DIFFERENT SEQUENCES. Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards T 2 T 3
|
|
|
- Cecily Gibson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 21 DIFFERENT SEQUENCES Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 1: Number and number relationships Assessment Standard Investigate number patterns including but not limited to those where there is a constant difference and hence. Make conjectures and generalisations, Provide explanations and justifications and attempt to prove conjectures. Overview In this lesson you will: Look at unusual sequences where there is no first or second difference. If possible find the nth term. Prove conjectures. DVD Lesson Example 1 What will the next three terms be in the sequence 2; 6; 18; 54; T 4 Þ 2 ; 6 ; 18 ; 54 ; 1_ 3 6 ; 1 6 ; 3 6 ; 9 6 ; = ; ; ; ; ; So the next 3 terms will be: 162; 486; 1458 and T n = 3 n 2 6 = 3 n = 2.3 n 1 Alternatively: T 4 Þ 2 ; 6 ; 18 ; 54; = 2 1 ; 2 3 ; 2 9 ; 2 27 = ; ; ; ; ; ; So the next 3 terms will be: = = = 1458 Example 2 Again they all are multiples of 6: 84 Þ 24 ; 12 ; 6 = 4 6 ; 2 6 ; 1 6 ; _ ; _ 1 4 ; _ 1 8 = ; ; ; ; ; 2 3 6
2 = ; ; ; ; ; Next 3 terms will be: 3; _ 3 2 ; _ 3 4 T n = 2 4 n.3 Alternatively 24; 12; 6; 24; _ 24 2 ; _ 24 4 ; _ 24 ; _ 14; _ ; Tn = 24. _ 1 2 n 1 Both these general terms are the same: T n = 2 4 n.3 and T n = 24. ( _ 1 2 )n 1 = n = n = n Example 3 (Problem solving) A rubber ball is dropped from a height of 30m. After each bounce, it returns to a height that is 4/5 of the previous height. a) express the first three heights as a sequence Solution 30( _ 4 5 ); 30( _ 4 5 ) 2, 30( _ 4 5 ) 3 b) how high will the ball be after 21 bounces? Solution 1 = 30( 4 _ 5 ) 21 Activity 1 Example 4 (The Fibonacci sequence) Write down the next three terms in the sequence 1; 1; 2; 3; 5; 8; Solution 13; 21; 34 These are fascinating numbers because they appear all over in our world. formative assessment PAIRS DVD 85
3 THE FAMILY (In this family tree a male is represented by the symbol ( ) and a female by the symbol ) Generation back Number of bees in each generation 1st 1 2nd 2 3rd 3 4th 5 5th 8 6th 13 The 13 keys shown below form one octave of a piano. If we spread them out What do we notice? 5 black keys 8 white keys 13 keys ALL Fibonacci numbers In the 6th generation back of the male bee we have Males are the black keys and females the white keys. Look at this example from the internet. 86
4 The golden ratio 1; 1; 2; 3; 5; 8; 13; 21; 34; 55; 89; 144 _ T2 = 1; _ T1 T2T T3=T2; _ T3T T4 =T1,5; _ T5 T4 = 1,666; _ T6 T5T =T1,6 _ 13 8 = 1,625; _ 13 21= 1,61538 ; _ = 1,61904; _ = 1,6176 _ 89 = 1, ; _ = 1, Notice, as the sequence gets larger so the ratio gets closer to 1,62. We call this the GOLDEN RATIO. Workbook: Lesson 21 Activity 2 Triangular numbers Numbers that form triangles PORTFOLIO Individual Look at the picture and find the rule. Lets make rectangles DVD = 1 = 2 _ 3 2 = 3 4 _ 2 T 4 = 4 _ 5 2 T n = _ n(n + 1) 2 Show the 6th square number is equal to the 5th triangular number plus the 6th triangular number. Square numbers: T n = n 2 T 6 = 36 Triangular numbers T n = _ n(n + 1) 2 T 5 = 15 T 6 = = 36 Try more examples Alternate exploration: T 4 _ 1 2 n2 _ _ snt _ 2 1 _ 2 2 _ 2 3 _
5 Make a conjecture The nth square is equal to the some of the nth and the (n 1) th triangular numbers. Now prove it: Formula for the triangular numbers _ n(n + 1) so _ n(n + 1) + (n 1)(n) = n2 + n +n 2 n = _ 2n2 2 = n 2 PASCAL S TRIANGLE Complete the next three lines a) Look for a linear sequence b) Look for triangular numbers c) Find the sum of the terms in the 51 st row Row Sum Gen st Row 1 2 nd Row 2 3 rd Row 4 4th Row 8 5th Row 2 4 6th Row 2 5 nth Row 2 n 1 51 st Row = 2 50 So T n = 2 n 1 T 51 =
6 WORKBOOK: Lesson21 Activity 1 1. Find the nth term of the following sequences. a) 4; 2, 1; _ 1 2 ; _ 1 4 b) _ 1 8 ; _ 2 1 ; 2; 8; c) 32; 16; 8; 4; 2; d) 3a; 6a 2 ; 9a 3 ; 18a 4 2. a) Find T n b) Find the 8th term 9; 3;1 3. Which term of the sequence 1; _ 3 2 ; _ 4 9 is equal to _ ? (Hint; Find T first) n 4. A tree grows 120 cm during the first year. Each year it grows _ 9 of the 10 previous year s growth. How much in the 58th year? PORTFOLIO Individual DVD Activity 2 Write a paragraph on Leonardo Fibonacci. Find out all you can about the Fibonacci numbers and where we find them in nature (you may look at various flowers, spirals, shells, the pineapple). Generate the Fibonacci sequence by looking at the reproduction of rabbits. Investigate the Golden Ratio and why it represents a mathematically ideal ratio. Investigate the history of the golden ratio, including its role in the ancient Greek architecture. Learn how to construct the Golden Rectangle. You must supply a reference to the sources you used including web addresses. PORTFOLIO Activity 3 1. a) Show why the 5th triangular number is T 5 = _ b) Find an expression in n for the nth triangular number. 2. a) Use the diagrams of the 3rd and 4th triangular numbers, and T 4 to show that their sum that their sum is the 4th square number, i.e. S 4 = + T 4 b) Generalise with a formula the connection between triangular and square numbers. 3. a) Write down a table of square numbers from the 1 st to the tenth. b) Find two square numbers which add to give a square number. c) Repeat part (b) for at least three other pairs of square numbers. 89
