Mathematical Investigations
|
|
|
- Milton Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mathematical Investigations We are learning to investigate problems We are learning to look for patterns and generalise We are developing multiplicative thinking Exercise 1: Crossroads Equipment needed: rulers or long straight sticks. AC EA AA AM AP You are to investigate the number of intersections or crossroads that are made when a number of roads are made to intersect. Use the metre rulers or sticks as your roads. Lay them across each other so that each new road crosses all others and record the number of crossroads that are made each time you add a new road. The diagram shows three cross roads when three sticks are laid across each other. Build your crossroads and record the results in a table like this. Roads Intersections (a) (b) (c) How many crossroads are made when five roads intersect? How many crossroads are made when six roads intersect? Explain your pattern. (d) (e) (f) How many crossroads are made when 20 roads intersect? How many crossroads are made when 101 roads intersect? What is the rule for n roads? Is it better to travel though an intersection quickly or slowly?
2 Exercise 2: Different Coins Equipment needed is a selection of 10c, 20c, 50c, $1 and $2 coins. These can be plastic or drawn on card as required. How many different amounts can be made using just a 10c, a 20c and a 50 cent coin? Complete the following: We can make 30c ( ), 60c ( ),,,,, and 10c. Investigate how many amounts can be made using a selection of different coins and record your results in a table like this. (Note that you can only use each coin once). Number of different coins Coins used Amounts made Number of amounts 1 10c 10, c, 20c 50, 70, (a) (b) (c) How many amounts can you make using 9 different coins? How many using 20 different coins? Explain any patterns you see. Write a rule for predicting how many amounts can be made for lots of n coins. Why do you think your rule works? SECRET CLUE..add 1 to all the numbers in the Number of amounts.
3 Exercise 3: Blaise Pascal and his Triangle. You might need a calculator, a highlighter pencil and if you have a computer with a spreadsheet programme you might be able to use that. Instructions Complete the grid below. Look carefully and leave the gaps. Row Total You could try and do this if you have a computer and a spreadsheet programme but it is quite hard because of the gaps. It can be done starting in the cell A1 but that problem is left for you to explore if you are interested. What do you see in the triangle? Find the following patterns and shade them using a highlighter. a) b) By adding numbers you should be able to find: c) d) By being imaginative you might see e) x x 11 x x 11 x 11 x 11 Pascal s Triangle is a very famous and well used pattern of numbers. Look for more information and write down anything you discover about Pascal. Who was Blaise Pascal?
4 Exercise 4: Triangular Based Pyramids Equipment needed: Lots of marbles. Marbles are best because each layer fits nicely on top in the gaps. The bottom layer will need to be secured with plasticine or rulers. You are to investigate the number of marbles needed to make a pyramid on a triangular base. Make a grid of marbles as in the diagram and push them into plasticine or use some other ingenious way to prevent them rolling away. On this layer place the other layers. The base will look a bit like this. Now count the number of marbles you used. Repeat your pyramid building with bases of different sizes and make a table of your results. Base side Total number of Pattern marbles (1+2) (1+2) + ( 1+2+3) (a) How many marbles are needed for a pyramid of base 7? (b) How many for a pyramid of base 10? (c) Can you find the pattern in Pascal s Triangle? (d) How many layers are there in a triangular pyramid that uses 35 balls? (e) How many layers are there in a triangular pyramid that uses 56 balls? (f) How many layers are there in a triangular pyramid that uses 165 balls? (g) How many for a base of size n? (Warning this is quite difficult!) An estimate for the n formula for the number of balls needed is one half of the number of balls in the base times the number of layers. Is this estimate useful?
5 Exercise 5: The Balls on the Brass Monkey Equipment needed: Lots of marbles. Marbles are better because each layer fits nicely on top in the gaps. The bottom layer will need to be secured with plasticine or rulers. You are to investigate the number of marbles needed to make a pyramid on a square base. Make a 4 x 4 grid of marbles and push them into plasticine or use some other ingenious way to prevent them rolling away. On this layer place a 3 x 3 layer of marbles and then 2 x 2 and finally 1 x 1 or just 1 marble at the very top. The base will look a bit like this. Now count the number of marbles you used. Repeat your pyramid building with square bases of different sizes and make a table of your results. Base side Total number of Explanation marbles 1 x 1 1 1x1 2 x x x 2 3 x 3 4 x 4 5 x 5 6 x 6 (a) How many marbles are needed for a pyramid of base 7 x 7? (b) How many for a pyramid of base 10 x 10? (c) How many for a base of size n? (Secret Clue n x n x n) The answer to (c) is the formula for adding the first n square numbers. Good luck! Why is the title The Balls on the Brass Monkey? It comes from an urban legend about the days of cannon balls and sailing ships. The myth says that in the old sailing ship days the sailors had piles of cannon balls stacked beside the cannons. The ships rocked around a lot and when they fired all the cannons on one side (broadside) the ship rolled wildly. The cannon balls were held securely by a brass plate called a monkey. In very cold weather the brass would shrink more than the cannon balls so the balls would fall off. Hence the expression it is cold enough to freeze the balls off a brass monkey.
6 Exercise 6: Investigate Zero! No Unity Here! You need some paper, a pencil You might need a calculator. Which of the answers to these calculations ends in a zero? 1) 2 5 (2) (3) ) (5) (6) ) (8) (9) ) (11) 65 2 (12) ) (14) (15) ) (17) (18) ) (20) (21) ) (23) (24) ) (26) 75 2 (27) ) (29) (30) (a) List all the factors of 10. Factors = { }. (b) List all the factors of 100. Factors = { }. (c) List all the factors of Factors = { }. (d) (e) (f) (g) What pattern did you notice in the problems 1 to 30 above? Write ten problems that have an answer that end in zero. Find two numbers that multiply and have the answer of 1000, but don t end in zero Find two numbers that multiply and have the answer 1,000,000, but don t end in zero The Trick is.
