22\ US B2. (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this. (12) United States Patent Hui et al.
|
|
|
- Cecil Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
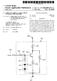
1 III III 0 II III III US B2 lid II0I II 0I II (12) United States Patent Hui et al. (10) Patent o.: US 9,678,370 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2017 (54) CARRIER-DEPLETIO BASED SILICO WAVEGUIDE RESOAT CAVITY MODULATOR WITH ITEGRATED OPTICAL POWER MOITOR (71) Applicants:IMEC VZW, Leuven (BE); Universiteit Gent, Ghent (BE) (72) Inventors: Yu Hui, Hangzhou (C); Wi Bogaerts, Melle (BE) (73) Assignees: IMEC VZW, Leuven (BE); Universiteit Gent, Ghent (BE) (*) otice: Subject to any disclaier, the ter of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 81 days. (21) Appl. o.: 14/338,564 (22) Filed: Jul. 23, 2014 (65) Prior Publication Data US 2015/ Al ov. 5, 2015 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Jul. 23, 2013 (EP) (51) Int. Cl. G02F 1/025 ( ) G02F 1/01 ( ) G02F 1/313 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl. CPC...G02F 1/025 ( ); G02F 1/0121 ( ); G02F 1/3132 ( ); GO2F 2201/58 ( ); G02F 2203/15 ( ) (58) Field of Classification Search one See application file for coplete search history. (56) References Cited U.S. PATET DOCUMETS 2002/ Al* 10/2002 Wagner...H01L31/ / / Al * 4/2003 Doash...G02B 6/ / / Al* 3/2012 Costa...H01L27/ /2 2014/ Al* 4/2014 Li...G01J1/ / Yu, Hui et al., "Using Carrier-Depletion Silicon Modulators for Optical Power Monitoring", Optics Letters, vol. 37, o. 22, ov. 15, 2012, pp Tu, Xiaoguang et al., "Fabrication of Low Loss and High Speed Silicon Optical Modulator Using Doping Copensation Method", Optics Express, vol. 19, o. 19, Sep. 12, 2011, pp * cited by exainer Priary Exainer Uyen Chau Le Assistant Exainer Chad Sith (74) Attorney, Agent, or Fir McDonnell Boehnen Hulbert & Berghoff LLP (57) ABSTRACT A carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator includes a silicon waveguide based resonant cavity. The resonant cavity includes an optical odulation section and an optical power onitoring section. The optical power onitoring section includes an integrated lateral PI diode including a doping copensated I region having a high defect density and a low net free carrier concentration. The doping copensated I region ay be fored by perforing a P-type iplantation step and an -type iplantation step with overlapping ion iplantation windows. 9 Clais, 3 Drawing Sheets 22\ 21 B A' 10
2 U.S. Patent Jun. 13, 2017 Sheet 1 of 3 US 9,678,370 B2 0 J 0 c
3 U.S. Patent Jun. 13, 2017 Sheet 2 of 3 US 9,678,370 B2 LU L
4 U.S. Patent Jun. 13, 2017 Sheet 3 of 3 US 9,678,370 B2 LU L
5 1 CARRIER-DEPLETIO BASED SILICO WAVEGUIDE RESOAT CAVITY MODULATOR WITH ITEGRATED OPTICAL POWER MOITOR CROSS-REFERECE TO RELATED APPLICATIO US 9,678,370 B2 This application clais priority to European Patent Application o filed on Jul. 23, 2013, the contents of 10 which are hereby incorporated by reference. FIELD The present disclosure is related to carrier-depletion based 15 silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulators having an integrated optical power onitor, and to ethods for fabricating such resonant cavity odulators with an integrated power onitor. A carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cay- 20 ity odulator of the present disclosure ay be integrated on a silicon photonics platfor without the need for additional process steps. BACKGROUD 25 An objective of silicon photonics is to integrate different functionalities, including wavelength ultiplexing and deultiplexing, routing, optical eission, odulation, and detection on a silicon based platfor, such as a silicon-on- 30 insulator (SOI) based platfor. A copact, power-efficient and high-speed integrated silicon odulator is a key building block of silicon photonics. The carrier-depletion odulator is becoing a preferred solution for electro-optic odulation in silicon, because of 35 its copatibility with copleentary etal-oxide seiconductor (CMOS) process technology, its processing siplicity, and its high operation speed. For exaple, a carrier-depletion based icro-ring odulator ay coprise a icro-ring resonator with an integrated 40 Pjunction. The icro-ring can be coupled to a neighboring waveguide. The resonant wavelength ay be odified by tuning the effective refractive index of the icro-ring waveguide. Tuning is obtained by reverse biasing the P junction integrated with the icro-ring. 45 Due to its resonant nature, the icro-ring odulator has the advantages of copact size, low power consuption, and low driving voltage. However, a drawback of this structure is that optical odulation occurs only within a narrow wavelength range near the resonance wavelength. A 50 typical optical bandwidth of effective odulation is less than 0.1 n. Further, a silicon waveguide is very sensitive to teperature variations. For exaple, a change in the abient teperature of 1 C. results in a shift of the resonance 55 wavelength of a silicon icro-ring odulator by about 0.1 n. This akes the silicon icro-ring odulator very sensitive to any teperature fluctuation. Therefore, a silicon icro-ring odulator generally needs to be integrated with a dynaic theral stabilization syste. 60 Such dynaic theral stabilization syste ay include a heater to change the teperature, a feedback circuit to control the heater power, and an optical power onitor that onitors the ring dynaics and that provides a feedback signal to the circuit controlling the heater power. 65 The 1.12 ev band gap of silicon akes it transparent in the teleco wavelength band around 1.55 ti. In order to 2 enable onitoring of the optical power inside a silicon icro-ring odulator, several solutions have been proposed, such as: integration of a Geraniu photodetector by eptiaxial growth; bonding of a Ill-V seiconductor based photodetector; or using a dedicated ion iplantation step (typically Si+ iplantation) to introduce lattice defects in the silicon waveguide in a predeterined area. These lattice defects ay lead to defect-state ediated sub-bandgap absorption and result in the generation of a photocurrent. While the observed effect is generally uch weaker than in case of direct absorption in a Ge or Ill-V photo-detector, it is an advantage of this approach that the functionality ay be ipleented relying exclusively on silicon carrier-depletion odulation without adding processing steps. A silicon icro-ring odulator wherein defect-state ediated absorption is used for integrated power onitoring has been described by Hui Yu et al. in "Using carrierdepletion silicon odulators for optical power onitoring", Optics Letters Vol. 37, o. 22, A icro-ring resonator with a lateral P junction is described, wherein the P junction is ebedded in an SOI waveguide by ion iplantation. After ion iplantation, a rapid theral annealing (RTA) ay be perfored at a teperature above 1000 C. to activate the dopants and to repair daage in the silicon lattice without causing uch dopant redistribution. Still, there ay reain soe residual crystal defects that can ediate sub-bandgap absorption. It is shown that, after being heated to 1075 C., a reverse-biased P diode still produces a substantial photocurrent, based on defect-ediated absorption in the ion-iplanted SOI waveguides. This photocurrent is used as a power onitor feedback signal. This eans that the widely utilized carrier-depletion odulator ay also be used for optical power onitoring without any additional processing. For exaple, a sall section of a P-junction-ebedded ring ay be used to onitor the optical power inside the ring. It is suggested that the responsivity of both the odulator and the onitor ay be enhanced by using an interdigitated P junction instead of a lateral P junction, to enlarge the overlap between the optical ode and the carrier-depletion region, or by reducing the RTA teperature to increase the crystal defect density. SUMMARY The present disclosure ais to provide a carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator with an integrated optical power onitor based on defect-ediated sub-bandgap absorption, wherein the power onitor has a good responsivity, and wherein the power onitor ay be integrated without the need for additional processing steps and without introducing any additional absorption aterials. The present disclosure further ais to provide a ethod for fabricating such resonant cavity odulator with an integrated power onitor. The present disclosure is related to a carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator that includes a silicon waveguide based resonant cavity. In an exaple, the resonant cavity has an optical odulation section and an optical power onitoring section. The optical odulation section ay include an integrated lateral P diode, and the optical power onitoring section ay include an integrated lateral PI diode coprising a doping copensated I region having a high defect density and a low net free carrier concentration. In the context of the present disclosure, the ter "PI diode" refers to a diode having a p-type seiconductor region (P) and an n-type seiconductor region (), with
