(51) Int Cl.: A63F 13/25 ( ) A63F 13/5255 ( ) A63F 13/90 ( ) G02B 27/01 ( ) H04N 13/04 ( )
|
|
|
- Jewel Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) TEPZZ Z4788 B_T (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: Bulletin 17/37 (21) Application number: (1) Int Cl.: A63F 13/2 (14.01) A63F 13/2 (14.01) A63F 13/90 (14.01) G02B 27/01 (06.01) H04N 13/04 (06.01) (22) Date of filing: (4) COMPRESSIBLE EYECUP ASSEMBLIES IN A VIRTUAL REALITY HEADSET KOMPRIMIERBARE AUGENMUSCHELANORDNUNG IN EINER BRILLE FÜR VIRTUELLE REALITÄT ENSEMBLES OEILLÈRE COMPRESSIBLE DANS UN CASQUE DE RÉALITÉ VIRTUELLE (84) Designated Contracting States: AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR () Priority: US PCT/US1/02431 (43) Date of publication of application: Bulletin 16/ (73) Proprietor: Oculus VR, LLC Menlo Park, CA 92 (US) (72) Inventor: THOMAS, Matt Lee Menlo Park, CA California 92 (US) (6) References cited: WO-A1-9/061 JP-A JP-A JP-A BRANDTBERG H ET AL: "HEAD-MOUNTED DISPLAYS", ERICSSON REVIEW (INCL. ON), TELEFONAKTIEBOLAGET L M ERICSSON, SE, vol. 74, no. 1, 1 January 1997 ( ), pages 41-48, XP , ISSN: SCHREYER H ET AL: "INTEGRATED HELMET SYSTEM WITH IMAGE INTENSIFIER TUBES", DISPLAYS DEVICES, DEMPA PUBLICATIONS, TOKYO, JP, vol. 1, no. 2, 1 January 1994 ( ), pages 98-, XP , ISSN: , DOI:.16/ (94) (74) Representative: Schröer, Gernot H. Meissner Bolte Patentanwälte Rechtsanwälte Partnerschaft mbb Bankgasse Nürnberg (DE) EP B1 Note: Within nine months of the publication of the mention of the grant of the European patent in the European Patent Bulletin, any person may give notice to the European Patent Office of opposition to that patent, in accordance with the Implementing Regulations. Notice of opposition shall not be deemed to have been filed until the opposition fee has been paid. (Art. 99(1) European Patent Convention). Printed by Jouve, 7001 PARIS (FR)
2 1 EP B1 2 Description BACKGROUND [0001] The present disclosure generally relates virtual reality headsets, and specifically relates to extendible eyecup assemblies in a virtual reality headset. [0002] Virtual reality (VR) headsets include eyecup assemblies, which pass light from an electronic display to the eyes of a user. The distance from a portion of an eyecup assembly to a user s eye generally affects the comfort of the user when wearing the VR headset and may also affect the user s field of view of content displayed by the VR headset. Conventional VR headsets include multiple rigid eyecup assemblies having different sizes to accommodate multiple users. [0003] When installed in a VR headset, a size of rigid eyecup assembly, when installed in the VR headset, results in a different fixed distance from a user s eye to a portion of the installed rigid eyecup (e.g., a rear portion of the rigid eyecup assembly), which affects comfort or field of view of the user. To use a VR headset, the user chooses a size of rigid eyecup assembly resulting in comfortable wear of the VR headset and a desired field of view. For example, a user wearing eyeglasses would likely select an eyecup assembly with a greater distance between a portion of the eyecup assembly and the user s eye than a different user who does not wear eyeglasses to comfortably accommodate the user s eyeglasses when using the VR headset. However, producing various sets of rigid eyecup assemblies for use in a VR headset increases production costs of a VR headset. [0004] Document WO 9/061 A1 describes a binocular head mounted display system utilizing an aspheric lens in each of the user s right-eye and left-eye optical paths. The aspheric lens is formed with a number of concentric zones for controlling the distance at which an image of displayed information is projected from the user and to minimize distortions across the virtual image. The distance between each lens and its respective display is independently variable. Further, the distance between the optical system as a whole and the user s eyes is variable. Document BRANDENBERG H. et. al.: "HEAD_MOUNTED DISPLAYS", 1997 provides an overview of the state of technology and future prospects of head mounted displays from the point of view of Year Document SCHREYER et. al.: "INTEGRATED HELMET SYSTEM WITH IMAGE INTENSIFIER TUBES", 1994 describes a helmet mounted sight system with a combined image intensifier tube system and cathode ray tube system, intended and specifically adapted for flight applications. SUMMARY [000] A virtual reality (VR) headset includes an electronic display element and an optics block having two eyecup assemblies. Each eyecup assembly includes a lens and a cone, or other structure, coupled to the lens and coupled to a mounting surface of a rigid body of the VR headset. The cone comprises an opaque material (e.g., a material that is opaque to wavelengths of visible light) that is deformable to adjust (e.g., increase or decrease) a distance between a top portion of the cone and a base portion of the cone. In some embodiments, adjustment to the distance between the top portion of the cone and the base portion of the cone is made via an adjustment mechanism included in the VR headset. Adjusting the distance between the top and bottom positions of the cone allows a user to adjust spacing between the outer surfaces of the lenses in each eyecup assembly and the user s eyes to comfortably use the VR headset. In some embodiments, the adjustment mechanism also allows the user to adjust a center spacing distance between each of the eyecup assemblies so the center spacing distance corresponds to the user s interpupillary distance (i.e., a distance between the centers of the pupils for each of the user s eyes). Adjusting the center spacing distance allows a user to align the locations of the exit pupils of the VR headset with the locations of the user s eyes. These adjustments allow use of a single VR headset by different users having different characteristics (e.g., different interpupillary distances, do not wear eyeglasses, wear eyeglasses, etc.). [0006] In some embodiments, an eyecup assembly includes one or more compression adjusters. A compression adjuster adjusts a distance between a point on a top portion of a cone within the eyecup assembly and a point on a bottom portion of the cone. For example, a compression adjuster is a mechanical device, an electrical device, or some combination thereof. In some embodiments, a compression adjuster is a spring configured to compress in response to application of an electric current to the spring. [0007] The invention is defined by appended independent claim 1. [0008] In an embodiment according to the invention, a virtual reality (VR) headset comprises: an electronic display element configured to output image light; an optics block configured to receive the image light, the optics block comprising: a lens and an additional lens each configured to direct portions of the image light to corresponding exit pupils that correspond to locations of eyes of a user of the VR headset; a cone including a base portion and a top portion, the base portion coupled to a mounting surface of a rigid body of the VR headset and the top portion coupled to the lens, the cone configured to receive image light through the base portion and direct the image light toward the lens and the cone comprising an opaque material that is deformable to adjust a distance between the top portion and the base portion; 2
3 3 EP B1 4 an additional cone including an additional base portion and an additional top portion, the additional base portion coupled to the mounting surface of the rigid body of the VR headset and the additional top portion coupled to the additional lens, the additional cone configured to receive image light through the additional base portion and direct the image light toward the additional lens, the additional cone comprising the opaque material that is deformable to adjust a distance between the additional top portion and the additional base portion; and an adjustment mechanism configured to adjust the distance between the top portion and the base portion of the cone or the distance between the additional top portion and the additional base portion of the additional cone based on a received input. [0009] In an embodiment according to the invention, the VR headset further may comprise: a compression adjuster coupled to the top portion and the base portion of the cone, the compression adjuster configured to reduce the distance between the top portion and the base portion in response to an input received from the adjustment mechanism. [00] The compression adjuster may be a spring that is configured to compress in response to receiving an electrical current. [0011] The cone may comprise thermoplastic polyurethane. [0012] In an embodiment according to the invention, the VR headset further may comprise: 1 2 of a rigid body of the VR headset and the top portion coupled to the lens, the cone configured to receive image light through the base portion and direct the image light toward the lens and the cone comprising an opaque material that is deformable to adjust a distance between the top portion and the base portion; and an adjustment mechanism configured to adjust the distance between the top portion and the base portion of the cone based on a received input. [001] The optics block further may comprise: an additional lens configured to direct portions of the image light to a corresponding exit pupil that corresponds to a location of another eye of the user of the VR headset; an additional cone including an additional base portion and an additional top portion, the additional base portion coupled to the mounting surface of the rigid body of the VR headset and the additional top portion coupled to the additional lens, the additional cone configured to receive image light through the additional base portion and direct the image light toward the additional lens, the additional cone comprising the opaque material that is deformable to adjust a distance between the additional top portion and the additional base portion; and the adjustment mechanism is further configured to adjust the distance between the additional top portion and the additional base portion of the additional cone based on the received input. a rail coupled to a base portion and an additional rail coupled to the additional base portion, wherein the adjustment mechanism is configured to adjust a center spacing distance between a center of the base portion and a center of the additional base portion in response to receiving a center spacing adjustment input. [0013] The opaque material may be opaque to wavelengths of visible light. [0014] In an embodiment according to the invention, a virtual reality (VR) headset comprises: an electronic display element configured to output image light; an optics block configured to receive the image light, the optics block comprising: a lens configured to direct portions of the image light to a corresponding exit pupil that corresponds to a location of an eye of a user of the VR headset; a cone including a base portion and a top portion, the base portion coupled to a mounting surface [0016] In an embodiment according to the invention, the VR headset further may comprise: a rail coupled to a base portion and an additional rail coupled to the additional base portion, wherein the adjustment mechanism is configured to adjust a center spacing distance between a center of the base portion and a center of the additional base portion in response to a center spacing adjustment input. [0017] In an embodiment according to the invention, a virtual reality (VR) headset comprises: an electronic display element configured to output image light; an optics block configured to receive the image light, the optics block comprising: a lens configured to direct portions of the image light to a corresponding exit pupil that corresponds to a location of an eye of a user of the VR headset; a cone including a base portion and a top portion, 3
