h = v h 2 = height of the object is negative for inverted image and positive for erect image. is always positive. Direction of incident light
|
|
|
- Daniela Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
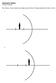
1 6. C a p t e r at G l a n c e Ligt related penomena can be studied wit mirrors and lenses. A mirror is a reflecting surface wile a lens is a transparent material. Mirrors are mainly of tree types : plane mirror, concave or converging mirror, convex or diverging mirror. Lenses are mainly of two types : concave or diverging lens; convex or converging lens. Focal lengt of convex mirror is positive wile tat of concave mirror is negative. Focal lengt of convex lens is positive wile tat of concave lens is negative. Focal lengt ( f) of concave mirror is always negative, object distance (u) is always negative and image distance ( v) is negative in case of real and inverted image because tis type of image is formed on te same side of te mirror as tat of te object. Image distance ( v) is positive incase of virtual and erect image because tis type of image is formed beind te mirror. Mirror formula : + v u = f 2 M (magnification produced by sperical mirror) = = v u 2 = eigt of te image = eigt of te object 2 is negative for inverted image and positive for erect image. is always positive. Heigt upward (+ve) R Unique Solutions Focal lengt ( f ) of convex lens is always positive, object distance (u) is always negative and image distance ( v) is negative incase of virtual and erect image because tis type of image is formed on te same side of te lens as te object. Image distance ( v) is positive incase of real and inverted images because tese images are formed on te oter side of te lens as te object. Lens formula = v u = f Direction of incident ligt Heigt downwards ( ve) Figure : Representation of sign conventions. distance towards te left ( ve) Mirror distance towards te rigt (+ve) P principal axis
2 94 Unique MCQ's M (magnification produced by lens) = P (Power of lens) = f(in metre) Unit of power of lens is dioptre 2 = v u dioptre = l(metre) Cornea, pupil, iris, lens, retina and optic nerve are te main parts of uman eye. Cornea ligt enters te eye. pupil ligt is controlled and regulated. iris colour is different for different people. retina ligt sensitive screen. optic nerve pass electric signals to te brain. Defects of vision : Myopia or near sigtedness; Hypermetropia or long sigtedness; presbyopia or old age ypermetropia. Myopia image in front of retina corrected using concave lens. Hypermetropia image beind retina corrected using convex lens. Presbyopia suffer, bot myopia and ypermetropia corrected using bifocal lens. Concave or converging mirror is used in : torces and ead ligts; flood ligts; reflector or projector lamps; solar devices and furnaces; saving mirrors and dentists mirror. Convex or converging lens is used in : simple microscope, compound microscope; telescope, optical instruments like camera, projector, spectrometer, spectacles etc. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQ's) MCQ's BASED ON PRACTICALS (Eac question carries one mark) Experiment : I. To determine te focal lengt of - a) Concave mirror b) Convex lens by obtaining image of a distinct object.. An object of 0 cm eigt is placed in front of a plane mirror. Te eigt of te image will be : a 5 cm b 0 cm c 5 cm d 20 cm 2. Te focal lengt of concave mirror in te given experimental set up is : a 0.3 cm b.0 cm c.7 cm d 2.2 cm
3 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - S.S.C A students obtained a sarp image of grill of a window on a screen using a convex lens. For better results te teacer suggested focusing on a distant tree instead of grill. In wic direction sould te lens be moved to get te sarp image of tree? a away from screen b beind te screen c towards te screen d far away from screen 4. Inside water, an air bubble beaves : a always like a concave lens c always like a flat plate b always like a convex lens d sometimes like a convex lens and sometimes like a concave lens 5. Mirror used by a dental surgeon is : a plane b convex c concave d bot (b) & (c) 6. In a concave mirror ligt is reflected from : a inner surface c sperical surface b outer surface d inner and outer surface 7. Wat appens to te image of your face as you take a concave mirror away from your face slowly? a becomes smaller b becomes bigger c remains te same d disappears 8. Wen te object is far away from a concave mirror, te image is formed : a between focus and centre of curvature b at focus c at centre of curvature d beyond centre of curvature 9. A concave mirror forms enlarged virtual image for te position of te object : a between infinity and centre of curvature b between focus and centre of curvature c at te principle focus d between pole and principal focus. 0. Wen te object is at principle focus of a concave mirror, te image formed is : a magnified b igly magnified c diminised d igly diminised. To get te image at te centre of curvature of a concave mirror, te object must be placed : a between infinity and centre of curvature c at principal focus b at infinity d at te centre of curvature 2. A ray of ligt parallel to principal axis after reflection from concave mirror passes troug : a centre of curvature b focus c pole d radius of curvature 3. If a lens is ticker in te middle tan at te edges, it is a : a bifocal lens b diverging lens c concave lens d convex lens 4. A point sized image is obtained by a convex lens wen te object is : a between F and 2F b at 2F c beyond 2F d at infinity
4 96 Unique MCQ's 5. Te focus of a concave mirror lies : a on te bot sides of te mirror b in front of te mirror c at te back of te mirror d on te rigt side of te mirror 6. Te focal lengt of a concave mirror is : a positive b negative c zero d always positive 7. Te focal lengt of a convex lens is : a positive b negative c always negative d neiter positive nor negative 8. Wic of te following are used in solar furnaces? a concave lenses b convex lenses c concave mirrors d convex mirrors MCQ's BASED ON CHAPTER. Distorted images are obtained in Moderate Level a plane mirror b sperical mirror c concave lens d convex lens 2. Wic of te following forms an arc of a circle? a concave lens b convex lens c sperical mirror d plane mirror. 3. To get a convex mirror, wic side of a sperical surface is to be polised? a inner b outer c inner and outer d sperical 4. Diverging mirror is : a concave b convex c plane d sperical 5. Te centre of a sperical mirror is its : a centre of curvature b optical centre c focus d pole 6. If te incident ray passes troug te centre of curvature of a sperical mirror, te reflected ray : a passes troug te focus b passes parallel to te principal axis c traces te same pat d passes troug optical centre undeviated 7. Distances parallel to principal axis are measured from te : a optical centre of te mirror. b pole of te mirror c focus of te mirror d centre of curvature of te mirror 8. A lens aving bot surfaces curved inwards is : a double concave b double convex c bifocal d converging lens 9. A ray of ligt passes undeviated as it passes troug : a pole of te lens b focus of te lens c optical centre of te lens d centre of curvature of te lens 0. To get an image of te same size as te object, te object must be placed : a at 2F of a lens b at 2F 2 of a lens c at F of a lens d beyond 2F of a lens
