Topic 3: Fourier Series (FS)
|
|
|
- Randell Daniels
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELEC361: Signals And Systems Tpic 3: Furier Series (FS) Dr. Aishy Amer Cncrdia University Electrical and Cmputer Engineering Intrductin t frequency analysis f signals Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t cmplex expnential Summary Appendix: Applicatins (nt in the exam) Figures and examples in these curse slides are taken frm the fllwing surces: A. Oppenheim, A.S. Willsky and S.H. Nawab, Signals and Systems, 2nd Editin, Prentice-Hall, 1997 M.J. Rberts, Signals and Systems, McGraw Hill, 2004 J. McClellan, R. Schafer, M. Yder, Signal Prcessing First, Prentice Hall, 2003
2 Signal Representatin Time-dmain representatin Wavefrm based Peridic / nn-peridic signals Frequency-dmain representatin Peridic signals Sinusidal signals Frequency analysis fr peridic signals Cncepts f frequency, bandwidth, filtering 2
3 Wavefrm Representatin Wavefrm representatin Plt f the signal value vs. time Sund amplitude, temperature reading, stck price,.. Mathematical representatin: x(t) x: variable value T: independent variable 3
4 4 Sample Speech Wavefrm
5 5 Sample Music Wavefrm
6 Sinusidal Signals Sinusidal signals: imprtant because they can be used t synthesize any signal An arbitrary signal can be expressed as a sum f many sinusidal signals with different frequencies, amplitudes and phases Phase shift: hw much the max. f the sinusidal signal is shifted away frm t=0 Music ntes are essentially sinusids at different frequencies 6
7 Cmplex Expnential Signals 7 Cmplex Number : Cartesian representatin : z Magnitude f Phase f Plar representatin : Cmplex Expnential Signal : x( t) = z e z is θ is the phase shift (initial phase) Cmplex Cnjugate : z * ( jω t+ θ ) Euler Frumla : e θ = a + e θ jb 0 z is = Nte : = 2cs( θ ) z = z ( z + z e θ = a + a z e 0 * 2 φ = z = = jφ z cs( ω t + θ ) + e + b 2 1 b tan a = z csφ + ) and θ = jb ( zz j z sin( ω t + θ ) * ) are real j2sin( θ ) j z sinφ 0
8 Real and Cmplex Sinusids 8
9 Peridic CT Signals A CT signal is peridic if there is a psitive value fr which Perid T f : The interval n which x(t) repeats Fundamental perid T 0 : the smallest such repetitin interval T 0 =1/f 0 Fundamental perid: the smallest psitive value fr which the equatin abve hlds Example: x(t) = cs(4*pi*t); T=1/2; T 0 =1/4 Harmnic frequencies f x(t): kf 0, k is integer, Example: is peridic with 9
10 Sums f CT peridic signals The perid f the sum f CT peridic functins is the least cmmn multiple f the perids f the individual functins summed If the least cmmn multiple is infinite, the sum is aperidic 10
11 Peridic DT Signals A DT signal is peridic with perid where is a psitive integer if The fundamental perid f is the smallest psitive value f fr which the equatin hlds Example: is peridic with fundamental perid 11
12 What is frequency f an arbitrary signal? Sinusidal signals have a distinct (unique) frequency An arbitrary signal x(t) des nt have a unique frequency x(t) can be decmpsed int many sinusidal signals with different frequencies, each with different magnitude and phase Spectrum f x(t): the plt f the magnitudes and phases f different frequency cmpnents Furier analysis: find spectrum fr signals Bandwidth f x(t): the spread f the frequency cmpnents with significant energy existing in a signal 12
13 13 Frequency cntent in signals
14 Frequency cntent in signals A cnstant : nly zer frequency cmpnent (DC cmpnent) A sinusid : Cntain nly a single frequency cmpnent Peridic signals : Cntain the fundamental frequency and harmnics : Line spectrum Slwly varying : cntain lw frequency nly Fast varying : cntain very high frequency Sharp transitin : cntain frm lw t high frequency Music: : cntain bth slwly varying and fast varying cmpnents, wide bandwidth 14
15 Transfrming Signals X(t) is the signal representatin in time dmain Often we transfrm signals in a different dmain Furier analysis allws us t view signals in the frequency dmain In the frequency dmain we examine which frequencies are present in the signal Frequency dmain techniques reveal things abut the signal that are difficult t see therwise in the time dmain 15
16 Furier representatin f signals The study f signals and systems using sinusidal representatins is termed Furier analysis, after Jseph Furier ( ) The develpment f Furier analysis has a lng histry invlving a great many individuals and the investigatin f many different physical phenmena, such as the mtin f a vibrating string, the phenmenn f heat prpagatin and diffusin Furier methds have widespread applicatin beynd signals and systems, being used in every branch f engineering and science The thery f integratin, pint-set tplgy, and eigenfunctin expansins are just a few examples f tpics in mathematics that have their rts in the analysis f Furier series and integrals 16
17 17 Furier representatin f signals: Types f signals
18 Furier representatin f signals: Cntinuus-Value / Cntinuus-Time Signals All cntinuus signals are CT but nt all CT signals are cntinuus 18
19 Furier representatin f signals: Types f signals 19
20 Furier representatin f signals Fur distinct Furier representatins: Each applicable t a different class f signals Determined by the peridicity prperties f the signal and whether the signal is discrete r cntinuus in time A Furier representatin is unique, i.e., n tw same signals in time dmain give the same functin in frequency dmain 20
21 Overview f Furier Analysis Methds Cntinuus in Time Aperidic in Frequency Discrete in Time Peridic in Frequency Peridic in Time Discrete in Frequency CT Furier Series : a k 1 = T x( t) = T 0 x( t) e jkω t CT Inverse Furier Series : X[ k] = a k k = N 1 n= 0 N 1 k = 0 e jkω t DT Furier Series 0 0 dt jω kn CT - P Inverse DT Furier Series 1 x[ n] = N x[ n] e 0 X[ k] e DT - P jω kn 0 N T DT DT CT - P DT - P DT - P N N T DT - P N Aperidic in Time Cntinuus in Frequency CT Furier Transfrm : X ( jω) = x( t) = DT Furier Transfrm : X ( e jω x[ n] = ) = n= Inverse DT Furier Transfrm : 1 2 π 2 π x[ n] e X ( e jω jωt Inverse CT Furier Transfrm : 1 2π x( t) e X ( jω) e jωn ) e dt jωt jωn dω dω CT CT DT CT + P CT CT CT + P 2π 2π DT 21
22 Furier representatin: Peridic Signals Furier Series Synthesis (inverser transfrm) x( t) = a = 0 + k = a k = 1 k e a 0 k jω kt cs( ω kt + φ ) (single sided, fr real signal nly) 0 k (duble sided, fr bth real and cmplex) Furier Series Analysis(frward transfrm) X[ k] = a a k k 1 = T T is, in general, a 0 x( t) e jω kt 0 dt; cmplex number k = 0, ± 1, ± 2,... Fr real signals : a k = a * k a k = a k (symmetric spectrum) 22 R(z) = z + z 2
23 23 FS: Example Nn - cnstant Cmpnents Cnstant Cmpnent ) ( ) ( ) 2 8cs(500 ) 3 14 cs( ) ( = = = t x e e e e e e e e t x t t t x t j j t j j t j j t j j π π π π π π π π π π π π
24 24 Cncept f Furier analysis
25 25 Cncept f Furier analysis
26 Apprximatin f Peridic Signals by Sinusids Any peridic signal can be apprximated by a sum f many sinusids at harmnic frequencies f the signal (kf 0 ) with apprpriate amplitude and phase The mre harmnic cmpnents are added, the mre accurate the apprximatin becmes Instead f using sinusidal signals, mathematically, we can use the cmplex expnential functins with bth psitive and negative harmnic frequencies 26
27 Apprximatin f Peridic Signals by Sum f Sinusids 27
28 Furier representatin: Peridic CT Signals 28
29 Example: Furier Series f Square Wave 1 The Furier series analysis: 29
30 Example: Spectrum f Square Wave 1 Each line crrespnds t ne harmnic frequency. The line magnitude (height) indicates the cntributin f that frequency t the signal The line magnitude drps expnentially, which is nt very fast. The very sharp transitin in square waves calls fr very high frequency sinusids t synthesize 30
31 31 Negative Frequency?
32 32 Negative Frequency?
