Improving GPU Performance via Large Warps and Two-Level Warp Scheduling
|
|
|
- Ross Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Improving GPU Performance via Large Warps and Two-Level Warp Scheduling Veynu Narasiman The University of Texas at Austin Michael Shebanow NVIDIA Chang Joo Lee Intel Rustam Miftakhutdinov The University of Texas at Austin Onur Mutlu Carnegie Mellon University Yale N. Patt The University of Texas at Austin MICRO-44 December 6 th, 2011 Porto Alegre, Brazil
2 Rise of GPU Computing GPUs have become a popular platform for general purpose applications New Programming Models CUDA ATI Stream Technology OpenCL Order of magnitude speedup over single-threaded CPU
3 How GPUs Exploit Parallelism Multiple GPU cores (i.e., Streaming Multiprocessors) Focus on a single GPU core Exploit parallelism in 2 major ways: Threads grouped into warps Single PC per warp Warps executed in SIMD fashion Multiple warps concurrently executed Round-robin scheduling Helps hide long latencies
4 The Problem Despite these techniques, computational resources can still be underutilized Two reasons for this: Branch divergence Long latency operations
5 Branch Divergence A 1111 Current PC: Current Active Mask: A B Taken Not Taken B 1001 C 0110 D 0110 C D 1111 D D 1111 Reconverge PC Active Mask Execute PC
6 Long Latency Operations Core Memory System All Warps Compute All Warps Compute Req Warp 0 Req Warp 1 Req Warp 15 Round Robin Scheduling, 16 total warps time
7 Computational Resource Utilization 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% to to 23 8 to 15 1 to 7 0 Good Bad 32 warps, 32 threads per warp, SIMD width = 32, round-robin scheduling
8 Large Warp Microarchitecture (LWM) Alleviates branch divergence Fewer, but larger warps Warp size much greater than SIMD width Total thread count and SIMD-width stay the same Dynamically breaks down large warp into sub-warps Can be executed on existing SIMD pipeline Rearrange active mask as 2D structure Number of columns = SIMD width Search each column for an active thread to create new sub-warp
9 Large Warp Microarchitecture Example Decode Stage Sub-warp 10 2 mask Sub-warp 10 mask Sub-warp 0 mask
10 More Large Warp Microarchitecture Divergence stack still used Handled at the large warp level How large should we make the warps? More threads per warp more potential for sub-warp creation Too large a warp size can degrade performance Re-fetch policy for conditional branches Must wait till last sub-warp finishes Optimization for unconditional branch instructions Don t create multiple sub-warps Sub-warping always completes in a single cycle
11 Two Level Round Robin Scheduling Split warps into equal sized fetch groups Create initial priority among the fetch groups Round-robin scheduling among warps in same fetch group When all warps in the highest priority fetch group are stalled Rotate fetch group priorities Highest priority fetch group becomes least Warps arrive at a stalling point at slightly different points in time Better overlap of computation and memory latency
12 Round Robin vs Two Level Round Robin Core Memory System All Warps Compute All Warps Compute Req Warp 0 Req Warp 1 Req Warp 15 Round Robin Scheduling, 16 total warps time Core Group 0 Compute Req Warp 0 Req Warp 1 Group 1 Compute Group 0 Compute Group 1 Compute Saved Cycles Memory System Req Warp 7 Req Warp 8 Req Warp 9 Req Warp 15 time Two Level Round Robin Scheduling, 2 fetch groups, 8 warps each
13 More on Two Level Scheduling What should the fetch group size be? Enough warps to keep pipeline busy in the absence of long latency stalls Too small Uneven progression of warps in the same fetch group Destroys data locality among warps Too large Reduces benefits of two-level scheduling More warps stall at the same time Not just for hiding memory latency Complex instructions (e.g., sine, cosine, sqrt, etc.) Two-level scheduling allows warps to arrive at such instructions at slightly different points in time
14 Combining LWM and Two Level Scheduling 4 large warps, 256 threads each Fetch group size = 1 large warp Problematic for applications with few long latency stalls No stalls no fetch group priority changes Single large warp starved Branch re-fetch policy for large warps bubbles in pipeline Timeout invoked fetch group priority change 32K instruction timeout period Alleviates starvation
15 Methodology Simulate single GPU core with 1024 thread contexts divided into 32 warps each with 32 threads Scalar Front End SIMD Back End Register File and On Chip Memories Memory System 1-wide fetch, decode 4KB single ported I-Cache Round-robin scheduling In order, 5 stages, 32 parallel SIMD lanes 64KB Register File 128KB, 4-way, D-Cache with 128B line size 128KB, 32-banked private memory Open row, first-come first-serve scheduling 8 banks, 4KB row buffer per bank 100-cycle row hit latency, 300-cycle row conflict latency 32 GB/s memory bandwidth
16 blackjack sort viterbi kmeans decrypt blackscholes needleman hotspot matrix_mult reduction histogram bfs gmean IPC Overall IPC Results Baseline TBC LWM 2Lev LWM+2Lev LWM+2Lev improves performance by 19.1% over baseline and by 11.5% over TBC
17 IPC IPC IPC and Computational Resource Utilization IPC for blackjack IPC for histogram baseline LWM 2LEV LWM+2LEV 5 0 baseline LWM 2LEV LWM+2LEV Computational Resource Utilization for blackjack Computational Resource Utilization for histogram 120% 120% 100% % 32 80% 24 to 31 80% 24 to 31 60% 16 to 23 60% 16 to 23 40% 8 to 15 40% 8 to 15 20% 1 to 7 20% 1 to 7 0% baseline LWM 2LEV LWM+2LEV 0 0% baseline LWM 2LEV LWM+2LEV 0
18 Conclusion For maximum performance, the computational resources on GPUs must be effectively utilized Branch divergence and long latency operations cause them to be underutilized or unused We proposed two mechanism to alleviate this Large Warp Microarchitecture for branch divergence Two-level scheduling for long latency operations Improves performance by 19.1% over traditional GPU cores Increases scope of applications that can run efficiently on a GPU Questions
CUDA Threads. Terminology. How it works. Terminology. Streaming Multiprocessor (SM) A SM processes block of threads
 Terminology CUDA Threads Bedrich Benes, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Streaming Multiprocessor (SM) A SM processes block of threads Streaming Processors (SP) also called CUDA
Terminology CUDA Threads Bedrich Benes, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Streaming Multiprocessor (SM) A SM processes block of threads Streaming Processors (SP) also called CUDA
Warp-Aware Trace Scheduling for GPUS. James Jablin (Brown) Thomas Jablin (UIUC) Onur Mutlu (CMU) Maurice Herlihy (Brown)
