Nebraska Social Studies Standards High School
|
|
|
- George Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Correlation of 2016 To the Nebraska High School
2 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson meets the for High School. Pearson is excited to announce its NEW United States History program! Designed to help prepare students to be college and career ready all while unlocking the exciting story of our nation s history, Pearson United States History invites students to explore the enduring issues that continue to shape our nation s history. The program bridges time-tested best practices, curriculum standard expectations, and technology to help prepare students to be college and career ready all while unlocking the exciting story of our nation s history. The program is available in print, digital, and blended options. The Pearson United States History program uses a research tested four-part learning model to enhance teaching and understanding. 1. Connect: Students make learning personal as they connect to content through a story and activate their prior knowledge, personal experience, and perspective. 2. Investigate: Students actively learn, investigate, and acquire key content knowledge through a variety of components both in print and digital. 3. Synthesize: Students extend their understanding by applying what they just learned in a quick recap and pull-it-all-together exercise before they move on to the next lesson. 4. Demonstrate: Students demonstrate their understanding through a variety of authentic, formative, and summative assessments. Technology Reimagined with Pearson s Realize Platform etext Student Edition with valuable tools for individualized instruction, remediation, or enrichment NBC Learn MyStory Videos that engage students in every chapter Interactive Reading and Note Taking Study Guide allows for differentiated instruction and assessments Online Lesson Planner; Standards-based planner that helps to save prep time. Assessments; built-in progress monitoring includes both formative and summative assessments Teacher Lesson Plans with point-of-use resources Flipped Videos available to assign to students or serve as quick refreshers 2
3 Table of Contents Civics... 4 Economics... 9 Geography History Chronological Thinking
4 Civics K-12 Civics: Students will develop and apply the skills of civic responsibility to make informed decisions based upon knowledge of government at local, state, national and international levels. Forms and Functions of Government High School (United States/World) SS Students will analyze and evaluate the foundation, structures, and functions of the United States government as well as local, state, and international governments. SS a Summarize the historical foundation that influenced the creation of the United States Constitution (e.g., philosophers, social contract theory, natural rights, Constitutional Convention, Federalist, and Anti-Federalist Papers) SE: Mayflower Compact, 5; Democratic Ideals in the American Colonies, 6; The Struggle for Ratification, 14 15; Principles of the Constitution, 15 16; United States Constitution, Topic Assessment: Review (3. Analyze and Evaluate the Declaration of Independence), 43; (6. Analyze and Evaluate Intent of the U.S. Constitution), 43; (7. Analyze and Evaluate Importance of Constitution and Bill of Rights), 43 SS b Analyze and evaluate the structure of American constitutional government (e.g., federalism, democracy, representative government, branches of the government, separation of powers, checks and balances, amendment process, concurrent/enumerated/implied powers, electoral college) SS c Analyze and evaluate the functions of United States government (e.g., national security, legislative lawmaking, executive implementation, judicial interpretation, constitutionalism, taxation, naturalization of citizens) SE: The Struggle for Ratification, 14 15; Principles of the Constitution, 15 16; United States Constitution, Topic Assessment: Review (6. Analyze and Evaluate Intent of the U.S. Constitution), 43; (7. Analyze and Evaluate Importance of Constitution and Bill of Rights), 43; (8. Analyze and Evaluate the Meaning of Federalism), 43 SE: Principles of the Constitution, 15 16; The Struggle Over Foreign Policy, 17 18; Judicial Review, 18; The Young Republic, 21; Monetary Policy, 142, 143; United States Constitution, Topic Assessment: Review (6. Analyze and Evaluate Intent of the U.S. Constitution), 43; (7. Analyze and Evaluate Importance of Constitution and Bill of Rights), 43; (8. Analyze and Evaluate the Meaning of Federalism), 43; Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152 4
5 SS d Analyze and evaluate the foundation, structures, and functions of local government (e.g., city council, school board, county government, regional boards) SS e Analyze and evaluate the foundation, structures, and functions of state government (e.g., bicameral/unicameral, reapportionment/redistricting, branches of government) SS f Analyze and evaluate the foundation, structures, and functions of supranational organizations (e.g., United Nations, NATO, European Union, treaties, trade organizations) SE: Federalism, 15 16; Local Government, 41, 55, 297, 301, 318, 441, 482, 623, 632, 634 Topic Assessment: Review (8. Analyze and Evaluate the Meaning of Federalism), 43 SE: States Establish Republican Governments, 11; State Government, 11, 15, 20, 53, 55, 68, 72 73, 163, 297, 321, 328, 436, 464, 469, 482 Topic Assessment: Review (8. Analyze and Evaluate the Meaning of Federalism), 43 SE: United Nations, 388, 392, 395, 408, 413, 419, 544, 588; SALT I, 545; SALT II, 557, 569; Brest Litovsk, 231; NAFTA, , 637; NATO, 400, ; United States Constitution, Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (4. Describe Impact of Gulf of Tonkin Resolution), 518; Topic 6 Assessment (1. Describe NAFTA), 637 SS g Analyze and evaluate the roles that political parties have played in the United States SE: Political Parties, 27, 34, 49, 63, 67, 140, 142, 181, , 237, 428, , 477, , 570, 573 Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (15. Evaluate Impact of Populist Party), 152; Topic 4 (10. Evaluate Impact of Progressive Party), 209; Topic 5 (12. Analyze Impact of Third Parties), 604; Topic 6 (5. Analyze 2000 Presidential Election), 637 5
6 SS h Analyze and evaluate United States foreign policy issues (e.g. methods, approaches, events) SE: This standard is met throughout the program. Examples include the following references: The Spanish-American War, ; The United States Emerges as a World Power, ; America Enters World War I, ; America Enters World War II, ; The Cold War Intensifies, ; The Cold War and Vietnam, ; A New Era in Foreign Policy, ; Free Trade and Treaties, ; The United States and Global Business, 610; Competing in a Global Economy & China s GDP (graph), 612; The Role of the United States in the Future Economy, ; Competing in a Global Economy, Topic Assessment: Topic 10 Assessment (2. Explain Reasons for and Outcomes of U.S. Foreign Involvement), 518; Topic 10 Assessment (3. Explain Reasons for U.S. Foreign Involvement), 518; Topic 10 Assessment (14. Explain Outcomes of Vietnam War), 519; Topic 12 Assessment (9. Describe Iran-Contra Affair), 604 6
7 Civic Participation SS Students will address local, state, national or international issues and policies through meaningful civic participation. SS a Evaluate how individuals and groups can effectively use the structure and functions of various levels of government to shape policy (e.g., lobbying, voting, contacting government officials, petitioning) SE: 21 st Century Skills: Participate in a Discussion or Debate, ; Being an Informed Citizen, ; Political Participation, 710; Voting, 711; Serving on a Jury, ; Citizenship, 51, 54, 62 64, 68, 70, 174, 367, 395, 458, 533; also see: The Organized Labor Movement, 91 97; Women Gain Rights, ; Striving for Equality, ; Reformers in the White House, ; Civil Rights, Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (4. Evaluate Methods of Expanding Right to Participate in Democratic Process), 484; Topic 2 (13. Trace Historical Development of Political Equality), 721 SS b Analyze the significance and benefits of patriotic symbols, songs, holidays, and activities (e.g. Pledge of Allegiance, "The Star Spangled Banner", "America", Veteran's Day, Martin Luther King, Jr. Day, American Indian Day, Constitution Day) SS c Engage in civic activities (e.g., discussing current issues, advocating for personal rights and the rights of others, influencing governmental actions, participating in civil discourse, registering for selective service, participating in community improvement activities, service learning) SE: For related material see: Image of the Constitution, 2 3; Painting of George Washington, 4; Image of Lincoln and the Emancipation Proclamation, 38; Photograph of Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr., SE: 21 st Century Skills: Participate in a Discussion or Debate, ; Being an Informed Citizen, ; Political Participation, 710; Voting, 711; Serving on a Jury, ; Citizenship, 51, 54, 62 64, 68, 70, 174, 367, 395, 458, 533 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (4. Evaluate Methods of Expanding Right to Participate in Democratic Process), 484; Topic 2 (13. Trace Historical Development of Political Equality), 721 7
8 SS d Analyze an issue and determine which level of government is most appropriate to utilize in addressing the issue SE: Federalism, 15 16; State Government, 11, 15, 20, 53, 55, 68, 72 73, 163, 297, 321, 328, 436, 464, 469, 482; Local Government, 41, 55, 297, 301, 318, 441, 482, 623, 632, 634; 21st Century Skills: Being an Informed Citizen, ; Political Participation, 710; Voting, 711; Serving on a Jury, Topic Assessment: Review (8. Analyze and Evaluate the Meaning of Federalism), 43 SS e Describe the roles and influences of individuals, groups, and the media as checks on governmental practices (e.g., interest groups, political action committees, lobbyists, public opinion polls) SE: The Organized Labor Movement, 91 97; Women Gain Rights, ; Striving for Equality, ; Reformers in the White House, ; Civil Rights, ; 21 st Century Skills: Participate in a Discussion or Debate, ; Being an Informed Citizen, ; Political Participation, 710; Voting, 711; Serving on a Jury, ; also see: Citizenship, 51, 54, 62 64, 68, 70, 174, 367, 395, 458, 533 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (4. Evaluate Methods of Expanding Right to Participate in Democratic Process), 484; Topic 2 (13. Trace Historical Development of Political Equality), 721 SS f Critique various media sources for accuracy and perspective SE: Mass Media, 193, 320, 528, 569; Analyze Political Cartoons, 52, 56, 88, 89, 94, 149, 157, 179, 181, 197, 219, 248, 297, 304, 338, 345, 370, 412, 511, 541; 21 st Century Skills: Analyze Primary and Secondary Sources, ; Compare Viewpoints, ; Identify Bias, 703 Projects involving research (examples): Topic 3 (10. Use Historical Inquiry), 152; Topic 7 (13. Evaluate Participation in International Treaties and Organizations), 396; Topic 8 (1. Describe Berlin Airlift), 444; Topic 12 (14. Identify Issues Across Political Spectrum), 604; Topic 13 (17. Explain Innovations in Medicine), 638 8
9 Economics K-12 Economics: Students will utilize economic reasoning skills to make informed judgments and become effective participants in the economy at the local, state, national and international levels. Markets High School (United States/World) SS Students will assess how market forces guide the owners of land, labor, and capital and determine the allocation of wealth in the economy. SS a Explain how the factors of production are bought and sold in the market SE: This standard is met throughout the program. Examples include the following references: Economic Development in the North and South, 37; Innovation Boosts Growth, 76 77; Innovation Drives Economic Development, 78 80; Mass Production, 80 81; Industrialization and the New South, 81 82; The Effects of Industrialization, 83 84; Economies of Scale, 86; Mass production, 241; Assembly lines, 242; Science, Technology, and the Free Enterprise System, 244; The Impact of Henry Ford and the Automobile, ; The Production Miracle, 354; Technological Progress Enhances Productivity, 425; Transforming Business and Industry, 600 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (1. Explain Economic Effects of Technological Innovations), 117; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; Topic 8 (9. Explain Economic Impact of Computers), 445; Topic 12 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 9
