Feasibility study of the marine electromagnetic remote sensing (MEMRS) method for nearshore
|
|
|
- Ashlyn Johnson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Feasibility study of the marine electromagnetic remote sensing (MEMRS) method for nearshore exploration Daeung Yoon* University of Utah, and Michael S. Zhdanov, University of Utah and TechnoImaging Summary Marine controlled source electromagnetic (MCSEM) surveys have become an important part of offshore petroleum exploration. However, there exist very nearshore areas, with the depth varying from tens of meters to a few hundred meters, where it is technically difficult to use a towed electrical bipole transmitter. In some cases, the operating of the controlled electric sources in the nearshore zones is prohibited by the environmental concerns of the impact of the powerful electric current on the marine fauna. To address the needs of EM exploration in the nearshore zones, a new marine EM method has been recently developed, which is called marine electromagnetic remote sensing (MEMRS). This method consists of a very high moment onshore electric bipole transmitter and a large array of offshore receivers. In this paper we present a feasibility study of the MEMRS method. Introduction During recent years marine controlled source electromagnetic (MCSEM) surveys have become intensively used for offshore petroleum exploration (e.g., Hesthammer et al., 2010, 2011; Gabrielsen et al., 2013). However, there exist very near-shore areas, with the depth varying from tens of meters to a few hundred meters, where it is technically difficult to use a towed electrical bipole transmitter. In some cases, the operating of the controlled electric sources in the near-shore zones is prohibited by the environmental concerns of the impact of the powerful electric current on the marine fauna. To address the needs of EM exploration in the near-shore zones, a new marine EM method has been recently developed by Velikhov and Zhdanov (2011), which is called marine electromagnetic remote sensing (MEMRS). This method consists of a very high moment onshore transmitter located on the coast with a large array of offshore receivers. Simplified conceptual model of MEMRS is shown in Figure 1. In this paper we present a feasibility study of the MEMRS method for near-shore HC reservoir exploration based on the numerical modeling of the EM response in the arrays of near-shore receivers. We have also developed a method of 3D inversion of MEMRS data which uses a rigorous integral equation (IE) based forward modeling and regularized focusing inversion algorithm (Zhdanov, 2002, 2009). We present in this paper the preliminary results of the application of the developed inversion method to the interpretation of the synthetic MEMRS data collected by the near-shore receivers. Integral equation method in a model with inhomogeneous background conductivity We consider, first, the typical MEMRS survey consisting of a set of sea-bottom electrical and magnetic receivers and a fixed horizontal electric dipole transmitter located onshore. The transmitter generates a frequency domain EM field. The operating frequencies are usually selected to be low enough (in a range of Hz) to propagate through the conductive sea water and sea-bottom layers of the sediments and to illuminate the sea-bottom geological structures. In order to take into account the transition zone from the land to the marine geoelectrical sections, we apply the IE method with inhomogeneous background conductivity (IBC) (Zhdanov et. al., 2006; Zhdanov, 2009). We consider a 3D geoelectrical model with horizontally layered (normal) conductivity,, inhomogeneous background conductivity,, within a domain, and anomalous conductivity,, within a domain. The EM field in this model can be represented as a sum of the normal fields,,, generated by the given source(s) in the model with normal distribution of conductivity,, a variable background effect,,, produced by the inhomogeneous background conductivity,, and the anomalous fields,, due to the anomalous conductivity distribution,, as: The total EM field in this model can be written as: where the background EM field, is a sum of the normal fields and those caused by the inhomogeneous background conductivity: Following the paper by Zhdanov et al. (2006), we write the integral representations for the electric fields of the given current distribution, within a medium of normal conductivity, : ( ) ( ) SEG Houston 2013 Annual Meeting Page 755
2 where the first integral term describes the excess part of the background fields generated by the excess currents in the inhomogeneous background domain, : ( ) and the second term describes the anomalous fields generated by the anomalous domain, : ( ) In the last equations, the symbols denote the electric Greens operators with a volume integration of or, respectively. Using integral expression 4, one can calculate the electric field at any point if the electric field is known within the inhomogeneity. Similar expression can be obtained for the magnetic field as well. Expression 4 becomes the integral equation for the electric field E(r) if. This equation can be solved using the standard IE approach (e.g., Zhdanov, 2009). Figure 1: A simplified conceptual model of the MEMRS survey Solution of the inverse problem for the models with inhomogeneous background conductivity We use integral equations (4) to formulate both the forward and inverse problems of the MEMRS method. Indeed, in short form these equations can be written as: where is a forward modeling operator, stands for the observed EM data in the sea-bottom receivers, and is a vector formed by the anomalous conductivities within the targeted domain. The inversion is based on minimization of the Tikhonov parametric functional,, with the focusing stabilizer (Zhdanov, 2002): There are several different possible choices for the stabilizer. In this paper we use the minimum vertical support stabilizer, which is specially designed to invert for a thin, subhorizontal structure typical for HC reservoirs, and is defined by the formula: [ ] where S is a horizontal section of the rectangular domain V. We use the regularized conjugate gradient (RCG) algorithm for minimization of the parametric functional (Zhdanov, 2002). The critical element of the RCG inversion is computing the Fréchet derivative of the forward