PHY-2464 Physical Basis of Music
|
|
|
- Ralph Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physical Basis of Music Presentation 19 Characteristic Sound (Timbre) of Wind Instruments Adapted from Sam Matteson s Unit 3 Session 30 and Unit 1 Session 10 Sam Trickey Mar. 15, 2005 REMINDERS: Brass instruments are characterized by buzzing the lips in a mouth piece. KEY FACTS Pipe is closed at mouthpiece end to an excellent approximation. The buzzing is stabilized by feedback from the open pipe end which matches impedance peaks. There are valved and valveless brass instruments There are brasses made with little or no metal.
2 What is the key physical difference among a Cornet, Trumpet, and Flügelhorn gelhorn? Trumpet Cornet The fraction of the horn that is cone/cylinder/flare. Trumpet most cylindrical Cornet -- more conical Flugel Horn most conical Flügelhorn Transverse Flute open pipe instrument Driven by air flow against the edge of the embochure hole. A pressure node exists there. Pitch is controlled by holes in the tube. Air flow Embrochure hole
3 Single Reed instruments stopped pipe The reed opens and closes like a valve, pressurizing the pipe when open, closing due to the Bernoulli effect when the air flows. A pressure anti-node node exists at the reed. Pitch is controlled by holes in the pipe. Air flow Tonguing Reed Double Reed instruments stopped pipe As with single reeds, the reed opens and closes like a valve, pressurizing the pipe when open, closing due to the Bernoulli effect when the air flows. A pressure anti-node node exists at the reed. Pitch is controlled by holes in the pipe. Air flow Pressure Pulses Reed Tip
4 Brass instruments stopped pipe Brass instruments are played by the player s s lips that form a lip valve. The lip valve admits pressure pulses into the pipe. The frequency is determined by the breath air pressure, the lip tension and the resonances of the pipe. A pressure anti-node node exists at the player s s lips. Pitch is controlled by valves and extra tubing, and/or slides, and/or overblowing. Louis Armstrong trumpet ( ) 1971) Wind instrument comparison f 5f 1 4f 1 3f 1 2f 1 f 1 5f 1 3f 1 f 1 6f 1 5f 1 4f 1 3f 1 2f 1 f 1 6f O 5f O 4f O 3f O 2f O f O f 1 Pedal Tone L f 1 = v/2l f 1 = v/4l Flute = v/4l f 1 = v/2(l+c) Clarinet Other Woodwinds c f o = (1+ξ)v/4(L+c) Brass
5 More wind instrument comparison Open Cylinder Stopped Cylinder Stopped Cone Stopped Combination N p N p f n = nf 1 f 1 = v/2l A p N p f 2n-1 = (2n-1)f 1 f 1 = v/4l A p N p f n = nf 1 f 1 = v/2(l+c) A p N p f n = nf 0 f 0 = (1+ξ)v/4(L+c) L f 1 = v/2l f 1 = v/4l Flute = v/4l f 1 = v/2(l+c) Clarinet Other Woodwinds c f o = (1+ξ)v/4(L+c) Brass In the flute, feedback from the acoustic standing wave locks the frequency of the oscillation if the edge tone is near the fundamental frequency. Matches impedance minima. Displacement wave f edge = 0.2 v jet /b f n = n v/ 2L; f edge f n
6 In reed instruments, pressure standing wave feedback locks the frequency of the oscillation of the reed; matches impedance maxima. Pressure wave f 2n 2n-1 = (2n-1) v/ 4L L = L r Pressure inverts 0.6 r Brass Instruments are stopped pipes. The player s s lips produce a displace- ment node (pressure antinode) ) at the mouth- piece. A displacement anti-node node (pressure node) exists at the bell. Winton Marsalis Trumpet
7 Feedback from Resonances KEY FACT: Wind instrument pitch is determined by the influence on the jet/reed/lip-valve of feedback from the pressure/displacement standing waves in the pipe. The near matching of impedance maxima or minima determines the stable ( playable )) pitches. Interlude regarding basics of SPECTRA: The energy of an oscillator or of sound dissipates in an exponential decay. An oscillator can be caused to vibrate in sympathy when the driving frequency is close to that of a natural mode of oscillation. The timbre of an instrument is determined by its spectrum The spectrum of an instrument changes with time because of transients.
8 Exponential Decay (pressure as example) p envelope = p / 1/2 0, /2 t t env A Fourier Decomposition is a representation of all the components that comprise a waveform, amplitude versus frequency and phase versus frequency.
