Standard Puzzle Format
|
|
|
- Lesley Hall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Standard Puzzle Format Specification. bstract This specification defines the Standard Puzzle Format (SPF). SPF is a format to describe the diagrams used for logical puzzles (such as sudoku, fences and tapa). The format is designed to be human readable as well as accessible by computers. It is embedded in the postscript language, which makes it easy to display and print the puzzle diagrams.. General description The general layout of the format is given as follows: prolog << key-value-pair* >> epilog file in SPF-format consists of a prolog, an EPS dictionary and an epilog. The prolog and the epilog can be anything, with the only exception, that the prolog might not contain the sequence <<. The dictionary starts with << and ends with >>. The >> must be preceded by a newline character. etween this two delimiters, the dictionary consists of key-value-pairs. The key always starts at the beginning of a line, that is it is preceded by a newline, and it s first character is a slash (/), immediately followed by the name of the key. Key and value are separated by a space. The key must not contain a space and should consist only of letters (lower and uppercase, which are considered different), digits and underscores.. Some special keys The dictionary has to contain a key called /type with the value being a postscript string containing the name of the puzzletype. This type defines the puzzle specific entries of the dictionary. If there are several formats, the/format can be specified as a version number. If no format is given, it can be assumed to be. The key /sol should also be defined as an boolean value (true or false). This defines, whether the puzzle or the solution of the puzzle should be shown. Of course, this only matters, if the puzzle is to be displayed. The key /author is used to specify the author of the puzzle as a postscript string. description of the puzzle can be given using the /description key. The value is an array of strings. In most cases, the puzzle diagram is given as an SII art image as value of the key /puzzle and the solution is given as value of the key /solution. In both cases, the type of the values is almost always an array of strings. s some applications may need to know the size of the diagram, before they read it, the size should also be given, eighter as X and Y or as size if the diagram has to be a square.. n example The example given on the next page defines the kropki puzzle given on the next page. The prolog consists of some postscript comments which are typical of encapsulated postscript files (EPS). The three dots indicate, that more postscript code can be added at this place. We ll soon have a closer look at the dictionary that follows. fter the dictionary more postscript code can follow. The dictionary defines five key-value-pairs with keys /type, /sol, /size, /puzzle and /description. The value of the type-key is (kropki). The parenthesis are used in postscript to describe a string literal. The value of the sol-key is false, as the file should not show the solution. Indeed no solution is given, which is fine, if the value of the sol-key is false. Next, the size of the diagram is specified. s kropkis are always squares, the size is given with the size-key and has the value of. The value associated with the puzzle-key is the main puzzle. It is defined as an array the brackets, which contains some strings. The strings are arranged to make up for a nice SII art of the puzzle. Last, a description follows, which is in this case only one line: size times. The description should be stuff, the user might know, before he starts to solve the puzzle. In this case the size is given in human readable form.
2 .. -ox %!PS-dobe-. EPSF-. %%Pages: %%oundingox: 7 7 %%ropox: 7 7 %%DocumentData: lean7it %%Page: %%Endomments... << /type (kropki) /sol false /size ( ) ( O ) (+O+ +*+) ( * ) (+ +O+O+) ( O O ) ( ) ] /description [ (size times ) ] >> currentdict copy pop... %%EOF ppendix. Specification of some puzzle types In the following puzzle specific specification the words vertice, edge and cell are used to describe the intersection of the lines, the line segment between such intersections and the area inside of line segments. /X /Y /max /left /top /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ( +---) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] () () () ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional max-key can be given, which denotes the number of letters, starting at the beginning of the alphabet, that can appear in the puzzle. If omitted, is assumed. The max-key cannot be greater than 6. The left-key and the top-key give the maximum number of numbers at the left and at the top of the puzzle. They should be given, as some programms might need them to know in advance the size of the puzzle-key. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers outside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is x + dl + and the height of the diagram is y +dt+, where x is the width of the puzzle, y is the height of the puzzle, l and t are the values of the left- and top-key and d is the value of the digits-key. The place dl dt is marked with a plus. Right of that plus are minuses and below that plus are pipes. They primarily serve to help humans, but the plus might be used by programms to decide upon the values of the left- and top-key if they are omitted. Minuses and pipes might be omitted. Inside the diagram, every cell of the puzzle contains a space or a letter, which has to be in the range given by the max-key. Outside the diagram, the hints are given. The content can be a question mark, a letter in the range specified by the max-key or a number greater or equal to. Rows or columns might also be completely
3 empty, which denotes, that there is no given information about this row or column. If the digits-key is greater than, the numbers at the top are written from top down. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given as single character... D /X /Y /max /digits ( ) ( ) ( +---) ( ) ( #) ( ) ] (D) (#) (D) ] D D D D D D oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional max-key can be given, which denotes the maximum letter in the alphabet, that can appear in the puzzle. If omitted, is assumed. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is x+dm+ and the height of the diagram is y+dm+, where x is the width of the puzzle, y is the height of the puzzle, d is the value of the digits-key and m is the value of the max-key. The place dm dm is marked with a plus. Right of that plus are minuses and below that plus are pipes. They primarily serve to help humans, but the plus might be used by programms to decide upon the value of the max-key if omitted. Minuses and pipes might be omitted. Inside the diagram, every cell of the puzzle contains one character, which can be a letter, a space or a hash key, the later one denoting a field that is blackend. Outside the diagram, the hints are given. t the left they are as many charakters wide, as the digits-key gives. t the top they are as many charakters high, as the digits-key gives. Numbers have to be right or bottom aligned. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the inner cells is given as single character.
4 .. D Diagonal Same as D, but the default for the max key is 5... quarium /digits ( ) ( ) ( # # # ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] (#####) (# ) ( ###) ( # #) (#####) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers outside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is x + d + and the height of the diagram is y +d+, where x and y are the width and the height of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, the edges between two areas are marked by pipes and minuses as well. In the cells, # and - can be given to denote a filled or an empty cell. t the left and the top numbers can be given. Numbers at the left have to be right alligned. Numbers at the top are written top-down and have to be bottom alligned. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given.
5 .5. rukone.6. asic ( ) ( ) ( # ) ( ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( - - ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional digits-key can be given. If given, numbers are used instead of letters. The key gives the maximum number of digits of these numbers. width of the diagram is dx + and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at The cells may contain an uppercase letter or # which is a cell, that must not be used by a path. In case of numbers, the cell may contain a number, which has to be right aligned. etween two cells, there might be minus and pipe symbols to show part of the path. The pipe symbol has to be centered, if not possible it has to be slightly right of the center. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key. /size /digits ( ) ( x ) ( 8 ) ( ) ( + ) ( ) ( ) ( : ) ( ) ( ) ( + - ) ( ) ( ) ] () () () () ] 8 8 The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to and less or equal to 9. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of small numbers inside the diagram. If omitted or less than, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is (d+)s+ and the height of the diagram is s+, where s is the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, the edges between two areas are marked by pipes and minuses as well. In the cells, at the top left a number can be given, which is a large number in this cell. t the top right an operator can be given, which is +, -, x, : or a space. In the bottom row a right aligned number can be given. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the numbers are given. 5
6 .7. ave.8. hatroom /digits ( 5) ( 7 ) ( 6 ) ( 5 ) ( 6## --) ] (# #) ( # ) (# # #) ( # ) ] 7 6 oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is dx and the height of the diagram is y, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the value of the digits-key. ells can contain # to denote part of the walls, - to denote part of the cave or a number, which has to be right alligned. The solution-key has one symbol per cell. The hashsymbol for walls and a space else /X 6 /Y 6 ( - # # ) ( ( ) ( ) ) ( ) ( ) ( ( ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( - - -* -* ) ( ) ( * - - ) ( ) * - ) ( ) ( *- - -@ - ) ( ) ( - -* - ) ( ) ( -@- - - ) ( ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is (d+)x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at The cells are d+ characters wide. If the rightmost character is the hash-key, the symbol in that cell is black. Else it s white. The rest of the cell contains either the which is a phone, or a questionmark or a number, which has to be right alligned. etween two cells, there might be minus and pipe symbols to show part of the path. 6
7 The solution-key gives the puzzle as ascii art. The width of the diagram is x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at The cells are one characters wide. nd might be completely empty. For better reading, the phones might be shown and the numbers as *. etween two cells, there are minus and pipe symbols to show the solution..9. ompass /X /Y /digits (.....) (... 6) ( ) (... ) (.. ) (... ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] 6 6 oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is dx and the height of the diagram is y, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the value of the digits-key. The cells of the puzzle are given as blocks of size d, that contain the clues. The first clue is the top value, the second clue is the right value, the third clue is the left value and the last clue is the bottom value. lues can be numbers, right-alligned, or dots for empty clues. The solution-key gives the puzzle as ascii art. The width of the diagram is x+ and the height of the diagram is y +. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, the edges between two areas are marked by pipes and minuses as well. 7
8 .. oral to upper. /left /top /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( #) ( - ) ( ) ] (## ##) ( ### ) (## ##) (# #) (### ) ] Rows or columns might also be completely empty, which denotes, that there is no given information about this row or column. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given. oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is x + dl + and the height of the diagram is y +dt+, where x is the width of the puzzle, y is the height of the puzzle, l and t are the values of the left- and top-key and d ist the value of the digits-key. The place dl dt is marked with a plus. Right of that plus are minuses and below that plus are pipes. They primarily serve to help humans, but the plus might be used by programms to decide upon the values of the left- and top-key if they are omitted. Minuses and pipes might be omitted. Inside the diagram, every cell of the puzzle contains one character, which can be a # to denote part of the coral and - to a cell which is not part of the coral. Outside the diagram, the hints are given. t the left they are as many charakters wide, as the digits-key gives. t the top they are as many charakters high, as the digits-key gives. Numbers have to be right or bottom aligned. Instead of a number, a questionmark can be used. The order of the numbers can be arbitrary, but as a convenience they should be ordered: First the questionmarks, than the number vom lower 8
9 .. urve Data /X /Y /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ## - ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] /shapes [ [ (+ ) ( ) (+-+) ] [ (+-+) ] [ ( +-+) ( ) (+---+) ( ) (+---+) ] ] ( ) ( ) (+... +) ( ) (+... +) ( # +-+ ) (+... +) ( ) ( ) ] symbols to show part of the path. The shapes-key is an array, where each entry corresponds to the number in the diagram. rray entries start with number. Each entry gives a shape in ascii art. Each shape consists of vertices marked with a plus symbol and edges marked with minus and pipe symbols. Vertices may only occur at places that are in odd rows and columns. Edges must end in a vertice and the whole graph of one shape must be connected. Vertices must not touch orthogonally. There should not be any remaining white space at the borders of a shape, but programs must not rely on this. Shapes must not contain abnormal vertices, that is, vertices, where the shape neigher dissects nor bends nor ends. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. The width of the diagram is x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle. ll vertices at the border are marked as plus symbols, all other vertices are marked as dots. The edges at Inside the diagram, cells can contain a hash symbol which denotes a black cell or a plus symbol which denotes a vertice of a curve. The edges of the curves are given by minus and pipe symbols between cells. If an edge of the graph goes straigt through a cell, that cell must also contain a minus or a pipe symbol. oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is (d+)x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, cells can contain a number, which has to be right aligned or hash symbols, where all places inside of the cell have to be filled with this symbol. etween two cells, there might be minus and pipe 9
10 .. Domino Hunt.. Doubleblock /min /max /digits ( ) ( ## ## ) ( ) ( ## ## ) ( ) ( ## ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ## ## ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ## ## ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ## ) ( ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is (d+)x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, cells can contain a number, which has to be right aligned or hash symbols, where all places inside of the cell have to be filled with this symbol. Horizontal and vertical lines, that separate, can be given as minuses and pipes. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key. /size 5 /digits ( 5 ) ( ) ( ## ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ## ##) ( ## ## ) (## ## ) ( ## ##) (## ## ) ] 5 5 The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is d(x +) + and the height of the diagram is y+, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the value of the digits-key. Each cell can contain a number, which is right alligned, be completely filled with hash-symbols to denote a block or be blank. t the left and the top numbers can be given. They also have to be right alligned. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key, but only the content of the cells is given.
