Remote Sensing. in Agriculture. Dr. Baqer Ramadhan CRP 514 Geographic Information System. Adel M. Al-Rebh G Term Paper.
|
|
|
- Diana Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Remote Sensing in Agriculture Term Paper to Dr. Baqer Ramadhan CRP 514 Geographic Information System By Adel M. Al-Rebh G May 2012
2 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction Objective Methodology Remote sensing Remote sensing in agriculture Active and Passive Remote Sensing Electromagnetic Energy and plant s spectral signature Crop Health Assessment The Electromagnetic Spectrum System Resolution Spatial resolution Spectral resolution Radiometric resolution Temporal resolution Agricultural Remote Sensing Process Historical Imagery in Google Earth Coastal Land Filling Recommendation Conclusion References
3 Table of Figures FIGURE 1 SPECTRAL SIGNATURE... 6 FIGURE 2 SPECTRAL SIGNATURES OF CROPS... 7 FIGURE 3 SPECTRAL SIGNATURES OF HEALTHY AND STRESSED SUGAR BEETS... 8 FIGURE 4 THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM... 9 FIGURE 5 THE REMOTE SENSING PROCESS FIGURE 6 SOME OF QATIF FARMS BEFORE URBAN EXPANSION (2005) FIGURE 7 SOME OF QATIF FARMS AFTER URBAN EXPANSION (2011) FIGURE 8 QATIF SHORELINE NORTH TAROUT BAY BEFORE URBAN EXPANSION (2004) FIGURE 9 QATIF SHORELINE NORTH TAROUT BAY AFTER URBAN EXPANSION AND SEA LANDFILLING (2011)
4 1.0 Introduction Land evaluation is an effective approach to measure the suitability of lands for Agricultural utilization. The availability of fertile lands is limited in Saudi Arabia due to the shortage of rainwater and underground water. Agricultural areas should be protected and considered as reservations. Land evaluation is of great importance in guiding decisions on land uses for the sake of their potential for usage and also for the sake of conserving natural resources for future generations. Remote sensing is one of reliable and effective method used for land evaluation and potential for agricultural utilization. Remotely sensed image can be used to observe the colors of leaves or the overall appearances of plants which aid in the determination of the plant s condition and further for assessing land fertility. According to (Nowatzki et al. 2004), Remotely sensed images can be used to identify nutrient deficiencies, diseases, water deficiency or surplus, weed infestations, insect damage, hail damage, wind damage, herbicide damage, and plant populations. 2.0 Objective This objective of this term paper is: To study remote sensing technology used in agricultural, the process of analyzing the obtained data and its importance in planning. To assess current condition of Agricultural area in Eastern Province specifically Qatif city. To bring awareness to Qatif residence and municipal the loss of the natural agricultural resources in the city. 4
5 3.0 Methodology The research uses remotely sensed imagery and Google earth s Historical Imagery feature to assess the effect of urban expansion in Qatif city on mainly the agricultural lands and touch basis on the problem of sea land filling. 4.0 Remote sensing It is the collection of data about an object from a distance such as satellite or airplane. Geographers use remote sensing to monitor or asses and measure phenomena found in the Earth's surface, and atmosphere. Remote sensors are the mechanical devices usually used by geographers to perform remote sensing of the environment. Similar to human eye, remote sensors spot the same visible wavelengths of light. Furthermore, energy from wavelengths that are undetectable to the human eye can be detected by remote sensors. The sensors can also observe the reflection and the radiation of energy from objects which enable geographers to obtain information about the nature of these objects. 4.1 Remote sensing in agriculture Remote sensing technology is significant for agricultural producers. Satellites and aircraft images provide a means to assess agricultural land and crop conditions. Since 1950s, large agricultural producers utilize this technology to assess their fields. Recently, this technology became easy to get to most agricultural producers (1). Plant s conditions can be assessed through the observation of the colors of leaves or the general look of plants. The remotely sensed image can be viewed, studied, and stored for future comparison. Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in almost all 5
6 plants. Healthy vegetation appears green as the absorption in chlorophyll bands outside the green wavelengths. One portion of the light is absorbed, the other get reflected as green light scattered at the cellular boundaries to appear green both in reflection and transmission. The emerged multiple reflections, natural light create a non-polarized image. The higher the wavelengths the strong the reflection; which represent strong absorption in the leaf, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Spectral Signature 4.2 Active and Passive Remote Sensing Several types of remote sensing technologies are available; Active Remote Sensing refers to the reflection of radiation and electromagnetic energy from manmade source such as Radar or Sonar Systems, which produce microwave radiation that reflect to a receiver. This system is not common in agricultural. Passive Remote Sensing, unlike active, refers to the reflection of radiation and electromagnetic energy from natural source such as the Sun. passive system is the most used system to for agricultural. Passive system senses the electromagnetic energy reflected from the plants. The sensors of this system can be mounted on either satellite or Aircraft. 6
7 4.3 Electromagnetic Energy and plant s spectral signature In passive remote system, when sunlight approaches the plant, it will be reflected, absorbed or transmitted. What dictate the proportions of energy among these three are the intensity of the wavelength of the energy and the individual features of the plants such as the color of the plant s leaves and the way leaves are attached to the plants. Chlorophyll and the absorbed wave s energy, which represent the first proportion of sun electromagnetic energy, are what give the plant s leaves the green color. The second proportion of sun electromagnetic energy will be transmitted through the leaves and the third proportion will be reflected. The three electromagnetic waves proportions will be deducted by the remote sensors. The difference of the ratios of these proportions will give each plant type its unique spectral signature. More illustration can be seen in Figure 2 Figure 2 Spectral signatures of crops 7
8 4.4 Crop Health Assessment One major advantage of remote sensing is the assessment of the crop health. Stressed plants, for example, can be identified. Figure 3 illustrates a comparison between healthy and stressed sugar beets. Figure 3 Spectral signatures of healthy and stressed sugar beets The spectral signature of typical healthy sugar beets should be used as basis for the comparison. The stressed plants will show different reflectance level from those that are healthy. Vegetation index compares the reflectance level of the plants along different wavelength to better assess the plant s health condition. 4.5 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic spectrum is the energy transmitted from the sun. Light or electromagnetic energy waves travel similar to water waves; wavelength is the distance between two subsequent waves peaks. Electromagnetic spectrum range consists of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. Remote sensing for 8
9 agricultural application cover small portion of the electromagnetic spectrum wide range. It extends from Visible Region which starts at around 400 nm to Infrared Region that ends at around 25 µm. Figure 4 illustrate the range of the electromagnetic spectrum. The green color wavelength should locate somewhere around 500 nm. Figure 4 the Electromagnetic Spectrum 4.6 System Resolution A wide view of earth s surface and features can be remotely sensed. Various techniques are available to analyze the collected data. The remotely sensed ground reflection can be utilized to assess the property of vegetation. Resolution is the intensity of details of an image. It is usually measured to the smallest object/details that can be captured. Extend on the other hand is more related to the width of coverage. Both resolution and extend are used to measure the quality of an image or the feature of an object. Several factors need to be considered to assess the capability of remote sensing for certain application such as vegetation. The remote sensing system includes four resolutions: Spatial resolution, Spectral resolution, Radiometric resolution, and Temporal resolution. 9
