CHARACTERISTICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE
|
|
|
- Bruce Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exp. No #1 CHARACTERISTICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine characteristics of a silicon diode and to determine the barrier potential of the diode. From the characteristic curve determine the dc resistance, ac resistance, for forward biased conditions and reverse resistance for reverse biased conditions. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS USED 1N4007 silicon rectifier diode 1 kω resistor, ¼ W 0-15 V dc regulated power supply (0-100)mA, (0 100)µA dc ammeter (0 1)V, (0-30)V dc voltmeter Breadboard THEORY The diode is a device made up of a junction of n-type and p-type semiconductor material. An ideal diode has two regions: a conduction region of zero resistance and a non-conduction region of infinite resistance. In forward bias operation, the silicon diode will not conduct significant current until the voltage reaches about 0.7V, called cut-in voltage. After the point of cut-in voltage small change in voltage causes large increase in current. In reverse bias operation, the diode will not conduct significant current until certain threshold voltage called breakdown voltage. DC resistance or static resistance is the ratio of voltage to current in the forward bias characteristics. AC or dynamic resistance is the reciprocal of the slope of the characteristic curve. The resistance offered by the diode under reverse bias is the reverse resistance. FURTHER READING 1. Robert Boylstad, Louis Nashelsky, Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, PHI, Theodore F.Bogart, Jeffrey S.Beasley, Electron Devices and Circuits, PHI 3. Robert Diffenderfer, Electronic Devices, Delmar Cengage Learning,
2 CIRCUIT DIAGRAM Figure1: Forward Biased Diode Figure2: Reverse Biased Diode PRACTICE PROCEDURE 1. Forward Bias 1. Construct the circuit as per the diagram shown in figure1. 2. Vary the power supply voltage in steps of 0.1V upto cut-in voltage and thereafter in steps of 1V upto a maximum of 10V. 3. Note down the voltage drop across the diode and the corresponding current. 4. Plot the graph: I F against V F 5. From the plot, find the static resistance, R = V F / I F. 6. Find also the dynamic resistance, r = Δ V F /Δ I F. 2. Reverse Bias 1. Connect the circuit as per the diagram shown in figure2. 2. Vary the power supply voltage in steps of 1V upto 15V. 3. Note down the voltage drop across the diode and the corresponding current. 4. Plot the graph: I R against V R. 12
3 PRELAB Read the specifications of the following diodes from its datasheet and compare the types of diodes offered by different manufacturers: Device Part Number: 1N4001 Device Manufacturer: Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage, V RRM = Average Rectified Forward Current, I F(av) = Maximum RMS Voltage, V RMS = DC Reverse Voltage, V R = Maximum reverse current I RM = Maximum instantaneous forward voltage drop V F = Device Manufacturer: Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage, V RRM = Average Rectified Forward Current, I F(av) = Maximum RMS Voltage, V RMS = DC Reverse Voltage, V R = Maximum reverse current I RM = Maximum instantaneous forward voltage drop V F = Device Part Number: 1N4007 Device Manufacturer: Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage, V RRM = Average Rectified Forward Current, I F(av) = Maximum RMS Voltage, V RMS = DC Reverse Voltage, V R = Maximum reverse current I RM = Maximum instantaneous forward voltage drop V F = Device Part Number: 1N914 Device Manufacturer: Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage, V RRM = Average Rectified Forward Current, I F(av) = Maximum RMS Voltage, V RMS = DC Reverse Voltage, V R = Maximum reverse current I RM = Maximum instantaneous forward voltage drop V F = 13
4 Exp. No.: OBJECTIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF SEMICONDUCTOR DIODE Date: OBSERVATION Forward Bias Circuit Diagram Table 1: Forward Bias Bias voltage, Vin Volts Diode Forward voltage, V F Volts Diode forward current, I F ma 14
5 Inference Reverse Bias Circuit Diagram 15
6 Table 2: Reverse Bias Bias voltage, Vin Volts Diode Reverse voltage, V R volts Diode Reverse current, I R µa Inference 16
7 UNDERSTANDING & LEARNING 17
8 RESULTS AND CONCLUSION Prepared by: Name: Reg. No.: Experiment Date: ASSESSMENT Report Submission Date: Submission Delay:... Student Task Max. Marks Graded Marks Pre-lab Preparation 20 Inference 10 Signature Results & Conclusion 10 Post-lab / Viva-voce 10 Total 50 18
STATIC CHARACTERISTICS OF TRANSISTOR
 STAT CHARACTERISTS OF TRANSISTOR OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to study the characteristics of bipolar transistor in common emitter (CE) configuration. From the characteristic curve it is
STAT CHARACTERISTS OF TRANSISTOR OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to study the characteristics of bipolar transistor in common emitter (CE) configuration. From the characteristic curve it is
FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER
 Exp. No #5 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to analyze and plot the frequency response of a common collector amplifier. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
Exp. No #5 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to analyze and plot the frequency response of a common collector amplifier. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER
 Exp. No #6 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to analyze and plot the frequency response of a common collector amplifier. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
Exp. No #6 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to analyze and plot the frequency response of a common collector amplifier. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
15EEE282 Electronic Circuits and Simulation Lab - I Lab # 6
 Exp. No #6 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON EMITTER AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design a common emitter amplifier. To analyze and plot the frequency response of the amplifier with
