LASER SAFETY. 5 Dye lasers (3-6) to 1 mj/pulse 20 Hz or 1 khz up to 1
|
|
|
- Anthony Wilkerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LASER SAFETY Abstract - This is an in-house manual on safe laser practice. It is designed to supplement government and University regulations, but it is strictly subordinate to them. Introduction Our laboratory resides in rooms 1081 and 1087 of Smith Laboratory. With the exception of a small Helium-Neon laser, every laser in this laboratory is a "Class 4" laser. The Helium-Neon is Class 2. Class 4 is a federal classification meaning that a laser constitutes a hazard to eyes and skin, and can start fires (see the Appendix). Here is a list of the lasers in our lab: Laser Wavelength (nm) Pulse Energy Pulse rate Power (Watts) 1 Millenia 532 (not a pulsed laser) 5 2 Merlin mj/pulse 1 khz 15 3 GCR , 532, , 150, 50 mj/pulse 20 Hz 12, 1.8, Kerr Lens nj/pulse 87 MHz 0.5 Modelocker 5 Dye lasers (3-6) to 1 mj/pulse 20 Hz or 1 khz up to 1 All of the above lasers are pulsed, except for the Millenia, which runs continuously. The pulse width of the others varies from 10 ns to 30 fs, depending on the laser. The visible wavelength range is roughly 400 nm to 750 nm (blue to red). Nonetheless, the Kerr Lens Modelocker is visible because of its power. The GCR 150 wavelength list begins with 1060 nm followed by other values. This laser actually only produces light at 1060 nm, but nonlinear crystals are used to generate the other colors. This raises an important point: non-linear techniques can produce any color in the spectrum besides the many listed above. Finally, most of the lasers in our lab do not operate independently, but jointly in a system. For example, at any time our lab may have several dye lasers in use, and these are pumped either by the Merlin or the GCR 150. Currently, the Millenia, Merlin, and Kerr Lens Modelocker are combined to form a short pulse laser system with these specifications: Short Pulse Laser System Wavelength Pulse Energy Pulse Rate Pulse Width Power nm 1 mj 1 khz 30 fs 1 W The key point is this: There is a broad range of laser wavelengths and energies present in this lab. You will typically have to protect yourself from multiple beams at multiple wavelengths simultaneously. 1
2 Laser Hazards Electrical: More people have been killed by electrocution from the laser electronics than blinded from exposure to a laser beam. Lethal voltages are present in the power supplies of all of our lasers, as well as in the lasers themselves. If you are not experienced working with high voltages in general, and laser power supplies in particular, you have no business doing any work inside a power supply except the regular maintenance described in the relevant laser manual (invariably done with the power off and the power supply unplugged from its electrical outlet). Fire: The only lasers that could easily start a fire are the Millenia and the Merlin. If their beams hit anything flammable, you are almost guaranteed of ignition. Care must be taken with all the lasers, of course. Eye and Skin Damage: The greatest daily hazards are in this area. All of the Class 4 lasers in our lab can easily cause total blindness or painful sores. The type of damage inflicted depends on the wavelength, pulse energy, pulse width, power, and repetition rate. Damage from ultraviolet radiation tends to reside in the outer layers of the skin for body exposure or in the cornea if the eyes are exposed. Low energy/power beams can cause burns like sunburns. Higher energy/power can ablate skin. In general, long-term exposure to ultraviolet beams or even diffuse scatter may lead to cataracts, glaucoma, and skin cancer. Optical and infrared radiation penetrate more deeply into the body. Beams entering the eye are focused by the cornea onto the fovea. The intensity of the beam at the focus can be enormous, even though the total energy present in the beam may be small. Not only can the region of the fovea at the focus be damaged, but the laser can generate a shock wave damaging other parts of the eye. Eye and skin damage may be immediately painful, or not noticed for a time. It is difficult to place an upper limit on the energy a laser pulse can have and not cause blindness because of the many factors involved. Any beam should be considered hazardous. Even diffuse scatter can be dangerous, especially if the radiation is in the ultra-violet. There will in general be many more beams in the lab than the ones coming directly from the lasers. Every time a laser beam passes through any object, there will be reflections from the input and output surfaces. Suppose a laser passes through a lens. One or both of the surfaces will be curved, hence, the reflections that leave the lens will either converge or diverge. The converging beams can hurt nearby people or damage optics. Diverging beams are also dangerous because they can fill a large area with laser radiation. Unless everyone in the lab is careful, the lab will be filled with dangerous light. We work hard to contain all the beams in the lab. 2
3 Personal Safety The next section will cover controlling stray beams. Given that this has been done, an enormous step has already been taken toward protecting yourself. The main threat, then, lies to your hands and eyes. Typically, you will be continuously adjusting optical components, and so necessarily placing your hands close to a beam. Invariably, you will get hit once and awhile. Usually this will just sting a little. There are a few beams in the lab, however, that can give a nasty bruise. Before you modify or work on any system, you must know exactly where all the beams are and how powerful they are. Every intense infrared or ultraviolet beam must have its path clearly marked, or it must be shielded. When you are planning a new beam path, at any wavelength, try to place the optics so they may be easily reached without your hand crossing any beams. Your eyes are your greatest concern - they are the most easily damaged. We have laser goggles which provide some protection from the Millenia, Merlin, and GCR 150 lasers. The degree of protection will vary depending on the wavelength and pulse energy involved (see the Appendix). There is a problem with using goggles, however. Our goggles are nothing more than absorbing filters which try to block certain laser lines while permitting enough ambient room light to transmit so the user can see. Typically, if you tried to block all the wavelengths present in an experiment, you would be unable to see anything at all. Worse the lab is often darkened for one reason or another. Moreover, if you are trying to align a beam you need to be able to see it - just the thing our goggles try to prevent. There will be many times, then, when you will not want to wear goggles or wearing them will not be sufficient protection. Nonetheless, there is much you can do to protect yourself. Eye glasses offer extra protection against ultra-violet light without degrading overall vision. There is often diffuse UV scatter present in the lab and the hazards from long term exposure to such radiation have already been noted. The amount of protection offered varies with wavelength and lens type, but is easy to measure. Eye glasses also present a hazard. No beam should ever be at eye level, but if one were, a user's eye glasses could direct light into his or her eyes that would otherwise miss. The principle threat comes from surface reflections off the lenses from beams directed towards the side of the face. In effect, glasses make the user's eyes bigger targets. As described in the next section, by design beams produced by stray reflections and diffuse scatter travel mostly in a plane at waist height and parallel to the floor. You must never allow your open eyes to intersect this plane. For example, if you drop a tool on the floor, you put yourself at risk when you bend down to pick it up. You can protect yourself by simply keeping your eyes closed until you are below this plane - make this a habit. Often, you will want to look at some part of your apparatus that requires you to place your eyes in a dangerous position if the lasers are present. Do not depend on electronically controlled beam stops to protect your 3
