Design and Performance Analysis of an Indoor Position Tracking Technique for Smart Rollators
|
|
|
- Allan Norris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3 Design and Pefomance Analysis of an Indoo Position Tacing Technique fo Smat Rollatos Payam Nazemzadeh, Daniele Fontanelli, David Macii, Tiza Rizano, Luigi Palopoli Depatment of Infomation Engineeing and Compute Science Depatment of Industial Engineeing Univesity of Tento, Tento, Italy E mail: {payam.nazemzadeh,daniele.fontanelli,david.macii}@unitn.it, {izano,palopoli}@disi.unitn.it Abstact This pape pesents a position tacing technique based on multisenso data fusion fo ollatos helping eldely people to move safely in lage indoo spaces such as public buildings, shopping malls o aipots. The poposed technique has been developed within the FP7 poject DALi, and elies on an extended Kalman filte pocessing data fom dead-econing sensos (i.e. encodes and gyoscopes), a shot-ange adio fequency identification (RFID) system and a font Kinect camea. As nown, position tacing based on dead-econing sensos only is intinsically affected by gowing uncetainty. In ode to eep such uncetainty within wanted boundaies, the position values ae occasionally updated using a coase-gained gid of low-cost passive RFID tags with nown coodinates in a given map-based efeence fame. Unfotunately, RFID tag detection does not povide any infomation about the oientation of the ollato. Theefoe, a font camea detecting some maes on the walls is used to adjust diection. Of couse, the data ate fom both the RFID eade and the camea is not constant, as it depends on the actual use s tajectoy and on the distance between pais of RFID tags and pais of maes. Theefoe, the aveage distance between tags and maes should be popely set to achieve a good tade-off between oveall deployment costs and accuacy. In the pape, the esults of a simulation-based pefomance analysis ae epoted in view of implementing the poposed localization and tacing technique in a eal envionment. Index Tems Indoo localization, position tacing, Kalman filte, data fusion, pefomance evaluation I. INTRODUCTION Today s obots ae no longe (and not only) the stiff and dangeous machines used in factoy automation thoughout the last decades. They have evolved into intelligent and flexible agents that inteact closely with thei uses, impove thei quality of life and do not pose significant safety theats. A pefect application aena fo this technology is the socalled Ambient Assisted Living (AAL). In the potfolio of the technological solutions fo AAL, obotic assistants play aleady an impotant ole and many eseaches believe that this is expected to gow futhe. DALi is a eseach poject with the aim of developing a cognitive wale (called c- Wale) assisting eldely people with deambulation poblems to navigate in complex envionment, such as shopping malls, aipots o stations that they could peceive as intimidating []. The DALi poject has offeed a pactical motivation to the wo pesented in this pape. The poblem can be shotly summaized in the following tems: in ode to assist uses in thei activities in a lage and patially stuctued envionment, a obotic assistant equies eal-time position tacing. This poblem can be hadly solved with conventional GPS eceives, because the GPS signals ae geneally too wea to be detected indoos and, in any case, GPS positioning accuacy is not sufficient fo the consideed application. What we need is instead an accuate local positioning system (LPS) (i.e. with accuacy bette than one mete) at an affodable cost. The impotance of indoo localization in seveal application aeas has stimulated consideable eseach effots in the last few yeas. Localization techniques can be oughly classified in two goups, i.e. elative and absolute localization methods. In elative localization methods, the distance of a device fom an initial position is measued using dead-econing sensos such as encodes, gyoscopes and acceleometes [], [3]. An inevitable poblem of such techniques is the accumulation of the measuement uncetainty contibutions. As a esult, the estimation eos tend to gow indefinitely, thus maing measued position values useless afte some time. This poblem can be avoided if absolute localization methods ae used. In fact, these techniques leveage extenal devices o landmas deployed in the envionment in nown positions, which ae detected by sensing systems such as cameas [4], ulta-sound sensos [5] o lase scannes [6]. Well-nown wieless solutions fo localization ae based on tiangulation fom fixed anchos and ely on: adio signal stength intensity (RSSI) measuements [7], [8], [9] time-of-flight (ToF) o time-of-aival (ToA) measuements of Radio Fequency (RF) signals [], [] o a combination theeof []. Anothe possibility fo absolute localization is the use of shot-ange Radio Fequency Identification (RFID) systems, which have the ey advantage of being less affected by the level of cowdedness of the envionment. A suvey on wieless systems fo indoo localization (including netwos of passive and active RFIDs) can be found in [3]. Active RFID-based solutions equie a smalle numbe of tags in the envionment [4], [5]. Howeve, passive RFIDs ae much cheape and do not need any maintenance (e.g. battey eplacement). Theefoe, they ae pefeable fo localization in lage envionments. In [6] passive RFID tags ae buied in capets. Anothe tigonometic algoithm fo indoo localization of mobile obots based on passive RFID // $3. IEEE
2 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3 tags has been poposed by Pa et al. [7]. An impotant dawbac of localization based on RFID technologies is that at least one tag within the ange of the eade has to be found at each sampling time. As a esult, a vey lage numbe of tags can be needed fo position tacing, which could not be economically pofitable in lage envionments. Kulyouin et al. [8] popose to educe the numbe of tags by using RFID mats. This solution is viable in coidos, but not in lage ooms without obstacles o foced paths. Fo all the easons above, position tacing pefomance can be impoved if elative and absolute localization techniques ae combined togethe, e.g. using multi-senso data fusion algoithms [9]. In [] a Bayesian estimation algoithm fuses vaious data eceived fom GPS, ange sensos, inetial and magnetic sensos and a baomete. A method fo fusing data fom inetial sensos and data eceived fom a wieless camea is descibed in []. Choi et. al. popose to solve the position tacing poblem by fusing data fom RFID tags, odometes [], cameas [3] and ultasonic sensos [4]. In [5] an extended Kalman filte (EKF) is used to fuse odomety data, measued by two encodes, and data sent fom a gyoscope to localize a smat ollato. Although Kalman filtes can stongly educe the estimation uncetainty, both measuement systems used in [5] ae dead econing. Hence, the total uncetainty accumulates ove time. A diffeent appoach is followed in [6], whee an automated wheelchai is localized by a camea ecognizing landmas on the ceiling, while two encodes and an azimuth senso ae used when the landmas ae out of view. A clea conclusion fom the discussion of the elated wo is that a eliable and cost effective LPS equies the integation of diffeent measuement devices, with complementay chaacteistics in tems of cost, accuacy, ange, availability and computational equiements. The appoach descibed in the est of this pape extends and efines the basic idea pesented in [7]. Lie in othe simila solutions, a Kalman filte is used to fuse the data coming fom a elative localization system woing at a high sampling ate with those collected fom an absolute localization system. Howeve, the infastuctue of the absolute system has to be configued so as to minimize its cost, with a little impact on accuacy. In the est of the pape, at fist, in Section II, ou specific poblem is fomalized. Then in Section III the position tacing algoithm is descibed. Finally, in Section IV the simulation settings ae defined and seveal esults ae epoted and commented. II. PROBLEM OVERVIEW The position tacing technique poposed in this pape elies on a multi-senso data fusion technique based on the data collected fom: two incemental encodes installed in both ea wheels; a tiaxial gyoscope located in the cental top pat of the ollato; an RFID eade with a ange of some tens of cm placed below the ollato and with the antenna appoximately cm above the gound; a font camea, paticulaly a Kinect. The encodes ae used to estimate the elative position and oientation of the c-wale smat ollato by using a simple inematic model. Relative oientation estimation can be impoved also by integating the angula velocity values collected fom a high-pefomance gyoscope (i.e., exhibiting a vey small dift). Unfotunately, model-elated as well as encode and gyoscope measuement uncetainty contibutions accumulate ove time and completely disupt localization pefomance afte some time. Such unbounded uncetainty gowth is common to all pue dead-econing localization appoaches elying on incemental sensos subject to measuement bias and dift [], [8]. Theefoe, absolute position and oientation data ae necessay not only to initialize the system, but also to adjust taget location peiodically. As fa as the position updates ae concened, an RFID eade can be used to detect some low-cost passive tags deployed in the envionment at nown locations, e.g., stuc on the gound o embedded in the tiles. Shot-ange RFID tag eading is a quite attactive solution in this context since passive tags ae cheap. Also, position measuement uncetainty can be ept smalle than the RFID eading ange (i.e., in the ode of a few tens of cm). The font camea is used as a beaing-only senso, a solution often used in obotics fo localization and map constuction due to its elatively low computational buden and good accuacy [9], [3]. In this way, just the oientation estimation eo is diectly adjusted. Since the system can ely also on a map of the chosen envionment and an absolute efeence is needed fo dift and bias emoval, we will assume that the camea is able to detect specified maes inside the envionment (e.g., wallpapes, signs, elevatos, paintings) whose position inside the map is assumed to be nown a pioi. As a Kinect device will be used in this poject fo such duties as object ecognition, we do not need to add any additional camea to the system. Kinect is a motion sensing device made by Micosoft based on an RGB camea and a depth senso which can captue 3D video data in vaious light conditions. Best pefomances ae achieved at distances between 8 cm and 4 m fom the camea with a hoizontal field of view of about 6 degees. The depth senso is a combination of an infaed lase pojecto and a CMOS senso which gives the Kinect the ability of estimating the distance between diffeent objects. The appopiate accuacy of Kinect as well as its low pice have made it quite inteesting fo indoo obot navigation [3], [3]. In this pape the depth maps collected by the Kinect ae used to estimate the oientation of the c-wale ollato with espect to nown maes. In ode to limit the computational and communication bandwidth equiements associated to Kinect image pocessing, mae detection is not epeated at evey fame, but only evey few seconds. In this way, the Kinect pocesses its depth map data and etuns ollato oientation (if a mae is detected) at a vey low ate, which is expected not to satuate the communication and computational esouces available on boad of the c-wale.
3 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3 Walls Maes Camea Gyoscope RFID eade RFID tags Encodes Fig.. The c-wale ollato of DALi within the efeence fame hw i = {OW, XW, YW, ZW }. A moe detailed desciption of the context whee the cwale pototype is supposed to be used is shown in Fig.. hw i = {Ow, Xw, Yw, Zw } epesents a fixed, ight-handed wold efeence fame, whee Π = Xw Yw descibes the plane of motion, Zw points outwads plane Π and, finally, Ow is the oigin of the efeence fame. With the descibed choice of hw i, the tags can be placed egulaly on a gid of plane Π (possibly embedding the tags in the floo). Conside that if DR epesents the distance between adjacent tags, the numbe of RFID tags must be ept quite limited and DR should be quite lage than the RFID eading ange (which typically is in the ode of a few tens of cm), to assue estimation with acceptable eo anges and to avoid simultaneous (ambiguous) eadings fom multiple tags. Simila consideations hold fo the visual maes to be detected by the Kinect: they can be assumed to be placed on the walls at a distance DM fom one anothe, with DM lage than the maximum eading ange of the Kinect. Fom a inematic view point, the ollato consists of two passive font caste wheels and two fixed ea wheels. If d is the wheel axle length, the adius of the wheels and ω and ωl ae the angula velocities of the ight and left wheels, espectively, it follows that (ω + ωl ), ω = (ω ωl ), d v= () whee v is the tangential velocity of the ollato and ω is its angula velocity aound the mid point of the wheels axle. The Catesian coodinates of this point on plane Π (denoted as (x, y) in Fig. ) detemine the actual position of the ollato. The oientation of the c-wale with espect to axis Xw is expessed instead by vaiable θ. Theefoe, the system descibing the motion of the ollato is given by x cos(θ) cos(θ) cos(θ) ω v. s = y = sin(θ) = sin(θ) sin(θ) ωl ω θ d d () whee s = [x, y, θ]t epesents the state of the system. The position tacing algoithm poposed in this pape must be able to eep the diffeence s s between actual and estimated state within a given inteval ±εs with 9% pobability. It is woth emphasizing that the poposed localization solution elies on a mixtue of event-based and time based measuement esults. Indeed, the RFID tags ae detected only when the ollato moves close to them (which depends on tajectoy), while the Kinect can detect one of the maes only if it is within the field of view of the camea. Evidently, the lage the values of DR and DM, the lowe the aveage ate of position and oientation adjustments. In ode to limit the computational buden associated with mae detection and ecognition, maes ae not continuously taced by the camea. In fact, the fame acquisition peiod can be so low as a few seconds. The data eceived fom diffeent sensing devices ae fused by means of an extended Kalman filte (EKF). The behavio of the poposed algoithm is summaized by the bloc diagam in Fig.. The encodes ae used to pedict position and oientation. The gyoscope is used to update the oientation in the shot-tem. The event based measues fom the RFID eade and the Kinect camea ae used, when available, to update the estimated state of the system. The poblem of selecting the best configuation in a given envionment can be tacled using a Monte Calo appoach. At fist, the state estimation eos ove a lage set of andom tajectoies ae computed fo diffeent values of DR and DM. Then, the values of DR and DM ae chosen so as to mae uncetainty smalle than ±εs with a minimum numbe of tags and maes in the chosen envionment. III. A LGORITHM D ESCRIPTION The senso data fom encodes and gyoscope ae collected with a sampling peiod Ts. Theefoe, the continuous time inematic model () can be discetized with peiod Ts, yielding to cos(θ ) cos(θ ) Ts ω sin(θ ) sin(θ ). (3) s+ = s + Ts ωl d d The integation algoithm adopted to obtain (3) is the Eule fowad method and elies on the assumption that the wheel velocities ae constant duing evey sample peiod. As a consequence, Φ = Ts ω and Φl = Ts ωl epesent the angula displacements of the ight and left wheels, espectively, duing the th integation peiod. Note that (3) can be
4 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3 at (+)Ts RFID eade at (+)Ts Camea Gyoscope Pocess Data at (+)Ts Plana position measued (RFID tag ead) Oientation measued (camea o gyoscope) at Ts Left encode Right encode Pedict the position (EKF pedict step) Position Tacing esult at Ts Update the position using the available data (EKF update step) Fig.. Bloc diagam of the poposed multi-senso data fusion technique fo ollato position tacing. ewitten as s + = s + f(s ) Φ, (4) whee Φ = [ Φ, Φ l ] T. Since the values of Φ ae measued by the encodes, they will be affected by the additive independent uncetainty contibutions ɛ = [ɛ, ɛ l ] T. Theefoe, (4) can be changed as follows, i.e. s + = s + f(s )( Φ + ɛ ). (5) whee Φ = [ Φ, Φ l ] T is the vecto of values actually measued at time T s. The output of (4) is simply a linea function of the state, i.e. o = C s + ζ, (6) whee the dimension of C changes in time as a function of the available measuement data coming fom the gyoscope, the RFID eade and/o the camea, espectively, and ζ is the vecto of the coesponding uncetainty contibutions at time T s. In paticula, depending on the available measues, the tems of the system output equation can be expessed as follows, i.e. in the case of gyoscope only: o = θ g, C = C g, ζ = ζ g θ ; (7) whee θ g denotes the oientation measued by the gyoscope and ζ g θ is the coesponding uncetainty; in the case of gyoscope + RFID: x [ ] o = y C ζ x, C = θ g C g, ζ = ζ y ; (8) ζ g θ whee (x, y ) ae the coodinates of the detected RFID tag in fame W and ζ x and ζ y epesent the coesponding position offsets along axes X w and Y w ; in the case of gyoscope + camea: [ θ g] ] o = θ c, C =, ζ = [ C g C c [ ζ g ] θ ζθ c ; (9) whee the meaning of θ g and ζg θ is the same as above, θ c is the oientation measued by the Kinect when a mae is detected and ζθ c is the coesponding measuement uncetainty, and finally in the case of gyoscope + RFID + Camea: x o = y C ζ x θ g, C = C g, ζ = ζ y θ c C c ζ g. () θ ζθ c Obseve that in (7)-() C esults fom the combination of one o moe of the following matices: C = [ I ], fo RFID, C g = [ ], fo Gyoscope, C c = [ ], fo Camea, () whee is a two-element, all-zeo column vecto and I is the identity matix. IV. EXTENDED KALMAN FILTER (EKF) As nown, fo a given dynamic system the Kalman filte is the optimal minimum mean-squae-eo (MMSE) state estimato when pocess and measuement noises ae white and gaussian. In this pape, (4) epesents a nonlinea system. Theefoe, an extended Kalman Filte (EKF) must be used to combine the data collected fom encodes, RFID tags, gyoscope and Kinect. In geneal, an EKF is able to combine the data collected fom vaious sensos by weighing vaiances and covaiances associated with diffeent uncetainty contibutions. Since extenal position and oientation data ae not always available and some uncetainty contibutions ae not stationay, the EKF descibed in the following can be hadly consideed as the optimal state estimato. Nonetheless, it is still the best linea MSE estimato [33]. Potentially, the system model (4) and the elated EKF could be extended to include the inputs descibing the effect of systematic measuement uncetainty contibutions (e.g. gyoscope and encode offsets). Howeve, in the est of this pape such tems will be assumed to have been peliminaily estimated and compensated though senso calibation, as customay in this ind of applications. Thus, the elements of ɛ and ζ can be supposed to have a negligible mean. The specific poblem of dynamic systematic offset estimation using the same EKF will be instead investigated in a futue wo. In the following, the ight and left wheel encodes will be assumed to be nominally identical, but affected by uncoelated noise tems. Due to the supeimposition of vaious andom uncetainty contibutions (e.g. limited esolution, mechanical vibations) we can easonably assume that ɛ N (, σ )
5 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3 and ɛ l N (, σ l ). Also, the vaiances σ and σ l of both encodes change ove time, as they depend on the wheels displacement in the time inteval between T s and ( + )T s. As a consequence, the pediction equation of the EKF is given by ŝ + + = ŝ + f(ŝ ) Φ, () whee ŝ denotes the state estimated at time T s and supescipt + stands fo pediction [33]. Moeove, by lineaizing (4) the state pediction covaiance matix esults fom P + + = F P F T + G Q G T. (3) whee F is the Jacobian of () with espect to s at [ŝ, Φ ], i.e., F = I 3 + [f(s ) Φ ] [ŝ s, Φ ] = ) ( Φ + Φ l sin ˆθ ) = ( Φ + Φ l cos ˆθ, (4) G is the Jacobian of () with espect to Φ and Φ l computed at [ŝ, Φ ], i.e., G = [f(s ) Φ ] [ŝ Φ, Φ ] = cos ˆθ cos ˆθ sin ˆθ sin ˆθ, (5) d d and Q is the covaiance matix associated with ɛ. Since the encodes noises ae wealy coelated in pactice, Q is a diagonal matix with σ and σ l on the main diagonal. The Kalman gain is given by K + = P + + CT + ( C+ P + + CT + + D + ), (6) whee C + is defined in (7)-() depending on the set of available measuement data at time T s, as descibed in Section III. Similaly, the covaiance matix D + associated to ζ + ae defined as follows, i.e. Gyoscope only: D + =σ θ+; g gyoscope + RFID: σx + ρ + σ x+ σ y+ D + = ρ + σ x+ σ y+ σy + ; σ θ g + Gyoscope + camea: D + = [ σ θ g + σ θ c + ] ; In the matices listed above, ρ + is the coelation coefficient between ζ x+ and ζ y+, while σx + and σy + ae the coesponding vaiances. Similaly, σ and σ θ g θ ae the c + + vaiances of ζ g θ + and ζθ c +, espectively. Afte the Kalman gain is computed, the estimated system state and the coesponding covaiance matix can be updated using the measuement data ecod o + collected at time (+ )T s, i.e. ŝ + = ŝ K + ( o+ C + ŝ + +), P + = (I 3 K + C + )P + +. (7) The position measuement uncetainty associated with RFID tag eading can be modeled by a unifom distibution with a cicula symmety aound evey tag and with adius equal to the eading ange R. This assumption is easonable if the shot-ange RFID eade installed on the ollato is quite isotopic. In this case the pobability of eading a tag is appoximately the same in evey point of the cicle centeed in the tag, egadless of ollato speed o movement diection. On the contay, the pobability of eading a tag when the ollato is fathe than R is zeo (since the passive tag is off and it cannot be tuned on). Unde these assumptions, it can be poved that the mean values of the position eos along axes X w and Y w ae zeo, while the espective vaiances ae σx + = σy + = R 4 with ρ + =. Such expessions show that the uncetainty associated with the coodinates measued along axes X w and Y w ae uncoelated and stationay. of the oientation data On the othe hand, the vaiance σ θ g + measued with the gyoscope is typically non-stationay and monotonically inceasing. In fact, it is a function of both angula speed and time because of the dead econing effects. A detailed desciption of gyoscope measuement uncetainty is out of the scope of this pape. To a fist appoximation, it is easonable to assume that ζ g θ N (, σ with σ θ), g θ g gowing linealy as a function of time in the case of constant motion. This assumption has been veified also expeimentally, as shown in Section V-B. The case of the oientation measuements based on the Kinect is instead quite diffeent. In fact, if a mae is within the field of view of the Kinect, the uncetainty affecting the measued angle depends mostly on the elative oientation between the mae and the Kinect senso, on the distance at which the mae is ecognized and on the esolution of the collected image. Since such factos ae independent fom each othe and the oientation measuement data may diffe consideably at diffeent distances fom a given mae, we can easonably assume that ζθ c N (, σθ It is woth noticing ). c that σ θ c is independent of time. Theefoe, the camea-based oientation values can be also used to eset the uncetainty accumulated by the gyoscope, thus impoving shot-tem pefomance. Gyoscope + RFID + camea: σ x + ρ + σ x+ σ y+ ρ + σ x+ σ y+ σy + D + = σ θ g. V. PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS AND SETUP OPTIMIZATION + σθ As mentioned in the Intoduction, the objective of the pape + c is to evaluate the pefomance of the poposed technique with
6 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe F 3F S S 3 5 F 5 3S Fig. 3. Examples of ollato tajectoies used fo Monte Calo simulations. The map efes to the Depatment of Infomation Engineeing and Compute Science of the Univesity of Tento. Symbols S, S and 3S denote the stating positions, wheeas F, F and 3F epesent the finishing points. RFID tags and maes fo the camea ae epesented with * and, espectively. diffeent configuation settings in ode to find a good tadeoff between deployment costs and accuacy, while eeping the computational buden due to image pocessing quite low. To this aim, seveal multi-paametic simulations have been pefomed by changing those quantities that most seiously influence system complexity, i.e. (which affects the RFID gid ganulaity and, consequently, the costs of a possible setup) and (which has a elevant impact on accuacy, computational load and setup costs). In ode to extend significantly the esults epoted in [7], multiple andom, but ealistic tajectoies have been geneated. The chosen envionment is the Depatment of Infomation Engineeing and Compute Science of the Univesity of Tento, Tento, Italy. The details of the algoithm used to geneate the testing tajectoies ae epoted in Section V-A. The senso paamete values used in simulations have been estimated by following the pocedues descibed in Section V-B. Finally, the esults associated with diffeent possible configuations ae epoted in Section V-C. A. Tajectoy geneation The tajectoies used fo Monte Calo simulations ae geneated by a path planning algoithm that can be applied to any map of a eal indoo envionment. The geometic entities (e.g. walls, patitions, funitue) in the map ae descibed as closed polylines. An algoithm based on appoximate cell decomposition is applied to divide the map into ectangula cells of diffeent sizes [34]. By intesecting these cells with the closed polylines, evey cell can be classified into thee possible types: fully occupied, patially occupied o empty. The empty cells epesent those aeas which ae accessible to the ollato. In the map of the Depatment thee ae 76 empty cells. A gaph is constucted fom these empty cells using the position of the cell centes as nodes of the gaph. Two nodes in the gaph ae connected if the coesponding cells ae adjacent. The weights of the edges between two nodes epesent the Euclidean distance between the cell centes. The Dijsta s shotest path algoithm is applied to the gaph to find a sequence of cells that connects the initial position of the ollato with the finishing point. Using the coodinates of the cente of these cells, a path consisting of line segments lining pais of subsequent cell centes is constucted. The esulting piecewise linea tajectoy povides a good appoximation of the path that the c-wale has to follow. In ode to povide a smoothe tansition between segments, a potion of evey pai of subsequent segments is eplaced by acs of a cicle. Fig. 3 shows thee possible ollato tajectoies on the map. Symbols S, S and 3S denote the stating positions, wheeas F, F and 3F epesent the coesponding finishing points. RFID tags and visual maes ae highlighted by symbols * and, espectively. B. Senso chaacteization In ode to evaluate position tacing accuacy though simulations in ealistic conditions, some of the sensos that ae expected to be used on the c-wale ollato have been tested on the field. At fist, two E5-seies optical incemental encodes have been installed on the ea wheels of a at emulating the ollato pototype. Seveal data ecods have been collected with the at moving along both staight and cicula paths. The distance values ead fom the encodes have been measued at nown positions. The efeence points wee maed by
7 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3 Encode Uncetainty (ad) std Left std Right mean Left mean Right Standad deviation Mean (afte calibation) Gyoscope Uncetainty (ad) std mean Standad Deviation Mean Wheels angula displacement (ad) time (s) Fig. 4. Mean values (afte calibation) and standad deviations of leftwheel and ight-wheel encodes. The maes efe to the expeimental esults collected in 3 expeiments ove a staight-line path and in futhe expeiments ove a cicula path. Dotted and continuous lines esult fom least-squaes linea fitting. Fig. 5. Mean values (afte calibation) and standad deviations of the oientation measued though a gyoscope as a function of time. The maes efe to the esults extapolated fom the andomization of multiple expeimental data ove elementay tajectoies. Dotted and continuous lines esult instead fom least-squaes linea fitting. some stices put on the floo of ou laboatoy. Encodes pefomance is evaluated accoding to the following pocedue: In all expeiments the diffeences between the angula displacements measued by both ight and left wheel encodes and the coesponding values estimated at evey efeence point ae calculated. The obtained eo histogams as well as thei mean and standad deviation ae computed. The mean and standad deviation pattens ae plotted as a function of the total angula displacements of both wheels. Given that the mean eos mae the measued distances dift away fom the actual values, such systematic contibutions have been compensated though a peliminay calibation. Finally, mean and standad deviation have been intepolated though least-squaes linea fitting, as a function of the total angula displacement, as shown in Fig. 4. In unning the Monte Calo simulations we have assumed that the encodes ae calibated and that the esidual offsets ae zeo. The standad deviation values ae used instead to build Q in (3). A simila appoach has been followed to test the pefomance of a tiaxial gyoscope Invensense IMU3. In paticula, seveal sets of data have been collected using a custom embedded platfom placed on top of the ollato pushed epeatedly ove staight and ectangula paths. It is woth eminding that the gyoscope measues angula velocity and not its oientation, which is instead obtained by integating the angula velocity data in time. The main steps of the testing pocedue ae listed below. In all expeiments the diffeences between measued and actual oientation angles with espect to X w have been computed at the same time. The measuement eos have been used to build diffeent histogams elated to homogeneous tajectoies. The mean and the standad deviation pattens of such histogams have been plotted as a function of time. As peviously discussed fo the encodes, the systematic contibutions coming fom the mean eo have been compensated though a peliminay senso calibation. Afte calibation, Monte Calo simulations based on the combination of the esults of the elementay paths have been pefomed ove diffeent andom tajectoies to extapolate a moe tustwothy histogam of gyoscope uncetainty as a function of time in multiple scenaios (which could not be easily detemined expeimentally). Both mean values and standad deviations have been estimated though least-squaes linea fitting, as shown in Fig. 5. Again, in unning the Monte Calo simulations, we have assumed that the gyoscope is calibated and that the esidual offset is zeo. The standad deviation values ae used instead to compute σ θ+. g The pefomances of the RFID eade fo localization puposes have been analyzed using a high-fequency (HF) ISC.MR-USB evaluation it by Feig Electonics opeating at 3.56 MHz. The eade is designed to detect passive tags compliant with Standads ISO 5693 (Vicinity Cads) and ISO 8-3 (Smat Labels). The main steps of the testing pocedue ae listed below. A tag is placed on the floo and the RFID eade is moved adially towads the tag and bacwads in eight diections (i.e. noth, noth-east, east, south-east, south, south-west, west, noth-west), while eeping the antenna paallel to gound. The eading ange of the device in evey diection is estimated by measuing epeatedly the distances at which
8 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3 the tag is detected o stops being detected. Afte checing the ommidiectional behavio of the eade, a histogam of the measued ange values is built. The esulting mean value of R is used to compute σ x + and σ y +, as descibed in Section IV. Since the algoithm fo mae ecognition is still unde development, the Kinect-based oientation measuement accuacy could not be evaluated on the field. Theefoe, it was deduced fom infomation and data available in the liteatue [35], [36]. Estimation eo of x (m) time (s) (a) C. Simulation esults In ode to evaluate the pefomance of the poposed technique in diffeent configuations and to find a good tade-off between accuacy and cost, the position tacing algoithm has been applied to diffeent paths geneated as descibed in Section V-A. All the tajectoies have a duation of 8 s, but the total taveled distance is diffeent because the aveage velocity of the use vaies fom case to case. The senso paametes used in all the simulations esult fom the chaacteization pocedues descibed in Section V-B and ae shotly summaized in the following, i.e. Encodes and gyoscope sample time: T s = 4 ms; Encodes standad deviation: σ = σ l =.66 Φ +.6 ad; Standad deviation of gyoscope-based oientation measuements: σ θ g =.98T s; Standad deviation of camea-based oientation measuements: σ θ c = π/8 ad, assuming a ange between.8 m and 3.5 m with a hoizontal field of view of 6 ; RFID eade ange: R = 5 cm with a toleance of ±5 cm; Fig. 6 shows the estimation eos of state vaiables x (a), y (b) and θ (c) as a function of time fo the tajectoy numbe (i.e., between positions S and F) shown in Fig. 3. The distances between pais of RFID tags and pais of visual maes ae equal to = 3 m and = 8 m, espectively. Obseve that the state estimation eos lie safely within ±ε s, whee ε s = [ m, m,. ad]. Simila esults can be deived fo all the othe tajectoies in the set. Fig. 7 shows the aveage oot mean squae (RMS) eos of the Euclidean distances between measued and actual positions as a function of { m,.5 m, m,.5 m, 3 m, 3.5 m, 4 m} and {6 m, 8 m, m, m, 4 m, 6 m, 8 m, m} fo all the tajectoies. The values of and ae chosen puposely lage than the maximum anges of RFID eade and Kinect, espectively, not to detect multiple tags o maes at the same time. A toleance of ±5 cm affects mae and tags placement on the map due to the physical constaints of the envionment (e.g. doos o passages). Each point of the suface in Fig. 7 is obtained as follows. At fist, the RMS values of the Euclidean distances between measued and actual positions ae computed at evey simulation time. Estimation eo of y (m) Estimation eo of θ (ad) time (s)... (b) time (s) (c) Fig. 6. Estimation eos of state vaiables x, y and θ as a function of time fo the tajectoy no. shown in Fig. 3. The distances between pais of RFID tags and pais of visual maes ae equal to = 3 m and = 8 m, espectively. Then the RMS eos elated to the last 6 s of simulation ae aveaged, because the EKF eaches the steady state afte s in all conditions. The points of the suface confim that the positioning uncetainty tends to gow when eithe o inceases, as expected. Fig. 7 shows also that the positioning standad uncetainty is below m fo.5 m (egadless of the value of ) and, dually, fo 8 m when 3.5 m. In such conditions the RMS eos lie between.5 m and.9 m in most cases. Howeve, the total numbe of maes and tags to be deployed in the chosen envionment diffes consideably. In fact, it anges fom about 95 items when = 3 m and = 8 m to moe than 3 items when = m and = 6 m. Evidently, in tems of tade-off between cost and accuacy the fome solution is pefeable and easie to deploy. Fig. 8 depicts the box-and-whises plots of the estimation eos of state vaiables x (a), y (b) and θ (c), espectively, ove 8 s in diffeent configuations of inteest (namely fo vaious pais of and values). Obseve that when = 3.5 m and = 8 m, the eos along X w and Y w ae within ± m
9 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3.5 Aveage RMS position eo (m) (m) 5 (m) 3 4 x axis estimation eo (m) =m =m =.5m =6m =m =4m =.5m =m (a) =3m =m =3.5m =8m =4m =6m Fig. 7. Steady-state RMS eos of the Euclidean distances between measued and actual positions computed ove tajectoies as a function of and. with almost 9% pobability. Also, the oientation eos ae much smalle than in othe cases due to quite fequent updates fom the Kinect. On the othe hand, the configuations in the cente of the suface (e.g. when =.5 m and = m) tend to be quite bad in all espects. Indeed, not only the oientation coections ae not fequent enough to eep x and y position eos below m, but they ae also quite expensive in tems of numbe of maes and tags. VI. CONCLUSIONS The analysis descibed in this pape povides essential guidelines fo the design of a localization and position tacing system to be implemented on a smat ollato called c-wale. The taget positioning uncetainty should be steadily below m. The esults epoted in the pape can be summaized as follows: Encodes accuacy is essential to achieve good pefomance. As a ule of thumb, encode esolution should be at least. degees. Also, possible systematic offsets must be popely estimated and compensated (e.g. though a peliminay calibation). The poposed technique is able to meet the specified accuacy equiements (to be used also fo long-tem tajectoy planning), even when the distance between the RFID tags embedded in the floo is one ode magnitude lage than the antenna eading ange. A distance of about 3.5 m between tags loos adequate. This esult is vey impotant because it dastically educes deployment costs and complexity. If no platfom oientation measues ae available, localization accuacy tends to degade quite quicly, even if a good gyoscope is used. A font Kinect collecting fames evey s and detecting suitable visual maes on the walls at a distance of about 8 m fom each othe y axis estimation eo (m) Oientation estimation eo (ad) =m =m =m =m =.5m =6m =.5m =6m =m =4m =m =4m =.5m =m (b) =.5m =m (c) =3m =m =3m =m =3.5m =8m =3.5m =8m =4m =6m =4m =6m Fig. 8. Box-and-whises plots epesenting the estimation eos of state vaiables x, y and θ fo diffeent pais of and values. can effectively solve this poblem, while eeping the computational buden within easonable limits. VII. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The eseach leading to these esults has eceived funding fom the Euopean Union Seventh Famewo Pogamme
10 3 Intenational Confeence on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation, 8-3st Octobe 3 (FP7/7-3) unde gant ageement n ICT DALi - Devices fo Assisted Living. REFERENCES [] The DALi Poject, Novembe. [] Ching-Hsien Hsu and Chia-Hao Yu, An acceleomete based appoach fo indoo localization, in Poc. Symposia and Woshops on Ubiquitous, Autonomic and Tusted Computing (UIC-ATC), Bisbane, Austalia, Jul. 9, pp [3] M. D. Cecco, Senso fusion of inetial-odometic navigation as a function of the actual manoeuves of autonomous guided vehicles, Measuement Science and Technology, vol. 4, no. 5, pp , May 3. [4] S. Se, D. Lowe, and J. Little, Mobile obot localization and mapping with uncetainty using scale-invaiant visual landmas, The intenational Jounal of obotics Reseach, vol., no. 8, pp , Aug.. [5] W. D. Rencen, Concuent localisation and map building fo mobile obots using ultasonic sensos, in Poc. IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), vol. 3, Yoohama, Japan, Jul. 993, pp [6] K. Lingemann, A. Nüchte, J. Hetzbeg, and H. Sumann, High-speed lase localization fo mobile obots, Robotics and Autonomous Systems, vol. 5, no. 4, pp , Jun. 5. [7] Y. Touati, H. Aoudia, and A. Ali-Cheif, Intelligent wheelchai localization in wieless senso netwo envionment: a fuzzy logic appoach, in Poc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Systems (IS), London, UK, Jul., pp [8] K. Whitehouse, C. Kalof, and D. Culle, A Pactical Evaluation of Radio Signal Stength fo Ranging-based Localization, SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev., vol., no., pp. 4 5, Jan. 7. [9] P. Pivato, L. Palopoli, and D. Peti, Accuacy of RSS-Based Centoid Localization Algoithms in an Indoo Envionment, IEEE Tans. on Instumentation and Measuement, vol. 6, no., pp , Oct.. [] I. Guvenc and Chia-Chin Chong, A Suvey on TOA Based Wieless Localization and NLOS Mitigation Techniques, IEEE Communications Suveys & Tutoials, vol., no. 3, pp. 7 4, Thid Quate 9. [] A. De Angelis, M. Dionigi, A. Moschitta, and P. Cabone, A Low-Cost Ulta-Wideband Indoo Ranging System, IEEE Tans. on Instumentation and Measuement, vol. 58, no., pp , Dec. 9. [] D. Macii, A. Colombo, P. Pivato, and D. Fontanelli, A data fusion technique fo wieless anging pefomance impovement, IEEE Tans. on Instumentation and Measuement, vol. 6, no., pp. 7 37, Jan. 3. [3] Hui Liu, H. Daabi, P. Banejee, and Jing Liu, Suvey of wieless indoo positioning techniques and systems, IEEE Tans. on Systems, Man, and Cybenetics, Pat C: Applications and Reviews, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 67 8, Nov. 7. [4] Guang-Yao Jin, Xiao-Yi Lu, and Myong-Soon Pa, An indoo localization mechanism using active RFID tag, in Poc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Senso Netwos, Ubiquitous, and Tustwothy Computing, Taichung, Taiwan, Jun. 6, pp [5] S. Jain, A. Sabhawal, and S. Chanda, An impovised localization scheme using active fid fo accuate tacing in smat homes, in Poc. Int. Conf. on Compute Modelling and Simulation (UKSim), Cambidge, UK, Ma., pp [6] A. A. Nazai Shiehjini, A. Yassine, and S. Shimohammadi, An RFID-based position and oientation measuement system fo mobile objects in intelligent envionments, IEEE Tans. on Instumentation and Measuement, vol. 6, no. 6, pp , Jun.. [7] S. Pa and S. Hashimoto, Autonomous mobile obot navigation using passive RFID in indoo envionment, IEEE Tans. on Industial Electonics, vol. 56, no. 7, pp , Jul. 9. [8] V. Kulyuin, A. Kutiyanawala, E. LoPesti, J. Matthews, and R. Simpson, iwale: Towad a ollato-mounted wayfinding system fo the eldely, in Poc. IEEE Int. Conf. on RFID, Las Vegas, NV, USA, Ap. 8, pp [9] D. Macii, A. Boni, M. De Cecco, and D. Peti, Tutoial 4: multisenso data fusion, IEEE Instumentation Measuement Magazine, vol., no. 3, pp. 4 33, Jun. 8. [] L. Klingbeil, M. Romanovas, P. Schneide, M. Taechtle, and Y. Manoli, A modula and mobile system fo indoo localization, in Poc. Int. Conf. on Indoo Positioning and Indoo Navigation (IPIN), Zuich, Switzeland, Sep., pp.. [] A. Colombo, D. Fontanelli, D. Macii, and L. Palopoli, A Weaable Embedded Inetial Platfom with Wieless Connectivity fo Indoo Position Tacing, in Poc. IEEE Intl. Instumentation and Measuement Technology Confeence (IMTC), Hangzhou, China, May, pp. 6. [] Byoung-Su Choi, Joon-Woo Lee, and Ju-Jang Lee, Localization and map-building of mobile obot based on RFID senso fusion system, in Poc. Intenational Confeence on Industial Infomatics (INDIN), Daejeon, Koea, Jul. 8, pp [3] Byoung-Su Choi and Ju-Jang Lee, Senso netwo based localization algoithm using fusion senso-agent fo indoo sevice obot, IEEE Tans. on Consume Electonics, vol. 56, no. 3, pp , Aug.. [4] Byoung-Su Choi, Joon-Woo Lee, Ju-Jang Lee, and Kyoung-Tai Pa, A hieachical algoithm fo indoo mobile obot localization using RFID senso fusion, IEEE Tans. on Industial Electonics, vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 6 35, Jun.. [5] M. Ibaheem, Gyoscope-enhanced dead econing localization system fo an intelligent wale, in Poc.Int. Conf. on Infomation Netwoing and Automation (ICINA), vol., Kunming, China, Oct., pp. V 67 V 7. [6] H. Wang, C.-U. Kang, T. Ishimatsu, and T. Ochiai, Auto-navigation of a wheelchai, Atificial Life and Robotics, vol., no. 3, pp. 4 46, Sep [7] P. Nazemzadeh, D. Fontanelli, and D. Macii, An Indoo Position Tacing Technique based on Data Fusion fo Ambient Assisted Living, in Poc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Computational Intelligence and Vitual Envionments fo Measuement Systems and Applications (CIVEMSA), Milan, Italy, Jul. 3, pp. 7. [8] F. Evennou and F. Max, Advanced integation of WIFI and inetial navigation systems fo indoo mobile positioning, EURASIP Jounal Appl. Signal Pocess., vol. 6, pp , Jan. 6. [9] P. Jensfelt, D. Kagic, J. Folesson, and M. Bjoman, A famewo fo vision based beaing only 3D SLAM, in Poc. IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Olando, FL, USA, May 6, pp [3] T. Lemaie, S. Lacoix, and J. Sola, A pactical 3d beaing-only SLAM algoithm, in Poc. Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Edmonton, Albeta, Canada, Aug. 5, pp [3] P. Heny, M. Kainin, E. Hebst, X. Ren, and D. Fox, RGB-D mapping: Using Kinect-style depth cameas fo dense 3D modeling of indoo envionments, The intenational Jounal of Robotics Reseach, vol. 3, no. 5, pp , Ap.. [3] D. Coea, D. Sciotti, M. Pado, D. Sales, D. Wolf, and F. Osoio, Mobile obots navigation in indoo envionments using inect senso, in Poc. nd Bazilian Confeence on Citical Embedded Systems (CBSEC), Campinas, São Paulo, Bazil, May, pp [33] T. K. Y. Ba-Shalom, X. Rong Li, Estimation with Application to Tacing and Navigation Theoy, Algoithm and Softwae. John. Wiley and Sons,. [34] R. A. Boos and T. Lozano-Peez, A subdivision algoithm in configuation space fo findpath with otation, IEEE Tans. on Systems, Man and Cybenetics, vol. SMC-5, no., pp. 4 33, Ma. Ap [35] S. Obdzale, G. Kuillo, F. Ofli, R. Bajcsy, E. Seto, H. Jimison, and M. Pavel, Accuacy and obustness of inect pose estimation in the context of coaching of eldely population, in Poc. Annual Int. Conf. of the IEEE Engineeing in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), San Diego, CA, USA, Aug.-Sep., pp [36] J. Han, L. Shao, D. Xu, and J. Shotton, Enhanced compute vision with micosoft inect senso: A eview, IEEE Tans. on Cybenetics, vol. 43, no. 5, pp , Oct. 3.
where and are polynomials with real coefficients and of degrees m and n, respectively. Assume that and have no zero on axis.
 function whee is an unknown constant epesents fo the un-modeled dynamics The pape investigates the position contol of electical moto dives that can be configued as stuctue of Fig 1 This poblem is fomulated
function whee is an unknown constant epesents fo the un-modeled dynamics The pape investigates the position contol of electical moto dives that can be configued as stuctue of Fig 1 This poblem is fomulated
Low-Complexity Time-Domain SNR Estimation for OFDM Systems
 Low-Complexity Time-Domain SR Estimation fo OFDM Systems A. jaz, A.B. Awoseyila and B.G. Evans A low-complexity SR estimation algoithm fo OFDM systems in fequency-selective fading channels is poposed.
Low-Complexity Time-Domain SR Estimation fo OFDM Systems A. jaz, A.B. Awoseyila and B.G. Evans A low-complexity SR estimation algoithm fo OFDM systems in fequency-selective fading channels is poposed.
Localization Algorithm for a mobile robot using igs
 Poceedings of the 17th Wold Congess The Intenational Fedeation of Automatic Contol Seoul, Koea, July 6-11, 008 Localization Algoithm fo a mobile obot using igs DaeGeun Seo *, JangMyung Lee** * Electical
Poceedings of the 17th Wold Congess The Intenational Fedeation of Automatic Contol Seoul, Koea, July 6-11, 008 Localization Algoithm fo a mobile obot using igs DaeGeun Seo *, JangMyung Lee** * Electical
Parameters of spinning AM reticles
 Paametes of spinning AM eticles onald G. Digges, Cal E. Halfod, and Glenn D. Boeman A new method of obtaining amplitude modulation (AM) fo detemining taget location with spinning eticles is pesented. The
Paametes of spinning AM eticles onald G. Digges, Cal E. Halfod, and Glenn D. Boeman A new method of obtaining amplitude modulation (AM) fo detemining taget location with spinning eticles is pesented. The
Design of A Circularly Polarized E-shaped Patch Antenna with Enhanced Bandwidth for 2.4 GHz WLAN Applications
 VNU Jounal of Science: Comp. Science & Com. Eng., Vol. 31, No. 2 (2015) 1-7 Design of A Ciculaly Polaized E-shaped Patch Antenna with Enhanced Bandwidth fo 2.4 GHz WLAN Applications Hong Van Tam 1, Luong
VNU Jounal of Science: Comp. Science & Com. Eng., Vol. 31, No. 2 (2015) 1-7 Design of A Ciculaly Polaized E-shaped Patch Antenna with Enhanced Bandwidth fo 2.4 GHz WLAN Applications Hong Van Tam 1, Luong
Demosaicking using Adaptive Bilateral Filters
 Demosaicking using Adaptive Bilateal Filtes Ekine Akuiyibo Timothy Atobatele EE 362, Winte 2006 0. Abstact Digital cameas sample the continuous spectum using an aay of colo filtes such that each pixel
Demosaicking using Adaptive Bilateal Filtes Ekine Akuiyibo Timothy Atobatele EE 362, Winte 2006 0. Abstact Digital cameas sample the continuous spectum using an aay of colo filtes such that each pixel
Figure Geometry for Computing the Antenna Parameters.
 Spheical Coodinate Systems Definitions Figue 1.2.1 Geomety fo Computing the Antenna Paametes. Antenna Radiation Patten: The distibution of adiated enegy fom an antenna ove a suface of constant adius centeed
Spheical Coodinate Systems Definitions Figue 1.2.1 Geomety fo Computing the Antenna Paametes. Antenna Radiation Patten: The distibution of adiated enegy fom an antenna ove a suface of constant adius centeed
Published in: International Journal of Material Forming. Document Version: Peer reviewed version
 A Vitual Inspection Technique fo Assessing the Dimensional Accuacy of Foged Compesso Blades Using FE Modeling and CMM Inspection Makem, J., Ou, H., Amstong, C., Rennie, A., & Nikov, S. (2008). A Vitual
A Vitual Inspection Technique fo Assessing the Dimensional Accuacy of Foged Compesso Blades Using FE Modeling and CMM Inspection Makem, J., Ou, H., Amstong, C., Rennie, A., & Nikov, S. (2008). A Vitual
Optimal Design of Smart Mobile Terminal Antennas for Wireless Communication and Computing Systems
 Optimal Design of Smat Mobile Teminal Antennas fo Wieless Communication and Computing Systems Autho Lu, Junwei, Yang, Shiyou Published 2007 Confeence Title 2007 4th Intenational Symposium on Electomagnetic
Optimal Design of Smat Mobile Teminal Antennas fo Wieless Communication and Computing Systems Autho Lu, Junwei, Yang, Shiyou Published 2007 Confeence Title 2007 4th Intenational Symposium on Electomagnetic
UNCERTAINTY ESTIMATION OF SIZE-OF-SOURCE EFFECT MEASUREMENT FOR 650 NM RADIATION THERMOMETERS
 XIX IMEKO Wold Congess Fundamental and Applied Metology Septembe 6 11, 29, Lisbon, Potugal UNCERTAINTY ESTIMATION OF SIZE-OF-SOURCE EFFECT MEASUREMENT FOR 65 NM RADIATION THERMOMETERS Fumihio Sakuma, Laina
XIX IMEKO Wold Congess Fundamental and Applied Metology Septembe 6 11, 29, Lisbon, Potugal UNCERTAINTY ESTIMATION OF SIZE-OF-SOURCE EFFECT MEASUREMENT FOR 65 NM RADIATION THERMOMETERS Fumihio Sakuma, Laina
PERFORMANCE OF TOA ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES IN INDOOR MULTIPATH CHANNELS
 PERFORMANCE OF TOA ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES IN INDOOR MULTIPATH CHANNELS Xinong Li, Kaveh Pahlavan, and Jacques Beneat Cente fo Wiele Infomation Netwo Studies Electical and Compute Engineeing Depatment, Woceste
PERFORMANCE OF TOA ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES IN INDOOR MULTIPATH CHANNELS Xinong Li, Kaveh Pahlavan, and Jacques Beneat Cente fo Wiele Infomation Netwo Studies Electical and Compute Engineeing Depatment, Woceste
Design of Microstrip Antenna for Wireless Local Area Network
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com Intenational Jounal of Compute Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Jounal of Compute Science and Infomation Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 4, Apil 205, pg.36 365
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com Intenational Jounal of Compute Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Jounal of Compute Science and Infomation Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 4, Issue. 4, Apil 205, pg.36 365
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 1 Due on Nov. 8, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes. ii)
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 1 Due on Nov. 8, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes. ii)
N2-1. The Voltage Source. V = ε ri. The Current Source
 DC Cicuit nalysis The simplest cicuits to undestand and analyze ae those that cay diect cuent (DC). n this note we continue ou study of DC cicuits with the topics of DC voltage and cuent souces, the idea
DC Cicuit nalysis The simplest cicuits to undestand and analyze ae those that cay diect cuent (DC). n this note we continue ou study of DC cicuits with the topics of DC voltage and cuent souces, the idea
AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD
 ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Inteface Pactices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 48-1 2015 Test Method fo Measuing Shielding Effectiveness of Passive and Active Devices Using a GTEM Cell NOTICE
ENGINEERING COMMITTEE Inteface Pactices Subcommittee AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD ANSI/SCTE 48-1 2015 Test Method fo Measuing Shielding Effectiveness of Passive and Active Devices Using a GTEM Cell NOTICE
Near-field Computation and. Uncertainty Estimation using Basic. Cylindrical-Spherical Formulae
 Nea-field Computation and Uncetainty Estimation using Basic Cylindical-Spheical Fomulae Poject... IEC 63 Subject... Basic Nea-Field Computation Document numbe... N/A Revision... 3 Autho... F.D. du Plessis
Nea-field Computation and Uncetainty Estimation using Basic Cylindical-Spheical Fomulae Poject... IEC 63 Subject... Basic Nea-Field Computation Document numbe... N/A Revision... 3 Autho... F.D. du Plessis
Design of FIR Filter using Filter Response Masking Technique
 Design of FIR Filte using Filte Response Masking Technique Sandeep Shivastava, Alok Jain, Ram Kuma Soni Abstact- In this pape autho is tying to implement Fequency esponse masking (FRM) technique. In this
Design of FIR Filte using Filte Response Masking Technique Sandeep Shivastava, Alok Jain, Ram Kuma Soni Abstact- In this pape autho is tying to implement Fequency esponse masking (FRM) technique. In this
Analysis of a Fractal Microstrip Patch Antenna
 124 Analysis of a Factal Micostip Patch Antenna Vibha Rani Gupta and Nisha Gupta* Bila Institute of Technology, Mesa, Ranchi-835215, Jhakhand, India. vgupta@bitmesa.ac.in, ngupta@bitmesa.ac.in Abstact-
124 Analysis of a Factal Micostip Patch Antenna Vibha Rani Gupta and Nisha Gupta* Bila Institute of Technology, Mesa, Ranchi-835215, Jhakhand, India. vgupta@bitmesa.ac.in, ngupta@bitmesa.ac.in Abstact-
Multiagent Reinforcement Learning Dynamic Spectrum Access in Cognitive Radios
 Sensos & Tansduces 204 by IFSA Publishing, S L http://wwwsensospotalcom Multiagent Reinfocement Leaning Dynamic Spectum Access in Cognitive Radios Wu Chun, 2 Yin Mingyong, 2 Ma Shaoliang, Jiang Hong School
Sensos & Tansduces 204 by IFSA Publishing, S L http://wwwsensospotalcom Multiagent Reinfocement Leaning Dynamic Spectum Access in Cognitive Radios Wu Chun, 2 Yin Mingyong, 2 Ma Shaoliang, Jiang Hong School
IAS 2.4. Year 12 Mathematics. Contents. Trigonometric Relationships. ulake Ltd. Robert Lakeland & Carl Nugent
 Yea 12 Mathematics IS 2.4 Tigonometic Relationships Robet Lakeland & al Nugent ontents chievement Standad.................................................. 2 icula Measue.......................................................
Yea 12 Mathematics IS 2.4 Tigonometic Relationships Robet Lakeland & al Nugent ontents chievement Standad.................................................. 2 icula Measue.......................................................
Anti-Forensics of Chromatic Aberration
 Anti-Foensics of Chomatic Abeation Owen Maye and Matthew C. Stamm Dept. of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Dexel Univesity, Philadelphia, PA, USA ABSTRACT Ove the past decade, a numbe of infomation foensic
Anti-Foensics of Chomatic Abeation Owen Maye and Matthew C. Stamm Dept. of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Dexel Univesity, Philadelphia, PA, USA ABSTRACT Ove the past decade, a numbe of infomation foensic
HYBRID FUZZY PD CONTROL OF TEMPERATURE OF COLD STORAGE WITH PLC
 Jounal of Theoetical and Applied Infomation Technology 28 th Febuay 2013. Vol. 48 No.3 2005-2013 JATIT & LLS. All ights eseved. ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.og E-ISSN: 1817-3195 HYBRID FUZZY PD CONTROL OF
Jounal of Theoetical and Applied Infomation Technology 28 th Febuay 2013. Vol. 48 No.3 2005-2013 JATIT & LLS. All ights eseved. ISSN: 1992-8645 www.jatit.og E-ISSN: 1817-3195 HYBRID FUZZY PD CONTROL OF
Investigation. Name: a About how long would the threaded rod need to be if the jack is to be stored with
 Think Unit bout 6 This Lesson Situation 1 Investigation 1 Name: Think about the design and function of this automobile jack. Use the uto Jack custom tool to test ou ideas. a bout how long would the theaded
Think Unit bout 6 This Lesson Situation 1 Investigation 1 Name: Think about the design and function of this automobile jack. Use the uto Jack custom tool to test ou ideas. a bout how long would the theaded
MIMO OTA Testing in Small Multi-Probe Anechoic Chamber Setups Llorente, Ines Carton; Fan, Wei; Pedersen, Gert F.
 Aalbog Univesitet MIMO OTA Testing in Small Multi-Pobe Anechoic Chambe Setups Lloente, Ines Caton; Fan, Wei; Pedesen, Get F. Published in: I E E E Antennas and Wieless Popagation Lettes DOI (link to publication
Aalbog Univesitet MIMO OTA Testing in Small Multi-Pobe Anechoic Chambe Setups Lloente, Ines Caton; Fan, Wei; Pedesen, Get F. Published in: I E E E Antennas and Wieless Popagation Lettes DOI (link to publication
The Periodic Ambiguity Function Its Validity and Value
 The Peiodic Ambiguity Function Its Validity and Value Nadav Levanon Dept. of Electical Engineeing Systems Tel Aviv Univesity Tel Aviv, Isael nadav@eng.tau.ac.il Abstact The peiodic ambiguity function (PAF)
The Peiodic Ambiguity Function Its Validity and Value Nadav Levanon Dept. of Electical Engineeing Systems Tel Aviv Univesity Tel Aviv, Isael nadav@eng.tau.ac.il Abstact The peiodic ambiguity function (PAF)
Chamber Influence Estimation for Radiated Emission Testing in the Frequency Range of 1 GHz to 18 GHz
 Chambe Influence Estimation fo Radiated Emission Testing in the Fequency Range of 1 GHz to 18 GHz Alexande Kiz Electomagnetic Compatibility and RF-Engineeing ARC eibesdof eseach GmbH eibesdof, Austia alexande.kiz@acs.ac.at
Chambe Influence Estimation fo Radiated Emission Testing in the Fequency Range of 1 GHz to 18 GHz Alexande Kiz Electomagnetic Compatibility and RF-Engineeing ARC eibesdof eseach GmbH eibesdof, Austia alexande.kiz@acs.ac.at
GAMMA SHAPED MONOPOLE PATCH ANTENNA FOR TABLET PC
 GAMMA SHAPED MONOPOLE PATCH ANTENNA FOR TABLET PC Islam Md. Rafiqul, Mohammad Shawkat Habib and Khaizuan Abdullah Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Intenational Islamic Univesity Malaysia,
GAMMA SHAPED MONOPOLE PATCH ANTENNA FOR TABLET PC Islam Md. Rafiqul, Mohammad Shawkat Habib and Khaizuan Abdullah Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Intenational Islamic Univesity Malaysia,
ScienceDirect. Simplified Generation of Electromagnetic Field within EMC Immunity Test Area
 Available online at www.sciencediect.com ScienceDiect Pocedia Engineeing 69 ( 014 ) 7 34 4th DAAAM Intenational Symposium on Intelligent Manufactuing and Automation, 013 Simplified Geneation of Electomagnetic
Available online at www.sciencediect.com ScienceDiect Pocedia Engineeing 69 ( 014 ) 7 34 4th DAAAM Intenational Symposium on Intelligent Manufactuing and Automation, 013 Simplified Geneation of Electomagnetic
1 Performance and Cost
 Pefomance and Cost Analysis and Reseach of Ai-Cooled Using Small Diamete Coppe Tubes Wu Yang, Li Changsheng and Deng Bin Abstact Replacing coppe tubes with aluminum tubes and using coppe tubes with smalle
Pefomance and Cost Analysis and Reseach of Ai-Cooled Using Small Diamete Coppe Tubes Wu Yang, Li Changsheng and Deng Bin Abstact Replacing coppe tubes with aluminum tubes and using coppe tubes with smalle
Antenna fundamentals: With answers to questions and problems (See also Chapter 9 in the textbook.)
 adio Technology Metopolia/A. Koivumäki Antenna fundamentals: With answes to questions and poblems (See also Chapte 9 in the textbook.) 1. a) Make up a definition fo the tem "antenna". Answe: One definition:
adio Technology Metopolia/A. Koivumäki Antenna fundamentals: With answes to questions and poblems (See also Chapte 9 in the textbook.) 1. a) Make up a definition fo the tem "antenna". Answe: One definition:
Realistic Simulation of a Wireless Signal Propagation in an Urban Environment
 Realistic Simulation of a Wieless Signal Popagation in an Uban Envionment Keyukuma J. Patel Univesity of Southen Queensland Toowoomba, Austalia e-mail: keyupatel@ieee.og Andew Y. J. Lee Nanyang Technological
Realistic Simulation of a Wieless Signal Popagation in an Uban Envionment Keyukuma J. Patel Univesity of Southen Queensland Toowoomba, Austalia e-mail: keyupatel@ieee.og Andew Y. J. Lee Nanyang Technological
NICKEL RELEASE REGULATIONS, EN 1811:2011 WHAT S NEW?
 NICKEL RELEASE REGULATIONS, EN 1811:2011 WHAT S NEW? BACKGROUND: EN 1811 is the intenationally ecognised test method which was devised almost 12 yeas ago to detemine the ate of nickel elease fom jewelley,
NICKEL RELEASE REGULATIONS, EN 1811:2011 WHAT S NEW? BACKGROUND: EN 1811 is the intenationally ecognised test method which was devised almost 12 yeas ago to detemine the ate of nickel elease fom jewelley,
PSO driven RBFNN for design of equilateral triangular microstrip patch antenna
 Indian Jounal of Radio & Space Physics Vol. 38, August 009, pp 33-37 PSO diven RBF fo design of equilateal tiangula micostip patch antenna Vidya Saga Chintakindi,$, Shyam Sunda Pattnaik,#,*, O P Bajpai
Indian Jounal of Radio & Space Physics Vol. 38, August 009, pp 33-37 PSO diven RBF fo design of equilateal tiangula micostip patch antenna Vidya Saga Chintakindi,$, Shyam Sunda Pattnaik,#,*, O P Bajpai
WIRELESS SENSORS EMBEDDED IN CONCRETE
 7th Euopean Wokshop on Stuctual Health Monitoing July 8-11, 2014. La Cité, Nantes, Fance Moe Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17296 WIRELESS SENSORS EMBEDDED IN CONCRETE Amal Abbadi 1 Phd Student,
7th Euopean Wokshop on Stuctual Health Monitoing July 8-11, 2014. La Cité, Nantes, Fance Moe Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17296 WIRELESS SENSORS EMBEDDED IN CONCRETE Amal Abbadi 1 Phd Student,
Design and Characterization of Conformal Microstrip Antennas Integrated into 3D Orthogonal Woven Fabrics
 Design and Chaacteization of Confomal Micostip Antennas Integated into 3D Othogonal Woven Fabics Xin Wang 1, Lan Yao 1, Fujun Xu 2, Dongchun Zhou 1, Yiping Qiu 1 1 College of Textiles, Donghua Univesity,
Design and Chaacteization of Confomal Micostip Antennas Integated into 3D Othogonal Woven Fabics Xin Wang 1, Lan Yao 1, Fujun Xu 2, Dongchun Zhou 1, Yiping Qiu 1 1 College of Textiles, Donghua Univesity,
VLSI Implementation of Low Complexity MIMO Detection Algorithms
 , Impact Facto :.643 eissn : 349-000 & pissn : 394-4544 Intenational Jounal of Reseach and Applications (Ap-Jun 015 Tansactions) (6): 309-313 Intenational Confeence on Emeging Tends in Electonics & Telecommunications
, Impact Facto :.643 eissn : 349-000 & pissn : 394-4544 Intenational Jounal of Reseach and Applications (Ap-Jun 015 Tansactions) (6): 309-313 Intenational Confeence on Emeging Tends in Electonics & Telecommunications
Discussion #7 Example Problem This problem illustrates how Fourier series are helpful tools for analyzing electronic circuits. Often in electronic
 Discussion #7 Example Poblem This poblem illustates how Fouie seies ae helpful tools fo analyzing electonic cicuits. Often in electonic cicuits we need sinusoids of vaious fequencies But we may aleady
Discussion #7 Example Poblem This poblem illustates how Fouie seies ae helpful tools fo analyzing electonic cicuits. Often in electonic cicuits we need sinusoids of vaious fequencies But we may aleady
A New Buck-Boost DC/DC Converter of High Efficiency by Soft Switching Technique
 A New Buck-Boost D/D onvete of High Efficiency by Soft Switching Technique Dong-Kul Kwak, Seung-Ho Lee, and Do-Young Jung Pofessional Gaduate School of Disaste Pevention, Kangwon National Univesity, 45-711,
A New Buck-Boost D/D onvete of High Efficiency by Soft Switching Technique Dong-Kul Kwak, Seung-Ho Lee, and Do-Young Jung Pofessional Gaduate School of Disaste Pevention, Kangwon National Univesity, 45-711,
Sliding Mode Control for Half-Wave Zero Current Switching Quasi-Resonant Buck Converter
 Sliding Mode Contol fo Half-Wave Zeo Cuent Switching Quasi-Resonant Buck Convete M. Ahmed, Student membe, IEEE, M. Kuisma, P. Silventoinen Abstact This pape focuses on the pactical implementation of sliding
Sliding Mode Contol fo Half-Wave Zeo Cuent Switching Quasi-Resonant Buck Convete M. Ahmed, Student membe, IEEE, M. Kuisma, P. Silventoinen Abstact This pape focuses on the pactical implementation of sliding
Efficient Power Control for Broadcast in Wireless Communication Systems
 Efficient Powe Contol fo Boadcast in Wieless Communication Systems A. T. Chonopoulos Compute Science Depatment Univesity of Texas at San Antonio San Antonio, TX Email:atc@cs.utsa.edu P. Cotae Depatment
Efficient Powe Contol fo Boadcast in Wieless Communication Systems A. T. Chonopoulos Compute Science Depatment Univesity of Texas at San Antonio San Antonio, TX Email:atc@cs.utsa.edu P. Cotae Depatment
Analysis of the optimized low-nonlinearity lateral effect sensing detector
 Jounal of hysics: Confeence Seies Analysis of the optimized low-nonlineaity lateal effect sensing detecto To cite this aticle: Saeed Olyaee et al J. hys.: Conf. Se. 76 4 Related content - Neual netwok
Jounal of hysics: Confeence Seies Analysis of the optimized low-nonlineaity lateal effect sensing detecto To cite this aticle: Saeed Olyaee et al J. hys.: Conf. Se. 76 4 Related content - Neual netwok
Hexagonal Shaped Microstrip Patch Antenna for Satellite and Military Applications
 Intenational Jounal of Engineeing and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 49 8958, Volume-7 Issue-5, June 08 Hexagonal Shaped Micostip Patch Antenna fo Satellite and Militay Applications Jayaenjini N, Unni
Intenational Jounal of Engineeing and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 49 8958, Volume-7 Issue-5, June 08 Hexagonal Shaped Micostip Patch Antenna fo Satellite and Militay Applications Jayaenjini N, Unni
The Experimental Study of Possibility for Radar Target Detection in FSR Using L1-Based Non-Cooperative Transmitter
 The Expeimental Study of Possibility fo Rada Taget Detection in FSR Using L1-Based on-coopeative Tansmitte Ch. Kabakchiev 1, I. Gavanov, V. Beha 3, H. Rohling 4 1 Faculty of Mathematics & Infomatics,Sofia
The Expeimental Study of Possibility fo Rada Taget Detection in FSR Using L1-Based on-coopeative Tansmitte Ch. Kabakchiev 1, I. Gavanov, V. Beha 3, H. Rohling 4 1 Faculty of Mathematics & Infomatics,Sofia
INVESTIGATION OF CLOSE-TO-WALL WIRELESS SENSOR DEPLOYMENT USING 2D FINITE-DIFFERENCE TIME-DOMAIN MODELLING. Y. Wu and I. J.
 2 nd Intenational Confeence on Wieless Communications in Undegound and Confined Aeas August 25-27, 2008 Val-d O - Québec - Canada INVESTIGATION OF CLOSE-TO-WALL WIRELESS SENSOR DEPLOYMENT USING 2D FINITE-DIFFERENCE
2 nd Intenational Confeence on Wieless Communications in Undegound and Confined Aeas August 25-27, 2008 Val-d O - Québec - Canada INVESTIGATION OF CLOSE-TO-WALL WIRELESS SENSOR DEPLOYMENT USING 2D FINITE-DIFFERENCE
An Efficient Control Approach for DC-DC Buck-Boost Converter
 2016 Published in 4th Intenational Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineeing and Science 3-5 Novembe 2016 (ISITES2016 Alanya/Antalya - Tukey) An Efficient Contol Appoach fo DC-DC Buck-Boost Convete
2016 Published in 4th Intenational Symposium on Innovative Technologies in Engineeing and Science 3-5 Novembe 2016 (ISITES2016 Alanya/Antalya - Tukey) An Efficient Contol Appoach fo DC-DC Buck-Boost Convete
Cyclic Constellation Mapping Method for PAPR Reduction in OFDM system
 2013 8th Intenational Confeence on Communications and Netwoking in China (CHINACOM) Cyclic Constellation Mapping Method fo PAPR Reduction in OFDM system Yong Cheng, Jianhua Ge, Jun Hou, and Fengkui Gong
2013 8th Intenational Confeence on Communications and Netwoking in China (CHINACOM) Cyclic Constellation Mapping Method fo PAPR Reduction in OFDM system Yong Cheng, Jianhua Ge, Jun Hou, and Fengkui Gong
Comparison Between Known Propagation Models Using Least Squares Tuning Algorithm on 5.8 GHz in Amazon Region Cities
 106 Compaison Between Known Popagation Models Using Least Squaes Tuning Algoithm on 5.8 GHz in Amazon Region Cities Buno S. L. Casto, Mácio R. Pinheio, Gevásio P. S. Cavalcante Fedeal Univesity of Paá
106 Compaison Between Known Popagation Models Using Least Squaes Tuning Algoithm on 5.8 GHz in Amazon Region Cities Buno S. L. Casto, Mácio R. Pinheio, Gevásio P. S. Cavalcante Fedeal Univesity of Paá
PPP-RTK PLATFORM PERFORMANCE BASED ON SINGLE-FREQUENCY GPS DATA
 PPP-RTK PLATFORM PERFORMANCE BASED ON SINGLE-FREQUENCY GPS DATA Dennis Odik *, Pete J.G. Teunissen, and Baocheng Zhang Reseach Fellow, GNSS Reseach Cente, Depatment of Spatial Sciences, Cutin Univesity,
PPP-RTK PLATFORM PERFORMANCE BASED ON SINGLE-FREQUENCY GPS DATA Dennis Odik *, Pete J.G. Teunissen, and Baocheng Zhang Reseach Fellow, GNSS Reseach Cente, Depatment of Spatial Sciences, Cutin Univesity,
Ubiquitous Sensory Intelligence
 Ubiquitous Sensoy Intelligence Péte Koondi, Péte Szemes and Hideki Hashimoto Integated Intelligent Systems Japanese-Hungaian Joint Laboatoy Univesity of Tokyo, Komaba 4-6-1, Meguo-ku, Tokyo, JAPAN 153-8505
Ubiquitous Sensoy Intelligence Péte Koondi, Péte Szemes and Hideki Hashimoto Integated Intelligent Systems Japanese-Hungaian Joint Laboatoy Univesity of Tokyo, Komaba 4-6-1, Meguo-ku, Tokyo, JAPAN 153-8505
Experimental Investigation of Influence on Non-destructive Testing by Form of Eddy Current Sensor Probe
 Expeimental Investigation of Influence on Non-destuctive Testing by Fom of Eddy Cuent Senso Pobe Fengyun Xie * and Jihui Zhou School of Mechanical and Electonical Engineeing, East China Jiaotong Univesity,
Expeimental Investigation of Influence on Non-destuctive Testing by Fom of Eddy Cuent Senso Pobe Fengyun Xie * and Jihui Zhou School of Mechanical and Electonical Engineeing, East China Jiaotong Univesity,
ISSN: [Reddy & Rao* et al., 5(12): December, 2016] Impact Factor: 4.116
![ISSN: [Reddy & Rao* et al., 5(12): December, 2016] Impact Factor: 4.116 ISSN: [Reddy & Rao* et al., 5(12): December, 2016] Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/95/122747775.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY SIMULATION COMPARISONS OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE WITH ESTIMATOR AND PLL V. Nasi Reddy *, S. Kishnajuna Rao*, S.Nagenda Kuma * Assistant
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY SIMULATION COMPARISONS OF INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE WITH ESTIMATOR AND PLL V. Nasi Reddy *, S. Kishnajuna Rao*, S.Nagenda Kuma * Assistant
Key Laboratory of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, China Earthquake Administration, China
 Shake Table Test fo Lage Indiect-Ai-Cooling Towe Stuctue of Fie Powe Plant Pat I Junwu DAI, Yongqiang YANG & Xuan WNG Key Laboatoy of athquake ngineeing and ngineeing Vibation, China athquake Administation,
Shake Table Test fo Lage Indiect-Ai-Cooling Towe Stuctue of Fie Powe Plant Pat I Junwu DAI, Yongqiang YANG & Xuan WNG Key Laboatoy of athquake ngineeing and ngineeing Vibation, China athquake Administation,
DESIGN AND PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF RECTANGULAR MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA FOR GSM APPLICATION
 DESIGN AND PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF RECTANGULAR MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA FOR GSM APPLICATION RAHUL T. DAHATONDE, SHANKAR B. DEOSARKAR Dept. of E & TC, D. Babasaheb Ambedka Technological Univesity, Lonee,
DESIGN AND PARAMETRIC EVALUATION OF RECTANGULAR MICROSTRIP PATCH ANTENNA FOR GSM APPLICATION RAHUL T. DAHATONDE, SHANKAR B. DEOSARKAR Dept. of E & TC, D. Babasaheb Ambedka Technological Univesity, Lonee,
A New Method of VHF Antenna Gain Measurement Based on the Two-ray Interference Loss
 7 nd Intenational Confeence on Atificial Intelligence and Engineeing Applications (AIEA 7) ISBN: 978--6595-485- A New Method of VH Antenna Gain Measuement Based on the Two-ay Intefeence Loss ZHIEI YANG,
7 nd Intenational Confeence on Atificial Intelligence and Engineeing Applications (AIEA 7) ISBN: 978--6595-485- A New Method of VH Antenna Gain Measuement Based on the Two-ay Intefeence Loss ZHIEI YANG,
Absolute calibration of null correctors using twin computer-generated holograms
 Absolute calibation of null coectos using twin compute-geneated hologams Poteep C.V. Mallik a, Rene Zehnde a, James H. Buge a, Alexande Poleshchuk b a College of Optical Sciences, The Univesity of Aizona,
Absolute calibation of null coectos using twin compute-geneated hologams Poteep C.V. Mallik a, Rene Zehnde a, James H. Buge a, Alexande Poleshchuk b a College of Optical Sciences, The Univesity of Aizona,
Small Loop Antenna and Duality Theorem
 Small Loop Antenna and Duality Theoem Page 1 Small Loop Antenna and Duality Theoem Having studied the ideal electic dipole we now tun ou attention to an inteesting antenna closely elated to the electic
Small Loop Antenna and Duality Theoem Page 1 Small Loop Antenna and Duality Theoem Having studied the ideal electic dipole we now tun ou attention to an inteesting antenna closely elated to the electic
Spectrum Sharing between Public Safety and Commercial Users in 4G-LTE
 1 Spectum Shaing between Public Safety and Commecial Uses in 4G-LTE Haya Shajaiah, Ahmed Abdel-Hadi and Chales Clancy Badley Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing Viginia Tech, Alington, VA, 22203,
1 Spectum Shaing between Public Safety and Commecial Uses in 4G-LTE Haya Shajaiah, Ahmed Abdel-Hadi and Chales Clancy Badley Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing Viginia Tech, Alington, VA, 22203,
THE USE OF WAVELETS FOR NOISE DETECTION IN THE IMAGES TAKEN BY THE ANALOG AND DIGITAL PHOTOGRAMMETRIC CAMERAS
 THE USE OF WAVELETS FO NOISE DETECTION IN THE IMAGES TAKEN BY THE ANALOG AND DIGITAL PHOTOGAMMETIC CAMEAS K. Pyka a, *, J. Siedlik b a Depatment of Geoinfomation, Photogammety and emote Sensing of Envionment
THE USE OF WAVELETS FO NOISE DETECTION IN THE IMAGES TAKEN BY THE ANALOG AND DIGITAL PHOTOGAMMETIC CAMEAS K. Pyka a, *, J. Siedlik b a Depatment of Geoinfomation, Photogammety and emote Sensing of Envionment
The Marginal Utility of Cooperation in Sensor Networks
 e Maginal Utility of Coopeation in Senso Netwoks Yu-Ching Tong, Geg Pottie Depatment of Electical Engineeing Univesity of Califonia, Los Angeles Los Angeles, Califonia 99 Email: yuching@ee.ucla.edu, pottie@icsl.ucla.edu
e Maginal Utility of Coopeation in Senso Netwoks Yu-Ching Tong, Geg Pottie Depatment of Electical Engineeing Univesity of Califonia, Los Angeles Los Angeles, Califonia 99 Email: yuching@ee.ucla.edu, pottie@icsl.ucla.edu
4 Trigonometric and Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 MATH983/954 Mathematics 0C/C. Geneal infomation fo the academic yea 0-03: Lectue: D Theodoe Voonov, Room.09, School of Mathematics, Alan Tuing Building, email: theodoe.voonov@mancheste.ac.uk. Lectues:
MATH983/954 Mathematics 0C/C. Geneal infomation fo the academic yea 0-03: Lectue: D Theodoe Voonov, Room.09, School of Mathematics, Alan Tuing Building, email: theodoe.voonov@mancheste.ac.uk. Lectues:
Optimization of the law of variation of shunt regulator impedance for Proximity Contactless Smart Card Applications to reduce the loading effect.
 Optimization of the law of vaiation of shunt egulato impedance fo Poximity Contactless Smat Cad Applications to educe the loading effect. Catheine Maechal, Dominique Paet. Laboatoie LIT ESIGETEL, ue du
Optimization of the law of vaiation of shunt egulato impedance fo Poximity Contactless Smat Cad Applications to educe the loading effect. Catheine Maechal, Dominique Paet. Laboatoie LIT ESIGETEL, ue du
Coarse Initial Orbit Determination for a Geostationary Satellite Using Single-Epoch GPS Measurements
 Sensos 15, 15, 7878-7897; doi:1.339/s157878 Aticle OPEN ACCESS sensos ISSN 1-8 www.mdpi.com/jounal/sensos Coase Initial Obit Detemination fo a Geostationay Satellite Using Single-Epoch GPS Measuements
Sensos 15, 15, 7878-7897; doi:1.339/s157878 Aticle OPEN ACCESS sensos ISSN 1-8 www.mdpi.com/jounal/sensos Coase Initial Obit Detemination fo a Geostationay Satellite Using Single-Epoch GPS Measuements
Discrepancies Between Euclidean and Spherical Trigonometry. David Eigen
 Discepancies Between Euclidean and Spheical Tigonomety David Eigen 1 Non-Euclidean geomety is geomety that is not based on the postulates of Euclidean geomety. The five postulates of Euclidean geomety
Discepancies Between Euclidean and Spheical Tigonomety David Eigen 1 Non-Euclidean geomety is geomety that is not based on the postulates of Euclidean geomety. The five postulates of Euclidean geomety
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 100 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencediect.com ScienceDiect Pocedia Engineeing 1 (215 ) 1 14 25th DAAAM Intenational Symposium on Intelligent Manufactuing and Automation DAAAM 214 Measuement of Complex Pemittivity
Available online at www.sciencediect.com ScienceDiect Pocedia Engineeing 1 (215 ) 1 14 25th DAAAM Intenational Symposium on Intelligent Manufactuing and Automation DAAAM 214 Measuement of Complex Pemittivity
cos s Presentation Layout HIGH ACCURACY REAL-TIME DAM MONITORING USING LOW COST GPS EQUIPMENT
 HIGH ACCURACY REAL-TIME DAM MONITORING USING LOW COST GPS EQUIPMENT Pesentation Layout GPS in Engineeing Monitoing. GPS Caie Phase Multipath Eo Multipath Sideeal-day Coection Technique Poposed Technique
HIGH ACCURACY REAL-TIME DAM MONITORING USING LOW COST GPS EQUIPMENT Pesentation Layout GPS in Engineeing Monitoing. GPS Caie Phase Multipath Eo Multipath Sideeal-day Coection Technique Poposed Technique
CCSDS Coding&Synchronization Working Group March Washington DC, USA SLS-C&S_08-CNES02
 CCSDS Coding&Synchonization Woking Goup Mach 2008 1 Washington DC, USA DVB-S2 like fame constuction and LDPC codes ate o/and size extension fo use of Vaiable Coding & Modulation suitable fo X and Ka bands
CCSDS Coding&Synchonization Woking Goup Mach 2008 1 Washington DC, USA DVB-S2 like fame constuction and LDPC codes ate o/and size extension fo use of Vaiable Coding & Modulation suitable fo X and Ka bands
A Walking Beacon-Assisted Localization in Wireless Sensor Networks
 This full text pape was pee eviewed at the diection of IEEE Communications Society subject matte expets fo publication in the ICC 007 poceedings. A Walking Beacon-Assisted Localization in Wieless Senso
This full text pape was pee eviewed at the diection of IEEE Communications Society subject matte expets fo publication in the ICC 007 poceedings. A Walking Beacon-Assisted Localization in Wieless Senso
A Gain Measurement in the Liquid Based on Friis Transmission Formula in the Near-Field Region
 A Gain Measuement in the Liquid Based on Fiis Tansmission Fomula in the Nea-Field Region # Takuhei Akagawa 1, Nozomu Ishii 2,3, Ken-ichi Sato 4, Lia Hamada 3 and Soichi Watanabe 3 1 Gaduate School of Science
A Gain Measuement in the Liquid Based on Fiis Tansmission Fomula in the Nea-Field Region # Takuhei Akagawa 1, Nozomu Ishii 2,3, Ken-ichi Sato 4, Lia Hamada 3 and Soichi Watanabe 3 1 Gaduate School of Science
ABSTRACTT FFT FFT-' Proc. of SPIE Vol U-1
 Phase econstuction stategies in phase-locking system based on multi-apetue wave font sensos P.A. Semenov, S.D. Pol skikh Shvabe-Reseach, Moscow, Russian Fedeation; e-mail: pite@bk.u ABSTRACTT System of
Phase econstuction stategies in phase-locking system based on multi-apetue wave font sensos P.A. Semenov, S.D. Pol skikh Shvabe-Reseach, Moscow, Russian Fedeation; e-mail: pite@bk.u ABSTRACTT System of
Signal Extraction Technology
 Extaction Technology Intoduction Masimo SET pulse oximety is a new and fundamentally distinct method of acquiing, pocessing and epoting ateial oxygen satuation and pulse ate. As illustated below, Masimo
Extaction Technology Intoduction Masimo SET pulse oximety is a new and fundamentally distinct method of acquiing, pocessing and epoting ateial oxygen satuation and pulse ate. As illustated below, Masimo
Electrical characterization of thin film ferroelectric capacitors
 1 Electical chaacteization of thin film feoelectic capacitos M. P. J. Tiggelman, K. Reimann, M. Klee, D. Beelen, W. Keu, J. Schmitz, and R. J. E. Hueting Abstact Tunable capacitos can be used to facilitate
1 Electical chaacteization of thin film feoelectic capacitos M. P. J. Tiggelman, K. Reimann, M. Klee, D. Beelen, W. Keu, J. Schmitz, and R. J. E. Hueting Abstact Tunable capacitos can be used to facilitate
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS VTU RESULTS FORUM BOOKSPAR ANDROID APP UNIT-4
 NTENN & PROPGTION 6EC6 1EC6 UNIT- Unit : Loop and Hon ntenna: Intoduction, small loop, compaison of fa field of small loop and shot dipole, loop antenna geneal case, fa field pattens of cicula loop, adiation
NTENN & PROPGTION 6EC6 1EC6 UNIT- Unit : Loop and Hon ntenna: Intoduction, small loop, compaison of fa field of small loop and shot dipole, loop antenna geneal case, fa field pattens of cicula loop, adiation
Optic Cable Tracking and Positioning Method Based on Distributed Optical Fiber Vibration Sensing
 08 5th Intenational Confeence on Electical & Electonics Engineeing and Compute Science (ICEEECS 08) Optic Cable Tacking and Positioning Method Based on Distibuted Optical Fibe Vibation Sensing Zhang Chao,
08 5th Intenational Confeence on Electical & Electonics Engineeing and Compute Science (ICEEECS 08) Optic Cable Tacking and Positioning Method Based on Distibuted Optical Fibe Vibation Sensing Zhang Chao,
Wireless Communication (Subject Code: 7EC3)
 COMPUCOM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT, JAIPUR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION) Notes Wieless Communication (Subject Code: 7EC3) Pepaed By: LOKESH KUMAR ARYA Class: B. Tech. IV Yea, VII
COMPUCOM INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT, JAIPUR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION) Notes Wieless Communication (Subject Code: 7EC3) Pepaed By: LOKESH KUMAR ARYA Class: B. Tech. IV Yea, VII
On Reducing Blocking Probability in Cooperative Ad-hoc Networks
 On educing Blocking Pobability in Coopeative Ad-hoc Netwoks Ayda Basyouni, Walaa Hamouda ept of Electical and Compute Engineeing Concodia Univesity, Monteal, Canada Email: {a basy,hamouda}@ececoncodiaca
On educing Blocking Pobability in Coopeative Ad-hoc Netwoks Ayda Basyouni, Walaa Hamouda ept of Electical and Compute Engineeing Concodia Univesity, Monteal, Canada Email: {a basy,hamouda}@ececoncodiaca
A multichannel Satellite Scheduling Algorithm
 A multichannel Satellite Scheduling Algoithm J.S. Gilmoe and R. Wolhute Depatment of Electonic Engineeing Univesity of Stellenbosch 7600 Stellenbosch, South Afica Email: jgilmoe@dsp.sun.ac.za, wolhute@sun.ac.za
A multichannel Satellite Scheduling Algoithm J.S. Gilmoe and R. Wolhute Depatment of Electonic Engineeing Univesity of Stellenbosch 7600 Stellenbosch, South Afica Email: jgilmoe@dsp.sun.ac.za, wolhute@sun.ac.za
Optimised Wireless Network Using Smart Mobile Terminal Antenna (SMTA) System
 Optimised Wieless Netwok Using Smat Mobile Teminal Antenna (SMTA) System Autho Lu, Junwei, Sciven, Ian, Wate, Wayne Published 2010 Confeence Title Poceedings of IEEE APEMC2010 DOI https://doi.og/10.1109/apemc.2010.5475858
Optimised Wieless Netwok Using Smat Mobile Teminal Antenna (SMTA) System Autho Lu, Junwei, Sciven, Ian, Wate, Wayne Published 2010 Confeence Title Poceedings of IEEE APEMC2010 DOI https://doi.og/10.1109/apemc.2010.5475858
Noise Attenuation Due to Vegetation
 Noise Attenuation Due to Vegetation Vasile BACRIA Politehnica Univesity of Timisoaa, Bd. M.Viteazu,1, 300222 Timisoaa, bacia@mec.upt.o Nicolae HERISANU Politehnica Univesity of Timisoaa, Bd. M. Viteazu,
Noise Attenuation Due to Vegetation Vasile BACRIA Politehnica Univesity of Timisoaa, Bd. M.Viteazu,1, 300222 Timisoaa, bacia@mec.upt.o Nicolae HERISANU Politehnica Univesity of Timisoaa, Bd. M. Viteazu,
OPTIMUM MEDIUM ACCESS TECHNIQUE FOR NEXT GENERATION WIRELESS SYSTEMS
 9 th Febuay. Vol. 3 No. 5 - JATIT & LLS. All ights eseved. ISSN: 99-5 www.jatit.og E-ISSN: 7-395 OPTIMUM MEDIUM ACCESS TECHNIQUE FOR NEXT GENERATION WIRELESS SYSTEMS N.AMUTHA PRABHA, V.MANIANDAN VIT UNIVERSITY,
9 th Febuay. Vol. 3 No. 5 - JATIT & LLS. All ights eseved. ISSN: 99-5 www.jatit.og E-ISSN: 7-395 OPTIMUM MEDIUM ACCESS TECHNIQUE FOR NEXT GENERATION WIRELESS SYSTEMS N.AMUTHA PRABHA, V.MANIANDAN VIT UNIVERSITY,
ONE-WAY RADAR EQUATION / RF PROPAGATION
 ONE-WAY RADAR EQUATION / RF PROPAGATION The one-way (tansmitte to eceive) ada equation is deived in this section. This equation is most commonly used in RWR o ESM type of applications. The following is
ONE-WAY RADAR EQUATION / RF PROPAGATION The one-way (tansmitte to eceive) ada equation is deived in this section. This equation is most commonly used in RWR o ESM type of applications. The following is
TECHNICAL DATA. JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard) Screw Thread. Specifications
 JIS (Japanese Industial Standad) Scew Thead Specifications TECNICAL DATA Note: Although these specifications ae based on JIS they also apply to and DIN s. Some comments added by Mayland Metics Coutesy
JIS (Japanese Industial Standad) Scew Thead Specifications TECNICAL DATA Note: Although these specifications ae based on JIS they also apply to and DIN s. Some comments added by Mayland Metics Coutesy
S11 PHY114 Problem Set 8
 S11 PHY114 Poblem Set 8 S. G. Rajeev Apil 4, 2011 Due Monday 4 Ap 2011 1. Find the wavelength of the adio waves emitted by the Univesity of Rocheste adio station (88.5 Mhz)? The numbe of bits pe second
S11 PHY114 Poblem Set 8 S. G. Rajeev Apil 4, 2011 Due Monday 4 Ap 2011 1. Find the wavelength of the adio waves emitted by the Univesity of Rocheste adio station (88.5 Mhz)? The numbe of bits pe second
Design of guided shell inclination measurement and display system. based-on MEMS accelerometer
 ey Engineeing Mateials Online: 2014-04-09 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vols. 609-610, pp 1040-1045 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/em.609-610.1040 2014 ans ech Publications, Switzeland Design of guided shell inclination
ey Engineeing Mateials Online: 2014-04-09 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vols. 609-610, pp 1040-1045 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/em.609-610.1040 2014 ans ech Publications, Switzeland Design of guided shell inclination
Design of an LLC Resonant Converter Using Genetic Algorithm
 Design of an LLC Resonant Convete Using Genetic Algoithm H. H. Nien, C. K. Huang, S. K. Changchien, C. H Chan Dept. of Electical Engineeing, Chienkuo Technology Univesity E-mail: nien@ctu.edu.tw Dept,
Design of an LLC Resonant Convete Using Genetic Algoithm H. H. Nien, C. K. Huang, S. K. Changchien, C. H Chan Dept. of Electical Engineeing, Chienkuo Technology Univesity E-mail: nien@ctu.edu.tw Dept,
Current Compensation Techniques for Lowvoltage High-performance Current Mirror Circuits
 Southen Illinois Univesity Cabondale OpenSIUC Aticles Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing 7-06 Cuent Compensation Techniques fo Lowvoltage High-pefomance Cuent Mio Cicuits Stefan Leitne Haibo
Southen Illinois Univesity Cabondale OpenSIUC Aticles Depatment of Electical and Compute Engineeing 7-06 Cuent Compensation Techniques fo Lowvoltage High-pefomance Cuent Mio Cicuits Stefan Leitne Haibo
Impact of bilateral filter parameters on medical image noise reduction and edge preservation
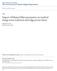 The Univesity of Toledo The Univesity of Toledo Digital Repositoy Theses and Dissetations 2009 Impact of bilateal filte paametes on medical image noise eduction and edge pesevation Michael D. Lekan Medical
The Univesity of Toledo The Univesity of Toledo Digital Repositoy Theses and Dissetations 2009 Impact of bilateal filte paametes on medical image noise eduction and edge pesevation Michael D. Lekan Medical
Investigation and Analysis of Inception Voltage and Field Distribution in Power Cables with Internal Cavities in Dielectric
 Investigation and Analysis of Inception Voltage and Field Distibution in Powe Cables with Intenal Cavities in Dielectic A. A. Hossam-Eldin Electical Eng. Depatment Faculty of Engineeing Alexandia Univesity,
Investigation and Analysis of Inception Voltage and Field Distibution in Powe Cables with Intenal Cavities in Dielectic A. A. Hossam-Eldin Electical Eng. Depatment Faculty of Engineeing Alexandia Univesity,
MACRO-DIVERSITY VERSUS MICRO-DIVERSITY SYSTEM CAPACITY WITH REALISTIC RECEIVER RFFE MODEL
 MACRO-DIVERSITY VERSUS MICRO-DIVERSITY SYSTEM CAACITY WITH REALISTIC RECEIVER RFFE MODEL I Ouachani, Duhamel, K Gosse, S Rouquette-Léveil and D Bateman *Laboatoie des Signaux et Systèmes 3 ue Joliot-Cuie
MACRO-DIVERSITY VERSUS MICRO-DIVERSITY SYSTEM CAACITY WITH REALISTIC RECEIVER RFFE MODEL I Ouachani, Duhamel, K Gosse, S Rouquette-Léveil and D Bateman *Laboatoie des Signaux et Systèmes 3 ue Joliot-Cuie
Fault severity diagnosis of rolling element bearings based on kurtogram and envelope analysis
 Fault seveity diagnosis of olling element beaings based on kutogam and envelope analysis Fengshou Gu, Xiange Tian, Zhi Chen, Tie Wang, Ibahim Rehab and Andew Ball Abstact Faults in olling element beaing
Fault seveity diagnosis of olling element beaings based on kutogam and envelope analysis Fengshou Gu, Xiange Tian, Zhi Chen, Tie Wang, Ibahim Rehab and Andew Ball Abstact Faults in olling element beaing
Short-Circuit Fault Protection Strategy of Parallel Three-phase Inverters
 Shot-Cicuit Fault Potection Stategy of Paallel Thee-phase Invetes Hongliang Wang, Membe, IEEE, Xuejun Pei, Membe, IEEE, Yu Chen, Membe, IEEE,Yong Kang College of Electical and Electonics Engineeing Huazhong
Shot-Cicuit Fault Potection Stategy of Paallel Thee-phase Invetes Hongliang Wang, Membe, IEEE, Xuejun Pei, Membe, IEEE, Yu Chen, Membe, IEEE,Yong Kang College of Electical and Electonics Engineeing Huazhong
Tightly Coupled Precise Point Positioning and Attitude Determination
 I. INTRODUCTION Tightly Coupled Pecise Point Positioning and Attitude Detemination PATRICK S. HENKEL Technische Univesität München Munich, Gemany A method is descibed fo joint pecise point positioning
I. INTRODUCTION Tightly Coupled Pecise Point Positioning and Attitude Detemination PATRICK S. HENKEL Technische Univesität München Munich, Gemany A method is descibed fo joint pecise point positioning
Study and Design of Dual Frequency High Gain and Conformal Microstrip Patch Antenna
 , pp.236-243 http://dx.doi.og/10.14257/astl.2017.147.33 Study and Design of Dual Fequency High Gain and Confomal Micostip Patch Antenna S. Auna 1, K. Sinivasa Naik 2, J. Ramesh 2 and D. Madhu 2 1 Andha
, pp.236-243 http://dx.doi.og/10.14257/astl.2017.147.33 Study and Design of Dual Fequency High Gain and Confomal Micostip Patch Antenna S. Auna 1, K. Sinivasa Naik 2, J. Ramesh 2 and D. Madhu 2 1 Andha
Mitigation of GPS Multipath Using Polarization and Spatial Diversities
 Mitigation of GPS Multipath Using Polaization and Spatial ivesities Matthew Benneman, Jade Moton Chun Yang Fank van Gaas Miami Univesity Sigtem Technology, Inc. Ohio Univesity BIOGRAPIES Matthew Benneman
Mitigation of GPS Multipath Using Polaization and Spatial ivesities Matthew Benneman, Jade Moton Chun Yang Fank van Gaas Miami Univesity Sigtem Technology, Inc. Ohio Univesity BIOGRAPIES Matthew Benneman
Diagnosis method of radiated emission from battery management system for electric vehicle
 Available online at www.sciencediect.com ScienceDiect Enegy Pocedia 88 (2016 ) 662 667 CUE2015-Applied Enegy Symposium and Summit 2015: Low cabon cities and uban enegy systems Diagnosis method of adiated
Available online at www.sciencediect.com ScienceDiect Enegy Pocedia 88 (2016 ) 662 667 CUE2015-Applied Enegy Symposium and Summit 2015: Low cabon cities and uban enegy systems Diagnosis method of adiated
IEEE Broadband Wireless Access Working Group < Modifications to the Feedback Methodologies in UL Sounding
 Poject Title Date Submitted IEEE 802.16 Boadband Wieless Access Woking Goup Modifications to the Feedback Methodologies in UL Sounding 2008-01-14 Souce(s) Fed Vook, Jeff Zhuang,
Poject Title Date Submitted IEEE 802.16 Boadband Wieless Access Woking Goup Modifications to the Feedback Methodologies in UL Sounding 2008-01-14 Souce(s) Fed Vook, Jeff Zhuang,
Study on Arc Envelope Grinding Process of Revolving Curved Surface Lingye Kong1, a,qiusheng Yan2,b,Yongliang Qiu1,c and Tengxiong Qiu1,d
 nd Intenational Confeence on Machiney, Mateials Engineeing, Chemical Engineeing and iotechnology (MMECE 015 Study on Ac Envelope Ginding Pocess of Revolving Cuved Suface Lingye Kong1, a,qiusheng Yan,b,Yongliang
nd Intenational Confeence on Machiney, Mateials Engineeing, Chemical Engineeing and iotechnology (MMECE 015 Study on Ac Envelope Ginding Pocess of Revolving Cuved Suface Lingye Kong1, a,qiusheng Yan,b,Yongliang
10! !. 3. Find the probability that a five-card poker hand (i.e. 5 cards out of a 52-card deck) will be:
 MATH 0(001 Fall 2018 Homewok 2 Solutions Please infom you instucto if you find any eos in the solutions 1 Suppose that thee ae duck huntes, each with a pefect shot A flock of ducks fly ove, and each hunte
MATH 0(001 Fall 2018 Homewok 2 Solutions Please infom you instucto if you find any eos in the solutions 1 Suppose that thee ae duck huntes, each with a pefect shot A flock of ducks fly ove, and each hunte
Microwave Finite Element Modeling Applications to Coupled Electromagnetic-Thermal Problems and Characterization of Dielectric Materials
 Micowave Finite Element Modeling Applications to Coupled Electomagnetic-Themal Poblems and Chaacteization of Dielectic Mateials Hulusi Acikgoz, Yann Le Bihan, Olivie Meye, and Lionel Pichon Laboatoie de
Micowave Finite Element Modeling Applications to Coupled Electomagnetic-Themal Poblems and Chaacteization of Dielectic Mateials Hulusi Acikgoz, Yann Le Bihan, Olivie Meye, and Lionel Pichon Laboatoie de
Channel Frequency Optimization of a Future AMSU-B-Like Millimeter-Wave Radiometer for Integrated Water Vapor Retrieval in polar regions
 Poceedings of the 4th WSEAS Intenational Confeence on REMOTE SENSING (REMOTE'8) Channel Fequency Optimization of a Futue AMSU-B-Like Millimete-Wave Radiomete fo Integated Wate Vapo Retieval in pola egions
Poceedings of the 4th WSEAS Intenational Confeence on REMOTE SENSING (REMOTE'8) Channel Fequency Optimization of a Futue AMSU-B-Like Millimete-Wave Radiomete fo Integated Wate Vapo Retieval in pola egions
Analytical Performance Evaluation of Mixed Services with Variable Data Rates for the Uplink of UMTS
 Analytical Pefomance Evaluation of Mixed Sevices with Vaiable Data Rates fo the Uplink of UMTS Laissa Popova and Wolfgang Koch Lehstuhl fü Mobilkommunikation, Univesität Elangen-Nünbeg, Gemany Email: {popova,
Analytical Pefomance Evaluation of Mixed Sevices with Vaiable Data Rates fo the Uplink of UMTS Laissa Popova and Wolfgang Koch Lehstuhl fü Mobilkommunikation, Univesität Elangen-Nünbeg, Gemany Email: {popova,
