Problems with TNM 3.0
|
|
|
- Percival Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Problems with TNM 3.0 from the viewpoint of SoundPLAN International LLC TNM 2.5 TNM 2.5 had some restrictions that hopefully are lifted in the up-coming version of TNM 3.0. TNM 2.5 for example did not allow an elevation line to intersect with a road or a noise barrier. In the past, models were small and it was relatively easy to clip elevation lines at the edge of the road, with the vast amount of data typically used in GIS operations, this may be a lot more cumbersome. Other problems such as the 2D spreading for sure are resolved but some of the problems remain. The assessment of TNM errors is based on the TNM calculation kernel from July It is our understanding that the Consistency Test Suite is using the same version to produce the master results. In May 2015 SoundPLAN sent the Volpe Center our first feedback on the results of the Consistency Test Suite. SoundPLAN has no information if these evaluations so far led to changes in the TNM coding. Problem #1 : Geometrical Spreading TNM up to its version TNM 2.5 calculated the spreading only with 2 dimensional coordinates, thus only taking the horizontal distance into account. Receivers that were close to a road but high above it experienced basically the same noise levels as a receiver close to the ground. TNM 3.0 has introduced 3 dimensional coordinates for the calculation of the spreading but now calculates the spreading for all vehicle types from the road surface position and not from the actual source location. For receivers close to the road this error can change the results up to 1 db. Instead of calculation the spreading for the sources position (A) TNM 3.0 uses the road surface (B) as the source position for the spreading calculation for all vehicle types. Action needed: Calculate the spreading for the position of the source, not the road surface! Re-do the master values for the consistency test. TNM 3.0 problems Page 1
2 Problem #2 : Dissection of the road All formulas pertaining to line sources first need to break down a line source to one or multiple point sources depending on the geometrical situation, the length of the line source and distance between the source and the receiver. TNM is converting the line source using an angular method. The road is divided so that each segment does not exceed an angular width of 10 degrees. For multiple reasons this opening is too coarse and will cause uncertainties exceeding the envisioned accuracy of 0.25 db. The problem occurs at the end of the source line and in places where the road is partially shielded. Dissecting the sources should be done in a way where inserting extra coordinates in the road and thus forcing a finer resolution, should not cause differences. We found that the dissection caused deviations of up to 1 db. Dissecting the road in segments should not be done like in the left sketch below but like in the one on the right. If the ratio between the size of the segment and the distance from the middle of the segment to the receiver exceeds a certain value, the road needs to be divided and the checking needs to be done again until all segments have a ration that is bigger that the threshold value. A value of 4 seems to be appropriate. For practical reasons dissection should also been stopped if the length of segment is below a certain value (e.g. 1 m). Dissection is not only necessary for the geometrical spreading but is rather important for ground effect and screening. When a road segment is intersected at a shallow angle, it is not enough to regard a segment of the road as it fits into a 10 degree slot, the segment needs to also have the ratio of length of the segment versus distance from the source point observed. Consider a road segment of a kilometer in length and the receiver point 10 meters away from the road. What would be the distance for the spreading? TNM 3.0 problems Page 2
3 Another problem associated with a fixed angular opening for a road segment to be considered as a point source is the question where the effect of changing ground from soft to hard be assessed reliably. Here some examples: TNM 3.0 problems Page 3
4 It can be argued that uncertainties as were seen in the previous pictures do not occur in a live example because a road of 300 meters normally would not be entered with just 2 or 3 coordinates. One thing is absolutely certain, it should not matter where the user divides the road, the results should not depend on this. If we take the example in the last pictures and divide the road so that each road segment is just one meter long, this should give us the most accurate prediction. It does! The next picture shows the outcome of this idea. Calculated with steps of 10 degrees but with road segments of one meter of length, the road looks like the example in the SoundPLAN 8.0 case with a full projection. The uncertainty that for bigger distances was in excess of 5 db is gone. This example can easily be repeated with the original TNM. Have fun experimenting! TNM 3.0 problems Page 4
5 The projection method not only applied to obstacles but also to ground type and mitigation areas is clearly superior to projecting at obstacles but leaving a fixed scanning angle of 10 degrees. The angular incremented pictures were created with SoundPLAN 6.5 varying the angular increments, the picture with full projection was created using SoundPLAN 8.0. It is clear that 10 degrees as the standard angular scanning is not sufficient! Action needed: Dynamically check and reduce the ratio of length of the segment / distance source to receiver and reduce the size of the scanning angle to at least 1 degree! Re-do the master values for the consistency test. Problem #3 : Receivers in the extended roadway The consistency test suite in section has a systematic problem recognizing hard ground close to the end of a road segment. When receivers are positioned in an angle to the road segment where the linear connection between the road source and the receiver is no longer intersecting with the extended edge of road line, TNM 3.0 does not recognize that the roadway is hard ground and calculates the ground effect with soft ground only. Here some examples: A line source without directivity, line source and end of line with the road as source A road source would look a little bit different than the line source in the example above as the road source has an implicit directivity associated with the line source and the ground is not the same for the entire example. The roadway is hard ground and the terrain around the road is soft ground. For this reason the example 2 below shows on the left side that the noise from cars and trucks carries farther if the transmission has a lot of the reflective road surface in its path instead of the more absorbent soft ground. For this reason the contour lines in the example on the left experience a wider and wider spacing in the direct path of the road. The example on the left was calculated with the TNM 3.0 adaptation in SoundPLAN, the right example was calculated with the original TNM 3.0 software where we extracted the receivers from the grid of receivers and made them stand alone receivers. We transferred the receiver coordinated to TNM 3.0, did the noise calculation and then transferred the results back into a grid to be mapped by the SoundPLAN graphics. TNM 3.0 problems Page 5
6 TNM 3.0 calculations with SoundPLAN and with TNM 3.0 original. Why are there differences between the two versions, and why does it matter? The TNM 3.0 calculation contains a systematic error for cases where the transmission from source to receiver is not passing over the outer edge of the road segment. Below see the sequence in pictograms. TNM 3.0 problems Page 6
7 Apparently TNM 3.0 needs to intersect with the edge of the extended road segment in order to understand that the ground between the source and the receiver is partly hard ground. The diagram from the TNM Consistency Test Suite shows the inconsistency, the road is 12 ft wide and all receivers less than 7 ft from the road center line have the same value. Between 6 and 7 ft the value jumps 4dB because all of the sudden the road edge was intersected and the transmission was partly on hard ground. Situations like the one described above are common for example with a T-junction of a road. It is not clear what will happen with the overlap of hard ground in such a case. When the Test Suite was generated the levels between the road axis and the extended edge of the road should have raised flags as there is no acoustical reason for this behavior and the directivity is definitive not the culprit. TNM 3.0 problems Page 7