4 eyes and do not use your hands as beam blocks. Use a beam block - a stable mounted shield, or a "beam eater" - a box designed to contain laser beams. There will be times when you wish to view your experiment in progress, and can do so only by placing your eyes near a beam. This is unacceptable. You must be willing to take the time to devise a safe means to view it. Alignment Procedures Most laser accidents occur while aligning an optical system. When you first place a mirror in a beam, you do not know where the reflected beam will go. If the vertical adjustment happens to be near the end of its range from the last time it was used, the beam could be sent careening upward - eventually to reach eye level. Fortunately, it is easy to align a laser system safely. The first rule is to align using the lowest beam power you can. There will usually be times when high power beams must be aligned, but the coarse alignment must always be done at low powers. If you want to direct a beam into an area where someone else is working, you must inform this person and agree amongst yourselves how to do this safely. It may be that one of you will have to wait until the other is done. (This is all obvious, of course. This document does not wish to suggest that safe practice requires much more than common sense. The goal of this document is to guarantee that everyone sees these ideas formally, at least once.) The greatest danger occurs when a mirror is first placed in the beam. This danger is completely nullified if a beam block is placed in the reflected path before the mirror is placed. Since you are doing this coarse alignment with low powers, almost anything will serve as a block. Once the mirror is in place, you can carefully move the block to the location of the next optical component, always keeping the beam on the block. You should follow the same procedure with any optical component. Lenses require a little extra care, however. Here you must also know where the reflections will go and how they are focused, before you place the lens. Also, note that a focusing reflection can easily damage any nearby optic. (If you notice a spark appearing just before or after a lens, that is probably a reflected beam breaking down the air.) The lasers that generate the beams are all at roughly waist height. You should strive to keep your beams at this level. This tends to keep spurious reflections in this plane where they are easy to block. Also, everyone is careful to keep their eyes well above or below this level. However, there will certainly be times when you have to send a beam from one level to another. Just be aware that this is when you are most likely to create a reflected beam moving upward at some random direction. We have a large laboratory, and if this beam is not blocked it will reach eye level. This is simply not acceptable. 4
5 You will often have high power beams present that you no longer need. For example, you could send a 1064 nm beam through a nonlinear, doubling crystal to generate 532 nm light, after which you may no longer need the 1064 nm light. We have high power "beam eaters" that can swallow any (non-focused) beam generated in the laboratory. If none are available, they are easy to construct. Ask someone. Special Hazards This is a description of some components that pose special hazards. Dielectric Mirrors: If a mirror is a dielectric mirror, than it can actually transmit if it is placed at the wrong angle initially. Even if it is at the correct angle, there can be leakage light through it. Usually this can be blocked with black tape. Glan-Thompson Polarizers: These polarizers work by transmitting light of one polarization and reflecting light of the orthogonal polarization. They are often placed in mounts that allow them to be rotated. As one is rotated, the reflected beam traces out a cone which can easily intersect your eye or anyone else's in the laboratory. The output port for the reflected light must be blocked unless you intend to use this light. (Note: if the output port is blocked, you can damage the polarizer if you send a high power beam through it.) Gratings: Here, you just need to be aware that a grating will typically have multiple beams leaving it from the different diffraction orders. Each one must be blocked if it is not used. Dye lasers: These tend to produce a large number of extra beams as well as copious diffuse scatter. This light should be well contained, but do not assume it is. This is difficult to arrange during alignment. Infra-red Viewing Cards: These cards glow red when exposed to infra-red light. They are essential when working with weak infra-red beams. The problem is they are often laminated and the lamination acts as a good reflector. You must always hold one of these cards such that a specular reflection would be directed downward. Actually, this is a good idea for anything you place in the beam path. These cards must not be used in high power beams. Infra-red Viewer: This is a device that converts IR light to electrons which then create an image on a screen. It looks a little like a camera or monocular, however it should not be treated as such. A beam that enters the device can reach your eye. This is for surveying a scene only. Machined Hardware: You will probably have to machine your own mounting hardware on occasion. Generally, this presents no difficulty. Still, you must avoid creating shiny surfaces. These can cause dangerous reflections. If you use aluminum, the hardware can be anodized after the machining is complete if there is a dangerous surface present. Anodization is a 5
6 chemical process that gives aluminum a flat black outer layer. Most of our optical hardware is made from anodized aluminum. Watches and Jewelry: The face of a wrist watch is reflective, as are rings, metal wristbands, and jewelry. If you are wearing a wrist watch and, as you reach towards an optical component, the face intersects a laser beam, you will send a dangerous reflection in an uncontrolled direction. All such apparel should be removed before working with laser radiation. Conclusion This document has described how to work with lasers safely in our lab. The guidelines given should be followed not only for your protection, but to keep you from endangering others. Safe laser practice is mostly common sense - it is easy to be safe. You should keep in mind that most laser accidents have not involved novices, but experienced workers. In part, this may be because experienced workers have had more time to make a mistake. Most likely, however, the problem is lack of caution. A beginning user is especially aware of the dangers involved, and perhaps even a little intimidated. As time goes by, this initial caution is slowly forgotten. There is no reason to be intimidated, but your safety depends on your continued caution. 6