7 Exercise 7: Powers of powers of powers You will definitely need a calculator. You will need a lot of multilink blocks. What to do Make a model of the problem if you have enough blocks. Complete the sheet and be prepared to explain an answer. Make a model with the multilink blocks of 1) 2 x 2 (2) 2 x 2 x 2 (3) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 Make a model with the multilink blocks of 4) 2 2 (5) 2 3 (6) 2 4 Make a model with the multilink blocks of 7) (2 2 ) 2 (8) (2 2 ) 3 (9) (2 2 ) 4 How many blocks in 10) 2 x 2 (11) 2 x 2 x 2 (12) 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 How many blocks in 13) 2 2 (14) 2 3 (15) 2 4 How many blocks in 16) (2 2 ) 2 (17) (2 2 ) 3 (18) (2 2 ) 4 Which of these could be sensibly modelled with blocks? 19) (2 3 ) 4 (20) (2 5 ) 7 (21) (2 8 ) 9 Which looks bigger 23 4 or 4 23? Which is bigger?
8 Exercise 8: Divisibility Rules! You will need a calculator. We often need to know without actually doing the division problem whether or not a number will divide into another number evenly or with no remainder. For example the number is divisible by the number 9. In fact it does not matter how those digits are scrambled they will be divisible by 9. Try it! The rule for 9 is Write 5 numbers that are divisible by 9 Now investigate the multiples of these digits and try and write a rule that will tell you the divisibility secret. Some are easy and some are hard but they all have rules. a) The number 5 My rule is Thinking Space b) The number 10 My rule is c) The number 3 My rule is d) The number 4 My rule is e) The number 8 My rule is f) The number 6 My rule is g) The number 2 My rule is
9 Exercise 9: A Diagonal Problem You will need a ruler and a pencil. How many diagonals are there in a polygon with 20 sides? What is the general rule for the polygon with n sides? These are the two questions you are going to investigate. A diagonal line joins two corners (or vertices) of a polygon that are not next (or adjacent) to one another. In a triangle there are no diagonals. In a quadrilateral (4 sides) there are two diagonals. Draw a pentagon (5 sided) and all the diagonals and add the numbers to the table. Continue the pattern for hexagon, heptagon, octagon, nonogon, decagon and 11-gon, 12-gon. Name Number of sides Number of Diagonals triangle or trilateral 3 0 quadrilateral 4 2 pentagon 5 hexagon heptagon octagon 8 nonogon decagon Now to find the rule to predict the number of diagonals in any polygon. Secret handshake clue! Everyone in a room shakes hands with everyone else in the room just once. How many handshakes happen? (You shaking hands with me is the same as me shaking hands with you so you will need to divide by two somewhere). The answer to this problem is the same as the one above with a slight modification. My Rule is What is the correct name for a 100 sided polygon? How many diagonals does it have?
10 Exercise 10: A Timely Problem You will need a few pipe cleaners and a pencil to record your answer. Task 1 Use a pipe cleaner and divide the numbers on the clock face so the two parts add to the same number Task 2 Use two pipe cleaners and divide the numbers into three parts on the clock face so they add to the same number. Task 3 Now divide the numbers on the clock face into 6 parts so they add to the same number. Task 4 How many times does the minute hand overtake the hour hand in one 12 hour period? Task 5 The hands on a clock are together at Noon. When, exactly, are they next together?
11 Mathematical Investigations Answers Exercise 1 Roads Intersections (a) 10 (b) 15 (c) Each road must cross all others before it. (d) (20 19) 2 = 190 (e) ( ) 2 = 5050 (f) n(n - 1) 2 or a sentence in words like however many roads you ve got, multiply this by one more and halve the answer. It may pay to check your word explanation here with your teacher as there are lots of ways of describing this relationship. It is of course better to travel through intersections slowly and very carefully to minimise collision damage. The roundabout is a wonderful invention because it makes drivers slow down, and all travel in the same direction, resulting in almost fatal injury free collisions (even though there are more of them). Exercise 2 Number Coins Used Amounts Number of Amounts 1 10c 10c , 20 50, 70, , 20, 50 10, 20, 50, 30, 60, 70, , 20, 50 $ , 20, 50, $1, $2 31 and so on. (a) = 511 (b) = (c) The answer to this question should be discussed with your teacher The rule for n coins is 2 n -1 Each coin combines with all the others, which doubles the number of choices each time. Exercise 3 The completion of the triangle is left as an exercise as it is straight forward. The computer spreadsheet is formed by =A2 + B1 and FILLING the formula as far RIGHT and as far DOWN as you have ones. Worth doing. (a) 2 nd diagonal (b) 3 rd diagonal (c) row totals (d) 4 th diagonal (e) Reading the rows as numbers
12 Exercise 4 Base Total Explanation (1+2) (1+2) + ( 1+2+3) (1+2) + ( 1+2+3) + ( ) (a) 84 (b) 220 (c) 4 th diagonal (d) 5 (e) 6 (f) 9 (g) xxxx (h) The estimate is quite useful for small pyramids. Can you find a better one? Exercise 5 Base Number Explanation (a) 140 (b) 385 (c) n(n+1)(2n+1)/6 Exercise 6 (a) F 10 = {1,2,5,10} (b) F 100 = {1,2,4,5,10,20,25,50,100} (c) F 1000 = {1,2,4,5, 8, 10,20,25,50,100, 125, 200, 250, 500, 1000} (d) All end in a zero. All have 2 5 or zero in the factors. (e) Various (f) or (g) or The trick is to make a factor tree Exercise 7 7) 4 8) 8 9) 16 10) 4 11) 8 12) 16 13) 16 14) 64 15) ) 4096 Maybe 17) Never, 34, 359, 738,368 blocks 18) Never never! 4 to the 23 rd power is the biggest by a long way. Why? Listen to other students answers.