7 4. Without using a calculator explain whether: a) 441 b) 2001 c) 1007 d) 4096 is a square number 5. Show that the difference between any two consecutive square numbers is an odd number. 6. Show that the difference between a) The 7th square number and the 4th square number is a multiple of b) The 8th square number and the 5th square number is a multiple of c) The 11th square number and the 7th square number is a multiple of 4. d) Generalise the statement implied in parts (a) (b) and (c). e) 64 is equal to the 8th square number S 8 = is equal to the 4th cube number C 4 = 4 3 Find other cube numbers which are also square numbers. If you can, make a general comment about such cube numbers. 7. For any positive whole number n its Tan function t(n) is defined as the number of positive whole number factors of n. 7 is a prime number. It has two factors so t(7) = 2 a) Show that if p is any prime number the t(p) = 2 b) For any prime number p and any positive value of n, find an expression for t(p n ). c) 6 7 = 42 The factors of 42 are: 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21, 42 so t(42) = 8 and t(6) = 4 t(7) = 2 t(6) t(7) n = 8 so t(6 7) = t(6) t(7) Investigate to see whether t(n m) = t(n) t(m) 8. One way of making the number 5 by adding ones and threes is: 5 = and another different way is: 5 = Investigate the number of different ways of making any number by adding ones and threes = = 9 = 3 2 = (1 + 2) = = 100 = 10 2 = ( ) = = 36 = 6 2 = ( ) 2 Investigate this situation further. Try other powers.
8 10. The last digit of 146 is 6. this is written LD(146) = 6. What comments can you make about a) LD(n m) b) LD(any square number) c) Show that 10n + 7 can never be a square number for any positive whole number value of n. 11. Mystery sequences Find the next three terms of the following sequences: 6; 8; 12; 14; ; 294; 72; 1; 5; 12; 22 and find T n 91
13 Searching for Pattern
 13 Searching for Pattern 13.1 Pictorial Logic In this section we will see how to continue patterns involving simple shapes. Example Continue these patterns by drawing the next 5 shapes in each case: Solution
13 Searching for Pattern 13.1 Pictorial Logic In this section we will see how to continue patterns involving simple shapes. Example Continue these patterns by drawing the next 5 shapes in each case: Solution
Fibonacci Numbers ANSWERS Lesson 1 of 10, work individually or in pairs
 Lesson 1 of 10, work individually or in pairs In 1202, the mathematician Leonardo Pisano Fibonacci (pronounced fi-buh-nah-chee) published a book with the famous Fibonacci sequence in it. (A sequence is
Lesson 1 of 10, work individually or in pairs In 1202, the mathematician Leonardo Pisano Fibonacci (pronounced fi-buh-nah-chee) published a book with the famous Fibonacci sequence in it. (A sequence is
repeated multiplication of a number, for example, 3 5. square roots and cube roots of numbers
 NUMBER 456789012 Numbers form many interesting patterns. You already know about odd and even numbers. Pascal s triangle is a number pattern that looks like a triangle and contains number patterns. Fibonacci
NUMBER 456789012 Numbers form many interesting patterns. You already know about odd and even numbers. Pascal s triangle is a number pattern that looks like a triangle and contains number patterns. Fibonacci
RIPPLES. 14 Patterns/Functions Grades 7-8 ETA.hand2mind. Getting Ready. The Activity On Their Own (Part 1) What You ll Need.
 RIPPLES Pattern recognition Growth patterns Arithmetic sequences Writing algebraic expressions Getting Ready What You ll Need Pattern Blocks, set per pair Colored pencils or markers Activity master, page
RIPPLES Pattern recognition Growth patterns Arithmetic sequences Writing algebraic expressions Getting Ready What You ll Need Pattern Blocks, set per pair Colored pencils or markers Activity master, page
Lesson 1. Unit 4. Golden Ratio. Ratio
 Lesson 1 Ratio Golden Ratio The golden ratio is a special ratio that is found in nature. In a nautilus shell it is found in the spiral. The spiral forms squares as shown. The rectangle formed reflects
Lesson 1 Ratio Golden Ratio The golden ratio is a special ratio that is found in nature. In a nautilus shell it is found in the spiral. The spiral forms squares as shown. The rectangle formed reflects
Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, Patterns - Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, 2017 Patterns - Solutions Tower of Hanoi The Tower of Hanoi is a
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, 2017 Patterns - Solutions Tower of Hanoi The Tower of Hanoi is a
Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, Patterns
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, 2017 Patterns Tower of Hanoi The Tower of Hanoi is a puzzle with
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, 2017 Patterns Tower of Hanoi The Tower of Hanoi is a puzzle with
Ideas beyond Number. Activity worksheets
 Ideas beyond Number Activity sheet 1 Task 1 Some students started to solve this equation in different ways: For each statement tick True or False: = = = = Task 2: Counter-examples The exception disproves
Ideas beyond Number Activity sheet 1 Task 1 Some students started to solve this equation in different ways: For each statement tick True or False: = = = = Task 2: Counter-examples The exception disproves
Figurate Numbers. by George Jelliss June 2008 with additions November 2008
 Figurate Numbers by George Jelliss June 2008 with additions November 2008 Visualisation of Numbers The visual representation of the number of elements in a set by an array of small counters or other standard
Figurate Numbers by George Jelliss June 2008 with additions November 2008 Visualisation of Numbers The visual representation of the number of elements in a set by an array of small counters or other standard
MAT 1160 Mathematics, A Human Endeavor
 MAT 1160 Mathematics, A Human Endeavor Syllabus: office hours, grading Schedule (note exam dates) Academic Integrity Guidelines Homework & Quizzes Course Web Site : www.eiu.edu/ mathcs/mat1160/ 2005 09,