4 EP B1 6 the base portion coupled to a mounting surface of a rigid body of the VR headset and the top portion coupled to the lens, the cone configured to receive image light through the base portion and direct the image light toward the lens and the cone comprising an opaque material that is deformable to adjust a distance between the top portion and the base portion; an adjustment mechanism configured to adjust the distance between the top portion and the base portion of the cone based on a received input; and a compression adjuster that is coupled to the top portion and the base portion of the cone, and is configured to reduce the distance between the top portion and the base portion in response to the received input. [0018] The compression adjuster may be a spring that is configured to compress in response receiving an electric current. [0019] The electric current may be received by the spring in response to the received input. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS [00] FIG. 1 FIG. 2A FIG. 2B FIG. 3 FIG. 4 FIG. A FIG. B is a block diagram of a system environment including a virtual reality (VR) system, in accordance with an embodiment. is a wire diagram of a virtual reality headset, in accordance with an embodiment. is a cross section of a front rigid body of the VR headset in FIG. 2A, in accordance with an embodiment. is a wire diagram of an embodiment of the front rigid body of the VR headset shown in FIG. 2A, in accordance with an embodiment. is a wire diagram of an embodiment of two eyecup assemblies coupled to a mounting surface of the front rigid body shown in FIG. 3, in accordance with an embodiment. is a cross section of an eyecup assembly in a full extension state, in accordance with an embodiment. is a cross section of the eyecup assembly in a full compression state, in accordance with an embodiment. [0021] The figures depict embodiments of the present disclosure for purposes of illustration only. One skilled in the art will readily recognize from the following description that alternative embodiments of the structures and methods illustrated herein may be employed without departing from the principles, or benefits touted, of the disclosure described herein DETAILED DESCRIPTION System Overview [0022] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a virtual reality (VR) system environment 0 in which a VR console 1 operates. The system environment 0 shown by FIG. 1 comprises a VR headset, an imaging device 13, and a VR input interface 1 that are each coupled to the VR console 1. While FIG. 1 shows an example system environment 0 including one VR headset, one imaging device 13, and one VR input interface 1, in other embodiments any number of these components may be included in the system environment 0. For example, there may be multiple VR headsets each having an associated VR input interface 1 and being monitored by one or more imaging devices 13, with each VR headset, VR input interface 1, and imaging devices 13 communicating with the VR console 1. In alternative configurations, different and/or additional components may be included in the system environment 0. [0023] The VR headset is a head-mounted display that presents media to a user. Examples of media presented by the VR head set include one or more images, video, audio, or some combination thereof. In some embodiments, audio is presented via an external device (e.g., speakers and/or headphones) that receives audio information from the VR headset, the VR console 1, or both, and presents audio data based on the audio information. An embodiment of the VR headset is further described below in conjunction with FIGS. 2A and 2B. The VR headset may comprise one or more rigid bodies, which may be rigidly or non-rigidly coupled to each other together. A rigid coupling between rigid bodies causes the coupled rigid bodies to act as a single rigid entity. In contrast, a non-rigid coupling between rigid bodies allows the rigid bodies to move relative to each other. [0024] The VR headset includes an electronic display 11, an optics block 118, one or more locators 1, one or more position sensors 12, and an inertial measurement unit (IMU) 1. The electronic display 11 displays images to the user in accordance with data received from the VR console 1. In various embodiments, the electronic display 11 may comprise a single electronic display or multiple electronic displays (e.g., a display for each eye of a user). Examples of the electronic display 11 include: a liquid crystal display (LCD), an organic light emitting diode (OLED) display, an active-matrix organic light-emitting diode display (AMOLED), some other display, or some combination thereof. [002] The optics block 118 magnifies received light, corrects optical errors associated with the image light, and presents the corrected image light to a user of the VR headset. In various embodiments, the optics block 118 includes one or more optical elements. Example optical elements included in the optics block 118 include: an aperture, a Fresnel lens, a convex lens, a con- 4
5 7 EP B cave lens, a filter, or any other suitable optical element that affects image light. Moreover, the optics block 118 may include combinations of different optical elements. In some embodiments, one or more of the optical elements in the optics block 118 may have one or more coatings, such as anti-reflective coatings. [0026] Magnification of the image light by the optics block 118 allows the electronic display 11 to be physically smaller, weigh less, and consume less power than larger displays. Additionally, magnification may increase a field of view of the content presented by the electronic display 11. For example, the field of view of the displayed content is such that the displayed content is presented using almost all (e.g., 1 degrees diagonal), and in some cases all, of the user s field of view. Additionally, in some embodiments, the amount of magnification may be adjusted by adding or removing optical elements. [0027] The optics block 118 may be designed to correct one or more types of optical error. Examples of optical error include: two dimensional optical errors, three dimensional optical errors, or some combination thereof. Two dimensional errors are optical aberrations that occur in two dimensions. Example types of two dimensional errors include: barrel distortion, pincushion distortion, longitudinal chromatic aberration, transverse chromatic aberration, or any other type of two-dimensional optical error. Three dimensional errors are optical errors that occur in three dimensions. Example types of three dimensional errors include spherical aberration, comatic aberration, field curvature, astigmatism, or any other type of three-dimensional optical error. In some embodiments, content provided to the electronic display 11 for display is pre-distorted, and the optics block 118 corrects the distortion when it receives image light from the electronic display 11 generated based on the content. [0028] The optics block 118 includes an eyecup assembly for each eye. Each eyecup assembly includes a lens and is configured to receive image light from the electronic display 11 and direct the image light to the lens, which directs the image light to a corresponding eye of a user wearing the VR headset. In some embodiments, one or more of the eyecup assemblies are deformable, so an eyecup assembly may be compressed or stretched to, respectively, increase or decrease the space between an eye of the user and a portion of the eyecup assembly, as further described below in conjunction with FIGS. 3-B. [0029] In some embodiments, the optics block 118 includes an adjustment mechanism, which is a mechanical or electrical device allowing a user to adjust a position of one or both of the eyecup assemblies with respect to the user s eyes. In some embodiments, the adjustment mechanism adjusts a spacing between an outer surface of each eyecup assembly and the user s eyes so the user is able to more comfortably use the VR headset. For example, a user not wearing eyeglasses positions the eyecup assemblies closer to their eyes than a user who wears eyeglasses via the adjustment mechanism. Additionally, in some embodiments, the adjustment mechanism enables the user to adjust a center spacing distance between each of the eyecup assemblies to correspond to the user s interpupillary distance (i.e., a distance between the centers of the pupils for each eye of the user). By adjusting the center spacing distance, a user is able to align the locations of the exit pupils of the VR headset with the locations of the user s eyes. Accordingly, the adjustment mechanism allows a single VR headset to be used by different users who have different interpupillary distances, who do not wear eyeglasses, who wear eyeglasses, or who have any other suitable characteristics. [00] The locators 1 are objects located in specific positions on the VR headset relative to one another and relative to a specific reference point on the VR headset. A locator 1 may be a light emitting diode (LED), a corner cube reflector, a reflective marker, a type of light source that contrasts with an environment in which the VR headset operates, or some combination thereof. In embodiments where the locators 1 are active (i.e., an LED or other type of light emitting device), the locators 1 may emit light in the visible band ( 380 nm to 70 nm), in the infrared (IR) band ( 70 nm to 1 mm), in the ultraviolet band ( nm to 380 nm), in some other portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, or in some combination thereof. [0031] In some embodiments, the locators 1 are located beneath an outer surface of the VR headset, which is transparent to the wavelengths of light emitted or reflected by the locators 1 or is thin enough to not substantially attenuate the wavelengths of light emitted or reflected by the locators 1. Additionally, in some embodiments, the outer surface or other portions of the VR headset are opaque in the visible band of wavelengths of light. Thus, the locators 1 may emit light in the IR band under an outer surface that is transparent in the IR band but opaque in the visible band. [0032] The IMU 1 is an electronic device that generates fast calibration data indicating an estimated position of the VR headset relative to an initial position of the VR headset based on measurement signals received from one or more of the position sensors 12. A position sensor 12 generates one or more measurement signals in response to motion of the VR headset. Examples of position sensors 12 include: one or more accelerometers, one or more gyroscopes, one or more magnetometers, another suitable type of sensor that detects motion, a type of sensor used for error correction of the IMU 1, or some combination thereof. The position sensors 12 may be located external to the IMU 1, internal to the IMU 1, or some combination thereof. [0033] Based on the one or more measurement signals generated by the one or more position sensors 12, the IMU 1 generates fast calibration data indicating an estimated position of the VR headset relative to an initial position of the VR headset. For example, the