Exp. No #6 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON EMITTER AMPLIFIER OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design a common emitter amplifier. To analyze and plot the frequency response of the amplifier with
WAVE SHAPING CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 WAVE SHAPING CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design the wave shaping circuits like Clippers, Clampers and Schmitt trigger using op-amps. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
WAVE SHAPING CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design the wave shaping circuits like Clippers, Clampers and Schmitt trigger using op-amps. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
15EEE282 Electronic Circuits and Simulation Lab - I Lab #4
 Exp. No #4 TRANSISTOR AS SWITCH OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and analyze the operation of transistor as switch. Also, to design a suitable driver circuit for a given load using
Exp. No #4 TRANSISTOR AS SWITCH OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and analyze the operation of transistor as switch. Also, to design a suitable driver circuit for a given load using
DIODE CLIPPERS AND CLAMPERS
 Exp. No #2 OBJECTIVE DIODE CLIPPERS AND CLAMPERS The purpose of the experiment is to design and analyze diode clipping, limiting and clamping circuits. Also to measure the voltage limits of both biased
Exp. No #2 OBJECTIVE DIODE CLIPPERS AND CLAMPERS The purpose of the experiment is to design and analyze diode clipping, limiting and clamping circuits. Also to measure the voltage limits of both biased
ACTIVE FILTERS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 ACTIVE FILTERS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and compare the frequency plots of second order low pass and high pass active filters. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
ACTIVE FILTERS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and compare the frequency plots of second order low pass and high pass active filters. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I
 CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
LINEAR APPLICATIONS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 LINEAR APPLICATIONS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine the linear applications of an operational amplifier. The applications that are designed and analyzed
LINEAR APPLICATIONS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine the linear applications of an operational amplifier. The applications that are designed and analyzed
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - II
 CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - II OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - II OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
Electronic Circuits I - Tutorial 03 Diode Applications I
 Electronic Circuits I - Tutorial 03 Diode Applications I -1 / 13 - T & F # Question 1 A diode can conduct current in two directions with equal ease. F 2 When reverse-biased, a diode ideally appears as
Electronic Circuits I - Tutorial 03 Diode Applications I -1 / 13 - T & F # Question 1 A diode can conduct current in two directions with equal ease. F 2 When reverse-biased, a diode ideally appears as
WAVEFORM GENERATOR CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 15EEE287 Electronic Circuits & Simulation Lab - II Lab #8 WAVEFORM GENERATOR CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and construct circuits to generate
15EEE287 Electronic Circuits & Simulation Lab - II Lab #8 WAVEFORM GENERATOR CIRCUITS USING OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and construct circuits to generate
Physics 281 EXPERIMENT 7 I-V Curves of Non linear Device
 Physics 281 EXPERIMENT 7 I-V Curves of Non linear Device Print this page to start your lab report (1 copy) Bring a diskette to save your data. OBJECT: To study the method of obtaining the characteristics
Physics 281 EXPERIMENT 7 I-V Curves of Non linear Device Print this page to start your lab report (1 copy) Bring a diskette to save your data. OBJECT: To study the method of obtaining the characteristics
1 Diodes. 1.1 Diode Models Ideal Diode. ELEN 236 Diodes
 ELEN 236 Diodes 1 Diodes 1.1 Diode Models 1.1.1 Ideal Diode Current through diode is zero for any voltage less than zero i.e. reverse biased case Current through diode is not limited by diode if voltage
ELEN 236 Diodes 1 Diodes 1.1 Diode Models 1.1.1 Ideal Diode Current through diode is zero for any voltage less than zero i.e. reverse biased case Current through diode is not limited by diode if voltage
EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION
 EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION Component List Resistors, one of each o 2 1010W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic
EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION Component List Resistors, one of each o 2 1010W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE
 EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
LABORATORY 8 DIODE CIRCUITS
 LABORATORY 8 DIODE CIRCUITS A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the
LABORATORY 8 DIODE CIRCUITS A solid state diode consists of a junction of either dissimilar semiconductors (pn junction diode) or a metal and a semiconductor (Schottky barrier diode). Regardless of the
TO INVESTIGATE THE VARIATION OF CURRENT (I) WITH P.D. (V) FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR
 FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR Low voltage power supply, rheostat, voltmeter, ammeter, length of nichrome wire. 6 A - Nichrome wire 1. Set up the circuit as shown and set the voltage supply at 6 d.c. 2.
FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR Low voltage power supply, rheostat, voltmeter, ammeter, length of nichrome wire. 6 A - Nichrome wire 1. Set up the circuit as shown and set the voltage supply at 6 d.c. 2.