 Warp-Aware Trace Scheduling for GPUS James Jablin (Brown) Thomas Jablin (UIUC) Onur Mutlu (CMU) Maurice Herlihy (Brown) Historical Trends in GFLOPS: CPUs vs. GPUs Theoretical GFLOP/s 3250 3000 2750 2500
Warp-Aware Trace Scheduling for GPUS James Jablin (Brown) Thomas Jablin (UIUC) Onur Mutlu (CMU) Maurice Herlihy (Brown) Historical Trends in GFLOPS: CPUs vs. GPUs Theoretical GFLOP/s 3250 3000 2750 2500
Computer Architecture ( L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS
 Computer Architecture (263-2210-00L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS Instructor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Mohammad Sadr, Lois Orosa, Juan Gomez Luna Assigned:
Computer Architecture (263-2210-00L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS Instructor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Mohammad Sadr, Lois Orosa, Juan Gomez Luna Assigned:
Supporting x86-64 Address Translation for 100s of GPU Lanes. Jason Power, Mark D. Hill, David A. Wood
 Supporting x86-64 Address Translation for 100s of GPU s Jason Power, Mark D. Hill, David A. Wood Summary Challenges: CPU&GPUs physically integrated, but logically separate; This reduces theoretical bandwidth,
Supporting x86-64 Address Translation for 100s of GPU s Jason Power, Mark D. Hill, David A. Wood Summary Challenges: CPU&GPUs physically integrated, but logically separate; This reduces theoretical bandwidth,
DASH: Deadline-Aware High-Performance Memory Scheduler for Heterogeneous Systems with Hardware Accelerators
 DASH: Deadline-Aware High-Performance Memory Scheduler for Heterogeneous Systems with Hardware Accelerators Hiroyuki Usui, Lavanya Subramanian Kevin Chang, Onur Mutlu DASH source code is available at GitHub
DASH: Deadline-Aware High-Performance Memory Scheduler for Heterogeneous Systems with Hardware Accelerators Hiroyuki Usui, Lavanya Subramanian Kevin Chang, Onur Mutlu DASH source code is available at GitHub
Dynamic Warp Resizing in High-Performance SIMT
 Dynamic Warp Resizing in High-Performance SIMT Ahmad Lashgar 1 a.lashgar@ece.ut.ac.ir Amirali Baniasadi 2 amirali@ece.uvic.ca 1 3 Ahmad Khonsari ak@ipm.ir 1 School of ECE University of Tehran 2 ECE Department
Dynamic Warp Resizing in High-Performance SIMT Ahmad Lashgar 1 a.lashgar@ece.ut.ac.ir Amirali Baniasadi 2 amirali@ece.uvic.ca 1 3 Ahmad Khonsari ak@ipm.ir 1 School of ECE University of Tehran 2 ECE Department
Track and Vertex Reconstruction on GPUs for the Mu3e Experiment
 Track and Vertex Reconstruction on GPUs for the Mu3e Experiment Dorothea vom Bruch for the Mu3e Collaboration GPU Computing in High Energy Physics, Pisa September 11th, 2014 Physikalisches Institut Heidelberg
Track and Vertex Reconstruction on GPUs for the Mu3e Experiment Dorothea vom Bruch for the Mu3e Collaboration GPU Computing in High Energy Physics, Pisa September 11th, 2014 Physikalisches Institut Heidelberg
Mosaic: A GPU Memory Manager with Application-Transparent Support for Multiple Page Sizes
 Mosaic: A GPU Memory Manager with Application-Transparent Support for Multiple Page Sizes Rachata Ausavarungnirun Joshua Landgraf Vance Miller Saugata Ghose Jayneel Gandhi Christopher J. Rossbach Onur
Mosaic: A GPU Memory Manager with Application-Transparent Support for Multiple Page Sizes Rachata Ausavarungnirun Joshua Landgraf Vance Miller Saugata Ghose Jayneel Gandhi Christopher J. Rossbach Onur
Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors
 Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 16 - Superscalar Processors 1 / 78 Table of Contents I 1 Overview
Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 16 - Superscalar Processors 1 / 78 Table of Contents I 1 Overview
7/11/2012. Single Cycle (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. Multi-Cycle Implementation. Single Cycle with Jump. Pipelining Analogy
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
Synthetic Aperture Beamformation using the GPU
 Paper presented at the IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Orlando, Florida, 211: Synthetic Aperture Beamformation using the GPU Jens Munk Hansen, Dana Schaa and Jørgen Arendt Jensen Center for Fast
Paper presented at the IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Orlando, Florida, 211: Synthetic Aperture Beamformation using the GPU Jens Munk Hansen, Dana Schaa and Jørgen Arendt Jensen Center for Fast
Chapter 4. Pipelining Analogy. The Processor. Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution. Parallelism improves performance. Four loads: Non-stop:
 Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
GPU-accelerated track reconstruction in the ALICE High Level Trigger
 GPU-accelerated track reconstruction in the ALICE High Level Trigger David Rohr for the ALICE Collaboration Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies CHEP 2016, San Francisco ALICE at the LHC The Large
GPU-accelerated track reconstruction in the ALICE High Level Trigger David Rohr for the ALICE Collaboration Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies CHEP 2016, San Francisco ALICE at the LHC The Large
Overview. 1 Trends in Microprocessor Architecture. Computer architecture. Computer architecture
 Overview 1 Trends in Microprocessor Architecture R05 Robert Mullins Computer architecture Scaling performance and CMOS Where have performance gains come from? Modern superscalar processors The limits of
Overview 1 Trends in Microprocessor Architecture R05 Robert Mullins Computer architecture Scaling performance and CMOS Where have performance gains come from? Modern superscalar processors The limits of
Performance Evaluation of Recently Proposed Cache Replacement Policies
 University of Jordan Computer Engineering Department Performance Evaluation of Recently Proposed Cache Replacement Policies CPE 731: Advanced Computer Architecture Dr. Gheith Abandah Asma Abdelkarim January
University of Jordan Computer Engineering Department Performance Evaluation of Recently Proposed Cache Replacement Policies CPE 731: Advanced Computer Architecture Dr. Gheith Abandah Asma Abdelkarim January
Multi-core Platforms for
 20 JUNE 2011 Multi-core Platforms for Immersive-Audio Applications Course: Advanced Computer Architectures Teacher: Prof. Cristina Silvano Student: Silvio La Blasca 771338 Introduction on Immersive-Audio
20 JUNE 2011 Multi-core Platforms for Immersive-Audio Applications Course: Advanced Computer Architectures Teacher: Prof. Cristina Silvano Student: Silvio La Blasca 771338 Introduction on Immersive-Audio
PARALLEL ALGORITHMS FOR HISTOGRAM-BASED IMAGE REGISTRATION. Benjamin Guthier, Stephan Kopf, Matthias Wichtlhuber, Wolfgang Effelsberg
 This is a preliminary version of an article published by Benjamin Guthier, Stephan Kopf, Matthias Wichtlhuber, and Wolfgang Effelsberg. Parallel algorithms for histogram-based image registration. Proc.
