire trajectory using approxiately 10 inutes of data, and coputing a solution every 10 seconds. This was done in order to avoid having repeated geoetry when the vehicle was stopped and also to avoid huge processing load. The error statistics is shown in Table 2. Table 2: Coparison of RMS of horizontal error for entire trajectory using different grid sizes Horizontal Error for 30x30 grid and grid resolution 5 Horizontal Error for 200x200 grid and grid resolution Figure 5: RSS of residuals due to all PRNs present at this epoch; size of position grid is 30x30 etres. The white star represents the final estiated position. Results in Table 2 show the RMS error is approxiately sae for two different grid sizes. These results indicate ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 5 of 11
6 that the algorith is arginally sensitive to the size of position grid. Sensitivity To Resolution of Position Grid The resolution of the position grid, or grid resolution, is an iportant factor in ters of obtaining the final position estiate. Increasing the grid resolution results in increased nuber of candidate points for a given grid size. This, in turn, should increase the likelihood of obtaining a candidate point closer to the true location but the processing load will have to increase to accoodate the increased nuber of candidate points under consideration. In order to analyze the effect of the grid resolution on the final estiated position accuracy and on the processing load, different grid resolution of 0.5, 1 and 5 were considered for a position grid of 30x30. The 2D error in final estiated position and nuber of Candidate Points for a grid resolution of 0.5, 1 and 5 are presented in Table 3. As expected, the horizontal error (2D error) for the finer grid resolution is better than for the larger grid resolution. Also shown in Table 3, this coes with a draatic increase in processing load, as reflected by the nuber of candidate points. Table 3: Perforance coparison for different grid resolutions for a 30x30 grid Grid Resolution (GR) Nuber of CPs change in CPs (with respect to 1 GR) N/A 2D error 5.7 Relative Error (with respect to 1 GR) N/A These results are as expected, since the increase in grid resolution is expected to give better positioning accuracy at the cost of increased processing load and vice-versa. Based solely on these results, it would see that a 0.5 resolution is not worth the coputational tradeoff but a 1 or 5 resolution would be sufficient, depending on the accuracy requireents. These results also suggest that the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning algorith can be ade ore efficient by ipleenting a ulti-stage approach. More precisely, a coarser gird can be used to obtain a refined position estiate (copared to the approxiate position used to initialize the algorith); then a saller, finer grid could be generated around that point to get the final estiate; this is left as future work. Sensitivity to Error in Transit Tie In traditional pseudorange-based positioning, because of satellite otion (~4 k/s), an error of 1 s corresponds to an error in range rate of up to about 800 ; which eventually leads to hundreds of etres of error in the position estiate (Van Diggelen 2009). Since proposed ethod is based on positioning with a snapshot of data, eaning that precise tiing inforation cannot be extracted, the effect of receiver tiing error becoes a crucial part of analysis. In order to analyze the sensitivity of the 3DBM-assisted positioning algorith with respect to the tiing error, Figure 7 shows a satellite at location a at a particular tie, along with the signal path that is incident on a reflector located near the receiver. The reflector is at a perpendicular distance d fro the reflector and θ is the angle of incidence defined with respect to the noral vector of the reflecting surface. Although Figure 7 is shown in 2D, the 3D scenario is effectively the sae but is also a function of aziuth % (ore) % (better) % (less) % (poor) Copared to the case of a 1 grid spacing: - The horizontal error for the 0.5 grid resolution is only slightly better (reduction of 0.4 copared to the case of 1 grid spacing) but at the cost of a nearly three-fold increase in the nuber of CPs, and hence processing load. - The horizontal error for the 5 spacing increased by 1.4 (25% increase) with a 95% reduction in processing load. Figure 7: Scenario with a reflector near-by receiver and reflections reaching the receiver ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 6 of 11
7 For this given scenario the path delay (D) of the reflected signal, is given by D = 2*d*cos(θ) (1) Any error in satellite transit tie (as derived fro the receiver tie), would lead to a wrong satellite position. Hence, assuing an error in transit tie, the satellite would be at a different location along the orbit, say at b in Figure 7. Taking the tie derivative of the above equation yields dd dθ = -2*d*sin(θ) * (2) dt dt where, ( dθ/ dt ) is the rate of the incident angle. An approxiate worst-case (largest) value for this is the angular rate of the satellites as viewed fro the centre of the Earth (i.e., the satellite s ean anoaly): Table 4: Error in path delay, aziuth and elevation of point of intersection of incident ray and reflector as a function of transit tie error Error in Transit tie 0 s (true transit tie) Aziuth to point of intersection Elevation to point of intersection s s s Path delay Error in delta path delay NA V s ax( dθ/ dt) (3) R where V is the satellite orbit speed and R is the distance s fro the centre of the Earth to the satellite. Continuing with the pessiistic analysis, d = 0.5 code chips and θ=90 (such that sin(θ) = 1); this would yield a axiu path delay of 1 chip which is the largest that can ipact the correlation function peak. Then, using GPS specific values for V s and R, the worst-case error in path delay is less than 5 c per second of tiing error. Given the level of code-phase noise and the agnitude of orbit and atosphere errors, this level of error is quite sall. It is also worth noting that the value above (5 c per second of tiing error) is uch saller than the absolute code phase error that is used for traditional coarse-tie positioning approaches (Van Diggelen 2009), which are proportional to the geoetric range rate between the receiver and satellite (up to about 900 /s). In this regard, the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning approach should be uch better suited to coarse-tie positioning applications. To confir the above, Table 4 shows the error in path delay coputed for PRN 1 for tiing errors up to 10 s; as can be seen, the path delay errors are 2 c or less. These values are less than the worst case error analysis perfored above, which is 50 c per 10 second tiing error (as explained above). In order to show the effect of transit tie error on the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning algorith, Figure 8 shows the difference in RSS of residuals for PRN 1 copared to what was shown in Figure 3, after introducing an error of 10 s in the transit tie. The difference in RSS of residuals is nearly zero everywhere. Figure 8: Difference in RSS of residuals for PRN 1 (Az: 297⁰, Ele: 42⁰), relative to Figure 3, due to a transit tie error of 10 s The difference sees larger at one of the CP (difference of ore than 0.9) because of a change in the nuber of paths at that CP due to tiing error of 10 s (copared to the true tie case). Since predicting the wrong nuber ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 7 of 11