TRANSISTOR AS SWITCH
 Exp. No #3 TRANSISTOR AS SWITCH Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and analyze the operation of transistor as switch. Also, to design a suitable driver circuit for a given load
Exp. No #3 TRANSISTOR AS SWITCH Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to design and analyze the operation of transistor as switch. Also, to design a suitable driver circuit for a given load
Introduction PNP C NPN C
 Introduction JT Transistors: A JT (or any transistor) can be used either as a switch with positions of on or off, or an amplifier that controls its output at all levels in between the extreme on or off
Introduction JT Transistors: A JT (or any transistor) can be used either as a switch with positions of on or off, or an amplifier that controls its output at all levels in between the extreme on or off
Electric Circuit Fall 2017 Lab3 LABORATORY 3. Diode. Guide
 LABORATORY 3 Diode Guide Diodes Overview Diodes are mostly used in practice for emitting light (as Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs) or controlling voltages in various circuits. Typical diode packages in same
LABORATORY 3 Diode Guide Diodes Overview Diodes are mostly used in practice for emitting light (as Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs) or controlling voltages in various circuits. Typical diode packages in same
EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification
 Name & Surname: ID: Date: EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification Objective To calculate, compare, draw, and measure the DC output voltages of half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits. Tools
Name & Surname: ID: Date: EXPERIMENT 3 Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectification Objective To calculate, compare, draw, and measure the DC output voltages of half-wave and full-wave rectifier circuits. Tools
INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I
 INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I Laboratory 4 Wave Shaping Diode Circuits Author: ID CoAuthors: 1. ID 2. ID 3. ID Experiment Date: Report received Date: Comments For Instructor Full Marks Pre
INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I Laboratory 4 Wave Shaping Diode Circuits Author: ID CoAuthors: 1. ID 2. ID 3. ID Experiment Date: Report received Date: Comments For Instructor Full Marks Pre
EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT
 EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT 1. OBJECTIVES 1.1 To practice how to test NPN and PNP transistors using multimeter. 1.2 To demonstrate the relationship between collector current
EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT 1. OBJECTIVES 1.1 To practice how to test NPN and PNP transistors using multimeter. 1.2 To demonstrate the relationship between collector current
Applications of diodes
 Applications of diodes Learners should be able to: (a) describe the I V characteristics of a silicon diode (b) describe the use of diodes for component protection in DC circuits and half-wave rectification
Applications of diodes Learners should be able to: (a) describe the I V characteristics of a silicon diode (b) describe the use of diodes for component protection in DC circuits and half-wave rectification
Lecture (03) Diodes and Diode Applications I
 Lecture (03) Diodes and Diode Applications I By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Agenda VOLTAGE CURRENT CHARACTERISTIC OF A DIODE Forward bias Reverse Bias V I Characteristic for Forward Bias V I Characteristic for
Lecture (03) Diodes and Diode Applications I By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Agenda VOLTAGE CURRENT CHARACTERISTIC OF A DIODE Forward bias Reverse Bias V I Characteristic for Forward Bias V I Characteristic for
BME/ISE 3512 Laboratory - Three Diode (1N4001)
 BME/ISE 3512 Laboratory Three Diode (1N4001) Learning Objectives: Understand the concept of PN junction diodes, their application as rectifiers, the nature and application of halfwave and fullwave rectifiers,
BME/ISE 3512 Laboratory Three Diode (1N4001) Learning Objectives: Understand the concept of PN junction diodes, their application as rectifiers, the nature and application of halfwave and fullwave rectifiers,
Light Emitting Diodes
 Light Emitting Diodes Topics covered in this presentation: LED operation LED Characteristics Display devices Protection and limiting 1 of 9 Light Emitting Diode - LED A special type of diode is the Light
Light Emitting Diodes Topics covered in this presentation: LED operation LED Characteristics Display devices Protection and limiting 1 of 9 Light Emitting Diode - LED A special type of diode is the Light
AIM:-To observe and draw the Forward bias V-I Characteristics of a P-N Junction diode and study of L.E.D characteristics.
 KARNAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT KUNJPURA, KARNAL LAB MANUAL OF ------- SUBJECT CODE DATE OF ISSUE: SEMESTER: BRANCH: REV NO EXPERIMENT NO 1 P-N JUNCTION DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AIM:-To observe
KARNAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT KUNJPURA, KARNAL LAB MANUAL OF ------- SUBJECT CODE DATE OF ISSUE: SEMESTER: BRANCH: REV NO EXPERIMENT NO 1 P-N JUNCTION DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AIM:-To observe
2) The larger the ripple voltage, the better the filter. 2) 3) Clamping circuits use capacitors and diodes to add a dc level to a waveform.
