Logical Thinking. Lesson
|
|
|
- Barnaby Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 2 Logical Thinking Aim In this lesson you will learn: Step by step approach and reasoning to solve problems. How to use what you already know to solve problems. How to tackle a task when you do not know anything about it. How logical thinking can help solve problems. Tejas: Fruits! I like fruits. They are good for health. Moz: Correct. You can have them. But first you have to solve this puzzle. There are four types of fruits: Apples, Oranges, Bananas and Grapes. Each one of you must pick two types of fruits. Note the following conditions: If you pick apple you cannot pick orange. If you pick orange you cannot pick banana. If you pick grapes you cannot pick apple. Tejas: I want an apple. With apple I cannot pick an orange or grapes. So I pick apple and banana. We know: There are four types of fruits Apples, oranges, bananas and grapes. Goal: Tejas has to pick two fruits. He likes apples. What other fruit can he take? Answer: Banana 24
2 Jyoti: I like oranges. With orange I cannot pick banana or apple. Hence I pick orange and grapes. Moz: Very good logical thinking. Can I pick banana and grapes? Tejas and Jyoti: Yes you can! Main steps in logical thinking I. Task: Read the problem carefully. Example problem: What comes next in the sequence below? II. Identify: As you are reading make a note of the following: 1. Goal- What is the goal? To find the fourth shape in the sequence. 2. Information- What is the information available? A sequence of geometrical shapes is given. In the sequence, the first shape has 3 sides, the second has 4 sides, and the third has 5 sides. CONCEPTS 3. Conditions- What are the conditions? The number of sides is increasing by 1, from one shape to the next, in the given sequence. III. Solve: Achieve the goal by using the given information and following the conditions. 1. Reasoning- The fourth shape should have 5+1 = 6 sides. 2. Solution- Work out the solution in a step-wise manner. The Problem is solved! Moz: Let us look at another example. You are walking towards a play ground. But the playground is on the other side of the road. So what do you do? 25
3 Jyoti: We know that we have to first reach a crossing where there are traffic lights. Tejas: Next, we check that the vehicles on both sides of the road have stopped before crossing. Then we can cross Jyoti: The condition is that we should follow traffic light rules. Moz: Good. It is very important to learn about the traffic rules and follow them. I. Task: To cross the road. II. Identify: 1. Goal- Cross the road. 2. Information available- There are vehicles on the road. There is a zebra crossing with a traffic signal. 3. Conditions- Wait for the green signal before crossing the road. No vehicles should be moving while we cross. III. Solve: 1. Reasoning- We should wait till Green signal for crossing is on and the vehicles have stopped moving. 2. Solution- Steps: 1) Come to a zebra crossing. 2) Wait for green signal. 3) Ensure vehicles are stopped. 4) Cross the road.. 26
4 Moz: If you do not know the rules then what do you do? Tejas: Ask parents, teachers, other elders whom you know. Jyoti: Observe others who are performing the task. ex: Observe, how people wait till the green signal to cross is on, and all the vehicles in both directions stop. Moz: Why do you follow the traffic rules? Jyoti: To be safe. Tejas: If we do not follow traffic rules, we can get hit by a vehicle and get hurt. CONCEPTS We use logical thinking to solve problems. You have to first identify the goal, then understand the given information, the rules and conditions. Finally, you have to work out the solution step-wise. What, when and why, are questions that can help in thinking logically, to find out How to reach the goal. Moz: Did you know that you already use logical reasoning to solve puzzles, maths problems, science experiments and other subjects? Moz brings out four pieces of a chain and gives Tejas and Jyoti the following problem: You are given four pieces of a chain. Each piece has three links in it. The links can be opened and closed. Join all 12 links of the chain into a single circle, as shown below. At the beginning of the problem all the links are closed. Each of the actions opening a link and closing a link is counted as one action. Total number of actions to form the single circular chain should not exceed 6. A B C D 27
5 Tejas and Jyoti make a note of the information available and the conditions of the problem as follows: I. Task: To make a circular chain. II. Note: 1. Goal- Join all the 12 links into a single circle. 2. Information available- Four pieces of chain. Each chain has three closed links inter connected. The links can be closed and opened. 3. Conditions- Opening a link or closing a link is counted as one action. Number of actions to complete the task should not be more than six. Tejas: Let us open link at the end of chain A and connect it to the beginning link of chain B. Jyoti: Then we will open the end link of B and connect it to the beginning link of the chain C. Moz: The number of actions are now 4. You have two more actions to complete the circular chain. Tejas: Oh! We cannot complete in two more actions as we still have to connect the D chain and then close the circle. What should we do? A Tejas and Jyoti start thinking of other options and they keep playing with one chain. Tejas accidentally opens the links of chain A. Then he exclaims, B C D Tejas: Look! The three links of a chain are open. Let us try connecting other chains B, C and D with these links. Jyoti: We have already used three actions for opening the three links of chain A. We have to achieve the goal with three more actions! 28
6 Jyoti: With link 1 of chain A let us connect chains B and C. We have seven links interconnected. Total number of actions is 4. Tejas: Now connect the chain D to these 7 links using the link 2 of chain A. We have a long chain of 11 links. Total number of actions is 5. Jyoti: Complete the circle using link 3 of chain A! Problem solved using 6 actions. Moz: Very good. Solving a problem: 1. Reasoning- Try various options for the solution. Find one option that leads to the goal without breaking the conditions given. Example: Circular chain problem: Option 1: Open a link from each chain to make the circular chain. Does not satisfiy the conditions. Option 2: Open all the three links of the chain. Can satisfy the conditions. 2. Solution- Achieve the goal by choosing the option that satisfies the conditions. Work out the detailed steps requried to reach the goal. Moz: You have been able to solve the problem very easily. You already know how to think logically. Would you like to solve a different type of puzzle? Tejas: Oh! yes. Moz: Here is the problem of a farmer, I met yesterday. Farmer s problem: Kishan, the farmer has to take a fox, a chicken, and a bag of corn safely across a river in a boat. He can take only one thing at a time in the boat. He cannot leave the fox and the chicken together on either side of the river, since the fox will eat the chicken. Likewise, he cannot leave the chicken along with the bag of corn, since the chicken will eat the corn. How can the farmer get everything across the river without anything being eaten? 29
7 Tejas and Jyoti discuss the problem and first list out the information, goal and conditions. CONCEPTS I. Task: The farmer, fox, chicken, and corn have to cross the river. II. Identify: 1. Goal- Farmer has to take the chicken, fox and the corn to the other side of the river in the boat. 2. Information available- A river that can be crossed on boat. A farmer who owns a boat. The farmer has with him a fox, chicken and some corn. 3. Conditions- The farmer can take only one item at a time in his boat( Either the fox or the chicken or corn). On either side of the river the farmer cannot leave: fox and chicken together. chicken and corn together. Tejas: Suppose the farmer takes the chicken first and leaves it on the other side. Moz: Why did you choose chicken first. Tejas: If we take the fox then chicken and corn will be left together. The chicken will eat the corn. Jyoti: The farmer cannot leave the fox and chicken together because the fox will eat the chicken. Moz: Good reasoning. fox and chicken together Chicken and corn together But he can leave fox and corn together 30