33 Why Frequency Dmain Representatin f signals? 33 Shws the frequency cmpsitin f the signal Change the magnitude f any frequency cmpnent arbitrarily by a filtering peratin Lwpass -> smthing, nise remval Highpass -> edge/transitin detectin High emphasis -> edge enhancement Shift the central frequency by mdulatin A cre technique fr cmmunicatin, which uses mdulatin t multiplex many signals int a single cmpsite signal, t be carried ver the same physical medium
34 Why Frequency Dmain Representatin f signals? Typical Filtering applied t x(t): Lwpass -> smthing, nise remval Highpass -> edge/transitin detectin Bandpass -> Retain nly a certain frequency range 34
35 Outline Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t cmplex expnential Summary 35
36 Furier series f CT peridic signals Cnsider the fllwing cntinuus-time cmplex expnentials: T 0 is the perid f all f these expnentials and it can be easily verified that the fundamental perid is equal t Any linear cmbinatin f is als peridic with perid T 0 36
37 Furier series f CT peridic signals fundamental cmpnents r the first harmnic cmpnents The crrespnding fundamental frequency is ω 0 Furier series representatin f a peridic signal x(t): 37 (4.1)
38 38 Furier series f a CT peridic signal
39 39 Furier series f a CT peridic signal
40 Furier series f a CT peridic signal: Example
41 Furier series f a CT peridic signal: Example 4.1 The Furier series cefficients are shwn in the Figures Nte that the Furier cefficients are cmplex numbers in general Thus ne shuld use tw figures t demnstrate them cmpletely: shw real and imaginary parts r magnitude and angle 41
42 Furier series f CT REAL peridic signals If x(t) is real This means that 42
43 Furier series f CT REAL peridic signals 43
44 44 sinc Functin
45 Furier series f a CT peridic signal:example
46 Furier series f a CT peridic signal: Example The Furier series cefficients are shwn in Figures fr T=4T 1 and T=16T 1 Nte that the Furier series cefficients fr this particular example are real
47 47
48 48 Inverse CT Furier Series: Example: Magnitude and Phase Spectra f the harmnic functin X[k]
49 Inverse CT Furier series: Example The CT Furier Series representatin xf(t) f the abve csine signal X[k] is xf(t) is dd The discntinuities make X[k] have significant higher harmnic cntent xf(t) 49
50 Nte: Lg-Magnitude Frequency Respnse Plts 50
51 Nte: Lg-Magnitude Frequency Respnse Plts 51
52 Outline Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t cmplex expnential Summary 52
53 Effect f Signal Symmetry n CT Furier Series 53
54 Effect f Signal Symmetry n CT Furier Series 54
55 Effect f Signal Symmetry n CT Furier Series 55
56 Effect f Signal Symmetry n CT Furier Series 56
57 Effect f Signal Symmetry n CT Furier Series 57
58 Effect f Signal Symmetry n CT Furier Series: Example 58
59 Outline Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t cmplex expnential Summary 59
60 Prperties f CT Furier series The prperties are useful in determining the Furier series r inverse Furier series They help t represent a given signal in term f peratins (e.g., cnvlutin, differentiatin, shift) n anther signal fr which the Furier series is knwn Operatins n {x(t)} Operatins n {X[k]} Help find analytical slutins t Furier Series prblems f cmplex signals Example: t FS{ y( t) = a u( t 5) } delay and multiplicatin 60
61 Prperties f CT Furier series Let x(t): have a fundamental perid T 0x Let y(t): have a fundamental perid T 0y Let X[k]=a k and Y[k]=b k The Furier Series harmnic functins each using the fundamental perid T F as the representatin time In the Furier series prperties which fllw: Assume the tw fundamental perids are the same T= T 0x =T 0y (unless therwise stated) The fllwing prperties can easily been shwn using equatin (4.5) fr Furier series 61
62 Prperties f CT Furier series 62
63 Prperties f CT Furier series 63
64 Prperties f CT Furier series 64
65 Prperties f CT Furier series 65
66 Prperties f CT Furier series 66
67 Prperties f CT Furier series 67
68 Prperties f CT Furier series 68
69 Prperties f CT Furier series 69
70 Prperties f CT Furier series 70
71 Prperties f CT Furier series 71
72 Prperties f CT Furier series: Example
73 Prperties f CT Furier series: Example
74 Prperties f CT Furier series: Example
75 Prperties f CT Furier series: Example 75
76 Outline Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t cmplex expnential Summary 76
77 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series The Furier series representatin f a peridic signal x(t) cnverges t x(t) if the Dirichlet cnditins are satisfied Three Dirichlet cnditins are as fllws: 1. Over any perid, x(t) must be abslutely integrable. Fr example, the fllwing signal des nt satisfy this cnditin 77
78 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series 2. x(t) must have a finite number f maxima and minima in ne perid Fr example, the fllwing signal meets Cnditin 1, but nt Cnditin 2 78
79 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series 3. x(t) must have a finite number f discntinuities, all f finite size, in ne perid Fr example, the fllwing signal vilates Cnditin 3 79
80 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Every cntinuus peridic signal has an FS representatin Many nt cntinuus signals has an FS representatin If a signal x(t) satisfies the Dirichlet cnditins and is nt cntinuus, then the Furier series cnverges t the midpint f the left and right limits f x(t) at each discntinuity Almst all physical peridic signals encuntered in engineering practice, including all f the signals with which we will be cncerned, satisfy the Dirichlet cnditins 80
81 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series: Summary 81
82 82 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series: Cntinuus signals
83 83 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series: Discntinuus signals
84 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series: Gibb s phenmenn 84
85 Cnvergence f the CT Furier series: Gibbs Phenmenn 85
86 Outline Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t cmplex expnential Summary 86
87 87 The DT Furier Series
88 88 The DT Furier Series
89 89 The DT Furier Series
90 90 Cncept f DT Furier Series
91 91 The DT Furier Series
92 92 The DT Furier Series
93 93 The DT Furier Series
94 The DT Furier Series: Example
95 The DT Furier Series: Example
96 The DT Furier Series: Example
97 The DT Furier Series: Example
98 Outline Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t cmplex expnential Summary 98
99 Prperties f DT Furier Series 99
100 Prperties f DT Furier Series 100
101 Outline Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential Summary 101
102 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential Eigen-functin f a linear peratr S: a nn-zer functin that returns frm the peratr exactly as is except fr a multiplicatr (r a scaling factr) Eigenfunctin f a system S: characteristic functin f S System applied n a functin x( t) : S{ x( t)} = λx( t) λ :eigen - value (a nn - null vectr) x( t) :eigen - functin 102
103 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential Eigenfunctin f an LTI system = the cmplex j k expnential e ω t Any LTI system S excited by a cmplex sinusid respnds with anther cmplex sinusid f the same frequency, but generally a different amplitude and phase The eigen-values are either real r, if cmplex, ccur in cmplex cnjugate pairs 103
104 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential 104 Cnvlutin represents: The input as a linear cmbinatin f impulses The respnse as a linear cmbinatin f impulse respnses Furier Series represents: x ( t) = x( τ ) δ ( t τ ) dτ y ( t) = x( τ ) h( t τ ) dτ a peridic signal as a linear cmbinatin f cmplex sinusids jωkt x( t) = ake ωk = 2π fk = 2π k f0 k =
105 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential : Linearity and Superpsitin If x(t) can be expressed as a sum f cmplex sinusids the respnse can be expressed as the sum f respnses t jω t cmplex sinusids k y( t) e ω = 2πf = bk k = k k 105
106 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential Let a cntinuus-time LTI system be excited by a cmplex expnential f the frm, The respnse is the cnvlutin f the excitatin with the impulse respnse r The quantity 106 will later be designated the Laplace transfrm f the impulse respnse and will be an imprtant transfrm methd fr CT system analysis
107 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential CT system: x( t) = e st = e ( σ + jω) t ; s = σ + jω This leads t the fllwing equatin fr CT LTI systems: 107
108 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential H(s) is a cmplex cnstant whse value depends n s and is given by: Cmplex expnential e st are eigenfunctins f CT LTI systems H(s) is the eigenvalue assciated with the eigenfunctin e st 108
109 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential DT systems: This leads t the fllwing equatin fr DT LTI systems: 109
110 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential H(z) is a cmplex cnstant whse value depends n z and is given by: Cmplex expnential z n are eigenfunctins f DT LTI systems H(z) is the eigenvalue assciated with the eigenfunctin z n 110
111 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential Frm superpsitin: 111
112 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential: Example 3.3 Cnsider an LTI system whse input x(t) and utput y(t) are related by a time shift as fllws: Find the utput f the system t the fllwing inputs: 112
113 113 Example Slutin
114 114 Example Slutin
115 jωt Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential : x( t) = e ; s = 0 + jω 115
116 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential: Example 116
117 Respnse f LTI systems t Cmplex Expnential: Example 117
118 Outline Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t peridic signals Summary 118