This is a preliminary version of an article published by Benjamin Guthier, Stephan Kopf, Matthias Wichtlhuber, and Wolfgang Effelsberg. Parallel algorithms for histogram-based image registration. Proc.
Processors Processing Processors. The meta-lecture
 Simulators 5SIA0 Processors Processing Processors The meta-lecture Why Simulators? Your Friend Harm Why Simulators? Harm Loves Tractors Harm Why Simulators? The outside world Unfortunately for Harm you
Simulators 5SIA0 Processors Processing Processors The meta-lecture Why Simulators? Your Friend Harm Why Simulators? Harm Loves Tractors Harm Why Simulators? The outside world Unfortunately for Harm you
Out-of-Order Execution. Register Renaming. Nima Honarmand
 Out-of-Order Execution & Register Renaming Nima Honarmand Out-of-Order (OOO) Execution (1) Essence of OOO execution is Dynamic Scheduling Dynamic scheduling: processor hardware determines instruction execution
Out-of-Order Execution & Register Renaming Nima Honarmand Out-of-Order (OOO) Execution (1) Essence of OOO execution is Dynamic Scheduling Dynamic scheduling: processor hardware determines instruction execution
EECS 470 Lecture 5. Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont
 Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides.
Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides.
SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation
 SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation Mark Wolff Linda Wills School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology {wolff,linda.wills}@ece.gatech.edu
SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation Mark Wolff Linda Wills School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology {wolff,linda.wills}@ece.gatech.edu
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel
 Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
Computational Efficiency of the GF and the RMF Transforms for Quaternary Logic Functions on CPUs and GPUs
 5 th International Conference on Logic and Application LAP 2016 Dubrovnik, Croatia, September 19-23, 2016 Computational Efficiency of the GF and the RMF Transforms for Quaternary Logic Functions on CPUs
5 th International Conference on Logic and Application LAP 2016 Dubrovnik, Croatia, September 19-23, 2016 Computational Efficiency of the GF and the RMF Transforms for Quaternary Logic Functions on CPUs
Final Report: DBmbench
 18-741 Final Report: DBmbench Yan Ke (yke@cs.cmu.edu) Justin Weisz (jweisz@cs.cmu.edu) Dec. 8, 2006 1 Introduction Conventional database benchmarks, such as the TPC-C and TPC-H, are extremely computationally
18-741 Final Report: DBmbench Yan Ke (yke@cs.cmu.edu) Justin Weisz (jweisz@cs.cmu.edu) Dec. 8, 2006 1 Introduction Conventional database benchmarks, such as the TPC-C and TPC-H, are extremely computationally
Freeway: Maximizing MLP for Slice-Out-of-Order Execution
 Freeway: Maximizing MLP for Slice-Out-of-Order Execution Rakesh Kumar Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) rakesh.kumar@ntnu.no Mehdi Alipour, David Black-Schaffer Uppsala University {mehdi.alipour,
Freeway: Maximizing MLP for Slice-Out-of-Order Execution Rakesh Kumar Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) rakesh.kumar@ntnu.no Mehdi Alipour, David Black-Schaffer Uppsala University {mehdi.alipour,
SOFTWARE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE
 SOFTWARE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE IEEE 802.11A/P PHYSICAL LAYER SDR`12 WInnComm Europe 27 29 June, 2012 Brussels, Belgium T. Cupaiuolo, D. Lo Iacono, M. Siti and M. Odoni Advanced System Technologies STMicroelectronics,
SOFTWARE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE IEEE 802.11A/P PHYSICAL LAYER SDR`12 WInnComm Europe 27 29 June, 2012 Brussels, Belgium T. Cupaiuolo, D. Lo Iacono, M. Siti and M. Odoni Advanced System Technologies STMicroelectronics,
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
CUDA-Accelerated Satellite Communication Demodulation
 CUDA-Accelerated Satellite Communication Demodulation Renliang Zhao, Ying Liu, Liheng Jian, Zhongya Wang School of Computer and Control University of Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline Motivation Related
CUDA-Accelerated Satellite Communication Demodulation Renliang Zhao, Ying Liu, Liheng Jian, Zhongya Wang School of Computer and Control University of Chinese Academy of Sciences Outline Motivation Related
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining
 Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
EECS 470. Tomasulo s Algorithm. Lecture 4 Winter 2018
 omasulo s Algorithm Winter 2018 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Martin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, yson, Vijaykumar, and Wenisch of Carnegie Mellon University,
omasulo s Algorithm Winter 2018 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Martin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, yson, Vijaykumar, and Wenisch of Carnegie Mellon University,
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
Suggested Readings! Lecture 12" Introduction to Pipelining! Example: We have to build x cars...! ...Each car takes 6 steps to build...! ! Readings!