11 .. Easy as /size 5 /max ( ) ( - ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. The max-key gives the position in the alphabet of the last used letter. width and height of the diagram are s +, where s is the size of the puzzle. The letters at the border are given in the leftmost, rightmost column and top and bottom row. In the center, letters and minus-signs can be given. minus sign denotes a cell, that cannot be occupied by a letter. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the center is given..5. Fences There are two formats defined for the fences puzzle: Format is a special format for rectangular grids, than might contain holes of size, but not larger. Format is a more general format, that can handle arbitrary planar graphs..5.. Format /X /Y ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] 6 6 oth have to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, all edges, that belong to the grid (that is, all edges, that are not inside the hole) are marked by pipes and minuses. In the center of all cells, a one digit number can be given. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key, but only the edges, that are part of the solution are marked by minuses and pipes.
12 .5.. Format /node [ [.69. ] [.86 ] [.78. ] [.77 ] [.6. ] [.6 ] [.69. ] [.86.6 ] [.78. ] [.77.6 ] [.6. ] [.57.6 ] [. ] [.69.8 ] [.86. ] [.78.8 ] [.77. ] [.6.8 ] [.57. ] [.69.6 ] [.86 ] [.78.6 ] [.77 ] [.6.6 ] ] /edge [ [ true ] [ true ] [ true ] [ true ] [ 5 6 false ] [ 6 7 true ] [ 7 8 false ] [ 8 9 false ] [ 9 false ] [ true ] [ false ] [ false ] [ 5 true ] [ 5 6 true ] [ 6 7 true ] [ 7 8 true ] [ 9 false ] [ false ] [ false ] [ false ] [ 6 true ] [ 8 false ] [ true ] [ 5 false ] [ 7 true ] [ 9 6 false ] [ 8 true ] [ 9 false ] [ 5 false ] [ 7 false ] ] /area [ [ ] [.77.8 ] [.69 ] [.78 - ] [.6 ] [.86. ] [ ] ] /style [ [ ] ] /area_outline [ [ ] [ ] [ 6 5 ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] ] The node-key describes the nodes of the graph. It s a list of pairs, describing the x- and y-coordinate of the node as floating point numbers. The edge-key describes the edges of the node, as well as the solution of the puzzle. It s a list of three items per entry: The index of the node in the node-key, where the edge starts, the index of the node in the node-key, where the edge ends and a boolean value, telling if this edge is part of the solution or not. The area-key is a list with four items per entry: The first two give x- and y-coordinate of the center of the area. The point defined by this coordinates has to be inside that area. It is often the balance point, but not necessary. The third entry is the value to be placed at that point, with - as a place holder for an empty areas. The last number gives the number of style to use when rendering this number. s some programs my rely upon it, all empty areas have to be given in this list. The style-key is a list with six items per entry. They define an affine transformation, the first four define the matrix and the last two the translation vector. This transformation is used to describe the rendering style of that number. n optional area_outline-key can be given. It is a list of polygons. The first entry of a polygon is the number of edges of that polygon. The other entries are indices to the list of edges. They have to be sorted to form a path arround the area. The information provided by the area_outline-key can be deduced from
13 the values of the other keys. ut as this is not an easy task to do, some programs might not work without this information..6. Fillomino There are two formats defined for the fillomino puzzle: Format is a special format for rectangular grids. Format is a more general format, that can handle arbitrary planar graphs..6.. Format /X /Y /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is dx + and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols. Edges can be marked by minus or pipe symbols. In the center of all cells, a number can be given. It has to be right aligned. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key, but only the content of the cells is given.
14 .6.. Format /edge [ [ true ] [ false ] [ false ] [ false ] [ 5 true ] [ 5 true ] [ 6 7 true ] [ 7 8 true ] [ 8 9 false ] [ 9 false ] [ 6 true ] [ false ] [ false ] [ true ] [ true ] [ true ] [ 9 true ] [ 5 false ] [ 5 false ] [ 8 6 true ] [ 6 7 true ] [ 7 8 true ] [ 8 false ] [ 5 9 false ] [ 9 true ] [ true ] [ true ] [ 8 true ] [ true ] [ 9 true ] ] /area [ [ ] [.77.8 ] [ ] [.78 ] [.6 - ] [ ] [ ] ] /style [ [ ] ] /node [ [.856 ] [.78. ] [.78. ] [ ] [.698. ] [.698. ] [.77 ] [.6. ] [.6. ] [.77.6 ] [.856. ] [ ] [. ] [.6 ] [.77. ] [.78.8 ] [ ] [.568. ] [.6.8 ] [.78.6 ] [.856 ] [ ] [.6.6 ] [.77 ] ] /area_outline [ [ 6 5 ] [ ] [ 6 5 ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] ] The node-key describes the nodes of the graph. It s a list of pairs, describing the x- and y-coordinate of the node as floating point numbers. The edge-key describes the edges of the node. It s a list of three items per entry: The index of the node in the node-key, where the edge starts, the index of the node in the node-key, where the edge ends and a boolean value which tells, if this edge should be a given border. The area-key is a list with five items per entry: The first two give x- and y-coordinate of the center of the area. The point defined by this coordinates has to be inside that area. It is often the balance point, but not necessary. The third entry is the value to be placed at that point, with - as a place holder for empty areas. The fourth number gives the number of style to use when rendering this number. The last number is the solution. s some programs my rely upon it, all empty areas have to be given in this list. The style-key is a list with six items per entry. They define an affine transformation, the first four define the matrix and the last two the translation vector. This transformation is used to describe the rendering style of that number. n optional area_outline-key can be given. It is a list of polygons. The first entry of a polygon is the number of edges of that polygon. The other entries are indices to the list of edges. They have to be sorted to form a path arround the area. The information provided by the area_outline-key can be deduced from
15 the values of the other keys. ut as this is not an easy task to do, some programs might not work without this information..7. Galaxies ( ) ( O ) ( O +) ( O ) ( O ) ( O+) ( ) (+ +O ) ( O O ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Vertices, edges and cells may contain a O, to denote the center of a galaxy. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle key. The borders of the areas are marked by minuses an pipes. 5
16 .8. Greater-Than-Sudoku.9. Hashi /size /digits ( ) ( > ) ( ^+) ( ) (+ + +-V+--+) ( D ) (+-+ + v+ +) ( < ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is ds + and the height of the diagram is s+, where s is the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, the edges between two areas are marked by pipes and minuses as well. In the cells, numbers can be given. If the digit-key is greater than, the numbers have to be right aligned. omparison symbols can be placed at the edges inside the puzzle. The symbols can be <, >, v and ^ on edges that do not separate areas and, D, V and on edges that do separate areas. The symbols have to be centered in the edge. If digits is even, the place right to the center is used. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given. ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) (===) ] ( ==) (--H) (H H) (H=H) (===) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is x and the height of the diagram is y, where x and y are the size of the puzzle. The symbols inside the puzzle can be a number from to 8, which denote an island with this number inside it, a question mark, which denotes an island without known number, and bridges, which are marked by -, =,, H. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key. In the solution, question marks may be replaced by the correct number. 6
17 .. Heyawake.. Hitori /X /Y /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ( -- ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ## ) ( ) ] (# # ) ( # ) (# #) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is (d+)x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, the edges between two areas are marked by pipes and minuses as well. Programs may assume, that all areas are rectangular. In the cells, numbers can be given. If the digit-key is greater than, the numbers have to be right aligned. Programs may assume, that there is only one number inside an area. The number should be placed at top left of the area, but programs must not rely on this. The cells can also be filled by hash keys as well as minus keys to denote a cell marked as filled or empty. The solution-key has one symbol per cell. black cell is written as # and non-black cells are written as space or dots. /X /Y /digits ( ) ( 9 9 ) ( ) ( ##) ] (..#.) (#...) (..#.) (#..#) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is dx and the height of the diagram is y, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the value of the digits-key. The cells may contain a number, which is placed at the rightmost position, a black cell, which is written by the hash symbol # or be empty. If the cell is black, all symbols should be hashes, but a program might only check one position. The solution-key has one symbol per cell. black cell is written as # and non-black cells are written as space or dots. 7
18 .. House-Tree-nimal.. Japanese Sums /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ( # ) ( * ) ( ) ( -) ( & ) ] ( &*#&) (*# *) (& &#) (# * ) (*& # ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is x + d + and the height of the diagram is y +d+, where x is the width of the puzzle, y is the height of the puzzle and d is the value of the digits-key. The place d d is marked with a plus. Right of that plus are minuses and below that plus are pipes. They primarily serve to help humans. Inside the diagram, every cell of the puzzle contains one character, which can be # to denote a house, * to denote a tree, & to denote an animal and - to denote an empty cell. Outside the diagram, the hints are given. t the left they are as many charakters wide, as the digits-key gives. t the top they are as many charakters high, as the digits-key gives. Numbers have to be right or bottom aligned. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the inner cells is given as single character. /X /Y /max /left /top ( ) ( 5 ) ( ) (...) (....) ( 5.. #.) (....) ] (#) (##) (#) (##) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional max-key can be given, which denotes the maximum digit, that can appear in the puzzle. If omitted, 9 is assumed. The max-key cannot be greater than 9. The left-key and the top-key give the maximum number of numbers at the left and at the top of the puzzle. They should be given, as some programms might need them to know in advance the size of the puzzle-key. width of the diagram is x + l + and the height of the diagram is y+t+, where x is the width of the puzzle, y is the height of the puzzle and l and t are the values of the left- and top-key. The place l t is marked with a plus. Right of that plus are minuses and below that plus are pipes. They primarily serve to help humans, but the plus might be used by programms to decide upon the values of the left- and top-key if they are omitted. Minuses and pipes might be omitted. Inside the diagram, every cell of the puzzle contains two characters, of which the left one should always be a space. The right one can be a space or a dot which are considered equivalent, but the dot should be used, as it helps humans. Furthermore, there can be a hash denoting a given black cell and digits from to max. Outside the diagram, the hints are given. They are always two cells wide. The content can be a number between and m(m+), wheremis the maximum digit given bei the max-key, or a question mark, which denotes an unknown number. Rows or columns might 8
19 also be completely empty, which denotes, that there is no given information about this row or column... Kakuro The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given as single character. /X /Y (########) (#####) (## ##) (## ##) (## ) (###5 ) (#### ) ] (####) (#9#) (#8) (##) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. In the size of the puzzle, the leftmost column and the topmost row, which both contain no empty cell, are included. width of the diagram is x and the height of the diagram is y, where x is the width of the puzzle, y is the height of the puzzle. The cells of the puzzle are given as blocks of size. They can either be completely made of spaces, which denotes an empty cell. In that case, the top left place might contain a number to be displayed in this cell. Or, they might denote clues. In that case the block is filled with hash signs. In the top two cells, the clue for the horicontal block can be given flushing to the right and in the bottom two cells, the clue for the vertical block can be given, again flushing to the right. lues might be omitted. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. The solution is made of hash keys which denote all non empty cells or digits. 9