119 Furier series: summary 119 Sinusid signals: Can determine the perid, frequency, magnitude and phase f a sinusid signal frm a given frmula r plt Furier series fr peridic signals Understand the meaning f Furier series representatin Can calculate the Furier series cefficients fr simple signals (nly require duble sided) Can sketch the line spectrum frm the Furier series cefficients
120 120 Furier series: summary
121 Furier series: summary Steps fr cmputing Furier series: 1. Identify perid 2. Write dwn equatin fr x(t) 3. Observe if the signal has any summitry (even r dd) 4. Use the expnential equatin (1) in previus slide, and if needed use Eq. (2) fr the trignmetric cefficients 121
122 FS Summary: a quiz Prblem: Find the Furier series cefficients f the peridic π cntinuus signal: x( t) = cs( t), 0 t < 3 3 and T = 3 is the perid f the signal. Plt the spectrum (magnitude and phase) f x(t). What is the spectrum f x(t-4)? Slutin: Using the definitin f Furier cefficients fr a peridic cntinuus signal, the cefficients are: a k = π π 1 T 3 2π 3 j t j t π 1 jk t 1 e + e jk t jkω 3 3 ( ) 0 t π x t e dt = cs( t) e dt = e T 2 dt which wuld be simplified after sme manipulatins t: a k 4kj = π (1 4k 2 ) 122
123 Outline 123 Intrductin t frequency analysis Furier series f CT peridic signals Signal Symmetry and CT Furier Series Prperties f CT Furier series Cnvergence f the CT Furier series Furier Series f DT peridic signals Prperties f DT Furier series Respnse f LTI systems t cmplex expnential Summary Appendix: Applicatins (nt in the exam)
124 Applicatins f frequency- dmain representatin 124 Clearly shws the frequency cmpsitin a signal Can change the magnitude f any frequency cmpnent arbitrarily by a filtering peratin Lwpass -> smthing, nise remval Highpass -> edge/transitin detectin High emphasis -> edge enhancement Can shift the central frequency by mdulatin A cre technique fr cmmunicatin, which uses mdulatin t multiplex many signals int a single cmpsite signal, t be carried ver the same physical medium Prcessing f speech and music signals
125 Typical Filters Lwpass -> smthing, nise remval Highpass -> edge/transitin detectin Bandpass -> Retain nly a certain frequency range 125
126 Lw Pass Filtering (Remve high freq, make signal smther) 126
127 High Pass Filtering (remve lw freq, detect edges) 127
128 Filtering in Tempral Dmain (Cnvlutin) 128
129 Cmmunicatin: Signal Bandwidth 129 Bandwidth f a signal is a critical feature when dealing with the transmissin f this signal A cmmunicatin channel usually perates nly at certain frequency range (called channel bandwidth) The signal will be severely attenuated if it cntains frequencies utside the range f the channel bandwidth T carry a signal in a channel, the signal needed t be mdulated frm its baseband t the channel bandwidth Multiple narrwband signals may be multiplexed t use a single wideband channel
130 Signal bandwidth Highest frequency estimatin in a signal: Find the shrtest interval between peak and valleys 130
131 131 Signal Bandwidth
132 Estimatin f Maximum Frequency 132
133 Prcessing Speech & Music Signals 133 Typical speech and music wavefrms are semi-peridic The fundamental perid is called pitch perid The fundamental frequency (f 0 ) Spectral cntent Within each shrt segment, a speech r music signal can be decmpsed int a pure sinusidal cmpnent with frequency f 0, and additinal harmnic cmpnents with frequencies that are multiples f f 0. The maximum frequency is usually several multiples f the fundamental frequency Speech has a frequency span up t 4 KHz Audi has a much wider spectrum, up t 22KHz
134 134 Sample Speech Wavefrm 1
135 Numerical Calculatin f CT Furier Series The riginal signal is digitized, and then a Fast Furier Transfrm (FFT) algrithm is applied, which yields samples f the FT at equally spaced intervals Fr a signal that is very lng, e.g. a speech signal r a music piece, spectrgram is used. Furier transfrms ver successive verlapping shrt intervals 135
136 Sample Speech Spectrgram 1 136
137 137 Sample Speech Wavefrm 2
138 138 Speech Spectrgram 2
139 139 Sample Music Wavefrm
140 140 Sample Music Spectrgram
Communication Theory II
 Cmmunicatin Thery II Lecture 3: Review n Furier analysis (cnt d) Ahmed Elnakib, PhD Assistant Prfessr, Mansura University, Egypt Febraury 15 th, 2015 1 Sectin plicy Gal: slve assciated prblems related
Cmmunicatin Thery II Lecture 3: Review n Furier analysis (cnt d) Ahmed Elnakib, PhD Assistant Prfessr, Mansura University, Egypt Febraury 15 th, 2015 1 Sectin plicy Gal: slve assciated prblems related
Phasor Representation
 Phasr Representatin Phase Phase difference Phasrs Phasr Transfrmatins Phase f sine wave An angular measurement that specifies the psitin f that sine wave relative t a reference When the sine wave is shifted
Phasr Representatin Phase Phase difference Phasrs Phasr Transfrmatins Phase f sine wave An angular measurement that specifies the psitin f that sine wave relative t a reference When the sine wave is shifted
Communication Theory II
 Cmmunicatin Thery II Lecture 2: Review n Furier analysis f signals and systems Ahmed Elnakib, PhD Assistant Prfessr, Mansura University, Egypt Febraury 12 th, 2015 1 Quiz 1 In a blank paper write yur name
Cmmunicatin Thery II Lecture 2: Review n Furier analysis f signals and systems Ahmed Elnakib, PhD Assistant Prfessr, Mansura University, Egypt Febraury 12 th, 2015 1 Quiz 1 In a blank paper write yur name
Spectrum Representation
 Spectrum Representatin Lecture #4 Chapter 3 99 What Is this Curse All Abut? T Gain an Appreciatin f the Varius Types f Signals and Systems T Analyze The Varius Types f Systems T Learn the Sills and Tls
Spectrum Representatin Lecture #4 Chapter 3 99 What Is this Curse All Abut? T Gain an Appreciatin f the Varius Types f Signals and Systems T Analyze The Varius Types f Systems T Learn the Sills and Tls
EE 311: Electrical Engineering Junior Lab Phase Locked Loop
 Backgrund Thery EE 311: Electrical Engineering Junir Lab Phase Lcked Lp A phase lcked lp is a cntrlled scillatr whse instantaneus frequency is dynamically adjusted thrugh multiplicative feedback and lw
Backgrund Thery EE 311: Electrical Engineering Junir Lab Phase Lcked Lp A phase lcked lp is a cntrlled scillatr whse instantaneus frequency is dynamically adjusted thrugh multiplicative feedback and lw
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY II EEE 209 EXPERIMENT-6. Operational Amplifiers II
 ADANA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY II EEE 209 EXPERIMENT-6 Operatinal Amplifiers II OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS Objectives The
ADANA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY II EEE 209 EXPERIMENT-6 Operatinal Amplifiers II OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS Objectives The
From definition (3.8a), find the Fourier transfonns of the signals get) shown in Fig. P3.l-4. (a)
 Prblems 43 3.-3 f get) C(w), then shw that g*(t) C*(-w). Frm definitin (3.8a), find the Furier transfnns f the signals get) shwn in Fig. P3.l-4. T {- T (... d.,mcgra l,newy Figure P3.-4 Frm definitin
Prblems 43 3.-3 f get) C(w), then shw that g*(t) C*(-w). Frm definitin (3.8a), find the Furier transfnns f the signals get) shwn in Fig. P3.l-4. T {- T (... d.,mcgra l,newy Figure P3.-4 Frm definitin
The demand for a successful flaw analysis is that the test equipment produces no distortion on the echos no noise. I _... I i.j J...
 SYSTEM ANALYSIS FOR WIDE BAND ULTRASONIC TEST SET-UPS Ulrich Opara Krautkramer GmbH Clgne, West Germany INTRODUCTION In the last years, the discussins abut ultrasnic test equipment fcussed n amplifier
SYSTEM ANALYSIS FOR WIDE BAND ULTRASONIC TEST SET-UPS Ulrich Opara Krautkramer GmbH Clgne, West Germany INTRODUCTION In the last years, the discussins abut ultrasnic test equipment fcussed n amplifier
INTRODUCTION TO PLL DESIGN
 INTRODUCTION TO PLL DESIGN FOR FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER Thanks Sung Tae Mn and Ari Valer fr part f this material A M S C Analg and Mixed-Signal Center Cntents Intrductin t Frequency Synthesizer Specificatin
INTRODUCTION TO PLL DESIGN FOR FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZER Thanks Sung Tae Mn and Ari Valer fr part f this material A M S C Analg and Mixed-Signal Center Cntents Intrductin t Frequency Synthesizer Specificatin
Operational Amplifiers High Speed Operational Amplifiers
 F Electrnics: Operatinal Amplifiers Page 11.1 Operatinal Amplifiers High Speed Operatinal Amplifiers Operatinal amplifiers with 3 db bandwidths f up t 1.5 GHz are nw available, such peratinal amplifiers
F Electrnics: Operatinal Amplifiers Page 11.1 Operatinal Amplifiers High Speed Operatinal Amplifiers Operatinal amplifiers with 3 db bandwidths f up t 1.5 GHz are nw available, such peratinal amplifiers
Chapter 4 DC to AC Conversion (INVERTER)
 Chapter 4 DC t AC Cnversin (INERTER) General cncept Single-phase inverter Harmnics Mdulatin Three-phase inverter Drives (ersin 3-003): 1 DC t AC Cnverter (Inverter) DEFINITION: Cnverts DC t AC pwer by
Chapter 4 DC t AC Cnversin (INERTER) General cncept Single-phase inverter Harmnics Mdulatin Three-phase inverter Drives (ersin 3-003): 1 DC t AC Cnverter (Inverter) DEFINITION: Cnverts DC t AC pwer by
Waves Unit / Mechanical Waves Sub-Unit
 Waves Unit / Mechanical Waves Sub-Unit 5.1.1 Oscillatins - time fr ne scillatin - number f scillatins per secnd Equatin Pendulum Mass n a Spring PRACTICE Regents Physics 1. A pendulum is timed as it mves
Waves Unit / Mechanical Waves Sub-Unit 5.1.1 Oscillatins - time fr ne scillatin - number f scillatins per secnd Equatin Pendulum Mass n a Spring PRACTICE Regents Physics 1. A pendulum is timed as it mves
Fourier Series LABVIEW GUI Documentation
 Furier Series LABVIEW GUI Dcumentatin INTRODUCTION The Furier Series GUI is meant t be used as a learning tl t better understand the Furier Series. The user is able t input the amplitude and frequency
Furier Series LABVIEW GUI Dcumentatin INTRODUCTION The Furier Series GUI is meant t be used as a learning tl t better understand the Furier Series. The user is able t input the amplitude and frequency