10 SS b Analyze the role of the product market and the resource market SE: This standard is met throughout the program. Examples include the following references: Growing Demand for Cotton, 21 22; Economic Development in the North and South, 37; How to Rebuild the Southern Economy, 49; Land Distribution in the South, 59 60; Natural Resources Fuel Economic Development, 76 77; Steel, Innovation, and Economic Development, 79; Mass Production, 80 81; New Industries Develop, 81; The Southern Economy Lags Behind, 82; Farm Issues in the South, 82 83; Conspicuous Consumerism, 111; Mining and the Growth of Railroads, ; The Cattle Industry Boom, ; Tension Over Economic Resources, 137; Farmers Face Economic Difficulty, ; Crop Prices Fall, ; The Production Miracle, 354; Fuel shortages, 556; Competing in a Global Economy & China s GDP (graph), 612; American Recovery & Reinvestment Act (ARRA), 623 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (1. Explain Economic Effects of Technological Innovations), 117; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; Topic 8 (9. Explain Economic Impact of Computers), 445; Topic 12 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 SS c Understand productivity as a measure of the quantity of goods and services produced with a given amount of resources (e.g., Gross Domestic Product) SE: U.S. Economy in World War I (GDP), 224; Competing in a Global Economy & China s GDP (graph), 612; American Recovery & Reinvestment Act (ARRA), 623 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 Assessment (1. Explain Economic Effects of Technological Innovations),
11 SS d Analyze how market forces determine what producers choose to produce and which combination of productive resources will be most productive SE: This standard is met throughout the program. Examples include the following references: Innovation Boosts Growth, 76 77; Free Enterprise Encourages the Rise of Entrepreneurship, 77 78; Laissez-Faire Policies Encourage Growth, 78 79; Mass Production, 80 81; The Effects of Industrialization, 83 84; Big Business Rises, 85 90; Free Enterprise Improves Life, ; Conspicuous Consumerism, 111; U.S. Exports, 205; Mass production, 241; The Postwar Economy Booms, ; Hidden Economic Problems in the Roaring Twenties, ; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; The Role of Entrepreneurs, 427, 428; Goals and Impacts of Reagonomics, 575; Free Trade and Treaties, Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (1. Explain Economic Effects of Technological Innovations), 117; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; Topic 8 (9. Explain Economic Impact of Computers), 445; Topic 12 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 SS e Explain how wages/earnings are affected by the market (e.g., value of products, supply and demand of labor, worker skills and qualifications) SE: Economic Development in the North and South, 37; The Workforce Grows, 77; Company Towns and Wage Slavery, 92; Miners pay/wage raise, 177; An Evolving Job Market Emphasizes Education, ; Unemployment Leaves Families Struggling, ; Moving Wherever Work Can Be Found, ; Minimum Wage, 310; Unemployment, 313; The Production Miracle, 354; Changes in the Labor Force, 427; Effects of Prosperity on Labor, 428; Reagan and Organized Labor, ; Dot.com Boom, 602; Transforming Business and Industry, 600; Economic Issues and Reform (unemployment), 624 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 Assessment (4. Understand Impact of Mass Production),
12 SS f Explain the role and importance of profit and return on investments to producers. (e.g. increase in supply and expansion of industries) SE: Innovation Boosts Growth, 76 77; Free Enterprise Encourages the Rise of Entrepreneurship, 77 78; Laissez-Faire Policies Encourage Growth, 78 79; New Industries Develop, 81; Corporations Find New Ways of Doing Business, 85 88; Free Enterprise Improves Life, ; Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Science, Technology, and the Free Enterprise System, 244; The Postwar Economy Booms, ; The Impact of Henry Ford and the Automobile, ; Business Cycle, 280 Speculation, 284; The Role of Entrepreneurs, 427, 428; Competing in a Global Economy, Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (1. Explain Economic Effects of Technological Innovations), 117; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; Topic 8 (9. Explain Economic Impact of Computers), 445; Topic 12 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector),
13 SS Students will illustrate how markets determine prices and allocate goods and services. SS a Understand demand, quantity SE: Growing Demand for Cotton, 21 22; demanded, and changes in demand Innovation Drives Economic Development, 78 80; Steel, Innovation, and Economic Development, 79; Mass Production, 80 81; New Industries Develop, 81; The Corporation Meets New Needs, 85 86; The Cattle Industry Boom, ; Mass production, 241; Science, Technology, and the Free Enterprise System, 244; The Impact of Henry Ford and the Automobile, ; Economic Growth in the 1920s, ; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Technological Progress Enhances Productivity, 425; Dot.com Boom, 602 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (1. Explain Economic Effects of Technological Innovations), 117; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; Topic 8 (9. Explain Economic Impact of Computers), 445; Topic 12 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector),
14 SS b Understand supply, quantity supplied, and changes in supply SE: Growing Demand for Cotton, 21 22; Innovation Drives Economic Development, 78 80; Steel, Innovation, and Economic Development, 79; Mass Production, 80 81; New Industries Develop, 81; The Corporation Meets New Needs, 85 86; The Cattle Industry Boom, ; Mass production, 241; Science, Technology, and the Free Enterprise System, 244; The Impact of Henry Ford and the Automobile, ; Economic Growth in the 1920s, ; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Technological Progress Enhances Productivity, 425; Dot.com Boom, 602 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (1. Explain Economic Effects of Technological Innovations), 117; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; Topic 8 (9. Explain Economic Impact of Computers), 445; Topic 12 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 SS c Understand that equilibrium price and quantity are determined by supply and demand SE: Growing Demand for Cotton, 21 22; Wholesale Price of Cotton, 82; Economies of Scale, 86; Units and pricing, 86; Buying on Margin, 243; The Stock Market Hits Bottom, 284; Crop Prices Fall, ; Dot.com Boom, 602 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 Assessment (5. Analyze Farm Issues in the South), 117 SS d Hypothesize how competition between sellers could results in lower prices, higher quality products, and better customer service SE: Growing Demand for Cotton, 21 22; Wholesale Price of Cotton, 82; Economies of Scale, 86; Units and pricing, 86; Buying on Margin, 243; The Stock Market Hits Bottom, 284; Crop Prices Fall, ; Dot.com Boom, 602 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 Assessment (5. Analyze Farm Issues in the South),
15 SS e Hypothesize how producers and consumers affect market prices and quantities through the goods and services they produce and buy (e.g., shifts in supply and demand, price elasticity) SE: Growing Demand for Cotton, 21 22; Free Enterprise Encourages the Rise of Entrepreneurship, 77 78; Innovation Drives Economic Development, 78 80; Wholesale Price of Cotton, 82; Corporations Find New Ways of Doing Business, 85 88; Economies of Scale, 86; Units and pricing, 86; Buying on Margin, 243; Business Cycle, 280; The Stock Market Hits Bottom, 284; Crop Prices Fall, ; Dot.com Boom, 602 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (5. Analyze Farm Issues in the South), 117; Topic 10 (8. Describe Impact of Defense Spending),
16 Institutions SS Students will analyze how economic institutions impact individuals and groups. SS a Analyze how various economic institutions have played a role in United States economic policy and practice (e.g., corporations, labor unions, financial institutions, stock markets, cooperatives, and business partnerships) SE: This standard is met throughout the program. Examples include the following references: Banking, 20, 142, 280, , 293, 300, 302; Free Enterprise Encourages the Rise of Entrepreneurship, 77 78; New Industries Develop, 81; Corporations Find New Ways of Doing Business, 85 88; The Corporation Meets New Needs, 85 86; Business Management Innovations, 86 87; The Pros and Cons of Big Business, 88; Company Towns and Wage Slavery, 92; National Consumers League (NCL), 165; Antitrust legislation, 85, 89 90, 97, 117, 157, 178, 181, 185, 209; Regulation of Commercial Banks, 184; Federal Trade Commission, ; Lack of government intervention in the economy, 286; Reconstruction Finance Corporation, 298; Two Presidents Respond, ; The New Deal Expands, ; Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), 302; An Expansion of Executive Power, ; The Role of Entrepreneurs, 427, 428; Franchise Businesses, 427; American Corporations Go Multinational, 428; Community Reinvestment Act, 557; Goals and Impacts of Reagonomics, 575; The United States and Global Business, 610; The Role of the United States in the Future Economy, Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 4 (1. Describe Benefits and Costs of Antitrust Acts), 209; (12. Evaluate Pros and Cons of International Treaties), 210; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; (9. Identify Impact of Tariffs), 275; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression), 327; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603; Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA),
17 SS b Describe how measures used by economic institutions are calculated (e.g., trends and business cycles using GDP, unemployment rates, inflation rates) SE: U.S. Economy in World War I (GDP), 224; Business Cycle, 280; Unemployment Leaves Families Struggling, ; Unemployment, 313; Minimum Wage, 310; Increased Opportunities in Employment, 369; Postwar Inflation, 424; U.S. Inflation, 570; Competing in a Global Economy & China s GDP (graph), 612; American Recovery & Reinvestment Act (ARRA), 623; Economic Issues and Reform (unemployment), 624 Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 4 (1. Describe Benefits and Costs of Antitrust Acts), 209; (12. Evaluate Pros and Cons of International Treaties), 210; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; (9. Identify Impact of Tariffs), 275; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression), 327; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603; Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA), 637 SS c Explain how banks and a sound monetary system are critical to a functioning economy SE: Banking, 20, 142, 280, , 293, 300, 302; Monetary Policy, 142, 143; Regulation of Commercial Banks, 184; Federal Trade Commission, ; Reconstruction Finance Corporation, 298; Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), 302 Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 4 (15. Describe Federal Reserve Act), 210 SS d Describe the functions and role of the Federal Reserve System and its influence through monetary policy (e.g., balancing inflation and unemployment) SE: Federal Reserve, 285, 302, 557, 575, Topic Assessment: Topic 4 (15. Describe Federal Reserve Act),
18 SS e Understand how financial markets determine the cost of borrowing and influence the level of economic activity SE: Bank Politics and Economic Woes, 20; Debt, interest, and sharecropping, 59 60; Conspicuous Consumerism, 111; Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Americans Rely on Credit, 283; Speculation, 284; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Savings and Loan Crisis, 576 Topic Assessment: Topic 6 (2. Identify Impact of Stock Market Speculation on Great Depression), 327 SS Students will assess how private ownership of property is a basic institution of a market economy. SS a Assess how property rights are SE: Private Property, 6, 78, 93, 97, 178, defined, enforced, and limited by , 254, 400, 541; Patent, 76, 78, government (e.g., zoning laws, eminent 80, 103, 131, 612; Homestead Act, 99, domain, Homestead Act, copyright laws, 130, 134, 152, 292 patents, and intellectual property) Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (8. Describe Economic Impact of Homestead Act), 152 SS b Describe the role of market economy in United States history (e.g., periods of prosperity, recessions, and overall growth) SE: Innovation Boosts Growth, 76 77; Free Enterprise Encourages the Rise of Entrepreneurship, 77 78; Innovation Drives Economic Development, 78 80; New Industries Develop, 81; Big Business Rises, 85 90; Conspicuous Consumerism, 111; New Ways of Shopping, 112; Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; The Postwar Economy Booms, ; Economic Prosperity Under Coolidge, ; Business Cycle, 280; Economic Trends & The Great Depression, 285; Trickle-down economics, 298; An Increasingly Significant Role Promoting Economic Growth, ; Postwar Prosperity, ; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; The Role of Entrepreneurs, 427, 428; Private Sector Creates Economic Opportunities, 577; Dot.com Boom, 602; The Service Sector Expands & The Decline of Organized Labor, 611 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (2. Analyze the Rise of Entrepreneurship), 117; Topic 8 (11. Analyze Innovations in Transportation),