8 1. Reasoning- For the first step Option 1: First take fox in the boat. Then chicken and corn will be together. Chicken will eat the corn. Option 1 does not satisfy the conditions. Option 2: First take corn in the boat. Then fox and chicken will be together. Fox will eat the chicken. Option 2 does not satisfy the conditions. Option 3: First take chicken in the boat. Then fox and corn will be together. Fox does not eat the corn. Option 3 satisfies the conditions. 2. Solution- Choose option 3. Detailed steps are shown below. 1 Step 1: Farmer takes the chicken in the boat and leaves it on the other side of the river and come backs empty. Jyoti: Next the farmer comes back alone and takes the corn. Tejas: But he cannot leave the corn and chicken together on the other side of the river. So the farmer leaves the corn and brings back the chicken. 2 Step 2: The farmer takes the corn to the other side of the river. He leaves the corn and brings back the chicken. 31
9 Tejas: Next the farmer takes the fox and leaves it on the other side. 3 Step 3: The farmer takes the fox and leaves it on the other side and comes back. Moz: Good. So the fox and corn on the other side can be left together. Jyoti: Yes. He comes back and then takes the chicken. 4 Step 4: The farmer takes the chicken to the other side of the river. Tejas: Farmer s problem solved! That was fun to solve. Moz: Now consider the second step again. Can the farmer take the fox instead of the corn? Tejas: Oh! Yes. Either fox or corn can be taken in the boat to the other side. Jyoti: But he has to bring back the chicken. Step 2: The farmer takes the fox and brings back the chicken. Moz: Correct. Now what will be the next step? Tejas: The farmer takes the corn to the other side and comes back. Step 3: The farmer takes the corn to the other side and comes back. Jyoti: Then he takes the chicken in the last step. Step 4: The farmer comes back and then takes the chicken. Step 1: Farmer takes the chicken in the boat and leaves it on the other side of the river and come backs empty. Step 2: The farmer takes the fox and brings back the chicken. Step 3: The farmer takes the corn to the other side and comes back. Step 4: The farmer comes back and then takes the chicken. 32
10 Moz: See how easy it is to solve a problem by first understanding the given information, the conditions and the goal. Jyoti: And then solve it step by step! Tejas: We have also found out that there can be many ways in which we can solve a problem. A problem can have more than one correct solution. CONCEPTS Logical thinking is about understanding, the information given, goal and conditions of a problem. Then solve it in a step-wise manner to reach the goal. CONCEPTS Step wise thinking is about identifing the main steps of a solution. Then detailed steps for each main step is listed. The sequence of steps may be fixed sometimes or interchangable (then there are more than one solution). Moz: Correct. Now apply step by step thinking and logical reasoning while you solve problems in other subjects. Tomorrow we can use what you learned and build some interesting games using Scratch. Chin Chinaki... Lesson Outcome After you have studied this lesson, you will be able to: Understand simple logical problems. Identify the information given, conditions and goal. Solve the problem step by step by logical reasoning. 33
11 WORKSHEETS 1. Solve anagrams and match the columns. In anagrams, alphabets in a word are presented in jumbled order. You have to set it in correct order to form the word. For instance, an anagram as D R E would mean RED. Following are some things you carry to the school everyday. Solve the anagrams by matching the columns. S.No. Anagram Word 1 K B O O 2 F I T F I N 3 G A B 4 C I P E N L 5 X O B 34
12 WORKSHEETS b. Following are names of the vehicles that are used for transportation. Solve the anagrams by matching the columns. S.No Anagram Word 1 R N T I A 2 P S I H 3 L C Y E C 4 S B U 5 R A C 35
13 WORKSHEETS 2. Chiku, the rabbit has to hop his way to find the carrots on the island. With each hop, he crosses five tiles. How many times will he have to hop to reach the carrots I. Task: Rabbit has to find the carrots on the island. II. Identify: 1. Information: tiles 2. Conditions: hops of 3. Goal: Reach carrots on tile II. Solution: Hop on tile number 5, 10,,, 25. So the number of hops = Another way of solving: 25/5 = hops Munmun, the squirrel has to eat the groundnut. Help her reach it. 36
14 WORKSHEETS 4. Complete the following sequences by writing the steps as given in the first problem: a) 9, 10, 12, 15,? 1. Goal: Find the 5 th number in the sequence. 2. Information: 4 numbers of a sequence in ascending order. 3. Condition: We observe that 9+1=10,10+2=12,12+3=15 4. Reasoning: We added 1 to first number and got second number. 9+1=10 We added 2 to second number and got third number. 10+2=12 We added 3 to third number and got fourth number. 12+3=15 We should add 4 to fourth number to get the fifth number. Solution: 15+4=19 b) 1, 2, 4, 7,? a) 10 b) 11 c) 10, 9, 7, 4,? a) 8 b) 1 c) 2 c) 5 d) 12 d) 0 d) 12, 8, 5, 3,? a) 2 b) 10 c) 1 d) 7 5. Can you help Jyoti to solve the following puzzles. a. Some figures are given below. Observe them. Now match the shapes with their colour. YELLOW RED BLUE GREEN 37
15 WORKSHEETS b. Observe the following figures. Fill in the blanks and colour the triangles in the grid below. The Red triangle should be between yellow and blue triangles. The first triangle is the Yellow one. 1. Goal: Colour the grid. 2. Information: First triangle is. 3. Condition: Red triangle should be between and triangles. 4. Reasoning: --> So the third triangle is. --> The second triangle is. --> The fourth triangle is. c. Study the following figures. The Red square comes in between the brown and yellow squares. Blue square is the first square in the grid. Black square is directly above the yellow square. Fill in the blanks and colour the squares in the grid that follows: 1. Goal: Colour the squares in the grid. 2. Information: square is the first square in the grid. 38
16 WORKSHEETS 3. Condition: --> Red square comes in between the and yellow squares. --> square is directly above the yellow square. 4. Reasoning and solution: The squares in the second row are brown,, yellow. The remaining square next to blue is square. 5. Minu will go hiking with her friend in 2 weeks. Today is January 3rd. What is the date on which Minu will go hiking? 6. Can you tell what comes next? Circle the correct option from a,b,c given below. i. 1. Information: --> Today is _. --> Minu will go hiking in weeks. 2. Reasoning: --> Two weeks means days. 4. Solution: --> 3+ _ =. --> Minu will go hiking on January.? a. b. c. 39
17 WORKSHEETS ii.? a. b. c. iii.? a. b. c. iv.? a. b. c. 40
18 WORKSHEETS 7. a. Solve the following puzzles: Kartar, Seema and Rahul collect different items. One collects stamps, one collects insect pictures and one collects toy car pictures. Rahul exchanged his car pictures for insect pictures. Seema doesn t like cars but likes getting letters. Kartar thinks insects are too small to worry about. What do Kartar, Seema and Rahul collect? Kartar Seema Rahul Information: , and are collectors. Conditions: i swapped his car pictures for pictures. ii. Seema doesn t like cars but likes getting iii. Kartar thinks are too small to worry about. Reasoning and solution: 1. By condition (i) Rahul collects pictures. 2. By condition (ii) Since Seema likes getting letters. Letters have stuck on them, so Seema collects By condition (iii) Kartar collects pictures. 41
19 WORKSHEETS b. Amina, Manish, and Jeet each ate something different for breakfast. One had toast, one had chapati, and one had an apple for breakfast. i. ii. iii. Amina likes to eat either an apple or toast for breakfast. Only Manish and Jeet like chapati for breakfast. Jeet did not have chapati or toast for breakfast. What did each person have for breakfast? Amina Manish Jeet Goal: Find who ate what for breakfast. Information: i. Jeet did not have chapati or toast. Condition: i. likes to eat either an or toast for breakfast. ii. and Jeet like chapati for. Reasoning: 1. From information, Jeet ate. 2. Since Jeet ate, by condition (i). Amina ate. 3. From 1 and 2 above, we find that is left. Hence, Manish ate _. (Note that condition is not used.) Solution: Jeet ate. Amina ate. Manish ate. 42
20 1. Sudoku: Select Sudoku from Applications ---> Games To play sudoku, select Sudoku from the Games submenu of the Applications menu. The rules of Sudoku are quite simple. In order to complete the puzzle, you must fill each square with a number between 1 to 5. Each row and each column contains the digits from 1 to 5 only once. That means, you must fill each square such that no number appears twice in the same row or column. Ask questions like: How can I fit all the numbers in this box? What numbers can fit in a square satisfying the given conditions? Think logically and solve the puzzle. As the level of the game increases the difficulty level and the number of grids also increases. 43