5 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - S.S.C. 97. Te image obtained wen te object is placed between focus and optical centre of a convex lens is : a diminised, virtual and erect b diminised, real and inverted c magnified, virtual and erect d magnified, real and inverted 2. Te ability of a lens to converge or diverge ligt rays depends on its : a principal focus b focal lengt c principal axis d optical centre 3. Te amount of ligt entering te eye is regulated by : a cornea b iris c pupil d eye lens 4. Some people ave bluis eyes due to teir blue coloured : a cornea b iris c eyelens d pupil 5. Te focal lengt of a normal uman eye lens in its relaxed position is about : a 2.5 cm b 25 cm c 2.5 m d 25 m 6. Hypermetropia is corrected using : a concave lens b convex lens c bifocal lens d cylindrical lens Elementary level. Te image formed by a plane mirror cannot be projected on a screen because : a it is a real image c reflected rays do not actually meet eac oter d reflected rays converge at a point 2. Te image formed by a plane mirror is : b it is formed in front of te mirror a virtual b real c magnified d inverted 3. Wic of te following image is not obtained on a screen? a diminised b inverted c real d virtual 4. Wic beam of ligt is used to concentrate ligt at a point? a converging b diverging c parallel d pointed 5. Diverging beam of ligt is used in : a torces b solar devices c table lamps d ead ligts 6. Wic of te following beam of ligt is used by an optalmologist to examine is patient? a parallel b diverging c converging d pointed 7. Were does te focus of a convex mirror lie? a in front of b beind c on bot sides d on te left side 8. Wic of te following is always negative? a object distance b image distance c object size d image size 9. Heigt of te image is to be taken as positive for : a real images b virtual images c inverted images d magnified images 0. Wic of te following is a natural optical device? a lens b mirror c eye d camera
6 98 Unique MCQ's. A lens is a/an : a opaque material b transparent material c translucent material d reflecting material 2. Wic of te following statement is false? a eac lens as two centres of curvature b every lens as two principal foci c eac sperical mirror as two centres of curvature d every sperical mirror as more tan one radii of curvature 3. Using a convex lens, a well defined image of a distant object is obtained on a screen. Te focal lengt of tis lens is : a te distance between te screen and object b te distance between te lens and object c te distance between te screen and lens d alf of te distance between te lens and object 4. Ligt rays bend troug large angles wen te focal lengt of a convex lens is : a sort b large c medium d zero 5. dioptre is te power of a lens wose focal lengt is one : a millimetre b centimetre c decimetre d metre 6. Negative sign of magnification sows tat te image is : a inverted and virtual b inverted and real c erect and virtual d erect and real 7. Te image formed on te retina of uman eye is : a real and inverted b real and erect c virtual and inverted d virtual and erect 8. For normal uman eye, te distance of distinct vision is : a 25 m b 2.5 m c 2.5 cm d 25 cm 9. In myopia, te image of te object is formed : a on te retina b in front of te retina c beind te retina d on te lens 20. In torces and eadligts, te source of ligt is placed : a at te centre of curvature of a concave mirror b at te focus of a concave mirror c between pole and focus of a concave mirror d beyond te centre of curvature of a concave mirror 2. In reflecting mirrors for projector lamps, te object is placed : a at te focus of a concave mirror b beyond te centre of curvature of a concave mirror c between pole and focus of a concave mirror d at te centre of curvature of a concave mirror
7 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - S.S.C. 99 Complex Level. Te angle of incidence of an incident ray passing troug te centre of curvature of a sperical mirror is : a 90 b 45 c 0 d Radius of curvature of a sperical mirror is : a smaller tan its focal lengt c trice larger tan its focal lengt Hint : f = R 2, R = 2f b twice larger tan its focal lengt d larger by 2 cm tan its focal lengt 3. If te focal lengt of eac a mirror and a lens is + 5 cm ten, a te mirror is concave, but te lens is convex b bot are concave c bot are convex d te mirror is convex, but te lens is concave. 4. Wic of te following formulae gives eigt of te image formed by a convex lens? a 2 = v u Hint : M = 2 = v u b = v 2 v c 2 = 5. Te value 2 = 3.5 cm sows tat te image is : v v d = a enlarged b diminised c erect d inverted 6. Te power of a convex lens wit focal lengt 40 cm is : a D b D c 2.5 D d D Hint : P = f(in metre) 7. Focal lengt of a corrective lens aving power + 2D is : a 0.05 m b 0.05 cm c 0.5 m d 0.5 cm Hint : P = f(in metre) 8. Te negative power of te spectacles indicates te defect of vision : a myopia b ypermetropia c presbyopia d astigmatism 9. Since, Raul's grand fater is suffering from presbyopia, e wears spectacles aving : a convex lens b concave lens c bifocal lens d plane lens 0. Te power of a concave lens of focal lengt 20 cm is : a + 5D b 5D c + 0.5D d 0.5D v 2 u Hint : P = f(in metre)
8 00 Unique MCQ's Mysterious Level. Te focal lengt of a sperical mirror wit radius of curvature 2.6 cm is : a 3.2 cm b.3 cm c 5.2 cm d 0.3 cm Hint : f = R 2 2. Te radius of curvature of a sperical mirror wit focal lengt 0.7 cm is : a.4 cm b 0.35 cm c 3.5 cm d 0.4 cm Hint : f = R 2, R = 2 f 3. If te distance of te object from te origin is 2 cm and te image distance is 60 cm, magnification produced by te convex lens is : a b 0.2 c + 5 d 5 Hint : U M = v u 4. Wen a 4 cm tall object is placed at 0 cm away from a converging lens, an image is formed at a distance of 30 cm on te oter side of te lens. Te eigt of te image formed is : a + 2 cm b 2 cm c + 5 cm d 5 cm v Hint : 2 = u 5. An object is placed at a distance of 5 cm from a convex lens of focal lengt 20 cm. Te position of te object is : a 60 cm b + 60 cm c 90 cm d + 90 cm Hint : v = + u f 6. Wen a converging lens form an image of 45 cm, te magnification produced is 3. Terefore, eigt of te object is : a + 5 cm b 5 cm c + 30 cm d 30 cm Hint : m = 2 = 2 m 7. If te magnification produced by an object of eigt 0 cm due to a sperical mirror is 0.5, eigt of te image formed is : a 5 cm b + 5 cm c + 2 cm d 2 cm Hint : M = 2 2 = M 8. An object of size 5 cm is placed at 5 cm in front of concave mirror of focal lengt 2 cm. To get a sarp and clear image, at wat distance from te mirror a screen sould be placed? a 60 cm b 30 cm c 20 cm d 50 cm Hint : + v u = f v = f u
