Reverse Chromatic Aberration and its Numerical Optimization in a Metamaterial Lens
|
|
|
- Cody Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reverse Chromatic Aberration and its Numerical Optimization in a Metamaterial Lens William J. Capecchi*, Nader Behdad, and Francesco A. Volpe University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI USA *capecchi@wisc.edu Abstract: In planar metamaterial lenses, the focal point moves with the frequency. Here it is shown numerically that this movement can be controlled by properly engineering the dimensions of the metamaterialbased phase shifters that constitute the lens. In particular, such lenses can be designed to exhibit unusual chromatic aberration with the focal length increasing, rather than decreasing, with the frequency. It is proposed that such an artificial reverse chromatic aberration may optimize the transverse resolution of millimeter wave diagnostics of plasmas and be useful in compensating for the natural ordinary chromatic aberration of other components in an optical system. More generally, optimized chromatic aberration will allow to simultaneously focus on several objects located at different distances and emitting or reflecting at different frequencies Optical Society of America OCIS codes: ( ) Metamaterials; ( ) Aberration compensation; ( ) Lenses; ( ) Plasma diagnostics. References and links 1. H. J. Hartfuss, T. Geist, M. Hirsch, Plasma Phys Contr F 39, 1693 (1997) 2. I. Hutchinson, Principles of Plasma Diagnostics, Cambridge Univ. Press N. C. Luhnann et al., Fusion Sci Technol 53, 335 (2008) 4. P. K. Chattopadhyay, J. K. Anderson, T. M. Biewer, D. Craig, C. B. Forest, R. W. Harvey, and A. P. Smirnov, Phys. Plasmas 9, 752 (2002); doi: / J. Wesson, Tokamaks. Oxford, NY: Oxford, M. Al-Joumayly and N. Behdad, Wideband Planar Microwave Lenses Using Sub-Wavelength Spatial Phase Shifters, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 59, no. 12, pp , Dec M. Al-Joumayly and N. Behdad, "A Generalized Method for Synthesizing Low-Profile, Band- Pass Frequency Selective Surfaces With Non resonant Constituting Elements," IEEE Trans. Antennas and Prop. Vol. 58, No. 12, pp , Dec N. Behdad, Mudar Al-Joumayly, and Mohsen Salehi, IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag., Vol. 57, pp Feb J.L. Luxon, Nucl. Fusion 42 (2002) R. F. Ellis, M. E. Austin, and D. Taussig, New High Spatial Resolution Optics for the DIII-D ECE Radiometer, in Proc. Of the 14th Joint Workshop on Electron Cyclotron Emission and Electron Cyclotron Resonance Heating (EC 14), Santorini, GR, May 9-12, Introduction Many optical systems suffer from chromatic aberration (CA). A typical lens focuses higher frequencies f closer to the lens and lower frequencies further away, due to the fact that the refractive index typically increases with frequency. A lens exhibiting reverse CA (RCA), meaning that it focuses higher f at longer focal lengths l, could be used to correct for CA in these systems. There are also cases in which finite amounts of CA or RCA are desirable but need to be 1
2 optimized. Some of these cases can be found in millimeter wave diagnostics [1-4] of plasmas [5]: electron cyclotron emission depends on the local magnetic field; as a result, different f are emitted at different locations in a non-uniformly magnetized plasma. Similarly, externally injected waves of different frequency f are reflected at different locations in a plasma of nonuniform density. These considerations translate in f-dependent focusing requirements: for the highest resolution, the focal length l (of the order of m) needs to increase with f (typical central frequency: 4-140GHz) by up to 2cm/GHz over ranges f of several GHz or tens of GHz. Finally there are cases, for instance in photography and surveillance, in which objects located at different distances and emitting or reflecting at different frequencies need to be imaged on the same focal plane. RCA was recently observed in a metamaterial lens [6] developed for phased array antenna applications at 8-12GHz. RCA is an undesired property for that application. In this work, we examine metamaterial lenses of the type reported in [6] and numerically optimize them for plasma diagnostics in the same range of frequencies. The optimization method, however, can be easily extended to the other applications mentioned above, as well as to different frequencies, including visible, where similar geometries are utilized, although not optimized for RCA. Fig. 1. Topology of a third-order bandpass MEFSS. (a) Exploded view of overall lens design. (b) Top views of a unit cell capacitive and inductive layers. (c) Equivalent circuit model valid for normal incidence. 2