10 Spatial resolution It refers to the smallest object that can be detected on the ground. In photograph, pixel is the smallest data crystal. Spatial is the reflection of the photographic pixels on the ground. The higher resolution of an image, the smaller the area covered in one pixel Spectral resolution The smallest portion of the electromagnetic spectrum is called band. The higher the spectrum resolution, the shorter the width of the wave length. Spectral signature can be used to identify the different material and minerals. If enough detail of wave length interval are available that cover the spectral range, a more sophisticate type such as multispectral or hyperspectral used to measure the energy as they are more sensitive. Crop condition can be assessed using these technologies Radiometric resolution Refer to the ability of sensing the miner difference in the reflection level. More precise picture can be obtained with higher radiometric resolution as it can detect precisely the small difference of the reflection level and electromagnetic spectrum Temporal resolution It refers to the frequency of area coverage. Normal satellite provides data every time orbiting over an area, while Geo-satellite has the ability to continuously provide remote sensing. Airplane remote sensing can be used for higher frequency sensing which is more expensive that satellite imagery. One advantage that flight timing can take the weather condition in consideration. 10
11 4.7 Agricultural Remote Sensing Process The process of agricultural remote sensing involves an interaction between Sun s electromagnetic radiation and the targets of interest, the plants. Figure 5 illustrates the seven steps required for agricultural assessment. The illustration is applicable to both imaging and non-imaging (Electromagnetic) sensing systems. Figure 5 The remote sensing process A. Illumination (Sun) - the first step for remote sensing is to have an energy source that illuminates and provides electromagnetic energy to the target of interest, in agricultural, the sun is the source of illumination. B. Radiation - as the electromagnetic waves travels from the sun, it will be interacted with the atmosphere as travel to the target and back to the sensors. C. The Target (Plants) - after the electromagnetic wave makes its way to the plants, the intensity of the interaction with plants will depend on the characteristics of the target plants and the quality of the arrived radiation. A proportion of the electromagnetic wave will transmit through the leaves. 11
12 D. Sensors - The sensor that can be mounted to satellite or aircraft detects the reflected electromagnetic waves. They collect and record the reflected electromagnetic radiation after traveling through the atmosphere. E. Processing Station - after the electromagnetic energy recorded by the sensor, the collected data will be transmitted to the ground, to a receiving and processing station. F. Analysis - the received data about the plants will be processed and interpreted into useful information such as images, numbers and graphs the target. G. Implementation - the final step of the remote sensing process is the assessment of the vegetation and, also problem solving and field correction incorporating the received and analyzed information. The whole of these seven steps are essential for remote sensing, the collected data and imagery should be stored for future comparison and assessment. 5.0 Historical Imagery in Google Earth It is a feature that Google Earth provides to travel back in time and view the various places. The feature gives us the ability to see the require information for the analysis of past records of various places and to see how places have changed over time. Currently, the important places in US can be traced back to as far as 1950, and UK to around Unfortunately, for Saud Arabia the tool provides imagery back to This interesting tool enables the comparisons, and could provide valuable information, that can assist in the studying of urban growth and it effect to the surrounding agricultural lands. For example, below are before and after shots for some location of what used to be called Qatif oasis: 12
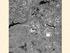
13 Figure 6 Some of Qatif Farms Before Urban Expansion (2005) Figure 7 Some of Qatif Farms After Urban Expansion (2011) 13
14 Figure 8 Qatif Shoreline North Tarout Bay Before Urban Expansion (2004) Figure 9 Qatif Shoreline North Tarout Bay After Urban Expansion and Sea Landfilling (2011) 14
15 Change is obviously, a dramatic shrinking of agricultural lands due to the unplanned urban expansion. The impact of this expansion is irreversible. Satellite images highlights the urban expansion in Qatif, the before, satellite images were taken back only as far as Agricultural lands were a lot healthier than what they are right now; in six years, a tremendous damage has been occurred, and if this expansion kept unplanned, Agricultural lands will be vanished. 6.0 Coastal Land Filling It is the process of filling the sea to prepare it for urban expansion; the process in much of the cases ends up damaging the marine biology. A report on coastal land filling (UNEP, 1997) has shown Saudi Arabia along with some other Arab countries, Jordan and Egypt, had performed physical alteration and destruction of habitats on the coastline for the purpose of urbanization and coastal development. Filling had caused significant destruction of marine habitats and marine environment. Mangroves, sea grass and algae are essential for fishery in the Arab Gulf. Filling does not just damage the covered areas but also the surrounding areas due to the increase of the turbidity in the water. 7.0 Recommendation Agricultural researchers should utilize Google earth historical imagery to study the condition of the vegetation and to observe how fields have changed over time. People need to realize the importance of reserving the natural resources of agricultural beauty for the future generation. 15
16 Municipals, Ministry of Economy and Planning and other governmental agencies should put restrictions on urban development and expansion to protect the agricultural area. Urban expansion should be planned through the municipals and planning ministry. City zoning should be clear to real state offices and legislation should govern the trading. 8.0 Conclusion Agricultural areas are limited in Saudi Arabia. This natural resource should be protected and preserved for the future generation. Remote sensing is one of reliable and effective method used for agricultural lands evaluation. It can be used to observe the colors of leaves and appearances of plants which aid in the determination of the plant s condition, crop health and, also can be used further to assess land fertility. Urban growth has negative effect on the surrounding agricultural lands. Citizens and concerned government agencies need to realize the importance of reserving the natural resources of agricultural. Google Earth Historical Imagery is a tool that researchers should utilize to study the condition of the vegetation and to observe how fields have changed over time. 16
17 9.0 References Canadian Environmental Grantmakers' Network (2005). Urban Environment Issues. Available at: < > [Accessed 21 April, 2012] Hatfield, J.L. & Pinter, P.J.Jr. (1993). Remote sensing for crop protection (Publication No /93/06/ ). Ames, IA: USDA - Agricultural Research Service. Nowatzki, J., Andres, R., & Kyllo, K. (2004). Agricultural Remote Sensing Basics. North Dakota State University. NDSU Extension Service Publication AE Available at: < [Accessed 21 April, 2012] Rai, A. (2003). Remote Sensing and GIS Application in Agricultural. Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute. Available at: < Remote%20Sensing%20and%20GIS.pdf > [Accessed 21 April, 2012] United Nations Environment Programme (1997). UNEP/PERSGA: Assessment of Land-based Sources and Activities Affecting the Marine Environment in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden. UNEP Regional Seas Reports and Studies No Available at: < > [Accessed 21 April, 2012] 17
Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing. Mads Olander Rasmussen
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing Mads Olander Rasmussen (mora@dhi-gras.com) 01. Introduction to Remote Sensing DHI What is remote sensing? the art, science, and technology
Introduction to Remote Sensing Fundamentals of Satellite Remote Sensing Mads Olander Rasmussen (mora@dhi-gras.com) 01. Introduction to Remote Sensing DHI What is remote sensing? the art, science, and technology
Final Examination Introduction to Remote Sensing. Time: 1.5 hrs Max. Marks: 50. Section-I (50 x 1 = 50 Marks)
 Final Examination Introduction to Remote Sensing Time: 1.5 hrs Max. Marks: 50 Note: Attempt all questions. Section-I (50 x 1 = 50 Marks) 1... is the technology of acquiring information about the Earth's
Final Examination Introduction to Remote Sensing Time: 1.5 hrs Max. Marks: 50 Note: Attempt all questions. Section-I (50 x 1 = 50 Marks) 1... is the technology of acquiring information about the Earth's
Introduction to Remote Sensing
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Daniel McInerney Urban Institute Ireland, University College Dublin, Richview Campus, Clonskeagh Drive, Dublin 14. 16th June 2009 Presentation Outline 1 2 Spaceborne Sensors