7 APPENDIX Laser Safety Classification Scheme Laser safety standards, accepted world wide, group all lasers into four general hazard classes described in the table. LASER CLASSIFICATIONS Class Description Maximum Power (assuming a cw Argon ion laser) 1 Eye Safe 0.4 µw 2 Theoretical eye hazard 1 mw 3a Marginal eye hazard 5 mw 3b Significant eye hazard 500 mw 4 Serious eye hazard >500 mw Theoretical eye hazard, refers to a case where a person stares into a visible laser source. The maximum power for a given class depends on the wavelength and pulse width. The values given are for an Argon ion laser, which lases at a number of green, blue, and ultraviolet wavelengths, running continuously. Optical Density and Laser Goggles The filtering capability of our lab s laser goggles is listed here (and on the goggles themselves). The transmission as a function of wavelength is specified in terms of "optical density" (OD). If the optical density at some wavelength is d, then the transmission, T, at that wavelength is given by: T = 10 -d. Thus, an OD of 3 would attenuate the intensity by a factor of Note that these goggles will not give much protection from the Short Pulse Laser System. Glendale LGB Laser Goggles Wavelength (nm) Comment OD Ultraviolet to blue > Green, primary Argon laser line > Green > Green, 532 nm = doubled Nd:YAG fundamental > Near infra-red (IR) > ,070 Near IR to IR > ,000 IR > 7 7
880 Quantum Electronics Optional Lab Construct A Pulsed Dye Laser
 880 Quantum Electronics Optional Lab Construct A Pulsed Dye Laser The goal of this lab is to give you experience aligning a laser and getting it to lase more-or-less from scratch. There is no write-up
880 Quantum Electronics Optional Lab Construct A Pulsed Dye Laser The goal of this lab is to give you experience aligning a laser and getting it to lase more-or-less from scratch. There is no write-up
Laser Safety & the Human Eye Recall the human eye is a simple single lens system Crystalline lens provide focus Cornea: outer surface protection
 Laser Safety & the Human Eye Recall the human eye is a simple single lens system Crystalline lens provide focus Cornea: outer surface protection Iris: control light Retina: where image is focused Note
Laser Safety & the Human Eye Recall the human eye is a simple single lens system Crystalline lens provide focus Cornea: outer surface protection Iris: control light Retina: where image is focused Note
National 3 Physics Waves and Radiation. 1. Wave Properties
 1. Wave Properties What is a wave? Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We see waves all the time, for example, ripples on a pond
1. Wave Properties What is a wave? Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We see waves all the time, for example, ripples on a pond
Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light
 Grade 8 Unit 1 Test Student Class Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light 2. Light-producing technologies, such as
Grade 8 Unit 1 Test Student Class Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light 2. Light-producing technologies, such as
NDFG Non-collinear difference frequency generator
 NDFG Non-collinear difference frequency generator Last Rev. 2011.09.21 PREFACE This manual contains user information for the non-collinear deference frequency generator (NDFG). Please, read this part of
NDFG Non-collinear difference frequency generator Last Rev. 2011.09.21 PREFACE This manual contains user information for the non-collinear deference frequency generator (NDFG). Please, read this part of
LASERS. & Protective Glasses. Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection.
 LASERS & Protective Glasses Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection. FACTS Light & Wavelengths Light is a type of what is called electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves, x-rays,
LASERS & Protective Glasses Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection. FACTS Light & Wavelengths Light is a type of what is called electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves, x-rays,
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Unit 1.5 Waves. The number waves per second. 1 Hz is 1waves per second. If there are 40 waves in 10 seconds then the frequency is 4 Hz.
 Unit 1.5 Waves Basic information Transverse: The oscillations of the particles are at right angles (90 ) to the direction of travel (propagation) of the wave. Examples: All electromagnetic waves (Light,
Unit 1.5 Waves Basic information Transverse: The oscillations of the particles are at right angles (90 ) to the direction of travel (propagation) of the wave. Examples: All electromagnetic waves (Light,
Science Focus 8. Light and Optical Systems. Pop Quiz Master (5 questions) for each Topic A C B D C C B C C A D B C A B B C C A C A C D B A C B B C D
 Science Focus 8 Pop Quiz Master (5 questions) for each Topic Light and Optical Systems Answer Key Science Focus 8 Questions Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Topic 1 - What is Light? A C B D C Topic 2 Reflection C
Science Focus 8 Pop Quiz Master (5 questions) for each Topic Light and Optical Systems Answer Key Science Focus 8 Questions Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Topic 1 - What is Light? A C B D C Topic 2 Reflection C
Experimental Physics. Experiment C & D: Pulsed Laser & Dye Laser. Course: FY12. Project: The Pulsed Laser. Done by: Wael Al-Assadi & Irvin Mangwiza
 Experiment C & D: Course: FY1 The Pulsed Laser Done by: Wael Al-Assadi Mangwiza 8/1/ Wael Al Assadi Mangwiza Experiment C & D : Introduction: Course: FY1 Rev. 35. Page: of 16 1// In this experiment we
Experiment C & D: Course: FY1 The Pulsed Laser Done by: Wael Al-Assadi Mangwiza 8/1/ Wael Al Assadi Mangwiza Experiment C & D : Introduction: Course: FY1 Rev. 35. Page: of 16 1// In this experiment we
Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13)
 Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13) Complete the following questions in preparation for your test on FRIDAY. The notes that you need are in italics. Try to answer it on your own first, then check with
Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13) Complete the following questions in preparation for your test on FRIDAY. The notes that you need are in italics. Try to answer it on your own first, then check with
Light has some interesting properties, many of which are used in medicine:
 LIGHT IN MEDICINE Light has some interesting properties, many of which are used in medicine: 1- The speed of light changes when it goes from one material into another. The ratio of the speed of light in
LIGHT IN MEDICINE Light has some interesting properties, many of which are used in medicine: 1- The speed of light changes when it goes from one material into another. The ratio of the speed of light in
Nd: YAG Laser Energy Levels 4 level laser Optical transitions from Ground to many upper levels Strong absorber in the yellow range None radiative to
 Nd: YAG Lasers Dope Neodynmium (Nd) into material (~1%) Most common Yttrium Aluminum Garnet - YAG: Y 3 Al 5 O 12 Hard brittle but good heat flow for cooling Next common is Yttrium Lithium Fluoride: YLF
Nd: YAG Lasers Dope Neodynmium (Nd) into material (~1%) Most common Yttrium Aluminum Garnet - YAG: Y 3 Al 5 O 12 Hard brittle but good heat flow for cooling Next common is Yttrium Lithium Fluoride: YLF
Longitudinal No, Mechanical wave ~340 m/s (in air) 1,100 feet per second More elastic/denser medium = Greater speed of sound
 Type of wave Travel in Vacuum? Speed Speed vs. Medium Light Sound vs. Sound Longitudinal No, Mechanical wave ~340 m/s (in air) 1,100 feet per second More elastic/denser medium = Greater speed of sound
Type of wave Travel in Vacuum? Speed Speed vs. Medium Light Sound vs. Sound Longitudinal No, Mechanical wave ~340 m/s (in air) 1,100 feet per second More elastic/denser medium = Greater speed of sound
Lecture 5: Introduction to Lasers
 Lecture 5: Introduction to Lasers http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/laser History of the Laser v Invented in 1958 by Charles Townes (Nobel prize in Physics 1964) and Arthur Schawlow of Bell Laboratories v Was
Lecture 5: Introduction to Lasers http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/laser History of the Laser v Invented in 1958 by Charles Townes (Nobel prize in Physics 1964) and Arthur Schawlow of Bell Laboratories v Was
Autotracker III. Applications...