3 Each lens consists of several spatial phase shifters, or pixels, that populate its aperture. Each spatial phase shifter is the unit cell of a miniaturized-element frequency selective surface (MEFSS) of the type reported in [7]. MEFSSs are composed of periodic arrangements of subwavelength capacitive patches and inductive wire grids. An MEFSS composed of N capacitive layers alternated by N-1 inductive layers acts as an N th -order coupled-resonator bandpass filter [7]. Fig. 1a-b shows an exploded view of an MEFSS with a 3 rd -order bandpass response. The phase delay provided by an MEFSS is controllable by varying the physical and geometrical parameters of its constituting unit cell (e.g., dimensions of the capacitive and inductive layers, the thickness and material of the dielectric layers, etc.). In the design considered in this paper, each cell has a width D=6.1mm which is much smaller than the wavelength (λ=30mm at f=10ghz). Fig. 2 illustrates the benefit of this feature. For a typical lens, a smooth variation in phase delay can be achieved by light rays at different distances from the optical axis experiencing different path lengths through the lens (Fig. 2a). In constructing a lens with discrete electrically large unit cells (e.g. microwave lenses based on arrays of receiving antennas connected to arrays of transmitting antennas using transmission lines with variable lengths) the phase delay does not change smoothly with the distance from the optical axis (Fig. 2b). However, the continuous nature of a traditional lens is regained in the limit that cells much smaller than the wavelength can be constructed and assembled (Fig. 2c). Fig. 2. The phase delay profile of a typical glass lens is a smooth function of radial distance (a). This is lost in discretized lens systems (b) but regained in the limit of small aperture features (c). A better understanding of the operation of this structure can be gained by considering the equivalent circuit in Fig. 1c, which is valid for normal incidence. The patches in the first, third, and fifth metallic layers are modeled with parallel capacitors and the wire grid layers are modeled with parallel inductors. The dielectric substrates separating these layers are modeled with short transmission lines of length equal to the thickness of the dielectric in Fig. 1a and characteristic impedance, where is the dielectric constant of the substrate and is the free space impedance. Free space on each side of the cell is modeled with semi-infinite transmission lines with characteristic impedances. The effective capacitance of a 2-D periodic array of square metallic patches separated by gaps as in Fig. 1 is [7]: [ ] where is the effective permittivity of the medium in which the capacitive patches are immersed. A similar expression relates the capacitance of the inner capacitive layer to the spacing between adjacent capacitive patches in that layer. 3
4 The effective inductance of a periodic wire mesh as pictured in Fig. 1a-b is described by [7]: [ ] Here is the free space permeability, is the effective permeability of the medium, and is the strip width (Fig. 1b). Equations (1)-(2) are valid only when the structure is placed in a homogenous medium away from metallic objects and when the parameters and are not varied over the array. The similarity between this circuit model and a 3 rd order coupled resonator frequency bandpass filter can be seen by replacing the transmission line sections with their equivalent circuit models, composed of a series inductor and shunt capacitor. A discussion of this can be found in [7]. A wave passing through the metamaterial lens in Fig. 1a experiences a frequencydependent attenuation and phase shift. These can be calculated from the transfer function describing the equivalent circuit in Fig. 1c: where A, B, C and D are given by [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] Here Z and are respectively the characteristic impedance and propagation constant of Fig. 3. Parameter sweeps highlighting the behavior of a 3 rd order MEFSS when varying (a) (b) or (c), all the rest remaining fixed. 4
5 the transmission line. The substitution of Eqs.1-2 in Eqs.3-4 and extraction of phase from Eq.3 yields a conceptually straightforward, but algebraically complicated relationship between, f, w, g 1 and g 2, that suggests that the frequency dependence of can be altered by varying the geometrical parameters w, g 1 and g 2. That complicated expression, however, is approximate, in the measure in which Fig.1c is only an approximate description of the array in Fig.1a. Instead, for more realistic estimates (for example to take into account the finite number of cells), the device in Fig. 1a was modeled numerically for various choices of,, and, and the corresponding transmission and phase shift were calculated using full-wave EM simulations in CST Microwave Studio. Fig.3 illustrates how the function (f) varies with (Fig.3a), (Fig.3b) and (Fig.3c), all the rest remaining fixed. Fig.4 illustrates how at a fixed f varies with,, and. This discussion and numerical optimization applies to a single, uniform array. Then, similar to Fig. 2c, we combine seven concentric zones about the optical axis. Each zone is separately optimized to yield a certain phase shift as a function of the frequency,. Note in Fig.4 that in general there are many (in fact, infinite) sets of,, solutions yielding the desired phase-shift for a certain frequency and zone. However, note also that, for each zone, different phases are required for each frequency. Fig 4. 