MAT 1160 Mathematics, A Human Endeavor Syllabus: office hours, grading Schedule (note exam dates) Academic Integrity Guidelines Homework & Quizzes Course Web Site : www.eiu.edu/ mathcs/mat1160/ 2005 09,
NUMBER PATTERNS. The first 3 triangular numbers can be illustrated as follows: 1 2 3
 1 NUMBER PATTERNS EXERCISE 1 1. Write down the first 20 Natural Numbers. 2. Provide answers to the following: a. What are the 4 th, 5 th and 6 th even numbers? b. What relationship is between an even number
1 NUMBER PATTERNS EXERCISE 1 1. Write down the first 20 Natural Numbers. 2. Provide answers to the following: a. What are the 4 th, 5 th and 6 th even numbers? b. What relationship is between an even number
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Sequences. like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a dance or movement? Have you ever group things into
 Math of the universe Paper 1 Sequences Kelly Tong 2017/07/17 Sequences Introduction Have you ever stamped your foot while listening to music? Have you ever counted like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a
Math of the universe Paper 1 Sequences Kelly Tong 2017/07/17 Sequences Introduction Have you ever stamped your foot while listening to music? Have you ever counted like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a
Exploring and Analyzing Patterns
 PATTERNS: THEY RE GRRRRRoWING! Student Text copyright 205 carnegie learning, Inc. Patterns: They re Grrrrrowing! Exploring and Analyzing Patterns LEArnInG GoALS In this lesson, you will: Identify multiple
PATTERNS: THEY RE GRRRRRoWING! Student Text copyright 205 carnegie learning, Inc. Patterns: They re Grrrrrowing! Exploring and Analyzing Patterns LEArnInG GoALS In this lesson, you will: Identify multiple
Ten Calculator Activities- Teacher s Notes
 Ten Calculator Activities- Teacher s Notes Introduction These ten activity sheets can be photocopied and given to pupils at Key Stage 2. It is intended that the teacher introduces and discusses each activity
Ten Calculator Activities- Teacher s Notes Introduction These ten activity sheets can be photocopied and given to pupils at Key Stage 2. It is intended that the teacher introduces and discusses each activity
Section 8.1. Sequences and Series
 Section 8.1 Sequences and Series Sequences Definition A sequence is a list of numbers. Definition A sequence is a list of numbers. A sequence could be finite, such as: 1, 2, 3, 4 Definition A sequence
Section 8.1 Sequences and Series Sequences Definition A sequence is a list of numbers. Definition A sequence is a list of numbers. A sequence could be finite, such as: 1, 2, 3, 4 Definition A sequence
The (Fabulous) Fibonacci Numbers. Alfred S. Posamentier & Ingmar Lehmann. Afterword by Herbert Hauptman, Nobel Laureate
 The (abulous) ibonacci Numbers Alfred S. Posamentier & Ingmar Lehmann Afterword by Herbert Hauptman, Nobel Laureate Amherst (New York), Prometheus Books, 007, 385 p. ISBN 978--590-475-0 Translation by
The (abulous) ibonacci Numbers Alfred S. Posamentier & Ingmar Lehmann Afterword by Herbert Hauptman, Nobel Laureate Amherst (New York), Prometheus Books, 007, 385 p. ISBN 978--590-475-0 Translation by
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission. Junior Certificate Examination Mathematics. Paper 2 Higher Level
 2016. S35 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Junior Certificate Examination 2016 Mathematics Paper 2 Higher Level Monday 13 June Morning 9:30 to 12:00 300 marks Examination number
2016. S35 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Junior Certificate Examination 2016 Mathematics Paper 2 Higher Level Monday 13 June Morning 9:30 to 12:00 300 marks Examination number
Warm Up Classify each angle. Holt McDougal Geometry
 Warm Up Classify each angle. Objectives EQ: How do you use inductive reasoning to identify patterns and make conjectures? How do you find counterexamples to disprove conjectures? Unit 2A Day 4 inductive
Warm Up Classify each angle. Objectives EQ: How do you use inductive reasoning to identify patterns and make conjectures? How do you find counterexamples to disprove conjectures? Unit 2A Day 4 inductive
I.G.C.S.E. Solving Linear Equations. You can access the solutions from the end of each question
 I.G.C.S.E. Solving Linear Equations Inde: Please click on the question number you want Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 You can access the solutions
I.G.C.S.E. Solving Linear Equations Inde: Please click on the question number you want Question 1 Question 2 Question 3 Question 4 Question 5 Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 You can access the solutions
Combinatorial Proofs
 Combinatorial Proofs Two Counting Principles Some proofs concerning finite sets involve counting the number of elements of the sets, so we will look at the basics of counting. Addition Principle: If A
Combinatorial Proofs Two Counting Principles Some proofs concerning finite sets involve counting the number of elements of the sets, so we will look at the basics of counting. Addition Principle: If A
Maths lesson. Exploring sequences and the Fibonacci sequence. Learning objectives. Knowledge. Skills. Resources
 Exploring sequences and the Fibonacci sequence Learning objectives 1. Explore the exponential sequences, leading to negative powers. 2. Discover the Fibonacci sequence and the Golden Number or Golden Ratio.
Exploring sequences and the Fibonacci sequence Learning objectives 1. Explore the exponential sequences, leading to negative powers. 2. Discover the Fibonacci sequence and the Golden Number or Golden Ratio.