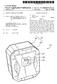
6 3 therein between a seiconductor region (I) having a net doping concentration that is lower than the net P-type doping concentration of the P region and lower than the net -type doping concentration of the region. In ebodients of the present disclosure, the doping copensated region (I region) ay be an intrinsic region or a near intrinsic region, or it ay be a lowly doped p-type region or a lowly doped n-type region. In operation, when light propagates through the resonant cavity silicon waveguide, free photo-carriers ay be generated in the PI diode through defect ediated absorption, resulting in a photocurrent. The photocurrent is a easure for the optical power inside the resonant cavity and ay be used as a feedback signal to a circuit controlling a heater power. In a fabrication process of a carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator of the present disclosure, the doping copensated region ay for exaple be fored by perforing a P-type iplantation step using a first iplantation window and by perforing an -type iplantation step using a second iplantation window, with overlapping first and second ion iplantation windows at the location where the doping copensated region is to be provided. The sae ion iplantation steps as used in the fabrication of the optical odulation section of the carrierdepletion based odulator ay be used to realize the in-waveguide optical power onitor. Therefore, a PI photodiode wherein photocarriers are generated through defect ediated absorption ay be obtained inside a waveguide based resonant cavity using the sae process flow as used for fabricating the carrier-depletion based odulator. In ebodients of the present disclosure, the waveguide resonant cavity ay for exaple coprise a icro-ring resonator or a Fabry-Pérot cavity, the present disclosure not being liited thereto. It is a potential advantage of devices and ethods of the present disclosure that there is no need for using non-silicon photoactive aterials, such as Ge or Ill-V seiconductor aterials, to enable optical power onitoring. It is a potential advantage of devices and ethods of the present disclosure that the doping copensated region ay have a high defect density, resulting in a good photocurrent (good responsivity) through defect ediated absorption, while having a low net free carrier concentration, thus avoiding or reducing undesired free carrier absorption losses. It is a potential advantage of devices and ethods of the present disclosure that there is no need for additional processing steps to realize the PI photodiode. The processing of the PI photodiode is fully copatible with the processing of the silicon carrier-depletion odulator. Therefore, the power onitor (PI diode) ay be integrated without additional cost. It is a potential advantage of ebodients of the present disclosure that the optical power onitor ay be provided directly inside the waveguide based resonant cavity odulator, thus leading to a reduced coplexity of the photonics circuit. Certain objects and advantages of various inventive aspects have been described hereinabove, Of course, it is to be understood that not necessarily all such objects or advantages ay be achieved in accordance with any particular ebodient of the disclosure. Thus, for exaple, those skilled in the art will recognize that the disclosure ay be ebodied or carried out in a anner that achieves or optiizes one advantage or group of advantages as taught herein without necessarily achieving other objects or advan- US 9,678,370 B2 4 tages as ay be taught or suggested herein. Further, it is understood that this suary is erely an exaple and is not intended to liit the scope of the disclosure. The disclosure, both as to organization and ethod of operation, 5 together with features and advantages thereof, ay best be understood by reference to the following detailed description when read in conjunction with the accopanying drawings. 10 BRIEF DESCRIPTIO OF THE FIGURES FIG. 1 scheatically illustrates a icro-ring coprising an optical odulation section and an optical power onitoring section in accordance with an ebodient of the 15 present disclosure. FIG. 2 scheatically shows a cross section along line A-A' (FIG. 1) of the optical odulation section of a icroring according to an ebodient of the present disclosure. FIG. 3 scheatically shows a cross section along line 20 B-B' (FIG. 1) of the optical power onitoring section of a icro-ring according to an ebodient of the present disclosure. Any reference signs in the clais shall not be construed as liiting the scope of the present disclosure. 25 In the different drawings, the sae reference signs refer to the sae or analogous eleents. DETAILED DESCRIPTIO 30 In the following detailed description, nuerous specific details are set forth in order to provide a thorough understanding of the disclosure and how it ay be practiced in particular ebodients. However, it will be understood that the present disclosure ay be practiced without these spe- 35 cific details. In other instances, well-known ethods, procedures and techniques have not been described in detail, so as not to obscure the present disclosure. The present disclosure will be described with respect to particular ebodients and with reference to certain draw- 40 ings but the disclosure is not liited thereto but only by the clais. The drawings described are only scheatic and are non-liiting. In the drawings, the size of soe of the eleents ay be exaggerated and not drawn on scale for illustrative purposes. The diensions and the relative 45 diensions do not necessarily correspond to actual reductions to practice of the disclosure. Furtherore, the ters first, second, third and the like in the description and in the clais, are used for distinguishing between siilar eleents and not necessarily for describing 50 a sequential or chronological order. The ters are interchangeable under appropriate circustances and the ebodients of the disclosure can operate in other sequences than described or illustrated herein. Moreover, the ters top, botto, over, under and the like 55 in the description and the clais are used for descriptive purposes and not necessarily for describing relative positions. It is to be understood that the ters so used are interchangeable under appropriate circustances and that the ebodients of the disclosure described herein are 60 capable of operation in other orientations than described or illustrated herein. The ter "coprising", used in the clais, should not be interpreted as being restricted to the eans listed thereafter; it does not exclude other eleents or steps. Rather, it should 65 generally be interpreted as specifying the presence of the stated features, integers, steps or coponents as referred to, but does not preclude the presence or addition of one or
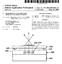
