Selective Excitation of Circular Helical Modes in Power-Law Index Fibers
|
|
|
- Avice Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modern Applied Science; Vol. 8, No. 1; 2014 ISSN E-ISSN Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Selective Excitation of Circular Helical Modes in Power-Law Index Fibers S. Al-Sowayan 1 1 EE Department, Al Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Correspondence: S. Al-Sowayan, EE Department, Al Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University, P. O. Box 93718, Riyadh 11683, Saudi Arabia. sssowayan@imamu.edu.sa Received: December 28, 2013 Accepted: January 12, 2014 Online Published: January 19, 2014 doi: /mas.v8n1p134 URL: Abstract Selective excitation of circular helical modes in power-law index fibers is shown to have an impact on their capacity. This is analyzed using a model for propagation delay variation with launch offset and angle that resulted from misalignment of source and fiber axis. Results show promising technique to improve power law-index fibers capacities. Keywords: fiber measurements, fiber optics, powe-law index profile, propagation modes 1. Introduction It is a fact that when the bandwidth demand increased by the high bandwidth applications required from communication networks, the capacity of the already installed thousands of kilometers of multimode fibers (MMF) will be a bottleneck by Raddatz (1998, 1999), Coleman (2006), Gu (2006) and McInally (2002). Despite availability of alternatives such as single mode fibers and ribbon link fibers analyzed by Hahn (1995), the cost of replacing already installed infrastructure will be high shown by Amphawan (2010). Legacy MMF with 62.5 μm core can have bandwidth as low as 160 MHz.km at 850 nm wavelength, and the observed bandwidth can be sensitive to launch angle and offset shown by Webster (1999). If the launch condition makes perfect alignment between source and fiber axis, what is so called meridional modes will only be excited. Meridional modes are the propagation modes that follow a path cross the fiber axis. The axial mode, which is the lowest order mode, is the mode of propagation that travels along the longitudinal axis of the fiber. If there is misalignment in both angle and offset between the source and the fiber axis what is called helical modes of propagation will be excited. Helical modes are the type of modes that propagate in a helix shape inside the core of the fiber along the longitudinal direction that do not cross the fiber axis and bounded by the total internal reflection inside the core of the fiber by Murshid (2008). In particular, low angle, on-axis power excites a selection of low-order modes which can result in excessive and unstable pulse broadening relative to over filled launch conditions by Sargent (1998). Since the bandwidth is sensitive to launch parameters, it is important to consider which groups of modes are being excited by laser sources. In this paper a computer model for propagation delay in graded index fibers was used to quantify the impact of selective excitation of circular helical modes only on link performance. 2. Computer Model The model refers the coupling angle and offset from the center of the fiber to the order of helical path that the optical energy will follow, the equation of the circular helix is stated in Equation (1). x Acost y Asint z bt Where x and y are the transverse plane coardinates and z is the longitudinal direction of the fiber, A and 2πb are the radius and pitch of the helical mode that will be determined by the coupling (entrance) angle with the fiber core face, and the offset from the center of the fiber core. In graded index (GI) fibers power law profile, the common profile is the parabola shape of refractive index with the peak at the center of the fiber. Though the model general idea is valid for all power law profiles, the parabolic profile is considered here. It has been 134 (1)
2 reported in literature such as Raddatz (Sep 1999) that during the manufacturing process of GI fibers there, a common defect that introduces a peak or dip in the value of refractive index at the center of the fiber is generated, which in turn reduces the capacity of the GI fibers when used with lasers at center launch in an underfilled launch regime. To avoid this defect, in this paper the entering rays will be offseted from the center by 10 µm. Without considering the defect at the center of the fiber the power-law index profile is described in Equation (2). n r 2 2 r 1 n 12 for 0 r a a n1 12 for r a Where n 1 is the refractive index of center of the core typical value for the glass is 1.5, is the change in the refractive index profile typically 0.01, r is the radial position, and a is the radius of the core which is µm. The coupling between the optical ray and fiber shall make an angle (θ) with the transverse plane of the fiber, to ensure no meridional modes nor elliptical helical modes are excited this angle shall make an entrance angle greater than the acceptance angle of the fiber (in this case it is 12 degrees) another condition is that the projection of the ray into the face of the fiber should be perpendicular to the radial vector from the center of the fiber to point of ray entrance to the core as shown in Figure 1. This means θ shall vary from 10 to 78 degrees, the 10 degrees are chosen for the helix to be realistic enough to propagate in the longitudinal direction. Table 1 shows for each entrance angle, measured from the transverse plane of the face of the fiber to the ray, the corresponding helical mode order parameters for a certain offset of 10 µm. Figure 2 gives a bigger picture of the relationship between the launch offset from the center of the fiber, the angle of entrance and the helical mode path length (normalized to the longest one) which can be calculated from the resulting helix parameters. Figure 2 clearly shows that as the offset gets larger the path of the optical pulse increases and as the angle θ becomes larger the optical pulse path decreases. (2) Figure 1. Misaligned coupling in both offset and angle that yield to excitation of circular helical modes 3 x 10-5 Traveled distance Normalized to maximum 0.9 Offset from center of fiber (m) Optical pulse coupling angle from the transverse plane of fiber (deg) Figure 2. Distance travelled in one rotation of circular helix for a particular coupling angle and offset 135
3 Table 1. Coupling angle with corresponding helix parameters θ Normalized helix parameters (A,b) 10 (10, 4.39) 30 (10, 5.41) 50 (10, 8.05) 75 (10, 21.8) It is of interest to consider the experimentally generated short optical pulse by gain switching an 850 nm laser to produce a ~200 ps pulse shown in Figure 3. as an input parameter to the model, the model then shall consider the arrival time of the mentioned pulse by calculating the required propagation time down the fiber normalized to the maximum time. The propagation time will be calculated based on the distance the pulse shall travel and the optical pulse group velocity which will defiantly be affected by the refractive index faced by the propagating mode. Usually, in some cases, the beam waist of the optical ray entering the fiber is around 4 µm by Tsekrekos (2004). Using the same beam waist and considering the optical pulse that enters the fiber with an offset from 10 µm to 14 µm, µm, µm, and µm offsets to avoid the defective area around the center of the fiber core. For each offset range the optical pulse is considered as a group of rays having the same θ angle (described before) with an increment of 0.1 µm. The distance traveled by each helical mode excited is calculated then the propagation time needed by each helical mode is calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the speed of the specific helical mode, which is the speed of light divided by the corresponding refractive index at the specified offset from Equation (1). This process is repeated for different θ angles of 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 degrees. Note that after calculating the traveled distances by each helical mode for different offsets and angles, the distances have been normalized to their maximum value. Figure 3. Optical short pulse from an 850nm laser source For a specific angle θ, the optical pulse shown in Figure 3. is then copied by each helical mode path and arrives at a reference distance at different arrival time. By adding these copies of arrived pulses at their corresponding arrival time, the result gives good approximation of the impulse response of the fiber when exciting only circular helical modes at the certain angle and offset with the mentioned beam waist. 3. Results and Discussion Figure 4 shows the result of the response of the 62.5/125 µm GI fiber when exciting only circular helical modes at θ = 10, 30, and 50 degrees tilt from the transverse plane of the fiber core perpendicular to the radial vector with offsets of µm in Figure 4 (a), and µm in Figure 4(b). It is clear from Figure 4 that as θ angle gets smaller the response gets narrower, and as the offset gets larger the response gets also narrower. 136
4 Figure 4. Optical 850 nm pulse response with 4 µm beam waist of a 62.5/125 μm fiber with a tilt θ angle of 10, 30, 50 degrees at an offset of (a) µm and (b) µm m m m m FWHM (ns) Angle () Figure 5. FWHM of the response of the 61.5/125 µm fiber with different angles of launch θ and offsets Figure 5 shows the resulting FWHM of the response of the fiber with respect to θ angle considering offsets at µm, µm, µm, and µm. It is also clear from Figure 5 that for the same offset as the coupling angle increases the propagation delay difference increases because the helix pitch increases which in turn make the traveled distance difference more. Bandwidth of the fiber can be approximated from this result by assuming Gaussian response of the fiber shown in Figure 4, which is a good approximation. If the fiber response is given by Equation (3), the resulting bandwidth will be the one given in Equation (4). To relate that to the FWHM of the response we use Equation (5). 2 t 2 1 ht e (3) 2 137
5 BW. (4) BW. FWHM (5) Using Equation (5) the resulting BW of the fiber by conditioning the launch to be at angle θ=10 degrees and an offset of µm from the center of the fiber core is about 660 MHz.km. Comparing this results with the fiber BW when used with VCSEL with no launch conditioning, the presented launch scheme gives four times better bandwidth. By comparing the presented launch scheme with previous work that has been reported in the literature such as Raddatz (1998), Raddatz (1999) and Webster (1999), it almost has the same bandwidth improvement, but with no additional expensive components such as single mode fiber patch cord to condition the launch. 4. Conclusion This paper reported a launch scheme to be used for launching light from an 850 nm laser that produces a 4 µm beam waist into 62.5/125 μm GI fiber. The scheme involves offset from the center of the fiber core and an angle with the transverse plane of the fiber that makes the projection of the ray into the face of the fiber perpendicular to the radial vector. The presented launch scheme has been shown to ensure excitation of only circular helical modes of the fiber. An improvement in the capacity of GI fibers when selectively excite few number of helical modes of propagation was demonstrated. Acknowledgements S Al-Sowayan would like to thank Al Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University for supporting this work, also would like to acknowledge Mr. Mohammed Asad Ali from Electrical Engineering Department at Al Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University for helping in organizing the article. References Amphawan, A., Payne, F., O Brien, D., & Shah, N. (2010). Derivation of an Analytical Expression for the Power Coupling Coefficient for Offset Launch Into Multimode Fiber. J. of Lightwave Tech, 28(6), Coleman, D. (2006). Migration to 50/125-µm in Local Area Network. Hicory, NC, Mar. 2006, Corning Cable Systems. Gu, X. J., Mohammed, W., & Smith, P. W. (2006). Demonstration of all-fiber WDM for multimode fiber local area networks. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 18(1), Hahn, K. H. (1995). POLO-parallel optical links for Gigabit/s data communications. Proc. LEOS\'95 (pp ). McInally, V. (2002). Multimode Fibre: The Progression towards Multi-Gigabit Speeds & The 850 nm Operating Wavelength. Corning U.K. Murshid, S., Grossman, B., & Narakorn, P. (2008). Spatial domain multiplexing: A new dimension in fiber multiplexing. Optics and Laser Technology, 40(8), Raddatz, L., White, I. H., Cunningham, D. G., & Nowell, M. C. (1998). An experimental and theoretical study of the offset launch technique for the enhancement of the bandwidth of multimode fiber links. J. of Lightwave Technol., 16, Raddatz, L., & White, I. H. (1999). Overcoming the modal bandwidth limitation of multimode fiber by using passband modulation. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett., 11(2), Sargent, L. J., Webster, M., White, I. H., Heard, P. J., Penty, R. V., Tan, M. R. T., & Cunningham, D. G. (1998). Simple technique for bandwidth enhancement of multimode fiber links using controlled spatial emission from vertical cavity surface emitting lasers. Electron. Lett., 34(21), Tsekrekos, C. P., Koonen, A. M. J., & van den Boom, H. P. A. (2004). Selective Excitation of Graded Multimode Fibers Resulting in Annular Near Field Patterns. Proceedings Symposium IEEE/LEOS Benelux Chapter, 2004, Ghent. 138
6 Webster, M., Raddatz, L., White, I. H., & Cunningham, D. G. (1999). A statistical analysis of conditioned launch for gigabit ethernet links using multimode fiber. J. of Lightwave Tech, 17(9), Copyrights Copyright for this article is retained by the author(s), with first publication rights granted to the journal. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( 139
Aberrated Microlenses to Reduce Crosstalk in Free Space Optical Interconnects Systems
 Modern Applied Science; Vol., No. 5; 8 ISSN 93-844 E-ISSN 93-85 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Aberrated Microlenses to Reduce Crosstalk in Free Space Optical Interconnects Systems
Modern Applied Science; Vol., No. 5; 8 ISSN 93-844 E-ISSN 93-85 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Aberrated Microlenses to Reduce Crosstalk in Free Space Optical Interconnects Systems
Fiber Optic Communications Communication Systems
 INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
Migration to 50/125 µm in the Local Area Network
 Migration to 50/125 µm in the Local Area Network By Doug Coleman Introduction Enterprise local area networks (LAN) should be designed to support legacy applications as well as emerging high-data-rate applications.
Migration to 50/125 µm in the Local Area Network By Doug Coleman Introduction Enterprise local area networks (LAN) should be designed to support legacy applications as well as emerging high-data-rate applications.
Study of Optical Fiber Design Parameters in Fiber Optics Communications
 Kurdistan Journal of Applied Research (KJAR) Print-ISSN: 2411-7684 Electronic-ISSN: 2411-7706 kjar.spu.edu.iq Volume 2 Issue 3 August 2017 DOI: 10.24017/science.2017.3.52 Study of Optical Fiber Design
Kurdistan Journal of Applied Research (KJAR) Print-ISSN: 2411-7684 Electronic-ISSN: 2411-7706 kjar.spu.edu.iq Volume 2 Issue 3 August 2017 DOI: 10.24017/science.2017.3.52 Study of Optical Fiber Design
Variation of Waveforms in Multimode Fibre
 Due to polarization, mechanical stress and wavelength changes Simon Meadowcroft David Cunningham Fibre Optics Product Division Introduction Observations are reported for the effects of polarisation, mechanical
Due to polarization, mechanical stress and wavelength changes Simon Meadowcroft David Cunningham Fibre Optics Product Division Introduction Observations are reported for the effects of polarisation, mechanical
Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS. Unit-03
 Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS Unit-03 INTRODUCTION FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS ABOUT OPTICAL FIBRE Multimode Fibres Multimode Step Index Fibres Multimode Graded Index Fibres INTRODUCTION In communication systems, there
Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS Unit-03 INTRODUCTION FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS ABOUT OPTICAL FIBRE Multimode Fibres Multimode Step Index Fibres Multimode Graded Index Fibres INTRODUCTION In communication systems, there
Spiral Launch Method for Enhanced MMF Bandwidth
 Spiral Launch Method for Enhanced MMF Bandwidth D. Vernooy and H. Blauvelt Xponent Photonics March 2004 IEEE 802.2 10Gb/s on FDDI-grade MM fiber Study Group hblauvelt@xponentinc.com 1 Outline I. Overview
Spiral Launch Method for Enhanced MMF Bandwidth D. Vernooy and H. Blauvelt Xponent Photonics March 2004 IEEE 802.2 10Gb/s on FDDI-grade MM fiber Study Group hblauvelt@xponentinc.com 1 Outline I. Overview
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 4
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 4 Modal Propagation of Light in an Optical Fiber Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 4 Modal Propagation of Light in an Optical Fiber Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems
 OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-I : OPTICAL FIBERS STRUCTURE: 1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems The operating range of optical fiber system term and the characteristics of the four key components of
OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION UNIT-I : OPTICAL FIBERS STRUCTURE: 1. Evolution Of Fiber Optic Systems The operating range of optical fiber system term and the characteristics of the four key components of
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY
 NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Course : Prepared by: TCET 4102 Fiber-optic communications Module
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE of TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY Course : Prepared by: TCET 4102 Fiber-optic communications Module
2062 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2005
 2062 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2005 Analysis of Graded-Index Polymer Optical Fiber Link Performance Under Fiber Bending Kenji Makino, Takuhiro Nakamura, Takaaki Ishigure, Member,
2062 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 6, JUNE 2005 Analysis of Graded-Index Polymer Optical Fiber Link Performance Under Fiber Bending Kenji Makino, Takuhiro Nakamura, Takaaki Ishigure, Member,
Ratiometric Wavelength Monitor Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fiber Structure
 Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Articles School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 8-1-1 Ratiometric Wavelength Monitor Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fiber Structure Agus Hatta
Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Articles School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 8-1-1 Ratiometric Wavelength Monitor Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fiber Structure Agus Hatta
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings
 A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
Variation in Multimode Fiber Response: Summary of Experimental Results
 Summary of Experimental Results IEEE P802.3aq 10GBASE-LRM, Task Group 4 November, 2004, San Antonio Infineon Fiber Optics, Infineon Fiber Optics Page 1 Summary of Experimental Results! Introduction A variation
Summary of Experimental Results IEEE P802.3aq 10GBASE-LRM, Task Group 4 November, 2004, San Antonio Infineon Fiber Optics, Infineon Fiber Optics Page 1 Summary of Experimental Results! Introduction A variation
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber. Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson Comm. Lab The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
UNIT Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion?
 UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
UNIT 3 1. Write notes on broadening of pulse in the fiber dispersion? Ans: The dispersion of the transmitted optical signal causes distortion for both digital and analog transmission along optical fibers.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance
 Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Spatial Investigation of Transverse Mode Turn-On Dynamics in VCSELs
 Spatial Investigation of Transverse Mode Turn-On Dynamics in VCSELs Safwat W.Z. Mahmoud Data transmission experiments with single-mode as well as multimode 85 nm VCSELs are carried out from a near-field
Spatial Investigation of Transverse Mode Turn-On Dynamics in VCSELs Safwat W.Z. Mahmoud Data transmission experiments with single-mode as well as multimode 85 nm VCSELs are carried out from a near-field
Assembly and Experimental Characterization of Fiber Collimators for Low Loss Coupling
 Assembly and Experimental Characterization of Fiber Collimators for Low Loss Coupling Ruby Raheem Dept. of Physics, Heriot Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland EH14 4AS, UK ABSTRACT The repeatability of
Assembly and Experimental Characterization of Fiber Collimators for Low Loss Coupling Ruby Raheem Dept. of Physics, Heriot Watt University, Edinburgh, Scotland EH14 4AS, UK ABSTRACT The repeatability of
Analysis of Efficiency and Misalignment Tolerances in Laser Diode Pigtailing Using Single Ball Lens
 Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 3(12): 1778-1787, 2007 2007, INSInet Publication Analysis of Efficiency and Misalignment Tolerances in Laser Diode Pigtailing Using Single Ball Lens M. Fadhali, Saktioto,
Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 3(12): 1778-1787, 2007 2007, INSInet Publication Analysis of Efficiency and Misalignment Tolerances in Laser Diode Pigtailing Using Single Ball Lens M. Fadhali, Saktioto,
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave Ray Theory Light
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic wave Ray Theory Light
The Development of the 1060 nm 28 Gb/s VCSEL and the Characteristics of the Multi-mode Fiber Link
 Special Issue Optical Communication The Development of the 16 nm 28 Gb/s VCSEL and the Characteristics of the Multi-mode Fiber Link Tomofumi Kise* 1, Toshihito Suzuki* 2, Masaki Funabashi* 1, Kazuya Nagashima*
Special Issue Optical Communication The Development of the 16 nm 28 Gb/s VCSEL and the Characteristics of the Multi-mode Fiber Link Tomofumi Kise* 1, Toshihito Suzuki* 2, Masaki Funabashi* 1, Kazuya Nagashima*
Title. CitationIEEE photonics journal, 8(3): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information.
 Title Theoretical Investigation of Six-Mode Multi/Demultip Author(s)Nishimoto, Shoko; Fujisawa, Takeshi; Sasaki, Yusuke; CitationIEEE photonics journal, 8(3): 7802908 Issue Date 2016-06 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/62373
Title Theoretical Investigation of Six-Mode Multi/Demultip Author(s)Nishimoto, Shoko; Fujisawa, Takeshi; Sasaki, Yusuke; CitationIEEE photonics journal, 8(3): 7802908 Issue Date 2016-06 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/62373
Effective Cutoff Wavelength Measurement of Bend-insensitive Fiber by Longitudinal Misalignment Loss Method. Won-Taek Han
 Advanced Materials Research Vols. 123-125 (2010) pp 419-422 Online available since 2010/Aug/11 at www.scientific.net (2010) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.123-125.419
Advanced Materials Research Vols. 123-125 (2010) pp 419-422 Online available since 2010/Aug/11 at www.scientific.net (2010) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.123-125.419
Test procedures Page: 1 of 5
 Test procedures Page: 1 of 5 1 Scope This part of document establishes uniform requirements for measuring the numerical aperture of optical fibre, thereby assisting in the inspection of fibres and cables
Test procedures Page: 1 of 5 1 Scope This part of document establishes uniform requirements for measuring the numerical aperture of optical fibre, thereby assisting in the inspection of fibres and cables
Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing
 Journal of Computer Science 2 (): 09-3, 2006 ISSN 549-3636 Science Publications, 2006 Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing Yas A. Alsultanny Computer Science Department, Amman Arab University for
Journal of Computer Science 2 (): 09-3, 2006 ISSN 549-3636 Science Publications, 2006 Laser Beam Analysis Using Image Processing Yas A. Alsultanny Computer Science Department, Amman Arab University for
High-Bandwidth Graded-Index Polymer Optical Fiber Enabling Power Penalty-Free Gigabit Data Transmission
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 21, NO. 11, NOVEMER 2003 2923 High-Bandwidth Graded-Index Polymer Optical Fiber Enabling Power Penalty-Free Gigabit Data Transmission Takaaki Ishigure, Member, IEEE,
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 21, NO. 11, NOVEMER 2003 2923 High-Bandwidth Graded-Index Polymer Optical Fiber Enabling Power Penalty-Free Gigabit Data Transmission Takaaki Ishigure, Member, IEEE,
Trends in Optical Transceivers:
 Trends in Optical Transceivers: Light sources for premises networks Peter Ronco Corning Optical Fiber Asst. Product Line Manager Premises Fibers January 24, 2006 Outline: Introduction: Transceivers and
Trends in Optical Transceivers: Light sources for premises networks Peter Ronco Corning Optical Fiber Asst. Product Line Manager Premises Fibers January 24, 2006 Outline: Introduction: Transceivers and
DESIGN OF COMPACT PULSED 4 MIRROR LASER WIRE SYSTEM FOR QUICK MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRON BEAM PROFILE
 1 DESIGN OF COMPACT PULSED 4 MIRROR LASER WIRE SYSTEM FOR QUICK MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRON BEAM PROFILE PRESENTED BY- ARPIT RAWANKAR THE GRADUATE UNIVERSITY FOR ADVANCED STUDIES, HAYAMA 2 INDEX 1. Concept
1 DESIGN OF COMPACT PULSED 4 MIRROR LASER WIRE SYSTEM FOR QUICK MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRON BEAM PROFILE PRESENTED BY- ARPIT RAWANKAR THE GRADUATE UNIVERSITY FOR ADVANCED STUDIES, HAYAMA 2 INDEX 1. Concept
Polarization Dependence of an Edge Filter Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fibre
 Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Articles School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 21-1-1 Polarization Dependence of an Edge Filter Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fibre Agus Hatta
Dublin Institute of Technology ARROW@DIT Articles School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering 21-1-1 Polarization Dependence of an Edge Filter Based on Singlemode-Multimode-Singlemode Fibre Agus Hatta
2 in the multipath dispersion of the optical fibre. (b) Discuss the merits and drawbacks of cut bouls method of measurement of alternation.
 B.TECH IV Year I Semester (R09) Regular Examinations, November 2012 1 (a) Derive an expression for multiple time difference tt 2 in the multipath dispersion of the optical fibre. (b) Discuss the merits
B.TECH IV Year I Semester (R09) Regular Examinations, November 2012 1 (a) Derive an expression for multiple time difference tt 2 in the multipath dispersion of the optical fibre. (b) Discuss the merits
The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack To cite this article: Yuanyuan Gu et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack To cite this article: Yuanyuan Gu et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Attenuation and Time Dispersion Measurements of Graded Index Polymer Optical Fiber for. Indoor Cellular Coverage
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 2, 2009, no. 2, 47-58 Attenuation and Time Dispersion Measurements of Graded Index Polymer Optical Fiber for Indoor Cellular Coverage S. Louvros and I. E. Kougias
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 2, 2009, no. 2, 47-58 Attenuation and Time Dispersion Measurements of Graded Index Polymer Optical Fiber for Indoor Cellular Coverage S. Louvros and I. E. Kougias
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
Multimode fiber media types for 802.3cd
 1 Multimode fiber media types for 802.3cd P802.3cd, Fort Worth, Texas September 12-16, 2016 Rick Pimpinella Jose Castro Brett Lane Panduit Labs, Panduit Corp. 2 Laser Optimized Multimode Fiber Types Fiber
1 Multimode fiber media types for 802.3cd P802.3cd, Fort Worth, Texas September 12-16, 2016 Rick Pimpinella Jose Castro Brett Lane Panduit Labs, Panduit Corp. 2 Laser Optimized Multimode Fiber Types Fiber
Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating
 International Journal of Computational Engineering & Management, Vol. 15 Issue 5, September 2012 www..org 16 Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating P. K. Raghav 1,
International Journal of Computational Engineering & Management, Vol. 15 Issue 5, September 2012 www..org 16 Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating P. K. Raghav 1,
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
Total care for networks. Introduction to Dispersion
 Introduction to Dispersion Introduction to PMD Version1.0- June 01, 2000 Copyright GN Nettest 2000 Introduction To Dispersion Contents Definition of Dispersion Chromatic Dispersion Polarization Mode Dispersion
Introduction to Dispersion Introduction to PMD Version1.0- June 01, 2000 Copyright GN Nettest 2000 Introduction To Dispersion Contents Definition of Dispersion Chromatic Dispersion Polarization Mode Dispersion
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber. Xavier Fernando Ryerson University
 Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson University The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Guided Propagation Along the Optical Fiber Xavier Fernando Ryerson University The Nature of Light Quantum Theory Light consists of small particles (photons) Wave Theory Light travels as a transverse electromagnetic
Analysis of Laser and Detector Placement in MIMO Multimode Optical Fiber Systems
 Analysis of Laser and Detector Placement in MIMO Multimode Optical Fiber Systems Kumar Appaiah, Sagi Zisman, Sriram Vishwanath, Seth R Bank Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University
Analysis of Laser and Detector Placement in MIMO Multimode Optical Fiber Systems Kumar Appaiah, Sagi Zisman, Sriram Vishwanath, Seth R Bank Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University
Modal Characteristics of Coupled Resonator Vertical Cavity Laser Diode
 Advances in Optoelectronic Materials (AOM) Volume 4, 06 doi: 0.4355/aom.06.04.00 www.seipub.org/aom Modal Characteristics of Coupled Resonator Vertical Cavity Laser Diode Kaikai Xu *, David Cheng, Xingfa
Advances in Optoelectronic Materials (AOM) Volume 4, 06 doi: 0.4355/aom.06.04.00 www.seipub.org/aom Modal Characteristics of Coupled Resonator Vertical Cavity Laser Diode Kaikai Xu *, David Cheng, Xingfa
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING
 CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology E-ISSN
 Research Article ANALYTICAL STUDY OF HELICALLY CLADDED OPTICAL WAVEGUIDE WITH DIFFERENT PITCH ANGLES Mishra V.* Gautam A. K. Taunk B. R. Address for Correspondence Sr. Member IEEE, Electronics Engineering
Research Article ANALYTICAL STUDY OF HELICALLY CLADDED OPTICAL WAVEGUIDE WITH DIFFERENT PITCH ANGLES Mishra V.* Gautam A. K. Taunk B. R. Address for Correspondence Sr. Member IEEE, Electronics Engineering
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
White Paper: The Ins and Outs of Testing Bend Insensitive Multimode Fiber (BIMMF): The Need for Encircled Flux
 White Paper: The Ins and Outs of Testing Bend Insensitive Multimode Fiber (BIMMF): The Need for Encircled Flux White Paper: The Ins and Outs of Testing Bend Insensitive Multimode Fiber (BIMMF): The Need
White Paper: The Ins and Outs of Testing Bend Insensitive Multimode Fiber (BIMMF): The Need for Encircled Flux White Paper: The Ins and Outs of Testing Bend Insensitive Multimode Fiber (BIMMF): The Need
Faraday Rotators and Isolators
 Faraday Rotators and I. Introduction The negative effects of optical feedback on laser oscillators and laser diodes have long been known. Problems include frequency instability, relaxation oscillations,
Faraday Rotators and I. Introduction The negative effects of optical feedback on laser oscillators and laser diodes have long been known. Problems include frequency instability, relaxation oscillations,
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus
 Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides
 Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
Multimode Optical Fiber
 Multimode Optical Fiber 1 OBJECTIVE Determine the optical modes that exist for multimode step index fibers and investigate their performance on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB The backbone of optical systems
Multimode Optical Fiber 1 OBJECTIVE Determine the optical modes that exist for multimode step index fibers and investigate their performance on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB The backbone of optical systems
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG
 http:// PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF 1.25 16 GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG Arashdeep Kaur 1, Ramandeep Kaur 2 1 Student, M.Tech, Department of Electronics and Communication
http:// PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF 1.25 16 GB/S BIDIRECTIONAL DWDM PASSIVE OPTICAL NETWORK BASED ON CYCLIC AWG Arashdeep Kaur 1, Ramandeep Kaur 2 1 Student, M.Tech, Department of Electronics and Communication
EFFECTS OF POLARIZATION MODE DISPERSION INOPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 I J C T A, 9(28) 2016, pp. 383-389 International Science Press EFFECTS OF POLARIZATION MODE DISPERSION INOPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Jabeena A* Ashna Jain* and N. Sardar Basha** Abstract : The effects
I J C T A, 9(28) 2016, pp. 383-389 International Science Press EFFECTS OF POLARIZATION MODE DISPERSION INOPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Jabeena A* Ashna Jain* and N. Sardar Basha** Abstract : The effects
Optical Fiber Technology. Photonic Network By Dr. M H Zaidi
 Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Deliverable Report. Deliverable No: D2.9 Deliverable Title: OAM waveguide transmission
 Deliverable Report Deliverable No: D2.9 Deliverable Title: OAM waveguide transmission Grant Agreement number: 255914 Project acronym: PHORBITECH Project title: A Toolbox for Photon Orbital Angular Momentum
Deliverable Report Deliverable No: D2.9 Deliverable Title: OAM waveguide transmission Grant Agreement number: 255914 Project acronym: PHORBITECH Project title: A Toolbox for Photon Orbital Angular Momentum
τ mod = T modal = longest ray path shortest ray path n 1 L 1 = L n 2 1
 S. Blair February 15, 2012 23 2.2. Pulse dispersion Pulse dispersion is the spreading of a pulse as it propagates down an optical fiber. Pulse spreading is an obvious detrimental effect that limits the
S. Blair February 15, 2012 23 2.2. Pulse dispersion Pulse dispersion is the spreading of a pulse as it propagates down an optical fiber. Pulse spreading is an obvious detrimental effect that limits the
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
Integrated Optoelectronic Chips for Bidirectional Optical Interconnection at Gbit/s Data Rates
 Bidirectional Optical Data Transmission 77 Integrated Optoelectronic Chips for Bidirectional Optical Interconnection at Gbit/s Data Rates Martin Stach and Alexander Kern We report on the fabrication and
Bidirectional Optical Data Transmission 77 Integrated Optoelectronic Chips for Bidirectional Optical Interconnection at Gbit/s Data Rates Martin Stach and Alexander Kern We report on the fabrication and
Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF
 Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF Koji Ieda a), Kenji Kurokawa, Katsusuke Tajima, and Kazuhide Nakajima NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories, NTT Corporation, 1 7 1 Hanabatake,
Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF Koji Ieda a), Kenji Kurokawa, Katsusuke Tajima, and Kazuhide Nakajima NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories, NTT Corporation, 1 7 1 Hanabatake,
Photonic Microwave Filter Employing an Opto- VLSI-Based Adaptive Optical Combiner
 Research Online ECU Publications 211 211 Photonic Microwave Filter Employing an Opto- VLSI-Based Adaptive Optical Combiner Haithem Mustafa Feng Xiao Kamal Alameh 1.119/HONET.211.6149818 This article was
Research Online ECU Publications 211 211 Photonic Microwave Filter Employing an Opto- VLSI-Based Adaptive Optical Combiner Haithem Mustafa Feng Xiao Kamal Alameh 1.119/HONET.211.6149818 This article was
RECENTLY, using near-field scanning optical
 1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
Fundamentals of Electromagnetics With Engineering Applications by Stuart M. Wentworth Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons. All rights reserved.
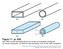 Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Figure 7-1 (p. 339) Non-TEM mmode waveguide structures include (a) rectangular waveguide, (b) circular waveguide., (c) dielectric slab waveguide, and (d) fiber optic waveguide. Figure 7-2 (p. 340) Cross
Publication II. c [2003] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology.
![Publication II. c [2003] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology. Publication II. c [2003] IEEE. Reprinted, with permission, from IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology.](/thumbs/77/76567042.jpg) II Publication II J. Oksanen and J. Tulkki, On crosstalk and noise in an optical amplifier with gain clamping by vertical laser field, IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 21, pp. 1914-1919 (2003). c [2003]
II Publication II J. Oksanen and J. Tulkki, On crosstalk and noise in an optical amplifier with gain clamping by vertical laser field, IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 21, pp. 1914-1919 (2003). c [2003]
Theory of Helix Antenna
 Theory of Helix Antenna Tariq Rahim School of Electronic and information, NWPU, Xian china Review on Helix Antenna 1 Introduction The helical antenna is a hybrid of two simple radiating elements, the dipole
Theory of Helix Antenna Tariq Rahim School of Electronic and information, NWPU, Xian china Review on Helix Antenna 1 Introduction The helical antenna is a hybrid of two simple radiating elements, the dipole
Measuring the Modal Properties of Multimode Fibres. FOToN 6th May 2004
 Measuring the Modal Properties of Multimode Fibres Andrew G Hallam David A Robinson FOToN 6th May 24 Structure of Talk Basic mode theory Measuring the mode distribution Measurement results Theory: modes
Measuring the Modal Properties of Multimode Fibres Andrew G Hallam David A Robinson FOToN 6th May 24 Structure of Talk Basic mode theory Measuring the mode distribution Measurement results Theory: modes
Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors
 846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
The fundamental differences between OM5 and OM4+ fiber
 The fundamental differences between OM5 and OM4+ fiber Pressure continues to build for data center operators to migrate to faster applications and longer link distances. In response, infrastructure OEMs
The fundamental differences between OM5 and OM4+ fiber Pressure continues to build for data center operators to migrate to faster applications and longer link distances. In response, infrastructure OEMs
Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume No. 7, July, 01 Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides 1 Trung-Thanh Le,
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume No. 7, July, 01 Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides 1 Trung-Thanh Le,
R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Semiconductor Lasers (2 weeks) Semiconductor (diode) lasers are by far the most widely used lasers today. Their small size and properties of the light output
R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Semiconductor Lasers (2 weeks) Semiconductor (diode) lasers are by far the most widely used lasers today. Their small size and properties of the light output
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Wavelength Stabilization of HPDL Array Fast-Axis Collimation Optic with integrated VHG
 Wavelength Stabilization of HPDL Array Fast-Axis Collimation Optic with integrated VHG C. Schnitzler a, S. Hambuecker a, O. Ruebenach a, V. Sinhoff a, G. Steckman b, L. West b, C. Wessling c, D. Hoffmann
Wavelength Stabilization of HPDL Array Fast-Axis Collimation Optic with integrated VHG C. Schnitzler a, S. Hambuecker a, O. Ruebenach a, V. Sinhoff a, G. Steckman b, L. West b, C. Wessling c, D. Hoffmann
Splice losses in holey optical fibers
 Splice losses in holey optical fibers J.T. Lizier and G.E. Town School of Electrical and Information Engineering (J03), University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia. Tel: +612-9351-2110, Fax: +612-9351-3847,
Splice losses in holey optical fibers J.T. Lizier and G.E. Town School of Electrical and Information Engineering (J03), University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia. Tel: +612-9351-2110, Fax: +612-9351-3847,
Fiber Optic Principles. Oct-09 1
 Fiber Optic Principles Oct-09 1 Fiber Optic Basics Optical fiber Active components Attenuation Power budget Bandwidth Oct-09 2 Reference www.flukenetworks.com/fiber Handbook Fiber Optic Technologies (Vivec
Fiber Optic Principles Oct-09 1 Fiber Optic Basics Optical fiber Active components Attenuation Power budget Bandwidth Oct-09 2 Reference www.flukenetworks.com/fiber Handbook Fiber Optic Technologies (Vivec
Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre
 Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre AMANDEEP KAUR (Assist. Prof.) ECE department GIMET Amritsar Abstract: In this paper, the polarization mode dispersion
Polarization Mode Dispersion compensation in WDM system using dispersion compensating fibre AMANDEEP KAUR (Assist. Prof.) ECE department GIMET Amritsar Abstract: In this paper, the polarization mode dispersion
Key Features for OptiSystem 14
 14.0 New Features Created to address the needs of research scientists, photonic engineers, professors and students; OptiSystem satisfies the demand of users who are searching for a powerful yet easy to
14.0 New Features Created to address the needs of research scientists, photonic engineers, professors and students; OptiSystem satisfies the demand of users who are searching for a powerful yet easy to
Lecture 10. Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers
 Lecture 10 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersions Step-Index Fiber, Multimode and Single Mode Fibers Numerical Aperture, Coupling
Lecture 10 Dielectric Waveguides and Optical Fibers Slab Waveguide, Modes, V-Number Modal, Material, and Waveguide Dispersions Step-Index Fiber, Multimode and Single Mode Fibers Numerical Aperture, Coupling
Optimized Dispersion Compensation with Post Fiber Bragg Grating in WDM Optical Network
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 10, October-2012 1 Optimized Dispersion Compensation with Post Fiber Bragg Grating in WDM Optical Network P.K. Raghav, M. P.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 10, October-2012 1 Optimized Dispersion Compensation with Post Fiber Bragg Grating in WDM Optical Network P.K. Raghav, M. P.
Modeling MM Light Propagation using measured index error, DMD, and bandwidth
 Modeling MM Light Propagation using measured index error, DMD, and bandwidth John Abbott Corning Incorporated IEEE 8.3aq meeting at July 4 Portland plenary Summary a. Predicting mode delays, DMD & BW from
Modeling MM Light Propagation using measured index error, DMD, and bandwidth John Abbott Corning Incorporated IEEE 8.3aq meeting at July 4 Portland plenary Summary a. Predicting mode delays, DMD & BW from
Stabilisation of Linear-cavity Fibre Laser Using a Saturable Absorber
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2011 2011 Stabilisation of Linear-cavity Fibre Laser Using a Saturable Absorber David Michel Edith Cowan University Feng Xiao Edith Cowan University
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2011 2011 Stabilisation of Linear-cavity Fibre Laser Using a Saturable Absorber David Michel Edith Cowan University Feng Xiao Edith Cowan University
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers
 Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Elimination of Self-Pulsations in Dual-Clad, Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Lasers 1.0 Modulation depth 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Laser 3 Laser 2 Laser 4 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Absorbed pump power (W) Laser 1 W. Guan and J. R.
Coupling effects of signal and pump beams in three-level saturable-gain media
 Mitnick et al. Vol. 15, No. 9/September 1998/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2433 Coupling effects of signal and pump beams in three-level saturable-gain media Yuri Mitnick, Moshe Horowitz, and Baruch Fischer Department
Mitnick et al. Vol. 15, No. 9/September 1998/J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2433 Coupling effects of signal and pump beams in three-level saturable-gain media Yuri Mitnick, Moshe Horowitz, and Baruch Fischer Department
Graded-Index Core Polymer Optical Waveguide for High-bandwidth-density On-Board Interconnect
 European Cluster for Optical Interconnects (ECO) Workshop Sep. 25, 2013 Graded-Index Core Polymer Optical Waveguide for High-bandwidth-density On-Board Interconnect Takaaki Ishigure Faculty of Science
European Cluster for Optical Interconnects (ECO) Workshop Sep. 25, 2013 Graded-Index Core Polymer Optical Waveguide for High-bandwidth-density On-Board Interconnect Takaaki Ishigure Faculty of Science
Novel multi-core fibers for mode division multiplexing: proposal and design principle
 Novel multi-core fibers for mode division multiplexing: proposal and design principle Yasuo Kokubun 1a) and Masanori Koshiba 2 1 Graduate School of Engineering, Yokohama National University, 79 5 Tokiwadai,
Novel multi-core fibers for mode division multiplexing: proposal and design principle Yasuo Kokubun 1a) and Masanori Koshiba 2 1 Graduate School of Engineering, Yokohama National University, 79 5 Tokiwadai,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication
 InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Rays. Wavefronts. Aberrations. Outline
 Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II
 Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches
 Annual report 998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches Safwat William Zaki Mahmoud We analyze the transverse mode structure
Annual report 998, Dept. of Optoelectronics, University of Ulm Mode analysis of Oxide-Confined VCSELs using near-far field approaches Safwat William Zaki Mahmoud We analyze the transverse mode structure
RECENTLY, studies have begun that are designed to meet
 838 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 43, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2007 Design of a Fiber Bragg Grating External Cavity Diode Laser to Realize Mode-Hop Isolation Toshiya Sato Abstract Recently, a unique
838 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 43, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2007 Design of a Fiber Bragg Grating External Cavity Diode Laser to Realize Mode-Hop Isolation Toshiya Sato Abstract Recently, a unique
Optical Splitters Based on Self-Imaging Effect in Multi-Mode Waveguide Made by Ion Exchange in Glass
 352 O. BARKMAN, V. JEŘÁBEK, V. PRAJZLER, OPTICAL SPLITTERS BASED ON SELF-IMAGING EFFECT IN MULTI-MODE Optical Splitters Based on Self-Imaging Effect in Multi-Mode Waveguide Made by Ion Exchange in Glass
352 O. BARKMAN, V. JEŘÁBEK, V. PRAJZLER, OPTICAL SPLITTERS BASED ON SELF-IMAGING EFFECT IN MULTI-MODE Optical Splitters Based on Self-Imaging Effect in Multi-Mode Waveguide Made by Ion Exchange in Glass
WHITE PAPER LINK LOSS BUDGET ANALYSIS TAP APPLICATION NOTE LINK LOSS BUDGET ANALYSIS
 TAP APPLICATION NOTE LINK LOSS BUDGET ANALYSIS WHITE PAPER JULY 2017 1 Table of Contents Basic Information... 3 Link Loss Budget Analysis... 3 Singlemode vs. Multimode... 3 Dispersion vs. Attenuation...
TAP APPLICATION NOTE LINK LOSS BUDGET ANALYSIS WHITE PAPER JULY 2017 1 Table of Contents Basic Information... 3 Link Loss Budget Analysis... 3 Singlemode vs. Multimode... 3 Dispersion vs. Attenuation...
Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas. EE-4382/ Antenna Engineering
 Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas EE-4382/5306 - Antenna Engineering Outline Traveling Wave Antennas Introduction Traveling Wave Antennas: Long Wire, V Antenna, Rhombic Antenna
Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas EE-4382/5306 - Antenna Engineering Outline Traveling Wave Antennas Introduction Traveling Wave Antennas: Long Wire, V Antenna, Rhombic Antenna
Introduction to Fiber Optics
 Introduction to Fiber Optics Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior Milestones in Electrical Communication 1838 Samuel F.B. Morse
Introduction to Fiber Optics Dr. Anurag Srivastava Atal Bihari Vajpayee Indian Institute of Information Technology and Manegement, Gwalior Milestones in Electrical Communication 1838 Samuel F.B. Morse
Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser
 Chapter 4 Optical-pumped Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser The booming laser techniques named VECSEL combine the flexibility of semiconductor band structure and advantages of solid-state
Chapter 4 Optical-pumped Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser The booming laser techniques named VECSEL combine the flexibility of semiconductor band structure and advantages of solid-state
COMPARISON OF MODULATION SCHEMES USED IN FSO COMMUNICATION M. Rama Narmada 1, K. Nithya 2, P. Ashok 3 1,2,3
 COMPARISON OF MODULATION SCHEMES USED IN FSO COMMUNICATION M. Rama Narmada 1, K. Nithya 2, P. Ashok 3 1,2,3 Prince Shri Venkateshwara Padmavathy Engineering College Abstract The semiconductor diode called
COMPARISON OF MODULATION SCHEMES USED IN FSO COMMUNICATION M. Rama Narmada 1, K. Nithya 2, P. Ashok 3 1,2,3 Prince Shri Venkateshwara Padmavathy Engineering College Abstract The semiconductor diode called
EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES
 EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES OBJECTIVES In this lab, firstly you will learn to couple semiconductor sources, i.e., lightemitting diodes (LED's), to optical fibers. The coupling
EXPRIMENT 3 COUPLING FIBERS TO SEMICONDUCTOR SOURCES OBJECTIVES In this lab, firstly you will learn to couple semiconductor sources, i.e., lightemitting diodes (LED's), to optical fibers. The coupling
The absorption of the light may be intrinsic or extrinsic
 Attenuation Fiber Attenuation Types 1- Material Absorption losses 2- Intrinsic Absorption 3- Extrinsic Absorption 4- Scattering losses (Linear and nonlinear) 5- Bending Losses (Micro & Macro) Material
Attenuation Fiber Attenuation Types 1- Material Absorption losses 2- Intrinsic Absorption 3- Extrinsic Absorption 4- Scattering losses (Linear and nonlinear) 5- Bending Losses (Micro & Macro) Material
Polymer Interconnects for Datacom and Sensing. Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge
 Polymer Interconnects for Datacom and Sensing Richard Penty, Ian White, Nikos Bamiedakis, Ying Hao, Fendi Hashim Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge Outline Introduction and Motivation Material
Polymer Interconnects for Datacom and Sensing Richard Penty, Ian White, Nikos Bamiedakis, Ying Hao, Fendi Hashim Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge Outline Introduction and Motivation Material
High-power All-Fiber components: The missing link for high power fiber lasers
 High- All-Fiber components: The missing link for high lasers François Gonthier, Lilian Martineau, Nawfel Azami, Mathieu Faucher, François Séguin, Damien Stryckman, Alain Villeneuve ITF Optical Technologies
High- All-Fiber components: The missing link for high lasers François Gonthier, Lilian Martineau, Nawfel Azami, Mathieu Faucher, François Séguin, Damien Stryckman, Alain Villeneuve ITF Optical Technologies
EC Optical Communication And Networking TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWERS UNIT -1 INTRODUCTION
 EC6702 - Optical Communication And Networking TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWERS UNIT -1 INTRODUCTION Ray Theory Transmission 1. Write short notes on ray optics theory. Laws governing the nature of light are
EC6702 - Optical Communication And Networking TWO MARKS QUESTION AND ANSWERS UNIT -1 INTRODUCTION Ray Theory Transmission 1. Write short notes on ray optics theory. Laws governing the nature of light are
Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology
 Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology Chapter 18 Objectives At the conclusion of this chapter, the reader will be able to: Describe the construction of fiber optic cable. Describe the propagation
Chapter 18: Fiber Optic and Laser Technology Chapter 18 Objectives At the conclusion of this chapter, the reader will be able to: Describe the construction of fiber optic cable. Describe the propagation
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL FIBERS 9 Evolution of fiber optic system Element of an Optical Fiber Transmission link Total internal reflection Acceptance angle Numerical aperture Skew rays Ray Optics
UNIT I INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL FIBERS 9 Evolution of fiber optic system Element of an Optical Fiber Transmission link Total internal reflection Acceptance angle Numerical aperture Skew rays Ray Optics
Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Fiber Bragg Gratings With Different Lengths for Ultrasonic Detection
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 2, 2016: 187 192 Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Fiber Bragg Gratings With Different Lengths for Ultrasonic Detection Zhouzhou YU, Qi JIANG *, Hao ZHANG, and
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 2, 2016: 187 192 Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Fiber Bragg Gratings With Different Lengths for Ultrasonic Detection Zhouzhou YU, Qi JIANG *, Hao ZHANG, and