20 .5. Killer-Sudoku small area, have to be filled with two hash signs. /size ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] /smallareas [ ( ) ( ## ## ) ( ) ( 5 ## ## ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( 7 ## ## ) ( ) ] () () () () ] 5 7 The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given. The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is s+ and the height of the diagram is s+, where s is the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, the edges between two areas are marked by pipes and minuses as well. In the cells, numbers can be given. The smallareas-key gives the small areas as ascii art. The width of the diagram is s+ and the height of the diagram is s+, where s is the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, the edges of small areas are marked by pipes and minuses as well. In the cells, numbers can be given. If they are single digit, they have to be right aligned. It s possible to have small areas without number but each small area can only contain one number. ells, that are not part of a
21 .6. Kropki.7. Laser /size /digits ( ) ( * * O ) (+ + O+ + O+) ( O O ) (+ O+ + *+ *+) ( O * ) (+ O+ + O+ +) ( * O ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is ds + and the height of the diagram is s+, where s is the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Dots can be placed at the edges inside the puzzle. Two types of dots are known: O for white dots and * for black dots. The dots have to be centered in the edge. If digits is even, the place right to the center is used. In the cells, numbers can be given. If the digit-key is greater than, the numbers have to be right aligned. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given. /digits ( ) ( ) ( / ) ( N ) ( ) ( + X ) ( ) ( ) ( # N ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( /N ) (N/ / ) (/N N ) ( N N) ( N/) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers outside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is x+d+ and the height of the diagram is y + d +, where x is the width of the puzzle, y is the height of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, starting at position d d, the edges at the border are marked by minus and pipe symbols to indicate the border of the puzzle diagram. The cells can contain an hash-key to indicate an unused cell. It can also contain a N or a slash-key to indicate a given piece of the laser beam. The plus symbols at the vertices can be replaced by an X to mark a crossing, by minus- or pipe-symbol to mark a mirror or by one of the symbols n, 7, N or / to mark the arrow entering (first two symbols) and leaving the diagram. t the left and the top numbers can be given. t the right and the bottom also numbers can be given, but at the position of the grid lines. Numbers at the left and at the right have to be right aligned, while num-
22 bers at the top and at the bottom are written from top down and are bottom aligned. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. The cells in the solution are made up of N and / to denote the laser beams or stay empty..8. LITS ( ) ( # ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ] (-#-##) (###-#) (#--##) (#-##-) (###--) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at Inside the diagram, the edges between two areas are marked by pipes and minuses as well. The cells can be filled by a hash key as well as a minus key to denote a cell marked as filled or empty. The solution-key has one symbol per cell. black cell is written as # and non-black cells are written as space or dots.
23 .9. LITS plus.. Magic Labyrinth Same as LITS. /size /max ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ] The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. The max-key gives the largest number to be inserted in the puzzle. width of the diagram is s+ and the height of the diagram is s+, where s is the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at indicate the border of the puzzle diagram, except the one at the entrance of the labyrinth. Inside the diagram, the edges that form the walls of the labyrinth are marked by pipes and minuses as well. In the cells, numbers can be given. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given.
24 .. Magnets /digits ( ) ( + ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( # ) ( ) ( # # ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( - + ) ( ) ] (+-+-+) (-##+#) (#+#-#) (#-##+) (-+-+-) ] In the cells, +, - and # can be given, to indicate plus, minus and neutral cells. ll cells of a plate have to be given. Programms might only check one of the two cells and calculate the other one. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the content of the cells is given. oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is x + d + and the height of the diagram is y +d+, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at The top left corner is separated by minus and pipe symbols and a plus and a minus sign are placed in the corner. They are ment as help for human viewers only. t the left and at the top numbers can be given. If d is greater than, the numbers at the top are given top down, that is, the decade is given above the unit position. Inside the puzzle, the magnet plates are drawn using minus and pipes. ll plates have to occupy two cells. There might be single cell plates, which all have to be neutral, that is, they have to be filled with a hash key #.
25 .. Masyu ( ) ( * O ) ( - ) ( # ) ( O ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( *- -O- ) ( ) ( - - ) ( ) ( - # # ) ( ) ( O - ) ( ) ( - -O- ) ( ) ].. Narrow ave Same as ave. oth have to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at The cells may contain an O or a * to denote white or black circles, or a #, which is a cell, that might not be used by the path. etween two cells, there might be minus and pipe symbols to show part of the path. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key. 5
26 .. Nurikabe.5. Pentomino Search /digits ( ) ( ## ) ( 6 ) ( 5 ) ] ( # ) ( ###) ( # ) (#####) ] 6 oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is dx and the height of the diagram is y, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the value of the digits-key. ells can contain # to denote part of the walls or a number, which has to be right alligned. The solution-key has one symbol per cell. The hashsymbol for walls and a space else /X 6 /Y 6 /used (LLY) /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ( #) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ##) ( # #) (## # #) ( # # #) ( # # ) ( ## ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. The usedkey gives a string with the pentominos used. It consists out of letters F,I,L,N,P,T,U,V,W,X,Y and Z. If a letter is given several times, the pentomino has to be placed that amout of times in the diagram. The used-key can be omitted. In that case, the set of the pentominos is unknown. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is x + d + and the height of the diagram is y+d+, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. Each cell can be completely filled with hash-symbols to denote a block, completely filled with minussymbols to denote an empty cell or be blank. t the left and the top numbers can be given. The numbers at the left have to be right alligned, the number at the top have to be bottom alligned. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key, but only the content of the cells is given. 6
27 .6. Pentopia.7. Pills ( v) (> ) ( ) (v S) ] ( ## ) ( ###) ( # ) (#### ) ] /X /Y /max /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( - ) ( - ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is x and the height of the diagram is y, where x and y are the width and the height of the puzzle. Each cell can contain various symbols. See the table at the end of this section for more details. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key. rrows can be omitted. > right arrow < left arrow ^ top arrow v bottom arrow - left-right arrow top-bottom arrow Q right-bottom arrow W left-bottom arrow right-top arrow S left-top-arrow T T-shape arrow down F T-shape arrow right G T-shape arrow left V T-shape arrow up + arrow in all four directions # black cell X white cell oth have to be greater or equal to. The max-key gives the largest value of a pill. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is d(x + ) and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the value of the digits-key. Each cell must contain a number, which is right alligned. t the left and the top numbers can be given. They also have to be right alligned. The solution-key has one symbol per cell. pipe symbol for the center of a vertical cell and a minus sign for the center of an horizontal cell. 7
28 .8. Pyramid.9. Skyscrapers /size (#. ) (# 7. ) (=... ) (# 7) ] ( ) ( 7 5 ) ( 6 6 ) ( 7) ] /size /digits ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is s and the height of the diagram is s, where s is the size of the puzzle. The leftmost symbol in every row must be = (a white row) or # (a grey row). In the rest of the grid, the cells of the pyramid are given to form a pyramid. n empty cell can be either a space symbol or a dot. The solution is the same as the puzzle grid, with one exception: The leftmost column is missing. The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width and height of the diagram are d(s+), where s is the size of the puzzle anddis the maximum number of digits. The numbers at the border are given in the leftmost, rightmost column and top and bottom row. In the center, numbers can be given. ll numbers are right aligned. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the center is given. 8
29 .. Skyscrapers with Parks.. Slalom /size /parks /digits ( - ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. The parks-key gives the number of parks in each row and column. width and height of the diagram are d(s+), where s is the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. The numbers at the border are given in the leftmost, rightmost column and top and bottom row. In the center, numbers or a minus sign can be given. ll numbers and signs are right aligned. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the center is given. /X /Y (+ + +) ( N ) ( ) ( ) ( / ) (+ + +) ( ) ] (NNNN) (/NNN) (/N//) (////) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. width of the diagram is x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle. Vertices can be numbers from to or a plus symbol to denote an empty vertice. The cells may contain a slash or a an N which serves as a replacement for the backslash. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key, but only the content of the cells is given. 9
30 .. Snake.. Starbattle /max /digits ( ) ( ### 7 ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ### 7 8 9) ( 6 ) ( 5 ) ( ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. The max-key gives the length of the snake. It can be omitted. In that case, the length of the snake is unknown. n optional digits-key can be given, which denotes the maximum number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is d(x + ) and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the value of the digits-key. Each cell can contain a number, which is right alligned, be completely filled with hash-symbols to denote a cell, that is not used by the snake, or be blank. t the left and the top numbers can be given. They also have to be right alligned. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key, but the leftmost column and the topmost row are removed. 9 /stars /size 5 ( ) ( * ) ( ) ( ) ( # ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ] ( * ) ( *) ( * ) ( * ) (* ) ] The size-key defines the size of the puzzle. It has to be greater or equal to. n optional stars-key can be given, which denotes the number of stars used in the puzzle. If omitted is assumed. width and height of the diagram are x +, where x is the size of the puzzle. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at the border and between areas are marked by minus and pipe symbols. The cells may contain *, -, # or be empty. starsymbol marks a star, that is already given. minus marks a cell, that cannot contain a star. The hashsign is used to mark cells, that do not belong to any area. To understand the difference between - and # is important. onsider the following diagram: If a hash-symbol is placed inside the cell marked with an the area would be separated in two areas, while a minus sign would not separate the area. The solution-key gives the solution as ascii art. In the solution diagram, only the stars are given.
31 .. Starry Sky.5. Stations /digits ( ) ( c *) (d q ) ( d-x ) (ee ) ] ( * *) ( ** ) ( *) ( ** ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is d(x + ) and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. The content of a cell of the puzzle-key can either be a number, which has to be right aligned, or a symbol, which is placed at the rightmost place of the cell. The symbol can be a star or a minus. Letters are used to symbolize arrows. The letters q, w, e, a, d, y, x and c are used to give arrows that point away from the s on a keyboard. Note, that on a german keyboard y is in place of a z on several other keyboards... The solution-key has one symbol per cell. star is written as *. /digits ( ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ( + ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] ( ) ( ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ( - ) ( ) ( - +- ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ] oth have to be greater or equal to. n optional number of digits of numbers inside the diagram. If omitted, it is assumed to be. width of the diagram is (d+)x+ and the height of the diagram is y +, where x and y are the size of the puzzle and d is the maximum number of digits. ll vertices are marked as plus symbols, the edges at The cells are d characters wide. The cell can contain the symbol + which is a crossing and has to be centered. If digits is even, the place right to the center is used. The cell can also contain a number, which has to be right alligned. etween two cells, there might be minus and pipe symbols to show part of the path. The solution-key is the same as the puzzle-key.