 Autotracker III Harmonic Generation System Model AT-III Applications... Automatic Second Harmonic and Third Harmonic Generation of UV Wavelengths Automatic Production of IR Wavelengths by Difference Frequency
Autotracker III Harmonic Generation System Model AT-III Applications... Automatic Second Harmonic and Third Harmonic Generation of UV Wavelengths Automatic Production of IR Wavelengths by Difference Frequency
Human Retina. Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve
 I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Energy of Light 6 10 ev 10 ev 4 1 2eV 40eV KeV MeV Energy
I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Energy of Light 6 10 ev 10 ev 4 1 2eV 40eV KeV MeV Energy
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Science 8 Unit 2 Pack:
 Science 8 Unit 2 Pack: Name Page 0 Section 4.1 : The Properties of Waves Pages By the end of section 4.1 you should be able to understand the following: Waves are disturbances that transmit energy from
Science 8 Unit 2 Pack: Name Page 0 Section 4.1 : The Properties of Waves Pages By the end of section 4.1 you should be able to understand the following: Waves are disturbances that transmit energy from
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Fall 2010 Solid-State
Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Fall 2010 Solid-State
Lab #1 Lenses and Imaging
 Lab #1 Lenses and Imaging (1 week) Contents: 1. Optics Lab Safety 2. New tools: HeNe Laser Optical mounts and positioners 3. Lens focal length measurement 4. Imaging with a lens 5. Compound lens: beam
Lab #1 Lenses and Imaging (1 week) Contents: 1. Optics Lab Safety 2. New tools: HeNe Laser Optical mounts and positioners 3. Lens focal length measurement 4. Imaging with a lens 5. Compound lens: beam
combustion diagnostics
 3. Instrumentation t ti for optical combustion diagnostics Equipment for combustion laser diagnostics 1) Laser/Laser system 2) Optics Lenses Polarizer Filters Mirrors Etc. 3) Detector CCD-camera Spectrometer
3. Instrumentation t ti for optical combustion diagnostics Equipment for combustion laser diagnostics 1) Laser/Laser system 2) Optics Lenses Polarizer Filters Mirrors Etc. 3) Detector CCD-camera Spectrometer
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II
 Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
ID: A. Optics Review Package Answer Section TRUE/FALSE
 Optics Review Package Answer Section TRUE/FALSE 1. T 2. F Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface Refraction is the bending of light as it travels from one medium to another. 3. T 4. F 5. T
Optics Review Package Answer Section TRUE/FALSE 1. T 2. F Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface Refraction is the bending of light as it travels from one medium to another. 3. T 4. F 5. T
Name: Date: Block: Light Unit Study Guide Matching Match the correct definition to each term. 1. Waves
 Name: Date: Block: Light Unit Study Guide Matching Match the correct definition to each term. 1. Waves 2. Medium 3. Mechanical waves 4. Longitudinal waves 5. Transverse waves 6. Frequency 7. Reflection
Name: Date: Block: Light Unit Study Guide Matching Match the correct definition to each term. 1. Waves 2. Medium 3. Mechanical waves 4. Longitudinal waves 5. Transverse waves 6. Frequency 7. Reflection
Technical Notes. Introduction. Optical Properties. Issue 6 July Figure 1. Specular Reflection:
 Technical Notes This Technical Note introduces basic concepts in optical design for low power off-grid lighting products and suggests ways to improve optical efficiency. It is intended for manufacturers,
Technical Notes This Technical Note introduces basic concepts in optical design for low power off-grid lighting products and suggests ways to improve optical efficiency. It is intended for manufacturers,
RENISHAW INVIA RAMAN SPECTROMETER
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE: RENISHAW INVIA RAMAN SPECTROMETER Purpose of this Instrument: The Renishaw invia Raman Spectrometer is an instrument used to analyze the Raman scattered light from samples
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE: RENISHAW INVIA RAMAN SPECTROMETER Purpose of this Instrument: The Renishaw invia Raman Spectrometer is an instrument used to analyze the Raman scattered light from samples
improved stability (compared with
 Picosecond Tunable Systems Nanosecond Lasers NT230 SERIES NT230 series lasers deliver high up to 10 mj energy pulses at 100 Hz pulse repetition rate, tunable over a broad spectral range. Integrated into
Picosecond Tunable Systems Nanosecond Lasers NT230 SERIES NT230 series lasers deliver high up to 10 mj energy pulses at 100 Hz pulse repetition rate, tunable over a broad spectral range. Integrated into
Atlantic. Industrial High Power Picosecond Lasers. features
 Atlantic Industrial High Power Picosecond Lasers lasers have been designed as a versatile tool for a variety of industrial material processing applications. They are compact, OEM rugged, with up to 8 W
Atlantic Industrial High Power Picosecond Lasers lasers have been designed as a versatile tool for a variety of industrial material processing applications. They are compact, OEM rugged, with up to 8 W
Laser Protective Eyewear Guide
 Laser Protective Eyewear Use of Laser Protective Eyewear According to the directives from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare [On Measures to Prevent Injury from Laser Radiation], laser protective
Laser Protective Eyewear Use of Laser Protective Eyewear According to the directives from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare [On Measures to Prevent Injury from Laser Radiation], laser protective
Optics Laboratory Spring Semester 2017 University of Portland
 Optics Laboratory Spring Semester 2017 University of Portland Laser Safety Warning: The HeNe laser can cause permanent damage to your vision. Never look directly into the laser tube or at a reflection
Optics Laboratory Spring Semester 2017 University of Portland Laser Safety Warning: The HeNe laser can cause permanent damage to your vision. Never look directly into the laser tube or at a reflection
Diode Pointer Quick Start Guide
 Important Note: Read all Danger, Warning, Caution terms, symbols, and instructions located in the (Safety & Hazard information) on our website. Reference the Diode Pointer Specifications located on our
Important Note: Read all Danger, Warning, Caution terms, symbols, and instructions located in the (Safety & Hazard information) on our website. Reference the Diode Pointer Specifications located on our
1. INTRODUCTION 2. LASER ABSTRACT
 Compact solid-state laser to generate 5 mj at 532 nm Bhabana Pati*, James Burgess, Michael Rayno and Kenneth Stebbins Q-Peak, Inc., 135 South Road, Bedford, Massachusetts 01730 ABSTRACT A compact and simple
Compact solid-state laser to generate 5 mj at 532 nm Bhabana Pati*, James Burgess, Michael Rayno and Kenneth Stebbins Q-Peak, Inc., 135 South Road, Bedford, Massachusetts 01730 ABSTRACT A compact and simple
Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When you look at yourself in a plane mirror, you
Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When you look at yourself in a plane mirror, you
Atlantic. series. Industrial High Power Picosecond DPSS Lasers
 Atlantic series Industrial High Power Picosecond DPSS Lasers Laser description Laser micromachining is rapidly becoming the material processing technology of choice for numerous small scale, real world
Atlantic series Industrial High Power Picosecond DPSS Lasers Laser description Laser micromachining is rapidly becoming the material processing technology of choice for numerous small scale, real world
ECEN. Spectroscopy. Lab 8. copy. constituents HOMEWORK PR. Figure. 1. Layout of. of the
 ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
ECEN 4606 Lab 8 Spectroscopy SUMMARY: ROBLEM 1: Pedrotti 3 12-10. In this lab, you will design, build and test an optical spectrum analyzer and use it for both absorption and emission spectroscopy. The
Unit 8: Light and Optics
 Objectives Unit 8: Light and Optics Explain why we see colors as combinations of three primary colors. Explain the dispersion of light by a prism. Understand how lenses and mirrors work. Explain thermal
Objectives Unit 8: Light and Optics Explain why we see colors as combinations of three primary colors. Explain the dispersion of light by a prism. Understand how lenses and mirrors work. Explain thermal
LAB 11 Color and Light
 Cabrillo College Name LAB 11 Color and Light Bring colored pencils or crayons to lab if you already have some. What to learn and explore In the previous lab, we discovered that some sounds are simple,
Cabrillo College Name LAB 11 Color and Light Bring colored pencils or crayons to lab if you already have some. What to learn and explore In the previous lab, we discovered that some sounds are simple,
High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers
 High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average powers. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical
High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average powers. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical
NL300 series. Compact Flash-Lamp Pumped Q-switched Nd:YAG Lasers FEATURES APPLICATIONS NANOSECOND LASERS
 NL200 NL210 NL230 NL300 NL740 electro-optically Q-switched nanosecond Nd:YAG lasers produce high energy pulses with 3 6 ns duration. Pulse repetition rate can be selected in range of 5 20 Hz. NL30 HT models
NL200 NL210 NL230 NL300 NL740 electro-optically Q-switched nanosecond Nd:YAG lasers produce high energy pulses with 3 6 ns duration. Pulse repetition rate can be selected in range of 5 20 Hz. NL30 HT models
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department. Waves. Pupil Notes Name:
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Waves Pupil Notes Name: Learning intentions for this unit? Be able to state that waves transfer energy. Be able to describe the difference between longitudinal and
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Waves Pupil Notes Name: Learning intentions for this unit? Be able to state that waves transfer energy. Be able to describe the difference between longitudinal and
Vision 1. Physical Properties of Light. Overview of Topics. Light, Optics, & The Eye Chaudhuri, Chapter 8
 Vision 1 Light, Optics, & The Eye Chaudhuri, Chapter 8 1 1 Overview of Topics Physical Properties of Light Physical properties of light Interaction of light with objects Anatomy of the eye 2 3 Light A
Vision 1 Light, Optics, & The Eye Chaudhuri, Chapter 8 1 1 Overview of Topics Physical Properties of Light Physical properties of light Interaction of light with objects Anatomy of the eye 2 3 Light A
Vixar High Power Array Technology
 Vixar High Power Array Technology I. Introduction VCSELs arrays emitting power ranging from 50mW to 10W have emerged as an important technology for applications within the consumer, industrial, automotive
Vixar High Power Array Technology I. Introduction VCSELs arrays emitting power ranging from 50mW to 10W have emerged as an important technology for applications within the consumer, industrial, automotive
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
Surprises with Light JoAnne Dombrowski
 SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 6.29-2 Figure 1 3. Hold the card with the arrow in front of you at the same distance as the far side of the jars. From this position, move the card away from
SCIENCE EXPERIMENTS ON FILE Revised Edition 6.29-2 Figure 1 3. Hold the card with the arrow in front of you at the same distance as the far side of the jars. From this position, move the card away from
1. Draw the Ray Diagram, name lens or mirror shown and determine the SALT for each picture
 Honors Physics Chapter 22 and 23 Test Name: 1. Draw the Ray Diagram, name lens or mirror shown and determine the SALT for each picture 2. Type of Mirror above: i. SALT of image: S: A: L: T: b. Type of
Honors Physics Chapter 22 and 23 Test Name: 1. Draw the Ray Diagram, name lens or mirror shown and determine the SALT for each picture 2. Type of Mirror above: i. SALT of image: S: A: L: T: b. Type of
Laser processing of materials. Laser safety
 Laser processing of materials Laser safety Prof. Dr. Frank Mücklich Dr. Andrés Lasagni Lehrstuhl für Funktionswerkstoffe Sommersemester 2007 Contents: LASER Safety Laser-tissue interaction Type of interaction
Laser processing of materials Laser safety Prof. Dr. Frank Mücklich Dr. Andrés Lasagni Lehrstuhl für Funktionswerkstoffe Sommersemester 2007 Contents: LASER Safety Laser-tissue interaction Type of interaction
SER: Biological Stains Visualization with Alternate Light Sources
 Sources Safety SAFETY WARNING! Do not look directly into the beam. Safety glasses with the proper viewing filters must always be worn to protect the eyes from the intense light emitted by a forensic light
Sources Safety SAFETY WARNING! Do not look directly into the beam. Safety glasses with the proper viewing filters must always be worn to protect the eyes from the intense light emitted by a forensic light
Physics Learning Guide Name:
 Physics Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have this
Physics Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have this
How-to guide. Working with a pre-assembled THz system
 How-to guide 15/06/2016 1 Table of contents 0. Preparation / Basics...3 1. Input beam adjustment...4 2. Working with free space antennas...5 3. Working with fiber-coupled antennas...6 4. Contact details...8
How-to guide 15/06/2016 1 Table of contents 0. Preparation / Basics...3 1. Input beam adjustment...4 2. Working with free space antennas...5 3. Working with fiber-coupled antennas...6 4. Contact details...8
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
Term Info Picture. A wave that has both electric and magnetic fields. They travel through empty space (a vacuum).
