Maths lesson. Exploring sequences and the Fibonacci sequence. Learning objectives. Knowledge. Skills. Resources
|
|
|
- Maximilian Ford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exploring sequences and the Fibonacci sequence Learning objectives 1. Explore the exponential sequences, leading to negative powers. 2. Discover the Fibonacci sequence and the Golden Number or Golden Ratio. 3. Connect this number to nature sense of awe and wonder! 4. Make a Golden rectangle. Knowledge Maths lesson To develop understanding of Fibonacci sequences and application within nature. To create a Golden rectangle. Skills Mathematical skills. Enquiry skills investigate, research and evaluate. Resources Power point presentation PHI The Golden Number. Calculators, rulers, a pineapple. Strips of paper, graph paper.
2 Main activity Introduction to sequences (25 minutes) Write some sequences on the board, look at next terms and nth terms. Try some arithmetic sequences, geometric sequences, quadratics, etc. Use some tricky examples that could have been generated by more than one rule. Suggested examples: Easy: 3, 6 could be 3, 6, 9, 12 or 3, 6, 10, 15, 21 Harder: 2, 4, 8 could be 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 (powers of 2) or 2, 4, 8, 14, 22 (differences go up by 2 each time, or equivalently nth term is n 2 n + 2) Even harder and kind of obscure: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 could be 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 (powers of 2) or 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 31, 57 (nth term is (n 4 6 n n 2 18n + 24)/24 try it, it works!) rief discussion: How many terms do we need to be sure we ve got the right rule? (Strictly, we can never have enough terms!) Look at powers of 2 and extend to the left to introduce negative powers. Can a number raised to a negative power ever be negative? What is (-1) to the power of 100? Etc. PowerPoint journey of discovery (10 minutes) Use this is a stimulus to start discussing Fibonacci and where one finds sequences Fibonacci sequence (15 minutes) The "greatest European mathematician of the middle ages", his full name was Leonardo of Pisa or Leonardo Pisano in Italian since he was born in Pisa (Italy), the city with the famous Leaning Tower, about Leonardo's father was called Guglielmo onacci. He called himself Fibonacci: a shortening of the Latin "filius onacci", which means "the son of onaccio", The sequence Start with two 1 s, add them to give 2, add 1 and 2 to give 3, then 2 and 3 to give 5, then 3 and 5 to five Continue the sequence to 20 terms at least. Calculate fib(n)/ fib(n-1) (i.e. one term divide the term before it). What do you notice? Page 2 of 9
3 Start with any two numbers, not 1 and 1. Do the same, find 30 terms and calculate fib(n) / fib(n- 1). Share your results with the group, what do you notice? This number is so important that it has a special name, a Greek letter Phi written as. Choose any large number term and divide by the term before it, what do you get? Group work (35 minutes) Activity 1 Fibonacci numbers and the Golden Number or Golden Ratio If we take the ratio of two successive numbers in Fibonacci's series, (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 ) and we divide each by the number before it, we will find the following series of numbers: n fib(n)/fib(n-1) 2 1/1=1 3 2/1=2 4 3/2= /5= /8= /13= Plot the ratios on a graph. What do you notice The value that the ratio seems to be settling down towards is called the golden ratio or the golden number. It has a value of approximately Try this (need a calculator) Pick any positive number (like 10 or pi or.78 or whatever), add 1, take the square root, add 1, take the square root, add 1, take the square root, etc. forever. What happens? Page 3 of 9
4 Activity 2 Fibonacci rectangles and shell spirals You need some graph paper for this, a pencil and ruler We can make another picture showing the Fibonacci numbers 1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21 if we start with two small squares of size 1 next to each other. On top of both of these draw a square of size 2 (=1+1). Here is a spiral drawn in the squares, a quarter of a circle in each square. The spiral is not a true mathematical spiral but it is a good approximation to a kind of spiral that does appear often in nature Here is a cross-section of a Nautilus sea shell. It shows the spiral curve of the shell and the internal chambers that the animal using it adds on as it grows. The chambers provide buoyancy in the water. Spirals Coneflower 34/55 Pine cone 8/13 Cauliflower 5/8 1. Collect some pine cones for yourself and count the spirals in both directions. A tip: Soak the cones in water so that they close up to make counting the spirals easier. Are all the cones identical in that the steep spiral (the one with most spiral arms) goes in the same direction? 2. What about a pineapple? Can you spot the same spiral pattern? How many spirals are there in each direction? Page 4 of 9
5 Activity 3 Fibonacci fingers? Look at your own hand You have... 2 hands each of which has... 5 fingers, each of which has... 3 parts separated by... 2 knuckles Is this just a coincidence or not? However, if you measure the lengths of the bones in your finger (best seen by slightly bending the finger) does it look as if the ratio of the longest bone in a finger to the middle bone is Phi? What about the ratio of the middle bone to the shortest bone (at the end of the finger) - Phi again? Can you find any ratios in the lengths of the fingers that look like Phi? ---or does it look as if it could be any other similar ratio also? Why not measure your friends'hands and gather some statistics? Page 5 of 9
6 Activity 4 The exact value of As we ve seen, the ratios of successive terms in the Fibonacci sequence get closer and closer to a certain value, which we call. Now, suppose we take a large term in the sequence, fib(n), and call it a. fib(n) = a Explain why fib(n+1) is almost exactly equal to a What is fib(n+2) equal to? Explain why. Explain why a 2 = a + a What equation do we get if we cancel the a s? Show that = (5 + 1)/2 is one of the solutions of this equation. [Note: students who know the quadratic formula can get it from that; otherwise, substituting into the equation is fine.] Work out this value on your calculator. Write down all the numbers on the display = Now find the square of and write down all the numbers on the display 2 = Now find 1/ and write all the numbers (this is called the reciprocal) 1/ = What do you notice? Page 6 of 9