 1! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 12"
1! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 12"
Recent Advances in Simulation Techniques and Tools
 Recent Advances in Simulation Techniques and Tools Yuyang Li, li.yuyang(at)wustl.edu (A paper written under the guidance of Prof. Raj Jain) Download Abstract: Simulation refers to using specified kind
Recent Advances in Simulation Techniques and Tools Yuyang Li, li.yuyang(at)wustl.edu (A paper written under the guidance of Prof. Raj Jain) Download Abstract: Simulation refers to using specified kind
Liu Yang, Bong-Joo Jang, Sanghun Lim, Ki-Chang Kwon, Suk-Hwan Lee, Ki-Ryong Kwon 1. INTRODUCTION
 Liu Yang, Bong-Joo Jang, Sanghun Lim, Ki-Chang Kwon, Suk-Hwan Lee, Ki-Ryong Kwon 1. INTRODUCTION 2. RELATED WORKS 3. PROPOSED WEATHER RADAR IMAGING BASED ON CUDA 3.1 Weather radar image format and generation
Liu Yang, Bong-Joo Jang, Sanghun Lim, Ki-Chang Kwon, Suk-Hwan Lee, Ki-Ryong Kwon 1. INTRODUCTION 2. RELATED WORKS 3. PROPOSED WEATHER RADAR IMAGING BASED ON CUDA 3.1 Weather radar image format and generation
Computer Hardware. Pipeline
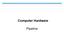 Computer Hardware Pipeline Conventional Datapath 2.4 ns is required to perform a single operation (i.e. 416.7 MHz). Register file MUX B 0.6 ns Clock 0.6 ns 0.2 ns Function unit 0.8 ns MUX D 0.2 ns c. Production
Computer Hardware Pipeline Conventional Datapath 2.4 ns is required to perform a single operation (i.e. 416.7 MHz). Register file MUX B 0.6 ns Clock 0.6 ns 0.2 ns Function unit 0.8 ns MUX D 0.2 ns c. Production
Use Nvidia Performance Primitives (NPP) in Deep Learning Training. Yang Song
 Use Nvidia Performance Primitives (NPP) in Deep Learning Training Yang Song Outline Introduction Function Categories Performance Results Deep Learning Specific Further Information What is NPP? Image+Signal
Use Nvidia Performance Primitives (NPP) in Deep Learning Training Yang Song Outline Introduction Function Categories Performance Results Deep Learning Specific Further Information What is NPP? Image+Signal
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
EECS 470. Lecture 9. MIPS R10000 Case Study. Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont
 MIPS R10000 Case Study Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Multiprocessor SGI Origin Using MIPS R10K Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for
MIPS R10000 Case Study Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Multiprocessor SGI Origin Using MIPS R10K Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for
7/19/2012. IF for Load (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. EX for Load (Review) ID for Load (Review) WB for Load (Review) MEM for Load (Review)
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-19-2012 2 ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-19-2012
CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-19-2012 2 ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-19-2012
RISC Central Processing Unit
 RISC Central Processing Unit Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Spring, 2014 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/
RISC Central Processing Unit Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Spring, 2014 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/
CUDA 를활용한실시간 IMAGE PROCESSING SYSTEM 구현. Chang Hee Lee
 1 CUDA 를활용한실시간 IMAGE PROCESSING SYSTEM 구현 Chang Hee Lee Overview Thin film transistor(tft) LCD : Inspection Object Type of Defect Type of Inspection Instrument Brief Lighting / Focusing Optic Magnification
1 CUDA 를활용한실시간 IMAGE PROCESSING SYSTEM 구현 Chang Hee Lee Overview Thin film transistor(tft) LCD : Inspection Object Type of Defect Type of Inspection Instrument Brief Lighting / Focusing Optic Magnification
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
An evaluation of debayering algorithms on GPU for real-time panoramic video recording
 An evaluation of debayering algorithms on GPU for real-time panoramic video recording Ragnar Langseth, Vamsidhar Reddy Gaddam, Håkon Kvale Stensland, Carsten Griwodz, Pål Halvorsen University of Oslo /
An evaluation of debayering algorithms on GPU for real-time panoramic video recording Ragnar Langseth, Vamsidhar Reddy Gaddam, Håkon Kvale Stensland, Carsten Griwodz, Pål Halvorsen University of Oslo /
Game Architecture. 4/8/16: Multiprocessor Game Loops
 Game Architecture 4/8/16: Multiprocessor Game Loops Monolithic Dead simple to set up, but it can get messy Flow-of-control can be complex Top-level may have too much knowledge of underlying systems (gross
Game Architecture 4/8/16: Multiprocessor Game Loops Monolithic Dead simple to set up, but it can get messy Flow-of-control can be complex Top-level may have too much knowledge of underlying systems (gross
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
Characterizing and Improving the Performance of Intel Threading Building Blocks
 Characterizing and Improving the Performance of Intel Threading Building Blocks Gilberto Contreras, Margaret Martonosi Princeton University IISWC 08 Motivation Chip Multiprocessors are the new computing
Characterizing and Improving the Performance of Intel Threading Building Blocks Gilberto Contreras, Margaret Martonosi Princeton University IISWC 08 Motivation Chip Multiprocessors are the new computing
Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
Tomasolu s s Algorithm
 omasolu s s Algorithm Fall 2007 Prof. homas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4 70 Floating Point Buffers (FLB) ag ag ag Storage Bus Floating Point 4 3 Buffers FLB 6 5 5 4 Control 2 1 1 Result
omasolu s s Algorithm Fall 2007 Prof. homas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4 70 Floating Point Buffers (FLB) ag ag ag Storage Bus Floating Point 4 3 Buffers FLB 6 5 5 4 Control 2 1 1 Result
Towards Warp-Scheduler Friendly STT-RAM/SRAM Hybrid GPGPU Register File Design
 Towards Warp-Scheduler Friendly STT-RAM/SRAM Hybrid GPGPU Register File Design Quan Deng, Youtao Zhang, Minxuan Zhang, Jun Yang College of Computer, National University of Defense Technolog, Changsha,