 Waves S8P4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to support the claim that electromagnetic (light) waves behave differently than mechanical (sound) waves. A. Ask questions to develop explanations
Waves S8P4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to support the claim that electromagnetic (light) waves behave differently than mechanical (sound) waves. A. Ask questions to develop explanations
Technische Universität Chemnitz Physikalische Chemie. Laser Safety
 Technische Universität Chemnitz Physikalische Chemie Laser Safety. Lasers and laser systems are classified by their ability to cause biological damage to the eye or skin during use. Class I: Lasers or
Technische Universität Chemnitz Physikalische Chemie Laser Safety. Lasers and laser systems are classified by their ability to cause biological damage to the eye or skin during use. Class I: Lasers or
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2013
 PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2013 Laboratory #1 Week of January 14 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp. 150-170 of "Optics" by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2013 Laboratory #1 Week of January 14 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp. 150-170 of "Optics" by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
Oriel Flood Exposure Sources
 218 Oriel Flood Exposure Sources High intensity outputs CALIBRATION SOURCES Highly uniform, large collimated beams Efficient out of band rejection Timed exposures DEUTERIUM SOURCES ARC SOURCES INCANDESCENT
218 Oriel Flood Exposure Sources High intensity outputs CALIBRATION SOURCES Highly uniform, large collimated beams Efficient out of band rejection Timed exposures DEUTERIUM SOURCES ARC SOURCES INCANDESCENT
Green Team Science - Mrs. Ferdinand
 Date: Homework: May 15, 2018 Waves Study Guide: start reviewing NOW Reminders: Unit Test: Friday, May 18 Unit Test Review: Thursday Turn In Activity 9: Wave Refraction Challenge Question None Agenda /
Date: Homework: May 15, 2018 Waves Study Guide: start reviewing NOW Reminders: Unit Test: Friday, May 18 Unit Test Review: Thursday Turn In Activity 9: Wave Refraction Challenge Question None Agenda /
Operating Instructions for ISSI Series LM2X, LM2X-DM, LM2X-DMHP
 Operating Instructions for ISSI Series LM2X, LM2X-DM, LM2X-DMHP and LM2X-DMHP-RGB LED Modules August 31, 2006 Rev. 1 Caution This LED illuminator is manufactured with very high power LEDs. Please be aware
Operating Instructions for ISSI Series LM2X, LM2X-DM, LM2X-DMHP and LM2X-DMHP-RGB LED Modules August 31, 2006 Rev. 1 Caution This LED illuminator is manufactured with very high power LEDs. Please be aware
PiXL Independence: GCSE Physics Student Booklet KS4. I. Level 1- Multiple Choice Quiz 20 credits. Level 3 - Science in The News 100 credits
 PiXL Independence: GCSE Physics Student Booklet KS4 Topic: Light and electromagnetic waves Contents: I. Level 1- Multiple Choice Quiz 20 credits II. III. IV. Level 2-5 questions, 5 sentences, 5 words 10
PiXL Independence: GCSE Physics Student Booklet KS4 Topic: Light and electromagnetic waves Contents: I. Level 1- Multiple Choice Quiz 20 credits II. III. IV. Level 2-5 questions, 5 sentences, 5 words 10
Devices & Services Company
 Devices & Services Company 10290 Monroe Drive, Suite 202 - Dallas, Texas 75229 USA - Tel. 214-902-8337 - Fax 214-902-8303 Web: www.devicesandservices.com Email: sales@devicesandservices.com D&S Technical
Devices & Services Company 10290 Monroe Drive, Suite 202 - Dallas, Texas 75229 USA - Tel. 214-902-8337 - Fax 214-902-8303 Web: www.devicesandservices.com Email: sales@devicesandservices.com D&S Technical
Basic concepts. Optical Sources (b) Optical Sources (a) Requirements for light sources (b) Requirements for light sources (a)
 Optical Sources (a) Optical Sources (b) The main light sources used with fibre optic systems are: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) Semiconductor lasers (diode lasers) Fibre laser and other compact solid-state
Optical Sources (a) Optical Sources (b) The main light sources used with fibre optic systems are: Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) Semiconductor lasers (diode lasers) Fibre laser and other compact solid-state
UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS
 UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS What is light? Light is simply a name for a range of electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. What characteristic does light have? Light is electromagnetic
UNIT 12 LIGHT and OPTICS What is light? Light is simply a name for a range of electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the human eye. What characteristic does light have? Light is electromagnetic
FPPO 1000 Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual
 Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual 2012 858 West Park Street, Eugene, OR 97401 www.mtinstruments.com Table of Contents Specifications and Overview... 1 General Layout...
Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual 2012 858 West Park Street, Eugene, OR 97401 www.mtinstruments.com Table of Contents Specifications and Overview... 1 General Layout...
Physical Science Physics
 Name Physical Science Physics C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points PSP 5W4 Seeing Problems (divide by 11) Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers
Name Physical Science Physics C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points PSP 5W4 Seeing Problems (divide by 11) Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
Z500. High-Precision Sensor that Measures and Displays an Object's Profile. Profile Measuring System
 Profile Measuring System High-Precision Sensor that Measures and Displays an Object's Profile. Features OMRON's original line beam method provides a complete solution to profile measurement problems. Conventional
Profile Measuring System High-Precision Sensor that Measures and Displays an Object's Profile. Features OMRON's original line beam method provides a complete solution to profile measurement problems. Conventional
The extremely compact laser head is approximately 480 mm long and can
 Compact Flash-Lamp Pumped Q-switched Nd:YAG Lasers FEATURES Rugged sealed laser cavity Up to 1200 mj pulse energy Better than 1 % StDev pulse energy stability 5 20 Hz pulse repetition rate 3 6 ns pulse
Compact Flash-Lamp Pumped Q-switched Nd:YAG Lasers FEATURES Rugged sealed laser cavity Up to 1200 mj pulse energy Better than 1 % StDev pulse energy stability 5 20 Hz pulse repetition rate 3 6 ns pulse
Lesson Title: The Science of Light and Photography Subject Grade Level Timeline. Physical Science minutes. Objectives
 Lesson Title: The Science of Light and Photography Subject Grade Level Timeline Physical Science 5-12 60-90 minutes Objectives This lesson explores some of the ways in which light can be manipulated to
Lesson Title: The Science of Light and Photography Subject Grade Level Timeline Physical Science 5-12 60-90 minutes Objectives This lesson explores some of the ways in which light can be manipulated to
Home-made Infrared Goggles & Lighting Filters. James Robb
 Home-made Infrared Goggles & Lighting Filters James Robb University Physics II Lab: H1 4/19/10 Trying to build home-made infrared goggles was a fun and interesting project. It involved optics and electricity.