7 US 9,678,370 B2 5 ore other features, integers, steps or coponents, or ing, e.g. Rapid Theral Annealing, for dopant activation. groups thereof. Thus, the scope of the expression "a device The doping concentration in the P-type region 33 and in the coprising eans A and B" should not be liited to devices -type region 34 ay for exaple be in the order of 1018 consisting only of coponents A and B. c 3, the present disclosure not being liited thereto. The present disclosure relates to a carrier-depletion based 5 In ebodients of the present disclosure, the location of silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator with an integrated optical power onitor based on defect ediated tially the sae lateral position along the length of the optical the P junction in the strip portion 202 ay be at substan- carrier absorption, wherein the power onitor has an odulation section 21. In other ebodients of the present iproved responsivity as copared to prior art power onitors, and wherein the power onitor ay be integrated 10 portion 202 ay vary along the length of the optical odu- disclosure, the location of the P junction in the strip without the need for additional processing steps and without lation section 21: the P junction ay for exaple be introducing any additional absorption aterials. interdigitated. The present disclosure is further described for ebodients wherein the silicon waveguide resonant cavity odu- P-type contact 37 and an -type contact 38, to enable tuning As illustrated in FIG. 2, the icro-ring also contains a lator is a silicon icro-ring odulator. However, the present 15 of the effective refractive index in the optical odulation disclosure is not liited thereto. The silicon waveguide section 21 by depleting the P junction (reverse biasing) resonant cavity ay for exaple be a Fabry-Pérot cavity or inside the icro-ring waveguide 20. A heavily doped P any other suitable cavity known by a person skilled in the region 35 and a heavily doped region 36 are fored in art. the silicon layer at the location of respectively the P-type FIG. 1 scheatically illustrates a icro-ring odulator 20 contact 37 and the -type contact 38 to enable the foration according to an ebodient of the present disclosure (top of good ohic contacts. The Pttype region and the ttype view). The odulator coprises a first waveguide 10, which region ay for exaple be fored by ion iplantation ay for exaple be a straight waveguide as shown in FIG. followed by annealing, e.g. Rapid Theral Annealing, for 1, the present disclosure not being liited thereto, and a dopant activation. The doping concentration in the Pttype second waveguide 20 having a icro-ring shape, the second 25 region and in the ttype region ay for exaple be in the waveguide 20 being optically coupled to the first waveguide order of 1020 c 3, the present disclosure not being liited 10 by evanescent coupling. The icro-ring waveguide 20 thereto. The P-type contact 37 ay for exaple be electrically connected to the heavily doped P region 35 though the coprises an optical odulation section 21 and an optical power onitoring section 22. upper cladding layer 32 by eans of electrically conductive In the exaple shown in FIG. 1, the second waveguide plugs 39. Siilarly, the -type contact 38 ay for exaple has a ring shape. However, the present disclosure is not be electrically connected to the heavily doped + region 36 liited thereto and any other suitable (closed) shape known though the upper cladding layer 32 by eans of electrically to a person skilled in the art ay be used for second conductive plugs 39. waveguide 20, such as for exaple a racetrack shape or a Although in FIG. 2 the icro-ring waveguide shown is a rectangular shape with rounded corners. 35 rib waveguide, wherein an electrical path between the heavily doped P region 35 (p-type contact 37) and the P In ebodients of the present disclosure, the first waveguide 10 and the second waveguide 20 (e.g. icro-ring) ay junction in the strip portion 202 of the waveguide and for exaple have a silicon core layer and silicon oxide between the heavily doped region 36 (-type contact 38) cladding layers. For exaple, the waveguide core ay be and the P junction is established through the doped slab fored in the device layer of an SQl substrate. However, the 40 portions 201, the present disclosure is not liited thereto. present disclosure is not liited thereto and other suitable For exaple, the icro-ring waveguide ay be a strip aterial cobinations ay be used. waveguide, wherein an electrical path is established between In ebodients of the present disclosure, the icro-ring the contacts and a P junction in the strip waveguide by odulator is a carrier depletion-based odulator with an foring doped silicon bridges between the contact areas and integrated P junction. 45 the strip waveguide. Other suitable configurations ay be FIG. 2 shows a cross-section along line A-A' (optical used. odulation section 21) and FIG. 3 shows a cross-section In the optical power onitoring section 22, scheatically along line B-B' (optical power onitoring section 22) of the illustrated in FIG. 3, the rib waveguide coprises a P-type icro-ring waveguide 20 of FIG. 1. In the exaple illustrated in FIG. 2 and FIG. 3, the icro-ring waveguide is a 50 -type region 34 at a second lateral side of the strip portion, region 33 at a first lateral side of the strip portion 202, an rib waveguide, containing slab portions 201 (shallow etched and a doping copensated region 40 between the P-type portions) and a strip portion 202 (unetched portion) wherein region 33 and the -type region 34, the doping copensated light ay be confined. The core of the icro-ring waveguide region 40 being located in the strip portion 202. In this way 20 is stacked between a lower cladding layer 31 and an a lateral PI diode is fored, with the doping copensated, upper cladding layer 32. The lower cladding layer 31 ay 55 e.g. intrinsic, region located in the strip portion of the for exaple be a silicon oxide layer, such as an oxide layer icro-ring. Although in the exaple illustrated in FIG. 3, of a SQl substrate. The upper cladding layer 32 ay for the P-type region 33 and the -type region 34 both extend exaple be a deposited silicon oxide layer. into the strip portion of the icro-ring, the present disclosure In the optical odulation section 21 of the icro-ring is not liited thereto. (FIG. 2), the rib waveguide coprises an integrated P 60 In ebodients of the present disclosure, the doping junction fored by a P-type region 33 at a first lateral side copensated region 40 is a region with a high defect density. of the strip portion 202 and an -type region 34 at a second This high defect density ay for exaple be obtained by lateral side of the strip portion 202. The P-type region 33 and doping copensation. In ebodients of the present disclosure, the doping copensated region 40 ay for exaple the -type region 34 for a lateral P junction that is located in the strip portion 202 of the icro-ring waveguide 65 be fored as a result of the ion iplantation steps that are 20. The P-type region 33 and the -type region 34 ay for used for foring the P-type region 33 and the -type region exaple be fored by ion iplantation followed by anneal- 34 (both in the optical power onitoring section 22 and in
8 US 9,678,370 B2 7 the optical odulation section 21), by providing an overlap between both ion iplantation windows. In other ebodients, the doping copensated region 40 ay for exaple be fored as a result of the ion iplantation steps that are perfored for foring the Pttype region 35 and the 5 ttype region 36, by providing an overlap between both ion iplantation windows. In still other ebodients an overlap between ion iplantation windows ay be provided for both the P-type and -type iplantation and the Pttype and ttype iplantation to for the copensated region By providing an overlap between the P-type (Pttype) ion iplantation window and the -type (ttype) ion iplantation window in the optical power onitoring section 22, in the strip portion 202 of the waveguide, the -type dopants 15 and the P-type dopants ay at least partially, e.g. copletely, copensate each other and a doping copensated region 40, such as for exaple an intrinsic region, ay be fored. As a result, the free carrier concentration reains low in the doping copensated region 40, which eliinates 20 undesired free carrier absorption. On the other hand, the density of lattice defects doubles in this region 40 due to the repeated ion iplantations. The lattice defects result in defect states in the forbidden band of silicon. Through these states, photons at 1.55 t whose energy is below the gap of 25 the forbidden band ay excite electrons fro the valence band to the conduction band, which is well-known as defect ediated sub-bandgap absorption. Generally, the optical-toelectrical conversion quantu efficiency of the defect ediated absorption is proportional to the defect density. 30 It is a potential advantage of ebodiens of the present disclosure that only existing ion iplantation steps that are indispensable to ipleent a carrier-depletion based odulator ay be used, so no additional processing steps are required. 