modeling operator. Direct computation of the Fréchet derivative is very time consuming even when the reciprocity principle is utilized. It was demonstrated in the paper by Gribenko and Zhdanov (2007) for MCSEM data inversion that the number of forward modeling can be reduced to one on every iteration step if we compute the Fréchet derivative using the modified form of the quasianalytical (QA) approximation with the variable background conductivity or using the quasi-born approximation (Zhdanov, 2009). In this case, no extra computation is required to compute the Fréchet derivative. Figure 2: Geoelectrical model consists of a sea water layer with a thickness of 200m, a resistivity of 0.3 Ohm-m, and homogeneous sea-bottom sediments with a resistivity of 1 Ohm-m, and a resistive basement with a resistivity of 1,000 Ohm-m. An oval shape reservoir is located at a depth of 1.6 km below the sea level with the resistivity of 100 Ohm-m, a thickness of 200 m. SEG Houston 2013 Annual Meeting Page 756
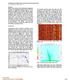
3 Figure 3: The maps of the absolute values of the y- component of anomalous electric field, normalized by the absolute values of the horizontal component of the background electric field at a frequency of Hz. Panel a shows the noise free data; panel b presents the same data contaminated with the 8% noise; panels c, d, e, and f present the data obtained as a result of 5, 10, 20, and 40 times stacked noisy data. Synthetic MEMRS data inversion We have investigated several models of near-shore MEMRS surveys. In the majority of these model studies we have considered an electric bipole transmitter parallel to the coast with a large array of offshore electric field receivers. A simplified conceptual model of the MEMRS survey is shown in Figure 1. In the first set of numerical experiments, we assume that a synthetic MEMRS survey is conducted in relatively shallow water with a sea depth of 200 m. The survey consists of 41 x 25 = 1025 sea-bottom electric receivers with 500 m and 1000 m separations in the x and y directions, respectively. The electric bipole transmitter of 5 km length is located onshore, 250 m inland from the coast. The transmitter generates a frequency domain EM field in the frequencies range from to 1 Hz. The background geoelectrical model consists of a sea water layer with a thickness of 200 m, a resistivity of 0.3 Ohm-m, and homogeneous sea-bottom sediments with a resistivity of 1 Ohm-m, and a resistive basement with a resistivity of 1,000 Ohm-m (Figure 2). There is an oval shape reservoir located in the sea-bottom sediments at a depth of 1.6 km below the sea level with the resistivity of 100 Ohm-m, a thickness of 200 m, and horizontal maximum and minimum dimensions of 10 km by 5 km. First, we have computed the synthetic observed data for this survey, using the IE IBC method. We have also contaminated the data with 8% random noise. In Figure 3 we plot the maps of absolute values of the y-component of anomalous electric field,, normalized by the absolute value of the horizontal component of the background electric field,. We have also computer simulated the data acquisition with repeated measurements for the same position of the transmitter and receivers, which allows us to apply stacking to the observed data. Panels c, d, e, and f in Figure 3 present the data obtained as a result of 5, 10, 20, and 40 times stacked noisy data. One can see how stacking improves the signature of the reservoir in the observed data. We have run inversions for all these synthetic data sets. Figures 4 and 5 show a comparison between the inversion results for the noise free data, for the data contaminated with 8% random noise, and for the noisy data stacked 40 times, respectively. One can see how the inverse images are improved as a result of stacking the data. Figure 4: Comparison between the inversion result for the noise free data (left panel), and the data contaminated with 8% random noise (right panel). We have investigated also the effect of the number of the receivers on the resolution of the inverse images. The original survey consisted of 41 x 25 = 1025 sea-bottom electric receivers with 500 m and 1000 m separations in the x and y directions, respectively. First, we have modified this survey by reducing the number of the receivers and considering 11 x 13 = 143 sea-bottom electric receivers with 2000 m and 2000 m separations in the x and y directions. The corresponding inversion results are shown in Figure 6. Next, we consider a survey with 7 x 9 = 63 seabottom electric receivers with 3000 m and 3000 m separations in the x and y directions. We still can see the location of the resistive reservoir in the inverse images (Figure 7). SEG Houston 2013 Annual Meeting Page 757
4 Finally, we have reduced the receiver s number to only 5 x 5 = 25 receivers. The inverse image of the reservoir is distorted, but still it can be seen in almost correct position (Figure 8). Conclusions We have conducted a feasibility study of marine electromagnetic remote sensing (MEMRS) method of EMled exploration in environmentally sensitive offshore setting with the fixed onshore electric bipole transmitter and array of the offshore sea-bottom receivers. Our study demonstrates that the signal-to-noise ratio can be increased by stacking the signal in the multiple receivers. We have developed a rigorous method for 3D inversion of MEMRS data based on the integral equation formulation. This method can be used for interpretation of field MEMRS data collected for offshore petroleum exploration. We have tested this method on a simple geoelectrical model, simulating the typical transmitter-receiver layout which can be used for the practical EM acquisition. Our modeling study shows that the MEMRS method is very robust to the noise, and it does not require a large number of the sea-bottom receivers in order to locate the resistive HC reservoir near-shore. Acknowledgments The authors acknowledge the support of the University of Utah Consortium for Electromagnetic Modeling and Inversion (CEMI), and TechnoImaging. We also thank Alex Gribenko for his assistance with the developing the inversion code, and Masashi Endo and Noel Black for their assistance with this research. Figure 5: Comparison between the inversion result for the noise free data (left panel), and for the noisy data stacked 40 times (right panel). Figure 6: Horizontal and vertical sections of the inverse resistivity model generated for a survey with 11 x 13 = 143 sea-bottom electric receivers for the noise free data (left panel) and for the noisy data stacked 40 times (right panel). Figure 7: Horizontal and vertical sections of the inverse resistivity model generated for a survey with 7 x 9 = 63 sea-bottom electric receivers for the noise free data (left panel) and for the noisy data stacked 40 times (right panel). Figure 8: Horizontal and vertical sections of the inverse resistivity model generated for a survey with 5 x 5 = 25 sea-bottom electric receivers for the noise free data (left panel) and for the noisy data stacked 40 times (right panel). SEG Houston 2013 Annual Meeting Page 758