Comparative analysis of influence of the type line supplying nonlinear load on deformation of voltage and current in the power system
 Cmputer Applicatins in Electrical Engineering Cmparative analysis f influence f the type line supplying nnlinear lad n defrmatin f vltage and current in the pwer system tanisław Blkwski, Wiesław Brciek
Cmputer Applicatins in Electrical Engineering Cmparative analysis f influence f the type line supplying nnlinear lad n defrmatin f vltage and current in the pwer system tanisław Blkwski, Wiesław Brciek
ELT COMMUNICATION THEORY
 ELT-41307 COMMUNICATION THEORY Matlab Exercise #5 Carrier mdulated digital transmissin: Transmitter and receiver structures QAM signals, up/dwncnversin, timing and phase synchrnizatin, and symbl detectin
ELT-41307 COMMUNICATION THEORY Matlab Exercise #5 Carrier mdulated digital transmissin: Transmitter and receiver structures QAM signals, up/dwncnversin, timing and phase synchrnizatin, and symbl detectin
Continuous Wavelet Transform
 Chapter 2 Cntinuus Wavelet Transfrm 2. Intrductin t the -Dimensinal Cntinuus Wavelet Transfrm Wavelet transfrms are time-frequency transfrms which map the time-frequency plane in the manner f Figure. (c)
Chapter 2 Cntinuus Wavelet Transfrm 2. Intrductin t the -Dimensinal Cntinuus Wavelet Transfrm Wavelet transfrms are time-frequency transfrms which map the time-frequency plane in the manner f Figure. (c)
CS5530 Mobile/Wireless Systems Key Wireless Physical Layer Concepts
 Mbile/Wireless Systems Key Wireless Physical Layer Cncepts Yanyan Zhuang Department f Cmputer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang UC. Clrad Springs Outline Electrmagnetic spectrum Reflectin, diffractin
Mbile/Wireless Systems Key Wireless Physical Layer Cncepts Yanyan Zhuang Department f Cmputer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang UC. Clrad Springs Outline Electrmagnetic spectrum Reflectin, diffractin
Lab3 Audio Amplifier (Sep 25)
 GOAL Lab3 Audi Amplifier (Sep 25) The gal f Lab 3 is t demnstrate an audi amplifier based n an p amp and ttem-ple stage. OBJECTIVES 1) Observe crssver distrtin in a Class B ttem-ple stage. 2) Measure frequency
GOAL Lab3 Audi Amplifier (Sep 25) The gal f Lab 3 is t demnstrate an audi amplifier based n an p amp and ttem-ple stage. OBJECTIVES 1) Observe crssver distrtin in a Class B ttem-ple stage. 2) Measure frequency
PASSIVE FILTERS (LCR BASED)
 EXPEIMENT PAIVE FILTE (LC BAED) (IMULATION) OBJECTIVE T build highpass, lwpass and bandpass LC filters using circuit simulatin tls. INTODUCTION Ladder netwrks are filters f the first kind, built in the
EXPEIMENT PAIVE FILTE (LC BAED) (IMULATION) OBJECTIVE T build highpass, lwpass and bandpass LC filters using circuit simulatin tls. INTODUCTION Ladder netwrks are filters f the first kind, built in the
Output Stages. Microelectronic Circuits. Ching-Yuan Yang. National Chung-Hsing University Department of Electrical Engineering.
 Micrelectrnic Circuits Output Stages Ching-Yuan Yang Natinal Chung-Hsing University Department f Electrical Engineering Outline Classificatin f Output Stages Class A Output Stage Class B Output Stage Class
Micrelectrnic Circuits Output Stages Ching-Yuan Yang Natinal Chung-Hsing University Department f Electrical Engineering Outline Classificatin f Output Stages Class A Output Stage Class B Output Stage Class
Math 3201 Unit 8: SINUSODIAL FUNCTIONS NAME: Up until now we can measure angles using degrees.
 Math 0 Unit 8: SINUSODIAL FUNCTIONS NAME: Sectin 8.: Understanding Angles p. 8 Hw can we measure things? Eamples: Length - meters (m) r ards (d.) Temperature - degrees Celsius ( C) r Fahrenheit (F) Hw
Math 0 Unit 8: SINUSODIAL FUNCTIONS NAME: Sectin 8.: Understanding Angles p. 8 Hw can we measure things? Eamples: Length - meters (m) r ards (d.) Temperature - degrees Celsius ( C) r Fahrenheit (F) Hw
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics II
 Pulse Width Mdulatin (PWM) Crnerstne Electrnics Technlgy and Rbtics II Administratin: Prayer PicBasic Pr Prgrams Used in This Lessn: General PicBasic Pr Prgram Listing: http://www.crnerstnerbtics.rg/picbasic.php
Pulse Width Mdulatin (PWM) Crnerstne Electrnics Technlgy and Rbtics II Administratin: Prayer PicBasic Pr Prgrams Used in This Lessn: General PicBasic Pr Prgram Listing: http://www.crnerstnerbtics.rg/picbasic.php
Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits
 Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits Purpse: In this experiment, yu will learn abut peratinal amplifiers (r p-amps). Simple circuits cntaining peratinal amplifiers can be used t perfrm mathematical peratins, such
Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits Purpse: In this experiment, yu will learn abut peratinal amplifiers (r p-amps). Simple circuits cntaining peratinal amplifiers can be used t perfrm mathematical peratins, such
BV4115. RF Packet Transmitter. Product specification. February ByVac 2007 ByVac Page 1 of 5
 Prduct Specificatin Prduct specificatin. February 2007 ByVac 2007 ByVac Page 1 f 5 Prduct Specificatin Cntents 1. Dcument Versins... 2 2. Intrductin... 2 3. Features... 2 4. Battery Life... 2 5. Blck Diagram...
Prduct Specificatin Prduct specificatin. February 2007 ByVac 2007 ByVac Page 1 f 5 Prduct Specificatin Cntents 1. Dcument Versins... 2 2. Intrductin... 2 3. Features... 2 4. Battery Life... 2 5. Blck Diagram...
Switched and Sectored Beamforming 1 c Raviraj Adve,
 Switched and Sectred Beamfrming c Raviraj Adve, 2005. rsadve@cmm.utrnt.ca Intrductin Having investigated the use f antenna arrays fr directin f arrival estimatin we nw turn t the use f arrays fr data prcessing.
Switched and Sectred Beamfrming c Raviraj Adve, 2005. rsadve@cmm.utrnt.ca Intrductin Having investigated the use f antenna arrays fr directin f arrival estimatin we nw turn t the use f arrays fr data prcessing.
Hospital Task Scheduling using Constraint Programming
 Hspital Task Scheduling using Cnstraint Prgramming Authr: Chaman Chahal Supervisr: Dr. P. Bse, Schl f Cmputer Science Organizatin: Carletn University Curse: COMP4905 Date: Dec. 11, 2012 1 Abstract Hspitals
Hspital Task Scheduling using Cnstraint Prgramming Authr: Chaman Chahal Supervisr: Dr. P. Bse, Schl f Cmputer Science Organizatin: Carletn University Curse: COMP4905 Date: Dec. 11, 2012 1 Abstract Hspitals
Specification for Learning and Qualifications for Physical Intervention Skills
 Specificatin fr Learning and Qualificatins fr Physical Interventin Skills September 2018 Security Industry Authrity www.sia.hmeffice.gv.uk Frewrd The Security Industry Authrity (SIA) recgnises that it
Specificatin fr Learning and Qualificatins fr Physical Interventin Skills September 2018 Security Industry Authrity www.sia.hmeffice.gv.uk Frewrd The Security Industry Authrity (SIA) recgnises that it
Experiment 7 Digital Logic Devices and the 555-Timer
 Experiment 7 Digital Lgic Devices and the 555-Timer Purpse: In this experiment we address the cncepts f digital electrnics and lk at the 555-timer, a device that uses digital devices and ther electrnic
Experiment 7 Digital Lgic Devices and the 555-Timer Purpse: In this experiment we address the cncepts f digital electrnics and lk at the 555-timer, a device that uses digital devices and ther electrnic
Algebra2/Trig Honors: Trig Unit 2 Packet
 Algebra2/Trig Hnrs: Trig Unit 2 Packet In this unit, students will be able t: Learn and apply c-functin relatinships between trig functins Learn and apply the sum and difference identities Learn and apply
Algebra2/Trig Hnrs: Trig Unit 2 Packet In this unit, students will be able t: Learn and apply c-functin relatinships between trig functins Learn and apply the sum and difference identities Learn and apply
COMPLEX FILTERS AS CASCADE OF BUFFERED GINGELL STRUCTURES: DESIGN FROM BAND-PASS CONSTRAINTS
 COMPLEX FILTERS AS CASCADE OF BUFFERED GINGELL STRUCTURES: DESIGN FROM BAND-PASS CONSTRAINTS A Thesis presented t the Faculty f Califrnia Plytechnic State University, San Luis Obisp In Partial Fulfillment
COMPLEX FILTERS AS CASCADE OF BUFFERED GINGELL STRUCTURES: DESIGN FROM BAND-PASS CONSTRAINTS A Thesis presented t the Faculty f Califrnia Plytechnic State University, San Luis Obisp In Partial Fulfillment
A Novel Matrix Converter Topology With Simple Commutation
 A Nvel Matrix Cnverter Tplgy With Simple Cmmutatin Abstract-Matrix cnverter is very simple in structure and has pwerful cntrllability. Hwever, cmmutatin prblem and cmplicated PWM methd keep it frm being
A Nvel Matrix Cnverter Tplgy With Simple Cmmutatin Abstract-Matrix cnverter is very simple in structure and has pwerful cntrllability. Hwever, cmmutatin prblem and cmplicated PWM methd keep it frm being
Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits
 Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits Purpse: In this experiment, yu will learn abut peratinal amplifiers (r p-amps). Simple circuits cntaining peratinal amplifiers can be used t perfrm mathematical peratins, such
Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits Purpse: In this experiment, yu will learn abut peratinal amplifiers (r p-amps). Simple circuits cntaining peratinal amplifiers can be used t perfrm mathematical peratins, such
Experiment 7 Digital Logic Devices and the 555-Timer
 Experiment 7 Digital Lgic Devices and the 555-Timer Purpse: In this experiment we address the cncepts f digital electrnics and lk at the 555-timer, a device that uses digital devices and ther electrnic
Experiment 7 Digital Lgic Devices and the 555-Timer Purpse: In this experiment we address the cncepts f digital electrnics and lk at the 555-timer, a device that uses digital devices and ther electrnic
Application for Drive Technology
 Applicatin fr Drive Technlgy MICROMASTER 4 Applicatin Descriptin Warranty, Liability and Supprt 1 Warranty, Liability and Supprt We d nt accept any liability fr the infrmatin cntained in this dcument.
Applicatin fr Drive Technlgy MICROMASTER 4 Applicatin Descriptin Warranty, Liability and Supprt 1 Warranty, Liability and Supprt We d nt accept any liability fr the infrmatin cntained in this dcument.
θ = radians; where s = arc length, r = radius
 TRIGONOMETRY: 2.1 Degrees & Radians Definitins: 1 degree - 1 radian θ r s FORMULA: s θ = radians; where s = arc length, r = radius r IMPLICATION OF FORMULA: If s = r then θ = 1 radian EXAMPLE 1: What is
TRIGONOMETRY: 2.1 Degrees & Radians Definitins: 1 degree - 1 radian θ r s FORMULA: s θ = radians; where s = arc length, r = radius r IMPLICATION OF FORMULA: If s = r then θ = 1 radian EXAMPLE 1: What is
VLBA Electronics Memo No. 737
 VLBA Electrnics Mem N. 737 U S I N G PULSECAL A M P L I T U D E S TO D E T E R M I N E SYSTEM T E M P E R A T U R E D.S.Bagri 1993Mar05 INTRODUCTION System temperature is nrmally measured using mdulated
VLBA Electrnics Mem N. 737 U S I N G PULSECAL A M P L I T U D E S TO D E T E R M I N E SYSTEM T E M P E R A T U R E D.S.Bagri 1993Mar05 INTRODUCTION System temperature is nrmally measured using mdulated
ELEC 7250 VLSI TESTING. Term Paper. Analog Test Bus Standard
 ELEC 7250 VLSI TESTING Term Paper On Analg Test Bus Standard Muthubalaji Ramkumar 1 Analg Test Bus Standard Muthubalaji Ramkumar Dept. f Electrical and Cmputer Engineering Auburn University Abstract This
ELEC 7250 VLSI TESTING Term Paper On Analg Test Bus Standard Muthubalaji Ramkumar 1 Analg Test Bus Standard Muthubalaji Ramkumar Dept. f Electrical and Cmputer Engineering Auburn University Abstract This
EE 3323 Electromagnetics Laboratory
 EE 3323 Electrmagnetics Labratry Experiment #1 Waveguides and Waveguide Measurements 1. Objective The bjective f Experiment #1 is t investigate waveguides and their use in micrwave systems. Yu will use
EE 3323 Electrmagnetics Labratry Experiment #1 Waveguides and Waveguide Measurements 1. Objective The bjective f Experiment #1 is t investigate waveguides and their use in micrwave systems. Yu will use
Processors with Sub-Microsecond Response Times Control a Variety of I/O. *Adapted from PID Control with ADwin, by Doug Rathburn, Keithley Instruments
 PID Cntrl with ADwin Prcessrs with Sub-Micrsecnd Respnse Times Cntrl a Variety f I/O CHESTERLAND OH March 9, 2015 *Adapted frm PID Cntrl with ADwin, by Dug Rathburn, Keithley Instruments By Terry Nagy,
PID Cntrl with ADwin Prcessrs with Sub-Micrsecnd Respnse Times Cntrl a Variety f I/O CHESTERLAND OH March 9, 2015 *Adapted frm PID Cntrl with ADwin, by Dug Rathburn, Keithley Instruments By Terry Nagy,
1. Give an example of how one can exploit the associative property of convolution to more efficiently filter an image.
 CS 376 Cmputer Visin Spring 2011 Prblem set 1 Out: Tuesday Feb 1 Due: Mnday Feb 14 11:59 PM See the end f this dcument fr submissin instructins. Visit us during ffice hurs t discuss any questins n the
CS 376 Cmputer Visin Spring 2011 Prblem set 1 Out: Tuesday Feb 1 Due: Mnday Feb 14 11:59 PM See the end f this dcument fr submissin instructins. Visit us during ffice hurs t discuss any questins n the
Study of Dipole Antenna Height for Radio Telescope According to Baghdad Location
 Study f Diple Antenna Height fr Radi Telescpe Accrding t Baghdad Lcatin Kamal M. Abd 1, Mretadha J. Kadhim and Zinah F. Kadhim 3 1 Department f Astrnmy and Space, Cllege f Science, University f Baghdad,
Study f Diple Antenna Height fr Radi Telescpe Accrding t Baghdad Lcatin Kamal M. Abd 1, Mretadha J. Kadhim and Zinah F. Kadhim 3 1 Department f Astrnmy and Space, Cllege f Science, University f Baghdad,
GRFX 1801: Game Development for Platforms
 GRFX 1801: Game Develpment fr Platfrms Instructr Camern Buckley Email cbuckley@astate.edu Office Lcatin Fine Arts Center 123 Office Hurs Friday 10a 1p Curse Overview Intermediate and advanced techniques
GRFX 1801: Game Develpment fr Platfrms Instructr Camern Buckley Email cbuckley@astate.edu Office Lcatin Fine Arts Center 123 Office Hurs Friday 10a 1p Curse Overview Intermediate and advanced techniques
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL (ADC) & DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG (DAC) CONVERTERS
 ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL (ADC) & DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG (DAC) CONVERTERS 37 Many events mnitred and cntrlled by the micrprcessr are analg events. ADC & DAC CONVERTERS These range frm mnitring all frms f events, even
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL (ADC) & DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG (DAC) CONVERTERS 37 Many events mnitred and cntrlled by the micrprcessr are analg events. ADC & DAC CONVERTERS These range frm mnitring all frms f events, even
Summary of High Energy Particle Detector Elements
 1 Summary f High Energy Particle Detectr Elements Cntents Abstract... 1 Phtmultipliers vs. Phtdides... 2 Phtmultiplier tube... 2 Phtdides... 3 Preamplifier... 4 Amplifier... 5 Multi-Channel Analyser (MCA)...
1 Summary f High Energy Particle Detectr Elements Cntents Abstract... 1 Phtmultipliers vs. Phtdides... 2 Phtmultiplier tube... 2 Phtdides... 3 Preamplifier... 4 Amplifier... 5 Multi-Channel Analyser (MCA)...
Passive detection of Gaussian signals with narrow-band and broad-band components
 Passive detectin f Gaussian signals with narrw-band and brad-band cmpnents S. Pasupathy Department f Electrical Enineering, University f Trnt, Trnt, MSSIA4, Canada P.M. Schultheiss Department f Engineering
Passive detectin f Gaussian signals with narrw-band and brad-band cmpnents S. Pasupathy Department f Electrical Enineering, University f Trnt, Trnt, MSSIA4, Canada P.M. Schultheiss Department f Engineering
Four Switch Three Phase Inverter with Modified Z-Source
 Fur Switch Three Phase Inverter with Mdified Z-Surce Ragubathi. D, Midhusha. S and Ashk Rangaswamy, Department f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering, Sri Shakthi Instititute f Engineering and Technlgy,
Fur Switch Three Phase Inverter with Mdified Z-Surce Ragubathi. D, Midhusha. S and Ashk Rangaswamy, Department f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering, Sri Shakthi Instititute f Engineering and Technlgy,
Rectifiers convert DC to AC. Inverters convert AC to DC.