 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) A diode conducts current when forward-biased and blocks current when reverse-biased. 1) 2) The larger the ripple voltage,
TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) A diode conducts current when forward-biased and blocks current when reverse-biased. 1) 2) The larger the ripple voltage,
PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 PCC-Cascade. Lab: AC Circuits
 PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 Lab: AC Circuits OBJECTIVES: EQUIPMENT: Universal Breadboard (Archer 276-169) 2 Simpson Digital Multimeters (464) Function Generator (Global Specialties 2001)*
PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 Lab: AC Circuits OBJECTIVES: EQUIPMENT: Universal Breadboard (Archer 276-169) 2 Simpson Digital Multimeters (464) Function Generator (Global Specialties 2001)*
Electronics 1 Lab (CME 2410) School of Informatics & Computing German Jordanian University Laboratory Experiment (10) Junction FETs
 Electronics 1 Lab (CME 2410) School of Informatics & Computing German Jordanian University Laboratory Experiment (10) 1. Objective: Junction FETs - the operation of a junction field-effect transistor (J-FET)
Electronics 1 Lab (CME 2410) School of Informatics & Computing German Jordanian University Laboratory Experiment (10) 1. Objective: Junction FETs - the operation of a junction field-effect transistor (J-FET)
LABORATORY MODULE. Analog Electronics. Semester 2 (2005/2006)
 LABORATORY MODULE ENT 162 Analog Electronics Semester 2 (2005/2006) EXPERIMENT 1 : Introduction to Diode Name Matric No. : : PUSAT PENGAJIAN KEJURUTERAAN MEKATRONIK KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA
LABORATORY MODULE ENT 162 Analog Electronics Semester 2 (2005/2006) EXPERIMENT 1 : Introduction to Diode Name Matric No. : : PUSAT PENGAJIAN KEJURUTERAAN MEKATRONIK KOLEJ UNIVERSITI KEJURUTERAAN UTARA
Fig [5]
![Fig [5] Fig [5]](/thumbs/82/85456687.jpg) 1 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows the I-V characteristic of a light-emitting diode (LED). 40 I / 10 3 A 30 20 10 0 1.0 1.5 2.0 V / V Fig. 4.1 (i) In Describe the significant features of the graph in terms of current,
1 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows the I-V characteristic of a light-emitting diode (LED). 40 I / 10 3 A 30 20 10 0 1.0 1.5 2.0 V / V Fig. 4.1 (i) In Describe the significant features of the graph in terms of current,
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram
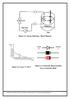 Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
Lec (03) Diodes and Applications
 Lec (03) Diodes and Applications Diode Models 1 Diodes and Applications Diode Operation V-I Characteristics of a Diode Diode Models Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Power Supply Filters and Regulators
Lec (03) Diodes and Applications Diode Models 1 Diodes and Applications Diode Operation V-I Characteristics of a Diode Diode Models Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Power Supply Filters and Regulators
Figure 1: Diode Measuring Circuit
 Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characteristics signal diode Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. The purpose of the back-to-back
Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characteristics signal diode Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. The purpose of the back-to-back
Figure 1: Diode Measuring Circuit
 Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characteristics signal diode Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. The purpose of the back-to-back
Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characteristics signal diode Measure the voltage-current characteristic of a standard signal diode, the 1N914, using the circuit shown in Figure 1 below. The purpose of the back-to-back
Chapter 5: Diodes. I. Theory. Chapter 5: Diodes
 Chapter 5: Diodes This week we will explore another new passive circuit element, the diode. We will also explore some diode applications including conversion of an AC signal into a signal that never changes
Chapter 5: Diodes This week we will explore another new passive circuit element, the diode. We will also explore some diode applications including conversion of an AC signal into a signal that never changes
Figure 1 Diode schematic symbol (left) and physical representation (right)
 Page 1/7 Revision 1 20-Jul-10 OBJECTIVES To reinforce the concepts behind diode circuit analysis Verification of diode theory and operation To understand certain diode applications, such as rectification
Page 1/7 Revision 1 20-Jul-10 OBJECTIVES To reinforce the concepts behind diode circuit analysis Verification of diode theory and operation To understand certain diode applications, such as rectification
EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10
 DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10 In this experiment we will measure the I vs V characteristics of Si, Ge, and Zener p-n junction diodes, and
DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS EXPERIMENT 7: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AND CIRCUITS 10/24/10 In this experiment we will measure the I vs V characteristics of Si, Ge, and Zener p-n junction diodes, and
NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
 NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE ECE-270 Experiment #4 X-Y DISPLAY TECHNIQUES: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS PRELAB Use your textbook and/or the library to answer the following questions about diodes.
NORTHWESTERN UNIVERSITY TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE ECE-270 Experiment #4 X-Y DISPLAY TECHNIQUES: DIODE CHARACTERISTICS PRELAB Use your textbook and/or the library to answer the following questions about diodes.
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE
 EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (I max = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6V pp, 12.6 V RMS ) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (I max = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6V pp, 12.6 V RMS ) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
Experiment No. 2 Half Wave Rectifier using RC-Triggering
 Experiment No. 2 Half Wave Rectifier using RC-Triggering Pre-Lab Reading: 1. Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices and Applications, by M. H. Rashid, 3e. (See page 790 to get help for this experiment).
Experiment No. 2 Half Wave Rectifier using RC-Triggering Pre-Lab Reading: 1. Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices and Applications, by M. H. Rashid, 3e. (See page 790 to get help for this experiment).
