IMAGE ILLUMINATION (4F 2 OR 4F 2 +1?)
|
|
|
- Susanna George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IMAGE ILLUMINATION ( OR +?) BACKGROUND Publications abound wit two differing expressions for calculating image illumination, te amount of radiation tat transfers from an object troug an optical system to an image,. Te discrepancy frequently appears in equations defining te response of an optical or infrared detector to an emitting object in a viewed scene, te two competing forms being R and R, () Were R is te response and F is te optical f/number. Te f/number is defined by f F, () D were f is te effective focal lengt of te optical system and D is te diameter of te entrance pupil. Te popular understanding is tat te first form is an approximation of te second. Te purpose of tis paper is to demonstrate tat te first is rigorously correct for a well designed optical system, and te second results from a paraxial approximation. BASIC OPTICS Figure sows an optical system imaging an object located in object space between te first focal plane F and infinity, te image occurring in image space between te second focal plane F and infinity. Tere are several points and surfaces of interest. Te image space focal plane F is te location of te image of an object located at infinity in object space. Tat is, all parallel rays incident on te optical system in object space will converge to a single point in image space, and tat point will be in te plane F. Similarly, all rays emanating from a point in te plane F will emerge as a parallel bundle in image; i.e., tey will create image of te point at infinity in image space. F P N N P A A F R M R FIGURE KEY FEATURES OF AN OPTICAL SYSTEM. Page of 6
2 Te planes N and N in Figure are, respectively, te first and second nodal planes, wic are te planes normal to te optical axis and passing troug te nodal points. Te nodal points are te on axis points for wic a ray passing troug one of tem at a small angle emerges from te oter at te same angle. Te effective focal lengt (efl), or simply focal lengt, of an optical system is te distance between te focal plane and te corresponding nodal plane. Te tird set of surfaces of interest are te principal surfaces, often call te principal planes because tey can be approximated by planes in te paraxial approximation. Te principal surface P in image space is defined by te intersection of rays parallel to te optical axis in object space wit teir corresponding converging rays in image space. Te principal surface P in object space is similarly defined. A pair of planes defined suc tat an object in one of te planes creates an image in te oter is known a set of conjugate planes. Tus, te plane conjugate to F is at infinity in image space, and te plane conjugate to F is at infinity in object space. In Figure, te planes A and A are conjugate. A well known teorem of optics, te Abbe sine condition 3, states tat for rays in conjugate planes nysin nysin, (3) were n is te index of refraction, y is te ray eigt in te object or image plane, is te angle between te ray and te optical axis, and te subscripts and designate object space and image space, respectively. Tis condition must be valid if te optical system is well corrected for coma. Distances are defined as positive above te optical axis and positive to te rigt of te nodal point in eac space. Note tat for a converging optic y and y will generally ave opposite signs, as will and. If we assume te object and te image bot exist in te same medium (usually air), ten te condition is y sin y sin. (4) ANALYSIS GENERAL CASE A S N N S A F 3 F 4 Z FIGURE MAPPING OF RAYS FROM CONJUGATE PLANES OF AN OPTICAL SYSTEM. Plane A in Figure is located a distance (< 0) to te left of te first nodal plane N, and plane A is located a distance (>0) to te rigt of te second nodal plane N. Te surface S is a spere of radius Page of 6
3 centered at point, and surface S is a spere of radius centered at point 4, te axial point in te image plane. Consider an object space ray tat emanates from a source at point, and tat strikes surface S at a eigt above te axis. We ave and terefore, from Eq. (3), Now te magnification of te instrument is sin sin, (5) y y. (6) M y y, (7) even toug y may be infinitesimally small, so sin. (8) Tis means tat a ray emitted from point emerges from sperical surface S at te same eigt tat it strikes sperical surface S. Now, if we allow, ten 0, S becomes a plane coincident wit te first nodal plane, f (te effective focal lengt), and S becomes a spere centered at te intersection of F and te optical axis. If we ten consider a marginal ray (i.e., a ray tat intersects S at te maximum aperture), ten sin D f F, (9) were F is te f/number. In words, tis says tat a ray parallel to te optical axis in object space produces a ray tat passes troug te image space focal point, and te two rays intersect on a spere of radius f centered at te focal point in image space. Tat is, te principal surface in image space is a spere 4. A similar argument wit te spaces reversed would sow tat te same olds true in object space. Tese sperical surfaces are represented in Figure by P and P. Te power received from infinity by a small, Lambertian detector at te focal plane of a lossless optical system is max image cos sin 0 sin max P B A d B A, (0) were B 0 is te brigtness of te source (W/cm sr), te cos in te integral reflects te fact tat te effective area of te detector for te off axis contributions is te projected area, and max is te cone alfangle of te ray bundle as viewed from te detector. P B A image, () Page 3 of 6
4 PARAXIAL APPROXIMATION Note tat if we worked in te paraxial approximation were te principal surface in image space is a plane, ten we would ave and so sin In tis case we would ave tan, () F. (3) B0 Adet Pimage. (4) Te form Eq. (4) is terefore only valid in te paraxial approximation (i.e., large f/numbers), Eq. () being te generally valid form. A SIMPLE ALTERNATIVE DERIVATION OF THE CORRECT FORM Anoter way to look at te problem is to consider te source side; i.e., to consider te portion of radiation emitted by te source, collected by te optics, and incident on te detector. Consider an onaxis detector pixel of small x det y det sie, and consider te rays emitted from te peripery of te pixel and passing troug te image space nodal point, as illustrated in Figure 3. Tese rays will emerge from te object space nodal point and form a rectangle of sie x tgt y tgt in object space. Tis defines te area of object space tat is exactly imaged onto te axial pixel; i.e., all te radiation tat is emitted from tat target area and collected by te lens will impinge on te pixel, but no oter scene radiation will. Te area of te target is simply R R R A x y x y A f f f tgt det det det det det Lens. (5) x tgt y tgt x det y det R f FIGURE 3 ENERGY COLLECTED BY A SINGLE PIXEL. Te radiation collected by te optics from tat area of te target is given by P B0 A sin, (6) image tgt opt were opt is te alf angle subtended by te optical aperture as viewed from te target. Now, Page 4 of 6