Towards Warp-Scheduler Friendly STT-RAM/SRAM Hybrid GPGPU Register File Design Quan Deng, Youtao Zhang, Minxuan Zhang, Jun Yang College of Computer, National University of Defense Technolog, Changsha,
GPU Acceleration of the HEVC Decoder Inter Prediction Module
 GPU Acceleration of the HEVC Decoder Inter Prediction Module Diego F. de Souza, Aleksandar Ilic, Nuno Roma and Leonel Sousa INESC-ID, IST, Universidade de Lisboa Rua Alves Redol 9, 000-09, Lisbon, Portugal
GPU Acceleration of the HEVC Decoder Inter Prediction Module Diego F. de Souza, Aleksandar Ilic, Nuno Roma and Leonel Sousa INESC-ID, IST, Universidade de Lisboa Rua Alves Redol 9, 000-09, Lisbon, Portugal
COTSon: Infrastructure for system-level simulation
 COTSon: Infrastructure for system-level simulation Ayose Falcón, Paolo Faraboschi, Daniel Ortega HP Labs Exascale Computing Lab http://sites.google.com/site/hplabscotson MICRO-41 tutorial November 9, 28
COTSon: Infrastructure for system-level simulation Ayose Falcón, Paolo Faraboschi, Daniel Ortega HP Labs Exascale Computing Lab http://sites.google.com/site/hplabscotson MICRO-41 tutorial November 9, 28
escience: Pulsar searching on GPUs
 escience: Pulsar searching on GPUs Alessio Sclocco Ana Lucia Varbanescu Karel van der Veldt John Romein Joeri van Leeuwen Jason Hessels Rob van Nieuwpoort And many others! Netherlands escience center Science
escience: Pulsar searching on GPUs Alessio Sclocco Ana Lucia Varbanescu Karel van der Veldt John Romein Joeri van Leeuwen Jason Hessels Rob van Nieuwpoort And many others! Netherlands escience center Science
Topics. Low Power Techniques. Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J.
 Topics Low Power Techniques Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J. Rabaey Review: Energy & Power Equations E = C L V 2 DD P 0 1 +
Topics Low Power Techniques Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J. Rabaey Review: Energy & Power Equations E = C L V 2 DD P 0 1 +
IBM Research Report. GPUVolt: Modeling and Characterizing Voltage Noise in GPU Architectures
 RC55 (WAT1-3) April 1, 1 Electrical Engineering IBM Research Report GPUVolt: Modeling and Characterizing Voltage Noise in GPU Architectures Jingwen Leng, Yazhou Zu, Minsoo Rhu University of Texas at Austin
RC55 (WAT1-3) April 1, 1 Electrical Engineering IBM Research Report GPUVolt: Modeling and Characterizing Voltage Noise in GPU Architectures Jingwen Leng, Yazhou Zu, Minsoo Rhu University of Texas at Austin
A B C D. Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold. Time
 Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry A B C D Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry A B C D Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining A B C D. Readings: Example: Doing the laundry. Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave. each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold
 Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave A B C D each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave A B C D each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
CMP 301B Computer Architecture. Appendix C
 CMP 301B Computer Architecture Appendix C Dealing with Exceptions What should be done when an exception arises and many instructions are in the pipeline??!! Force a trap instruction in the next IF stage
CMP 301B Computer Architecture Appendix C Dealing with Exceptions What should be done when an exception arises and many instructions are in the pipeline??!! Force a trap instruction in the next IF stage
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H ) Next: continued. Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2)
 Lecture Topics Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H 4.5-4.10) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2) 2 1 ISA Implementations Three different strategies: single-cycle
Lecture Topics Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H 4.5-4.10) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2) 2 1 ISA Implementations Three different strategies: single-cycle
Analysis of Image Compression Algorithm: GUETZLI
 Analysis of Image Compression Algorithm: GUETZLI Lingyi Li August 18, 2017 Abstract How to balance picture size and quality is the core of image compression. This paper evaluates Google's jpeg image compression
Analysis of Image Compression Algorithm: GUETZLI Lingyi Li August 18, 2017 Abstract How to balance picture size and quality is the core of image compression. This paper evaluates Google's jpeg image compression
Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling
 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling Reading: Appendix A (A-67) H&P Chapter 2 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling 1 his Unit: Dynamic Scheduling Application OS Compiler
Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling Reading: Appendix A (A-67) H&P Chapter 2 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling 1 his Unit: Dynamic Scheduling Application OS Compiler
Performance Lessons from Porting Source 2 to Vulkan. Dan Ginsburg
 Performance Lessons from Porting Source 2 to Vulkan Dan Ginsburg Overview Dota 2 Vulkan Performance Results Performance Lessons Learned Overview Dota 2 Vulkan Performance Results Performance Lessons Learned
Performance Lessons from Porting Source 2 to Vulkan Dan Ginsburg Overview Dota 2 Vulkan Performance Results Performance Lessons Learned Overview Dota 2 Vulkan Performance Results Performance Lessons Learned
Ramon Canal NCD Master MIRI. NCD Master MIRI 1
 Wattch, Hotspot, Hotleakage, McPAT http://www.eecs.harvard.edu/~dbrooks/wattch-form.html http://lava.cs.virginia.edu/hotspot http://lava.cs.virginia.edu/hotleakage http://www.hpl.hp.com/research/mcpat/
Wattch, Hotspot, Hotleakage, McPAT http://www.eecs.harvard.edu/~dbrooks/wattch-form.html http://lava.cs.virginia.edu/hotspot http://lava.cs.virginia.edu/hotleakage http://www.hpl.hp.com/research/mcpat/
SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE
 SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE FOR VOLTAGE SCALABILITY Bhargava Gopireddy, Choungki Song, Josep Torrellas, Nam Sung Kim, Aditya Agrawal, Asit Mishra University of Illinois, University of Wisconsin, Nvidia,
SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE FOR VOLTAGE SCALABILITY Bhargava Gopireddy, Choungki Song, Josep Torrellas, Nam Sung Kim, Aditya Agrawal, Asit Mishra University of Illinois, University of Wisconsin, Nvidia,
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
ΕΠΛ 605: Προχωρημένη Αρχιτεκτονική
 ΕΠΛ 605: Προχωρημένη Αρχιτεκτονική Υπολογιστών Presentation of UniServer Horizon 2020 European project findings: X-Gene server chips, voltage-noise characterization, high-bandwidth voltage measurements,
ΕΠΛ 605: Προχωρημένη Αρχιτεκτονική Υπολογιστών Presentation of UniServer Horizon 2020 European project findings: X-Gene server chips, voltage-noise characterization, high-bandwidth voltage measurements,
Performance Evaluation of Multi-Threaded System vs. Chip-Multi-Processor System
 Performance Evaluation of Multi-Threaded System vs. Chip-Multi-Processor System Ho Young Kim, Robert Maxwell, Ankil Patel, Byeong Kil Lee Abstract The purpose of this study is to analyze and compare the
Performance Evaluation of Multi-Threaded System vs. Chip-Multi-Processor System Ho Young Kim, Robert Maxwell, Ankil Patel, Byeong Kil Lee Abstract The purpose of this study is to analyze and compare the
Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance
 Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance Michael D. Powell, Arijit Biswas, Shantanu Gupta, and Shubu Mukherjee SPEARS Group, Intel Massachusetts EECS, University
Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance Michael D. Powell, Arijit Biswas, Shantanu Gupta, and Shubu Mukherjee SPEARS Group, Intel Massachusetts EECS, University
Memory-Level Parallelism Aware Fetch Policies for Simultaneous Multithreading Processors
 Memory-Level Parallelism Aware Fetch Policies for Simultaneous Multithreading Processors STIJN EYERMAN and LIEVEN EECKHOUT Ghent University A thread executing on a simultaneous multithreading (SMT) processor
Memory-Level Parallelism Aware Fetch Policies for Simultaneous Multithreading Processors STIJN EYERMAN and LIEVEN EECKHOUT Ghent University A thread executing on a simultaneous multithreading (SMT) processor
Matthew Grossman Mentor: Rick Brownrigg
 Matthew Grossman Mentor: Rick Brownrigg Outline What is a WMS? JOCL/OpenCL Wavelets Parallelization Implementation Results Conclusions What is a WMS? A mature and open standard to serve georeferenced imagery
Matthew Grossman Mentor: Rick Brownrigg Outline What is a WMS? JOCL/OpenCL Wavelets Parallelization Implementation Results Conclusions What is a WMS? A mature and open standard to serve georeferenced imagery
A Polyphase Filter for GPUs and Multi-Core Processors
 A Polyphase Filter for GPUs and Multi-Core Processors Karel van der Veldt Universiteit van Amsterdam The Netherlands karel.vd.veldt@uva.nl Ana Lucia Varbanescu Technische Universiteit Delft The Netherlands
A Polyphase Filter for GPUs and Multi-Core Processors Karel van der Veldt Universiteit van Amsterdam The Netherlands karel.vd.veldt@uva.nl Ana Lucia Varbanescu Technische Universiteit Delft The Netherlands
Simulating GPGPUs ESESC Tutorial
 ESESC Tutorial Speaker: ankaranarayanan Department of Computer Engineering, University of California, Santa Cruz http://masc.soe.ucsc.edu 1 Outline Background GPU Emulation Setup GPU Simulation Setup Running
ESESC Tutorial Speaker: ankaranarayanan Department of Computer Engineering, University of California, Santa Cruz http://masc.soe.ucsc.edu 1 Outline Background GPU Emulation Setup GPU Simulation Setup Running
An Evaluation of Speculative Instruction Execution on Simultaneous Multithreaded Processors
 An Evaluation of Speculative Instruction Execution on Simultaneous Multithreaded Processors STEVEN SWANSON, LUKE K. McDOWELL, MICHAEL M. SWIFT, SUSAN J. EGGERS and HENRY M. LEVY University of Washington
An Evaluation of Speculative Instruction Execution on Simultaneous Multithreaded Processors STEVEN SWANSON, LUKE K. McDOWELL, MICHAEL M. SWIFT, SUSAN J. EGGERS and HENRY M. LEVY University of Washington
CSE502: Computer Architecture Welcome to CSE 502
 Welcome to CSE 502 Introduction & Review Today s Lecture Course Overview Course Topics Grading Logistics Academic Integrity Policy Homework Quiz Key basic concepts for Computer Architecture Course Overview
Welcome to CSE 502 Introduction & Review Today s Lecture Course Overview Course Topics Grading Logistics Academic Integrity Policy Homework Quiz Key basic concepts for Computer Architecture Course Overview
U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I
 U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I Prof. Karu Sankaralingam Unit 5: Dynamic Scheduling I Slides developed by Amir Roth of University of Pennsylvania with sources that included University
U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I Prof. Karu Sankaralingam Unit 5: Dynamic Scheduling I Slides developed by Amir Roth of University of Pennsylvania with sources that included University
PROBE: Prediction-based Optical Bandwidth Scaling for Energy-efficient NoCs
 PROBE: Prediction-based Optical Bandwidth Scaling for Energy-efficient NoCs Li Zhou and Avinash Kodi Technologies for Emerging Computer Architecture Laboratory (TEAL) School of Electrical Engineering and
PROBE: Prediction-based Optical Bandwidth Scaling for Energy-efficient NoCs Li Zhou and Avinash Kodi Technologies for Emerging Computer Architecture Laboratory (TEAL) School of Electrical Engineering and
MUVR: Supporting Multi-User Mobile Virtual Reality with Resource Constrained Edge Cloud
 2018 Third ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing MUVR: Supporting Multi-User Mobile Virtual Reality with Resource Constrained Edge Cloud Yong Li Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
2018 Third ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing MUVR: Supporting Multi-User Mobile Virtual Reality with Resource Constrained Edge Cloud Yong Li Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Outline Simulators and such. What defines a simulator? What about emulation?