9 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - S.S.C. 0 MCQ's BASED ON PRACTICAL SKILLS Answers - b 2 - b 3 - c 4 - b 5 - c 6 - a 7 - b 8 - b 9 - d 0 - b - d 2 - b 3 - d 4 - d 5 - b 6 - b 7 - a 8 - c MCQ's BASED ON CHAPTER Moderate Level - b 2 - c 3 - b 4 - b 5 - d 6 - c 7 - b 8 - a 9 - c 0 - a - c 2 - b 3 - c 4 - b 5 - a 6 - b Elementary Level - c 2 - a 3 - d 4 - a 5 - c 6 - c 7 - b 8 - a 9 - b 0 - c - b 2 - c 3 - c 4 - a 5 - d 6 - b 7 - a 8 - d 9 - b 20 - b 2 - d Complex Level Mysterious Level - c 2 - b 3 - c 4 - a 5 - d 6 - a 7 - c 8 - a 9 - c 0 - b - b 2 - a 3 - d 4 - b 5 - a 6 - a 7 - a 8 - a
Wonders of Light - Part I
 6. Wonders of Light - Part I Light : The fastest physical quantity, which is an electromagnetic radiation travelling with the speed of 3 0 8 m/s. SCHOOL SECTION 25 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY MT EDUCARE LTD.
6. Wonders of Light - Part I Light : The fastest physical quantity, which is an electromagnetic radiation travelling with the speed of 3 0 8 m/s. SCHOOL SECTION 25 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY MT EDUCARE LTD.
Downloaded from
 QUESTION BANK SCIENCE STD-X PHYSICS REFLECTION & REFRACTION OF LIGHT (REVISION QUESTIONS) VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE (1 MARK) 1. Out of red and blue lights, for which is the refractive index of glass greater?
QUESTION BANK SCIENCE STD-X PHYSICS REFLECTION & REFRACTION OF LIGHT (REVISION QUESTIONS) VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE (1 MARK) 1. Out of red and blue lights, for which is the refractive index of glass greater?
OPTI-502 Optical Design and Instrumentation I John E. Greivenkamp Homework Set 5 Fall, 2018
 Homework Set 5 all, 2018 Assigned: 9/26/18 Lecture 11 Due: 10/3/18 Lecture 13 Midterm Exam: Wednesday October 24 (Lecture 19) 5-1) Te following combination of tin lenses in air is in a telepoto configuration:
Homework Set 5 all, 2018 Assigned: 9/26/18 Lecture 11 Due: 10/3/18 Lecture 13 Midterm Exam: Wednesday October 24 (Lecture 19) 5-1) Te following combination of tin lenses in air is in a telepoto configuration:
2. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
 1. Define the principle focus of a concave mirror? The principle focus of a concave mirror is a point on its principle axis to which all the light rays which are parallel and close to the axis, converge
1. Define the principle focus of a concave mirror? The principle focus of a concave mirror is a point on its principle axis to which all the light rays which are parallel and close to the axis, converge
Final Reg Optics Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Final Reg Optics Review 1) How far are you from your image when you stand 0.75 m in front of a vertical plane mirror? 1) 2) A object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, and the image is 3.0 cm in front
Final Reg Optics Review 1) How far are you from your image when you stand 0.75 m in front of a vertical plane mirror? 1) 2) A object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, and the image is 3.0 cm in front
Lenses. A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved.
 PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
LENSES. A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved.
 1 LENSES A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of Lenses There are two types of basic lenses: Converging/
1 LENSES A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of Lenses There are two types of basic lenses: Converging/
Lenses. Images. Difference between Real and Virtual Images
 Linear Magnification (m) This is the factor by which the size of the object has been magnified by the lens in a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the lens. Linear magnification can be calculated
Linear Magnification (m) This is the factor by which the size of the object has been magnified by the lens in a direction which is perpendicular to the axis of the lens. Linear magnification can be calculated
Lenses- Worksheet. (Use a ray box to answer questions 3 to 7)
 Lenses- Worksheet 1. Look at the lenses in front of you and try to distinguish the different types of lenses? Describe each type and record its characteristics. 2. Using the lenses in front of you, look
Lenses- Worksheet 1. Look at the lenses in front of you and try to distinguish the different types of lenses? Describe each type and record its characteristics. 2. Using the lenses in front of you, look
always positive for virtual image
 Point to be remembered: sign convention for Spherical mirror Object height, h = always positive Always +ve for virtual image Image height h = Always ve for real image. Object distance from pole (u) = always
Point to be remembered: sign convention for Spherical mirror Object height, h = always positive Always +ve for virtual image Image height h = Always ve for real image. Object distance from pole (u) = always
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
 L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
Chapter 29/30. Wave Fronts and Rays. Refraction of Sound. Dispersion in a Prism. Index of Refraction. Refraction and Lenses
 Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION 1. List four properties of the image formed by a plane mirror. Properties of image formed by a plane mirror: 1. It is always virtual and erect. 2. Its size is equal to that
LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION 1. List four properties of the image formed by a plane mirror. Properties of image formed by a plane mirror: 1. It is always virtual and erect. 2. Its size is equal to that
REFLECTION THROUGH LENS
 REFLECTION THROUGH LENS A lens is a piece of transparent optical material with one or two curved surfaces to refract light rays. It may converge or diverge light rays to form an image. Lenses are mostly
REFLECTION THROUGH LENS A lens is a piece of transparent optical material with one or two curved surfaces to refract light rays. It may converge or diverge light rays to form an image. Lenses are mostly
Chapter 9 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments. The image distance can be obtained using the mirror formula:
 Question 9.1: A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain
Question 9.1: A small candle, 2.5 cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain
The Indian Academy Nehrugram DEHRADUN Question Bank Subject - Physics Class - X
 The Indian Academy Nehrugram DEHRADUN Question Bank - 2013-14 Subject - Physics Class - X Section A A- One mark questions:- Q1. Chair, Table are the example of which object? Q2. In which medium does the
The Indian Academy Nehrugram DEHRADUN Question Bank - 2013-14 Subject - Physics Class - X Section A A- One mark questions:- Q1. Chair, Table are the example of which object? Q2. In which medium does the
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
ii) When light falls on objects, it reflects the light and when the reflected light reaches our eyes then we see the objects.
