UNCLASSIFIED AD NUMBER LIMITATION CHANGES
|
|
|
- Shona Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TO: UNCLASSIFIED AD NUMBER AD LIMITATION CHANGES Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. FROM: Distribution authorized to U.S. Gov't. agencies and their contractors; Administrative/Operational Use; JUN Other requests shall be referred to Office of Naval Research, Washington, DC. onr ltr, 26 oct 1977 AUTHORITY THIS PAGE IS UNCLASSIFIED
2 THIS REPORT HAS BEEN DELIMITED AND CLEARED FOR PUBLIC RELEASE UNDER DOD DIRECTIVE AND NO RESTRICTIONS ARE IMPOSED UPON ITS USE AND DISCLOSURE, DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A APPROVED FOR PUBLIC RELEASEj DISTRIBUTION UNLIMITED,
3 -. I eniiceneeii nformation r limited supply, you are requested to return this copy WHEN IT HAS SERVED >SE so that it may be made available to other requesters. Your cooperation iated. IMENT OR OTHER DRAWINGS, SPECIFICATIONS OR OTHER DATA POSE OTHER THAN IN CONNECTION WITH A DEFINITELY RELATED MENT OPERATION, THE U. S. GOVERNMENT THEREBY INCURS R ANY OBLIGATION WHATSOEVER; AND THE FACT THAT THE E FORMULATED, FURNISHED, OR IN ANY WAY SUPPLIED THE ICATIONS, OR OTHER DATA IS NOT TO BE REGARDED BY :WISE AS IN ANY MANNER LICENSING THE HOLDER OR ANY OTHER DN, OR CONVEYING ANY RIGHTS OR PERMISSION TO MANUFACTURE, NTED INVENTION THAT MAY D* ANY WAY BE RELATED THERETO. Reproduced by MENT SERVICE CENTER TT BUILDING, DAYTON, 2, OHIO
4 CARNEGIE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PITTSBURGH 13, PENNSYLVANIA LU o <--^ ~r/~s A TRANSDUCTOR TYPE FIELD RIPPLE DETECTOR FOR SYNCHRONOUS GENERATORS H. M. McCONNELL MAGNETIC AMPLIFIERS TECHNICAL REPORT NO. 18 WORK PERFORMED UNDER OFFICE OF NAVAL. RESEARCH CONTRACTS N7 ONR AND PROJECTS NO AND 275
5 MAGNETIC AMPLIFIERS-TECHNICAL REPORT No. 18 A TRANSDUCTOR TYPE FIELD RIPPLE DETECTOR FOR SYNCHRONOUS GENERATORS by H. K. McConnell Work performed under Office of Naval Research Contracts N70NR and 30308, Projects no ?- and 275 SYNOPSIS Magnetic amplifier techniques are used to synthesize a device which acts as a current transformer, to detect the alternating component of a current in the presence of large amounts of superposed direct current. Conventional current transformers for this service must be prohibitively large in order to avoid saturation oi' the magnetic circuit. The present device is small, light in weight, and has accuracy suitable for instrumentation. The particular application for which the device was designed is the detection and measurement of double-frequency ripples in the fioid current of a synchronous generator. This ripple current is proportional to the negative-sequence component of stator current. Large negative sequence currents are objectior ble, since corresponding induced currents in the rotor structure cause destructive heating. The device described in this report forms the detecting element for a protection scheme. It replaces more elaborate negative-sequence segregating networks. Department of Electrical Engineering Carnegie Institute of Technology Pittsburgh 13, Pennsylvania June, 1954
6 - n A TRANSDUCTOR TYPE FIELD RIPPLE DETECTOR FOR SYNCHRONOUS GENERATORS Introduction It has been recognized that negative sequence stator currents in synchronous generators, if allowed to persist, may cause dangerous heating of the rotor structure due to induced currents. The problem of protecting synchronous* generator against rotor heating from this cause has stimulated an active discussion among those responsible for relay application. 'ine present method of detecting negative sequence stator current is to employ well known sequence filtering networks fed by current transformers. The output of the network is used to operate a relay which actuates protective equipment if the permissible "I 2 T M, or integrated square of negative sequence current, is exceeded. A group of recent papers, references 1 to 5 inclusive, summarize the present state of development in this matter. At the time of presentation of these papers, it was mentioned in oral discussion that a method of detection of negative sequence currents based on the induced a-c component of field current would be desirable. It is well known that a proportionality exists between these quantities. However, a conventional current transformer is not satisfactory to detect the a-c component of field current, due to the presence of the steady d-c component which saturates the transformer* This paper presents a circuit for the measurement of the a-c component of a current which has a considerable d-c level, with particular application to tho field ripole problem at hand. The circuit consists of current transformer with an additional compensating winding supplied by a current transductor, whose function is to cancel the d-c ampere turns. Tne circuit is shown in Figure 1. The cores are made in gapless (toroidal) form, of a material having essentially a rectangular hysteresis loop. Design Objectives The objectives in designing the circuit are to achieve (a) a useful output current I 0 into the burden Z Q ; (b) faithful response to sudden changes in either the d-c or a-c components of the current I*.j (c> acceptable liuearity between I Q and the a-c component of I*. An approximate analysis of the circuit indicates the way in which th'2 various circuit components must be chosen in order to meet these objectives. Analysis* The transductor will be idealised by stating that the instantaneous current 1l (see Figure l) is the image of the instantaneous current I*. Reasonably close agreement between this idealization and actual performance is obtained if the resistance drop in the a-c windings of the transductor, 2 r ( L ( is small 4
7 - 2 - compared with the maximum applied voltage, and the capacitor C offers low impedance to the a-c component of I]_. A detailed analysis of the transductor operation is beyond the scope of this paper; in fact, the performance of the series-connected magnetic amolifier with high impedance control circuit is not well understood due to unexplained core behavior. It is sufficient to note hsre that trie compensating turns of the current transformer may be adjusted to account for linear departures of the transductor performance from the ideal. Thus, 1-. l il (l) N. J ' where ki is the proportionality factor which accounts for the current ratio error of the transductor. therefore For perfect compensation of the current transformer, Hilled = Ifwo j (2) Nz- "r ' (3) fel The current transformer is idealized by neglecting its magnetizing current. Then, the ampere-turn relationship states that The common flux Q ^ windings N Q and N2 require that W)(r 2 +^L) = 3u»M 2 (6) The reactance offered by C at the ripple frequency t&l 2 TV is not included in equation (6) because the conducting arms of the rectifier bridge effectively shortcircuit C to this component of current. Combining equations (4), (5), and (6) yields the complex ratio of transformation T I. = (7) AfGic) N 0 ) 1 +