9 Example: Synthesis of a Square wave- The Fourier Spectrum Fundamental 1 st Harmonic Amplitude 1 st Overtone 3 rd 2 nd Harmonic Overtone 5 th Harmonic f o 3f o 5f o Frequency 7f o Waveform Synthesis Harmonic n = Overtone f0 f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 f6 f7 f8 Amplitude = Amplitude (Pa) all modes =1/odd=2: Phase Frequency (Hz) = Component Amplitude (Pa) Fourier Spectrum Amplitude (Pa) Composite Waveform Frequency (Hz) Time (ms)
10 ADSR: Attack, Decay, Sustain, Release The envelope of the amplitude of all musical sound is described by ADSR. amplitude Attack Decay Sustain Release time Wind Instruments A jet produces a fluctuating air flow, while a reed or the lips produce pressure pulsations, the frequencies of which are controlled by impedance matching feedback from standing waves in the horn. Flow fluctuations or Pressure Feedback pulsations Standing waves in horn f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 ~ ~ f n
11 Effect of Excitation The mode of excitation of the horn significantly influences the harmonic recipe (spectrum) of the air column. The relative strengths (amplitudes) of the harmonics are determined by the excitation of the jet/reed/lip-valve. The spectrum of the radiated sound determines the timbre. Driven Pipe Vibrational Spectrum ( Recipe( Recipe ) A Pipe Spectrum A A Mouthpiece Spectrum Driven Pipe Spectrum Frequency
12 Effect of the Pipe A pipe is three dimensional; therefore, 3-D 3 modes of oscillation are possible in the pipe. Only those modes with frequency above a cut- off frequency f c (low frequency cut-off) will exist in the pipe. f > f c for propagation. Transverse Modes of Vibration of an Air Column (0,0) D (1,0) (2,0) Cut-off Frequency f c = q n m v/d; for f < f c no propagation q 00 = 0; q 10 = 0.59; q 20 = 0.97
13 Effect of Transverse Modes on Spectrum More transverse modes implies more intensity. Most influential in high frequency harmonics. Shape and relative diameter of pipe influence transverse modes. Thus, a square, triangular, and circular cross- section organ pipes have different timbres. Reflections from the array of holes in a woodwind affect the relative strength of the high frequency harmonics in the pipe. Displacement wave Reflections from holes (closed and open)
14 Effect of Holes on Transmission Larger holes have greater effect. A high pass filter: Low frequencies tend to be reflected more and high frequencies transmitted more. Thus the holes make a brighter sounding instrument. Reflections from joints and imperfections affect the relative amplitude of the high frequency harmonics in the pipe. Reflections
15 Filtering of Wind Instrument Sound The specifics of transmission of the various frequency components in the pipe produce a filtering effect on the frequency spectrum of the sound. Transmission through horn f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 ~ ~ f n Radiation of Sound from Wind Instruments The radiation characteristics of the bell alter ( shape )) the harmonic recipe, hence strongly influence the timbre of the instrument. Radiation Characteristics f 1 f 2 f 3 f 4 ~ ~ f n
16 The diameter of the mouth and the flare rate of the bell determine the radiation characteristics of brass instruments. Trumpet The larger the bore diameter, the more intense the low frequency harmonics. The more rapid the flare,, the more the low frequencies are reflected, and thus, the more high frequency harmonics are radiated. Cornet Flügelhorn The Bell Exponential Horn a = a o exp(m x)+ b m = flare constant. Larger m means more rapid flare accentuate high frequencies x
17 French Horn Bell Bessel Horn a a = a o e -(εx ) +b x Called Bessel Horns because the standing wave follows a Bessel Function. Mutes The French Horn player s s hand modifies the radiation characteristics of the horn, as well as the effective flare. Mutes reduce the effective area of the horn and, therefore, reduce the intensity. Mutes tend to reduce more the first and second harmonic of the pipe than higher frequency harmonics due to their internal modes of oscillation. Mutes make brass sound thin and reedy.
18 Summary - The pitch of a wind instrument is determined by the length and shape of its air column. The effective length of the air column is controlled with holes, valves and slides. Feedback from the resonances of the pipe select the frequency of oscillation of the jet, reed or lip-valve. The excitation, transmission and emittance of the sound in the horn determine the timbre of the instrument.
Chapter 18. Superposition and Standing Waves
 Chapter 18 Superposition and Standing Waves Particles & Waves Spread Out in Space: NONLOCAL Superposition: Waves add in space and show interference. Do not have mass or Momentum Waves transmit energy.
Chapter 18 Superposition and Standing Waves Particles & Waves Spread Out in Space: NONLOCAL Superposition: Waves add in space and show interference. Do not have mass or Momentum Waves transmit energy.
A Look at Un-Electronic Musical Instruments
 A Look at Un-Electronic Musical Instruments A little later in the course we will be looking at the problem of how to construct an electrical model, or analog, of an acoustical musical instrument. To prepare
A Look at Un-Electronic Musical Instruments A little later in the course we will be looking at the problem of how to construct an electrical model, or analog, of an acoustical musical instrument. To prepare
The Physics of Musical Instruments
 Neville H. Fletcher Thomas D. Rossing The Physics of Musical Instruments Second Edition With 485 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface Preface to the First Edition v vii I. Vibrating Systems 1. Free
Neville H. Fletcher Thomas D. Rossing The Physics of Musical Instruments Second Edition With 485 Illustrations Springer Contents Preface Preface to the First Edition v vii I. Vibrating Systems 1. Free
Chapter 21 Musical Instruments
 Lecture 22 Chapter 21 Musical Instruments CR/NC Deadline Oct. 19 Musical Instruments Now that we understand some of the physics of sound, let s analyze how musical sound is produced by different types
Lecture 22 Chapter 21 Musical Instruments CR/NC Deadline Oct. 19 Musical Instruments Now that we understand some of the physics of sound, let s analyze how musical sound is produced by different types
Dept. of Computer Science, University of Copenhagen Universitetsparken 1, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark
 NORDIC ACOUSTICAL MEETING 12-14 JUNE 1996 HELSINKI Dept. of Computer Science, University of Copenhagen Universitetsparken 1, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark krist@diku.dk 1 INTRODUCTION Acoustical instruments
NORDIC ACOUSTICAL MEETING 12-14 JUNE 1996 HELSINKI Dept. of Computer Science, University of Copenhagen Universitetsparken 1, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark krist@diku.dk 1 INTRODUCTION Acoustical instruments
Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990.
 Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990. Acoustics 1 1 Introduction Acoustics 2! The word acoustics refers to the science of sound and is a subcategory of physics! Room acoustics
Sound, acoustics Slides based on: Rossing, The science of sound, 1990. Acoustics 1 1 Introduction Acoustics 2! The word acoustics refers to the science of sound and is a subcategory of physics! Room acoustics
Review of Standing Waves on a String
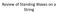 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30 m A.
Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30 m A.
L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String
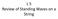 L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30
L 5 Review of Standing Waves on a String Below is a picture of a standing wave on a 30 meter long string. What is the wavelength of the running waves that the standing wave is made from? 30
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Sound 16-1 Characteristics of Sound Sound can travel through h any kind of matter, but not through a vacuum. The speed of sound is different in different materials; in general, it is slowest
Chapter 16 Sound 16-1 Characteristics of Sound Sound can travel through h any kind of matter, but not through a vacuum. The speed of sound is different in different materials; in general, it is slowest
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 14-7 Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same medium combine, or superpose, by simple addition. 14-7 Superposition and Interference If two pulses combine to give
14-7 Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same medium combine, or superpose, by simple addition. 14-7 Superposition and Interference If two pulses combine to give
Sound & Music. how musical notes are produced and perceived. calculate the frequency of the pitch produced by a string or pipe
 Add Important Sound & Music Page: 53 NGSS Standards: N/A Sound & Music MA Curriculum Frameworks (2006): N/A AP Physics Learning Objectives: 6.D.3., 6.D.3.2, 6.D.3.3, 6.D.3.4, 6.D.4., 6.D.4.2, 6.D.5. Knowledge/Understanding
Add Important Sound & Music Page: 53 NGSS Standards: N/A Sound & Music MA Curriculum Frameworks (2006): N/A AP Physics Learning Objectives: 6.D.3., 6.D.3.2, 6.D.3.3, 6.D.3.4, 6.D.4., 6.D.4.2, 6.D.5. Knowledge/Understanding
Q15.9. Monday, May 2, Pearson Education, Inc.
 Q15.9 While a guitar string is vibrating, you gently touch the midpoint of the string to ensure that the string does not vibrate at that point. The lowest-frequency standing wave that could be present
Q15.9 While a guitar string is vibrating, you gently touch the midpoint of the string to ensure that the string does not vibrate at that point. The lowest-frequency standing wave that could be present
Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase. Out of Phase
 Superposition Interference Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere,
Superposition Interference Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere,
Musical instruments: strings and pipes
 Musical instruments: strings and pipes Physics 211 Syracuse University, Physics 211 Spring 2017 Walter Freeman April 24, 2017 W. Freeman Musical instruments: strings and pipes April 24, 2017 1 / 11 Announcements
Musical instruments: strings and pipes Physics 211 Syracuse University, Physics 211 Spring 2017 Walter Freeman April 24, 2017 W. Freeman Musical instruments: strings and pipes April 24, 2017 1 / 11 Announcements
Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns
 Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Some types of headphones use the phenomena of constructive and destructive interference to cancel out outside noises.
Sound Interference and Resonance: Standing Waves in Air Columns Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Some types of headphones use the phenomena of constructive and destructive interference to cancel out outside noises.
Waves and Sound. AP Physics 1
 Waves and Sound AP Physics 1 What is a wave A WAVE is a vibration or disturbance in space. A MEDIUM is the substance that all SOUND WAVES travel through and need to have in order to move. Classes of waves
Waves and Sound AP Physics 1 What is a wave A WAVE is a vibration or disturbance in space. A MEDIUM is the substance that all SOUND WAVES travel through and need to have in order to move. Classes of waves
A-110 VCO. 1. Introduction. doepfer System A VCO A-110. Module A-110 (VCO) is a voltage-controlled oscillator.
 doepfer System A - 100 A-110 1. Introduction SYNC A-110 Module A-110 () is a voltage-controlled oscillator. This s frequency range is about ten octaves. It can produce four waveforms simultaneously: square,
doepfer System A - 100 A-110 1. Introduction SYNC A-110 Module A-110 () is a voltage-controlled oscillator. This s frequency range is about ten octaves. It can produce four waveforms simultaneously: square,
Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear mathematical relationship between them.
 The Sound of Music Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear mathematical relationship between them. How is music formed? By STANDING WAVES Formed due to
The Sound of Music Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear mathematical relationship between them. How is music formed? By STANDING WAVES Formed due to
Simple Plucked and Blown Free Reeds from Southeast Asia
 Simple Plucked and Blown Free Reeds from Southeast Asia J. Cottingham Coe College, 1220 First Avenue NE, Cedar Rapids, IA 52402, USA jcotting@coe.edu 383 The origins of the free reed mouth organs of Southeast
Simple Plucked and Blown Free Reeds from Southeast Asia J. Cottingham Coe College, 1220 First Avenue NE, Cedar Rapids, IA 52402, USA jcotting@coe.edu 383 The origins of the free reed mouth organs of Southeast
In Phase. Out of Phase
 Superposition Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere, and keep
Superposition Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere, and keep
Physics 1240: Sound and Music Scott Parker 1/31/06. Today: Sound sources, resonance, nature of sound waves (begin wave motion)
 Physics 1240: Sound and Music Scott Parker 1/31/06 Today: Sound sources, resonance, nature of sound waves (begin wave motion) Next Time: Wave motion Outline Last time: Sound sources (string, reed, brass,
Physics 1240: Sound and Music Scott Parker 1/31/06 Today: Sound sources, resonance, nature of sound waves (begin wave motion) Next Time: Wave motion Outline Last time: Sound sources (string, reed, brass,
What is Sound? Part II
 What is Sound? Part II Timbre & Noise 1 Prayouandi (2010) - OneOhtrix Point Never PSYCHOACOUSTICS ACOUSTICS LOUDNESS AMPLITUDE PITCH FREQUENCY QUALITY TIMBRE 2 Timbre / Quality everything that is not frequency
What is Sound? Part II Timbre & Noise 1 Prayouandi (2010) - OneOhtrix Point Never PSYCHOACOUSTICS ACOUSTICS LOUDNESS AMPLITUDE PITCH FREQUENCY QUALITY TIMBRE 2 Timbre / Quality everything that is not frequency
Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase. Out of Phase
 Superposition Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere, and keep
Superposition Interference Waves ADD: Constructive Interference. Waves SUBTRACT: Destructive Interference. In Phase Out of Phase Superposition Traveling waves move through each other, interfere, and keep
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 2. A string is firmly attached at both ends. When a frequency of 60 Hz is applied, the string vibrates in the standing wave
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 2. A string is firmly attached at both ends. When a frequency of 60 Hz is applied, the string vibrates in the standing wave
Music. Sound Part II
 Music Sound Part II What is the study of sound called? Acoustics What is the difference between music and noise? Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear
Music Sound Part II What is the study of sound called? Acoustics What is the difference between music and noise? Music: Sound that follows a regular pattern; a mixture of frequencies which have a clear
INSTRUMENTS OF THE ORCHESTRA
 https://www.sfponline.org/uploads/271/instruments%20of%20the%20orchestra.pdf INSTRUMENTS OF THE ORCHESTRA String Family Violin The violin is the smallest of the string family. It has 4 strings and is played
https://www.sfponline.org/uploads/271/instruments%20of%20the%20orchestra.pdf INSTRUMENTS OF THE ORCHESTRA String Family Violin The violin is the smallest of the string family. It has 4 strings and is played
ACOUSTICS OF THE AIR-JET FAMILY OF INSTRUMENTS ABSTRACT
 104-1 The Seventh Western Pacific Regional Acoustics Conference Kumamoto, Japan, 3-5 October 2000 ACOUSTICS OF THE AIR-JET FAMILY OF INSTRUMENTS Joe WOLFE, John SMITH School of Physics, The University
104-1 The Seventh Western Pacific Regional Acoustics Conference Kumamoto, Japan, 3-5 October 2000 ACOUSTICS OF THE AIR-JET FAMILY OF INSTRUMENTS Joe WOLFE, John SMITH School of Physics, The University
Sound Synthesis. A review of some techniques. Synthesis
 Sound Synthesis A review of some techniques Synthesis Synthesis is the name given to a number of techniques for creating new sounds. Early synthesizers used electronic circuits to create sounds. Modern
Sound Synthesis A review of some techniques Synthesis Synthesis is the name given to a number of techniques for creating new sounds. Early synthesizers used electronic circuits to create sounds. Modern
No Brain Too Small PHYSICS
 WAVES: STANDING WAVES QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS PAN FLUTES (2016;1) Assume the speed of sound in air is 343 m s -1. A pan flute is a musical instrument made of a set of pipes that are closed
WAVES: STANDING WAVES QUESTIONS No Brain Too Small PHYSICS PAN FLUTES (2016;1) Assume the speed of sound in air is 343 m s -1. A pan flute is a musical instrument made of a set of pipes that are closed
Resonance in Air Columns
 Resonance in Air Columns When discussing waves in one dimension, we observed that a standing wave forms on a spring when reflected waves interfere with incident waves. We learned that the frequencies at
Resonance in Air Columns When discussing waves in one dimension, we observed that a standing wave forms on a spring when reflected waves interfere with incident waves. We learned that the frequencies at
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER MUSIC PHYSICAL MODELS. Professor of Computer Science, Art, and Music. Copyright by Roger B.
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER MUSIC PHYSICAL MODELS Roger B. Dannenberg Professor of Computer Science, Art, and Music Copyright 2002-2013 by Roger B. Dannenberg 1 Introduction Many kinds of synthesis: Mathematical
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER MUSIC PHYSICAL MODELS Roger B. Dannenberg Professor of Computer Science, Art, and Music Copyright 2002-2013 by Roger B. Dannenberg 1 Introduction Many kinds of synthesis: Mathematical
Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points]
![Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points]](/thumbs/87/96934113.jpg) Name Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] 1. To demonstrate standing waves, one end of a string is attached to a tuning fork with frequency 120 Hz. The other end
Name Waves and Sound Practice Test 43 points total Free- response part: [27 points] 1. To demonstrate standing waves, one end of a string is attached to a tuning fork with frequency 120 Hz. The other end
Physics Standing Waves. Tues. 4/18, and Thurs. 4/20
 Physics 116 2017 Standing Waves Tues. 4/18, and Thurs. 4/20 A long string is firmly connected to a stationary metal rod at one end. A student holding the other end moves her hand rapidly up and down to
Physics 116 2017 Standing Waves Tues. 4/18, and Thurs. 4/20 A long string is firmly connected to a stationary metal rod at one end. A student holding the other end moves her hand rapidly up and down to
Waves Q1. MockTime.com. (c) speed of propagation = 5 (d) period π/15 Ans: (c)
 Waves Q1. (a) v = 5 cm (b) λ = 18 cm (c) a = 0.04 cm (d) f = 50 Hz Q2. The velocity of sound in any gas depends upon [1988] (a) wavelength of sound only (b) density and elasticity of gas (c) intensity
Waves Q1. (a) v = 5 cm (b) λ = 18 cm (c) a = 0.04 cm (d) f = 50 Hz Q2. The velocity of sound in any gas depends upon [1988] (a) wavelength of sound only (b) density and elasticity of gas (c) intensity
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
Novel Designer Plastic Trumpet Bells for Brass Instruments
 http://dx.doi.org/1.14236/ewic/eva216.3 Novel Designer Plastic Trumpet Bells for Brass Instruments Birmingham City University Faculty of Computing, Engineering and the Built Environment Millennium Point,
http://dx.doi.org/1.14236/ewic/eva216.3 Novel Designer Plastic Trumpet Bells for Brass Instruments Birmingham City University Faculty of Computing, Engineering and the Built Environment Millennium Point,
constructive interference results when destructive interference results when two special interference patterns are the and the
 Interference and Sound Last class we looked at interference and found that constructive interference results when destructive interference results when two special interference patterns are the and the
Interference and Sound Last class we looked at interference and found that constructive interference results when destructive interference results when two special interference patterns are the and the
A NEW TECHNIQUE FOR THE RAPID MEASUREMENT OF THE ACOUSTIC IMPEDANCE OF WIND INSTRUMENTS
 A NEW TECHNIQUE FOR THE RAPID MEASUREMENT OF THE ACOUSTIC IMPEDANCE OF WIND INSTRUMENTS Abstract John Smith, Claudia Fritz, Joe Wolfe School of Physics, University of New South Wales UNSW Sydney, 2052
A NEW TECHNIQUE FOR THE RAPID MEASUREMENT OF THE ACOUSTIC IMPEDANCE OF WIND INSTRUMENTS Abstract John Smith, Claudia Fritz, Joe Wolfe School of Physics, University of New South Wales UNSW Sydney, 2052
Musical Acoustics, C. Bertulani. Musical Acoustics. Lecture 13 Timbre / Tone quality I
 1 Musical Acoustics Lecture 13 Timbre / Tone quality I Waves: review 2 distance x (m) At a given time t: y = A sin(2πx/λ) A -A time t (s) At a given position x: y = A sin(2πt/t) Perfect Tuning Fork: Pure
1 Musical Acoustics Lecture 13 Timbre / Tone quality I Waves: review 2 distance x (m) At a given time t: y = A sin(2πx/λ) A -A time t (s) At a given position x: y = A sin(2πt/t) Perfect Tuning Fork: Pure
Preview. Sound Section 1. Section 1 Sound Waves. Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance. Section 3 Harmonics
 Sound Section 1 Preview Section 1 Sound Waves Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance Section 3 Harmonics Sound Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and
Sound Section 1 Preview Section 1 Sound Waves Section 2 Sound Intensity and Resonance Section 3 Harmonics Sound Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 7A examine and describe oscillatory motion and
CHAPTER 12 SOUND ass/sound/soundtoc. html. Characteristics of Sound
 CHAPTER 12 SOUND http://www.physicsclassroom.com/cl ass/sound/soundtoc. html Characteristics of Sound Intensity of Sound: Decibels The Ear and Its Response; Loudness Sources of Sound: Vibrating Strings
CHAPTER 12 SOUND http://www.physicsclassroom.com/cl ass/sound/soundtoc. html Characteristics of Sound Intensity of Sound: Decibels The Ear and Its Response; Loudness Sources of Sound: Vibrating Strings
Demonstrating Acoustic Resonance: with the CircuitGear CGR-101 and Power Supply PSM-101
 Demonstrating Acoustic Resonance: with the CircuitGear CGR-101 and Power Supply PSM-101 Peter D. Hiscocks, James Gaston Syscomp Electronic Design Limited phiscock@ee.ryerson.ca www.syscompdesign.com August
Demonstrating Acoustic Resonance: with the CircuitGear CGR-101 and Power Supply PSM-101 Peter D. Hiscocks, James Gaston Syscomp Electronic Design Limited phiscock@ee.ryerson.ca www.syscompdesign.com August
Sound Spectra. Periodic Complex Waves 4/6/09
 Sound Spectra The frequencies of all the sinusoidal component that make it up The amplitude of each sinusoidal component present Periodic Complex Waves The repetition frequency determines the pitch The
Sound Spectra The frequencies of all the sinusoidal component that make it up The amplitude of each sinusoidal component present Periodic Complex Waves The repetition frequency determines the pitch The
Sound. DEF: A pressure variation that is transmitted through matter. Collisions are high pressure / compressions.
 Sound Sound DEF: A pressure variation that is transmitted through matter. Link to pic of bell animation Collisions are high pressure / compressions. Pulls are low pressure / rarefacation. Have same properties
Sound Sound DEF: A pressure variation that is transmitted through matter. Link to pic of bell animation Collisions are high pressure / compressions. Pulls are low pressure / rarefacation. Have same properties
Lecture 2: Acoustics
 ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 2: Acoustics 1. Acoustics, Sound & the Wave Equation 2. Musical Oscillations 3. The Digital Waveguide Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 2: Acoustics 1. Acoustics, Sound & the Wave Equation 2. Musical Oscillations 3. The Digital Waveguide Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
CMPT 468: Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis
 CMPT 468: Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 6, 23 Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) Till now we ve seen signals
CMPT 468: Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University October 6, 23 Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) Till now we ve seen signals
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
PHYSICS 102N Spring Week 6 Oscillations, Waves, Sound and Music
 PHYSICS 102N Spring 2009 Week 6 Oscillations, Waves, Sound and Music Oscillations Any process that repeats itself after fixed time period T Examples: Pendulum, spring and weight, orbits, vibrations (musical
PHYSICS 102N Spring 2009 Week 6 Oscillations, Waves, Sound and Music Oscillations Any process that repeats itself after fixed time period T Examples: Pendulum, spring and weight, orbits, vibrations (musical
Ch17. The Principle of Linear Superposition and Interference Phenomena. The Principle of Linear Superposition
 Ch17. The Principle of Linear Superposition and Interference Phenomena The Principle of Linear Superposition 1 THE PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR SUPERPOSITION When two or more waves are present simultaneously at
Ch17. The Principle of Linear Superposition and Interference Phenomena The Principle of Linear Superposition 1 THE PRINCIPLE OF LINEAR SUPERPOSITION When two or more waves are present simultaneously at
Interference of sound waves. Sound II. Interference due to path difference. Noise canceling headphones. Interference. Interference
 Sound II. of sound waes Standing waes Complex sound waes of sound waes Two sound waes superimposed Constructie Destructie Noise canceling headphones Noise Wae Wae Anti-noise Wae Wae due to path difference
Sound II. of sound waes Standing waes Complex sound waes of sound waes Two sound waes superimposed Constructie Destructie Noise canceling headphones Noise Wae Wae Anti-noise Wae Wae due to path difference
Waves are generated by an oscillator which has to be powered.
 Traveling wave is a moving disturbance. Can transfer energy and momentum from one place to another. Oscillations occur simultaneously in space and time. Waves are characterized by 1. their velocity 2.
Traveling wave is a moving disturbance. Can transfer energy and momentum from one place to another. Oscillations occur simultaneously in space and time. Waves are characterized by 1. their velocity 2.
Standing Waves and Musical Instruments
 OpenStax-CNX module: m12413 1 Standing Waves and Musical Instruments Catherine Schmidt-Jones This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m12413 1 Standing Waves and Musical Instruments Catherine Schmidt-Jones This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 12 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Musical Acoustics, C. Bertulani. Musical Acoustics. Lecture 14 Timbre / Tone quality II
 1 Musical Acoustics Lecture 14 Timbre / Tone quality II Odd vs Even Harmonics and Symmetry Sines are Anti-symmetric about mid-point If you mirror around the middle you get the same shape but upside down
1 Musical Acoustics Lecture 14 Timbre / Tone quality II Odd vs Even Harmonics and Symmetry Sines are Anti-symmetric about mid-point If you mirror around the middle you get the same shape but upside down
Honors Physics-121B Sound and Musical Acoustics Introduction: Production of Sounds by Various Sources: Media That Transmit Sound:
 Honors Physics-121B Sound and Musical Acoustics Introduction: This unit deals with the properties of longitudinal (compressional) waves traveling through various media. As these waves travel through the
Honors Physics-121B Sound and Musical Acoustics Introduction: This unit deals with the properties of longitudinal (compressional) waves traveling through various media. As these waves travel through the
Worksheet 15.2 Musical Instruments
 Worksheet 15.2 Musical Instruments 1. You and your group stretch a spring 12 feet across the floor and you produce a standing wave that has a node at each end and one antinode in the center. Sketch this
Worksheet 15.2 Musical Instruments 1. You and your group stretch a spring 12 feet across the floor and you produce a standing wave that has a node at each end and one antinode in the center. Sketch this
Fundamentals of Music Technology
 Fundamentals of Music Technology Juan P. Bello Office: 409, 4th floor, 383 LaFayette Street (ext. 85736) Office Hours: Wednesdays 2-5pm Email: jpbello@nyu.edu URL: http://homepages.nyu.edu/~jb2843/ Course-info:
Fundamentals of Music Technology Juan P. Bello Office: 409, 4th floor, 383 LaFayette Street (ext. 85736) Office Hours: Wednesdays 2-5pm Email: jpbello@nyu.edu URL: http://homepages.nyu.edu/~jb2843/ Course-info:
AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR
 AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR NAME: HB: ACTIVITY I. BOUNDARY BEHAVIOR As a wave travels through a medium, it will often reach the end of the medium and encounter an obstacle or perhaps another medium through
AP PHYSICS WAVE BEHAVIOR NAME: HB: ACTIVITY I. BOUNDARY BEHAVIOR As a wave travels through a medium, it will often reach the end of the medium and encounter an obstacle or perhaps another medium through
Acoustical Investigations of the French Horn and the Effects of the Hand in the Bell
 Acoustical Investigations of the French Horn and the Effects of the Hand in the Bell Phys498POM Spring 2009 Adam Watts Introduction: The purpose of this experiment was to investigate the effects of the
Acoustical Investigations of the French Horn and the Effects of the Hand in the Bell Phys498POM Spring 2009 Adam Watts Introduction: The purpose of this experiment was to investigate the effects of the
Inexpensive impedance head for classroom use The input impedance is defined as
 Building and using an inexpensive impedance head 1 Workshop given at CCRMA, 20 January, 2006 Peter L. Hoekje Department of Physics and Astronomy, Baldwin-Wallace College, Berea, OH 44017 Inexpensive impedance
Building and using an inexpensive impedance head 1 Workshop given at CCRMA, 20 January, 2006 Peter L. Hoekje Department of Physics and Astronomy, Baldwin-Wallace College, Berea, OH 44017 Inexpensive impedance
YAMAHA. Modifying Preset Voices. IlU FD/D SUPPLEMENTAL BOOKLET DIGITAL PROGRAMMABLE ALGORITHM SYNTHESIZER
 YAMAHA Modifying Preset Voices I IlU FD/D DIGITAL PROGRAMMABLE ALGORITHM SYNTHESIZER SUPPLEMENTAL BOOKLET Welcome --- This is the first in a series of Supplemental Booklets designed to provide a practical
YAMAHA Modifying Preset Voices I IlU FD/D DIGITAL PROGRAMMABLE ALGORITHM SYNTHESIZER SUPPLEMENTAL BOOKLET Welcome --- This is the first in a series of Supplemental Booklets designed to provide a practical
Linguistics 401 LECTURE #2. BASIC ACOUSTIC CONCEPTS (A review)
 Linguistics 401 LECTURE #2 BASIC ACOUSTIC CONCEPTS (A review) Unit of wave: CYCLE one complete wave (=one complete crest and trough) The number of cycles per second: FREQUENCY cycles per second (cps) =
Linguistics 401 LECTURE #2 BASIC ACOUSTIC CONCEPTS (A review) Unit of wave: CYCLE one complete wave (=one complete crest and trough) The number of cycles per second: FREQUENCY cycles per second (cps) =
Sound waves. septembre 2014 Audio signals and systems 1
 Sound waves Sound is created by elastic vibrations or oscillations of particles in a particular medium. The vibrations are transmitted from particles to (neighbouring) particles: sound wave. Sound waves
Sound waves Sound is created by elastic vibrations or oscillations of particles in a particular medium. The vibrations are transmitted from particles to (neighbouring) particles: sound wave. Sound waves
Reed chamber resonances and attack transients in free reed instruments
 PROCEEDINGS of the 22 nd International Congress on Acoustics Wind Instruments: Paper ICA2016-748 Reed chamber resonances and attack transients in free reed instruments James Cottingham (a) (a) Coe College,
PROCEEDINGS of the 22 nd International Congress on Acoustics Wind Instruments: Paper ICA2016-748 Reed chamber resonances and attack transients in free reed instruments James Cottingham (a) (a) Coe College,
Date Period Name. Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat
 Date Period Name CHAPTER 15 Study Guide Sound Vocabulary Review Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat Doppler effect closed-pipe resonator fundamental consonance
Date Period Name CHAPTER 15 Study Guide Sound Vocabulary Review Write the term that corresponds to the description. Use each term once. beat Doppler effect closed-pipe resonator fundamental consonance
Vibrato and Tremolo Analysis. Antonio DiCristofano Amanda Manaster May 13, 2016 Physics 406 L1
 Vibrato and Tremolo Analysis Antonio DiCristofano Amanda Manaster May 13, 2016 Physics 406 L1 1 Abstract In this study, the effects of vibrato and tremolo are observed and analyzed over various instruments
Vibrato and Tremolo Analysis Antonio DiCristofano Amanda Manaster May 13, 2016 Physics 406 L1 1 Abstract In this study, the effects of vibrato and tremolo are observed and analyzed over various instruments
Trumpet Wind Controller
 Design Proposal / Concepts: Trumpet Wind Controller Matthew Kelly Justin Griffin Michael Droesch The design proposal for this project was to build a wind controller trumpet. The performer controls the
Design Proposal / Concepts: Trumpet Wind Controller Matthew Kelly Justin Griffin Michael Droesch The design proposal for this project was to build a wind controller trumpet. The performer controls the
Principles of Musical Acoustics
 William M. Hartmann Principles of Musical Acoustics ^Spr inger Contents 1 Sound, Music, and Science 1 1.1 The Source 2 1.2 Transmission 3 1.3 Receiver 3 2 Vibrations 1 9 2.1 Mass and Spring 9 2.1.1 Definitions
William M. Hartmann Principles of Musical Acoustics ^Spr inger Contents 1 Sound, Music, and Science 1 1.1 The Source 2 1.2 Transmission 3 1.3 Receiver 3 2 Vibrations 1 9 2.1 Mass and Spring 9 2.1.1 Definitions
Sound Spectra. Periodic Complex Waves. Ohm s law of hearing 4/6/09. What is the spectrum of the complex wave (thick dotted line)?
 Sound Spectra The frequencies of all the sinusoidal component that make it up The amplitude of each sinusoidal component present Periodic Complex Waves The repetition frequency determines the pitch The
Sound Spectra The frequencies of all the sinusoidal component that make it up The amplitude of each sinusoidal component present Periodic Complex Waves The repetition frequency determines the pitch The
Lecture Presentation Chapter 16 Superposition and Standing Waves
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 16 Superposition and Standing Waves Suggested Videos for Chapter 16 Prelecture Videos Constructive and Destructive Interference Standing Waves Physics of Your Vocal System
Lecture Presentation Chapter 16 Superposition and Standing Waves Suggested Videos for Chapter 16 Prelecture Videos Constructive and Destructive Interference Standing Waves Physics of Your Vocal System
Spectrum. Additive Synthesis. Additive Synthesis Caveat. Music 270a: Modulation
 Spectrum Music 7a: Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) October 3, 7 When sinusoids of different frequencies are added together, the
Spectrum Music 7a: Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) October 3, 7 When sinusoids of different frequencies are added together, the
Music 270a: Modulation
 Music 7a: Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) October 3, 7 Spectrum When sinusoids of different frequencies are added together, the
Music 7a: Modulation Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) October 3, 7 Spectrum When sinusoids of different frequencies are added together, the
Chapter4: Superposition and Interference
 Chapter4: Superposition and Interference 1. Superposition and Interference Many interesting wave phenomena in nature cannot be described by a single traveling wave. Instead, one must analyze complex waves
Chapter4: Superposition and Interference 1. Superposition and Interference Many interesting wave phenomena in nature cannot be described by a single traveling wave. Instead, one must analyze complex waves
TIMPANI-HORN INTERACTIONS AT THE PLAYER S LIPS
 TIMPANI-HORN INTERACTIONS AT THE PLAYER S LIPS Jer-Ming Chen John Smith Joe Wolfe School of Physics, The University of New South Wales, Sydney jerming@unsw.edu.au john.smith@unsw.edu.au j.wolfe@unsw.edu.au
TIMPANI-HORN INTERACTIONS AT THE PLAYER S LIPS Jer-Ming Chen John Smith Joe Wolfe School of Physics, The University of New South Wales, Sydney jerming@unsw.edu.au john.smith@unsw.edu.au j.wolfe@unsw.edu.au
Part I. Open Open Pipes. A 35 cm long string is played at its fundamental frequency.
 Part I Open Open Pipes A 35 cm long pipe is played at its fundamental frequency. 1. What does the waveform look like inside the pipe? 2. What is this frequency s wavelength? 3. What is this frequency being
Part I Open Open Pipes A 35 cm long pipe is played at its fundamental frequency. 1. What does the waveform look like inside the pipe? 2. What is this frequency s wavelength? 3. What is this frequency being
Chapter 12. Preview. Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect. Section 1 Sound Waves
 Section 1 Sound Waves Preview Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect Section 1 Sound Waves Objectives Explain how sound waves are produced. Relate frequency
Section 1 Sound Waves Preview Objectives The Production of Sound Waves Frequency of Sound Waves The Doppler Effect Section 1 Sound Waves Objectives Explain how sound waves are produced. Relate frequency
Chapter 17. Linear Superposition and Interference
 Chapter 17 Linear Superposition and Interference Linear Superposition If two waves are traveling through the same medium, the resultant wave is found by adding the displacement of the individual waves
Chapter 17 Linear Superposition and Interference Linear Superposition If two waves are traveling through the same medium, the resultant wave is found by adding the displacement of the individual waves
Examination of Organ Flue Pipe Resonator Eigenfrequencies by Means of the Boundary Element Method
 Examination of Organ Flue Pipe Resonator Eigenfrequencies by Means of the Boundary Element Method Gábor Szoliva Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Telecommunications, H-1117
Examination of Organ Flue Pipe Resonator Eigenfrequencies by Means of the Boundary Element Method Gábor Szoliva Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Telecommunications, H-1117
ABC Math Student Copy
 Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 9(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Waves and Sound Cont d 2 Principle of Linear Superposition Sound is a pressure wave. Often two or more sound waves are present at the same place
Page 1 of 17 Physics Week 9(Sem. 2) Name Chapter Summary Waves and Sound Cont d 2 Principle of Linear Superposition Sound is a pressure wave. Often two or more sound waves are present at the same place
Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) Chirp Signal. Chirp Signal cont. CMPT 468: Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis
 Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) CMPT 468: Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 26, 29 Till now we
Linear Frequency Modulation (FM) CMPT 468: Lecture 7 Frequency Modulation (FM) Synthesis Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 26, 29 Till now we
Quarterly Progress and Status Report. An ionophone for acoustical measurements
 Dept. for Speech, Music and Hearing Quarterly Progress and Status Report An ionophone for acoustical measurements Fransson, F. journal: STL-QPSR volume: 3 number: 4 year: 1962 pages: 022-026 http://www.speech.kth.se/qpsr
Dept. for Speech, Music and Hearing Quarterly Progress and Status Report An ionophone for acoustical measurements Fransson, F. journal: STL-QPSR volume: 3 number: 4 year: 1962 pages: 022-026 http://www.speech.kth.se/qpsr
Sound All sound begins with a vibrating object Ex. Vibrating tuning fork Vibrating prong sets molecules near it in motion
 Sound All sound begins with a vibrating object Ex. Vibrating tuning fork Vibrating prong sets molecules near it in motion As prong swings right, air molecules in front of the movement are forced closer
Sound All sound begins with a vibrating object Ex. Vibrating tuning fork Vibrating prong sets molecules near it in motion As prong swings right, air molecules in front of the movement are forced closer
Physics in Entertainment and the Arts
 Physics in Entertainment and the Arts Chapter VIII Control of Sound The sound characteristics (acoustics) of a room depend upon a great many complex factors room size/shape wall/floor/ceiling materials
Physics in Entertainment and the Arts Chapter VIII Control of Sound The sound characteristics (acoustics) of a room depend upon a great many complex factors room size/shape wall/floor/ceiling materials
Structure of Speech. Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping
 Structure of Speech Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping Speech acoustics Source-Filter Theory Speech Source characteristics Speech Filter characteristics
Structure of Speech Physical acoustics Time-domain representation Frequency domain representation Sound shaping Speech acoustics Source-Filter Theory Speech Source characteristics Speech Filter characteristics
1. Introduction. 2. Digital waveguide modelling
 ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 27, 4, 303317 (2002) DIGITAL WAVEGUIDE MODELS OF THE PANPIPES A. CZY EWSKI, J. JAROSZUK and B. KOSTEK Sound & Vision Engineering Department, Gda«sk University of Technology, Gda«sk,
ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 27, 4, 303317 (2002) DIGITAL WAVEGUIDE MODELS OF THE PANPIPES A. CZY EWSKI, J. JAROSZUK and B. KOSTEK Sound & Vision Engineering Department, Gda«sk University of Technology, Gda«sk,
Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound. Period T time taken for one complete vibrational cycle
 Unit 1: Waves Lesson: Sound Sound is a mechanical wave, a longitudinal wave, a pressure wave Periodic sound waves have: Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound Period
Unit 1: Waves Lesson: Sound Sound is a mechanical wave, a longitudinal wave, a pressure wave Periodic sound waves have: Frequency f determined by the source of vibration; related to pitch of sound Period
Pitch Bending PITCH BENDING AND ANOMALOUS BEHAVIOR IN A FREE REED COUPLED TO A PIPE RESONATOR
 PITCH BENDING AND ANOMALOUS BEHAVIOR IN A FREE REED COUPLED TO A PIPE RESONATOR James P. Cottingham Phys. Dept., Coe College, Cedar Rapids, IA 52402 USA, jcotting@coe.edu Abstract The reed-pipe system
PITCH BENDING AND ANOMALOUS BEHAVIOR IN A FREE REED COUPLED TO A PIPE RESONATOR James P. Cottingham Phys. Dept., Coe College, Cedar Rapids, IA 52402 USA, jcotting@coe.edu Abstract The reed-pipe system
I. Orchestra Scope Note Top term A. String Instruments Scope Note 1. Bowed String Instruments Scope Note a) Violin Scope Note b) Viola Scope Note
 I. Orchestra Scope Note: An ensemble of instrumentalists composed of string, woodwind, brass, and percussion sections that typically plays classical music; often includes one or more keyboard instruments.
I. Orchestra Scope Note: An ensemble of instrumentalists composed of string, woodwind, brass, and percussion sections that typically plays classical music; often includes one or more keyboard instruments.
RS380 MODULATION CONTROLLER
 RS380 MODULATION CONTROLLER The RS380 is a composite module comprising four separate sub-modules that you can patch together or with other RS Integrator modules to generate and control a wide range of
RS380 MODULATION CONTROLLER The RS380 is a composite module comprising four separate sub-modules that you can patch together or with other RS Integrator modules to generate and control a wide range of
Phys Homework Set 1 Fall 2015 Exam Name
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is a children s drawing toy that uses a circle within a circle
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is a children s drawing toy that uses a circle within a circle
Interference & Superposition. Creating Complex Wave Forms
 Interference & Superposition Creating Complex Wave Forms Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing
Interference & Superposition Creating Complex Wave Forms Waves & Interference I. Definitions and Types II. Parameters and Equations III. Sound IV. Graphs of Waves V. Interference - superposition - standing
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S. Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED Instructions: Please answer all questions in the examination booklet(s) provided. Completely
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science MOCK EXAMINATION PHY207H1S Duration 3 hours NO AIDS ALLOWED Instructions: Please answer all questions in the examination booklet(s) provided. Completely
= 2n! 1 " L n. = 2n! 1 # v. = 2n! 1 " v % v = m/s + ( m/s/ C)T. f 1. = 142 Hz
 Chapter 9 Review, pages 7 Knowledge 1. (b). (c) 3. (b). (d) 5. (b) 6. (d) 7. (d) 8. (b) 9. (a) 10. (c) 11. (a) 1. (c) 13. (b) 1. (b) 15. (d) 16. False. Interference does not leave a wave permanently altered.
Chapter 9 Review, pages 7 Knowledge 1. (b). (c) 3. (b). (d) 5. (b) 6. (d) 7. (d) 8. (b) 9. (a) 10. (c) 11. (a) 1. (c) 13. (b) 1. (b) 15. (d) 16. False. Interference does not leave a wave permanently altered.
MODELING AND MEASUREMENT OF WIND INSTRUMENT BORES
 9 INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 27 MODELING AND MEASUREMENT OF WIND INSTRUMENT BORES PACS: 443.75.Zz Smyth, Tamara ; Abel, Jonathan 2 School of Computing Science; Simon Fraser
9 INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 27 MODELING AND MEASUREMENT OF WIND INSTRUMENT BORES PACS: 443.75.Zz Smyth, Tamara ; Abel, Jonathan 2 School of Computing Science; Simon Fraser
From Last Time Wave Properties. Description of a Wave. Water waves? Water waves occur on the surface. They are a kind of transverse wave.
 From Last Time Wave Properties Amplitude is the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position Wavelength,, is the distance between two successive points that behave identically Period: time required
From Last Time Wave Properties Amplitude is the maximum displacement from the equilibrium position Wavelength,, is the distance between two successive points that behave identically Period: time required
From Last Time Wave Properties. Doppler Effect for a moving source. Question. Shock Waves and Sonic Booms. Breaking the sound barrier.
 From Last Time Wave Properties Interference: waves can superimpose constructively or destructively Two speakers can be quieter than one! Doppler effect Frequency shift (up or down) from moving source.
From Last Time Wave Properties Interference: waves can superimpose constructively or destructively Two speakers can be quieter than one! Doppler effect Frequency shift (up or down) from moving source.
AP Homework (Q2) Does the sound intensity level obey the inverse-square law? Why?
 AP Homework 11.1 Loudness & Intensity (Q1) Which has a more direct influence on the loudness of a sound wave: the displacement amplitude or the pressure amplitude? Explain your reasoning. (Q2) Does the
AP Homework 11.1 Loudness & Intensity (Q1) Which has a more direct influence on the loudness of a sound wave: the displacement amplitude or the pressure amplitude? Explain your reasoning. (Q2) Does the
Sound. Production of Sound
 Sound Production o Sound Sound is produced by a vibrating object. A loudspeaker has a membrane or diaphragm that is made to vibrate by electrical currents. Musical instruments such as gongs or cymbals
Sound Production o Sound Sound is produced by a vibrating object. A loudspeaker has a membrane or diaphragm that is made to vibrate by electrical currents. Musical instruments such as gongs or cymbals

 Journal of Sound and
Journal of Sound and