Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring
|
|
|
- Raymond Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty are distinct. Resolution refers to the size and shape of the focused event image, while location uncertainty describes the effect of noise on the estimates of the image position. Synthetic modeling and comparison to case studies are used to characterize the relationship between the two and to demonstrate that positional uncertainties for surface based monitoring are similar to those for down-hole monitoring, but with a much broader viewing area. Introduction Microseismic monitoring can provide important information to help optimize well placement and stimulation programs in unconventional reservoirs (Maxwell, 2010). Surface microseismic monitoring offers several operational advantages over borehole monitoring. Surface arrays do not require dedicated monitoring borehole, and are well disposed for long-term field monitoring. Additionally, the increased distance between event and receiver offers a much larger field of view, allowing long laterals or multi-well pads to be monitored in their entirety (Duncan and Eisner, 2010). Surface deployment of large 2D or 3D arrays captures a large portion of the emitted microseismic wave field, enabling well constrained event imaging with only compressional waves, significantly reducing the sensitivity to velocity model assumptions. While the surface arrays offer several advantages, there are two main challenges: 1) reduced signal amplitude due to increased distance between event hypocenter and receiver, 2) generally higher levels of noise at surface. While borehole monitoring schemes typically rely on detection of events followed by event location, the reduced signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) at the surface does not generally allow detection of signals in the unstacked data (e.g., Zhebel et al., 2010). Migration based imaging schemes address this problem by simultaneously improving the SNR through stacking and positioning the events at their proper location. In this approach one must then rely on signal detection after migration which leads to two levels of uncertainty: 1) uncertainty in the detection of signal, 2) uncertainty in the localization of the event. In this paper, synthetic modeling will be used to illustrate the performance characteristics of the migration process in terms of signal detection and false-alarm rates, along with uncertainties in positional estimates. Examples from two case studies illustrate the magnitude of uncertainties achievable in actual monitoring surveys. Method GeoConvention 2012: Vision 1
2 Migration based approach to microseismic imaging involves three steps: downward continuation by beamforming, followed by event detection, then event localization (estimation of event location and timing). Beamforming is accomplished by a progressive scan of potential hypocenter locations in the subsurface. For each potential source location, the data recorded across the array are summed along diffraction curves, forming a beamformed trace, a continuous estimate of the potential source history at the subsurface location over the course of the recording. As microseismic events are transient events, potential events in the beamformed trace are then identified and extracted. Identification of an event is accomplished via amplitude ratio test. The ratio of RMS amplitude within a sliding event window (the signal estimate) to the RMS amplitude in a trailing window (the noise estimate) is used to compute an estimated SNR. If the SNR exceeds a specified threshold, the event window is marked as a potential trigger. Once all triggers are detected over all potential hypocenter locations, the catalog is analyzed to localize the event. Due to the finite extent of the array and the restriction of the array to the near surface, the point response of the migration is spread across many subsurface locations. For a surface array with an aperture twice the depth of interest, this point spread function will be elongated in the vertical direction by roughly a factor of three compared to the horizontal response. This elongated shape is primarily due to the trade-off between time of the event (i.e., origin time) and depth of the event when origin time of the event is unknown (Eisner et al., 2009). The actual size of this response is determined by the frequency of the received signal, the velocity of the overburden, distance to the event as well as the array configuration. The localization step consists of identification and evaluation of triggers related to a given event and a secondary diffraction sum along the time/depth trade-off trajectory (Duncan et. al., 2010). This secondary diffraction sum, allows one to estimate the timing and location of optimal energy focus and hence the event position. Uncertainty Uncertainty in migration based microseismic imaging arises in two primary contexts. First, is uncertainty in the detection step: How certain can we be that the detected events are, in fact, true microseismic events and not spurious noise? The second context relates to the event localization: How accurate are the positional estimates, especially in the vertical direction? In the case of large events that are visible in the unstacked data, the pattern of moveout and wavelet variation can be readily identified by an experienced analyst as a valid event. However, as one pursues weaker and weaker events, this approach soon fails as the signal disappears into the noise. The statisitics of signal detection (McDonough and Whalen, 1995) provides a framework that allows one to provide quantitative estimates of the probability of valid detections along with the probabilities of false alarms. By specifying the detection step as a likelihood ratio test using SNR, it is possible to show that one effectively fixes the probability of false-alarms in the system while maximizing the probability of detection. In general, it is not possible to choose a likelihood ratio test that reduces the probability of false-alarms to zero, so one must accept some probability of false-alarms. In practice, one must balance the false-alarm probability against the probability of failing to detect valid signal. GeoConvention 2012: Vision 2
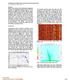
3 Figure 1: Count of detected events as a function of SNR after migration. Detected events matched to modeled events are shown as hits, events without a match are shown as false alarms. While it is difficult to assign a certainty to an individual detected event, detection theory does supply some useful insights to the event catalog as a whole. First, we know that the event catalog will contain some percentage of false-alarms. Secondly, theory predicts that the probability of detection should show three distinct zones as a function of SNR. Above some threshold, detection should be nearly certain; below a second threshold, detection should be nearly impossible, and a third relatively narrow transition zone in between. Estimating an event location ultimately comes down to selection of an optimal focusing point. Uncertainty in this estimate is driven by the effect of noise in this selection process. While the particulars of how noise interacts with the selection process are specific to the selection algorithm, we can predict that noise will tend to move the estimated location along contours of the migration point response and that the impact of noise should decrease with increasing SNR. Synthetic Modeling Synthetic modeling is used to assess both types of uncertainty in our imaging algorithm. Synthetic events at known locations were generated and contaminated with varying levels of noise to simulate variable SNR levels. Various array geometries and signal configurations can be simulated, all with similar uncertainty performance characteristics. Figure 1 shows number of hits and false-alarms for each output SNR level. For SNR > 2, all 100 of the seeded events were detected. For SNR < 2, the detection rate rapidly drops, effectively reaching zero for SNR < 1. This behavior suggests that we can use SNR as an indicator of reliability in the performance in the algorithm. Above some SNR threshold valid events are reliably detected, while below this threshold valid events are missed. GeoConvention 2012: Vision 3
4 Figure 2: Standard deviation of positional errors as a function of SNR after migration. Figure 2 shows the standard deviations of positional errors computed from the matched events (hits) shown above. Not shown in the figure are the average errors, for SNR > 1 average errors are very close to zero for all three dimensions indicating the estimates are unbiased. For SNR > 1, we see an exponential decline in variability of the errors, with horizontal and vertical uncertainties converging to near zero for very high SNR values. Variability in X and Y are approximately equal and 2-3 times smaller than variability in Z. The rate of decline in variability in all three dimensions is approximately the same. The estimates with SNR < 1 should be discounted as it contains only 2 hits, and origin time errors associated with these two hits are significantly larger than the other hits (50ms vs. 5ms), indicating these are not likely valid matches. As predicted, sensitivity to noise in the vertical direction is greater than in the lateral direction. The relative magnitude of the vertical and horizontal sensitivity is roughly proportional to the elongation of the migration point spread response. Furthermore, the impact of noise on the positional estimates diminishes rapidly with increasing SNR. Case Study Number of events Depth Of Target (ft) SNR Range Std. Dev. X error (ft) Std. Dev. Y error (ft) Std. Dev. Z error (ft) , , Table 1: Summary of uncertainty in calibration errors in two case studies. Case Studies Table 1 summarizes the analysis of uncertainty in two calibration studies from separate hydraulic fracture monitoring surveys in two different shale plays in North America. Both utilized radial surface arrays consisting of approximately 1000 channels in each. In both cases, perforation shots were used to calibrate the velocity and static corrections for the array. Once the calibration was determined, the imaged positions of the detected perforation shots were compared to the measured location of the gun. The SNR range for the set of shots and the standard deviation of the errors are reported. The estimated uncertainties in positions may be subject to a systematic bias as measured locations of perforation shots can be offset due to errors in deviation surveys (see Bulant et al. 2007). GeoConvention 2012: Vision 4
5 In Case #1, 85 shots were imaged over a pad of 5 lateral wells. Even though all the shots used similar charges, the SNR range varied from 3 to 10, with 60% of the shots having a SNR < 5. The difference SNR is likely result of variable conversion of charge energy to seismic energy as also observed by Chambers et al. (2010). We consider SNR < 5 to be fairly low SNR for calibration. Average errors in all three dimensions were less than 30 feet. In Case #2, 28 shots were imaged over a single lateral well. Although the target here was much deeper than the first case, the SNR range is considerably higher, with 78% of the shots having a SNR >15. We consider this to be very good SNR for calibration. Average errors in all three dimensions were less than 20 feet. While the positional uncertainties in both cases are larger than those shown in the synthetic model, they do show a similar behavior. Case #2 which is characterized by a larger SNR shows a smaller uncertainty indicated by a smaller standard deviation of the errors. Case #2 also shows similar uncertainties in horizontal and vertical directions comparable to the convergence zone noted in the synthetic model. The increased uncertainty compared to the model is likely due to the real-world need to estimate both velocity and static corrections and the presence of coherent noise in real data. In both cases, the uncertainties reported here were deemed acceptable by the operator. Conclusions Signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) is a key indicator of the uncertainty in migration based imaging of microseismic events. Reliability, in terms of the ability to detect the complete set of events is nearly a step-function of SNR. Events with SNR above a threshold of 2-3 are readily detected, while events with SNR below the threshold are missed. Positional uncertainties likewise are driven by SNR. While vertical uncertainty is more sensitive to noise, both horizontal and vertical uncertainties decrease rapidly with increasing SNR. While SNR can be used to infer the relative likelihood that given event is real, falsealarms will occur. Discriminating the real event from the false will require additional information beyond SNR. While synthetic modeling is useful in assessing the performance characteristic of the imaging method, a number of simplifying assumptions were made that differ from actual application of the method. First, our model assumed that travel-times were known exactly. In practice, velocity and static corrections must be estimated from calibration shots (sources at known locations in the subsurface). While travel time errors are most likely to decrease the SNR after migration, long period errors in travel times could cause spurious focusing and add uncertainty. Secondly, the model assumed the additive noise was Gaussian. While this is a reasonable first approximation, it does not take into account coherent noises, which are ubiquitous in surface microseismic monitoring. Appropriate preprocessing can reduce the impact of coherent noise, but residual coherent noise will trigger false-alarms. References Bulant, P., L. Eisner, I. Psencik, and J. L. Calvez, 2007, Importance of borehole deviation surveys for monitoring of hydraulic fracturing treatments: Geophysical Prospecting, 55, Chambers, K., S. Brandsberg-Dahl, J.-M. Kendall, and J. Rueda, 2008, Testing the ability of surface arrays to locate microseismicity: 78th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, GeoConvention 2012: Vision 5
6 Duncan P., Eisner L., 2010: Reservoir characterization using surface microseismic monitoring. Geophysics, 75, pp. 75A139 75A146; doi: / Duncan, P.M., J.D. Lakings, and R.A. Flores, 2010, Method for Passive Seismic Emission Tomography: U.S. Patent 7,663,970 B2. Eisner L., Heigl W.M., Duncan P.M., Keller W.R., 2009: Uncertainties in passive seismic monitoring. The Leading Edge; v. 28; no. 6; p ; DOI: / Maxwell, S., 2010, Microseismic: Growth born from success. The Leading Edge, vol. 29, No. 3, p McDonough, R. N., and A. D. Whalen, 1995, Detection of signals in noise. Academic Press, Waltham, MA. Zhebel, O., Gajewski D., and Venelle C., 2010, SEG Expanded Abstracts 29, GeoConvention 2012: Vision 6
Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques
 Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques Kit Chambers, Aaron Booterbaugh Nanometrics Inc. Summary Microseismic data always contains noise and its effect is to reduce the quality
Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques Kit Chambers, Aaron Booterbaugh Nanometrics Inc. Summary Microseismic data always contains noise and its effect is to reduce the quality
=, (1) Summary. Theory. Introduction
 Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Ambient Passive Seismic Imaging with Noise Analysis Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc.
 Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data
 A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc.
 Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc. Summary Common techniques for locating fracture events, from large earthquakes to
Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc. Summary Common techniques for locating fracture events, from large earthquakes to
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data
 Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
Cmin. Cmax. Frac volume. SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting. Summary (1),
 Improving signal-to-noise ratio of passsive seismic data with an adaptive FK filter Chuntao Liang*, Mike P. Thornton, Peter Morton, BJ Hulsey, Andrew Hill, and Phil Rawlins, Microseismic Inc. Summary We
Improving signal-to-noise ratio of passsive seismic data with an adaptive FK filter Chuntao Liang*, Mike P. Thornton, Peter Morton, BJ Hulsey, Andrew Hill, and Phil Rawlins, Microseismic Inc. Summary We
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. different curvatures at different times (see figure 1a and 1b).
 APERTURE WIDTH SELECTION CRITERION IN KIRCHHOFF MIGRATION Richa Rastogi, Sudhakar Yerneni and Suhas Phadke Center for Development of Advanced Computing, Pune University Campus, Ganesh Khind, Pune 411007,
APERTURE WIDTH SELECTION CRITERION IN KIRCHHOFF MIGRATION Richa Rastogi, Sudhakar Yerneni and Suhas Phadke Center for Development of Advanced Computing, Pune University Campus, Ganesh Khind, Pune 411007,
WS15-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise
 WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
SEPTEMBER VOL. 38, NO. 9 ELECTRONIC DEFENSE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL ERRORS IN WIDEBAND IFM RECEIVERS WIDE, WIDER, WIDEST SYNTHETIC APERTURE ANTENNAS
 r SEPTEMBER VOL. 38, NO. 9 ELECTRONIC DEFENSE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL ERRORS IN WIDEBAND IFM RECEIVERS WIDE, WIDER, WIDEST SYNTHETIC APERTURE ANTENNAS CONTENTS, P. 10 TECHNICAL FEATURE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL
r SEPTEMBER VOL. 38, NO. 9 ELECTRONIC DEFENSE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL ERRORS IN WIDEBAND IFM RECEIVERS WIDE, WIDER, WIDEST SYNTHETIC APERTURE ANTENNAS CONTENTS, P. 10 TECHNICAL FEATURE SIMULTANEOUS SIGNAL
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis
 Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events
 Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data
 Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements
 Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements David C. Henley Radial traces revisited ABSTRACT Filtering seismic data in the radial trace (R-T) domain is an effective technique for
Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements David C. Henley Radial traces revisited ABSTRACT Filtering seismic data in the radial trace (R-T) domain is an effective technique for
Contents of this file 1. Text S1 2. Figures S1 to S4. 1. Introduction
 Supporting Information for Imaging widespread seismicity at mid-lower crustal depths beneath Long Beach, CA, with a dense seismic array: Evidence for a depth-dependent earthquake size distribution A. Inbal,
Supporting Information for Imaging widespread seismicity at mid-lower crustal depths beneath Long Beach, CA, with a dense seismic array: Evidence for a depth-dependent earthquake size distribution A. Inbal,
Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector
 Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic
Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data
 Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Multipole Sonic-While-Drilling Technology Delivers Quality Data Regardless of Mud Slowness
 YOUNG TECHNOLOGY SHOWCASE Multipole Sonic-While-Drilling Technology Delivers Quality Data Regardless of Mud Slowness Julio Loreto, Eduardo Saenz, and Vivian Pistre, Schlumberger As the pace of exploration
YOUNG TECHNOLOGY SHOWCASE Multipole Sonic-While-Drilling Technology Delivers Quality Data Regardless of Mud Slowness Julio Loreto, Eduardo Saenz, and Vivian Pistre, Schlumberger As the pace of exploration
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure
 Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile
 Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a
 Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a a Published in SEP report, 89, 167-178 (1995) Arnaud Berlioux and William S. Harlan 1 ABSTRACT Variations in source strength and receiver amplitude
Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a a Published in SEP report, 89, 167-178 (1995) Arnaud Berlioux and William S. Harlan 1 ABSTRACT Variations in source strength and receiver amplitude
Summary. Methodology. Selected field examples of the system included. A description of the system processing flow is outlined in Figure 2.
 Halvor Groenaas*, Svein Arne Frivik, Aslaug Melbø, Morten Svendsen, WesternGeco Summary In this paper, we describe a novel method for passive acoustic monitoring of marine mammals using an existing streamer
Halvor Groenaas*, Svein Arne Frivik, Aslaug Melbø, Morten Svendsen, WesternGeco Summary In this paper, we describe a novel method for passive acoustic monitoring of marine mammals using an existing streamer
Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. II: Using GAIN=2 to Minimize the Effect
 Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. II: Using GAIN=2 to Minimize the Effect Mauro Giavalisco August 10, 2004 ABSTRACT Cross talk is observed in images taken with ACS WFC between the four CCD quadrants
Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. II: Using GAIN=2 to Minimize the Effect Mauro Giavalisco August 10, 2004 ABSTRACT Cross talk is observed in images taken with ACS WFC between the four CCD quadrants
A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection
 A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection Jubran Akram*,1, Daniel Peter 1, and David Eaton 2 1 King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia 2 University
A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection Jubran Akram*,1, Daniel Peter 1, and David Eaton 2 1 King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia 2 University
Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting
 Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting Xianzheng Zhao, Xishuang Wang, A.P. Zhukov, Ruifeng Zhang, Chuanzhang Tang Abstract: Seismic data from conventional vibroseis prospecting
Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting Xianzheng Zhao, Xishuang Wang, A.P. Zhukov, Ruifeng Zhang, Chuanzhang Tang Abstract: Seismic data from conventional vibroseis prospecting
Summary. D Receiver. Borehole. Borehole. Borehole. tool. tool. tool
 n off center quadrupole acoustic wireline : numerical modeling and field data analysis Zhou-tuo Wei*, OSL-UP llied coustic Lab., hina University of Petroleum (UP); Hua Wang, Earth Resources Lab., Massachusetts
n off center quadrupole acoustic wireline : numerical modeling and field data analysis Zhou-tuo Wei*, OSL-UP llied coustic Lab., hina University of Petroleum (UP); Hua Wang, Earth Resources Lab., Massachusetts
Presented on. Mehul Supawala Marine Energy Sources Product Champion, WesternGeco
 Presented on Marine seismic acquisition and its potential impact on marine life has been a widely discussed topic and of interest to many. As scientific knowledge improves and operational criteria evolve,
Presented on Marine seismic acquisition and its potential impact on marine life has been a widely discussed topic and of interest to many. As scientific knowledge improves and operational criteria evolve,
Enhanced subsurface response for marine CSEM surveying Frank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA
 rank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA Summary A new robust method for enhancing marine CSEM subsurface response is presented. The method is demonstrated to enhance resolution and depth penetration
rank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA Summary A new robust method for enhancing marine CSEM subsurface response is presented. The method is demonstrated to enhance resolution and depth penetration
OILFIELD DATA ANALYTICS
 A Short Course for the Oil & Gas Industry Professionals OILFIELD DATA ANALYTICS INSTRUCTOR: Shahab D. Mohaghegh, Ph. D. Intelligent Solution, Inc. Professor of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering West
A Short Course for the Oil & Gas Industry Professionals OILFIELD DATA ANALYTICS INSTRUCTOR: Shahab D. Mohaghegh, Ph. D. Intelligent Solution, Inc. Professor of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering West
Summary. Page SEG SEG Denver 2014 Annual Meeting
 Seismo-acoustic characterization of a seismic vibrator Claudio Bagaini*, Martin Laycock and Colin Readman, WesternGeco; Emmanuel Coste, Schlumberger; Colin Anderson, Siemens PLM Software Summary A seismic
Seismo-acoustic characterization of a seismic vibrator Claudio Bagaini*, Martin Laycock and Colin Readman, WesternGeco; Emmanuel Coste, Schlumberger; Colin Anderson, Siemens PLM Software Summary A seismic
EEE508 GÜÇ SİSTEMLERİNDE SİNYAL İŞLEME
 EEE508 GÜÇ SİSTEMLERİNDE SİNYAL İŞLEME Signal Processing for Power System Applications Triggering, Segmentation and Characterization of the Events (Week-12) Gazi Üniversitesi, Elektrik ve Elektronik Müh.
EEE508 GÜÇ SİSTEMLERİNDE SİNYAL İŞLEME Signal Processing for Power System Applications Triggering, Segmentation and Characterization of the Events (Week-12) Gazi Üniversitesi, Elektrik ve Elektronik Müh.
Introduction. Figure 2: Source-Receiver location map (to the right) and geometry template (to the left).
 Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS
 Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise
 Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Understanding Seismic Amplitudes
 Understanding Seismic Amplitudes The changing amplitude values that define the seismic trace are typically explained using the convolutional model. This model states that trace amplitudes have three controlling
Understanding Seismic Amplitudes The changing amplitude values that define the seismic trace are typically explained using the convolutional model. This model states that trace amplitudes have three controlling
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods
 Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
Seismic reflection method
 Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
ISSN Volume 28 Issue 6 June A New Spring for Geoscience. Special Topic
 ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
Applied Methods MASW Method
 Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
2D field data applications
 Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments. Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft
 Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft Outline Micro Seismic Technology in the Oil industry Velocity Structure Examples Fault interaction
Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft Outline Micro Seismic Technology in the Oil industry Velocity Structure Examples Fault interaction
Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study
 Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study M.Das, Maharaj Singh, M.Muruganandan* & Dr.D.V.R. Murti RCC, GPS, A&AA Basin, ONGC Jorhat Summary Multiple attenuation is a long standing problem in reflection seismic
Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study M.Das, Maharaj Singh, M.Muruganandan* & Dr.D.V.R. Murti RCC, GPS, A&AA Basin, ONGC Jorhat Summary Multiple attenuation is a long standing problem in reflection seismic
Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION
 Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION Innovative Solutions, from Access to Production Uncertainty Knowledge ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT
Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION Innovative Solutions, from Access to Production Uncertainty Knowledge ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results
 Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging To cite this article: Y. Bashir et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging To cite this article: Y. Bashir et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation
 Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation Xinxiang Li and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd. Summary The method of time-frequency adaptive
Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation Xinxiang Li and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd. Summary The method of time-frequency adaptive
A HILBERT TRANSFORM BASED RECEIVER POST PROCESSOR
 A HILBERT TRANSFORM BASED RECEIVER POST PROCESSOR 1991 Antenna Measurement Techniques Association Conference D. Slater Nearfield Systems Inc. 1330 E. 223 rd Street Bldg. 524 Carson, CA 90745 310-518-4277
A HILBERT TRANSFORM BASED RECEIVER POST PROCESSOR 1991 Antenna Measurement Techniques Association Conference D. Slater Nearfield Systems Inc. 1330 E. 223 rd Street Bldg. 524 Carson, CA 90745 310-518-4277
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
SHALE ANALYTICS. INTELLIGENT SOLUTIONS, INC.
 A Short Course for the Oil & Gas Industry Professionals SHALE INSTRUCTOR: Shahab D. Mohaghegh, Ph. D. Intelligent Solution, Inc. Professor of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering West Virginia University
A Short Course for the Oil & Gas Industry Professionals SHALE INSTRUCTOR: Shahab D. Mohaghegh, Ph. D. Intelligent Solution, Inc. Professor of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering West Virginia University
Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes
 Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes Christopher C. Petten*, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta ccpetten@ucalgary.ca and Gary F.
Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes Christopher C. Petten*, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta ccpetten@ucalgary.ca and Gary F.
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain
 High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
South Africa CO2 Seismic Program
 1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
Abstract. Introduction
 TARGET PRIORITIZATION IN TEM SURVEYS FOR SUB-SURFACE UXO INVESTIGATIONS USING RESPONSE AMPLITUDE, DECAY CURVE SLOPE, SIGNAL TO NOISE RATIO, AND SPATIAL MATCH FILTERING Darrell B. Hall, Earth Tech, Inc.,
TARGET PRIORITIZATION IN TEM SURVEYS FOR SUB-SURFACE UXO INVESTIGATIONS USING RESPONSE AMPLITUDE, DECAY CURVE SLOPE, SIGNAL TO NOISE RATIO, AND SPATIAL MATCH FILTERING Darrell B. Hall, Earth Tech, Inc.,
3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion. Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas
 P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
(Refer Slide Time: 00:10)
 Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 03 Unit-6 Instrumental details
Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 03 Unit-6 Instrumental details
Coda Waveform Correlations
 Chapter 5 Coda Waveform Correlations 5.1 Cross-Correlation of Seismic Coda 5.1.1 Introduction In the previous section, the generation of the surface wave component of the Green s function by the correlation
Chapter 5 Coda Waveform Correlations 5.1 Cross-Correlation of Seismic Coda 5.1.1 Introduction In the previous section, the generation of the surface wave component of the Green s function by the correlation
Analysis and design of filters for differentiation
 Differential filters Analysis and design of filters for differentiation John C. Bancroft and Hugh D. Geiger SUMMARY Differential equations are an integral part of seismic processing. In the discrete computer
Differential filters Analysis and design of filters for differentiation John C. Bancroft and Hugh D. Geiger SUMMARY Differential equations are an integral part of seismic processing. In the discrete computer
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo
 Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Site-specific seismic hazard analysis
 Site-specific seismic hazard analysis ABSTRACT : R.K. McGuire 1 and G.R. Toro 2 1 President, Risk Engineering, Inc, Boulder, Colorado, USA 2 Vice-President, Risk Engineering, Inc, Acton, Massachusetts,
Site-specific seismic hazard analysis ABSTRACT : R.K. McGuire 1 and G.R. Toro 2 1 President, Risk Engineering, Inc, Boulder, Colorado, USA 2 Vice-President, Risk Engineering, Inc, Acton, Massachusetts,
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System
 A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION
 MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION by Delaine Thompson Earth Resources Laboratory Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION by Delaine Thompson Earth Resources Laboratory Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Application of Surface Consistent Amplitude Corrections as a Manual Editing Tool
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 4, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov-Dec. 2016), PP 59-65 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Surface Consistent
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 4, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov-Dec. 2016), PP 59-65 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Surface Consistent
Downloaded 11/02/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
On Determination of Focal Laws for Linear Phased Array Probes as to the Active and Passive Element Size
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 On Determination of Focal Laws for Linear Phased Array Probes as to the Active and Passive Element Size Andreas GOMMLICH 1, Frank SCHUBERT 2 1 Institute
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 On Determination of Focal Laws for Linear Phased Array Probes as to the Active and Passive Element Size Andreas GOMMLICH 1, Frank SCHUBERT 2 1 Institute
Ocean Acoustics and Signal Processing for Robust Detection and Estimation
 Ocean Acoustics and Signal Processing for Robust Detection and Estimation Zoi-Heleni Michalopoulou Department of Mathematical Sciences New Jersey Institute of Technology Newark, NJ 07102 phone: (973) 596
Ocean Acoustics and Signal Processing for Robust Detection and Estimation Zoi-Heleni Michalopoulou Department of Mathematical Sciences New Jersey Institute of Technology Newark, NJ 07102 phone: (973) 596
Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain
 Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
A SHEAR WAVE TRANSDUCER ARRAY FOR REAL-TIME IMAGING. R.L. Baer and G.S. Kino. Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
 A SHEAR WAVE TRANSDUCER ARRAY FOR REAL-TIME IMAGING R.L. Baer and G.S. Kino Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 INTRODUCTION In this paper we describe a contacting shear
A SHEAR WAVE TRANSDUCER ARRAY FOR REAL-TIME IMAGING R.L. Baer and G.S. Kino Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 INTRODUCTION In this paper we describe a contacting shear
Instrumental Considerations
 Instrumental Considerations Many of the limits of detection that are reported are for the instrument and not for the complete method. This may be because the instrument is the one thing that the analyst
Instrumental Considerations Many of the limits of detection that are reported are for the instrument and not for the complete method. This may be because the instrument is the one thing that the analyst
How to Attenuate Diffracted Noise: (DSCAN) A New Methodology
 How to Attenuate Diffracted Noise: (DSCAN) A New Methodology Ali Karagul* CGG Canada Service Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada akaragul@cgg.com Todd Mojesky and XinXiang Li CGG Canada Service Ltd., Calgary,
How to Attenuate Diffracted Noise: (DSCAN) A New Methodology Ali Karagul* CGG Canada Service Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada akaragul@cgg.com Todd Mojesky and XinXiang Li CGG Canada Service Ltd., Calgary,
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG)
 Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Dependence of Predicted Dewatering on Size of Hydraulic Stress Used for Groundwater Model Calibration
 Proceedings of Mine Water Solutions 2018 June 12 15, 2018, Vancouver, Canada Published by the University of British Columbia, 2018 Dependence of Predicted Dewatering on Size of Hydraulic Stress Used for
Proceedings of Mine Water Solutions 2018 June 12 15, 2018, Vancouver, Canada Published by the University of British Columbia, 2018 Dependence of Predicted Dewatering on Size of Hydraulic Stress Used for
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
Evaluation of a broadband marine source
 Evaluation of a broadband marine source Rob Telling 1*, Stuart Denny 1, Sergio Grion 1 and R. Gareth Williams 1 evaluate far-field signatures and compare processing results for a 2D test-line acquired
Evaluation of a broadband marine source Rob Telling 1*, Stuart Denny 1, Sergio Grion 1 and R. Gareth Williams 1 evaluate far-field signatures and compare processing results for a 2D test-line acquired
NPAL Acoustic Noise Field Coherence and Broadband Full Field Processing
 NPAL Acoustic Noise Field Coherence and Broadband Full Field Processing Arthur B. Baggeroer Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 Phone: 617 253 4336 Fax: 617 253 2350 Email: abb@boreas.mit.edu
NPAL Acoustic Noise Field Coherence and Broadband Full Field Processing Arthur B. Baggeroer Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 Phone: 617 253 4336 Fax: 617 253 2350 Email: abb@boreas.mit.edu
Isolation Scanner. Advanced evaluation of wellbore integrity
 Isolation Scanner Advanced evaluation of wellbore integrity Isolation Scanner* cement evaluation service integrates the conventional pulse-echo technique with flexural wave propagation to fully characterize
Isolation Scanner Advanced evaluation of wellbore integrity Isolation Scanner* cement evaluation service integrates the conventional pulse-echo technique with flexural wave propagation to fully characterize
TREBALL FI DE CARRERA
 - TREBALL FI DE CARRERA Títol Development of an automated microseismic event detection method and analysis of a microseismic dataset from hydraulic fracture stimulation to characterise natural and induced
- TREBALL FI DE CARRERA Títol Development of an automated microseismic event detection method and analysis of a microseismic dataset from hydraulic fracture stimulation to characterise natural and induced
Downloaded 01/03/14 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 : a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
: a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
Northing (km)
 Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 22.
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 22 Optical Receivers Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical Engineering,
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 22 Optical Receivers Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical Engineering,
Why not narrowband? Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology
 Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Lecture 8: GIS Data Error & GPS Technology
 Lecture 8: GIS Data Error & GPS Technology A. Introduction We have spent the beginning of this class discussing some basic information regarding GIS technology. Now that you have a grasp of the basic terminology
Lecture 8: GIS Data Error & GPS Technology A. Introduction We have spent the beginning of this class discussing some basic information regarding GIS technology. Now that you have a grasp of the basic terminology
Accurate Utility Depth Measurements Using the Spar 300
 Accurate Utility Depth Measurements Using the Spar 3 This Application Note addresses how to obtain accurate subsurface utility depths using the model-based methods employed by the Spar 3. All electromagnetic
Accurate Utility Depth Measurements Using the Spar 3 This Application Note addresses how to obtain accurate subsurface utility depths using the model-based methods employed by the Spar 3. All electromagnetic
Assessing & Mitigation of risks on railways operational scenarios
 R H I N O S Railway High Integrity Navigation Overlay System Assessing & Mitigation of risks on railways operational scenarios Rome, June 22 nd 2017 Anja Grosch, Ilaria Martini, Omar Garcia Crespillo (DLR)
R H I N O S Railway High Integrity Navigation Overlay System Assessing & Mitigation of risks on railways operational scenarios Rome, June 22 nd 2017 Anja Grosch, Ilaria Martini, Omar Garcia Crespillo (DLR)
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas
 The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
McArdle, N.J. 1, Ackers M. 2, Paton, G ffa 2 - Noreco. Introduction.
 An investigation into the dependence of frequency decomposition colour blend response on bed thickness and acoustic impedance: results from wedge and thin bed models applied to a North Sea channel system
An investigation into the dependence of frequency decomposition colour blend response on bed thickness and acoustic impedance: results from wedge and thin bed models applied to a North Sea channel system
Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition
 Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition Authors: Alexandre Egreteau, John Gibson, Forest Lin and Julien Meunier (CGGVeritas) Main objectives: Promote the use of long sweeps to compensate for the
Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition Authors: Alexandre Egreteau, John Gibson, Forest Lin and Julien Meunier (CGGVeritas) Main objectives: Promote the use of long sweeps to compensate for the
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events
 A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events Zuolin Chen and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT There exist a variety of algorithms for the detection
A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events Zuolin Chen and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT There exist a variety of algorithms for the detection
Tu A D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study
 Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
2 Gain Variation from the Receiver Output through the IF Path
 EVLA Memo #185 Bandwidth- and Frequency-Dependent Effects in the T34 Total Power Detector Keith Morris September 17, 214 1 Introduction The EVLA Intermediate Frequency (IF) system employs a system of power
EVLA Memo #185 Bandwidth- and Frequency-Dependent Effects in the T34 Total Power Detector Keith Morris September 17, 214 1 Introduction The EVLA Intermediate Frequency (IF) system employs a system of power
MAKING TRANSIENT ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS
 MAKING TRANSIENT ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS Roger Dygert, Steven R. Nichols MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Boulevard, Suite 100 Suwanee, GA 30024-4629 ABSTRACT In addition to steady state performance, antennas
MAKING TRANSIENT ANTENNA MEASUREMENTS Roger Dygert, Steven R. Nichols MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Boulevard, Suite 100 Suwanee, GA 30024-4629 ABSTRACT In addition to steady state performance, antennas
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Noise Attenuation in Seismic Data Iterative Wavelet Packets vs Traditional Methods Lionel J. Woog, Igor Popovic, Anthony Vassiliou, GeoEnergy, Inc.
 Noise Attenuation in Seismic Data Iterative Wavelet Packets vs Traditional Methods Lionel J. Woog, Igor Popovic, Anthony Vassiliou, GeoEnergy, Inc. Summary In this document we expose the ideas and technologies
Noise Attenuation in Seismic Data Iterative Wavelet Packets vs Traditional Methods Lionel J. Woog, Igor Popovic, Anthony Vassiliou, GeoEnergy, Inc. Summary In this document we expose the ideas and technologies