19 Financial Literacy SS Students will recognize and predict the impact that various economic systems will have on people. SS a Develop a logical argument debating the merits of various economic systems (e.g., traditional, command, market, mixed) SE: Free Enterprise Encourages the Rise of Entrepreneurship, 77 78; Socialism, 93; Free Enterprise Improves Life, ; Technology and Free Enterprise Lead to Higher Standards of Living, 112; Science, Technology, and the Free Enterprise System, 244; Free Enterprise Improves U.S. Standard of Living, ; Communism, ; Free Trade and Treaties, Topic Assessment: Topic 6 (2. Identify Impact of Stock Market Speculation on Great Depression), 327; Topic 8 (2. Analyze the Rise of Entrepreneurship), 117; Topic 8 (11. Analyze Innovations in Transportation),
20 SS b Evaluate the historical use of various economic systems SE: This standard is met throughout the program. Examples include the following references: Banking, 20, 142, 280, , 293, 300, 302; Free Enterprise Encourages the Rise of Entrepreneurship, 77 78; Antitrust legislation, 85, 89 90, 97, 117, 157, 178, 181, 185, 209; Regulation of Commercial Banks, 184; Federal Trade Commission, ; Reconstruction Finance Corporation, 298; Two Presidents Respond, ; The New Deal Expands, ; Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), 302; An Expansion of Executive Power, ; The Role of Entrepreneurs, 427, 428; Franchise Businesses, 427; American Corporations Go Multinational, 428; Community Reinvestment Act, 557; Goals and Impacts of Reagonomics, 575; The United States and Global Business, 610; The Role of the United States in the Future Economy, Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 4 (1. Describe Benefits and Costs of Antitrust Acts), 209; (12. Evaluate Pros and Cons of International Treaties), 210; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; (9. Identify Impact of Tariffs), 275; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression), 327; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603; Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA), 637 SS c Compare the standard of living with other countries (Germany, Brazil, Russia, India, China) SE: Technology and Free Enterprise Lead to Higher Standards of Living, 112; Miners pay/wage raise, 177; Minimum Wage, 310; Free Enterprise Improves U.S. Standard of Living, Topic Assessment: Topic 2 (13. Analyze Social Issues Affecting Women), 118; (14. Analyze How Transportation Improved Standard of Living),
21 SS Students will understand economic concepts that support rational decision making SS a Explore employment trends SE: The Workforce Grows, 77; Company and reasons for growth and decline in Towns and Wage Slavery, 92; Miners employment pay/wage raise, 177; An Evolving Job Market Emphasizes Education, ; Unemployment Leaves Families Struggling, ; Moving Wherever Work Can Be Found, ; Minimum Wage, 310; Unemployment, 313; The Production Miracle, 354; Changes in the Labor Force, 427; Effects of Prosperity on Labor, 428; Reagan and Organized Labor, ; Dot.com Boom, 602; Transforming Business and Industry, 600; Economic Issues and Reform (unemployment), 624 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 Assessment (4. Understand Impact of Mass Production), 117 SS b Make career decisions by systematically considering alternatives and consequences through the use of cost benefit analysis SE: For related material see: An Evolving Job Market Emphasizes Education, ; Unemployment Leaves Families Struggling, ; Moving Wherever Work Can Be Found, ; Minimum Wage, 310; Changes in the Labor Force, 427; Dot.com Boom, 602; Transforming Business and Industry, 600; The Service Sector Expands & The Decline of Organized Labor, 611 Topic Assessment: Topic 2 Assessment (4. Understand Impact of Mass Production), 117 SS c Assess the incentives for investing in personal education, skills, and talents SE: For related material see: An Evolving Job Market Emphasizes Education, ; Unemployment Leaves Families Struggling, ; Moving Wherever Work Can Be Found, ; Minimum Wage, 310; Changes in the Labor Force, 427; Dot.com Boom, 602; Transforming Business and Industry, 600; The Service Sector Expands & The Decline of Organized Labor, 611 Topic Assessment: Topic 6 Assessment (17. Explain Innovations in Medicine),
22 SS d Identify various ways people earn a living by using career programs to explore opportunities (e.g., Nebraska Career Education) SE: For related material see: The Service Sector Expands, 611; The Role of the United States in the Future Economy, ; Technology Transforms Life, Topic Assessment: Topic 6 Assessment (17. Explain Innovations in Medicine), 638 SS Students will apply effective money management concepts. SS a Organize personal finances and SE: For related material see: A New Tax on use a budget to manage cash flow Income, 183; Income Tax Rates, 249; 21 st Century Skills: Paying Taxes, ; also see: Minimum Wage, 310 SS b Compare and contrast checking and savings accounts SS c Assess the effects of taxes on personal income SE: For related material see: Bank Politics and Economic Woes, 20; Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Americans Rely on Credit, 283; Speculation, 284; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Savings and Loan Crisis, 576 SE: A New Tax on Income, 183; Income Tax Rates, 249; Tax Cuts and Deregulation, ; 21st Century Skills: Paying Taxes,
23 SS Students will critique strategies used to establish, build, maintain, monitor, and control credit. SS a Analyze factors that affect the SE: Bank Politics and Economic Woes, 20; choice of credit, the cost of credit, and the Debt, interest, and sharecropping, 59 60; legal aspects of using credit Conspicuous Consumerism, 111; Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Americans Rely on Credit, 283; Speculation, 284; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Savings and Loan Crisis, 576 Topic Assessment: Topic 5 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 SS b Identify strategies of establishing and maintaining a good credit rating for effective credit management (e.g., credit cards, auto loans, mortgages) SE: For related material see: Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Americans Rely on Credit, 283; Speculation, 284; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Savings and Loan Crisis, 576 Topic Assessment: Topic 5 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 SS c Compare and contrast the cost and benefits of various lending institutions (e.g., banks, credit unions, paycheck advance businesses, pawn shops) SS d Students will identify situations when borrowing money and paying interest may be a wise or unwise decision SE: For related material see: Banking, 20, 142, 280, , 293, 300, 302 Topic Assessment: Topic 5 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 SE: For related material see: Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Americans Rely on Credit, 283; Speculation, 284; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Savings and Loan Crisis, 576 Topic Assessment: Topic 5 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector),
24 SS Students will evaluate savings, investment, and risk management strategies to achieve financial goals. SS a Explain the importance of SE: For related material see: Banking, 20, saving to ensure financial security 142, 280, , 293, 300, 302; Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Americans Rely on Credit, 283; Speculation, 284; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Savings and Loan Crisis, 576 Topic Assessment: Topic 5 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 SS b Implement an investment strategy that is compatible with personal goals (e.g., stocks, bonds, mutual funds, retirement plans) SE: For related material see: Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Americans Rely on Credit, 283; Speculation, 284; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Savings and Loan Crisis, 576 Topic Assessment: Topic 5 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector), 603 SS c Analyze appropriate and cost effective risk management strategies (e.g., health, disability, life, auto insurance) SE: For related material see: Advertising and Installment Buying, 243; Americans Rely on Credit, 283; Speculation, 284; Increased Consumption and Consumerism, ; Savings and Loan Crisis, 576 Topic Assessment: Topic 5 Assessment (5. Analyze Unintended Consequences in the Private Sector),
25 Government SS Students will analyze the roles and responsibilities of government in various economic systems. SS a Examine how governments utilize taxation to provide goods and services to society (e.g., disaster relief, flood control, police protection) SE: A New Tax on Income, 183; Income Tax Rates, 249; Tax Cuts and Deregulation, ; 21st Century Skills: Paying Taxes, Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603 SS b Investigate multiple roles of government in a market economy (e.g., forms of taxation, enforcing private property and zoning laws, collecting sales tax) SE: Protective tariffs, 19 20, 78, 142, ; Bank Politics and Economic Woes, 20; Second Bank of the United States, 20; The Changing Relationship Between Government and Business, 89 90; Monetary Policy, 142, 143; Antitrust legislation, 85, 89 90, 97, 117, 157, 178, 181, 185, 209; The ICC Takes on the Railroads, ; A New Tax on Income, 183; Regulation of Commercial Banks, 184; Federal Trade Commission, ; Economic Prosperity Under Coolidge, ; Reconstruction Finance Corporation, 298; Reforming the Financial System, ; Two Presidents Respond, ; The New Deal Expands, ; Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), 302; An Increasingly Significant Role Promoting Economic Growth, ; An Expansion of Executive Power, ; Tax Cuts and Deregulation, ; Federal Budget (Surpluses, Deficits), 599 Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 4 (1. Describe Benefits and Costs of Antitrust Acts), 209; (12. Evaluate Pros and Cons of International Treaties), 210; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; (9. Identify Impact of Tariffs), 275; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression), 327; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603; Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA),
26 SS c Explore various forms of taxation (earning, consumption, or wealth) and discuss outcomes of various tax philosophies as drivers of economic activity SE: A New Tax on Income, 183; Income Tax Rates, 249; Tax Cuts and Deregulation, ; 21st Century Skills: Paying Taxes, Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603 SS d Research the role of government in the development of economic systems (e.g., historic and current examples of command, market, traditional, mixed systems) SE: This standard is met throughout the program. Examples include the following references: Banking, 20, 142, 280, , 293, 300, 302; Free Enterprise Encourages the Rise of Entrepreneurship, 77 78; Antitrust legislation, 85, 89 90, 97, 117, 157, 178, 181, 185, 209; Regulation of Commercial Banks, 184; Federal Trade Commission, ; Reconstruction Finance Corporation, 298; Two Presidents Respond, ; The New Deal Expands, ; Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), 302; An Expansion of Executive Power, ; The Role of Entrepreneurs, 427, 428; Franchise Businesses, 427; American Corporations Go Multinational, 428; Community Reinvestment Act, 557; Goals and Impacts of Reagonomics, 575; The United States and Global Business, 610; The Role of the United States in the Future Economy, Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 4 (1. Describe Benefits and Costs of Antitrust Acts), 209; (12. Evaluate Pros and Cons of International Treaties), 210; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; (9. Identify Impact of Tariffs), 275; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression), 327; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603; Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA),