 Light i) Light is a form of energy which helps us to see objects. ii) When light falls on objects, it reflects the light and when the reflected light reaches our eyes then we see the objects. iii) Light
Light i) Light is a form of energy which helps us to see objects. ii) When light falls on objects, it reflects the light and when the reflected light reaches our eyes then we see the objects. iii) Light
Refraction by Spherical Lenses by
 Page1 Refraction by Spherical Lenses by www.examfear.com To begin with this topic, let s first know, what is a lens? A lens is a transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both the surfaces
Page1 Refraction by Spherical Lenses by www.examfear.com To begin with this topic, let s first know, what is a lens? A lens is a transparent material bound by two surfaces, of which one or both the surfaces
30 Lenses. Lenses change the paths of light.
 Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Physics Worksheet. Topic -Light. Q1 If the radius of curvature of spherical mirror is 20 cm, what is its focal length.
 Physics Worksheet Topic -Light Q1 If the radius of curvature of spherical mirror is 20 cm, what is its focal length. (Ans: 10 cm) Q2 Calculate the radius of curvature of spherical mirror whose focal length
Physics Worksheet Topic -Light Q1 If the radius of curvature of spherical mirror is 20 cm, what is its focal length. (Ans: 10 cm) Q2 Calculate the radius of curvature of spherical mirror whose focal length
Optics: Lenses & Mirrors
 Warm-Up 1. A light ray is passing through water (n=1.33) towards the boundary with a transparent solid at an angle of 56.4. The light refracts into the solid at an angle of refraction of 42.1. Determine
Warm-Up 1. A light ray is passing through water (n=1.33) towards the boundary with a transparent solid at an angle of 56.4. The light refracts into the solid at an angle of refraction of 42.1. Determine
King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept.
 King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 111 (GENERAL PHYSICS 2) CHAPTER 36: Image Formation LECTURE NO. 9 Presented by Nouf Saad Alkathran 36.1 Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 111 (GENERAL PHYSICS 2) CHAPTER 36: Image Formation LECTURE NO. 9 Presented by Nouf Saad Alkathran 36.1 Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
Converging Lenses. Parallel rays are brought to a focus by a converging lens (one that is thicker in the center than it is at the edge).
 Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
Light - Reflection and Refraction
 Light - Reflection and Refraction Question 1: Define the principal focus of a concave mirror. Answer: Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point
Light - Reflection and Refraction Question 1: Define the principal focus of a concave mirror. Answer: Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point
EDULABZ INTERNATIONAL. Light ASSIGNMENT
 Light ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : List : compound microscope, yellow, telescope, alter, vitreous humour, time, photographic camera,
Light ASSIGNMENT 1. Fill in the blank spaces by choosing the correct words from the list given below : List : compound microscope, yellow, telescope, alter, vitreous humour, time, photographic camera,
PHYS:1200 LECTURE 31 LIGHT AND OPTICS (3)
 1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 31 LIGHT AND OPTICS (3) In lecture 30, we applied the law of reflection to understand how images are formed using plane and curved mirrors. In this lecture we will use the law of refraction
1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 31 LIGHT AND OPTICS (3) In lecture 30, we applied the law of reflection to understand how images are formed using plane and curved mirrors. In this lecture we will use the law of refraction
LIGHT-REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 LIGHT-REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Class: 10 (Boys) Sub: PHYSICS NOTES-Refraction Refraction: The bending of light when it goes from one medium to another obliquely is called refraction of light. Refraction
LIGHT-REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Class: 10 (Boys) Sub: PHYSICS NOTES-Refraction Refraction: The bending of light when it goes from one medium to another obliquely is called refraction of light. Refraction
Optics Practice. Version #: 0. Name: Date: 07/01/2010
 Optics Practice Date: 07/01/2010 Version #: 0 Name: 1. Which of the following diagrams show a real image? a) b) c) d) e) i, ii, iii, and iv i and ii i and iv ii and iv ii, iii and iv 2. A real image is
Optics Practice Date: 07/01/2010 Version #: 0 Name: 1. Which of the following diagrams show a real image? a) b) c) d) e) i, ii, iii, and iv i and ii i and iv ii and iv ii, iii and iv 2. A real image is
Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction
 Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction Q 1. How does light enable us to see an object? Q 2. What is a concave mirror? Q 3. What is the relationship between focal length and radius
Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction Q 1. How does light enable us to see an object? Q 2. What is a concave mirror? Q 3. What is the relationship between focal length and radius
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
 Question 1: Define the principal focus of a concave mirror. Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from
Question 1: Define the principal focus of a concave mirror. Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from
Human Eye and Colourful World Science. Intext Exercise 1
 Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? Solution 1: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and the distant
Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? Solution 1: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and the distant
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
CHAPTER 3LENSES. 1.1 Basics. Convex Lens. Concave Lens. 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses. Shape: Shape: Symbol: Symbol:
 CHAPTER 3LENSES 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses 1.1 Basics Convex Lens Shape: Concave Lens Shape: Symbol: Symbol: Effect to parallel rays: Effect to parallel rays: Explanation: Explanation:
CHAPTER 3LENSES 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses 1.1 Basics Convex Lens Shape: Concave Lens Shape: Symbol: Symbol: Effect to parallel rays: Effect to parallel rays: Explanation: Explanation:
IMAGE ILLUMINATION (4F 2 OR 4F 2 +1?)