21 2. Chess: Select Sudoku from Applications ---> Games ---> Chess Goal: The object of the game is to checkmate the opponent s king. This occurs when the king is under immediate attack (in check) and there is no way to remove it from attack on the next move. Learn to play by trial and error. Information: Chess is a two-player board game. You can play this game with the computer (as a second player). Chess is played on a square chessboard, consisting of 64 squares of alternating color. Each player begins the game with sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, two knights, two bishops, and eight pawns. Rules: One player controls the white pieces and the other player controls the black pieces; the player that controls white is the first to move. The players take turns moving pieces; certain moves involve a capturing of an opponent s piece, removing it from the chessboard. Movement of each type of piece has a rule. Find these rules using help. Discover more rules on your own by playing with computer. 44
22 3. Tux math: Select Sudoku from Applications ---> Games ---> Tux math Your mission is to save the penguins igloo from the falling comets. Stop a comet by typing the correct answer to the math problem and pressing the space bar or enter. If an igloo gets hits by a comet, it melts. But dont worry, the penguin is ok! Type the correct answer on the comet before it hits the igloo. Group activity: Enact the following story in the class. Answer the questions given at the end of the story. Unity is Strength Once upon a time, there was a flock of doves that flew in search of food led by their king. One day, they had flown a long distance and were very tired. The dove king encouraged them to fly a little further. The smallest dove picked up speed and found some rice scattered beneath a banyan tree. So all the doves landed and began to eat. Suddenly a net fell over them and they were all trapped. They saw a hunter approaching carrying a huge club. The doves desperately fluttered their wings trying to get out, but to no avail. The king had an idea. He advised all the doves to fly up together carrying the net with them. He said that there was strength in unity. 45
23 Each dove picked up a portion of the net and together they flew off carrying the net with them. The hunter looked up in astonishment. He tried to follow them, but they were flying high over hills and valleys. They flew to a hill near a city of temples where there lived a mouse who could help them. He was a faithful friend of the dove king. When the mouse heard the loud noise of their approach, he went into hiding. The dove king gently called out to him and then the mouse was happy to see him. The dove king explained that they had been caught in a trap and needed the mouse s help. He asked the move to gnaw at the net with his teeth and set them free. The mouse agreed saying that he would set the king free first. The king insisted that his subjects be freed first and the king last. The mouse understood the king s feelings and compled with his wishes. He began to cut the net and one by one all the doves were freed, including the dove king. They all thanked the mouse and flew away together, united in their strength. Questions to be answered: i. How were the doves saved? ii. What would have happened if all the doves did not listen to their king? iii. Why is it important to be united? iv. Finally, list out the information, conditions, reasoning and the solution, using the step-wise manner given in this lesson. Explore! A shoe can be used for several activities besides covering your feet. Write 20 different uses of a shoe. What are the conditions in constructing a building? Can you put beams before columns? 46
24 Teacher s Corner Book IV Lesson 2 Start the class by revising the step-wise thinking lesson. Now bring out the importance of thinking capabilities. Ask students what they do to keep physically fit. They may say, We exercise our body to remain physically fit. Tell them, that exercise of mind is important for mental fitness. Tell them that solving puzzles, mental sums, stories and computer games can be an effective mechanism for exercise of the mind. To teach logical thinking, discuss examples where children use logical thinking in every day life. For instance, you may ask the students, why they do not cross the road when vehicles are moving. You can elaborate that while crossing the road, they reason out that they should not cross the road when the vehicles are passing and they may be hit if they are not careful. They wait for the walk signal to be green, so that the vehicles stop and they cross the road safely. Ask several WHY questions. For example: i. Why are vegetables washed before cooking? ii. Why do you not put your finger in the flame of a burning candle? iii. Why should we learn good manners? iv. Why should we help others? v. Why should we speak truth? Explain that in step wise thinking, they detail out the solution and there may be only one rule to follow. For logical reasoning, they have to understand the rules and conditions. You can give the example of cooking a vegetable. First ask them about the steps to follow. Tell them that this is an example of making a vegetable. Now question them on why to follow the steps in the order. Tell them the questionning is an example of logical thinking. Narrate a story to the students that highlights logical thinking. Ask them questions that require logical reasoning after you have told them the story. For example, stories of Akbar and Birbal. Summarize the lesson emphasizing the importance of thinking. Give them puzzles to solve where they have to detail the steps and understand the condition to arrive at the answer. Furhter Reading :
Logical Thinking. Lesson
 Lesson 2 Logical Thinking Aim In this lesson you will learn: Step by step approach and reasoning to solve problems. How to use what you already know to solve problems. How to tackle a task when you do
Lesson 2 Logical Thinking Aim In this lesson you will learn: Step by step approach and reasoning to solve problems. How to use what you already know to solve problems. How to tackle a task when you do
Logical Thinking. Lesson
 Lesson 2 Logical Thinking Aim In this lesson you will learn: Step by step approach and reasoning to solve problems. How to use what you already know to solve problems. How to tackle a task when you do
Lesson 2 Logical Thinking Aim In this lesson you will learn: Step by step approach and reasoning to solve problems. How to use what you already know to solve problems. How to tackle a task when you do
Math Stories and Games: Logic, Patterns and Mathematical Thinking
 Math Stories and Games: Logic, Patterns and Mathematical Thinking Anna Shevyakova, Alexey Shevyakov............... Lesson 1. Attributes of Objects Dad, play with me, I am bored! Nicky called his father.
Math Stories and Games: Logic, Patterns and Mathematical Thinking Anna Shevyakova, Alexey Shevyakov............... Lesson 1. Attributes of Objects Dad, play with me, I am bored! Nicky called his father.
LEARN TO PLAY CHESS CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION. Terry Marris December 2004
 LEARN TO PLAY CHESS Terry Marris December 2004 CONTENTS 1 Kings and Queens 2 The Rooks 3 The Bishops 4 The Pawns 5 The Knights 6 How to Play 1 INTRODUCTION Chess is a game of war. You have pieces that
LEARN TO PLAY CHESS Terry Marris December 2004 CONTENTS 1 Kings and Queens 2 The Rooks 3 The Bishops 4 The Pawns 5 The Knights 6 How to Play 1 INTRODUCTION Chess is a game of war. You have pieces that
I am Kittu. This is my home. Isn't it huge? It has 100 rooms. Help me in painting some of the rooms.
 3 Give and Take I am Kittu. This is my home. Isn't it huge? It has 100 rooms. Help me in painting some of the rooms. I start from room 2. I add 10 to 2 to reach room 12 and paint it. To add 10 to 2, we
3 Give and Take I am Kittu. This is my home. Isn't it huge? It has 100 rooms. Help me in painting some of the rooms. I start from room 2. I add 10 to 2 to reach room 12 and paint it. To add 10 to 2, we
I am Kittu. This is my home. Isn't it huge? It has 100 rooms. Help me in painting some of the rooms. NCERT
 3 Give and Take I am Kittu. This is my home. Isn't it huge? It has 100 rooms. Help me in painting some of the rooms. I start from room 2. I add 10 to 2 to reach room 12 and paint it. To add 10 to 2, we
3 Give and Take I am Kittu. This is my home. Isn't it huge? It has 100 rooms. Help me in painting some of the rooms. I start from room 2. I add 10 to 2 to reach room 12 and paint it. To add 10 to 2, we
Class Work 16. Problem 2 Circle all of the objects that have a cylinder shape.