Introduction to Remote Sensing Daniel McInerney Urban Institute Ireland, University College Dublin, Richview Campus, Clonskeagh Drive, Dublin 14. 16th June 2009 Presentation Outline 1 2 Spaceborne Sensors
An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS. Introduction
 An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS Introduction Remote sensing is the measurement of object properties on Earth s surface using data acquired from aircraft and satellites. It attempts to measure something
An Introduction to Remote Sensing & GIS Introduction Remote sensing is the measurement of object properties on Earth s surface using data acquired from aircraft and satellites. It attempts to measure something
GIS Data Collection. Remote Sensing
 GIS Data Collection Remote Sensing Data Collection Remote sensing Introduction Concepts Spectral signatures Resolutions: spectral, spatial, temporal Digital image processing (classification) Other systems
GIS Data Collection Remote Sensing Data Collection Remote sensing Introduction Concepts Spectral signatures Resolutions: spectral, spatial, temporal Digital image processing (classification) Other systems
Monitoring agricultural plantations with remote sensing imagery
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Monitoring agricultural plantations with remote sensing imagery Camelia Slave and Anca Rotman University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine - Bucharest Romania,
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Monitoring agricultural plantations with remote sensing imagery Camelia Slave and Anca Rotman University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine - Bucharest Romania,
Geo/SAT 2 INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING
 Geo/SAT 2 INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING Paul R. Baumann, Professor Emeritus State University of New York College at Oneonta Oneonta, New York 13820 USA COPYRIGHT 2008 Paul R. Baumann Introduction Remote
Geo/SAT 2 INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING Paul R. Baumann, Professor Emeritus State University of New York College at Oneonta Oneonta, New York 13820 USA COPYRIGHT 2008 Paul R. Baumann Introduction Remote
Interpreting land surface features. SWAC module 3
 Interpreting land surface features SWAC module 3 Interpreting land surface features SWAC module 3 Different kinds of image Panchromatic image True-color image False-color image EMR : NASA Echo the bat
Interpreting land surface features SWAC module 3 Interpreting land surface features SWAC module 3 Different kinds of image Panchromatic image True-color image False-color image EMR : NASA Echo the bat
An NDVI image provides critical crop information that is not visible in an RGB or NIR image of the same scene. For example, plants may appear green
 Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) Spectral Band calculation that uses the visible (RGB) and near-infrared (NIR) bands of the electromagnetic spectrum NDVI= + An NDVI image provides critical
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) Spectral Band calculation that uses the visible (RGB) and near-infrared (NIR) bands of the electromagnetic spectrum NDVI= + An NDVI image provides critical
REMOTE SENSING. Topic 10 Fundamentals of Digital Multispectral Remote Sensing MULTISPECTRAL SCANNERS MULTISPECTRAL SCANNERS
 REMOTE SENSING Topic 10 Fundamentals of Digital Multispectral Remote Sensing Chapter 5: Lillesand and Keifer Chapter 6: Avery and Berlin MULTISPECTRAL SCANNERS Record EMR in a number of discrete portions
REMOTE SENSING Topic 10 Fundamentals of Digital Multispectral Remote Sensing Chapter 5: Lillesand and Keifer Chapter 6: Avery and Berlin MULTISPECTRAL SCANNERS Record EMR in a number of discrete portions
Outline for today. Geography 411/611 Remote sensing: Principles and Applications. Remote sensing: RS for biogeochemical cycles
 Geography 411/611 Remote sensing: Principles and Applications Thomas Albright, Associate Professor Laboratory for Conservation Biogeography, Department of Geography & Program in Ecology, Evolution, & Conservation
Geography 411/611 Remote sensing: Principles and Applications Thomas Albright, Associate Professor Laboratory for Conservation Biogeography, Department of Geography & Program in Ecology, Evolution, & Conservation
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS
 746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 1 Concepts of remote sensing and Basic principle of Photogrammetry Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University What
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 1 Concepts of remote sensing and Basic principle of Photogrammetry Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University What
Introduction to Remote Sensing
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Spatial, spectral, temporal resolutions Image display alternatives Vegetation Indices Image classifications Image change detections Accuracy assessment Satellites & Air-Photos
Introduction to Remote Sensing Spatial, spectral, temporal resolutions Image display alternatives Vegetation Indices Image classifications Image change detections Accuracy assessment Satellites & Air-Photos
Int n r t o r d o u d c u ti t on o n to t o Remote Sensing
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Definition of Remote Sensing Remote sensing refers to the activities of recording/observing/perceiving(sensing)objects or events at far away (remote) places. In remote sensing,
Introduction to Remote Sensing Definition of Remote Sensing Remote sensing refers to the activities of recording/observing/perceiving(sensing)objects or events at far away (remote) places. In remote sensing,
Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS
 Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS Time: Max. Marks: Q1. What is remote Sensing? Explain the basic components of a Remote Sensing system. Q2. What is
Govt. Engineering College Jhalawar Model Question Paper Subject- Remote Sensing & GIS Time: Max. Marks: Q1. What is remote Sensing? Explain the basic components of a Remote Sensing system. Q2. What is
An Introduction to Geomatics. Prepared by: Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq خاص بطلبة مساق مقدمة في علم. Associate Professor of Surveying IUG
 An Introduction to Geomatics خاص بطلبة مساق مقدمة في علم الجيوماتكس Prepared by: Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor of Surveying IUG 1 Airborne Imagery Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor
An Introduction to Geomatics خاص بطلبة مساق مقدمة في علم الجيوماتكس Prepared by: Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor of Surveying IUG 1 Airborne Imagery Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq Associate Professor
First Exam: New Date. 7 Geographers Tools: Gathering Information. Photographs and Imagery REMOTE SENSING 2/23/2018. Friday, March 2, 2018.
 First Exam: New Date Friday, March 2, 2018. Combination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation. Bring a #2 pencil with eraser. Based on class lectures supplementing chapter 1. Review lecture
First Exam: New Date Friday, March 2, 2018. Combination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation. Bring a #2 pencil with eraser. Based on class lectures supplementing chapter 1. Review lecture
APCAS/10/21 April 2010 ASIA AND PACIFIC COMMISSION ON AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS TWENTY-THIRD SESSION. Siem Reap, Cambodia, April 2010
 APCAS/10/21 April 2010 Agenda Item 8 ASIA AND PACIFIC COMMISSION ON AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS TWENTY-THIRD SESSION Siem Reap, Cambodia, 26-30 April 2010 The Use of Remote Sensing for Area Estimation by Robert
APCAS/10/21 April 2010 Agenda Item 8 ASIA AND PACIFIC COMMISSION ON AGRICULTURAL STATISTICS TWENTY-THIRD SESSION Siem Reap, Cambodia, 26-30 April 2010 The Use of Remote Sensing for Area Estimation by Robert
Lecture 2. Electromagnetic radiation principles. Units, image resolutions.
 NRMT 2270, Photogrammetry/Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Electromagnetic radiation principles. Units, image resolutions. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
NRMT 2270, Photogrammetry/Remote Sensing Lecture 2 Electromagnetic radiation principles. Units, image resolutions. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
First Exam. Geographers Tools: Gathering Information. Photographs and Imagery. SPIN 2 Image of Downtown Atlanta, GA 1995 REMOTE SENSING 9/19/2016
 First Exam Geographers Tools: Gathering Information Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0616. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to
First Exam Geographers Tools: Gathering Information Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0616. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to
Sommersemester Prof. Dr. Christoph Kleinn Institut für Waldinventur und Waldwachstum Arbeitsbereich Fernerkundung und Waldinventur.