Number Fun December 3,
 Number Fun December 3, 2008 John L. Lehet jlehet@mathmaverick.com www.mathmaverick.com Numbers Fibonacci Numbers Digital Roots Vedic Math Original Puzzles MathMagic Tricks Predict the Sum? (PredictTheSum.xls)
Number Fun December 3, 2008 John L. Lehet jlehet@mathmaverick.com www.mathmaverick.com Numbers Fibonacci Numbers Digital Roots Vedic Math Original Puzzles MathMagic Tricks Predict the Sum? (PredictTheSum.xls)
Lesson 3. Translating Patterns
 Lesson 3 Translating Patterns Poultry Farming Poultry farming once consisted of the farmer s wife throwing out feed to the chickens. The chickens would wander about the farm yard. She would collect the
Lesson 3 Translating Patterns Poultry Farming Poultry farming once consisted of the farmer s wife throwing out feed to the chickens. The chickens would wander about the farm yard. She would collect the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *3620551787* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICS 0607/05 Paper 5 (Core) October/November 2010
*3620551787* UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL MATHEMATICS 0607/05 Paper 5 (Core) October/November 2010
Number Patterns - Grade 10 [CAPS] *
![Number Patterns - Grade 10 [CAPS] * Number Patterns - Grade 10 [CAPS] *](/thumbs/87/96010508.jpg) OpenStax-CNX module: m38376 1 Number Patterns - Grade 10 [CAPS] * Free High School Science Texts Project Based on Number Patterns by Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Mark Horner Heather
OpenStax-CNX module: m38376 1 Number Patterns - Grade 10 [CAPS] * Free High School Science Texts Project Based on Number Patterns by Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Mark Horner Heather
Arithmetic Sequences Read 8.2 Examples 1-4
 CC Algebra II HW #8 Name Period Row Date Arithmetic Sequences Read 8.2 Examples -4 Section 8.2 In Exercises 3 0, tell whether the sequence is arithmetic. Explain your reasoning. (See Example.) 4. 2, 6,
CC Algebra II HW #8 Name Period Row Date Arithmetic Sequences Read 8.2 Examples -4 Section 8.2 In Exercises 3 0, tell whether the sequence is arithmetic. Explain your reasoning. (See Example.) 4. 2, 6,
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important. There are many patterns you can see in nature. You can use numbers to describe many of these patterns.
 There are many patterns you can see in nature. You can use numbers to describe many of these patterns. At the end of this unit, you will investigate a famous set of numbers, the Fibonacci Numbers. You
There are many patterns you can see in nature. You can use numbers to describe many of these patterns. At the end of this unit, you will investigate a famous set of numbers, the Fibonacci Numbers. You
Whole Numbers. Whole Numbers. Curriculum Ready.
 Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
PARTICIPANT Guide. Unit 2
 PARTICIPANT Guide Unit 2 UNIT 02 participant Guide ACTIVITIES NOTE: At many points in the activities for Mathematics Illuminated, workshop participants will be asked to explain, either verbally or in
PARTICIPANT Guide Unit 2 UNIT 02 participant Guide ACTIVITIES NOTE: At many points in the activities for Mathematics Illuminated, workshop participants will be asked to explain, either verbally or in
Answer keys to the assessment tasks 61 Answer keys to the challenge questions 63 Achievement Profile 64
 Contents page Introduction 4 1. Odd and even numbers 5 Assessment task 1 8 2. Counting techniques: Consecutive numbers 9 3. Counting techniques: How many digits? 11 Assessment task 2 13 4. Number chains
Contents page Introduction 4 1. Odd and even numbers 5 Assessment task 1 8 2. Counting techniques: Consecutive numbers 9 3. Counting techniques: How many digits? 11 Assessment task 2 13 4. Number chains
Whole Numbers WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT.
 WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
Ideas beyond Number. Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets
 Ideas beyond Number Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets Learning objectives To explore reasoning, logic and proof through practical, experimental, structured and formalised methods of communication
Ideas beyond Number Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets Learning objectives To explore reasoning, logic and proof through practical, experimental, structured and formalised methods of communication
A natural number is called a perfect cube if it is the cube of some. some natural number.
 A natural number is called a perfect square if it is the square of some natural number. i.e., if m = n 2, then m is a perfect square where m and n are natural numbers. A natural number is called a perfect
A natural number is called a perfect square if it is the square of some natural number. i.e., if m = n 2, then m is a perfect square where m and n are natural numbers. A natural number is called a perfect
1.3 Number Patterns: Part 2 31
 (a) Create a sequence of 13 terms showing the number of E. coli cells after 12 divisions or a time period of four hours. (b) Is the sequence in part (a) an arithmetic sequence, a quadratic sequence, a
(a) Create a sequence of 13 terms showing the number of E. coli cells after 12 divisions or a time period of four hours. (b) Is the sequence in part (a) an arithmetic sequence, a quadratic sequence, a
YEAR 2 MID-PROGRAMME ENTRY EXAMINATIONS Time allowed: 2 hours
 YEAR 2 MID-PROGRAMME ENTRY EXAMINATIONS 2018 MATHEMATICS SATURDAY 2 nd JUNE 2018 Instructions to candidates Time allowed: 2 hours Answer the questions in the spaces provided there may be more space than
YEAR 2 MID-PROGRAMME ENTRY EXAMINATIONS 2018 MATHEMATICS SATURDAY 2 nd JUNE 2018 Instructions to candidates Time allowed: 2 hours Answer the questions in the spaces provided there may be more space than
1999 Mathcounts National Sprint Round Solutions
 999 Mathcounts National Sprint Round Solutions. Solution: 5. A -digit number is divisible by if the sum of its digits is divisible by. The first digit cannot be 0, so we have the following four groups
999 Mathcounts National Sprint Round Solutions. Solution: 5. A -digit number is divisible by if the sum of its digits is divisible by. The first digit cannot be 0, so we have the following four groups
3301/2I. MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 3301/2I Intermediate Tier Paper 2 Calculator. General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2004
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2004 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 3301/2I Intermediate Tier Paper 2 Calculator
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Secondary Education June 2004 MATHEMATICS (SPECIFICATION A) 3301/2I Intermediate Tier Paper 2 Calculator
100 IDEAS FOR USING A HUNDRED SQUARE
 100 IDEAS FOR USING A HUNDRED SQUARE These ideas are in no particular order and can be adapted to any age range or ability. The objectives are for children to learn to recognise numbers, understand numbers
100 IDEAS FOR USING A HUNDRED SQUARE These ideas are in no particular order and can be adapted to any age range or ability. The objectives are for children to learn to recognise numbers, understand numbers
First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed
 Mathematics First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Mathematics First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION AND REPRESENTATION. Date: Lesson: Chapter 1: Introduction and Representation
 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION AND REPRESENTATION Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Toolkit 2013 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved. 1 Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Toolkit 2013 CPM Educational
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION AND REPRESENTATION Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Toolkit 2013 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved. 1 Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Toolkit 2013 CPM Educational
Representing Square Numbers. Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array.