Home-made Infrared Goggles & Lighting Filters James Robb University Physics II Lab: H1 4/19/10 Trying to build home-made infrared goggles was a fun and interesting project. It involved optics and electricity.
BASIC LASER SAFETY. 1. Review of Light Waves 5. Stimulated emission 6. II. The Unique Characteristics of Laser Light 6
 BASIC LASER SAFETY SUBJECT PAGE 1. Review of Light Waves 5 Stimulated emission 6 II. The Unique Characteristics of Laser Light 6 A. Monochromaticity 6 B. Directionality 6 C. Coherence 6 111. How a Laser
BASIC LASER SAFETY SUBJECT PAGE 1. Review of Light Waves 5 Stimulated emission 6 II. The Unique Characteristics of Laser Light 6 A. Monochromaticity 6 B. Directionality 6 C. Coherence 6 111. How a Laser
PHYS General Physics II Lab Diffraction Grating
 1 PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab Diffraction Grating In this lab you will perform an experiment to understand the interference of light waves when they pass through a diffraction grating and to determine
1 PHYS 1040 - General Physics II Lab Diffraction Grating In this lab you will perform an experiment to understand the interference of light waves when they pass through a diffraction grating and to determine
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014
 PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014 Laboratory #1 Week of January 13 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp.150-170 of Optics by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014 Laboratory #1 Week of January 13 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp.150-170 of Optics by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
DESIGN OF COMPACT PULSED 4 MIRROR LASER WIRE SYSTEM FOR QUICK MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRON BEAM PROFILE
 1 DESIGN OF COMPACT PULSED 4 MIRROR LASER WIRE SYSTEM FOR QUICK MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRON BEAM PROFILE PRESENTED BY- ARPIT RAWANKAR THE GRADUATE UNIVERSITY FOR ADVANCED STUDIES, HAYAMA 2 INDEX 1. Concept
1 DESIGN OF COMPACT PULSED 4 MIRROR LASER WIRE SYSTEM FOR QUICK MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRON BEAM PROFILE PRESENTED BY- ARPIT RAWANKAR THE GRADUATE UNIVERSITY FOR ADVANCED STUDIES, HAYAMA 2 INDEX 1. Concept
Section 1: Sound. Sound and Light Section 1
 Sound and Light Section 1 Section 1: Sound Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Properties of Sound Sound Intensity and Decibel Level Musical Instruments Hearing and the Ear The Ear Ultrasound and Sonar Sound
Sound and Light Section 1 Section 1: Sound Preview Key Ideas Bellringer Properties of Sound Sound Intensity and Decibel Level Musical Instruments Hearing and the Ear The Ear Ultrasound and Sonar Sound
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color
 Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
4.2W 445nm Laser Diode Component
 1 4.2W 445nm Laser Diode Component This multi-mode laser diode component is pressed fit mounted in an aluminum housing and has an aluminum mountable heat-sink. The laser is set in the heat sink with thermally
1 4.2W 445nm Laser Diode Component This multi-mode laser diode component is pressed fit mounted in an aluminum housing and has an aluminum mountable heat-sink. The laser is set in the heat sink with thermally
INTRODUCTION. 5. Electromagnetic Waves
 INTRODUCTION An electric current produces a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field produces an electric field Because of such a connection, we refer to the phenomena of electricity and magnetism
INTRODUCTION An electric current produces a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field produces an electric field Because of such a connection, we refer to the phenomena of electricity and magnetism
LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points
 WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
Optics looks at the properties and behaviour of light!
 Optics looks at the properties and behaviour of light! Chapter 4: Wave Model of Light Past Theories Pythagoras believed that light consisted of beams made up of tiny particles that carried information
Optics looks at the properties and behaviour of light! Chapter 4: Wave Model of Light Past Theories Pythagoras believed that light consisted of beams made up of tiny particles that carried information
Flash-lamp Pumped Q-switched
 NL120 NL200 NL220 NL230 NL300 NL303D NL310 NL300 series electro-optically Q-switched nanosecond Nd:YAG lasers produce high energy pulses with 3 6 ns duration. Pulse repetition rate can be selected in range
NL120 NL200 NL220 NL230 NL300 NL303D NL310 NL300 series electro-optically Q-switched nanosecond Nd:YAG lasers produce high energy pulses with 3 6 ns duration. Pulse repetition rate can be selected in range
EUV Plasma Source with IR Power Recycling
 1 EUV Plasma Source with IR Power Recycling Kenneth C. Johnson kjinnovation@earthlink.net 1/6/2016 (first revision) Abstract Laser power requirements for an EUV laser-produced plasma source can be reduced
1 EUV Plasma Source with IR Power Recycling Kenneth C. Johnson kjinnovation@earthlink.net 1/6/2016 (first revision) Abstract Laser power requirements for an EUV laser-produced plasma source can be reduced
How to align your laser for two-photon imaging
 How to align your laser for two-photon imaging Two-photon microscopy uses a laser to excite fluorescent molecules (fluorophores) within a sample through emitting short pulses of light at high power. This
How to align your laser for two-photon imaging Two-photon microscopy uses a laser to excite fluorescent molecules (fluorophores) within a sample through emitting short pulses of light at high power. This
OPTICS DIVISION B. School/#: Names:
 OPTICS DIVISION B School/#: Names: Directions: Fill in your response for each question in the space provided. All questions are worth two points. Multiple Choice (2 points each question) 1. Which of the
OPTICS DIVISION B School/#: Names: Directions: Fill in your response for each question in the space provided. All questions are worth two points. Multiple Choice (2 points each question) 1. Which of the
PGx11 series. Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA APPLICATIONS. Available models
 PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA optical parametric devices employ advanced design concepts in order to produce broadly tunable picosecond pulses with nearly Fourier-transform
PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA optical parametric devices employ advanced design concepts in order to produce broadly tunable picosecond pulses with nearly Fourier-transform
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
SCI-PS Light and Optics Pre Assessment Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 SCI-PS Light and Optics Pre Assessment Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1TL2E1 1 If the angle of incidence is 45, what is the angle of reflection? A 120 B 50 C 90 D 45 2 The wave
SCI-PS Light and Optics Pre Assessment Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:1TL2E1 1 If the angle of incidence is 45, what is the angle of reflection? A 120 B 50 C 90 D 45 2 The wave
Physics 9 Wednesday, February 1, 2012
 Physics 9 Wednesday, February 1, 2012 learningcatalytics.com class session ID: 542970 Today: repeat soap bubble; measure λ for laser Today: telescope, human eye Friday: first of 3 days on fluids (liquids,
Physics 9 Wednesday, February 1, 2012 learningcatalytics.com class session ID: 542970 Today: repeat soap bubble; measure λ for laser Today: telescope, human eye Friday: first of 3 days on fluids (liquids,
SELECTION GUIDE MULTIPLE-ORDER QUARTZ WAVEPLATES ZERO-ORDER QUARTZ WAVEPLATES DUAL-WAVELENGTH WAVEPLATES... 85
 WAVEPLATES Mirrors Waveplates are used in applications where the control, synthesis, or analysis of the polarization state of an incident beam of light is required. Our waveplates are constructed of very
WAVEPLATES Mirrors Waveplates are used in applications where the control, synthesis, or analysis of the polarization state of an incident beam of light is required. Our waveplates are constructed of very
CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images. Joshua Levine
 CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images Joshua Levine levinej@clemson.edu Lecture 04 Displays and Optics Sept. 1, 2015 Slide Credits: Kenny A. Hunt Don House Torsten Möller Hanspeter Pfister Agenda Open
CPSC 4040/6040 Computer Graphics Images Joshua Levine levinej@clemson.edu Lecture 04 Displays and Optics Sept. 1, 2015 Slide Credits: Kenny A. Hunt Don House Torsten Möller Hanspeter Pfister Agenda Open
Lens: Lenses are usually made of and have 2 curved surfaces. Draw figure 5.23 on Page 191. Label it clearly and use a ruler for the light rays.
 5.3 Lenses We have seen lenses in our microscopes, cameras or eyeglasses. Lens: Lenses are usually made of and have 2 curved surfaces. Concave lens: A lens curved inward Thinner at the centre than at the
5.3 Lenses We have seen lenses in our microscopes, cameras or eyeglasses. Lens: Lenses are usually made of and have 2 curved surfaces. Concave lens: A lens curved inward Thinner at the centre than at the
Physics 1520, Spring 2013 Quiz 2, Form: A
 Physics 1520, Spring 2013 Quiz 2, Form: A Name: Date: Section 1. Exercises 1. The index of refraction of a certain type of glass for red light is 1.52. For violet light, it is 1.54. Which color of light,
Physics 1520, Spring 2013 Quiz 2, Form: A Name: Date: Section 1. Exercises 1. The index of refraction of a certain type of glass for red light is 1.52. For violet light, it is 1.54. Which color of light,
Draw and label this wave: - What do waves transfer? (They do this without transferring what?) What do all electromagnetic waves have in common?
 What do waves transfer? Draw and label this wave: - (They do this without transferring what?) What do all electromagnetic waves have in common? Name the electromagnetic spectrum from shortest to longest
What do waves transfer? Draw and label this wave: - (They do this without transferring what?) What do all electromagnetic waves have in common? Name the electromagnetic spectrum from shortest to longest
Q1. The diagram shows the oscilloscope traces of two different sounds P and Q. The oscilloscope setting is exactly the same in both cases.
 Q1. The diagram shows the oscilloscope traces of two different sounds P and Q. The oscilloscope setting is exactly the same in both cases. P and Q sound different. Write down two differences in the way
Q1. The diagram shows the oscilloscope traces of two different sounds P and Q. The oscilloscope setting is exactly the same in both cases. P and Q sound different. Write down two differences in the way
Chapter 28. Reflection and Refraction
 Chapter 28 Reflection and Refraction Light takes the path from one point to another that is a. quickest. b. shortest. c. closest to a straight line. d. None of these. Light takes the path from one point
Chapter 28 Reflection and Refraction Light takes the path from one point to another that is a. quickest. b. shortest. c. closest to a straight line. d. None of these. Light takes the path from one point
THEIMER - lamps. The optimal type for every application. Ga - Fe doped: Multi spectrum type TH...2 Ga - Pb doped: Dual spectrum type THS...
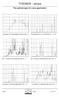 The optimal type for every application 12 12 1 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 3 35 4 45 5 55 6 65 7 Xenon puls: For reprographic camera type KX... 3 32 34 36 38 4 42 44 46 48 5 52 54 56 58 6 Hg undoped: For UV curing
The optimal type for every application 12 12 1 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 3 35 4 45 5 55 6 65 7 Xenon puls: For reprographic camera type KX... 3 32 34 36 38 4 42 44 46 48 5 52 54 56 58 6 Hg undoped: For UV curing
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Physics for Kids. Science of Light. What is light made of?
 Physics for Kids Science of Light What is light made of? This is not an easy question. Light has no mass and is not really considered matter. So does it even exist? Of course it does! We couldn't live
Physics for Kids Science of Light What is light made of? This is not an easy question. Light has no mass and is not really considered matter. So does it even exist? Of course it does! We couldn't live
Ph 77 ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY ATOMIC AND OPTICAL PHYSICS
 Ph 77 ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY ATOMIC AND OPTICAL PHYSICS Diode Laser Characteristics I. BACKGROUND Beginning in the mid 1960 s, before the development of semiconductor diode lasers, physicists mostly
Ph 77 ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY ATOMIC AND OPTICAL PHYSICS Diode Laser Characteristics I. BACKGROUND Beginning in the mid 1960 s, before the development of semiconductor diode lasers, physicists mostly
Light sources can be natural or artificial (man-made)
 Light The Sun is our major source of light Light sources can be natural or artificial (man-made) People and insects do not see the same type of light - people see visible light - insects see ultraviolet
Light The Sun is our major source of light Light sources can be natural or artificial (man-made) People and insects do not see the same type of light - people see visible light - insects see ultraviolet
Chapter: Sound and Light
 Table of Contents Chapter: Sound and Light Section 1: Sound Section 2: Reflection and Refraction of Light Section 3: Mirrors, Lenses, and the Eye Section 4: Light and Color 1 Sound Sound When an object
Table of Contents Chapter: Sound and Light Section 1: Sound Section 2: Reflection and Refraction of Light Section 3: Mirrors, Lenses, and the Eye Section 4: Light and Color 1 Sound Sound When an object
This series of lasers are available with a choice of Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, and Nd:YVO 4. System Reliability
 Photonics Industries DS Series of UV (351/355 nm) diode pumped solid-state Q-switched lasers offer a compact, hands-free system with the long-term reliability that the manufacturing industry demands. Utilizing
Photonics Industries DS Series of UV (351/355 nm) diode pumped solid-state Q-switched lasers offer a compact, hands-free system with the long-term reliability that the manufacturing industry demands. Utilizing