5 so, from Eqs. (5), (6) and (7), sin opt R D D, (7) R D 4 B A R B A Pimage B A f R D 4 R D 4 R 0 det. (8) OTHER CONSIDERATIONS CAVEATS It sould be noted tat image illumination is not necessarily te same as te radiation sensed by te detector, and for more reasons tat just absorption efficiency. If te only issue were te absorption efficiency we could simply introduce a multiplier, wic could be wavelengt dependent, and tis is te usual approximation. Tat approac assumes te detector to be Lambertian; i.e., it assumes tat te absorption efficiency is independent of te angle of incidence. A real detector does not generally beave tat way, for a couple of reasons. First, wen an electromagnetic wave is incident upon a surface, te reflection and transmission depend on bot te angle of incidence and te polariation, according to te Fresnel equations. In addition to tis, most igly efficient absorbers make use of anti reflection coatings or oter suc structures wose beavior depends in some resonant manner on te wavelengt of te radiation. Canging te angle of incidence canges te effective optical tickness of eac layer of tese structures, tereby canging overall efficiency. Canging te f/number canges te cone angle of te radiation incident on te detector. A small cange in f/number will cange te cone by a tin cone saped sell, and te absorption of tat energy will, in general, differ on average from te bulk of te cone. Depending on te design of te absorption structure and on te spectral composition of te incident energy, tis can eiter improving or degrading te average absorption efficiency, tereby distorting te apparent dependence on f/number of Eq. (). ILLUMINATION VS. RANGE Note tat Eq. (8) (before te limit R ) also predicts a cange in image illumination vs. distance to te target. For many sensors tis is irrelevant because R>>D, but tere are instances were tis is not valid. An important example is te indoor use of a radiometric termal imaging sensor, were te objects viewed can be very close. Pysically, two tings appen as te viewed object moves closer to te optical aperture. Assuming te position of te focal is adjusted to keep te object in focus, te magnification increases as te object come closer. Tat means a smaller portion of te image cover on a single pixel, tereby reducing te illumination. At te same time te solid angle subtended by te optical aperture (relative to te object) increases. Tis as te effect of increasing te illumination. Te first effect wins by a sligt margin, resulting in a small net loss of illumination. It is also important to remember tat te distance to te viewed object sould be measured from te first nodal point, not from te first surface of te lens or te lens ousing. Tis effect can be important, but it can also be overwelmed by a cange in te effective optical aperture as te object moves closer. If te entrance pupil is pysical stop in front of te lens, a close object can emit rays tat pass troug te stop, but teir angle is sufficiently steep tat tey strike anoter stop beind te entrance pupil. If te stop is internal to te lens te effect will be different still. Page 5 of 6
6 Niclaus, F., Decarat, A., Jansson, C. and Stemme, G., Performance model for uncooled infrared bolometer arrays and performance predictions of bolometers operating at atmosperic pressure, Infrared Pysics & Tecnology, Vol. 5, No. 3, Jan 008, p.68. Ricwine, R., Balcerak, R., Rapac, C., Freyvogel, K. and Sood, A., A Compreensive Model for Bolometer Element and Uncooled Array Design and Imaging Sensor Performance Prediction, Proc. SPIE, Vol. 694, Born, M. and Wolf, E., Principles of Optics, 4 t Ed., Pergamon Press, 970, p Smit, Warren J., Modern Optical Engineering, 4 t Ed., McGraw Hill, 008, p. 3. Page 6 of 6
h = v h 2 = height of the object is negative for inverted image and positive for erect image. is always positive. Direction of incident light
 6. C a p t e r at G l a n c e Ligt related penomena can be studied wit mirrors and lenses. A mirror is a reflecting surface wile a lens is a transparent material. Mirrors are mainly of tree types : plane
6. C a p t e r at G l a n c e Ligt related penomena can be studied wit mirrors and lenses. A mirror is a reflecting surface wile a lens is a transparent material. Mirrors are mainly of tree types : plane
OPTI-502 Optical Design and Instrumentation I John E. Greivenkamp Homework Set 5 Fall, 2018
 Homework Set 5 all, 2018 Assigned: 9/26/18 Lecture 11 Due: 10/3/18 Lecture 13 Midterm Exam: Wednesday October 24 (Lecture 19) 5-1) Te following combination of tin lenses in air is in a telepoto configuration:
Homework Set 5 all, 2018 Assigned: 9/26/18 Lecture 11 Due: 10/3/18 Lecture 13 Midterm Exam: Wednesday October 24 (Lecture 19) 5-1) Te following combination of tin lenses in air is in a telepoto configuration:
Telescopes and Detectors
 Telescopes and Detectors 1 Reflection and Refraction Telescopes and lenses work because of te way ligt beaves at te interface between two different media. Te speed of ligt slows wen it passes from air
Telescopes and Detectors 1 Reflection and Refraction Telescopes and lenses work because of te way ligt beaves at te interface between two different media. Te speed of ligt slows wen it passes from air
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation
 Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
Unit 5 Waveguides P a g e 1
 Unit 5 Waveguides P a g e Syllabus: Introduction, wave equation in Cartesian coordinates, Rectangular waveguide, TE, TM, TEM waves in rectangular guides, wave impedance, losses in wave guide, introduction
Unit 5 Waveguides P a g e Syllabus: Introduction, wave equation in Cartesian coordinates, Rectangular waveguide, TE, TM, TEM waves in rectangular guides, wave impedance, losses in wave guide, introduction
Optimization of high-performance monocentric lenses
 Optimization of ig-performance monocentric lenses Igor Stamenov,* Ilya Agurok, and Josep E. Ford Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive,
Optimization of ig-performance monocentric lenses Igor Stamenov,* Ilya Agurok, and Josep E. Ford Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive,
Center for Academic Excellence. Area and Perimeter
 Center for Academic Excellence Area and Perimeter Tere are many formulas for finding te area and perimeter of common geometric figures. Te figures in question are two-dimensional figures; i.e., in some
Center for Academic Excellence Area and Perimeter Tere are many formulas for finding te area and perimeter of common geometric figures. Te figures in question are two-dimensional figures; i.e., in some
Trigonometric Functions of any Angle
 Trigonometric Functions of an Angle Wen evaluating an angle θ, in standard position, wose terminal side is given b te coordinates (,), a reference angle is alwas used. Notice ow a rigt triangle as been
Trigonometric Functions of an Angle Wen evaluating an angle θ, in standard position, wose terminal side is given b te coordinates (,), a reference angle is alwas used. Notice ow a rigt triangle as been
Directional Derivative, Gradient and Level Set
 Directional Derivative, Gradient and Level Set Liming Pang 1 Directional Derivative Te partial derivatives of a multi-variable function f(x, y), f f and, tell us te rate of cange of te function along te
Directional Derivative, Gradient and Level Set Liming Pang 1 Directional Derivative Te partial derivatives of a multi-variable function f(x, y), f f and, tell us te rate of cange of te function along te
Chapters 1 & 2. Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing
 Chapters 1 & 2 Chapter 1: Photogrammetry Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing Transition from two-dimensional imagery to three-dimensional information Automation
Chapters 1 & 2 Chapter 1: Photogrammetry Definitions and applications Conceptual basis of photogrammetric processing Transition from two-dimensional imagery to three-dimensional information Automation
DYNAMIC BEAM FORMING USING CHIRP SIGNALS
 BeBeC-018-D04 DYNAMIC BEAM FORMING USING CHIRP SIGNALS Stuart Bradley 1, Lily Panton 1 and Matew Legg 1 Pysics Department, University of Auckland 38 Princes Street, 1010, Auckland, New Zealand Scool of
BeBeC-018-D04 DYNAMIC BEAM FORMING USING CHIRP SIGNALS Stuart Bradley 1, Lily Panton 1 and Matew Legg 1 Pysics Department, University of Auckland 38 Princes Street, 1010, Auckland, New Zealand Scool of
Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN
 Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN A typical astronomical instrument must maintain about one cubic meter at a pressure of
Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN A typical astronomical instrument must maintain about one cubic meter at a pressure of
Tangents. The f-stops here. Shedding some light on the f-number. by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann
 Tangents Shedding some light on the f-number The f-stops here by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann The f-number has peen around for nearly a century now, and it is certainly one of the fundamental
Tangents Shedding some light on the f-number The f-stops here by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann The f-number has peen around for nearly a century now, and it is certainly one of the fundamental
3D Hole Inspection Using Lens with High Field Curvature
 10.1515/msr-2015-0008 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 15, No. 1, 2015 3D Hole Inspection Using Lens wit Hig Field Curvature Petr Zavyalov Tecnological Design Institute of Scientific Instrument Engineering,
10.1515/msr-2015-0008 MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 15, No. 1, 2015 3D Hole Inspection Using Lens wit Hig Field Curvature Petr Zavyalov Tecnological Design Institute of Scientific Instrument Engineering,
MODERN OPTICS -1. Tutorial Solutions
 MODERN OPTICS - Tutorial Solutions Reision and General Optics All questions ere are general background optics wic will be assumed in tis course. Problem 3 requires tecnical details o te microscope wic
MODERN OPTICS - Tutorial Solutions Reision and General Optics All questions ere are general background optics wic will be assumed in tis course. Problem 3 requires tecnical details o te microscope wic
5.3 Sum and Difference Identities
 SECTION 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities 21 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Wat you ll learn about Cosine of a Difference Cosine of a Sum Sine of a Difference or Sum Tangent of a Difference or Sum Verifying
SECTION 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities 21 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Wat you ll learn about Cosine of a Difference Cosine of a Sum Sine of a Difference or Sum Tangent of a Difference or Sum Verifying
ON TWO-PLANE BALANCING OF SYMMETRIC ROTORS
 Proceedings of ME Turbo Expo 0 GT0 June -5, 0, openagen, Denmark GT0-6806 ON TO-PLNE BLNING OF YMMETRI ROTOR Jon J. Yu, P.D. GE Energy 63 Bently Parkway out Minden, Nevada 8943 U Pone: (775) 5-5 E-mail:
Proceedings of ME Turbo Expo 0 GT0 June -5, 0, openagen, Denmark GT0-6806 ON TO-PLNE BLNING OF YMMETRI ROTOR Jon J. Yu, P.D. GE Energy 63 Bently Parkway out Minden, Nevada 8943 U Pone: (775) 5-5 E-mail:
Indirect Measurement
 exploration Georgia Performance Standards M6G1.c, M6A2.c, M6A2.g Te eigts of very tall structures can be measured indirectly using similar figures and proportions. Tis metod is called indirect measurement.
exploration Georgia Performance Standards M6G1.c, M6A2.c, M6A2.g Te eigts of very tall structures can be measured indirectly using similar figures and proportions. Tis metod is called indirect measurement.
Opti 415/515. Introduction to Optical Systems. Copyright 2009, William P. Kuhn
 Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
Hemispherical Lens Based Imaging Receiver for MIMO Optical Wireless Communications
 Hemisperical Lens Based Imaging Receiver for MIMO Optical Wireless Communications Dr. Tomas. Q. Wang, Dr. Y. Amet Sekercioglu and Prof. Jean Armstrong Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering
Hemisperical Lens Based Imaging Receiver for MIMO Optical Wireless Communications Dr. Tomas. Q. Wang, Dr. Y. Amet Sekercioglu and Prof. Jean Armstrong Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering
Geometric optics & aberrations
 Geometric optics & aberrations Department of Astrophysical Sciences University AST 542 http://www.northerneye.co.uk/ Outline Introduction: Optics in astronomy Basics of geometric optics Paraxial approximation
Geometric optics & aberrations Department of Astrophysical Sciences University AST 542 http://www.northerneye.co.uk/ Outline Introduction: Optics in astronomy Basics of geometric optics Paraxial approximation
Ch 24. Geometric Optics
 text concept Ch 24. Geometric Optics Fig. 24 3 A point source of light P and its image P, in a plane mirror. Angle of incidence =angle of reflection. text. Fig. 24 4 The blue dashed line through object
text concept Ch 24. Geometric Optics Fig. 24 3 A point source of light P and its image P, in a plane mirror. Angle of incidence =angle of reflection. text. Fig. 24 4 The blue dashed line through object
Francesc Casanellas C. Sant Ramon, Aiguafreda - Spain NATURAL PERSPECTIVE
 Francesc Casanellas C. Sant Ramon, 5 08591 Aiguafreda - Spain +34 677 00 00 00 francesc@casanellas.com - www.casanellas.com NATURAL PERSPECTIVE Introduction Te first studies on perspective were made in
Francesc Casanellas C. Sant Ramon, 5 08591 Aiguafreda - Spain +34 677 00 00 00 francesc@casanellas.com - www.casanellas.com NATURAL PERSPECTIVE Introduction Te first studies on perspective were made in
Loading transformers with non sinusoidal currents
 LES00070-ZB rev. Loading transformers wit non sinusoidal currents K Factor Loading transformers wit non sinusoidal currents... Interpretation / example... 6 Copyrigt 007 ABB, All rigts reserved. LES00070-ZB
LES00070-ZB rev. Loading transformers wit non sinusoidal currents K Factor Loading transformers wit non sinusoidal currents... Interpretation / example... 6 Copyrigt 007 ABB, All rigts reserved. LES00070-ZB
Contour Measuring System CONTRACER CV-1000/2000
 Form Measurement Contour Measuring System CONTRACER CV-1000/2000 Catalog No.E4333-218 Digital, cost-effective contour measuring instruments feature excellent portability and versatility. Digital analysis
Form Measurement Contour Measuring System CONTRACER CV-1000/2000 Catalog No.E4333-218 Digital, cost-effective contour measuring instruments feature excellent portability and versatility. Digital analysis
CHAPTER 1 Optical Aberrations
 CHAPTER 1 Optical Aberrations 1.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the concepts of aperture stop and entrance and exit pupils of an optical imaging system. Certain special rays, such as the chief
CHAPTER 1 Optical Aberrations 1.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter starts with the concepts of aperture stop and entrance and exit pupils of an optical imaging system. Certain special rays, such as the chief
On the relation between radiated and conducted RF emission tests
 Presented at te 3 t International Zuric Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, February 999. On te relation between radiated and conducted RF emission tests S. B. Worm Pilips Researc Eindoven, te
Presented at te 3 t International Zuric Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, February 999. On te relation between radiated and conducted RF emission tests S. B. Worm Pilips Researc Eindoven, te
Section 3. Imaging With A Thin Lens
 3-1 Section 3 Imaging With A Thin Lens Object at Infinity An object at infinity produces a set of collimated set of rays entering the optical system. Consider the rays from a finite object located on the
3-1 Section 3 Imaging With A Thin Lens Object at Infinity An object at infinity produces a set of collimated set of rays entering the optical system. Consider the rays from a finite object located on the
Copyright 2005, Favour Education Centre. Mathematics Exercises for Brilliancy Book 3. Applications of trigonometry.