 Outline Simulators and such Mats Brorsson & Mladen Nikitovic ICT Dept of Electronic, Computer and Software Systems (ECS) What defines a simulator? Why are simulators needed? Classifications Case studies
Outline Simulators and such Mats Brorsson & Mladen Nikitovic ICT Dept of Electronic, Computer and Software Systems (ECS) What defines a simulator? Why are simulators needed? Classifications Case studies
ESE532: System-on-a-Chip Architecture. Today. Message. Crossbar. Interconnect Concerns
 ESE532: System-on-a-Chip Architecture Day 19: March 29, 2017 Network-on-a-Chip (NoC) Today Ring 2D Mesh Networks Design Issues Buffering and deflection Dynamic and static routing Penn ESE532 Spring 2017
ESE532: System-on-a-Chip Architecture Day 19: March 29, 2017 Network-on-a-Chip (NoC) Today Ring 2D Mesh Networks Design Issues Buffering and deflection Dynamic and static routing Penn ESE532 Spring 2017
On the Rules of Low-Power Design
 On the Rules of Low-Power Design (and Why You Should Break Them) Prof. Todd Austin University of Michigan austin@umich.edu A long time ago, in a not so far away place The Rules of Low-Power Design P =
On the Rules of Low-Power Design (and Why You Should Break Them) Prof. Todd Austin University of Michigan austin@umich.edu A long time ago, in a not so far away place The Rules of Low-Power Design P =
Dynamic MIPS Rate Stabilization in Out-of-Order Processors
 Dynamic Rate Stabilization in Out-of-Order Processors Jinho Suh and Michel Dubois Ming Hsieh Dept of EE University of Southern California Outline Motivation Performance Variability of an Out-of-Order Processor
Dynamic Rate Stabilization in Out-of-Order Processors Jinho Suh and Michel Dubois Ming Hsieh Dept of EE University of Southern California Outline Motivation Performance Variability of an Out-of-Order Processor
Image Processing Architectures (and their future requirements)
 Lecture 17: Image Processing Architectures (and their future requirements) Visual Computing Systems Smart phone processing resources Qualcomm snapdragon Image credit: Qualcomm Apple A7 (iphone 5s) Chipworks
Lecture 17: Image Processing Architectures (and their future requirements) Visual Computing Systems Smart phone processing resources Qualcomm snapdragon Image credit: Qualcomm Apple A7 (iphone 5s) Chipworks
Monte Carlo integration and event generation on GPU and their application to particle physics
 Monte Carlo integration and event generation on GPU and their application to particle physics Junichi Kanzaki (KEK) GPU2016 @ Rome, Italy Sep. 26, 2016 Motivation Increase of amount of LHC data (raw &
Monte Carlo integration and event generation on GPU and their application to particle physics Junichi Kanzaki (KEK) GPU2016 @ Rome, Italy Sep. 26, 2016 Motivation Increase of amount of LHC data (raw &
IMPLEMENTATION OF SOFTWARE-BASED 2X2 MIMO LTE BASE STATION SYSTEM USING GPU
 IMPLEMENTATION OF SOFTWARE-BASED 2X2 MIMO LTE BASE STATION SYSTEM USING GPU Seunghak Lee (HY-SDR Research Center, Hanyang Univ., Seoul, South Korea; invincible@dsplab.hanyang.ac.kr); Chiyoung Ahn (HY-SDR
IMPLEMENTATION OF SOFTWARE-BASED 2X2 MIMO LTE BASE STATION SYSTEM USING GPU Seunghak Lee (HY-SDR Research Center, Hanyang Univ., Seoul, South Korea; invincible@dsplab.hanyang.ac.kr); Chiyoung Ahn (HY-SDR
COSC4201. Scoreboard
 COSC4201 Scoreboard Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) 1 Overcoming Data Hazards with Dynamic Scheduling In the pipeline, if there is
COSC4201 Scoreboard Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) 1 Overcoming Data Hazards with Dynamic Scheduling In the pipeline, if there is
Experience with new architectures: moving from HELIOS to Marconi
 Experience with new architectures: moving from HELIOS to Marconi Serhiy Mochalskyy, Roman Hatzky 3 rd Accelerated Computing For Fusion Workshop November 28 29 th, 2016, Saclay, France High Level Support
Experience with new architectures: moving from HELIOS to Marconi Serhiy Mochalskyy, Roman Hatzky 3 rd Accelerated Computing For Fusion Workshop November 28 29 th, 2016, Saclay, France High Level Support
HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING USING GPGPU FOR RADAR APPLICATIONS
 HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING USING GPGPU FOR RADAR APPLICATIONS Viswam Gampala 1 (visgam@yahoo.co.in), Akshay BM 1, A Vengadarajan 1, PS Avadhani 2 1. Electronics & Radar Development Establishment, DRDO,
HIGH PERFORMANCE COMPUTING USING GPGPU FOR RADAR APPLICATIONS Viswam Gampala 1 (visgam@yahoo.co.in), Akshay BM 1, A Vengadarajan 1, PS Avadhani 2 1. Electronics & Radar Development Establishment, DRDO,
Signal Processing on GPUs for Radio Telescopes
 Signal Processing on GPUs for Radio Telescopes John W. Romein Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy (ASTRON) Dwingeloo, the Netherlands 1 Overview radio telescopes motivation processing pipelines signal-processing
Signal Processing on GPUs for Radio Telescopes John W. Romein Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy (ASTRON) Dwingeloo, the Netherlands 1 Overview radio telescopes motivation processing pipelines signal-processing
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on
 EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
Challenges in Transition
 Challenges in Transition Keynote talk at International Workshop on Software Engineering Methods for Parallel and High Performance Applications (SEM4HPC 2016) 1 Kazuaki Ishizaki IBM Research Tokyo kiszk@acm.org
Challenges in Transition Keynote talk at International Workshop on Software Engineering Methods for Parallel and High Performance Applications (SEM4HPC 2016) 1 Kazuaki Ishizaki IBM Research Tokyo kiszk@acm.org