 1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
MATHEMATICS ON THE CHESSBOARD
 MATHEMATICS ON THE CHESSBOARD Problem 1. Consider a 8 8 chessboard and remove two diametrically opposite corner unit squares. Is it possible to cover (without overlapping) the remaining 62 unit squares
MATHEMATICS ON THE CHESSBOARD Problem 1. Consider a 8 8 chessboard and remove two diametrically opposite corner unit squares. Is it possible to cover (without overlapping) the remaining 62 unit squares
Exploring Concepts with Cubes. A resource book
 Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Facilitator Guide. Unit 2
 Facilitator Guide Unit 2 UNIT 02 Facilitator Guide ACTIVITIES NOTE: At many points in the activities for Mathematics Illuminated, workshop participants will be asked to explain, either verbally or in
Facilitator Guide Unit 2 UNIT 02 Facilitator Guide ACTIVITIES NOTE: At many points in the activities for Mathematics Illuminated, workshop participants will be asked to explain, either verbally or in
Consecutive Numbers. Madhav Kaushish. November 23, Learning Outcomes: 1. Coming up with conjectures. 2. Coming up with proofs
 Consecutive Numbers Madhav Kaushish November 23, 2017 Learning Outcomes: 1. Coming up with conjectures 2. Coming up with proofs 3. Generalising theorems The following is a dialogue between a teacher and
Consecutive Numbers Madhav Kaushish November 23, 2017 Learning Outcomes: 1. Coming up with conjectures 2. Coming up with proofs 3. Generalising theorems The following is a dialogue between a teacher and
FIBONACCI KOLAMS -- AN OVERVIEW
 FIBONACCI KOLAMS -- AN OVERVIEW S. Naranan This paper is an overview of all my work on Fibonacci Kolams as of end of the year 2015 that is included in my website www.vindhiya.com/snaranan/fk/index.htm
FIBONACCI KOLAMS -- AN OVERVIEW S. Naranan This paper is an overview of all my work on Fibonacci Kolams as of end of the year 2015 that is included in my website www.vindhiya.com/snaranan/fk/index.htm
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Honors Precalculus Chapter 9 Summary Basic Combinatorics
 Honors Precalculus Chapter 9 Summary Basic Combinatorics A. Factorial: n! means 0! = Why? B. Counting principle: 1. How many different ways can a license plate be formed a) if 7 letters are used and each
Honors Precalculus Chapter 9 Summary Basic Combinatorics A. Factorial: n! means 0! = Why? B. Counting principle: 1. How many different ways can a license plate be formed a) if 7 letters are used and each
40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016
 THE CALGARY MATHEMATICAL ASSOCIATION 40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016 NAME: PLEASE PRINT (First name Last name) GENDER: SCHOOL: GRADE: (9,8,7,...) You have 90 minutes for the examination.
THE CALGARY MATHEMATICAL ASSOCIATION 40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016 NAME: PLEASE PRINT (First name Last name) GENDER: SCHOOL: GRADE: (9,8,7,...) You have 90 minutes for the examination.
Name Date. Chapter 15 Final Review
 Name Date Chapter 15 Final Review Tell whether the events are independent or dependent. Explain. 9) You spin a spinner twice. First Spin: You spin a 2. Second Spin: You spin an odd number. 10) Your committee
Name Date Chapter 15 Final Review Tell whether the events are independent or dependent. Explain. 9) You spin a spinner twice. First Spin: You spin a 2. Second Spin: You spin an odd number. 10) Your committee
Number Relationships. Chapter GOAL
 Chapter 1 Number Relationships GOAL You will be able to model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies to estimate and calculate
Chapter 1 Number Relationships GOAL You will be able to model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies to estimate and calculate
Key Stage 3 Mathematics. Common entrance revision
 Key Stage 3 Mathematics Key Facts Common entrance revision Number and Algebra Solve the equation x³ + x = 20 Using trial and improvement and give your answer to the nearest tenth Guess Check Too Big/Too
Key Stage 3 Mathematics Key Facts Common entrance revision Number and Algebra Solve the equation x³ + x = 20 Using trial and improvement and give your answer to the nearest tenth Guess Check Too Big/Too
Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot)
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot) Unit 2 Geometry and Algebra Monday 11 November 2013
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot) Unit 2 Geometry and Algebra Monday 11 November 2013
Meet # 1 October, Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet # 1 October, 2000 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet # 1 October, 2000 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the picture shown below, the top half of the clock is obstructed from view
Meet # 1 October, 2000 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet # 1 October, 2000 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the picture shown below, the top half of the clock is obstructed from view
Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions.