7 Activity 5 The perfect rectangle or golden rectangle The length is equal to, the width is 1 unit A A = C = 1 D C A + C = A Explain this equation in words. A C If C=1 then this equation becomes + 1 = gives + 1 = i.e. 2-1 = 0 solution is = -b + (b 2 4ac) 2a where a=1, b=-1, c=-1 Use this formula to show that = Constructing a golden rectangle Start with a long strip of paper width 10cm A C 1. Fold corner over to, make a crease then unfold 2. Fold side A over to C, make a crease then unfold Page 7 of 9
8 A A C Fold long end over like this and make a mark at D D A D This is a golden rectangle Measure AD and see! Page 8 of 9
9 Plenary session Students feed back what they have learnt. Questions for focus 1. Why do the Fibonacci numbers often appear in family trees? For suggested answers: 2. Sunflowers can contain the number 89, or even 144. Many other plants, such as succulents, also show the numbers. Some coniferous trees show these numbers in the bumps on their trunks. And palm trees show the numbers in the rings on their trunks. Why do these arrangements occur? 3. Look at this example of Muslim art and explain how the Fibonacci sequence is implemented. Page 9 of 9
Fibonacci Numbers ANSWERS Lesson 1 of 10, work individually or in pairs
 Lesson 1 of 10, work individually or in pairs In 1202, the mathematician Leonardo Pisano Fibonacci (pronounced fi-buh-nah-chee) published a book with the famous Fibonacci sequence in it. (A sequence is
Lesson 1 of 10, work individually or in pairs In 1202, the mathematician Leonardo Pisano Fibonacci (pronounced fi-buh-nah-chee) published a book with the famous Fibonacci sequence in it. (A sequence is
Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, Patterns - Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, 2017 Patterns - Solutions Tower of Hanoi The Tower of Hanoi is a
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, 2017 Patterns - Solutions Tower of Hanoi The Tower of Hanoi is a
Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, Patterns
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, 2017 Patterns Tower of Hanoi The Tower of Hanoi is a puzzle with
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles February 21/22, 2017 Patterns Tower of Hanoi The Tower of Hanoi is a puzzle with
Objectives. Materials
 . Objectives Activity 8 To plot a mathematical relationship that defines a spiral To use technology to create a spiral similar to that found in a snail To use technology to plot a set of ordered pairs
. Objectives Activity 8 To plot a mathematical relationship that defines a spiral To use technology to create a spiral similar to that found in a snail To use technology to plot a set of ordered pairs
GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE The Mathematics of Shell Construction. and other patterns
 GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 The Mathematics of Shell Construction and other patterns The Mathematics of Shell Construction and other patterns Contents 3 Fibonnaci Numbers
GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 GROWING UP IN MORECAMBE 2008 The Mathematics of Shell Construction and other patterns The Mathematics of Shell Construction and other patterns Contents 3 Fibonnaci Numbers
First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed
 Mathematics First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Mathematics First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
DIFFERENT SEQUENCES. Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards T 2 T 3
 Lesson 21 DIFFERENT SEQUENCES Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 1: Number and number relationships Assessment Standard Investigate number patterns including but not limited to
Lesson 21 DIFFERENT SEQUENCES Learning Outcomes and Assessment Standards Learning Outcome 1: Number and number relationships Assessment Standard Investigate number patterns including but not limited to
Section 8.1. Sequences and Series
 Section 8.1 Sequences and Series Sequences Definition A sequence is a list of numbers. Definition A sequence is a list of numbers. A sequence could be finite, such as: 1, 2, 3, 4 Definition A sequence
Section 8.1 Sequences and Series Sequences Definition A sequence is a list of numbers. Definition A sequence is a list of numbers. A sequence could be finite, such as: 1, 2, 3, 4 Definition A sequence
Algebra 2. TMT 3 Algebra 2: Student Lesson 2 140
 A.1(B) collect and organize data, make and interpret scatterplots, fit the graph of a function to the data, interpret the results, and proceed to model, predict, and make decisions and critical judgments.
A.1(B) collect and organize data, make and interpret scatterplots, fit the graph of a function to the data, interpret the results, and proceed to model, predict, and make decisions and critical judgments.
Number Fun December 3,
 Number Fun December 3, 2008 John L. Lehet jlehet@mathmaverick.com www.mathmaverick.com Numbers Fibonacci Numbers Digital Roots Vedic Math Original Puzzles MathMagic Tricks Predict the Sum? (PredictTheSum.xls)
Number Fun December 3, 2008 John L. Lehet jlehet@mathmaverick.com www.mathmaverick.com Numbers Fibonacci Numbers Digital Roots Vedic Math Original Puzzles MathMagic Tricks Predict the Sum? (PredictTheSum.xls)
Sequences. like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a dance or movement? Have you ever group things into
 Math of the universe Paper 1 Sequences Kelly Tong 2017/07/17 Sequences Introduction Have you ever stamped your foot while listening to music? Have you ever counted like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a
Math of the universe Paper 1 Sequences Kelly Tong 2017/07/17 Sequences Introduction Have you ever stamped your foot while listening to music? Have you ever counted like 1, 2, 3, 4 while you are doing a
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
PROBLEM 1 Do You See a Pattern?
 PROBLEM 1 Do You See a Pattern? A sequence is a pattern involving an ordered arrangement of numbers, geometric figures, letters, or other objects. A term of a sequence is an individual number, figure,
PROBLEM 1 Do You See a Pattern? A sequence is a pattern involving an ordered arrangement of numbers, geometric figures, letters, or other objects. A term of a sequence is an individual number, figure,
Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering. By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys.
 Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys Unit 2 Page 1 2.1: Place Values We just looked at graphing ordered
Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys Unit 2 Page 1 2.1: Place Values We just looked at graphing ordered
MATHEMATICS IN DESIGN
 MATHEMATICS IN DESIGN An exploration of the use of math in the fields of Fine Art and Graphic Design Spring 2017, EMPACTS Project Gary Bender, Instructor, gbender@nwacc.edu Northwest Arkansas Community
MATHEMATICS IN DESIGN An exploration of the use of math in the fields of Fine Art and Graphic Design Spring 2017, EMPACTS Project Gary Bender, Instructor, gbender@nwacc.edu Northwest Arkansas Community
Lesson 1. Unit 4. Golden Ratio. Ratio
 Lesson 1 Ratio Golden Ratio The golden ratio is a special ratio that is found in nature. In a nautilus shell it is found in the spiral. The spiral forms squares as shown. The rectangle formed reflects
Lesson 1 Ratio Golden Ratio The golden ratio is a special ratio that is found in nature. In a nautilus shell it is found in the spiral. The spiral forms squares as shown. The rectangle formed reflects
Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions.
 Student Outcomes Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions. Lesson Notes It is recommended that students have access to a calculator as they work
Student Outcomes Students apply the Pythagorean Theorem to real world and mathematical problems in two dimensions. Lesson Notes It is recommended that students have access to a calculator as they work
NUMBER PATTERNS. The first 3 triangular numbers can be illustrated as follows: 1 2 3
 1 NUMBER PATTERNS EXERCISE 1 1. Write down the first 20 Natural Numbers. 2. Provide answers to the following: a. What are the 4 th, 5 th and 6 th even numbers? b. What relationship is between an even number
1 NUMBER PATTERNS EXERCISE 1 1. Write down the first 20 Natural Numbers. 2. Provide answers to the following: a. What are the 4 th, 5 th and 6 th even numbers? b. What relationship is between an even number
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 5 7
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem
 UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
Divine Composition With Fibonacci s Ratio (The Rule of Thirds on Steroids)- AC Core
 Are you a stickler for little details? Well, if you re a photographer, you had better be. Discovering the rule of thirds is a big milestone for any photographer. Suddenly, you realize that all you ever
Are you a stickler for little details? Well, if you re a photographer, you had better be. Discovering the rule of thirds is a big milestone for any photographer. Suddenly, you realize that all you ever
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2008 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2008 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES.
 AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
Study Guide and Review - Chapter 3. Find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the graph of each linear function.
 Find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the graph of each linear function. 11. The x-intercept is the point at which the y-coordinate is 0, or the line crosses the x-axis. So, the x-intercept is 8. The
Find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the graph of each linear function. 11. The x-intercept is the point at which the y-coordinate is 0, or the line crosses the x-axis. So, the x-intercept is 8. The
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2008 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2008 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
PATTERN and RELATIONSHIPS
 PATTERN and RELATIONSHIPS Patterns are all around us outside in both the natural and built environments. They come in many guises: Number patterns are part of the joy and wonder of maths. Forms such as
PATTERN and RELATIONSHIPS Patterns are all around us outside in both the natural and built environments. They come in many guises: Number patterns are part of the joy and wonder of maths. Forms such as
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 3 5. satspapers.org
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 3 5 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 3 5 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Representing Square Numbers. Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array.
 1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
Study Guide and Intervention
 NAME DATE PERIOD Study Guide and Intervention Sequences An arithmetic sequence is a list in which each term is found by adding the same number to the previous term. 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 3 3 3 3 A geometric
NAME DATE PERIOD Study Guide and Intervention Sequences An arithmetic sequence is a list in which each term is found by adding the same number to the previous term. 2, 5, 8, 11, 14, 3 3 3 3 A geometric
Before How does the painting compare to the original figure? What do you expect will be true of the painted figure if it is painted to scale?
 Dilations LAUNCH (7 MIN) Before How does the painting compare to the original figure? What do you expect will be true of the painted figure if it is painted to scale? During What is the relationship between
Dilations LAUNCH (7 MIN) Before How does the painting compare to the original figure? What do you expect will be true of the painted figure if it is painted to scale? During What is the relationship between
UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet 5.1 Fractions: Parts and Wholes Identify the whole and its parts. Find and compare areas of different shapes. Identify congruent
Name Period Date UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet 5.1 Fractions: Parts and Wholes Identify the whole and its parts. Find and compare areas of different shapes. Identify congruent
Folding Activity 3. Compass Colored paper Tape or glue stick
 Folding Activity 3 Part 1 You re not done until everyone in your group is done! If you finish before someone else, help them finish before starting on the next part. You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie
Folding Activity 3 Part 1 You re not done until everyone in your group is done! If you finish before someone else, help them finish before starting on the next part. You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie
WITH MATH INTERMEDIATE/MIDDLE (IM) GRADE 6
 May 06 VIRGINIA MATHEMATICS STANDARDS OF LEARNING CORRELATED TO MOVING WITH MATH INTERMEDIATE/MIDDLE (IM) GRADE 6 NUMBER AND NUMBER SENSE 6.1 The student will identify representations of a given percent
May 06 VIRGINIA MATHEMATICS STANDARDS OF LEARNING CORRELATED TO MOVING WITH MATH INTERMEDIATE/MIDDLE (IM) GRADE 6 NUMBER AND NUMBER SENSE 6.1 The student will identify representations of a given percent
By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys
 Math Fundamentals for Statistics I (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Math Fundamentals for Statistics I (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike
1.3 Number Patterns: Part 2 31
 (a) Create a sequence of 13 terms showing the number of E. coli cells after 12 divisions or a time period of four hours. (b) Is the sequence in part (a) an arithmetic sequence, a quadratic sequence, a
(a) Create a sequence of 13 terms showing the number of E. coli cells after 12 divisions or a time period of four hours. (b) Is the sequence in part (a) an arithmetic sequence, a quadratic sequence, a
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 6 8 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2007 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Basic Mathematics Review 5232
 Basic Mathematics Review 5232 Symmetry A geometric figure has a line of symmetry if you can draw a line so that if you fold your paper along the line the two sides of the figure coincide. In other words,
Basic Mathematics Review 5232 Symmetry A geometric figure has a line of symmetry if you can draw a line so that if you fold your paper along the line the two sides of the figure coincide. In other words,
Overview: These flying oddities aren t your typical paper airplane. They may be strange to look at, but they re simple to make and fun to fly.
 17 THESE THINGS FLY! Overview: These flying oddities aren t your typical paper airplane. They may be strange to look at, but they re simple to make and fun to fly. Paper Paper or foam cups Straw Elastic
17 THESE THINGS FLY! Overview: These flying oddities aren t your typical paper airplane. They may be strange to look at, but they re simple to make and fun to fly. Paper Paper or foam cups Straw Elastic
Folding Activity 1. Colored paper Tape or glue stick
 Folding Activity 1 We ll do this first activity as a class, and I will model the steps with the document camera. Part 1 You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie Colored paper Tape or glue stick As you do
Folding Activity 1 We ll do this first activity as a class, and I will model the steps with the document camera. Part 1 You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie Colored paper Tape or glue stick As you do
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
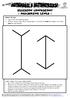 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
Home Connection 19 H Worksheet
 NAME For use after Unit Three, Session 1. DATE Home Connection 19 H Worksheet Doubles & Halves 1 Draw rectangle A with dimensions of 4 by 8 on the grid below 2 The perimeter of rectangle A is. Please show
NAME For use after Unit Three, Session 1. DATE Home Connection 19 H Worksheet Doubles & Halves 1 Draw rectangle A with dimensions of 4 by 8 on the grid below 2 The perimeter of rectangle A is. Please show
Objective: Use the addition of adjacent angle measures to solve problems using a symbol for the unknown angle measure.
 Lesson 10 Objective: Use the addition of adjacent angle measures to solve problems using a Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time
Lesson 10 Objective: Use the addition of adjacent angle measures to solve problems using a Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time
Patterns and Graphing Year 10
 Patterns and Graphing Year 10 While students may be shown various different types of patterns in the classroom, they will be tested on simple ones, with each term of the pattern an equal difference from
Patterns and Graphing Year 10 While students may be shown various different types of patterns in the classroom, they will be tested on simple ones, with each term of the pattern an equal difference from
Shimmer Braid. Month 4
 Shimmer Braid Month 4 4 star blocks 1 center block Star Block Size 10 square = Finished Block Size. Finished means after it is sewn into the quilt. 10 ½ square = Unfinished Size. Unfinished means before
Shimmer Braid Month 4 4 star blocks 1 center block Star Block Size 10 square = Finished Block Size. Finished means after it is sewn into the quilt. 10 ½ square = Unfinished Size. Unfinished means before
8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER. Paper 1. Year 8 mathematics test. Calculator not allowed. First name. Last name. Class. Date YEAR
 Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER 1 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the
Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 5 7 PAPER 1 Year 8 mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the
First Group Second Group Third Group How to determine the next How to determine the next How to determine the next number in the sequence:
 MATHEMATICIAN DATE BAND PUZZLES! WHAT COMES NEXT??? PRECALCULUS PACKER COLLEGIATE INSTITUTE Warm Up: 1. You are going to be given a set of cards. The cards have a sequence of numbers on them Although there
MATHEMATICIAN DATE BAND PUZZLES! WHAT COMES NEXT??? PRECALCULUS PACKER COLLEGIATE INSTITUTE Warm Up: 1. You are going to be given a set of cards. The cards have a sequence of numbers on them Although there
Arithmetic Sequences Read 8.2 Examples 1-4
 CC Algebra II HW #8 Name Period Row Date Arithmetic Sequences Read 8.2 Examples -4 Section 8.2 In Exercises 3 0, tell whether the sequence is arithmetic. Explain your reasoning. (See Example.) 4. 2, 6,
CC Algebra II HW #8 Name Period Row Date Arithmetic Sequences Read 8.2 Examples -4 Section 8.2 In Exercises 3 0, tell whether the sequence is arithmetic. Explain your reasoning. (See Example.) 4. 2, 6,
Paper 2 - The Business of Fibonacci. Leonardo of Pisa, who went by the nickname Fibonacci, was born in Pisa, Italy in 1170
 Paper 2 - The Business of Fibonacci Leonardo of Pisa, who went by the nickname Fibonacci, was born in Pisa, Italy in 1170 (O Connor & Robertson, 1998). He contributed much to the field of mathematics,
Paper 2 - The Business of Fibonacci Leonardo of Pisa, who went by the nickname Fibonacci, was born in Pisa, Italy in 1170 (O Connor & Robertson, 1998). He contributed much to the field of mathematics,
Sequence and Series Lesson 6. March 14, th Year HL Maths. March 2013
 j 6th Year HL Maths March 2013 1 arithmetic arithmetic arithmetic quadratic arithmetic quadratic geometric 2 3 Arithmetic Sequence 4 5 check: check: 6 check 7 First 5 Terms Count up in 3's from 4 simplify
j 6th Year HL Maths March 2013 1 arithmetic arithmetic arithmetic quadratic arithmetic quadratic geometric 2 3 Arithmetic Sequence 4 5 check: check: 6 check 7 First 5 Terms Count up in 3's from 4 simplify
MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS
 MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS Manipulative Mathematics Using Manipulatives to Promote Understanding of Elementary Algebra Concepts Lynn Marecek MaryAnne Anthony-Smith This file is copyright 07,
MANIPULATIVE MATHEMATICS FOR STUDENTS Manipulative Mathematics Using Manipulatives to Promote Understanding of Elementary Algebra Concepts Lynn Marecek MaryAnne Anthony-Smith This file is copyright 07,
KSF selected problems Student
 3 point problems 1. Andrea was born in 1997, her younger sister Charlotte in 2001. The age difference of the two sisters is therefore in any case. (A) less than 4 years (B) at least 4 years (C) exactly
3 point problems 1. Andrea was born in 1997, her younger sister Charlotte in 2001. The age difference of the two sisters is therefore in any case. (A) less than 4 years (B) at least 4 years (C) exactly
Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB
 Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB It s the Right Thing Subject: Mathematics: Geometry: Ratio and Proportion Level: Grade 7 Abstract: Students will learn the six types of triangles and the characteristics
Mathematics Geometry Grade 6AB It s the Right Thing Subject: Mathematics: Geometry: Ratio and Proportion Level: Grade 7 Abstract: Students will learn the six types of triangles and the characteristics
8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER. Paper 1. Year 8 mathematics test. Calculator not allowed. First name. Last name. Class. Date YEAR
 Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER Year 8 mathematics test Paper Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Ma YEAR 8 LEVELS 4 6 PAPER Year 8 mathematics test Paper Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your details in the spaces
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2005 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2005 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
In this section, you will learn the basic trigonometric identities and how to use them to prove other identities.
 4.6 Trigonometric Identities Solutions to equations that arise from real-world problems sometimes include trigonometric terms. One example is a trajectory problem. If a volleyball player serves a ball
4.6 Trigonometric Identities Solutions to equations that arise from real-world problems sometimes include trigonometric terms. One example is a trajectory problem. If a volleyball player serves a ball
Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern
 Published on Sew4Home Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern Editor: Liz Johnson Thursday, 25 August 2016 1:00 The circle is, in my humble opinion, the Queen of the geometric shapes. Don't get me
Published on Sew4Home Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern Editor: Liz Johnson Thursday, 25 August 2016 1:00 The circle is, in my humble opinion, the Queen of the geometric shapes. Don't get me
The Golden Ratio and the Elegance of Limits
 MathString Zentangle Workshop: The Golden Ratio and the Elegance of Limits Presented by: Pilar Pulido, CZT Class designed by: Pilar Pulido, CZT Lynn Mead, CZT About the class designers: Pilar Pulido, CZT
MathString Zentangle Workshop: The Golden Ratio and the Elegance of Limits Presented by: Pilar Pulido, CZT Class designed by: Pilar Pulido, CZT Lynn Mead, CZT About the class designers: Pilar Pulido, CZT
Draw an enlargement of this rectangle with scale factor 2 Use point A as the centre of enlargement.
 Enlargement 2. Look at the rectangle drawn on a square grid. Draw an enlargement of this rectangle with scale factor 2 Use point A as the centre of enlargement. A KS3/05/Ma/Tier 6 8/P2 4 Heron of Alexandria
Enlargement 2. Look at the rectangle drawn on a square grid. Draw an enlargement of this rectangle with scale factor 2 Use point A as the centre of enlargement. A KS3/05/Ma/Tier 6 8/P2 4 Heron of Alexandria
repeated multiplication of a number, for example, 3 5. square roots and cube roots of numbers
 NUMBER 456789012 Numbers form many interesting patterns. You already know about odd and even numbers. Pascal s triangle is a number pattern that looks like a triangle and contains number patterns. Fibonacci
NUMBER 456789012 Numbers form many interesting patterns. You already know about odd and even numbers. Pascal s triangle is a number pattern that looks like a triangle and contains number patterns. Fibonacci
Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 4 Lesson 6 Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 4 Lesson 6 Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
STUDENT'S BOOKLET. Inclination: Explorations on Slopes Part 1. Contents. 1 Flights 2 The slope of a line. 3 How Tall are you? 4 Duplicating Squares
 Meeting 3 Student s Booklet Inclination: Explorations on Slopes Part 1 February 1 2017 @ UCI Contents 1 Flights 2 The slope of a line STUDENT'S BOOKLET 3 How Tall are you? 4 Duplicating Squares UC IRVINE
Meeting 3 Student s Booklet Inclination: Explorations on Slopes Part 1 February 1 2017 @ UCI Contents 1 Flights 2 The slope of a line STUDENT'S BOOKLET 3 How Tall are you? 4 Duplicating Squares UC IRVINE
GCSE style questions arranged by topic
 Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Mathematics Sequences GCSE style questions arranged by topic Candidate Number Higher Tier
Write your name here Surname Other names In the style of: Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Mathematics Sequences GCSE style questions arranged by topic Candidate Number Higher Tier
Art and Science of Golden proportion a g rao
 Workshop on Art and Science of Golden proportion a g rao Preamble I thought many people might have heard of Golden Proportion. To my surprise I found that few among engineers had heard of it. Many Architects
Workshop on Art and Science of Golden proportion a g rao Preamble I thought many people might have heard of Golden Proportion. To my surprise I found that few among engineers had heard of it. Many Architects
Catty Corner. Side Lengths in Two and. Three Dimensions
 Catty Corner Side Lengths in Two and 4 Three Dimensions WARM UP A 1. Imagine that the rectangular solid is a room. An ant is on the floor situated at point A. Describe the shortest path the ant can crawl
Catty Corner Side Lengths in Two and 4 Three Dimensions WARM UP A 1. Imagine that the rectangular solid is a room. An ant is on the floor situated at point A. Describe the shortest path the ant can crawl
Ideal Crochet Rectangle
 Ideal Crochet Rectangle A pattern by Ms Premise-Conclusion Ms Premise-Conclusion Do you already know the dimensions or aspect ratio of your rectangle? Then you can figure out your entire pattern beforehand!
Ideal Crochet Rectangle A pattern by Ms Premise-Conclusion Ms Premise-Conclusion Do you already know the dimensions or aspect ratio of your rectangle? Then you can figure out your entire pattern beforehand!
Area of Composite Figures. ESSENTIAL QUESTION do you find the area of composite figures? 7.9.C
 ? LESSON 9.4 Area of Composite Figures ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area of composite figures? Equations, expressions, and relationships Determine the area of composite figures containing combinations
? LESSON 9.4 Area of Composite Figures ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do you find the area of composite figures? Equations, expressions, and relationships Determine the area of composite figures containing combinations
Whole Numbers. Whole Numbers. Curriculum Ready.
 Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Lesson 16. Opening Exploration A Special Case
 Opening Exploration A Special Case 1. Consuela ran across the quadratic equation y = 4x 2 16 and wondered how it could be factored. She rewrote it as y = 4x 2 + 0x 16. A. Use one of the methods you ve
Opening Exploration A Special Case 1. Consuela ran across the quadratic equation y = 4x 2 16 and wondered how it could be factored. She rewrote it as y = 4x 2 + 0x 16. A. Use one of the methods you ve
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES.
 AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
AREA & PERIMETER LESSON 1 OBJ ECTIVE: OBJECTIVE: INVESTIGATE AND USE THE FORMULAS FOR AREA AND PERIMETER OF RECTANGLES. Learning Goal By the end of the unit... students will apply the area and perimeter
Number Relationships. Chapter GOAL
 Chapter 1 Number Relationships GOAL You will be able to model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies to estimate and calculate
Chapter 1 Number Relationships GOAL You will be able to model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies to estimate and calculate
Squares and Square Roots Algebra 11.1
 Squares and Square Roots Algebra 11.1 To square a number, multiply the number by itself. Practice: Solve. 1. 1. 0.6. (9) 4. 10 11 Squares and Square Roots are Inverse Operations. If =y then is a square
Squares and Square Roots Algebra 11.1 To square a number, multiply the number by itself. Practice: Solve. 1. 1. 0.6. (9) 4. 10 11 Squares and Square Roots are Inverse Operations. If =y then is a square
math6thgradecrctreview (6thgrademathcrct)
 Name: Date: 1. Ethan is making a necklace. He has only 16 glass beads. He wants to know all the factors of 16 so he can create a longer necklace with a pattern of the glass beads and gold spacers he has.
Name: Date: 1. Ethan is making a necklace. He has only 16 glass beads. He wants to know all the factors of 16 so he can create a longer necklace with a pattern of the glass beads and gold spacers he has.
Information for teachers
 Topic Drawing line graphs Level Key Stage 3/GCSE (or any course for students aged - 6) Outcomes. Students identify what is wrong with a line graph 2. Students use a mark scheme to peer assess a line graph
Topic Drawing line graphs Level Key Stage 3/GCSE (or any course for students aged - 6) Outcomes. Students identify what is wrong with a line graph 2. Students use a mark scheme to peer assess a line graph
Measuring in Centimeters
 MD2-3 Measuring in Centimeters Pages 179 181 Standards: 2.MD.A.1 Goals: Students will measure pictures of objects in centimeters using centimeter cubes and then a centimeter ruler. Prior Knowledge Required:
MD2-3 Measuring in Centimeters Pages 179 181 Standards: 2.MD.A.1 Goals: Students will measure pictures of objects in centimeters using centimeter cubes and then a centimeter ruler. Prior Knowledge Required:
Ten Calculator Activities- Teacher s Notes
 Ten Calculator Activities- Teacher s Notes Introduction These ten activity sheets can be photocopied and given to pupils at Key Stage 2. It is intended that the teacher introduces and discusses each activity
Ten Calculator Activities- Teacher s Notes Introduction These ten activity sheets can be photocopied and given to pupils at Key Stage 2. It is intended that the teacher introduces and discusses each activity
Section D: "Square and Unsquare" Sec D class 1.notebook. November 15, Oct 11 9:29 AM. Oct 11 8:31 AM. Oct 24 10:41 AM.
 Draw a square with the dimensions 3 cm by 3cm. Section D: "Square and Unsquare" How many cm by cm squares completely cover this square? How is squaring related to the area of the square you drew? Oct 8:8
Draw a square with the dimensions 3 cm by 3cm. Section D: "Square and Unsquare" How many cm by cm squares completely cover this square? How is squaring related to the area of the square you drew? Oct 8:8
OCEAN WAVES Free Quilt Pattern Scrappy and 2-Color Quilt Directions Cindy Carter 2009
 OCEAN WAVES Free Quilt Pattern Scrappy and 2-Color Quilt Directions Cindy Carter 2009 http://carterquilter.wordpress.com/ Cindy Carter 2009 Ocean Waves 1 Copyright Information I have created all of my
OCEAN WAVES Free Quilt Pattern Scrappy and 2-Color Quilt Directions Cindy Carter 2009 http://carterquilter.wordpress.com/ Cindy Carter 2009 Ocean Waves 1 Copyright Information I have created all of my
Your Task. Unit 3 (Chapter 1): Number Relationships. The 5 Goals of Chapter 1
 Unit 3 (Chapter 1): Number Relationships The 5 Goals of Chapter 1 I will be able to: model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies
Unit 3 (Chapter 1): Number Relationships The 5 Goals of Chapter 1 I will be able to: model perfect squares and square roots use a variety of strategies to recognize perfect squares use a variety of strategies
Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills
 Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills Aim: to be able to present results and draw appropriate types of graphs Must: identify mistakes in data recording Should: be
Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills Aim: to be able to present results and draw appropriate types of graphs Must: identify mistakes in data recording Should: be
A C E. Applications. Applications Connections Extensions. 1. For parts (a) (c), use the parallelograms below.
 A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. For parts (a) (c), use the parallelograms below. a. List all the pairs of similar parallelograms. Explain your reasoning. b. For each pair of similar
A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. For parts (a) (c), use the parallelograms below. a. List all the pairs of similar parallelograms. Explain your reasoning. b. For each pair of similar
A proposal outline for K-12 curriculum development and research
 1 A proposal outline for K-12 curriculum development and research Integrated instruction of mathematics, geometry and biology using a daisy prime number sieve. by Dr. Scot Nelson University of Hawaii at
1 A proposal outline for K-12 curriculum development and research Integrated instruction of mathematics, geometry and biology using a daisy prime number sieve. by Dr. Scot Nelson University of Hawaii at
Describe Plane Shapes
 LESSON 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses,
LESSON 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes FOCUS COHERENCE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANCE F C R Focus: Common Core State Standards Learning Objective 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses,
Pythagorean Theorem Unit
 Pythagorean Theorem Unit TEKS covered: ~ Square roots and modeling square roots, 8.1(C); 7.1(C) ~ Real number system, 8.1(A), 8.1(C); 7.1(A) ~ Pythagorean Theorem and Pythagorean Theorem Applications,
Pythagorean Theorem Unit TEKS covered: ~ Square roots and modeling square roots, 8.1(C); 7.1(C) ~ Real number system, 8.1(A), 8.1(C); 7.1(A) ~ Pythagorean Theorem and Pythagorean Theorem Applications,
Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper
 THOMAS WHITHAM SIXTH FORM Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper Year 7 B U R N L E Y C@M P U S, B U R N L E Y, L A N C A S H I R E, B B 1 0 1 J D. T EL. 6 8 2 2 7 2 Algebra (1) Simplif each of the following
THOMAS WHITHAM SIXTH FORM Algebra Mathematics S. J. Cooper Year 7 B U R N L E Y C@M P U S, B U R N L E Y, L A N C A S H I R E, B B 1 0 1 J D. T EL. 6 8 2 2 7 2 Algebra (1) Simplif each of the following
Year 9 mathematics test
 Ma KeY STAGe 3 Year 9 mathematics test Tier 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name Class Date Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start.
Ma KeY STAGe 3 Year 9 mathematics test Tier 5 7 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name Class Date Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start.
Paper 1. Mathematics test. Calculator not allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2003 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2003 Mathematics test Paper 1 Calculator not allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
2.3: The Human Cannonball
 2.3: The Human Cannonball Parabola Equations and Graphs As a human cannonball Rosa is shot from a special cannon. She is launched into the air by a spring. Rosa lands in a horizontal net 150 ft. from the
2.3: The Human Cannonball Parabola Equations and Graphs As a human cannonball Rosa is shot from a special cannon. She is launched into the air by a spring. Rosa lands in a horizontal net 150 ft. from the
Meet #3 January Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet #3 January 2009 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #3 January 2009 Category 1 Mystery 1. How many two-digit multiples of four are there such that the number is still a
Meet #3 January 2009 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #3 January 2009 Category 1 Mystery 1. How many two-digit multiples of four are there such that the number is still a
SURDS, SPIRALS, DYNAMIC GEOMETRY AND CAS
 SURDS, SPIRALS, DYNAMIC GEOMETRY AND CAS Kaye Stacey and Elizabeth Price University of Melbourne and Canterbury Girls Secondary College This paper aims to enrich the teaching of surds. We use explorations
SURDS, SPIRALS, DYNAMIC GEOMETRY AND CAS Kaye Stacey and Elizabeth Price University of Melbourne and Canterbury Girls Secondary College This paper aims to enrich the teaching of surds. We use explorations
Mathematics Success Grade 8
 T936 Mathematics Success Grade 8 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the line of best fit for a scatter plot, interpret the equation and y-intercept of the linear representation, and make predictions based
T936 Mathematics Success Grade 8 [OBJECTIVE] The student will find the line of best fit for a scatter plot, interpret the equation and y-intercept of the linear representation, and make predictions based
Page 1 part 1 PART 2
 Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
Page 1 part 1 PART 2 Page 2 Part 1 Part 2 Page 3 part 1 Part 2 Page 4 Page 5 Part 1 10. Which point on the curve y x 2 1 is closest to the point 4,1 11. The point P lies in the first quadrant on the graph
Anthony Chan. September, Georgia Adult Education Conference
 Anthony Chan September, 2018 1 2018 Georgia Adult Education Conference Attendees will be able to: Make difficult math concepts simple and help their students discover math principles on their own. This
Anthony Chan September, 2018 1 2018 Georgia Adult Education Conference Attendees will be able to: Make difficult math concepts simple and help their students discover math principles on their own. This
YEAR 8 SRING TERM PROJECT ROOTS AND INDICES
 YEAR 8 SRING TERM PROJECT ROOTS AND INDICES Focus of the Project The aim of this The aim of this is to engage students in exploring ratio and/or probability. There is no expectation of teaching formal
YEAR 8 SRING TERM PROJECT ROOTS AND INDICES Focus of the Project The aim of this The aim of this is to engage students in exploring ratio and/or probability. There is no expectation of teaching formal
Decide how many topics you wish to revise at a time (let s say 10)
 1 Minute Maths for the Higher Exam (grades B, C and D topics*) Too fast for a first-time use but... brilliant for topics you have already understood and want to quickly revise. for the Foundation Exam
1 Minute Maths for the Higher Exam (grades B, C and D topics*) Too fast for a first-time use but... brilliant for topics you have already understood and want to quickly revise. for the Foundation Exam
Summer Work th Grade Skills that are necessary for success in 7 th grade and beyond:
 Summer Work 208 6 th Grade Math to 7 th Grade Math 6 th Grade Skills that are necessary for success in 7 th grade and beyond: - ability to add subtract, multiply and divide decimals and fractions - solve
Summer Work 208 6 th Grade Math to 7 th Grade Math 6 th Grade Skills that are necessary for success in 7 th grade and beyond: - ability to add subtract, multiply and divide decimals and fractions - solve
Easy Twist Pop-Up Panel Card
 Easy Twist Pop-Up Panel Card These cards are very popular, and the instructions online vary greatly. Some are just way to complicated. This is the easiest way I ve found to make it. I hope it helps you.
Easy Twist Pop-Up Panel Card These cards are very popular, and the instructions online vary greatly. Some are just way to complicated. This is the easiest way I ve found to make it. I hope it helps you.
REFLECTIONS AND STANDING WAVE RATIO
 Page 1 of 9 THE SMITH CHART.In the last section we looked at the properties of two particular lengths of resonant transmission lines: half and quarter wavelength lines. It is possible to compute the impedance
Page 1 of 9 THE SMITH CHART.In the last section we looked at the properties of two particular lengths of resonant transmission lines: half and quarter wavelength lines. It is possible to compute the impedance
3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers
 Math 1201 Date: 3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers Prime Number: a whole number greater than 1, whose only two whole-number factors are 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7,
Math 1201 Date: 3.1 Factors and Multiples of Whole Numbers Prime Number: a whole number greater than 1, whose only two whole-number factors are 1 and itself. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7,
GCSE 9-1 Higher Edexcel Set B Paper 1 - Non Calculator
 Name: GCSE 9-1 Higher Edexcel Set B Paper 1 - Non Calculator Equipment 1. A black ink ball-point pen. 2. A pencil. 3. An eraser. 4. A ruler. 5. A pair of compasses. 6. A protractor. Guidance 1. Read each
Name: GCSE 9-1 Higher Edexcel Set B Paper 1 - Non Calculator Equipment 1. A black ink ball-point pen. 2. A pencil. 3. An eraser. 4. A ruler. 5. A pair of compasses. 6. A protractor. Guidance 1. Read each
Equations of Lines and Linear Models
 8. Equations of Lines and Linear Models Equations of Lines If the slope of a line and a particular point on the line are known, it is possible to find an equation of the line. Suppose that the slope of
8. Equations of Lines and Linear Models Equations of Lines If the slope of a line and a particular point on the line are known, it is possible to find an equation of the line. Suppose that the slope of
