Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector
|
|
|
- Benjamin Scot Phelps
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic events can be induced in hydrocarbon reservoirs due to human activities. Automated detection and location of these events is desirable in monitoring reservoir changes and revealing extent of fracture growth in real time. Most detection algorithms produce initial estimates of arrival times which sometimes contain large errors, degrading the accuracy of earthquake location procedures. The uncertainty associated with the estimated hypocenter locations can sometimes be larger than the source dimensions as a result, restricting the resolution of the seismicity image. We have developed an efficient method for reprocessing arrival time measurements using the subspace detector. Previously detected events are used to construct a signal subspace which represents similar but significantly variable microseismic signals. The basis waveforms comprising the subspace representation have improved signalto-noise ratios permitting a more accurate definition of the absolute arrival time. These are then used to correct arrival time inconsistencies via cross correlation. A workflow for implementing this procedure from event detection to location is shown and tested on real data. We find the performance of the repicking method is comparable with manually picked arrival times and dependent on the signal-to-noise ratio of the basis waveforms. Introduction Activities such as fluid injection and wastewater disposal can cause an increase in pore pressure in the subsurface, which allow faults to slide under pre-existing shear stress (van der Elst et al., 2013). The resulting stress perturbations reactivates faults and opens or closes new fracture sets, resulting in the generation of microseismic events (De Meersman et al., 2009). Automated detection and location of these microseismic events is a valuable tool in monitoring reservoir changes. Finding the exact location of a seismic source is one of the most important tasks as it can reveal fracture geometry and progress of fluid fronts during production (Oye & Roth, 2003). Most microseismic events have low magnitudes and are usually contaminated by high amplitude noise. This tends to reduce the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), reducing the accuracy of P and S waves arrival time picks (Song et al., 2014). Standard location techniques utilize arrival times and back azimuths across stations to determine event hypocenters and origin times. This is achieved by minimizing the sum of the difference between the predicted and observed parameters (arrival times and back azimuths). However, the effects of unmodeled velocity structure as well as the effects of limited source-receiver configuration and arrival time picking errors tend to decrease the accuracy of the event locations (Schaff et al., 2004; Pavlis, 1992). In this article we introduce an efficient means of repicking arrival times using the subspace detector. The subspace detector (Harris, 2006; Scharf & Friedlander, 1994) projects a sliding window of continuous data onto a vector subspace spanning a collection of signals expected from a particular source(s). The signals to be detected are modeled as a linear combination of orthogonal basis waveforms. One advantage of the subspace detector is the improvement in the SNR in the basis waveforms. Improvements in arrival time picks can then be obtained by cross correlation in a search region around our events with the basis waveforms. A workflow showing a practical implementation from event detection to repicking will be outlined, and the performance will be evaluated real life examples. GeoConvention
2 the Theory The standard method for obtaining phase arrival time picks involves visual inspection of the traces to determine onset times. Due to large data volumes and the subjectivity involved this method is usually inefficient, especially in real time monitoring. Numerous algorithms exist to this effect such as the short time average over long time average detector (Allen, 1978; Trnkoczy, 1999), autoregressive modeling (Sleeman and Van Eck, 1999) and correlation techniques (Molyneux and Schmitt, 1999; De Meersman et al., 2009). However, they are heavily influenced by the SNR conditions present. In this study correlation techniques are used as they can provide very high precision arrival time measurements. This is especially useful for correcting time picking inconsistencies between microseismic multiplets. A multiplet is defined as groups of more than 2 similar events which have separation distances of less than a quarter of the dominant wavelength (Geller & Mueller, 1980). If two microseismic events are highly similar, their time picks must be at the same position. The time lag corresponding to the maximum peak of the cross correlation function between both events can be used to correct inconsistencies in arrival time picks. De Meersman et al., 2009 use an iterative stacking procedure to improve arrival time picks across a receiver array. If there is little variation in signal between the stations, the stack is used to improve arrival time picks. This is due to the improvement in the signal to noise ratio allowing a more accurate definition of the absolute arrival time. In most cases, there is significant variation across the receiver array, making this technique non-feasible. An efficient means of repicking arrival times involves the subspace detector. The subspace detector projects a sliding window of data onto a vector subspace spanning a collection of events expected from a particular source(s) (Harris, 2006). The projected data is a leastsquares estimate of the signal in the detection window, and gives a measure of the linear dependence between the windowed data and the signals comprising the signal subspace. Construction of the signal subspace begins with detection of high signal-to-noise ratio events assumed to characterize the source(s) signals of interest. The waveforms are then clustered based on correlations between them, andand cluster of interest selected. The waveforms are then aligned and a singular value decomposition (SVD) is applied to the aligned set to obtain an orthonormal representation of the waveforms. A truncation of the orthonormal representation may be done such that signal energy is best represented while noise energy is minimized. The SVD tries to capture the essential features present in the data i.e. it contains information common to the template waveforms. The basis vectors obtained from the SVD represent the direction of the maximum variance possible. This usually results in a modest amount of noise reduction on the basis vectors and a subsequent improvement in their signal-to-noise ratio. Barrett & Beroza (2014) found the first basis vector closely approximates the stack, with the other singular vectors contributing the remaining information common to the templates within the design set in decreasing amounts. Thus it is possible to obtain more accurate estimate of the arrival times on these basis vectors. These can then be used to correct initial arrival time picks from detection by searching in a time window within the vicinity of the picks. The basis vector which corresponds to the highest peak correlation value with the windowed data is subsequently selected to correct the inconsistency in arrival time picks for a certain event. Examples Workflow We analyze microseismic data that occur over a 2 day period during a hydraulic fracture treatment of 2 wells near Rimbey, in Alberta (Eaton et al., 2014). A total of 68 events were selected for analysis from an hour of data and used to test and demonstrate the performance of the repicking method. These events were located using 3 different subspace detectors. The first singular vector for the P-waves and the first two singular vectors for the S-waves are used in the repicking procedure. Figure 1 and 2 shows the workflow for implementing the repicking procedure using the singular vectors from singular value decomposition and an example of repicked arrival times for an event respectively. GeoConvention
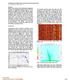
3 Figure 1: Workflow highlighting how initial arrival time picks are corrected using the basis vectors of the subspace detector. P and S wave vectors are utilized in this procedure. Figure 2: Vertical component of an event file highlighting the S-wave arrival. Manual arrival time picks (green dots) as well as subspace repicked arrival times (yellow dots) are shown. Absolute locations For events in a multiplet, it is assumed that the hypocentral separation between the 2 earthquakes is small compared to the event-station distance (Geller & Mueller, 1980; Waldhauser & Ellsworth, 2000). Therefore we can perform some quality control by comparing the average event distances obtained from both manually picked and repicked arrival times. We focus our analysis on the 2 largest groups containing 13 and 10 events respectively. We removed events which could not be located within our model space and the events with locations using both manual and repicked arrival times are shown in figure 3. The quality of the templates influences the accuracy to which the arrival time picks can be corrected. The SVD operation at the heart of the subspace detector captures variability present within the design set of waveforms to be described, and as such the basis vectors produced display high similarity with the source waveforms. The use of only one basis vector does not always guarantee a high correlation with the signals to be detected, therefore a search over the representative singular basis waveforms is more robust. Increased noise levels degrade the quality of the templates making it difficult to use higher number of basis or pick accurate starting positions on the basis waveforms. Our application of the repicking procedure revealed some key points. Comparing the locations obtained using repicked and manually picked times for the larger cluster, the locations obtained using the manually picked arrival times are more tightly clustered than those GeoConvention
4 obtained from repicking. Most of the events in this cluster displayed higher correlations with the noisier basis vectors. The onset times for these vectors were harder to determine accurately and could have introduced bias in our estimates of arrival times. Correlation with noise could also have influenced the picking accuracy. However the locations are still reasonably close together. In contrast, the locations of events from the smaller cluster using the repicked time are more tightly clustered than those manually picked. All the events in this cluster had high correlation with basis vectors with high SNR which had more accurate onset picks. The closeness of the locations acts as quality control since we expect these events to be spatially close to each other. Figure 3: Hypocenter locations of events from 2 multi event clusters. Receivers shown as black triangles, and locations displayed as red stars (a) Manual picking locations for largest group (b) Repicked locations for largest group (c) Manual picking locations for second largest group (d) Repicked locations for second largest group Conclusions This study shows that is possible to accurately repick arrival times using the subspace detector, and this procedure can be implemented in an automated detection and location workflow. However, the accuracy of the picks are dependent on the noise levels of the signals used in detection and the ability to select the right starting window on our template waveforms. The use of a 1-D velocity model in our analysis of the real data set introduced some biases into our locations, and the poor station coverage increased uncertainty in azimuthal information. Nevertheless, the repicking procedure was still shown to perform quite well, revealing tight clusters of events for multiplet groups where accurate picking was possible, and performing reasonably well compared to manual picking. Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank the sponsors of the Microseismic Industry Consortium for financial support. We would also like to thank ConocoPhillips Canada for granting permission to use the microseimsic dataset. GeoConvention
5 References Allen, R. V., Automatic earthquake recognition and timing from single traces. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America}, 68(5), Barrett, A., & Beroza, C., An empirical approach to subspace detection. Seismological Research Letters, 85(3), Eaton, D., Caffagni, E., van der Baan, M., & Matthews, L., Passive seismic monitoring and integrated geomechanical analysis of a tight-sand reservoir during hydraulic-fracture treatment, flowback and production. Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Denver, Colorado, August Society of Exploration Geophysicists, American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Geller, J., & Mueller, S., Four similar earthquakes in central California. Geophysical Research Letters, 7(10), Harris, D., Subspace Detectors: Theory. Internal Report UCRL-TR , University of California, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. De Meersman, K., Kendall, J., Van der Baan, M., The 1998 Valhall microseismic data set: An integrated study of relocated sources, seismic multiplets, and S-wave splitting. Geophysics, 74, B183-B195. Molyneux, J. B., & Schmitt, D. R., Firstbreak timing: Arrival onset times by direct correlation. Geophysics, 64(5), Molyneux, B., & Schmitt, R., First-break timing: Arrival onset times by direct correlation. Geophysics, 64(5), Oye, V., & Roth, M., Automated seismic event location for hydrocarbon reservoirs. Computers & Geosciences, 29(7), Pavlis, G. L., Appraising relative earthquake location errors. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 82(2), Scharf, L. L., & Friedlander, B., Matched subspace detectors. IEEE Transactions on signal processing, 42(8), Schaff, D. P., Bokelmann, G. H., Ellsworth, W. L., Zanzerkia, E., Waldhauser, F., & Beroza, G. C., Optimizing correlation techniques for improved earthquake location. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 94(2), Sleeman, R., & Van Eck, T., Robust automatic P-phase picking: an on-line implementation in the analysis of broadband seismogram recordings}. Physics of the earth and planetary interiors, 113(1), Song, F., Warpinski, N., Toksoz, M., & Kuleli, H. (2014). Full-waveform based microseismic event detection and signal enhancement; An application of the subspace approach. Geophys. Prospect., 62, Trnkoczy, A. (1999). Understanding and parameter setting of STA/LTA trigger algorithm Van der Elst, N. J., Savage, H. M., Keranen, K. M., & Abers, G. A., Enhanced remote earthquake triggering at fluidinjection sites in the Midwestern United States. Science, 341(6142), Waldhauser, F., & Ellsworth, W. L., A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: Method and application to the northern Hayward fault, California. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 90(6), GeoConvention
A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection
 A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection Jubran Akram*,1, Daniel Peter 1, and David Eaton 2 1 King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia 2 University
A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection Jubran Akram*,1, Daniel Peter 1, and David Eaton 2 1 King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia 2 University
Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques
 Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques Kit Chambers, Aaron Booterbaugh Nanometrics Inc. Summary Microseismic data always contains noise and its effect is to reduce the quality
Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques Kit Chambers, Aaron Booterbaugh Nanometrics Inc. Summary Microseismic data always contains noise and its effect is to reduce the quality
=, (1) Summary. Theory. Introduction
 Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events
 A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events Zuolin Chen and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT There exist a variety of algorithms for the detection
A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events Zuolin Chen and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT There exist a variety of algorithms for the detection
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring
 Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Th P6 01 Retrieval of the P- and S-velocity Structure of the Groningen Gas Reservoir Using Noise Interferometry
 Th P6 1 Retrieval of the P- and S-velocity Structure of the Groningen Gas Reservoir Using Noise Interferometry W. Zhou* (Utrecht University), H. Paulssen (Utrecht University) Summary The Groningen gas
Th P6 1 Retrieval of the P- and S-velocity Structure of the Groningen Gas Reservoir Using Noise Interferometry W. Zhou* (Utrecht University), H. Paulssen (Utrecht University) Summary The Groningen gas
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data
 A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events
 Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise
 Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments. Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft
 Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft Outline Micro Seismic Technology in the Oil industry Velocity Structure Examples Fault interaction
Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft Outline Micro Seismic Technology in the Oil industry Velocity Structure Examples Fault interaction
Cmin. Cmax. Frac volume. SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting. Summary (1),
 Improving signal-to-noise ratio of passsive seismic data with an adaptive FK filter Chuntao Liang*, Mike P. Thornton, Peter Morton, BJ Hulsey, Andrew Hill, and Phil Rawlins, Microseismic Inc. Summary We
Improving signal-to-noise ratio of passsive seismic data with an adaptive FK filter Chuntao Liang*, Mike P. Thornton, Peter Morton, BJ Hulsey, Andrew Hill, and Phil Rawlins, Microseismic Inc. Summary We
Ambient Passive Seismic Imaging with Noise Analysis Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc.
 Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 197, 458 463 Advance Access publication 2014 January 20 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt516 An earthquake detection algorithm with pseudo-probabilities of
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 197, 458 463 Advance Access publication 2014 January 20 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt516 An earthquake detection algorithm with pseudo-probabilities of
Passive (Micro-)Seismic Event Detection
 Passive (Micro-)Seismic Event Detection Introduction Among engineers there is considerable interest in the real-time identification of events within time series data with a low signal to noise ratio (S/N).
Passive (Micro-)Seismic Event Detection Introduction Among engineers there is considerable interest in the real-time identification of events within time series data with a low signal to noise ratio (S/N).
TREBALL FI DE CARRERA
 - TREBALL FI DE CARRERA Títol Development of an automated microseismic event detection method and analysis of a microseismic dataset from hydraulic fracture stimulation to characterise natural and induced
- TREBALL FI DE CARRERA Títol Development of an automated microseismic event detection method and analysis of a microseismic dataset from hydraulic fracture stimulation to characterise natural and induced
Contents of this file 1. Text S1 2. Figures S1 to S4. 1. Introduction
 Supporting Information for Imaging widespread seismicity at mid-lower crustal depths beneath Long Beach, CA, with a dense seismic array: Evidence for a depth-dependent earthquake size distribution A. Inbal,
Supporting Information for Imaging widespread seismicity at mid-lower crustal depths beneath Long Beach, CA, with a dense seismic array: Evidence for a depth-dependent earthquake size distribution A. Inbal,
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) Geophysical Journal International Advance Access published January 22, 2014 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt433 Improvements in magnitude precision, using
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) Geophysical Journal International Advance Access published January 22, 2014 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt433 Improvements in magnitude precision, using
27th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 GLOBAL GROUND TRUTH DATA SET WITH WAVEFORM AND IMPROVED ARRIVAL DATA István Bondár 1, Ben Kohl 1, Eric Bergman 2, Keith McLaughlin 1, Hans Israelsson 1, Yu-Long Kung 1, Paul Piraino 1, and Bob Engdahl
GLOBAL GROUND TRUTH DATA SET WITH WAVEFORM AND IMPROVED ARRIVAL DATA István Bondár 1, Ben Kohl 1, Eric Bergman 2, Keith McLaughlin 1, Hans Israelsson 1, Yu-Long Kung 1, Paul Piraino 1, and Bob Engdahl
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure
 Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
The COMPLOC Earthquake Location Package
 The COMPLOC Earthquake Location Package Guoqing Lin and Peter Shearer Guoqing Lin and Peter Shearer Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California San Diego INTRODUCTION This article describes
The COMPLOC Earthquake Location Package Guoqing Lin and Peter Shearer Guoqing Lin and Peter Shearer Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California San Diego INTRODUCTION This article describes
Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms
 Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms Jean Baptiste Tary 1, Mirko van der Baan 1, and Roberto Henry Herrera 1 1 Department
Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms Jean Baptiste Tary 1, Mirko van der Baan 1, and Roberto Henry Herrera 1 1 Department
Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery
 Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery Gabriela Melo and A lison Malcolm Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Massachusetts
Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery Gabriela Melo and A lison Malcolm Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Massachusetts
CS229: Machine Learning
 CS229: Machine Learning Event Identification in Continues Seismic Data Please print out, fill in and include this cover sheet as the first page of your submission. We strongly recommend that you use this
CS229: Machine Learning Event Identification in Continues Seismic Data Please print out, fill in and include this cover sheet as the first page of your submission. We strongly recommend that you use this
28th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 SEISMIC SOURCE LOCATIONS AND PARAMETERS FOR SPARSE NETWORKS BY MATCHING OBSERVED SEISMOGRAMS TO SEMI-EMPIRICAL SYNTHETIC SEISMOGRAMS: IMPROVEMENTS TO THE PHASE SPECTRUM PARAMETERIZATION David. Salzberg
SEISMIC SOURCE LOCATIONS AND PARAMETERS FOR SPARSE NETWORKS BY MATCHING OBSERVED SEISMOGRAMS TO SEMI-EMPIRICAL SYNTHETIC SEISMOGRAMS: IMPROVEMENTS TO THE PHASE SPECTRUM PARAMETERIZATION David. Salzberg
29th Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 SEISMIC SOURCE LOCATIONS AND PARAMETERS FOR SPARSE NETWORKS BY MATCHING OBSERVED SEISMOGRAMS TO SEMI-EMPIRICAL SYNTHETIC SEISMOGRAMS: APPLICATIONS TO LOP NOR AND NORTH KOREA David Salzberg and Margaret
SEISMIC SOURCE LOCATIONS AND PARAMETERS FOR SPARSE NETWORKS BY MATCHING OBSERVED SEISMOGRAMS TO SEMI-EMPIRICAL SYNTHETIC SEISMOGRAMS: APPLICATIONS TO LOP NOR AND NORTH KOREA David Salzberg and Margaret
REMOTE MONITORING OF WEAK AFTERSHOCK ACTIVITY WITH WAVEFORM CROSS CORRELATION: THE CASE OF THE DPRK SEPTEMBER 9, 2016 UNDERGROUND TEST
 REMOTE MONITORING OF WEAK AFTERSHOCK ACTIVITY WITH WAVEFORM CROSS CORRELATION: THE CASE OF THE DPRK SEPTEMBER 9, 2016 UNDERGROUND TEST Bobrov D.I., I.O. Kitov, and M.V. Rozhkov Abstract The method of waveform
REMOTE MONITORING OF WEAK AFTERSHOCK ACTIVITY WITH WAVEFORM CROSS CORRELATION: THE CASE OF THE DPRK SEPTEMBER 9, 2016 UNDERGROUND TEST Bobrov D.I., I.O. Kitov, and M.V. Rozhkov Abstract The method of waveform
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas
 Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION GROUP VELOCITY
 Surface-wave inversion for near-surface shear-wave velocity estimation at Coronation field Huub Douma (ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging solutions) and Matthew Haney (Boise State University) SUMMARY We study
Surface-wave inversion for near-surface shear-wave velocity estimation at Coronation field Huub Douma (ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging solutions) and Matthew Haney (Boise State University) SUMMARY We study
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Travel time estimation methods for mode tomography
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Distribution approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Travel time estimation methods for mode tomography Tarun K. Chandrayadula George Mason University Electrical
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Distribution approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Travel time estimation methods for mode tomography Tarun K. Chandrayadula George Mason University Electrical
27th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 INTEGRATED SEISMIC EVENT DETECTION AND LOCATION BY ADVANCED ARRAY PROCESSING T. Kvaerna 1, S. J. Gibbons 1, F. Ringdal 1, and D. B. Harris 2 NORSAR 1 and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 2 Sponsored
INTEGRATED SEISMIC EVENT DETECTION AND LOCATION BY ADVANCED ARRAY PROCESSING T. Kvaerna 1, S. J. Gibbons 1, F. Ringdal 1, and D. B. Harris 2 NORSAR 1 and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 2 Sponsored
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation
 WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
28th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 8th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies A LOWER BOUND ON THE STANDARD ERROR OF AN AMPLITUDE-BASED REGIONAL DISCRIMINANT D. N. Anderson 1, W. R. Walter, D. K.
8th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies A LOWER BOUND ON THE STANDARD ERROR OF AN AMPLITUDE-BASED REGIONAL DISCRIMINANT D. N. Anderson 1, W. R. Walter, D. K.
Microseismic events enhancement and detection in sensor arrays using autocorrelation-based filtering
 Geophysical Prospecting, 7 doi:./3-78.9 Microseismic events enhancement and detection in sensor arrays using autocorrelation-based filtering Entao Liu, Lijun Zhu, Anupama Govinda Raj, James H. McClellan,
Geophysical Prospecting, 7 doi:./3-78.9 Microseismic events enhancement and detection in sensor arrays using autocorrelation-based filtering Entao Liu, Lijun Zhu, Anupama Govinda Raj, James H. McClellan,
EXPLOITING AMBIENT NOISE FOR SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS
 EXPLOITING AMBIENT NOISE FOR SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS ABSTRACT Michael H. Ritzwoller, Anatoli L. Levshin, and Mikhail P. Barmin University of Colorado at Boulder Sponsored by
EXPLOITING AMBIENT NOISE FOR SOURCE CHARACTERIZATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS ABSTRACT Michael H. Ritzwoller, Anatoli L. Levshin, and Mikhail P. Barmin University of Colorado at Boulder Sponsored by
Improved Locations Through Waveform Cross-Correlation Within the Antelope Environment
 Improved Locations Through Waveform Cross-Correlation Within the Antelope Environment David von Seggern Nevada Seismological Laboratory Antelope Users Group Meeting June 7, 2008 Outline of This Talk history
Improved Locations Through Waveform Cross-Correlation Within the Antelope Environment David von Seggern Nevada Seismological Laboratory Antelope Users Group Meeting June 7, 2008 Outline of This Talk history
Earthquakes: Nucleation, Triggering, Rupture, and Relationships to Aseismic Processes October 3, 2017, Cargese. ( Haar transform ), window #1267
 The FAST Method for Earthquake Detection: Application to Seismicity During the Initial Stages of the Guy- Greenbrier, Arkansas, Earthquake Sequence Clara Yoon, Karianne Bergen, Ossian O Reilly, Fantine
The FAST Method for Earthquake Detection: Application to Seismicity During the Initial Stages of the Guy- Greenbrier, Arkansas, Earthquake Sequence Clara Yoon, Karianne Bergen, Ossian O Reilly, Fantine
Basis Pursuit for Seismic Spectral decomposition
 Basis Pursuit for Seismic Spectral decomposition Jiajun Han* and Brian Russell Hampson-Russell Limited Partnership, CGG Geo-software, Canada Summary Spectral decomposition is a powerful analysis tool used
Basis Pursuit for Seismic Spectral decomposition Jiajun Han* and Brian Russell Hampson-Russell Limited Partnership, CGG Geo-software, Canada Summary Spectral decomposition is a powerful analysis tool used
Company profile... 4 Our Teams... 4 E&P Software Solutions Software Technical and Software Support Training...
 Company profile... 4 Our Teams... 4 E&P Software Solutions... 4 2.1 Software... 5 2.2 Technical and Software Support... 6 2.3 Training... 6 3.1 Privileged Access to State of the Art Technology... 7 3.2
Company profile... 4 Our Teams... 4 E&P Software Solutions... 4 2.1 Software... 5 2.2 Technical and Software Support... 6 2.3 Training... 6 3.1 Privileged Access to State of the Art Technology... 7 3.2
Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION
 Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION Innovative Solutions, from Access to Production Uncertainty Knowledge ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT
Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION Innovative Solutions, from Access to Production Uncertainty Knowledge ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas
 The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays
 Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays J. Wang 1, F. Tilmann 1, R. S. White 1, H. Soosalu 1 and P. Bordoni 2 1. Bullard Laboratories,
Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays J. Wang 1, F. Tilmann 1, R. S. White 1, H. Soosalu 1 and P. Bordoni 2 1. Bullard Laboratories,
Coda Waveform Correlations
 Chapter 5 Coda Waveform Correlations 5.1 Cross-Correlation of Seismic Coda 5.1.1 Introduction In the previous section, the generation of the surface wave component of the Green s function by the correlation
Chapter 5 Coda Waveform Correlations 5.1 Cross-Correlation of Seismic Coda 5.1.1 Introduction In the previous section, the generation of the surface wave component of the Green s function by the correlation
Data-Driven Earthquake Location Method Project Report
 Data-Driven Earthquake Location Method Project Report Weiqiang Zhu (6118474), Kaiwen Wang (6122739) Department of Geophysics, School of Earth, Energy and Environmental Science 1 Abstract 12/16/216 Earthquake
Data-Driven Earthquake Location Method Project Report Weiqiang Zhu (6118474), Kaiwen Wang (6122739) Department of Geophysics, School of Earth, Energy and Environmental Science 1 Abstract 12/16/216 Earthquake
Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site
 Number of pages Number of appendices 33 (incl. appendices) 3 TNO report Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site Date
Number of pages Number of appendices 33 (incl. appendices) 3 TNO report Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site Date
Multicomponent seismic polarization analysis
 Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
WS15-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise
 WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
Automatic P-onset precise determination based on local maxima and minima
 CTBT: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE 2015, 22-26 June, Hofburg palace, Vienna, Austria LETSMP Automatic P-onset precise determination based on local maxima and minima Presented by: Dr. Ait Laasri El
CTBT: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY CONFERENCE 2015, 22-26 June, Hofburg palace, Vienna, Austria LETSMP Automatic P-onset precise determination based on local maxima and minima Presented by: Dr. Ait Laasri El
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data
 Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
Introduction. Figure 2: Source-Receiver location map (to the right) and geometry template (to the left).
 Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
Multipole Sonic-While-Drilling Technology Delivers Quality Data Regardless of Mud Slowness
 YOUNG TECHNOLOGY SHOWCASE Multipole Sonic-While-Drilling Technology Delivers Quality Data Regardless of Mud Slowness Julio Loreto, Eduardo Saenz, and Vivian Pistre, Schlumberger As the pace of exploration
YOUNG TECHNOLOGY SHOWCASE Multipole Sonic-While-Drilling Technology Delivers Quality Data Regardless of Mud Slowness Julio Loreto, Eduardo Saenz, and Vivian Pistre, Schlumberger As the pace of exploration
P1-3-8 Avoiding False Amplitude Anomalies by 3D Seismic Trace Detuning Introduction Wedge Model of Tuning
 P1-3-8 Avoiding False Amplitude Anomalies by 3D Seismic Trace Detuning Ashley Francis, Samuel Eckford Earthworks Reservoir, Salisbury, Wiltshire, UK Introduction Amplitude maps derived from 3D seismic
P1-3-8 Avoiding False Amplitude Anomalies by 3D Seismic Trace Detuning Ashley Francis, Samuel Eckford Earthworks Reservoir, Salisbury, Wiltshire, UK Introduction Amplitude maps derived from 3D seismic
Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes
 Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes Christopher C. Petten*, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta ccpetten@ucalgary.ca and Gary F.
Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes Christopher C. Petten*, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta ccpetten@ucalgary.ca and Gary F.
Picking microseismic first arrival times by Kalman filter and wavelet transform
 Picking first arrival times Picking microseismic first arrival times by Kalman filter and wavelet transform Baolin Qiao and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT Due to the high energy content of the ambient noise,
Picking first arrival times Picking microseismic first arrival times by Kalman filter and wavelet transform Baolin Qiao and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT Due to the high energy content of the ambient noise,
A Rayleigh wave back-projection method applied to the 2011 Tohoku earthquake
 A Rayleigh wave back-projection method applied to the 2011 Tohoku earthquake Daniel Roten, Hiroe Miyake, and Kazuki Koketsu (2012), GRL Earthquake of the Week - 27 January 2012 Roten, D., H. Miyake, and
A Rayleigh wave back-projection method applied to the 2011 Tohoku earthquake Daniel Roten, Hiroe Miyake, and Kazuki Koketsu (2012), GRL Earthquake of the Week - 27 January 2012 Roten, D., H. Miyake, and
Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Group Array Stack of single sensor data
 P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
RESERVOIR CHARACTERIZATION
 A Short Course for the Oil & Gas Industry Professionals INSTRUCTOR: Shahab D. Mohaghegh, Ph. D. Intelligent Solution, Inc. Professor, Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering West Virginia University Morgantown,
A Short Course for the Oil & Gas Industry Professionals INSTRUCTOR: Shahab D. Mohaghegh, Ph. D. Intelligent Solution, Inc. Professor, Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering West Virginia University Morgantown,
Automatic Picker Developments and Optimization: FilterPicker a Robust, Broadband Picker for Real-Time Seismic Monitoring and Earthquake Early Warning
 Automatic Picker Developments and Optimization: FilterPicker a Robust, Broadband Picker for Real-Time Seismic Monitoring and Earthquake Early Warning Anthony Lomax, Claudio Satriano, and Maurizio Vassallo
Automatic Picker Developments and Optimization: FilterPicker a Robust, Broadband Picker for Real-Time Seismic Monitoring and Earthquake Early Warning Anthony Lomax, Claudio Satriano, and Maurizio Vassallo
Location of Remote Harmonics in a Power System Using SVD *
 Location of Remote Harmonics in a Power System Using SVD * S. Osowskil, T. Lobos2 'Institute of the Theory of Electr. Eng. & Electr. Measurements, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, POLAND email:
Location of Remote Harmonics in a Power System Using SVD * S. Osowskil, T. Lobos2 'Institute of the Theory of Electr. Eng. & Electr. Measurements, Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, POLAND email:
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
TOWARD A RAYLEIGH WAVE ATTENUATION MODEL FOR EURASIA AND CALIBRATING A NEW M S FORMULA
 TOWARD A RAYLEIGH WAVE ATTENUATION MODEL FOR EURASIA AND CALIBRATING A NEW M S FORMULA Xiaoning (David) Yang 1, Anthony R. Lowry 2, Anatoli L. Levshin 2 and Michael H. Ritzwoller 2 1 Los Alamos National
TOWARD A RAYLEIGH WAVE ATTENUATION MODEL FOR EURASIA AND CALIBRATING A NEW M S FORMULA Xiaoning (David) Yang 1, Anthony R. Lowry 2, Anatoli L. Levshin 2 and Michael H. Ritzwoller 2 1 Los Alamos National
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 6b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO
 Antennas and Propagation b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO Introduction From last lecture How do we model H p? Discrete path model (physical, plane waves) Random matrix models (forget H p and
Antennas and Propagation b: Path Models Rayleigh, Rician Fading, MIMO Introduction From last lecture How do we model H p? Discrete path model (physical, plane waves) Random matrix models (forget H p and
HIGH-FREQUENCY ACOUSTIC PROPAGATION IN THE PRESENCE OF OCEANOGRAPHIC VARIABILITY
 HIGH-FREQUENCY ACOUSTIC PROPAGATION IN THE PRESENCE OF OCEANOGRAPHIC VARIABILITY M. BADIEY, K. WONG, AND L. LENAIN College of Marine Studies, University of Delaware Newark DE 19716, USA E-mail: Badiey@udel.edu
HIGH-FREQUENCY ACOUSTIC PROPAGATION IN THE PRESENCE OF OCEANOGRAPHIC VARIABILITY M. BADIEY, K. WONG, AND L. LENAIN College of Marine Studies, University of Delaware Newark DE 19716, USA E-mail: Badiey@udel.edu
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS
 Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
A TECHNIQUE FOR AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF ONSET TIME OF P- AND S-PHASES IN STRONG MOTION RECORDS
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 786 A TECHNIQUE FOR AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF ONSET TIME OF P- AND S-PHASES IN STRONG MOTION RECORDS Takashi
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 786 A TECHNIQUE FOR AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF ONSET TIME OF P- AND S-PHASES IN STRONG MOTION RECORDS Takashi
29th Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 ADAPTIVE WAVEFORM CORRELATION DETECTORS FOR ARRAYS: ALGORITHMS FOR AUTONOMOUS CALIBRATION ABSTRACT Frode Ringdal 1, Steven J. Gibbons 1, and David B. Harris 2 NORSAR 1 and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
ADAPTIVE WAVEFORM CORRELATION DETECTORS FOR ARRAYS: ALGORITHMS FOR AUTONOMOUS CALIBRATION ABSTRACT Frode Ringdal 1, Steven J. Gibbons 1, and David B. Harris 2 NORSAR 1 and Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Study of Low-frequency Seismic Events Sources in the Mines of the Verkhnekamskoye Potash Deposit
 Study of Low-frequency Seismic Events Sources in the Mines of the Verkhnekamskoye Potash Deposit D.A. Malovichko Mining Institute, Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences ABSTRACT Seismic networks operated
Study of Low-frequency Seismic Events Sources in the Mines of the Verkhnekamskoye Potash Deposit D.A. Malovichko Mining Institute, Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences ABSTRACT Seismic networks operated
Northing (km)
 Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to
 Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic
 Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
CDP noise attenuation using local linear models
 CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
ASSESSING LOCATION CAPABILITY WITH GROUND TRUTH EVENTS: THE DEAD SEA AND SOUTH AFRICA REGIONS. Clifford Thurber, Haijiang Zhang, and William Lutter
 ASSESSING LOCATION CAPABILITY WITH GROUND TRUTH EVENTS: THE DEAD SEA AND SOUTH AFRICA REGIONS Clifford Thurber, Haijiang Zhang, and William Lutter University of Wisconsin-Madison Sponsored by Defense Threat
ASSESSING LOCATION CAPABILITY WITH GROUND TRUTH EVENTS: THE DEAD SEA AND SOUTH AFRICA REGIONS Clifford Thurber, Haijiang Zhang, and William Lutter University of Wisconsin-Madison Sponsored by Defense Threat
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
27th Seismic Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 IMPROVING M s ESTIMATES BY CALIBRATING VARIABLE PERIOD MAGNITUDE SCALES AT REGIONAL DISTANCES Heather Hooper 1, Ileana M. Tibuleac 1, Michael Pasyanos 2, and Jessie L. Bonner 1 Weston Geophysical Corporation
IMPROVING M s ESTIMATES BY CALIBRATING VARIABLE PERIOD MAGNITUDE SCALES AT REGIONAL DISTANCES Heather Hooper 1, Ileana M. Tibuleac 1, Michael Pasyanos 2, and Jessie L. Bonner 1 Weston Geophysical Corporation
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System
 A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain
 High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis
 Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Short Notes Characterization of a Continuous, Very Narrowband Seismic Signal near 2.08 Hz
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 91, 6, pp. 1910 1916, December 2001 Short Notes Characterization of a Continuous, Very Narrowband Seismic Signal near 2.08 Hz by Kelly H. Liu and Stephen
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 91, 6, pp. 1910 1916, December 2001 Short Notes Characterization of a Continuous, Very Narrowband Seismic Signal near 2.08 Hz by Kelly H. Liu and Stephen
Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology
 Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology M S Maklad* Signal Estimation Technology Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada msm@signalestimation.com and J K Dirstein Total Depth Pty Ltd, Perth, Western Australia,
Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology M S Maklad* Signal Estimation Technology Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada msm@signalestimation.com and J K Dirstein Total Depth Pty Ltd, Perth, Western Australia,
JUMPSTARTING NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING FOR SEISMIC PROBLEMS
 JUMPSTARTING NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING FOR SEISMIC PROBLEMS Fantine Huot (Stanford Geophysics) Advised by Greg Beroza & Biondo Biondi (Stanford Geophysics & ICME) LEARNING FROM DATA Deep learning networks
JUMPSTARTING NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING FOR SEISMIC PROBLEMS Fantine Huot (Stanford Geophysics) Advised by Greg Beroza & Biondo Biondi (Stanford Geophysics & ICME) LEARNING FROM DATA Deep learning networks
of Seismic Wave Propagation In Jordan
 UCRL-JC-134329 PREPRINT Calibration of Seismic Wave Propagation In Jordan D. Harris, K. Mayeda, K. Nakanishi, A. Rodgers, S. Ruppert, F. Ryall, K. Skinnell, A-Q Amrat, T. Al-Yazjeen, A. Al-Husien F. Simon
UCRL-JC-134329 PREPRINT Calibration of Seismic Wave Propagation In Jordan D. Harris, K. Mayeda, K. Nakanishi, A. Rodgers, S. Ruppert, F. Ryall, K. Skinnell, A-Q Amrat, T. Al-Yazjeen, A. Al-Husien F. Simon
2011 Monitoring Research Review: Ground-Based Nuclear Explosion Monitoring Technologies
 COMBINING ANALYST AND WAVEFORM-CORRELATION-BASED ARRIVAL TIME MEASUREMENTS IN THE BAYESLOC MULTIPLE-EVENT LOCATION ALGORITHM Stephen C. Myers, Gardar Johannesson, Douglas A. Dodge, and Nathan A. Simmons
COMBINING ANALYST AND WAVEFORM-CORRELATION-BASED ARRIVAL TIME MEASUREMENTS IN THE BAYESLOC MULTIPLE-EVENT LOCATION ALGORITHM Stephen C. Myers, Gardar Johannesson, Douglas A. Dodge, and Nathan A. Simmons
( ) ( ) (1) GeoConvention 2013: Integration 1
 Regular grids travel time calculation Fast marching with an adaptive stencils approach Zhengsheng Yao, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada zyao2@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, Randy Kolesar, WesternGeco,
Regular grids travel time calculation Fast marching with an adaptive stencils approach Zhengsheng Yao, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada zyao2@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, Randy Kolesar, WesternGeco,
Method to Improve Location Accuracy of the GLD360
 Method to Improve Location Accuracy of the GLD360 Ryan Said Vaisala, Inc. Boulder Operations 194 South Taylor Avenue, Louisville, CO, USA ryan.said@vaisala.com Amitabh Nag Vaisala, Inc. Boulder Operations
Method to Improve Location Accuracy of the GLD360 Ryan Said Vaisala, Inc. Boulder Operations 194 South Taylor Avenue, Louisville, CO, USA ryan.said@vaisala.com Amitabh Nag Vaisala, Inc. Boulder Operations
McArdle, N.J. 1, Ackers M. 2, Paton, G ffa 2 - Noreco. Introduction.
 An investigation into the dependence of frequency decomposition colour blend response on bed thickness and acoustic impedance: results from wedge and thin bed models applied to a North Sea channel system
An investigation into the dependence of frequency decomposition colour blend response on bed thickness and acoustic impedance: results from wedge and thin bed models applied to a North Sea channel system
Attenuation estimation with continuous wavelet transforms. Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston.
 . Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston. SUMMARY Seismic attenuation measurements from surface seismic data using spectral ratios are particularly sensitive to
. Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston. SUMMARY Seismic attenuation measurements from surface seismic data using spectral ratios are particularly sensitive to
Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet transform
 Joint Time/Frequency, Computation of Q, Dr. M. Turhan (Tury Taner, Rock Solid Images Page: 1 Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet
Joint Time/Frequency, Computation of Q, Dr. M. Turhan (Tury Taner, Rock Solid Images Page: 1 Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet
Corresponding Author William Menke,
 Waveform Fitting of Cross-Spectra to Determine Phase Velocity Using Aki s Formula William Menke and Ge Jin Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Corresponding Author William Menke, MENKE@LDEO.COLUMBIA.EDU,
Waveform Fitting of Cross-Spectra to Determine Phase Velocity Using Aki s Formula William Menke and Ge Jin Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Corresponding Author William Menke, MENKE@LDEO.COLUMBIA.EDU,
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION
 MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION by Delaine Thompson Earth Resources Laboratory Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION by Delaine Thompson Earth Resources Laboratory Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile
 Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
EPICENTRAL LOCATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS BASED ON EMPIRICAL GREEN FUNCTIONS FROM AMBIENT NOISE
 EPICENTRAL LOCATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS BASED ON EMPIRICAL GREEN FUNCTIONS FROM AMBIENT NOISE Michael H. Ritzwoller, Mikhail P. Barmin, Anatoli L. Levshin, and Yingjie Yang University of Colorado
EPICENTRAL LOCATION OF REGIONAL SEISMIC EVENTS BASED ON EMPIRICAL GREEN FUNCTIONS FROM AMBIENT NOISE Michael H. Ritzwoller, Mikhail P. Barmin, Anatoli L. Levshin, and Yingjie Yang University of Colorado
(Gibbons and Ringdal 2006, Anstey 1964), but the method has yet to be explored in the context of acoustic damage detection of civil structures.
 ABSTRACT There has been recent interest in using acoustic techniques to detect damage in instrumented civil structures. An automated damage detection method that analyzes recorded data has application
ABSTRACT There has been recent interest in using acoustic techniques to detect damage in instrumented civil structures. An automated damage detection method that analyzes recorded data has application
FOUR TOTAL TRANSFER CAPABILITY. 4.1 Total transfer capability CHAPTER
 CHAPTER FOUR TOTAL TRANSFER CAPABILITY R structuring of power system aims at involving the private power producers in the system to supply power. The restructured electric power industry is characterized
CHAPTER FOUR TOTAL TRANSFER CAPABILITY R structuring of power system aims at involving the private power producers in the system to supply power. The restructured electric power industry is characterized
Estimating the epicenters of local and regional seismic sources, using the circle and chord method (Tutorial with exercise by hand and movies)
 Topic Estimating the epicenters of local and regional seismic sources, using the circle and chord method (Tutorial with exercise by hand and movies) Author Version Peter Bormann (formerly GFZ German Research
Topic Estimating the epicenters of local and regional seismic sources, using the circle and chord method (Tutorial with exercise by hand and movies) Author Version Peter Bormann (formerly GFZ German Research
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (015) 03, 1896 1908 GJI Seismology doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv419 Comparison of the STA/LTA and power spectral density methods for microseismic event detection
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (015) 03, 1896 1908 GJI Seismology doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv419 Comparison of the STA/LTA and power spectral density methods for microseismic event detection
Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging To cite this article: Y. Bashir et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of Frequency and Migration Aperture on Seismic Diffraction Imaging To cite this article: Y. Bashir et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.:
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method
 P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
24th Seismic Research Review Nuclear Explosion Monitoring: Innovation and Integration
 ON INFRASOUND DETECTION AND LOCATION STRATEGIES Rodney Whitaker, Douglas ReVelle, and Tom Sandoval Los Alamos National Laboratory Sponsored by National Nuclear Security Administration Office of Nonproliferation
ON INFRASOUND DETECTION AND LOCATION STRATEGIES Rodney Whitaker, Douglas ReVelle, and Tom Sandoval Los Alamos National Laboratory Sponsored by National Nuclear Security Administration Office of Nonproliferation
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data
 Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