INSTRUCTION BOOKLET (v2)
 CZECH PUZZLE CHAMPIONSHIP 7 Prague, - June 7 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET (v) SATURDAY JUNE 7 : : INDIVIDUAL ROUND - SHADING MINUTES POINTS : : INDIVIDUAL ROUND LOOPS 6 MINUTES 6 POINTS : : INDIVIDUAL ROUND - NUMBERS
CZECH PUZZLE CHAMPIONSHIP 7 Prague, - June 7 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET (v) SATURDAY JUNE 7 : : INDIVIDUAL ROUND - SHADING MINUTES POINTS : : INDIVIDUAL ROUND LOOPS 6 MINUTES 6 POINTS : : INDIVIDUAL ROUND - NUMBERS
Inside Outside Circles Outside Circles Inside. Regions Circles Inside Regions Outside Regions. Outside Inside Regions Circles Inside Outside
 START Inside Outside Circles Outside Circles Inside Regions Circles Inside Regions Outside Regions Outside Inside Regions Circles Inside Outside Circles Regions Outside Inside Regions Circles FINISH Each
START Inside Outside Circles Outside Circles Inside Regions Circles Inside Regions Outside Regions Outside Inside Regions Circles Inside Outside Circles Regions Outside Inside Regions Circles FINISH Each
FEATURES 24 PUZZLES, ASSORTED MIX, MOSTLY THEMED ON 24 HPC. HINTS FOR EACH PUZZLE. SOLUTIONS FOR EACH PUZZLE.
 FEATURES 4 PUZZLES, ASSORTED MIX, MOSTLY THEMED ON 4 HPC. HINTS FOR EACH PUZZLE. SOLUTIONS FOR EACH PUZZLE. Nanro 80 Points Turning Fences 95 Points Toroidal Skyscrapers 85 Points (50 + 5) Tents 0 Points
FEATURES 4 PUZZLES, ASSORTED MIX, MOSTLY THEMED ON 4 HPC. HINTS FOR EACH PUZZLE. SOLUTIONS FOR EACH PUZZLE. Nanro 80 Points Turning Fences 95 Points Toroidal Skyscrapers 85 Points (50 + 5) Tents 0 Points
1. Hex Tapa (12 points) 2. Hex Dominos (13 points)
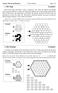 lassics: Hexed and Remixed Puzzle ooklet Page /5. Hex Tapa ( points) Paint some empty cells black to form a continuous wall. Each clue indicates the lengths of the consecutive blocks of black cells among
lassics: Hexed and Remixed Puzzle ooklet Page /5. Hex Tapa ( points) Paint some empty cells black to form a continuous wall. Each clue indicates the lengths of the consecutive blocks of black cells among
Prague. Prague th WSC 27th WPC HALAS. 27th World Puzzle Championship. Instruction booklet. Partners
 Prague Prague th WS th WP HLS th World Puzzle hampionship Instruction booklet Partners Schedule Thursday.. 9:-9: Individual round Shading :-: Individual round bjects :-: Individual round Skyscrapers :-:
Prague Prague th WS th WP HLS th World Puzzle hampionship Instruction booklet Partners Schedule Thursday.. 9:-9: Individual round Shading :-: Individual round bjects :-: Individual round Skyscrapers :-:
We hope you enjoy the set. Good luck for the Indian Puzzle Championship! 3 A B C 4 H D 5 G F E 7 A B 8 H 9 G F
 Notes:. All Puzzle rules have been copied from the IP 0 Instruction booklet. Participants are advised to have a look at the booklet before trying out these puzzles, as they contain easier examples with
Notes:. All Puzzle rules have been copied from the IP 0 Instruction booklet. Participants are advised to have a look at the booklet before trying out these puzzles, as they contain easier examples with
WPF PUZZLE GP 2018 ROUND 7 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET. Host Country: Netherlands. Bram de Laat. Special Notes: None.
 W UZZLE G 0 NSTRUCTON BOOKLET Host Country: Netherlands Bram de Laat Special Notes: None. oints:. Balance 7. Letter Bags 5. Letter Bags. Letter Weights 5 5. Letter Weights 7 6. Masyu 7 7. Masyu. Tapa 6
W UZZLE G 0 NSTRUCTON BOOKLET Host Country: Netherlands Bram de Laat Special Notes: None. oints:. Balance 7. Letter Bags 5. Letter Bags. Letter Weights 5 5. Letter Weights 7 6. Masyu 7 7. Masyu. Tapa 6
WPF PUZZLE GP 2014 COMPETITION BOOKLET ROUND 1 WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRAND PRIX 2014
 WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRAND PRX 04 WPF PUZZLE GP 04 COMPETTON BOOKLET Puzzle authors: Germany Rainer Biegler (6, ) Gabi Penn-Karras (5, 7, 9) Roland Voigt (, 3, 8) Ulrich Voigt (, 5, 0) Robert Vollmert (4,
WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRAND PRX 04 WPF PUZZLE GP 04 COMPETTON BOOKLET Puzzle authors: Germany Rainer Biegler (6, ) Gabi Penn-Karras (5, 7, 9) Roland Voigt (, 3, 8) Ulrich Voigt (, 5, 0) Robert Vollmert (4,
WPF PUZZLE GP 2016 ROUND 8 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET. Host Country: Russia. Andrey Bogdanov. Special Notes: No special notes for this round.
 WPF PUZZLE GP 01 INSTRUTION OOKLET Host ountry: Russia ndrey ogdanov Special Notes: No special notes for this round. Points, asual Section: Points, ompetitive Section: 1. Not Like the Others 1. Not Like
WPF PUZZLE GP 01 INSTRUTION OOKLET Host ountry: Russia ndrey ogdanov Special Notes: No special notes for this round. Points, asual Section: Points, ompetitive Section: 1. Not Like the Others 1. Not Like
Swaroop Guggilam, Ashish Kumar, Rajesh Kumar, Rakesh Rai, Prasanna Seshadri
 ROUND WPF PUZZLE GP 0 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET Host Country: India Swaroop Guggilam, Ashish Kumar, Rajesh Kumar, Rakesh Rai, Prasanna Seshadri Special Notes: The round is presented with similar-style puzzles
ROUND WPF PUZZLE GP 0 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET Host Country: India Swaroop Guggilam, Ashish Kumar, Rajesh Kumar, Rakesh Rai, Prasanna Seshadri Special Notes: The round is presented with similar-style puzzles
IN THIS ISSUE
 7 IN THIS ISSUE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Hula-hoop Sudoku Matchmaker Sudoku 10 Mediator Sudoku Slitherlink Sudoku Numberlink Sudoku Marked Sudoku Multiplication Sudoku Top Heavy Sudoku Fortress Sudoku Meta
7 IN THIS ISSUE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Hula-hoop Sudoku Matchmaker Sudoku 10 Mediator Sudoku Slitherlink Sudoku Numberlink Sudoku Marked Sudoku Multiplication Sudoku Top Heavy Sudoku Fortress Sudoku Meta
Indian Puzzle Championship 2013
 Indian Puzzle Championship 03 07-July-03 http://logicmastersindia.com/03/ipc/ Important Links Submission: http://logicmastersindia.com/03/ipc/ Discussion: http://logicmastersindia.com/t/?tid=694 Results:
Indian Puzzle Championship 03 07-July-03 http://logicmastersindia.com/03/ipc/ Important Links Submission: http://logicmastersindia.com/03/ipc/ Discussion: http://logicmastersindia.com/t/?tid=694 Results:
15/03/23: BACA by John Bulten Theme: Beach Booty
 15/0/: by John ulten Theme: each ooty (This pirates' map depicts eastern Palm each ounty, Florida, showing the locations of the communities of bacoa, oynton each, and oca Raton, in relation to the coastal
15/0/: by John ulten Theme: each ooty (This pirates' map depicts eastern Palm each ounty, Florida, showing the locations of the communities of bacoa, oynton each, and oca Raton, in relation to the coastal
IN THIS ISSUE. Cave vs. Pentagroups
 3 IN THIS ISSUE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cave vs. Pentagroups Brokeback loop Easy as skyscrapers Breaking the loop L-oop Triple loop Octave Total rising Dead end cells Pentamino in half Giant tents Cave vs. Pentagroups
3 IN THIS ISSUE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cave vs. Pentagroups Brokeback loop Easy as skyscrapers Breaking the loop L-oop Triple loop Octave Total rising Dead end cells Pentamino in half Giant tents Cave vs. Pentagroups
Dutch Sudoku Advent 1. Thermometers Sudoku (Arvid Baars)
 1. Thermometers Sudoku (Arvid Baars) The digits in each thermometer-shaped region should be in increasing order, from the bulb to the end. 2. Search Nine Sudoku (Richard Stolk) Every arrow is pointing
1. Thermometers Sudoku (Arvid Baars) The digits in each thermometer-shaped region should be in increasing order, from the bulb to the end. 2. Search Nine Sudoku (Richard Stolk) Every arrow is pointing
WPF PUZZLE GP 2015 COMPETITION BOOKLET ROUND 7. Puzzle authors: Switzerland Roger Kohler Fred Stalder Markus Roth Esther Naef Carmen Günther
 0 COMPETITION BOOKLET Puzzle authors: Switzerland Roger Kohler Fred Stalder Markus Roth Esther Naef Carmen Günther Organized by Points:. Fillomino. Fillomino. Fillomino. Fillomino 8. Tapa. Tapa 8. Tapa
0 COMPETITION BOOKLET Puzzle authors: Switzerland Roger Kohler Fred Stalder Markus Roth Esther Naef Carmen Günther Organized by Points:. Fillomino. Fillomino. Fillomino. Fillomino 8. Tapa. Tapa 8. Tapa
WPF PUZZLE GP 2018 ROUND 4 COMPETITION BOOKLET. Host Country: Czech Republic
 WPF PUZZLE GP 0 COMPETITION BOOKLET Host Country: Czech Republic ROUND Jakub Hrazdira, Jiří Hrdina, Pavel Kadlečík, Petr Lichý, Jan Novotný, Zuzana Vytisková, Jan Zvěřina Special Notes: An earlier version
WPF PUZZLE GP 0 COMPETITION BOOKLET Host Country: Czech Republic ROUND Jakub Hrazdira, Jiří Hrdina, Pavel Kadlečík, Petr Lichý, Jan Novotný, Zuzana Vytisková, Jan Zvěřina Special Notes: An earlier version
WPF PUZZLE GP 2018 ROUND 3 COMPETITION BOOKLET. Host Country: India + = 2 = = 18 = = = = = =
 Host Country: India WPF PUZZLE GP 0 COMPETITION BOOKLET ROUND Swaroop Guggilam, Ashish Kumar, Rajesh Kumar, Rakesh Rai, Prasanna Seshadri Special Notes: The round is presented with similar-style puzzles
Host Country: India WPF PUZZLE GP 0 COMPETITION BOOKLET ROUND Swaroop Guggilam, Ashish Kumar, Rajesh Kumar, Rakesh Rai, Prasanna Seshadri Special Notes: The round is presented with similar-style puzzles
WPF PUZZLE GP 2019 ROUND 3 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET. Host Country: Serbia. Čedomir Milanović, Zoran Tanasić, Nikola Živanović NOMNONMON B NOMNONMON
 9 9 NRUCN BKE Host Country: erbia Čedomir Milanović, Zoran anasić, Nikola Živanović pecial Notes: Point values are not finalized. Points:. Palindromes or Not XX. etter Weights XX. crabble XX. Password
9 9 NRUCN BKE Host Country: erbia Čedomir Milanović, Zoran anasić, Nikola Živanović pecial Notes: Point values are not finalized. Points:. Palindromes or Not XX. etter Weights XX. crabble XX. Password
WPF PUZZLE GP 2015 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET ROUND 7. Puzzle authors: Switzerland Roger Kohler Fred Stalder Markus Roth Esther Naef Carmen Günther
 05 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET Puzzle authors: Switzerland Roger Kohler Fred Stalder Markus Roth Esther Naef Carmen Günther Organized by Points:. Fillomino 6. Fillomino 3. Fillomino. Fillomino 58 5. Tapa 5 6.