Dynamic Reconfiguration of 3D Photonic Networks-on-Chip for Maximizing Performance and Improving Fault Tolerance
 Dynamic Reconfiguration of 3D Photonic Networks-on-Chip for Maximizing Performance and Improving Fault Tolerance Randy Morris Ϯ, Avinash Kodi Ϯ and Ahmed Louri School of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Dynamic Reconfiguration of 3D Photonic Networks-on-Chip for Maximizing Performance and Improving Fault Tolerance Randy Morris Ϯ, Avinash Kodi Ϯ and Ahmed Louri School of Electrical Engineering and Computer
Pre-Silicon Validation of Hyper-Threading Technology
 Pre-Silicon Validation of Hyper-Threading Technology David Burns, Desktop Platforms Group, Intel Corp. Index words: microprocessor, validation, bugs, verification ABSTRACT Hyper-Threading Technology delivers
Pre-Silicon Validation of Hyper-Threading Technology David Burns, Desktop Platforms Group, Intel Corp. Index words: microprocessor, validation, bugs, verification ABSTRACT Hyper-Threading Technology delivers
An Energy-Efficient Heterogeneous CMP based on Hybrid TFET-CMOS Cores
 An Energy-Efficient Heterogeneous CMP based on Hybrid TFET-CMOS Cores Abstract The steep sub-threshold characteristics of inter-band tunneling FETs (TFETs) make an attractive choice for low voltage operations.
An Energy-Efficient Heterogeneous CMP based on Hybrid TFET-CMOS Cores Abstract The steep sub-threshold characteristics of inter-band tunneling FETs (TFETs) make an attractive choice for low voltage operations.
Ben Baker. Sponsored by:
 Ben Baker Sponsored by: Background Agenda GPU Computing Digital Image Processing at FamilySearch Potential GPU based solutions Performance Testing Results Conclusions and Future Work 2 CPU vs. GPU Architecture
Ben Baker Sponsored by: Background Agenda GPU Computing Digital Image Processing at FamilySearch Potential GPU based solutions Performance Testing Results Conclusions and Future Work 2 CPU vs. GPU Architecture
Pipeline Damping: A Microarchitectural Technique to Reduce Inductive Noise in Supply Voltage
 Pipeline Damping: A Microarchitectural Technique to Reduce Inductive Noise in Supply Voltage Michael D. Powell and T. N. Vijaykumar School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University {mdpowell,
Pipeline Damping: A Microarchitectural Technique to Reduce Inductive Noise in Supply Voltage Michael D. Powell and T. N. Vijaykumar School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University {mdpowell,
Contents. Basic Concepts. Histogram of CPU-burst Times. Diagram of Process State CHAPTER 5 CPU SCHEDULING. Alternating Sequence of CPU And I/O Bursts
 Contents CHAPTER 5 CPU SCHEDULING Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time Scheduling Basic Concepts Maximum CPU utilization obtained with multiprogramming
Contents CHAPTER 5 CPU SCHEDULING Basic Concepts Scheduling Criteria Scheduling Algorithms Multiple-Processor Scheduling Real-Time Scheduling Basic Concepts Maximum CPU utilization obtained with multiprogramming
ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Pipeline: Introduction
 Computer Architecture and Organization Pipeline: Introduction Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 11.1 The Laundry Analogy Student A,
Computer Architecture and Organization Pipeline: Introduction Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 11.1 The Laundry Analogy Student A,
NRC Workshop on NASA s Modeling, Simulation, and Information Systems and Processing Technology
 NRC Workshop on NASA s Modeling, Simulation, and Information Systems and Processing Technology Bronson Messer Director of Science National Center for Computational Sciences & Senior R&D Staff Oak Ridge
NRC Workshop on NASA s Modeling, Simulation, and Information Systems and Processing Technology Bronson Messer Director of Science National Center for Computational Sciences & Senior R&D Staff Oak Ridge
Convolution Engine: Balancing Efficiency and Flexibility in Specialized Computing
 Convolution Engine: Balancing Efficiency and Flexibility in Specialized Computing Paper by: Wajahat Qadeer Rehan Hameed Ofer Shacham Preethi Venkatesan Christos Kozyrakis Mark Horowitz Presentation by:
Convolution Engine: Balancing Efficiency and Flexibility in Specialized Computing Paper by: Wajahat Qadeer Rehan Hameed Ofer Shacham Preethi Venkatesan Christos Kozyrakis Mark Horowitz Presentation by:
Early Adopter : Multiprocessor Programming in the Undergraduate Program. NSF/TCPP Curriculum: Early Adoption at the University of Central Florida
 Early Adopter : Multiprocessor Programming in the Undergraduate Program NSF/TCPP Curriculum: Early Adoption at the University of Central Florida Narsingh Deo Damian Dechev Mahadevan Vasudevan Department
Early Adopter : Multiprocessor Programming in the Undergraduate Program NSF/TCPP Curriculum: Early Adoption at the University of Central Florida Narsingh Deo Damian Dechev Mahadevan Vasudevan Department
Parallel Programming Design of BPSK Signal Demodulation Based on CUDA
 Int. J. Communications, Network and System Sciences, 216, 9, 126-134 Published Online May 216 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcns http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijcns.216.9511 Parallel Programming
Int. J. Communications, Network and System Sciences, 216, 9, 126-134 Published Online May 216 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcns http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijcns.216.9511 Parallel Programming
