Suppression of Co-Channel Interference in High Duty Ratio Pulsed Radar Receivers
|
|
|
- Spencer Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Suppresson of Co-Channel Interference n Hgh Duty Rato Pulsed Radar Recevers C M Alabaster* *Whte Horse Radar Lmted, K, emal: clve@whradar.com Keywords: Co-Channel Interference, Pulsed Radar, Recever, Hgh duty rato. Abstract Ths paper descrbes a technque for the suppresson of nterference, partcularly co-channel components arsng from nterference on neghbourng channels, wthn a pulsed radar recever operatng on a hgh duty rato. The technque employs two RF swtches wth a band pass flter between them and nestng the gatng control of the second swtch to le wthn the gatng control of the frst swtch. Smulatons ndcate that rejecton of n-band nterference components arsng from nterference that s offset by 60MHz from the channel centre frequency some 0dB greater than that of a conventonal flterng s possble. The technque s most effectve at hgh duty ratos. Introducton One of the most damagng forms of nterference for any radar s co-channel nterference from another, smlar radar, snce the nterference sgnal closely resembles that expected by the vctm radar. Interference on a neghbourng channel frequency but wthn the front-end bandwdth of the radar can be accepted nto the radar causng saturaton of front-end components and ntermodulaton products wthn the channel bandwdth. Furthermore, the recever protecton swtchng can modulate the nterference resultng n addtonal frequency components wthn the channel bandwdth. Consequently, the nterference can cause a flood of false alarms, saturate the processng and corrupt the operaton of the constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detector. To combat ths problem, a radar may cancel nterference sgnals wthn ts sgnal processor or use auxlary antenna cancellaton technques, or steerable antenna nulls, n the drecton of the nterference sources; orthogonal waveforms may be used by lke radars operatng wthn range of each other n order to suppress mutual nterference. It would, however, be preferable to reject nterference wthn the recever before t reaches the processor snce ths reduces the processng burden, does not dstort antenna beams f steered close to nulls n ther radaton patterns and does not requre coordnaton of waveforms between smlar radars. A smple technque s descrbed here that can provde hgh levels of nterference rejecton n pulsed radars operatng on a hgh duty rato. Hgh duty ratos are often assocated wth hgh PRF waveforms but ths need not always be the case. The soluton uses standard components wthn the rado frequency (RF) radar recever; namely two RF swtches and a band pass flter (BPF) between the two swtches. The frst swtch pulse modulates the nterference at the pulse repetton frequency (PRF) of the vctm radar and the BPF passes only hgh order PRF components that are manfest as mpulses of n-band nterference at the swtchng edges of the frst swtch. The gatng control of the second swtch s nested wthn the gatng control of the frst swtch such that the mpulses of nterference are gated out. The crtcal and novel elements descrbed here are the relatve tmngs of the swtch gatng sgnals and the flter requrements. Secton descrbes the technque n more detal and secton 3 provdes an analytcal bass. The fourth secton descrbes detals of a smulaton, ncludng some smulaton results. Fnally, secton 5 draws some conclusons. Descrpton of the Technque. The Problem Consder a stuaton whereby a pulsed radar s recevng nterference from another pulsed radar. The stuaton s portrayed n Fgure for a source of pulsed nterference and a vctm recever both operatng on nomnally the same PRF wth a 50% duty rato. The top trace (a) n Fgure shows the transmtted pulses from an nterference source. The mddle trace (b) of Fgure s the gatng functon of a vctm recever that, when low, solates the recever durng the transmsson of ts own pulses and, when hgh, permts the recepton of sgnals. The bottom trace (c) of Fgure shows the noneclpsed fragments of the nterference pulses that are accepted nto the vctm recever. Snce the tmngs of the transmtted pulses and the gatng of the vctm recever wll, n general, be asynchronous, n addton to an unknown range delay between the two, there wll be a random tmng offset between the two. Ths means that only fragments of the transmtted pulses wll be receved correspondng to perods when the transmtted pulses are present durng the recevng tme of the vctm radar. For 50% duty ratos, one edge of the fragment of nterference wll be defned by the transmtted modulaton (the tralng edge, as shown n Fgure ) and the other edge wll be defned by the recever gatng (the leadng edge, as shown n Fgure ). Although the two radars may both be runnng on notonally the same PRF, n practce, there
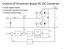
2 wll always be a slght dfference n ther PRFs. Furthermore, the range between the transmtter of the nterference and the recever may constantly be changng. Both the PRF dfference and changng range wll ensure that the tmngs of the transmtted pulses and recever gatng drft n and out of phase wth each other and, as a result, the wdth of the fragment of nterference s constantly changng. Addtonally, the defnton of the leadng/tralng edges of ths fragment swaps perodcally between the transmtted modulaton and recever gatng. The bandwdth of the nterference s gven by the recprocal of the pulse fragment wdth and wll therefore constantly be changng. The rate at whch the spectrum of the nterference decays at hgher offset frequences from ts carrer frequency depends on the rse and fall tmes of the transmtted modulaton and recever gatng. Snce both these sgnals tend to have sharp edges, there wll be consderable spectral spread nto neghbourng channels. As the duty rato of the transmtter and recever reduce, or the wdth of the transmtted pulses becomes much less than the vctm recever s open tme, both edges of the nterference pulses become more lkely to be defned by the transmtted modulaton. Notwthstandng ths, there s always some lkelhood that fragments of nterference wll have one edge defned by the recever gatng. A complete soluton to mutual nterference must therefore address both the transmsson of pulses and the recever. If, however, only one edge of the pulse has the 0ns cosne profle and the other edge has a ns rse tme, then the mprovement s only 4.5dB at a 60MHz offset frequency. Clearly, t s mportant that both edges of the nterference pulse fragment be shaped n order to reduce co-channel nterference. Whlst t s possble to shape the recever gatng functon n much the same way that transmtted pulses may be shaped, t s not always practcal to do so. Frstly, f the nterference s powerful enough to drve any subsequent amplfer stages nto saturaton, the profled edges wll be re-sharpened. Secondly, the extended rse and fall tmes on the recever gatng functon ncrease eclpsng losses and the mnmum range []. The reducton n spectral spread can be mparted wthn the recever usng a combnaton of two swtches wth a flter between them. A block dagram of a typcal superheterodyne recever front-end s shown n Fgure. The crucal and novel elements are the two swtches, and specfcally, the tmng controls to these swtches, wth the band pass flter (BPF) sandwched between them and these components are hghlghted usng the lght grey shadng n Fgure. Any pulsed radar recever requres a protecton swtch before the low nose amplfer (LNA) n order to solate t from damagng levels of transmtter leakage power durng ts transmtted pulses; ths forms the frst RF swtch. Receved sgnals are then amplfed n the LNA and down-converted to an ntermedate frequency (IF) usng a mxer. The BPF s desgned to flter out nterference fallng outsde the channel bandwdth of the radar and so may typcally have a bandwdth of a several MHz; t s not ntended to be the matched flter, whch would typcally come further along the processng chan. The BPF s more easly mplemented n the IF sgnal path, rather than at the ncomng (mcrowave) RF secton, snce t requres a more modest Q-factor here. The solaton provded by the protecton swtch may typcally be around 60dB and, although adequate to protect the LNA from saturaton, stll results n a detectable level of transmtter leakage power wthn the recever. Ths should be removed usng an addtonal hgh solaton swtch before the hgh gan amplfer chan; ths s the second swtch shown on the rght of Fgure. Fgure : Interference from pulsed radar operatng on a 50% duty rato. (a) Pulsed nterference, (b) Gatng control of vctm recever (hgh = recever open, low = recever closed), (c) Fragment of nterference pulse accepted nto recever.. The Soluton The classc soluton to lmt the spectral spread of transmtted pulses s to shape the pulses wth a weghtng functon []. Ths extends the rse and fall tmes of the transmtted pulses. Even the smple expedent of mpartng a cosne functon rse and fall (voltage) profle over the frst and last 0ns of a.5μs pulse can reduce the spectral envelope by 5dB at an offset frequency of 60MHz compared wth ns rse and fall tmes. Fgure : Radar superheterodyne recever front-end block dagram. In order to solate the recever effects from those of shapng the transmtted pulses, t s most convenent to consder contnuous wave (CW) nterference. If CW nterference s receved on a neghbourng channel t should be subject to a
3 hgh degree of rejecton by the BPF, however, the acton of the protecton swtch pulse modulates the nterference at the recevng system s PRF and causes sgnfcant spectral spread nto the pass band of the BPF, especally f the protecton swtch mparts fast rse and fall tmes. Ironcally, the protecton swtch has exacerbated the problem. The BPF passes hgh order PRF harmoncs that result n an output sgnal comprsng short bursts (mpulses) of nterference occurrng at the rsng and fallng edges of the pulses of nterference,.e. at the rsng and fallng edges of the gatng functon of the protecton swtch. The BPF has dfferentated the pulses of nterference. The duraton of these mpulses s proportonal to the rse and fall tmes of the protecton swtch and nversely proportonal to the bandwdth of the BPF and the frequency of the nterference; they may typcally last for a few tens of nano-seconds for a flter bandwdth of 5-30MHz. The hgh solaton swtch that follows the BPF must now have a gatng control nested wthn that of the protecton swtch such that these mpulses are gated out. The gatng tmngs are llustrated n Fgure 3 and a close-up vew of the rsng and fallng edges wth 30ns nested tmngs s shown n Fgure 4. In gatng out the mpulses, the n-band nterference s removed. Should ths nterference not be removed t could cause false target ndcatons, mask smaller genune target responses fallng concdent n range and velocty as the nterference, sap effort from the tracker whch may attempt to track these responses and corrupt the operaton of the constant false alarm rate (CFAR) detecton; n short, the nterference could have smlar effects as would false target jammng. The only n-band nterference that remans are hgh order PRF harmoncs assocated wth the fltered nterference. Consequently, the n-band nterference s reduced by approxmately the level of the flter rejecton at the centre frequency of the nterference and wll be sgnfcantly lower than that seen on the BPF output, or f the gatng functon to the hgh solaton swtch was not properly nested wthn the gatng functon of the protecton swtch. The exact tmngs n a practcal system would have to be adjusted to account for the group delay between the two swtches. The (small) penalty pad for the hgh degree of nterference rejecton s the slghtly ncreased dead tme due to the nestng and subsequent ncreases n eclpsng losses. It s therefore advantageous to ensure that these mpulses be as short-lved as possble, such that the dead tme due to swtch nestng may be mnmsed, and so ths demands rapd swtchng of the protecton swtch, a wde pass band of the BPF and mnmal dsperson n all the crcuts between the two swtches. To ths end, the BPF should have a lnear phase flter response across ts (wde) pass band, whch s most readly acheved f ts pass band s centred at a hgh frequency,.e. a hgh value of IF s used (VHF (30-300MHz) or HF ( MHz) beng better than HF (3-30MHz) [3]). The desgn of the BPF s crucal to the success of the nterference rejecton. The mpulses represent the flter s transent response to the rsng and fallng edges of the pulse of out-of-band nterference. The duraton of the mpulses s reduced for a large offset between the flter pass band and the nterference and for a wde pass band. The pass band should not be so wde, however, that t compromses the rejecton of out-of-band nterference. Resstve flter losses ntroduce dampng whch lengthens the mpulses; dsperson n the flter, and other components before the solaton swtch, also stretches the mpulses and should be avoded. Fgure 3: Sgnal waveforms. (a) protecton swtch gatng, (b) BPF output sgnal, (c) solaton swtch gatng, (d) sgnal at solaton swtch output. Fgure 4: Close-up of waveforms at swtchng rse/fall tmes. (a) protecton swtch gatng, (b) BPF output sgnal, (c) solaton swtch gatng, (d) sgnal at solaton swtch output. 3 Theory The processng of a receved sgnal by the analogue recever components hghlghted n grey n Fgure entals swtchng between the tme and frequency domans. The gatng functon provded by the two swtches s most convenently appled n the tme doman whereas the flterng functon of the BPF s most convenently appled n the frequency doman. The Fourer transform, together wth the nverse Fourer transform, enables one to transform from the tme (t) to frequency (ω) domans and back agan [4]. Let the CW nterference sgnal be gven by: s0t cos t () where ω s the angular frequency of the nterference. 3
4 It s necessary to consder just a sngle cycle of the pulsng operaton of the protecton swtch whch can therefore be represented by the dealsed tme gatng functon: gt 0 t () 0 elsewhere Ths swtch modulates the nterference sgnal wth zero nserton loss when the swtch s closed and nfnte solaton when open. It results n a rectangular pulse of nterference havng a pulse wdth, τ, of nfntely fast rse and fall tmes. The pulse modulated nterference sgnal on the swtch output s therefore: st s0t gt cos t 0 t (3) 0 elsewhere (The amplfcaton and down-converson process s nconsequental to the rejecton of nterference and so the same nterference carrer frequency has been retaned throughout.) The s (t) sgnal s a sngle pulse of the orgnal nterference from tme, t = 0 to t = τ. The spectrum of ths sgnal s gven by ts Fourer transform, whch s defned as: jt s t s e dt S F. (4) In ths case, the functon s (t) s gven by the product of two functons, so: s t g t S S F 0. 0 G (5) where S 0 (ω) represents the Fourer transform of s 0 (t), G (ω) represents the Fourer transform of g (t) and * represents the convoluton of the two. In practce, t s not necessary to use convoluton snce the Fourer transform of s (t) may be derved drectly from the defnton of the Fourer transform gven by Equaton (4) over three tme ntervals; t < 0, 0 t τ and t > τ. The resultng spectrum s gven by: j.. e.sn. j j j. e.cos S (6) Ths s the classc snc functon spectrum centred at ω wth an angular frequency offset to the nulls at multples of. Should the analyss be extended to capture at least two perods of the gatng functon, g (t), ts perodcty would be evdent and would result n a set of dscrete spectral responses offset by harmoncs of the PRF and whose envelope conforms to the snc functon gven by Equaton (6). Let the BPF have an dealsed transfer functon gven by: j F cos jsn e L (7) 0 elsewhere where ω L and ω are the lower and upper frequency lmts of the pass band, respectvely, and β s the phase constant of the flter. Wthn ts pass band, the flter has a magntude response of and a phase response of β. Thus, the flter has a rectangular response of zero pass band nserton loss and nfnte stop band solaton and has a lnear phase response wthn ts pass band; the flter s therefore non-dspersve. It may be assumed that ω s well outsde the pass band, ω L to ω, and so the flter passes only low-level, hgh order sdelobes of the snc functon that are offset well away from ω represented by Equaton (6). The flter output therefore has a spectrum gven by: S S F (8) Substtuton of Equatons (6) and (7) nto Equaton (8) gves: S j j e.cos.. e.sn. j j. e L j (9) S 0 elsewhere The tme doman representaton of ths sgnal may be obtaned va an nverse Fourer transform,.e.: j s t S S e t F. d (0) In ths case, the upper expresson for S (ω) gven by Equaton (9) can be substtuted n Equaton (0) and the lmts of ntegraton can be reduced to ω L and ω. Note also that: () v p where v p s the phase velocty through the flter. The tme doman representaton of the flter output s therefore gven by: s t j L j. e j t v p j t v p j. e.cos.... t vp.sn. d.... e () Ths sgnal s ncdent on the solaton swtch. Agan, t s necessary to consder just a sngle cycle of the pulsng operaton of the solaton swtch whch can therefore be represented by the dealsed gatng functon: gt tn t tn (3) 0 elsewhere where t n s the nestng margn of the solaton swtch wthn the tmngs of the protecton swtch, g (t). The gatng functon to the solaton swtch s a pulse of wdth τ-t n delayed by t n wth respect to g (t). As for the protecton swtch, the solaton swtch exhbts nfntely fast rse and fall tmes, zero nserton loss when the swtch s closed and nfnte solaton when open and t provdes further modulaton of the nterference sgnal. The waveform on the output of the solaton swtch s therefore gven by: t s t g t (4) s3 The spectrum of the output sgnal s gven by the Fourer transform of s 3(t),.e.: S3 F s 3t S G (5) where G (ω) represents the Fourer transform of g (t). 4
5 Ascertanng the spectra and waveforms of the sgnals on the nput and output of the solaton swtch entals an evaluaton of the ntegral of Equaton (). The precse nature of these sgnals depends on the values of ω and τ wth respect to ω L and ω. Of partcular nterest here, s the case of both ω L and ω beng offset from ω by many tmes π/τ,.e. typcally,, 00. L Evaluaton of Equaton (9) and the ntegral of Equaton () s awkward but some general trends may be observed for the partcular choce of parameter values of nterest here that ad understandng. Equaton (9) s of the general form: j a j e (6) j a c j The e term n Equaton (9) merely ntroduces a phase offset to the spectrum or a tme shft equvalent to the delay through the flter nto the waveform, Equaton (0), and may be gnored here. The nverse Fourer transform of Equaton (6) represents the waveform of an exponentally decayng cosne wave startng at tme t = 0 followed by an exponentally decayng negatve cosne wave startng at tme t = τ. The frequency of the cosne waves s gven by ω c and the factor a s the tme constant of the exponental decay and wll be large and postve for a wde pass band flter centred well away from the carrer frequency of the nterference.e.: s large and, 00 L. L The exponentally decayng cosne waves are the underdamped transent responses of a resonant crcut,.e. the response of the deal, loss-less flter to the rsng and fallng edges of the nput pulse. The frequency, ω c, corresponds to the resonant frequency of the crcut,.e. the centre frequency of the flter pass band. The duraton of a flter s response s gven by the nverse of ts bandwdth, therefore a. As the flter bandwdth ncreases, a becomes L ncreasngly large and the exponental decay becomes more rapd wth the result that the waveform tends towards a postve mpulse at t = 0 and a negatve mpulse at t = τ. Ths waveform represents the dfferental of the nput pulse whose j spectrum s of the form: e. It may therefore be understood that, for the partcular choce of parameters descrbed here, the waveform, s (t) approxmates the dfferental of the s (t) pulse and resembles the mpulses shown n Fgure 4, trace (b). The exponentally decayng cosne mpulses reduce to 37%. Settng the of ther ntal ampltude after a tme L nestng offset to the nverse of the BPF bandwdth, t, enables waveform g (t) to gate out most of n L the mpulses. Increasng t n to allows the L mpulses to decay to 4% of ther ntal ampltude, and so more of the mpulses are gated out but the dead tme and eclpsng losses are doubled. The waveform on the solaton swtch output s now very low: s t 0 for all t. In ths way, 3 sgnfcant rejecton of the nterference wthn the pass band can be acheved. 4 Smulaton Results The sgnals wthn the IF secton of a hypothetcal recever have been smulated n accordance wth the technques and theory descrbed n the earler sectons. An 8 pole Butterworth flter desgn has been modelled. A hgh PRF wth a hgh duty rato s assumed and would be typcal parameters for a hgh PRF ar-to-ar velocty search mode of an arborne ntercept or fre control radar [5]. The followng parameters have been assumed: PRF of recever 50 khz Duty rato 37.5% (recever open tme.5 μs) IF centre frequency 00 MHz BPF nserton loss at 00MHz.6 db BPF 3dB bandwdth 7.5 MHz Interference centre frequency n IF 60 MHz (.e. 60MHz above IF centre) BPF nserton loss at 60MHz 6.0 db (Rejecton wrt to pass band 4.4 db) It was further assumed that the protecton swtch had a rse and fall (voltage) profle of a cosne functon over 0ns. The solaton swtch had a ns rse and fall tme that was nested 30ns wthn the 50% ponts of the rse and fall of the protecton swtch edges (Fgure 4). The fast rse and fall tmes of the solaton swtch was ntended to gve rse to the slowest spectral decay n the nterference and hence the most pessmstc result for nterference rejecton; slower rse/fall tmes would result n reduced n-band nterference. The extra 30ns nestng margn at the begnnng and end of each recevng perod ncurs a dead tme totallng 60ns. Ths dead tme reduces the recever open tme to.5μs 60ns =.44μs that results n an extra eclpsng loss of: 0.log 0(.44/.50) = 0.dB. A smaller ncrease n eclpsng loss would be ncurred at a lower PRF. The spectra of the varous sgnals are shown n Fgure 5. These spectra were obtaned va a unformly weghted FFT over two complete cycles of the recever pulsed waveform (8μs). The nterference, pulse modulated by the protecton swtch, and down-converted by the mxer, s shown n the dark blue and ts peak level at 60MHz s normalsed to 0dB. Its envelope at 00MHz s at -56.5dB and s due entrely to the pulse modulaton mparted by the protecton swtch. The flter characterstc n decbels s shown n red. The flter provdes 4.4dB rejecton of nterference at +60MHz offset from ts centre frequency. The green spectrum corresponds to the nterference sgnal seen on the output of the BPF. Its peak at 60MHz s at -6.04dB and corresponds to the flter nserton loss at ths frequency. Its envelope at 00MHz s at -58.dB whch s only.6db lower than the nterference level at the IF centre frequency seen at the mxer output (due to the.6db nserton loss of the BPF at 00MHz). Ths llustrates that the flter wll prevent the out-of-band nterference from saturatng further amplfcaton and processng stages but provdes almost no rejecton of n-band nterference components ncurred by the pulsng of the protecton swtch. The nterference seen on the solaton swtch output s shown 5
6 n cyan and has a peak level of -6.6dB at 60MHz. The small decrease wth respect to the BPF output (green) of 0.dB s due to the slght reducton n the wdth of the nterference pulse, totallng 60ns, due to the 30ns of nestng at each edge, and s consstent wth the extra eclpsng loss. From the lower trace of Fgure 4, one may observe how the mpulses of n-band nterference have been removed, leavng the (suppressed) pulse modulated 60MHz sgnal. Its envelope at 00MHz s at -79.3dB, whch shows a.db decrease wth respect to the nterference at 00MHz on the flter output (green). The.dB mprovement s somewhat less than the 4.4dB rejecton provded by the flter at 60MHz offset; the dscrepancy beng due to the slower decay of the spectrum due to the faster edges of the solaton swtch (plus a mnor dscrepancy due to the slght change n ts pulse wdth, as noted earler). +00MHz MHz Table : Improvement of n-band rejecton of nterference versus offset frequency. () the greater degree of rejecton of n-band nterference results from extendng the nestng to 50ns. Very hgh levels of nterference rejecton are acheved n these cases due to the hgh flter rejecton close to zero Hertz. These results are gven for smple, unmodulated pulses. If ntra-pulse modulatons are used for the purposes of pulse compresson, there wll be addtonal spectral components wthn the IF pass band, however, these would also be rejected by the levels gven n Table. 5 Conclusons Fgure 5: Sgnal spectra. Blue = nterference at mxer output, Red = flter characterstc, Green = nterference at flter output, Cyan = nterference at solaton swtch output. The mprovements for nterference at other frequency offsets are tabulated n Table. The maxmum mprovement wll be lmted to ether the flter rejecton at the centre frequency of the nterference or the solaton of the solaton swtch, whchever s the least. Snce several hgh solaton swtches can be ganged n seres, t s the flter rejecton that sets the practcal lmt on nterference rejecton. Frequency offset of Interference Flter rejecton wrt pass band [db] Improvement of n-band nterference rejecton [db] - 80MHz , 6 () -60MHz , 53 () -40MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz MHz A full soluton to the rejecton of mutual nterference entals spectral contanment of the transmtted pulses through pulse shapng and rejecton wthn the recever. The use of two swtches wth a band pass flter between them as part of a typcal superheterodyne recever archtecture can provde a hgh degree of rejecton of neghbourng-channel nterference. The rejecton of nterference s dependent on the nondspersve nature of the crcutry between the two swtches, the characterstcs of the flter and the relatve tmngs of the gatng functons to the swtches; the gatng of the second swtch beng nested wthn the gatng tmngs of the frst. Rejecton of n-band, co-channel, spectral components of mutual nterference up to the level of the flter rejecton at the centre frequency of the nterference s possble. Ths offers consderable mprovements over flterng on ts own and would probably be benefcal n suppressng all forms of nterference. A small ncrease n eclpsng losses s ncurred due to the nestng margns between the two gatng sgnals. Acknowledgements I would lke to acknowledge the nvaluable contrbuton to ths work of the late Chrs Bourne, an ex-colleague and frend. References [] D. Emery. The Dgtal Synthess of HF Surfacewave Radar Waveforms, MSC thess, Cranfeld nversty, Shrvenham, K, (004). [] C. M. Alabaster. Pulse Doppler Radar, Sctech (now IET), (0). [3] IEEE Std Standard Letter Desgnatons for Radar-Frequency Bands. (976, revsed 984, 00). [4] James W. Nlsson, Electrc Crcuts, 4 th Ed., Addson- Wesley, ISBN (993). [5] Davd Lynch, Jr and Carlo Kopp, Multfunctonal Radar Systems for Fghter Arcraft, chapter 5 n Radar Handbook 3 rd Edton, Ed M. I. Skolnk, McGraw-Hll, ISBN (008). 6
antenna antenna (4.139)
 .6.6 The Lmts of Usable Input Levels for LNAs The sgnal voltage level delvered to the nput of an LNA from the antenna may vary n a very wde nterval, from very weak sgnals comparable to the nose level,
.6.6 The Lmts of Usable Input Levels for LNAs The sgnal voltage level delvered to the nput of an LNA from the antenna may vary n a very wde nterval, from very weak sgnals comparable to the nose level,
High Speed ADC Sampling Transients
 Hgh Speed ADC Samplng Transents Doug Stuetzle Hgh speed analog to dgtal converters (ADCs) are, at the analog sgnal nterface, track and hold devces. As such, they nclude samplng capactors and samplng swtches.
Hgh Speed ADC Samplng Transents Doug Stuetzle Hgh speed analog to dgtal converters (ADCs) are, at the analog sgnal nterface, track and hold devces. As such, they nclude samplng capactors and samplng swtches.
Rejection of PSK Interference in DS-SS/PSK System Using Adaptive Transversal Filter with Conditional Response Recalculation
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol., No., November 23, 3-9 Rejecton of PSK Interference n DS-SS/PSK System Usng Adaptve Transversal Flter wth Condtonal Response Recalculaton Zorca Nkolć, Bojan
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol., No., November 23, 3-9 Rejecton of PSK Interference n DS-SS/PSK System Usng Adaptve Transversal Flter wth Condtonal Response Recalculaton Zorca Nkolć, Bojan
NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia SPECTRAL PROCESSOR MEMO NO. 25. MEMORANDUM February 13, 1985
 NATONAL RADO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Vrgna SPECTRAL PROCESSOR MEMO NO. 25 MEMORANDUM February 13, 1985 To: Spectral Processor Group From: R. Fsher Subj: Some Experments wth an nteger FFT
NATONAL RADO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Vrgna SPECTRAL PROCESSOR MEMO NO. 25 MEMORANDUM February 13, 1985 To: Spectral Processor Group From: R. Fsher Subj: Some Experments wth an nteger FFT
Calculation of the received voltage due to the radiation from multiple co-frequency sources
 Rec. ITU-R SM.1271-0 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1271-0 * EFFICIENT SPECTRUM UTILIZATION USING PROBABILISTIC METHODS Rec. ITU-R SM.1271 (1997) The ITU Radocommuncaton Assembly, consderng a) that communcatons
Rec. ITU-R SM.1271-0 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1271-0 * EFFICIENT SPECTRUM UTILIZATION USING PROBABILISTIC METHODS Rec. ITU-R SM.1271 (1997) The ITU Radocommuncaton Assembly, consderng a) that communcatons
Walsh Function Based Synthesis Method of PWM Pattern for Full-Bridge Inverter
 Walsh Functon Based Synthess Method of PWM Pattern for Full-Brdge Inverter Sej Kondo and Krt Choesa Nagaoka Unversty of Technology 63-, Kamtomoka-cho, Nagaoka 9-, JAPAN Fax: +8-58-7-95, Phone: +8-58-7-957
Walsh Functon Based Synthess Method of PWM Pattern for Full-Brdge Inverter Sej Kondo and Krt Choesa Nagaoka Unversty of Technology 63-, Kamtomoka-cho, Nagaoka 9-, JAPAN Fax: +8-58-7-95, Phone: +8-58-7-957
Passive Filters. References: Barbow (pp ), Hayes & Horowitz (pp 32-60), Rizzoni (Chap. 6)
 Passve Flters eferences: Barbow (pp 6575), Hayes & Horowtz (pp 360), zzon (Chap. 6) Frequencyselectve or flter crcuts pass to the output only those nput sgnals that are n a desred range of frequences (called
Passve Flters eferences: Barbow (pp 6575), Hayes & Horowtz (pp 360), zzon (Chap. 6) Frequencyselectve or flter crcuts pass to the output only those nput sgnals that are n a desred range of frequences (called
A High-Sensitivity Oversampling Digital Signal Detection Technique for CMOS Image Sensors Using Non-destructive Intermediate High-Speed Readout Mode
 A Hgh-Senstvty Oversamplng Dgtal Sgnal Detecton Technque for CMOS Image Sensors Usng Non-destructve Intermedate Hgh-Speed Readout Mode Shoj Kawahto*, Nobuhro Kawa** and Yoshak Tadokoro** *Research Insttute
A Hgh-Senstvty Oversamplng Dgtal Sgnal Detecton Technque for CMOS Image Sensors Usng Non-destructve Intermedate Hgh-Speed Readout Mode Shoj Kawahto*, Nobuhro Kawa** and Yoshak Tadokoro** *Research Insttute
Harmonic Balance of Nonlinear RF Circuits
 MICROWAE AND RF DESIGN Harmonc Balance of Nonlnear RF Crcuts Presented by Mchael Steer Readng: Chapter 19, Secton 19. Index: HB Based on materal n Mcrowave and RF Desgn: A Systems Approach, nd Edton, by
MICROWAE AND RF DESIGN Harmonc Balance of Nonlnear RF Crcuts Presented by Mchael Steer Readng: Chapter 19, Secton 19. Index: HB Based on materal n Mcrowave and RF Desgn: A Systems Approach, nd Edton, by
IEE Electronics Letters, vol 34, no 17, August 1998, pp ESTIMATING STARTING POINT OF CONDUCTION OF CMOS GATES
 IEE Electroncs Letters, vol 34, no 17, August 1998, pp. 1622-1624. ESTIMATING STARTING POINT OF CONDUCTION OF CMOS GATES A. Chatzgeorgou, S. Nkolads 1 and I. Tsoukalas Computer Scence Department, 1 Department
IEE Electroncs Letters, vol 34, no 17, August 1998, pp. 1622-1624. ESTIMATING STARTING POINT OF CONDUCTION OF CMOS GATES A. Chatzgeorgou, S. Nkolads 1 and I. Tsoukalas Computer Scence Department, 1 Department
1 GSW Multipath Channel Models
 In the general case, the moble rado channel s pretty unpleasant: there are a lot of echoes dstortng the receved sgnal, and the mpulse response keeps changng. Fortunately, there are some smplfyng assumptons
In the general case, the moble rado channel s pretty unpleasant: there are a lot of echoes dstortng the receved sgnal, and the mpulse response keeps changng. Fortunately, there are some smplfyng assumptons
To: Professor Avitabile Date: February 4, 2003 From: Mechanical Student Subject: Experiment #1 Numerical Methods Using Excel
 To: Professor Avtable Date: February 4, 3 From: Mechancal Student Subject:.3 Experment # Numercal Methods Usng Excel Introducton Mcrosoft Excel s a spreadsheet program that can be used for data analyss,
To: Professor Avtable Date: February 4, 3 From: Mechancal Student Subject:.3 Experment # Numercal Methods Usng Excel Introducton Mcrosoft Excel s a spreadsheet program that can be used for data analyss,
TECHNICAL NOTE TERMINATION FOR POINT- TO-POINT SYSTEMS TN TERMINATON FOR POINT-TO-POINT SYSTEMS. Zo = L C. ω - angular frequency = 2πf
 TECHNICAL NOTE TERMINATION FOR POINT- TO-POINT SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION Because dgtal sgnal rates n computng systems are ncreasng at an astonshng rate, sgnal ntegrty ssues have become far more mportant to
TECHNICAL NOTE TERMINATION FOR POINT- TO-POINT SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION Because dgtal sgnal rates n computng systems are ncreasng at an astonshng rate, sgnal ntegrty ssues have become far more mportant to
Digital Transmission
 Dgtal Transmsson Most modern communcaton systems are dgtal, meanng that the transmtted normaton sgnal carres bts and symbols rather than an analog sgnal. The eect o C/N rato ncrease or decrease on dgtal
Dgtal Transmsson Most modern communcaton systems are dgtal, meanng that the transmtted normaton sgnal carres bts and symbols rather than an analog sgnal. The eect o C/N rato ncrease or decrease on dgtal
Section 5. Signal Conditioning and Data Analysis
 Secton 5 Sgnal Condtonng and Data Analyss 6/27/2017 Engneerng Measurements 5 1 Common Input Sgnals 6/27/2017 Engneerng Measurements 5 2 1 Analog vs. Dgtal Sgnals 6/27/2017 Engneerng Measurements 5 3 Current
Secton 5 Sgnal Condtonng and Data Analyss 6/27/2017 Engneerng Measurements 5 1 Common Input Sgnals 6/27/2017 Engneerng Measurements 5 2 1 Analog vs. Dgtal Sgnals 6/27/2017 Engneerng Measurements 5 3 Current
The Performance Improvement of BASK System for Giga-Bit MODEM Using the Fuzzy System
 Int. J. Communcatons, Network and System Scences, 10, 3, 1-5 do:10.36/jcns.10.358 Publshed Onlne May 10 (http://www.scrp.org/journal/jcns/) The Performance Improvement of BASK System for Gga-Bt MODEM Usng
Int. J. Communcatons, Network and System Scences, 10, 3, 1-5 do:10.36/jcns.10.358 Publshed Onlne May 10 (http://www.scrp.org/journal/jcns/) The Performance Improvement of BASK System for Gga-Bt MODEM Usng
A study of turbo codes for multilevel modulations in Gaussian and mobile channels
 A study of turbo codes for multlevel modulatons n Gaussan and moble channels Lamne Sylla and Paul Forter (sylla, forter)@gel.ulaval.ca Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng Laval Unversty, Ste-Foy,
A study of turbo codes for multlevel modulatons n Gaussan and moble channels Lamne Sylla and Paul Forter (sylla, forter)@gel.ulaval.ca Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng Laval Unversty, Ste-Foy,
Parameter Free Iterative Decoding Metrics for Non-Coherent Orthogonal Modulation
 1 Parameter Free Iteratve Decodng Metrcs for Non-Coherent Orthogonal Modulaton Albert Gullén Fàbregas and Alex Grant Abstract We study decoder metrcs suted for teratve decodng of non-coherently detected
1 Parameter Free Iteratve Decodng Metrcs for Non-Coherent Orthogonal Modulaton Albert Gullén Fàbregas and Alex Grant Abstract We study decoder metrcs suted for teratve decodng of non-coherently detected
AC-DC CONVERTER FIRING ERROR DETECTION
 BNL- 63319 UC-414 AGS/AD/96-3 INFORMAL AC-DC CONVERTER FIRING ERROR DETECTION O.L. Gould July 15, 1996 OF THIS DOCUMENT IS ALTERNATING GRADIENT SYNCHROTRON DEPARTMENT BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY ASSOCIATED
BNL- 63319 UC-414 AGS/AD/96-3 INFORMAL AC-DC CONVERTER FIRING ERROR DETECTION O.L. Gould July 15, 1996 OF THIS DOCUMENT IS ALTERNATING GRADIENT SYNCHROTRON DEPARTMENT BROOKHAVEN NATIONAL LABORATORY ASSOCIATED
Chapter 13. Filters Introduction Ideal Filter
 Chapter 3 Flters 3.0 Introducton Flter s the crcut that capable o passng sgnal rom nput to output that has requency wthn a speced band and attenuatng all others outsde the band. Ths s the property o selectvty.
Chapter 3 Flters 3.0 Introducton Flter s the crcut that capable o passng sgnal rom nput to output that has requency wthn a speced band and attenuatng all others outsde the band. Ths s the property o selectvty.
RC Filters TEP Related Topics Principle Equipment
 RC Flters TEP Related Topcs Hgh-pass, low-pass, Wen-Robnson brdge, parallel-t flters, dfferentatng network, ntegratng network, step response, square wave, transfer functon. Prncple Resstor-Capactor (RC)
RC Flters TEP Related Topcs Hgh-pass, low-pass, Wen-Robnson brdge, parallel-t flters, dfferentatng network, ntegratng network, step response, square wave, transfer functon. Prncple Resstor-Capactor (RC)
Control of Chaos in Positive Output Luo Converter by means of Time Delay Feedback
 Control of Chaos n Postve Output Luo Converter by means of Tme Delay Feedback Nagulapat nkran.ped@gmal.com Abstract Faster development n Dc to Dc converter technques are undergong very drastc changes due
Control of Chaos n Postve Output Luo Converter by means of Tme Delay Feedback Nagulapat nkran.ped@gmal.com Abstract Faster development n Dc to Dc converter technques are undergong very drastc changes due
Uncertainty in measurements of power and energy on power networks
 Uncertanty n measurements of power and energy on power networks E. Manov, N. Kolev Department of Measurement and Instrumentaton, Techncal Unversty Sofa, bul. Klment Ohrdsk No8, bl., 000 Sofa, Bulgara Tel./fax:
Uncertanty n measurements of power and energy on power networks E. Manov, N. Kolev Department of Measurement and Instrumentaton, Techncal Unversty Sofa, bul. Klment Ohrdsk No8, bl., 000 Sofa, Bulgara Tel./fax:
Multicarrier Modulation
 Multcarrer Modulaton Wha Sook Jeon Moble Computng & Communcatons Lab Contents Concept of multcarrer modulaton Data transmsson over multple carrers Multcarrer modulaton wth overlappng Chap. subchannels
Multcarrer Modulaton Wha Sook Jeon Moble Computng & Communcatons Lab Contents Concept of multcarrer modulaton Data transmsson over multple carrers Multcarrer modulaton wth overlappng Chap. subchannels
Figure 1. DC-DC Boost Converter
 EE46, Power Electroncs, DC-DC Boost Converter Verson Oct. 3, 11 Overvew Boost converters make t possble to effcently convert a DC voltage from a lower level to a hgher level. Theory of Operaton Relaton
EE46, Power Electroncs, DC-DC Boost Converter Verson Oct. 3, 11 Overvew Boost converters make t possble to effcently convert a DC voltage from a lower level to a hgher level. Theory of Operaton Relaton
Revision of Lecture Twenty-One
 Revson of Lecture Twenty-One FFT / IFFT most wdely found operatons n communcaton systems Important to know what are gong on nsde a FFT / IFFT algorthm Wth the ad of FFT / IFFT, ths lecture looks nto OFDM
Revson of Lecture Twenty-One FFT / IFFT most wdely found operatons n communcaton systems Important to know what are gong on nsde a FFT / IFFT algorthm Wth the ad of FFT / IFFT, ths lecture looks nto OFDM
Development of a High Bandwidth, High Power Linear Amplifier for a Precision Fast Tool Servo System
 Development of a Hgh Bandwdth, Hgh Power near Amplfer for a Precson Fast Tool Servo System S. Rakuff 1, J. Cuttno 1, D. Schnstock 2 1 Dept. of Mechancal Engneerng, The Unversty of North Carolna at Charlotte,
Development of a Hgh Bandwdth, Hgh Power near Amplfer for a Precson Fast Tool Servo System S. Rakuff 1, J. Cuttno 1, D. Schnstock 2 1 Dept. of Mechancal Engneerng, The Unversty of North Carolna at Charlotte,
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P Multipath propagation and parameterization of its characteristics
 Rec. ITU-R P.47-3 RECOMMEDATIO ITU-R P.47-3 Multpath propagaton and parameterzaton of ts characterstcs (Queston ITU-R 3/3) (999-3-5-7) Scope Recommendaton ITU-R P.47 descrbes the nature of multpath propagaton
Rec. ITU-R P.47-3 RECOMMEDATIO ITU-R P.47-3 Multpath propagaton and parameterzaton of ts characterstcs (Queston ITU-R 3/3) (999-3-5-7) Scope Recommendaton ITU-R P.47 descrbes the nature of multpath propagaton
29. Network Functions for Circuits Containing Op Amps
 9. Network Functons for Crcuts Contanng Op Amps Introducton Each of the crcuts n ths problem set contans at least one op amp. Also each crcut s represented by a gven network functon. These problems can
9. Network Functons for Crcuts Contanng Op Amps Introducton Each of the crcuts n ths problem set contans at least one op amp. Also each crcut s represented by a gven network functon. These problems can
ECE315 / ECE515 Lecture 5 Date:
 Lecture 5 Date: 18.08.2016 Common Source Amplfer MOSFET Amplfer Dstorton Example 1 One Realstc CS Amplfer Crcut: C c1 : Couplng Capactor serves as perfect short crcut at all sgnal frequences whle blockng
Lecture 5 Date: 18.08.2016 Common Source Amplfer MOSFET Amplfer Dstorton Example 1 One Realstc CS Amplfer Crcut: C c1 : Couplng Capactor serves as perfect short crcut at all sgnal frequences whle blockng
Figure.1. Basic model of an impedance source converter JCHPS Special Issue 12: August Page 13
 A Hgh Gan DC - DC Converter wth Soft Swtchng and Power actor Correcton for Renewable Energy Applcaton T. Selvakumaran* and. Svachdambaranathan Department of EEE, Sathyabama Unversty, Chenna, Inda. *Correspondng
A Hgh Gan DC - DC Converter wth Soft Swtchng and Power actor Correcton for Renewable Energy Applcaton T. Selvakumaran* and. Svachdambaranathan Department of EEE, Sathyabama Unversty, Chenna, Inda. *Correspondng
AIR FORCE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 MULTIPLE ACCESS INTERFERENCE CHARACTERIZATION FOR DIRECT-SEQUENCE SPREAD-SPECTRUM COMMUNICATIONS USING CHIP WAVEFORM SHAPING THESIS Matthew G. Glen, Captan, USAF AFIT/GE/ENG/04-10 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR
MULTIPLE ACCESS INTERFERENCE CHARACTERIZATION FOR DIRECT-SEQUENCE SPREAD-SPECTRUM COMMUNICATIONS USING CHIP WAVEFORM SHAPING THESIS Matthew G. Glen, Captan, USAF AFIT/GE/ENG/04-10 DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR
Graph Method for Solving Switched Capacitors Circuits
 Recent Advances n rcuts, ystems, gnal and Telecommuncatons Graph Method for olvng wtched apactors rcuts BHUMIL BRTNÍ Department of lectroncs and Informatcs ollege of Polytechncs Jhlava Tolstého 6, 586
Recent Advances n rcuts, ystems, gnal and Telecommuncatons Graph Method for olvng wtched apactors rcuts BHUMIL BRTNÍ Department of lectroncs and Informatcs ollege of Polytechncs Jhlava Tolstého 6, 586
Effect of Time-Interleaved Analog-to-Digital Converter Mismatches on OFDM Performance
 Effect of Tme-Interleaved Analog-to-Dgtal Converter Msmatches on OFDM Performance Vo-Trung-Dung Huynh, Nele Noels, Peter Rombouts 2, Jean Armstrong 3, Hed Steendam Department of Telecommuncatons and Informaton
Effect of Tme-Interleaved Analog-to-Dgtal Converter Msmatches on OFDM Performance Vo-Trung-Dung Huynh, Nele Noels, Peter Rombouts 2, Jean Armstrong 3, Hed Steendam Department of Telecommuncatons and Informaton
PRACTICAL, COMPUTATION EFFICIENT HIGH-ORDER NEURAL NETWORK FOR ROTATION AND SHIFT INVARIANT PATTERN RECOGNITION. Evgeny Artyomov and Orly Yadid-Pecht
 68 Internatonal Journal "Informaton Theores & Applcatons" Vol.11 PRACTICAL, COMPUTATION EFFICIENT HIGH-ORDER NEURAL NETWORK FOR ROTATION AND SHIFT INVARIANT PATTERN RECOGNITION Evgeny Artyomov and Orly
68 Internatonal Journal "Informaton Theores & Applcatons" Vol.11 PRACTICAL, COMPUTATION EFFICIENT HIGH-ORDER NEURAL NETWORK FOR ROTATION AND SHIFT INVARIANT PATTERN RECOGNITION Evgeny Artyomov and Orly
Triferential Subtraction in Strain Gage Signal Conditioning. Introduction
 Trferental Subtracton n Stran Gage Sgnal Condtonng Karl F. Anderson Vald Measurements 3751 W. Ave. J-14 Lancaster, CA 93536 (661) 722-8255 http://www.vm-usa.com Introducton The general form of NASA's Anderson
Trferental Subtracton n Stran Gage Sgnal Condtonng Karl F. Anderson Vald Measurements 3751 W. Ave. J-14 Lancaster, CA 93536 (661) 722-8255 http://www.vm-usa.com Introducton The general form of NASA's Anderson
Figure 1. DC-DC Boost Converter
 EE36L, Power Electroncs, DC-DC Boost Converter Verson Feb. 8, 9 Overvew Boost converters make t possble to effcently convert a DC voltage from a lower level to a hgher level. Theory of Operaton Relaton
EE36L, Power Electroncs, DC-DC Boost Converter Verson Feb. 8, 9 Overvew Boost converters make t possble to effcently convert a DC voltage from a lower level to a hgher level. Theory of Operaton Relaton
Analysis and Optimization of the Performance of OFDM on Frequency- Selective Time-Selective Fading Channels
 Analyss and Optmzaton of the erformance of OFDM on Frequency- Selectve Tme-Selectve Fadng Channels Hed Steendam, Marc Moeneclaey Communcatons Engneerng Lab. Unversty of Ghent B-9 GET, BELGIUM Abstract
Analyss and Optmzaton of the erformance of OFDM on Frequency- Selectve Tme-Selectve Fadng Channels Hed Steendam, Marc Moeneclaey Communcatons Engneerng Lab. Unversty of Ghent B-9 GET, BELGIUM Abstract
MTBF PREDICTION REPORT
 MTBF PREDICTION REPORT PRODUCT NAME: BLE112-A-V2 Issued date: 01-23-2015 Rev:1.0 Copyrght@2015 Bluegga Technologes. All rghts reserved. 1 MTBF PREDICTION REPORT... 1 PRODUCT NAME: BLE112-A-V2... 1 1.0
MTBF PREDICTION REPORT PRODUCT NAME: BLE112-A-V2 Issued date: 01-23-2015 Rev:1.0 Copyrght@2015 Bluegga Technologes. All rghts reserved. 1 MTBF PREDICTION REPORT... 1 PRODUCT NAME: BLE112-A-V2... 1 1.0
THE ARCHITECTURE OF THE BROADBAND AMPLIFIERS WITHOUT CLASSICAL STAGES WITH A COMMON BASE AND A COMMON EMITTER
 VOL. 0, NO. 8, OCTOBE 205 ISSN 89-6608 2006-205 Asan esearch Publshng Network (APN. All rghts reserved. THE ACHITECTUE OF THE BOADBAND AMPLIFIES WITHOUT CLASSICAL STAGES WITH A COMMON BASE AND A COMMON
VOL. 0, NO. 8, OCTOBE 205 ISSN 89-6608 2006-205 Asan esearch Publshng Network (APN. All rghts reserved. THE ACHITECTUE OF THE BOADBAND AMPLIFIES WITHOUT CLASSICAL STAGES WITH A COMMON BASE AND A COMMON
Analysis of Time Delays in Synchronous and. Asynchronous Control Loops. Bj rn Wittenmark, Ben Bastian, and Johan Nilsson
 37th CDC, Tampa, December 1998 Analyss of Delays n Synchronous and Asynchronous Control Loops Bj rn Wttenmark, Ben Bastan, and Johan Nlsson emal: bjorn@control.lth.se, ben@control.lth.se, and johan@control.lth.se
37th CDC, Tampa, December 1998 Analyss of Delays n Synchronous and Asynchronous Control Loops Bj rn Wttenmark, Ben Bastan, and Johan Nlsson emal: bjorn@control.lth.se, ben@control.lth.se, and johan@control.lth.se
Microelectronic Circuits
 Mcroelectronc Crcuts Slde 1 Introducton Suggested textbook: 1. Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C. Smth, Mcroelectronc Crcuts Theory and Applcatons, Sxth edton Internatonal Verson, Oxford Unersty Press, 2013.
Mcroelectronc Crcuts Slde 1 Introducton Suggested textbook: 1. Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C. Smth, Mcroelectronc Crcuts Theory and Applcatons, Sxth edton Internatonal Verson, Oxford Unersty Press, 2013.
Dynamic Optimization. Assignment 1. Sasanka Nagavalli January 29, 2013 Robotics Institute Carnegie Mellon University
 Dynamc Optmzaton Assgnment 1 Sasanka Nagavall snagaval@andrew.cmu.edu 16-745 January 29, 213 Robotcs Insttute Carnege Mellon Unversty Table of Contents 1. Problem and Approach... 1 2. Optmzaton wthout
Dynamc Optmzaton Assgnment 1 Sasanka Nagavall snagaval@andrew.cmu.edu 16-745 January 29, 213 Robotcs Insttute Carnege Mellon Unversty Table of Contents 1. Problem and Approach... 1 2. Optmzaton wthout
A Current Differential Line Protection Using a Synchronous Reference Frame Approach
 A Current Dfferental Lne rotecton Usng a Synchronous Reference Frame Approach L. Sousa Martns *, Carlos Fortunato *, and V.Fernão res * * Escola Sup. Tecnologa Setúbal / Inst. oltécnco Setúbal, Setúbal,
A Current Dfferental Lne rotecton Usng a Synchronous Reference Frame Approach L. Sousa Martns *, Carlos Fortunato *, and V.Fernão res * * Escola Sup. Tecnologa Setúbal / Inst. oltécnco Setúbal, Setúbal,
Strain Gauge Measuring Amplifier BA 660
 Stran Gauge Measurng Amplfer BA 660 Orgnal of the Manual BA660 / IP20 BA660 / IP66 Table of Contents 1. Safety precautons...2 1.1. Feld of applcaton...2 1.2. Installaton...2 1.3. Mantenance...2 2. Functon...2
Stran Gauge Measurng Amplfer BA 660 Orgnal of the Manual BA660 / IP20 BA660 / IP66 Table of Contents 1. Safety precautons...2 1.1. Feld of applcaton...2 1.2. Installaton...2 1.3. Mantenance...2 2. Functon...2
Tunable Wideband Receiver (TWB) Data Processing Description December, 2013
 Page 1 of 5 Tunable Wdeband Recever (TWB) Data Processng Descrpton December, 2013 The tunable wdeband recever (TWB) can be manually tuned to any frequency of nterest between 17 and 33 MHz. The recever
Page 1 of 5 Tunable Wdeband Recever (TWB) Data Processng Descrpton December, 2013 The tunable wdeband recever (TWB) can be manually tuned to any frequency of nterest between 17 and 33 MHz. The recever
Detection and parameters interception of a radar pulse signal based on interrupt driven algorithm
 Scentfc Research and Essays Vol. 6(6), pp. 1380-1387, 18 March, 2011 Avalable onlne at http://www.academcjournals.org/sre DOI: 10.5897/SRE11.122 ISSN 1992-2248 2011 Academc Journals Full Length Research
Scentfc Research and Essays Vol. 6(6), pp. 1380-1387, 18 March, 2011 Avalable onlne at http://www.academcjournals.org/sre DOI: 10.5897/SRE11.122 ISSN 1992-2248 2011 Academc Journals Full Length Research
Keywords LTE, Uplink, Power Control, Fractional Power Control.
 Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X Internatonal Journal of Advanced Research n Computer Scence and Software Engneerng Research Paper Avalable onlne at: www.jarcsse.com Uplnk Power Control Schemes
Volume 3, Issue 6, June 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X Internatonal Journal of Advanced Research n Computer Scence and Software Engneerng Research Paper Avalable onlne at: www.jarcsse.com Uplnk Power Control Schemes
Application of Intelligent Voltage Control System to Korean Power Systems
 Applcaton of Intellgent Voltage Control System to Korean Power Systems WonKun Yu a,1 and HeungJae Lee b, *,2 a Department of Power System, Seol Unversty, South Korea. b Department of Power System, Kwangwoon
Applcaton of Intellgent Voltage Control System to Korean Power Systems WonKun Yu a,1 and HeungJae Lee b, *,2 a Department of Power System, Seol Unversty, South Korea. b Department of Power System, Kwangwoon
Phasor Representation of Sinusoidal Signals
 Phasor Representaton of Snusodal Sgnals COSC 44: Dgtal Communcatons Instructor: Dr. Amr Asf Department of Computer Scence and Engneerng York Unversty Handout # 6: Bandpass odulaton Usng Euler dentty e
Phasor Representaton of Snusodal Sgnals COSC 44: Dgtal Communcatons Instructor: Dr. Amr Asf Department of Computer Scence and Engneerng York Unversty Handout # 6: Bandpass odulaton Usng Euler dentty e
ANNUAL OF NAVIGATION 11/2006
 ANNUAL OF NAVIGATION 11/2006 TOMASZ PRACZYK Naval Unversty of Gdyna A FEEDFORWARD LINEAR NEURAL NETWORK WITH HEBBA SELFORGANIZATION IN RADAR IMAGE COMPRESSION ABSTRACT The artcle presents the applcaton
ANNUAL OF NAVIGATION 11/2006 TOMASZ PRACZYK Naval Unversty of Gdyna A FEEDFORWARD LINEAR NEURAL NETWORK WITH HEBBA SELFORGANIZATION IN RADAR IMAGE COMPRESSION ABSTRACT The artcle presents the applcaton
Design of Shunt Active Filter for Harmonic Compensation in a 3 Phase 3 Wire Distribution Network
 Internatonal Journal of Research n Electrcal & Electroncs Engneerng olume 1, Issue 1, July-September, 2013, pp. 85-92, IASTER 2013 www.aster.com, Onlne: 2347-5439, Prnt: 2348-0025 Desgn of Shunt Actve
Internatonal Journal of Research n Electrcal & Electroncs Engneerng olume 1, Issue 1, July-September, 2013, pp. 85-92, IASTER 2013 www.aster.com, Onlne: 2347-5439, Prnt: 2348-0025 Desgn of Shunt Actve
AN ALL DIGITAL QAM MODULATOR WITH RADIO FREQUENCY OUTPUT
 AN ALL DIGITAL QAM MODULATOR WITH RADIO FREQUENCY OUTPUT Zhuan Ye (Motorola Labs, 131 E. Algonqun Rd., Schaumburg, IL 6196 zhuan.ye@motorola.com); John Grosspetsch (Motorola Labs, Schaumburg, IL 6196 john.grosspetsch@motorola.com)
AN ALL DIGITAL QAM MODULATOR WITH RADIO FREQUENCY OUTPUT Zhuan Ye (Motorola Labs, 131 E. Algonqun Rd., Schaumburg, IL 6196 zhuan.ye@motorola.com); John Grosspetsch (Motorola Labs, Schaumburg, IL 6196 john.grosspetsch@motorola.com)
THE GENERATION OF 400 MW RF PULSES AT X-BAND USING RESONANT DELAY LINES *
 SLAC PUB 874 3/1999 THE GENERATION OF 4 MW RF PULSES AT X-BAND USING RESONANT DELAY LINES * Sam G. Tantaw, Arnold E. Vleks, and Rod J. Loewen Stanford Lnear Accelerator Center, Stanford Unversty P.O. Box
SLAC PUB 874 3/1999 THE GENERATION OF 4 MW RF PULSES AT X-BAND USING RESONANT DELAY LINES * Sam G. Tantaw, Arnold E. Vleks, and Rod J. Loewen Stanford Lnear Accelerator Center, Stanford Unversty P.O. Box
Control of Drivetrain Boost DC DC Converter
 Control of Drvetran Boost DC DC Converter Small sgnal model Converter transfer functons Current control loop bat current sensng c 2 v ge2 _ S 2 Q 2 D 2 v s S 1 C c voltage sensng I v v bat _ c 1 v ge1
Control of Drvetran Boost DC DC Converter Small sgnal model Converter transfer functons Current control loop bat current sensng c 2 v ge2 _ S 2 Q 2 D 2 v s S 1 C c voltage sensng I v v bat _ c 1 v ge1
The Application of Interpolation Algorithms in OFDM Channel Estimation
 The Applcaton of Interpolaton Algorthms n OFDM Estmaton Xjun ZHANG 1,, Zhantng YUAN 1, 1 School of Electrcal and Informaton Engneerng, Lanzhou Unversty of Technology, Lanzhou, Gansu 730050, Chna School
The Applcaton of Interpolaton Algorthms n OFDM Estmaton Xjun ZHANG 1,, Zhantng YUAN 1, 1 School of Electrcal and Informaton Engneerng, Lanzhou Unversty of Technology, Lanzhou, Gansu 730050, Chna School
ETSI TS V8.4.0 ( )
 TS 100 959 V8.4.0 (2001-11) Techncal Specfcaton Dgtal cellular telecommuncatons system (Phase 2+); Modulaton (3GPP TS 05.04 verson 8.4.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS R 1 TS 100
TS 100 959 V8.4.0 (2001-11) Techncal Specfcaton Dgtal cellular telecommuncatons system (Phase 2+); Modulaton (3GPP TS 05.04 verson 8.4.0 Release 1999) GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS R 1 TS 100
Research on Peak-detection Algorithm for High-precision Demodulation System of Fiber Bragg Grating
 , pp. 337-344 http://dx.do.org/10.1457/jht.014.7.6.9 Research on Peak-detecton Algorthm for Hgh-precson Demodulaton System of Fber ragg Gratng Peng Wang 1, *, Xu Han 1, Smn Guan 1, Hong Zhao and Mngle
, pp. 337-344 http://dx.do.org/10.1457/jht.014.7.6.9 Research on Peak-detecton Algorthm for Hgh-precson Demodulaton System of Fber ragg Gratng Peng Wang 1, *, Xu Han 1, Smn Guan 1, Hong Zhao and Mngle
STUDY OF MATRIX CONVERTER BASED UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER APPLIED PI-D CONTROLLER
 Journal of Engneerng Scence and Technology Specal Issue on Appled Engneerng and Scences, October (214) 3-38 School of Engneerng, Taylor s Unversty STUDY OF MATRIX CONVERTER BASED UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER
Journal of Engneerng Scence and Technology Specal Issue on Appled Engneerng and Scences, October (214) 3-38 School of Engneerng, Taylor s Unversty STUDY OF MATRIX CONVERTER BASED UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER
Control of Venturini Method Based Matrix Converter in Input Voltage Variations
 IMECS 9, March 8 -, 9, Hong Kong Control of Venturn Method Based Matrx Converter n Input Voltage Varatons Hulus Karaca, Ramazan Akkaya Abstract Matrx converter s a sngle-stage converter whch drectly connects
IMECS 9, March 8 -, 9, Hong Kong Control of Venturn Method Based Matrx Converter n Input Voltage Varatons Hulus Karaca, Ramazan Akkaya Abstract Matrx converter s a sngle-stage converter whch drectly connects
Chapter 2 Two-Degree-of-Freedom PID Controllers Structures
 Chapter 2 Two-Degree-of-Freedom PID Controllers Structures As n most of the exstng ndustral process control applcatons, the desred value of the controlled varable, or set-pont, normally remans constant
Chapter 2 Two-Degree-of-Freedom PID Controllers Structures As n most of the exstng ndustral process control applcatons, the desred value of the controlled varable, or set-pont, normally remans constant
AN ADVANCED ALGORITHM FOR IMPROVING DVB-T COVERAGE IN SFN. V. Mignone, A. Morello, M. Visintin. RAI Research Centre, Italy ABSTRACT
 AN ADVANCED ALGORITHM FOR IMPROVING DVB-T COVERAGE IN SFN V. Mgnone, A. Morello, M. Vsntn RAI Research Centre, Italy ABSTRACT The paper analyses the coverage achevable n sngle frequency networks (SFN)
AN ADVANCED ALGORITHM FOR IMPROVING DVB-T COVERAGE IN SFN V. Mgnone, A. Morello, M. Vsntn RAI Research Centre, Italy ABSTRACT The paper analyses the coverage achevable n sngle frequency networks (SFN)
NOVEL ITERATIVE TECHNIQUES FOR RADAR TARGET DISCRIMINATION
 NOVEL ITERATIVE TECHNIQUES FOR RADAR TARGET DISCRIMINATION Phaneendra R.Venkata, Nathan A. Goodman Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Unversty of Arzona, 30 E. Speedway Blvd, Tucson, Arzona
NOVEL ITERATIVE TECHNIQUES FOR RADAR TARGET DISCRIMINATION Phaneendra R.Venkata, Nathan A. Goodman Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Unversty of Arzona, 30 E. Speedway Blvd, Tucson, Arzona
Multipath Propagation. Outline. What is OFDM? (OFDM) for Broadband Communications and. Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
 Orthogonal Dvson Multplexng (OFDM) for Broadband Communcatons and Dgtal Audo Broadcastng (DAB) Klaus Wtrsal wtrsal@nw.tugraz.at VL: Dgtale Audotechnk, 21. März, 2002 What s OFDM? Modulaton technque Requres
Orthogonal Dvson Multplexng (OFDM) for Broadband Communcatons and Dgtal Audo Broadcastng (DAB) Klaus Wtrsal wtrsal@nw.tugraz.at VL: Dgtale Audotechnk, 21. März, 2002 What s OFDM? Modulaton technque Requres
EE 508 Lecture 6. Degrees of Freedom The Approximation Problem
 EE 508 Lecture 6 Degrees of Freedom The Approxmaton Problem Revew from Last Tme Desgn Strategy Theorem: A crcut wth transfer functon T(s) can be obtaned from a crcut wth normalzed transfer functon T n
EE 508 Lecture 6 Degrees of Freedom The Approxmaton Problem Revew from Last Tme Desgn Strategy Theorem: A crcut wth transfer functon T(s) can be obtaned from a crcut wth normalzed transfer functon T n
Equivalent Circuit Model of Electromagnetic Behaviour of Wire Objects by the Matrix Pencil Method
 ERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 5, No., May 008, -0 Equvalent Crcut Model of Electromagnetc Behavour of Wre Objects by the Matrx Pencl Method Vesna Arnautovsk-Toseva, Khall El Khamlch Drss,
ERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 5, No., May 008, -0 Equvalent Crcut Model of Electromagnetc Behavour of Wre Objects by the Matrx Pencl Method Vesna Arnautovsk-Toseva, Khall El Khamlch Drss,
A Comparison of Two Equivalent Real Formulations for Complex-Valued Linear Systems Part 2: Results
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH VOL. 1 NO. () A Comparson of Two Equvalent Real Formulatons for Complex-Valued Lnear Systems Part : Results Abnta Munankarmy and Mchael A. Heroux Department of
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF UNDERGRADUATE RESEARCH VOL. 1 NO. () A Comparson of Two Equvalent Real Formulatons for Complex-Valued Lnear Systems Part : Results Abnta Munankarmy and Mchael A. Heroux Department of
... -J to send radio signals through the air, how modulation , IJ."~ UNITED STATES~~ FREQUENCY ALLOCATIONS
 ..., J."..J What would lfe be lke wthout rado and televson? Only a hundred years ago the fastest way to send a message between Amerca and Europe or Asa was a fast shp. Now we get lve televson coverage
..., J."..J What would lfe be lke wthout rado and televson? Only a hundred years ago the fastest way to send a message between Amerca and Europe or Asa was a fast shp. Now we get lve televson coverage
Channel Alternation and Rotation in Narrow Beam Trisector Cellular Systems
 Channel Alternaton and Rotaton n Narrow Beam Trsector Cellular Systems Vncent A. Nguyen, Peng-Jun Wan, Ophr Freder Illnos Insttute of Technology-Communcaton Laboratory Research Computer Scence Department-Chcago,
Channel Alternaton and Rotaton n Narrow Beam Trsector Cellular Systems Vncent A. Nguyen, Peng-Jun Wan, Ophr Freder Illnos Insttute of Technology-Communcaton Laboratory Research Computer Scence Department-Chcago,
Analysis, Design, and Simulation of a Novel Current Sensing Circuit
 Analyss, Desgn, and Smulaton of a Noel Current Sensng Crcut Louza Sellam Electrcal and Computer Engneerng Department US Naal Academy Annapols, Maryland, USA sellam@usna.edu obert W. Newcomb Electrcal and
Analyss, Desgn, and Smulaton of a Noel Current Sensng Crcut Louza Sellam Electrcal and Computer Engneerng Department US Naal Academy Annapols, Maryland, USA sellam@usna.edu obert W. Newcomb Electrcal and
Comparative Analysis of Reuse 1 and 3 in Cellular Network Based On SIR Distribution and Rate
 Comparatve Analyss of Reuse and 3 n ular Network Based On IR Dstrbuton and Rate Chandra Thapa M.Tech. II, DEC V College of Engneerng & Technology R.V.. Nagar, Chttoor-5727, A.P. Inda Emal: chandra2thapa@gmal.com
Comparatve Analyss of Reuse and 3 n ular Network Based On IR Dstrbuton and Rate Chandra Thapa M.Tech. II, DEC V College of Engneerng & Technology R.V.. Nagar, Chttoor-5727, A.P. Inda Emal: chandra2thapa@gmal.com
Micro-grid Inverter Parallel Droop Control Method for Improving Dynamic Properties and the Effect of Power Sharing
 2015 AASRI Internatonal Conference on Industral Electroncs and Applcatons (IEA 2015) Mcro-grd Inverter Parallel Droop Control Method for Improvng Dynamc Propertes and the Effect of Power Sharng aohong
2015 AASRI Internatonal Conference on Industral Electroncs and Applcatons (IEA 2015) Mcro-grd Inverter Parallel Droop Control Method for Improvng Dynamc Propertes and the Effect of Power Sharng aohong
Space Time Equalization-space time codes System Model for STCM
 Space Tme Eualzaton-space tme codes System Model for STCM The system under consderaton conssts of ST encoder, fadng channel model wth AWGN, two transmt antennas, one receve antenna, Vterb eualzer wth deal
Space Tme Eualzaton-space tme codes System Model for STCM The system under consderaton conssts of ST encoder, fadng channel model wth AWGN, two transmt antennas, one receve antenna, Vterb eualzer wth deal
Evaluate the Effective of Annular Aperture on the OTF for Fractal Optical Modulator
 Global Advanced Research Journal of Management and Busness Studes (ISSN: 2315-5086) Vol. 4(3) pp. 082-086, March, 2015 Avalable onlne http://garj.org/garjmbs/ndex.htm Copyrght 2015 Global Advanced Research
Global Advanced Research Journal of Management and Busness Studes (ISSN: 2315-5086) Vol. 4(3) pp. 082-086, March, 2015 Avalable onlne http://garj.org/garjmbs/ndex.htm Copyrght 2015 Global Advanced Research
Shunt Active Filters (SAF)
 EN-TH05-/004 Martt Tuomanen (9) Shunt Actve Flters (SAF) Operaton prncple of a Shunt Actve Flter. Non-lnear loads lke Varable Speed Drves, Unnterrupted Power Supples and all knd of rectfers draw a non-snusodal
EN-TH05-/004 Martt Tuomanen (9) Shunt Actve Flters (SAF) Operaton prncple of a Shunt Actve Flter. Non-lnear loads lke Varable Speed Drves, Unnterrupted Power Supples and all knd of rectfers draw a non-snusodal
Soft-Switched CCM Boost Converter with High Voltage Gain for High Power Applications
 Soft-Swtched CCM Boost Converter wth Hgh oltage Gan for Hgh Power Applcatons Sungsk Park and Sewan Cho, IEEE Senor Member Seoul Natonal Unversty of Technology Dept. of Control and Instrumentaton Eng. 17
Soft-Swtched CCM Boost Converter wth Hgh oltage Gan for Hgh Power Applcatons Sungsk Park and Sewan Cho, IEEE Senor Member Seoul Natonal Unversty of Technology Dept. of Control and Instrumentaton Eng. 17
Calculation model for SFN reception and reference receiver characteristics of ISDB-T system
 Report ITU-R BT.9-1 (5/13) Calculaton model for SFN recepton and reference recever characterstcs of ISDB-T system BT Seres Broadcastng servce (televson) Rep. ITU-R BT.9-1 Foreword The role of the Radocommuncaton
Report ITU-R BT.9-1 (5/13) Calculaton model for SFN recepton and reference recever characterstcs of ISDB-T system BT Seres Broadcastng servce (televson) Rep. ITU-R BT.9-1 Foreword The role of the Radocommuncaton
Low Switching Frequency Active Harmonic Elimination in Multilevel Converters with Unequal DC Voltages
 Low Swtchng Frequency Actve Harmonc Elmnaton n Multlevel Converters wth Unequal DC Voltages Zhong Du,, Leon M. Tolbert, John N. Chasson, Hu L The Unversty of Tennessee Electrcal and Computer Engneerng
Low Swtchng Frequency Actve Harmonc Elmnaton n Multlevel Converters wth Unequal DC Voltages Zhong Du,, Leon M. Tolbert, John N. Chasson, Hu L The Unversty of Tennessee Electrcal and Computer Engneerng
A Spreading Sequence Allocation Procedure for MC-CDMA Transmission Systems
 A Spreadng Sequence Allocaton Procedure for MC-CDMA Transmsson Systems Davd Motter, Damen Castelan Mtsubsh Electrc ITE 80, Avenue des Buttes de Coësmes, 35700 Rennes FRAE e-mal: {motter,castelan}@tcl.te.mee.com
A Spreadng Sequence Allocaton Procedure for MC-CDMA Transmsson Systems Davd Motter, Damen Castelan Mtsubsh Electrc ITE 80, Avenue des Buttes de Coësmes, 35700 Rennes FRAE e-mal: {motter,castelan}@tcl.te.mee.com
DIMENSIONAL SYNTHESIS FOR WIDE-BAND BAND- PASS FILTERS WITH QUARTER-WAVELENGTH RES- ONATORS
 Progress In Electromagnetcs Research B, Vol. 17, 213 231, 29 DIMENSIONAL SYNTHESIS FOR WIDE-BAND BAND- PASS FILTERS WITH QUARTER-WAVELENGTH RES- ONATORS Q. Zhang and Y. Lu School of Electrcal and Electroncs
Progress In Electromagnetcs Research B, Vol. 17, 213 231, 29 DIMENSIONAL SYNTHESIS FOR WIDE-BAND BAND- PASS FILTERS WITH QUARTER-WAVELENGTH RES- ONATORS Q. Zhang and Y. Lu School of Electrcal and Electroncs
BER Performances of a Differential OFDM System in Fading Channels
 Buletnul Ştnţfc al Unverstăţ "Poltehnca" dn Tmşoara era ELECTRONICĂ ş TELECOMUNICAŢII TRANACTION on ELECTRONIC and COMMUNICATION Tom 49(63), Fasccola, 4 BER Performances of a Dfferental OFDM ystem n Fadng
Buletnul Ştnţfc al Unverstăţ "Poltehnca" dn Tmşoara era ELECTRONICĂ ş TELECOMUNICAŢII TRANACTION on ELECTRONIC and COMMUNICATION Tom 49(63), Fasccola, 4 BER Performances of a Dfferental OFDM ystem n Fadng
Performance Analysis of Power Line Communication Using DS-CDMA Technique with Adaptive Laguerre Filters
 Internatonal Conference on Informaton and Electroncs Engneerng IPCSIT vol.6 ( ( IACSIT Press, Sngapore Performance Analyss of Power Lne Communcaton Usng DS-CDMA Technque wth Adaptve Laguerre Flters S.
Internatonal Conference on Informaton and Electroncs Engneerng IPCSIT vol.6 ( ( IACSIT Press, Sngapore Performance Analyss of Power Lne Communcaton Usng DS-CDMA Technque wth Adaptve Laguerre Flters S.
ITU-T O.172. Amendment 1 (06/2008)
 Internatonal Telecommuncaton Unon ITU-T O.72 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU Amendment (6/8) SERIES O: SPECIFICATIONS OF MEASURING EQUIPMENT Equpment for the measurement of dgtal and analogue/dgtal
Internatonal Telecommuncaton Unon ITU-T O.72 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU Amendment (6/8) SERIES O: SPECIFICATIONS OF MEASURING EQUIPMENT Equpment for the measurement of dgtal and analogue/dgtal
PULSEWIDTH-modulated (PWM) voltage-source inverters
 674 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 13, NO. 4, JULY 1998 Carrer-Based PWM-VSI Overmodulaton Strateges: Analyss, Comparson, and Desgn Ahmet M. Hava, Student Member, IEEE, Russel J. Kerkman,
674 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER ELECTRONICS, VOL. 13, NO. 4, JULY 1998 Carrer-Based PWM-VSI Overmodulaton Strateges: Analyss, Comparson, and Desgn Ahmet M. Hava, Student Member, IEEE, Russel J. Kerkman,
Unit 1. Current and Voltage U 1 VOLTAGE AND CURRENT. Circuit Basics KVL, KCL, Ohm's Law LED Outputs Buttons/Switch Inputs. Current / Voltage Analogy
 ..2 nt Crcut Bascs KVL, KCL, Ohm's Law LED Outputs Buttons/Swtch Inputs VOLTAGE AND CRRENT..4 Current and Voltage Current / Voltage Analogy Charge s measured n unts of Coulombs Current Amount of charge
..2 nt Crcut Bascs KVL, KCL, Ohm's Law LED Outputs Buttons/Swtch Inputs VOLTAGE AND CRRENT..4 Current and Voltage Current / Voltage Analogy Charge s measured n unts of Coulombs Current Amount of charge
4.3- Modeling the Diode Forward Characteristic
 2/8/2012 3_3 Modelng the ode Forward Characterstcs 1/3 4.3- Modelng the ode Forward Characterstc Readng Assgnment: pp. 179-188 How do we analyze crcuts wth juncton dodes? 2 ways: Exact Solutons ffcult!
2/8/2012 3_3 Modelng the ode Forward Characterstcs 1/3 4.3- Modelng the ode Forward Characterstc Readng Assgnment: pp. 179-188 How do we analyze crcuts wth juncton dodes? 2 ways: Exact Solutons ffcult!
Prevention of Sequential Message Loss in CAN Systems
 Preventon of Sequental Message Loss n CAN Systems Shengbng Jang Electrcal & Controls Integraton Lab GM R&D Center, MC: 480-106-390 30500 Mound Road, Warren, MI 48090 shengbng.jang@gm.com Ratnesh Kumar
Preventon of Sequental Message Loss n CAN Systems Shengbng Jang Electrcal & Controls Integraton Lab GM R&D Center, MC: 480-106-390 30500 Mound Road, Warren, MI 48090 shengbng.jang@gm.com Ratnesh Kumar
Digital Differential Protection of Power Transformer Using Matlab
 Chapter 10 Dgtal Dfferental Protecton of Power Transformer Usng Matlab Adel Aktab and M. Azzur Rahman Addtonal nformaton s avalable at the end of the chapter http://dx.do.org/10.5772/48624 1. Introducton
Chapter 10 Dgtal Dfferental Protecton of Power Transformer Usng Matlab Adel Aktab and M. Azzur Rahman Addtonal nformaton s avalable at the end of the chapter http://dx.do.org/10.5772/48624 1. Introducton
Pseudo Peak Suppression in Generating Range Profile with Multi-carrier Chirp
 Pseudo Peak Suppresson n Generatng Range Profle wth Mult-carrer Chrp YANG Chao, ZHENG Ln,, BAI Yunhao. Key Lab. of Cogntve Rado & Informaton Processng, the Mnstry of Educaton, Guln, P. R. Chna. Sc. and
Pseudo Peak Suppresson n Generatng Range Profle wth Mult-carrer Chrp YANG Chao, ZHENG Ln,, BAI Yunhao. Key Lab. of Cogntve Rado & Informaton Processng, the Mnstry of Educaton, Guln, P. R. Chna. Sc. and
Performance Analysis of Multi User MIMO System with Block-Diagonalization Precoding Scheme
 Performance Analyss of Mult User MIMO System wth Block-Dagonalzaton Precodng Scheme Yoon Hyun m and Jn Young m, wanwoon Unversty, Department of Electroncs Convergence Engneerng, Wolgye-Dong, Nowon-Gu,
Performance Analyss of Mult User MIMO System wth Block-Dagonalzaton Precodng Scheme Yoon Hyun m and Jn Young m, wanwoon Unversty, Department of Electroncs Convergence Engneerng, Wolgye-Dong, Nowon-Gu,
Chaotic Filter Bank for Computer Cryptography
 Chaotc Flter Bank for Computer Cryptography Bngo Wng-uen Lng Telephone: 44 () 784894 Fax: 44 () 784893 Emal: HTwng-kuen.lng@kcl.ac.ukTH Department of Electronc Engneerng, Dvson of Engneerng, ng s College
Chaotc Flter Bank for Computer Cryptography Bngo Wng-uen Lng Telephone: 44 () 784894 Fax: 44 () 784893 Emal: HTwng-kuen.lng@kcl.ac.ukTH Department of Electronc Engneerng, Dvson of Engneerng, ng s College
Novel Sampling Clock Offset Estimation for DVB-T OFDM
 Novel Samplng Cloc Offset Estmaton for DVB-T OFD Hou-Shn Chen Yumn Lee Graduate Insttute of Communcaton Eng. and Department of Electrcal Eng. Natonal Tawan Unversty Tape 67 Tawan Abstract Samplng cloc
Novel Samplng Cloc Offset Estmaton for DVB-T OFD Hou-Shn Chen Yumn Lee Graduate Insttute of Communcaton Eng. and Department of Electrcal Eng. Natonal Tawan Unversty Tape 67 Tawan Abstract Samplng cloc
High Speed, Low Power And Area Efficient Carry-Select Adder
 Internatonal Journal of Scence, Engneerng and Technology Research (IJSETR), Volume 5, Issue 3, March 2016 Hgh Speed, Low Power And Area Effcent Carry-Select Adder Nelant Harsh M.tech.VLSI Desgn Electroncs
Internatonal Journal of Scence, Engneerng and Technology Research (IJSETR), Volume 5, Issue 3, March 2016 Hgh Speed, Low Power And Area Effcent Carry-Select Adder Nelant Harsh M.tech.VLSI Desgn Electroncs
Introduction to Amplifiers
 Introducton to Amplfers Dad W. Graham West Vrgna Unersty Lane Department of Computer Scence and Electrcal Engneerng Dad W. Graham, 07 Small Wggles To Bg Wggles Amplfcaton s extremely mportant n electroncs
Introducton to Amplfers Dad W. Graham West Vrgna Unersty Lane Department of Computer Scence and Electrcal Engneerng Dad W. Graham, 07 Small Wggles To Bg Wggles Amplfcaton s extremely mportant n electroncs
Ultra Sonic Flow Rate Measurements in Large Pipes and open Channels
 Ultra Sonc Flow Rate Measurements n Large Ppes and open Channels Dr. Mchael Teufel I Summary Correlaton s a mathematcal tool whch, enabled by developments of fast and powerful mcroprocessors n last few
Ultra Sonc Flow Rate Measurements n Large Ppes and open Channels Dr. Mchael Teufel I Summary Correlaton s a mathematcal tool whch, enabled by developments of fast and powerful mcroprocessors n last few
EEC173B/ECS152C, Winter Fundamentals of Wireless Communications
 EEC173B/ECS152C, Wnter 2006 Fundamentals of Wreless Communcatons #1: Frequences #2: Rado Propagaton Model #3: Modulaton Acknowledgment: Selected sldes from Prof. Schller & Prof. Goldsmth Characterstcs
EEC173B/ECS152C, Wnter 2006 Fundamentals of Wreless Communcatons #1: Frequences #2: Rado Propagaton Model #3: Modulaton Acknowledgment: Selected sldes from Prof. Schller & Prof. Goldsmth Characterstcs
Multiple Error Correction Using Reduced Precision Redundancy Technique
 Multple Error Correcton Usng Reduced Precson Redundancy Technque Chthra V 1, Nthka Bhas 2, Janeera D A 3 1,2,3 ECE Department, Dhanalakshm Srnvasan College of Engneerng,Combatore, Tamlnadu, Inda Abstract
Multple Error Correcton Usng Reduced Precson Redundancy Technque Chthra V 1, Nthka Bhas 2, Janeera D A 3 1,2,3 ECE Department, Dhanalakshm Srnvasan College of Engneerng,Combatore, Tamlnadu, Inda Abstract
Lecture 10: Bipolar Junction Transistor Construction. NPN Physical Operation.
 Whtes, EE 320 Lecture 10 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 10: Bpolar Juncton Transstor Constructon. NPN Physcal Operaton. For the remander of ths semester we wll be studyng transstors and transstor crcuts. The transstor
Whtes, EE 320 Lecture 10 Page 1 of 9 Lecture 10: Bpolar Juncton Transstor Constructon. NPN Physcal Operaton. For the remander of ths semester we wll be studyng transstors and transstor crcuts. The transstor
Sensors for Motion and Position Measurement
 Sensors for Moton and Poston Measurement Introducton An ntegrated manufacturng envronment conssts of 5 elements:- - Machne tools - Inspecton devces - Materal handlng devces - Packagng machnes - Area where
Sensors for Moton and Poston Measurement Introducton An ntegrated manufacturng envronment conssts of 5 elements:- - Machne tools - Inspecton devces - Materal handlng devces - Packagng machnes - Area where

 _'x,'_l _ 3_+ tl / j'...... t...! "t
_'x,'_l _ 3_+ tl / j'...... t...! "t