EXPERIMENT 10: SCHOTTKY DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
 EXPERIMENT 10: SCHOTTKY DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AIM: To plot forward and reverse characteristics of Schottky diode (Metal Semiconductor junction) APPARATUS: D.C. Supply (0 15 V), current limiting resistor
EXPERIMENT 10: SCHOTTKY DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AIM: To plot forward and reverse characteristics of Schottky diode (Metal Semiconductor junction) APPARATUS: D.C. Supply (0 15 V), current limiting resistor
Field - Effect Transistor
 Page 1 of 6 Field - Effect Transistor Aim :- To draw and study the out put and transfer characteristics of the given FET and to determine its parameters. Apparatus :- FET, two variable power supplies,
Page 1 of 6 Field - Effect Transistor Aim :- To draw and study the out put and transfer characteristics of the given FET and to determine its parameters. Apparatus :- FET, two variable power supplies,
Electronics I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo Section s7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s7ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
The University of Toledo Section s7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s7ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
Class XII - Physics Semiconductor Electronics. Chapter-wise Problems
 lass X - Physics Semiconductor Electronics Materials, Device and Simple ircuit hapter-wise Problems Multiple hoice Question :- 14.1 The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature
lass X - Physics Semiconductor Electronics Materials, Device and Simple ircuit hapter-wise Problems Multiple hoice Question :- 14.1 The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature
Experiment No. 1 Half Wave Rectifier using R-Triggering
 Experiment No. 1 Half Wave Rectifier using R-Triggering Pre-Lab Reading: Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices and Applications, by M. H. Rashid, 3e. Objectives: To analyze resistive firing/triggering of
Experiment No. 1 Half Wave Rectifier using R-Triggering Pre-Lab Reading: Power Electronics: Circuits, Devices and Applications, by M. H. Rashid, 3e. Objectives: To analyze resistive firing/triggering of
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 2 - Semiconductor Diodes Overview: In this lab session students will investigate I-V characteristics
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Experiment No. 2 - Semiconductor Diodes Overview: In this lab session students will investigate I-V characteristics
Chapter 1 Introduction to Electronics
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Electronics Section 1-1 Atomic Structure 1. An atom with an atomic number of 6 has 6 electrons and 6 protons.. The third shell of an atom can have n = (3) = 18 electrons. Section
Chapter 1 Introduction to Electronics Section 1-1 Atomic Structure 1. An atom with an atomic number of 6 has 6 electrons and 6 protons.. The third shell of an atom can have n = (3) = 18 electrons. Section
7. Bipolar Junction Transistor
 41 7. Bipolar Junction Transistor 7.1. Objectives - To experimentally examine the principles of operation of bipolar junction transistor (BJT); - To measure basic characteristics of n-p-n silicon transistor
41 7. Bipolar Junction Transistor 7.1. Objectives - To experimentally examine the principles of operation of bipolar junction transistor (BJT); - To measure basic characteristics of n-p-n silicon transistor
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015
 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
Diodes and Applications
 Diodes and Applications Diodes and Applications 2 1 Diode Operation 2 2 Voltage-Current (V-I) Characteristics 2 3 Diode Models 2 4 Half-Wave Rectifiers 2 5 Full-Wave Rectifiers 2 6 Power Supply Filters
Diodes and Applications Diodes and Applications 2 1 Diode Operation 2 2 Voltage-Current (V-I) Characteristics 2 3 Diode Models 2 4 Half-Wave Rectifiers 2 5 Full-Wave Rectifiers 2 6 Power Supply Filters
Silicon Controlled Rectifier
 Page 1 of 5 Silicon Controlled Rectifier Aim :- To draw and study the forward and reverse volt ampere characteristics of the Silicon Controlled Rectifier. Apparatus :- Silicon Controlled Rectifier, voltmeter,
Page 1 of 5 Silicon Controlled Rectifier Aim :- To draw and study the forward and reverse volt ampere characteristics of the Silicon Controlled Rectifier. Apparatus :- Silicon Controlled Rectifier, voltmeter,
REV NO EXPERIMENT NO 1 AIM: To study the PN junction diode characteristics under Forward & Reverse bias conditions. APPARATUS REQUIRED:
 KARNAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT KUNJPURA, KARNAL LAB MANUAL OF ------- SUBJECT CODE DATE OF ISSUE: SEMESTER: BRANCH: REV NO EXPERIMENT NO 1 AIM: To study the PN junction diode characteristics
KARNAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT KUNJPURA, KARNAL LAB MANUAL OF ------- SUBJECT CODE DATE OF ISSUE: SEMESTER: BRANCH: REV NO EXPERIMENT NO 1 AIM: To study the PN junction diode characteristics
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics. Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers
 BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and
EXPERIMENT 4 LIMITER AND CLAMPER CIRCUITS
 EXPERIMENT 4 LIMITER AND CLAMPER CIRCUITS 1. OBJECTIVES 1.1 To demonstrate the operation of a diode limiter. 1.2 To demonstrate the operation of a diode clamper. 2. INTRODUCTION PART A: Limiter Circuit
EXPERIMENT 4 LIMITER AND CLAMPER CIRCUITS 1. OBJECTIVES 1.1 To demonstrate the operation of a diode limiter. 1.2 To demonstrate the operation of a diode clamper. 2. INTRODUCTION PART A: Limiter Circuit
Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits
 1. Learning Outcomes Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits At the end of this lab, the students should be able to compare the experimental data to the theoretical curve of the diodes. The students