05 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET Puzzle authors: Switzerland Roger Kohler Fred Stalder Markus Roth Esther Naef Carmen Günther Organized by Points:. Fillomino 6. Fillomino 3. Fillomino. Fillomino 58 5. Tapa 5 6.
puzzles may not be published without written authorization
 Presentational booklet of various kinds of puzzles by DJAPE In this booklet: - Hanjie - Hitori - Slitherlink - Nurikabe - Tridoku - Hidoku - Straights - Calcudoku - Kakuro - And 12 most popular Sudoku
Presentational booklet of various kinds of puzzles by DJAPE In this booklet: - Hanjie - Hitori - Slitherlink - Nurikabe - Tridoku - Hidoku - Straights - Calcudoku - Kakuro - And 12 most popular Sudoku
LMI October Puzzle Test 1 9/10 October Minutes N I K O LI SELECTION. by Tom detuned Collyer http//blogs.warwick.ac.
 LMI October Puzzle Test 1 9/10 October 2010 100 Minutes N I K O LI SELECTION by Tom detuned Collyer http//blogs.warwick.ac.uk/tcollyer/ Tested and coordinated by Deb Mohanty & Co. SUMISSION LINK: http//logicmastersindia.com/m201010p1
LMI October Puzzle Test 1 9/10 October 2010 100 Minutes N I K O LI SELECTION by Tom detuned Collyer http//blogs.warwick.ac.uk/tcollyer/ Tested and coordinated by Deb Mohanty & Co. SUMISSION LINK: http//logicmastersindia.com/m201010p1
Episode 3 16 th 19 th March Made In India and Regions by Prasanna Seshadri
 and Episode 3 16 th 19 th March 2018 by Prasanna Seshadri Puzzle Ramayan rounds will also serve as qualifiers for Indian Puzzle Championship for year 2018. Please check http://logicmastersindia.com/pr/2018pr.asp
and Episode 3 16 th 19 th March 2018 by Prasanna Seshadri Puzzle Ramayan rounds will also serve as qualifiers for Indian Puzzle Championship for year 2018. Please check http://logicmastersindia.com/pr/2018pr.asp
LMI Monthly Puzzle Test. 9 th /10 th July minutes
 NIKOLI SELECTION P U Z Z L E O O K L E T LMI Monthly Puzzle Test 9 th /10 th July 2011 90 minutes Y T O M detuned C O L L Y E R Solvers are once again reminded that it is highly recommended that you do
NIKOLI SELECTION P U Z Z L E O O K L E T LMI Monthly Puzzle Test 9 th /10 th July 2011 90 minutes Y T O M detuned C O L L Y E R Solvers are once again reminded that it is highly recommended that you do
WPF PUZZLE GP 2017 ROUND 5A COMPETITION BOOKLET. Host Country: Czech Republic C D. Author: Jan Novotný
 WPF PUZZLE GP 0 OMPETITION OOKLET Host ountry: zech Republic uthor: Jan Novotný Special Notes: For puzzles with hexagonal grids, the word row in the puzzle description refers to the diagonal rows (slanted
WPF PUZZLE GP 0 OMPETITION OOKLET Host ountry: zech Republic uthor: Jan Novotný Special Notes: For puzzles with hexagonal grids, the word row in the puzzle description refers to the diagonal rows (slanted
Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, Magic and Latin Squares
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, 2017 Magic and Latin Squares Today we will be solving math and logic puzzles!
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, 2017 Magic and Latin Squares Today we will be solving math and logic puzzles!
WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRAND PRIX 2014 WPF PUZZLE GP 2014 COMPETITION BOOKLET ROUND 3. Puzzle authors: Japan. Organised by
 WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRND PRIX 0 WPF PUZZLE GP 0 OMPETITION BOOKLET ROUND Puzzle authors: Japan Shinichi oki Masahiro Kaneko Tetsuya Nishio Naoki Inaba Masatoshi Kengo Yukari Nishiyama Yousuke Imai Minako
WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRND PRIX 0 WPF PUZZLE GP 0 OMPETITION BOOKLET ROUND Puzzle authors: Japan Shinichi oki Masahiro Kaneko Tetsuya Nishio Naoki Inaba Masatoshi Kengo Yukari Nishiyama Yousuke Imai Minako
WPF PUZZLE GP 2016 ROUND 6 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET. Host Country: Serbia. Nikola Živanović, Čedomir Milanović, Branko Ćeranić
 WPF PUZZLE GP 26 NSTRUTON BOOKLET Host ountry: Serbia Nikola Živanović, Čedomir Milanović, Branko Ćeranić Special Notes: None for this round. Points, asual Section:. Letter Weights 8 2. Letter Weights
WPF PUZZLE GP 26 NSTRUTON BOOKLET Host ountry: Serbia Nikola Živanović, Čedomir Milanović, Branko Ćeranić Special Notes: None for this round. Points, asual Section:. Letter Weights 8 2. Letter Weights
Logic Masters Instructions, First round
 Organised member of by Logic Masters 2018 Instructions, First round Welcome to the first round of the Logic Masters 2018. The contest begins on Friday, March 2 2018 at 12:00 CET and ends on Monday, March
Organised member of by Logic Masters 2018 Instructions, First round Welcome to the first round of the Logic Masters 2018. The contest begins on Friday, March 2 2018 at 12:00 CET and ends on Monday, March
Sudoku Mock Test 5. Instruction Booklet. 28 th December, IST (GMT ) 975 points + Time Bonus. Organized by. Logic Masters: India
 Sudoku Mock Test 5 Instruction Booklet 28 th December, 2008 14.30 16.30 IST (GMT + 5.30) 975 points + Time Bonus Organized by Logic Masters: India Points Distribution No. Sudoku Points Puzzle Creator 1
Sudoku Mock Test 5 Instruction Booklet 28 th December, 2008 14.30 16.30 IST (GMT + 5.30) 975 points + Time Bonus Organized by Logic Masters: India Points Distribution No. Sudoku Points Puzzle Creator 1
5CHAMPIONSHIP. Individual Round Puzzle Examples SUDOKU. th WORLD. from PHILADELPHIA. Lead Sponsor
 th WORLD SUDOKU CHAMPIONSHIP PHILADELPHIA A P R M A Y 0 0 0 Individual Round Puzzle Examples from http://www.worldpuzzle.org/wiki/ Lead Sponsor Classic Sudoku Place the digits through into the empty cells
th WORLD SUDOKU CHAMPIONSHIP PHILADELPHIA A P R M A Y 0 0 0 Individual Round Puzzle Examples from http://www.worldpuzzle.org/wiki/ Lead Sponsor Classic Sudoku Place the digits through into the empty cells
Name. WPC French Qualifier Part I
 Name. Battleships 0 points. Coral finder 5 + 0 points. Crack it on 0 points 4. Parthenon 5 points 5. Loopfinder 5 + 5 points 6. End view 5 + 0 points 7. Magnets 5 points 8. Word jungle 40 points 9. Four
Name. Battleships 0 points. Coral finder 5 + 0 points. Crack it on 0 points 4. Parthenon 5 points 5. Loopfinder 5 + 5 points 6. End view 5 + 0 points 7. Magnets 5 points 8. Word jungle 40 points 9. Four
Name. Part 2. Part 2 Swimming 55 minutes
 Name Swimming 55 minutes 1. Moby Dick...................... 15. Islands (Nurikabe).................. 0. Hashiwokakero (Bridges).............. 15 4. Coral Finder..................... 5 5. Sea Serpent......................
Name Swimming 55 minutes 1. Moby Dick...................... 15. Islands (Nurikabe).................. 0. Hashiwokakero (Bridges).............. 15 4. Coral Finder..................... 5 5. Sea Serpent......................