 Basics of Remote Sensing Some literature references Franklin, SE 2001 Remote Sensing for Sustainable Forest Management Lewis Publishers 407p Lillesand, Kiefer 2000 Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation
Basics of Remote Sensing Some literature references Franklin, SE 2001 Remote Sensing for Sustainable Forest Management Lewis Publishers 407p Lillesand, Kiefer 2000 Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS. Multi spectral, thermal and hyper spectral sensing and usage
 746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 3 Multi spectral, thermal and hyper spectral sensing and usage Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University Multi
746A27 Remote Sensing and GIS Lecture 3 Multi spectral, thermal and hyper spectral sensing and usage Chandan Roy Guest Lecturer Department of Computer and Information Science Linköping University Multi
High Resolution Multi-spectral Imagery
 High Resolution Multi-spectral Imagery Jim Baily, AirAgronomics AIRAGRONOMICS Having been involved in broadacre agriculture until 2000 I perceived a need for a high resolution remote sensing service to
High Resolution Multi-spectral Imagery Jim Baily, AirAgronomics AIRAGRONOMICS Having been involved in broadacre agriculture until 2000 I perceived a need for a high resolution remote sensing service to
earthobservation.wordpress.com
 Dirty REMOTE SENSING earthobservation.wordpress.com Stuart Green Teagasc Stuart.Green@Teagasc.ie 1 Purpose Give you a very basic skill set and software training so you can: find free satellite image data.
Dirty REMOTE SENSING earthobservation.wordpress.com Stuart Green Teagasc Stuart.Green@Teagasc.ie 1 Purpose Give you a very basic skill set and software training so you can: find free satellite image data.
Module 3 Introduction to GIS. Lecture 8 GIS data acquisition
 Module 3 Introduction to GIS Lecture 8 GIS data acquisition GIS workflow Data acquisition (geospatial data input) GPS Remote sensing (satellites, UAV s) LiDAR Digitized maps Attribute Data Management Data
Module 3 Introduction to GIS Lecture 8 GIS data acquisition GIS workflow Data acquisition (geospatial data input) GPS Remote sensing (satellites, UAV s) LiDAR Digitized maps Attribute Data Management Data
First Exam: Thurs., Sept 28
 8 Geographers Tools: Gathering Information Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0917. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
8 Geographers Tools: Gathering Information Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College Geography Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0917. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
MSB Imagery Program FAQ v1
 MSB Imagery Program FAQ v1 (F)requently (A)sked (Q)uestions 9/22/2016 This document is intended to answer commonly asked questions related to the MSB Recurring Aerial Imagery Program. Table of Contents
MSB Imagery Program FAQ v1 (F)requently (A)sked (Q)uestions 9/22/2016 This document is intended to answer commonly asked questions related to the MSB Recurring Aerial Imagery Program. Table of Contents
FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry. Lecture 2. Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics
 FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics Lecture Outline Electromagnetic Radiation Theory Digital vs. Analog (i.e. film ) Systems
FOR 353: Air Photo Interpretation and Photogrammetry Lecture 2 Electromagnetic Energy/Camera and Film characteristics Lecture Outline Electromagnetic Radiation Theory Digital vs. Analog (i.e. film ) Systems
MULTISPECTRAL AGRICULTURAL ASSESSMENT. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index. Federal Robotics INSPECTION & DOCUMENTATION
 MULTISPECTRAL AGRICULTURAL ASSESSMENT Normalized Difference Vegetation Index INSPECTION & DOCUMENTATION Federal Robotics Clearwater Dr. Amherst, New York 14228 716-221-4181 Sales@FedRobot.com www.fedrobot.com
MULTISPECTRAL AGRICULTURAL ASSESSMENT Normalized Difference Vegetation Index INSPECTION & DOCUMENTATION Federal Robotics Clearwater Dr. Amherst, New York 14228 716-221-4181 Sales@FedRobot.com www.fedrobot.com
The studies began when the Tiros satellites (1960) provided man s first synoptic view of the Earth s weather systems.
 Remote sensing of the Earth from orbital altitudes was recognized in the mid-1960 s as a potential technique for obtaining information important for the effective use and conservation of natural resources.
Remote sensing of the Earth from orbital altitudes was recognized in the mid-1960 s as a potential technique for obtaining information important for the effective use and conservation of natural resources.
Blacksburg, VA July 24 th 30 th, 2010 Remote Sensing Page 1. A condensed overview. For our purposes
 A condensed overview George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) The art and science
A condensed overview George McLeod Prepared by: With support from: NSF DUE-0903270 in partnership with: Geospatial Technician Education Through Virginia s Community Colleges (GTEVCC) The art and science
Spectral Signatures. Vegetation. 40 Soil. Water WAVELENGTH (microns)
 Spectral Signatures % REFLECTANCE VISIBLE NEAR INFRARED Vegetation Soil Water.5. WAVELENGTH (microns). Spectral Reflectance of Urban Materials 5 Parking Lot 5 (5=5%) Reflectance 5 5 5 5 5 Wavelength (nm)
Spectral Signatures % REFLECTANCE VISIBLE NEAR INFRARED Vegetation Soil Water.5. WAVELENGTH (microns). Spectral Reflectance of Urban Materials 5 Parking Lot 5 (5=5%) Reflectance 5 5 5 5 5 Wavelength (nm)
NON-PHOTOGRAPHIC SYSTEMS: Multispectral Scanners Medium and coarse resolution sensor comparisons: Landsat, SPOT, AVHRR and MODIS
 NON-PHOTOGRAPHIC SYSTEMS: Multispectral Scanners Medium and coarse resolution sensor comparisons: Landsat, SPOT, AVHRR and MODIS CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS PASSIVE ACTIVE DIGITAL
NON-PHOTOGRAPHIC SYSTEMS: Multispectral Scanners Medium and coarse resolution sensor comparisons: Landsat, SPOT, AVHRR and MODIS CLASSIFICATION OF NONPHOTOGRAPHIC REMOTE SENSORS PASSIVE ACTIVE DIGITAL
Introduction of Satellite Remote Sensing
 Introduction of Satellite Remote Sensing Spatial Resolution (Pixel size) Spectral Resolution (Bands) Resolutions of Remote Sensing 1. Spatial (what area and how detailed) 2. Spectral (what colors bands)
Introduction of Satellite Remote Sensing Spatial Resolution (Pixel size) Spectral Resolution (Bands) Resolutions of Remote Sensing 1. Spatial (what area and how detailed) 2. Spectral (what colors bands)
Important Missions. weather forecasting and monitoring communication navigation military earth resource observation LANDSAT SEASAT SPOT IRS
 Fundamentals of Remote Sensing Pranjit Kr. Sarma, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Geography Mangaldai College Email: prangis@gmail.com Ph. No +91 94357 04398 Remote Sensing Remote sensing is defined
Fundamentals of Remote Sensing Pranjit Kr. Sarma, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Geography Mangaldai College Email: prangis@gmail.com Ph. No +91 94357 04398 Remote Sensing Remote sensing is defined
IKONOS High Resolution Multispectral Scanner Sensor Characteristics
 High Spatial Resolution and Hyperspectral Scanners IKONOS High Resolution Multispectral Scanner Sensor Characteristics Launch Date View Angle Orbit 24 September 1999 Vandenberg Air Force Base, California,
High Spatial Resolution and Hyperspectral Scanners IKONOS High Resolution Multispectral Scanner Sensor Characteristics Launch Date View Angle Orbit 24 September 1999 Vandenberg Air Force Base, California,
CORN BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES CHAPTER 22. Matching Remote Sensing to Problems
 CORN BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES CHAPTER 22 USDA photo by Regis Lefebure Matching Remote Sensing to Problems Jiyul Chang (Jiyul.Chang@sdstate.edu) and David Clay (David.Clay@sdstate.edu) Remote sensing can
CORN BEST MANAGEMENT PRACTICES CHAPTER 22 USDA photo by Regis Lefebure Matching Remote Sensing to Problems Jiyul Chang (Jiyul.Chang@sdstate.edu) and David Clay (David.Clay@sdstate.edu) Remote sensing can
Viewing New Hampshire from Space
 Viewing New Hampshire from Space A Bird s-eye View of the Granite State! Introduction Environmental changes are a major concern for researchers and policy makers today since these changes have both human
Viewing New Hampshire from Space A Bird s-eye View of the Granite State! Introduction Environmental changes are a major concern for researchers and policy makers today since these changes have both human
7 Geographers Tools: Gathering Information
 FIRST EXAM TODAY ExCr ATLAS EXERCISE for EXAM I is DUE. Bubble in your vtues., Feb. 26, 2019. Pass Scantrons forward. name on the back. Combination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation.