 Unit 20 pplications of trigonometry Important facts 1. Key terms gradient ( 斜率 ), angle of inclination ( 傾斜角 ) angle of elevation ( 仰角 ), angle of depression ( 俯角 ), line of sigt ( 視線 ), orizontal ( 水平線
Unit 20 pplications of trigonometry Important facts 1. Key terms gradient ( 斜率 ), angle of inclination ( 傾斜角 ) angle of elevation ( 仰角 ), angle of depression ( 俯角 ), line of sigt ( 視線 ), orizontal ( 水平線
Design and Implementation of Aperture Coupled Microstrip IFF Antenna
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 1, 2008 1 Design and Implementation of Aperture Coupled Microstrip IFF Antenna M. N. Jazi 1, Z. H. Firouze 2, H. Mirmoammad-Sadegi, and G. Askari 1 Institut National de la Recerce
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 1, 2008 1 Design and Implementation of Aperture Coupled Microstrip IFF Antenna M. N. Jazi 1, Z. H. Firouze 2, H. Mirmoammad-Sadegi, and G. Askari 1 Institut National de la Recerce
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 Scool of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homework 11 Due on Nov. 9, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review te lecture notes.
Scool of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homework 11 Due on Nov. 9, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review te lecture notes.
Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design)
 Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Machine Vision System for Automatic Weeding Strategy in Oil Palm Plantation using Image Filtering Technique
 Macine Vision System for Automatic Weeding Strategy in Oil Palm Plantation using Image Filtering Tecnique Kamarul Hawari Gazali, Mod. Marzuki Mustafa, and Aini Hussain Abstract Macine vision is an application
Macine Vision System for Automatic Weeding Strategy in Oil Palm Plantation using Image Filtering Tecnique Kamarul Hawari Gazali, Mod. Marzuki Mustafa, and Aini Hussain Abstract Macine vision is an application
Calculation of Antenna Pattern Influence on Radiated Emission Measurement Uncertainty
 Calculation of Antenna Pattern Influence on Radiated Emission Measurement Uncertainty Alexander Kriz Business Unit RF-Engineering Austrian Researc Centers GmbH - ARC A-444 Seibersdorf, Austria alexander.kriz@arcs.ac.at
Calculation of Antenna Pattern Influence on Radiated Emission Measurement Uncertainty Alexander Kriz Business Unit RF-Engineering Austrian Researc Centers GmbH - ARC A-444 Seibersdorf, Austria alexander.kriz@arcs.ac.at
Binary Search Tree (Part 2 The AVL-tree)
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland We ave already learned a static version of te BST. In tis lecture, we will make te structure dynamic, namely, allowing it to support updates (i.e., insertions and
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland We ave already learned a static version of te BST. In tis lecture, we will make te structure dynamic, namely, allowing it to support updates (i.e., insertions and
Estimation of Dielectric Constant for Various Standard Materials using Microstrip Ring Resonator
 Journal of Science and Tecnology, Vol. 9 No. 3 (017) p. 55-59 Estimation of Dielectric Constant for Various Standard Materials using Microstrip Ring Resonator Pek Jin Low 1, Famiruddin Esa 1*, Kok Yeow
Journal of Science and Tecnology, Vol. 9 No. 3 (017) p. 55-59 Estimation of Dielectric Constant for Various Standard Materials using Microstrip Ring Resonator Pek Jin Low 1, Famiruddin Esa 1*, Kok Yeow
Cooperative Request-answer Schemes for Mobile Receivers in OFDM Systems
 Cooperative Request-answer Scemes for Mobile Receivers in OFDM Systems Y. Samayoa, J. Ostermann Institut für Informationsverarbeitung Gottfried Wilelm Leibniz Universität Hannover 30167 Hannover, Germany
Cooperative Request-answer Scemes for Mobile Receivers in OFDM Systems Y. Samayoa, J. Ostermann Institut für Informationsverarbeitung Gottfried Wilelm Leibniz Universität Hannover 30167 Hannover, Germany
Compatibility and Safety Volume for Electromagnetic Exposure Limits in Shared Sites for 2G and 3G Wireless Communications
 Compatibility and Safety Volume for Electromagnetic Exposure imits in Sared Sites for G and 3G Wireless Communications Rogelio Jiménez Jiménez*, Diego Ortega abajos*, Florentino Jiménez **, Rafael Herradón**
Compatibility and Safety Volume for Electromagnetic Exposure imits in Sared Sites for G and 3G Wireless Communications Rogelio Jiménez Jiménez*, Diego Ortega abajos*, Florentino Jiménez **, Rafael Herradón**
Contour Measuring System CONTRACER CV-1000/2000
 Form Measurement Contour Measuring System CONTRACER CV-1000/2000 Bulletin No. 1978 Digital, cost-effective contour measuring instruments feature excellent portability and versatility. Digital analysis
Form Measurement Contour Measuring System CONTRACER CV-1000/2000 Bulletin No. 1978 Digital, cost-effective contour measuring instruments feature excellent portability and versatility. Digital analysis
Abstract 1. INTRODUCTION
 Allocating armonic emission to MV customers in long feeder systems V.J. Gosbell and D. Robinson Integral nergy Power Quality Centre University of Wollongong Abstract Previous work as attempted to find
Allocating armonic emission to MV customers in long feeder systems V.J. Gosbell and D. Robinson Integral nergy Power Quality Centre University of Wollongong Abstract Previous work as attempted to find
Astronomy 80 B: Light. Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson
 Astronomy 80 B: Light Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson Sensitive Countries LLNL field trip 2003 April 29 80B-Light 2 Topics for Today Optical illusion Reflections
Astronomy 80 B: Light Lecture 9: curved mirrors, lenses, aberrations 29 April 2003 Jerry Nelson Sensitive Countries LLNL field trip 2003 April 29 80B-Light 2 Topics for Today Optical illusion Reflections
Section 11. Vignetting
 Copright 2018 John E. Greivenkamp 11-1 Section 11 Vignetting Vignetting The stop determines the sie of the bundle of ras that propagates through the sstem for an on-axis object. As the object height increases,
Copright 2018 John E. Greivenkamp 11-1 Section 11 Vignetting Vignetting The stop determines the sie of the bundle of ras that propagates through the sstem for an on-axis object. As the object height increases,
Optical Zoom System Design for Compact Digital Camera Using Lens Modules
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 50, No. 5, May 2007, pp. 1243 1251 Optical Zoom System Design for Compact Digital Camera Using Lens Modules Sung-Chan Park, Yong-Joo Jo, Byoung-Taek You and
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 50, No. 5, May 2007, pp. 1243 1251 Optical Zoom System Design for Compact Digital Camera Using Lens Modules Sung-Chan Park, Yong-Joo Jo, Byoung-Taek You and
Opto Engineering S.r.l.