27 SS e Analyze government policies and regulations in areas of market failure (e.g., monopolies, externalities, nonenforcement of property rights) SE: This standard is met throughout the program. Examples include the following references: Banking, 20, 142, 280, , 293, 300, 302; National Consumers League (NCL), 165; Antitrust legislation, 85, 89 90, 97, 117, 157, 178, 181, 185, 209; Regulation of Commercial Banks, 184; Federal Trade Commission, ; Lack of government intervention in the economy, 286; Reconstruction Finance Corporation, 298; Two Presidents Respond, ; The New Deal Expands, ; Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), 302; An Expansion of Executive Power, ; Community Reinvestment Act, 557; Goals and Impacts of Reagonomics, 575; The United States and Global Business, 610 Topic Assessment: Topic 1 (2. Compare and Contrast Rival Plans for Reconstruction), 72; (3. Describe the Effects of Reconstruction), 72; Topic 2 (9. Describe Benefits and Costs of Sherman Antitrust Act), 117; Topic 2 (10. Explain Actions to Expand Economic Opportunities for Minorities), 117; Topic 3 (6. Explain Actions to Expand Economic Opportunities and Political Rights), 151; (8. Describe Economic Impact of Homestead Act), 152; Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 4 (1. Describe Benefits and Costs of Antitrust Acts), 209; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression),
28 SS Students will examine the government s influence on economic systems through fiscal policy. SS a Examine how governments SE: Monetary Policy, 142, 143; A New Tax can use taxing and spending policies to on Income, 183; Income Tax Rates, 249; influence behavior (e.g., alcohol tax, home Tax Cuts and Deregulation, ; Goals mortgage interest deduction) and Impacts of Reagonomics, 575; Federal Budget (Surpluses, Deficits), 599; 21st Century Skills: Paying Taxes, Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603 SS b Examine the impact of fiscal policy on budget deficits\surpluses and national debt SE: Monetary Policy, 142, 143; Tax Cuts and Deregulation, ; Goals and Impacts of Reagonomics, 575; Federal Budget (Surpluses, Deficits), 599 Topic Assessment: Topic 3 (13. Describe Emergence of Monetary Policy), 152; Topic 5 (8. Explain Economic Development), 275; Topic 12 (3. Describe Reaganomics), 603 SS c Examine the impact of the unemployment rate on the economy (frictional, structural, cyclical) SE: Business Cycle, 280; Unemployment Leaves Families Struggling, ; Unemployment, 313; Minimum Wage, 310; Increased Opportunities in Employment, 369; American Recovery & Reinvestment Act (ARRA), 623; Economic Issues and Reform (unemployment), 624 Topic Assessment: Topic 3 Assessment (8. Describe Impact of Defense Spending),
29 Globalization SS Students will evaluate how international trade benefits individuals, organizations, and nations SS a Analyze the effects of various trade policies (e.g., identify short term/long term impacts) SE: Protective tariffs, 19 20, 78, 142, ; Federal Trade Commission, ; U.S. Trade Deficit with Japan, 576; Free Trade and Treaties, Topic Assessment: Topic 5 (9. Identify Impact of Tariffs), 275; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression), 327; Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA), 637 SS b Identify goods which are available at a lower price because of international trade SS c Explain how trade barriers impact the prices and quantity of goods in the domestic market SE: For related material see: Free Trade and Treaties, Topic Assessment: Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA), 637 SE: Protective tariffs, 19 20, 78, 142, ; Federal Trade Commission, ; U.S. Trade Deficit with Japan, 576; Free Trade and Treaties, Topic Assessment: Topic 5 (9. Identify Impact of Tariffs), 275; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression), 327; Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA), 637 SS Students will evaluate how international trade affects the domestic economy. SS a Identify goods which are SE: For related material see: Free Trade available at a lower price because of and Treaties, international trade Topic Assessment: Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA), 637 SS b Explain how trade barriers impact the prices and quantity of goods in the domestic market SE: Protective tariffs, 19 20, 78, 142, ; Federal Trade Commission, ; U.S. Trade Deficit with Japan, 576; Free Trade and Treaties, Topic Assessment: Topic 5 (9. Identify Impact of Tariffs), 275; Topic 6 (3. Identify Impact of Tariffs on the Great Depression), 327; Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA),
30 Geography K-12 Geography: Students will develop and apply spatial perspective and geographic skills to make informed decisions regarding issues and current events at local, state, national and international levels. The World in Spatial Terms High School (United States/World) SS Students will analyze where (spatial) and why people, places, and environments are organized on the Earth s surface. SS a Analyze geographical information sources (e.g., map, globe, atlas, remote sensing, GPS, and GIS) SE: 21 st Century Skills: Read Physical Maps, ; Read Political Maps, ; Read Special Purpose Maps, ; Use Parts of a Map, ; Analyze Maps, 53, 80, 123, 125, 131, 133, 148, 150, 168, 179, 183, 194, 195, 201, 203, 204, 215, 217, 221, 228, 232, 242, 292, 301, 303, 355, 357, 363, 375, 377, 378, 384, 415, 426, 450, 490, 492, 498, 506, 540, 549, 560, 572, 585, 591, 593, 594, 609, 615 Topic Assessment (activities involving maps and spatial data): Topic 8 (1. Describe Berlin Airlift), 444; Topic 9 (5. Describe Role of Groups in Maintaining Status Quo), 484; Topic 11 (11. Analyze Sunbelt Migration), 564; Topic 12 (16. Understand Global Positioning Products), 604 SS b Apply map scale as a geographical tool and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of projections (e.g., large scale/small scale, Peters, Mercator, plane, conical, cylindrical) SS c Analyze mental maps and spatial relationships. (e.g., city development, urban planning based on railroads, location of natural resources) SE: 21 st Century Skills: Read Physical Maps, ; Read Political Maps, ; Read Special Purpose Maps, ; Use Parts of a Map, Topic Assessment (activities involving maps and spatial data): Topic 8 (1. Describe Berlin Airlift), 444; Topic 9 (5. Describe Role of Groups in Maintaining Status Quo), 484; Topic 11 (11. Analyze Sunbelt Migration), 564 SE: For related material see: 21 st Century Skills: Read Physical Maps, ; Read Political Maps, ; Read Special Purpose Maps, ; Use Parts of a Map,
31 SS d Apply spatial thinking to investigate issues and justify decisions. (e.g., consolidation of schools, closing of post offices) SE: Topic Assessment: Environmental Issues: Topic 9 (14. Identify Roles in Managing Environment), 485; Topic 11 (7. Identify Roles in Managing the Environment), 563 Topic Assessment: Activities Involving Maps and Spatial Data: Topic 8 (1. Describe Berlin Airlift), 444; Topic 9 (5. Describe Role of Groups in Maintaining Status Quo), 484; Topic 11 (11. Analyze Sunbelt Migration), 564 Topic Assessment: Human Interaction with Environment: Topic 1 (10. Analyze the Problems of New Farming Systems), 73; Topic 2 (5. Analyze Farm Issues in the South), 117; (6. Explain Technological Innovations in Agriculture), 117; Topic 3 (4. Analyze Impact of Geographic Factors on Klondike Gold Rush), 151; Topic 6 (12. Identify Roles in Managing the Environment), st Century Skills: Create Charts and Maps, ; Read Physical Maps, ; Read Political Maps, ; Read Special Purpose Maps, ; Use Parts of a Map, Mastered Mastered 31
32 Places and Regions SS Students will examine how regions form and change over time. SS a Analyze physical and human SE: Migration & Immigration, 74, 77, 78, processes that shape places and regions 79 81, 83 84, 86 88, 90, 92, 94 98, 100, (e.g., erosion, international trade, , 119, 156, 256, 259, 482, 532, weathering, climate, migration, 536, 537, 563, 593, 630, 636; international trade ) Urbanization, 83, 105, 106, 107, 114, 118, 173, 245, 269, 276, 426, , 482, 533; Free Trade and Treaties, ; Competing in a Global Economy, ; Innovation Boosts Growth, Topic Assessment: Topic 5 (14. Analyze Causes and Effects of Great Migration), 276; Topic 6 (1. Analyze Causes and Effects of Changing Demographic Patterns), 327; Topic 8 (7. Analyze Effects of Demographic Patterns), 445; Topic 9 (9. Analyze Demographic Patterns), 485 SS b Examine the importance of places and regions to individual and social identity (e.g., nationalism, national monuments, local legends, parks, subcultures, nationalism, territoriality, iconography) SS c Analyze the changes in places and regions over time (e.g., migration, urbanization, fertility and mortality, industrialization) SE: The West Is Transformed, ; Farm Issues and Populism, ; The United States Emerges as a World Power, ; The Environmental Movement, Environmental Issues: Topic 8 (1. Describe Berlin Airlift), 444; Topic 9 (14. Identify Roles in Managing Environment), 485; Topic 11 (7. Identify Roles in Managing the Environment), 563; (11. Analyze Sunbelt Migration), 564 SE: Immigration, 74, 77, 78, 79 81, 83 84, 86 88, 90, 92, 94 98, 100, , 119, 156, 256, 259, 482, 532, 536, 537, 563, 593, 630, 636; Urbanization, 83, 105, 106, 107, 114, 118, 173, 245, 269, 276, 426, , 482, 533 Environmental Issues: Topic 9 (14. Identify Roles in Managing Environment), 485; Topic 11 (7. Identify Roles in Managing the Environment),
33 SS d Analyze the interdependence of places and regions. (e.g., international trade, NAFTA, EU) SS e Analyze critical issues and problems of places and regions. (e.g., current events) SE: America and the World Economy, Topic Assessment: Topic 13 (1. Describe NAFTA), 637; Assessment (2. Explain Economic Impact of Technological Innovations), 637; (3. Identify Impact of Multinational Corporations), 637 SE: Farm Issues and Populism, ; The Environmental Movement, ; Energy and the Environment, ; Oil Embargo, 547, 548, 564 Environmental Issues: Topic 9 (14. Identify Roles in Managing Environment), 485; Topic 11 (7. Identify Roles in Managing the Environment), 563 SS f Apply regional analysis of geographic issues and questions. (e.g., discussing current events and issues of the day in a geographical context) SE: For related material see: Analyze Maps, 53, 80, 123, 125, 131, 133, 148, 150, 168, 179, 183, 194, 195, 201, 203, 204, 215, 217, 221, 228, 232, 242, 292, 301, 303, 355, 357, 363, 375, 377, 378, 384, 415, 426, 450, 490, 492, 498, 506, 540, 549, 560, 572, 585, 591, 593, 594, 609, 615 Topic Assessment: Topic 6 Assessment (12. Identify Roles in Managing the Environment), 328; Topic 9 (14. Identify Roles in Managing Environment), 485; Topic 8 (1. Describe Berlin Airlift), 444; Topic 9 (5. Describe Role of Groups in Maintaining Status Quo), 484; Topic 11 (11. Analyze Sunbelt Migration),
A Correlation of. To the. Nebraska Social Studies Standards High School
 A Correlation of To the Nebraska High School A Correlation of, to the Nebraska Introduction This document demonstrates how, meets the Nebraska Social Studies Standards, High School. Correlation page references
A Correlation of To the Nebraska High School A Correlation of, to the Nebraska Introduction This document demonstrates how, meets the Nebraska Social Studies Standards, High School. Correlation page references
A Correlation of. To the. College, Career, & Civic Life (C3) Framework for Social Studies State Standards Grades 6-8
 A Correlation of 2016 To the College, Career, & Civic Life (C3) Framework for Social Studies State Standards Introduction This document demonstrates how, 2016 meets the C3 Curriculum Frameworks for Social
A Correlation of 2016 To the College, Career, & Civic Life (C3) Framework for Social Studies State Standards Introduction This document demonstrates how, 2016 meets the C3 Curriculum Frameworks for Social
Illinois Learning Standards for Social Science
 A Correlation of Survey Edition, To the Social Science Grade 6-8 Social Science Inquiry Skills Developing Questions and Planning Inquiries Constructing Essential Questions SS.IS.1.6-8: Create essential
A Correlation of Survey Edition, To the Social Science Grade 6-8 Social Science Inquiry Skills Developing Questions and Planning Inquiries Constructing Essential Questions SS.IS.1.6-8: Create essential
A Correlation of. To the. Illinois Learning Standards for Social Science Grades 9-12
 A Correlation of 2016 To the Illinois Learning Standards for Social Science Grades 9-12 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson meets the Illinois Learning Standards for Social Science, Grades
A Correlation of 2016 To the Illinois Learning Standards for Social Science Grades 9-12 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson meets the Illinois Learning Standards for Social Science, Grades
Unit 1: The Economic Fundamentals Weeks How does scarcity impact the decisions individuals and societies must make?
 Economics Teacher: Vida Unit 1: The Economic Fundamentals Weeks 1-4 Essential Questions 1. How does scarcity impact the decisions individuals and societies must make? 2. What roles do individuals and businesses
Economics Teacher: Vida Unit 1: The Economic Fundamentals Weeks 1-4 Essential Questions 1. How does scarcity impact the decisions individuals and societies must make? 2. What roles do individuals and businesses
State Content Standards for New Mexico
 Episode 101 What Is a Biz Kid? Episode 102 What Is Money? Episode 103 How Do You Get Money? Episode 104 What Can You Do with Money? Episode 105 Money Moves Episode 106 Taking Charge of Your Financial Future
Episode 101 What Is a Biz Kid? Episode 102 What Is Money? Episode 103 How Do You Get Money? Episode 104 What Can You Do with Money? Episode 105 Money Moves Episode 106 Taking Charge of Your Financial Future
Colorado Academic Standards Social Studies
 2016 To the High School Introduction This document demonstrates how, 2016 meets the, High School. Pearson is excited to announce its NEW United States History program! Designed to help prepare students
2016 To the High School Introduction This document demonstrates how, 2016 meets the, High School. Pearson is excited to announce its NEW United States History program! Designed to help prepare students
Prentice Hall The American Nation: Civil War to the Present 2003 Correlated to: Arkansas Social Studies Curriculum Frameworks (Grades 5 8)
 Arkansas Social Studies Curriculum Frameworks (Grades 5 8) STRAND 1: TIME, CONTINUITY, AND CHANGE CONTENT STANDARD 1: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the chronology and concepts of history
Arkansas Social Studies Curriculum Frameworks (Grades 5 8) STRAND 1: TIME, CONTINUITY, AND CHANGE CONTENT STANDARD 1: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the chronology and concepts of history
Core Content for Social Studies Assessment
 Core Content for Social Studies Assessment Middle School Version 4.1 August 2006 Kentucky Department or Education Kentucky Department of Education 1 Introduction Core Content for Social Studies Assessment
Core Content for Social Studies Assessment Middle School Version 4.1 August 2006 Kentucky Department or Education Kentucky Department of Education 1 Introduction Core Content for Social Studies Assessment
2010 Alabama Course of Study for Social Studies - Economics & Common Core Standards for Literacy in History/Social Studies
 Two Correlations Economics Alabama Edition 2015 To the 2010 Alabama Course of Study for Social Studies - Economics & Common Core Standards for Literacy in History/Social Studies Table of Contents Alabama
Two Correlations Economics Alabama Edition 2015 To the 2010 Alabama Course of Study for Social Studies - Economics & Common Core Standards for Literacy in History/Social Studies Table of Contents Alabama
The Kenton County School District A System of Excellence
 Big Idea: Government and Civics The study of government and civics allows students to understand the nature of government and the unique characteristics of American democracy, including its fundamental
Big Idea: Government and Civics The study of government and civics allows students to understand the nature of government and the unique characteristics of American democracy, including its fundamental
ILLINOIS LICENSURE TESTING SYSTEM
 ILLINOIS LICENSURE TESTING SYSTEM FIELD 244: SOCIAL SCIENCE: ECONOMICS January 2017 Effective beginning May 14, 2018 ILLINOIS LICENSURE TESTING SYSTEM FIELD 244: SOCIAL SCIENCE: ECONOMICS January 2017
ILLINOIS LICENSURE TESTING SYSTEM FIELD 244: SOCIAL SCIENCE: ECONOMICS January 2017 Effective beginning May 14, 2018 ILLINOIS LICENSURE TESTING SYSTEM FIELD 244: SOCIAL SCIENCE: ECONOMICS January 2017
Academic Standards for Civics and Government Principles and Documents of Government PENNSYLVANIA ACADEMIC STANDARDS, SOCIAL STUDIES
 Civics and Government, Economics, Geography, and History (5.1-5.4, 6.1-6.3, 6.5, 7.1, 7.3, 8.1, 8.3) (Grade 12) Academic Standards for Civics and Government 5.1. Principles and Documents of Government
Civics and Government, Economics, Geography, and History (5.1-5.4, 6.1-6.3, 6.5, 7.1, 7.3, 8.1, 8.3) (Grade 12) Academic Standards for Civics and Government 5.1. Principles and Documents of Government
State Content Standards for Florida
 Episode 101 What Is a Biz Kid? Episode 102 What Is Money? Episode 103 How Do You Get Money? Episode 104 What Can You Do with Money? Episode 105 Money Moves Episode 106 Taking Charge of Your Financial Future
Episode 101 What Is a Biz Kid? Episode 102 What Is Money? Episode 103 How Do You Get Money? Episode 104 What Can You Do with Money? Episode 105 Money Moves Episode 106 Taking Charge of Your Financial Future
Correlations to NATIONAL SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS
 Correlations to NATIONAL SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS This chart indicates which of the activities in this guide teach or reinforce the National Council for the Social Studies standards for middle grades and
Correlations to NATIONAL SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS This chart indicates which of the activities in this guide teach or reinforce the National Council for the Social Studies standards for middle grades and
Correlation Guide. Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text
 Presented by the Center for Civic Education, The National Conference of State Legislatures, and The State Bar of Wisconsin Correlation Guide For Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text Jack
Presented by the Center for Civic Education, The National Conference of State Legislatures, and The State Bar of Wisconsin Correlation Guide For Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text Jack
Social Studies: RESOURCES
 Social Studies Key Themes: Grade 8 To be productive members of society, students must be critical consumers of information they read, hear, and observe and communicate effectively about their ideas. They
Social Studies Key Themes: Grade 8 To be productive members of society, students must be critical consumers of information they read, hear, and observe and communicate effectively about their ideas. They
A Correlation of. To the Wyoming Social Studies Content and Performance Standards Grade 12
 A Correlation of To the Wyoming Social Studies Content and Performance Standards Grade 12 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson, meets the, Grade 12. Pearson is excited to announce its NEW
A Correlation of To the Wyoming Social Studies Content and Performance Standards Grade 12 Introduction This document demonstrates how Pearson, meets the, Grade 12. Pearson is excited to announce its NEW
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved
 Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
6th Grade Key Terms What do the Students Have to Know to Master the Standard? How will you assess mastery of the standard?
 Government & Civics The study of government and civics equips students to understand the nature of government and the unique characteristics of representative democracy in the United States, including
Government & Civics The study of government and civics equips students to understand the nature of government and the unique characteristics of representative democracy in the United States, including
The Economy and the United States Government s-1930 s
 The Economy and the United States Government 1870 s-1930 s 1850 s-1870 s 1850 s-1870 s Two of the biggest changes in the economy of the United States during this time period was the end of slavery and
The Economy and the United States Government 1870 s-1930 s 1850 s-1870 s 1850 s-1870 s Two of the biggest changes in the economy of the United States during this time period was the end of slavery and
Academic Standards for Civics and Government Principles and Documents of Government PENNSYLVANIA ACADEMIC STANDARDS, SOCIAL STUDIES
 Civics and Government, Economics, Geography, and History (5.1-5.4, 6.1-6.5, 7.1,7.3, 8.1, 8.3) Academic Standards for Civics and Government 5.1. Principles and Documents of Government 5.1.9. GRADE 9 potential
Civics and Government, Economics, Geography, and History (5.1-5.4, 6.1-6.5, 7.1,7.3, 8.1, 8.3) Academic Standards for Civics and Government 5.1. Principles and Documents of Government 5.1.9. GRADE 9 potential
TEACHERS OF SOCIAL STUDIES FORM I-C MATRIX
 8710.4800 TECHERS OF SOCIL STUDIES FORM I-C MTRIX Professional Education Program Evaluation Report (PEPER II) MTRIX Form I-C 8710.4800 Teachers of Social Studies = opportunities to gain the nowledge or
8710.4800 TECHERS OF SOCIL STUDIES FORM I-C MTRIX Professional Education Program Evaluation Report (PEPER II) MTRIX Form I-C 8710.4800 Teachers of Social Studies = opportunities to gain the nowledge or
From Prosperity to Depression: From Prosperity to Depression:
 Topics of Discussion A. Role of the Federal Government B. Democrats: Divided C. Republicans: Pro-Business D. Warren Harding, 1921-23 E. Calvin Coolidge, 1923-1929 F. Hoover Inherits a Troubled Economy
Topics of Discussion A. Role of the Federal Government B. Democrats: Divided C. Republicans: Pro-Business D. Warren Harding, 1921-23 E. Calvin Coolidge, 1923-1929 F. Hoover Inherits a Troubled Economy
Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS)
 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) 113.32. United States History Studies Since Reconstruction (One Credit). Category Student Expectation Strategy/Assessment (a) General requirements. Students
Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) 113.32. United States History Studies Since Reconstruction (One Credit). Category Student Expectation Strategy/Assessment (a) General requirements. Students
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core U.S. Government & Citizenship This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core U.S. Government & Citizenship This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan
 Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan Concept / Topic To Teach: Period 6: (1865-1898) Week 1: 03/21-03/25 Week 2: 03/28-03/31 Week 3: 04/18-04/22 Week 4: 04/25-04/29 Reconstruction, Gilded Age,
Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan Concept / Topic To Teach: Period 6: (1865-1898) Week 1: 03/21-03/25 Week 2: 03/28-03/31 Week 3: 04/18-04/22 Week 4: 04/25-04/29 Reconstruction, Gilded Age,
Curriculum Standards for Social Studies of the National Council for the Social Studies NCSS
 A Correlation of to the Curriculum Standards for Social Studies of the National Council for the Social Studies NCSS Grades K - 6 N/SS-116 Introduction This document cites pages references to demonstrate
A Correlation of to the Curriculum Standards for Social Studies of the National Council for the Social Studies NCSS Grades K - 6 N/SS-116 Introduction This document cites pages references to demonstrate
Alaska Content and Performance Standards Science Grade: 4 - Adopted: Concepts of Life Science (SC1, SC2, SC3)
 Main Criteria: Alaska Content and Performance Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 4 Correlation Options: Show Correlated AK.C1. Alaska Content and Performance Standards
Main Criteria: Alaska Content and Performance Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 4 Correlation Options: Show Correlated AK.C1. Alaska Content and Performance Standards
Alaska Content and Performance Standards Science Grade: 1 - Adopted: Concepts of Earth Science (SD1, SD2, SD3, SD4)
 Main Criteria: Alaska Content and Performance Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 1 Correlation Options: Show Correlated AK.D1. Alaska Content and Performance Standards
Main Criteria: Alaska Content and Performance Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 1 Correlation Options: Show Correlated AK.D1. Alaska Content and Performance Standards
SOCIAL STUDIES 10-1: Perspectives on Globalization
 SOCIAL STUDIES 10-1: Perspectives on Globalization Overview Students will explore multiple perspectives on the origins of globalization and the local, national and international impacts of globalization
SOCIAL STUDIES 10-1: Perspectives on Globalization Overview Students will explore multiple perspectives on the origins of globalization and the local, national and international impacts of globalization
The Social Studies Curriculum: Scope and Sequence
 The Social Studies Curriculum: Scope and Sequence Miquon s Social Studies content is tied to the thematic and the discipline standards set forth by National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS). Social
The Social Studies Curriculum: Scope and Sequence Miquon s Social Studies content is tied to the thematic and the discipline standards set forth by National Council for the Social Studies (NCSS). Social
FOR05664 Constructing Social Education Curriculum for the Twenty-first Century: the Role and Importance of Economics Education
 FOR05664 Constructing Social Education Curriculum for the Twenty-first Century: the Role and Importance of Economics Education Anita Forsyth Monash University Abstract: The place of economics education
FOR05664 Constructing Social Education Curriculum for the Twenty-first Century: the Role and Importance of Economics Education Anita Forsyth Monash University Abstract: The place of economics education
New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Science Grade: K - Adopted: 2006
 Main Criteria: New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: K Correlation Options: Show Correlated New Hampshire College and Career Ready
Main Criteria: New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: K Correlation Options: Show Correlated New Hampshire College and Career Ready
Dr. Greg Hallman Director, Real Estate Finance and Investment Center (REFIC) McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin
 Dr. Greg Hallman Director, Real Estate Finance and Investment Center (REFIC) McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin POWERPOINT PARTNER } The US Economy today, with a close look at jobs
Dr. Greg Hallman Director, Real Estate Finance and Investment Center (REFIC) McCombs School of Business University of Texas at Austin POWERPOINT PARTNER } The US Economy today, with a close look at jobs
An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy
 An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy SHANG Yong, Ph.D. Vice Minister Ministry of Science and Technology, China and Senior Fellow Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy SHANG Yong, Ph.D. Vice Minister Ministry of Science and Technology, China and Senior Fellow Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
THE INTERNATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS OF ECONOMIES IN TRANSITION THE UNTAPPED POTENTIAL: A CHALLENGE FOR BUSINESS AND GOVERNMENT BELARUS
 THE INTERNATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS OF ECONOMIES IN TRANSITION THE UNTAPPED POTENTIAL: A CHALLENGE FOR BUSINESS AND GOVERNMENT BELARUS NATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS ISSUES, CONSTRAINTS AND STRATEGIC IMPLICATIONS
THE INTERNATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS OF ECONOMIES IN TRANSITION THE UNTAPPED POTENTIAL: A CHALLENGE FOR BUSINESS AND GOVERNMENT BELARUS NATIONAL COMPETITIVENESS ISSUES, CONSTRAINTS AND STRATEGIC IMPLICATIONS
The Industrialization of the United States s 1910 s
 The Industrialization of the United States 1860 s 1910 s The South Builds Railways O After the Civil War, the South began building more railroads to rival those of the North. O South now relied on its
The Industrialization of the United States 1860 s 1910 s The South Builds Railways O After the Civil War, the South began building more railroads to rival those of the North. O South now relied on its
Kindergarten U.S. History Grade Standards, Supporting Skills, and Examples
 Kindergarten U.S. History Grade s, Supporting Skills, and Examples Indicator 1: Analyze U.S. historical eras to determine connections and cause/effect relationships in reference to chronology. Students
Kindergarten U.S. History Grade s, Supporting Skills, and Examples Indicator 1: Analyze U.S. historical eras to determine connections and cause/effect relationships in reference to chronology. Students
Case 4:74-cv DCB Document Filed 09/01/17 Page 293 of 322 APPENDIX V 156
 Case 4:74-cv-00090-DCB Document 2061-10 Filed 09/01/17 Page 293 of 322 APPENDIX V 156 4:74-cv-00090-DCB Document 2061-10 Filed 09/01/17 Page 294 of 322 TUSD MC Curriculum Recommendations Grades 6-12 Initiative
Case 4:74-cv-00090-DCB Document 2061-10 Filed 09/01/17 Page 293 of 322 APPENDIX V 156 4:74-cv-00090-DCB Document 2061-10 Filed 09/01/17 Page 294 of 322 TUSD MC Curriculum Recommendations Grades 6-12 Initiative
Content Standard Students in Wisconsin will learn about geography through the study of the relationships among people, places, and environments.
 and Accompanying Performance Standards (Grade 8) WISCONSIN MODEL ACADEMIC WISCONSIN MODEL ACADEMIC FOR SOCIAL STUDIES A. GEOGRAPHY: PEOPLE, PLACES, AND ENVIRONMENTS Content Standard Students in Wisconsin
and Accompanying Performance Standards (Grade 8) WISCONSIN MODEL ACADEMIC WISCONSIN MODEL ACADEMIC FOR SOCIAL STUDIES A. GEOGRAPHY: PEOPLE, PLACES, AND ENVIRONMENTS Content Standard Students in Wisconsin
Unit Plan: 11 th Grade US History
 Unit Plan: 11 th Grade US History Unit #3: The Roaring Twenties 14 Instructional Days Unit Overview Big Idea: After WW1 America enters a period of economic growth and isolationism which leads to excess
Unit Plan: 11 th Grade US History Unit #3: The Roaring Twenties 14 Instructional Days Unit Overview Big Idea: After WW1 America enters a period of economic growth and isolationism which leads to excess
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US Revolution to Civil War,1776-1860 Lecture #5 Peter Allen Econ 120 Financial Issues, 1776-1860 Revolutionary War, 1775-81 Articles of Confederation, 1781-89 Practical aim, victory
Economic History of the US Revolution to Civil War,1776-1860 Lecture #5 Peter Allen Econ 120 Financial Issues, 1776-1860 Revolutionary War, 1775-81 Articles of Confederation, 1781-89 Practical aim, victory
Maine Learning Results Science Grade: 3 - Adopted: 2007
 Main Criteria: Maine Learning Results Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 3 Correlation Options: Show Correlated Maine Learning Results Science Grade: 3 - Adopted: 2007 STRAND
Main Criteria: Maine Learning Results Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 3 Correlation Options: Show Correlated Maine Learning Results Science Grade: 3 - Adopted: 2007 STRAND
Innovation. Key to Strengthening U.S. Competitiveness. Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology
 Innovation Key to Strengthening U.S. Competitiveness Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology PDMA Annual Meeting October 23, 2005 Innovation Key to strengthening U.S. competitiveness
Innovation Key to Strengthening U.S. Competitiveness Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology PDMA Annual Meeting October 23, 2005 Innovation Key to strengthening U.S. competitiveness
Fifth Grade United States History
 Fifth Grade United States History Year 3: Industrialization to the Digital Age In fifth grade, students are in the final year of a three year study of United States history in which all four strands (history,
Fifth Grade United States History Year 3: Industrialization to the Digital Age In fifth grade, students are in the final year of a three year study of United States history in which all four strands (history,
Historical Development of Management in Japan
 Historical Development of Management in Japan Copyright 2007 Keio University Quote of the Day Ganbare, Nippon!!! Copyright 2007 Keio University 2 This Lecture Overview of the historical development of
Historical Development of Management in Japan Copyright 2007 Keio University Quote of the Day Ganbare, Nippon!!! Copyright 2007 Keio University 2 This Lecture Overview of the historical development of
An Uneven Planet. Globalization, Capital, & Inequality in the 21 st Century
 An Uneven Planet Globalization, Capital, & Inequality in the 21 st Century Today s Discussion Brief Review Globalization The Problem of Inequality Picketty & the Politics of Redistribution Brief Review
An Uneven Planet Globalization, Capital, & Inequality in the 21 st Century Today s Discussion Brief Review Globalization The Problem of Inequality Picketty & the Politics of Redistribution Brief Review
Getting Started. This Lecture
 Getting Started Entrepreneurship (MGT-271) Lecture 9-11 This Lecture Intellectual Property Rights Forms of intellectual property Patent, its types and steps to obtaining patent Potential financing sources
Getting Started Entrepreneurship (MGT-271) Lecture 9-11 This Lecture Intellectual Property Rights Forms of intellectual property Patent, its types and steps to obtaining patent Potential financing sources
New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Science Grade: 1 - Adopted: 2006
 Main Criteria: New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 1 Correlation Options: Show Correlated New Hampshire College and Career Ready
Main Criteria: New Hampshire College and Career Ready Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 1 Correlation Options: Show Correlated New Hampshire College and Career Ready
Gifted and Talented AIM Learning Outcomes Framework
 Gifted and Talented AIM Learning Outcomes Framework Grade: Sixth Nine Weeks: 2nd Subject: 1920s Big Ideas: (Topics/Concepts): Cultural and Technological Impacts on Society Enduring Understanding (What
Gifted and Talented AIM Learning Outcomes Framework Grade: Sixth Nine Weeks: 2nd Subject: 1920s Big Ideas: (Topics/Concepts): Cultural and Technological Impacts on Society Enduring Understanding (What
Lecture 1: The Rise of Big Business in the Gilded Age
 Lecture 1: The Rise of Big Business in the Gilded Age Famous photograph taken by A.J. Russell, the photographer of the Union Pacific Railroad, commemorabng the Last Spike of May 10, 1869, in Promontory
Lecture 1: The Rise of Big Business in the Gilded Age Famous photograph taken by A.J. Russell, the photographer of the Union Pacific Railroad, commemorabng the Last Spike of May 10, 1869, in Promontory
Huntsville City Schools Pacing Guide Course: U.S. History from 1900 Grade: 11 First Nine Weeks
 First Nine Weeks Please Note: There are a total of 34 instructional days plus 6 review days in the first 9 weeks, not including the first week of school (you need to review the Civil War and Reconstruction).