13 Exercise 8 The rules in the notes are repeated here. DIVISIBILITY RULES An integer, N, is a multiple of b if b can be evenly divided into N. If N is a multiple of b, then N is divisible by b. If N is a multiple of b, then b is a factor of N: N = b a Divisibility Rule for 1: 1 is a factor of every number, and every number is a factor of itself. Divisibility Rule for 2: 2 is a factor of every even number. Divisibility Rule for 3: If the sum of the individual digits of a number is a multiple of 3, then N is also a multiple of 3 Divisibility Rule for 4: If the last two digits of a number are a multiple of 4, then the entire number is a multiple of 4. (This rule is used for numbers that have at least three digits.) Divisibility Rule for 5: 5 is a factor of every number that ends in either 5 or 0; in other words, the ones digit is either 0 or 5. Divisibility Rule for 6: If a number is a multiple of both 2 and 3, then it is also a multiple of 6. Divisibility Rule for 7: If a number, N, is a multiple of 7, then another multiple of 7 can be found by (i) subtracting the ones digit from N, (ii) dividing the result by 10, and (iii) subtracting, from that result, twice the original ones digit. Divisibility Rule for 8: If the last three digits of a number is a multiple of 8, then the entire number is a multiple of 8. (This rule is used for numbers that have at least four digits.) Divisibility Rule for 9: If the sum of the individual digits is a multiple of 9, then the original number is also a multiple of 9 (and 9 is a factor of that original number). Divisibility Rule for 10: 10 is a factor of every number that ends in is a factor of every number that has both 2 and 5 as factors. Divisibility Rule for 11: In a number, N, if the difference of the sum of the even place digits and the sum of the odd place digits is 0 or a multiple of 11, then N is a multiple of 11. Exercise 9 Name Sides Diagonals Triangle 3 0 Quadrilateral 4 2 Pentagon 5 5 Hexagon 6 9 Heptagon 7 14 Octagon 8 20 Nonagon 9 27 Decagon The general rule for n-sides is n(n - 1)/2 n = n(n - 3)/2. The handshake solution is of course n(n - 1)/2 from which the sides n is subtracted. A 100-gon is possibly called a centagon or maybe a deca-decagon and will have 4950 diagonals.
14 Exercise 10 Task 1 Diagonally between the 9, 10 and the 3, 4. Why? Task 2 Diagonally between the 10, 11 and the 2, 3; the 9, 8 and the 4, 5. Why? Task 3 Diagonally between the 8, 7 and 5, 6 and every oppostie pair above. Why? Task 4 Exactly 11 times. Why? Task 5 One eleventh of the way around the clock. This is almost a third of a second more than 1:05:27 and it is quite tricky to convert 12/11 into hours minutes and seconds.
Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting
 Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting Week Four Solutions 1. An ice-cream store specializes in super-sized deserts. Their must famous is the quad-cone which has 4 scoops of ice-cream stacked one on top
Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting Week Four Solutions 1. An ice-cream store specializes in super-sized deserts. Their must famous is the quad-cone which has 4 scoops of ice-cream stacked one on top
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
Maths Makes Sense. 1 Medium-term plan
 Maths Makes Sense 1 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Copy addition and subtraction Maths Stories with 1-digit, zero, a half and a quarter, e.g. 2 + 1
Maths Makes Sense 1 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 1 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Copy addition and subtraction Maths Stories with 1-digit, zero, a half and a quarter, e.g. 2 + 1
JIGSAW ACTIVITY, TASK # Make sure your answer in written in the correct order. Highest powers of x should come first, down to the lowest powers.
 JIGSAW ACTIVITY, TASK #1 Your job is to multiply and find all the terms in ( 1) Recall that this means ( + 1)( + 1)( + 1)( + 1) Start by multiplying: ( + 1)( + 1) x x x x. x. + 4 x x. Write your answer
JIGSAW ACTIVITY, TASK #1 Your job is to multiply and find all the terms in ( 1) Recall that this means ( + 1)( + 1)( + 1)( + 1) Start by multiplying: ( + 1)( + 1) x x x x. x. + 4 x x. Write your answer
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 4237, 4,
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 4237, 4,
Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting
 Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting Week Four Problems Please read through the entire menu and try to classify each problem into one of the following types: Counting Subsets, Distinct Partitions, Block
Combinatorics: The Fine Art of Counting Week Four Problems Please read through the entire menu and try to classify each problem into one of the following types: Counting Subsets, Distinct Partitions, Block
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Maths Makes Sense. 3 Medium-term plan
 Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
repeated multiplication of a number, for example, 3 5. square roots and cube roots of numbers
 NUMBER 456789012 Numbers form many interesting patterns. You already know about odd and even numbers. Pascal s triangle is a number pattern that looks like a triangle and contains number patterns. Fibonacci
NUMBER 456789012 Numbers form many interesting patterns. You already know about odd and even numbers. Pascal s triangle is a number pattern that looks like a triangle and contains number patterns. Fibonacci
Exploring Concepts with Cubes. A resource book
 Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
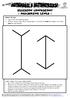 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
Introduction. It gives you some handy activities that you can do with your child to consolidate key ideas.
 (Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
(Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy
 The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
Complete the following patterns (NO CALCULATORS)
 Complete the following patterns (NO CALCULATORS) 1. 1 1 = 1 2. 3 4 = 12 11 11 = 121 33 34 = 1122 111 111 = 12321 333 334 = 111222 1111 1111 = 1234321 3333 3334 = 11112222 11111 11111 = 123454321 33333
Complete the following patterns (NO CALCULATORS) 1. 1 1 = 1 2. 3 4 = 12 11 11 = 121 33 34 = 1122 111 111 = 12321 333 334 = 111222 1111 1111 = 1234321 3333 3334 = 11112222 11111 11111 = 123454321 33333
Use of Sticks as an Aid to Learning of Mathematics for classes I-VIII Harinder Mahajan (nee Nanda)
 Use of Sticks as an Aid to Learning of Mathematics for classes I-VIII Harinder Mahajan (nee Nanda) Models and manipulatives are valuable for learning mathematics especially in primary school. These can
Use of Sticks as an Aid to Learning of Mathematics for classes I-VIII Harinder Mahajan (nee Nanda) Models and manipulatives are valuable for learning mathematics especially in primary school. These can
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET
 DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
DOWNSEND SCHOOL YEAR 5 EASTER REVISION BOOKLET This booklet is an optional revision aid for the Summer Exam Name: Maths Teacher: Revision List for Summer Exam Topic Junior Maths Bk 3 Place Value Chapter
PARENT PACKET Splash into Summer with Math!
 PARENT PACKET Splash into Summer with Math! For Students Completing Fourth Grade This summer math booklet was developed to provide students in 4 th Grade Math to review grade level math objectives and
PARENT PACKET Splash into Summer with Math! For Students Completing Fourth Grade This summer math booklet was developed to provide students in 4 th Grade Math to review grade level math objectives and
RIPPLES. 14 Patterns/Functions Grades 7-8 ETA.hand2mind. Getting Ready. The Activity On Their Own (Part 1) What You ll Need.
 RIPPLES Pattern recognition Growth patterns Arithmetic sequences Writing algebraic expressions Getting Ready What You ll Need Pattern Blocks, set per pair Colored pencils or markers Activity master, page
RIPPLES Pattern recognition Growth patterns Arithmetic sequences Writing algebraic expressions Getting Ready What You ll Need Pattern Blocks, set per pair Colored pencils or markers Activity master, page
Math Review Questions
 Math Review Questions Working with Feet and Inches A foot is broken up into twelve equal parts called inches. On a tape measure, each inch is divided into sixteenths. To add or subtract, arrange the feet
Math Review Questions Working with Feet and Inches A foot is broken up into twelve equal parts called inches. On a tape measure, each inch is divided into sixteenths. To add or subtract, arrange the feet
Contents. PART 1 Unit 1: Number Sense: Numbers to 10. Unit 2: Number Sense: Numbers to 20. Unit 3: Patterns and Algebra: Repeating Patterns
 Contents PART 1 Unit 1: Number Sense: Numbers to 10 NS2-1 Counting and Matching 1 NS2-2 One-to-One Correspondence 3 NS2-3 More, Fewer, and Less 5 NS2-4 How Many More? 7 NS2-5 Reading Number Words to Ten
Contents PART 1 Unit 1: Number Sense: Numbers to 10 NS2-1 Counting and Matching 1 NS2-2 One-to-One Correspondence 3 NS2-3 More, Fewer, and Less 5 NS2-4 How Many More? 7 NS2-5 Reading Number Words to Ten
36 th NEW BRUNSWICK MATHEMATICS COMPETITION
 UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK UNIVERSITÉ DE MONCTON 36 th NEW BRUNSWICK MATHEMATICS COMPETITION Thursday, May 3 rd, 2018 GRADE 8 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE STUDENT: 1. Do not start the examination until you are
UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK UNIVERSITÉ DE MONCTON 36 th NEW BRUNSWICK MATHEMATICS COMPETITION Thursday, May 3 rd, 2018 GRADE 8 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE STUDENT: 1. Do not start the examination until you are
Meet #3 January Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet #3 January 2009 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #3 January 2009 Category 1 Mystery 1. How many two-digit multiples of four are there such that the number is still a
Meet #3 January 2009 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #3 January 2009 Category 1 Mystery 1. How many two-digit multiples of four are there such that the number is still a
Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme
 Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme Every student is assigned to a Stage, based on their academic year and assessed study level. Stage 2 students are approximately 8 to 10 years old. The sheets
Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme Every student is assigned to a Stage, based on their academic year and assessed study level. Stage 2 students are approximately 8 to 10 years old. The sheets
SAMPLE. Mathematics CAMBRIDGE PRIMARY. Challenge. Cherri Moseley and Janet Rees. Original material Cambridge University Press 2016
 CAMBRIDGE PRIMARY Mathematics Challenge 3 Cherri Moseley and Janet Rees CAMBRIDGE PRIMARY Mathematics Name: Contents Three-digit numbers... 4 7 Addition several small numbers... 8 9 Doubling and halving
CAMBRIDGE PRIMARY Mathematics Challenge 3 Cherri Moseley and Janet Rees CAMBRIDGE PRIMARY Mathematics Name: Contents Three-digit numbers... 4 7 Addition several small numbers... 8 9 Doubling and halving
Upper Primary Division Round 2. Time: 120 minutes
 3 rd International Mathematics Assessments for Schools (2013-2014 ) Upper Primary Division Round 2 Time: 120 minutes Printed Name Code Score Instructions: Do not open the contest booklet until you are
3 rd International Mathematics Assessments for Schools (2013-2014 ) Upper Primary Division Round 2 Time: 120 minutes Printed Name Code Score Instructions: Do not open the contest booklet until you are
These tests contain questions ranging from Level 2 to Level 3. Children should have five seconds to answer questions 1 3 in each test,
 These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test, ten seconds to answer questions and fifteen seconds to answer questions -.
These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test, ten seconds to answer questions and fifteen seconds to answer questions -.
Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. RBKC SMILE 2001
 Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. A B D C RBKC SMILE 2001 50 110 104 37 48 32 100 140 60 70 120 119 45 76 Carefully cut out the following shapes. Angle Fit 20 d a c 39 101 b 105 64
Prism or Pyramid? Which nets make pyramids? Find out. A B D C RBKC SMILE 2001 50 110 104 37 48 32 100 140 60 70 120 119 45 76 Carefully cut out the following shapes. Angle Fit 20 d a c 39 101 b 105 64
Number Shapes. Professor Elvis P. Zap
 Number Shapes Professor Elvis P. Zap January 28, 2008 Number Shapes 2 Number Shapes 3 Chapter 1 Introduction Hello, boys and girls. My name is Professor Elvis P. Zap. That s not my real name, but I really
Number Shapes Professor Elvis P. Zap January 28, 2008 Number Shapes 2 Number Shapes 3 Chapter 1 Introduction Hello, boys and girls. My name is Professor Elvis P. Zap. That s not my real name, but I really
Section 1: Whole Numbers
 Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
Grade 6 Play! Mathematics Answer Book 67 Section : Whole Numbers Question Value and Place Value of 7-digit Numbers TERM 2. Study: a) million 000 000 A million has 6 zeros. b) million 00 00 therefore million
St Thomas of Canterbury Catholic Primary School Where every child is special
 Helping your child with Maths games and FUN! Helping with Maths at home can often be an issue we ve all been there, tears and frustration and your children aren t happy either! The key is to try to make
Helping your child with Maths games and FUN! Helping with Maths at home can often be an issue we ve all been there, tears and frustration and your children aren t happy either! The key is to try to make
Just One Fold. Each of these effects and the simple mathematical ideas that can be derived from them will be examined in more detail.
 Just One Fold This pdf looks at the simple mathematical effects of making and flattening a single fold in a sheet of square or oblong paper. The same principles, of course, apply to paper of all shapes.
Just One Fold This pdf looks at the simple mathematical effects of making and flattening a single fold in a sheet of square or oblong paper. The same principles, of course, apply to paper of all shapes.
Mathematical J o u r n e y s. Departure Points
 Mathematical J o u r n e y s Departure Points Published in January 2007 by ATM Association of Teachers of Mathematics 7, Shaftesbury Street, Derby DE23 8YB Telephone 01332 346599 Fax 01332 204357 e-mail
Mathematical J o u r n e y s Departure Points Published in January 2007 by ATM Association of Teachers of Mathematics 7, Shaftesbury Street, Derby DE23 8YB Telephone 01332 346599 Fax 01332 204357 e-mail
SHAPE level 2 questions. 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. 1 mark. International School of Madrid 1
 SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
Summer Solutions Problem Solving Level 4. Level 4. Problem Solving. Help Pages
 Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Hundreds Grid. MathShop: Hundreds Grid
 Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Name Date Class Practice A. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see.
 Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Sequences. like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a dance or movement? Have you ever group things into
 Math of the universe Paper 1 Sequences Kelly Tong 2017/07/17 Sequences Introduction Have you ever stamped your foot while listening to music? Have you ever counted like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a
Math of the universe Paper 1 Sequences Kelly Tong 2017/07/17 Sequences Introduction Have you ever stamped your foot while listening to music? Have you ever counted like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a
UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE. April 25th 2013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS
 UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE April 5th 013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS These solutions augment the printed solutions that we send to schools. For convenience, the solutions sent to schools are confined to two
UK JUNIOR MATHEMATICAL CHALLENGE April 5th 013 EXTENDED SOLUTIONS These solutions augment the printed solutions that we send to schools. For convenience, the solutions sent to schools are confined to two
Counting Problems
 Counting Problems Counting problems are generally encountered somewhere in any mathematics course. Such problems are usually easy to state and even to get started, but how far they can be taken will vary
Counting Problems Counting problems are generally encountered somewhere in any mathematics course. Such problems are usually easy to state and even to get started, but how far they can be taken will vary
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Released January Years 3/4. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area
 Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
Shapes. Practice. Family Note. Unit. show 3-sided, 4-sided, 5-sided, and 6-sided shapes. Ask an adult for permission first. Add.
 Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Home Link 8-1 Shapes In this lesson children examined different shapes, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. They also discussed these shapes attributes or characteristics such as
Mathematics, Grade 8
 Session 1, Multiple-Choice Questions Use the scatter plot to answer question 1. 1. In the scatter plot, each dot represents one student who participated in the 50-meter race. Ben is 15 years old. Based
Session 1, Multiple-Choice Questions Use the scatter plot to answer question 1. 1. In the scatter plot, each dot represents one student who participated in the 50-meter race. Ben is 15 years old. Based
CONNECT: Divisibility
 CONNECT: Divisibility If a number can be exactly divided by a second number, with no remainder, then we say that the first number is divisible by the second number. For example, 6 can be divided by 3 so
CONNECT: Divisibility If a number can be exactly divided by a second number, with no remainder, then we say that the first number is divisible by the second number. For example, 6 can be divided by 3 so
Table of Contents. Table of Contents 1
 Table of Contents 1) The Factor Game a) Investigation b) Rules c) Game Boards d) Game Table- Possible First Moves 2) Toying with Tiles a) Introduction b) Tiles 1-10 c) Tiles 11-16 d) Tiles 17-20 e) Tiles
Table of Contents 1) The Factor Game a) Investigation b) Rules c) Game Boards d) Game Table- Possible First Moves 2) Toying with Tiles a) Introduction b) Tiles 1-10 c) Tiles 11-16 d) Tiles 17-20 e) Tiles
Whole Numbers WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT.
 WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
Hyde Community College
 Hyde Community College Numeracy Booklet 1 Introduction What is the purpose of this booklet? This booklet has been produced to give guidance to pupils and parents on how certain common Numeracy topics are
Hyde Community College Numeracy Booklet 1 Introduction What is the purpose of this booklet? This booklet has been produced to give guidance to pupils and parents on how certain common Numeracy topics are
Angles and. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
Geometry. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
Whole Numbers. Whole Numbers. Curriculum Ready.
 Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles. Angle Bisector. Perpendicular Bisector
 Lessons and Activities GEOMETRY Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles Angle Bisector Perpendicular Bisector 1 Lessons and Activities POLYGONS are PLANE SHAPES (figures) with at least 3 STRAIGHT sides and
Lessons and Activities GEOMETRY Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles Angle Bisector Perpendicular Bisector 1 Lessons and Activities POLYGONS are PLANE SHAPES (figures) with at least 3 STRAIGHT sides and
S1/2 Checklist S1/2 Checklist. Whole Numbers. No. Skill Done CfE Code(s) 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting
 Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet Learner s name: School name: _ Day 1 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 273, 2,
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet Learner s name: School name: _ Day 1 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 273, 2,
Meet # 1 October, Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet # 1 October, 2000 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet # 1 October, 2000 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the picture shown below, the top half of the clock is obstructed from view
Meet # 1 October, 2000 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet # 1 October, 2000 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the picture shown below, the top half of the clock is obstructed from view
Solving Problems. PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1. Activities. PS1.1 Number stories 1.
 PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1 PS1.1 Number stories 1 PS1.2 Difference arithmagons PS1.3 Changing orders PS1.4 Making shapes PS1.5 Odd or even? PS1.6 Odd
PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1 PS1.1 Number stories 1 PS1.2 Difference arithmagons PS1.3 Changing orders PS1.4 Making shapes PS1.5 Odd or even? PS1.6 Odd
Pascal Contest (Grade 9)
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Thursday, February 20, 201 (in North America and South America) Friday, February 21, 201 (outside of North
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Pascal Contest (Grade 9) Thursday, February 20, 201 (in North America and South America) Friday, February 21, 201 (outside of North
Common Core State Standard I Can Statements 2 nd Grade
 CCSS Key: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT) Measurement and Data (MD) Geometry (G) Common Core State Standard 2 nd Grade Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
CCSS Key: Operations and Algebraic Thinking (OA) Number and Operations in Base Ten (NBT) Measurement and Data (MD) Geometry (G) Common Core State Standard 2 nd Grade Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
Figurate Numbers. by George Jelliss June 2008 with additions November 2008
 Figurate Numbers by George Jelliss June 2008 with additions November 2008 Visualisation of Numbers The visual representation of the number of elements in a set by an array of small counters or other standard
Figurate Numbers by George Jelliss June 2008 with additions November 2008 Visualisation of Numbers The visual representation of the number of elements in a set by an array of small counters or other standard
Counting Things. Tom Davis March 17, 2006
 Counting Things Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles March 17, 2006 Abstract We present here various strategies for counting things. Usually, the things are patterns, or
Counting Things Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles March 17, 2006 Abstract We present here various strategies for counting things. Usually, the things are patterns, or
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII. Mathematics Laboratory
 LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
Question No: 1 If you join all the vertices of a heptagon, how many quadrilaterals will you get?
 Volume: 427 Questions Question No: 1 If you join all the vertices of a heptagon, how many quadrilaterals will you get? A. 72 B. 36 C. 25 D. 35 E. 120 Question No: 2 Four students have to be chosen 2 girls
Volume: 427 Questions Question No: 1 If you join all the vertices of a heptagon, how many quadrilaterals will you get? A. 72 B. 36 C. 25 D. 35 E. 120 Question No: 2 Four students have to be chosen 2 girls
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures. Grade 9 Mathematics
 Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Second Grade Mathematics Goals
 Second Grade Mathematics Goals Operations & Algebraic Thinking 2.OA.1 within 100 to solve one- and twostep word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart,
Second Grade Mathematics Goals Operations & Algebraic Thinking 2.OA.1 within 100 to solve one- and twostep word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart,
SCHOOL OF EDUCATION (Edgewood Campus) MAIN EXAMINATIONS - NOVEMBER 2015 BACHELOR OF EDUCATION
 SCHOOL OF EDUCATION (Edgewood Campus) MAIN EXAMINATIONS - NOVEMBER 2015 BACHELOR OF EDUCATION Module Name Primary Mathematics Education 310 Code EDMA311 Duration 3 hours Marks 120 Internal Examiners Ms
SCHOOL OF EDUCATION (Edgewood Campus) MAIN EXAMINATIONS - NOVEMBER 2015 BACHELOR OF EDUCATION Module Name Primary Mathematics Education 310 Code EDMA311 Duration 3 hours Marks 120 Internal Examiners Ms
Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards. Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction
 Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction AR.Math.Content.2.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100
Grade 2 Arkansas Mathematics Standards Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction AR.Math.Content.2.OA.A.1 Use addition and subtraction within 100
Good Luck To. DIRECTIONS: Answer each question and show all work in the space provided. The next two terms of the sequence are,
 Good Luck To Period Date DIRECTIONS: Answer each question and show all work in the space provided. 1. Find the next two terms of the sequence. 6, 36, 216, 1296, _?_, _?_ The next two terms of the sequence
Good Luck To Period Date DIRECTIONS: Answer each question and show all work in the space provided. 1. Find the next two terms of the sequence. 6, 36, 216, 1296, _?_, _?_ The next two terms of the sequence
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 04
 Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Find Closed Lines. Put an on the lines that are not closed. Circle the closed lines. Who wins:,, or nobody?
 Find Closed Lines Put an on the lines that are not closed. Circle the closed lines. Who wins:,, or nobody? F-34 Blackline Master Geometry Teacher s Guide for Grade 2 CA 2.1 BLM Unit 5 p34-52 V8.indd 34
Find Closed Lines Put an on the lines that are not closed. Circle the closed lines. Who wins:,, or nobody? F-34 Blackline Master Geometry Teacher s Guide for Grade 2 CA 2.1 BLM Unit 5 p34-52 V8.indd 34
Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies?
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies? Let s explore scaled copies. 1.1: Printing Portraits m.openup.org/1/7-1-1-1 Here is a portrait of a student. 1. Look at Portraits A E. How is each one the same
Unit 1, Lesson 1: What are Scaled Copies? Let s explore scaled copies. 1.1: Printing Portraits m.openup.org/1/7-1-1-1 Here is a portrait of a student. 1. Look at Portraits A E. How is each one the same
Job Cards and Other Activities. Write a Story for...
 Job Cards and Other Activities Introduction. This Appendix gives some examples of the types of Job Cards and games that we used at the Saturday Clubs. We usually set out one type of card per table, along
Job Cards and Other Activities Introduction. This Appendix gives some examples of the types of Job Cards and games that we used at the Saturday Clubs. We usually set out one type of card per table, along
Intermediate A. Help Pages & Who Knows
 & Who Knows 83 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication problem.
& Who Knows 83 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication problem.
Statue of Liberty Eiffel Tower Gothic Cathedral (p1) Gothic Cathedral (p2) Gothic Cathedral (p3) Medieval Manor (p1)
 ARCHITECTURE Statue of Liberty Eiffel Tower Gothic Cathedral (p1) Gothic Cathedral (p2) Gothic Cathedral (p3) Medieval Manor (p1) Medieval Manor (p1) Toltec sculpture Aqueduct Great Pyramid of Khufu (p1)
ARCHITECTURE Statue of Liberty Eiffel Tower Gothic Cathedral (p1) Gothic Cathedral (p2) Gothic Cathedral (p3) Medieval Manor (p1) Medieval Manor (p1) Toltec sculpture Aqueduct Great Pyramid of Khufu (p1)
DCSD Common Core State Standards Math Pacing Guide 2nd Grade Trimester 1
 Trimester 1 OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction. 1. Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve oneand two-step word problems involving
Trimester 1 OA: Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction. 1. Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve oneand two-step word problems involving
1st Grade Math. Please complete the activity below for the day indicated. Day 1: Double Trouble. Day 2: Greatest Sum. Day 3: Make a Number
 1st Grade Math Please complete the activity below for the day indicated. Day 1: Double Trouble Day 2: Greatest Sum Day 3: Make a Number Day 4: Math Fact Road Day 5: Toy Store Double Trouble Paper 1 Die
1st Grade Math Please complete the activity below for the day indicated. Day 1: Double Trouble Day 2: Greatest Sum Day 3: Make a Number Day 4: Math Fact Road Day 5: Toy Store Double Trouble Paper 1 Die
Part II For the Teacher
 Part II: For the Teacher Curriculum Areas Problem 1 - Measurement and Number Sense Problem 2 - Number Sense and Pattern/Algebra Problem 3 - Probability and Number Sense Problem 4 - Data Management and
Part II: For the Teacher Curriculum Areas Problem 1 - Measurement and Number Sense Problem 2 - Number Sense and Pattern/Algebra Problem 3 - Probability and Number Sense Problem 4 - Data Management and
MEP: Feeder Primary Project. R: Addition and subtraction (mental and written work) C: Revision: numbers to 100 E: Roman numerals.
 R: Addition and subtraction (mental and written work) C: Revision: numbers to 100 E: Roman numerals. Puzzles Week 1 Lesson Plan 1 1 Mental counting Listen carefully, do the calculations in your head and
R: Addition and subtraction (mental and written work) C: Revision: numbers to 100 E: Roman numerals. Puzzles Week 1 Lesson Plan 1 1 Mental counting Listen carefully, do the calculations in your head and
Line Op Art. In the mid-20th century, artists such as Josef Albers, Victor Vasarely, and M.C. Escher experimented with Optical Art.
 Intro Basic line, space Line Op Art Concept/Skill:When lines are close together in patterns, colors, motion or other optical illusions are created. OHS line - A1, A2, C4, C5, D3 Objective: The learner
Intro Basic line, space Line Op Art Concept/Skill:When lines are close together in patterns, colors, motion or other optical illusions are created. OHS line - A1, A2, C4, C5, D3 Objective: The learner
Yr 4: Unit 4E Modelling effects on screen
 ICT SCHEME OF WORK Modelling on screen in LOGO PoS: KS 2 1c 2a 2c Yr 4: Unit 4E Modelling effects on screen Class: Date: Theme: Children learn to enter instructions to control a screen turtle and will
ICT SCHEME OF WORK Modelling on screen in LOGO PoS: KS 2 1c 2a 2c Yr 4: Unit 4E Modelling effects on screen Class: Date: Theme: Children learn to enter instructions to control a screen turtle and will
Objective: Describe the systematic construction of flat shapes using ordinal
 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (5 minutes) (25 minutes) (8 minutes) (50 minutes) Fluency Practice
Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (5 minutes) (25 minutes) (8 minutes) (50 minutes) Fluency Practice
4 th Grade Math Notebook
 4 th Grade Math Notebook By: Aligned to the VA SOLs Table of Contents Quarter 1 Table of Contents Quarter 2 Table of Contents Quarter 3 Table of Contents Quarter 4 Hundred Millions Ten Millions Millions
4 th Grade Math Notebook By: Aligned to the VA SOLs Table of Contents Quarter 1 Table of Contents Quarter 2 Table of Contents Quarter 3 Table of Contents Quarter 4 Hundred Millions Ten Millions Millions
American Mathematics Competitions. Practice 8 AMC 8
 American Mathematics Competitions Practice 8 AMC 8 (American Mathematics Contest 8) INSTRUCTIONS 1. DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOUR PROCTOR TELLS YOU.. This is a twenty-five question multiple choice
American Mathematics Competitions Practice 8 AMC 8 (American Mathematics Contest 8) INSTRUCTIONS 1. DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOUR PROCTOR TELLS YOU.. This is a twenty-five question multiple choice
Paper 2. Calculator allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 2 Calculator allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 2 Calculator allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You may use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
(1). We have n different elements, and we would like to arrange r of these elements with no repetition, where 1 r n.
 BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Two Important Terms (1.1). Permutations A permutation is an arrangement or a listing of objects in which the order is important. For example, if we have three numbers 1, 5, 9, there
BASIC KNOWLEDGE 1. Two Important Terms (1.1). Permutations A permutation is an arrangement or a listing of objects in which the order is important. For example, if we have three numbers 1, 5, 9, there
4.2.4 What if both events happen?
 4.2.4 What if both events happen? Unions, Intersections, and Complements In the mid 1600 s, a French nobleman, the Chevalier de Mere, was wondering why he was losing money on a bet that he thought was
4.2.4 What if both events happen? Unions, Intersections, and Complements In the mid 1600 s, a French nobleman, the Chevalier de Mere, was wondering why he was losing money on a bet that he thought was
2nd Grade Math Curriculum Map
 Standards Quarter 1 2.OA.2. Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies.* By end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. 2.OA.3. Determine whether a group of objects
Standards Quarter 1 2.OA.2. Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies.* By end of Grade 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. 2.OA.3. Determine whether a group of objects
Follow each step of the procedure to fold a strip of 10 equilateral triangles into a flexagon with 3 faces.
 Assignment 1 Start with an arbitrary folding line on your paper roll. Do action Folding Up (U) to create a new folding line Do action Folding down (D) to create a new folding line Repeat this (doing U,
Assignment 1 Start with an arbitrary folding line on your paper roll. Do action Folding Up (U) to create a new folding line Do action Folding down (D) to create a new folding line Repeat this (doing U,
2. Approximately how many seconds are there in two-sevenths of a 2. seconds minute? Round your answer to the nearest second.
 litz, Page 1 1. Simplify: 1 2 + 3 4 + 5 6 5 12 1. 2. pproximately how many seconds are there in two-sevenths of a 2. seconds minute? Round your answer to the nearest second. 3. lphonse has equal numbers
litz, Page 1 1. Simplify: 1 2 + 3 4 + 5 6 5 12 1. 2. pproximately how many seconds are there in two-sevenths of a 2. seconds minute? Round your answer to the nearest second. 3. lphonse has equal numbers
Counting Things Solutions
 Counting Things Solutions Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles March 7, 006 Abstract These are solutions to the Miscellaneous Problems in the Counting Things article at:
Counting Things Solutions Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles March 7, 006 Abstract These are solutions to the Miscellaneous Problems in the Counting Things article at:
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT
 Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Mathematics Challenge 2015
 Name Candidate number Mathematics Challenge 2015 by Children s Well-wishers Network (CWN) YEAR 1 45 minutes Do NOT open this booklet until instructed Calculators must NOT be used Write your name and candidate
Name Candidate number Mathematics Challenge 2015 by Children s Well-wishers Network (CWN) YEAR 1 45 minutes Do NOT open this booklet until instructed Calculators must NOT be used Write your name and candidate
2016 RSM Olympiad 3-4
 1. In the puzzle below, each card hides a digit. What digit is hidden under the card with the question mark? Answer: 9 Solution 1. Note that 999 is the largest 3-digit number. Therefore, if we add to it
1. In the puzzle below, each card hides a digit. What digit is hidden under the card with the question mark? Answer: 9 Solution 1. Note that 999 is the largest 3-digit number. Therefore, if we add to it
Standard Indicator Lines Of Symmetry. Students will identify and draw lines of symmetry in polygons.
 TIMSS NAEP Standard Indicator 4.4.5 Lines Of Symmetry Purpose Students will identify and draw lines of symmetry in polygons. Materials For the teacher: square and rectangle of construction paper, marker,
TIMSS NAEP Standard Indicator 4.4.5 Lines Of Symmetry Purpose Students will identify and draw lines of symmetry in polygons. Materials For the teacher: square and rectangle of construction paper, marker,
Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define rectangles and rhombuses based on those attributes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 18 5 5 Lesson 18 Objective: Draw rectangles and rhombuses to clarify their attributes, and define Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD
 THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD The following list of suggestions is indicative of exercises and examples that can be worked on the geoboard. Simpler, as well as, more difficult suggestions can easily be
THINGS TO DO WITH A GEOBOARD The following list of suggestions is indicative of exercises and examples that can be worked on the geoboard. Simpler, as well as, more difficult suggestions can easily be
16.1 Introduction Numbers in General Form
 16.1 Introduction You have studied various types of numbers such as natural numbers, whole numbers, integers and rational numbers. You have also studied a number of interesting properties about them. In
16.1 Introduction You have studied various types of numbers such as natural numbers, whole numbers, integers and rational numbers. You have also studied a number of interesting properties about them. In
Downloaded from
 Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER. Paper 1. Year 8 mathematics test. Calculator not allowed. First name. Last name. Class. Date YEAR
 Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER 1 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the
Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER 1 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the
SENIOR DIVISION COMPETITION PAPER
 A u s t r a l i a n M at h e m at i c s C o m p e t i t i o n a n a c t i v i t y o f t h e a u s t r a l i a n m at h e m at i c s t r u s t THURSDAY 2 AUGUST 2012 NAME SENIOR DIVISION COMPETITION PAPER
A u s t r a l i a n M at h e m at i c s C o m p e t i t i o n a n a c t i v i t y o f t h e a u s t r a l i a n m at h e m at i c s t r u s t THURSDAY 2 AUGUST 2012 NAME SENIOR DIVISION COMPETITION PAPER
Simple Solutions Mathematics Level 3. Level 3. Help Pages & Who Knows Drill
 Level 3 & Who Knows Drill 283 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and 1 is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication
Level 3 & Who Knows Drill 283 Vocabulary Arithmetic Operations Difference the result or answer to a subtraction problem. Example: The difference of 5 and 1 is 4. Product the result or answer to a multiplication
Mathematics Challenge 2015
 Mathematics Challenge 2015 by Children s Well-wishers Network (CWN) YEAR 1 Mark Scheme We provide mark schemes of our CWN Mathematics Challenge 2015 examination papers to help parents. Please note that
Mathematics Challenge 2015 by Children s Well-wishers Network (CWN) YEAR 1 Mark Scheme We provide mark schemes of our CWN Mathematics Challenge 2015 examination papers to help parents. Please note that