8 of paths would lead to larger RSS of residuals copared to that corresponding to true nuber of paths, these results ake sense. More iportantly, the final estiated position was at sae location (sae CP) for a grid resolution of 1. By extension, in worst case scenarios where the tiing error results in wrong nuber of paths for ost of CPs, the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning algorith is expected to provide an estiated position corresponding to a CP with a valid and least RSS of residuals, taking care of over-fitting and under-fitting of LSQ (details in Kuar & Petovello 2016). Hence, even with 10 s error in transit tie, the error in estiated position is significantly saller than that observed in traditional coarse tie approaches where errors can be as large as 800 per second of tiing error. In other words, using path delay for position coputation is nearly insensitive to the transit tie error. The process of tiing error injection was repeated for the entire trajectory of 2.5 k for an error injection of 5 s. It was observed that the ean error in path delay was 0.08 etres which eventually ended up in sae candidate point as final estiated position. Sensitivity To Error in 3DBM Accuracy of 3DBM is an iportant factor for 3DBMassisted snapshot positioning ethod. In order to analyze the effect of the error on the final estiated position, bias of 1 and 3 were injected in the vertices coordinates of the given 3DBM. In order to analyze the effect of errors in 3DBM along and across the trajectory, errors of agnitude 1 and 3 were injected in east direction (along-track) and north direction (across-track) respectively, at the epoch under consideration (yellow star in Figure 2). Table 5 copares the 2D positioning accuracy due to errors of different agnitude in the 3DBM. The 2D position error corresponding to the case with no injected error is considered as reference for coparison purposes. Based on the results fro Table 5 and copared to the reference (no error injection) case: - Error up to 3 along track direction has no effect on the 2D position error. - 2D position error reains the sae (as copared to no injected error in 3DBM) for an error of 1 across track. - The 2D position error increases by 58% approxiately, for an error injection of 3 across track in the 3DBM. Table 5: Effect of 3DBM error on estiated position for a grid size of 30x30 and resolution of 5 3DBM Error 2D RMS Error () Change in 2D RMS Error due to biases N/A 1 along track 7.1 No change 1 across track 7.1 No change 3 along track 7.1 No change 3 across track % These results are as expected, since the effect of across track error (injecting error in north coordinate of the vertices) in 3DBM would be ore profound; this fact is indirectly explained by equation (1) above. Since the epoch considered (yellow star in Figure 2) lies on the trajectory along east-west directions and buildings (possible reflectors) are present in north-south direction, error injection (in vertices coordinates of the 3DBM) in north-south direction (across track) would result in an obvious position error (as suggested by equation (1)). Since the grid resolution considered here is 5, the effect of across track error of 1 is effectively absorbed by the grid resolution. By extension, the effect of across track error in 3DBM would be visible as an additional error in the final estiated position, for finer grid resolution. Sensitivity To Coherent Integration Tie The sensitivity of the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning algorith with respect to the coherent integration tie (CIT) was analyzed for CIT of 10 s, 20 s and 100 s. The resulting RMS horizontal position errors along with ean and standard deviation for these cases are shown in Table 6. Table 6: Effect of coherent integration tie on 3DBMassisted snapshot positioning algorith Coherent Integration Tie Mean Std. Deviation RMS Horizontal Position Error 100 s s s ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 8 of 11
9 Copared with the 100 s case, the RMS of horizontal error for 20 s CIT differed by only 20 c. There is arginal degradation of positioning perforance (RMS error increases by 10 %) when CIT was reduced to 10 s fro 100 s. This arginal degradation in case of 10 s CIT-based correlators can be attributed to noisier correlator output in case of 10 s CIT, as can be seen fro the statistics in Table 6 and noralized correlator plots in Figure 9. Figure 9: Noralized correlator outputs for 10 s and 100 s coherent integration ties. The correlator output corresponding to 10 s is noisier copared to that of 100 s. Hence based on the results the perforance of the 3DBMassisted snapshot positioning ethod is considered arginally sensitive to CIT. The result further suggests that external data bit aiding would be unnecessary while using 3DBM-asisted snapshot positioning ethod; which in turn iplies a siplified architecture of receiver for positioning in dense urban areas. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS This paper provides a sensitivity analysis of 3DBMasisted positioning ethod with respect to size of the position grid, resolution of the position grid, tiing errors, error in 3DBM and coherent integration ties. The sensitivity of 3DBM-assisted positioning algorith to the size of the PG was deterined by coparing results for a 30x30 with those of a 200x200. It was observed that the effect of size of position grid on the algorith was entirely based on geoetry of the reflectors around the receiver position, as expected. It was also observed that the algorith s perforance in ters of final estiated position, does not change with the change in size of the position grid; i.e., 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning ethod is nearly insensitive to size of positon grid. The perforance of the algorith in ters of accuracy and processing load was observed to be dependent on the grid resolution. It was observed that erely increasing the resolution to 50 c fro 1 resulted in a 287% increase in processing load with a arginal iproveent in accuracy of 7% (0.4 ). On the other hand, decreasing the grid resolution to 5, the processing load was reduced by 95% at the cost of 1.4 ore error (25% increase). The algorith s sensitivity in ters of positioning accuracy with respect to tiing error was analyzed for transit error up to 10 s. Results indicated that even with an error of 10 s in transit tie, the error in estiated position was less than a etre. Hence it can be concluded that the 3DBM-assisted snapshot positioning algorith is nearly insensitive to tiing error. Hence, the 3DBMassisted positioning technique proposed by sae authors (Kuar & Petovello 2016), can be used for low cost urban navigation, for exaple, in autootive applications and in weak signal environents, with a snapshot of GNSS data without tracking. The algorith s sensitivity with respect to error in 3DBM was analyzed for error of 1 and 3, along and across track. The analysis was done by coparing the 2D position accuracy of the algorith, with and without additional (injected) error in 3DBM. It was perceived that the effect of error in 3DBM, across track, was ore profound; an increase in 2D position error of 57 % was observed due to an additional error of 3 across track. Hence, the algorith sees ore sensitive to 3DBM error s coponent in across track and less sensitive to the error coponent towards along track. Finally, the algorith s sensitivity with respect to coherent integration tie was analyzed. The RMS error of horizontal position was copared for 100 s, 20 s and 10 s coherent integration ties. The arginal iproveent of positioning perforance by 10% for 100 s coherent integration copared to 10 s coherent integration, suggests external data bit aiding is unnecessary even while navigating in dense urban areas and hence siplifies receiver architecture. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Alberta Innovates Technology Futures (AITF) is acknowledged for supporting the first author via an AITF Graduate Student Scholarship. ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 9 of 11