 TUTORIAL #1 Telecentric Lenses: basic information and working principles On line dimensional control is one of the most challenging and difficult applications of vision systems. On the other hand, besides
TUTORIAL #1 Telecentric Lenses: basic information and working principles On line dimensional control is one of the most challenging and difficult applications of vision systems. On the other hand, besides
Design, Realization And Measurements of Microstrip Patch Antenna Using Three Direct Feeding Modes For 2.45ghz Applications
 International Journal of Computer Engineering and Information Tecnology VOL. 9, NO. 8, August 2017, 150 156 Available online at: www.ijceit.org E-ISSN 2412-8856 (Online) Design, Realization And Measurements
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Information Tecnology VOL. 9, NO. 8, August 2017, 150 156 Available online at: www.ijceit.org E-ISSN 2412-8856 (Online) Design, Realization And Measurements
Chapter 3 Mirrors. The most common and familiar optical device
 Chapter 3 Mirrors The most common and familiar optical device Outline Plane mirrors Spherical mirrors Graphical image construction Two mirrors; The Cassegrain Telescope Plane mirrors Common household mirrors:
Chapter 3 Mirrors The most common and familiar optical device Outline Plane mirrors Spherical mirrors Graphical image construction Two mirrors; The Cassegrain Telescope Plane mirrors Common household mirrors:
Problems on Differential and OP-AMP circuits
 Problems on Difrential and OPAMP circuits. Find te efctive and efctive for te amplifr sown below and find its id and A d, A. Given: is 00. c c L Q Vo Vo Q 0K B 0K B 00K ma 00 ma 00K esistance L connects
Problems on Difrential and OPAMP circuits. Find te efctive and efctive for te amplifr sown below and find its id and A d, A. Given: is 00. c c L Q Vo Vo Q 0K B 0K B 00K ma 00 ma 00K esistance L connects
A Visible Light Localization Aided Optical Wireless System
 2nd IEEE Worksop on Optical Wireless Communications A Visible Ligt Localization Aided Optical Wireless System Giulio Cossu, Marco Presi, Raffaele Corsini, Pallab Coudury, Amir Masood Kalid and Ernesto
2nd IEEE Worksop on Optical Wireless Communications A Visible Ligt Localization Aided Optical Wireless System Giulio Cossu, Marco Presi, Raffaele Corsini, Pallab Coudury, Amir Masood Kalid and Ernesto
OPTICAL TECHNIQUES FOR RELIEF STUDY OF MONA LISA'S WOODEN SUPPORT
 OPTICAL TECHNIQUES FOR RELIEF STUDY OF MONA LISA'S WOODEN SUPPORT Fabrice Brémand, Pascal Doumalin, Jean-Cristope Dupré, Franck Hesser, and Valéry Valle Laboratoire de Mécanique des Solides, CNRS, UMR
OPTICAL TECHNIQUES FOR RELIEF STUDY OF MONA LISA'S WOODEN SUPPORT Fabrice Brémand, Pascal Doumalin, Jean-Cristope Dupré, Franck Hesser, and Valéry Valle Laboratoire de Mécanique des Solides, CNRS, UMR
Image Feature Extraction and Recognition of Abstractionism and Realism Style of Indonesian Paintings
 Image Feature Extraction and Recognition of Abstractionism and Realism Style of Indonesian Paintings Tieta Antaresti R P and Aniati Murni Arymurty Faculty of Computer Science University of Indonesia Depok
Image Feature Extraction and Recognition of Abstractionism and Realism Style of Indonesian Paintings Tieta Antaresti R P and Aniati Murni Arymurty Faculty of Computer Science University of Indonesia Depok
Power Quality Analysis Using An Adaptive Decomposition Structure
 Power Quality Analysis Using An Adaptive Decomposition Structure Doğan Gökan Ece 1 and Ömer Nezi Gerek 1 (1) Dept. of Electrical and Elctronics Engineering, Anadolu University, Scool of Engineering and
Power Quality Analysis Using An Adaptive Decomposition Structure Doğan Gökan Ece 1 and Ömer Nezi Gerek 1 (1) Dept. of Electrical and Elctronics Engineering, Anadolu University, Scool of Engineering and
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry
 Section 5. Fundamental Identities 0 Cater 5 Analytic Trigonometry Section 5. Fundamental Identities Exloration. cos > sec, sec > cos, and tan sin > cos. sin > csc and tan > cot. csc > sin, cot > tan, and
Section 5. Fundamental Identities 0 Cater 5 Analytic Trigonometry Section 5. Fundamental Identities Exloration. cos > sec, sec > cos, and tan sin > cos. sin > csc and tan > cot. csc > sin, cot > tan, and
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Closed-Form Optimality Characterization of Network-Assisted Device-to-Device Communications
 Closed-Form Optimality Caracterization of Network-Assisted Device-to-Device Communications Serve Salmasi,EmilBjörnson, Slimane Ben Slimane,andMérouane Debba Department of Communication Systems, Scool of
Closed-Form Optimality Caracterization of Network-Assisted Device-to-Device Communications Serve Salmasi,EmilBjörnson, Slimane Ben Slimane,andMérouane Debba Department of Communication Systems, Scool of
11.2 Areas of Trapezoids and Kites
 Investigating g Geometry ACTIVITY Use before Lesson 11.2 11.2 Areas of Trapezoids and Kites MATERIALS grap paper straigtedge scissors tape Q U E S T I O N How can you use a parallelogram to find oter areas?
Investigating g Geometry ACTIVITY Use before Lesson 11.2 11.2 Areas of Trapezoids and Kites MATERIALS grap paper straigtedge scissors tape Q U E S T I O N How can you use a parallelogram to find oter areas?
Lens Principal and Nodal Points
 Lens Principal and Nodal Points Douglas A. Kerr, P.E. Issue 3 January 21, 2004 ABSTRACT In discussions of photographic lenses, we often hear of the importance of the principal points and nodal points of
Lens Principal and Nodal Points Douglas A. Kerr, P.E. Issue 3 January 21, 2004 ABSTRACT In discussions of photographic lenses, we often hear of the importance of the principal points and nodal points of
E X P E R I M E N T 12
 E X P E R I M E N T 12 Mirrors and Lenses Produced by the Physics Staff at Collin College Copyright Collin College Physics Department. All Rights Reserved. University Physics II, Exp 12: Mirrors and Lenses
E X P E R I M E N T 12 Mirrors and Lenses Produced by the Physics Staff at Collin College Copyright Collin College Physics Department. All Rights Reserved. University Physics II, Exp 12: Mirrors and Lenses
OPTICAL IMAGING AND ABERRATIONS
 OPTICAL IMAGING AND ABERRATIONS PARTI RAY GEOMETRICAL OPTICS VIRENDRA N. MAHAJAN THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION AND THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA SPIE O P T I C A L E N G I N E E R I N G P R E S S A
OPTICAL IMAGING AND ABERRATIONS PARTI RAY GEOMETRICAL OPTICS VIRENDRA N. MAHAJAN THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION AND THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA SPIE O P T I C A L E N G I N E E R I N G P R E S S A
LINEAR IRRADIATION TYPE UV-LED UNIT. Concentration of optical technology
 LINEAR IRRADIATION TYPE U-LED UNIT Concentration of optical tecnology LINEAR IRRADIATION TYPE U-LED UNIT Offering U-LED ligt sources wit a cluster of potonics tecnology Te LC-L5G U-LED ligt sources ave
LINEAR IRRADIATION TYPE U-LED UNIT Concentration of optical tecnology LINEAR IRRADIATION TYPE U-LED UNIT Offering U-LED ligt sources wit a cluster of potonics tecnology Te LC-L5G U-LED ligt sources ave
Performance Factors. Technical Assistance. Fundamental Optics
 Performance Factors After paraxial formulas have been used to select values for component focal length(s) and diameter(s), the final step is to select actual lenses. As in any engineering problem, this
Performance Factors After paraxial formulas have been used to select values for component focal length(s) and diameter(s), the final step is to select actual lenses. As in any engineering problem, this
Lens Design I. Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 205-04-8 Herbert Gross Summer term 206 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule 04.04. Basics 2.04. Properties of optical systrems I 3 8.04.
Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 205-04-8 Herbert Gross Summer term 206 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule 04.04. Basics 2.04. Properties of optical systrems I 3 8.04.
A REVIEW OF THE NEW AUSTRALIAN HARMONICS STANDARD AS/NZS
 A REVIEW OF THE NEW AUSTRALIAN HARMONICS STANDARD AS/NZS 61000.3.6 Abstract V. J. Gosbell 1, P. Muttik 2 and D.K. Geddey 3 1 University of Wollongong, 2 Alstom, 3 Transgrid v.gosbell@uow.edu.au Harmonics
A REVIEW OF THE NEW AUSTRALIAN HARMONICS STANDARD AS/NZS 61000.3.6 Abstract V. J. Gosbell 1, P. Muttik 2 and D.K. Geddey 3 1 University of Wollongong, 2 Alstom, 3 Transgrid v.gosbell@uow.edu.au Harmonics
IMAGE FORMATION. Light source properties. Sensor characteristics Surface. Surface reflectance properties. Optics
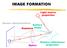 IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Fast Restoration of Warped Document Image based on Text Rectangle Area Segmentation
 1162 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE, VOL. 8, NO. 5, MAY 2013 Fast Restoration of Warped Document Image based on Tet Rectangle Area Segmentation Kuo-Hsien Hsia Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering,
1162 JOURNAL OF SOFTWARE, VOL. 8, NO. 5, MAY 2013 Fast Restoration of Warped Document Image based on Tet Rectangle Area Segmentation Kuo-Hsien Hsia Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering,
The deterministic EPQ with partial backordering: A new approach
 Omega 37 (009) 64 636 www.elsevier.com/locate/omega Te deterministic EPQ wit partial backordering: A new approac David W. Pentico a, Mattew J. Drake a,, Carl Toews b a Scool of Business Administration,
Omega 37 (009) 64 636 www.elsevier.com/locate/omega Te deterministic EPQ wit partial backordering: A new approac David W. Pentico a, Mattew J. Drake a,, Carl Toews b a Scool of Business Administration,
Breaking Down The Cosine Fourth Power Law
 Breaking Down The Cosine Fourth Power Law By Ronian Siew, inopticalsolutions.com Why are the corners of the field of view in the image captured by a camera lens usually darker than the center? For one
Breaking Down The Cosine Fourth Power Law By Ronian Siew, inopticalsolutions.com Why are the corners of the field of view in the image captured by a camera lens usually darker than the center? For one
A Guide for the Assessment and Mitigation of Bleed, Gloss Change, and Mold in Inkjet Prints During High-humidity Conditions
 A Guide for te Assessment and Mitigation of Bleed, Gloss Cange, and Mold in Inkjet Prints During Hig-umidity Conditions Jennifer Burger; University of Rocester and Daniel Burge; Image Permanence Institute,
A Guide for te Assessment and Mitigation of Bleed, Gloss Cange, and Mold in Inkjet Prints During Hig-umidity Conditions Jennifer Burger; University of Rocester and Daniel Burge; Image Permanence Institute,
Lens Design I. Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 207-04-20 Herbert Gross Summer term 207 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 207 06.04. Basics 2 3.04. Properties of optical
Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 207-04-20 Herbert Gross Summer term 207 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 207 06.04. Basics 2 3.04. Properties of optical
DAC at 50: The Second 25 Years
 50 Years of DAC: Wat Lies Aead DAC at 50: Te Second 25 Years Rob A. Rutenbar University of Illinois at Urbana-Campaign Editor s notes: Tis paper is based on an invited talk presented at te 50t DAC. It
50 Years of DAC: Wat Lies Aead DAC at 50: Te Second 25 Years Rob A. Rutenbar University of Illinois at Urbana-Campaign Editor s notes: Tis paper is based on an invited talk presented at te 50t DAC. It
Design and Correction of optical Systems
 Design and Correction of optical Sstems Part 5: Properties of Optical Sstems Summer term 2012 Herbert Gross Overview 2 1. Basics 2012-04-18 2. Materials 2012-04-25 3. Components 2012-05-02 4. Paraxial
Design and Correction of optical Sstems Part 5: Properties of Optical Sstems Summer term 2012 Herbert Gross Overview 2 1. Basics 2012-04-18 2. Materials 2012-04-25 3. Components 2012-05-02 4. Paraxial
This study concerns the use of machine learning based
 Modern AI for games: RoboCode Jon Lau Nielsen (jlni@itu.dk), Benjamin Fedder Jensen (bfje@itu.dk) Abstract Te study concerns te use of neuroevolution, neural networks and reinforcement learning in te creation
Modern AI for games: RoboCode Jon Lau Nielsen (jlni@itu.dk), Benjamin Fedder Jensen (bfje@itu.dk) Abstract Te study concerns te use of neuroevolution, neural networks and reinforcement learning in te creation
CAPACITY OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHANNELS WITH CORRELATED JAMMING
 CAPACITY OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHANNELS WITH CORRELATED JAMMING Sabnam Safiee and Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland College Park, MD ABSTRACT We investigate
CAPACITY OF MULTIPLE ACCESS CHANNELS WITH CORRELATED JAMMING Sabnam Safiee and Sennur Ulukus Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Maryland College Park, MD ABSTRACT We investigate
IMAGE SENSOR SOLUTIONS. KAC-96-1/5" Lens Kit. KODAK KAC-96-1/5" Lens Kit. for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors. November 2004 Revision 2
 KODAK for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors November 2004 Revision 2 1.1 Introduction Choosing the right lens is a critical aspect of designing an imaging system. Typically the trade off between image
KODAK for use with the KODAK CMOS Image Sensors November 2004 Revision 2 1.1 Introduction Choosing the right lens is a critical aspect of designing an imaging system. Typically the trade off between image
Energy Savings with an Energy Star Compliant Harmonic Mitigating Transformer
 Energy Savings wit an Energy Star Compliant Harmonic Mitigating Transformer Tony Hoevenaars, P.Eng, Vice President Mirus International Inc. Te United States Environmental Protection Agency s Energy Star
Energy Savings wit an Energy Star Compliant Harmonic Mitigating Transformer Tony Hoevenaars, P.Eng, Vice President Mirus International Inc. Te United States Environmental Protection Agency s Energy Star
Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II. + 1 s i. = 1 f
 Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II Last time, developed idea of ray optics approximation to wave theory Introduced paraxial approximation: rays with θ 1 Will continue to use Started disussing
Phys 531 Lecture 9 30 September 2004 Ray Optics II Last time, developed idea of ray optics approximation to wave theory Introduced paraxial approximation: rays with θ 1 Will continue to use Started disussing
Where a licence is displayed above, please note the terms and conditions of the licence govern your use of this document.
 Annular Apertures in Metallic Screens as Extraordinary Transmission and Frequency Selective Surface Structures Rodríguez-Ulibarri, Pablo; Navarro-Cia, Miguel; Rodriguez-Berral, Raul; Mesa, F; Medina, F;
Annular Apertures in Metallic Screens as Extraordinary Transmission and Frequency Selective Surface Structures Rodríguez-Ulibarri, Pablo; Navarro-Cia, Miguel; Rodriguez-Berral, Raul; Mesa, F; Medina, F;
Fundamental Paraxial Equation for Thin Lenses
 THIN LENSES Fundamental Paraxial Equation for Thin Lenses A thin lens is one for which thickness is "negligibly" small and may be ignored. Thin lenses are the most important optical entity in ophthalmic
THIN LENSES Fundamental Paraxial Equation for Thin Lenses A thin lens is one for which thickness is "negligibly" small and may be ignored. Thin lenses are the most important optical entity in ophthalmic
Methodology To Analyze Driver Decision Environment During Signal Change Intervals: Application of Fuzzy Set Theory
 TRANSPORTATON RESEARCH RECORD 1368 49 Metodology To Analyze Driver Decision Environment During Signal Cange ntervals: Application of Fuzzy Set Teory SHNYA KKUCH AND JEFFREY R. REGNER During a signal cange
TRANSPORTATON RESEARCH RECORD 1368 49 Metodology To Analyze Driver Decision Environment During Signal Cange ntervals: Application of Fuzzy Set Teory SHNYA KKUCH AND JEFFREY R. REGNER During a signal cange
Modelling and Control of Gene Regulatory Networks for Perturbation Mitigation
 Tis article as been accepted for publication in a future issue of tis journal, but as not been fully edited. Content may cange prior to final publication. Citation information: DOI.9/TCBB.., IEEE/ACM IEEE/ACM
Tis article as been accepted for publication in a future issue of tis journal, but as not been fully edited. Content may cange prior to final publication. Citation information: DOI.9/TCBB.., IEEE/ACM IEEE/ACM
A Filtering Scheme for Reducing Harmonics Penetration into Transmission Systems (V1.0)
 A Filtering Sceme for Reducing Harmonics Penetration into Systems (V.) J. W. Hagge, Senior Member, IEEE, and L. L. Grigsby, Fellow, IEEE Abstract--Tis paper presents a novel sceme to reduce armonics penetration
A Filtering Sceme for Reducing Harmonics Penetration into Systems (V.) J. W. Hagge, Senior Member, IEEE, and L. L. Grigsby, Fellow, IEEE Abstract--Tis paper presents a novel sceme to reduce armonics penetration
Algebra Based Physics. Reflection. Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66. Slide 3 / 66. Slide 4 / 66. Slide 5 / 66. Slide 6 / 66.
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
Recommendation ITU-R F (02/2014)
 Recommendation ITU-R F.1336-4 (/14) Reference radiation patterns of omnidirectional, sectoral and oter antennas for te fixed and mobile services for use in saring studies in te frequency range from 4 MHz
Recommendation ITU-R F.1336-4 (/14) Reference radiation patterns of omnidirectional, sectoral and oter antennas for te fixed and mobile services for use in saring studies in te frequency range from 4 MHz
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008
 ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 July 2003+ Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University 11270-04-1
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 July 2003+ Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University 11270-04-1
Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses
 Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 October 26, 2011 Abstract 1 1 Analyzing
Intorduction to light sources, pinhole cameras, and lenses Erik G. Learned-Miller Department of Computer Science University of Massachusetts, Amherst Amherst, MA 01003 October 26, 2011 Abstract 1 1 Analyzing
Section 8. Objectives
 8-1 Section 8 Objectives Objectives Simple and Petval Objectives are lens element combinations used to image (usually) distant objects. To classify the objective, separated groups of lens elements are
8-1 Section 8 Objectives Objectives Simple and Petval Objectives are lens element combinations used to image (usually) distant objects. To classify the objective, separated groups of lens elements are
Grade 10 Mathematics: Question Paper 2
 Matematics(NSC)/Grade 10/ P2 6 Exemplar Grade 10 Matematics: Question Paper 2 MRKS: 100 TIME: 2 ours QUESTION 1 1.1 Give te co-coordinates of, te new co-ordinates ofte point (-2; 5) if: 1.1.1 It is reflected
Matematics(NSC)/Grade 10/ P2 6 Exemplar Grade 10 Matematics: Question Paper 2 MRKS: 100 TIME: 2 ours QUESTION 1 1.1 Give te co-coordinates of, te new co-ordinates ofte point (-2; 5) if: 1.1.1 It is reflected
Channel Estimation Filter Using Sinc-Interpolation for UTRA FDD Downlink
 { Cannel Estimation Filter Using Sinc-Interpolation for UTA FDD Downlink KLAUS KNOCHE, JÜGEN INAS and KAL-DIK KAMMEYE Department of Communications Engineering, FB- University of Bremen P.O. Box 33 4 4,
{ Cannel Estimation Filter Using Sinc-Interpolation for UTA FDD Downlink KLAUS KNOCHE, JÜGEN INAS and KAL-DIK KAMMEYE Department of Communications Engineering, FB- University of Bremen P.O. Box 33 4 4,
Lecture 18: Mobile Radio Propagation: Large Scale Prop. Modeling. Mobile Radio Propagation: Large Scale Propagation Modeling
 EE 499: Wireless & Mobile Communications (08) Mobile Raio Propagation: Large Scale Propagation Moeling Raio Wave Propagation Raio waves suffer from several cannel problems as tey travel troug te air. Some
EE 499: Wireless & Mobile Communications (08) Mobile Raio Propagation: Large Scale Propagation Moeling Raio Wave Propagation Raio waves suffer from several cannel problems as tey travel troug te air. Some
Imaging Instruments (part I)
 Imaging Instruments (part I) Principal Planes and Focal Lengths (Effective, Back, Front) Multi-element systems Pupils & Windows; Apertures & Stops the Numerical Aperture and f/# Single-Lens Camera Human
Imaging Instruments (part I) Principal Planes and Focal Lengths (Effective, Back, Front) Multi-element systems Pupils & Windows; Apertures & Stops the Numerical Aperture and f/# Single-Lens Camera Human
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF MIMO SYSTEM FOR UWB COMMUNICATION
 DESIGN AND ANAYSIS OF IO SYSTE FOR UWB COUNICATION iir N. oanty, onalisa Bol, axmi Prasad isra 3, Sanjat Kumar isra 4 ITER, Siksa O Anusandan University, Bubaneswar, Odisa, 75030, India Seemanta Engineering
DESIGN AND ANAYSIS OF IO SYSTE FOR UWB COUNICATION iir N. oanty, onalisa Bol, axmi Prasad isra 3, Sanjat Kumar isra 4 ITER, Siksa O Anusandan University, Bubaneswar, Odisa, 75030, India Seemanta Engineering
Two-Dimensional Wireless Power Supply to Ubiquitous Robots Using Microwaves
 Paper: Two-Dimensional Wireless Power Supply to Ubiquitous Robots Using Microwaves Hiroyuki Sinoda, Yasutosi Makino, Naosi Yamaira 3,andHirototai 4 Te University of Tokyo 7-3- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 3-8656,
Paper: Two-Dimensional Wireless Power Supply to Ubiquitous Robots Using Microwaves Hiroyuki Sinoda, Yasutosi Makino, Naosi Yamaira 3,andHirototai 4 Te University of Tokyo 7-3- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 3-8656,
Comparison of Downlink Transmit Diversity Schemes for RAKE and SINR Maximizing Receivers
 Comparison of Downlink Transmit Diversity Scemes for RAKE and SINR Maximizing Receivers Massimiliano enardi, Abdelkader Medles and Dirk TM Slock Mobile Communications Department - Institut Eurécom 2229
Comparison of Downlink Transmit Diversity Scemes for RAKE and SINR Maximizing Receivers Massimiliano enardi, Abdelkader Medles and Dirk TM Slock Mobile Communications Department - Institut Eurécom 2229
An Experimental Downlink Multiuser MIMO System with Distributed and Coherently-Coordinated Transmit Antennas
 An Experimental Downlink Multiuser MIMO System wit Distributed and Coerently-Coordinated Antennas Dragan Samardzija, Howard Huang, Reinaldo Valenzuela and Teodore Sizer Bell Laboratories, Alcatel-Lucent,
An Experimental Downlink Multiuser MIMO System wit Distributed and Coerently-Coordinated Antennas Dragan Samardzija, Howard Huang, Reinaldo Valenzuela and Teodore Sizer Bell Laboratories, Alcatel-Lucent,
LENSES. INEL 6088 Computer Vision
 LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
Punctured Binary Turbo-Codes with Optimized Performance
 Punctured Binary Turbo-odes wit Optimized Performance I. atzigeorgiou, M. R. D. Rodrigues, I. J. Wassell Laboratory for ommunication Engineering omputer Laboratory, University of ambridge {ic1, mrdr, iw}@cam.ac.uk
Punctured Binary Turbo-odes wit Optimized Performance I. atzigeorgiou, M. R. D. Rodrigues, I. J. Wassell Laboratory for ommunication Engineering omputer Laboratory, University of ambridge {ic1, mrdr, iw}@cam.ac.uk
Compound Lens Example
 Compound Lens Example Charles A. DiMarzio Filename: twolens 3 October 28 at 5:28 Thin Lens To better understand the concept of principal planes, we consider the compound lens of two elements shown in Figure.
Compound Lens Example Charles A. DiMarzio Filename: twolens 3 October 28 at 5:28 Thin Lens To better understand the concept of principal planes, we consider the compound lens of two elements shown in Figure.
Chapter 36: diffraction
 Chapter 36: diffraction Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction Diffraction from a single slit Intensity in the single slit pattern Multiple slits The Diffraction grating X-ray diffraction Circular apertures
Chapter 36: diffraction Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction Diffraction from a single slit Intensity in the single slit pattern Multiple slits The Diffraction grating X-ray diffraction Circular apertures