3D iso-phase contour plot over,, and for =10GHz. Note that for every desired, parameter solution,, is not unique for a given. However, constraining at multiple reduces the choices of,, and. 2. Numerical Optimization The starting point for our RCA optimization was an existing experimentally and numerically well-characterized 3 rd order MEFSS design with a bandpass of 9-11GHz [6-8]. For proof of principle, we initially set the goal of modifying that design in such a way that it had a focal length =30cm at =8GHz and =126cm at =12GHz. These focal lengths were chosen since similar focal lengths will be needed in the DIII-D [9] tokamak [5], but at 10 times higher frequencies ( =80-130GHz) [10]. The relative variation of focal length considered here is the same. The miniaturization and other issues associated with the higher frequencies are left as future work. The requirement on the dependence of on translates into requirements on the dependencies in the various zones [6]. 5
6 The order of an MEFSS puts a constraint on the aperture size. For a 3 rd order MEFSS for example, there is a 270 phase variation between 9 and 11GHz. The technique used to obtain the desired phase delay as a function of frequency,, is to detune the center frequency of the MEFSS by varying the dimensions,, and (Fig. 1). The dielectric thickness is kept constant. The detuned, however, should remain within the passing band to ensure high transmission. At the same time, it is desired here that varies linearly with. These two requirements limit the phase variation at any frequency (within the passing band) to 270. For a planar lens simple geometry gives the aperture limitation for a given frequency and focal length as: [ ] where is the aperture diameter, is the focal length, is the frequency dependent wave number, and is the phase variation between the optical axis and the edge of the aperture. This gives an aperture constraint of at 8GHz. What is desired is the largest phase variation possible so that a large amount of control over the focus is maintained. There is, however, a tradeoff. The phase response required for the m-th zone is determined by the radial distance from the optical axis to a point half way between the inner and outer radius of the zone. Increasing the number of zones decreases the width of each zone due to the limitation of the aperture which means that for the outermost zone, approaches, and therefore the maximum phase variation, for a large number of zones. However, using more zones requires fewer cells to be used in each zone, with the result that the infinite array used in the numerical modeling of a single zone is no longer a satisfactory approximation. The use of 7 zones was chosen as a reasonable compromise between the two competing effects. The phase delay for the center zone (z=0) is found from the aperture (Eq. 5) and focal lengths to be: ( ) where is a constant phase to be added to all zones of the lens. The phase delay introduced by the m-th zone, located at a radial distance axis, is: from the optical ( ) ( ) Therefore the phase difference between zones 0 and 6 is: ( ) For =8GHz and =30cm this phase difference (which will be one of the goals of our optimization) evaluates to: For =12GHz and =126cm it evaluates to: It is evident from the goals set in equations (9)-(10) that the desired effect is to have phase responses that converge towards higher frequencies. Converging phase responses would mean that for high the phase delay differences between zones become small, and so since all zones would be phase-shifting the wave by nearly the same amount an incident plane wave would remain approximately planar, i.e. that it s focal length is very large which is the behavior we want at high. 6
7 To ensure a high degree of accuracy in finding parameters that not only match the desired phase at 8 and 12GHz but also have a linear phase response a computerized optimization was carried out in two steps. First, a 3D parameter scan was conducted: the dimensions,, and were varied and the corresponding phase shift was calculated for various frequencies. A contour plot of in 3D (as a function of,, and ) is shown in Fig. 4 for =10GHz. Similar sets of data were generated for =8, 8.5, 9,,12GHz. For each zone then, Mathematica can be used to locate the set of parameters that approximately minimizes the goal function value (GFV) : [ ] where is the actual phase value obtained in CST simulations at frequency for a specific set of parameters,, and. By contrast, is the desired phase value at frequency f and for zone i. Minimizing is equivalent to a least-square minimization of the discrepancy between the actual and desired phases at frequencies =8,8.5, 12GHz in the X-band. Note however, that Eq. 6-8 only determine the phase differences between zones at certain frequencies and does not