10 REFERENCES Adjrd M., and Paul D Groves (2015), Enhancing Conventional GNSS Positioning with 3D Mapping without Accurate Prior Knowledge, Proceeding of ION GNSS 2015, Septeber 14-18, Tapa, FL, USA Ben-Moshe, B., E. Elkin, H. Levi, and A. Weissan (2011), Iproving Accuracy of GNSS Devices in Urban Canyons, in the Proceeding of Canadian Conference on Coputational Geoetry 2011, August 10-12, Toronto, ON Bourdeau, A. (2012) "Constructive Use of GNSS NLOS- Multipath: Augenting the Navigation Kalan Filter with a 3D Model of the Environent," in Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Inforation Fusion, Singapore, IEEE, pp Bradbury, J., M. Ziebart, and P.A. Cross (2007), Code Multipath Modelling in the Urban Environent Using Large Virtual Reality City Models: Deterining the Local Environent, THE JOURNAL OF NAVIGATION (2007), Vol. 60, Frere D, Vandekerckhove J, Moon T, Van Gool L (1998) Autoatic Modelling and 3D Reconstruction of Urban 376 Buildings fro Aerial Iagery. IEEE International Geoscience and Reote Sensing Syposiu 377 Proceedings, pp Groves, P D, Z Jiang, M Rudi, and P Strode (2013), A Portfolio Approach to NLOS and Multipath Mitigation in Dense Urban Areas, Proceeding of ION GNSS 2013, Septeber 16-20, Nashville, TN Groves, P.D., Z. Jiang, L. Wang, and M K Ziebart (2012), Intelligent Urban Positioning Using Multi-Constellation GNSS with 3D Mapping and NLOS Signal Detection, in the Proceeding of ION ITM 2012, Septeber 17-21, Nashville, TN Groves, P.D. (2011), Shadow Matching: A New GNSS Positioning Technique for Urban Canyons, Journal of Navigation, Vol. 64, Issue 03 Gu Y., Li-Ta Hsu, Y. Wada and S. Kaijo (2015), Integration of 3D Map based GPS Positioning and Onboard Sensors for Vehicle Self-Localization in Urban canyons, in the Proceeding of ION PNT 2015, Honolulu, Hawaii, April 2015, pp He, Z., and M.G. Petovello (2013), Multipath Mitigation by Voting Channel Ipulse Response in Navigation Doain with High-Sensitivity GNSS, Proceeding of ION GNSS 2013, Septeber 16-20, Nashville, TN. Hsu, LT., Y. Gu and S. Kaijo (2016), 3D building odel-based Pedestrian Positioning Method Using GPS/GLONASS/QZSS and Its Reliability Calculation GPS solutions July 2016, Volue 20, Issue-3 pp Hsu, LT., Y. Gu and S. Kaijo (2016 a), Autonoous driving positioning using building odel and DGNSS ENC 2016, Helsinki, Finland, 30 May-2 June 2016, IEEE. Kuar, R. and M.G. Petovello (2016), 3D Building Model- assisted Snapshot Positioning Algorith, subitted to GPS-Solutions. Kuar, R. and M.G. Petovello (2015), 3D Building Model-assisted Multipath Paraeter Estiation, IEEE IPIN 2015, Banff, AB, Canada, October 2015 Kuar, R. and M.G. Petovello (2014), A Novel GNSS Positioning Technique for Iproved Accuracy in Urban Canyon Scenarios using 3D City Model, ION GNSS+ 2014, Session D6, Tapa, FL, 8-12 Septeber 2014 Misra, P., and P. Enge (2011) Global Positioning Syste: Signals, Measureents and Perforance, Ganga-Jauna Press, Licoln, Massachusetts Obst, M., S. Bauer, and G. Wanielik (2012) "Urban Multipath Detection and Mitigation with Dynaic 3D Maps for Reliable Land Vehicle Localization," in Proceedings of the Position Location and Navigation Syposiu (PLANS), IEEE/ION, Myrtle Beach, SC, IEEE/ION, pp O Driscoll,C., G. Lachapelle, and M.E. Taazin (2010), Investigation of the Benefits of Cobined GPS/GLONASS Receivers in Urban Enviornents, Royal Inst. Of Nav. NAV10 Conference, London Nov 30- Dec 2, 2010 Petovello, M., and Z. He (2016) Skyline Positioning in Urban Areas Using a Low-Cost Infrared Caera, ENC 2016, Helsinki, Finland, 30 May-2 June 2016, IEEE Petovello, M.G., C. O Driscoll, G. Lachapelle, D. Borio and H. Murtaza (2009) Architecture and Benefits of an Advanced GNSS Software Receiver. Journal of Global Positioning Systes, 7, 2, pp Petovello, M., C. O Driscoll and G. Lachapelle (2008) Weak Signal Carrier Tracking Using Coherent Integration with an Ultra-Tight GNSS/IMU Receiver, Proceedings of European Navigation Conference (Toulouse, April), 11 pages Petovello, M., and G. Lachapelle (2006) Coparison of Vector-Based Software Receiver Ipleentations with Application to Ultra-Tight GPS/INS Integration, in Proceedings of ION GNSS 2006, Sept., Fort Worth TX, pp , U.S. Institute of Navigation, Fairfax VA. Soloviev, A., and F. V. Graas (2009) Use of deeply integrated GPS/INS architecture and laser scanners for the identification of ultipath reflections in urban environents, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, vol. 3, no. 5, pp , Oct ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 10 of 11
11 Suzuki, T., and N. Kubo (2012), GNSS Positioning with Multipath Siulation using 3D Surface Model in Urban Canyon, in Proceedings of the ION GNSS, Nashville, Tennessee, 2012, pp Suzuki T, Kubo N (2013), Correcting GNSS ultipath errors using a 3D surface odel and particle filter, in Proceedings ION GNSS , Institute of Navigation, Nashville, TN, Septeber 16 20, pp Van Diggelen, F., (2009) A-GPS: Assisted GPS, GNSS and SBAS, Artech House, Boston London Van Graas, F., A. Soloviev, M. Uijt de Haag, and S. Gunawardena (2009), Closed-Loop Sequential Signal Processing and Open-loop Batch Processing Approaches for GNSS Receiver Design, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, Vol. 3, No. 4, August 2009 Van Nee, R.D.J. (1992), The Multipath Estiating Delay Lock, IEEE 2nd syposiu on spread spectru Techniques and applications, (ISSTA 92), Yokolohaa, Japan, Nov 29 Dec 02, Wang, L., P D Groves, and M.K. Ziebart, (2015), Sartphone Shadow Matching for Better Cross-street GNSS Positioning in Urban Environents, The Journal of Navigation, Vol. 68, Wang L, Groves PD, Ziebart MK (2013), GNSS shadow atching: iproving urban positioning accuracy using a 3D city odel with optiized visibility scoring schee, Journal of The Institute of Navigation, Vol. 60, No. 3, 2013, pp Ward, P. W., J. W. Betz, and Christopher J. Hegarty, (2006) Interference, Multipath, and Scintillation, Chapter 6, Understanding GPS: Principles and Applications, Edited by Elliott D. Kaplan and Christopher J. Hegarty, second edition, Artech House Xie, P., and M. G. Petovello (2014) Measuring GNSS Multipath Distributions in Urban Canyon Environents," IEEE Transactions on Instruentation and Measureent, 2014, Feb 2015, Vol. 64 Issue 2, p366, 11 p Yozevitch R and B. Ben Moshe (2015), A Robust Shadow Matching Algorith for GNSS Positioning, Navigation: Journal of The Institute of Navigation, Vol. 62, No. 2, Suer 2015, pp ION GNSS+ 2016, Session B6, Portland, OR, Septeber 2016 Page 11 of 11
S(Q)=A R(Δτ )sinc( πtcδf )sin( πtcδf + Δθ ) + M k=1 L L L L L (A R(Δτ ) sinc( πtcδf ) sin( πtcδf +Δθ )) + η Nk Nk Nk Nk Nk Q where, A is the signal am
 3D Building Model-Assisted Multipath Signal Parameter Estimation Rakesh Kumar and M. G. Petovello Position, Location And Navigation (PLAN) Group Dept. of Geomatics Engineering University Of Calgary Calgary,
3D Building Model-Assisted Multipath Signal Parameter Estimation Rakesh Kumar and M. G. Petovello Position, Location And Navigation (PLAN) Group Dept. of Geomatics Engineering University Of Calgary Calgary,
EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS
 1 EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS M. Malicorne*, M. Bousquet**, V. Calettes*** SUPAERO, 1 avenue Edouard Belin BP 43, 3155 Toulouse Cedex, France.
1 EFFECTS OF MASKING ANGLE AND MULTIPATH ON GALILEO PERFORMANCES IN DIFFERENT ENVIRONMENTS M. Malicorne*, M. Bousquet**, V. Calettes*** SUPAERO, 1 avenue Edouard Belin BP 43, 3155 Toulouse Cedex, France.
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK
 PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
Kalman Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environment
 16 Kalan Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environent Chin-Der Wann National Sun Yat-Sen University Taiwan 1. Introduction Kalan filter and its nonlinear extension, extended
16 Kalan Filtering for NLOS Mitigation and Target Tracking in Indoor Wireless Environent Chin-Der Wann National Sun Yat-Sen University Taiwan 1. Introduction Kalan filter and its nonlinear extension, extended
Adaptive Harmonic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor
 Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless Positioning System
 2 3rd International Conference on Coputer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2) IPCSIT vol. 53 (22) (22) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT.22.V53.No..54 A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless
2 3rd International Conference on Coputer and Electrical Engineering (ICCEE 2) IPCSIT vol. 53 (22) (22) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT.22.V53.No..54 A Novel NLOS Mitigation Approach for Wireless
Energy-Efficient Cellular Communications Powered by Smart Grid Technology
 Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorithm Zhong Danmei 1, a, Wang zhan 1, a, Cheng zhu 1, a, Huang Da 1, a
 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
Power Improvement in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Embedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3
 Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition
 International Journal of Signal Processing Systes Vol., No. Deceber 03 DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition David Levy Infineon Austria AG, Autootive Power Train Systes,
International Journal of Signal Processing Systes Vol., No. Deceber 03 DSI3 Sensor to Master Current Threshold Adaptation for Pattern Recognition David Levy Infineon Austria AG, Autootive Power Train Systes,
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0?
 WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
It is well known that GNSS signals
 GNSS Solutions: Multipath vs. NLOS signals GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to the columnist,
GNSS Solutions: Multipath vs. NLOS signals GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions to the columnist,
A New Localization and Tracking Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things
 Sensors & Transducers 203 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.co A New Localization and Tracking Algorith for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things, 2 Zhang Feng, Xue Hui-Feng, 2 Zhang Yong-Heng,
Sensors & Transducers 203 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.co A New Localization and Tracking Algorith for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Internet of Things, 2 Zhang Feng, Xue Hui-Feng, 2 Zhang Yong-Heng,
Introduction Traditionally, studying outage or cellular systes has been based on the signal-to-intererence ratio (SIR) dropping below a required thres
 Miniu Duration Outages in Rayleigh Fading Channels Jie Lai and Narayan B. Mandaya WINLAB, Rutgers University 73 Brett Rd., Piscataway, NJ 8854-86 Eail: jlai@winlab.rutgers.edu, narayan@winlab.rutgers.edu
Miniu Duration Outages in Rayleigh Fading Channels Jie Lai and Narayan B. Mandaya WINLAB, Rutgers University 73 Brett Rd., Piscataway, NJ 8854-86 Eail: jlai@winlab.rutgers.edu, narayan@winlab.rutgers.edu
RAKE Receiver. Tommi Heikkilä S Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications, Autumn II.
 S-72333 Postgraduate Course in Radio Counications, Autun 2004 1 RAKE Receiver Toi Heikkilä toiheikkila@teliasoneraco Abstract RAKE receiver is used in CDMA-based (Code Division Multiple Access) systes
S-72333 Postgraduate Course in Radio Counications, Autun 2004 1 RAKE Receiver Toi Heikkilä toiheikkila@teliasoneraco Abstract RAKE receiver is used in CDMA-based (Code Division Multiple Access) systes
PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF THE ADAPTIVE MVDR QR-BASED BEAMFORMER FOR JAMMING AND MULTIPATH SUPRESSION IN GPS/GLONASS RECEIVERS
 PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF THE ADAPTIVE MVDR QR-BASED BEAMFORMER FOR JAMMING AND MULTIPATH SUPRESSION IN GPS/GLONASS RECEIVERS V. Behar 1, Ch. Kabakchiev 2, G. Gaydadjiev 3, G.Kuzanov 4, P. Ganchosov 5
PARAMETER OPTIMIZATION OF THE ADAPTIVE MVDR QR-BASED BEAMFORMER FOR JAMMING AND MULTIPATH SUPRESSION IN GPS/GLONASS RECEIVERS V. Behar 1, Ch. Kabakchiev 2, G. Gaydadjiev 3, G.Kuzanov 4, P. Ganchosov 5
EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM
 EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM Guangrong Zou, Maro Antila, Antti Lanila and Jari Kataja Sart Machines, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland P.O. Box 00, FI-0 Tapere,
EQUALIZED ALGORITHM FOR A TRUCK CABIN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM Guangrong Zou, Maro Antila, Antti Lanila and Jari Kataja Sart Machines, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland P.O. Box 00, FI-0 Tapere,
COMBINED FREQUENCY AND SPATIAL DOMAINS POWER DISTRIBUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRANSMISSION
 The 8th nnual IEEE International Syposiu on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Counications (PIMRC 07) COMINED FREQUENCY ND SPTIL DOMINS POWER DISTRIUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRNSMISSION Wladiir ocquet, Kazunori
The 8th nnual IEEE International Syposiu on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Counications (PIMRC 07) COMINED FREQUENCY ND SPTIL DOMINS POWER DISTRIUTION FOR MIMO-OFDM TRNSMISSION Wladiir ocquet, Kazunori
Precise Indoor Localization System For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorithm
 Precise Indoor Localization Syste For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorith Sung-Bu Ki, JangMyung Lee, and I.O. Lee : Pusan National University, http://robotics.ee.pusan.ac.r, : Ninety syste Abstract:
Precise Indoor Localization Syste For a Mobile Robot Using Auto Calibration Algorith Sung-Bu Ki, JangMyung Lee, and I.O. Lee : Pusan National University, http://robotics.ee.pusan.ac.r, : Ninety syste Abstract:
Modeling Beam forming in Circular Antenna Array with Directional Emitters
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volue 5 Issue 3 ǁ Mar. 2017 ǁ PP.01-05 Modeling Bea foring in Circular Antenna Array
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volue 5 Issue 3 ǁ Mar. 2017 ǁ PP.01-05 Modeling Bea foring in Circular Antenna Array
Improved GPS Carrier Phase Tracking in Difficult Environments Using Vector Tracking Approach
 Improved GPS Carrier Phase Tracking in Difficult Environments Using Vector Tracking Approach Scott M. Martin David M. Bevly Auburn University GPS and Vehicle Dynamics Laboratory Presentation Overview Introduction
Improved GPS Carrier Phase Tracking in Difficult Environments Using Vector Tracking Approach Scott M. Martin David M. Bevly Auburn University GPS and Vehicle Dynamics Laboratory Presentation Overview Introduction
SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS
 Latin Aerican Applied Research 39:187-192 (2009) SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS L. ARNONE, C. GONZÁLEZ, C. GAYOSO, J. CASTIÑEIRA MOREIRA and M. LIBERATORI
Latin Aerican Applied Research 39:187-192 (2009) SECURITY AND BER PERFORMANCE TRADE-OFF IN WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS L. ARNONE, C. GONZÁLEZ, C. GAYOSO, J. CASTIÑEIRA MOREIRA and M. LIBERATORI
OTC Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker. sensitive to lateral loading such as the SAL5 and
 OTC 61 78 Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker by J.A..Pinkster, Maritie Research Inst. Netherlands Copyright 1989, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was presented at
OTC 61 78 Statistics of High- and Low-Frequency Motions of a Moored Tanker by J.A..Pinkster, Maritie Research Inst. Netherlands Copyright 1989, Offshore Technology Conference This paper was presented at
TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue 5, Nuber /004, pp.000-000 TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE Daniel BELEGA
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue 5, Nuber /004, pp.000-000 TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE Daniel BELEGA
VEHICLE LOCALIZATION IN URBAN CANYONS USING GEO-REFERENCED DATA AND FEW GNSS SATELLITES
 VEHICLE LOCALIZATION IN URBAN CANYONS USING GEO-REFERENCED DATA AND FEW GNSS SATELLITES Cleent Fouque Philippe Bonnifait Heudiasyc UMR CNRS 6599, Universite de Technologie de Copiegne, France. firstnae.nae@hds.utc.fr
VEHICLE LOCALIZATION IN URBAN CANYONS USING GEO-REFERENCED DATA AND FEW GNSS SATELLITES Cleent Fouque Philippe Bonnifait Heudiasyc UMR CNRS 6599, Universite de Technologie de Copiegne, France. firstnae.nae@hds.utc.fr
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 10M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 10M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors
A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and peak-factor reduction in OFDM
 A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and pea-factor reduction in OFDM Yves LOUET *, Annic LE GLAUNEC ** and Pierre LERAY ** * PhD Student and ** Professors, Departent
A soft decision decoding of product BCH and Reed-Müller codes for error control and pea-factor reduction in OFDM Yves LOUET *, Annic LE GLAUNEC ** and Pierre LERAY ** * PhD Student and ** Professors, Departent
Research Article Dynamic Beamforming for Three-Dimensional MIMO Technique in LTE-Advanced Networks
 Antennas and Propagation Volue 213, Article ID 76457, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/76457 Research Article Dynaic Beaforing for Three-Diensional MIMO Technique in LTE-Advanced Networks Yan Li, Xiaodong
Antennas and Propagation Volue 213, Article ID 76457, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/76457 Research Article Dynaic Beaforing for Three-Diensional MIMO Technique in LTE-Advanced Networks Yan Li, Xiaodong
Cross-correlation tracking for Maximum Length Sequence based acoustic localisation
 Cross-correlation tracking for Maxiu Length Sequence based acoustic localisation Navinda Kottege Research School of Inforation Sciences and Engineering The Australian National University, ACT, Australia
Cross-correlation tracking for Maxiu Length Sequence based acoustic localisation Navinda Kottege Research School of Inforation Sciences and Engineering The Australian National University, ACT, Australia
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio
 Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
Iterative Receiver Signal Processing for Joint Mitigation of Transmitter and Receiver Phase Noise in OFDM-Based Cognitive Radio Link
 Iterative Receiver Signal Processing for Joint Mitigation of Transitter and Receiver Phase Noise in OFDM-Based Cognitive Radio Link Ville Syrjälä and Mikko Valkaa Departent of Counications Engineering
Iterative Receiver Signal Processing for Joint Mitigation of Transitter and Receiver Phase Noise in OFDM-Based Cognitive Radio Link Ville Syrjälä and Mikko Valkaa Departent of Counications Engineering
Performance Analysis of Atmospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays
 Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
Fundamental study for measuring microflow with Michelson interferometer enhanced by external random signal
 Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
Using Adaptive Modulation in a LEO Satellite Communication System
 Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUNICATIONS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 26-28, 27 255 Using Adaptive Modulation in a LEO Satellite Counication Syste L. HADJ
Proceedings of the 11th WSEAS International Conference on COMMUNICATIONS, Agios Nikolaos, Crete Island, Greece, July 26-28, 27 255 Using Adaptive Modulation in a LEO Satellite Counication Syste L. HADJ
Keywords Frequency-domain equalization, antenna diversity, multicode DS-CDMA, frequency-selective fading
 Joint Frequency-doain Equalization and Antenna Diversity Cobining for Orthogonal Multicode DS-CDMA Signal Transissions in A Frequency-selective Fading Channel Taeshi ITAGAKI *1 and Fuiyui ADACHI *2 Dept.