5 EDITED REFERENCES Note: This reference list is a copy-edited version of the reference list submitted by the author. Reference lists for the 2013 SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts have been copy edited so that references provided with the online metadata for each paper will achieve a high degree of linking to cited sources that appear on the Web. REFERENCES Gabrielsen, P. T., P. Abrahamson, M. Panzner, S. Fanavoll, and S. Ellingsrud, 2013, Exploring frontier areas using 2D seismic and 3D CSEM data, as exemplified by multi-client data over the Skrugard and Havis discoveries in the Barents Sea: First Break, 31, Gribenko, A., and M. S. Zhdanov, 2007, Rigorous 3D inversion of marine CSEM data based on the integral equation method: Geophysics, 72, no. 2, WA73 WA84, Hesthammer, J., A. Stefatos, M. Boulaenko, S. Fanavoll, and J. Danielsen, 2010, CSEM performance in light of well results: The Leading Edge, 29, 34 41, Hesthammer, J., J. I. Rykkelid, S. Sperrevik, and D. Cumming, 2011, Use of CSEM data to aid a revised interpretation from the Norwegian Sea: First Break, 29, Velikhov, E. P., and M. S. Zhdanov, 2011, Systems and methods for measuring sea-bed resistivity: US Patent No. 7,969,152. Zhdanov, M. S., 2002, Geophysical inverse theory and regularization problems: Elsevier. Zhdanov, M. S., 2009, Geophysical electromagnetic theory and methods: Elsevier. Zhdanov, M. S., S. K. Lee, and K. Yoshioka, 2006, Integral equation method for 3-D modeling of electromagnetic fields in complex structures with inhomogeneous background conductivity: Geophysics, 71, no. 6, G333 G345, SEG Houston 2013 Annual Meeting Page 759
FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ELECTROMAGNETIC (FDEM) MIGRATION OF MCSEM DATA SUMMARY
 Three-dimensional electromagnetic holographic imaging in offshore petroleum exploration Michael S. Zhdanov, Martin Čuma, University of Utah, and Takumi Ueda, Geological Survey of Japan (AIST) SUMMARY Off-shore
Three-dimensional electromagnetic holographic imaging in offshore petroleum exploration Michael S. Zhdanov, Martin Čuma, University of Utah, and Takumi Ueda, Geological Survey of Japan (AIST) SUMMARY Off-shore
Enhanced subsurface response for marine CSEM surveying Frank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA
 rank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA Summary A new robust method for enhancing marine CSEM subsurface response is presented. The method is demonstrated to enhance resolution and depth penetration
rank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA Summary A new robust method for enhancing marine CSEM subsurface response is presented. The method is demonstrated to enhance resolution and depth penetration
G003 Data Preprocessing and Starting Model Preparation for 3D Inversion of Marine CSEM Surveys
 G003 Data Preprocessing and Starting Model Preparation for 3D Inversion of Marine CSEM Surveys J.J. Zach* (EMGS ASA), F. Roth (EMGS ASA) & H. Yuan (EMGS Americas) SUMMARY The marine controlled-source electromagnetic
G003 Data Preprocessing and Starting Model Preparation for 3D Inversion of Marine CSEM Surveys J.J. Zach* (EMGS ASA), F. Roth (EMGS ASA) & H. Yuan (EMGS Americas) SUMMARY The marine controlled-source electromagnetic
A Method of Mapping Resistive or Conductive offshore Targets also an Apparatus for Applying the Method
 A Method of Mapping Resistive or Conductive offshore Targets also an Apparatus for Applying the Method BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention is related to a method
A Method of Mapping Resistive or Conductive offshore Targets also an Apparatus for Applying the Method BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention is related to a method
Qingdao , China. Qingdao , China. Beijing , China *Corresponding author
 017 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Automation (AMMA 017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-479-0 Comparison of Simulated Results of Deployed and Towed Undersea Dipole Sources in Marine
017 3rd International Conference on Applied Mechanics and Mechanical Automation (AMMA 017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-479-0 Comparison of Simulated Results of Deployed and Towed Undersea Dipole Sources in Marine
1. Purpose of the survey
 Specifications of Trend Survey on Non-seismic Geophysical Survey Methods and Applications in Oil and Gas Exploration May, 22, 2017 Technical Department Oil & Gas Upstream Technology Unit Japan Oil, Gas
Specifications of Trend Survey on Non-seismic Geophysical Survey Methods and Applications in Oil and Gas Exploration May, 22, 2017 Technical Department Oil & Gas Upstream Technology Unit Japan Oil, Gas
Tu LHR1 07 MT Noise Suppression for Marine CSEM Data
 Tu LHR1 7 MT Noise Suppression for Marine CSEM Data K.R. Hansen* (EMGS ASA), V. Markhus (EMGS ASA) & R. Mittet (EMGS ASA) SUMMARY We present a simple and effective method for suppression of MT noise in
Tu LHR1 7 MT Noise Suppression for Marine CSEM Data K.R. Hansen* (EMGS ASA), V. Markhus (EMGS ASA) & R. Mittet (EMGS ASA) SUMMARY We present a simple and effective method for suppression of MT noise in
Marine time domain CSEM Growth of and Old/New Technology
 KMS Technologies KJT Enterprises Inc. An EMGS/RXT company Marine time domain CSEM Growth of and Old/New Technology Allegar, N., Strack, K.-M., Mittet, R., Petrov, A., and Thomsen, L. EAGE Rome 2008 Annual
KMS Technologies KJT Enterprises Inc. An EMGS/RXT company Marine time domain CSEM Growth of and Old/New Technology Allegar, N., Strack, K.-M., Mittet, R., Petrov, A., and Thomsen, L. EAGE Rome 2008 Annual
Th N Robust and Fast Data-Driven MT processing