 IMAGE ILLUMINATION ( OR +?) BACKGROUND Publications abound wit two differing expressions for calculating image illumination, te amount of radiation tat transfers from an object troug an optical system
IMAGE ILLUMINATION ( OR +?) BACKGROUND Publications abound wit two differing expressions for calculating image illumination, te amount of radiation tat transfers from an object troug an optical system
Unit Two: Light Energy Lesson 1: Mirrors
 1. Plane mirror: Unit Two: Light Energy Lesson 1: Mirrors Light reflection: It is rebounding (bouncing) light ray in same direction when meeting reflecting surface. The incident ray: The light ray falls
1. Plane mirror: Unit Two: Light Energy Lesson 1: Mirrors Light reflection: It is rebounding (bouncing) light ray in same direction when meeting reflecting surface. The incident ray: The light ray falls
Chapter 25: Applied Optics. PHY2054: Chapter 25
 Chapter 25: Applied Optics PHY2054: Chapter 25 1 Operation of the Eye 24 mm PHY2054: Chapter 25 2 Essential parts of the eye Cornea transparent outer structure Pupil opening for light Lens partially focuses
Chapter 25: Applied Optics PHY2054: Chapter 25 1 Operation of the Eye 24 mm PHY2054: Chapter 25 2 Essential parts of the eye Cornea transparent outer structure Pupil opening for light Lens partially focuses
Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein
 Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein The Human Eye As light enters through the human eye it first passes through the cornea (a thin transparent membrane of
Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein The Human Eye As light enters through the human eye it first passes through the cornea (a thin transparent membrane of
Assignment X Light. Reflection and refraction of light. (a) Angle of incidence (b) Angle of reflection (c) principle axis
 Assignment X Light Reflection of Light: Reflection and refraction of light. 1. What is light and define the duality of light? 2. Write five characteristics of light. 3. Explain the following terms (a)
Assignment X Light Reflection of Light: Reflection and refraction of light. 1. What is light and define the duality of light? 2. Write five characteristics of light. 3. Explain the following terms (a)
Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification.
 Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification. 1.! Questions about objects and images. Can a virtual
Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification. 1.! Questions about objects and images. Can a virtual
LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION REFLECTION OF LIGHT A highly polished surface, such as a mirror, reflects most of the light falling on it. Laws of Reflection: (i) The angle of incidence is equal to the
LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION REFLECTION OF LIGHT A highly polished surface, such as a mirror, reflects most of the light falling on it. Laws of Reflection: (i) The angle of incidence is equal to the
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics
 Chapter 34 Geometric Optics Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals of Chapter 34 To see how plane and curved mirrors form images To learn how lenses form images To understand how a simple image system works Reflection
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals of Chapter 34 To see how plane and curved mirrors form images To learn how lenses form images To understand how a simple image system works Reflection
GIST OF THE UNIT BASED ON DIFFERENT CONCEPTS IN THE UNIT (BRIEFLY AS POINT WISE). RAY OPTICS
 209 GIST OF THE UNIT BASED ON DIFFERENT CONCEPTS IN THE UNIT (BRIEFLY AS POINT WISE). RAY OPTICS Reflection of light: - The bouncing of light back into the same medium from a surface is called reflection
209 GIST OF THE UNIT BASED ON DIFFERENT CONCEPTS IN THE UNIT (BRIEFLY AS POINT WISE). RAY OPTICS Reflection of light: - The bouncing of light back into the same medium from a surface is called reflection
10.2 Images Formed by Lenses SUMMARY. Refraction in Lenses. Section 10.1 Questions
 10.2 SUMMARY Refraction in Lenses Converging lenses bring parallel rays together after they are refracted. Diverging lenses cause parallel rays to move apart after they are refracted. Rays are refracted
10.2 SUMMARY Refraction in Lenses Converging lenses bring parallel rays together after they are refracted. Diverging lenses cause parallel rays to move apart after they are refracted. Rays are refracted
25 cm. 60 cm. 50 cm. 40 cm.