 Class Work 16 Problem 1 This is traffic light. Trace and color in the lights according to the traffic light rule. Problem 2 Circle all of the objects that have a cylinder shape. Problem 3 Color in the
Class Work 16 Problem 1 This is traffic light. Trace and color in the lights according to the traffic light rule. Problem 2 Circle all of the objects that have a cylinder shape. Problem 3 Color in the
Unit. The double attack. Types of double attack. With which pieces? Notes and observations
 Unit The double attack Types of double attack With which pieces? Notes and observations Think Colour in the drawing with the colours of your choice. These types of drawings are called mandalas. They are
Unit The double attack Types of double attack With which pieces? Notes and observations Think Colour in the drawing with the colours of your choice. These types of drawings are called mandalas. They are
FIRST GRADE FIRST GRADE HIGH FREQUENCY WORDS FIRST 100 HIGH FREQUENCY WORDS FIRST 100
 HIGH FREQUENCY WORDS FIRST 100 about Preprimer, Primer or 1 st Grade lists 1 st 100 of again 100 HF words for Grade 1 all am an are as away be been before big black blue boy brown but by came cat come
HIGH FREQUENCY WORDS FIRST 100 about Preprimer, Primer or 1 st Grade lists 1 st 100 of again 100 HF words for Grade 1 all am an are as away be been before big black blue boy brown but by came cat come
All games have an opening. Most games have a middle game. Some games have an ending.
 Chess Openings INTRODUCTION A game of chess has three parts. 1. The OPENING: the start of the game when you decide where to put your pieces 2. The MIDDLE GAME: what happens once you ve got your pieces
Chess Openings INTRODUCTION A game of chess has three parts. 1. The OPENING: the start of the game when you decide where to put your pieces 2. The MIDDLE GAME: what happens once you ve got your pieces
Phrases for 2 nd -3 rd Grade Sight Words (9) for for him for my mom it is for it was for. (10) on on it on my way On the day I was on
 (1) the on the bus In the school by the dog It was the cat. Phrases for 2 nd -3 rd Grade Sight Words (9) for for him for my mom it is for it was for (17) we If we go we can sit we go out Can we go? (2)
(1) the on the bus In the school by the dog It was the cat. Phrases for 2 nd -3 rd Grade Sight Words (9) for for him for my mom it is for it was for (17) we If we go we can sit we go out Can we go? (2)
Anna Hibiscus loves the village. She plays with her village friends all day long. But Anna Hibiscus has to work as well! There is too much work in
 ABC and 123 Anna Hibiscus lives in Africa. Amazing Africa. She lives in a big white house in a big busy city with her whole entire family. But Anna Hibiscus is not in the city now. She is on holiday with
ABC and 123 Anna Hibiscus lives in Africa. Amazing Africa. She lives in a big white house in a big busy city with her whole entire family. But Anna Hibiscus is not in the city now. She is on holiday with
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Game Theory October 27/28, 2015
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Game Theory October 27/28, 2015 Chomp Chomp is a simple 2-player game. There is
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Game Theory October 27/28, 2015 Chomp Chomp is a simple 2-player game. There is
SUDOKU1 Challenge 2013 TWINS MADNESS
 Sudoku1 by Nkh Sudoku1 Challenge 2013 Page 1 SUDOKU1 Challenge 2013 TWINS MADNESS Author : JM Nakache The First Sudoku1 Challenge is based on Variants type from various SUDOKU Championships. The most difficult
Sudoku1 by Nkh Sudoku1 Challenge 2013 Page 1 SUDOKU1 Challenge 2013 TWINS MADNESS Author : JM Nakache The First Sudoku1 Challenge is based on Variants type from various SUDOKU Championships. The most difficult
Movement of the pieces
 Movement of the pieces Rook The rook moves in a straight line, horizontally or vertically. The rook may not jump over other pieces, that is: all squares between the square where the rook starts its move
Movement of the pieces Rook The rook moves in a straight line, horizontally or vertically. The rook may not jump over other pieces, that is: all squares between the square where the rook starts its move
NUMERATION AND NUMBER PROPERTIES
 Section 1 NUMERATION AND NUMBER PROPERTIES Objective 1 Order three or more whole numbers up to ten thousands. Discussion To be able to compare three or more whole numbers in the thousands or ten thousands
Section 1 NUMERATION AND NUMBER PROPERTIES Objective 1 Order three or more whole numbers up to ten thousands. Discussion To be able to compare three or more whole numbers in the thousands or ten thousands
How to use these Addition Cards.
 How to use these Addition Cards. Throw out your dice, and replace them with Mental Math. Your child will be adding faster than a calculator soon! Each card is an Addition Fact question. The cards use values
How to use these Addition Cards. Throw out your dice, and replace them with Mental Math. Your child will be adding faster than a calculator soon! Each card is an Addition Fact question. The cards use values
Parable - The Prodigal Son
 Parable - The Prodigal Son With this lesson the children will have a good idea of what matters in life. The choice between material possessions or relationship will determine how they would want to live
Parable - The Prodigal Son With this lesson the children will have a good idea of what matters in life. The choice between material possessions or relationship will determine how they would want to live
Unit 1 Number Sense: Numbers to 10
 Unit 1 Number Sense: Numbers to 10 Introduction In this unit, students will review counting (this includes equating written numerals, quantities, spoken numbers, and numbers written as words). Students
Unit 1 Number Sense: Numbers to 10 Introduction In this unit, students will review counting (this includes equating written numerals, quantities, spoken numbers, and numbers written as words). Students
Wordy Problems for MathyTeachers
 December 2012 Wordy Problems for MathyTeachers 1st Issue Buffalo State College 1 Preface When looking over articles that were submitted to our journal we had one thing in mind: How can you implement this
December 2012 Wordy Problems for MathyTeachers 1st Issue Buffalo State College 1 Preface When looking over articles that were submitted to our journal we had one thing in mind: How can you implement this
Make 10. Operations and Algebraic Thinking. Objective. Common Core State Standards. Talk About It. Solve It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 9 Objective Common Core State Standards Make 10 To begin building a strong foundation for the base ten system and addition, children need to understand how two parts make up 10. By using concrete objects
9 Objective Common Core State Standards Make 10 To begin building a strong foundation for the base ten system and addition, children need to understand how two parts make up 10. By using concrete objects
ShillerMath Book 1 Test Answers
 LESSON 1-56 REVIEW TEST #1-1 Now we will have a test to see what you have learned. This will help me understand what I need to do to make our math work more fun. You may take as much time and use whatever
LESSON 1-56 REVIEW TEST #1-1 Now we will have a test to see what you have learned. This will help me understand what I need to do to make our math work more fun. You may take as much time and use whatever
Essentials. Week by. Week. Investigations. Let s Write Write a story about. Seeing Math $ $ $ $ What Do You Think? Patterns, Patterns, Patterns
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 21 Let s Write Write a story about 1 2 Seeing Math What Do You Think? Suppose you hit the target with three darts. How could you score 15? Is there more
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 21 Let s Write Write a story about 1 2 Seeing Math What Do You Think? Suppose you hit the target with three darts. How could you score 15? Is there more
LEVEL I. 3. In how many ways 4 identical white balls and 6 identical black balls be arranged in a row so that no two white balls are together?
 LEVEL I 1. Three numbers are chosen from 1,, 3..., n. In how many ways can the numbers be chosen such that either maximum of these numbers is s or minimum of these numbers is r (r < s)?. Six candidates
LEVEL I 1. Three numbers are chosen from 1,, 3..., n. In how many ways can the numbers be chosen such that either maximum of these numbers is s or minimum of these numbers is r (r < s)?. Six candidates
An End Game in West Valley City, Utah (at the Harman Chess Club)
 An End Game in West Valley City, Utah (at the Harman Chess Club) Can a chess book prepare a club player for an end game? It depends on both the book and the game Basic principles of the end game can be
An End Game in West Valley City, Utah (at the Harman Chess Club) Can a chess book prepare a club player for an end game? It depends on both the book and the game Basic principles of the end game can be
This chapter gives you everything you
 Chapter 1 One, Two, Let s Sudoku In This Chapter Tackling the basic sudoku rules Solving squares Figuring out your options This chapter gives you everything you need to know to solve the three different
Chapter 1 One, Two, Let s Sudoku In This Chapter Tackling the basic sudoku rules Solving squares Figuring out your options This chapter gives you everything you need to know to solve the three different
After learning the Rules, What should beginners learn next?