1. Learning Outcomes Lab 2: Diode Characteristics and Diode Circuits At the end of this lab, the students should be able to compare the experimental data to the theoretical curve of the diodes. The students
SKEU 3741 BASIC ELECTRONICS LAB
 Faculty: Subject Subject Code : SKEU 3741 FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING : 2 ND YEAR ELECTRONIC DESIGN LABORATORY Review Release Date Last Amendment Procedure Number : 1 : 2013 : 2013 : PK-UTM-FKE-(0)-10
Faculty: Subject Subject Code : SKEU 3741 FACULTY OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING : 2 ND YEAR ELECTRONIC DESIGN LABORATORY Review Release Date Last Amendment Procedure Number : 1 : 2013 : 2013 : PK-UTM-FKE-(0)-10
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers
 BME 351 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and real
BME 351 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and real
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit
 Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 204 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University at Rangsit School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 204 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR
Concepts to be Covered
 Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 2 Semiconductors, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Covered Semiconductors
Introductory Medical Device Prototyping Analog Circuits Part 2 Semiconductors, http://saliterman.umn.edu/ Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota Concepts to be Covered Semiconductors
Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers
 Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers # Student ID Student Name Grade (10) 1 Instructor signature 2 3 4 5 Delivery Date -1 / 18 - Objectives In this experiment, you will get to know a group of
Electronic Circuits I Laboratory 03 Rectifiers # Student ID Student Name Grade (10) 1 Instructor signature 2 3 4 5 Delivery Date -1 / 18 - Objectives In this experiment, you will get to know a group of
Practical Manual. Deptt.of Electronics &Communication Engg. (ECE)
 Practical Manual LAB: BASICS OF ELECTRONICS 1 ST SEM.(CSE/CV) Deptt.of Electronics &Communication Engg. (ECE) RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDER GARH)12302 Prepared By. Mr.SANDEEP KUMAR
Practical Manual LAB: BASICS OF ELECTRONICS 1 ST SEM.(CSE/CV) Deptt.of Electronics &Communication Engg. (ECE) RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDER GARH)12302 Prepared By. Mr.SANDEEP KUMAR
Diode Characteristics and Applications
 Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
Physics 15b, Lab 3: The Capacitor... and a glimpse of Diodes
 Phys 15b: Lab 3, Sprng 2007 1 Due Friday, March 23, 2007. Physics 15b, Lab 3: The Capacitor... and a glimpse of Diodes REV0 1 ; March 14, 2007 NOTE that this is the first of the labs that you are invited
Phys 15b: Lab 3, Sprng 2007 1 Due Friday, March 23, 2007. Physics 15b, Lab 3: The Capacitor... and a glimpse of Diodes REV0 1 ; March 14, 2007 NOTE that this is the first of the labs that you are invited
The Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit
 The Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit In the Bipolar Transistor tutorial, we saw that the most common circuit configuration for an NPN transistor is that of the Common Emitter Amplifier circuit and that
The Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit In the Bipolar Transistor tutorial, we saw that the most common circuit configuration for an NPN transistor is that of the Common Emitter Amplifier circuit and that
Chapter 2. Diodes & Applications
 Chapter 2 Diodes & Applications The Diode A diode is made from a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon, in which half is doped as a p region and half is doped as an n region with a pn
Chapter 2 Diodes & Applications The Diode A diode is made from a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon, in which half is doped as a p region and half is doped as an n region with a pn
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET
 Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE:
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE:
Downloaded from
 Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants. (b) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent
Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants. (b) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent
Electro - Principles I
 The PN Junction Diode Introduction to the PN Junction Diode Note: In this chapter we consider conventional current flow. Page 11-1 The schematic symbol for the pn junction diode the shown in Figure 1.
The PN Junction Diode Introduction to the PN Junction Diode Note: In this chapter we consider conventional current flow. Page 11-1 The schematic symbol for the pn junction diode the shown in Figure 1.
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY
 SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BHATEWAR-3360 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING [[ Objective: ) P-N JUNCTION
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BHATEWAR-3360 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING [[ Objective: ) P-N JUNCTION
Unijunction Transistor (Volt-Ampere Characteristics)
 Page 1 of 5 Unijunction Transistor (Volt-Ampere Characteristics) Aim :- To draw the volt-ampere characteristics of the unijunction transistor and to find the UJT pameters. Apparatus :- UJT, two variable
Page 1 of 5 Unijunction Transistor (Volt-Ampere Characteristics) Aim :- To draw the volt-ampere characteristics of the unijunction transistor and to find the UJT pameters. Apparatus :- UJT, two variable
Theory. Week. Lecture Day. TOPICS Week TOPICS. Intoduction Overview of DC Circuits. 1.use of measuring instruments-multimeter,cro etc.