3 rd -4 th September minutes
 rd - th September 7 minutes y astien «Ours brun» Vial-Jaime http://ile-logique.blogspot.com With the help of Deb Mohanty Testers : Sylvain Caudmont, Robert Vollmert, Nikola Zivanovic Contest page : http://logicmastersindia.com/m9p/
rd - th September 7 minutes y astien «Ours brun» Vial-Jaime http://ile-logique.blogspot.com With the help of Deb Mohanty Testers : Sylvain Caudmont, Robert Vollmert, Nikola Zivanovic Contest page : http://logicmastersindia.com/m9p/
PART 2 VARIA 1 TEAM FRANCE WSC minutes 750 points
 Name : PART VARIA 1 TEAM FRANCE WSC 00 minutes 0 points 1 1 points Alphabet Triplet No more than three Circles Quad Ring Consecutive Where is Max? Puzzle Killer Thermometer Consecutive irregular Time bonus
Name : PART VARIA 1 TEAM FRANCE WSC 00 minutes 0 points 1 1 points Alphabet Triplet No more than three Circles Quad Ring Consecutive Where is Max? Puzzle Killer Thermometer Consecutive irregular Time bonus
Rounds: 2780 points 3 hours 45 minutes
 INSTRUCTION BOOK UK Open Puzzle Tournament 0 Rounds: Online start time Warm Up 0 minutes 80 :0pm 8th April Classics 60 minutes 70 :0pm 8th April Japanese Puzzles 5 minutes 60 5:0pm 8th April UK Themes
INSTRUCTION BOOK UK Open Puzzle Tournament 0 Rounds: Online start time Warm Up 0 minutes 80 :0pm 8th April Classics 60 minutes 70 :0pm 8th April Japanese Puzzles 5 minutes 60 5:0pm 8th April UK Themes
Part III F F J M. Name
 Name 1. Pentaminoes 15 points 2. Pearls (Masyu) 20 points 3. Five Circles 30 points 4. Mastermindoku 35 points 5. Unequal Skyscrapers 40 points 6. Hex Alternate Corners 40 points 7. Easy Islands 45 points
Name 1. Pentaminoes 15 points 2. Pearls (Masyu) 20 points 3. Five Circles 30 points 4. Mastermindoku 35 points 5. Unequal Skyscrapers 40 points 6. Hex Alternate Corners 40 points 7. Easy Islands 45 points
IN THIS ISSUE. WPC Placement. WPC Placement Puzzles of the th Belarusian Puzzle Championship. Puzzles of the
 6 IN THIS ISSUE 1. 2-8. WPC Placement Puzzles of the 7th Belarusian Puzzle Championship 9-14. Puzzles of the 10th Russian Puzzle Championship WPC Placement Author - Andrey Bogdanov Place all the given
6 IN THIS ISSUE 1. 2-8. WPC Placement Puzzles of the 7th Belarusian Puzzle Championship 9-14. Puzzles of the 10th Russian Puzzle Championship WPC Placement Author - Andrey Bogdanov Place all the given
Standard Sudoku point. 1 point. P a g e 1
 P a g e 1 Standard 1-2 Place a digit from 1 to 6 in each empty cell so that each digit appears exactly once in each row, column and 2X box. 1 point A 6 2 6 2 1 5 1 point B 5 2 2 4 1 1 6 5 P a g e 2 Standard
P a g e 1 Standard 1-2 Place a digit from 1 to 6 in each empty cell so that each digit appears exactly once in each row, column and 2X box. 1 point A 6 2 6 2 1 5 1 point B 5 2 2 4 1 1 6 5 P a g e 2 Standard
17/01/14: Pentominous by Carl Worth Theme: Just One (in Roman Numerals)
 //: Pentominous by Carl Worth Theme: Just One (in Roman Numerals) U N T W Y Z F L X P V //: Fillomino (Symmetry) by Murat Can Tonta Theme: Clue Symmetry and Logic Rules: Standard Fillomino Rules. lso,
//: Pentominous by Carl Worth Theme: Just One (in Roman Numerals) U N T W Y Z F L X P V //: Fillomino (Symmetry) by Murat Can Tonta Theme: Clue Symmetry and Logic Rules: Standard Fillomino Rules. lso,
13 TH 24 HOURS PUZZLE CHAMPIONSHIP
 NM: NTY: PNT: T M PZZ Y: N PÄNT & TT VN NYM PNT ( +) & P 0 PNT ( + 0) MMMT V 0 PNT (+) -- N 0 PNT (+) G VW T TT 0 PNT 0 PNT N TN 0 PNT (0 + 0) N W PNT (0 + 0) Y TTP T Y 0 PNT PNT PNT W MZ PNT ( +0) PYGP
NM: NTY: PNT: T M PZZ Y: N PÄNT & TT VN NYM PNT ( +) & P 0 PNT ( + 0) MMMT V 0 PNT (+) -- N 0 PNT (+) G VW T TT 0 PNT 0 PNT N TN 0 PNT (0 + 0) N W PNT (0 + 0) Y TTP T Y 0 PNT PNT PNT W MZ PNT ( +0) PYGP
T G D T LMI PUZZLE TEST DUTCH TREAT WITH A GERMAN TWIST 7 TH 9 TH SEPTEMBER 2013 BY RICHARD STOLK INSTRUCTION BOOKLET GOOD LUCK AND HAVE FUN!
 LMI PUZZLE TEST UTH TRET WITH GERMN TWIST 7 TH TH SEPTEMER Y RIHR STOLK T T G INSTRUTION OOKLET Since I don t have my own weblog, I consider my user page in the puzzle portal of Logic Masters Germany my
LMI PUZZLE TEST UTH TRET WITH GERMN TWIST 7 TH TH SEPTEMER Y RIHR STOLK T T G INSTRUTION OOKLET Since I don t have my own weblog, I consider my user page in the puzzle portal of Logic Masters Germany my
1st UKPA Sudoku Championship
 st UKPA Sudoku Championship COMPETITION PUZZLES Saturday 6th Sunday 7th November 00 Championship Duration: hours. Puzzles designed by Tom Collyer # - Classic Sudoku ( 4) 0pts #8 - No Touch Sudoku 5pts
st UKPA Sudoku Championship COMPETITION PUZZLES Saturday 6th Sunday 7th November 00 Championship Duration: hours. Puzzles designed by Tom Collyer # - Classic Sudoku ( 4) 0pts #8 - No Touch Sudoku 5pts
WPF PUZZLE GP 2016 ROUND 2 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET. Puzzle Authors: Slovakia. Matus Demiger. General Notes: None for this round. Points, Casual Section:
 ROUND WP PUZZL GP 016 INSTRUCTION BOOKLT Puzzle uthors: Slovakia Matus Demiger General Notes: None for this round. Points, Casual Section: Points, Competitve Section: 1. Mastermind 10. Mastermind 15 3.
ROUND WP PUZZL GP 016 INSTRUCTION BOOKLT Puzzle uthors: Slovakia Matus Demiger General Notes: None for this round. Points, Casual Section: Points, Competitve Section: 1. Mastermind 10. Mastermind 15 3.
Sudoku Xtra. Sudoku Xtra 1. >> The Logic Puzzle Brain Workout. Issue 8 - July Expanded Community Section! >> Samurai Sudoku 6x6: S
 Sudoku Xtra Issue - July TM Sudoku Xtra >> The Logic Puzzle Brain Workout All main section puzzles by Dr Gareth Moore For back issues and subscriptions, visit www.sudokuxtra.com >> Samurai Sudoku x: S
Sudoku Xtra Issue - July TM Sudoku Xtra >> The Logic Puzzle Brain Workout All main section puzzles by Dr Gareth Moore For back issues and subscriptions, visit www.sudokuxtra.com >> Samurai Sudoku x: S
Quintessence A Packet of Puzzles by John Bulten
 Quintessence A Packet of Puzzles by John Bulten Editor s Note: The last, giant grid here is one of the hardest puzzles we have ever presented. If I knew in advance John wanted to make a puzzle like this,
Quintessence A Packet of Puzzles by John Bulten Editor s Note: The last, giant grid here is one of the hardest puzzles we have ever presented. If I knew in advance John wanted to make a puzzle like this,
SUDOKU1 Challenge 2013 TWINS MADNESS
 Sudoku1 by Nkh Sudoku1 Challenge 2013 Page 1 SUDOKU1 Challenge 2013 TWINS MADNESS Author : JM Nakache The First Sudoku1 Challenge is based on Variants type from various SUDOKU Championships. The most difficult
Sudoku1 by Nkh Sudoku1 Challenge 2013 Page 1 SUDOKU1 Challenge 2013 TWINS MADNESS Author : JM Nakache The First Sudoku1 Challenge is based on Variants type from various SUDOKU Championships. The most difficult
Colossal Cave Collection Sampler
 Collection Sampler by Roger Barkan GRANDMASTER PUZZLES LE UZZ Z S P E Z S U U G M E SZ P L Z UZ M www. GMPUZZLES.com Notes: This sampler contains (out of 100) puzzles from the full title, as well as the
Collection Sampler by Roger Barkan GRANDMASTER PUZZLES LE UZZ Z S P E Z S U U G M E SZ P L Z UZ M www. GMPUZZLES.com Notes: This sampler contains (out of 100) puzzles from the full title, as well as the
WPF PUZZLE GP 2018 ROUND 2 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET. Host Country: Switzerland. Markus Roth, Roger Kohler, Esther Naef
 ROUND WPF PUZZLE GP 0 INSTRUCTION OOKLET Host Country: Switzerland Markus Roth, Roger Kohler, Esther Naef Special Notes: CH is short for Confoederatio Helvetica, the Latin name for Switzerland, and appears
ROUND WPF PUZZLE GP 0 INSTRUCTION OOKLET Host Country: Switzerland Markus Roth, Roger Kohler, Esther Naef Special Notes: CH is short for Confoederatio Helvetica, the Latin name for Switzerland, and appears
Instruction booklet EVOLVED TERRESTRIALS. 16th-17th April 2011
 Instruction booklet EVOLVED TERRESTRIALS th-7th April 0 Puzzles by Anurag Sahay This test contains variations of a few popular puzzle types. Thanks to Zoltan Horvath, who tested the puzzles and helped
Instruction booklet EVOLVED TERRESTRIALS th-7th April 0 Puzzles by Anurag Sahay This test contains variations of a few popular puzzle types. Thanks to Zoltan Horvath, who tested the puzzles and helped
WPF PUZZLE GP 2018 ROUND 1 COMPETITION BOOKLET. Host Country: Turkey. Serkan Yürekli, Salih Alan, Fatih Kamer Anda, Murat Can Tonta A B H G A B I H
 Host Country: urkey WPF PUZZE GP 0 COMPEON BOOKE Serkan Yürekli, Salih Alan, Fatih Kamer Anda, Murat Can onta ROUND Special Notes: Note that there is partial credit available on puzzle for a close answer.
Host Country: urkey WPF PUZZE GP 0 COMPEON BOOKE Serkan Yürekli, Salih Alan, Fatih Kamer Anda, Murat Can onta ROUND Special Notes: Note that there is partial credit available on puzzle for a close answer.
WPF PUZZLE GP 2015 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET ROUND 6. Puzzle authors: Germany Rainer Biegler Gabi Penn-Karras Roland Voigt Ulrich Voigt.