8 - 3 - The rapidity with which the bias current Io(dc^ ^- s a^e ^ adjust to transients in the d-c level of I will have an effect upon the current transformer behavior. During transient intervals both the d-c and a-c components of field current change suddenly. The current transformer can by itself reproduce such symmetrical currents in its output winding for a short time only; thi3 time is dictated by the rate at which the average flux level of the current transformer core increases, which is in turn dictated by the burden. It will be assumed here that the current transformer is unable to reproduce asymmetrical currents at all unless perfect compensation in the bias winding exists. Then a suitable transient response of the bias current Lj will be defined as follows: the bias current should reach a level such that compensation is restored within an interval wnich is short in comparison with the short circuit transient time constant (T^') of the generator. Taking 20 cycles to be a representative value of T^', then the bias current should be able to reach the level for comoensation in about 4 cycles at fundamental frequency. Transients in the bi=s circuit- will be calculated unaer assumptions that \&) the transductor delivers a direct current 1-^ proportional to the d-c component of I.*; (b) tho current transformer is saturated. Then, the bias winding (N2) may be treated as a resistance, and the circuit L, T2> C may be considered to receive a prescribed current. Rapid response with a ndnimum tendency to overshoot in a circuit of this type is achieved if the damping is somewhat less than the critical value. Accordingly, a damping ratio of 0.7 will be assumed. Previous discussion of response time has indicated that about (l/l5) second ma: r be allowed between initiation of a sudden change in 1^ and a corresponding response of I 2» As shown in any treatment of second-order systems of this type, the following relationships are established: (8) or r t C = &0373 ^ (9) Wiether the conditions of equations (9) may be realized depends on whether the filter circuit Q prescribed by these equations is practical. It is found that at the ripple frequency of 120 cycles the ratio ( <jol./t\ ) dictated by (9) is about 14, which is readily obtained with commercial components. Let it be required to design a field ripple detector for a generator in which, during transients, the d.c. component of field current may reach 400 amperes. The initial value of a.c. component of field current under such circumstances will be less than 400 amperes peak, by an amount equal to the initial field current. However, let it be assumed for purposes of design that the peak a.c. component will be 400 amperes; the detector should be designed for an a.c. level of 283 amperes
9 - u - r.m.3. Let a burden of 10 volt-amperes at 1000 ohms be required at this a.c. level. These preliminary considerations fix. the current transformer output at. 100 m.a. r.m.s. and the current transformer output winding can have no more than 2830 turns. The current transformer core mu3t be capable of at least (100/2830) volts per turn at 120 cycles. Equation (7), together with the value of Q=14 dictated by equations (9), allows the determination of N 0 and N2 versus the parameter (N2/N 0 ) for a given value of the second parameter ^. If T2 ^s assume d to take a certain value, then B_ and N2 may be found such that the wire sizes, available winding spaces, and practically available choke fit the assumed value of ^. Several trials of this nature indicate the combination best suited to the particular application considered. It is found that in the present example N2 should be about 5000 and N should be about 2200 if it is assumed that T2 is 500 ohms. The corresponding value of L is 9*30 henries. The rated value of the compensating current I 0 becomes 80 m.a. and the rectifier must withstand 40 volts d.c. The capacitor should be about 75 microfarads, although the exact value i3 not critical (equation 8). Exuerimenx-iil Work A model of the circuit has been constructed and tested. The three cores f. were made of 0.004" "Orthonol" tape. Liner UJ.VIIO VX11 inches) are: Core ID Core 0D H ID Box 0D~ H Other constants of the circuit are: % N 2 2n? c 5000 turns # turns # turns # ohms (20 C) 501 ohms (20 C) 10.5 henry (nominal) 50 Kfd 50 volts electrolytic A factor kj. was introduced in equation (l) to account for the fact that the ampere-turn ratio of the transductor is slightly less than the ideal of unity. It will be noted that both N]_ and N are 5000 turns in the model. The factor k^ is introduced in an equivalent way in the model by placing more exciting turns upon the transductor cores than upon the current transformer core, turns being added until maximum output current is reached at rated dc and ac excitation levels. It was found that 72 turns on the transductor cores and 69 turns on the current transformer core achieved this result. Thus Iq. = 69/72 = Rated d-c current becomes 5.80 amperes and rated a-c ripple current becomes 4.08 amperes rms. (The example design began by assuming 400 amperes in a single conductor to be the exci'.ation level. In order to test the model on available machines, the nominal 70-turn exciting windings were installed. In a single conductor application it would be most convenient to add extra turns to the current transformer compensating winding, in about 1/2 per cent taps, in order to "tune" for best compensation).
10 - 5- The steady-state response of the unit at 60 cycles is giver, in Figure 2. Transient response, in the situation for which the unit was designed, is 3hovm in the oscillograms of Figures 3 and 4. (it will he rr>led that the d-c component of generator field current in Figure 4 rises to a value considerably greater than the designed level, resulting in some distortion of the output current wave form and a reduction in its r.m.s. value). Conclusions The device presented in this paper i=> shown to be a small, inexpensive, static apparatus for the measurement of the a-c component of field current in a synchronous generator, both in the transient and steady states. It has sufficient output to operate a relay or meter, Its design is simple and its components are readily obtained. Probably the most serious obstacle to the application of this device to generator protection is the determination, without dangerous test3, of the amount of a-c ripple in field ciirrent per unit of generator negative-sequence current. Accurate calculations are possible in the case of salient-pole generators. However, the presence of solid iron in the rotor forging of a turoo-generator upsets any formal calculation for those machines. Acknowledgements The author is grateful for the assistance of Mr. Hugh McK. Lynch, and to Magnetics, Incorporated or Butler, Pennsylvania, for some of the experimental apparatus. Reierences. 1. M. B. Ross and E. I. King, "Turbine Generator Heating During Single Phase Short Circuits," Transactions Amer. Inst. of Elect. Engrs., Vol. 72, Part III (1953). pages E. I. Pollard, "Effects of Negative Sequence Currents on Turbine Generator Rotor?.," Transactions Amer. Inst. of Elect. Engrs., Vol. 72, Part III (1953), pages P. L. Alger, R. F. Franklin, C. E. Kilbourne, and J. B. McClure, "Short Circuit Capabilities cf Synchronous Machines for Unbalanced Faults," Transactions American Inst. of Elec, Engrs., Vol. 72, Part III (1953), pages J. E. Barkle and W. E. Glassburn, "Protection of Generators Against Unbalanced Currents," Transactions Amer. In3t. of Elec. Engrs., Vol. 72, Part III (1953), pages J. E. Barkle and Frank Von Roeschlaub, "Applications of Relays for Unbalanced Faults on Generators," Transactions Amer. Inst. of Elec. Engrs., Vol. 72, Part III (1953), page =
11 TRANSDUCTOR *~ SECTION " FiUER SECTION OUTPUT SECTION" Figure 1. Circuit diagram of the traneductor type field ripple detector.
12 o 11 i i i 1 i. 1 (/) o CD // V r """CD < So a. 3g Jr4? /r y ^>." A ^ ^ <? <x * o 0! A.C. AMPERE-TURNS (RMS) Figure 2. Steady-state output characteristic at 60 cycles, with 400 ampereturns d.c., and 585 ohms resistive load. Dashed curvet Calculated by equation (7) Solid curvet Measured.