8 In the picture below all receivers that are inside the extended road edge lines calculate the ground effect only for soft ground! For a single road segment the error results in noise levels being up to 3.6 db too low, however for normal noise calculations the error described above is not as important as it appears as there are multiple road segments active at the same time. Many of these errors, glitches and unwanted patterns are only detected when the noise modeling software permits noise contours to be calculated and drawn. When SoundPLAN introduced Grid Noise Maps over 20 years ago, we had to correct many of these effects and it can be assumed that TNM will have to go through the same phase once noise contours bring these uncertainties to life. Action needed: Correct the problem for ignoring hard ground on the extended roadway! Re-do the master values for the consistency test. Problem #4 : Overlapping Roads in TNM 3.0 A road is defined as a hard surface with noise sources associated with it. As many roads have multiple lanes, it should be possible to simulate a multiple lane road with multiple roads as long as the edge of the asphalt band is consistent. Aside of simulating the source characteristic of a road with the types and numbers of vehicles, all the software needs to do with the road is to establish where the hard surface ends and where the soft ground begins. In TNM 3.0 there seems to be a problem with this. Most of the consistency tests are using multiple parallel roads. In half of the sets the road width overlap slightly in the other half the overlap is significant. Unfortunately the results of TNM 3.0 calculations vary up to 1.5 db when the road width is varied in a way where the source position remains identical and the overall edge of the road also is constant. As this error is not only an error in the near field of the road, it is very important to correct. TNM 3.0 users will think that TNM will calculate the overall edge of the road correctly but it does not, thus for the user the outcome is a random error of up to 1.5 db. TNM 3.0 problems Page 8
9 Road #1 and road #2 are overlapping. If the width of road #2 is varied so that the edge of road string is still within road #2, the noise received at the receiver changes up to 1.5 db, the emitting road axis remains in the same place! It seems that the edge of road string from road #2 needs to be eliminated for the part where another road is extending the pavement without a gap. There is also some evidence that some road segments are ignored in the calculations when road segments overlap. For sure noise contour maps also would show Moiré effects starting from these overlap areas. Action needed: Calculate the edge of the pavement correctly regardless of the degree of overlap of the road! Re-do the master values for the consistency test. Additional problems? So far we have tested Test Suite positions 1..3, further progress is not possible until the errors are fixed. With further test cases building on the basic cases, we cannot determine where deviations come from, if they are caused by the problems described above or if we have a problem in SoundPLAN or if TNM has additional problems. As the corrections not only will change the outcome of the Consistency Test Suite but all future work, the software should be updated quickly and the data for the Consistency Test Suite redone. This definitively should be done before even a limited release of the TNM 3.0 software. If the written text of the standard is the valid definition of TNM, then neither TNM 2.5 nor TNM 3.0 would pass the Consistency Test. TNM 3.0 problems Page 9
10 Why are these problems important? SoundPLAN GmbH, the parent company to SoundPLAN International LLC has continuously developed noise modeling software for the past 30 years. Currently they are involved in the development of the new ISO 17534: Acoustics Software for the calculation of sound outdoors Part 1: Quality requirements and quality assurance. Naturally we want to apply this quest for quality to our entire product and as an extension to the standards we use. We are interested in making TNM 3.0 the best road noise modeling standard available and thus want to make sure that it is consistent and that the results are as good an interpretation of the physics as possible. We also have an interest that the results of TNM fit the propagation of other noise sources such as railways that sometimes need to be evaluated in combination with the road noise model. As TNM itself cannot supply a solution for this, SoundPLAN offers an alternative capable of many options from true optimization/minimization of noise barriers to various graphics options to present noise contours on the terrain or in a vertical cutting. SoundPLAN is used worldwide for environmental impact studies, the mitigation of noise from roads and railways, the noise impact on residential buildings, the noise exposure of workers in the factory environment, the noise the study of the health effects of noise and the mitigation of aircraft noise. The software is standards based with currently over 75 national and international standards implemented and verified, the 1978 FHWA model as well as TNM 2.5 and TNM 3.0 are implemented. TNM officially is used to assess the need for noise barriers along roads in Federal Aid Projects. In practice the software is used in a much broader way to assess noise from highways, sometimes stand alone, sometimes along with other noise sources such as railways. So far TNM does not have the capabilities to draw noise contour lines or to superimpose noise from roads with the noise from railway or industrial sources. TNM is currently available as TNM 2.5 with the up-coming version TNM 3.0 in preparation. SoundPLAN has implemented the rules of TNM 2.5 and is preparing/testing the rules for TNM 3.0. SoundPLAN users in the USA and also in Canada, Israel, New Zealand, Australia and Singapore are interested in using the SoundPLAN software for road noise with the TNM model and want to make sure that the results are accepted by the departments of transport (Federal, State and local). The Federal Highway Administration has generated a Consistency Test Suite and defined Acceptable Margin Answer Keys for the FHWA TNM. SoundPLAN has started implementing the test questions as a SoundPLAN project and checked the results against the official results. Most of the answers from SoundPLAN are within the margin of 0.25 db but some answers are not. For the cases where SoundPLAN deviates in excess of the Acceptable Margin, we started researching why. Some of the results are laid out in the text above, unfortunately our tests can only complete when the errors in TNM are corrected. TNM is a complex standard, it was the first to calculate ground effect and screening with a phase correct algorithm. SoundPLAN started implementing TNM 17 years ago, since then we implemented and tested the other phase correct model, the Scandinavian Nord Implementing and testing Nord 2000 required our software developers to closely cooperate with the developer of the standard. In the process, errors were found on both software interpretations and were reconciled. Comparing the outcome of two software products will always help to find systematic errors, unfortunately not only in the software to be tested but also in the master program. Random deviations are much more difficult to identify with single receiver results. Often the numerical results in themselves seem correct but if they are compared to a receiver close by they are showing differences TNM 3.0 problems Page 10
11 that are bigger than expected. In SoundPLAN we found many inconsistencies when we mapped noise contours, something that TNM has not experienced yet. Scanning roads with 10 degrees of angular increment is such a problem that will only manifest itself if a noise map is drawn. As it can be assumed that the future of TNM 3.0 also will involve noise contour lines, it is wise to correct these problems before the users point out these inconsistencies. It is our opinion that TNM 3.0 could be much improved if reflections from individual buildings would be added to the portfolio. SoundPLAN has implemented this feature and for more than 30 years SoundPLAN users are successfully using this feature to predict noise levels where reflections from individual buildings cannot be ignored. Driving along Interstate 5 through downtown Seattle would support this concept. For all their users, SoundPLAN is interested in earning the status of equivalency to TNM, being part of the noise community we also offer our help in debugging the TNM software. Having implemented and tested TNM and Nord 2000, we know how valuable it is to have a review of the software against a second set of programmer s eyes. To get the best product, we have offered our cooperation in the past and still do! We offer our cooperation in trouble shooting the calculation core of TNM 3.0, helping establish the correct results of TNM and the TNM Consistency Test Suite. As we have been continuously involved in leading the development of noise modeling software for over 30 years, we have the expertise to improve and optimize noise modeling software so that it becomes cutting edge again. With best regards Arne Berndt; arne@soundplan.com SoundPLAN International LLC 80 E Aspley Ln; Shelton, WA For an overview of SoundPLAN please click here: or have a look at our website: TNM is a trademark of the US Government TNM 3.0 problems Page 11
Memorandum 1.0 Highway Traffic Noise
 Memorandum Date: September 18, 2009 To: Chris Hiniker, SEH From: Stephen B. Platisha, P.E. Re: Updated CSAH 14 Noise Analysis The purpose of this memorandum is to provide the results of the revised traffic
Memorandum Date: September 18, 2009 To: Chris Hiniker, SEH From: Stephen B. Platisha, P.E. Re: Updated CSAH 14 Noise Analysis The purpose of this memorandum is to provide the results of the revised traffic
Further Comparison of Traffic Noise Predictions Using the CadnaA and SoundPLAN Noise Prediction Models
 Proceedings of 20 th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia Further Comparison of Traffic Noise Predictions Using the CadnaA and SoundPLAN Noise Prediction Models
Proceedings of 20 th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia Further Comparison of Traffic Noise Predictions Using the CadnaA and SoundPLAN Noise Prediction Models
Noise Mitigation Study Pilot Program Summary Report Contract No