 0 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET Puzzle authors: Germany Rainer Biegler Gabi Penn-Karras Roland Voigt Ulrich Voigt Organised by Points:. Spiral Galaxies 6. Spiral Galaxies 6. Spiral Galaxies 7. Spiral Galaxies. Battleships
0 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET Puzzle authors: Germany Rainer Biegler Gabi Penn-Karras Roland Voigt Ulrich Voigt Organised by Points:. Spiral Galaxies 6. Spiral Galaxies 6. Spiral Galaxies 7. Spiral Galaxies. Battleships
WPF SUDOKU GP 2014 ROUND 2 WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRAND PRIX Puzzle authors: Serbia. Organised by
 WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRAND PRIX 2014 WPF SUDOKU GP 2014 Puzzle authors: Serbia Classic sudoku by Nikola Živanović Sudoku variations by Zoran Tanasić and Čedomir Milanović Organised by 1 Classic Sudoku (6
WPF SUDOKU/PUZZLE GRAND PRIX 2014 WPF SUDOKU GP 2014 Puzzle authors: Serbia Classic sudoku by Nikola Živanović Sudoku variations by Zoran Tanasić and Čedomir Milanović Organised by 1 Classic Sudoku (6
WPF PUZZLE GP 2016 ROUND 6 COMPETITION BOOKLET. Host Country: Serbia. Nikola Živanović, Čedomir Milanović, Branko Ćeranić COMPETITIVE
 OMEO OOKE Host ountry: erbia ikola Živanović, Čedomir Milanović, ranko Ćeranić pecial otes: one for this round. -. Yajilin [ikola Živanović] (,, points) lacken some white cells and then draw a single closed
OMEO OOKE Host ountry: erbia ikola Živanović, Čedomir Milanović, ranko Ćeranić pecial otes: one for this round. -. Yajilin [ikola Živanović] (,, points) lacken some white cells and then draw a single closed
LMI SUDOKU TEST 7X JULY 2014 BY RICHARD STOLK
 LMI SUDOKU TEST X x JULY 0 BY RICHARD STOLK The first logic puzzle that I ever designed was a scattered number place puzzle of size x. I was inspired by a puzzle from the USPC, around ten years ago. Ever
LMI SUDOKU TEST X x JULY 0 BY RICHARD STOLK The first logic puzzle that I ever designed was a scattered number place puzzle of size x. I was inspired by a puzzle from the USPC, around ten years ago. Ever
Tetsuya Nishio Cup. The Japan Number Place Championship. 3.8 sun 13:00-16:000
 Tetsuya Nishio up The Japan Number Place hampionship 3.8 sun 13:00-16:000 009 1 Relay Number Place 1 lassic Number Place 18 3 ± 1 Number Place 10 End View Number Place 1 5 Pips Number Place 1 6 Untouchable
Tetsuya Nishio up The Japan Number Place hampionship 3.8 sun 13:00-16:000 009 1 Relay Number Place 1 lassic Number Place 18 3 ± 1 Number Place 10 End View Number Place 1 5 Pips Number Place 1 6 Untouchable
Round minutes. Best results:
 Round 1 30 minutes Best results: Jakub Ondroušek Jan Zvěřina Matúš Demiger 410 points 390 points 350 points Round 1 Translation Sheet 1-3) Classic sudoku 6 6 Fill in the grid with digits 1 to 6 so that
Round 1 30 minutes Best results: Jakub Ondroušek Jan Zvěřina Matúš Demiger 410 points 390 points 350 points Round 1 Translation Sheet 1-3) Classic sudoku 6 6 Fill in the grid with digits 1 to 6 so that
LMI Monthly Test May 2010 Instruction Booklet
 Submit at http://www.logicmastersindia.com/m201005 LMI Monthly Test May 2010 Instruction Booklet Forum http://logicmastersindia.com/forum/forums/thread-view.asp?tid=53 Start Time 22-May-2010 20:00 IST
Submit at http://www.logicmastersindia.com/m201005 LMI Monthly Test May 2010 Instruction Booklet Forum http://logicmastersindia.com/forum/forums/thread-view.asp?tid=53 Start Time 22-May-2010 20:00 IST
Welcome to the Sudoku and Kakuro Help File.
 HELP FILE Welcome to the Sudoku and Kakuro Help File. This help file contains information on how to play each of these challenging games, as well as simple strategies that will have you solving the harder
HELP FILE Welcome to the Sudoku and Kakuro Help File. This help file contains information on how to play each of these challenging games, as well as simple strategies that will have you solving the harder
Episode 5 11 th 14 th May Casual & Word by Rakesh Rai
 and Episode 5 11 th 1 th May 018 by Rakesh Rai Puzzle Ramayan rounds will also serve as qualifiers for Indian Puzzle Championship for year 018. Please check http://logicmastersindia.com/pr/018pr.asp for
and Episode 5 11 th 1 th May 018 by Rakesh Rai Puzzle Ramayan rounds will also serve as qualifiers for Indian Puzzle Championship for year 018. Please check http://logicmastersindia.com/pr/018pr.asp for
Exploring Concepts with Cubes. A resource book
 Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Exploring Concepts with Cubes A resource book ACTIVITY 1 Gauss s method Gauss s method is a fast and efficient way of determining the sum of an arithmetic series. Let s illustrate the method using the
Tapa Variations Contest
 Tapa Variations Contest Feb 011 week TAPA RULE: Paint some cells black to create a continuous wall. Number/s in a cell indicate the length of black cell blocks on its neighbouring cells. If there is more
Tapa Variations Contest Feb 011 week TAPA RULE: Paint some cells black to create a continuous wall. Number/s in a cell indicate the length of black cell blocks on its neighbouring cells. If there is more
UKPA Presents. March 12 13, 2011 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET.
 UKPA Presents March 12 13, 2011 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET This contest deals with Sudoku and its variants. The Puzzle types are: No. Puzzle Points 1 ChessDoku 20 2 PanDigital Difference 25 3 Sequence Sudoku
UKPA Presents March 12 13, 2011 INSTRUCTION BOOKLET This contest deals with Sudoku and its variants. The Puzzle types are: No. Puzzle Points 1 ChessDoku 20 2 PanDigital Difference 25 3 Sequence Sudoku
Irish Collegiate Programming Contest Problem Set
 Irish Collegiate Programming Contest 2011 Problem Set University College Cork ACM Student Chapter March 26, 2011 Contents Instructions 2 Rules........................................... 2 Testing and Scoring....................................
Irish Collegiate Programming Contest 2011 Problem Set University College Cork ACM Student Chapter March 26, 2011 Contents Instructions 2 Rules........................................... 2 Testing and Scoring....................................
PASS Sample Size Software. These options specify the characteristics of the lines, labels, and tick marks along the X and Y axes.
 Chapter 940 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a scatter plot. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
Chapter 940 Introduction This section describes the options that are available for the appearance of a scatter plot. A set of all these options can be stored as a template file which can be retrieved later.
WPF PUZZLE GP 2018 ROUND 2. COMPETITION BOOKLET Host Country: Switzerland. ScHWeIZ. ScHWeiz. schweiz. SchWEIZ. SchwEiz. SchWEiZ. schweiz.
 WPF PUZZLE GP COMPETITION BOOKLET Host Country: Switzerland Markus Roth, Roger Kohler, Esther Naef Special Notes: CH is short for Confoederatio Helvetica, the Latin name for Switzerland, and appears in
WPF PUZZLE GP COMPETITION BOOKLET Host Country: Switzerland Markus Roth, Roger Kohler, Esther Naef Special Notes: CH is short for Confoederatio Helvetica, the Latin name for Switzerland, and appears in
ProCo 2017 Advanced Division Round 1
 ProCo 2017 Advanced Division Round 1 Problem A. Traveling file: 256 megabytes Moana wants to travel from Motunui to Lalotai. To do this she has to cross a narrow channel filled with rocks. The channel
ProCo 2017 Advanced Division Round 1 Problem A. Traveling file: 256 megabytes Moana wants to travel from Motunui to Lalotai. To do this she has to cross a narrow channel filled with rocks. The channel
Instructions Booklet. 26th WPC INDIA 2017 LOGIC MASTERS INDIA. THURSDAY, 19th OCTOBER Session 1. Session 2. FRIDAY, 20th OCTOBER Session 3.
 Instructions Booklet 6th WPC INDI 07 Final version THURSDY, 9th OCTOBER Session. Road To Bangalore 9:00-9:0 0m 50 points Individual. Indian Puzzle Land 9:50-0:50 60m 600 points Individual. Evergreens :05
Instructions Booklet 6th WPC INDI 07 Final version THURSDY, 9th OCTOBER Session. Road To Bangalore 9:00-9:0 0m 50 points Individual. Indian Puzzle Land 9:50-0:50 60m 600 points Individual. Evergreens :05
Preview Puzzle Instructions U.S. Sudoku Team Qualifying Test September 6, 2015
 Preview Puzzle Instructions U.S. Sudoku Team Qualifying Test September 6, 2015 The US Qualifying test will start on Sunday September 6, at 1pm EDT (10am PDT) and last for 2 ½ hours. Here are the instructions
Preview Puzzle Instructions U.S. Sudoku Team Qualifying Test September 6, 2015 The US Qualifying test will start on Sunday September 6, at 1pm EDT (10am PDT) and last for 2 ½ hours. Here are the instructions
The 2013 British Informatics Olympiad
 Sponsored by Time allowed: 3 hours The 2013 British Informatics Olympiad Instructions You should write a program for part (a) of each question, and produce written answers to the remaining parts. Programs
Sponsored by Time allowed: 3 hours The 2013 British Informatics Olympiad Instructions You should write a program for part (a) of each question, and produce written answers to the remaining parts. Programs
CSE Day 2016 COMPUTE Exam. Time: You will have 50 minutes to answer as many of the problems as you want to.
 CSE Day 2016 COMPUTE Exam Name: School: There are 21 multiple choice problems in this event. Time: You will have 50 minutes to answer as many of the problems as you want to. Scoring: You will get 4 points
CSE Day 2016 COMPUTE Exam Name: School: There are 21 multiple choice problems in this event. Time: You will have 50 minutes to answer as many of the problems as you want to. Scoring: You will get 4 points
UN DOS TREZ Sudoku Competition. Puzzle Booklet for Preliminary Round. 19-Feb :45PM 75 minutes
 Name: College: Email id: Contact: UN DOS TREZ Sudoku Competition Puzzle Booklet for Preliminary Round 19-Feb-2010 4:45PM 75 minutes In Association With www.logicmastersindia.com Rules of Sudoku A typical
Name: College: Email id: Contact: UN DOS TREZ Sudoku Competition Puzzle Booklet for Preliminary Round 19-Feb-2010 4:45PM 75 minutes In Association With www.logicmastersindia.com Rules of Sudoku A typical
1. Rectangles 20 points
 Name Rectangles points (+) Domino Hunt points Mirrors points (+) Skyscrapers points (+) ri-squares points (+) Meanders points (+) Fences points (+) ents points (+) Hungarian Count points Loopfinder points
Name Rectangles points (+) Domino Hunt points Mirrors points (+) Skyscrapers points (+) ri-squares points (+) Meanders points (+) Fences points (+) ents points (+) Hungarian Count points Loopfinder points
Booklet SUDOKUCUP 2. Kabròáci SUDOKUCUP.COM
 Booklet..COM .COM. Classical Sudoku Fill in the grid so that every row, column, and x box contains the digits through 9. 8 6 5 9 7 6 5 5 7 5 5 6 9-5 5 .COM. Diagonal Fill in the grid so that every row,
Booklet..COM .COM. Classical Sudoku Fill in the grid so that every row, column, and x box contains the digits through 9. 8 6 5 9 7 6 5 5 7 5 5 6 9-5 5 .COM. Diagonal Fill in the grid so that every row,
BmMT 2015 Puzzle Round November 7, 2015
 BMmT Puzzle Round 2015 The puzzle round is a team round. You will have one hour to complete the twelve puzzles on the round. Calculators and other electronic devices are not permitted. The puzzles are
BMmT Puzzle Round 2015 The puzzle round is a team round. You will have one hour to complete the twelve puzzles on the round. Calculators and other electronic devices are not permitted. The puzzles are
GENERALIZATION: RANK ORDER FILTERS
 GENERALIZATION: RANK ORDER FILTERS Definition For simplicity and implementation efficiency, we consider only brick (rectangular: wf x hf) filters. A brick rank order filter evaluates, for every pixel in
GENERALIZATION: RANK ORDER FILTERS Definition For simplicity and implementation efficiency, we consider only brick (rectangular: wf x hf) filters. A brick rank order filter evaluates, for every pixel in
Inductive Reasoning Practice Test. Solution Booklet. 1
 Inductive Reasoning Practice Test Solution Booklet 1 www.assessmentday.co.uk Question 1 Solution: B In this question, there are two rules to follow. The first rule is that the curved and straight-edged
Inductive Reasoning Practice Test Solution Booklet 1 www.assessmentday.co.uk Question 1 Solution: B In this question, there are two rules to follow. The first rule is that the curved and straight-edged
AKIL OYUNLARI MAGAZINE COMPETITION. 18 th - 20 th AUGUST 120 MINUTES
 August - 0 AKIL OYUNLARI MAGAZINE COMPETITION 8 th - 0 th AUGUST 0 MINUTES . Nurikabe Loop - Issue 7 0 x 0 - x.create some areas, surrounded with cells which are linked to a continuous loop..the numbers
August - 0 AKIL OYUNLARI MAGAZINE COMPETITION 8 th - 0 th AUGUST 0 MINUTES . Nurikabe Loop - Issue 7 0 x 0 - x.create some areas, surrounded with cells which are linked to a continuous loop..the numbers
Tile Number and Space-Efficient Knot Mosaics
 Tile Number and Space-Efficient Knot Mosaics Aaron Heap and Douglas Knowles arxiv:1702.06462v1 [math.gt] 21 Feb 2017 February 22, 2017 Abstract In this paper we introduce the concept of a space-efficient
Tile Number and Space-Efficient Knot Mosaics Aaron Heap and Douglas Knowles arxiv:1702.06462v1 [math.gt] 21 Feb 2017 February 22, 2017 Abstract In this paper we introduce the concept of a space-efficient
F F J M. Name. Part I
 Name 1. Battleships 20 points 2. No Four in a Row 20+20 points 3. Skyscrapers 25+25 points 4. Meanders 20 points 5. ABCD Connection 10+20 points 6. Crack It On 20+80 points 7. Loop Finder 25 points 8.