13 Lgure 3
14 Figure
15 Armed Services I echnical Information Hgency Because of our limited supply, you are requested to return this copy WHEN IT HAS SERVED YOUR PURPOSE so that it may be made available to other requesters. Your cooperation will be appreciated. I NOTICE: WHEN GOVERNMENT OR OTHER DRAWINGS, SPECIFICATIONS OR OTHER DATA ARE USED FOR ANY PURPOSE OTHER THAN IN CONNECTION WITH A DEFINITELY RELATED GOVERNMENT PROCUREMENT OPERATION, THE U. S. GOVERNMENT THEREBY INCURS NO RESPONSIBILITY, NOR ANY OBLIGATION WHATSOEVER; AND THE FACT THAT THE GOVERNMENT MAY HAVE FORMULATED, FURNISHED, OR IN ANY WAY SUPPLIED THE SAID DRAWINGS, SPECIFICATIONS, OR OTHER DATA IS NOT TO BE REGARDED BY IMPLICATION OR OTHERWISE AS IN ANS MANNER LICENSING THE HOLDER OR ANY OTHER PERSON OR CORPORATION, OR CONVEYING ANY RIGHTS OR PERMISSION TO MANUFACTURE, USE OR SELL ANY PATENTED INVENTION THAT MAY IN ANY WAY BE RELATED THERETO. Reproduced by DOCUMENT SERVICE CENTER KNOTT BUILDING, DAYTON, 2, OHiO \rx MMi n - in -,1,11- A ccinp»» ' I Mi * i " '"> ^f^^st 3^ M^» "
UNCLASSIFIED AD ARMED SERVICES TECHNICAL INFORMATION AGENCY ARLINGTON HALL STATION ARLINGTON 12, VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED
 UNCLASSIFIED AD- 258 735 ARMED SERVICES TECHNICAL INFORMATION AGENCY ARLINGTON HALL STATION ARLINGTON 12, VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED NOTICE: When government or other drawings, specifications or other data are
UNCLASSIFIED AD- 258 735 ARMED SERVICES TECHNICAL INFORMATION AGENCY ARLINGTON HALL STATION ARLINGTON 12, VIRGINIA UNCLASSIFIED NOTICE: When government or other drawings, specifications or other data are
Power System Dynamics and Control Prof. A. M. Kulkarni Department of Electrical Engineering Indian institute of Technology, Bombay
 Power System Dynamics and Control Prof. A. M. Kulkarni Department of Electrical Engineering Indian institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 25 Excitation System Modeling We discussed, the basic operating
Power System Dynamics and Control Prof. A. M. Kulkarni Department of Electrical Engineering Indian institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 25 Excitation System Modeling We discussed, the basic operating
CHAPTER 2 D-Q AXES FLUX MEASUREMENT IN SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
 22 CHAPTER 2 D-Q AXES FLUX MEASUREMENT IN SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES 2.1 INTRODUCTION For the accurate analysis of synchronous machines using the two axis frame models, the d-axis and q-axis magnetic characteristics
22 CHAPTER 2 D-Q AXES FLUX MEASUREMENT IN SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES 2.1 INTRODUCTION For the accurate analysis of synchronous machines using the two axis frame models, the d-axis and q-axis magnetic characteristics
UNCLASSIFIED. Armed S ervices Technical Information Agency. frt DOCUMENT SERVICE CENTER. Reproduced KNOTT BUILDING, DAYTON, 2, OHIO
 Armed S ervices Technical Information Agency Because of our limited supply, you are requested to return this copy WHEN IT HAS SERVED YOUR PURPOSE so that it may be made available to other requesters. Your
Armed S ervices Technical Information Agency Because of our limited supply, you are requested to return this copy WHEN IT HAS SERVED YOUR PURPOSE so that it may be made available to other requesters. Your
CHAPTER 2. Basic Concepts, Three-Phase Review, and Per Unit
 CHAPTER 2 Basic Concepts, Three-Phase Review, and Per Unit 1 AC power versus DC power DC system: - Power delivered to the load does not fluctuate. - If the transmission line is long power is lost in the
CHAPTER 2 Basic Concepts, Three-Phase Review, and Per Unit 1 AC power versus DC power DC system: - Power delivered to the load does not fluctuate. - If the transmission line is long power is lost in the
TO Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
 UNCLASSIFIED AD NUMBER AD442959 NEW LIMITATION CHANGE TO Approved for public release, distribution unlimited FROM Distribution authorized to U.S. Gov't. agencies and their contractors; Administrative/Operational
UNCLASSIFIED AD NUMBER AD442959 NEW LIMITATION CHANGE TO Approved for public release, distribution unlimited FROM Distribution authorized to U.S. Gov't. agencies and their contractors; Administrative/Operational
Type KLF Generator Field Protection-Loss of Field Relay
 Supersedes DB 41-745B pages 1-4, dated June, 1989 Mailed to: E, D, C/41-700A ABB Power T&D Company Inc. Relay Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA For Use With Delta Connected Potential Transformers
Supersedes DB 41-745B pages 1-4, dated June, 1989 Mailed to: E, D, C/41-700A ABB Power T&D Company Inc. Relay Division Coral Springs, FL Allentown, PA For Use With Delta Connected Potential Transformers
Electrical Drives I. Week 4-5-6: Solid state dc drives- closed loop control of phase controlled DC drives
 Electrical Drives I Week 4-5-6: Solid state dc drives- closed loop control of phase controlled DC drives DC Drives control- DC motor without control Speed Control Strategy: below base speed: V t control
Electrical Drives I Week 4-5-6: Solid state dc drives- closed loop control of phase controlled DC drives DC Drives control- DC motor without control Speed Control Strategy: below base speed: V t control
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK UNIT I BASIC CIRCUITS ANALYSIS PART A (2-MARKS)
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK YEAR / SEM : I / II SUBJECT CODE & NAME : EE 1151 CIRCUIT THEORY UNIT I BASIC CIRCUITS ANALYSIS PART A (2-MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK YEAR / SEM : I / II SUBJECT CODE & NAME : EE 1151 CIRCUIT THEORY UNIT I BASIC CIRCUITS ANALYSIS PART A (2-MARKS)
Dynamic Response of Wound Rotor Induction Generator for. Wind Energy Application
 Dynamic Response of Wound Rotor Induction Generator for Wind Energy Application Saurabh Gupta Kishor Thakre Gaurav Gupta Research scholar Research scholar Research Scholar UIT-RGPV BHOPAL UIT-RGPV BHOPAL
Dynamic Response of Wound Rotor Induction Generator for Wind Energy Application Saurabh Gupta Kishor Thakre Gaurav Gupta Research scholar Research scholar Research Scholar UIT-RGPV BHOPAL UIT-RGPV BHOPAL
Unit 3 Magnetism...21 Introduction The Natural Magnet Magnetic Polarities Magnetic Compass...21
 Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...4 Negative Atomic Charge...4 Positive
Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...4 Negative Atomic Charge...4 Positive
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Index
 Index Note: Bold italic type refers to entries in the Table of Contents, refers to a Standard Title and Reference number and # refers to a specific standard within the buff book 91, 40, 48* 100, 8, 22*,
Index Note: Bold italic type refers to entries in the Table of Contents, refers to a Standard Title and Reference number and # refers to a specific standard within the buff book 91, 40, 48* 100, 8, 22*,
148 Electric Machines
 148 Electric Machines 3.1 The emf per turn for a single-phase 2200/220- V, 50-Hz transformer is approximately 12 V. Calculate (a) the number of primary and secondary turns, and (b) the net cross-sectional
148 Electric Machines 3.1 The emf per turn for a single-phase 2200/220- V, 50-Hz transformer is approximately 12 V. Calculate (a) the number of primary and secondary turns, and (b) the net cross-sectional
EFFECT OF TRANSFORMER LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE ON THE THREE PHASE CAPACITIVE INPUT RECTIFIER
 EFFECT OF TRANSFORMER LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE ON THE THREE PHASE CAPACITIVE INPUT RECTIFIER James O'Loughlin Douglas Larson Air Force Weapons Laboratory/ARAY Kirtland Air Force Base NM 87117 Summary The characteristics
EFFECT OF TRANSFORMER LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE ON THE THREE PHASE CAPACITIVE INPUT RECTIFIER James O'Loughlin Douglas Larson Air Force Weapons Laboratory/ARAY Kirtland Air Force Base NM 87117 Summary The characteristics
Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals
 Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...5 Negative Atomic Charge...5
Preface...x Chapter 1 Electrical Fundamentals Unit 1 Matter...3 Introduction...3 1.1 Matter...3 1.2 Atomic Theory...3 1.3 Law of Electrical Charges...4 1.4 Law of Atomic Charges...5 Negative Atomic Charge...5
Transformer Waveforms
 OBJECTIVE EXPERIMENT Transformer Waveforms Steady-State Testing and Performance of Single-Phase Transformers Waveforms The voltage regulation and efficiency of a distribution system are affected by the
OBJECTIVE EXPERIMENT Transformer Waveforms Steady-State Testing and Performance of Single-Phase Transformers Waveforms The voltage regulation and efficiency of a distribution system are affected by the
Introduction. Inductors in AC Circuits.