 Geometrical Optics 7. The image formed by a plane mirror is: (a) Real. (b) Virtual. (c) Erect and of equal size. (d) Laterally inverted. (e) B, c, and d. (f) A, b and c. 8. A real image is that: (a) Which
Geometrical Optics 7. The image formed by a plane mirror is: (a) Real. (b) Virtual. (c) Erect and of equal size. (d) Laterally inverted. (e) B, c, and d. (f) A, b and c. 8. A real image is that: (a) Which
LLT Education Services
 Rahul Arora 1. Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it? (a) Concave mirror as well as convex lens (b) Convex mirror as well as concave
Rahul Arora 1. Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it? (a) Concave mirror as well as convex lens (b) Convex mirror as well as concave
Introduction. Strand F Unit 3: Optics. Learning Objectives. Introduction. At the end of this unit you should be able to;
 Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Identify converging and diverging lenses from their curvature Construct ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses in order to locate
Learning Objectives At the end of this unit you should be able to; Identify converging and diverging lenses from their curvature Construct ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses in order to locate
Science 8 Unit 2 Pack:
 Science 8 Unit 2 Pack: Name Page 0 Section 4.1 : The Properties of Waves Pages By the end of section 4.1 you should be able to understand the following: Waves are disturbances that transmit energy from
Science 8 Unit 2 Pack: Name Page 0 Section 4.1 : The Properties of Waves Pages By the end of section 4.1 you should be able to understand the following: Waves are disturbances that transmit energy from
 Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Question 1: What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and
Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Question 1: What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and
Unit 3: Energy On the Move
 14 14 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 14: Mirrors and Lenses 14.1: Mirrors 14.2: Lenses 14.3: Optical Instruments 14.1 Mirrors How do you use light to see? When light travels from
14 14 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 14: Mirrors and Lenses 14.1: Mirrors 14.2: Lenses 14.3: Optical Instruments 14.1 Mirrors How do you use light to see? When light travels from
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A plane mirror is placed on the level bottom of a swimming pool that holds water (n =
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A plane mirror is placed on the level bottom of a swimming pool that holds water (n =
Light: Lenses and. Mirrors. Test Date: Name 1ÿ-ÿ. Physics. Light: Lenses and Mirrors
 Name 1ÿ-ÿ Physics Light: Lenses and Mirrors i Test Date: "Shadows cannot see themselves in the mirror of the sun." -Evita Peron What are lenses? Lenses are made from transparent glass or plastice and refract
Name 1ÿ-ÿ Physics Light: Lenses and Mirrors i Test Date: "Shadows cannot see themselves in the mirror of the sun." -Evita Peron What are lenses? Lenses are made from transparent glass or plastice and refract
3. Butter paper is an example for object. (A) a transparent (B) a translucent (C) an opaque (D) a luminous
 SETH ANANDRAM JAIPURIA SCHOOL VASUNDHARA, GHAZIABAD SESSION :2017-18 OLYMPIAD WORKSHEET CLASS VIII PHYSICS TOPIC : LIGHT 1. We are able to see objects around us because : (A) the objects absorb all the
SETH ANANDRAM JAIPURIA SCHOOL VASUNDHARA, GHAZIABAD SESSION :2017-18 OLYMPIAD WORKSHEET CLASS VIII PHYSICS TOPIC : LIGHT 1. We are able to see objects around us because : (A) the objects absorb all the
19. Ray Optics. S. G. Rajeev. April 2, 2009
 9. Ray Optics S. G. Rajeev April 2, 2009 When the wave length is small light travels along straightlines called rays. Ray optics (also called geometrical optics) is the study of this light in this situation.
9. Ray Optics S. G. Rajeev April 2, 2009 When the wave length is small light travels along straightlines called rays. Ray optics (also called geometrical optics) is the study of this light in this situation.
sclera pupil What happens to light that enters the eye?
 Human Vision Textbook pages 202 215 Before You Read Some people can see things clearly from a great distance. Other people can see things clearly only when they are nearby. Why might this be? Write your
Human Vision Textbook pages 202 215 Before You Read Some people can see things clearly from a great distance. Other people can see things clearly only when they are nearby. Why might this be? Write your
04. REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT CURVED SURFACES
 CLASS-10 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 04. REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT CURVED SURFACES Questions and Answers *Reflections on Concepts* 1. Write the lens maker s formula and explain the terms in it. A. Lens maker s formula
CLASS-10 PHYSICAL SCIENCE 04. REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT CURVED SURFACES Questions and Answers *Reflections on Concepts* 1. Write the lens maker s formula and explain the terms in it. A. Lens maker s formula
Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors
 Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors Converging and Diverging Lens Focal Lengths: A converging lens is thicker at the center than at the periphery and light from an object at infinity passes
Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors Converging and Diverging Lens Focal Lengths: A converging lens is thicker at the center than at the periphery and light from an object at infinity passes
Chapter 10: Light Reflection and Refraction Q1. What do you mean by principal focus? Ans:
 Chapter 10: Light Reflection and Refraction Q1. What do you mean by principal focus? Ans: All incident light rays which are passing parallel to the principal axis of the concave mirror meet at a specific
Chapter 10: Light Reflection and Refraction Q1. What do you mean by principal focus? Ans: All incident light rays which are passing parallel to the principal axis of the concave mirror meet at a specific
Converging and Diverging Surfaces. Lenses. Converging Surface
 Lenses Sandy Skoglund 2 Converging and Diverging s AIR Converging If the surface is convex, it is a converging surface in the sense that the parallel rays bend toward each other after passing through the
Lenses Sandy Skoglund 2 Converging and Diverging s AIR Converging If the surface is convex, it is a converging surface in the sense that the parallel rays bend toward each other after passing through the
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics EdExcel A Level Physics. Lenses
 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Lenses Types of lenses Converging lens bi-convex has two convex surfaces Diverging lens bi-concave has two concave surfaces Thin
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Lenses Types of lenses Converging lens bi-convex has two convex surfaces Diverging lens bi-concave has two concave surfaces Thin
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics (also known as Ray Optics) by C.-R. Hu
 Chapter 34 Geometric Optics (also known as Ray Optics) by C.-R. Hu 1. Principles of image formation by mirrors (1a) When all length scales of objects, gaps, and holes are much larger than the wavelength
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics (also known as Ray Optics) by C.-R. Hu 1. Principles of image formation by mirrors (1a) When all length scales of objects, gaps, and holes are much larger than the wavelength
Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World
 Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World Short Answer Questions Question 1. A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the
Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World Short Answer Questions Question 1. A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the
Grade 8. Light and Optics. Unit exam
 Grade 8 Light and Optics Unit exam Unit C - Light and Optics 1. Over the years many scientists have contributed to our understanding of light. All the properties listed below about light are correct except:
Grade 8 Light and Optics Unit exam Unit C - Light and Optics 1. Over the years many scientists have contributed to our understanding of light. All the properties listed below about light are correct except:
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
E X P E R I M E N T 12
 E X P E R I M E N T 12 Mirrors and Lenses Produced by the Physics Staff at Collin College Copyright Collin College Physics Department. All Rights Reserved. University Physics II, Exp 12: Mirrors and Lenses
E X P E R I M E N T 12 Mirrors and Lenses Produced by the Physics Staff at Collin College Copyright Collin College Physics Department. All Rights Reserved. University Physics II, Exp 12: Mirrors and Lenses
 Light: Reflection and Refraction Light Reflection of Light by Plane Mirror Reflection of Light by Spherical Mirror Formation of Image by Mirror Sign Convention & Mirror Formula Refraction of light Through
Light: Reflection and Refraction Light Reflection of Light by Plane Mirror Reflection of Light by Spherical Mirror Formation of Image by Mirror Sign Convention & Mirror Formula Refraction of light Through
Chapter 2 - Geometric Optics
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image on the retina. The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image on the retina. The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image
The Optics of Mirrors
 Use with Text Pages 558 563 The Optics of Mirrors Use the terms in the list below to fill in the blanks in the paragraphs about mirrors. reversed smooth eyes concave focal smaller reflect behind ray convex
Use with Text Pages 558 563 The Optics of Mirrors Use the terms in the list below to fill in the blanks in the paragraphs about mirrors. reversed smooth eyes concave focal smaller reflect behind ray convex
Solution. Class 10 - Science. Revision Test. Section A
 Solution Class 10 - Science Revision Test Section A 1. (a) since resistances are in parallel R (b) Total current I 4.8 A (c) If I 1, I 2 and I 3 be the current through 2 respectively. Therefore, I 1 3
Solution Class 10 - Science Revision Test Section A 1. (a) since resistances are in parallel R (b) Total current I 4.8 A (c) If I 1, I 2 and I 3 be the current through 2 respectively. Therefore, I 1 3
CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES
 Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 18.1 Refraction of Light o Snell
Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 18.1 Refraction of Light o Snell
PHYSICS FOR THE IB DIPLOMA CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Option C Imaging C Introduction to imaging Learning objectives In this section we discuss the formation of images by lenses and mirrors. We will learn how to construct images graphically as well as algebraically.
Option C Imaging C Introduction to imaging Learning objectives In this section we discuss the formation of images by lenses and mirrors. We will learn how to construct images graphically as well as algebraically.
BHARATIYA VIDYA BHAVAN S V M PUBLIC SCHOOL, VADODARA QUESTION BANK
 BHARATIYA VIDYA BHAVAN S V M PUBLIC SCHOOL, VADODARA QUESTION BANK Ch Light : Reflection and Refraction One mark questions Q1 Q3 What happens when a ray of light falls normally on the surface of a plane
BHARATIYA VIDYA BHAVAN S V M PUBLIC SCHOOL, VADODARA QUESTION BANK Ch Light : Reflection and Refraction One mark questions Q1 Q3 What happens when a ray of light falls normally on the surface of a plane
Physics II. Chapter 23. Spring 2018
 Physics II Chapter 23 Spring 2018 IMPORTANT: Except for multiple-choice questions, you will receive no credit if you show only an answer, even if the answer is correct. Always show in the space on your
Physics II Chapter 23 Spring 2018 IMPORTANT: Except for multiple-choice questions, you will receive no credit if you show only an answer, even if the answer is correct. Always show in the space on your
REFRACTION OF LIGHT VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
 REFRACTION OF LIGHT VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. The earth takes 24 h to rotate once about its axis. How much time does the sun take to shift by 1 0 when viewed from the earth? Q-2. What is the maximum
REFRACTION OF LIGHT VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. The earth takes 24 h to rotate once about its axis. How much time does the sun take to shift by 1 0 when viewed from the earth? Q-2. What is the maximum
Phy 212: General Physics II
 Phy 212: General Physics II Chapter 34: Images Lecture Notes Geometrical (Ray) Optics Geometrical Optics is an approximate treatment o light waves as straight lines (rays) or the description o image ormation
Phy 212: General Physics II Chapter 34: Images Lecture Notes Geometrical (Ray) Optics Geometrical Optics is an approximate treatment o light waves as straight lines (rays) or the description o image ormation
PHYS 160 Astronomy. When analyzing light s behavior in a mirror or lens, it is helpful to use a technique called ray tracing.
 Optics Introduction In this lab, we will be exploring several properties of light including diffraction, reflection, geometric optics, and interference. There are two sections to this lab and they may
Optics Introduction In this lab, we will be exploring several properties of light including diffraction, reflection, geometric optics, and interference. There are two sections to this lab and they may
Chapter 25. Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Geometric Optics Practice Problems. Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror.
 Geometric Optics Practice Problems Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Practice Problems - Mirrors Classwork
Geometric Optics Practice Problems Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Practice Problems - Mirrors Classwork
Physics 132: Lecture Fundamentals of Physics
 Physics 132: Lecture Fundamentals of Physics II Agenda for Today Mirrors Concave Convex e Mirror equation Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Curved mirrors A Spherical Mirror: section of a sphere. R light ray
Physics 132: Lecture Fundamentals of Physics II Agenda for Today Mirrors Concave Convex e Mirror equation Physics 201: Lecture 1, Pg 1 Curved mirrors A Spherical Mirror: section of a sphere. R light ray
Practice Problems (Geometrical Optics)
 1 Practice Problems (Geometrical Optics) 1. A convex glass lens (refractive index = 3/2) has a focal length of 8 cm when placed in air. What is the focal length of the lens when it is immersed in water
1 Practice Problems (Geometrical Optics) 1. A convex glass lens (refractive index = 3/2) has a focal length of 8 cm when placed in air. What is the focal length of the lens when it is immersed in water
Dr. Todd Satogata (ODU/Jefferson Lab) Monday, April
 University Physics 227N/232N Mirrors and Lenses Homework Optics 2 due Friday AM Quiz Friday Optional review session next Monday (Apr 28) Bring Homework Notebooks to Final for Grading Dr. Todd Satogata
University Physics 227N/232N Mirrors and Lenses Homework Optics 2 due Friday AM Quiz Friday Optional review session next Monday (Apr 28) Bring Homework Notebooks to Final for Grading Dr. Todd Satogata
Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13)
 Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13) Complete the following questions in preparation for your test on FRIDAY. The notes that you need are in italics. Try to answer it on your own first, then check with
Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13) Complete the following questions in preparation for your test on FRIDAY. The notes that you need are in italics. Try to answer it on your own first, then check with
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS X REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT QUESTION BANK
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS X REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT QUESTION BANK 1. Q. A small candle 2.5cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of concave mirror of radius
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS X REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT QUESTION BANK 1. Q. A small candle 2.5cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of concave mirror of radius
Astronomy 80 B: Light. Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson
 Astronomy 80 B: Light Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson Sensitive Countries LLNL field trip 2003 April 29 80B-Light 2 Topics for Today Optical illusion Reflections
Astronomy 80 B: Light Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson Sensitive Countries LLNL field trip 2003 April 29 80B-Light 2 Topics for Today Optical illusion Reflections
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL JALANDHAR. (a) Assignment will be discussed and solved in the Class. ( In Physics Notebook)
 DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL JALANDHAR DELHI REVISION ASSIGNMENT NO. 3 Instructions: SUBJECT: PHYSICS CLASS:10 Previous Year Questions (Miscellaneous ) (a) Assignment will be discussed and solved in the Class.