Joint Frequency-doain Equalization and Antenna Diversity Cobining for Orthogonal Multicode DS-CDMA Signal Transissions in A Frequency-selective Fading Channel Taeshi ITAGAKI *1 and Fuiyui ADACHI *2 Dept.
ELEC2202 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Modulation (FM)
 ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS. M.E. Ulug
 COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS M.E. Ulug General Electric Corporate Research and Developent Schenectady, New York 1245 ABSTRACT Waiting ties have been calculated
COMPARISON OF TOKEN HOLDING TIME STRATEGIES FOR A STATIC TOKEN PASSING BUS M.E. Ulug General Electric Corporate Research and Developent Schenectady, New York 1245 ABSTRACT Waiting ties have been calculated
Comparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls
 Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
Assessing & Mitigation of risks on railways operational scenarios
 R H I N O S Railway High Integrity Navigation Overlay System Assessing & Mitigation of risks on railways operational scenarios Rome, June 22 nd 2017 Anja Grosch, Ilaria Martini, Omar Garcia Crespillo (DLR)
R H I N O S Railway High Integrity Navigation Overlay System Assessing & Mitigation of risks on railways operational scenarios Rome, June 22 nd 2017 Anja Grosch, Ilaria Martini, Omar Garcia Crespillo (DLR)
Sound recording with the application of microphone arrays
 Coputer Applications in Electrical Engineering Sound recording with the application of icrophone arrays Eugeniusz Kornatowski West Poeranian University of Technology 7-26 Szczecin, 26 Kwietnia, e-ail:
Coputer Applications in Electrical Engineering Sound recording with the application of icrophone arrays Eugeniusz Kornatowski West Poeranian University of Technology 7-26 Szczecin, 26 Kwietnia, e-ail:
NovAtel s. Performance Analysis October Abstract. SPAN on OEM6. SPAN on OEM6. Enhancements
 NovAtel s SPAN on OEM6 Performance Analysis October 2012 Abstract SPAN, NovAtel s GNSS/INS solution, is now available on the OEM6 receiver platform. In addition to rapid GNSS signal reacquisition performance,
NovAtel s SPAN on OEM6 Performance Analysis October 2012 Abstract SPAN, NovAtel s GNSS/INS solution, is now available on the OEM6 receiver platform. In addition to rapid GNSS signal reacquisition performance,
A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS
 A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS Jaal Moshtagh University of Bath, UK oshtagh79@yahoo.co Abstract
A NEW APPROACH TO UNGROUNDED FAULT LOCATION IN A THREE-PHASE UNDERGROUND DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM USING COMBINED NEURAL NETWORKS & WAVELET ANALYSIS Jaal Moshtagh University of Bath, UK oshtagh79@yahoo.co Abstract
Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization from 2 to 8 GHz
 Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization fro to 8 GHz Ada S Y Poon and Minnie Ho Counications and Interconnect Lab, Intel Corporation Abstract In ultiple-antenna channels, e optiality of a transission
Indoor Multiple-Antenna Channel Characterization fro to 8 GHz Ada S Y Poon and Minnie Ho Counications and Interconnect Lab, Intel Corporation Abstract In ultiple-antenna channels, e optiality of a transission
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
 Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
SPAN Technology System Characteristics and Performance
 SPAN Technology System Characteristics and Performance NovAtel Inc. ABSTRACT The addition of inertial technology to a GPS system provides multiple benefits, including the availability of attitude output
SPAN Technology System Characteristics and Performance NovAtel Inc. ABSTRACT The addition of inertial technology to a GPS system provides multiple benefits, including the availability of attitude output
Cross Correlation Mitigation Techniques for Software GPS C/A Code Receivers
 International Global Navigation Satellite Systes Society IGNSS Syposiu 27 The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia 4 6 Deceber, 27 Cross Correlation Mitigation Techniques for Software GPS C/A
International Global Navigation Satellite Systes Society IGNSS Syposiu 27 The University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia 4 6 Deceber, 27 Cross Correlation Mitigation Techniques for Software GPS C/A
ELECTROMAGNETIC COVERAGE CALCULATION IN GIS
 ELECTROMAGNETIC COVERAGE CALCULATION IN GIS M. Uit Guusay 1, Alper Sen 1, Uut Bulucu 2, Aktul Kavas 2 1 Yildiz Technical University, Departent of Geodesy and Photograetry Engineering, Besiktas, Istanbul,
ELECTROMAGNETIC COVERAGE CALCULATION IN GIS M. Uit Guusay 1, Alper Sen 1, Uut Bulucu 2, Aktul Kavas 2 1 Yildiz Technical University, Departent of Geodesy and Photograetry Engineering, Besiktas, Istanbul,
Performance Analysis of Reversible Fast Decimal Adders
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Coputer Science 7 WCECS 7, October 4-6, 7, San rancisco, USA Perforance Analysis of Reversible ast Decial Adders Rekha K. Jaes, Shahana T. K., K. Poulose
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Coputer Science 7 WCECS 7, October 4-6, 7, San rancisco, USA Perforance Analysis of Reversible ast Decial Adders Rekha K. Jaes, Shahana T. K., K. Poulose
An orthogonal multi-beam based MIMO scheme. for multi-user wireless systems
 An orthogonal ulti-bea based IO schee for ulti-user wireless systes Dong-chan Oh o and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Electrical Engineering and IC, Seoul ational University Kwana P.O. Box 34, Seoul, 151-600,
An orthogonal ulti-bea based IO schee for ulti-user wireless systes Dong-chan Oh o and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Electrical Engineering and IC, Seoul ational University Kwana P.O. Box 34, Seoul, 151-600,
Additive Synthesis, Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
 Additive Synthesis, Aplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation Pro Eduardo R Miranda Varèse-Gastproessor eduardo.iranda@btinternet.co Electronic Music Studio TU Berlin Institute o Counications Research
Additive Synthesis, Aplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation Pro Eduardo R Miranda Varèse-Gastproessor eduardo.iranda@btinternet.co Electronic Music Studio TU Berlin Institute o Counications Research