explicitly determine the desired phase values,, of an individual zone. Only in choosing the desired phase values for one zone are they then determined for the remaining zones. The desired phase response of a zone can be characterized by the phase value at 8GHz (offset) and the slope given by the difference in phase between 8-12GHz. For zone i then, using Mathematica and Eq. 11, the GFV was minimized not only by varying the parameters,, and, but also by varying the offset and slope which changes the desired phase values. An optimum offset and slope was found that simultaneously minimized the GFV for zone 0 and 6. This ensured that the largest GFV returned by any of the 7 zones would be as small as possible. Using this offset and slope, the desired phase responses were evaluated for all the zones. With the desired phase responses determined, a set of parameters was found for each zone that minimized the GFV. Once the approximate parameter minimum was found in Mathematica, further finer scans of,, and were performed by means of dedicated full-wave CST simulations. This led to identifying the best dimensions,, and for the closest match of with its goal for Fig. 5. Phase response of the numerically optimized zones (solid lines) and their corresponding desired phase responses (dashed lines) 7
8 zone i. The procedure was repeated for all zones. The results, summarized in Fig. 5 and Table 1 confirm that it is possible to engineer a zoned lens of reverse chromatic aberration as desired. The results vary in their tolerance. Zone 6 for example, exhibits behavior very close to the desired phase response over the 8-12GHz frequency range except near 8GHz where there is a deviation of approximately 30. This maximum deviation diminishes for the lower zones, but the overall behavior also becomes less linear and the phase response is seen to be alternatively above and below the desired linear response. Three parameters were varied for each zone:,, and, but it is expected that a higher degree of control of can be achieved by adding other free parameters such as,, or by allowing different layers to have different dimensions, or by considering MEFSS of higher order than N=3. Table 1. Optimal Parameter Dimensions by Zone Zone (mm) (mm) (mm) Conclusion In conclusion it has been shown by numerical scans of the phase shift introduced by a 3 rd order miniaturized element frequency selective surface (MEFSS) as a function of its geometrical properties, that the phase response in the various zones composing a composite metamaterial lens can be manipulated to craft the chromatic aberration in a desirable manner, hereby including reverse chromatic aberration. Modeling was performed in the 8-12GHz range, which is of interest for millimeter wave diagnostics in low-field fusion plasmas. Future work will address the extension to higher frequencies, relevant to fusion devices operating at higher magnetic field, as well as to non-fusion applications. Acknowledgments Author WJC wishes to thank Chien Hao Liu and Meng Li for their help with the optimization software, Mark A. Thomas for fruitful discussions and technical assistance and John S. Sarff and Jay K. Anderson for their support. NB is supported by a Young Investigator Program (YIP) Grant from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (Award No. FA ) and by the National Science Foundation (Award No. ECCS ) 8
CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
 43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
Determination of Transmission and Reflection Parameters by Analysis of Square Loop Metasurface
 Determination of Transmission and Reflection Parameters by Analysis of Square Loop Metasurface Anamika Sethi #1, Rajni *2 #Research Scholar, ECE Department, MRSPTU, INDIA *Associate Professor, ECE Department,
Determination of Transmission and Reflection Parameters by Analysis of Square Loop Metasurface Anamika Sethi #1, Rajni *2 #Research Scholar, ECE Department, MRSPTU, INDIA *Associate Professor, ECE Department,
Magnetic Response of Rectangular and Circular Split Ring Resonator: A Research Study
 Magnetic Response of Rectangular and Circular Split Ring Resonator: A Research Study Abhishek Sarkhel Bengal Engineering and Science University Shibpur Sekhar Ranjan Bhadra Chaudhuri Bengal Engineering
Magnetic Response of Rectangular and Circular Split Ring Resonator: A Research Study Abhishek Sarkhel Bengal Engineering and Science University Shibpur Sekhar Ranjan Bhadra Chaudhuri Bengal Engineering
Compact Broadband End-Fire Antenna with Metamaterial Transmission Line
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 73, 37 44, 2018 Compact Broadband End-Fire Antenna with Metamaterial Transmission Line Liang-Yuan Liu * and Jing-Qi Lu Abstract A broadband end-fire
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 73, 37 44, 2018 Compact Broadband End-Fire Antenna with Metamaterial Transmission Line Liang-Yuan Liu * and Jing-Qi Lu Abstract A broadband end-fire
2008 IEEE. Reprinted with permission.
 Pekka Alitalo, