MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY
|
|
|
- Margaret Simpson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/32 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options), maximum raw mark 50 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates, to indicate the requirements of the examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were instructed to award marks. It does not indicate the details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners meeting before marking began, which would have considered the acceptability of alternative answers. Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for Teachers. Cambridge will not enter into discussions about these mark schemes. Cambridge is publishing the mark schemes for the October/November 2015 series for most Cambridge IGCSE, Cambridge International A and AS Level components and some Cambridge O Level components. IGCSE is the registered trademark of Cambridge International Examinations.
2 Page 2 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper Production, location and change 1 (a) For one named agricultural system (arable or pastoral) which you have studied: Much depends, clearly, on the system chosen. In the past, systems which are identified clearly, named and located performed better. If a candidate chooses something which is not a system using the classic definition, such as the Green Revolution or the CAP, mark on merit up to the top of in (b) and its equivalent in (a), 7/10. If a different system is chosen for (ii) than (i), credit the better and allow 1 for the other if the terms are understood and treated robustly. (i) describe the system s inputs and its outputs; [5] This requires a little more development than a list. Inputs of land (extent, quality, soil, etc.), labour (and skills), capital (for machinery, seeds, livestock, fertilisers, etc.) and climate. Raw outputs and/or processed products if done on the farm or in an associated enterprise, plus wastes. For a list max. 2. For either inputs or outputs, max. 3. (ii) explain how physical factors affect agricultural land-use and practices in this system. [5] Here physical factors cover land, soil, aspect, climate, climatic hazards and pests and diseases. Mark holistically, bearing in mind three bands of marks, 1 2, 3 4 and 5. If only land-use or practices, max. 4. (b) To what extent are changes in agriculture the result of economic factors? [15] Candidates may interpret changes as they choose, given the material they have. In many cases other factors, such as social or behavioural ones (the farmers choices) and political ones, may be significant, enabling an assessment. Structure their response as an assessment, show detailed knowledge of agriculture in more than one context. Argue convincingly and critically, with respect to factors in at least one other dimension, using the example(s) effectively. [12 15] Produce a sound response, which may be good in parts, but which remains limited and/or unbalanced in overall detail or development. May offer evaluative comments after a satisfactory descriptive or narrative response. [7 11] Make a basic answer which may be general, have a weak focus on change in agriculture or be faulty conceptually. Make one or more valid points, but offer little or no meaningful assessment. Notes and fragments remain in this level. [1 6]
3 Page 3 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper 2 (a) Figs 1A and 1B show two stages in production and location of manufacturing industry in cities. Describe, and suggest reasons for, the changes between Fig. 1A and Fig. 1B. [10] A full description covers changes between Figs 1A and 1B in: spatial scale, describing the spread and dispersion of production the separation of production from control functions (6 to 12 units) the increasing complexity of flows which results. Reasons for this decentralisation are many, but should cover disadvantages for production of the existing central locations, e.g. traffic congestion, lack of room to expand, and the advantages of the new suburban locations, e.g. good access, purpose-built factories suited to modern methods, financial incentives, space, etc. Examples that support and develop the reasons may be credited, but a general or generic response could achieve full marks. Mark on overall quality, bearing in mind three bands of marks and levels of response: 1 4, 5 7 and For either the description or suggesting reasons, max. 6. (b) With the help of examples, explain the concept of functional linkages and assess their significance for manufacturing. [15] functional linkages are the relationships or links between one industry and another. They take a number of forms: forward to the industry that consumes the industrial product backward to the industry that provides the raw material/component vertical a raw material goes through several successive processes horizontal an industry relies on several/many others for supplies diagonal an industry makes something which can be used in several linked industries, e.g. screws A broader view of linkages includes related services, e.g. finance, maintenance, advertising, packaging, transport, etc. Significance is in terms of productivity, efficiency, production networks, just-in-time working and as a locational factor.
4 Page 4 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper Use detailed knowledge and strong conceptual understanding of linkages to explain them and assess their significance robustly. Impress by overall perspective and organisation of the response. [12 15] Show satisfactory knowledge and understanding of linkages, which may be good in parts. Make a response which is limited overall, in detail, development and/or in the assessment it contains. [7 11] Produce a response of basic quality which may remain general or broadly located. Struggle to select and apply material to this question. Take an approach which is more descriptive than explanatory, offering little or no effective assessment. Notes and fragments remain in this level. [1 6]
5 Page 5 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper Environmental management 3 (a) Explain why demand for energy is increasing in most countries. [10] The fundamental reason for increasing energy demand is that as countries develop, energy demand in all sectors (domestic, agriculture, manufacturing, services including transport) increases. This, if developed well, is fully acceptable as an answer. Candidates may link it to rising standard of living and increase in affluence and to resource-hungry machines, from white goods to large cars in multi-car households. It may be linked to urbanisation, as urban life demands more energy than rural life in most places, and to industrialisation and the growth of the secondary sector (both heavy industry and light industry). Credit the idea that increasing energy demand may be mitigated by energy-saving initiatives and appliances, by the environmentally aware, but that the upward trend remains. Mark on overall quality, bearing in mind three bands of marks and levels of response: 1 4, 5 7 and For a response without examples (countries, activities, sectors, locations, data, etc.) max. 6. (b) The future of energy production is in renewable resources. With the help of examples, how far do you agree with this statement? [15] Candidates are free to develop their own response, based on their view or diverse views of the relative contribution of non-renewable and renewable resources in future. Accept nuclear power as either type. Issues of sustainability cost and energy security may be seen, alongside the classic concerns about the depletion of fossil fuels and their environmental impact. Structure their whole response as an assessment, combining detailed exemplar knowledge of energy with strong conceptual understanding. Recognise that the issue is dynamic and that views differ. [12 15] Provide a response of sound quality which may be good in parts or as far as it goes. Give a satisfactory, but limited, assessment which may not be integrated with the rest of the answer and which is limited in scope. [7 11] Struggle to deal with the topic. Make one or more basic points about energy production which may remain general. Answer descriptively, offering little or no effective assessment. Notes and fragments remain in this level. [1 6]
6 Page 6 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper 4 (a) Fig. 2 shows the loss of forested area, by country, With the help of examples, suggest reasons why deforestation varies globally. [10] Candidates have the opportunity to develop a response in different ways using the knowledge and understanding they have about environments generally and deforestation as a process. Responses are likely to combine the causes of deforestation (for fuelwood, wood for construction, mining, land clearance, etc.) and why these vary globally, with reasoning based on global concerns about forest loss and environmental protection, afforestation, etc., and that these also vary with income, development, political regime, etc. Specific reference to Fig. 2 is not required in that it functions as a stimulus resource and description of what it shows is not creditable as the demand is explanatory. Mark on overall quality, bearing in mind three bands of marks and levels of response: 1 4, 5 7 and For a response without examples (countries, forests, locations, policies, etc.), max. 6. (b) Assess the success of one attempt to improve the quality of a degraded environment you have studied. [15] Following (a), there is no requirement that the environment be a forest, but some will be. This is a syllabus classic, using the case study from 2.4. Experience shows that many candidates spend too long explaining the causes of degradation, rather than making the success of the attempt the focus. Credit clear criteria for improvement (relative success or failure), such as for local people, vegetation and animals or environmental quality measures. Produce a high quality assessment, based on strong conceptual understanding of degradation and detailed knowledge of the chosen attempt. Demonstrate a high level of skill in analysis and argument, structuring the response well. Impress by overall perspective. [12 15] Develop a response of sound to good quality. While satisfactory as far as it goes, candidates may lack detailed knowledge, firm conceptual grasp of degradation and/or skills in assessment. At the lower end may deal with the environment or attempt quite generally. [7 11] Make a response which is more a description than an assessment. Offer a few basic observations about the environment and what was done. Notes and fragmentary responses remain in this level. [1 6]
7 Page 7 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper Global interdependence 5 (a) Fig. 3 shows the largest trade flows in 2010, the fastest growing trade flows and information about world output of selected commodities. (i) Describe the pattern of the fastest growing trade flows, supporting your response with evidence from Fig. 3. [4] Flows into South Asia (2) and China (3), from varying distances and from LEDCs, NICs and one MEDC (Australia). All have increased by similar percentages (20 to 26%). For the description 2 and use of evidence 2. (ii) How does resource endowment help explain the largest trade flows in Fig. 3? [6] Here resource endowment is a factor in syllabus 3.1. The idea is helpful in that resources, especially minerals (iron ore, coal, oil), are needed to supply existing and emerging industries, transport, energy production, etc. Flows out of the Middle East to Europe and to East Asia are of oil, for example, and of iron ore and coal from Australia to China. However, resource endowment is not fully explanatory and other factors matter also, e.g. cost, policy, trade agreements, etc. Mark on overall quality, scope and detail, bearing in mind three levels of response and the mark bands of 1 2, 3 4 and 5 6. (b) Discuss the view that trade is preferable to tourism as the basis for a country s economic development. [15] Candidates may consider issues such as stability, fragility, the global economic context and outlook, multiplier effect, cumulative causation, etc. For trade, ideas such as trade blocs and dependency on primary products are relevant; for tourism, those of fashion and leakage, etc. Any view may be taken, based on their own evidence and argument. Structure the response as an evaluation, demonstrating strong conceptual understanding of both trade and tourism. Convince by overall perspective, exemplar detail and analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of each. [12 15] Produce a satisfactory to good evaluation of sound quality overall. Show some knowledge of the economic potential of both sectors. Develop a response which is limited in one or more ways (perspective, examples, analysis and evaluation). [7 11] Make a few basic points about trade and/or tourism in an approach which is descriptive and may be general. Offer little or no evaluation or an unsupported opinion. Fragments and notes remain in this level. [1 6]
8 Page 8 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper 6 (a) Account for the growth of international tourism. [10] In the lifetime of 9696, this has been developed in the context of three sets of factors (whether candidates call them this, or not): demand factors supply factors facilitating factors e.g. time, affluence, fashion, interest, numbers e.g. TNCs, resort development, tourism strategy and planning, package holidays, niche tourism and new types such as ecotourism e.g. transport, media, advertising, ease of obtaining visas Reward the combination of the above three and use of evidence (data, locations, etc.). A contemporary account, for example recognising new markets among the middle classes in India and China; or affluent retired populations in MEDCs who holiday several times a year, may also indicate quality. Mark on overall quality, scope and detail, bearing in mind three levels of response and the mark bands of 1 4, 5 7 and For a response without examples, max. 6. (b) How far do you agree that for tourist destinations the benefits received from tourism are far greater than the costs? [15] The syllabus requires the study of impacts on environments, societies and economies (local and national). As such, costs should not be simply interpreted in the financial or economic sense. Much depends on the type of tourism, the point in the life cycle, if applicable, and the management of the destination. Responses may indicate that the analysis varies by location, group of people, etc. Provide a convincing personal assessment of the statement s validity. Impress by overall perspective and conceptual understanding of tourism s costs and benefits. Make evidencebased analysis and argument, using the chosen examples effectively. [12 15] Provide a response of sound to good quality which is fine as far as it goes but which remains underdeveloped in detail, dimensionality or in the assessment offered. At the lower end may simply agree with the statement and support it. For a well developed response on one tourist destination, max. 10. [7 11] Make one or more simple observations about tourism s benefits and costs. Answer superficially or generally with little or no exemplar content. Offer a description more than an assessment. Fragments and notes remain in this level. [1 6]
9 Page 9 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper Economic transition 7 (a) Fig. 4 shows gross national income (GNI) per person and one measure of happiness for selected countries in (i) Describe the relationship between the measures, supporting your response with information from Fig. 4. [4] There is a discernible happiness curve, where happiness increases with GNI per person. 2 The curve flattens out above US$30 000, as increased income brings relatively little further increase in happiness. 1 For the idea that below US$ the relationship between the two is indistinct (e.g. compare Indonesia, India, Moldova) or for an anomaly/ies. 1 (ii) Compare the strengths and limitations of the measures in Fig. 4 in showing social and economic wellbeing. [6] Strengths and limitations may include: GNI per person happiness strengths * easy to understand * single criterion/clear * allows global comparison * hard economic statistic * includes social * values individuals * other limitations * per person hides internal variation * economic not social * possible inaccuracies of statistic * other * definition/cultural? * social and economic basis unclear * may depend on character, mood, etc. * other Mark on overall quality, bearing in mind three bands of marks and levels of response: 1 2, 3 4 and 5 6. Both measures are needed for the top band.
10 Page 10 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper (b) To what extent does globalisation help to explain global inequalities in development? [15] A straightforward opportunity to develop a to some extent argument, based on knowledge and understanding of the process of globalisation (elements, actors, outcomes, etc.) and of global inequalities in development (measured in any way). There are many other factors which may also be explanatory: environmental (e.g. resource endowment, climate, accessibility); economic (e.g. finance, level or stage of development); social (e.g. education); political, (e.g. regime, colonisation, instability). Offer a convincing assessment which impresses by its perspective, detail and strength of approach to the topic. Analyse globalisation and other factors in a judging manner, structuring the response well. [12 15] Provide a response of sound quality overall, which may be good in parts, but which remains limited in detail, overall understanding of globalisation and other causes of global inequalities or the assessment made. [7 11] Make one or more simple observations about the causes of global inequalities. Struggle to select and apply learned material. Answer generally and/or descriptively, offering little or no assessment. [1 6] 8 With reference to one country: If a candidate covers more than one country, mark as separate responses and credit the better or best one, annotating the script to this effect. If the response is at the global scale, use the principle of generic credit to award marks within the first band and. (a) describe how social and economic development varies between regions; [10] Based on recall knowledge and understanding, detail and development are needed to access the higher marks. Look for detail such as named locations, data, dates, examples of social development (e.g. literacy, education, the empowerment of women, quality of and access to healthcare) and of economic development in any sectors and for individuals, communities, etc. Better descriptions may do more than take the core and one example of a peripheral region and may be reasonably up-to-date. Mark on overall quality, bearing in mind three bands of marks and levels of response: 1 4, 5 7 and 8 10.
11 Page 11 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper (b) assess the reasons why the country s regional development remains uneven. [15] For a combination of reasons from initial advantages, such as location and resource endowment which remain significant; through the process of development, such as spread and backwash effects; and currently, such as the lack of effective regional policy or its lack of success. Classical divergence and little or no convergence may be relevant, also other factors, e.g. political instability, hazards, selective choices of FDI, TNCs, government, migrants, etc. Provide an impressive assessment of the reasons why regional development in the chosen country remains uneven. Show detailed knowledge of the chosen country, skills in analysis and strong conceptual understanding of the theoretical context. Structure the response well. [12 15] Produce a sound response, which lacks full development, but which may be good in some respects. Show satisfactory understanding of the reasons for uneven regional development in the chosen country and some ability to assess. At the lower end may take a broad but shallow approach, with limited reasoning and partial evaluation. [7 11] Make more of an explanatory response about why development is uneven in the chosen country than one which assesses. Write quite generally or loosely, maybe repeating content in (a). Notes and fragmentary responses remain in this level. [1 6]
9696 GEOGRAPHY. Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for Teachers.
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/33 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options), maximum raw mark
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/33 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options), maximum raw mark
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level GEOGRAPHY 9696/31 Paper 3 Advanced Human Options October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 50 Published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level GEOGRAPHY 9696/31 Paper 3 Advanced Human Options October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 50 Published
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9696 GEOGRAPHY. 9696/03 Paper 3 (Human Options), maximum raw mark 50
 www.gceguide.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/03 Paper 3
www.gceguide.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/03 Paper 3
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/31 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/31 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options), maximum
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level GEOGRAPHY 9696/33 Paper 3 Advanced Human Options October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 50 Published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level GEOGRAPHY 9696/33 Paper 3 Advanced Human Options October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 50 Published
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/32 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options),
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/32 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options),
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/33 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9696 GEOGRAPHY 9696/33 Paper 3 (Advanced Human Options), maximum
Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History
 Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History 1. Identification Name of programme Scope of programme Level Programme code Master Programme in Economic History 60/120 ECTS Master level Decision
Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History 1. Identification Name of programme Scope of programme Level Programme code Master Programme in Economic History 60/120 ECTS Master level Decision
Teddington School Sixth Form
 Teddington School Sixth Form AS / A level Sociology Induction and Key Course Materials AS and A level Sociology Exam Board AQA This GCE Sociology specification has been designed so that candidates will
Teddington School Sixth Form AS / A level Sociology Induction and Key Course Materials AS and A level Sociology Exam Board AQA This GCE Sociology specification has been designed so that candidates will
Scenario Development Process
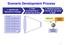 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
2011 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines
 0 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer C A C 4 D 5 A 6 B 7 C 8 A 9 D 0 C B D C 4 B 5 B 6 B 7 D 8 D 9 B 0 C 0 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section II
0 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer C A C 4 D 5 A 6 B 7 C 8 A 9 D 0 C B D C 4 B 5 B 6 B 7 D 8 D 9 B 0 C 0 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section II
EC Chapter 1. Burak Alparslan Eroğlu. October 13, Burak Alparslan Eroğlu EC Chapter 1
 EC 101 - Chapter 1 Burak Alparslan Eroğlu October 13, 2016 Outline Introduction to New Course Module Introduction to Unit 1 Hockey Stick Growth Capitalism Inequality Economics and Economy Introduction
EC 101 - Chapter 1 Burak Alparslan Eroğlu October 13, 2016 Outline Introduction to New Course Module Introduction to Unit 1 Hockey Stick Growth Capitalism Inequality Economics and Economy Introduction
Class 12 Geography Bk 1. Chapter 6 Secondary Economic Activities
 CHAPTER 6 SECONDARY ACTIVITIES Questions at the end of the Chapter A. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. 1. Which one of the following statements is wrong? 1.1 Cheap water
CHAPTER 6 SECONDARY ACTIVITIES Questions at the end of the Chapter A. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below. 1. Which one of the following statements is wrong? 1.1 Cheap water
Technology transfer: Challenges in Mongolia
 Technology transfer: Challenges in Mongolia Presenter: Mr. Enkh-Otgon.D /Senior Instructor, National University of Mongolia/ Mongolia is situated in Central Asia, between Russia and China, and population
Technology transfer: Challenges in Mongolia Presenter: Mr. Enkh-Otgon.D /Senior Instructor, National University of Mongolia/ Mongolia is situated in Central Asia, between Russia and China, and population
1.1 Students know how to use maps, globes, and other geographic tools to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective.
 Prentice Hall World Geography: Building a Global Perspective 2005 Colorado Model Academic Standards for Social Studies: Geography (Grades 9-12) GEOGRAPHY STANDARD 1: Students know how to use and construct
Prentice Hall World Geography: Building a Global Perspective 2005 Colorado Model Academic Standards for Social Studies: Geography (Grades 9-12) GEOGRAPHY STANDARD 1: Students know how to use and construct
GCE Media Studies. Mark Scheme for June Unit G325: Critical Perspectives in Media. Advanced GCE. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Media Studies Unit G325: Critical Perspectives in Media Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 2017 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Media Studies Unit G325: Critical Perspectives in Media Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 2017 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
Short Contribution to Panel Discussions on Africa s Industrialisation Machiko Nissanke
 Short Contribution to Panel Discussions on Africa s Industrialisation Machiko Nissanke At ODI, London, 14 January 2016 Issues and Questions Arising Industrialisation is a critical part of Africa s Structural
Short Contribution to Panel Discussions on Africa s Industrialisation Machiko Nissanke At ODI, London, 14 January 2016 Issues and Questions Arising Industrialisation is a critical part of Africa s Structural
2010 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines
 00 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section I Question Answer C D B 4 C 5 D 6 C 7 D 8 B 9 D 0 A D D C 4 B 5 A 6 A and D 7 C 8 B 9 A 0 B 00 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section II Question (a) Correctly
00 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section I Question Answer C D B 4 C 5 D 6 C 7 D 8 B 9 D 0 A D D C 4 B 5 A 6 A and D 7 C 8 B 9 A 0 B 00 HSC Economics Marking Guidelines Section II Question (a) Correctly
GCE Media Studies. Mark Scheme for June Unit G325: Critical Perspectives in Media. Advanced GCE. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Media Studies Unit G325: Critical Perspectives in Media Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Media Studies Unit G325: Critical Perspectives in Media Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 2014 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
Coal was king of the Industrial Revolution, but not always the path to a modern economy
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Law, Humanities and the Arts - Papers Faculty of Law, Humanities and the Arts 2016 Coal was king of the Industrial Revolution, but not always the path
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Law, Humanities and the Arts - Papers Faculty of Law, Humanities and the Arts 2016 Coal was king of the Industrial Revolution, but not always the path
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 0470 HISTORY. 0470/23 Paper 2, maximum raw mark 50
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 0470 HISTY 0470/23 Paper 2, maximum raw mark 50
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 0470 HISTY 0470/23 Paper 2, maximum raw mark 50
The Triple Bottom Line for London
 The Triple Bottom Line for London An index of London s sustainability Sponsored by Foreword by Jo Valentine, chief executive, London First Sustainability defined by the UK government as the simple idea
The Triple Bottom Line for London An index of London s sustainability Sponsored by Foreword by Jo Valentine, chief executive, London First Sustainability defined by the UK government as the simple idea
REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION SURVEY
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate A: Cooperation in the European Statistical System; international cooperation; resources Unit A2: Strategy and Planning REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate A: Cooperation in the European Statistical System; international cooperation; resources Unit A2: Strategy and Planning REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION
MSMES: OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES FOR THE SDG AGENDA
 MSMES: OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES FOR THE SDG AGENDA Global Symposium on the role of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) in the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) UN
MSMES: OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES FOR THE SDG AGENDA Global Symposium on the role of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) in the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) UN
Importance of SMEs in Greening the Economy in Georgia
 Importance of SMEs in Greening the Economy in Georgia EaP Green Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia February 12, 2015 Kiev, Ukraine Importance of Green Economy for Georgia
Importance of SMEs in Greening the Economy in Georgia EaP Green Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia February 12, 2015 Kiev, Ukraine Importance of Green Economy for Georgia
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/41 Paper 4 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 60 Published This mark
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/41 Paper 4 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 60 Published This mark
They all say it is about the economy. It is more than ratio s, percentages, and growth; it is about the Lives of people
 They all say it is about the economy It is more than ratio s, percentages, and growth; it is about the Lives of people Let me share my version of that vision based on the belief that Curaçao Connects Communities
They all say it is about the economy It is more than ratio s, percentages, and growth; it is about the Lives of people Let me share my version of that vision based on the belief that Curaçao Connects Communities
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MATHEMATICS 0580/ Paper (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 70 Published This mark scheme
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MATHEMATICS 0580/ Paper (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 70 Published This mark scheme
Common Terms of Reference for Regional/Country Studies on Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining for the MMSD Project Prepared by J.
 Common Terms of Reference for Regional/Country Studies on Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining for the MMSD Project Prepared by J. Davidson This outline is based on Latin American and Southern African plans
Common Terms of Reference for Regional/Country Studies on Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining for the MMSD Project Prepared by J. Davidson This outline is based on Latin American and Southern African plans
2005 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Food Technology
 2005 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Food Technology 2006 Copyright Board of Studies NSW for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales. This document contains Material prepared
2005 HSC Notes from the Marking Centre Food Technology 2006 Copyright Board of Studies NSW for and on behalf of the Crown in right of the State of New South Wales. This document contains Material prepared
Vietnam s Innovation System: Toward a Product Innovation Ecosystem.
 Session 1 Vietnam s Innovation System: Toward a Product Innovation Ecosystem. Ca Ngoc Tran General Secretary The National Council for Science and Technology Policy (NCSTP) Vietnam 1. Vietnam s innovation
Session 1 Vietnam s Innovation System: Toward a Product Innovation Ecosystem. Ca Ngoc Tran General Secretary The National Council for Science and Technology Policy (NCSTP) Vietnam 1. Vietnam s innovation
DIRECTION OF SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION POLICY IN THAILAND
 DIRECTION OF SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION POLICY IN THAILAND By Mr. Pichet Durongkaveroj Secretary General, National Science Technology and Innovation Policy Office, Thailand 99 I SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY
DIRECTION OF SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY AND INNOVATION POLICY IN THAILAND By Mr. Pichet Durongkaveroj Secretary General, National Science Technology and Innovation Policy Office, Thailand 99 I SCIENCE, TECHNOLOGY
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education HISTORY 0470/22 Paper 2 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 50 Published This mark scheme is published as an
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education HISTORY 0470/22 Paper 2 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 50 Published This mark scheme is published as an
Outcomes of the 2018 OECD Ministerial Conference on SMEs & the way forward
 Outcomes of the 2018 OECD Ministerial Conference on SMEs & the way forward SME Envoys Network 23 March 2018 Copenhagen Miriam Koreen Deputy Director Centre for Entrepreneurship, SMEs, Regions and Cities
Outcomes of the 2018 OECD Ministerial Conference on SMEs & the way forward SME Envoys Network 23 March 2018 Copenhagen Miriam Koreen Deputy Director Centre for Entrepreneurship, SMEs, Regions and Cities
High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development. UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017
 High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017 Edna dos Santos-Duisenberg creative.edna@gmail.com Policy Advisor
High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017 Edna dos Santos-Duisenberg creative.edna@gmail.com Policy Advisor
State Content Standards for New Mexico
 Episode 101 What Is a Biz Kid? Episode 102 What Is Money? Episode 103 How Do You Get Money? Episode 104 What Can You Do with Money? Episode 105 Money Moves Episode 106 Taking Charge of Your Financial Future
Episode 101 What Is a Biz Kid? Episode 102 What Is Money? Episode 103 How Do You Get Money? Episode 104 What Can You Do with Money? Episode 105 Money Moves Episode 106 Taking Charge of Your Financial Future
Werner Wobbe. Employed at the European Commission, Directorate General Research and Innovation
 Werner Wobbe Employed at the European Commission, Directorate General Research and Innovation Conference Paper, Call to Europe, September 2013 1 The current European Commission policies are guided by the
Werner Wobbe Employed at the European Commission, Directorate General Research and Innovation Conference Paper, Call to Europe, September 2013 1 The current European Commission policies are guided by the
The Internationalization of R&D in India: Opportunities and Challenges. Rajeev Anantaram National Interest Project March 2009
 The Internationalization of R&D in India: Opportunities and Challenges Rajeev Anantaram National Interest Project March 2009 Context of the Paper Part of the Private Sector Advisory Group constituted by
The Internationalization of R&D in India: Opportunities and Challenges Rajeev Anantaram National Interest Project March 2009 Context of the Paper Part of the Private Sector Advisory Group constituted by
Chapter 3 What Economies Do Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.)
 Chapter 3 What Economies Do Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview This chapter introduces the four essential economic activities: resource maintenance, the production of goods and
Chapter 3 What Economies Do Macroeconomics In Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview This chapter introduces the four essential economic activities: resource maintenance, the production of goods and
Building a common information architecture for the Commission. October 14, 2014
 Building a common information architecture for the Commission October 14, 2014 Introduction: what we did last time Explained process of building a common architecture Explained card sorting scope and planning
Building a common information architecture for the Commission October 14, 2014 Introduction: what we did last time Explained process of building a common architecture Explained card sorting scope and planning
Horizon 2020 and CAP towards 2020
 Horizon 2020 and CAP towards 2020 An update of contributions by the SCAR cwg AKIS Dublin, June, 2013 Pascal Bergeret, Krijn J. Poppe, Kevin Heanue Content of the presentation Summary of findings CWG AKIS
Horizon 2020 and CAP towards 2020 An update of contributions by the SCAR cwg AKIS Dublin, June, 2013 Pascal Bergeret, Krijn J. Poppe, Kevin Heanue Content of the presentation Summary of findings CWG AKIS
THE INTERNATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS OF ECONOMIES IN TRANSITION THE UNTAPPED POTENTIAL: A CHALLENGE FOR BUSINESS AND GOVERNMENT BELARUS
 THE INTERNATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS OF ECONOMIES IN TRANSITION THE UNTAPPED POTENTIAL: A CHALLENGE FOR BUSINESS AND GOVERNMENT BELARUS NATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS ISSUES, CONSTRAINTS AND STRATEGIC IMPLICATIONS
THE INTERNATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS OF ECONOMIES IN TRANSITION THE UNTAPPED POTENTIAL: A CHALLENGE FOR BUSINESS AND GOVERNMENT BELARUS NATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS ISSUES, CONSTRAINTS AND STRATEGIC IMPLICATIONS
Industries can be classified on the basis of raw materials, size and ownership.
 Industries Industry refers to an economic activity that is concerned with production of goods, extraction of minerals or the provision of services. Thus we have iron and steel industry (production of goods),
Industries Industry refers to an economic activity that is concerned with production of goods, extraction of minerals or the provision of services. Thus we have iron and steel industry (production of goods),
Years 9 and 10 standard elaborations Australian Curriculum: Design and Technologies
 Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Years 3 and 4 standard elaborations Australian Curriculum: Digital Technologies
 Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be as a tool for: making consistent
Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be as a tool for: making consistent
European Circular Economy Stakeholder Conference Brussels, February 2018 Civil Society Perspectives
 European Circular Economy Stakeholder Conference Brussels, 20-21 February 2018 Civil Society Perspectives On the 20 th and 21 st February 2018, the European Commission and the European Economic and Social
European Circular Economy Stakeholder Conference Brussels, 20-21 February 2018 Civil Society Perspectives On the 20 th and 21 st February 2018, the European Commission and the European Economic and Social
The$return$of$industrial$policy$on$the$African$ continent$and$the$drivers$of$this$revival$
 The$return$of$industrial$policy$on$the$African$ continent$and$the$drivers$of$this$revival$ Christopher Cramer SOAS, University of London Nicolas Meisel Agence Française de Développement (AFD) Issues Papers
The$return$of$industrial$policy$on$the$African$ continent$and$the$drivers$of$this$revival$ Christopher Cramer SOAS, University of London Nicolas Meisel Agence Française de Développement (AFD) Issues Papers
Building an enterprise-centred innovation system
 Building an enterprise-centred innovation system Ken Warwick Chair, OECD CIIE Deputy Chief Economic Adviser UK Department for Business, Enterprise and Regulatory Reform Themes Enterprise and innovation
Building an enterprise-centred innovation system Ken Warwick Chair, OECD CIIE Deputy Chief Economic Adviser UK Department for Business, Enterprise and Regulatory Reform Themes Enterprise and innovation
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/3 Paper 3 Practical Test MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/3 Paper 3 Practical Test MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and
FINLAND. The use of different types of policy instruments; and/or Attention or support given to particular S&T policy areas.
 FINLAND 1. General policy framework Countries are requested to provide material that broadly describes policies related to science, technology and innovation. This includes key policy documents, such as
FINLAND 1. General policy framework Countries are requested to provide material that broadly describes policies related to science, technology and innovation. This includes key policy documents, such as
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2010 Highlights
 OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 21 OECD 21 OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 21 Highlights Innovation can play an important role in the economic recovery Science, technology and
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 21 OECD 21 OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 21 Highlights Innovation can play an important role in the economic recovery Science, technology and
English National Curriculum Key Stage links to Meteorology
 English National Curriculum Key Stage links to Meteorology Subject KS1 (Programme of Study) links KS2 (Programme of Study) links KS3 (National Curriculum links) KS4 (National Curriculum links) Citizenship
English National Curriculum Key Stage links to Meteorology Subject KS1 (Programme of Study) links KS2 (Programme of Study) links KS3 (National Curriculum links) KS4 (National Curriculum links) Citizenship
Ministerial Conference on Nuclear Science and Technology: Addressing Current and Emerging Challenges Vienna, November 2018
 Ministerial Conference on Nuclear Science and Technology: Addressing Current and Emerging Challenges Vienna, 28-30 November 2018 Concluding Summary by the Co-Chairs of the Conference 1. The International
Ministerial Conference on Nuclear Science and Technology: Addressing Current and Emerging Challenges Vienna, 28-30 November 2018 Concluding Summary by the Co-Chairs of the Conference 1. The International
Information Societies: Towards a More Useful Concept
 IV.3 Information Societies: Towards a More Useful Concept Knud Erik Skouby Information Society Plans Almost every industrialised and industrialising state has, since the mid-1990s produced one or several
IV.3 Information Societies: Towards a More Useful Concept Knud Erik Skouby Information Society Plans Almost every industrialised and industrialising state has, since the mid-1990s produced one or several
Analysing Megatrends to Better shape the future of Tourism
 Issues Paper Analysing Megatrends to Better shape the future of Tourism 2-3 October 2017 OECD, Paris 2 Background information This note is provided as background information at the High Level Meeting on
Issues Paper Analysing Megatrends to Better shape the future of Tourism 2-3 October 2017 OECD, Paris 2 Background information This note is provided as background information at the High Level Meeting on
Original: English Rio de Janeiro, Brazil June 2012
 United Nations A/CONF.216/4 Distr.: General 29 May 2012 Original: English Rio de Janeiro, Brazil 20-22 June 2012 Item 9 of the provisional agenda* Reports of the round tables Background note for round
United Nations A/CONF.216/4 Distr.: General 29 May 2012 Original: English Rio de Janeiro, Brazil 20-22 June 2012 Item 9 of the provisional agenda* Reports of the round tables Background note for round
New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy
 Ninth Session of the Committee on Sustainable Development and the Africa Regional Forum on Sustainable Development New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 16-18 June
Ninth Session of the Committee on Sustainable Development and the Africa Regional Forum on Sustainable Development New and Emerging Issues Interface to Science Policy Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 16-18 June
Promoting Foreign Direct Investment in The United States. Christopher Clement International Investment Specialist Invest in America
 Promoting Foreign Direct Investment in The United States Christopher Clement International Investment Specialist Invest in America FDI in the U.S. Economy 5.2 million $40 billion $55 billion $190 billion
Promoting Foreign Direct Investment in The United States Christopher Clement International Investment Specialist Invest in America FDI in the U.S. Economy 5.2 million $40 billion $55 billion $190 billion
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights
 OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights Global dynamics in science, technology and innovation Investment in science, technology and innovation has benefited from strong economic
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights Global dynamics in science, technology and innovation Investment in science, technology and innovation has benefited from strong economic
Enacting Transformative Innovation Policy: A Comparative Study
 Enacting Transformative Innovation Policy: A Comparative Study Johan Schot - Director Science Policy Research Unit - SPRU University of Sussex @Johan_Schot Transformative Innovation Policy Consortium Aim
Enacting Transformative Innovation Policy: A Comparative Study Johan Schot - Director Science Policy Research Unit - SPRU University of Sussex @Johan_Schot Transformative Innovation Policy Consortium Aim
CGC1D Geography of Canada Exam Review
 CGC1D Geography of Canada Exam Review Exam Format Part A: Knowledge & Understanding: Multiple Choice, True and False, Fill in the Blank Part B: Application: Labelling Part C: Thinking & Inquiry: Short
CGC1D Geography of Canada Exam Review Exam Format Part A: Knowledge & Understanding: Multiple Choice, True and False, Fill in the Blank Part B: Application: Labelling Part C: Thinking & Inquiry: Short
Decoding jute plant genome an eye opener. Abdul Quader
 Decoding jute plant genome an eye opener Abdul Quader Decoding jute plant genome is a breakthrough in the field of genomics research and biotechnology. It is a great achievement on the part of a Bangladeshi
Decoding jute plant genome an eye opener Abdul Quader Decoding jute plant genome is a breakthrough in the field of genomics research and biotechnology. It is a great achievement on the part of a Bangladeshi
Activity Tourism and Special Interest Pursuits: An Introduction (SCQF level 6)
 National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H0BD 12 Superclass: NK Publication date: January 2012 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Summary This Unit is primarily intended
National Unit specification: general information Unit code: H0BD 12 Superclass: NK Publication date: January 2012 Source: Scottish Qualifications Authority Version: 02 Summary This Unit is primarily intended
Annotated Chapter Outline
 Annotated Chapter Outline Chapter 1: Context, Scope and Approach 1. Context. Access-poverty-economy linkages, need for substantive scale-up, global movement SE4ALL, SDGs, etc. 2. Rationale. Complementary
Annotated Chapter Outline Chapter 1: Context, Scope and Approach 1. Context. Access-poverty-economy linkages, need for substantive scale-up, global movement SE4ALL, SDGs, etc. 2. Rationale. Complementary
FOR05664 Constructing Social Education Curriculum for the Twenty-first Century: the Role and Importance of Economics Education
 FOR05664 Constructing Social Education Curriculum for the Twenty-first Century: the Role and Importance of Economics Education Anita Forsyth Monash University Abstract: The place of economics education
FOR05664 Constructing Social Education Curriculum for the Twenty-first Century: the Role and Importance of Economics Education Anita Forsyth Monash University Abstract: The place of economics education
Correlation Guide. Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text
 Presented by the Center for Civic Education, The National Conference of State Legislatures, and The State Bar of Wisconsin Correlation Guide For Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text Jack
Presented by the Center for Civic Education, The National Conference of State Legislatures, and The State Bar of Wisconsin Correlation Guide For Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text Jack
DPS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL CAMBRIDGE IGCSE [FOUNDATION] SYLLABUS Subject : BIOLOGY
![DPS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL CAMBRIDGE IGCSE [FOUNDATION] SYLLABUS Subject : BIOLOGY DPS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL CAMBRIDGE IGCSE [FOUNDATION] SYLLABUS Subject : BIOLOGY](/thumbs/95/124596435.jpg) DPS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL CAMBRIDGE IGCSE [FOUNDATION] SYLLABUS 2015-2016 Subject : BIOLOGY CELLS: CELL STRUCTURE, CELLS AND ORGANISMS MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF CELLS ENZYMES :CHEMICALS OF LIFE CHEMICALS OF
DPS INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL CAMBRIDGE IGCSE [FOUNDATION] SYLLABUS 2015-2016 Subject : BIOLOGY CELLS: CELL STRUCTURE, CELLS AND ORGANISMS MOVEMENT IN AND OUT OF CELLS ENZYMES :CHEMICALS OF LIFE CHEMICALS OF
Years 5 and 6 standard elaborations Australian Curriculum: Design and Technologies
 Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
The future agenda of research for sustainable development
 The future agenda of research for sustainable development Heide Hackmann Executive Director: International Social Science Council Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research Overview The global environment
The future agenda of research for sustainable development Heide Hackmann Executive Director: International Social Science Council Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research Overview The global environment
Towards a World in Common Strategy. #WorldInCommon
 Towards a World in Common 2018-2022 Strategy #WorldInCommon Our vision A World in Common AFD Group has a mission to help construct a world in common, a world that preserves and protects five important
Towards a World in Common 2018-2022 Strategy #WorldInCommon Our vision A World in Common AFD Group has a mission to help construct a world in common, a world that preserves and protects five important
9705 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 9705 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 9705/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 120 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2012 series 9705 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 9705/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 120 This mark scheme is published as
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND INNOVATION - DECISIVE FACTORS OF BUSINESS PERFORMANCE
 194ANNALS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CRAIOVA ECONOMIC SCIENCES Year XXXXI No. 39 2011 SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND INNOVATION - DECISIVE FACTORS OF BUSINESS PERFORMANCE Spiridon Cosmin Alexandru Ph. D Student University
194ANNALS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CRAIOVA ECONOMIC SCIENCES Year XXXXI No. 39 2011 SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND INNOVATION - DECISIVE FACTORS OF BUSINESS PERFORMANCE Spiridon Cosmin Alexandru Ph. D Student University
F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business
 The Australian Curriculum Subjects Year levels F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business Foundation Year, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, Year 4, Year
The Australian Curriculum Subjects Year levels F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business Foundation Year, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, Year 4, Year
AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION?
 *COMMON CORE TASK* 10/07/13 AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? Do Now: Collect Comparative Essays Hand out Common Core Task Common Core Task Did the benefits of the Industrial Revolution
*COMMON CORE TASK* 10/07/13 AIM: WHAT WAS THE IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION? Do Now: Collect Comparative Essays Hand out Common Core Task Common Core Task Did the benefits of the Industrial Revolution
MEGATRENDS THE TREND TOWARDS
 01: DEMOGRAPHIC CHANGE 02: INDIVIDUALISATION REACHES A NEW STAGE 03: HEALTH THRIVES 04: WOMEN ON THE RISE 05: CULTURAL DIVERSITY 06: NEW PATTERNS OF MOBILITY 07: DIGITAL LIFESTYLE 08: BIOMIMICRY, OR, LEARNING
01: DEMOGRAPHIC CHANGE 02: INDIVIDUALISATION REACHES A NEW STAGE 03: HEALTH THRIVES 04: WOMEN ON THE RISE 05: CULTURAL DIVERSITY 06: NEW PATTERNS OF MOBILITY 07: DIGITAL LIFESTYLE 08: BIOMIMICRY, OR, LEARNING
Years 3 and 4 standard elaborations Australian Curriculum: Design and Technologies
 Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
The role of radical and systemic changes for green transformation
 The role of radical and systemic changes for green transformation Fred Steward Professor of Innovation & Sustainability OECD Future of Ecoinnovation. Copenhagen, 19 January 2012 A new transitions policy
The role of radical and systemic changes for green transformation Fred Steward Professor of Innovation & Sustainability OECD Future of Ecoinnovation. Copenhagen, 19 January 2012 A new transitions policy
Central Idea: People s beliefs influence their behaviour. Key concepts: perspective; reflection. Related concepts: diversity; perception
 Who we are An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities, and cultures;
Who we are An inquiry into the nature of the self; beliefs and values; personal, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; human relationships including families, friends, communities, and cultures;
STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION PLAN
 STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION PLAN 2017 2021 Connecting knowledge to action EUROPEAN FOREST INSTITUTE Yliopistokatu 6 80100 Joensuu Tel. +358 10 773 4300 www.efi.int Table of Contents 1 Framework... 3 2 Operational
STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION PLAN 2017 2021 Connecting knowledge to action EUROPEAN FOREST INSTITUTE Yliopistokatu 6 80100 Joensuu Tel. +358 10 773 4300 www.efi.int Table of Contents 1 Framework... 3 2 Operational
Industrialisation. Industrial processes. Industrialisation in developing countries. D Mining in Namibia. Textile in Namibia
 Unit 1 Industrialisation In Module 1 Unit 5 we discussed how rural areas have been affected by development. Now we will look at the industrial development which began in European and North American cities
Unit 1 Industrialisation In Module 1 Unit 5 we discussed how rural areas have been affected by development. Now we will look at the industrial development which began in European and North American cities
Smart Cities, Concept and Coverage. Aziz Sisman, (Turkey) Key words: Smart cities, Sustainable development, Environment
 Smart Cities, Concept and Coverage Aziz Sisman, (Turkey) Key words: Smart cities, Sustainable development, Environment SUMMARY Smart city concept is a new fashionable approach in few years. It includes
Smart Cities, Concept and Coverage Aziz Sisman, (Turkey) Key words: Smart cities, Sustainable development, Environment SUMMARY Smart city concept is a new fashionable approach in few years. It includes
Australian Approaches to Innovation and Transitioning to a Low Carbon Economy Lessons for Quebec
 Australian Approaches to Innovation and Transitioning to a Low Carbon Economy Lessons for Quebec Andrew Pickford, Adjunct Research Fellow, University of Western Australia Mark Stickells, Director, Business
Australian Approaches to Innovation and Transitioning to a Low Carbon Economy Lessons for Quebec Andrew Pickford, Adjunct Research Fellow, University of Western Australia Mark Stickells, Director, Business
Home Economics Lower Secondary Subject Area Guidelines. November 2011
 Home Economics Lower Secondary Subject Area Guidelines November 2011 Contents Rationale... 1 Planning using these guidelines... 2 Mapping of Essential Learnings and Year 10 Guidelines... 3 Essential Learnings
Home Economics Lower Secondary Subject Area Guidelines November 2011 Contents Rationale... 1 Planning using these guidelines... 2 Mapping of Essential Learnings and Year 10 Guidelines... 3 Essential Learnings
GROWTH-STRATEGY FOR THE ENGINEERING INDUSTRY TO ACHIEVE RAPID INDUSTRIALIZATION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
 GROWTH-STRATEGY FOR THE ENGINEERING INDUSTRY TO ACHIEVE RAPID INDUSTRIALIZATION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH Javed Akhtar Paracha* ABSTRACT The paper focuses on the importance of the engineering sector in economic
GROWTH-STRATEGY FOR THE ENGINEERING INDUSTRY TO ACHIEVE RAPID INDUSTRIALIZATION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH Javed Akhtar Paracha* ABSTRACT The paper focuses on the importance of the engineering sector in economic
SPECIMEN. INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Answer both parts of question 1 from section A and one question from section B.
 Advanced GCE MEDIA STUDIES Unit G325: Critical Perspectives in Media G325 QP Specimen Paper Morning/Afternoon Additional Materials: Booklet (16 pages) INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES both parts of question
Advanced GCE MEDIA STUDIES Unit G325: Critical Perspectives in Media G325 QP Specimen Paper Morning/Afternoon Additional Materials: Booklet (16 pages) INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES both parts of question
Tourism research and policy
 Tourism research and policy Tim Quinn Manager Economic and Industry Analysis Tourism Research Australia Department of Resources, Energy and Tourism An overview of today s presentation Evidence-based policy
Tourism research and policy Tim Quinn Manager Economic and Industry Analysis Tourism Research Australia Department of Resources, Energy and Tourism An overview of today s presentation Evidence-based policy
Text Text. Cristian Matti 1,2, Irene Vivas 1,3, Julia Panny 1 and Blanca JuanAgullo 1. EIT Climate-KIC, 2 Utrecht University 3 Maastricht University
 Innovation platforms fostering communities of practice in low carbon economy towards 2030 Transformative mechanism and processes for realising SDG9 in Europe. UN/WASD International Conference on Public
Innovation platforms fostering communities of practice in low carbon economy towards 2030 Transformative mechanism and processes for realising SDG9 in Europe. UN/WASD International Conference on Public
THE INTERNATIONALIZATION OF CORPORATE R&D AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF AUTOMOTIVE R&D IN EAST-CENTRAL EUROPE
 THE INTERNATIONALIZATION OF CORPORATE R&D AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF AUTOMOTIVE R&D IN EAST-CENTRAL EUROPE Petr Pavlínek University of Nebraska at Omaha, USA Charles University in Prague, Czechia CHANGING
THE INTERNATIONALIZATION OF CORPORATE R&D AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF AUTOMOTIVE R&D IN EAST-CENTRAL EUROPE Petr Pavlínek University of Nebraska at Omaha, USA Charles University in Prague, Czechia CHANGING
Unit 1: The Economic Fundamentals Weeks How does scarcity impact the decisions individuals and societies must make?
 Economics Teacher: Vida Unit 1: The Economic Fundamentals Weeks 1-4 Essential Questions 1. How does scarcity impact the decisions individuals and societies must make? 2. What roles do individuals and businesses
Economics Teacher: Vida Unit 1: The Economic Fundamentals Weeks 1-4 Essential Questions 1. How does scarcity impact the decisions individuals and societies must make? 2. What roles do individuals and businesses
CAPITALISM, TECHNOLOGY AND A GREEN GLOBAL GOLDEN AGE: The Role of History in Helping to Shape the Future
 CAPITALISM, TECHNOLOGY AND A GREEN GLOBAL GOLDEN AGE: The Role of History in Helping to Shape the Future Carlota Perez Honorary Professor, SPRU, University of Sussex, UK Centennial Professor, London School
CAPITALISM, TECHNOLOGY AND A GREEN GLOBAL GOLDEN AGE: The Role of History in Helping to Shape the Future Carlota Perez Honorary Professor, SPRU, University of Sussex, UK Centennial Professor, London School
Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Innovation and Global Sustainable Development
 Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Innovation and Global Sustainable Development 1. Identification Name of programme Scope of programme Level Programme code Decision details Master Programme
Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Innovation and Global Sustainable Development 1. Identification Name of programme Scope of programme Level Programme code Decision details Master Programme
Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation
 Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation United Nations University October 18, 2018 Tokyo, Japan 0 Mahmoud Mohieldin Senior Vice President @wbg2030 worldbank.org/sdgs
Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation United Nations University October 18, 2018 Tokyo, Japan 0 Mahmoud Mohieldin Senior Vice President @wbg2030 worldbank.org/sdgs
Industrialization Spreads Close Read
 Industrialization Spreads Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Industrialization Spreads Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Level 4 exemplars and comments. Paper 1 Sample 1: Section A, Question 1
 Level 4 exemplars and comments Paper 1 Section A, Question 1 1 Section A, Question 1 2 Section A, Question 1 3 Section A, Question 1 4 Section A, Question 1 5 Section A, Question 1 6 Section A, Question
Level 4 exemplars and comments Paper 1 Section A, Question 1 1 Section A, Question 1 2 Section A, Question 1 3 Section A, Question 1 4 Section A, Question 1 5 Section A, Question 1 6 Section A, Question
How can public and social innovation build a more inclusive economy?
 How can public and social innovation build a more inclusive economy? Friday 27th January 2017 Nesta Guest seespark Welcome and Introduction Madeleine Gabriel Head of Inclusive Innovation, International
How can public and social innovation build a more inclusive economy? Friday 27th January 2017 Nesta Guest seespark Welcome and Introduction Madeleine Gabriel Head of Inclusive Innovation, International
Et Extension from an innovation systems perspective
 Et Extension from an innovation systems perspective Rasheed Sulaiman V Centre for Research on Innovation and Science Policy y( (CRISP) (LINK South Asia Rural Innovation Policy Studies Hub), Hyderabad,
Et Extension from an innovation systems perspective Rasheed Sulaiman V Centre for Research on Innovation and Science Policy y( (CRISP) (LINK South Asia Rural Innovation Policy Studies Hub), Hyderabad,
OECD Innovation Strategy: Key Findings
 The Voice of OECD Business March 2010 OECD Innovation Strategy: Key Findings (SG/INNOV(2010)1) BIAC COMMENTS General comments BIAC has strongly supported the development of the horizontal OECD Innovation
The Voice of OECD Business March 2010 OECD Innovation Strategy: Key Findings (SG/INNOV(2010)1) BIAC COMMENTS General comments BIAC has strongly supported the development of the horizontal OECD Innovation
Key words: Women, Labour, Local Economy, Technology, Women and Mines
 Women, Labour and Technology in Coal Mines: A Case Study of the Impact on Local Economy of Korba District (Chhattisgarh) Key words: Women, Labour, Local Economy, Technology, Women and Mines Women and labour
Women, Labour and Technology in Coal Mines: A Case Study of the Impact on Local Economy of Korba District (Chhattisgarh) Key words: Women, Labour, Local Economy, Technology, Women and Mines Women and labour
See the Preface for important information on the organization of the following material.
 GRADE 8 See the Preface for important information on the organization of the following material. The Arts (2009) A. DANCE A1. Creating and Presenting A1.1 create dance pieces to respond to issues that
GRADE 8 See the Preface for important information on the organization of the following material. The Arts (2009) A. DANCE A1. Creating and Presenting A1.1 create dance pieces to respond to issues that
SMART CITIES Presentation
 Chrysses Nicolaides Director, CNE Business Development Ltd Founder, Smart Cities Mediterranean Cluster Introduction SMART CITIES Presentation 1. The Smart Cities Mediterranean Cluster The Partnership is
Chrysses Nicolaides Director, CNE Business Development Ltd Founder, Smart Cities Mediterranean Cluster Introduction SMART CITIES Presentation 1. The Smart Cities Mediterranean Cluster The Partnership is