Radio Resource Management in a Coordinated Cellular Distributed Antenna System By Using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Radio Resource Manageent in a Coordinated Cellular Distributed Antenna Syste By Using Particle Swar Optiization Oer Haliloglu (1), Cenk Toker (1), Gurhan Bulu (1), Hali Yanikoeroglu (2) (1) Departent of
Radio Resource Manageent in a Coordinated Cellular Distributed Antenna Syste By Using Particle Swar Optiization Oer Haliloglu (1), Cenk Toker (1), Gurhan Bulu (1), Hali Yanikoeroglu (2) (1) Departent of
ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT
 ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT M. Lopatka a, B. Nicolas a, G. Le Touzé a,b, X. Cristol c, B. Chalindar c, J. Mars a, D. Fattaccioli d a GIPSA-Lab /DIS/
ROBUST UNDERWATER LOCALISATION OF ULTRA LOW FREQUENCY SOURCES IN OPERATIONAL CONTEXT M. Lopatka a, B. Nicolas a, G. Le Touzé a,b, X. Cristol c, B. Chalindar c, J. Mars a, D. Fattaccioli d a GIPSA-Lab /DIS/
Phase Noise Modelling and Mitigation Techniques in OFDM Communications Systems
 Phase Noise Modelling and Mitigation Techniques in OFDM Counications Systes Ville Syrjälä, Mikko Valkaa, Nikolay N. Tchaov, and Jukka Rinne Tapere University of Technology Departent of Counications Engineering
Phase Noise Modelling and Mitigation Techniques in OFDM Counications Systes Ville Syrjälä, Mikko Valkaa, Nikolay N. Tchaov, and Jukka Rinne Tapere University of Technology Departent of Counications Engineering
Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar
 17-20 Noveber 2013, Victor Harbor, Australia Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar Han X. Vu (1,2), Sauel J. Davey (1,2), Fiona K. Fletcher (1), Sanjeev Arulapala (1,2), Richard Elle (1)
17-20 Noveber 2013, Victor Harbor, Australia Track-Before-Detect for an Active Towed Array Sonar Han X. Vu (1,2), Sauel J. Davey (1,2), Fiona K. Fletcher (1), Sanjeev Arulapala (1,2), Richard Elle (1)
Utilizing Batch Processing for GNSS Signal Tracking
 Utilizing Batch Processing for GNSS Signal Tracking Andrey Soloviev Avionics Engineering Center, Ohio University Presented to: ION Alberta Section, Calgary, Canada February 27, 2007 Motivation: Outline
Utilizing Batch Processing for GNSS Signal Tracking Andrey Soloviev Avionics Engineering Center, Ohio University Presented to: ION Alberta Section, Calgary, Canada February 27, 2007 Motivation: Outline
Secondary-side-only Simultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynamic Wireless Power Transfer System
 069060 Secondary-side-only Siultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynaic Wireless Power Transfer Syste 6 Giorgio ovison ) Daita Kobayashi ) Takehiro Iura ) Yoichi Hori ) ) The University of Tokyo,
069060 Secondary-side-only Siultaneous Power and Efficiency Control in Dynaic Wireless Power Transfer Syste 6 Giorgio ovison ) Daita Kobayashi ) Takehiro Iura ) Yoichi Hori ) ) The University of Tokyo,
Performance Analysis of an AMC System with an Iterative V-BLAST Decoding Algorithm
 I. J. Counications, Network and Syste Sciences, 008,, 105-06 Published Online May 008 in SciRes (http://www.srpublishing.org/journal/ijcns/). Perforance Analysis of an AMC Syste with an Iterative V-BLAST
I. J. Counications, Network and Syste Sciences, 008,, 105-06 Published Online May 008 in SciRes (http://www.srpublishing.org/journal/ijcns/). Perforance Analysis of an AMC Syste with an Iterative V-BLAST
Interference Management in LTE Femtocell Systems Using Fractional Frequency Reuse
 Interference Manageent in LTE Fetocell Systes Using Fractional Frequency Reuse Poongup Lee and Jitae Shin School of Inforation and Counication Engineering Sungyunwan University, Suwon, 440-746, Korea {poongup,
Interference Manageent in LTE Fetocell Systes Using Fractional Frequency Reuse Poongup Lee and Jitae Shin School of Inforation and Counication Engineering Sungyunwan University, Suwon, 440-746, Korea {poongup,
Comparing structural airframe maintenance strategies based on probabilistic estimates of the remaining useful service life
 22 èe Congrès Français de Mécanique Lyon, 24 au 28 Août 2015 Coparing structural airfrae aintenance strategies based on probabilistic estiates of the reaining useful service life. WAG a, C.GOGU b,.biaud
22 èe Congrès Français de Mécanique Lyon, 24 au 28 Août 2015 Coparing structural airfrae aintenance strategies based on probabilistic estiates of the reaining useful service life. WAG a, C.GOGU b,.biaud
New Adaptive Linear Combination Structure for Tracking/Estimating Phasor and Frequency of Power System
 28 Journal of Electrical Engineering & echnology Vol. 5, No., pp. 28~35, 2 New Adaptive Linear Cobination Structure for racking/estiating Phasor and Frequency of Power Syste Choowong-Wattanasakpubal and
28 Journal of Electrical Engineering & echnology Vol. 5, No., pp. 28~35, 2 New Adaptive Linear Cobination Structure for racking/estiating Phasor and Frequency of Power Syste Choowong-Wattanasakpubal and
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF SMARTPHONE GNSS MEASUREMENTS WITH DIFFERENT ANTENNA CONFIGURATIONS
 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF SMARTPHONE GNSS MEASUREMENTS WITH DIFFERENT ANTENNA CONFIGURATIONS Ranjeeth Siddakatte, Ali Broumandan and Gérard Lachapelle PLAN Group, Department of Geomatics Engineering, Schulich
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF SMARTPHONE GNSS MEASUREMENTS WITH DIFFERENT ANTENNA CONFIGURATIONS Ranjeeth Siddakatte, Ali Broumandan and Gérard Lachapelle PLAN Group, Department of Geomatics Engineering, Schulich
This file is part of the following reference: Access to this file is available from:
 This file is part of the following reference: Page, Geoff (27) Mass Transport Evaluation using consolidated VHF Radar and Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler data. Masters (Research) thesis, Jaes Cook University.
This file is part of the following reference: Page, Geoff (27) Mass Transport Evaluation using consolidated VHF Radar and Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler data. Masters (Research) thesis, Jaes Cook University.
POWER QUALITY ASSESSMENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIMATION NUMERICAL ALGORITHM
 POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
Intermediate-Node Initiated Reservation (IIR): A New Signaling Scheme for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion
 Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
LETTER Adaptive Multi-Stage Parallel Interference Cancellation Receiver for Multi-Rate DS-CDMA System
 IEICE TRANS. COMMUN., VOL.E87 B, NO.8 AUGUST 2004 2401 LETTER Adaptive Multi-Stage Parallel Interference Cancellation Receiver for Multi-Rate DS-CDMA Syste Seung Hee HAN a), Student Meber and Jae Hong
IEICE TRANS. COMMUN., VOL.E87 B, NO.8 AUGUST 2004 2401 LETTER Adaptive Multi-Stage Parallel Interference Cancellation Receiver for Multi-Rate DS-CDMA Syste Seung Hee HAN a), Student Meber and Jae Hong
Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynamic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
 Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 5 Seville, Spain, Deceber -5, 5 WeIC8. Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynaic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, and the European Control Conference 5 Seville, Spain, Deceber -5, 5 WeIC8. Robust Acceleration Control of Electrodynaic Shaker Using µ Synthesis
David Carruthers 1, Xiangyu Sheng 2, Emilie Vanvyve 1
 REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS FOR DISPERSION MODELLING IN TAIWAN INCLUDING THE USE OF ADMS David Carruthers 1, Xiangyu Sheng, Eilie Vanvyve 1 1 CERC, 3 King s Parade, Cabridge CB 1SJ, UK Scott Wilson, Michael
REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS FOR DISPERSION MODELLING IN TAIWAN INCLUDING THE USE OF ADMS David Carruthers 1, Xiangyu Sheng, Eilie Vanvyve 1 1 CERC, 3 King s Parade, Cabridge CB 1SJ, UK Scott Wilson, Michael
Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaker Arrays
 Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaer Arrays Fotios Kontoichos, Nicolas Alexander Tatlas, and John Mourjopoulos Audio and Acoustic Technology Group, Wire Counications Laboratory, Electrical
Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaer Arrays Fotios Kontoichos, Nicolas Alexander Tatlas, and John Mourjopoulos Audio and Acoustic Technology Group, Wire Counications Laboratory, Electrical
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE HARTEBEESTHOEK94 CO-ORDINATE SYSTEM IN SOUTH AFRICA
 THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE HARTEBEESTHOEK94 CO-ORDINATE SYSTEM IN SOUTH AFRICA Richard Wonnacott Chief Directorate : Surveys and Mapping South Africa ABSTRACT : The Hartebeesthoek94 co-ordinate syste becae
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE HARTEBEESTHOEK94 CO-ORDINATE SYSTEM IN SOUTH AFRICA Richard Wonnacott Chief Directorate : Surveys and Mapping South Africa ABSTRACT : The Hartebeesthoek94 co-ordinate syste becae
Multitarget Direction Measurement Based on Bistatic Radar
 Sensors & ransducers Vol. 70 Issue 5 May 204 pp. 65-70 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co Multitarget Direction Measureent Based on Bistatic Radar Yubao ou School
Sensors & ransducers Vol. 70 Issue 5 May 204 pp. 65-70 Sensors & ransducers 204 by IFSA Publishing S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.co Multitarget Direction Measureent Based on Bistatic Radar Yubao ou School
FORWARD MASKING THRESHOLD ESTIMATION USING NEURAL NETWORKS AND ITS APPLICATION TO PARALLEL SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
 FORWARD MASKING THRESHOLD ESTIMATION USING NEURAL NETWORKS AND ITS APPLICATION TO PARALLEL SPEECH ENHANCEMENT T. S. GUNAWAN 1, O. O. KHALIFA 1, E. AMBIKAIRAJAH 2 1 Electrical and Coputer Engineering Departent,
FORWARD MASKING THRESHOLD ESTIMATION USING NEURAL NETWORKS AND ITS APPLICATION TO PARALLEL SPEECH ENHANCEMENT T. S. GUNAWAN 1, O. O. KHALIFA 1, E. AMBIKAIRAJAH 2 1 Electrical and Coputer Engineering Departent,
NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS
 NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Machine Design and Control Systes Section National Technical
NONLINEAR WAVELET PACKET DENOISING OF IMPULSIVE VIBRATION SIGNALS NIKOLAOS G. NIKOLAOU, IOANNIS A. ANTONIADIS Departent of Mechanical Engineering, Machine Design and Control Systes Section National Technical
Multicarrier Interleave-Division Multiple Access Communication in Multipath Channels
 Multicarrier Interleave-Division Multiple Access Counication in Multipath Channels Habib ur Rehan *, Muhaad Naee **, Iran Zaa *, Syed Isail Shah ** * Center for Advanced Studies in Engineering (CASE) Islaabad
Multicarrier Interleave-Division Multiple Access Counication in Multipath Channels Habib ur Rehan *, Muhaad Naee **, Iran Zaa *, Syed Isail Shah ** * Center for Advanced Studies in Engineering (CASE) Islaabad
HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE
 HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE T.W. Murray, O. Balogun, and N. Pratt Departent of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Boston University, Boston MA 0225 Abstract:
HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE T.W. Murray, O. Balogun, and N. Pratt Departent of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Boston University, Boston MA 0225 Abstract:
Detection of Faults in Power System Using Wavelet Transform and Independent Component Analysis
 Detection of Faults in Power Syste Using Wavelet Transfor and Independent Coponent Analysis 1 Prakash K. Ray, 2 B. K. Panigrahi, 2 P. K. Rout 1 Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, IIIT, Bhubaneswar,
Detection of Faults in Power Syste Using Wavelet Transfor and Independent Coponent Analysis 1 Prakash K. Ray, 2 B. K. Panigrahi, 2 P. K. Rout 1 Dept. of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, IIIT, Bhubaneswar,
Dynamic Model Displacement for Model-mediated Teleoperation
 Dynaic Model Displaceent for Model-ediated Teleoperation Xiao Xu Giulia Paggetti Eckehard Steinbach Institute for Media Technology, Technische Universität München, Munich, Gerany ABSTRACT In this paper,
Dynaic Model Displaceent for Model-ediated Teleoperation Xiao Xu Giulia Paggetti Eckehard Steinbach Institute for Media Technology, Technische Universität München, Munich, Gerany ABSTRACT In this paper,
Overlapped frequency-time division multiplexing
 April 29, 16(2): 8 13 www.sciencedirect.co/science/journal/158885 he Journal of China Universities of Posts and elecounications www.buptjournal.cn/xben Overlapped frequency-tie division ultiplexing JIANG
April 29, 16(2): 8 13 www.sciencedirect.co/science/journal/158885 he Journal of China Universities of Posts and elecounications www.buptjournal.cn/xben Overlapped frequency-tie division ultiplexing JIANG
Real-Time Attitude Determination of a Nanosatellite Using GPS Signal-to-Noise Ratio Observations
 Real-Tie Attitude Deterination of a Nanosatellite Using GPS Signal-to-Noise Ratio Oservations The University of Teas at Austin Shaun M. Stewart Greg N. Holt FASTRAC Mission Foration Autonoy Spacecraft
Real-Tie Attitude Deterination of a Nanosatellite Using GPS Signal-to-Noise Ratio Oservations The University of Teas at Austin Shaun M. Stewart Greg N. Holt FASTRAC Mission Foration Autonoy Spacecraft
This is an author-deposited version published in: Eprints ID: 5737
 Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and akes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Open Archive Toulouse Archive Ouverte (OATAO) OATAO is an open access repository that collects the work of Toulouse researchers and akes it freely available over the web where possible. This is an author-deposited
Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response
 Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response Thoas Kaalakis, Thoas Sphicopoulos and Diitris Syvridis (Departent of Inforatics and Telecounications, University of Athens, Panepistiiopolis,
Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response Thoas Kaalakis, Thoas Sphicopoulos and Diitris Syvridis (Departent of Inforatics and Telecounications, University of Athens, Panepistiiopolis,
Impact of the Reactive Power Compensation on Harmonic Distortion Level
 pact of the Reactive Power Copensation on Haronic Distortion Level J. A. M. eto,. C. Jesus, L. L. Piesanti Departaento de Tecnologia Universidade Regional do oroeste do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul juí
pact of the Reactive Power Copensation on Haronic Distortion Level J. A. M. eto,. C. Jesus, L. L. Piesanti Departaento de Tecnologia Universidade Regional do oroeste do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul juí
Efficient Non-linear Changed Mel-filter Bank VAD Algorithm
 Matheatical Models and Methods in Modern Science Efficient on-linear Changed Mel-filter Bank VAD Algorith DAMJA VLAJ, ZDRAVKO KAČIČ, MARKO KOS Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Coputer Science University
Matheatical Models and Methods in Modern Science Efficient on-linear Changed Mel-filter Bank VAD Algorith DAMJA VLAJ, ZDRAVKO KAČIČ, MARKO KOS Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Coputer Science University
Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium Claims, Targets, and Standard Alignment for Math
 Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu Clais, s, Stard Alignent for Math The Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu (SBAC) has created a hierarchy coprised of clais targets that together can be used to ake stateents
Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu Clais, s, Stard Alignent for Math The Sarter Balanced Assessent Consortiu (SBAC) has created a hierarchy coprised of clais targets that together can be used to ake stateents
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops October 11, 2006
 Experient 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase ocked oops October 11, 2006 Frequency Modulation Norally, we consider a voltage wave for with a fixed frequency of the for v(t) = V sin(ω c t + θ), (1) where
Experient 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase ocked oops October 11, 2006 Frequency Modulation Norally, we consider a voltage wave for with a fixed frequency of the for v(t) = V sin(ω c t + θ), (1) where
Yield Enhancement Techniques for 3D Memories by Redundancy Sharing among All Layers
 Yield Enhanceent Techniques for 3D Meories by Redundancy Sharing aong All Layers Joohwan Lee, Kihyun Park, and Sungho Kang Three-diensional (3D) eories using through-silicon vias (TSVs) will likely be
Yield Enhanceent Techniques for 3D Meories by Redundancy Sharing aong All Layers Joohwan Lee, Kihyun Park, and Sungho Kang Three-diensional (3D) eories using through-silicon vias (TSVs) will likely be
Parameter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB
 Paraeter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB Mato Fruk, Goran Vujisić, Toislav Špoljarić Departent of Electrical Engineering The Polytechnic of Zagreb Konavoska, Zagreb, Croatia ato.fruk@tvz.hr,
Paraeter Identification of Transfer Functions Using MATLAB Mato Fruk, Goran Vujisić, Toislav Špoljarić Departent of Electrical Engineering The Polytechnic of Zagreb Konavoska, Zagreb, Croatia ato.fruk@tvz.hr,
Optimal Modulation Index of the Mach-Zehnder Modulator in a Coherent Optical OFDM System Employing Digital Predistortion
 Optial Modulation Index of the Mach-Zehnder Modulator in a Coherent Optical OFDM yste Eploying Digital redistortion David Rörich, Xiaojie Wang, Michael Bernhard, Joachi peidel Universität tuttgart, Institut
Optial Modulation Index of the Mach-Zehnder Modulator in a Coherent Optical OFDM yste Eploying Digital redistortion David Rörich, Xiaojie Wang, Michael Bernhard, Joachi peidel Universität tuttgart, Institut
Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity
 Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity Aravind Kailas School of Electrical and Coputer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 3033-050,
Investigating Multiple Alternating Cooperative Broadcasts to Enhance Network Longevity Aravind Kailas School of Electrical and Coputer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology Atlanta, Georgia 3033-050,
Study and Implementation of Complementary Golay Sequences for PAR reduction in OFDM signals
 Study and Ipleentation of Copleentary Golay Sequences for PAR reduction in OFDM signals Abstract In this paper soe results of PAR reduction in OFDM signals and error correction capabilities by using Copleentary
Study and Ipleentation of Copleentary Golay Sequences for PAR reduction in OFDM signals Abstract In this paper soe results of PAR reduction in OFDM signals and error correction capabilities by using Copleentary
Torsion System. Encoder #3 ( 3 ) Third encoder/disk for Model 205a only. Figure 1: ECP Torsion Experiment
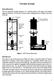 Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Keywords: Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance, Finite Element, Inrush Current.
 Discriination of Inrush fro Fault Currents in Power Transforers Based on Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance Technique Coupled with Finite Eleent Method Downloaded fro ijeee.iust.ac.ir at 5:47 IRST on
Discriination of Inrush fro Fault Currents in Power Transforers Based on Equivalent Instantaneous Inductance Technique Coupled with Finite Eleent Method Downloaded fro ijeee.iust.ac.ir at 5:47 IRST on
REPORT ITU-R SA Telecommunication characteristics and requirements for space VLBI systems
 Rep. ITU-R SA.2132 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2132 Telecounication characteristics and requireents for space VLBI systes (2008) This Report describes the characteristics of the space VLBI systes. These characteristics
Rep. ITU-R SA.2132 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2132 Telecounication characteristics and requireents for space VLBI systes (2008) This Report describes the characteristics of the space VLBI systes. These characteristics
Distributed Power Delivery for Energy Efficient and Low Power Systems
 Distributed Power Delivery for Energy Efficient and Low Power Systes Selçuk Köse Departent of Electrical Engineering University of South Florida Tapa, Florida 33620 kose@usf.edu Eby G. Friedan Departent
Distributed Power Delivery for Energy Efficient and Low Power Systes Selçuk Köse Departent of Electrical Engineering University of South Florida Tapa, Florida 33620 kose@usf.edu Eby G. Friedan Departent
A Novel TDS-FDMA Scheme for Multi-User Uplink Scenarios
 A Novel TDS-FDMA Schee for Multi-User Uplink Scenarios Linglong Dai, Zhaocheng Wang, Jun Wang, and Zhixing Yang Tsinghua National Laboratory for Inforation Science and Technology, Electronics Engineering
A Novel TDS-FDMA Schee for Multi-User Uplink Scenarios Linglong Dai, Zhaocheng Wang, Jun Wang, and Zhixing Yang Tsinghua National Laboratory for Inforation Science and Technology, Electronics Engineering
A New Simple Model for Land Mobile Satellite Channels
 A New Siple Model for Land Mobile Satellite Channels A. Abdi, W. C. Lau, M.-S. Alouini, and M. Kaveh Dept. of Elec. and Cop. Eng., University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Eails: {abdi, wlau, alouini,
A New Siple Model for Land Mobile Satellite Channels A. Abdi, W. C. Lau, M.-S. Alouini, and M. Kaveh Dept. of Elec. and Cop. Eng., University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455 Eails: {abdi, wlau, alouini,
Modeling and Parameter Identification of a DC Motor Using Constraint Optimization Technique
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volue 3, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 206), PP 46-56 www.iosrjournals.org Modeling and Paraeter Identification
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volue 3, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov. - Dec. 206), PP 46-56 www.iosrjournals.org Modeling and Paraeter Identification
Statistical Singing Voice Conversion with Direct Waveform Modification based on the Spectrum Differential
 INTERSPEECH 2014 Statistical Singing Voice Conversion with Direct Wavefor Modification based on the Spectru Differential Kazuhiro Kobayashi, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura Graduate
INTERSPEECH 2014 Statistical Singing Voice Conversion with Direct Wavefor Modification based on the Spectru Differential Kazuhiro Kobayashi, Tooki Toda, Graha Neubig, Sakriani Sakti, Satoshi Nakaura Graduate
Compensated Single-Phase Rectifier
 Copensated Single-Phase Rectifier Jānis DoniĦš Riga Technical university jdonins@gail.co Abstract- Paper describes ethods of rectified DC pulsation reduction adding a ensation node to a single phase rectifier.
Copensated Single-Phase Rectifier Jānis DoniĦš Riga Technical university jdonins@gail.co Abstract- Paper describes ethods of rectified DC pulsation reduction adding a ensation node to a single phase rectifier.
Waveform Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar
 Wavefor Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar John Jakabosky and Shannon D. Blunt Radar Systes Lab University of Kansas Lawrence, KS Braha Hied Sensors Directorate Air Force
Wavefor Design and Receive Processing for Nonrecurrent Nonlinear FMCW Radar John Jakabosky and Shannon D. Blunt Radar Systes Lab University of Kansas Lawrence, KS Braha Hied Sensors Directorate Air Force
Vector tracking loops are a type
 GNSS Solutions: What are vector tracking loops, and what are their benefits and drawbacks? GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are
GNSS Solutions: What are vector tracking loops, and what are their benefits and drawbacks? GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are