 After learning the Rules, What should beginners learn next? Chess Puzzling Presentation Nancy Randolph Capital Conference June 21, 2016 Name Introduction to Chess Test 1. How many squares does a chess
After learning the Rules, What should beginners learn next? Chess Puzzling Presentation Nancy Randolph Capital Conference June 21, 2016 Name Introduction to Chess Test 1. How many squares does a chess
Vocabulary: colon, equivalent ratios, fraction, part-to-part, part-to-whole, ratio
 EE8-39 Ratios and Fractions Pages 144 147 Standards: preparation for 8.EE.B.5 Goals: Students will review part-to-part and part-to-whole ratios, different notations for a ratio, and equivalent ratios.
EE8-39 Ratios and Fractions Pages 144 147 Standards: preparation for 8.EE.B.5 Goals: Students will review part-to-part and part-to-whole ratios, different notations for a ratio, and equivalent ratios.
Review I. October 14, 2008
 Review I October 14, 008 If you put n + 1 pigeons in n pigeonholes then at least one hole would have more than one pigeon. If n(r 1 + 1 objects are put into n boxes, then at least one of the boxes contains
Review I October 14, 008 If you put n + 1 pigeons in n pigeonholes then at least one hole would have more than one pigeon. If n(r 1 + 1 objects are put into n boxes, then at least one of the boxes contains
Unit 1 Money. 1 loves 2 usually saves 3 doesn t want 4 doesn t like 5 always wants 6 doesn t spend. countable nouns (e.g.
 Unit Money loves usually saves doesn t want doesn t like always wants doesn t spend like believe / know understands want know prefers don t like don t believe / don t know doesn t understand don t want
Unit Money loves usually saves doesn t want doesn t like always wants doesn t spend like believe / know understands want know prefers don t like don t believe / don t know doesn t understand don t want
Important Words in Mathematics
 1 P a g e Important Words in Mathematics... 2 Numbers... 3 Number Words... 4 EVEN OR ODD... 5 PLACE VALUE... 6 PLACE VALUE... 7 VALUE... 8 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 9 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 10
1 P a g e Important Words in Mathematics... 2 Numbers... 3 Number Words... 4 EVEN OR ODD... 5 PLACE VALUE... 6 PLACE VALUE... 7 VALUE... 8 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 9 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 10
Kodu Module 1: Eating Apples in the Kodu World
 Kodu Module 1: Eating Apples in the Kodu World David S. Touretzky Version of May 29, 2017 Learning Goals How to navigate through a world using the game controller. New idioms: Pursue and Consume, Let Me
Kodu Module 1: Eating Apples in the Kodu World David S. Touretzky Version of May 29, 2017 Learning Goals How to navigate through a world using the game controller. New idioms: Pursue and Consume, Let Me
Junior Circle Games with coins and chessboards
 Junior Circle Games with coins and chessboards 1. a.) There are 4 coins in a row. Let s number them 1 through 4. You are allowed to switch any two coins that have a coin between them. (For example, you
Junior Circle Games with coins and chessboards 1. a.) There are 4 coins in a row. Let s number them 1 through 4. You are allowed to switch any two coins that have a coin between them. (For example, you
I followed the steps to work through four examples. Conjecture: It is 3 times. It worked.
 1.6 Reasoning to Solve Problems GOAL Solve problems using inductive or deductive reasoning. INVESTIGATE the Math Emma was given this math trick: Choose a number. Multiply by 6. Add 4. Divide by 2. Subtract
1.6 Reasoning to Solve Problems GOAL Solve problems using inductive or deductive reasoning. INVESTIGATE the Math Emma was given this math trick: Choose a number. Multiply by 6. Add 4. Divide by 2. Subtract
List #1 Fluency. List #1 Fluency
 Your child has read and completed Sight Word list #1. Please have him/her read this list to practice fluency. Return this sheet in order to get sight word list #2. List #1 Fluency it is to we can go I
Your child has read and completed Sight Word list #1. Please have him/her read this list to practice fluency. Return this sheet in order to get sight word list #2. List #1 Fluency it is to we can go I
2. How many even 4 digit numbers can be made using 0, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9 if no repeats are allowed?
 Math 30-1 Combinatorics Practice Test 1. A meal combo consists of a choice of 5 beverages, main dishes, and side orders. The number of different meals that are available if you have one of each is A. 15
Math 30-1 Combinatorics Practice Test 1. A meal combo consists of a choice of 5 beverages, main dishes, and side orders. The number of different meals that are available if you have one of each is A. 15
Math Circle Beginners Group May 22, 2016 Combinatorics
 Math Circle Beginners Group May 22, 2016 Combinatorics Warm-up problem: Superstitious Cyclists The president of a cyclist club crashed his bicycle into a tree. He looked at the twisted wheel of his bicycle
Math Circle Beginners Group May 22, 2016 Combinatorics Warm-up problem: Superstitious Cyclists The president of a cyclist club crashed his bicycle into a tree. He looked at the twisted wheel of his bicycle
VERITAS CHRISTIAN ACADEMY CHESS CLUB
 VERITAS CHRISTIAN ACADEMY CHESS CLUB Why Chess? 2016 Club meetings 9/11 12/11 Sept 11th 1st day of Chess Club TBA Halloween Tournament TBA WNC Team Tournament at VCA Veritas Christian Academy invites your
VERITAS CHRISTIAN ACADEMY CHESS CLUB Why Chess? 2016 Club meetings 9/11 12/11 Sept 11th 1st day of Chess Club TBA Halloween Tournament TBA WNC Team Tournament at VCA Veritas Christian Academy invites your
The Basic Rules of Chess
 Introduction The Basic Rules of Chess One of the questions parents of young children frequently ask Chess coaches is: How old does my child have to be to learn chess? I have personally taught over 500
Introduction The Basic Rules of Chess One of the questions parents of young children frequently ask Chess coaches is: How old does my child have to be to learn chess? I have personally taught over 500
LESSON 2: THE INCLUSION-EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE
 LESSON 2: THE INCLUSION-EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE The inclusion-exclusion principle (also known as the sieve principle) is an extended version of the rule of the sum. It states that, for two (finite) sets, A
LESSON 2: THE INCLUSION-EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE The inclusion-exclusion principle (also known as the sieve principle) is an extended version of the rule of the sum. It states that, for two (finite) sets, A
Cato s Hike Quick Start
 Cato s Hike Quick Start Version 1.1 Introduction Cato s Hike is a fun game to teach children and young adults the basics of programming and logic in an engaging game. You don t need any experience to play
Cato s Hike Quick Start Version 1.1 Introduction Cato s Hike is a fun game to teach children and young adults the basics of programming and logic in an engaging game. You don t need any experience to play
Gough, John , Logic games, Australian primary mathematics classroom, vol. 7, no. 2, pp
 Deakin Research Online Deakin University s institutional research repository DDeakin Research Online Research Online This is the published version (version of record) of: Gough, John 2002-06, Logic games,
Deakin Research Online Deakin University s institutional research repository DDeakin Research Online Research Online This is the published version (version of record) of: Gough, John 2002-06, Logic games,
The Pieces Lesson. In your chess set there are six different types of piece.
 In your chess set there are six different types of piece. In this lesson you'll learn their names and where they go at the start of the game. If you happen to have a chess set there it will help you to
In your chess set there are six different types of piece. In this lesson you'll learn their names and where they go at the start of the game. If you happen to have a chess set there it will help you to
MATHEMATICS LEVEL: 3 4 (Γ - Δ Δημοτικού)
 MATHEMATICS LEVEL: 3 4 (Γ - Δ Δημοτικού) 10:00 11:00, 20 March 2010 THALES FOUNDATION 1 3 points 1. There is a hidden part of the path in the picture for a cat and a mouse. The cat can reach the milk,
MATHEMATICS LEVEL: 3 4 (Γ - Δ Δημοτικού) 10:00 11:00, 20 March 2010 THALES FOUNDATION 1 3 points 1. There is a hidden part of the path in the picture for a cat and a mouse. The cat can reach the milk,
LESSON 4. Second-Hand Play. General Concepts. General Introduction. Group Activities. Sample Deals
 LESSON 4 Second-Hand Play General Concepts General Introduction Group Activities Sample Deals 110 Defense in the 21st Century General Concepts Defense Second-hand play Second hand plays low to: Conserve
LESSON 4 Second-Hand Play General Concepts General Introduction Group Activities Sample Deals 110 Defense in the 21st Century General Concepts Defense Second-hand play Second hand plays low to: Conserve
DELUXE 3 IN 1 GAME SET
 Chess, Checkers and Backgammon August 2012 UPC Code 7-19265-51276-9 HOW TO PLAY CHESS Chess Includes: 16 Dark Chess Pieces 16 Light Chess Pieces Board Start Up Chess is a game played by two players. One
Chess, Checkers and Backgammon August 2012 UPC Code 7-19265-51276-9 HOW TO PLAY CHESS Chess Includes: 16 Dark Chess Pieces 16 Light Chess Pieces Board Start Up Chess is a game played by two players. One
Family and Friends 1 Time to talk! Student Audio CD Script
 Family and Friends 1 Time to talk! Student Audio CD Script Starter unit Listening 1. Listen and repeat. Rosy, Tim, Billy, Miss Jones Listening 2. Listen and sing. Hello, Rosy. Hello, Tim. Hello everyone.
Family and Friends 1 Time to talk! Student Audio CD Script Starter unit Listening 1. Listen and repeat. Rosy, Tim, Billy, Miss Jones Listening 2. Listen and sing. Hello, Rosy. Hello, Tim. Hello everyone.
D.A.V PUBLIC SCHOOL, KAILASH HILLS SUMMER BREAK HOLIDAY HOMEWORK
 D.A.V PUBLIC SCHOOL, KAILASH HILLS SUMMER BREAK HOLIDAY HOMEWORK CLASS LKG (Session 2017-18) Dear Parents, Summer Vacations is always one of the most awaited holidays for children when they can relax at
D.A.V PUBLIC SCHOOL, KAILASH HILLS SUMMER BREAK HOLIDAY HOMEWORK CLASS LKG (Session 2017-18) Dear Parents, Summer Vacations is always one of the most awaited holidays for children when they can relax at
OCTAGON 5 IN 1 GAME SET
 OCTAGON 5 IN 1 GAME SET CHESS, CHECKERS, BACKGAMMON, DOMINOES AND POKER DICE Replacement Parts Order direct at or call our Customer Service department at (800) 225-7593 8 am to 4:30 pm Central Standard
OCTAGON 5 IN 1 GAME SET CHESS, CHECKERS, BACKGAMMON, DOMINOES AND POKER DICE Replacement Parts Order direct at or call our Customer Service department at (800) 225-7593 8 am to 4:30 pm Central Standard
Reading at Home. Parents + Schools = Successful Children
 Parents + Schools = Successful Children Reading at Home This project was designed and developed by the National Center for Family Literacy (NCFL) with generous support from the Dollar General Literacy
Parents + Schools = Successful Children Reading at Home This project was designed and developed by the National Center for Family Literacy (NCFL) with generous support from the Dollar General Literacy
Math Circle Beginners Group May 22, 2016 Combinatorics
 Math Circle Beginners Group May 22, 2016 Combinatorics Warm-up problem: Superstitious Cyclists The president of a cyclist club crashed his bicycle into a tree. He looked at the twisted wheel of his bicycle
Math Circle Beginners Group May 22, 2016 Combinatorics Warm-up problem: Superstitious Cyclists The president of a cyclist club crashed his bicycle into a tree. He looked at the twisted wheel of his bicycle
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
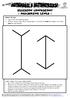 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
4th Pui Ching Invitational Mathematics Competition. Final Event (Secondary 1)
 4th Pui Ching Invitational Mathematics Competition Final Event (Secondary 1) 2 Time allowed: 2 hours Instructions to Contestants: 1. 100 This paper is divided into Section A and Section B. The total score
4th Pui Ching Invitational Mathematics Competition Final Event (Secondary 1) 2 Time allowed: 2 hours Instructions to Contestants: 1. 100 This paper is divided into Section A and Section B. The total score
2nd Grade Facts Presentation
 Slide 1 / 246 Slide 2 / 246 2nd Grade Facts Presentation 1 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 246 Presentation 1 Table of Contents Facts Click on a topic to go to that section. Recall from Memory Addition
Slide 1 / 246 Slide 2 / 246 2nd Grade Facts Presentation 1 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 246 Presentation 1 Table of Contents Facts Click on a topic to go to that section. Recall from Memory Addition
Introducing Numicon into Year 1
 Introducing Numicon into year page of 5 Introducing Numicon into Year Before using Numicon Shapes in your teaching, give children time to explore Numicon Shapes for themselves. To help you get started
Introducing Numicon into year page of 5 Introducing Numicon into Year Before using Numicon Shapes in your teaching, give children time to explore Numicon Shapes for themselves. To help you get started
Acing Math (One Deck At A Time!): A Collection of Math Games. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Introduction to Acing Math page 5 Card Sort (Grades K - 3) page 8 Greater or Less Than (Grades K - 3) page 9 Number Battle (Grades K - 3) page 10 Place Value Number Battle (Grades 1-6)
Table of Contents Introduction to Acing Math page 5 Card Sort (Grades K - 3) page 8 Greater or Less Than (Grades K - 3) page 9 Number Battle (Grades K - 3) page 10 Place Value Number Battle (Grades 1-6)
Movers Listening, Part 1
 Movers Listening, Part 1 01 Listen and draw lines. Peter Fred Jim Sally Daisy John Jill Movers Listening, Part 2 02 Listen and write. Mary Black 1 Goes to market: 2 Time: 3 Always buys: 4 Market is: 5
Movers Listening, Part 1 01 Listen and draw lines. Peter Fred Jim Sally Daisy John Jill Movers Listening, Part 2 02 Listen and write. Mary Black 1 Goes to market: 2 Time: 3 Always buys: 4 Market is: 5
Introduction. Firstly however we must look at the Fundamental Principle of Counting (sometimes referred to as the multiplication rule) which states:
 Worksheet 4.11 Counting Section 1 Introduction When looking at situations involving counting it is often not practical to count things individually. Instead techniques have been developed to help us count
Worksheet 4.11 Counting Section 1 Introduction When looking at situations involving counting it is often not practical to count things individually. Instead techniques have been developed to help us count
Perry High School. 2 nd Semester!
 2 nd Semester! Monday: Admin Review / Chess Tuesday: Admin Review / Chess Wednesday: The Code, Part 1, with worksheet Thursday: The Code, Part 2, with worksheet Friday: Chess, Chapter 5 Assignments Next
2 nd Semester! Monday: Admin Review / Chess Tuesday: Admin Review / Chess Wednesday: The Code, Part 1, with worksheet Thursday: The Code, Part 2, with worksheet Friday: Chess, Chapter 5 Assignments Next
2) Diaphantus was a Greek mathematician who lived in the third century. He was one of the first mathematicians to use algebraic symbols.
 1) Mismatched Joe is in a pitch dark room selecting socks from his drawer. He has only six socks in his drawer, a mixture of black and white. If he chooses two socks, the chance that he draws out a white
1) Mismatched Joe is in a pitch dark room selecting socks from his drawer. He has only six socks in his drawer, a mixture of black and white. If he chooses two socks, the chance that he draws out a white
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n
 Shoebox, page 1 In his book Chess Variants & Games, A. V. Murali suggests playing chess on the exterior surface of a cube. This playing surface has intriguing properties: We can think of it as three interlocked
Shoebox, page 1 In his book Chess Variants & Games, A. V. Murali suggests playing chess on the exterior surface of a cube. This playing surface has intriguing properties: We can think of it as three interlocked
A Simple Pawn End Game
 A Simple Pawn End Game This shows how to promote a knight-pawn when the defending king is in the corner near the queening square The introduction is for beginners; the rest may be useful to intermediate
A Simple Pawn End Game This shows how to promote a knight-pawn when the defending king is in the corner near the queening square The introduction is for beginners; the rest may be useful to intermediate
Counting Learning Outcomes
 1 Counting Learning Outcomes List all possible outcomes of an experiment or event. Use systematic listing. Use two-way tables. Use tree diagrams. Solve problems using the fundamental principle of counting.
1 Counting Learning Outcomes List all possible outcomes of an experiment or event. Use systematic listing. Use two-way tables. Use tree diagrams. Solve problems using the fundamental principle of counting.
Canadian Money Unit. By Jessicca Nielsen
 Canadian Money Unit By Jessicca Nielsen Table of Contents 1. Canadian money poster and worksheet 2. Counting nickels worksheet 3. Counting dimes worksheet 4. Counting money worksheet #1 5. Counting money
Canadian Money Unit By Jessicca Nielsen Table of Contents 1. Canadian money poster and worksheet 2. Counting nickels worksheet 3. Counting dimes worksheet 4. Counting money worksheet #1 5. Counting money
Chess Handbook: Course One
 Chess Handbook: Course One 2012 Vision Academy All Rights Reserved No Reproduction Without Permission WELCOME! Welcome to The Vision Academy! We are pleased to help you learn Chess, one of the world s
Chess Handbook: Course One 2012 Vision Academy All Rights Reserved No Reproduction Without Permission WELCOME! Welcome to The Vision Academy! We are pleased to help you learn Chess, one of the world s
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Kenken For Teachers. Tom Davis January 8, Abstract
 Kenken For Teachers Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles January 8, 00 Abstract Kenken is a puzzle whose solution requires a combination of logic and simple arithmetic
Kenken For Teachers Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles January 8, 00 Abstract Kenken is a puzzle whose solution requires a combination of logic and simple arithmetic
By Kelly Mikeselll. C. 2009
 By Kelly Mikeselll http://www.elementary-teacher-resources.com info@elementary-teacher-resources.com C. 2009 Many parents and teachers are looking for quick and easy skill-based routines for their classrooms.
By Kelly Mikeselll http://www.elementary-teacher-resources.com info@elementary-teacher-resources.com C. 2009 Many parents and teachers are looking for quick and easy skill-based routines for their classrooms.
Flyers. Reading & Writing. Cambridge Young Learners English. My name is:... There are 50 questions. You have 40 minutes.
 Centre Number Candidate Number *20 4 7 2 09378* Cambridge Young Learners English Flyers Reading & Writing Version 127 0761 There are 50 questions. You have 40 minutes. You will need a pen or pencil. My
Centre Number Candidate Number *20 4 7 2 09378* Cambridge Young Learners English Flyers Reading & Writing Version 127 0761 There are 50 questions. You have 40 minutes. You will need a pen or pencil. My
PUZZLES. Reasoning Ability TOP 50 QUESTIONS OF. IBPS RRB Prelims Exam Top 50 PUZZLES Questions For IBPS RRB Prelims 2018
 Reasoning Ability TOP 50 QUESTIONS OF PUZZLES IBPS RRB Prelims Exam 2018 Directions (1 to 5): Study the following Nine persons A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I were born in the months of March, April and May
Reasoning Ability TOP 50 QUESTIONS OF PUZZLES IBPS RRB Prelims Exam 2018 Directions (1 to 5): Study the following Nine persons A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I were born in the months of March, April and May
STUDENT'S BOOKLET. Shapes, Bees and Balloons. Meeting 20 Student s Booklet. Contents. April 27 UCI
 Meeting 20 Student s Booklet Shapes, Bees and Balloons April 27 2016 @ UCI Contents 1 A Shapes Experiment 2 Trinities 3 Balloons 4 Two bees and a very hungry caterpillar STUDENT'S BOOKLET UC IRVINE MATH
Meeting 20 Student s Booklet Shapes, Bees and Balloons April 27 2016 @ UCI Contents 1 A Shapes Experiment 2 Trinities 3 Balloons 4 Two bees and a very hungry caterpillar STUDENT'S BOOKLET UC IRVINE MATH
ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION number range 0-10
 ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION number range 0-10 1 ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION, number range 0 10 Addition and subtraction 0 10 contains 15 teaching sessions for practising addition and subtraction. Addition is
ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION number range 0-10 1 ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION, number range 0 10 Addition and subtraction 0 10 contains 15 teaching sessions for practising addition and subtraction. Addition is
Patterns and rules repeating patterns
 Patterns and rules repeating patterns We are used to continuing repeated patterns. But what if the pattern rule is in the middle? What strategies can you use to continue these patterns both ways? 1 ontinue
Patterns and rules repeating patterns We are used to continuing repeated patterns. But what if the pattern rule is in the middle? What strategies can you use to continue these patterns both ways? 1 ontinue
The game of Paco Ŝako
 The game of Paco Ŝako Created to be an expression of peace, friendship and collaboration, Paco Ŝako is a new and dynamic chess game, with a mindful touch, and a mind-blowing gameplay. Two players sitting
The game of Paco Ŝako Created to be an expression of peace, friendship and collaboration, Paco Ŝako is a new and dynamic chess game, with a mindful touch, and a mind-blowing gameplay. Two players sitting
Answer Key. Easy Peasy All-In-One-Homeschool
 Answer Key Easy Peasy All-In-One-Homeschool 3 Odd Numbers A. Odd numbers cannot be paired or divided into equal groups. Count the dots on each dice and circle the pairs. Is the count Odd or Even? + My
Answer Key Easy Peasy All-In-One-Homeschool 3 Odd Numbers A. Odd numbers cannot be paired or divided into equal groups. Count the dots on each dice and circle the pairs. Is the count Odd or Even? + My
Ask a Scientist Pi Day Puzzle Party Ask a Scientist Pi Day Puzzle Party Ask a Scientist Pi Day Puzzle Party 3.
 1. CHOCOLATE BARS Consider a chocolate bar that s a 3x6 grid of yummy squares. One of the squares in the corner of the bar has an X on it. With this chocolate bar, two people can play a game called Eat
1. CHOCOLATE BARS Consider a chocolate bar that s a 3x6 grid of yummy squares. One of the squares in the corner of the bar has an X on it. With this chocolate bar, two people can play a game called Eat
Building Concepts: Fractions and Unit Squares
 Lesson Overview This TI-Nspire lesson, essentially a dynamic geoboard, is intended to extend the concept of fraction to unit squares, where the unit fraction b is a portion of the area of a unit square.
Lesson Overview This TI-Nspire lesson, essentially a dynamic geoboard, is intended to extend the concept of fraction to unit squares, where the unit fraction b is a portion of the area of a unit square.
Puzzles to Play With
 Puzzles to Play With Attached are some puzzles to occupy your mind. They are not arranged in order of difficulty. Some at the back are easier than some at the front. If you think you have a solution but
Puzzles to Play With Attached are some puzzles to occupy your mind. They are not arranged in order of difficulty. Some at the back are easier than some at the front. If you think you have a solution but
URASHIMA TARO, the Fisherman (A Japanese folktale)
 URASHIMA TARO, the Fisherman (A Japanese folktale) (Urashima Taro is pronounced "Oo-rah-shee-ma Ta-roe") Cast: Narrator(s) Urashima Taro His Mother 3 Bullies Mother Tortoise 2 Swordfish Guards Sea King
URASHIMA TARO, the Fisherman (A Japanese folktale) (Urashima Taro is pronounced "Oo-rah-shee-ma Ta-roe") Cast: Narrator(s) Urashima Taro His Mother 3 Bullies Mother Tortoise 2 Swordfish Guards Sea King
MEP : Feeder Primary Project / Reception Year. R: Counting up to nine C: Decomposing nine E: Observational and manual skills.
 1 5 min 2 15 min 3 20 min : Counting up to nine C: Decomposing nine E: Observational and manual skills. Short term memory Nine shells T: Share nine shells with your partner. Explain your sharing A and
1 5 min 2 15 min 3 20 min : Counting up to nine C: Decomposing nine E: Observational and manual skills. Short term memory Nine shells T: Share nine shells with your partner. Explain your sharing A and
NS2-45 Skip Counting Pages 1-8
 NS2-45 Skip Counting Pages 1-8 Goals Students will skip count by 2s, 5s, or 10s from 0 to 100, and back from 100 to 0. Students will skip count by 5s starting at multiples of 5, and by 2s or 10s starting
NS2-45 Skip Counting Pages 1-8 Goals Students will skip count by 2s, 5s, or 10s from 0 to 100, and back from 100 to 0. Students will skip count by 5s starting at multiples of 5, and by 2s or 10s starting
Exercises and Problems 1.1
 Section 1.1 Introduction to Problem Solving 1.13 13 echnology Connection What is the least number of moves to transfer four disks from one tower to another if only one disk can be moved at a time and a
Section 1.1 Introduction to Problem Solving 1.13 13 echnology Connection What is the least number of moves to transfer four disks from one tower to another if only one disk can be moved at a time and a
Tactics Time. Interviews w/ Chess Gurus John Herron Interview Tim Brennan
 Tactics Time Interviews w/ Chess Gurus John Herron Interview Tim Brennan 12 John Herron Interview Timothy Brennan: Hello, this is Tim with http://tacticstime.com and today I have a very special guest,
Tactics Time Interviews w/ Chess Gurus John Herron Interview Tim Brennan 12 John Herron Interview Timothy Brennan: Hello, this is Tim with http://tacticstime.com and today I have a very special guest,
2. Advanced Image Editing
 2. Advanced Image Editing Aim: In this lesson, you will learn: The different options and tools to edit an image. The different ways to change and/or add attributes of an image. Jyoti: I want to prepare
2. Advanced Image Editing Aim: In this lesson, you will learn: The different options and tools to edit an image. The different ways to change and/or add attributes of an image. Jyoti: I want to prepare
Grade 6 Math Circles Combinatorial Games - Solutions November 3/4, 2015
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles Combinatorial Games - Solutions November 3/4, 2015 Chomp Chomp is a simple 2-player
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles Combinatorial Games - Solutions November 3/4, 2015 Chomp Chomp is a simple 2-player
Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, Magic and Latin Squares
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, 2017 Magic and Latin Squares Today we will be solving math and logic puzzles!
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, 2017 Magic and Latin Squares Today we will be solving math and logic puzzles!
Unit 8 Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Addition within 10
 Unit 8 Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Addition within 10 Introduction In this unit, students build on Unit 7 by adding numbers with a total less than or equal to 10. They will follow the sequence of
Unit 8 Operations and Algebraic Thinking: Addition within 10 Introduction In this unit, students build on Unit 7 by adding numbers with a total less than or equal to 10. They will follow the sequence of
Bruce and Alice learn some Algebra by Zoltan P. Dienes
 Bruce and Alice learn some Algebra by Zoltan P. Dienes It soon became the understood thing that Bruce, Alice, Unta, Ata and Alo went to school with the other local children. They soon got used to the base
Bruce and Alice learn some Algebra by Zoltan P. Dienes It soon became the understood thing that Bruce, Alice, Unta, Ata and Alo went to school with the other local children. They soon got used to the base
Nazmul, Anna and Rosie can t wait to start at St Helen s Primary School
 Nazmul, Anna and Rosie can t wait to start at St Helen s Primary School What happens when I get to school? When you get to school, you say goodbye to your grown-up at the door. Your teacher will be waiting
Nazmul, Anna and Rosie can t wait to start at St Helen s Primary School What happens when I get to school? When you get to school, you say goodbye to your grown-up at the door. Your teacher will be waiting
4 Complete the appleuestions with the correct verbs.
 Complete the appleuestions with the correct verbs. cook take pay phone wear wear Does she have to wear a tie? Do you have to the beans? Does she have to Jim at nine? Does he have to the medicine four times
Complete the appleuestions with the correct verbs. cook take pay phone wear wear Does she have to wear a tie? Do you have to the beans? Does she have to Jim at nine? Does he have to the medicine four times
Alternatives to Homework MATHEMATICS. Class VII
 Alternatives to Homework MATHEMATICS Class VII 1. Integers 1. Make the butterfly beautiful Draw butterfly as shown in sample. 1. Use red colour for negative integer and green colour for positive integer.
Alternatives to Homework MATHEMATICS Class VII 1. Integers 1. Make the butterfly beautiful Draw butterfly as shown in sample. 1. Use red colour for negative integer and green colour for positive integer.
2) Diaphanous was a Greek mathematician who lived in the third century. He was one of the first mathematicians to use algebraic symbols.
 1) Mismatched Joe is in a pitch dark room selecting socks from his drawer. He has only six socks in his drawer, a mixture of black and white. If he chooses two socks, the chances that he draws out a white
1) Mismatched Joe is in a pitch dark room selecting socks from his drawer. He has only six socks in his drawer, a mixture of black and white. If he chooses two socks, the chances that he draws out a white
Math Mania in the Primary Grades. Ginny A. Dowd
 Math Mania in the Primary Grades Ginny A. Dowd 1 Table of Contents Let s find attributes! Pages 4-6 Negative Numbers Page 130-132 Let s write numbers Pages 7-11 Calendar Fun Pages 12-25 The Magical Number
Math Mania in the Primary Grades Ginny A. Dowd 1 Table of Contents Let s find attributes! Pages 4-6 Negative Numbers Page 130-132 Let s write numbers Pages 7-11 Calendar Fun Pages 12-25 The Magical Number
Cheetah Math Superstars
 PARENTS: You may read the problem to your child and demonstrate a similar problem, but he/she should work the problems. Please encourage independent thinking and problem solving skills. SCORING: 20 paw
PARENTS: You may read the problem to your child and demonstrate a similar problem, but he/she should work the problems. Please encourage independent thinking and problem solving skills. SCORING: 20 paw
Unit 5. Exercise 1. Understanding Messages about Spending Money, p.122:
 71 Unit 5 Exercise 1. Understanding Messages about Spending Money, p.122: You will hear information about three people. They are each talking about buying something. Listen carefully. On the line, write
71 Unit 5 Exercise 1. Understanding Messages about Spending Money, p.122: You will hear information about three people. They are each talking about buying something. Listen carefully. On the line, write
Answer Keys for Calvert Math
 Answer Keys for Calvert Math Lessons 1 20 0613-0615 CONTENTS Math Textbook... 3 Math Workbook... 6 Answer Keys Math Textbook Lessons 1 20 CHAPTER 1 1.1 A There should be a ring around the chicken and
Answer Keys for Calvert Math Lessons 1 20 0613-0615 CONTENTS Math Textbook... 3 Math Workbook... 6 Answer Keys Math Textbook Lessons 1 20 CHAPTER 1 1.1 A There should be a ring around the chicken and
Foundation Stage. Using and applying mathematics. Framework review. Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems
 Foundation Stage Using and applying mathematics Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Look at the apples. Are there more green apples or more red apples? How can you
Foundation Stage Using and applying mathematics Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Look at the apples. Are there more green apples or more red apples? How can you
Time for Math. An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement!
 Time for Math Establishes a strong foundation in math through an interactive multimedia program! An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement! Numbers & Counting
Time for Math Establishes a strong foundation in math through an interactive multimedia program! An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement! Numbers & Counting
SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! Looking for a Pattern
 SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! Looking for a Pattern SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! 75 Teaching Notes Looking for a Pattern This strategy is an extension of Drawing a Table and Creating
SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! Looking for a Pattern SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! SOLVE THAT PROBLEM! 75 Teaching Notes Looking for a Pattern This strategy is an extension of Drawing a Table and Creating
Time for Math. An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement!
 Time for Math Establishes a strong foundation in math through an interactive multimedia program! An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement! Numbers & Counting
Time for Math Establishes a strong foundation in math through an interactive multimedia program! An extensive amount of content from numbers and counting, all the way to measurement! Numbers & Counting