35 In operation, when light propagates through the icroring 20, part of the propagating light is absorbed by defect ediated absorption in the power onitoring section 22 of the icro-ring. This absorption gives rise to a photocurrent that is a easure for the optical power inside the icro-ring. 40 This photocurrent ay be used as a feedback signal towards a feedback control circuit that adjusts the power of an integrated heater, so as to dynaically control the operation wavelength of the ring odulator. The foregoing description details certain ebodients of 45 the disclosure. It will be appreciated, however, that no atter how detailed the foregoing appears in text, the disclosure ay be practiced in any ways. It should be noted that the use of particular terinology when describing certain features or aspects of the disclosure should not be taken to 50 iply that the terinology is being re-defined herein to be restricted to including any specific characteristics of the features or aspects of the disclosure with which that terinology is associated. While the above detailed description has shown, 55 described, and pointed out novel features of the disclosure as 8 applied to various ebodients, it will be understood that various oissions, substitutions, and changes in the for and details of the device or process illustrated ay be ade by those skilled in the technology without departing fro the disclosure. The invention claied is: 1. A carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator coprising: a silicon waveguide based resonant cavity, wherein the resonant cavity includes an optical odulation section and an optical power onitoring section, wherein the optical power onitoring section includes an integrated lateral PI diode including a doping copensated I-region having a high defect density, wherein the doping copensated I-region is fored by perforing a P-type ion iplantation in the I-region and an -type ion iplantation in the I-region. 2. The carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator according to clai 1, wherein the lateral PI diode coprises a P-doped region having a net P-type doping concentration, an -doped region having a net -type doping concentration, and the doping copensated I-region is between the P-doped region and the -doped region, wherein the I-region has a net doping concentration that is lower than the net P-type doping concentration and lower than the net -type concentration. 3. The carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator according to clai 2, wherein the doping copensated region is an intrinsic region. 4. The carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator according to clai 3, wherein the resonant cavity includes a icro-ring resonator. 5. The carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator according to clai 3, wherein the resonant cavity coprises a Fabry-Pérot cavity. 6. The carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator according to clai 4, wherein icro-ring resonator includes an etched portion and an unetched portion, and wherein P-doped region, the -doped region, and the I-region extend into the unetched portion. 7. The carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator according to clai 4, wherein the optical odulation section includes an integrated P junction fored by a second P-doped region and a second -doped region. 8. The carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator according to clai 7, wherein icro-ring resonator includes an etched portion and an unetched portion, and wherein the P junction fored by the second P-doped region and the second -doped region is disposed in the unetched portion. 9. The carrier-depletion based silicon waveguide resonant cavity odulator according to clai 8, wherein first P-doped region, the first -doped region, and the I-region extend into the unetched portion. * * * * *
Silicon Carrier-Depletion-Based Mach-Zehnder and Ring Modulators with Different Doping Patterns for Telecommunication and Optical Interconnect
 Silicon Carrier-Depletion-Based Mach-Zehnder and Ring Modulators with Different Doping Patterns for Telecommunication and Optical Interconnect Hui Yu, Marianna Pantouvaki*, Joris Van Campenhout*, Katarzyna
Silicon Carrier-Depletion-Based Mach-Zehnder and Ring Modulators with Different Doping Patterns for Telecommunication and Optical Interconnect Hui Yu, Marianna Pantouvaki*, Joris Van Campenhout*, Katarzyna
POD-001 PolaDetect. Operation Manual
 POD-001 PolaDetect In-line high speed polarieter Operation Manual August 31, 2005 General Photonics Corp. Ph: (909) 590-5473 5228 Edison Ave. Fax: (909) 902-5536 Chino, CA 91710 USA www.generalphotonics.co
POD-001 PolaDetect In-line high speed polarieter Operation Manual August 31, 2005 General Photonics Corp. Ph: (909) 590-5473 5228 Edison Ave. Fax: (909) 902-5536 Chino, CA 91710 USA www.generalphotonics.co
Silicon Photonics Technology Platform To Advance The Development Of Optical Interconnects
 Silicon Photonics Technology Platform To Advance The Development Of Optical Interconnects By Mieke Van Bavel, science editor, imec, Belgium; Joris Van Campenhout, imec, Belgium; Wim Bogaerts, imec s associated
Silicon Photonics Technology Platform To Advance The Development Of Optical Interconnects By Mieke Van Bavel, science editor, imec, Belgium; Joris Van Campenhout, imec, Belgium; Wim Bogaerts, imec s associated
HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE
 HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE T.W. Murray, O. Balogun, and N. Pratt Departent of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Boston University, Boston MA 0225 Abstract:
HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE T.W. Murray, O. Balogun, and N. Pratt Departent of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Boston University, Boston MA 0225 Abstract:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Ironside et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004
 US 2004O247218A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0247218 A1 Ironside et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2004O247218A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0247218 A1 Ironside et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 9, 2004 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC DEVICE Publication Classification
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio
 Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Takahashi et al. USOO6553171B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2003 (54) OPTICAL COMPONENT HAVING POSITONING MARKERS AND METHOD FOR MAKING THE SAME (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Takahashi et al. USOO6553171B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 22, 2003 (54) OPTICAL COMPONENT HAVING POSITONING MARKERS AND METHOD FOR MAKING THE SAME (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
58 Field of Search /112, 113, short wave pass (SWP) filter between the LED and the
 USOO5813752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,813,752 Singer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 29, 1998 54 UV/BLUE LED-PHOSPHOR DEVICE WITH 5,557,115 9/1996 Shakuda... 257/81 SHORT WAVE PASS,
USOO5813752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,813,752 Singer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 29, 1998 54 UV/BLUE LED-PHOSPHOR DEVICE WITH 5,557,115 9/1996 Shakuda... 257/81 SHORT WAVE PASS,
Exploring the Electron Tunneling Behavior of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Semiconductor
 Page 110 Exploring the of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Seiconductor M. A. Rahan * and J. U. Ahed Departent of Applied Physics, Electronics & Counication Engineering, University of
Page 110 Exploring the of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Seiconductor M. A. Rahan * and J. U. Ahed Departent of Applied Physics, Electronics & Counication Engineering, University of
Electronic devices-i. Difference between conductors, insulators and semiconductors
 Electronic devices-i Semiconductor Devices is one of the important and easy units in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. It is easy to understand and learn. Generally the questions asked are simple. The unit
Electronic devices-i Semiconductor Devices is one of the important and easy units in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. It is easy to understand and learn. Generally the questions asked are simple. The unit
On the field of view of a Galilean telescope
 Transactions of the Optical Society On the field of view of a Galilean telescope To cite this article: H A Hughes and P F Everitt 1920 Trans. Opt. Soc. 22 15 View the article online for updates and enhanceents.
Transactions of the Optical Society On the field of view of a Galilean telescope To cite this article: H A Hughes and P F Everitt 1920 Trans. Opt. Soc. 22 15 View the article online for updates and enhanceents.
ELEC2202 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Modulation (FM)
 ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick. Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al.
 Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al. Abstract: Anti-syetric localized surface plasons are deonstrated on a single silver nanostrip sandwiched by SiC layers.
Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al. Abstract: Anti-syetric localized surface plasons are deonstrated on a single silver nanostrip sandwiched by SiC layers.
Power Improvement in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Embedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3
 Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
Optical fiber beamformer for processing two independent simultaneous RF beams
 Optical fiber beaforer for processing two independent siultaneous RF beas M. Jaeger, S. Granieri *, and A. Siahakoun Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering, Rose-Hulan Institute of Technology Terre
Optical fiber beaforer for processing two independent siultaneous RF beas M. Jaeger, S. Granieri *, and A. Siahakoun Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering, Rose-Hulan Institute of Technology Terre
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors
 Optical Fibres and Telecommunications Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors Introduction Where are we? A look at some real laser diodes. External modulators Mach-Zender Electro-absorption modulators
Optical Fibres and Telecommunications Lecture 9 External Modulators and Detectors Introduction Where are we? A look at some real laser diodes. External modulators Mach-Zender Electro-absorption modulators
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,557,649 B2
 US007557649B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 2009 (54) DC OFFSET CANCELLATION CIRCUIT AND 3,868,596 A * 2/1975 Williford... 33 1/108 R PROGRAMMABLE
US007557649B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 2009 (54) DC OFFSET CANCELLATION CIRCUIT AND 3,868,596 A * 2/1975 Williford... 33 1/108 R PROGRAMMABLE
A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz amplifier.
 University of Michigan, EECS413 Final project. A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz aplifier. 1 A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz aplifier. Mark Ferriss, Junghwan Han, Joshua Jaeyoung Kang, University of Michigan. Abstract
University of Michigan, EECS413 Final project. A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz aplifier. 1 A 1.2V rail-to-rail 100MHz aplifier. Mark Ferriss, Junghwan Han, Joshua Jaeyoung Kang, University of Michigan. Abstract
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
Design and Implementation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measurement System Based on STC12 Jian Huang
 International Conference on Education, Manageent and Coputer Science (ICEMC 2016) Design and Ipleentation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measureent Syste Based on STC12 Jian Huang Xijing University,
International Conference on Education, Manageent and Coputer Science (ICEMC 2016) Design and Ipleentation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measureent Syste Based on STC12 Jian Huang Xijing University,
Fabrication of High-Speed Resonant Cavity Enhanced Schottky Photodiodes
 Fabrication of High-Speed Resonant Cavity Enhanced Schottky Photodiodes Abstract We report the fabrication and testing of a GaAs-based high-speed resonant cavity enhanced (RCE) Schottky photodiode. The
Fabrication of High-Speed Resonant Cavity Enhanced Schottky Photodiodes Abstract We report the fabrication and testing of a GaAs-based high-speed resonant cavity enhanced (RCE) Schottky photodiode. The
UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Commutated AC to DC converters) Line Commutated Converter
 UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Coutated AC to DC converters) INTRODUCTION TO CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS Controlled rectifiers are line coutated ac to power converters which are used to convert a fixed
UNIT - II CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS (Line Coutated AC to DC converters) INTRODUCTION TO CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS Controlled rectifiers are line coutated ac to power converters which are used to convert a fixed
Real Time Etch-depth Measurement Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, (8): -7, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 Real Tie Etch-depth Measureent Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor 1 Reza Hosseini, Navid Rahany, 3 Behrad Soltanbeigi, Rouzbeh
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, (8): -7, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 Real Tie Etch-depth Measureent Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor 1 Reza Hosseini, Navid Rahany, 3 Behrad Soltanbeigi, Rouzbeh
High speed silicon-based optoelectronic devices Delphine Marris-Morini Institut d Electronique Fondamentale, Université Paris Sud
 High speed silicon-based optoelectronic devices Delphine Marris-Morini Institut d Electronique Fondamentale, Université Paris Sud Data centers Optical telecommunications Environment Interconnects Silicon
High speed silicon-based optoelectronic devices Delphine Marris-Morini Institut d Electronique Fondamentale, Université Paris Sud Data centers Optical telecommunications Environment Interconnects Silicon
AccuBridge TOWARDS THE DEVELOPMENT OF A DC CURRENT COMPARATOR RATIO STANDARD
 AccuBridge TOWARD THE DEVELOPMENT OF A DC CURRENT COMPARATOR RATO TANDARD Duane Brown,Andrew Wachowicz, Dr. hiping Huang 3 Measureents nternational, Prescott Canada duanebrown@intl.co, Measureents nternational,
AccuBridge TOWARD THE DEVELOPMENT OF A DC CURRENT COMPARATOR RATO TANDARD Duane Brown,Andrew Wachowicz, Dr. hiping Huang 3 Measureents nternational, Prescott Canada duanebrown@intl.co, Measureents nternational,
Study and Implementation of Complementary Golay Sequences for PAR reduction in OFDM signals
 Study and Ipleentation of Copleentary Golay Sequences for PAR reduction in OFDM signals Abstract In this paper soe results of PAR reduction in OFDM signals and error correction capabilities by using Copleentary
Study and Ipleentation of Copleentary Golay Sequences for PAR reduction in OFDM signals Abstract In this paper soe results of PAR reduction in OFDM signals and error correction capabilities by using Copleentary
Photodiode: LECTURE-5
 LECTURE-5 Photodiode: Photodiode consists of an intrinsic semiconductor sandwiched between two heavily doped p-type and n-type semiconductors as shown in Fig. 3.2.2. Sufficient reverse voltage is applied
LECTURE-5 Photodiode: Photodiode consists of an intrinsic semiconductor sandwiched between two heavily doped p-type and n-type semiconductors as shown in Fig. 3.2.2. Sufficient reverse voltage is applied
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006
 (19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(12) United States Patent
 US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
Design and Implementation of Block Based Transpose Form FIR Filter
 Design and Ipleentation of Bloc Based Transpose For FIR Filter O. Venata rishna 1, Dr. C. Venata Narasihulu 2, Dr.. Satya Prasad 3 1 (ECE, CVR College of Engineering, Hyderabad, India) 2 (ECE, Geethanjali
Design and Ipleentation of Bloc Based Transpose For FIR Filter O. Venata rishna 1, Dr. C. Venata Narasihulu 2, Dr.. Satya Prasad 3 1 (ECE, CVR College of Engineering, Hyderabad, India) 2 (ECE, Geethanjali
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
Micro valve arrays for fluid flow control
 ( 1 of 14 ) United States Patent 6,705,345 Bifano March 16, 2004 Micro valve arrays for fluid flow control Abstract An array of micro valves, and the process for its formation, used for control of a fluid
( 1 of 14 ) United States Patent 6,705,345 Bifano March 16, 2004 Micro valve arrays for fluid flow control Abstract An array of micro valves, and the process for its formation, used for control of a fluid
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops October 11, 2006
 Experient 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase ocked oops October 11, 2006 Frequency Modulation Norally, we consider a voltage wave for with a fixed frequency of the for v(t) = V sin(ω c t + θ), (1) where
Experient 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase ocked oops October 11, 2006 Frequency Modulation Norally, we consider a voltage wave for with a fixed frequency of the for v(t) = V sin(ω c t + θ), (1) where
Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices 6-28-2011 Jannick Rolland University of Central Florida Ozan Cakmakci University of Central Florida Find
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices 6-28-2011 Jannick Rolland University of Central Florida Ozan Cakmakci University of Central Florida Find
MICRO RING MODULATOR. Dae-hyun Kwon. High-speed circuits and Systems Laboratory
 MICRO RING MODULATOR Dae-hyun Kwon High-speed circuits and Systems Laboratory Paper preview Title of the paper Low Vpp, ultralow-energy, compact, high-speed silicon electro-optic modulator Publication
MICRO RING MODULATOR Dae-hyun Kwon High-speed circuits and Systems Laboratory Paper preview Title of the paper Low Vpp, ultralow-energy, compact, high-speed silicon electro-optic modulator Publication
Review of Semiconductor Physics
 Review of Semiconductor Physics k B 1.38 u 10 23 JK -1 a) Energy level diagrams showing the excitation of an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The resultant free electron can freely
Review of Semiconductor Physics k B 1.38 u 10 23 JK -1 a) Energy level diagrams showing the excitation of an electron from the valence band to the conduction band. The resultant free electron can freely
UNIT-III SOURCES AND DETECTORS. According to the shape of the band gap as a function of the momentum, semiconductors are classified as
 UNIT-III SOURCES AND DETECTORS DIRECT AND INDIRECT BAND GAP SEMICONDUCTORS: According to the shape of the band gap as a function of the momentum, semiconductors are classified as 1. Direct band gap semiconductors
UNIT-III SOURCES AND DETECTORS DIRECT AND INDIRECT BAND GAP SEMICONDUCTORS: According to the shape of the band gap as a function of the momentum, semiconductors are classified as 1. Direct band gap semiconductors
EXPERIMENTATION FOR ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL
 CHPTER - 6 EXPERIMENTTION FOR CTIVE VIBRTION CONTROL 6. INTRODUCTION The iportant issues in vibration control applications are odeling the sart structure with in-built sensing and actuation capabilities
CHPTER - 6 EXPERIMENTTION FOR CTIVE VIBRTION CONTROL 6. INTRODUCTION The iportant issues in vibration control applications are odeling the sart structure with in-built sensing and actuation capabilities
Yield Enhancement Techniques for 3D Memories by Redundancy Sharing among All Layers
 Yield Enhanceent Techniques for 3D Meories by Redundancy Sharing aong All Layers Joohwan Lee, Kihyun Park, and Sungho Kang Three-diensional (3D) eories using through-silicon vias (TSVs) will likely be
Yield Enhanceent Techniques for 3D Meories by Redundancy Sharing aong All Layers Joohwan Lee, Kihyun Park, and Sungho Kang Three-diensional (3D) eories using through-silicon vias (TSVs) will likely be
High-speed Ge photodetector monolithically integrated with large cross silicon-on-insulator waveguide
 [ APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS ] High-speed Ge photodetector monolithically integrated with large cross silicon-on-insulator waveguide Dazeng Feng, Shirong Liao, Roshanak Shafiiha. etc Contents 1. Introduction
[ APPLIED PHYSICS LETTERS ] High-speed Ge photodetector monolithically integrated with large cross silicon-on-insulator waveguide Dazeng Feng, Shirong Liao, Roshanak Shafiiha. etc Contents 1. Introduction
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,673,522 B2
 USOO6673522B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,673,522 B2 Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING CAPILLARY 2002/0058209 A1 5/2002 Kim et al.... 430/321 DISCHARGE
USOO6673522B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,673,522 B2 Kim et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING CAPILLARY 2002/0058209 A1 5/2002 Kim et al.... 430/321 DISCHARGE
Optical Amplifiers. Continued. Photonic Network By Dr. M H Zaidi
 Optical Amplifiers Continued EDFA Multi Stage Designs 1st Active Stage Co-pumped 2nd Active Stage Counter-pumped Input Signal Er 3+ Doped Fiber Er 3+ Doped Fiber Output Signal Optical Isolator Optical
Optical Amplifiers Continued EDFA Multi Stage Designs 1st Active Stage Co-pumped 2nd Active Stage Counter-pumped Input Signal Er 3+ Doped Fiber Er 3+ Doped Fiber Output Signal Optical Isolator Optical
don, G.B. U.S. P. DOCUMENTS spaced by an air gap from the collecting lens. The widths of
 United States Patent (19) Wartmann III US005708532A 11 Patent Number: 5,708,532 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 1998 (54) DOUBLE-SIDED TELECENTRC 573790 11/1977 U.S.S.R... 359/663 MEASUREMENT OBJECTIVE 1 248
United States Patent (19) Wartmann III US005708532A 11 Patent Number: 5,708,532 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 1998 (54) DOUBLE-SIDED TELECENTRC 573790 11/1977 U.S.S.R... 359/663 MEASUREMENT OBJECTIVE 1 248
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,654,911 B2
 USOO7654911B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 7,654,911 B2 Cartwright (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2010 (54) POOL TABLE LEVELIG SYSTEM 3,080,835 A * 3/1963 Guglielmi... 108,116 3,190.405 A
USOO7654911B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 7,654,911 B2 Cartwright (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2010 (54) POOL TABLE LEVELIG SYSTEM 3,080,835 A * 3/1963 Guglielmi... 108,116 3,190.405 A
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 27, 2017
 (19) United States US 20170214216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0214216 A1 Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HYBRID SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIS 5/1014 (2013.01);
(19) United States US 20170214216A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0214216 A1 Dong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HYBRID SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... HOIS 5/1014 (2013.01);
Lecture 18: Photodetectors
 Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Lecture 18: Photodetectors Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Photodetector principle 2 3 Photoconductor 4 4 Photodiodes 6 4.1 Heterojunction photodiode.................... 8 4.2 Metal-semiconductor photodiode................
Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics. Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI
 Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI Context The goal is to give optical functionalities to electronics integrated circuit (EIC) The objectives
Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI Context The goal is to give optical functionalities to electronics integrated circuit (EIC) The objectives
(*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this E. E. E. " "...O.E.
 USOO6957055B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,055 B2 Gamliel (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2005 (54) DOUBLE BALANCED FET MIXER WITH 5,361,409 A 11/1994 Vice... 455/326 HIGH IP3 AND
USOO6957055B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,055 B2 Gamliel (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2005 (54) DOUBLE BALANCED FET MIXER WITH 5,361,409 A 11/1994 Vice... 455/326 HIGH IP3 AND
Optodevice Data Book ODE I. Rev.9 Mar Opnext Japan, Inc.
 Optodevice Data Book ODE-408-001I Rev.9 Mar. 2003 Opnext Japan, Inc. Section 1 Operating Principles 1.1 Operating Principles of Laser Diodes (LDs) and Infrared Emitting Diodes (IREDs) 1.1.1 Emitting Principles
Optodevice Data Book ODE-408-001I Rev.9 Mar. 2003 Opnext Japan, Inc. Section 1 Operating Principles 1.1 Operating Principles of Laser Diodes (LDs) and Infrared Emitting Diodes (IREDs) 1.1.1 Emitting Principles
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a Fabry-Perot laser.
 Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a Fabry-Perot laser. Figure 1. Shows the structure of a typical edge-emitting laser. The dimensions of the active region are 200 m m in length, 2-10 m m lateral width and
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a Fabry-Perot laser. Figure 1. Shows the structure of a typical edge-emitting laser. The dimensions of the active region are 200 m m in length, 2-10 m m lateral width and
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
6,064,277 A * 5/2000 Gilbert 331/117 R 6,867,658 Bl * 3/2005 Sibrai et al 331/185 6,927,643 B2 * 8/2005 Lazarescu et al. 331/186. * cited by examiner
 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007274264B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 7,274,264 B2 Gabara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep.25,2007 (54) LOW-POWER-DISSIPATIO
111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007274264B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 7,274,264 B2 Gabara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep.25,2007 (54) LOW-POWER-DISSIPATIO
Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response
 Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response Thoas Kaalakis, Thoas Sphicopoulos and Diitris Syvridis (Departent of Inforatics and Telecounications, University of Athens, Panepistiiopolis,
Design of an Arrayed Waveguide Grating with flat spectral response Thoas Kaalakis, Thoas Sphicopoulos and Diitris Syvridis (Departent of Inforatics and Telecounications, University of Athens, Panepistiiopolis,
Defect mediated detection of wavelengths around 1550 nm in a ring resonant structure
 Defect mediated detection of wavelengths around 1550 nm in a ring resonant structure A P Knights* a, J K Doylend a, D F Logan a, J J Ackert a, P E Jessop b, P Velha c, M Sorel c and R M De La Rue c a Department
Defect mediated detection of wavelengths around 1550 nm in a ring resonant structure A P Knights* a, J K Doylend a, D F Logan a, J J Ackert a, P E Jessop b, P Velha c, M Sorel c and R M De La Rue c a Department
10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional)
 EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US008803599B2 (10) Patent No.: Pritiskutch (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) DENDRITE RESISTANT INPUT BIAS (52) U.S. Cl. NETWORK FOR METAL OXDE USPC... 327/581 SEMCONDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent US008803599B2 (10) Patent No.: Pritiskutch (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 12, 2014 (54) DENDRITE RESISTANT INPUT BIAS (52) U.S. Cl. NETWORK FOR METAL OXDE USPC... 327/581 SEMCONDUCTOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF PULSE TRANSFORMER CONSIDERING LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE AND CAPACITANCE
 ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF PULSE TRANSFORMER CONSIDERING LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE AND CAPACITANCE ABOLFAZL VAHEDI, HOSSEIN HEYDARI, and FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Electrical Engineering Departent, High Voltage & Magnetic
ANALYSIS AND SIMULATION OF PULSE TRANSFORMER CONSIDERING LEAKAGE INDUCTANCE AND CAPACITANCE ABOLFAZL VAHEDI, HOSSEIN HEYDARI, and FARAMARZ FAGHIHI Electrical Engineering Departent, High Voltage & Magnetic
Exam 1 ECE 410 Fall 2002
 NAME: Exa 1 ECE 410 Fall 2002 During this exa you are allowed to use a calculator and the equations sheet provided. You are not allowed to speak to or exchange books, papers, calculators, etc. with other
NAME: Exa 1 ECE 410 Fall 2002 During this exa you are allowed to use a calculator and the equations sheet provided. You are not allowed to speak to or exchange books, papers, calculators, etc. with other
Amplifiers and Feedback
 6 A Textbook of Operational Transconductance Aplifier and AIC Chapter Aplifiers and Feedback. INTRODUCTION Practically all circuits using Operational Transconductance Aplifiers are based around one of
6 A Textbook of Operational Transconductance Aplifier and AIC Chapter Aplifiers and Feedback. INTRODUCTION Practically all circuits using Operational Transconductance Aplifiers are based around one of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,009,450 B2
 USOO700945OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,009,450 B2 Parkhurst et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2006 (54) LOW DISTORTION AND HIGH SLEW RATE OUTPUT STAGE FOR WOLTAGE FEEDBACK (56)
USOO700945OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,009,450 B2 Parkhurst et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 7, 2006 (54) LOW DISTORTION AND HIGH SLEW RATE OUTPUT STAGE FOR WOLTAGE FEEDBACK (56)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication
 InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
InP-based Waveguide Photodetector with Integrated Photon Multiplication D.Pasquariello,J.Piprek,D.Lasaosa,andJ.E.Bowers Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of California, Santa Barbara,
LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells
 LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells Chapter 7 (Parker) ELEC 424 John Peeples Why the Interest in Photons? Answer: Momentum and Radiation High electrical current density destroys minute polysilicon and
LEDs, Photodetectors and Solar Cells Chapter 7 (Parker) ELEC 424 John Peeples Why the Interest in Photons? Answer: Momentum and Radiation High electrical current density destroys minute polysilicon and
Intermediate-Node Initiated Reservation (IIR): A New Signaling Scheme for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion
 Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
An Automatic Control Strategy of Strip Width in Cold Rolling
 Advanced Materials Research Subitted: 204-06-04 ISSN: 662-8985, Vols. 004-005, pp 22-225 Accepted: 204-06-08 doi:0.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.004-005.22 Online: 204-08-3 204 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland
Advanced Materials Research Subitted: 204-06-04 ISSN: 662-8985, Vols. 004-005, pp 22-225 Accepted: 204-06-08 doi:0.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.004-005.22 Online: 204-08-3 204 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland
Index. Cambridge University Press Silicon Photonics Design Lukas Chrostowski and Michael Hochberg. Index.
 absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
202 19' 19 19' (12) United States Patent 202' US 7,050,043 B2. Huang et al. May 23, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
REPORT ITU-R SA Telecommunication characteristics and requirements for space VLBI systems
 Rep. ITU-R SA.2132 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2132 Telecounication characteristics and requireents for space VLBI systes (2008) This Report describes the characteristics of the space VLBI systes. These characteristics
Rep. ITU-R SA.2132 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2132 Telecounication characteristics and requireents for space VLBI systes (2008) This Report describes the characteristics of the space VLBI systes. These characteristics
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
 Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
Notes on Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Discrete Fourier ransfor As a reinder, the analytic fors of Fourier and inverse Fourier transfors are X f x t t, f dt x t exp j2 ft dt (.) where
What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell?
 What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell? GT CRC Roof-Mounted PV System Largest single PV structure at the time of it s construction for the 1996 Olympic games Produced more than 1 billion watt hrs. of
What is the highest efficiency Solar Cell? GT CRC Roof-Mounted PV System Largest single PV structure at the time of it s construction for the 1996 Olympic games Produced more than 1 billion watt hrs. of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,774,758 B2
 USOO6774758B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,774,758 B2 Gokhale et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2004 (54) LOW HARMONIC RECTIFIER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (76) Inventors: Kalyan
USOO6774758B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,774,758 B2 Gokhale et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 2004 (54) LOW HARMONIC RECTIFIER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (76) Inventors: Kalyan
Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beamformer
 Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beaforer Sean Durrant a, Sergio Granieri a, Azad Siahakoun a, Bruce Black b a Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering b Departent of Electrical and Coputer
Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beaforer Sean Durrant a, Sergio Granieri a, Azad Siahakoun a, Bruce Black b a Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering b Departent of Electrical and Coputer
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
Modeling of All-Optical Even and Odd Parity Generator Circuits Using Metal-Insulator-Metal Plasmonic Waveguides
 PHOTONI SENSORS / Vol. 7, No., 7: 8 9 Modeling of ll-optical Even and Odd Parity Generator ircuits Using Metal-Insulator-Metal Plasonic Waveguides Lokendra SINGH, na BEDI, and Santosh KUMR * Photonics
PHOTONI SENSORS / Vol. 7, No., 7: 8 9 Modeling of ll-optical Even and Odd Parity Generator ircuits Using Metal-Insulator-Metal Plasonic Waveguides Lokendra SINGH, na BEDI, and Santosh KUMR * Photonics
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,080,983 B2
 US008080983B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: LOurens et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2011 (54) LOW DROP OUT (LDO) BYPASS VOLTAGE 6,465,994 B1 * 10/2002 Xi... 323,274 REGULATOR 7,548,051
US008080983B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: LOurens et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 20, 2011 (54) LOW DROP OUT (LDO) BYPASS VOLTAGE 6,465,994 B1 * 10/2002 Xi... 323,274 REGULATOR 7,548,051
Basic concepts. Optical Sources (b) Optical Sources (a) Requirements for light sources (b) Requirements for light sources (a)
 Optical Sources (a) Optical Sources (b) The main light sources used with fibre optic systems are: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) Semiconductor lasers (diode lasers) Fibre laser and other compact solid-state
Optical Sources (a) Optical Sources (b) The main light sources used with fibre optic systems are: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) Semiconductor lasers (diode lasers) Fibre laser and other compact solid-state
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014
 (19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0?
 WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O151349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0151349 A1 Andrews et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) TRADING CARD AND CONTAINER (76) Inventors: Robert
(19) United States US 2006O151349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0151349 A1 Andrews et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) TRADING CARD AND CONTAINER (76) Inventors: Robert
Chapter Semiconductor Electronics
 Chapter Semiconductor Electronics Q1. p-n junction is said to be forward biased, when [1988] (a) the positive pole of the battery is joined to the p- semiconductor and negative pole to the n- semiconductor
Chapter Semiconductor Electronics Q1. p-n junction is said to be forward biased, when [1988] (a) the positive pole of the battery is joined to the p- semiconductor and negative pole to the n- semiconductor
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 20
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 20 Photo-Detectors and Detector Noise Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept.
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 20 Photo-Detectors and Detector Noise Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept.
New advances in silicon photonics Delphine Marris-Morini
 New advances in silicon photonics Delphine Marris-Morini P. Brindel Alcatel-Lucent Bell Lab, Nozay, France New Advances in silicon photonics D. Marris-Morini, L. Virot*, D. Perez-Galacho, X. Le Roux, D.
New advances in silicon photonics Delphine Marris-Morini P. Brindel Alcatel-Lucent Bell Lab, Nozay, France New Advances in silicon photonics D. Marris-Morini, L. Virot*, D. Perez-Galacho, X. Le Roux, D.
LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES
 Page 1 of 10 LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES Hugh McPherson Spectral Line Systes Ltd, Units 1,2&3 Scott Road, Tarbert, Isle of Harris. www.spectral-line-systes.co.uk
Page 1 of 10 LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES Hugh McPherson Spectral Line Systes Ltd, Units 1,2&3 Scott Road, Tarbert, Isle of Harris. www.spectral-line-systes.co.uk
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
73 Assignee: Dialight Corporation, Manasquan, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 09/144, Filed: Aug. 31, 1998 (51) Int. Cl... G05F /158; 315/307
 United States Patent (19) Grossman et al. 54) LED DRIVING CIRCUITRY WITH VARIABLE LOAD TO CONTROL OUTPUT LIGHT INTENSITY OF AN LED 75 Inventors: Hyman Grossman, Lambertville; John Adinolfi, Milltown, both
United States Patent (19) Grossman et al. 54) LED DRIVING CIRCUITRY WITH VARIABLE LOAD TO CONTROL OUTPUT LIGHT INTENSITY OF AN LED 75 Inventors: Hyman Grossman, Lambertville; John Adinolfi, Milltown, both
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,227,109 B2
 US007227109B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,227,109 B2 Eke (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007 (54) MICROWAVE OVENS (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Kenneth Ian Eke, Franklin, TN (US)
US007227109B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,227,109 B2 Eke (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007 (54) MICROWAVE OVENS (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Kenneth Ian Eke, Franklin, TN (US)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2. Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004
 USOO6815941B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2 Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004 (54) BANDGAP REFERENCE CIRCUIT 6,052,020 * 4/2000 Doyle... 327/539 6,084,388 A 7/2000 Toosky
USOO6815941B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,815,941 B2 Butler (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 9, 2004 (54) BANDGAP REFERENCE CIRCUIT 6,052,020 * 4/2000 Doyle... 327/539 6,084,388 A 7/2000 Toosky
Optical Cavity Designs for Interferometric Gravitational Wave Detectors. Pablo Barriga 17 August 2009
 Optical Cavity Designs for Interferoetric Gravitational Wave Detectors Pablo Barriga 7 August 9 Assignents.- Assuing a cavity of 4k with an ITM of 934 radius of curvature and an ETM of 45 radius of curvature.
Optical Cavity Designs for Interferoetric Gravitational Wave Detectors Pablo Barriga 7 August 9 Assignents.- Assuing a cavity of 4k with an ITM of 934 radius of curvature and an ETM of 45 radius of curvature.
A Preprocessing Method to Increase High Frequency Response of A Parametric Loudspeaker
 A Preprocessing Method to Increase High Frequency Response of A Paraetric Loudspeaker Chuang Shi * and Woon-Seng Gan Digital Processing Laboratory School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang
A Preprocessing Method to Increase High Frequency Response of A Paraetric Loudspeaker Chuang Shi * and Woon-Seng Gan Digital Processing Laboratory School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang
Energy-Efficient Cellular Communications Powered by Smart Grid Technology
 Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150366008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0366008 A1 Barnetson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) LED RETROFIT LAMP WITH ASTRIKE (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150366008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0366008 A1 Barnetson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) LED RETROFIT LAMP WITH ASTRIKE (52) U.S. Cl.
United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen
 United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen USOO5856731A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 1999 54 ELECTRICSCREWDRIVER 75 Inventor: Hermann Rottmerhusen, Tellingstedt, Germany 73 Assignee: Metabowerke
United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen USOO5856731A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 1999 54 ELECTRICSCREWDRIVER 75 Inventor: Hermann Rottmerhusen, Tellingstedt, Germany 73 Assignee: Metabowerke
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822
 34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