FIRST EXAM TODAY ExCr ATLAS EXERCISE for EXAM I is DUE. Bubble in your vtues., Feb. 26, 2019. Pass Scantrons forward. name on the back. Combination of multiple choice questions and map interpretation.
Chapter 8. Remote sensing
 1. Remote sensing 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Remote sensing 8.3 Resolution 8.4 Landsat 8.5 Geostationary satellites GOES 8.1 Introduction What is remote sensing? One can describe remote sensing in different
1. Remote sensing 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Remote sensing 8.3 Resolution 8.4 Landsat 8.5 Geostationary satellites GOES 8.1 Introduction What is remote sensing? One can describe remote sensing in different
Remote Sensing and GIS
 Remote Sensing and GIS Atmosphere Reflected radiation, e.g. Visible Emitted radiation, e.g. Infrared Backscattered radiation, e.g. Radar (λ) Visible TIR Radar & Microwave 11/9/2017 Geo327G/386G, U Texas,
Remote Sensing and GIS Atmosphere Reflected radiation, e.g. Visible Emitted radiation, e.g. Infrared Backscattered radiation, e.g. Radar (λ) Visible TIR Radar & Microwave 11/9/2017 Geo327G/386G, U Texas,
Remote Sensing in Daily Life. What Is Remote Sensing?
 Remote Sensing in Daily Life What Is Remote Sensing? First time term Remote Sensing was used by Ms Evelyn L Pruitt, a geographer of US in mid 1950s. Minimal definition (not very useful): remote sensing
Remote Sensing in Daily Life What Is Remote Sensing? First time term Remote Sensing was used by Ms Evelyn L Pruitt, a geographer of US in mid 1950s. Minimal definition (not very useful): remote sensing
Digital Image Processing - A Remote Sensing Perspective
 ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) Digital Image Processing - A Remote Sensing Perspective D.Sarala Department of Physics & Electronics St. Ann s College for Women, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad, India Sunita Jacob Head,
ISSN 2278 0211 (Online) Digital Image Processing - A Remote Sensing Perspective D.Sarala Department of Physics & Electronics St. Ann s College for Women, Mehdipatnam, Hyderabad, India Sunita Jacob Head,
Remote Sensing for Rangeland Applications
 Remote Sensing for Rangeland Applications Jay Angerer Ecological Training June 16, 2012 Remote Sensing The term "remote sensing," first used in the United States in the 1950s by Ms. Evelyn Pruitt of the
Remote Sensing for Rangeland Applications Jay Angerer Ecological Training June 16, 2012 Remote Sensing The term "remote sensing," first used in the United States in the 1950s by Ms. Evelyn Pruitt of the
1. Theory of remote sensing and spectrum
 1. Theory of remote sensing and spectrum 7 August 2014 ONUMA Takumi Outline of Presentation Electromagnetic wave and wavelength Sensor type Spectrum Spatial resolution Spectral resolution Mineral mapping
1. Theory of remote sensing and spectrum 7 August 2014 ONUMA Takumi Outline of Presentation Electromagnetic wave and wavelength Sensor type Spectrum Spatial resolution Spectral resolution Mineral mapping
SATELLITE OCEANOGRAPHY
 SATELLITE OCEANOGRAPHY An Introduction for Oceanographers and Remote-sensing Scientists I. S. Robinson Lecturer in Physical Oceanography Department of Oceanography University of Southampton JOHN WILEY
SATELLITE OCEANOGRAPHY An Introduction for Oceanographers and Remote-sensing Scientists I. S. Robinson Lecturer in Physical Oceanography Department of Oceanography University of Southampton JOHN WILEY
How to Access Imagery and Carry Out Remote Sensing Analysis Using Landsat Data in a Browser
 How to Access Imagery and Carry Out Remote Sensing Analysis Using Landsat Data in a Browser Including Introduction to Remote Sensing Concepts Based on: igett Remote Sensing Concept Modules and GeoTech
How to Access Imagery and Carry Out Remote Sensing Analysis Using Landsat Data in a Browser Including Introduction to Remote Sensing Concepts Based on: igett Remote Sensing Concept Modules and GeoTech
Introduction to Remote Sensing
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Outline Remote Sensing Defined Resolution Electromagnetic Energy (EMR) Types Interpretation Applications Remote Sensing Defined Remote Sensing is: The art and science of
Introduction to Remote Sensing Outline Remote Sensing Defined Resolution Electromagnetic Energy (EMR) Types Interpretation Applications Remote Sensing Defined Remote Sensing is: The art and science of
Digitization and fundamental techniques
 Digitization and fundamental techniques Chapter 2.2-2.6 Robin Strand Centre for Image analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline Imaging Digitization Sampling Labeling
Digitization and fundamental techniques Chapter 2.2-2.6 Robin Strand Centre for Image analysis Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Uppsala University Outline Imaging Digitization Sampling Labeling
Lecture 1 Introduction to Remote Sensing
 Lecture 1 Introduction to Remote Sensing Dr Ian Leiper School of Environmental and Life Sciences Bldg Purple 12.2.27 1 2 Lecture Outline Introductions Unit admin Learning outcomes Unit outline Practicals
Lecture 1 Introduction to Remote Sensing Dr Ian Leiper School of Environmental and Life Sciences Bldg Purple 12.2.27 1 2 Lecture Outline Introductions Unit admin Learning outcomes Unit outline Practicals
Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing. DeeDee Whitaker SW Guilford High EES & Chemistry
 Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing DeeDee Whitaker SW Guilford High EES & Chemistry whitakd@gcsnc.com Outline What is remote sensing? How does remote sensing work? What role does the electromagnetic
Satellite Imagery and Remote Sensing DeeDee Whitaker SW Guilford High EES & Chemistry whitakd@gcsnc.com Outline What is remote sensing? How does remote sensing work? What role does the electromagnetic
Present and future of marine production in Boka Kotorska
 Present and future of marine production in Boka Kotorska First results from satellite remote sensing for the breeding areas of filter feeders in the Bay of Kotor INTRODUCTION Environmental monitoring is
Present and future of marine production in Boka Kotorska First results from satellite remote sensing for the breeding areas of filter feeders in the Bay of Kotor INTRODUCTION Environmental monitoring is
Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing. Lecture 2 August 31, 2005
 Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing Lecture 2 August 31, 2005 What is remote sensing Remote Sensing: remote sensing is science of acquiring, processing, and interpreting images and related data that
Some Basic Concepts of Remote Sensing Lecture 2 August 31, 2005 What is remote sensing Remote Sensing: remote sensing is science of acquiring, processing, and interpreting images and related data that
Remote sensing in archaeology from optical to lidar. Krištof Oštir ModeLTER Scientific Research Centre of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts
 Remote sensing in archaeology from optical to lidar Krištof Oštir ModeLTER Scientific Research Centre of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts Introduction Optical remote sensing Systems Search for
Remote sensing in archaeology from optical to lidar Krištof Oštir ModeLTER Scientific Research Centre of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts Introduction Optical remote sensing Systems Search for
Valuable New Information for Precision Agriculture. Mike Ritter Founder & CEO - SLANTRANGE, Inc.