Name 1. Battleships 20 points 2. No Four in a Row 20+20 points 3. Skyscrapers 25+25 points 4. Meanders 20 points 5. ABCD Connection 10+20 points 6. Crack It On 20+80 points 7. Loop Finder 25 points 8.
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
SUDOKU Mahabharat. Episode 7 21 st 23 rd March. Converse by Swaroop Guggilam
 Episode 7 21 st 23 rd March by Swaroop Guggilam Important Links Submission Page : http://logicmastersindia.com/sm/201503/ Discussion Thread : http://logicmastersindia.com/t/?tid=936 bout Sudoku Mahabharat
Episode 7 21 st 23 rd March by Swaroop Guggilam Important Links Submission Page : http://logicmastersindia.com/sm/201503/ Discussion Thread : http://logicmastersindia.com/t/?tid=936 bout Sudoku Mahabharat
Using KenKen to Build Reasoning Skills 1
 1 INTRODUCTION Using KenKen to Build Reasoning Skills 1 Harold Reiter Department of Mathematics, University of North Carolina Charlotte, Charlotte, NC 28223, USA hbreiter@email.uncc.edu John Thornton Charlotte,
1 INTRODUCTION Using KenKen to Build Reasoning Skills 1 Harold Reiter Department of Mathematics, University of North Carolina Charlotte, Charlotte, NC 28223, USA hbreiter@email.uncc.edu John Thornton Charlotte,
Figure 1: The Game of Fifteen
 1 FIFTEEN One player has five pennies, the other five dimes. Players alternately cover a number from 1 to 9. You win by covering three numbers somewhere whose sum is 15 (see Figure 1). 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9
1 FIFTEEN One player has five pennies, the other five dimes. Players alternately cover a number from 1 to 9. You win by covering three numbers somewhere whose sum is 15 (see Figure 1). 1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9
Laboratory 2: Graphing
 Purpose It is often said that a picture is worth 1,000 words, or for scientists we might rephrase it to say that a graph is worth 1,000 words. Graphs are most often used to express data in a clear, concise
Purpose It is often said that a picture is worth 1,000 words, or for scientists we might rephrase it to say that a graph is worth 1,000 words. Graphs are most often used to express data in a clear, concise
Junior Circle Games with coins and chessboards
 Junior Circle Games with coins and chessboards 1. a.) There are 4 coins in a row. Let s number them 1 through 4. You are allowed to switch any two coins that have a coin between them. (For example, you
Junior Circle Games with coins and chessboards 1. a.) There are 4 coins in a row. Let s number them 1 through 4. You are allowed to switch any two coins that have a coin between them. (For example, you
Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles February 2-3, 2016 Logic Puzzles
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles February 2-3, 2016 Logic Puzzles Introduction Math is not always numbers, equations
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles February 2-3, 2016 Logic Puzzles Introduction Math is not always numbers, equations
LMI-MONTHLY TEST JUN 2010 'SPEED SIXES'
 LMI-MONTHLY TEST JUN 2010 'SPEED SIXES' 6/6/2010 166 MINUTES 1666 POINTS INSTRUCTION BOOKLET (Sudokus by Tejal Phatak / Rohan Rao) http://rohanrao.blogspot.com/ WEBPAGE: http://logicmastersindia.com/forum/forums/thread-view.asp?
LMI-MONTHLY TEST JUN 2010 'SPEED SIXES' 6/6/2010 166 MINUTES 1666 POINTS INSTRUCTION BOOKLET (Sudokus by Tejal Phatak / Rohan Rao) http://rohanrao.blogspot.com/ WEBPAGE: http://logicmastersindia.com/forum/forums/thread-view.asp?
ISudoku. Jonathon Makepeace Matthew Harris Jamie Sparrow Julian Hillebrand
 Jonathon Makepeace Matthew Harris Jamie Sparrow Julian Hillebrand ISudoku Abstract In this paper, we will analyze and discuss the Sudoku puzzle and implement different algorithms to solve the puzzle. After
Jonathon Makepeace Matthew Harris Jamie Sparrow Julian Hillebrand ISudoku Abstract In this paper, we will analyze and discuss the Sudoku puzzle and implement different algorithms to solve the puzzle. After
Solving Problems. PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1. Activities. PS1.1 Number stories 1.
 PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1 PS1.1 Number stories 1 PS1.2 Difference arithmagons PS1.3 Changing orders PS1.4 Making shapes PS1.5 Odd or even? PS1.6 Odd
PS1 Use and apply mathematics to solve problems, communicate and reason Year 1 PS1.1 Number stories 1 PS1.2 Difference arithmagons PS1.3 Changing orders PS1.4 Making shapes PS1.5 Odd or even? PS1.6 Odd
This chapter gives you everything you
 Chapter 1 One, Two, Let s Sudoku In This Chapter Tackling the basic sudoku rules Solving squares Figuring out your options This chapter gives you everything you need to know to solve the three different
Chapter 1 One, Two, Let s Sudoku In This Chapter Tackling the basic sudoku rules Solving squares Figuring out your options This chapter gives you everything you need to know to solve the three different
Input. Output. Examples. Note. Input file: Output file: standard input standard output
 Problem AC. Art Museum file: 6 seconds 6 megabytes EPFL (Extreme Programmers For Life) want to build their 7th art museum. This museum would be better, bigger and simply more amazing than the last 6 museums.
Problem AC. Art Museum file: 6 seconds 6 megabytes EPFL (Extreme Programmers For Life) want to build their 7th art museum. This museum would be better, bigger and simply more amazing than the last 6 museums.
Fundamentals III CHAPTER PROJECT EXERCISE
 CHAPTER 4 Fundamentals III PROJECT EXERCISE This project exercise provides point-by-point instructions for setting up the drawing with layers and then creating the objects shown in Figure P4 1. FIGURE
CHAPTER 4 Fundamentals III PROJECT EXERCISE This project exercise provides point-by-point instructions for setting up the drawing with layers and then creating the objects shown in Figure P4 1. FIGURE
Sudoku Xtra. Packed with Puzzles! >> The Logic Puzzle Brain Workout. >> Daffodil Samurai Sudoku
 Sudoku Xtra TM ugust ll puzzles by Dr Gareth Moore ecept where otherwise credited For back issues and subscriptions, isit www.sudokuxtra.com >> Daffodil Samurai Sudoku Full instructions on page. >> The
Sudoku Xtra TM ugust ll puzzles by Dr Gareth Moore ecept where otherwise credited For back issues and subscriptions, isit www.sudokuxtra.com >> Daffodil Samurai Sudoku Full instructions on page. >> The
Creo Revolve Tutorial
 Creo Revolve Tutorial Setup 1. Open Creo Parametric Note: Refer back to the Creo Extrude Tutorial for references and screen shots of the Creo layout 2. Set Working Directory a. From the Model Tree navigate
Creo Revolve Tutorial Setup 1. Open Creo Parametric Note: Refer back to the Creo Extrude Tutorial for references and screen shots of the Creo layout 2. Set Working Directory a. From the Model Tree navigate
Three of these grids share a property that the other three do not. Can you find such a property? + mod
 PPMTC 22 Session 6: Mad Vet Puzzles Session 6: Mad Veterinarian Puzzles There is a collection of problems that have come to be known as "Mad Veterinarian Puzzles", for reasons which will soon become obvious.
PPMTC 22 Session 6: Mad Vet Puzzles Session 6: Mad Veterinarian Puzzles There is a collection of problems that have come to be known as "Mad Veterinarian Puzzles", for reasons which will soon become obvious.
Kenken For Teachers. Tom Davis January 8, Abstract
 Kenken For Teachers Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles January 8, 00 Abstract Kenken is a puzzle whose solution requires a combination of logic and simple arithmetic
Kenken For Teachers Tom Davis tomrdavis@earthlink.net http://www.geometer.org/mathcircles January 8, 00 Abstract Kenken is a puzzle whose solution requires a combination of logic and simple arithmetic
Introduction. EN Raster Graphics 6-1
 6 Raster Graphics Introduction A raster image is a made up of a series of discrete picture elements pixels. Pictures such as those in newspapers, television, and documents from Hewlett-Packard printers
6 Raster Graphics Introduction A raster image is a made up of a series of discrete picture elements pixels. Pictures such as those in newspapers, television, and documents from Hewlett-Packard printers
Chapter 4 Number Theory
 Chapter 4 Number Theory Throughout the study of numbers, students Á should identify classes of numbers and examine their properties. For example, integers that are divisible by 2 are called even numbers
Chapter 4 Number Theory Throughout the study of numbers, students Á should identify classes of numbers and examine their properties. For example, integers that are divisible by 2 are called even numbers
TASK NOP CIJEVI ROBOTI RELJEF. standard output
 Tasks TASK NOP CIJEVI ROBOTI RELJEF time limit (per test case) memory limit (per test case) points standard standard 1 second 32 MB 35 45 55 65 200 Task NOP Mirko purchased a new microprocessor. Unfortunately,
Tasks TASK NOP CIJEVI ROBOTI RELJEF time limit (per test case) memory limit (per test case) points standard standard 1 second 32 MB 35 45 55 65 200 Task NOP Mirko purchased a new microprocessor. Unfortunately,