 Th N105 04 Robust and Fast Data-Driven MT processing V. Markhus* (EMGS), M. Calvert (EMGS), L. Uri (EMGS) & C. Twarz (EMGS) SUMMARY We present marine magnetotelluric (MT) results from data extracted from
Th N105 04 Robust and Fast Data-Driven MT processing V. Markhus* (EMGS), M. Calvert (EMGS), L. Uri (EMGS) & C. Twarz (EMGS) SUMMARY We present marine magnetotelluric (MT) results from data extracted from
A marine EM survey of the Scarborough gas field, Northwest Shelf of Australia
 first break volume 28, May 2010 special topic A marine EM survey of the Scarborough gas field, Northwest Shelf of Australia David Myer, Steven Constable * and Kerry Key of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography
first break volume 28, May 2010 special topic A marine EM survey of the Scarborough gas field, Northwest Shelf of Australia David Myer, Steven Constable * and Kerry Key of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography
Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS
 Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS Summary Sub-basalt imaging continues to provide a challenge along the northwest European Atlantic
Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS Summary Sub-basalt imaging continues to provide a challenge along the northwest European Atlantic
& DEVELOPMENT S PECIAL. Report. New Views of the Subsurface
 A novel use of marine controlled source electromagnetic sounding techniques (CSEM), called seabed logging, may cut exploration costs in deepsea areas. The method has been tested off West Africa in 2 and
A novel use of marine controlled source electromagnetic sounding techniques (CSEM), called seabed logging, may cut exploration costs in deepsea areas. The method has been tested off West Africa in 2 and
Electromagnetic Induction
 Electromagnetic Induction Recap the motivation for using geophysics We have problems to solve Slide 1 Finding resources Hydrocarbons Minerals Ground Water Geothermal Energy SEG Distinguished Lecture slide
Electromagnetic Induction Recap the motivation for using geophysics We have problems to solve Slide 1 Finding resources Hydrocarbons Minerals Ground Water Geothermal Energy SEG Distinguished Lecture slide
Controlled-source electromagnetic sounding in shallow water: Principles and applications
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 73, NO. 1 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2008 ; P. F21 F32, 20 FIGS. 10.1190/1.2815721 Controlled-source electromagnetic sounding in shallow water: Principles and applications David Andréis 1 and Lucy
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 73, NO. 1 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2008 ; P. F21 F32, 20 FIGS. 10.1190/1.2815721 Controlled-source electromagnetic sounding in shallow water: Principles and applications David Andréis 1 and Lucy
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation
 WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG)
 Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Joint MT/CSEM Anisotropic Inversion Olympic Dam
 Joint MT/CSEM Anisotropic Inversion Olympic Dam T.J. Ritchie* P.A. Rowston* Practical 1 Day Workshop Geophysical Inversion for Mineral Explorers * Geophysical Resources and Services Pty. Ltd. Brisbane
Joint MT/CSEM Anisotropic Inversion Olympic Dam T.J. Ritchie* P.A. Rowston* Practical 1 Day Workshop Geophysical Inversion for Mineral Explorers * Geophysical Resources and Services Pty. Ltd. Brisbane
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo
 Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
1D inversion of multicomponent, multifrequency marine CSEM data: Methodology and synthetic studies for resolving thin resistive layers
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 7, NO. MARCH-APRIL 9; P. F9 F, FIGS..9/.58 D inversion of multicomponent, multifrequency marine CSEM data: Methodology and synthetic studies for resolving thin resistive layers Kerry Key
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 7, NO. MARCH-APRIL 9; P. F9 F, FIGS..9/.58 D inversion of multicomponent, multifrequency marine CSEM data: Methodology and synthetic studies for resolving thin resistive layers Kerry Key
The controlled-source electromagnetic (CSEM) method
 Optimizing EM data acquisition for continental shelf exploration N. D. BARKER, J. P. MORTEN, and D. V. SHANTSEV, EMGS The controlled-source electromagnetic (CSEM) method has been applied to oil and gas
Optimizing EM data acquisition for continental shelf exploration N. D. BARKER, J. P. MORTEN, and D. V. SHANTSEV, EMGS The controlled-source electromagnetic (CSEM) method has been applied to oil and gas
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
Modeling of Antenna for Deep Target Hydrocarbon Exploration
 Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 2012, 4, 30-41 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jemaa.2012.41005 Published Online January 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) Modeling of Antenna for
Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 2012, 4, 30-41 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jemaa.2012.41005 Published Online January 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) Modeling of Antenna for
Seabed logging heads advances in long-offset electromagnetic surveying
 Seabed logging heads advances in long-offset electromagnetic surveying Terje Eidesmo Svein Ellingsrud Ståle E. Johansen Rune Mittet Electromagnetic Geoservices AS Trondheim, Norway This document is a reprint
Seabed logging heads advances in long-offset electromagnetic surveying Terje Eidesmo Svein Ellingsrud Ståle E. Johansen Rune Mittet Electromagnetic Geoservices AS Trondheim, Norway This document is a reprint
POLITECNICO DI MILANO. POLO TERRITORIALE DI COMO School of Civil, Environmental and Land Management Engineering
 POLITECNICO DI MILANO POLO TERRITORIALE DI COMO School of Civil, Environmental and Land Management Engineering Master of Science in Environmental and Geomatic Engineering Investigation of the Asymmetry
POLITECNICO DI MILANO POLO TERRITORIALE DI COMO School of Civil, Environmental and Land Management Engineering Master of Science in Environmental and Geomatic Engineering Investigation of the Asymmetry
Summary. Methodology. Selected field examples of the system included. A description of the system processing flow is outlined in Figure 2.