 Module 3 AC Theory What you ll learn in Module 3. Section 3.1 Electromagnetic Induction. Magnetic Fields around Conductors. The Solenoid. Section 3.2 Inductance & Back e.m.f. The Unit of Inductance. Factors
Module 3 AC Theory What you ll learn in Module 3. Section 3.1 Electromagnetic Induction. Magnetic Fields around Conductors. The Solenoid. Section 3.2 Inductance & Back e.m.f. The Unit of Inductance. Factors
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
 SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES The geometry of a synchronous machine is quite similar to that of the induction machine. The stator core and windings of a three-phase synchronous machine are practically identical
Bahram Amin. Induction Motors. Analysis and Torque Control. With 41 Figures and 50 diagrams (simulation plots) Springer
 Bahram Amin Induction Motors Analysis and Torque Control With 41 Figures and 50 diagrams (simulation plots) Springer 1 Main Parameters of Induction Motors 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Structural Elements of
Bahram Amin Induction Motors Analysis and Torque Control With 41 Figures and 50 diagrams (simulation plots) Springer 1 Main Parameters of Induction Motors 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Structural Elements of
Power Factor. Power Factor Correction.
 Power Factor. Power factor is the ratio between the KW and the KVA drawn by an electrical load where the KW is the actual load power and the KVA is the apparent load power. It is a measure of how effectively
Power Factor. Power factor is the ratio between the KW and the KVA drawn by an electrical load where the KW is the actual load power and the KVA is the apparent load power. It is a measure of how effectively
Beyond the Knee Point: A Practical Guide to CT Saturation
 Beyond the Knee Point: A Practical Guide to CT Saturation Ariana Hargrave, Michael J. Thompson, and Brad Heilman, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Abstract Current transformer (CT) saturation,
Beyond the Knee Point: A Practical Guide to CT Saturation Ariana Hargrave, Michael J. Thompson, and Brad Heilman, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, Inc. Abstract Current transformer (CT) saturation,
Placement Paper For Electrical
 Placement Paper For Electrical Q.1 The two windings of a transformer is (A) conductively linked. (B) inductively linked. (C) not linked at all. (D) electrically linked. Ans : B Q.2 A salient pole synchronous
Placement Paper For Electrical Q.1 The two windings of a transformer is (A) conductively linked. (B) inductively linked. (C) not linked at all. (D) electrically linked. Ans : B Q.2 A salient pole synchronous
Design, Implementation, and Dynamic Behavior of a Power Plant Model
 Design, Implementation, and Dynamic Behavior of a Power Plant Model M.M. A. Rahman, Member ASEE Grand Valley State University Grand Rapids, MI rahmana@gvsu.edu Daniel Mutuku Consumers Energy West Olive,
Design, Implementation, and Dynamic Behavior of a Power Plant Model M.M. A. Rahman, Member ASEE Grand Valley State University Grand Rapids, MI rahmana@gvsu.edu Daniel Mutuku Consumers Energy West Olive,
3.1.Introduction. Synchronous Machines
 3.1.Introduction Synchronous Machines A synchronous machine is an ac rotating machine whose speed under steady state condition is proportional to the frequency of the current in its armature. The magnetic
3.1.Introduction Synchronous Machines A synchronous machine is an ac rotating machine whose speed under steady state condition is proportional to the frequency of the current in its armature. The magnetic
Literature Review for Shunt Active Power Filters
 Chapter 2 Literature Review for Shunt Active Power Filters In this chapter, the in depth and extensive literature review of all the aspects related to current error space phasor based hysteresis controller
Chapter 2 Literature Review for Shunt Active Power Filters In this chapter, the in depth and extensive literature review of all the aspects related to current error space phasor based hysteresis controller
Differential Protection with REF 542plus Feeder Terminal
 Differential Protection with REF 542plus Application and Setting Guide kansikuva_bw 1MRS 756281 Issued: 09.01.2007 Version: A Differential Protection with REF 542plus Application and Setting Guide Contents:
Differential Protection with REF 542plus Application and Setting Guide kansikuva_bw 1MRS 756281 Issued: 09.01.2007 Version: A Differential Protection with REF 542plus Application and Setting Guide Contents:
p. 1 p. 6 p. 22 p. 46 p. 58
 Comparing power factor and displacement power factor corrections based on IEEE Std. 18-2002 Harmonic problems produced from the use of adjustable speed drives in industrial plants : case study Theory for
Comparing power factor and displacement power factor corrections based on IEEE Std. 18-2002 Harmonic problems produced from the use of adjustable speed drives in industrial plants : case study Theory for
TECHNICAL BULLETIN 004a Ferroresonance
 May 29, 2002 TECHNICAL BULLETIN 004a Ferroresonance Abstract - This paper describes the phenomenon of ferroresonance, the conditions under which it may appear in electric power systems, and some techniques
May 29, 2002 TECHNICAL BULLETIN 004a Ferroresonance Abstract - This paper describes the phenomenon of ferroresonance, the conditions under which it may appear in electric power systems, and some techniques
DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS
 Unit 4 AC s UNIT OBJECTIVE After completing this unit, you will be able to demonstrate and explain the operation of ac induction motors using the Squirrel-Cage module and the Capacitor-Start Motor module.
Unit 4 AC s UNIT OBJECTIVE After completing this unit, you will be able to demonstrate and explain the operation of ac induction motors using the Squirrel-Cage module and the Capacitor-Start Motor module.
Bus protection with a differential relay. When there is no fault, the algebraic sum of circuit currents is zero
 Bus protection with a differential relay. When there is no fault, the algebraic sum of circuit currents is zero Consider a bus and its associated circuits consisting of lines or transformers. The algebraic
Bus protection with a differential relay. When there is no fault, the algebraic sum of circuit currents is zero Consider a bus and its associated circuits consisting of lines or transformers. The algebraic
Sequence Networks p. 26 Sequence Network Connections and Voltages p. 27 Network Connections for Fault and General Unbalances p. 28 Sequence Network
 Preface p. iii Introduction and General Philosophies p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Classification of Relays p. 1 Analog/Digital/Numerical p. 2 Protective Relaying Systems and Their Design p. 2 Design Criteria
Preface p. iii Introduction and General Philosophies p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Classification of Relays p. 1 Analog/Digital/Numerical p. 2 Protective Relaying Systems and Their Design p. 2 Design Criteria
Waterpower '97. Upgrading Hydroelectric Generator Protection Using Digital Technology
 Waterpower '97 August 5 8, 1997 Atlanta, GA Upgrading Hydroelectric Generator Protection Using Digital Technology Charles J. Beckwith Electric Company 6190-118th Avenue North Largo, FL 33773-3724 U.S.A.
Waterpower '97 August 5 8, 1997 Atlanta, GA Upgrading Hydroelectric Generator Protection Using Digital Technology Charles J. Beckwith Electric Company 6190-118th Avenue North Largo, FL 33773-3724 U.S.A.
Aligarh College of Engineering & Technology (College Code: 109) Affiliated to UPTU, Approved by AICTE Electrical Engg.
 Aligarh College of Engineering & Technology (College Code: 19) Electrical Engg. (EE-11/21) Unit-I DC Network Theory 1. Distinguish the following terms: (a) Active and passive elements (b) Linearity and
Aligarh College of Engineering & Technology (College Code: 19) Electrical Engg. (EE-11/21) Unit-I DC Network Theory 1. Distinguish the following terms: (a) Active and passive elements (b) Linearity and
UNDERSTANDING SUB-HARMONICS
 UNDERSTANDING SUB-HARMONICS Joe Perez, P.E., SynchroGrid, College Station, TX 77845, jperez@synchrogrid.com Introduction: Over the years, engineers have employed fundamental principles of electrical engineering
UNDERSTANDING SUB-HARMONICS Joe Perez, P.E., SynchroGrid, College Station, TX 77845, jperez@synchrogrid.com Introduction: Over the years, engineers have employed fundamental principles of electrical engineering
PART I THE USE OF A MAGNETIC PICKUP AS AN ALIGNMENT INDICATOR WITH A STRETCIIED-WIRF: TECHNIQUE. W. K. H. Panofsky PART II
 TN-55-74 September 1965 PART I THE USE OF A MAGNETIC PICKUP AS AN ALIGNMENT INDICATOR WITH A STRETCIIED-WIRF: TECHNIQUE W. K. H. Panofsky PART II PROPOSED SYSTEMS AND CIRCUITS FOR MAGNF,TIC ALIGNMENT PICKUPS
TN-55-74 September 1965 PART I THE USE OF A MAGNETIC PICKUP AS AN ALIGNMENT INDICATOR WITH A STRETCIIED-WIRF: TECHNIQUE W. K. H. Panofsky PART II PROPOSED SYSTEMS AND CIRCUITS FOR MAGNF,TIC ALIGNMENT PICKUPS
CONVERTERS IN POWER VOLTAGE-SOURCED SYSTEMS. Modeling, Control, and Applications IEEE UNIVERSITATSBIBLIOTHEK HANNOVER. Amirnaser Yazdani.
 VOLTAGE-SOURCED CONVERTERS IN POWER SYSTEMS Modeling, Control, and Applications Amirnaser Yazdani University of Western Ontario Reza Iravani University of Toronto r TECHNISCHE INFORMATIONSBIBLIOTHEK UNIVERSITATSBIBLIOTHEK
VOLTAGE-SOURCED CONVERTERS IN POWER SYSTEMS Modeling, Control, and Applications Amirnaser Yazdani University of Western Ontario Reza Iravani University of Toronto r TECHNISCHE INFORMATIONSBIBLIOTHEK UNIVERSITATSBIBLIOTHEK
Electronics for Analog Signal Processing - I Prof. K. Radhakrishna Rao Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Madras
 Electronics for Analog Signal Processing - I Prof. K. Radhakrishna Rao Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Madras Lecture - 6 Full Wave Rectifier and Peak Detector In
Electronics for Analog Signal Processing - I Prof. K. Radhakrishna Rao Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology - Madras Lecture - 6 Full Wave Rectifier and Peak Detector In
Module 1. Introduction. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 1 Introduction Lesson 1 Introducing the Course on Basic Electrical Contents 1 Introducing the course (Lesson-1) 4 Introduction... 4 Module-1 Introduction... 4 Module-2 D.C. circuits.. 4 Module-3
Module 1 Introduction Lesson 1 Introducing the Course on Basic Electrical Contents 1 Introducing the course (Lesson-1) 4 Introduction... 4 Module-1 Introduction... 4 Module-2 D.C. circuits.. 4 Module-3
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (AUTONOMOUS) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 CIVIL ENGINEERING ASSIGNMENT Name : Electrical and Electronics Engineering Code : A30203 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch
Enhancement of Fault Current and Overvoltage by Active Type superconducting fault current limiter (SFCL) in Renewable Distributed Generation (DG)
 Enhancement of Fault Current and Overvoltage by Active Type superconducting fault current limiter (SFCL) in Renewable Distributed Generation (DG) PATTI.RANADHEER Assistant Professor, E.E.E., PACE Institute
Enhancement of Fault Current and Overvoltage by Active Type superconducting fault current limiter (SFCL) in Renewable Distributed Generation (DG) PATTI.RANADHEER Assistant Professor, E.E.E., PACE Institute
CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY
 CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS 1 Electric Circuit Principles 2 Electronic Circuit Principles 3 Generation 4 Distribution 5 Utilisation The expected learning outcome is
CHIEF ENGINEER REG III/2 MARINE ELECTROTECHNOLOGY LIST OF TOPICS 1 Electric Circuit Principles 2 Electronic Circuit Principles 3 Generation 4 Distribution 5 Utilisation The expected learning outcome is
Design of a Regenerative Receiver for the Short-Wave Bands A Tutorial and Design Guide for Experimental Work. Part I
 Design of a Regenerative Receiver for the Short-Wave Bands A Tutorial and Design Guide for Experimental Work Part I Ramón Vargas Patrón rvargas@inictel-uni.edu.pe INICTEL-UNI Regenerative Receivers remain
Design of a Regenerative Receiver for the Short-Wave Bands A Tutorial and Design Guide for Experimental Work Part I Ramón Vargas Patrón rvargas@inictel-uni.edu.pe INICTEL-UNI Regenerative Receivers remain
Innovative Science and Technology Publications
 Innovative Science and Technology Publications Manuscript Title SATURATION ANALYSIS ON CURRENT TRANSFORMER Thilepa R 1, Yogaraj J 2, Vinoth kumar C S 3, Santhosh P K 4, 1 Department of Electrical and Electronics
Innovative Science and Technology Publications Manuscript Title SATURATION ANALYSIS ON CURRENT TRANSFORMER Thilepa R 1, Yogaraj J 2, Vinoth kumar C S 3, Santhosh P K 4, 1 Department of Electrical and Electronics
Generator Protection GENERATOR CONTROL AND PROTECTION
 Generator Protection Generator Protection Introduction Device Numbers Symmetrical Components Fault Current Behavior Generator Grounding Stator Phase Fault (87G) Field Ground Fault (64F) Stator Ground Fault
Generator Protection Generator Protection Introduction Device Numbers Symmetrical Components Fault Current Behavior Generator Grounding Stator Phase Fault (87G) Field Ground Fault (64F) Stator Ground Fault
United States Patent Office
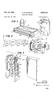 United States Patent Office Patented Feb. 14, 1961 1 AJ."\IPLIFIER CIRCUIT Richard Silberbach, Chicago, m., assignor to Motorola, Ine., Chicago, m., a corporation of Dlinois Filed Dec. 23, 1957, Ser. No.
United States Patent Office Patented Feb. 14, 1961 1 AJ."\IPLIFIER CIRCUIT Richard Silberbach, Chicago, m., assignor to Motorola, Ine., Chicago, m., a corporation of Dlinois Filed Dec. 23, 1957, Ser. No.
Module 7. Electrical Machine Drives. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 7 Electrical Machine Drives Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 34 Electrical Actuators: Induction Motor Drives Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After learning the lesson
Module 7 Electrical Machine Drives Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 34 Electrical Actuators: Induction Motor Drives Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After learning the lesson
Impact of transient saturation of Current Transformer during cyclic operations Analysis and Diagnosis
 1 Impact of transient saturation of Current Transformer during cyclic operations Analysis and Diagnosis BK Pandey, DGM(OS-Elect) Venkateswara Rao Bitra, Manager (EMD Simhadri) 1.0 Introduction: Current
1 Impact of transient saturation of Current Transformer during cyclic operations Analysis and Diagnosis BK Pandey, DGM(OS-Elect) Venkateswara Rao Bitra, Manager (EMD Simhadri) 1.0 Introduction: Current
Radar. Radio. Electronics. Television. .104f 4E011 UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES LOUISVILLE
 Electronics Radio Television.104f Radar UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES LOUISVILLE KENTUCKY REVISED 1967 4E011 1:1111E111611 COPYRIGHT 1956 UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES POWER SUPPLIES ASSIGNMENT 23
Electronics Radio Television.104f Radar UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES LOUISVILLE KENTUCKY REVISED 1967 4E011 1:1111E111611 COPYRIGHT 1956 UNITED ELECTRONICS LABORATORIES POWER SUPPLIES ASSIGNMENT 23
TABLE OF CONTENT
 Page : 1 of 34 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT SCOPE 3 REFERENCES
Page : 1 of 34 Project Engineering Standard www.klmtechgroup.com KLM Technology #03-12 Block Aronia, Jalan Sri Perkasa 2 Taman Tampoi Utama 81200 Johor Bahru Malaysia TABLE OF CONTENT SCOPE 3 REFERENCES
Design Considerations
 Design Considerations Ferrite beads provide a simple, economical method for attenuating high frequency noise or oscillations. By slipping a bead over a wire, a RF choke or suppressor is produced which
Design Considerations Ferrite beads provide a simple, economical method for attenuating high frequency noise or oscillations. By slipping a bead over a wire, a RF choke or suppressor is produced which
PAPER-II (Subjective)
 PAPER-II (Subjective) 1.(A) Choose and write the correct answer from among the four options given in each case for (a) to (j) below: (a) Improved commutation in d.c machines cannot be achieved by (i) Use
PAPER-II (Subjective) 1.(A) Choose and write the correct answer from among the four options given in each case for (a) to (j) below: (a) Improved commutation in d.c machines cannot be achieved by (i) Use
EVALUATION OF REACTANCES AND TIME CONSTANTS OF SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR
 EVALUATION OF REACTANCES AND TIME CONSTANTS OF SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR Shaheena Khanum 1, K.L Ratnakar 2, Ramesh K.N 3, Ravi.R 4 1 PG Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Sri Siddhartha
EVALUATION OF REACTANCES AND TIME CONSTANTS OF SYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR Shaheena Khanum 1, K.L Ratnakar 2, Ramesh K.N 3, Ravi.R 4 1 PG Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Sri Siddhartha
Course ELEC Introduction to electric power and energy systems. Additional exercises with answers December reactive power compensation
 Course ELEC0014 - Introduction to electric power and energy systems Additional exercises with answers December 2017 Exercise A1 Consider the system represented in the figure below. The four transmission
Course ELEC0014 - Introduction to electric power and energy systems Additional exercises with answers December 2017 Exercise A1 Consider the system represented in the figure below. The four transmission
Excitation systems and automatic voltage regulators
 ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Excitation systems and automatic voltage regulators Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct November 2017 1 / 16 Overview
ELEC0047 - Power system dynamics, control and stability Excitation systems and automatic voltage regulators Thierry Van Cutsem t.vancutsem@ulg.ac.be www.montefiore.ulg.ac.be/~vct November 2017 1 / 16 Overview
David L. Lockwood. Ralph I. McNall Jr., Richard F. Whitbeck Thermal Technology Laboratory, Inc., Buffalo, N.Y.
 ANALYSIS OF POWER TRANSFORMERS UNDER TRANSIENT CONDITIONS hy David L. Lockwood. Ralph I. McNall Jr., Richard F. Whitbeck Thermal Technology Laboratory, Inc., Buffalo, N.Y. ABSTRACT Low specific weight
ANALYSIS OF POWER TRANSFORMERS UNDER TRANSIENT CONDITIONS hy David L. Lockwood. Ralph I. McNall Jr., Richard F. Whitbeck Thermal Technology Laboratory, Inc., Buffalo, N.Y. ABSTRACT Low specific weight
Design of A Closed Loop Speed Control For BLDC Motor
 International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 3, Issue 11 (November 214), PP.17-111 Design of A Closed Loop Speed Control For BLDC
International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 3, Issue 11 (November 214), PP.17-111 Design of A Closed Loop Speed Control For BLDC
STEADY STATE REACTANCE
 INDEX NO. : M-53 TECHNICAL MANUAL FOR STEADY STATE REACTANCE Manufactured by : PREMIER TRADING CORPORATION (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company) 212/1, Mansarover Civil Lines, MEERUT. Phone : 0121-2645457,
INDEX NO. : M-53 TECHNICAL MANUAL FOR STEADY STATE REACTANCE Manufactured by : PREMIER TRADING CORPORATION (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company) 212/1, Mansarover Civil Lines, MEERUT. Phone : 0121-2645457,
Operation Analysis of Current Transformer with Transient Performance Analysis Using EMTP Software
 Operation Analysis of Current Transformer with Transient Performance Analysis Using EMTP Software Govind Pandya 1, Rahul Umre 2, Aditya Pandey 3 Assistant professor, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics,
Operation Analysis of Current Transformer with Transient Performance Analysis Using EMTP Software Govind Pandya 1, Rahul Umre 2, Aditya Pandey 3 Assistant professor, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics,
A Novel Control Method for Input Output Harmonic Elimination of the PWM Boost Type Rectifier Under Unbalanced Operating Conditions
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 16, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 2001 603 A Novel Control Method for Input Output Harmonic Elimination of the PWM Boost Type Rectifier Under Unbalanced Operating Conditions
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 16, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 2001 603 A Novel Control Method for Input Output Harmonic Elimination of the PWM Boost Type Rectifier Under Unbalanced Operating Conditions
SERIES ACTIVE power filters have proved to be an interesting
 928 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 14, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 1999 A Fault Protection Scheme for Series Active Power Filters Luis A. Morán, Senior Member, IEEE, Ivar Pastorini, Juan Dixon, Senior
928 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 14, NO. 5, SEPTEMBER 1999 A Fault Protection Scheme for Series Active Power Filters Luis A. Morán, Senior Member, IEEE, Ivar Pastorini, Juan Dixon, Senior
Generator Advanced Concepts
 Generator Advanced Concepts Common Topics, The Practical Side Machine Output Voltage Equation Pitch Harmonics Circulating Currents when Paralleling Reactances and Time Constants Three Generator Curves
Generator Advanced Concepts Common Topics, The Practical Side Machine Output Voltage Equation Pitch Harmonics Circulating Currents when Paralleling Reactances and Time Constants Three Generator Curves
Practical Tricks with Transformers. Larry Weinstein K0NA
 Practical Tricks with Transformers Larry Weinstein K0NA Practical Tricks with Transformers Quick review of inductance and magnetics Switching inductive loads How many voltages can we get out of a $10 Home
Practical Tricks with Transformers Larry Weinstein K0NA Practical Tricks with Transformers Quick review of inductance and magnetics Switching inductive loads How many voltages can we get out of a $10 Home
Experimental Observation of RF Radiation Generated by an Explosively Driven Voltage Generator
 Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 20375-5320 NRL/FR/5745--05-10,112 Experimental Observation of RF Radiation Generated by an Explosively Driven Voltage Generator MARK S. RADER CAROL SULLIVAN TIM
Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC 20375-5320 NRL/FR/5745--05-10,112 Experimental Observation of RF Radiation Generated by an Explosively Driven Voltage Generator MARK S. RADER CAROL SULLIVAN TIM
Line Frequency Transformer
 Line Frequency Transformer For frequencies of 50/60 Hz, specify a Frequency Transformer. Line Line Frequency Transformers are customized to meet customer requirements, and are available in various ratings.
Line Frequency Transformer For frequencies of 50/60 Hz, specify a Frequency Transformer. Line Line Frequency Transformers are customized to meet customer requirements, and are available in various ratings.
Type of loads Active load torque: - Passive load torque :-
 Type of loads Active load torque: - Active torques continues to act in the same direction irrespective of the direction of the drive. e.g. gravitational force or deformation in elastic bodies. Passive
Type of loads Active load torque: - Active torques continues to act in the same direction irrespective of the direction of the drive. e.g. gravitational force or deformation in elastic bodies. Passive
PART 2 - ACTUATORS. 6.0 Stepper Motors. 6.1 Principle of Operation
 6.1 Principle of Operation PART 2 - ACTUATORS 6.0 The actuator is the device that mechanically drives a dynamic system - Stepper motors are a popular type of actuators - Unlike continuous-drive actuators,
6.1 Principle of Operation PART 2 - ACTUATORS 6.0 The actuator is the device that mechanically drives a dynamic system - Stepper motors are a popular type of actuators - Unlike continuous-drive actuators,
SECTION SHORT CIRCUIT, COMPONENT PROTECTION, FLASH HAZARD AND SELECTIVE COORDINATION STUDY
 SECTION 16075 - SHORT CIRCUIT, COMPONENT PROTECTION, FLASH HAZARD AND SELECTIVE COORDINATION STUDY PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Provide a short-circuit, component protection, flash
SECTION 16075 - SHORT CIRCUIT, COMPONENT PROTECTION, FLASH HAZARD AND SELECTIVE COORDINATION STUDY PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Provide a short-circuit, component protection, flash
AGN 005 Fault Currents and Short Circuit Decrement Curves
 Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 005 Fault Currents and Short Circuit Decrement Curves DESCRIPTION To facilitate the correct design of an electrical
Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 005 Fault Currents and Short Circuit Decrement Curves DESCRIPTION To facilitate the correct design of an electrical
GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION APPLICATION Category 3 For All Projects with Aggregate Generator Output of More Than 150 kw but Less Than or Equal to 550 kw
 GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION APPLICATION Category 3 For All Projects with Aggregate Generator Output of More Than 150 kw but Less Than or Equal to 550 kw ELECTRIC UTILITY CONTACT INFORMATION Consumers Energy
GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION APPLICATION Category 3 For All Projects with Aggregate Generator Output of More Than 150 kw but Less Than or Equal to 550 kw ELECTRIC UTILITY CONTACT INFORMATION Consumers Energy
A 11/89. Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SF-8616 and 8617 COILS SET. Copyright November 1989 $15.
 Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SF-8616 and 8617 012-03800A 11/89 COILS SET Copyright November 1989 $15.00 How to Use This Manual The best way to learn to use the
Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SF-8616 and 8617 012-03800A 11/89 COILS SET Copyright November 1989 $15.00 How to Use This Manual The best way to learn to use the
IDAHO PURPA GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION REQUEST (Application Form)
 IDAHO PURPA GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION REQUEST (Application Form) Transmission Provider: IDAHO POWER COMPANY Designated Contact Person: Jeremiah Creason Address: 1221 W. Idaho Street, Boise ID 83702 Telephone
IDAHO PURPA GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION REQUEST (Application Form) Transmission Provider: IDAHO POWER COMPANY Designated Contact Person: Jeremiah Creason Address: 1221 W. Idaho Street, Boise ID 83702 Telephone
Comparison of Different Modulation Strategies Applied to PMSM Drives Under Inverter Fault Conditions
 Comparison of Different Modulation Strategies Applied to PMSM Drives Under Inverter Fault Conditions Jorge O. Estima and A.J. Marques Cardoso University of Coimbra, FCTUC/IT, Department of Electrical and
Comparison of Different Modulation Strategies Applied to PMSM Drives Under Inverter Fault Conditions Jorge O. Estima and A.J. Marques Cardoso University of Coimbra, FCTUC/IT, Department of Electrical and
DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM VOLTAGE SAGS: INTERACTION WITH MOTOR AND DRIVE LOADS
 DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM VOLTAGE SAGS: INTERACTION WITH MOTOR AND DRIVE LOADS Le Tang, Jeff Lamoree, Mark McGranaghan Members, IEEE Electrotek Concepts, Inc. Knoxville, Tennessee Abstract - Several papers have
DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM VOLTAGE SAGS: INTERACTION WITH MOTOR AND DRIVE LOADS Le Tang, Jeff Lamoree, Mark McGranaghan Members, IEEE Electrotek Concepts, Inc. Knoxville, Tennessee Abstract - Several papers have
Gertsch Products RatioTrans are high precision AC Voltage Dividers. They have the following useful features. 1. EXTREME ACCURACY
 INSTRUCTION BOOK FOR STANDARD RATIO TRANSFORMER RATIOTRAN SECTION I - GENERAL DESCRIPTION Gertsch Products RatioTrans are high precision AC Voltage Dividers. They have the following useful features. 1.
INSTRUCTION BOOK FOR STANDARD RATIO TRANSFORMER RATIOTRAN SECTION I - GENERAL DESCRIPTION Gertsch Products RatioTrans are high precision AC Voltage Dividers. They have the following useful features. 1.
. Armed Services Technical Information Agency
 «* «. Armed Services Technical Information Agency gh Because of our limited supply, you are requested to return this copy WHEN IT HAS SERVED YOUR PURPOSE so that it may be made available to other requesters.
«* «. Armed Services Technical Information Agency gh Because of our limited supply, you are requested to return this copy WHEN IT HAS SERVED YOUR PURPOSE so that it may be made available to other requesters.
GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION APPLICATION FOR ALL PROJECTS WITH AGGREGATE GENERATOR OUTPUT OF MORE THAN 150 KW BUT LESS THAN OR EQUAL TO 550 KW
 GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION APPLICATION FOR ALL PROJECTS WITH AGGREGATE GENERATOR OUTPUT OF MORE THAN 150 KW BUT LESS THAN OR EQUAL TO 550 KW Electric Utility Contact Information Detroit Edison Company Interconnection
GENERATOR INTERCONNECTION APPLICATION FOR ALL PROJECTS WITH AGGREGATE GENERATOR OUTPUT OF MORE THAN 150 KW BUT LESS THAN OR EQUAL TO 550 KW Electric Utility Contact Information Detroit Edison Company Interconnection
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY By: Fadhil A. Hasan ELECTRICAL MACHINES
 UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Year: Second 2016-2017 By: Fadhil A. Hasan ELECTRICAL MACHINES І Module-II: AC Transformers o Single phase transformers o Three-phase transformers
UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Year: Second 2016-2017 By: Fadhil A. Hasan ELECTRICAL MACHINES І Module-II: AC Transformers o Single phase transformers o Three-phase transformers
COMPARATIVE PERFORMANCE OF SMART WIRES SMARTVALVE WITH EHV SERIES CAPACITOR: IMPLICATIONS FOR SUB-SYNCHRONOUS RESONANCE (SSR)
 7 February 2018 RM Zavadil COMPARATIVE PERFORMANCE OF SMART WIRES SMARTVALVE WITH EHV SERIES CAPACITOR: IMPLICATIONS FOR SUB-SYNCHRONOUS RESONANCE (SSR) Brief Overview of Sub-Synchronous Resonance Series
7 February 2018 RM Zavadil COMPARATIVE PERFORMANCE OF SMART WIRES SMARTVALVE WITH EHV SERIES CAPACITOR: IMPLICATIONS FOR SUB-SYNCHRONOUS RESONANCE (SSR) Brief Overview of Sub-Synchronous Resonance Series
HISTORY: How we got to where we are. March 2015 Roy Boyer 1
 HISTORY: How we got to where we are March 2015 Roy Boyer 1 Traditional Stability Analysis: 1. Maintain synchronism of synchronous machines 2. Simplifying assumptions: 1. Balanced positive sequence system
HISTORY: How we got to where we are March 2015 Roy Boyer 1 Traditional Stability Analysis: 1. Maintain synchronism of synchronous machines 2. Simplifying assumptions: 1. Balanced positive sequence system
CHAPTER 2. Transformers. Dr Gamal Sowilam
 CHAPTER Transformers Dr Gamal Sowilam Introduction A transformer is a static machine. It is not an energy conversion device, it is indispensable in many energy conversion systems. A transformer essentially
CHAPTER Transformers Dr Gamal Sowilam Introduction A transformer is a static machine. It is not an energy conversion device, it is indispensable in many energy conversion systems. A transformer essentially
AGN 034 Alternator Reactance
 Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 034 Alternator Reactance DEFINITION Reactance Periods Inherent to the design of an alternator are certain internal
Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 034 Alternator Reactance DEFINITION Reactance Periods Inherent to the design of an alternator are certain internal
Design Considerations
 Design Considerations APPLICATION NOTES: Multi-hole cores provide specialized shapes that are sometimes more useful than single hole devices. One example is wide band transformers where good coupling between
Design Considerations APPLICATION NOTES: Multi-hole cores provide specialized shapes that are sometimes more useful than single hole devices. One example is wide band transformers where good coupling between
Central Electronics Model 600L Linear Amplifier
 INTRODUCTION This manual has been reproduced by James Lawrence, NA5RC, a 600L owner. Text no longer applicable such as insurance claim with the carrier has been deleted. Some capitalization and grammar
INTRODUCTION This manual has been reproduced by James Lawrence, NA5RC, a 600L owner. Text no longer applicable such as insurance claim with the carrier has been deleted. Some capitalization and grammar
ISSN: Page 298
 Sizing Current Transformers Rating To Enhance Digital Relay Operations Using Advanced Saturation Voltage Model *J.O. Aibangbee 1 and S.O. Onohaebi 2 *Department of Electrical &Computer Engineering, Bells
Sizing Current Transformers Rating To Enhance Digital Relay Operations Using Advanced Saturation Voltage Model *J.O. Aibangbee 1 and S.O. Onohaebi 2 *Department of Electrical &Computer Engineering, Bells
MILITARY STANDARD INTERFACE STANDARD FOR SHIPBOARD SYSTEMS SECTION 390
 MIL-STD-1399(NAVY) SECTION 390 2 October 1987 MILITARY STANDARD INTERFACE STANDARD FOR SHIPBOARD SYSTEMS SECTION 390 ELECTRIC POWER, DIRECT CURRENT, (OTHER THAN SHIP S BATTERY) FOR SUBMARINES (METRIC)
MIL-STD-1399(NAVY) SECTION 390 2 October 1987 MILITARY STANDARD INTERFACE STANDARD FOR SHIPBOARD SYSTEMS SECTION 390 ELECTRIC POWER, DIRECT CURRENT, (OTHER THAN SHIP S BATTERY) FOR SUBMARINES (METRIC)
Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination Fundamentals
 Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination Fundamentals NERC Protection Coordination Webinar Series June 2, 2010 Jon Gardell Agenda 2 Objective Introduction to Protection Generator and
Power Plant and Transmission System Protection Coordination Fundamentals NERC Protection Coordination Webinar Series June 2, 2010 Jon Gardell Agenda 2 Objective Introduction to Protection Generator and
May 1995 QST Volume 79, Number 5
 POWER WATT S IT ALL ABOUT? By Mike Gruber, WA1SVF ARRL Laboratory Engineer Q: Peak Envelope Power (PEP), RMS, average power...the list goes on and on. And I haven t even mentioned some of those strange
POWER WATT S IT ALL ABOUT? By Mike Gruber, WA1SVF ARRL Laboratory Engineer Q: Peak Envelope Power (PEP), RMS, average power...the list goes on and on. And I haven t even mentioned some of those strange
Electrical Systems - Course 135 UNBALANCED CURRENTS, THEIR EFFECTS
 135" 02-1 Electrical Systems - Course 135 UNBALANCED CURRENTS, THEIR EFFECTS -----_.._--- -. _------._------------- 1.0 INTRODUCTION The previous lesson, 135.01-1 explained that._ oala'1ced currents, caused
135" 02-1 Electrical Systems - Course 135 UNBALANCED CURRENTS, THEIR EFFECTS -----_.._--- -. _------._------------- 1.0 INTRODUCTION The previous lesson, 135.01-1 explained that._ oala'1ced currents, caused
Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM) with Reference Voltage Compensation (RVC) control scheme
 I J E E E C International Journal of Electrical, Electronics ISSN No. (Online) : 2277-2626 and Computer Engineering 2(1): 7-12(2013) Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM)
I J E E E C International Journal of Electrical, Electronics ISSN No. (Online) : 2277-2626 and Computer Engineering 2(1): 7-12(2013) Transient stability improvement by using shunt FACT device (STATCOM)
Harnessing of wind power in the present era system
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 1, January-2012 1 Harnessing of wind power in the present era system Raghunadha Sastry R, Deepthy N Abstract This paper deals
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 3, Issue 1, January-2012 1 Harnessing of wind power in the present era system Raghunadha Sastry R, Deepthy N Abstract This paper deals
Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL. Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two
 Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two convertor stations which are connected to each other by a transmission link consisting of an overhead
Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two convertor stations which are connected to each other by a transmission link consisting of an overhead
SATURATION OF CURRENT TRANSFORMERS AND ITS IMPACT ON DIGITAL OVERCURRENT RELAYS NABIL H. AL-ABBAS
 SATURATION OF CURRENT TRANSFORMERS AND ITS IMPACT ON DIGITAL OVERCURRENT RELAYS by NABIL H. AL-ABBAS A Thesis Presented to the DEANSHIP OF GRADUATE STUDIES In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
SATURATION OF CURRENT TRANSFORMERS AND ITS IMPACT ON DIGITAL OVERCURRENT RELAYS by NABIL H. AL-ABBAS A Thesis Presented to the DEANSHIP OF GRADUATE STUDIES In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER EI6402 ELECTRICAL MACHINES Regulation 2013 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK IV SEMESTER EI6402 ELECTRICAL MACHINES Regulation 2013 Academic
Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems
 Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems Introduction The two major problems that the modern power systems are facing are voltage and angle stabilities. There are various approaches to overcome
Chapter 10: Compensation of Power Transmission Systems Introduction The two major problems that the modern power systems are facing are voltage and angle stabilities. There are various approaches to overcome
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A
 Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
A VARIABLE SPEED PFC CONVERTER FOR BRUSHLESS SRM DRIVE
 A VARIABLE SPEED PFC CONVERTER FOR BRUSHLESS SRM DRIVE Mrs. M. Rama Subbamma 1, Dr. V. Madhusudhan 2, Dr. K. S. R. Anjaneyulu 3 and Dr. P. Sujatha 4 1 Professor, Department of E.E.E, G.C.E.T, Y.S.R Kadapa,
A VARIABLE SPEED PFC CONVERTER FOR BRUSHLESS SRM DRIVE Mrs. M. Rama Subbamma 1, Dr. V. Madhusudhan 2, Dr. K. S. R. Anjaneyulu 3 and Dr. P. Sujatha 4 1 Professor, Department of E.E.E, G.C.E.T, Y.S.R Kadapa,
IV/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION. Electrical &Electronics Engineering
 Hall Ticket Number: 14EE704 November, 2017 Seventh Semester Time: Three Hours Answer Question No.1 compulsorily. Answer ONE question from each unit. IV/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION Electrical
Hall Ticket Number: 14EE704 November, 2017 Seventh Semester Time: Three Hours Answer Question No.1 compulsorily. Answer ONE question from each unit. IV/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION Electrical
OPERATING, METERING AND EQUIPMENT PROTECTION REQUIREMENTS FOR PARALLEL OPERATION OF LARGE-SIZE GENERATING FACILITIES GREATER THAN 25,000 KILOWATTS
 OPERATING, METERING AND EQUIPMENT PROTECTION REQUIREMENTS FOR PARALLEL OPERATION OF LARGE-SIZE GENERATING FACILITIES GREATER THAN 25,000 KILOWATTS AND MEDIUM-SIZE FACILITIES (5,000-25,000KW) CONNECTED
OPERATING, METERING AND EQUIPMENT PROTECTION REQUIREMENTS FOR PARALLEL OPERATION OF LARGE-SIZE GENERATING FACILITIES GREATER THAN 25,000 KILOWATTS AND MEDIUM-SIZE FACILITIES (5,000-25,000KW) CONNECTED
Power systems 2: Transformation
 Power systems 2: Transformation Introduction In this series of articles, we will be looking at each of the main stages of the electrical power system in turn. s you will recall from our Introduction to
Power systems 2: Transformation Introduction In this series of articles, we will be looking at each of the main stages of the electrical power system in turn. s you will recall from our Introduction to
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE ROLE OF STABILIZERS IN THE ENHANCEMENT OF AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATORS PERFORMANCE
 Engineering Journal of Qatar University, Vol. 4, 1991, p. 91-102. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE ROLE OF STABILIZERS IN THE ENHANCEMENT OF AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATORS PERFORMANCE K. I. Saleh* and M.
Engineering Journal of Qatar University, Vol. 4, 1991, p. 91-102. EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF THE ROLE OF STABILIZERS IN THE ENHANCEMENT OF AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATORS PERFORMANCE K. I. Saleh* and M.