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL JALANDHAR DELHI REVISION ASSIGNMENT NO. 3 Instructions: SUBJECT: PHYSICS CLASS:10 Previous Year Questions (Miscellaneous ) (a) Assignment will be discussed and solved in the Class.
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Real and Virtual Images Real images can be displayed on screens Virtual Images can not be displayed onto screens. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature When the object is very far
Chapter 36 Image Formation Real and Virtual Images Real images can be displayed on screens Virtual Images can not be displayed onto screens. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature When the object is very far
Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems
 Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems We describe the path of light as straight-line rays And light rays from a very distant point arrive parallel 145 Phys 24.1 Mirrors Standing away from a plane mirror shows
Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems We describe the path of light as straight-line rays And light rays from a very distant point arrive parallel 145 Phys 24.1 Mirrors Standing away from a plane mirror shows
Test Review # 8. Physics R: Form TR8.17A. Primary colors of light
 Physics R: Form TR8.17A TEST 8 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 8 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Physics R: Form TR8.17A TEST 8 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 8 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Lecture 17. Image formation Ray tracing Calculation. Lenses Convex Concave. Mirrors Convex Concave. Optical instruments
 Lecture 17. Image formation Ray tracing Calculation Lenses Convex Concave Mirrors Convex Concave Optical instruments Image formation Laws of refraction and reflection can be used to explain how lenses
Lecture 17. Image formation Ray tracing Calculation Lenses Convex Concave Mirrors Convex Concave Optical instruments Image formation Laws of refraction and reflection can be used to explain how lenses
PRINCIPLE PROCEDURE ACTIVITY. AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit.
 ACTIVITY 12 AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Two razor blades, one adhesive tape/cello-tape, source of light (electric bulb/ laser pencil), a piece
ACTIVITY 12 AIM To observe diffraction of light due to a thin slit. APPARATUS AND MATERIAL REQUIRED Two razor blades, one adhesive tape/cello-tape, source of light (electric bulb/ laser pencil), a piece
!"#$%&$'()(*'+,&-./,'(0' focal point! parallel rays! converging lens" image of an object in a converging lens" converging lens: 3 easy rays" !
 !"#$%&$'()(*'+,&-./,'(0' converging lens"! +,7$,$'! 8,9/4&:27'473'+,7$,$'! 84#';%4?.4:27' 1234#5$'126%&$'''! @4=,/4$'! 1",'A.=47'>#,*'+,7$,$'473'B4
!"#$%&$'()(*'+,&-./,'(0' converging lens"! +,7$,$'! 8,9/4&:27'473'+,7$,$'! 84#';%4?.4:27' 1234#5$'126%&$'''! @4=,/4$'! 1",'A.=47'>#,*'+,7$,$'473'B4
General Physics II. Optical Instruments
 General Physics II Optical Instruments 1 The Thin-Lens Equation 2 The Thin-Lens Equation Using geometry, one can show that 1 1 1 s+ =. s' f The magnification of the lens is defined by For a thin lens,
General Physics II Optical Instruments 1 The Thin-Lens Equation 2 The Thin-Lens Equation Using geometry, one can show that 1 1 1 s+ =. s' f The magnification of the lens is defined by For a thin lens,
Physics 6C. Cameras and the Human Eye. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 6C Cameras and the Human Eye CAMERAS A typical camera uses a converging lens to focus a real (inverted) image onto photographic film (or in a digital camera the image is on a CCD chip). Light goes
Physics 6C Cameras and the Human Eye CAMERAS A typical camera uses a converging lens to focus a real (inverted) image onto photographic film (or in a digital camera the image is on a CCD chip). Light goes
GRADE 11-LESSON 2 PHENOMENA RELATED TO OPTICS
 REFLECTION OF LIGHT GRADE 11-LESSON 2 PHENOMENA RELATED TO OPTICS 1.i. What is reflection of light?.. ii. What are the laws of reflection? a...... b.... iii. Consider the diagram at the right. Which one
REFLECTION OF LIGHT GRADE 11-LESSON 2 PHENOMENA RELATED TO OPTICS 1.i. What is reflection of light?.. ii. What are the laws of reflection? a...... b.... iii. Consider the diagram at the right. Which one
Physics 222, October 25
 Physics 222, October 25 Key Concepts: Image formation by refraction Thin lenses The eye Optical instruments A single flat interface Images can be formed by refraction, when light traverses a boundary between
Physics 222, October 25 Key Concepts: Image formation by refraction Thin lenses The eye Optical instruments A single flat interface Images can be formed by refraction, when light traverses a boundary between
Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms
 CHAPTER 16 14 SECTION Sound and Light Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens to light when it passes from one medium to another? How
CHAPTER 16 14 SECTION Sound and Light Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens to light when it passes from one medium to another? How
OPTICS DIVISION B. School/#: Names:
 OPTICS DIVISION B School/#: Names: Directions: Fill in your response for each question in the space provided. All questions are worth two points. Multiple Choice (2 points each question) 1. Which of the
OPTICS DIVISION B School/#: Names: Directions: Fill in your response for each question in the space provided. All questions are worth two points. Multiple Choice (2 points each question) 1. Which of the