6 9 EP B1 position sensors 12 include multiple accelerometers to measure translational motion (forward/back, up/down, left/right) and multiple gyroscopes to measure rotational motion (e.g., pitch, yaw, roll). In some embodiments, the IMU 1 rapidly samples the measurement signals from various position sensors 12 and calculates the estimated position of the VR headset from the sampled data. For example, the IMU 1 integrates the measurement signals received from one or more accelerometers over time to estimate a velocity vector and integrates the velocity vector over time to determine an estimated position of a reference point on the VR headset. Alternatively, the IMU 1 provides the sampled measurement signals to the VR console 1, which determines the fast calibration data. The reference point is a point that may be used to describe the position of the VR headset. While the reference point may generally be defined as a point in space; however, in practice the reference point is defined as a point within the VR headset (e.g., a center of the IMU 1). [0034] The IMU 1 receives one or more calibration parameters from the VR console 1. As further discussed below, the one or more calibration parameters are used to maintain tracking of the VR headset. Based on a received calibration parameter, the IMU 1 may adjust one or more IMU parameters (e.g., sample rate). In some embodiments, certain calibration parameters cause the IMU 1 to update an initial position of the reference point so it corresponds to a next calibrated position of the reference point. Updating the initial position of the reference point as the next calibrated position of the reference point helps reduce accumulated error associated with the determined estimated position. The accumulated error, also referred to as drift error, causes the estimated position of the reference point to "drift" away from the actual position of the reference point over time. [003] The imaging device 13 generates slow calibration data in accordance with calibration parameters received from the VR console 1. Slow calibration data includes one or more images showing observed positions of the locators 1 that are detectable by the imaging device 13. The imaging device 13 may include one or more cameras, one or more video cameras, any other device capable of capturing images including one or more of the locators 1, or some combination thereof. Additionally, the imaging device 13 may include one or more filters (e.g., for increasing signal to noise ratio). The imaging device 13 is configured to detect light emitted or reflected from locators 1 in a field of view of the imaging device 13. In embodiments where the locators 1 include passive elements (e.g., a retroreflector), the imaging device 13 may include a light source that illuminates some or all of the locators 1, which retro-reflect the light towards the light source in the imaging device 13. Slow calibration data is communicated from the imaging device 13 to the VR console 1, and the imaging device 13 receives one or more calibration parameters from the VR console 1 to adjust one or more imaging parameters (e.g., focal length, focus, frame rate, ISO, sensor temperature, shutter speed, aperture, etc.). [0036] The VR input interface 1 is a device that allows a user to send action requests to the VR console 1. An action request is a request to perform a particular action. For example, an action request may be to start or to end an application or to perform a particular action within the application. The VR input interface 1 may include one or more input devices. Example input devices include: a keyboard, a mouse, a game controller, a joystick, a yoke, or any other suitable device for receiving action requests and communicating the received action requests to the VR console 1. An action request received by the VR input interface 1 is communicated to the VR console 1, which performs an action corresponding to the action request. In some embodiments, the VR input interface 1 may provide haptic feedback to the user in accordance with instructions received from the VR console 1. For example, haptic feedback is provided when an action request is received, or the VR console 1 communicates instructions to the VR input interface 1 causing the VR input interface 1 to generate haptic feedback when the VR console 1 performs an action. [0037] The VR console 1 provides content to the VR headset for presentation to the user in accordance with information received from one or more of: the imaging device 13, the VR headset, and the VR input interface 1. In the example shown in FIG. 1, the VR console 1 includes an application store 14, a tracking module 10, and a virtual reality (VR) engine 1. Some embodiments of the VR console 1 have different components than those described in conjunction with FIG. 1. Similarly, the functions further described below may be distributed among components of the VR console 1 in a different manner than is described here. [0038] The application store 14 stores one or more applications for execution by the VR console 1. An application is a group of instructions, that when executed by a processor, generates content for presentation to the user. Content generated by an application may be in response to inputs received from the user via movement of the VR headset or the VR interface device 1. Examples of applications include: gaming applications, conferencing applications, video playback application, or other suitable applications. [0039] The tracking module 10 calibrates the system environment 0 using one or more calibration parameters and may adjust one or more calibration parameters to reduce error in determination of the position of the VR headset. For example, the tracking module 10 adjusts the focus of the imaging device 13 to obtain a more accurate position for observed locators on the VR headset. Moreover, calibration performed by the tracking module 10 also accounts for information received from the IMU 1. Additionally, if tracking of the VR headset is lost (e.g., the imaging device 13 loses line of sight 6
7 11 EP B1 12 of at least a threshold number of the locators 1), the tracking module 1 re-calibrates some or all of the system environment 0. [00] The tracking module 10 tracks movements of the VR headset using slow calibration information from the imaging device 13. For example, the tracking module 10 determines positions of a reference point of the VR headset using observed locators 1 from the slow calibration information and a model of the VR headset. The tracking module 10 also determines positions of a reference point of the VR headset using position information from the fast calibration information. Additionally, in some embodiments, the tracking module 10 may use portions of the fast calibration information, the slow calibration information, or some combination thereof, to predict a future location of the headset. The tracking module 10 provides the estimated or predicted future position of the VR headset to the VR engine 1. [0041] The VR engine 1 executes applications within the system environment 0 and receives position information, acceleration information, velocity information, predicted future positions, or some combination thereof, of the VR headset from the tracking module 10. Based on the received information, the VR engine 1 determines content to provide to the VR headset for presentation to the user. For example, if the received information indicates that the user has looked to the left, the VR engine 1 generates content for the VR headset that mirrors the user s movement in a virtual environment. Additionally, the VR engine 1 performs an action within an application executing on the VR console 1 in response to an action request received from the VR input interface 1 and provides feedback to the user that the action was performed. The provided feedback may be visual or audible feedback via the VR headset or haptic feedback via the VR input interface 1. [0042] FIG. 2A is a wire diagram of a virtual reality (VR) headset 0, in accordance with an embodiment. The VR headset 0 is an embodiment of the VR headset, and includes a front rigid body and a band 2. The front rigid body includes one or more electronic display elements of the electronic display 11 (not shown), the IMU 1, the one or more position sensors 12, and the locators 1. In the embodiment shown by FIG. 2A, the position sensors 12 are located within the IMU 1, and neither the IMU 1 nor the position sensors 12 are visible to the user. [0043] The locators 1 are located in fixed positions on the front rigid body relative to one another and relative to a reference point 21. In the example of FIG. 2A, the reference point 21 is located at the center of the IMU 1. Each of the locators 1 emit light that is detectable by the imaging device 13. Locators 1, or portions of locators 1, are located on a front side 2A, a top side 2B, a bottom side 2C, a right side 2D, and a left side 2E of the front rigid body in the example of FIG. 2A [0044] FIG. 2B is a cross section 22 of the front rigid body of the embodiment of the VR headset 0 shown in FIG. 2A. As shown in FIG. 2B, the front rigid body includes an optical block 2 that provides altered image light to an exit pupil. The exit pupil is a location where a user s eye 24 is positioned while using the VR headset 0. For purposes of illustration, FIG. 2B shows a cross section 22 associated with a single eye 24, but another optical block, separate from the optical block 2, provides altered image light to another eye of the user. [004] The optical block 2 includes an electronic display element 23 of the electronic display 11, and the optics block 118. The electronic display element 23 emits image light toward the optics block 118. In some embodiments, the optics block 118 corrects for one or more optical errors (e.g., distortion, astigmatism, etc.) via one or more optical elements or other components. The optics block 118 directs, via an eyecup assembly, corrected image light to the exit pupil for presentation to the user. In some embodiments, optical elements for correcting one or more optical errors included in the eyecup assembly. [0046] FIG. 3 is a wire diagram of an embodiment of the front rigid body of the VR headset 0 shown in FIG. 2A. The front rigid body includes eyecup assemblies 3 and 31 that are coupled to mounting locations 3 and 3, respectively, on a mounting surface 3. As discussed below in conjunction with FIG. 4, portions of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 may be compressed, stretched, or otherwise deformed to adjust spacing between a user s eyes and outer surfaces 370 of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31. In some embodiments, an adjustment mechanism modifies one or more of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 to adjust the spacing between one or more of the user s eyes and outer surfaces 370 of one or more of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31. Alternatively, a user may manually adjust the spacing between the user s eyes and outer surfaces 370 of one or more of the eyecup assemblies by manually compressing or stretching an eyecup assembly 3, 31. Additionally, in some embodiments, the coupling of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 to the mounting surface 3 allows adjustment of a center spacing 360 between centerlines of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31. This allows a user to adjust the center spacing 360 to correspond to the user s interpupillary distance (i.e., a distance between the centers of the pupils for each eye of the user). [0047] FIG. 4 is a wire diagram of an embodiment of the two eyecup assemblies 3, 31 coupled to the mounting surface 3 of the front rigid body shown in FIG. 3. As shown in FIG. 4, the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 are coupled to the mounting surface 3 to allow adjustment of the center spacing 360 between the eyecup assemblies 3, 31. In the example of FIG. 4, the mounting surface 3 includes rails 4 that are coupled to the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 and coupled to the adjustment mechanism. In some embodiments, the 7