 Student Outcomes Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions. Lesson Notes It is recommended that students have access to a calculator as they work
Student Outcomes Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions. Lesson Notes It is recommended that students have access to a calculator as they work
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Applications. 30 Prime Time
 Applications For Exercises 1 6, give the dimensions of each rectangle that can be made from the given number of tiles. Then use the dimensions of the rectangles to list all the factor pairs for each number.
Applications For Exercises 1 6, give the dimensions of each rectangle that can be made from the given number of tiles. Then use the dimensions of the rectangles to list all the factor pairs for each number.
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring
 Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Your Task. Unit 3 (Chapter 1): Number Relationships. The 5 Goals of Chapter 1
 Unit 3 (Chapter 1): Number Relationships The 5 Goals of Chapter 1 I will be able to: model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies
Unit 3 (Chapter 1): Number Relationships The 5 Goals of Chapter 1 I will be able to: model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies
SCHOOL OF EDUCATION (Edgewood Campus) MAIN EXAMINATIONS - NOVEMBER 2015 BACHELOR OF EDUCATION
 SCHOOL OF EDUCATION (Edgewood Campus) MAIN EXAMINATIONS - NOVEMBER 2015 BACHELOR OF EDUCATION Module Name Primary Mathematics Education 310 Code EDMA311 Duration 3 hours Marks 120 Internal Examiners Ms
SCHOOL OF EDUCATION (Edgewood Campus) MAIN EXAMINATIONS - NOVEMBER 2015 BACHELOR OF EDUCATION Module Name Primary Mathematics Education 310 Code EDMA311 Duration 3 hours Marks 120 Internal Examiners Ms
MATHEMATICS IN DESIGN
 MATHEMATICS IN DESIGN An exploration of the use of math in the fields of Fine Art and Graphic Design Spring 2017, EMPACTS Project Gary Bender, Instructor, gbender@nwacc.edu Northwest Arkansas Community
MATHEMATICS IN DESIGN An exploration of the use of math in the fields of Fine Art and Graphic Design Spring 2017, EMPACTS Project Gary Bender, Instructor, gbender@nwacc.edu Northwest Arkansas Community
Student Book SAMPLE CHAPTERS
 Student Book SAMPLE CHAPTERS Nelson Student Book Nelson Math Focus... Eas Each lesson starts with a Lesson Goal. Chapter 6 You will need base ten blocks GOAL Multiply using a simpler, related question.
Student Book SAMPLE CHAPTERS Nelson Student Book Nelson Math Focus... Eas Each lesson starts with a Lesson Goal. Chapter 6 You will need base ten blocks GOAL Multiply using a simpler, related question.
Mathematics Enhancement Programme TEACHING SUPPORT: Year 3
 Mathematics Enhancement Programme TEACHING UPPORT: Year 3 1. Question and olution Write the operations without brackets if possible so that the result is the same. Do the calculations as a check. The first
Mathematics Enhancement Programme TEACHING UPPORT: Year 3 1. Question and olution Write the operations without brackets if possible so that the result is the same. Do the calculations as a check. The first
2Reasoning and Proof. Prerequisite Skills. Before VOCABULARY CHECK SKILLS AND ALGEBRA CHECK
 2Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning 2.2 Analyze Conditional Statements 2.3 Apply Deductive Reasoning 2.4 Use Postulates and Diagrams 2.5 Reason Using Properties from Algebra 2.6 Prove Statements
2Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning 2.2 Analyze Conditional Statements 2.3 Apply Deductive Reasoning 2.4 Use Postulates and Diagrams 2.5 Reason Using Properties from Algebra 2.6 Prove Statements
SHRIMATI INDIRA GANDHI COLLEGE
 SHRIMATI INDIRA GANDHI COLLEGE (Nationally Re-accredited at A Grade by NAAC) Trichy - 2. COMPILED AND EDITED BY : J.SARTHAJ BANU DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS 1 LOGICAL REASONING 1.What number comes inside
SHRIMATI INDIRA GANDHI COLLEGE (Nationally Re-accredited at A Grade by NAAC) Trichy - 2. COMPILED AND EDITED BY : J.SARTHAJ BANU DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS 1 LOGICAL REASONING 1.What number comes inside
Strings. A string is a list of symbols in a particular order.
 Ihor Stasyuk Strings A string is a list of symbols in a particular order. Strings A string is a list of symbols in a particular order. Examples: 1 3 0 4 1-12 is a string of integers. X Q R A X P T is a
Ihor Stasyuk Strings A string is a list of symbols in a particular order. Strings A string is a list of symbols in a particular order. Examples: 1 3 0 4 1-12 is a string of integers. X Q R A X P T is a
Algebra 2. TMT 3 Algebra 2: Student Lesson 2 140
 A.1(B) collect and organize data, make and interpret scatterplots, fit the graph of a function to the data, interpret the results, and proceed to model, predict, and make decisions and critical judgments.
A.1(B) collect and organize data, make and interpret scatterplots, fit the graph of a function to the data, interpret the results, and proceed to model, predict, and make decisions and critical judgments.
We congratulate you on your achievement in reaching the second round of the Ulpaniada Mathematics Competition and wish you continued success.
 BS D Dear Participant, Shevat 5774 /January 2014 We congratulate you on your achievement in reaching the second round of the Ulpaniada Mathematics Competition and wish you continued success. Please fill
BS D Dear Participant, Shevat 5774 /January 2014 We congratulate you on your achievement in reaching the second round of the Ulpaniada Mathematics Competition and wish you continued success. Please fill
The University of Melbourne BHPBilliton School Mathematics Competition, 2007 JUNIOR DIVISION, QUESTIONS & SOLUTIONS
 The University of Melbourne BHPBilliton School Mathematics Competition, 2007 JUNIOR DIVISION, QUESTIONS & SOLUTIONS Flower power. Rose is a teacher at Kinder and has 12 children in her class. She would
The University of Melbourne BHPBilliton School Mathematics Competition, 2007 JUNIOR DIVISION, QUESTIONS & SOLUTIONS Flower power. Rose is a teacher at Kinder and has 12 children in her class. She would
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet Learner s name: School name: _ Day 1 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 273, 2,
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet Learner s name: School name: _ Day 1 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 273, 2,
Mod 21 Test Review GEO
 Name: Class: Date: ID: Mod 2 Test Review GEO Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Let U be the set of all integers from to 20. Let = {, 3, 6,
Name: Class: Date: ID: Mod 2 Test Review GEO Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Let U be the set of all integers from to 20. Let = {, 3, 6,
LAMC Junior Circle February 3, Oleg Gleizer. Warm-up
 LAMC Junior Circle February 3, 2013 Oleg Gleizer oleg1140@gmail.com Warm-up Problem 1 Compute the following. 2 3 ( 4) + 6 2 Problem 2 Can the value of a fraction increase, if we add one to the numerator
LAMC Junior Circle February 3, 2013 Oleg Gleizer oleg1140@gmail.com Warm-up Problem 1 Compute the following. 2 3 ( 4) + 6 2 Problem 2 Can the value of a fraction increase, if we add one to the numerator
Answer questions 1-35 on your Scantron. Questions 1-30 will be scored for the Power Bowl event. In the
 Answer questions 1-35 on your Scantron. Questions 1-30 will be scored for the Power Bowl event. In the event of a tie, questions 31-35 will be used as the tiebreaker. 1. If a = 2, the largest number in
Answer questions 1-35 on your Scantron. Questions 1-30 will be scored for the Power Bowl event. In the event of a tie, questions 31-35 will be used as the tiebreaker. 1. If a = 2, the largest number in
Proportional Reasoning Learning Contract (page 1 of 3)
 Appendix A ratio and Proportion Grade 8 Mathematics Proportional Reasoning Learning Contract (page 1 of 3) Non-Negotiable Tasks Building Knowledge and Skills Work in a small group and complete all questions.
Appendix A ratio and Proportion Grade 8 Mathematics Proportional Reasoning Learning Contract (page 1 of 3) Non-Negotiable Tasks Building Knowledge and Skills Work in a small group and complete all questions.
Mathematics. Stage 7
 Mathematics Stage 7 V These tables give general guidelines on marking answers that involve number and place value, and units of length, mass, money or duration. If the mark scheme does not specify the
Mathematics Stage 7 V These tables give general guidelines on marking answers that involve number and place value, and units of length, mass, money or duration. If the mark scheme does not specify the
MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED FOUNDATION TIER
 Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U20-1 S17-3300U20-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED FOUNDATION TIER TUESDAY, 20 JUNE 2017 AFTERNOON 1 hour 30 minutes For s use
Surname Centre Number Candidate Number Other Names 0 GCSE NEW 3300U20-1 S17-3300U20-1 MATHEMATICS UNIT 2: CALCULATOR-ALLOWED FOUNDATION TIER TUESDAY, 20 JUNE 2017 AFTERNOON 1 hour 30 minutes For s use
Scoring Format: 3 points per correct response -1 each wrong response 0 for blank answers
 Eighth Grade Contest 2017 Pellissippi State Math Competition Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition 8 th Grade Exam Scoring Format: 3 points per correct response -1 each wrong response
Eighth Grade Contest 2017 Pellissippi State Math Competition Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition 8 th Grade Exam Scoring Format: 3 points per correct response -1 each wrong response
THE TAYLOR EXPANSIONS OF tan x AND sec x
 THE TAYLOR EXPANSIONS OF tan x AND sec x TAM PHAM AND RYAN CROMPTON Abstract. The report clarifies the relationships among the completely ordered leveled binary trees, the coefficients of the Taylor expansion
THE TAYLOR EXPANSIONS OF tan x AND sec x TAM PHAM AND RYAN CROMPTON Abstract. The report clarifies the relationships among the completely ordered leveled binary trees, the coefficients of the Taylor expansion
A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES
 Last update: Nov. 6, 2015. A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
Last update: Nov. 6, 2015. A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
PART I: NO CALCULATOR (115 points)
 Prealgebra Practice Midterm Math 40 OER (Ch. 1-4) PART I: NO CALCULATOR (115 points) (1.) 1. Find the difference. a) 578 80 480 b) 10 165 51 (1.). Multiply the given numbers. 684 9. Divide the given numbers.
Prealgebra Practice Midterm Math 40 OER (Ch. 1-4) PART I: NO CALCULATOR (115 points) (1.) 1. Find the difference. a) 578 80 480 b) 10 165 51 (1.). Multiply the given numbers. 684 9. Divide the given numbers.
Objectives. Materials
 . Objectives Activity 8 To plot a mathematical relationship that defines a spiral To use technology to create a spiral similar to that found in a snail To use technology to plot a set of ordered pairs
. Objectives Activity 8 To plot a mathematical relationship that defines a spiral To use technology to create a spiral similar to that found in a snail To use technology to plot a set of ordered pairs
RightStart Mathematics
 Most recent update: January, 019 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level C/Grade Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE CORRECTION OR UPDATE Lesson /01/01
Most recent update: January, 019 RightStart Mathematics Corrections and Updates for Level C/Grade Lessons and Worksheets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE CORRECTION OR UPDATE Lesson /01/01
1. The 14 digits of a credit card are written in the boxes shown. If the sum of any three consecutive digits is 20, what is the value of A?
 No calculator is allowed. Write the letter of the answer you choose on the provided answer form. Note that, all the questions are single-choice questions. 1. The 14 digits of a credit card are written
No calculator is allowed. Write the letter of the answer you choose on the provided answer form. Note that, all the questions are single-choice questions. 1. The 14 digits of a credit card are written
Number Series Workbook V-1
 Direction (1-5) : What value should come in place of question mark (?) in the following number series? 1. 22, 42, 64, 88,? 1. 112 2. 118 3. 116 4. 114 5. 115 2. 11, 61, 299, 1189,? 1. 3559 2. 3659 3. 3569
Direction (1-5) : What value should come in place of question mark (?) in the following number series? 1. 22, 42, 64, 88,? 1. 112 2. 118 3. 116 4. 114 5. 115 2. 11, 61, 299, 1189,? 1. 3559 2. 3659 3. 3569
UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space. LESSON 4.1 Skills Practice. Vocabulary. Problem Set
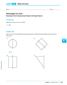 LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space Vocabulary Describe the term in your own words. 1. disc Problem Set Write the name of the solid figure
LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date Whirlygigs for Sale! Rotating Two-Dimensional Figures through Space Vocabulary Describe the term in your own words. 1. disc Problem Set Write the name of the solid figure
2004 Solutions Fryer Contest (Grade 9)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of The Centre for Education in Ma thematics and Computing, University of W aterloo, Wa terloo, Ontario 004 Solutions Fryer Contest (Grade 9) 004 Waterloo Mathematics
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of The Centre for Education in Ma thematics and Computing, University of W aterloo, Wa terloo, Ontario 004 Solutions Fryer Contest (Grade 9) 004 Waterloo Mathematics
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2009 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Year 2 Problems and Investigations Spring
 Year 2 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Racing riddles Children discuss the positions of four dogs in a set of four races using the information given. They attempt to use mathematical reasoning
Year 2 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Racing riddles Children discuss the positions of four dogs in a set of four races using the information given. They attempt to use mathematical reasoning
2.1 inductive reasoning and conjecture ink.notebook. September 07, Page 55. Ch 2. Reasoning. Page 56. and Proofs. 2.1 Inductive.
 2.1 inductive reasoning and conjecture ink.notebook Page 55 Ch 2 Reasoning and Proofs Page 56 2.1 Inductive Reasoning Lesson Objectives Page 57 Standards Lesson Notes Page 58 2.1 Inductive Reasoning and
2.1 inductive reasoning and conjecture ink.notebook Page 55 Ch 2 Reasoning and Proofs Page 56 2.1 Inductive Reasoning Lesson Objectives Page 57 Standards Lesson Notes Page 58 2.1 Inductive Reasoning and
GAP CLOSING. Powers and Roots. Intermediate / Senior Student Book GAP CLOSING. Powers and Roots. Intermediate / Senior Student Book
 GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots Intermediate / Senior Student Book Intermediate / Senior Student Book Powers and Roots Diagnostic...3 Perfect Squares and Square Roots...6 Powers...
GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots GAP CLOSING Powers and Roots Intermediate / Senior Student Book Intermediate / Senior Student Book Powers and Roots Diagnostic...3 Perfect Squares and Square Roots...6 Powers...
Key Concept Probability of Independent Events. Key Concept Probability of Mutually Exclusive Events. Key Concept Probability of Overlapping Events
 15-4 Compound Probability TEKS FOCUS TEKS (1)(E) Apply independence in contextual problems. TEKS (1)(B) Use a problemsolving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan or strategy,
15-4 Compound Probability TEKS FOCUS TEKS (1)(E) Apply independence in contextual problems. TEKS (1)(B) Use a problemsolving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan or strategy,
Grade 8 The Pythagorean Theorem
 THE NEWARK PUBLIC SCHOOLS THE OFFICE OF MATHEMATICS Grade 8 The Pythagorean Theorem 8.G.6-8 Student Pages Grade 8 - Lesson 1 Introductory Task Introductory Task Prerequisite Competencies 8.EE.2 Use square
THE NEWARK PUBLIC SCHOOLS THE OFFICE OF MATHEMATICS Grade 8 The Pythagorean Theorem 8.G.6-8 Student Pages Grade 8 - Lesson 1 Introductory Task Introductory Task Prerequisite Competencies 8.EE.2 Use square
Grade Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition Funded by ORAU 1. Pellissippi State. Middle School Mathematics Competition
 Grade 6 008 Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition Funded by ORAU Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition Sponsored by: Oak Ridge Associated Universities Sixth Grade Scoring
Grade 6 008 Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition Funded by ORAU Pellissippi State Middle School Mathematics Competition Sponsored by: Oak Ridge Associated Universities Sixth Grade Scoring
Assignment 5 unit3-4-radicals. Due: Friday January 13 BEFORE HOMEROOM
 Assignment 5 unit3-4-radicals Name: Due: Friday January 13 BEFORE HOMEROOM Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Write the prime factorization
Assignment 5 unit3-4-radicals Name: Due: Friday January 13 BEFORE HOMEROOM Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Write the prime factorization
Problem Solving Methods
 Problem olving Methods Blake Thornton One of the main points of problem solving is to learn techniques by just doing problems. o, lets start with a few problems and learn a few techniques. Patience. Find
Problem olving Methods Blake Thornton One of the main points of problem solving is to learn techniques by just doing problems. o, lets start with a few problems and learn a few techniques. Patience. Find
Cross Sections of Three-Dimensional Figures
 Domain 4 Lesson 22 Cross Sections of Three-Dimensional Figures Common Core Standard: 7.G.3 Getting the Idea A three-dimensional figure (also called a solid figure) has length, width, and height. It is
Domain 4 Lesson 22 Cross Sections of Three-Dimensional Figures Common Core Standard: 7.G.3 Getting the Idea A three-dimensional figure (also called a solid figure) has length, width, and height. It is
Math 122 Rough Guide to Studying for Exam 2 Spring, 2009
 Warning: Please don t take this as the final word on how to study. First of all, everybody learns differently, second of all, I am an expert at math, not at the theory of studying, and finally, I m squeezing
Warning: Please don t take this as the final word on how to study. First of all, everybody learns differently, second of all, I am an expert at math, not at the theory of studying, and finally, I m squeezing