 DT23-3 Inverter Ntes 3 January 23. The difference between Rectifiers and Inverters Rectifiers cnvert DC t AC. Inverters cnvert AC t DC. 2. Uses f Inverters Battery Backup. Batteries stre DC. Many appliances
DT23-3 Inverter Ntes 3 January 23. The difference between Rectifiers and Inverters Rectifiers cnvert DC t AC. Inverters cnvert AC t DC. 2. Uses f Inverters Battery Backup. Batteries stre DC. Many appliances
R.c. Addison, Jr. and A.D.W. McKie Rockwell Science Center Thousand Oaks, California 91358
 GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SINGLE MODE LAMB WA YES USING LASER-BASED ULTRASOUND R.c. Addisn, Jr. and A.D.W. McKie Rckwell Science Center Thusand Oaks, Califrnia 91358 INTRODUCTION Lamb waves have been
GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SINGLE MODE LAMB WA YES USING LASER-BASED ULTRASOUND R.c. Addisn, Jr. and A.D.W. McKie Rckwell Science Center Thusand Oaks, Califrnia 91358 INTRODUCTION Lamb waves have been
NATF CIP Requirement R1 Guideline
 Open Distributin NATF CIP 014-2 Requirement R1 Guideline Disclaimer This dcument was created by the Nrth American Transmissin Frum (NATF) t facilitate industry wrk t imprve physical security. NATF reserves
Open Distributin NATF CIP 014-2 Requirement R1 Guideline Disclaimer This dcument was created by the Nrth American Transmissin Frum (NATF) t facilitate industry wrk t imprve physical security. NATF reserves
PreLab5 Temperature-Controlled Fan (Due Oct 16)
 PreLab5 Temperature-Cntrlled Fan (Due Oct 16) GOAL The gal f Lab 5 is t demnstrate a temperature-cntrlled fan. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f temperature has many applicatins. A temperature-cntrlled
PreLab5 Temperature-Cntrlled Fan (Due Oct 16) GOAL The gal f Lab 5 is t demnstrate a temperature-cntrlled fan. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f temperature has many applicatins. A temperature-cntrlled
Consider a boost-buck converter with the following parameters (Fig. 1-1). R cs2. R s2a HV9930 VDD PWMD REF C3
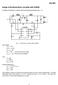 Design f the Bst-Buck cnverter with HV9930 Cnsider a bst-buck cnverter with the fllwing parameters (Fig. -. D L C L - VN Q d Cd D D3 C VO cs cs + s VN HV9930 VDD C sa sb GATE CS PWMD CS ref ref GND EF
Design f the Bst-Buck cnverter with HV9930 Cnsider a bst-buck cnverter with the fllwing parameters (Fig. -. D L C L - VN Q d Cd D D3 C VO cs cs + s VN HV9930 VDD C sa sb GATE CS PWMD CS ref ref GND EF
INLINE TE 01δ MODE DIELECTRIC-RESONATOR FIL- TERS WITH CONTROLLABLE TRANSMISSION ZERO FOR WIRELESS BASE STATIONS
 Prgress In Electrmagnetics Research Letters, Vl. 38, 11 11, 213 INLINE TE 1δ MODE DIELECTRIC-RESONATOR FIL- TERS WITH CONTROLLABLE TRANSMISSION ZERO FOR WIRELESS BASE STATIONS Xia Ouyang * and B-Yng Wang
Prgress In Electrmagnetics Research Letters, Vl. 38, 11 11, 213 INLINE TE 1δ MODE DIELECTRIC-RESONATOR FIL- TERS WITH CONTROLLABLE TRANSMISSION ZERO FOR WIRELESS BASE STATIONS Xia Ouyang * and B-Yng Wang
Application Note. Lock-in Milliohmmeter
 Applicatin Nte AN2207 Lck-in Millihmmeter Authr: Oleksandr Karpin Assciated Prject: Yes Assciated Part Family: CY8C24xxxA, CY8C27xxx PSC Designer Versin: 4.1 SP1 Assciated Applicatin Ntes: AN2028, AN2044,
Applicatin Nte AN2207 Lck-in Millihmmeter Authr: Oleksandr Karpin Assciated Prject: Yes Assciated Part Family: CY8C24xxxA, CY8C27xxx PSC Designer Versin: 4.1 SP1 Assciated Applicatin Ntes: AN2028, AN2044,
Maxon Motor & Motor Controller Manual
 Maxn Mtr & Mtr Cntrller Manual Nte: This manual is nly fr use fr the Maxn mtr and cntrller utlined belw. This infrmatin is based upn the tutrial vides fund nline and thrugh testing. NOTE: Maximum Permitted
Maxn Mtr & Mtr Cntrller Manual Nte: This manual is nly fr use fr the Maxn mtr and cntrller utlined belw. This infrmatin is based upn the tutrial vides fund nline and thrugh testing. NOTE: Maximum Permitted
Filter Design. Filter Design by INSERTION LOSS METHOD controls Γ(ω) to control passband and stopband of filter. sabarina/ppkkp 1
 Filter Desin Filter Desin by INSERTION LOSS METHOD cntrls Γ(ω) t cntrl passband and stpband f filter. sabarina/ppkkp 1 Filter parameters Passband -- frequencies that are passed by filter. Stpband -- frequencies
Filter Desin Filter Desin by INSERTION LOSS METHOD cntrls Γ(ω) t cntrl passband and stpband f filter. sabarina/ppkkp 1 Filter parameters Passband -- frequencies that are passed by filter. Stpband -- frequencies
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET Internatinal Jurnal f Electrical Engineering and Technlgy (IJEET, ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976 6545(Print ISSN 0976 6553(Online Vlume 4, Issue
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET Internatinal Jurnal f Electrical Engineering and Technlgy (IJEET, ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976 6545(Print ISSN 0976 6553(Online Vlume 4, Issue
King Saud University. College of Engineering. IE 341: Human Factors Engineering
 King Saud University Cllege f Engineering IE 341: Human Factrs Engineering Fall 2016 (1 st Sem. 1437-8H) Chapter 10. Human Cntrl f Systems Tracking (Part 1) Prepared by: Ahmed M. El-Sherbeeny, PhD 1 PART
King Saud University Cllege f Engineering IE 341: Human Factrs Engineering Fall 2016 (1 st Sem. 1437-8H) Chapter 10. Human Cntrl f Systems Tracking (Part 1) Prepared by: Ahmed M. El-Sherbeeny, PhD 1 PART
CM5530 GENERAL DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCU. Rev.1.0 0
 FEATURES Quasi-Resnant Primary Side Regulatin (QR-PSR) Cntrl with High Efficiency Multi-Mde PSR Cntrl Fast Dynamic Respnse Built-in Dynamic Base Drive Audi Nise Free Operatin ±4% CC and C Regulatin Lw
FEATURES Quasi-Resnant Primary Side Regulatin (QR-PSR) Cntrl with High Efficiency Multi-Mde PSR Cntrl Fast Dynamic Respnse Built-in Dynamic Base Drive Audi Nise Free Operatin ±4% CC and C Regulatin Lw
PROBABILITY OF DETECTION OF FLAWS IN A GAS TURBINE ENGINE. Gary L. Burkhardt and R.E. Beissner
 PROBABILITY OF DETECTION OF FLAWS IN A GAS TURBINE ENGINE COMPONENT USING ELECTRIC CURRENT PERTURBATION Gary L. Burkhardt and R.E. Beissner Suthwest Research Institute 6220 CUlebra Rad San Antni, Texas
PROBABILITY OF DETECTION OF FLAWS IN A GAS TURBINE ENGINE COMPONENT USING ELECTRIC CURRENT PERTURBATION Gary L. Burkhardt and R.E. Beissner Suthwest Research Institute 6220 CUlebra Rad San Antni, Texas
Theory of Electric Circuits II Lecture #1: Resonant Circuits
 Thery f Electric Circuits II Lecture #1: Resnant Circuits Fall 2009 Department f Electrnics and Cmmunicatins Engineering, Cair University Mahmud H. Ismail, 2009 Intrductin Outline 1 Intrductin Curse cntents,
Thery f Electric Circuits II Lecture #1: Resnant Circuits Fall 2009 Department f Electrnics and Cmmunicatins Engineering, Cair University Mahmud H. Ismail, 2009 Intrductin Outline 1 Intrductin Curse cntents,
Puget Sound Company Overview. Purpose of the Project. Solution Overview
 Puget Sund Cmpany Overview Puget Sund Energy is Washingtn State s largest and ldest energy utility, serving nearly 1 millin electric custmers and mre than 650,000 natural gas custmers, primarily within
Puget Sund Cmpany Overview Puget Sund Energy is Washingtn State s largest and ldest energy utility, serving nearly 1 millin electric custmers and mre than 650,000 natural gas custmers, primarily within
ME 4710 Motion and Control Frequency Domain Analysis
 ME 4710 Mtin and Cntl Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ME 4710 Mtin and Cntl Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
 Physics Department Electricity and Magnetism Labratry ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS 1. Aim. Learn t use measuring instruments: Digital multimeter. Analg scillscpe. Assembly f simple elementary circuit. Cllectin
Physics Department Electricity and Magnetism Labratry ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS 1. Aim. Learn t use measuring instruments: Digital multimeter. Analg scillscpe. Assembly f simple elementary circuit. Cllectin
Optimization of Monopole Four-Square Array Antenna Using a Decoupling Network and a Neural Network to Model Ground Plane Effects
 Optimizatin f Mnple Fur-Square Array Antenna Using a ecupling Netwrk and a Neural Netwrk t Mdel Grund Plane Effects Pedram azdanbakhsh, Klaus Slbach University uisburg-essen, Hchfrequenztechnik, Bismarckstr.8,
Optimizatin f Mnple Fur-Square Array Antenna Using a ecupling Netwrk and a Neural Netwrk t Mdel Grund Plane Effects Pedram azdanbakhsh, Klaus Slbach University uisburg-essen, Hchfrequenztechnik, Bismarckstr.8,
DXF2DAT 3.0 Professional Designed Computing Systems 848 W. Borton Road Essexville, Michigan 48732
 Prgram Infrmatin 1 DXF2DAT 3.0 Prfessinal Designed Cmputing Systems 848 W. Brtn Rad Essexville, Michigan 48732 Cntact: (989) 892-4376 website: http://www.famwrk.net General Infrmatin: inf@famwrk.net Technical
Prgram Infrmatin 1 DXF2DAT 3.0 Prfessinal Designed Cmputing Systems 848 W. Brtn Rad Essexville, Michigan 48732 Cntact: (989) 892-4376 website: http://www.famwrk.net General Infrmatin: inf@famwrk.net Technical
Human Psychoacoustics
 1 ESE250: Digital Audi Basics Week 6 February 19, 2013 Human Psychacustics Curse Map 2 Week 2 Received signal is sampled & quantized q = PCM[ r ] Week 4 Sampled signal first transfrmed int frequency dmain
1 ESE250: Digital Audi Basics Week 6 February 19, 2013 Human Psychacustics Curse Map 2 Week 2 Received signal is sampled & quantized q = PCM[ r ] Week 4 Sampled signal first transfrmed int frequency dmain
Performance of Switched-Capacitor Circuits Due to Finite Gain Amplifiers
 Perfrmance f Switched-apacitr ircuits Due t Finite Gain Amplifiers urse: EE35 Prepared by Rbert Wang 9743359 Prepared fr Prfessr K. Phang Due Date: Nv 5 th, 00 able f ntents PERFORMANE OF SWIED-APAIOR
Perfrmance f Switched-apacitr ircuits Due t Finite Gain Amplifiers urse: EE35 Prepared by Rbert Wang 9743359 Prepared fr Prfessr K. Phang Due Date: Nv 5 th, 00 able f ntents PERFORMANE OF SWIED-APAIOR
Experiment 2 Complex Impedance, Steady State Analysis, and Filters
 Experiment 2 Cmplex Impedance, Steady State Analysis, and Filters Purpse: The bjective f this experiment is t learn abut steady state analysis and basic filters. Backgrund: Befre ding this experiment,
Experiment 2 Cmplex Impedance, Steady State Analysis, and Filters Purpse: The bjective f this experiment is t learn abut steady state analysis and basic filters. Backgrund: Befre ding this experiment,
Security Exercise 12
 Security Exercise 12 Asynchrnus Serial Digital Baseband Transmissin Discussin: In this chapter, yu learned that bits are transmitted ver a cpper wire as a series f vltage pulses (a prcess referred t as
Security Exercise 12 Asynchrnus Serial Digital Baseband Transmissin Discussin: In this chapter, yu learned that bits are transmitted ver a cpper wire as a series f vltage pulses (a prcess referred t as
Waves Review Outline
 5.1 Mechanical Waves Waves Review Outline 5.1.1A-B Oscillating Systems T = 1 f perid the time that it takes fr ne scillatin t ccur frequency the number f scillatins that take place in ne secnd 5.1.2A-B
5.1 Mechanical Waves Waves Review Outline 5.1.1A-B Oscillating Systems T = 1 f perid the time that it takes fr ne scillatin t ccur frequency the number f scillatins that take place in ne secnd 5.1.2A-B
High Efficiency Frequency Tunable Inverse Class-E Amplifier in VHF Band
 High Efficiency Frequency Tunable Inverse Class-E Amplifier in VHF Band Kumh Natinal Institute f Technlgy, 1 Yangh-Dng, Gumi, Gyungbuk, 730-701, Krea yungk@kumh.ac.kr Abstract This paper prpses the use
High Efficiency Frequency Tunable Inverse Class-E Amplifier in VHF Band Kumh Natinal Institute f Technlgy, 1 Yangh-Dng, Gumi, Gyungbuk, 730-701, Krea yungk@kumh.ac.kr Abstract This paper prpses the use
MEASURING INDUCTANCES ON A DC MACHINE
 ESURING INDUCTNCES ON DC CHINE Ning Chuang, Timthy Gale, Richard Langman Schl f Engineering, University f Tasmania GPO Bx 252-65, Hbart, Tasmania 700 ustralia E-mail: T.Gale@utas.edu.au BSTRCT This paper
ESURING INDUCTNCES ON DC CHINE Ning Chuang, Timthy Gale, Richard Langman Schl f Engineering, University f Tasmania GPO Bx 252-65, Hbart, Tasmania 700 ustralia E-mail: T.Gale@utas.edu.au BSTRCT This paper
Enhanced Balance Bandwidth Quadrature Coupler Using Parallel Coupled Microstrip Lines
 VOL.6, NO., 211 228 Enhanced Balance Bandwidth Quadrature Cupler Using Parallel Cupled Micrstrip Lines Vamsi Krishna Velidi, Girja Shankar and Subrata Sanyal Department f Electrnics and Electrical Cmmunicatin
VOL.6, NO., 211 228 Enhanced Balance Bandwidth Quadrature Cupler Using Parallel Cupled Micrstrip Lines Vamsi Krishna Velidi, Girja Shankar and Subrata Sanyal Department f Electrnics and Electrical Cmmunicatin
Introduction to Optical Detectors (Nofziger)
 1 Intrductin t Optical Detectrs (Nfziger) Optical detectrs are at the heart f mst mdern-day ptical systems. They have largely replaced the human eye r tgraic film as the detectin medium. They may be categrized
1 Intrductin t Optical Detectrs (Nfziger) Optical detectrs are at the heart f mst mdern-day ptical systems. They have largely replaced the human eye r tgraic film as the detectin medium. They may be categrized
PhotoVu Digital Picture Frame Service & Repair Guide
 PhtVu Digital Picture Frame Service & Repair Guide PhtVu, LLC 2450 Central Ave, #G1 Bulder, CO 80301 USA www.phtvu.cm/supprt Versin: 1.0 Table f Cntents Getting Started... 3 Determine Yur Generatin f PhtVu
PhtVu Digital Picture Frame Service & Repair Guide PhtVu, LLC 2450 Central Ave, #G1 Bulder, CO 80301 USA www.phtvu.cm/supprt Versin: 1.0 Table f Cntents Getting Started... 3 Determine Yur Generatin f PhtVu
Tee (Not a Coupler) Open Circuit Line. Z Z Z jz d
 ECSE-2 Spring 22 Analysis Using Matlab Cable System R2 T2 Tee (Nt a Cupler) T TV Set Input R V 75 75 T3 Open Circuit Line The basic principle f this signal blcker is relatively simple. The CATV cable (T2
ECSE-2 Spring 22 Analysis Using Matlab Cable System R2 T2 Tee (Nt a Cupler) T TV Set Input R V 75 75 T3 Open Circuit Line The basic principle f this signal blcker is relatively simple. The CATV cable (T2
National Curriculum Programme of Study:
 Natinal Curriculum Prgramme f Study: Cunt in steps f 2, 3, and 5 frm 0, and in tens frm any number, frward and backward. Recall and use multiplicatin and divisin facts fr the 2, 5 and 10 multiplicatin
Natinal Curriculum Prgramme f Study: Cunt in steps f 2, 3, and 5 frm 0, and in tens frm any number, frward and backward. Recall and use multiplicatin and divisin facts fr the 2, 5 and 10 multiplicatin
Modulation: Introduction:
 Mdulatin: Intrductin: Inrmatin signals are transprted between transmitter and receiver thrugh a transmissin medium. Original inrmatin must be transrmed int a suitable rm r transmissin. Mdulatin is a prcess
Mdulatin: Intrductin: Inrmatin signals are transprted between transmitter and receiver thrugh a transmissin medium. Original inrmatin must be transrmed int a suitable rm r transmissin. Mdulatin is a prcess
Lab2 Digital Weighing Scale (Sep 18)
 GOAL Lab2 Digital Weighing Scale (Sep 18) The gal f Lab 2 is t demnstrate a digital weighing scale. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f mass has many applicatins. A digital weighing scale typically
GOAL Lab2 Digital Weighing Scale (Sep 18) The gal f Lab 2 is t demnstrate a digital weighing scale. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f mass has many applicatins. A digital weighing scale typically
The Modification of Simple Images by Fourier Transform Manipulation
 Rchester Institute f Technlgy RIT Schlar Wrks Theses Thesis/Dissertatin Cllectins 6-1-1979 The Mdificatin f Simple Images by Furier Transfrm Manipulatin Nel Chavez Fllw this and additinal wrks at: http://schlarwrks.rit.edu/theses
Rchester Institute f Technlgy RIT Schlar Wrks Theses Thesis/Dissertatin Cllectins 6-1-1979 The Mdificatin f Simple Images by Furier Transfrm Manipulatin Nel Chavez Fllw this and additinal wrks at: http://schlarwrks.rit.edu/theses
Implementation Of 12V To 330V Boost Converter With Closed Loop Control Using Push Pull Topology
 Implementatin Of 12V T 330V Bst Cnverter With Clsed Lp Cntrl Using Push Pull Tplgy Anande J.T 1, Odinya J.O.. 2, Yilwatda M.M. 3 1,2,3 Department f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering, Federal University
Implementatin Of 12V T 330V Bst Cnverter With Clsed Lp Cntrl Using Push Pull Tplgy Anande J.T 1, Odinya J.O.. 2, Yilwatda M.M. 3 1,2,3 Department f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering, Federal University
The Mathematics of the Rubik s Cube
 In this lessn, students will explre the pssible number ways the pieces f a Rubik's Cube can be arranged, and still fit the criteria fr a Rubik's Cube. Clrs are riented in a set way, s sme pieces (such
In this lessn, students will explre the pssible number ways the pieces f a Rubik's Cube can be arranged, and still fit the criteria fr a Rubik's Cube. Clrs are riented in a set way, s sme pieces (such
Application of Percents