8 13 EP B1 14 rails 4 are threaded and interface with a corresponding threading on one or both of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31. For example, as one or both rails 4 rotate in a direction, the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 move toward each other, while the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 move away from each other as one or both of the rails rotate in an opposite direction. [0048] Each eyecup assembly 3, 31 includes a cone 4, a lens assembly 4, and one or more compression adjusters 4. The lens assembly 4 of an eyecup assembly 3, 31 includes one or more optical elements and is configured to direct portions of image light to a corresponding exit pupil that corresponds to a location of an eye of a user of the VR headset 0. In some embodiments, the lens assembly 4 is also configured to correct one or more types of optical error and/or to magnify the image light. [0049] A cone 4 includes a top portion and a base portion 460. The top portion is coupled to the lens assembly 4 and is configured to hold the lens assembly 4. The cone 4 is configured to receive image light through the base portion 460 and direct the image light toward the lens assembly 4. In various embodiments, the cone 4 is composed of a material that is opaque to visible light and is deformable, so a deformation distance 470 between the top portion and the base portion 460 may be altered. For example, the cone 4 is made of thermoplastic polyurethane. In some embodiments, a user may manually compress or stretch the cone 4 to alter the deformation distance 470, and the cone 4 maintains the deformed state. In other embodiments, the deformation distance 470 may be adjusted using the adjustment mechanism or other suitable mechanism. [000] The cone 4 occupies various positional states corresponding to different distances between its top portion and its bottom portion 460. Example positional states include a full extension state, a partial compression state, and a full compression state. The full extension state is a state of the cone 4 where a distance between the top portion and the bottom portion 460 has a maximum value. The full compression state is a state of the cone 4 where the distance between the top portion and the bottom portion 460 has a minimum value. The partial compression state is a state of the cone 4 where the distance between the top portion and the bottom portion 460 has a value below the maximum value but greater than the minimum value. For example, FIG. A is a cross section of an embodiment of an eyecup assembly 00 in a full extension state. In contrast, FIG. B is a cross section of an embodiment of the eyecup assembly 00 in a full compression state. [001] Turning back to FIG. 4, a compression adjuster 4 adjusts the distance of a particular cone 4 between a point on the top portion of the cone 4 and a point on the bottom portion 460 of the cone. Each cone 4 includes at least one compression adjuster 4. In the embodiment illustrated in FIG. 4, each cone 4 includes three compression adjusters 4. A compression adjuster 4 may be a mechanical device, an electrical device, or some combination thereof. [002] In some embodiments, a compression adjuster 4 is a spring that is electrically coupled to the adjustment mechanism, or another suitable device. The spring is composed of an electrically conductive material, where application of an electrical current to the spring causes the spring to compress. When electrical current is not provided to the spring, the spring does not compress. In various embodiments, the amount by which the spring compresses when current is applied positively correlates with the amount of current applied to the spring. Compression of a spring when current is applied occurs because the coils of the spring have currents flowing in the same direction, which products a magnetic field causing each loop of the spring to be attracted toward each other. [003] The adjustment mechanism may be a mechanical and/or electrical adjustment device capable of causing one and/or both of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 to deform. Deformation of an eyecup assembly 3, 31 alters a deformation distance 470 between a top portion of the cone 4 of the eyecup assembly 3, 31 and a bottom portion 460 of the cone 4 of the eyecup assembly 3, 31. The adjustment mechanism is mechanically and/or electrically coupled to the one or more compression adjusters 4. Responsive to receiving an input from the user, the adjustment device causes one or more of the compression adjusters 4 to compress or to extend. [004] Additionally, in some embodiments, the adjustment mechanism may cause one or both of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 to move along the rails 4. For example, the adjustment mechanism may interface (electrically and/or mechanically) with the rails 4 so an adjustment by the user via the adjustment mechanism modifies the center spacing distance 360. In alternative embodiments, a different adjustment mechanism is used to adjust the center spacing distance 360 of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31. [00] The mounting surface 34 may also include one or more detectors 49 used to determine position information for the eyecup assemblies 3, 31. For example, during calibration the detectors 49 determine different positions of the rails 4 and the positions of the rails 4 are mapped to corresponding positions of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31. Thus, the VR headset determines positions of the eyecup assemblies 3, 31 using the positions of the rails 4 determined from the detectors 49. Summary [006] The foregoing description of the embodiments of the disclosure has been presented for the purpose of illustration; it is not intended to be exhaustive or to limit 8
9 1 EP B1 16 the disclosure to the precise forms disclosed. Persons skilled in the relevant art can appreciate that many modifications and variations are possible in light of the above disclosure. [007] The language used in the specification has been principally selected for readability and instructional purposes, and it may not have been selected to delineate or circumscribe the inventive subject matter. It is therefore intended that the scope of the disclosure be limited not by this detailed description, but rather by any claims that issue on an application based hereon. Accordingly, the disclosed embodiments are intended to be illustrative, but not limiting, of the scope of the disclosure, which is set forth in the following claims. 1 () of the VR headset (0) and the additional top portion () coupled to the additional lens (460), the additional cone (4) configured to receive image light through the additional base portion (460) and direct the image light toward the additional lens (4), the additional cone (4) comprising the opaque material that is deformable to adjust a distance (470) between the additional top portion () and the additional base portion (460); and the adjustment mechanism () is further configured to adjust the distance (470) between the additional top portion () and the additional base portion (460) of the additional cone (4) based on the received input. Claims 1. A virtual reality (VR) headset (0) comprising: an electronic display element (23) configured to output image light; an optics block (118) configured to receive the image light, the optics block (118) comprising: a lens (4) configured to direct portions of the image light to a corresponding exit pupil that corresponds to a location of an eye (24) of a user of the VR headset (0); characterized by a cone (4) including a base (460) portion and a top portion (), the base portion (460) coupled to a mounting surface (3) of a rigid body () of the VR headset (0) and the top portion () coupled to the lens (4), the cone (4) configured to receive image light through the base portion (460) and direct the image light toward the lens (4) and the cone (4) comprising an opaque material that is deformable to adjust a distance (470) between the top portion () and the base portion (460); and an adjustment mechanism () configured to adjust the distance (470) between the top portion () and the base portion (460) of the cone (4) based on a received input. 2. The VR headset (0) of claim 1, wherein the optics block (118) further comprises: an additional lens (4) configured to direct portions of the image light to a corresponding exit pupil that corresponds to a location of another eye (34) of the user of the VR headset (0); an additional cone (4) including an additional base portion (460) and an additional top portion (), the additional base portion (460) coupled to the mounting surface (3) of the rigid body The VR headset (0) of claim 1 or 2, further comprising: a rail (4) coupled to a base portion (460) and an additional rail (4) coupled to the additional base portion (460), wherein the adjustment mechanism () is configured to adjust a center spacing distance (360) between a center of the base portion (460) and a center of the additional base portion (460) in response to a center spacing adjustment input. 4. The VR headset (0) of any of claims 1 to 3, further comprising: a compression adjuster (4) that is coupled to the top portion () and the base portion (460) of the cone (4), and is configured to reduce the distance (470) between the top portion () and the base portion (460) in response to an input received from the adjustment mechanism ().. The VR headset (0) of claims 1, 2 and 4, comprising a first eyecup assembly (3) and a second eyecup assembly (31), the first eyecup assembly (3) including the cone (4), the lens (4) and one or more compression adjusters (4), and the second eyecup assembly (31) including the additional lens (4), the additional cone (4) and one or more additional compression adjusters (4), wherein the mounting surface (34) includes one or more detectors (49) for determining position information of the first and second eyecup assemblies (3, 31). 6. The VR headset (0) of claim, wherein the adjustment mechanism () is a mechanical and/or electrical adjustment device capable of causing the first and/or the second eyecup assembly (3, 31) to deform. 7. The VR headset (0) of any of claims 1 to 6, wherein 9
10 17 EP B1 18 the compression adjuster (4) is a spring that is configured to compress in response to receiving an electrical current. 8. The VR headset (0) of claim 7, wherein the spring is electrically coupled to the adjustment mechanism (), the spring being made from an electrically conductive material, where application of an electrical current to the spring causes the spring to compress, and when electrical current is not provided to the spring, the spring does not compress, the amount by which the spring compresses positively correlating with the amount of current applied to the spring. 9. The VR headset (0) of any of claims 1 to 8, wherein the cone (4) comprises thermoplastic polyurethane.. The VR headset (0) of any of claims 1 to 9, wherein the opaque material is opaque to wavelengths of visible light. Patentansprüche 1. Brille für virtuelle Realität, VR, (0), die umfasst: ein elektronisches Anzeigeelement (23), das so ausgeführt ist, dass es Bildlicht ausgibt; einen Optikblock (118), der so ausgeführt ist, dass er das Bildlicht empfängt, wobei der Optikblock (118) umfasst: eine Linse (4), die so ausgeführt ist, dass sie Teile des Bildlichts zu einer entsprechenden Ausgangspupille leitet, welche einer Stelle eines Auges (24) eines Benutzers der VR-Brille (0) entspricht; gekennzeichnet durch einen Konus (4), der einen Basisteil (460) und einen oberen Teil () aufweist, wobei der Basisteil (460) mit einer Befestigungsfläche (3) eines starren Körpers () der VR-Brille (0) gekoppelt ist und der obere Teil () mit der Linse (4) gekoppelt ist, der Konus (4) so ausgeführt ist, dass er Bildlicht durch den Basisteil (460) hindurch empfängt und das Bildlicht in Richtung der Linse (4) leitet und der Konus (4) ein undurchlässiges Material umfasst, das verformbar ist, um eine Distanz (470) zwischen dem oberen Teil () und dem Basisteil (460) einzustellen; und einen Einstellmechanismus (), der so ausgeführt ist, dass er die Distanz (470) zwischen dem oberen Teil () und dem Basisteil (460) des Konus (4) auf der Basis eines empfangenen Eingangssignals einstellt. 2. VR-Brille (0) nach Anspruch 1, wobei der Optikblock (118) ferner umfasst: eine weitere Linse (4), die so ausgeführt ist, dass sie Teile des Bildlichts zu einer entsprechenden Ausgangspupille leitet, welche einer Stelle eines anderen Auges (34) des Benutzers der VR-Brille (0) entspricht; einen weiteren Konus (4), der einen weiteren Basisteil (460) und einen weiteren oberen Teil () aufweist, wobei der weitere Basisteil (460) mit der Befestigungsfläche (3) des starren Körpers () der VR-Brille (0) gekoppelt ist und der weitere obere Teil () mit der weiteren Linse (460) gekoppelt ist, wobei der weitere Konus (4) so ausgeführt ist, dass er Bildlicht durch den weiteren Basisteil (460) hindurch empfängt und das Bildlicht in Richtung der weiteren Linse (4) leitet, wobei der weitere Konus (4) das undurchlässige Material umfasst, das verformbar ist, um eine Distanz (470) zwischen dem weiteren oberen Teil () und dem weiteren Basisteil (460) einzustellen; und der Einstellmechanismus () ferner so ausgeführt ist, dass er die Distanz (470) zwischen dem weiteren oberen Teil () und dem weiteren Basisteil (460) des weiteren Konus (4) auf der Basis des empfangenen Eingangssignals einstellt. 3. VR-Brille (0) nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, die ferner umfasst: eine Schiene (4), die mit einem Basisteil (460) gekoppelt ist und eine weitere Schiene (4), die mit dem weiteren Basisteil (460) gekoppelt ist, wobei der Einstellmechanismus () so ausgeführt ist, dass er eine Mittenbeabstandungsdistanz (360) zwischen einer Mitte des Basisteils (460) und einer Mitte des weiteren Basisteils (460) in Reaktion auf ein Mittenbeabstandungseinstell-Eingangssignal einstellt. 4. VR-Brille (0) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, die ferner umfasst: eine Zusammendrück-Einstelleinrichtung (4), die mit dem oberen Teil () und dem Basisteil (460) des Konus (4) gekoppelt ist und so ausgeführt ist, dass sie die Distanz (470) zwischen dem oberen Teil () und dem Basisteil (460) in Reaktion auf ein Eingangssignal, das aus dem Einstellmechanismus () erhalten wird, verringert.. VR-Brille (0) nach Anspruch 1, 2 und 4, die eine