 Ohio Turnpike Commission Noise Mitigation Study Pilot Program Summary Report Contract No. 71-08-02 Prepared For: Ohio Turnpike Commission 682 Prospect Street Berea, Ohio 44017 Prepared By: November 2009
Ohio Turnpike Commission Noise Mitigation Study Pilot Program Summary Report Contract No. 71-08-02 Prepared For: Ohio Turnpike Commission 682 Prospect Street Berea, Ohio 44017 Prepared By: November 2009
FINAL REPORT. On Project Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM) APPENDIX K Parallel Barriers
 FINAL REPORT On Project - Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM) APPENDIX K Parallel Barriers Prepared for: National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP) Transportation
FINAL REPORT On Project - Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM) APPENDIX K Parallel Barriers Prepared for: National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP) Transportation
Electricity Supply to Africa and Developing Economies. Challenges and opportunities. Planning for the future in uncertain times
 Electricity Supply to Africa and Developing Economies. Challenges and opportunities. Planning for the future in uncertain times 765 kv Substation Acoustic Noise Impact Study by Predictive Software and
Electricity Supply to Africa and Developing Economies. Challenges and opportunities. Planning for the future in uncertain times 765 kv Substation Acoustic Noise Impact Study by Predictive Software and
Session 8 Traffic Noise Modeling: Best Practices for Modeling and Review of Models
 Session 8 Traffic Noise Modeling: Best Practices for Modeling and Review of Models Facilitator: Tom Hanf, Michigan DOT Participants: Mark Ferroni, FHWA Josh Kozlowski, Virginia DOT Jim Ozment, Tennessee
Session 8 Traffic Noise Modeling: Best Practices for Modeling and Review of Models Facilitator: Tom Hanf, Michigan DOT Participants: Mark Ferroni, FHWA Josh Kozlowski, Virginia DOT Jim Ozment, Tennessee
Performance of Roadside Sound Barriers with Sound Absorbing Edges
 Performance of Roadside Sound Barriers with Sound Absorbing Edges Diffracted Path Transmitted Path Interference Source Luc Mongeau, Sanghoon Suh, and J. Stuart Bolton School of Mechanical Engineering,
Performance of Roadside Sound Barriers with Sound Absorbing Edges Diffracted Path Transmitted Path Interference Source Luc Mongeau, Sanghoon Suh, and J. Stuart Bolton School of Mechanical Engineering,
ACOUSTIC BARRIER FOR TRANSFORMER NOISE. Ruisen Ming. SVT Engineering Consultants, Leederville, WA 6007, Australia
 ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-12 July, 2007 ACOUSTIC BARRIER FOR TRANSFORMER NOISE Ruisen Ming SVT Engineering Consultants, Leederville, WA 6007, Australia Roy.Ming@svt.com.au Abstract In this paper, an acoustic
ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-12 July, 2007 ACOUSTIC BARRIER FOR TRANSFORMER NOISE Ruisen Ming SVT Engineering Consultants, Leederville, WA 6007, Australia Roy.Ming@svt.com.au Abstract In this paper, an acoustic
METHODOLOGY FOR VERIFICATION OF SOFTWARE FOR NOISE ATTENUATION CALCULATION ACCORDING TO ISO STANDARD
 METHODOLOGY FOR VERIFICATION OF SOFTWARE FOR NOISE ATTENUATION CALCULATION ACCORDING TO ISO 9613-2 STANDARD Jelena Tomić, Slobodan Todosijević, Nebojša Bogojević, Zlatan Šoškić Faculty of Mechanical and
METHODOLOGY FOR VERIFICATION OF SOFTWARE FOR NOISE ATTENUATION CALCULATION ACCORDING TO ISO 9613-2 STANDARD Jelena Tomić, Slobodan Todosijević, Nebojša Bogojević, Zlatan Šoškić Faculty of Mechanical and
FINAL REPORT. On Project Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM) APPENDIX L Tunnel Openings
 FINAL REPORT On Project 2-34 Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM) APPENDIX L Tunnel Openings Prepared for: National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP)
FINAL REPORT On Project 2-34 Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM) APPENDIX L Tunnel Openings Prepared for: National Cooperative Highway Research Program (NCHRP)
The SoundPLAN Expert System for Industry Noise
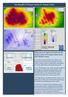 The SoundPLAN Expert System for Industry Noise Differences in approach between the optimization of transportation noise and industry noise In contrast to transportation noise where noise barriers are the
The SoundPLAN Expert System for Industry Noise Differences in approach between the optimization of transportation noise and industry noise In contrast to transportation noise where noise barriers are the
The Influence of Quieter Pavement & Absorptive Barriers on US 101 in Marin County
 The Influence of Quieter Pavement & Absorptive Barriers on US 101 in Marin County Paul R. Donavan Illingworth & Rodkin, Inc. Dana M. Lodico Lodico Acoustics, LLC TAM US 101 Widening Project in Marin County
The Influence of Quieter Pavement & Absorptive Barriers on US 101 in Marin County Paul R. Donavan Illingworth & Rodkin, Inc. Dana M. Lodico Lodico Acoustics, LLC TAM US 101 Widening Project in Marin County
Guide Sign Policy for Secondary State Highways Edition
 Massachusetts Highway Department, Ten Park Plaza, Boston, MA 02116-3973 ` Guide Sign Policy for Secondary State Highways 2005 Edition Revised September 2005 1. PURPOSE The Massachusetts Highway Department
Massachusetts Highway Department, Ten Park Plaza, Boston, MA 02116-3973 ` Guide Sign Policy for Secondary State Highways 2005 Edition Revised September 2005 1. PURPOSE The Massachusetts Highway Department
Exit 61 I-90 Interchange Modification Justification Study
 Exit 61 I-90 Interchange Modification Justification Study Introduction Exit 61 is a diamond interchange providing the connection between Elk Vale Road and I-90. Figure 1 shows the location of Exit 61.
Exit 61 I-90 Interchange Modification Justification Study Introduction Exit 61 is a diamond interchange providing the connection between Elk Vale Road and I-90. Figure 1 shows the location of Exit 61.
Technical Note. Noise reducing properties of crash barriers. Performed for WillumTech. AV 1217/11 Project no.: A Page 1 of 19 incl.
 Technical Note Noise reducing properties of crash barriers Performed for WillumTech Project no.: A581500 Page 1 of 19 incl. 1 annex 6 October 2011 DELTA Venlighedsvej 4 2970 Hørsholm Denmark Tel. +45 72
Technical Note Noise reducing properties of crash barriers Performed for WillumTech Project no.: A581500 Page 1 of 19 incl. 1 annex 6 October 2011 DELTA Venlighedsvej 4 2970 Hørsholm Denmark Tel. +45 72
Noise Impact Analysis. NW Bethany Boulevard Improvement Project NW Bronson Road to NW West Union Road. November Washington County.
 Noise Impact Analysis NW Bethany Boulevard Improvement Project NW Bronson Road to NW West Union Road Washington County November 2011 Prepared for: Washington County Department of Land Use and Transportation
Noise Impact Analysis NW Bethany Boulevard Improvement Project NW Bronson Road to NW West Union Road Washington County November 2011 Prepared for: Washington County Department of Land Use and Transportation
Appendix D. Traffic Noise Analysis Report. I-94 St. Michael to Albertville Minnesota Department of Transportation
 Appendix D Traffic Noise Analysis Report I-94 St. Michael to Albertville Minnesota Department of Transportation Traffic Noise Analysis Report I-94 St. Michael to Albertville Project SP 8680-172 Report
Appendix D Traffic Noise Analysis Report I-94 St. Michael to Albertville Minnesota Department of Transportation Traffic Noise Analysis Report I-94 St. Michael to Albertville Project SP 8680-172 Report
Road Noise Auralisation for Planning New Roads
 Road Noise Auralisation for Planning New Roads Per FINNE 1 ; Jakob FRYD 2 1 DELTA Acoustics, Denmark 2 Danish Road Administration, Denmark ABSTRACT This paper introduces a method to create auralisations
Road Noise Auralisation for Planning New Roads Per FINNE 1 ; Jakob FRYD 2 1 DELTA Acoustics, Denmark 2 Danish Road Administration, Denmark ABSTRACT This paper introduces a method to create auralisations
Problems with the INM: Part 2 Atmospheric Attenuation
 Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2006 20-22 November 2006, Christchurch, New Zealand Problems with the INM: Part 2 Atmospheric Attenuation Steven Cooper, John Maung The Acoustic Group, Sydney, Australia ABSTRACT
Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2006 20-22 November 2006, Christchurch, New Zealand Problems with the INM: Part 2 Atmospheric Attenuation Steven Cooper, John Maung The Acoustic Group, Sydney, Australia ABSTRACT
This page is intentionally blank. GARMIN G1000 SYNTHETIC VISION AND PATHWAYS OPTION Rev 1 Page 2 of 27
 This page is intentionally blank. 190-00492-15 Rev 1 Page 2 of 27 Revision Number Page Number(s) LOG OF REVISIONS Description FAA Approved Date of Approval 1 All Initial Release See Page 1 See Page 1 190-00492-15
This page is intentionally blank. 190-00492-15 Rev 1 Page 2 of 27 Revision Number Page Number(s) LOG OF REVISIONS Description FAA Approved Date of Approval 1 All Initial Release See Page 1 See Page 1 190-00492-15
Module 2. Milling calculations, coordinates and program preparing. 1 Pepared By: Tareq Al Sawafta
 Module 2 Milling calculations, coordinates and program preparing 1 Module Objectives: 1. Calculate the cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut 2. Recognize coordinate 3. Differentiate between Cartesian
Module 2 Milling calculations, coordinates and program preparing 1 Module Objectives: 1. Calculate the cutting speed, feed rate and depth of cut 2. Recognize coordinate 3. Differentiate between Cartesian
Please refer to the figure on the following page which shows the relationship between sound fields.
 Defining Sound s Near The near field is the region close to a sound source usually defined as ¼ of the longest wave-length of the source. Near field noise levels are characterized by drastic fluctuations
Defining Sound s Near The near field is the region close to a sound source usually defined as ¼ of the longest wave-length of the source. Near field noise levels are characterized by drastic fluctuations
Traffic Noise and Vibration Impact Assessment Technical Report for the North Meadows Extension to US 85 and Interstate 25
 Traffic Noise and Vibration Impact Assessment Technical Report for the North Meadows Extension to US 85 and Interstate 25 February 2010 Prepared for: Town of Castle Rock Douglas County Colorado Department
Traffic Noise and Vibration Impact Assessment Technical Report for the North Meadows Extension to US 85 and Interstate 25 February 2010 Prepared for: Town of Castle Rock Douglas County Colorado Department
REVIEW TOPICS CEEN 2320 FINAL EXAM
 REVIEW TOPICS CEEN 2320 FINAL EXAM Be familiar with all materials covered in class, your class handouts and the notes you took in class, your homework assignments, test questions, formulas, tables, figures.
REVIEW TOPICS CEEN 2320 FINAL EXAM Be familiar with all materials covered in class, your class handouts and the notes you took in class, your homework assignments, test questions, formulas, tables, figures.
FINAL REPORT. On Project Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM)
 FINAL REPORT On Project 25-34 Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM) APPENDIX A Structure Reflected Noise and Expansion Joint Noise Prepared for: National Cooperative
FINAL REPORT On Project 25-34 Supplemental Guidance on the Application of FHWA s Traffic Noise Model (TNM) APPENDIX A Structure Reflected Noise and Expansion Joint Noise Prepared for: National Cooperative
EPCWIN THE HIGH-END SOFTWARE
 EPCWIN THE HIGH-END SOFTWARE ZSK Stickmaschinen GmbH Magdeburger Str. 38-40 D-47800 Krefeld Tel: +49 (0) 2151 44 40 Fax: +49 (0) 2151 44 41 70 atelier@zsk.de www.zsk.com News 4.0 Version 4.0 (03/2009)
EPCWIN THE HIGH-END SOFTWARE ZSK Stickmaschinen GmbH Magdeburger Str. 38-40 D-47800 Krefeld Tel: +49 (0) 2151 44 40 Fax: +49 (0) 2151 44 41 70 atelier@zsk.de www.zsk.com News 4.0 Version 4.0 (03/2009)
Appendix L Noise Technical Report. Rehabilitation and Restoration of the Longfellow Bridge
 Appendix L Noise Technical Report Rehabilitation and Restoration of the Longfellow Bridge Noise Technical Report Rehabilitation and Restoration of the Longfellow Bridge Boston, MA May, 2011* Prepared by
Appendix L Noise Technical Report Rehabilitation and Restoration of the Longfellow Bridge Noise Technical Report Rehabilitation and Restoration of the Longfellow Bridge Boston, MA May, 2011* Prepared by
Problems with the INM: Part 1 Lateral Attenuation
 Problems with the INM: Part 1 Lateral Attenuation Steven Cooper The Acoustic Group. Sydney, Australia ABSTRACT Validation of INM predictions finds agreement when the monitoring position is close to or
Problems with the INM: Part 1 Lateral Attenuation Steven Cooper The Acoustic Group. Sydney, Australia ABSTRACT Validation of INM predictions finds agreement when the monitoring position is close to or
Sound Reflection from a Motorway Barrier
 Auckland Christchurch Kuala Lumpur Melbourne Sydney Wellington www.marshallday.com Sound Reflection from a Motorway Barrier Christopher W Day Paper revised June 2005 chrisday@marshallday.co.nz Abstract
Auckland Christchurch Kuala Lumpur Melbourne Sydney Wellington www.marshallday.com Sound Reflection from a Motorway Barrier Christopher W Day Paper revised June 2005 chrisday@marshallday.co.nz Abstract
Q. Will prevailing winds and wind speeds be taken into account in the noise study?
 Anthony Henday Noise Study Questions asked at Open House (October 24, 2016) March 2, 2017 Q. Will prevailing winds and wind speeds be taken into account in the noise study? Yes, engineers will review weather
Anthony Henday Noise Study Questions asked at Open House (October 24, 2016) March 2, 2017 Q. Will prevailing winds and wind speeds be taken into account in the noise study? Yes, engineers will review weather
Environmental noise mapping study for heterogeneous traffic conditions
 Proceedings of 20 th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia Environmental noise mapping study for heterogeneous traffic conditions R.Kalaiselvi (1), and A.Ramachandraiah
Proceedings of 20 th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia Environmental noise mapping study for heterogeneous traffic conditions R.Kalaiselvi (1), and A.Ramachandraiah
A low-budget road traffic noise model for individual building evaluation - a case study in Western Australia
 A low-budget road traffic noise model for individual building evaluation - a case study in Western Australia Martin Felder 1 ; Marion Burgess 2 ; Jörg Arnold 3 1 Gebäudeanayse Martin Felder, Switzerland
A low-budget road traffic noise model for individual building evaluation - a case study in Western Australia Martin Felder 1 ; Marion Burgess 2 ; Jörg Arnold 3 1 Gebäudeanayse Martin Felder, Switzerland
OPERATING PAVEMENT PROFILOGRAPH AND EVALUATING PROFILES
 Test Procedure for OPERATING PAVEMENT PROFILOGRAPH AND EVALUATING PROFILES Texas Department of Transportation TxDOT Designation: Tex-1000-S Effective Date: August 1999 1. SCOPE 1.1 This method covers the
Test Procedure for OPERATING PAVEMENT PROFILOGRAPH AND EVALUATING PROFILES Texas Department of Transportation TxDOT Designation: Tex-1000-S Effective Date: August 1999 1. SCOPE 1.1 This method covers the
Specifying, predicting and testing:
 Specifying, predicting and testing: Three steps to coverage confidence on your digital radio network EXECUTIVE SUMMARY One of the most important properties of a radio network is coverage. Yet because radio
Specifying, predicting and testing: Three steps to coverage confidence on your digital radio network EXECUTIVE SUMMARY One of the most important properties of a radio network is coverage. Yet because radio
PROPOSED MARYWOOD DEVELOPMENT
 ACOUSTICAL ANALYSIS PROPOSED MARYWOOD DEVELOPMENT CITY OF ORANGE, CALIFORNIA PREPARED FOR VCS Environmental 30900 RANCH VIEJO ROAD, SUITE 100 SAN JUAN CAPISTRANO, CALIFORNIA 92675 PREPARED BY A/E Tech
ACOUSTICAL ANALYSIS PROPOSED MARYWOOD DEVELOPMENT CITY OF ORANGE, CALIFORNIA PREPARED FOR VCS Environmental 30900 RANCH VIEJO ROAD, SUITE 100 SAN JUAN CAPISTRANO, CALIFORNIA 92675 PREPARED BY A/E Tech
describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves;
 1 Sound-Detailed Study Study Design 2009 2012 Unit 4 Detailed Study: Sound describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves; analyse sound using wavelength, frequency and speed
1 Sound-Detailed Study Study Design 2009 2012 Unit 4 Detailed Study: Sound describe sound as the transmission of energy via longitudinal pressure waves; analyse sound using wavelength, frequency and speed
8.EE. Development from y = mx to y = mx + b DRAFT EduTron Corporation. Draft for NYSED NTI Use Only
 8.EE EduTron Corporation Draft for NYSED NTI Use Only TEACHER S GUIDE 8.EE.6 DERIVING EQUATIONS FOR LINES WITH NON-ZERO Y-INTERCEPTS Development from y = mx to y = mx + b DRAFT 2012.11.29 Teacher s Guide:
8.EE EduTron Corporation Draft for NYSED NTI Use Only TEACHER S GUIDE 8.EE.6 DERIVING EQUATIONS FOR LINES WITH NON-ZERO Y-INTERCEPTS Development from y = mx to y = mx + b DRAFT 2012.11.29 Teacher s Guide:
Parallel Barrier Effects for Distant Receivers
 Parallel Barrier Effects for Distant Receivers Final Report July 2002 Stocker Center Ohio University Athens, OH 45701-2979 1. Report No. FHWA/OH2002/027 2. Government Accession No. 3. Recipient's Catalog
Parallel Barrier Effects for Distant Receivers Final Report July 2002 Stocker Center Ohio University Athens, OH 45701-2979 1. Report No. FHWA/OH2002/027 2. Government Accession No. 3. Recipient's Catalog
Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2
 www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.24 September-2014, Pages:4885-4889 Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2 1 Dept of Mechanical
www.semargroup.org, www.ijsetr.com ISSN 2319-8885 Vol.03,Issue.24 September-2014, Pages:4885-4889 Analysis on Acoustic Attenuation by Periodic Array Structure EH KWEE DOE 1, WIN PA PA MYO 2 1 Dept of Mechanical
Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory
 Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory 1. Introduction One of the purposes of the introductory physics laboratory is to train the student in the presentation and analysis of experimental
Appendix III Graphs in the Introductory Physics Laboratory 1. Introduction One of the purposes of the introductory physics laboratory is to train the student in the presentation and analysis of experimental
Noise walls Some Noise Facts
 What is noise? Noise is unwanted sound. Noise is perceived differently by every individual. A noise that is irritating one person may be tolerant to another. Sound is transmitted by pressure variations
What is noise? Noise is unwanted sound. Noise is perceived differently by every individual. A noise that is irritating one person may be tolerant to another. Sound is transmitted by pressure variations
Assessment of rail noise based on generic shape of the pass-by time history
 Proceedings of Acoustics 23 Victor Harbor 7-2 November 23, Victor Harbor, Australia Assessment of rail noise based on generic shape of the pass-by time history Valeri V. enchine, Jonathan Song Science
Proceedings of Acoustics 23 Victor Harbor 7-2 November 23, Victor Harbor, Australia Assessment of rail noise based on generic shape of the pass-by time history Valeri V. enchine, Jonathan Song Science
Copyrighted Material. Copyrighted Material. Copyrighted. Copyrighted. Material
 Engineering Graphics ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION People who work with drawings develop the ability to look at lines on paper or on a computer screen and "see" the shapes of the objects the lines represent.
Engineering Graphics ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTION People who work with drawings develop the ability to look at lines on paper or on a computer screen and "see" the shapes of the objects the lines represent.
Heuristic Drift Reduction for Gyroscopes in Vehicle Tracking Applications
 White Paper Heuristic Drift Reduction for Gyroscopes in Vehicle Tracking Applications by Johann Borenstein Last revised: 12/6/27 ABSTRACT The present invention pertains to the reduction of measurement
White Paper Heuristic Drift Reduction for Gyroscopes in Vehicle Tracking Applications by Johann Borenstein Last revised: 12/6/27 ABSTRACT The present invention pertains to the reduction of measurement
International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: , Volume 3, Issue 4 (July-August 2015), PP.
 www.ijtra.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (July-August 2015, PP. 97-105 THE EFFECT OF BUILDINGS ORGANIZATION ON TRAFFIC NOISE PROPAGATION IN THE URBAN ENVIRONMENT Dr. Hanan Al Jumaily Associated professor, Architectural
www.ijtra.com Volume 3, Issue 4 (July-August 2015, PP. 97-105 THE EFFECT OF BUILDINGS ORGANIZATION ON TRAFFIC NOISE PROPAGATION IN THE URBAN ENVIRONMENT Dr. Hanan Al Jumaily Associated professor, Architectural
Keysight Technologies Achieving Accurate E-band Power Measurements with E8486A Waveguide Power Sensors. Application Note
 Keysight Technologies Achieving Accurate E-band Power Measurements with Waveguide Power Sensors Application Note Introduction The 60 to 90 GHz spectrum, or E-band, has been gaining more millimeter wave
Keysight Technologies Achieving Accurate E-band Power Measurements with Waveguide Power Sensors Application Note Introduction The 60 to 90 GHz spectrum, or E-band, has been gaining more millimeter wave
MB1013, MB1023, MB1033, MB1043
 HRLV-MaxSonar - EZ Series HRLV-MaxSonar - EZ Series High Resolution, Low Voltage Ultra Sonic Range Finder MB1003, MB1013, MB1023, MB1033, MB1043 The HRLV-MaxSonar-EZ sensor line is the most cost-effective
HRLV-MaxSonar - EZ Series HRLV-MaxSonar - EZ Series High Resolution, Low Voltage Ultra Sonic Range Finder MB1003, MB1013, MB1023, MB1033, MB1043 The HRLV-MaxSonar-EZ sensor line is the most cost-effective
AutoCAD Civil 3D 2009 ESSENTIALS
 AutoCAD Civil 3D 2009 ESSENTIALS SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. Alignments and Profiles Section 2: Profiles In this section you learn how
AutoCAD Civil 3D 2009 ESSENTIALS SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. Alignments and Profiles Section 2: Profiles In this section you learn how
DELINEATOR REFERENCE POINT 200' TYPICAL SPACING (YELLOW DELINEATORS) END OF MERGE LANE TAPER DELINEATOR REFERENCE POINT
 200' TYP. 600' < EACH SIDE BOTH ROADWAYS END OF MERGE LANE TAPER TYPICAL FOR ALL 2-LANE MERGES EXCEPT WHERE THERE IS A MERGE FROM THE RIGHT AND NO OFFSET IN THE THROUGH LANES END OF MERGE LANE TAPER 200'
200' TYP. 600' < EACH SIDE BOTH ROADWAYS END OF MERGE LANE TAPER TYPICAL FOR ALL 2-LANE MERGES EXCEPT WHERE THERE IS A MERGE FROM THE RIGHT AND NO OFFSET IN THE THROUGH LANES END OF MERGE LANE TAPER 200'
Pave-IR Scan TM Primer
 SHRP2 Solution: Technologies to Enhance Quality Control on Asphalt Pavements Introduction Pave-IR Scan TM Primer In-place density is a critical factor in determining pavement durability in hot mix asphalt
SHRP2 Solution: Technologies to Enhance Quality Control on Asphalt Pavements Introduction Pave-IR Scan TM Primer In-place density is a critical factor in determining pavement durability in hot mix asphalt
A comparing overview on ECAC Doc.29 3 rd Edition and the new German AzB
 A comparing overview on ECAC Doc.29 3 rd Edition and the new German AzB Dr. Ullrich Isermann German Aerospace Center DLR Institute of Aerodynamics und Flow Technology JRC Workshop on Aircraft Noise, Brussels,
A comparing overview on ECAC Doc.29 3 rd Edition and the new German AzB Dr. Ullrich Isermann German Aerospace Center DLR Institute of Aerodynamics und Flow Technology JRC Workshop on Aircraft Noise, Brussels,
Appendix B: Noise Study
 Appendix B: Noise Study creating remarkable solutions for a higher quality of life NOISE STUDY Interstate 55 Route PP to County Road 311 Prepared for: MoDOT PROJECT NO. J010956 November 2014 Prepared
Appendix B: Noise Study creating remarkable solutions for a higher quality of life NOISE STUDY Interstate 55 Route PP to County Road 311 Prepared for: MoDOT PROJECT NO. J010956 November 2014 Prepared
Domain Understanding and Requirements Elicitation
 and Requirements Elicitation CS/SE 3RA3 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada Ryszard Janicki 1/24 Previous Lecture: The requirement engineering
and Requirements Elicitation CS/SE 3RA3 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada Ryszard Janicki 1/24 Previous Lecture: The requirement engineering
Analysis Techniques for WiMAX Network Design Simulations
 Technical White Paper Analysis Techniques for WiMAX Network Design Simulations The Power of Smart Planning 1 Analysis Techniques for WiMAX Network Jerome Berryhill, Ph.D. EDX Wireless, LLC Eugene, Oregon
Technical White Paper Analysis Techniques for WiMAX Network Design Simulations The Power of Smart Planning 1 Analysis Techniques for WiMAX Network Jerome Berryhill, Ph.D. EDX Wireless, LLC Eugene, Oregon
TxDOT Project : Evaluation of Pavement Rutting and Distress Measurements
 0-6663-P2 RECOMMENDATIONS FOR SELECTION OF AUTOMATED DISTRESS MEASURING EQUIPMENT Pedro Serigos Maria Burton Andre Smit Jorge Prozzi MooYeon Kim Mike Murphy TxDOT Project 0-6663: Evaluation of Pavement
0-6663-P2 RECOMMENDATIONS FOR SELECTION OF AUTOMATED DISTRESS MEASURING EQUIPMENT Pedro Serigos Maria Burton Andre Smit Jorge Prozzi MooYeon Kim Mike Murphy TxDOT Project 0-6663: Evaluation of Pavement
Photo Scale The photo scale and representative fraction may be calculated as follows: PS = f / H Variables: PS - Photo Scale, f - camera focal
 Scale Scale is the ratio of a distance on an aerial photograph to that same distance on the ground in the real world. It can be expressed in unit equivalents like 1 inch = 1,000 feet (or 12,000 inches)
Scale Scale is the ratio of a distance on an aerial photograph to that same distance on the ground in the real world. It can be expressed in unit equivalents like 1 inch = 1,000 feet (or 12,000 inches)
Deployment and Testing of Optimized Autonomous and Connected Vehicle Trajectories at a Closed- Course Signalized Intersection
 Deployment and Testing of Optimized Autonomous and Connected Vehicle Trajectories at a Closed- Course Signalized Intersection Clark Letter*, Lily Elefteriadou, Mahmoud Pourmehrab, Aschkan Omidvar Civil
Deployment and Testing of Optimized Autonomous and Connected Vehicle Trajectories at a Closed- Course Signalized Intersection Clark Letter*, Lily Elefteriadou, Mahmoud Pourmehrab, Aschkan Omidvar Civil
PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SOURCE LOCATION BY A WAVELET TRANSFORM
 PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SOURCE LOCATION BY A WAVELET TRANSFORM Abstract M. A. HAMSTAD 1,2, K. S. DOWNS 3 and A. O GALLAGHER 1 1 National Institute of Standards and Technology, Materials
PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SOURCE LOCATION BY A WAVELET TRANSFORM Abstract M. A. HAMSTAD 1,2, K. S. DOWNS 3 and A. O GALLAGHER 1 1 National Institute of Standards and Technology, Materials
LMD622 and LMD624 Series
 LMD622 and LMD624 Series Inductive Loop Monitor THIS MANUAL CONTAINS TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR THE LMD622, LMD622T, LMD624, LMD624H, and LMD624T SERIES INDUCTIVE LOOP MONITOR. REVISION: MARCH 2012 pn 888-062X-001
LMD622 and LMD624 Series Inductive Loop Monitor THIS MANUAL CONTAINS TECHNICAL INFORMATION FOR THE LMD622, LMD622T, LMD624, LMD624H, and LMD624T SERIES INDUCTIVE LOOP MONITOR. REVISION: MARCH 2012 pn 888-062X-001
4 th Grade Curriculum Map
 4 th Grade Curriculum Map 2017-18 MONTH UNIT/ CONTENT CORE GOALS/SKILLS STANDARDS WRITTEN ASSESSMENTS ROUTINES RESOURCES VOCABULARY September Chapter 1 8 days NUMBERS AND OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN WORKING
4 th Grade Curriculum Map 2017-18 MONTH UNIT/ CONTENT CORE GOALS/SKILLS STANDARDS WRITTEN ASSESSMENTS ROUTINES RESOURCES VOCABULARY September Chapter 1 8 days NUMBERS AND OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN WORKING
Regional detailed transport noise modelling issues and outcomes
 Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2016 9-11 November 2016, Brisbane, Australia Regional detailed transport noise modelling issues and outcomes S Zhang 1, MS Kanowski 1, NM Janssen 1, DJ Greaves 1, M Tuckwood 1,
Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2016 9-11 November 2016, Brisbane, Australia Regional detailed transport noise modelling issues and outcomes S Zhang 1, MS Kanowski 1, NM Janssen 1, DJ Greaves 1, M Tuckwood 1,
Book 10: Slope & Elevation
 Math 21 Home Book 10: Slope & Elevation Name: Start Date: Completion Date: Year Overview: Earning and Spending Money Home Travel and Transportation Recreation and Wellness 1. Budget 2. Personal Banking
Math 21 Home Book 10: Slope & Elevation Name: Start Date: Completion Date: Year Overview: Earning and Spending Money Home Travel and Transportation Recreation and Wellness 1. Budget 2. Personal Banking
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1996-2 Second edition 2007-03-15 Acoustics Description, measurement and assessment of environmental noise Part 2: Determination of environmental noise levels Acoustique Description,
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 1996-2 Second edition 2007-03-15 Acoustics Description, measurement and assessment of environmental noise Part 2: Determination of environmental noise levels Acoustique Description,
Trade of Sheet Metalwork. Module 7: Introduction to CNC Sheet Metal Manufacturing Unit 4: CNC Drawings & Documentation Phase 2
 Trade of Sheet Metalwork Module 7: Introduction to CNC Sheet Metal Manufacturing Unit 4: CNC Drawings & Documentation Phase 2 Table of Contents List of Figures... 5 List of Tables... 5 Document Release
Trade of Sheet Metalwork Module 7: Introduction to CNC Sheet Metal Manufacturing Unit 4: CNC Drawings & Documentation Phase 2 Table of Contents List of Figures... 5 List of Tables... 5 Document Release
ProMark 500 White Paper
 ProMark 500 White Paper How Magellan Optimally Uses GLONASS in the ProMark 500 GNSS Receiver How Magellan Optimally Uses GLONASS in the ProMark 500 GNSS Receiver 1. Background GLONASS brings to the GNSS
ProMark 500 White Paper How Magellan Optimally Uses GLONASS in the ProMark 500 GNSS Receiver How Magellan Optimally Uses GLONASS in the ProMark 500 GNSS Receiver 1. Background GLONASS brings to the GNSS
Chapter 4 Results. 4.1 Pattern recognition algorithm performance
 94 Chapter 4 Results 4.1 Pattern recognition algorithm performance The results of analyzing PERES data using the pattern recognition algorithm described in Chapter 3 are presented here in Chapter 4 to
94 Chapter 4 Results 4.1 Pattern recognition algorithm performance The results of analyzing PERES data using the pattern recognition algorithm described in Chapter 3 are presented here in Chapter 4 to
E/ECE/324/Rev.1/Add.47/Rev.6/Amend.1 E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.47/Rev.6/Amend.1
 4 October 2010 Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the Conditions for
4 October 2010 Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for Wheeled Vehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the Conditions for
PROGRAM RP83. Drawing of perspective views. User guide. Release: Pragoprojekt a.s
 ROADPAC 14 PROGRAM User guide Release: 25.02.2014 Pragoprojekt a.s. 1986-2014 PRAGOPROJEKT a.s., 147 54 Praha 4, K Rysance 16 1. Introduction Program DRAWING Of PERSPECTIVE VIEWS is part of ROADPAC system.
ROADPAC 14 PROGRAM User guide Release: 25.02.2014 Pragoprojekt a.s. 1986-2014 PRAGOPROJEKT a.s., 147 54 Praha 4, K Rysance 16 1. Introduction Program DRAWING Of PERSPECTIVE VIEWS is part of ROADPAC system.
37 Game Theory. Bebe b1 b2 b3. a Abe a a A Two-Person Zero-Sum Game
 37 Game Theory Game theory is one of the most interesting topics of discrete mathematics. The principal theorem of game theory is sublime and wonderful. We will merely assume this theorem and use it to
37 Game Theory Game theory is one of the most interesting topics of discrete mathematics. The principal theorem of game theory is sublime and wonderful. We will merely assume this theorem and use it to
Microsoft Scrolling Strip Prototype: Technical Description
 Microsoft Scrolling Strip Prototype: Technical Description Primary features implemented in prototype Ken Hinckley 7/24/00 We have done at least some preliminary usability testing on all of the features
Microsoft Scrolling Strip Prototype: Technical Description Primary features implemented in prototype Ken Hinckley 7/24/00 We have done at least some preliminary usability testing on all of the features
Strategic versus simplistic noise modelling of the Bay Area of California: comparing the impact on policy and the community
 Strategic versus simplistic noise modelling of the Bay Area of California: comparing the impact on policy and the community ABSTRACT Benjamin J.A. Hinze (1), Melanie J. Hinze (2) (1) Ambient Maps Pty Ltd,
Strategic versus simplistic noise modelling of the Bay Area of California: comparing the impact on policy and the community ABSTRACT Benjamin J.A. Hinze (1), Melanie J. Hinze (2) (1) Ambient Maps Pty Ltd,
JOHANN CATTY CETIM, 52 Avenue Félix Louat, Senlis Cedex, France. What is the effect of operating conditions on the result of the testing?
 ACOUSTIC EMISSION TESTING - DEFINING A NEW STANDARD OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION TESTING FOR PRESSURE VESSELS Part 2: Performance analysis of different configurations of real case testing and recommendations for
ACOUSTIC EMISSION TESTING - DEFINING A NEW STANDARD OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION TESTING FOR PRESSURE VESSELS Part 2: Performance analysis of different configurations of real case testing and recommendations for
Jitter Analysis Techniques Using an Agilent Infiniium Oscilloscope
 Jitter Analysis Techniques Using an Agilent Infiniium Oscilloscope Product Note Table of Contents Introduction........................ 1 Jitter Fundamentals................. 1 Jitter Measurement Techniques......
Jitter Analysis Techniques Using an Agilent Infiniium Oscilloscope Product Note Table of Contents Introduction........................ 1 Jitter Fundamentals................. 1 Jitter Measurement Techniques......
MicroStation XM Training Manual 2D Level 2
 You are viewing sample pages from our textbook: MicroStation XM Training Manual 2D Level 2 The full content of Module 9 is shown below, which discusses the generation of Complex Elements. The instruction
You are viewing sample pages from our textbook: MicroStation XM Training Manual 2D Level 2 The full content of Module 9 is shown below, which discusses the generation of Complex Elements. The instruction
5: SOUND WAVES IN TUBES AND RESONANCES INTRODUCTION
 5: SOUND WAVES IN TUBES AND RESONANCES INTRODUCTION So far we have studied oscillations and waves on springs and strings. We have done this because it is comparatively easy to observe wave behavior directly
5: SOUND WAVES IN TUBES AND RESONANCES INTRODUCTION So far we have studied oscillations and waves on springs and strings. We have done this because it is comparatively easy to observe wave behavior directly
VGLA COE Organizer Mathematics 4
 4.1 The Student will identify the place value for each digit in a whole number expressed through millions a) orally and in writing; b) compare two whole numbers expressed through millions, using symbols
4.1 The Student will identify the place value for each digit in a whole number expressed through millions a) orally and in writing; b) compare two whole numbers expressed through millions, using symbols
Resistive Circuits. Lab 2: Resistive Circuits ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 42/43/100 INTRODUCTION TO MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
 NAME: NAME: SID: SID: STATION NUMBER: LAB SECTION: Resistive Circuits Pre-Lab: /46 Lab: /54 Total: /100 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 42/43/100 INTRODUCTION TO MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
NAME: NAME: SID: SID: STATION NUMBER: LAB SECTION: Resistive Circuits Pre-Lab: /46 Lab: /54 Total: /100 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 42/43/100 INTRODUCTION TO MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUITS
Range Sensing strategies
 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart and Nourbakhsh 4.1.6 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called
Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart and Nourbakhsh 4.1.6 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called
18th World Conference on Non-destructive Testing, April 2012, Durban, South Africa
 18th World Conference on Non-destructive Testing, 16-20 April 20, Durban, South Africa Guided Wave Testing for touch point corrosion David ALLEYNE Guided Ultrasonics Ltd, London, UK; Phone: +44 2082329102;
18th World Conference on Non-destructive Testing, 16-20 April 20, Durban, South Africa Guided Wave Testing for touch point corrosion David ALLEYNE Guided Ultrasonics Ltd, London, UK; Phone: +44 2082329102;
Acoustic Emission Linear Location Cluster Analysis on Seam Welded Hot Reheat Piping
 Acoustic Emission Linear Location Cluster Analysis on Seam Welded Hot Reheat Piping The EPRI Guidelines for acoustic emission (AE) inspection of seamed hot reheat piping were published in November 1995.
Acoustic Emission Linear Location Cluster Analysis on Seam Welded Hot Reheat Piping The EPRI Guidelines for acoustic emission (AE) inspection of seamed hot reheat piping were published in November 1995.
Reflection and absorption of sound (Item No.: P )
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Reflection and absorption of sound (Item No.: P6012000) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: Age 14-16 Topic: Acoustics Subtopic: Generation, propagation
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Reflection and absorption of sound (Item No.: P6012000) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: Age 14-16 Topic: Acoustics Subtopic: Generation, propagation
Optimizing localization of noise monitoring stations for the purpose of inverse engineering applications
 Optimizing localization of noise monitoring stations for the purpose of inverse engineering applications M. Reiter, J. Kotus and A. Czyzewski Gdansk University of Technology, Multimedia Systems Department,
Optimizing localization of noise monitoring stations for the purpose of inverse engineering applications M. Reiter, J. Kotus and A. Czyzewski Gdansk University of Technology, Multimedia Systems Department,
OUTDOOR PORTRAITURE WORKSHOP
 OUTDOOR PORTRAITURE WORKSHOP SECOND EDITION Copyright Bryan A. Thompson, 2012 bryan@rollaphoto.com Goals The goals of this workshop are to present various techniques for creating portraits in an outdoor
OUTDOOR PORTRAITURE WORKSHOP SECOND EDITION Copyright Bryan A. Thompson, 2012 bryan@rollaphoto.com Goals The goals of this workshop are to present various techniques for creating portraits in an outdoor
Land Navigation / Map Reading
 Land Navigation / Map Reading What is the Field Manual for map reading and land navigation? FM 3-25.26 What are the basic colors of a map, and what does each color represent? Black - Indicates cultural
Land Navigation / Map Reading What is the Field Manual for map reading and land navigation? FM 3-25.26 What are the basic colors of a map, and what does each color represent? Black - Indicates cultural
Electronic Noise Effects on Fundamental Lamb-Mode Acoustic Emission Signal Arrival Times Determined Using Wavelet Transform Results
 DGZfP-Proceedings BB 9-CD Lecture 62 EWGAE 24 Electronic Noise Effects on Fundamental Lamb-Mode Acoustic Emission Signal Arrival Times Determined Using Wavelet Transform Results Marvin A. Hamstad University
DGZfP-Proceedings BB 9-CD Lecture 62 EWGAE 24 Electronic Noise Effects on Fundamental Lamb-Mode Acoustic Emission Signal Arrival Times Determined Using Wavelet Transform Results Marvin A. Hamstad University
SEPTEMBER VOL. 38, NO. 9 ELECTRONIC DEFENSE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL ERRORS IN WIDEBAND IFM RECEIVERS WIDE, WIDER, WIDEST SYNTHETIC APERTURE ANTENNAS
 r SEPTEMBER VOL. 38, NO. 9 ELECTRONIC DEFENSE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL ERRORS IN WIDEBAND IFM RECEIVERS WIDE, WIDER, WIDEST SYNTHETIC APERTURE ANTENNAS CONTENTS, P. 10 TECHNICAL FEATURE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL
r SEPTEMBER VOL. 38, NO. 9 ELECTRONIC DEFENSE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL ERRORS IN WIDEBAND IFM RECEIVERS WIDE, WIDER, WIDEST SYNTHETIC APERTURE ANTENNAS CONTENTS, P. 10 TECHNICAL FEATURE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL
Oakland International Airport Master Plan Update
 Oakland International Airport Master Plan Update - 200. Community-Requested Environmental Projects Port staff asked members of the Stakeholder Advisory Committee to consider any environmentally beneficial
Oakland International Airport Master Plan Update - 200. Community-Requested Environmental Projects Port staff asked members of the Stakeholder Advisory Committee to consider any environmentally beneficial
Sensor Troubleshooting Application Note
 Sensor Troubleshooting Application Note Rev. May 2008 Sensor Troubleshooting Application Note 2008 Argus Control Systems Limited. All Rights Reserved. This publication may not be duplicated in whole or
Sensor Troubleshooting Application Note Rev. May 2008 Sensor Troubleshooting Application Note 2008 Argus Control Systems Limited. All Rights Reserved. This publication may not be duplicated in whole or
University of Tennessee at. Chattanooga
 University of Tennessee at Chattanooga Step Response Engineering 329 By Gold Team: Jason Price Jered Swartz Simon Ionashku 2-3- 2 INTRODUCTION: The purpose of the experiments was to investigate and understand
University of Tennessee at Chattanooga Step Response Engineering 329 By Gold Team: Jason Price Jered Swartz Simon Ionashku 2-3- 2 INTRODUCTION: The purpose of the experiments was to investigate and understand
Blueprint Reading
 Western Technical College 31420302 Blueprint Reading Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 1.00 Total Hours 36.00 Introduction to ready
Western Technical College 31420302 Blueprint Reading Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 1.00 Total Hours 36.00 Introduction to ready
Technical Note 2. Standards-compliant test of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation on radar equipment
 Technical Note 2 Standards-compliant test of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation on radar equipment Technical Note: Standards-compliant test of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation on radar equipment
Technical Note 2 Standards-compliant test of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation on radar equipment Technical Note: Standards-compliant test of non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation on radar equipment
Math + 4 (Red) SEMESTER 1. { Pg. 1 } Unit 1: Whole Number Sense. Unit 2: Whole Number Operations. Unit 3: Applications of Operations
 Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Chapter 23. Signing and Pavement Marking Plans
 Chapter 23 Signing and Pavement Marking Plans 23.1 General... 23-3 23.2 Key Sheet... 23-4 23.3 Signature Sheet... 23-4 23.4 Tabulation of Quantities and Pay Item Notes... 23-4 23.4.1 Standard Notes...
Chapter 23 Signing and Pavement Marking Plans 23.1 General... 23-3 23.2 Key Sheet... 23-4 23.3 Signature Sheet... 23-4 23.4 Tabulation of Quantities and Pay Item Notes... 23-4 23.4.1 Standard Notes...
+ A Supply B. C Load D
 17 E7 E7.1 OHM'S LAW AND RESISTANCE NETWORKS OBJECT The objects of this experiment are to determine the voltage-current relationship for a resistor and to verify the series and parallel resistance formulae.
17 E7 E7.1 OHM'S LAW AND RESISTANCE NETWORKS OBJECT The objects of this experiment are to determine the voltage-current relationship for a resistor and to verify the series and parallel resistance formulae.
Learning Guide. ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. # Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6. Fax:
 Learning Guide ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. #1 20461 Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6 Toll free: 1-800-818-2051 e-mail: support@asrsoft.com Fax: 604-539-1334 www.asrsoft.com Copyright 1991-2013
Learning Guide ASR Automated Systems Research Inc. #1 20461 Douglas Crescent, Langley, BC. V3A 4B6 Toll free: 1-800-818-2051 e-mail: support@asrsoft.com Fax: 604-539-1334 www.asrsoft.com Copyright 1991-2013
Phased Array Velocity Sensor Operational Advantages and Data Analysis
 Phased Array Velocity Sensor Operational Advantages and Data Analysis Matt Burdyny, Omer Poroy and Dr. Peter Spain Abstract - In recent years the underwater navigation industry has expanded into more diverse
Phased Array Velocity Sensor Operational Advantages and Data Analysis Matt Burdyny, Omer Poroy and Dr. Peter Spain Abstract - In recent years the underwater navigation industry has expanded into more diverse
WHITE PAPER BENEFITS OF OPTICOM GPS. Upgrading from Infrared to GPS Emergency Vehicle Preemption GLOB A L TRAFFIC TE CHNOLOGIE S
 WHITE PAPER BENEFITS OF OPTICOM GPS Upgrading from Infrared to GPS Emergency Vehicle Preemption GLOB A L TRAFFIC TE CHNOLOGIE S 2 CONTENTS Overview 3 Operation 4 Advantages of Opticom GPS 5 Opticom GPS
WHITE PAPER BENEFITS OF OPTICOM GPS Upgrading from Infrared to GPS Emergency Vehicle Preemption GLOB A L TRAFFIC TE CHNOLOGIE S 2 CONTENTS Overview 3 Operation 4 Advantages of Opticom GPS 5 Opticom GPS
Rule of Thirds. Notice how the building and horizon are aligned along rule-of-thirds lines. Image by Trey Ratcliff.
 Rule of Thirds Imagine that your image is divided into 9 equal segments by 2 vertical and 2 horizontal lines. Therule of thirds says that you should position the most important elements in your scene along
Rule of Thirds Imagine that your image is divided into 9 equal segments by 2 vertical and 2 horizontal lines. Therule of thirds says that you should position the most important elements in your scene along
Until now, I have discussed the basics of setting
 Chapter 3: Shooting Modes for Still Images Until now, I have discussed the basics of setting up the camera for quick shots, using Intelligent Auto mode to take pictures with settings controlled mostly
Chapter 3: Shooting Modes for Still Images Until now, I have discussed the basics of setting up the camera for quick shots, using Intelligent Auto mode to take pictures with settings controlled mostly
Display and Draw Features
 CHAPTER 7 Display and Draw Features 7.1 Overview Feature / Function Tool Display or draw DTM features, such as contours, triangles, lattices, voids, islands, etc. DTM Menu Bar Load > DTM Features GEOPAK
CHAPTER 7 Display and Draw Features 7.1 Overview Feature / Function Tool Display or draw DTM features, such as contours, triangles, lattices, voids, islands, etc. DTM Menu Bar Load > DTM Features GEOPAK