 Valuable New Information for Precision Agriculture Mike Ritter Founder & CEO - SLANTRANGE, Inc. SENSORS Accurate, Platform- Agnostic ANALYTICS On-Board, On-Location SLANTRANGE Delivering Valuable New Information
Valuable New Information for Precision Agriculture Mike Ritter Founder & CEO - SLANTRANGE, Inc. SENSORS Accurate, Platform- Agnostic ANALYTICS On-Board, On-Location SLANTRANGE Delivering Valuable New Information
SUGAR_GIS. From a user perspective. Provides spatial distribution of a wide range of sugarcane production data in an easy to use and sensitive way.
 SUGAR_GIS From a user perspective What is Sugar_GIS? A web-based, decision support tool. Provides spatial distribution of a wide range of sugarcane production data in an easy to use and sensitive way.
SUGAR_GIS From a user perspective What is Sugar_GIS? A web-based, decision support tool. Provides spatial distribution of a wide range of sugarcane production data in an easy to use and sensitive way.
Application of Remote Sensing in the Monitoring of Marine pollution. By Atif Shahzad Institute of Environmental Studies University of Karachi
 Application of Remote Sensing in the Monitoring of Marine pollution By Atif Shahzad Institute of Environmental Studies University of Karachi Remote Sensing "Remote sensing is the science (and to some extent,
Application of Remote Sensing in the Monitoring of Marine pollution By Atif Shahzad Institute of Environmental Studies University of Karachi Remote Sensing "Remote sensing is the science (and to some extent,
A map says to you, 'Read me carefully, follow me closely, doubt me not.' It says, 'I am the Earth in the palm of your hand. Without me, you are alone
 A map says to you, 'Read me carefully, follow me closely, doubt me not.' It says, 'I am the Earth in the palm of your hand. Without me, you are alone and lost. Beryl Markham (West With the Night, 1946
A map says to you, 'Read me carefully, follow me closely, doubt me not.' It says, 'I am the Earth in the palm of your hand. Without me, you are alone and lost. Beryl Markham (West With the Night, 1946
INF-GEO Introduction to remote sensing
 INF-GEO 4310 Introduction to remote sensing Anne Solberg (anne@ifi.uio.no) Satellites, orbits and repeat cycles Optical remote sensings Based on a tutorial adapted from Canadian Center for Remote Sensing,
INF-GEO 4310 Introduction to remote sensing Anne Solberg (anne@ifi.uio.no) Satellites, orbits and repeat cycles Optical remote sensings Based on a tutorial adapted from Canadian Center for Remote Sensing,
Sensors and Data Interpretation II. Michael Horswell
 Sensors and Data Interpretation II Michael Horswell Defining remote sensing 1. When was the last time you did any remote sensing? acquiring information about something without direct contact 2. What are
Sensors and Data Interpretation II Michael Horswell Defining remote sensing 1. When was the last time you did any remote sensing? acquiring information about something without direct contact 2. What are
AR M. Sc. (Rural Technology) II Semester Fundamental of Remote Sensing Model Paper
 1. Multiple choice question ; AR- 7251 M. Sc. (Rural Technology) II Semester Fundamental of Remote Sensing Model Paper 1. Chlorophyll strongly absorbs radition of : (b) Red and Blue wavelength (ii) Which
1. Multiple choice question ; AR- 7251 M. Sc. (Rural Technology) II Semester Fundamental of Remote Sensing Model Paper 1. Chlorophyll strongly absorbs radition of : (b) Red and Blue wavelength (ii) Which
HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGERY FOR SAFEGUARDS APPLICATIONS. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria
 HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGERY FOR SAFEGUARDS APPLICATIONS G. A. Borstad 1, Leslie N. Brown 1, Q.S. Bob Truong 2, R. Kelley, 3 G. Healey, 3 J.-P. Paquette, 3 K. Staenz 4, and R. Neville 4 1 Borstad Associates Ltd.,
HYPERSPECTRAL IMAGERY FOR SAFEGUARDS APPLICATIONS G. A. Borstad 1, Leslie N. Brown 1, Q.S. Bob Truong 2, R. Kelley, 3 G. Healey, 3 J.-P. Paquette, 3 K. Staenz 4, and R. Neville 4 1 Borstad Associates Ltd.,
Outline. Introduction. Introduction: Film Emulsions. Sensor Systems. Types of Remote Sensing. A/Prof Linlin Ge. Photographic systems (cf(
 GMAT x600 Remote Sensing / Earth Observation Types of Sensor Systems (1) Outline Image Sensor Systems (i) Line Scanning Sensor Systems (passive) (ii) Array Sensor Systems (passive) (iii) Antenna Radar
GMAT x600 Remote Sensing / Earth Observation Types of Sensor Systems (1) Outline Image Sensor Systems (i) Line Scanning Sensor Systems (passive) (ii) Array Sensor Systems (passive) (iii) Antenna Radar
Introduction to Remote Sensing Part 1
 Introduction to Remote Sensing Part 1 A Primer on Electromagnetic Radiation Digital, Multi-Spectral Imagery The 4 Resolutions Displaying Images Corrections and Enhancements Passive vs. Active Sensors Radar
Introduction to Remote Sensing Part 1 A Primer on Electromagnetic Radiation Digital, Multi-Spectral Imagery The 4 Resolutions Displaying Images Corrections and Enhancements Passive vs. Active Sensors Radar
Introduction to Remote Sensing of the Environment. Dr. Anne Nolin Department of Geosciences
 Introduction to Remote Sensing of the Environment Dr. Anne Nolin Department of Geosciences Overview of today s lecture Course overview Definitions How measurements are made Analog vs. digital The remote
Introduction to Remote Sensing of the Environment Dr. Anne Nolin Department of Geosciences Overview of today s lecture Course overview Definitions How measurements are made Analog vs. digital The remote
Remote Sensing. Odyssey 7 Jun 2012 Benjamin Post
 Remote Sensing Odyssey 7 Jun 2012 Benjamin Post Definitions Applications Physics Image Processing Classifiers Ancillary Data Data Sources Related Concepts Outline Big Picture Definitions Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing Odyssey 7 Jun 2012 Benjamin Post Definitions Applications Physics Image Processing Classifiers Ancillary Data Data Sources Related Concepts Outline Big Picture Definitions Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing Part 3 Examples & Applications
 Remote Sensing Part 3 Examples & Applications Review: Spectral Signatures Review: Spectral Resolution Review: Computer Display of Remote Sensing Images Individual bands of satellite data are mapped to
Remote Sensing Part 3 Examples & Applications Review: Spectral Signatures Review: Spectral Resolution Review: Computer Display of Remote Sensing Images Individual bands of satellite data are mapped to
UNERSITY OF NAIROBI UNIT: PRICIPLES AND APPLICATIONS OF REMOTE SENSING AND APLLIED CLIMATOLOGY
 UNERSITY OF NAIROBI DEPARTMENT OF METEOROLOGY UNIT: PRICIPLES AND APPLICATIONS OF REMOTE SENSING AND APLLIED CLIMATOLOGY COURSE CODE: SMR 308 GROUP TWO: SENSORS MEMBERS OF GROUP TWO 1. MUTISYA J.M I10/2784/2006
UNERSITY OF NAIROBI DEPARTMENT OF METEOROLOGY UNIT: PRICIPLES AND APPLICATIONS OF REMOTE SENSING AND APLLIED CLIMATOLOGY COURSE CODE: SMR 308 GROUP TWO: SENSORS MEMBERS OF GROUP TWO 1. MUTISYA J.M I10/2784/2006
Ground Truth for Calibrating Optical Imagery to Reflectance