First Nine Weeks Please Note: There are a total of 34 instructional days plus 6 review days in the first 9 weeks, not including the first week of school (you need to review the Civil War and Reconstruction).
Policy recommendations. Digital literacy
 Policy recommendations The opportunity Computer and internet literacy, familiarity with productivity software, fluency using a wide range of digital devices these are all essential workplace skills for
Policy recommendations The opportunity Computer and internet literacy, familiarity with productivity software, fluency using a wide range of digital devices these are all essential workplace skills for
Maryland College and Career-Ready Standards Science Grade: 1 - Adopted: 2008
 Main Criteria: Maryland College and Career-Ready Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 1 Correlation Options: Show Correlated Maryland College and Career-Ready Standards
Main Criteria: Maryland College and Career-Ready Standards Secondary Criteria: Subjects: Science, Social Studies Grade: 1 Correlation Options: Show Correlated Maryland College and Career-Ready Standards
EC Chapter 1. Burak Alparslan Eroğlu. October 13, Burak Alparslan Eroğlu EC Chapter 1
 EC 101 - Chapter 1 Burak Alparslan Eroğlu October 13, 2016 Outline Introduction to New Course Module Introduction to Unit 1 Hockey Stick Growth Capitalism Inequality Economics and Economy Introduction
EC 101 - Chapter 1 Burak Alparslan Eroğlu October 13, 2016 Outline Introduction to New Course Module Introduction to Unit 1 Hockey Stick Growth Capitalism Inequality Economics and Economy Introduction
A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE
 A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE 1870-1900 EXPANSION OF INDUSTRY New innovations and inventions lead to the growth of industry and changes in the American economy. I. Expansion of Industry After the Civil War, the
A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE 1870-1900 EXPANSION OF INDUSTRY New innovations and inventions lead to the growth of industry and changes in the American economy. I. Expansion of Industry After the Civil War, the
Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical Thinking Skills
 AP World History 2015-2016 Nacogdoches High School Nacogdoches Independent School District Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical
AP World History 2015-2016 Nacogdoches High School Nacogdoches Independent School District Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical
HPISD CURRICULUM (SOCIAL STUDIES, GRADE 5)
 HPISD CURRICULUM (SOCIAL STUDIES, GRADE 5) EST. NUMBER OF DAYS: 9 WEEKS UNIT NAME Unit Overview Generalizations/Enduring Understandings Concepts Guiding/Essential Questions UNIT 3 IMMIGRATION, INDUSTRIALIZATION,
HPISD CURRICULUM (SOCIAL STUDIES, GRADE 5) EST. NUMBER OF DAYS: 9 WEEKS UNIT NAME Unit Overview Generalizations/Enduring Understandings Concepts Guiding/Essential Questions UNIT 3 IMMIGRATION, INDUSTRIALIZATION,
Mineral Policy Lessons from Canada and Australia
 Mineral Policy Lessons from Canada and Australia Philip Maxwell Mineral Economics program WA School of Mines Curtin University of Technology Western Australia Mineral Policy Lessons from Canada and Australia
Mineral Policy Lessons from Canada and Australia Philip Maxwell Mineral Economics program WA School of Mines Curtin University of Technology Western Australia Mineral Policy Lessons from Canada and Australia
Reaction of the European Alliance for Culture and the Arts to the European Commission s proposal for the EU future budget
 Reaction of the European Alliance for Culture and the Arts to the European Commission s proposal for the EU future budget Brussels, 18 June 2018 The Alliance argues for a long-term, considerable and balanced
Reaction of the European Alliance for Culture and the Arts to the European Commission s proposal for the EU future budget Brussels, 18 June 2018 The Alliance argues for a long-term, considerable and balanced
Scenario Development Process
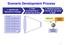 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Importance of SMEs in Greening the Economy in Georgia
 Importance of SMEs in Greening the Economy in Georgia EaP Green Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia February 12, 2015 Kiev, Ukraine Importance of Green Economy for Georgia
Importance of SMEs in Greening the Economy in Georgia EaP Green Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Protection of Georgia February 12, 2015 Kiev, Ukraine Importance of Green Economy for Georgia
BASED ECONOMIES. Nicholas S. Vonortas
 KNOWLEDGE- BASED ECONOMIES Nicholas S. Vonortas Center for International Science and Technology Policy & Department of Economics The George Washington University CLAI June 9, 2008 Setting the Stage The
KNOWLEDGE- BASED ECONOMIES Nicholas S. Vonortas Center for International Science and Technology Policy & Department of Economics The George Washington University CLAI June 9, 2008 Setting the Stage The
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: ASIAN SMES AND GLOBALIZATION
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: ASIAN SMES AND GLOBALIZATION 1. AIM OF THE STUDIES Large enterprises (LEs) and small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are the two important wheels of development in developing countries.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: ASIAN SMES AND GLOBALIZATION 1. AIM OF THE STUDIES Large enterprises (LEs) and small and medium enterprises (SMEs) are the two important wheels of development in developing countries.
English National Curriculum Key Stage links to Meteorology
 English National Curriculum Key Stage links to Meteorology Subject KS1 (Programme of Study) links KS2 (Programme of Study) links KS3 (National Curriculum links) KS4 (National Curriculum links) Citizenship
English National Curriculum Key Stage links to Meteorology Subject KS1 (Programme of Study) links KS2 (Programme of Study) links KS3 (National Curriculum links) KS4 (National Curriculum links) Citizenship
BRAZIL S COMPETITIVENESS CHALLENGES VIEWED FROM ITS COMPANIES
 BRAZIL S COMPETITIVENESS CHALLENGES VIEWED FROM ITS COMPANIES WOODROW WILSON CENTER S BRAZIL INSTITUTE June 2013 KELLIE MEIMAN HOCK, MANAGING PARTNER MCLARTY ASSOCIATES Overview ECONOMIC POLITICAL + Brazil
BRAZIL S COMPETITIVENESS CHALLENGES VIEWED FROM ITS COMPANIES WOODROW WILSON CENTER S BRAZIL INSTITUTE June 2013 KELLIE MEIMAN HOCK, MANAGING PARTNER MCLARTY ASSOCIATES Overview ECONOMIC POLITICAL + Brazil
The Industrial Revolution
 The Industrial Revolution Discussion Question What factors caused the Industrial Revolution to begin in England? Causes of the Industrial Revolution Favorable natural resources Agricultural Revolution
The Industrial Revolution Discussion Question What factors caused the Industrial Revolution to begin in England? Causes of the Industrial Revolution Favorable natural resources Agricultural Revolution
Korea s Industries in the World Market (Shares and Ranking)
 - 1 - - 2 - The Industrial Leader from an Unknown LDC in the 1960s Many think that HCI policies in the 70s established the basis of current Manufacturing-strong economy and HCI industries. Korea s Industries
- 1 - - 2 - The Industrial Leader from an Unknown LDC in the 1960s Many think that HCI policies in the 70s established the basis of current Manufacturing-strong economy and HCI industries. Korea s Industries
Plan I. Fostering innovation for long-term growth. 5 February Stian Westlake, Exec Dir of Policy &
 Plan I Fostering innovation for long-term growth 5 February 2013 Stian Westlake, Exec Dir of Policy & Research @stianwestlake 1 Two plans dominate the debate Plan A : Austerity Plan B : Stimulus Cut government
Plan I Fostering innovation for long-term growth 5 February 2013 Stian Westlake, Exec Dir of Policy & Research @stianwestlake 1 Two plans dominate the debate Plan A : Austerity Plan B : Stimulus Cut government
F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business
 The Australian Curriculum Subjects Year levels F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business Foundation Year, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, Year 4, Year
The Australian Curriculum Subjects Year levels F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business Foundation Year, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, Year 4, Year
INFORMATION DOCUMENT UNIFORM EXAMINATION NEW FEATURES. HISTORY OF QUÉBEC AND CANADA Secondary IV
 INFORMATION DOCUMENT UNIFORM EXAMINATION HISTORY OF QUÉBEC AND CANADA Secondary IV 585-44 NEW FEATURES June 005 August 005 January 006 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... SUMMARY OF NEW FEATURES OF THE EXAMINATION...3
INFORMATION DOCUMENT UNIFORM EXAMINATION HISTORY OF QUÉBEC AND CANADA Secondary IV 585-44 NEW FEATURES June 005 August 005 January 006 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION... SUMMARY OF NEW FEATURES OF THE EXAMINATION...3
The Making of Industrial Society (Bentley - Chapter 30)
 The Making of Industrial Society (Bentley - Chapter 30) Industrialization was essential to the modern world and its effects were global. It also had enormous effects on the economic, domestic, and social
The Making of Industrial Society (Bentley - Chapter 30) Industrialization was essential to the modern world and its effects were global. It also had enormous effects on the economic, domestic, and social
How New Jersey's Economy Benefits from International Trade & Investment
 How New Jersey's Economy Benefits from International Trade & Investment With more than 95 percent of the world s population and 80 percent of the world s purchasing power outside the United States, future
How New Jersey's Economy Benefits from International Trade & Investment With more than 95 percent of the world s population and 80 percent of the world s purchasing power outside the United States, future
Capital Planning Retreat Economic Outlook Alan E. Maguire
 Capital Planning Retreat Economic Outlook Alan E. Maguire Chandler-Gilbert Estrella Mountain GateWay Glendale Mesa Paradise Valley Phoenix Rio Salado Scottsdale South Mountain Economic Outlook Where are
Capital Planning Retreat Economic Outlook Alan E. Maguire Chandler-Gilbert Estrella Mountain GateWay Glendale Mesa Paradise Valley Phoenix Rio Salado Scottsdale South Mountain Economic Outlook Where are
Please send your responses by to: This consultation closes on Friday, 8 April 2016.
 CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
14.54 International Trade Lecture 2: The Basics
 14.54 International Trade Lecture 2: The Basics 14.54 Week 2 Fall 2016 14.54 (Week 2) The Basics Fall 2016 1 / 36 Today s Plan 1 2 What Does the World Economy Look Like? 1 2 What does the world trade?
14.54 International Trade Lecture 2: The Basics 14.54 Week 2 Fall 2016 14.54 (Week 2) The Basics Fall 2016 1 / 36 Today s Plan 1 2 What Does the World Economy Look Like? 1 2 What does the world trade?
Oregon. History and Social Science Standards of Learning United States History to 1865 Virginia
 History and Social Science Standards of Learning Virginia Oregon 2018 Students will use skills for historical and geographical analysis to explore the early history of the United States and understand
History and Social Science Standards of Learning Virginia Oregon 2018 Students will use skills for historical and geographical analysis to explore the early history of the United States and understand
Railroads and Rise of Big Business. Age. Transcontinental Railroad. Term coined by
 Railroads and Rise of Big Business Age Term coined by Refers to last quarter of the 19th century Looked glitzy, but not pure Transcontinental Railroad Central Pacific and Union Pacific Railroads met at
Railroads and Rise of Big Business Age Term coined by Refers to last quarter of the 19th century Looked glitzy, but not pure Transcontinental Railroad Central Pacific and Union Pacific Railroads met at
Adopted March 17, 2009 (Ordinance 09-15)
 ECONOMIC ELEMENT of the PINELLAS COUNTY COMPREHENSIVE PLAN Prepared By: The Pinellas County Planning Department as staff to the LOCAL PLANNING AGENCY for THE BOARD OF COUNTY COMMISSIONERS OF PINELLAS COUNTY,
ECONOMIC ELEMENT of the PINELLAS COUNTY COMPREHENSIVE PLAN Prepared By: The Pinellas County Planning Department as staff to the LOCAL PLANNING AGENCY for THE BOARD OF COUNTY COMMISSIONERS OF PINELLAS COUNTY,
Warm-UP. As the nation was growing (early stages) explain why it may have been tempting and perhaps easier to take part in illegal business activity.
 Warm-UP As the nation was growing (early stages) explain why it may have been tempting and perhaps easier to take part in illegal business activity. The Railroads The Transcontinental Railroad In 1862
Warm-UP As the nation was growing (early stages) explain why it may have been tempting and perhaps easier to take part in illegal business activity. The Railroads The Transcontinental Railroad In 1862
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights
 OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights Global dynamics in science, technology and innovation Investment in science, technology and innovation has benefited from strong economic
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights Global dynamics in science, technology and innovation Investment in science, technology and innovation has benefited from strong economic
Comparative study of SME development in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. Lyubov Tsoy CWRD intern Supervisor Dai Chai Song
 Comparative study of SME development in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan Lyubov Tsoy CWRD intern Supervisor Dai Chai Song 1. Background 2. SME development trends (1991-2013) 3. Factors that caused differences
Comparative study of SME development in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan Lyubov Tsoy CWRD intern Supervisor Dai Chai Song 1. Background 2. SME development trends (1991-2013) 3. Factors that caused differences
The seventh M&A wave. Marcos Cordeiro SEPTEMBER, 2014
 SEPTEMBER, 2014 The seventh M&A wave Marcos Cordeiro The history of mergers and acquisitions is probably as long as commerce itself, and it is difficult to determine a date for the first case of a merger
SEPTEMBER, 2014 The seventh M&A wave Marcos Cordeiro The history of mergers and acquisitions is probably as long as commerce itself, and it is difficult to determine a date for the first case of a merger
What type of Entrepreneurs (Entrepreneurship) do we need for Economic Development?
 Entrepreneurs and their role in Economic Development Entrepreneurs, firms and business membership organizations: their role in politics and development Leipzig, Germany, 29th 31th October 2014 Prof. Dr.
Entrepreneurs and their role in Economic Development Entrepreneurs, firms and business membership organizations: their role in politics and development Leipzig, Germany, 29th 31th October 2014 Prof. Dr.
From Paleolithic Times. to the Present FIFTH EDITION. LARRY NEAL University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 A CONCISE ECONOMIC HISTORY OF THE WORLD From Paleolithic Times to the Present FIFTH EDITION LARRY NEAL University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign RONDO CAMERON Emory University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY
A CONCISE ECONOMIC HISTORY OF THE WORLD From Paleolithic Times to the Present FIFTH EDITION LARRY NEAL University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign RONDO CAMERON Emory University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY
WARM UP. 1 You have 20 minutes to begin working on the study guide for your first test tomorrow
 WARM UP 1 You have 20 minutes to begin working on the study guide for your first test tomorrow 2 The study guide gives you an additional 15 points on the test 1 To pass test = study guide and 45 2 To get
WARM UP 1 You have 20 minutes to begin working on the study guide for your first test tomorrow 2 The study guide gives you an additional 15 points on the test 1 To pass test = study guide and 45 2 To get
AP World History SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP World History SCORING GUIDELINES Long Essay Question 2 In the period 1950 to 2001, scientific and technological innovations led to advances in communication, transportation, and industry that transformed
AP World History SCORING GUIDELINES Long Essay Question 2 In the period 1950 to 2001, scientific and technological innovations led to advances in communication, transportation, and industry that transformed
Social Studies: RESOURCES
 Social Studies Key Themes: Grade 6 To be productive members of society, students must be critical consumers of information they read, hear, and observe and communicate effectively about their ideas. They
Social Studies Key Themes: Grade 6 To be productive members of society, students must be critical consumers of information they read, hear, and observe and communicate effectively about their ideas. They
Overview of Venture Equity
 Overview of Venture Equity SVB Analytics Report 2017 Written by SVB Analytics: Steve Liu Managing Director sliu@svb.com Sean Lawson Senior Manager slawson2@svb.com Steven Pipp Senior Associate spipp@svb.com
Overview of Venture Equity SVB Analytics Report 2017 Written by SVB Analytics: Steve Liu Managing Director sliu@svb.com Sean Lawson Senior Manager slawson2@svb.com Steven Pipp Senior Associate spipp@svb.com
Small Business, Entrepreneurship, and Economic Recovery
 U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency Small Business, Entrepreneurship, and Economic Recovery Ivonne Cunarro Co- Hosted by the Kauffman Foundation, Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta,
U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency Small Business, Entrepreneurship, and Economic Recovery Ivonne Cunarro Co- Hosted by the Kauffman Foundation, Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta,
High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development. UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017
 High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017 Edna dos Santos-Duisenberg creative.edna@gmail.com Policy Advisor
High Level Seminar on the Creative Economy and Copyright as Pathways to Sustainable Development UN-ESCAP/ WIPO, Bangkok December 6, 2017 Edna dos Santos-Duisenberg creative.edna@gmail.com Policy Advisor
Higher Education for Science, Technology and Innovation. Accelerating Africa s Aspirations. Communique. Kigali, Rwanda.
 Higher Education for Science, Technology and Innovation Accelerating Africa s Aspirations Communique Kigali, Rwanda March 13, 2014 We, the Governments here represented Ethiopia, Mozambique, Rwanda, Senegal,
Higher Education for Science, Technology and Innovation Accelerating Africa s Aspirations Communique Kigali, Rwanda March 13, 2014 We, the Governments here represented Ethiopia, Mozambique, Rwanda, Senegal,
Service Science: A Key Driver of 21st Century Prosperity
 Service Science: A Key Driver of 21st Century Prosperity Dr. Bill Hefley Carnegie Mellon University The Information Technology and Innovation Foundation Washington, DC April 9, 2008 Topics Why a focus
Service Science: A Key Driver of 21st Century Prosperity Dr. Bill Hefley Carnegie Mellon University The Information Technology and Innovation Foundation Washington, DC April 9, 2008 Topics Why a focus
1.1 Students know how to use maps, globes, and other geographic tools to acquire, process, and report information from a spatial perspective.
 Prentice Hall World Geography: Building a Global Perspective 2005 Colorado Model Academic Standards for Social Studies: Geography (Grades 9-12) GEOGRAPHY STANDARD 1: Students know how to use and construct
Prentice Hall World Geography: Building a Global Perspective 2005 Colorado Model Academic Standards for Social Studies: Geography (Grades 9-12) GEOGRAPHY STANDARD 1: Students know how to use and construct
Learning Lessons Abroad on Funding Research and Innovation. 29 April 2016
 Learning Lessons Abroad on Funding Research and Innovation 29 April 2016 In South Africa universities contribute 2.1% of gross domestic product more than textiles and forestry and they employ 300,000 people
Learning Lessons Abroad on Funding Research and Innovation 29 April 2016 In South Africa universities contribute 2.1% of gross domestic product more than textiles and forestry and they employ 300,000 people
Macroeconomics: Principles, Applications, and Tools
 Macroeconomics: Principles, Applications, and Tools NINTH EDITION Chapter 8 Why Do Economies Grow? Learning Objectives 8.1 Calculate economic growth rates. 8.2 Explain the role of capital in economic growth.
Macroeconomics: Principles, Applications, and Tools NINTH EDITION Chapter 8 Why Do Economies Grow? Learning Objectives 8.1 Calculate economic growth rates. 8.2 Explain the role of capital in economic growth.
Industrialization. January 25th & 26th
 Industrialization January 25th & 26th Warm Up - January 25th & 26th Based on what we have talked about with Jim Crow South, Westward Expansion, Urbanization, and Immigration Is progress a good or bad thing?
Industrialization January 25th & 26th Warm Up - January 25th & 26th Based on what we have talked about with Jim Crow South, Westward Expansion, Urbanization, and Immigration Is progress a good or bad thing?
FINANCING OF THE INNOVATIONS COMPETITIVENESS OF THE COMPANIES AND THE NATIONAL ECONOMY
 FINANCING OF THE INNOVATIONS IN FUNCTION TO THE COMPETITIVENESS OF THE COMPANIES AND THE NATIONAL ECONOMY Miroslav Andonovski, PhD miroslav.andonovski@uklo.edu.mk University St. Kliment Ohridski Bitola,
FINANCING OF THE INNOVATIONS IN FUNCTION TO THE COMPETITIVENESS OF THE COMPANIES AND THE NATIONAL ECONOMY Miroslav Andonovski, PhD miroslav.andonovski@uklo.edu.mk University St. Kliment Ohridski Bitola,
Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum
 Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum Content Area: Social Studies Course Title/ Grade Level: Grade 5 Unit 1: Prehistory Month: 3rd & 4 th Marking Period Unit 2: Early Civilizations/Mesopotamia Month: 3rd
Pine Hill Public Schools Curriculum Content Area: Social Studies Course Title/ Grade Level: Grade 5 Unit 1: Prehistory Month: 3rd & 4 th Marking Period Unit 2: Early Civilizations/Mesopotamia Month: 3rd