 Halvor Groenaas*, Svein Arne Frivik, Aslaug Melbø, Morten Svendsen, WesternGeco Summary In this paper, we describe a novel method for passive acoustic monitoring of marine mammals using an existing streamer
Halvor Groenaas*, Svein Arne Frivik, Aslaug Melbø, Morten Svendsen, WesternGeco Summary In this paper, we describe a novel method for passive acoustic monitoring of marine mammals using an existing streamer
The Hodogram as an AVO Attribute
 The Hodogram as an AVO Attribute Paul F. Anderson* Veritas GeoServices, Calgary, AB Paul_Anderson@veritasdgc.com INTRODUCTION The use of hodograms in interpretation of AVO cross-plots is a relatively recent
The Hodogram as an AVO Attribute Paul F. Anderson* Veritas GeoServices, Calgary, AB Paul_Anderson@veritasdgc.com INTRODUCTION The use of hodograms in interpretation of AVO cross-plots is a relatively recent
HELICOPTER-BORNE GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY SYSTEMS
 HELICOPTER-BORNE GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS: base & precious metals exploration diamondiferous kimberlite exploration geological mapping mapping of fault zones for engineering and mining applications
HELICOPTER-BORNE GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY SYSTEMS APPLICATIONS: base & precious metals exploration diamondiferous kimberlite exploration geological mapping mapping of fault zones for engineering and mining applications
Tu A D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study
 Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization
 High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization Kevin D. Heaney Lockheed-Martin ORINCON Corporation, 4350 N. Fairfax Dr., Arlington VA 22203 Abstract. The Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization (RGC) algorithm
High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization Kevin D. Heaney Lockheed-Martin ORINCON Corporation, 4350 N. Fairfax Dr., Arlington VA 22203 Abstract. The Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization (RGC) algorithm
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data
 Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
=, (1) Summary. Theory. Introduction
 Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Time Reversal Ocean Acoustic Experiments At 3.5 khz: Applications To Active Sonar And Undersea Communications
 Time Reversal Ocean Acoustic Experiments At 3.5 khz: Applications To Active Sonar And Undersea Communications Heechun Song, P. Roux, T. Akal, G. Edelmann, W. Higley, W.S. Hodgkiss, W.A. Kuperman, K. Raghukumar,
Time Reversal Ocean Acoustic Experiments At 3.5 khz: Applications To Active Sonar And Undersea Communications Heechun Song, P. Roux, T. Akal, G. Edelmann, W. Higley, W.S. Hodgkiss, W.A. Kuperman, K. Raghukumar,
2D field data applications
 Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys
 Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys Lachlan Hennessy* RMIT University hennessylachlan@gmail.com James Macnae RMIT University *presenting author SUMMARY Lightning strikes generate
Sferic signals for lightning sourced electromagnetic surveys Lachlan Hennessy* RMIT University hennessylachlan@gmail.com James Macnae RMIT University *presenting author SUMMARY Lightning strikes generate
Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter, Thierry Klein, CGG
 Downloaded //6 to 9..7.. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter,
Downloaded //6 to 9..7.. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter,
Microseismic & Electromagnetic
 Microseismic Electromagnetic Array data acquisition system Product overview Main components Land data acquisition unit 32-bit interface module LEMI-701 non-polarizable, lead-free electrodes LEMI-120 induction
Microseismic Electromagnetic Array data acquisition system Product overview Main components Land data acquisition unit 32-bit interface module LEMI-701 non-polarizable, lead-free electrodes LEMI-120 induction
A New Scheme for Acoustical Tomography of the Ocean
 A New Scheme for Acoustical Tomography of the Ocean Alexander G. Voronovich NOAA/ERL/ETL, R/E/ET1 325 Broadway Boulder, CO 80303 phone (303)-497-6464 fax (303)-497-3577 email agv@etl.noaa.gov E.C. Shang
A New Scheme for Acoustical Tomography of the Ocean Alexander G. Voronovich NOAA/ERL/ETL, R/E/ET1 325 Broadway Boulder, CO 80303 phone (303)-497-6464 fax (303)-497-3577 email agv@etl.noaa.gov E.C. Shang
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION MOTIVATION
 Isabella Masoni, Total E&P, R. Brossier, University Grenoble Alpes, J. L. Boelle, Total E&P, J. Virieux, University Grenoble Alpes SUMMARY In this study, an innovative layer stripping approach for FWI
Isabella Masoni, Total E&P, R. Brossier, University Grenoble Alpes, J. L. Boelle, Total E&P, J. Virieux, University Grenoble Alpes SUMMARY In this study, an innovative layer stripping approach for FWI
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical
 A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
Computer modeling of acoustic modem in the Oman Sea with inhomogeneities
 Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences Vol.46 (08), August 2017, pp. 1651-1658 Computer modeling of acoustic modem in the Oman Sea with inhomogeneities * Mohammad Akbarinassab University of Mazandaran,
Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences Vol.46 (08), August 2017, pp. 1651-1658 Computer modeling of acoustic modem in the Oman Sea with inhomogeneities * Mohammad Akbarinassab University of Mazandaran,
Multi-transient EM technology in practice
 first break volume 26, March 2008 special topic Multi-transient EM technology in practice Chris Anderson, 1 Andrew Long, 2 Anton Ziolkowski, 3 Bruce Hobbs, 3 and David Wright 3 explain the principles of
first break volume 26, March 2008 special topic Multi-transient EM technology in practice Chris Anderson, 1 Andrew Long, 2 Anton Ziolkowski, 3 Bruce Hobbs, 3 and David Wright 3 explain the principles of
Main Menu. Summary: Introduction:
 UXO Detection and Prioritization Using Combined Airborne Vertical Magnetic Gradient and Time-Domain Electromagnetic Methods Jacob Sheehan, Les Beard, Jeffrey Gamey, William Doll, and Jeannemarie Norton,
UXO Detection and Prioritization Using Combined Airborne Vertical Magnetic Gradient and Time-Domain Electromagnetic Methods Jacob Sheehan, Les Beard, Jeffrey Gamey, William Doll, and Jeannemarie Norton,
Locating good conductors by using the B-field integrated from partial db/dt waveforms of timedomain
 Locating good conductors by using the integrated from partial waveforms of timedomain EM systems Haoping Huang, Geo-EM, LLC Summary An approach for computing the from time-domain data measured by an induction
Locating good conductors by using the integrated from partial waveforms of timedomain EM systems Haoping Huang, Geo-EM, LLC Summary An approach for computing the from time-domain data measured by an induction
ACMAC s PrePrint Repository
 ACMAC s PrePrint Repository Monitoring the sea environment using acoustics the role of the acoustical observatories Michael Taroudakis Original Citation: Taroudakis, Michael (2013) Monitoring the sea environment
ACMAC s PrePrint Repository Monitoring the sea environment using acoustics the role of the acoustical observatories Michael Taroudakis Original Citation: Taroudakis, Michael (2013) Monitoring the sea environment
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Why not narrowband? Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology
 Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Northing (km)
 Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Introduction. Figure 2: Source-Receiver location map (to the right) and geometry template (to the left).
 Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Laws of Attraction The use of electromagnetics in exploration is revolutionizing the way operators view their reservoirs.
 Laws of Attraction The use of electromagnetics in exploration is revolutionizing the way operators view their reservoirs. Inverted data using a geologic model, regional observations from seismic data,
Laws of Attraction The use of electromagnetics in exploration is revolutionizing the way operators view their reservoirs. Inverted data using a geologic model, regional observations from seismic data,
Summary. Introduction
 Multi survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Nathan Payne*, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION GX Technology UK; Reza Afrazmanech. Perenco UK.
Multi survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Nathan Payne*, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION GX Technology UK; Reza Afrazmanech. Perenco UK.
3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion. Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas
 P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
Th N Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data
 Th N103 16 Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data H. Masoomzadeh* (TGS), A. Hardwick (TGS) & S. Baldock (TGS) SUMMARY The frequency of ghost notches is naturally diversified by random variations,
Th N103 16 Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data H. Masoomzadeh* (TGS), A. Hardwick (TGS) & S. Baldock (TGS) SUMMARY The frequency of ghost notches is naturally diversified by random variations,
Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Characterization of noise in airborne transient electromagnetic data using Benford s law
 Characterization of noise in airborne transient electromagnetic data using Benford s law Dikun Yang, Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, University of British Columbia SUMMARY Given any
Characterization of noise in airborne transient electromagnetic data using Benford s law Dikun Yang, Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, University of British Columbia SUMMARY Given any
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
Th ELI1 07 How to Teach a Neural Network to Identify Seismic Interference
 Th ELI1 07 How to Teach a Neural Network to Identify Seismic Interference S. Rentsch* (Schlumberger), M.E. Holicki (formerly Schlumberger, now TU Delft), Y.I. Kamil (Schlumberger), J.O.A. Robertsson (ETH
Th ELI1 07 How to Teach a Neural Network to Identify Seismic Interference S. Rentsch* (Schlumberger), M.E. Holicki (formerly Schlumberger, now TU Delft), Y.I. Kamil (Schlumberger), J.O.A. Robertsson (ETH
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain
 High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
A Matlab-Based Virtual Propagation Tool: Surface Wave Mixed-path Calculator
 430 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 A Matlab-Based Virtual Propagation Tool: Surface Wave Mixed-path Calculator L. Sevgi and Ç. Uluışık Doğuş University,
430 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2006, Cambridge, USA, March 26-29 A Matlab-Based Virtual Propagation Tool: Surface Wave Mixed-path Calculator L. Sevgi and Ç. Uluışık Doğuş University,
DISTORTION OF VLF RADIO WAVE FIELD VERTICAL METAL POLES.
 Title DISTORTION OF VLF RADIO WAVE FIELD VERTICAL METAL POLES Author(s) KIKUCHI, Takashi; ARAKI, Tohru Citation Contributions of the Geophysical In (1972), 12: 1-5 Issue Date 1972-12 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/178624
Title DISTORTION OF VLF RADIO WAVE FIELD VERTICAL METAL POLES Author(s) KIKUCHI, Takashi; ARAKI, Tohru Citation Contributions of the Geophysical In (1972), 12: 1-5 Issue Date 1972-12 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/178624
Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a
 Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a a Published in SEP report, 89, 167-178 (1995) Arnaud Berlioux and William S. Harlan 1 ABSTRACT Variations in source strength and receiver amplitude
Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a a Published in SEP report, 89, 167-178 (1995) Arnaud Berlioux and William S. Harlan 1 ABSTRACT Variations in source strength and receiver amplitude
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
From Black Magic to Swarms: Hydrocarbon Exploration using Non-Seismic Technologies
 Index Table of contents From Black Magic to Swarms: Hydrocarbon Exploration using Non-Seismic Technologies Ed. K. Biegert Shell International Exploration and Production Summary Why don t hydrocarbon detection
Index Table of contents From Black Magic to Swarms: Hydrocarbon Exploration using Non-Seismic Technologies Ed. K. Biegert Shell International Exploration and Production Summary Why don t hydrocarbon detection
AVOID THE IRRESISTIBLE Daniel Baltar London February, 2015
 AVOID THE IRRESISTIBLE Daniel Baltar London February, 2015 Outline Challenges to exploration performance and value creation Impact of CSEM in exploration uncertainty Performance of CSEM in prospect evaluation
AVOID THE IRRESISTIBLE Daniel Baltar London February, 2015 Outline Challenges to exploration performance and value creation Impact of CSEM in exploration uncertainty Performance of CSEM in prospect evaluation
THE FEASIBILITY OF THE AIRBORNE FLUXGATE MAGNETOMETER AS AN EXPLORATION TOOL RESULTS FROM THREE DIMENSIONAL NUMERICAL MODELLING
 THE FEASIBILITY OF THE AIRBORNE FLUXGATE MAGNETOMETER AS AN EXPLORATION TOOL RESULTS FROM THREE DIMENSIONAL NUMERICAL MODELLING John Joseph CRC LEME, School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University
THE FEASIBILITY OF THE AIRBORNE FLUXGATE MAGNETOMETER AS AN EXPLORATION TOOL RESULTS FROM THREE DIMENSIONAL NUMERICAL MODELLING John Joseph CRC LEME, School of Earth and Environmental Sciences, University
Summary. Introduction
 Multiple attenuation for variable-depth streamer data: from deep to shallow water Ronan Sablon*, Damien Russier, Oscar Zurita, Danny Hardouin, Bruno Gratacos, Robert Soubaras & Dechun Lin. CGGVeritas Summary
Multiple attenuation for variable-depth streamer data: from deep to shallow water Ronan Sablon*, Damien Russier, Oscar Zurita, Danny Hardouin, Bruno Gratacos, Robert Soubaras & Dechun Lin. CGGVeritas Summary
TECHNICAL NOTE EXTREMELY LOW FREQUENCY (ELF) EM SYSTEM
 TECHNICAL NOTE 2012-01 EXTREMELY LOW FREQUENCY (ELF) EM SYSTEM Dave Hildes, Ph.D, P. Geol Aurora Geoscicences Ltd. 34A Laberge Road, Whitehorse, YT, Y1A 5Y9 techniques such as MT / CSAMT / large-loop TEM.
TECHNICAL NOTE 2012-01 EXTREMELY LOW FREQUENCY (ELF) EM SYSTEM Dave Hildes, Ph.D, P. Geol Aurora Geoscicences Ltd. 34A Laberge Road, Whitehorse, YT, Y1A 5Y9 techniques such as MT / CSAMT / large-loop TEM.
SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1. Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil)
 SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1 Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil) 2 That s how it looks! Wave Polarisation An electromagnetic (EM) plane wave has time-varying
SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1 Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil) 2 That s how it looks! Wave Polarisation An electromagnetic (EM) plane wave has time-varying
Here the goal is to find the location of the ore body, and then evaluate its size and depth.
 Geophysics 223 March 2009 D3 : Ground EM surveys over 2-D resistivity models D3.1 Tilt angle measurements In D2 we discussed approaches for mapping terrain conductivity. This is appropriate for many hydrogeology
Geophysics 223 March 2009 D3 : Ground EM surveys over 2-D resistivity models D3.1 Tilt angle measurements In D2 we discussed approaches for mapping terrain conductivity. This is appropriate for many hydrogeology
INVERSION OF EM DATA TO RECOVER 1-D CONDUCTIVITY AND A GEOMETRIC SURVEY PARAMETER. Sean Eugene Walker
 INVERSION OF EM DATA TO RECOVER 1-D CONDUCTIVITY AND A GEOMETRIC SURVEY PARAMETER By Sean Eugene Walker B. Sc. (Honours), Geology & Physics, McMaster University, 1996 a thesis submitted in partial fulfillment
INVERSION OF EM DATA TO RECOVER 1-D CONDUCTIVITY AND A GEOMETRIC SURVEY PARAMETER By Sean Eugene Walker B. Sc. (Honours), Geology & Physics, McMaster University, 1996 a thesis submitted in partial fulfillment
Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain
 Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010.
 This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
Ǥ CONFERENCE ABSTRACTS 161
 CONFERENCE ABSTRACTS 161 162 EXPANDED ABSTRACT SEG 2010 163 Qualitative seismic sensor array estimation and seafloor coupling by using incoherent ambient signals for reservoir-monitoring-systems Marcus
CONFERENCE ABSTRACTS 161 162 EXPANDED ABSTRACT SEG 2010 163 Qualitative seismic sensor array estimation and seafloor coupling by using incoherent ambient signals for reservoir-monitoring-systems Marcus
Determining the orientation of marine CSEM receivers using orthogonal Procrustes rotation analysis
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 7, NO. 3 MAY-JUNE ;P.F63 F7,7FIGS.,3TABLES..9/.33776 Determining the orientation of marine CSEM receivers using orthogonal Procrustes rotation analysis Kerry Key and Andrew Lockwood ABSTRACT
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 7, NO. 3 MAY-JUNE ;P.F63 F7,7FIGS.,3TABLES..9/.33776 Determining the orientation of marine CSEM receivers using orthogonal Procrustes rotation analysis Kerry Key and Andrew Lockwood ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. different curvatures at different times (see figure 1a and 1b).
 APERTURE WIDTH SELECTION CRITERION IN KIRCHHOFF MIGRATION Richa Rastogi, Sudhakar Yerneni and Suhas Phadke Center for Development of Advanced Computing, Pune University Campus, Ganesh Khind, Pune 411007,
APERTURE WIDTH SELECTION CRITERION IN KIRCHHOFF MIGRATION Richa Rastogi, Sudhakar Yerneni and Suhas Phadke Center for Development of Advanced Computing, Pune University Campus, Ganesh Khind, Pune 411007,
Ocean Ambient Noise Studies for Shallow and Deep Water Environments
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Ocean Ambient Noise Studies for Shallow and Deep Water Environments Martin Siderius Portland State University Electrical
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Ocean Ambient Noise Studies for Shallow and Deep Water Environments Martin Siderius Portland State University Electrical
A COMPARISON OF ELECTRODE ARRAYS IN IP SURVEYING
 A COMPARISON OF ELECTRODE ARRAYS IN IP SURVEYING John S. Sumner Professor of Geophysics Laboratory of Geophysics and College of Mines University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona This paper is to be presented
A COMPARISON OF ELECTRODE ARRAYS IN IP SURVEYING John S. Sumner Professor of Geophysics Laboratory of Geophysics and College of Mines University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona This paper is to be presented
Oil spill leakage avoidance with real time seismic monitoring. Helge Brandsæter, President OCTIO AS
 Oil spill leakage avoidance with real time seismic monitoring Helge Brandsæter, President OCTIO AS Injection wells - Pitfalls Oseberg - Norway Frade Brazil Veslefrikk Norway Tordis - Norway Challenges
Oil spill leakage avoidance with real time seismic monitoring Helge Brandsæter, President OCTIO AS Injection wells - Pitfalls Oseberg - Norway Frade Brazil Veslefrikk Norway Tordis - Norway Challenges
The fast marching method in Spherical coordinates: SEG/EAGE salt-dome model
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 97, July 8, 1998, pages 251 264 The fast marching method in Spherical coordinates: SEG/EAGE salt-dome model Tariq Alkhalifah 1 keywords: traveltimes, finite difference
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 97, July 8, 1998, pages 251 264 The fast marching method in Spherical coordinates: SEG/EAGE salt-dome model Tariq Alkhalifah 1 keywords: traveltimes, finite difference
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
Estimation of a time-varying sea-surface profile for receiver-side de-ghosting Rob Telling* and Sergio Grion Shearwater Geoservices, UK
 for receiver-side de-ghosting Rob Telling* and Sergio Grion Shearwater Geoservices, UK Summary The presence of a rough sea-surface during acquisition of marine seismic data leads to time- and space-dependent
for receiver-side de-ghosting Rob Telling* and Sergio Grion Shearwater Geoservices, UK Summary The presence of a rough sea-surface during acquisition of marine seismic data leads to time- and space-dependent
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System
 A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
Development of a TDEM Data Acquisition System Based on a SQUID Magnetometer for Mineral Exploration
 Development of a TDEM Data Acquisition System Based on a SQUID Magnetometer for Mineral Exploration Eiichi ARAI Toshihiko HAYASHI Tatsuoki NAGAISHI and Hajime OHTA Metals Exploration Group, Japan Oil,
Development of a TDEM Data Acquisition System Based on a SQUID Magnetometer for Mineral Exploration Eiichi ARAI Toshihiko HAYASHI Tatsuoki NAGAISHI and Hajime OHTA Metals Exploration Group, Japan Oil,
Low Frequency Bottom Reflectivity from Reflection
 Low Frequency Bottom Reflectivity from Reflection,Alexander Kritski 1 and Chris Jenkins 2 1 School of Geosciences, University of Sydney, NSW, 2 Ocean Sciences Institute, University of Sydney, NSW. Abstract
Low Frequency Bottom Reflectivity from Reflection,Alexander Kritski 1 and Chris Jenkins 2 1 School of Geosciences, University of Sydney, NSW, 2 Ocean Sciences Institute, University of Sydney, NSW. Abstract
DAVE MONK : APACHE CORP.
 DAVE MONK : APACHE CORP. KEY DRIVERS : SEISMIC TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT? In our industry the interpreter / exploration company is interested in only one thing: The direct and accurate identification of commercially
DAVE MONK : APACHE CORP. KEY DRIVERS : SEISMIC TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT? In our industry the interpreter / exploration company is interested in only one thing: The direct and accurate identification of commercially
Directional Imaging Stack (DIS) for Shot Based Pre-stack Depth Migrations Wilfred Whiteside*, Alex Yeh and Bin Wang
 Directional Imaging Stack (DIS) for Shot ased Pre-stack Depth Migrations Wilfred Whiteside*, lex Yeh and in Wang Summary Shot based pre-stack depth migrations such as RTM are used to generate a partial
Directional Imaging Stack (DIS) for Shot ased Pre-stack Depth Migrations Wilfred Whiteside*, lex Yeh and in Wang Summary Shot based pre-stack depth migrations such as RTM are used to generate a partial
Imaging Deep into the Gulf of
 Imaging Deep into the Gulf of Houston Houston The Gulf of Mexico as viewed from space. This Mediterranean-type sea is located at the southeastern corner of North America. It covers 1.5 million square kilometers
Imaging Deep into the Gulf of Houston Houston The Gulf of Mexico as viewed from space. This Mediterranean-type sea is located at the southeastern corner of North America. It covers 1.5 million square kilometers
Electrical Resistivity Imaging
 Approved for Public Release; Distribution Unlimited Electrical Resistivity Imaging David Hull US Army Research Lab hull@arl.army.mil 17 Jun 2009 ARL Workshop on Personnel, Vehicle, and Tunnel Detection
Approved for Public Release; Distribution Unlimited Electrical Resistivity Imaging David Hull US Army Research Lab hull@arl.army.mil 17 Jun 2009 ARL Workshop on Personnel, Vehicle, and Tunnel Detection
Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION
 Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION Innovative Solutions, from Access to Production Uncertainty Knowledge ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT
Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION Innovative Solutions, from Access to Production Uncertainty Knowledge ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT
RESISTIVITY METHODS MT
 Presented at Short Course V on Exploration for Geothermal Resources, organized by UNU-GTP, GDC and KenGen, at Lake Bogoria and Lake Naivasha, Kenya, Oct. 29 Nov. 19, 2010. GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME
Presented at Short Course V on Exploration for Geothermal Resources, organized by UNU-GTP, GDC and KenGen, at Lake Bogoria and Lake Naivasha, Kenya, Oct. 29 Nov. 19, 2010. GEOTHERMAL TRAINING PROGRAMME
Development of Mid-Frequency Multibeam Sonar for Fisheries Applications
 Development of Mid-Frequency Multibeam Sonar for Fisheries Applications John K. Horne University of Washington, School of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences Box 355020 Seattle, WA 98195 phone: (206) 221-6890
Development of Mid-Frequency Multibeam Sonar for Fisheries Applications John K. Horne University of Washington, School of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences Box 355020 Seattle, WA 98195 phone: (206) 221-6890
T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data
 T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data N. Gulunay* (CGGVeritas), N. Benjamin (CGGVeritas) & A. Khalil (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Interbed multiples for noisy land data that survives the stacking process
T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data N. Gulunay* (CGGVeritas), N. Benjamin (CGGVeritas) & A. Khalil (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Interbed multiples for noisy land data that survives the stacking process
IDENTIFICATION OF MIXED ACOUSTIC MODES IN THE DIPOLE FULL WAVEFORM DATA USING INSTANTANEOUS FREQUENCY-SLOWNESS METHOD
 IDENTIFICATION OF MIXED ACOUSTIC MODES IN THE DIPOLE FULL WAVEFORM DATA USING INSTANTANEOUS FREQUENCY-SLOWNESS METHOD Marek Kozak, Mirka Kozak., and Jefferson Williams, SuperSonic Geophysical LLC Copyright
IDENTIFICATION OF MIXED ACOUSTIC MODES IN THE DIPOLE FULL WAVEFORM DATA USING INSTANTANEOUS FREQUENCY-SLOWNESS METHOD Marek Kozak, Mirka Kozak., and Jefferson Williams, SuperSonic Geophysical LLC Copyright
Downloaded 11/02/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
Direct Imaging of Group Velocity Dispersion Curves in Shallow Water Christopher Liner*, University of Houston; Lee Bell and Richard Verm, Geokinetics
 Direct Imaging of Group Velocity Dispersion Curves in Shallow Water Christopher Liner*, University of Houston; Lee Bell and Richard Verm, Geokinetics Summary Geometric dispersion is commonly observed in
Direct Imaging of Group Velocity Dispersion Curves in Shallow Water Christopher Liner*, University of Houston; Lee Bell and Richard Verm, Geokinetics Summary Geometric dispersion is commonly observed in
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion
 Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Downloaded 01/03/14 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 : a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
: a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