 Visual Information Solutions Ground Truth for Calibrating Optical Imagery to Reflectance The by: Thomas Harris Whitepaper Introduction: Atmospheric Effects on Optical Imagery Remote sensing of the Earth
Visual Information Solutions Ground Truth for Calibrating Optical Imagery to Reflectance The by: Thomas Harris Whitepaper Introduction: Atmospheric Effects on Optical Imagery Remote sensing of the Earth
Fundamentals of Remote Sensing
 Climate Variability, Hydrology, and Flooding Fundamentals of Remote Sensing May 19-22, 2015 GEO-Latin American & Caribbean Water Cycle Capacity Building Workshop Cartagena, Colombia 1 Objective To provide
Climate Variability, Hydrology, and Flooding Fundamentals of Remote Sensing May 19-22, 2015 GEO-Latin American & Caribbean Water Cycle Capacity Building Workshop Cartagena, Colombia 1 Objective To provide
BASICS OF REMOTE SENSING
 BASICS OF REMOTE SENSING 23: Basics of Remote Sensing Shibendu Shankar Ray Mahalanobis National Crop Forecast Centre, Department of Agriculture & Cooperation, Krishi Vistar Sadan, Pusa Campus, New Delhi
BASICS OF REMOTE SENSING 23: Basics of Remote Sensing Shibendu Shankar Ray Mahalanobis National Crop Forecast Centre, Department of Agriculture & Cooperation, Krishi Vistar Sadan, Pusa Campus, New Delhi
remote sensing? What are the remote sensing principles behind these Definition
 Introduction to remote sensing: Content (1/2) Definition: photogrammetry and remote sensing (PRS) Radiation sources: solar radiation (passive optical RS) earth emission (passive microwave or thermal infrared
Introduction to remote sensing: Content (1/2) Definition: photogrammetry and remote sensing (PRS) Radiation sources: solar radiation (passive optical RS) earth emission (passive microwave or thermal infrared
9/10/2013. Incoming energy. Reflected or Emitted. Absorbed Transmitted
 Won Suk Daniel Lee Professor Agricultural and Biological Engineering University of Florida Non destructive sensing technologies Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) Time resolved reflectance spectroscopy
Won Suk Daniel Lee Professor Agricultural and Biological Engineering University of Florida Non destructive sensing technologies Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) Time resolved reflectance spectroscopy
Dr. P Shanmugam. Associate Professor Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras INDIA
 Dr. P Shanmugam Associate Professor Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras INDIA Biography Ph.D (Remote Sensing and Image Processing for Coastal Studies) - Anna University,
Dr. P Shanmugam Associate Professor Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras INDIA Biography Ph.D (Remote Sensing and Image Processing for Coastal Studies) - Anna University,
Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014
 Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014 Contents Introduction GMES Copernicus Six thematic areas Infrastructure Space data An introduction to Remote Sensing In-situ data Applications
Copernicus Introduction Lisbon, Portugal 13 th & 14 th February 2014 Contents Introduction GMES Copernicus Six thematic areas Infrastructure Space data An introduction to Remote Sensing In-situ data Applications
Satellite Remote Sensing: Earth System Observations
 Satellite Remote Sensing: Earth System Observations Land surface Water Atmosphere Climate Ecosystems 1 EOS (Earth Observing System) Develop an understanding of the total Earth system, and the effects of
Satellite Remote Sensing: Earth System Observations Land surface Water Atmosphere Climate Ecosystems 1 EOS (Earth Observing System) Develop an understanding of the total Earth system, and the effects of
The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural
 The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural Luxembourg, 12.03.2014 r. Tomasz Milewski NUTS for Poland: NUTS 1 macro-regions (grup of province, voivodships) (6), NUTS 2 - regions (province,
The use of satellite images to forecast agricultural Luxembourg, 12.03.2014 r. Tomasz Milewski NUTS for Poland: NUTS 1 macro-regions (grup of province, voivodships) (6), NUTS 2 - regions (province,
Figure 1: Percent reflectance for various features, including the five spectra from Table 1, at different wavelengths from 0.4µm to 1.4µm.
 Section 1: The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1. The wavelength range that has the highest reflectance for broadleaf vegetation and needle leaf vegetation is 0.75µm to 1.05µm. 2. Dry soil can be distinguished
Section 1: The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1. The wavelength range that has the highest reflectance for broadleaf vegetation and needle leaf vegetation is 0.75µm to 1.05µm. 2. Dry soil can be distinguished
The studies began when the Tiros satellites (1960) provided man s first synoptic view of the Earth s weather systems.
 Remote sensing of the Earth from orbital altitudes was recognized in the mid-1960 s as a potential technique for obtaining information important for the effective use and conservation of natural resources.
Remote sensing of the Earth from orbital altitudes was recognized in the mid-1960 s as a potential technique for obtaining information important for the effective use and conservation of natural resources.
AGRON / E E / MTEOR 518: Microwave Remote Sensing
 AGRON / E E / MTEOR 518: Microwave Remote Sensing Dr. Brian K. Hornbuckle, Associate Professor Departments of Agronomy, ECpE, and GeAT bkh@iastate.edu What is remote sensing? Remote sensing: the acquisition
AGRON / E E / MTEOR 518: Microwave Remote Sensing Dr. Brian K. Hornbuckle, Associate Professor Departments of Agronomy, ECpE, and GeAT bkh@iastate.edu What is remote sensing? Remote sensing: the acquisition
The Benefits of the 8 Spectral Bands of WorldView-2
 W H I T E P A P E R The Benefits of the 8 Spectral Bands of WorldView-2 A U G U S T 2 0 0 9 Corporate (U.S.) 303.684.4561 or 800.496.1225 London +44.20.8899.6801 Singapore +65.6389.4851 www.digitalglobe.com
W H I T E P A P E R The Benefits of the 8 Spectral Bands of WorldView-2 A U G U S T 2 0 0 9 Corporate (U.S.) 303.684.4561 or 800.496.1225 London +44.20.8899.6801 Singapore +65.6389.4851 www.digitalglobe.com
Introduction to Remote Sensing. Electromagnetic Energy. Data From Wave Phenomena. Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) Electromagnetic Energy
 A Basic Introduction to Remote Sensing (RS) ~~~~~~~~~~ Rev. Ronald J. Wasowski, C.S.C. Associate Professor of Environmental Science University of Portland Portland, Oregon 1 September 2015 Introduction
A Basic Introduction to Remote Sensing (RS) ~~~~~~~~~~ Rev. Ronald J. Wasowski, C.S.C. Associate Professor of Environmental Science University of Portland Portland, Oregon 1 September 2015 Introduction
Lecture 13: Remotely Sensed Geospatial Data
 Lecture 13: Remotely Sensed Geospatial Data A. The Electromagnetic Spectrum: The electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 1) indicates the different forms of radiation (or simply stated light) emitted by nature.
Lecture 13: Remotely Sensed Geospatial Data A. The Electromagnetic Spectrum: The electromagnetic spectrum (Figure 1) indicates the different forms of radiation (or simply stated light) emitted by nature.