 Grade 7 Mathematics, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1 Applicatin f Percents Overview Number f instructinal days: 15 (1 day = 45 60 minutes) Cntent t be learned Cnvert between different frms f ratinal numbers (psitive
Grade 7 Mathematics, Quarter 3, Unit 3.1 Applicatin f Percents Overview Number f instructinal days: 15 (1 day = 45 60 minutes) Cntent t be learned Cnvert between different frms f ratinal numbers (psitive
Input-Series Two-Stage DC-DC Converter with Inductor Coupling
 Input-Series w-stage DC-DC Cnverter with Inductr Cupling ing Qian Wei Sng Brad Lehman Nrtheastern University Dept. Electrical & Cmputer Engineering Bstn MA 0 USA Abstract: his paper presents an input-series
Input-Series w-stage DC-DC Cnverter with Inductr Cupling ing Qian Wei Sng Brad Lehman Nrtheastern University Dept. Electrical & Cmputer Engineering Bstn MA 0 USA Abstract: his paper presents an input-series
Valve train natural frequency measurement and analysis
 Rchester Institute f Technlgy RIT Schlar Wrks Theses Thesis/Dissertatin Cllectins 511997 Valve train natural frequency measurement and analysis Cynthia Greene Fllw this and additinal wrks at: http://schlarwrks.rit.edu/theses
Rchester Institute f Technlgy RIT Schlar Wrks Theses Thesis/Dissertatin Cllectins 511997 Valve train natural frequency measurement and analysis Cynthia Greene Fllw this and additinal wrks at: http://schlarwrks.rit.edu/theses
Transfer-Function Synthesis with Computer Amplifiers and Passive Networks
 955 WESTERN JOINT COMPUTER CONFERENCE 7 Transfer-Functin Synthesis with Cmputer Amplifiers Passive Netwrks M. v. MATHEWSt AND w. w. SEIFERTt Summary-The study f dynamic systems n an analg cmputer ften
955 WESTERN JOINT COMPUTER CONFERENCE 7 Transfer-Functin Synthesis with Cmputer Amplifiers Passive Netwrks M. v. MATHEWSt AND w. w. SEIFERTt Summary-The study f dynamic systems n an analg cmputer ften
Network Working Group. Category: Informational Cisco Systems A. Shaikh AT&T Labs (Research) April 2005
 Netwrk Wrking Grup Request fr Cmments: 4062 Categry: Infrmatinal V. Manral SiNett Crp. R. White Cisc Systems A. Shaikh AT&T Labs (Research) April 2005 Status f This Mem OSPF Benchmarking Terminlgy and
Netwrk Wrking Grup Request fr Cmments: 4062 Categry: Infrmatinal V. Manral SiNett Crp. R. White Cisc Systems A. Shaikh AT&T Labs (Research) April 2005 Status f This Mem OSPF Benchmarking Terminlgy and
Excel Step by Step Instructions Creating Lists and Charts. Microsoft
 Infrmatin Yu Can Enter in a Wrksheet: Labels: Any type f text r infrmatin nt used in any calculatins. Labels are used fr wrksheet headings and make wrksheets easy t read and understand. Labels can als
Infrmatin Yu Can Enter in a Wrksheet: Labels: Any type f text r infrmatin nt used in any calculatins. Labels are used fr wrksheet headings and make wrksheets easy t read and understand. Labels can als
Flux Bender Equalizer
 Lightning By Audi Flux Bender Equalizer Users Guide 2014 Revised 2015 Cngratulatins n an excellent purchase! This guide was put tgether t help yu get the mst ut f yur investment. Please read this thrughly
Lightning By Audi Flux Bender Equalizer Users Guide 2014 Revised 2015 Cngratulatins n an excellent purchase! This guide was put tgether t help yu get the mst ut f yur investment. Please read this thrughly
EE380: Exp. 2. Measurement of Op-Amp Parameters and Design/ Verification of an Integrator
 EE380: Exp. 2 Measurement Op-Amp Parameters and Design/ Veriicatin an Integratr Intrductin: An Opamp is a basic building blck a wide range analg circuits. T carry ut design circuits cnsisting ne r mre
EE380: Exp. 2 Measurement Op-Amp Parameters and Design/ Veriicatin an Integratr Intrductin: An Opamp is a basic building blck a wide range analg circuits. T carry ut design circuits cnsisting ne r mre
DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF AN AIRCRAFT CARRIER ^} DECK MOTION PREDICTION SYSTEM. Paul Kaplan. and
 ÜCEANICS- INC. DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF AN AIRCRAFT CARRIER ^} DECK MOTION PREDICTION SYSTEM by Paul Kaplan 9 and Thedre P. Sargent Oceanics, Inc. Plainview, New Yrk Prepared fr: Office f Naval Research
ÜCEANICS- INC. DEVELOPMENT AND TESTING OF AN AIRCRAFT CARRIER ^} DECK MOTION PREDICTION SYSTEM by Paul Kaplan 9 and Thedre P. Sargent Oceanics, Inc. Plainview, New Yrk Prepared fr: Office f Naval Research
3G Coverage Obligation Verification Methodology
 3G Cverage Obligatin Verificatin Methdlgy Statement Publicatin date: 9 May 2012 Main Heading Cntents Sectin Page 1 Intrductin 1 2 Summary f apprach 2 3 Key parameters t be used in the SINR calculatin
3G Cverage Obligatin Verificatin Methdlgy Statement Publicatin date: 9 May 2012 Main Heading Cntents Sectin Page 1 Intrductin 1 2 Summary f apprach 2 3 Key parameters t be used in the SINR calculatin
TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE
 TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE Cadence Virtus Schematic editing prvides a design envirnment cmprising tls t create schematics, symbls and run simulatins. This tutrial will
TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE Cadence Virtus Schematic editing prvides a design envirnment cmprising tls t create schematics, symbls and run simulatins. This tutrial will
LINE POWER SUPPLIES Low-Loss Supplies for Line Powered EnOcean Modules
 Lw-Lss Supplies fr Line Pwered EnOcean Mdules A line pwer supply has t ffer the required energy t supply the actuatr electrnic and t supply the EnOcean TCM/RCM radi cntrl mdule. This paper cntains sme
Lw-Lss Supplies fr Line Pwered EnOcean Mdules A line pwer supply has t ffer the required energy t supply the actuatr electrnic and t supply the EnOcean TCM/RCM radi cntrl mdule. This paper cntains sme
Design and Implementation of a Kalman Filter-Based Time-Varying Harmonics Analyzer
 Design and Implementatin f a Kalman Filter-Based Time-Varying Harmnics Analyzer Abstract: Nwadays with increasing use f numerus nnlinear lads, vltage and current harmnics in pwer systems are ne f the mst
Design and Implementatin f a Kalman Filter-Based Time-Varying Harmnics Analyzer Abstract: Nwadays with increasing use f numerus nnlinear lads, vltage and current harmnics in pwer systems are ne f the mst
Materials: Metals, timber, plastics, composites, smart and nanomaterials Candidates should:
 AQA Resistant Materials - Unit 1 Specificatin 2014-4560 Materials: Metals, timber, plastics, cmpsites, smart and nanmaterials Be aware f the surce f a range f materials. Understand they are prcessed fr
AQA Resistant Materials - Unit 1 Specificatin 2014-4560 Materials: Metals, timber, plastics, cmpsites, smart and nanmaterials Be aware f the surce f a range f materials. Understand they are prcessed fr
Review of Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain
 Internatinal Jurnal f Cmputer Science and Infrmatin Technlgy Research ISSN 2348-120X (nline) Vl. 2, Issue 4, pp: (194-200), Mnth: Octber - December 2014, Available at: www.researchpublish.cm Review f Image
Internatinal Jurnal f Cmputer Science and Infrmatin Technlgy Research ISSN 2348-120X (nline) Vl. 2, Issue 4, pp: (194-200), Mnth: Octber - December 2014, Available at: www.researchpublish.cm Review f Image
Single-arm 3-wave interferometer for measuring dispersion in short lengths of fiber
 Single-arm 3-wave interfermeter fr measuring dispersin in shrt lengths f fiber By Michael Anthny Galle St# 991 454 109 A thesis submitted in cnfrmity with the requirements fr the degree f Master f Applied
Single-arm 3-wave interfermeter fr measuring dispersin in shrt lengths f fiber By Michael Anthny Galle St# 991 454 109 A thesis submitted in cnfrmity with the requirements fr the degree f Master f Applied
ENGR-2300 ELCTRONIC INSTRUMENTATION Experiment 8. Experiment 8 Diodes
 Experiment 8 Dides Purpse: The bjective f this experiment is t becme familiar with the prperties and uses f dides. We will first cnsider the i-v characteristic curve f a standard dide that we can use in
Experiment 8 Dides Purpse: The bjective f this experiment is t becme familiar with the prperties and uses f dides. We will first cnsider the i-v characteristic curve f a standard dide that we can use in
Process Gain and Loop Gain
 Prcess Gain and Lp Gain By nw, it is evident that ne can calculate the sensitivity fr each cmpnent in a cntrlled prcess. Smetimes, this sensitivity is referred t as a gain. The cnfusin is understandable
Prcess Gain and Lp Gain By nw, it is evident that ne can calculate the sensitivity fr each cmpnent in a cntrlled prcess. Smetimes, this sensitivity is referred t as a gain. The cnfusin is understandable