11 19 EP B1 erste Augenmuschelanordnung (3) und eine zweite Augenmuschelanordnung (31) umfasst, wobei die erste Augenmuschelanordnung (3) den Konus (4), die Linse (4) und eine oder mehrere Zusammendrück-Einstelleinrichtungen (4) aufweist und die zweite Augenmuschelanordnung (31) die weitere Linse (4), den weiteren Konus (4) und eine oder mehrere weitere Zusammendrück-Einstelleinrichtungen (4) aufweist, wobei die Befestigungsfläche (34) einen oder mehrere Detektoren (49) zum Ermitteln von Positionsinformationen der ersten und der zweiten Augenmuschelanordnung (3, 31) aufweist. 6. VR-Brille (0) nach Anspruch, wobei der Einstellmechanismus () eine mechanische und/oder elektrische Einstellvorrichtung ist, die in der Lage ist zu bewirken, dass sich die erste und/oder die zweite Augenmuschelanordnung (3, 31) verformt. 7. VR-Brille (0) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6, wobei die Zusammendrück-Einstelleinrichtung (4) eine Feder ist, die so ausgeführt ist, dass sie in Reaktion auf das Empfangen eines elektrischen Stroms zusammengedrückt wird. 8. VR-Brille (0) nach Anspruch 7, wobei die Feder mit dem Einstellmechanismus () elektrisch gekoppelt ist, wobei die Feder aus einem elektrisch leitenden Material gefertigt ist, wobei das Anlegen eines elektrischen Stroms an die Feder bewirkt, dass die Feder zusammengedrückt wird, und wenn kein elektrischer Strom zu der Feder geliefert wird, die Feder nicht zusammengedrückt wird, wobei der Betrag, um den die Feder zusammengedrückt wird, mit dem Betrag an Strom, der an die Feder angelegt wird, positiv korreliert ist. 9. VR-Brille (0) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 8, wobei der Konus (4) ein thermoplastisches Urethan umfasst.. VR-Brille (0) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 9, wobei das undurchlässige Material gegenüber Wellenlängen des sichtbaren Lichts undurchlässig ist. Revendications 1. Casque de réalité virtuelle, RV, (0) comprenant : un élément d affichage électronique (23) configuré pour fournir en sortie une lumière d image ; un bloc optique (118) configuré pour recevoir la lumière d image, le bloc optique (118) comprenant : une lentille (4) configurée pour diriger des portions de la lumière d image vers une pupille de sortie correspondante qui correspond à un emplacement d un oeil (24) d un utilisateur du casque RV (0) ; caractérisé par un cône (4) comportant une portion de base (460) et une portion de dessus (), la portion de base (460) étant couplée à une surface de montage (3) d un corps rigide () du casque RV (0) et la portion de dessus () étant couplée à la lentille (4), le cône (4) étant configuré pour recevoir une lumière d image à travers la portion de base (460) et diriger la lumière de base vers la lentille (4) et le cône (4) comprenant un matériau opaque qui est déformable pour régler une distance (470) entre la portion de dessus () et la portion de base (460) ; et un mécanisme de réglage () configuré pour régler la distance (470) entre la portion de dessus () et la portion de base (460) du cône (4) d après une entrée reçue. 2. Casque RV (0) selon la revendication 1, dans lequel le bloc optique (118) comprend en outre : une lentille supplémentaire (4) configurée pour diriger des portions de la lumière d image vers une pupille de sortie correspondante qui correspond à un emplacement d un autre oeil (34) de l utilisateur du casque RV (0) ; un cône supplémentaire (4) comportant une portion de base supplémentaire (460) et une portion de dessus supplémentaire (), la portion de base supplémentaire (460) étant couplée à la surface de montage (3) du corps rigide () du casque RV (0) et la portion de dessus supplémentaire () étant couplée à la lentille supplémentaire (460), le cône supplémentaire (4) étant configuré pour recevoir une lumière d image à travers la portion de base supplémentaire (460) et diriger la lumière d image vers la lentille supplémentaire (4), le cône supplémentaire (4) comprenant le matériau opaque qui est déformable pour régler une distance (470) entre la portion de dessus supplémentaire () et la portion de base supplémentaire (460) ; et le mécanisme de réglage () est en outre configuré pour régler la distance (470) entre la portion de dessus supplémentaire () et la portion de base supplémentaire (460) du cône supplémentaire (4) d après l entrée reçue. 3. Casque RV (0) selon la revendication 1 ou 2, comprenant en outre : 11
(51) Int Cl.: H02M 1/32 ( ) H05K 5/02 ( ) H02M 5/45 ( ) H02M 5/458 ( ) H02M 7/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_99 _9B_T (11) EP 1 993 19 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 (21) Application number: 081862.9
(19) TEPZZ_99 _9B_T (11) EP 1 993 19 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 (21) Application number: 081862.9
(51) Int Cl.: B42D 25/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_8868 B_T (11) EP 1 886 83 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.08.201 Bulletin 201/33 (1) Int Cl.: B42D 2/00 (2014.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ_8868 B_T (11) EP 1 886 83 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.08.201 Bulletin 201/33 (1) Int Cl.: B42D 2/00 (2014.01) (21)
(51) Int Cl.: G03B 37/04 ( ) G03B 21/00 ( ) E04H 3/22 ( ) G03B 21/60 ( ) H04N 9/31 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 68 _ B_T (11) EP 2 68 312 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (21) Application number: 1317918. (1) Int
(19) TEPZZ 68 _ B_T (11) EP 2 68 312 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.03.16 Bulletin 16/13 (21) Application number: 1317918. (1) Int
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 765688A T (11) EP 2 765 688 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/33 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14154185.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 765688A T (11) EP 2 765 688 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 13.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/33 (51) Int Cl.: H02K 11/04 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 14154185.4 (22)
TEPZZ 879Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0354 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
TEPZZ_94787 B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ_94787 B_T (11) EP 1 947 872 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.04.14 Bulletin 14/16 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 24/02 (09.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ_94787 B_T (11) EP 1 947 872 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 16.04.14 Bulletin 14/16 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 24/02 (09.01) (21)
TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T (11) EP 2 607 223 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (21) Application number: 10858858.3
(19) TEPZZ 6Z7 A_T (11) EP 2 607 223 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 26.06.2013 Bulletin 2013/26 (21) Application number: 10858858.3
TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 ( ) G06F 3/0482 (2013.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T (11) EP 2 720 134 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/16 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01) G06F 3/0482 (2013.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T (11) EP 2 720 134 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/16 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01) G06F 3/0482 (2013.01) (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: G06K 19/07 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 724 706 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.02.2008 Bulletin 2008/09 (1) Int Cl.: G06K 19/07 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) (11) EP 1 724 706 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.02.2008 Bulletin 2008/09 (1) Int Cl.: G06K 19/07 (2006.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 774884A_T (11) EP 2 774 884 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.2014 Bulletin 2014/37 (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13158169.6 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 774884A_T (11) EP 2 774 884 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09.2014 Bulletin 2014/37 (51) Int Cl.: B66B 1/34 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13158169.6 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 ( ) B21D 41/00 ( ) B62D 1/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 56 5A_T (11) EP 3 115 635 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16177975.6 (51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 (2006.01) B21D
(19) TEPZZ 56 5A_T (11) EP 3 115 635 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16177975.6 (51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 (2006.01) B21D
(51) Int Cl.: G07D 9/00 ( ) G07D 11/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 4_48B_T (11) EP 2 341 48 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 088119.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 4_48B_T (11) EP 2 341 48 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (21) Application number: 088119.2 (22) Date
TEPZZ 8 5ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 8 ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (21) Application number: 13170674.9 (1) Int Cl.: G0B 19/042 (06.01) G06F 11/00 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 8 ZA_T (11) EP 2 811 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.12.14 Bulletin 14/0 (21) Application number: 13170674.9 (1) Int Cl.: G0B 19/042 (06.01) G06F 11/00 (06.01)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/51
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 263 736 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.12.2010 Bulletin 2010/51 (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/09 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10165921.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 263 736 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.12.2010 Bulletin 2010/51 (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/09 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10165921.7 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ Z7Z7 5A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H01F 30/12 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z7Z7 A_T (11) EP 3 070 72 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.09.16 Bulletin 16/38 (1) Int Cl.: H01F /12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 16161481.3 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ Z7Z7 A_T (11) EP 3 070 72 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.09.16 Bulletin 16/38 (1) Int Cl.: H01F /12 (06.01) (21) Application number: 16161481.3 (22) Date of
TEPZZ 7545 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2014/29
 (19) TEPZZ 74 A_T (11) EP 2 74 11 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (21) Application number: 1476.7 (1) Int Cl.: B21F 27/ (06.01) B21C 1/02 (06.01) C21D
(19) TEPZZ 74 A_T (11) EP 2 74 11 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.07.14 Bulletin 14/29 (21) Application number: 1476.7 (1) Int Cl.: B21F 27/ (06.01) B21C 1/02 (06.01) C21D
(51) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 3 239 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 0.06.13 Bulletin 13/23 (1) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 3 239 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 0.06.13 Bulletin 13/23 (1) Int Cl.: D03D 47/48 (06.01) (21) Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170134717A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0134717 A1 Trail et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DEPTH MAPPING WITH A HEAD G06T 9/00 (2006.01) MOUNTED DISPLAY
(19) United States US 20170134717A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0134717 A1 Trail et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) DEPTH MAPPING WITH A HEAD G06T 9/00 (2006.01) MOUNTED DISPLAY
TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T (11) EP 2 670 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/49 (21) Application number: 12169788.2 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/36 (2007.01) H02J
(19) TEPZZ 67ZZ A_T (11) EP 2 670 033 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/49 (21) Application number: 12169788.2 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 1/36 (2007.01) H02J
TEPZZ 9746 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9746 A_T (11) EP 2 974 611 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 20.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/03 (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15159454.6 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 9746 A_T (11) EP 2 974 611 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 20.01.2016 Bulletin 2016/03 (51) Int Cl.: A41F 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15159454.6 (22)
TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2015/35
 (19) TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T (11) EP 2 9 473 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.08.1 Bulletin 1/3 (21) Application number: 13836.0 (22) Date of filing: 04.02.1 (1) Int Cl.: B6B 9/093
(19) TEPZZ 9_Z47 A_T (11) EP 2 9 473 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 26.08.1 Bulletin 1/3 (21) Application number: 13836.0 (22) Date of filing: 04.02.1 (1) Int Cl.: B6B 9/093
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/50
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 261 890 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.12.20 Bulletin 20/50 (51) Int Cl.: GD 13/02 (2006.01) GH 3/14 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 160308.2 (22) Date
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 261 890 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.12.20 Bulletin 20/50 (51) Int Cl.: GD 13/02 (2006.01) GH 3/14 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 160308.2 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: G10L 19/24 ( ) G10L 21/038 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 48Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 48 029 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (21) Application number: 117746.0 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48Z 9B_T (11) EP 2 48 029 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (21) Application number: 117746.0 (22)
TEPZZ _64_69B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _64_69B_T (11) EP 2 164 169 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/32 (21) Application number: 07741714.5
(19) TEPZZ _64_69B_T (11) EP 2 164 169 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.08.2017 Bulletin 2017/32 (21) Application number: 07741714.5
TEPZZ 76 84_A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 76 84_A_T (11) EP 2 762 841 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/32 (21) Application number: 12835850.4
(19) TEPZZ 76 84_A_T (11) EP 2 762 841 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.08.2014 Bulletin 2014/32 (21) Application number: 12835850.4
TEPZZ Z47794A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z47794A_T (11) EP 3 047 794 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 27.07.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1478031.1
(19) TEPZZ Z47794A_T (11) EP 3 047 794 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 27.07.16 Bulletin 16/ (21) Application number: 1478031.1
TEPZZ 5496_6A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 ( ) H02M 7/493 (2007.
 (19) TEPZZ 496_6A_T (11) EP 2 49 616 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/04 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 (2006.01) H02M 7/493 (2007.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 496_6A_T (11) EP 2 49 616 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 23.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/04 (1) Int Cl.: H02J 3/38 (2006.01) H02M 7/493 (2007.01) (21) Application number:
TEPZZ 7 8 9ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 8 9ZA_T (11) EP 2 728 390 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 07.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/19 (21) Application number: 12804964.0
(19) TEPZZ 7 8 9ZA_T (11) EP 2 728 390 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 07.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/19 (21) Application number: 12804964.0
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: B65D 1/34 ( ) B29C 45/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7 6 8ZB_T (11) EP 2 726 380 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.08.201 Bulletin 201/3 (21) Application number: 12793.3 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 7 6 8ZB_T (11) EP 2 726 380 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.08.201 Bulletin 201/3 (21) Application number: 12793.3 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2012/33
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 486 833 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/33 (51) Int Cl.: A47J 43/07 (2006.01) A47J 43/046 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250148.1
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 486 833 A1 (43) Date of publication: 15.08.2012 Bulletin 2012/33 (51) Int Cl.: A47J 43/07 (2006.01) A47J 43/046 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 11250148.1
TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2017/09
 (19) TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T (11) EP 3 135 931 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: F16C 29/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 16190648.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ _ 59 _A_T (11) EP 3 135 931 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01.03.2017 Bulletin 2017/09 (51) Int Cl.: F16C 29/06 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 16190648.2 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B23K 9/095 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z_97 8B_T (11) EP 2 019 738 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.01.14 Bulletin 14/01 (21) Application number: 0770896.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z_97 8B_T (11) EP 2 019 738 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.01.14 Bulletin 14/01 (21) Application number: 0770896.4 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/31
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 213 476 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.08.2010 Bulletin 2010/31 (21) Application number: 09151785.4 (51) Int Cl.: B44C 5/04 (2006.01) E04F 13/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 213 476 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.08.2010 Bulletin 2010/31 (21) Application number: 09151785.4 (51) Int Cl.: B44C 5/04 (2006.01) E04F 13/00 (2006.01)
TEPZZ 674Z48A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 674Z48A_T (11) EP 2 674 048 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/1 (1) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 131713.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 674Z48A_T (11) EP 2 674 048 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 18.12.2013 Bulletin 2013/1 (1) Int Cl.: A42B 3/30 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 131713.4 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl. 7 : H04Q 7/32. (56) References cited: US-A
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00083337B1* (11) EP 0 833 37 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00083337B1* (11) EP 0 833 37 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of
TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T (11) EP 3 1 927 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 (06.01) (21) Application number: 118222.1 (22) Date of filing:
(19) TEPZZ _ Z9 7A_T (11) EP 3 1 927 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 1.02.17 Bulletin 17/07 (1) Int Cl.: G01P 3/66 (06.01) (21) Application number: 118222.1 (22) Date of filing:
(51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 ( ) G01B 11/24 ( ) G01N 21/47 ( )
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 939 581 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.07.2008 Bulletin 2008/27 (21) Application number: 07405346.3 (51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 (2006.01) G01B 11/24 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 939 581 A1 (43) Date of publication: 02.07.2008 Bulletin 2008/27 (21) Application number: 07405346.3 (51) Int Cl.: G01B 9/02 (2006.01) G01B 11/24 (2006.01)
TEPZZ_787_6_B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ_787_6_B_T (11) EP 1 787 161 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.09.2017 Bulletin 2017/39 (21) Application number: 05778009.0
(19) TEPZZ_787_6_B_T (11) EP 1 787 161 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.09.2017 Bulletin 2017/39 (21) Application number: 05778009.0
(51) Int Cl.: G01V 3/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 6 _B_T (11) EP 2 62 1 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.11.16 Bulletin 16/4 (21) Application number: 1177893.0 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 6 _B_T (11) EP 2 62 1 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 09.11.16 Bulletin 16/4 (21) Application number: 1177893.0 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: B05B 15/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_79 9 5B_T (11) EP 1 793 935 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 25.02.2009 Bulletin 2009/09 (21) Application number: 06768011.6
(19) TEPZZ_79 9 5B_T (11) EP 1 793 935 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 25.02.2009 Bulletin 2009/09 (21) Application number: 06768011.6
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160127717A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0127717 A1 PetroV (43) Pub. Date: (54) DIFFRACTIVE ELEMENT FOR REDUCING (52) U.S. Cl. FIXED PATTERN NOSE IN
US 20160127717A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0127717 A1 PetroV (43) Pub. Date: (54) DIFFRACTIVE ELEMENT FOR REDUCING (52) U.S. Cl. FIXED PATTERN NOSE IN
TEPZZ _79748A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 ( ) B60Q 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ _79748A_T (11) EP 3 179 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 (09.01) B60Q 1/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 119834.9
(19) TEPZZ _79748A_T (11) EP 3 179 748 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.06.17 Bulletin 17/24 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 4/04 (09.01) B60Q 1/00 (06.01) (21) Application number: 119834.9
(51) Int Cl.: B23K 9/095 ( ) B23K 9/10 ( ) B23K 9/32 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 96ZZZ_B_T (11) EP 2 960 001 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.04.17 Bulletin 17/1 (1) Int Cl.: B23K 9/09 (06.01) B23K 9/
(19) TEPZZ 96ZZZ_B_T (11) EP 2 960 001 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.04.17 Bulletin 17/1 (1) Int Cl.: B23K 9/09 (06.01) B23K 9/
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B29B 15/12 ( ) B32B 5/26 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ A_T (11) EP 3 112 111 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: B29B 1/12 (2006.01) B32B /26 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 117028.8
(19) TEPZZ A_T (11) EP 3 112 111 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: B29B 1/12 (2006.01) B32B /26 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 117028.8
APSI WIFI, LLC. Company S Monroe Plaza Way Suite A Sandy, UT 84070
 APSI WIFI, LLC Address 9121 S Monroe Plaza Way Suite A Sandy, UT 84070 Publication number WO/2015/161133 Application number PCT/US2015/026259 Publication date 2015-10-22 Filing Date 2015-04-16 Publication
APSI WIFI, LLC Address 9121 S Monroe Plaza Way Suite A Sandy, UT 84070 Publication number WO/2015/161133 Application number PCT/US2015/026259 Publication date 2015-10-22 Filing Date 2015-04-16 Publication
TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B21J 5/08 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T (11) EP 3 037 189 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/26 (1) Int Cl.: B21J /08 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 120098.9 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ Z 7_89A_T (11) EP 3 037 189 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 29.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/26 (1) Int Cl.: B21J /08 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 120098.9 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/044 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7469Z6B_T (11) EP 2 746 906 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 19.04.17 Bulletin 17/16 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/044 (06.01) (21)
(19) TEPZZ 7469Z6B_T (11) EP 2 746 906 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 19.04.17 Bulletin 17/16 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/044 (06.01) (21)
TEPZZ 56_495B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G08B 17/107 ( ) G08B 29/24 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 6_49B_T (11) EP 2 61 49 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 19.03.2014 Bulletin 2014/12 (21) Application number: 11719038.9
(19) TEPZZ 6_49B_T (11) EP 2 61 49 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 19.03.2014 Bulletin 2014/12 (21) Application number: 11719038.9
(51) Int Cl.: H05B 33/08 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_9 94B_T (11) EP 1 932 394 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/17 (21) Application number: 06821145.7
(19) TEPZZ_9 94B_T (11) EP 1 932 394 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 27.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/17 (21) Application number: 06821145.7
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 ( ) G01S 13/78 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 8789A_T (11) EP 2 87 89 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04.201 Bulletin 201/1 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 (2006.01) G01S 13/78 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
(19) TEPZZ 8789A_T (11) EP 2 87 89 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.04.201 Bulletin 201/1 (1) Int Cl.: G01S 7/40 (2006.01) G01S 13/78 (2006.01) (21) Application number:
EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) (11) EP 1 826 753 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21..2009 Bulletin 2009/43 (51) Int Cl.: G11B 7/0065 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) (11) EP 1 826 753 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 21..2009 Bulletin 2009/43 (51) Int Cl.: G11B 7/0065 (2006.01) (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z4Z9ZB_T (11) EP 3 0 90 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.02.18 Bulletin 18/07 (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ Z4Z9ZB_T (11) EP 3 0 90 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 14.02.18 Bulletin 18/07 (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ 48A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/335 ( ) H02M 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/48
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 390 891 A1 (43) Date of publication: 30.11.2011 Bulletin 2011/48 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 33/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10460018.4 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 390 891 A1 (43) Date of publication: 30.11.2011 Bulletin 2011/48 (51) Int Cl.: H01H 33/16 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10460018.4 (22) Date of filing:
TEPZZ Z_89_5A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2016/19
 (19) TEPZZ Z_89_A_T (11) EP 3 018 91 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.0.16 Bulletin 16/19 (1) Int Cl.: H04R 1/34 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1192976.7 (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ Z_89_A_T (11) EP 3 018 91 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.0.16 Bulletin 16/19 (1) Int Cl.: H04R 1/34 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1192976.7 (22) Date of
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04B 1/40 ( ) H04W 52/02 (2009.
 (19) TEPZZ 44 79A T (11) EP 2 44 379 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 09.01.13 Bulletin 13/02 (1) Int Cl.: H04B 1/ (06.01) H04W 2/02 (09.01) (21) Application number: 1210216.
(19) TEPZZ 44 79A T (11) EP 2 44 379 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 09.01.13 Bulletin 13/02 (1) Int Cl.: H04B 1/ (06.01) H04W 2/02 (09.01) (21) Application number: 1210216.
TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T (11) EP 3 029 821 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 08.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/23 (21) Application number: 14831328.1
(19) TEPZZ Z 98 _A_T (11) EP 3 029 821 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 153(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 08.06.2016 Bulletin 2016/23 (21) Application number: 14831328.1
TEPZZ Z 8867A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ Z 8867A_T (11) EP 3 028 867 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (21) Application number: 110888.4 (1) Int Cl.: B41M /0 (06.01) B41M /2 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ Z 8867A_T (11) EP 3 028 867 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 08.06.16 Bulletin 16/23 (21) Application number: 110888.4 (1) Int Cl.: B41M /0 (06.01) B41M /2 (06.01)
(51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/06 ( ) (54) Combined current and voltage measurement transformer of the capacitor bushing type
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 624 311 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.02.2006 Bulletin 2006/06 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 624 311 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.02.2006 Bulletin 2006/06 (51) Int Cl.:
TEPZZ 5Z 8 9B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04W 52/14 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z 8 9B_T (11) EP 2 03 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.0.16 Bulletin 16/18 (21) Application number: 83116.4 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ Z 8 9B_T (11) EP 2 03 829 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.0.16 Bulletin 16/18 (21) Application number: 83116.4 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: H02P 25/06 ( ) F04B 35/04 ( ) F04B 49/06 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z_6669B_T (11) EP 2 016 669 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.03.17 Bulletin 17/11 (21) Application number: 0774604.9 (22)
(19) TEPZZ Z_6669B_T (11) EP 2 016 669 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.03.17 Bulletin 17/11 (21) Application number: 0774604.9 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: B60J 10/00 ( ) B60P 3/34 ( ) F16J 15/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z6 4A_T (11) EP 3 6 334 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.12.2016 Bulletin 2016/51 (21) Application number: 16171482.9 (51) Int Cl.: B60J /00 (2016.01) B60P 3/34
(19) TEPZZ _Z6 4A_T (11) EP 3 6 334 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 21.12.2016 Bulletin 2016/51 (21) Application number: 16171482.9 (51) Int Cl.: B60J /00 (2016.01) B60P 3/34
TEPZZ B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 6 464 B_T (11) EP 2 624 643 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.03.1 Bulletin 1/13 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 64/00 (09.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6 464 B_T (11) EP 2 624 643 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 2.03.1 Bulletin 1/13 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 64/00 (09.01) (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: H04R 25/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z78 8B_T (11) EP 2 7 828 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 29.06.16 Bulletin 16/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04R 2/00 (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ _Z78 8B_T (11) EP 2 7 828 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 29.06.16 Bulletin 16/26 (1) Int Cl.: H04R 2/00 (06.01) (21) Application
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H04N 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 9 498 A_T (11) EP 2 924 983 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09. Bulletin / (1) Int Cl.: H04N 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1444.0 (22) Date of filing: 27.03.14
(19) TEPZZ 9 498 A_T (11) EP 2 924 983 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication:.09. Bulletin / (1) Int Cl.: H04N 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1444.0 (22) Date of filing: 27.03.14
TEPZZ 9 449B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 9 449B_T (11) EP 2 293 449 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.07.13 Bulletin 13/28 (21) Application number: 0984478.7 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 9 449B_T (11) EP 2 293 449 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.07.13 Bulletin 13/28 (21) Application number: 0984478.7 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: G02B 27/01 ( ) H04N 5/74 ( ) H04N 9/31 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_4_6 9B_T (11) EP 1 41 639 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.11.2016 Bulletin 2016/44 (21) Application number: 0278816.6
(19) TEPZZ_4_6 9B_T (11) EP 1 41 639 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.11.2016 Bulletin 2016/44 (21) Application number: 0278816.6
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 96 6 8A_T (11) EP 2 962 628 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.01.16 Bulletin 16/01 (21) Application number: 14781797.7
(19) TEPZZ 96 6 8A_T (11) EP 2 962 628 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 06.01.16 Bulletin 16/01 (21) Application number: 14781797.7
TEPZZ _74 6 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ _74 6 A_T (11) EP 3 174 363 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (21) Application number: 16872.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 84/04 (09.01) H04W 88/04 (09.01)
(19) TEPZZ _74 6 A_T (11) EP 3 174 363 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (21) Application number: 16872.1 (1) Int Cl.: H04W 84/04 (09.01) H04W 88/04 (09.01)
TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T (11) EP 3 002 860 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 15002058.4 (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/156 (2006.01) H02M
(19) TEPZZ ZZ 86ZA_T (11) EP 3 002 860 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 06.04.2016 Bulletin 2016/14 (21) Application number: 15002058.4 (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/156 (2006.01) H02M
(51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 ( ) B25J 9/00 ( ) (54) Robotic system for laser, plasma, water jet, milling etc. machining or processing of parts
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 011 609 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/02 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 (2006.01) B25J 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08104621.1
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 011 609 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.2009 Bulletin 2009/02 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 5/02 (2006.01) B25J 9/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 08104621.1
TEPZZ_9775 B_T EP B1 (19) (11) EP B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
 (19) TEPZZ_977 B_T (11) EP 1 977 32 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.11.14 Bulletin 14/46 (21) Application number: 07762632.3 (22)
(19) TEPZZ_977 B_T (11) EP 1 977 32 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 12.11.14 Bulletin 14/46 (21) Application number: 07762632.3 (22)
(51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 2 284 766 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 11.07.2012 Bulletin 2012/28 (51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) (11) EP 2 284 766 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 11.07.2012 Bulletin 2012/28 (51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 (2006.01) (21) Application
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2004/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001418491A2* (11) EP 1 418 491 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.0.04 Bulletin 04/ (1) Int
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP001418491A2* (11) EP 1 418 491 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 12.0.04 Bulletin 04/ (1) Int
(56) References cited: US-A US-A
 (19) Europllsches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 (11) EP 1 453 416 81 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
(19) Europllsches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen des brevets 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 (11) EP 1 453 416 81 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2009/18
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 052 672 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.04.2009 Bulletin 2009/18 (21) Application number: 08015309.1 (51) Int Cl.: A61B 1/005 (2006.01) A61M 25/00 (2006.01)
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 052 672 A1 (43) Date of publication: 29.04.2009 Bulletin 2009/18 (21) Application number: 08015309.1 (51) Int Cl.: A61B 1/005 (2006.01) A61M 25/00 (2006.01)
(51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ ZZ7Z97B_T (11) EP 3 007 097 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 30.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ ZZ7Z97B_T (11) EP 3 007 097 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 30.08.17 Bulletin 17/3 (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: G01S 5/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _794 B_T (11) EP 2 217 942 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.03.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 078192.4 (22)
(19) TEPZZ _794 B_T (11) EP 2 217 942 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 08.03.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 078192.4 (22)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 5/02 ( ) G01S 5/14 ( ) H04L 12/28 (2006.
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 720 032 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/45 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 720 032 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.11.2006 Bulletin 2006/45 (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: H04B 7/06 ( ) H04B 7/08 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 4 447B_T (11) EP 2 42 447 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.09.17 Bulletin 17/36 (21) Application number: 7332.7 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 4 447B_T (11) EP 2 42 447 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 06.09.17 Bulletin 17/36 (21) Application number: 7332.7 (22) Date
(51) Int Cl.: G01B 11/00 ( ) G01B 21/30 ( ) G01B 9/02 ( ) G01Q 20/02 ( ) B82Y 35/00 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_86Z 96B_T (11) EP 1 860 396 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/17 (21) Application number: 06715045.8
(19) TEPZZ_86Z 96B_T (11) EP 1 860 396 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 23.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/17 (21) Application number: 06715045.8
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2000/20
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 000 000 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.05.2000 Bulletin 2000/20 (21) Application
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 000 000 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 17.05.2000 Bulletin 2000/20 (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: B32B 27/32 ( ) B65D 65/40 ( )
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 483 116 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.01.06
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 483 116 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 04.01.06
(51) Int Cl.: B29C 45/16 ( ) B29K 55/02 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ _Z_8ZB_T (11) EP 2 3 180 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 0974786. (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ _Z_8ZB_T (11) EP 2 3 180 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent:.02.16 Bulletin 16/06 (21) Application number: 0974786. (22) Date
TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01S 5/06 ( ) G01S 5/02 (2010.
 (19) TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T (11) EP 3 173 809 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (1) Int Cl.: G01S /06 (06.01) G01S /02 (.01) (21) Application number: 1618084.8
(19) TEPZZ _7 8Z9A_T (11) EP 3 173 809 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 31.0.17 Bulletin 17/22 (1) Int Cl.: G01S /06 (06.01) G01S /02 (.01) (21) Application number: 1618084.8
TEPZZ _48_45A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ _48_4A_T (11) EP 3 148 14 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 1489422.7
(19) TEPZZ _48_4A_T (11) EP 3 148 14 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 29.03.17 Bulletin 17/13 (21) Application number: 1489422.7
(51) Int Cl.: D21F 11/00 ( ) D21H 27/30 ( ) D21H 27/32 ( ) D21H 27/10 ( ) D21H 21/48 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ Z_ 4_B_T (11) EP 2 013 41 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 19.11.2014 Bulletin 2014/47 (21) Application number: 07734239.2
(19) TEPZZ Z_ 4_B_T (11) EP 2 013 41 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 19.11.2014 Bulletin 2014/47 (21) Application number: 07734239.2
(51) Int Cl.: G06K 7/10 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 779Z ZB_T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28..1 Bulletin 1/44 (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1419196.6
(19) TEPZZ 779Z ZB_T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 28..1 Bulletin 1/44 (1) Int Cl.: G06K 7/ (06.01) (21) Application number: 1419196.6
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2006/40
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 708 303 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/40 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 708 303 A1 (43) Date of publication: 04.10.2006 Bulletin 2006/40 (51) Int Cl.:
(51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/041 ( ) H03K 17/96 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 46_ B_T (11) EP 2 461 233 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/14 (21) Application number: 10804118.7
(19) TEPZZ 46_ B_T (11) EP 2 461 233 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (45) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 02.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/14 (21) Application number: 10804118.7
(51) Int Cl.: B24D 11/00 ( )
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 22 386 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.03.06
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (11) EP 1 22 386 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 01.03.06
*EP A1* EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2005/39
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00180041A1* (11) EP 1 80 041 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.09.200 Bulletin 200/39 (1)
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00180041A1* (11) EP 1 80 041 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 28.09.200 Bulletin 200/39 (1)
TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 ( ) B25J 19/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T (11) EP 2 551 068 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/05 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 (2006.01) B25J 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 55_Z68A_T (11) EP 2 551 068 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 30.01.2013 Bulletin 2013/05 (51) Int Cl.: B25J 9/04 (2006.01) B25J 19/00 (2006.01) (21) Application
(51) Int Cl.: H04B 1/38 ( ) H01Q 1/24 ( )
 (19) (11) EP 1 162 73 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.09.07 Bulletin 07/39 (1) Int Cl.: H04B 1/38 (06.01) H01Q 1/24 (06.01) (21)
(19) (11) EP 1 162 73 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 26.09.07 Bulletin 07/39 (1) Int Cl.: H04B 1/38 (06.01) H01Q 1/24 (06.01) (21)
EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/11
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 296 072 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.03.11 Bulletin 11/11 (1) Int Cl.: G0D 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 170224.9 (22) Date of filing: 21.07.
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 296 072 A2 (43) Date of publication: 16.03.11 Bulletin 11/11 (1) Int Cl.: G0D 1/02 (06.01) (21) Application number: 170224.9 (22) Date of filing: 21.07.
EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Intel e B60M 1/13. Bayonne, New Jersey (US) Holborn London EC1N2QP (GB)
 (19) (12) Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen een des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION EP 0 888 924 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.1999 Bulletin 1999/01 (51) Intel e B60M
(19) (12) Europaisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office europeen een des brevets EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION EP 0 888 924 A2 (43) Date of publication: 07.01.1999 Bulletin 1999/01 (51) Intel e B60M
TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
 (19) TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T (11) EP 2 980 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.02.16 Bulletin 16/0 (21) Application number: 141792.6 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 13/00 (16.01) F03D 7/02 (06.01)
(19) TEPZZ 98Z4Z4A_T (11) EP 2 980 4 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.02.16 Bulletin 16/0 (21) Application number: 141792.6 (1) Int Cl.: F03D 13/00 (16.01) F03D 7/02 (06.01)
(51) Int Cl.: G06T 3/40 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ_99 89B_T (11) EP 1 99 389 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 1.11.17 Bulletin 17/46 (1) Int Cl.: G06T 3/ (06.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ_99 89B_T (11) EP 1 99 389 B1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT SPECIFICATION (4) Date of publication and mention of the grant of the patent: 1.11.17 Bulletin 17/46 (1) Int Cl.: G06T 3/ (06.01) (21) Application
*EP A2* EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2002/33
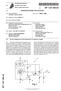 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00123128A2* (11) EP 1 231 28 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.02 Bulletin 02/33 (1)
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets *EP00123128A2* (11) EP 1 231 28 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.02 Bulletin 02/33 (1)