Microwave Remote Sensing
 Provide copy on a CD of the UCAR multi-media tutorial to all in class. Assign Ch-7 and Ch-9 (for two weeks) as reading material for this class. HW#4 (Due in two weeks) Problems 1,2,3 and 4 (Chapter 7)
Provide copy on a CD of the UCAR multi-media tutorial to all in class. Assign Ch-7 and Ch-9 (for two weeks) as reading material for this class. HW#4 (Due in two weeks) Problems 1,2,3 and 4 (Chapter 7)
Part I. The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing
 Part I The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing 1 Introduction jacqueline le moigne, nathan s. netanyahu, and roger d. eastman Despite the importance of image registration to data integration
Part I The Importance of Image Registration for Remote Sensing 1 Introduction jacqueline le moigne, nathan s. netanyahu, and roger d. eastman Despite the importance of image registration to data integration
DIGITALGLOBE SATELLITE IMAGERY AND CLOUD SERVICES FOR SUGARCANE MAPPING
 DIGITALGLOBE SATELLITE IMAGERY AND CLOUD SERVICES FOR SUGARCANE MAPPING PRESENTER: DILLON PANIZZOLO (TECHNICAL MANAGER) COMPANY: GEO DATA DESIGN DATE: 18 TH AUGUST 2015 SASTA Congress Sugar Cane Mapping
DIGITALGLOBE SATELLITE IMAGERY AND CLOUD SERVICES FOR SUGARCANE MAPPING PRESENTER: DILLON PANIZZOLO (TECHNICAL MANAGER) COMPANY: GEO DATA DESIGN DATE: 18 TH AUGUST 2015 SASTA Congress Sugar Cane Mapping
Remote Sensing. Measuring an object from a distance. For GIS, that means using photographic or satellite images to gather spatial data
 Remote Sensing Measuring an object from a distance For GIS, that means using photographic or satellite images to gather spatial data Remote Sensing measures electromagnetic energy reflected or emitted
Remote Sensing Measuring an object from a distance For GIS, that means using photographic or satellite images to gather spatial data Remote Sensing measures electromagnetic energy reflected or emitted
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies September 2, 2014
 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies September 2, 2014 The Earth from Above Introduction to Environmental Remote Sensing Lectures: Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm,
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies September 2, 2014 The Earth from Above Introduction to Environmental Remote Sensing Lectures: Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm,
CLASSIFICATION OF VEGETATION AREA FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES ABSTRACT
 CLASSIFICATION OF VEGETATION AREA FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES Arpita Pandya Research Scholar, Computer Science, Rai University, Ahmedabad Dr. Priya R. Swaminarayan Professor
CLASSIFICATION OF VEGETATION AREA FROM SATELLITE IMAGES USING IMAGE PROCESSING TECHNIQUES Arpita Pandya Research Scholar, Computer Science, Rai University, Ahmedabad Dr. Priya R. Swaminarayan Professor
Coral Reef Remote Sensing
 Coral Reef Remote Sensing Spectral, Spatial, Temporal Scaling Phillip Dustan Sensor Spatial Resolutio n Number of Bands Useful Bands coverage cycle Operation Landsat 80m 2 2 18 1972-97 Thematic 30m 7
Coral Reef Remote Sensing Spectral, Spatial, Temporal Scaling Phillip Dustan Sensor Spatial Resolutio n Number of Bands Useful Bands coverage cycle Operation Landsat 80m 2 2 18 1972-97 Thematic 30m 7
Plant Health Monitoring System Using Raspberry Pi
 Volume 119 No. 15 2018, 955-959 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ 1 Plant Health Monitoring System Using Raspberry Pi Jyotirmayee Dashᵃ *, Shubhangi
Volume 119 No. 15 2018, 955-959 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ 1 Plant Health Monitoring System Using Raspberry Pi Jyotirmayee Dashᵃ *, Shubhangi
Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites. The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning
 Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning Outline SPOT program and other moderate resolution systems High resolution satellite systems
Lecture 6: Multispectral Earth Resource Satellites The University at Albany Fall 2018 Geography and Planning Outline SPOT program and other moderate resolution systems High resolution satellite systems
2017 REMOTE SENSING EVENT TRAINING STRATEGIES 2016 SCIENCE OLYMPIAD COACHING ACADEMY CENTERVILLE, OH
 2017 REMOTE SENSING EVENT TRAINING STRATEGIES 2016 SCIENCE OLYMPIAD COACHING ACADEMY CENTERVILLE, OH This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some changes in the final copy of the
2017 REMOTE SENSING EVENT TRAINING STRATEGIES 2016 SCIENCE OLYMPIAD COACHING ACADEMY CENTERVILLE, OH This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may be some changes in the final copy of the
Ghazanfar A. Khattak National Centre of Excellence in Geology University of Peshawar
 INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING Ghazanfar A. Khattak National Centre of Excellence in Geology University of Peshawar WHAT IS REMOTE SENSING? Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about
INTRODUCTION TO REMOTE SENSING Ghazanfar A. Khattak National Centre of Excellence in Geology University of Peshawar WHAT IS REMOTE SENSING? Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about
Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing
 Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing Passive remote sensing system record EMR that was reflected (e.g., blue, green, red, and near IR) or emitted (e.g., thermal IR) from the surface of the Earth.
Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing Passive remote sensing system record EMR that was reflected (e.g., blue, green, red, and near IR) or emitted (e.g., thermal IR) from the surface of the Earth.
Summary. Introduction. Remote Sensing Basics. Selecting a Remote Sensing Product
 K. Dalsted, J.F. Paris, D.E. Clay, S.A. Clay, C.L. Reese, and J. Chang SSMG-40 Selecting the Appropriate Satellite Remote Sensing Product for Precision Farming Summary Given the large number of satellite
K. Dalsted, J.F. Paris, D.E. Clay, S.A. Clay, C.L. Reese, and J. Chang SSMG-40 Selecting the Appropriate Satellite Remote Sensing Product for Precision Farming Summary Given the large number of satellite
Remote Sensing of Environment (RSE)
 I N T R O Introduction to Introduction to Remote Sensing T O R S E Remote Sensing of Environment (RSE) with TNTmips page 1 TNTview Before Getting Started Imagery acquired by airborne or satellite sensors
I N T R O Introduction to Introduction to Remote Sensing T O R S E Remote Sensing of Environment (RSE) with TNTmips page 1 TNTview Before Getting Started Imagery acquired by airborne or satellite sensors
Remote Sensing. Division C. Written Exam
 Remote Sensing Division C Written Exam Team Name: Team #: Team Members: _ Score: /132 A. Matching (10 points) 1. Nadir 2. Albedo 3. Diffraction 4. Refraction 5. Spatial Resolution 6. Temporal Resolution
Remote Sensing Division C Written Exam Team Name: Team #: Team Members: _ Score: /132 A. Matching (10 points) 1. Nadir 2. Albedo 3. Diffraction 4. Refraction 5. Spatial Resolution 6. Temporal Resolution
A broad survey of remote sensing applications for many environmental disciplines
 1 2 3 4 A broad survey of remote sensing applications for many environmental disciplines 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. First definition is very general and applies to many types of remote sensing. You use your eyes
1 2 3 4 A broad survey of remote sensing applications for many environmental disciplines 5 6 7 8 9 10 1. First definition is very general and applies to many types of remote sensing. You use your eyes
Using Freely Available. Remote Sensing to Create a More Powerful GIS
 Using Freely Available Government Data and Remote Sensing to Create a More Powerful GIS All rights reserved. ENVI, E3De, IAS, and IDL are trademarks of Exelis, Inc. All other marks are the property of
Using Freely Available Government Data and Remote Sensing to Create a More Powerful GIS All rights reserved. ENVI, E3De, IAS, and IDL are trademarks of Exelis, Inc. All other marks are the property of