 Name of faculty: Sanjay Puri Discipline: Applied Science (Electronics and Communication Engg.) Subject: Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engg. Lesson Plan Duration: 36 weeks (From August 2018
Name of faculty: Sanjay Puri Discipline: Applied Science (Electronics and Communication Engg.) Subject: Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engg. Lesson Plan Duration: 36 weeks (From August 2018
Lesson 08. Name and affiliation of the author: Professor L B D R P Wijesundera Department of Physics, University of Kelaniya.
 Lesson 08 Title of the Experiment: Identification of active components in electronic circuits and characteristics of a Diode, Zener diode and LED (Activity number of the GCE Advanced Level practical Guide
Lesson 08 Title of the Experiment: Identification of active components in electronic circuits and characteristics of a Diode, Zener diode and LED (Activity number of the GCE Advanced Level practical Guide
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology
 Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology B.E. Semester III (EC) 131101: Basic Electronics INDEX Sr. No. Title Page Date Sign Grade 1 [A] To Study the V-I characteristic of PN junction diode. [B]
Shankersinh Vaghela Bapu Institute of Technology B.E. Semester III (EC) 131101: Basic Electronics INDEX Sr. No. Title Page Date Sign Grade 1 [A] To Study the V-I characteristic of PN junction diode. [B]
Sheet 2 Diodes. ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering. Problem (1) Draw the
 Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall 2014 Sheet 2 Diodes Problem (1) Draw the i) Charge density distribution, ii) Electric field distribution iii) Potential distribution,
Ain Shams University Faculty of Engineering ECE335: Electronic Engineering Fall 2014 Sheet 2 Diodes Problem (1) Draw the i) Charge density distribution, ii) Electric field distribution iii) Potential distribution,
6. Bipolar Diode. Owing to this one-direction conductance, current-voltage characteristic of p-n diode has a rectifying shape shown in Fig. 2.
 33 6. Bipolar Diode 6.1. Objectives - to experimentally observe temperature dependence of the current flowing in p-n junction silicon and germanium diodes; - to measure current-voltage characteristics
33 6. Bipolar Diode 6.1. Objectives - to experimentally observe temperature dependence of the current flowing in p-n junction silicon and germanium diodes; - to measure current-voltage characteristics
 Energy band diagrams Metals: 9. ELECTRONIC DEVICES GIST ρ= 10-2 to 10-8 Ω m Insulators: ρ> 10 8 Ω m Semiconductors ρ= 1 to 10 5 Ω m 109 A. Intrinsic semiconductors At T=0k it acts as insulator At room
Energy band diagrams Metals: 9. ELECTRONIC DEVICES GIST ρ= 10-2 to 10-8 Ω m Insulators: ρ> 10 8 Ω m Semiconductors ρ= 1 to 10 5 Ω m 109 A. Intrinsic semiconductors At T=0k it acts as insulator At room
POWER ELECTRONICS LAB MANUAL
 JIS College of Engineering (An Autonomous Institution) Department of Electrical Engineering POWER ELECTRONICS LAB MANUAL Exp-1. Study of characteristics of an SCR AIM: To obtain the V-I characteristics
JIS College of Engineering (An Autonomous Institution) Department of Electrical Engineering POWER ELECTRONICS LAB MANUAL Exp-1. Study of characteristics of an SCR AIM: To obtain the V-I characteristics
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits. Electrical Enginnering Departement. By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben. Instructor: Eng.
 Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
EE 330 Experiment 7 Fall Diodes and Diode Applications
 EE 330 Experiment 7 Fall 2007 Diodes and Diode Applications Objectives: The objective of this experiment is to develop familiarity with diodes and diode applications. The relationship between the actual
EE 330 Experiment 7 Fall 2007 Diodes and Diode Applications Objectives: The objective of this experiment is to develop familiarity with diodes and diode applications. The relationship between the actual
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS. Class XII : PHYSICS WORKSHEET
 SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
L MOSFETS, IDENTIFICATION, CURVES. PAGE 1. I. Review of JFET (DRAW symbol for n-channel type, with grounded source)
 L.107.4 MOSFETS, IDENTIFICATION, CURVES. PAGE 1 I. Review of JFET (DRAW symbol for n-channel type, with grounded source) 1. "normally on" device A. current from source to drain when V G = 0 no need to
L.107.4 MOSFETS, IDENTIFICATION, CURVES. PAGE 1 I. Review of JFET (DRAW symbol for n-channel type, with grounded source) 1. "normally on" device A. current from source to drain when V G = 0 no need to
MT..KB SERIES 130 A 160 A THREE PHASE BRIDGE. Power Modules. Features. Description. Major Ratings and Characteristics. Bulletin I /97
 MT..KB SERIES THREE PHASE BRIDGE Power Modules Features Package fully compatible with the industry standard INT-A-pak power modules series High thermal conductivity package, electrically insulated case
MT..KB SERIES THREE PHASE BRIDGE Power Modules Features Package fully compatible with the industry standard INT-A-pak power modules series High thermal conductivity package, electrically insulated case
Experiment #1: Solid State Diodes Testing & Characterization. Type Value Symbol Name Multisim Part Description Resistor 1MΩ R 2 Basic/Resistor ---
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #1: Solid State Diodes Testing & Characterization COMPONENTS
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #1: Solid State Diodes Testing & Characterization COMPONENTS
Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits EE 111 Electrical Engineering Majmaah University 2 nd Semester 1432/1433 H. Chapter 2. Diodes and Applications
 Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits EE 111 Electrical Engineering Majmaah University 2 nd Semester 1432/1433 H Chapter 2 Diodes and Applications 1 Diodes A diode is a semiconductor device with a single
Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits EE 111 Electrical Engineering Majmaah University 2 nd Semester 1432/1433 H Chapter 2 Diodes and Applications 1 Diodes A diode is a semiconductor device with a single
The George Washington University School of Engineering and Applied Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 20 - LAB
 The George Washington University School of Engineering and Applied Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 20 - LAB Components: Experiment # 1 Solid State Diodes Testing & Characterization
The George Washington University School of Engineering and Applied Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 20 - LAB Components: Experiment # 1 Solid State Diodes Testing & Characterization
Basic Electronics Lab Manual. School of Physical Sciences National Institute of Science Education and Research Bhubaneswar
 Basic Electronics Lab Manual School of Physical Sciences National Institute of Science Education and Research Bhubaneswar IDENTIFICATION OF CIRCUIT COMPONENTS Breadboards: In order to temporarily construct
Basic Electronics Lab Manual School of Physical Sciences National Institute of Science Education and Research Bhubaneswar IDENTIFICATION OF CIRCUIT COMPONENTS Breadboards: In order to temporarily construct
f14m1s_elct7.fm - 1 The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronocs I Electronics I Problems Points Total 15 Was the exam fair?
 f4ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm I Examination Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no f4ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit, mark your answers yes, no, or not
f4ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm I Examination Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no f4ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit, mark your answers yes, no, or not
STPS20S100C. 100 V power Schottky rectifier. Datasheet. Features. Applications. Description
 Datasheet 100 V power Schottky rectifier K A1 A2 A2 K A1 TO-220AB K K A2 A1 TO-220FPAB Features High junction temperature capability for converters located in confined environment Low leakage current at
Datasheet 100 V power Schottky rectifier K A1 A2 A2 K A1 TO-220AB K K A2 A1 TO-220FPAB Features High junction temperature capability for converters located in confined environment Low leakage current at
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES
 KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
Analog Electronics. Lecture 3. Muhammad Amir Yousaf
 Analog Electronics Lecture 3 Discrete Semiconductor Devices Rectifier (Diodes) Light Emitting Diodes Zener Diodes Photo Diodes Transistors Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) MOSFETs Diodes A diode is
Analog Electronics Lecture 3 Discrete Semiconductor Devices Rectifier (Diodes) Light Emitting Diodes Zener Diodes Photo Diodes Transistors Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) MOSFETs Diodes A diode is
Table of Contents. iii
 Table of Contents Subject Page Experiment 1: Diode Characteristics... 1 Experiment 2: Rectifier Circuits... 7 Experiment 3: Clipping and Clamping Circuits 17 Experiment 4: The Zener Diode 25 Experiment
Table of Contents Subject Page Experiment 1: Diode Characteristics... 1 Experiment 2: Rectifier Circuits... 7 Experiment 3: Clipping and Clamping Circuits 17 Experiment 4: The Zener Diode 25 Experiment
SAFEIR Series 10ETS12PbF
 Bulletin I9 /04 SAFEIR Series 0ETSPbF INPUT RECTIFIER DIODE Lead-Free ("PbF" suffix) V F < V @ 0A I FSM = 00A Description/ Features V RRM = 00V The 0ETSPbF rectifier SAFEIR series has been optimized for
Bulletin I9 /04 SAFEIR Series 0ETSPbF INPUT RECTIFIER DIODE Lead-Free ("PbF" suffix) V F < V @ 0A I FSM = 00A Description/ Features V RRM = 00V The 0ETSPbF rectifier SAFEIR series has been optimized for
Lecture (03) Diode applications
 Lecture (03) Diode applications By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Agenda The Basic DC Power Supply Half wave rectifier Full wave rectifier Filters Voltage Regulators ٢ The Basic DC Power Supply All active electronic
Lecture (03) Diode applications By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Agenda The Basic DC Power Supply Half wave rectifier Full wave rectifier Filters Voltage Regulators ٢ The Basic DC Power Supply All active electronic
ELECTRONICS DEVICE MANUAL (NEC-354)
 ELECTRONICS DEVICE MANUAL (NEC-354) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 27, Knowledge Park-III, Greater Noida, (U.P.) Phone : 0120-2323854-58 website :- www.dronacharya.info CONTENTS
ELECTRONICS DEVICE MANUAL (NEC-354) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 27, Knowledge Park-III, Greater Noida, (U.P.) Phone : 0120-2323854-58 website :- www.dronacharya.info CONTENTS
ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A. Name. Section. Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points)
 ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A Name Section Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points) Total (100 points): Please do not write on the crib sheets. On all questions:
ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A Name Section Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points) Total (100 points): Please do not write on the crib sheets. On all questions:
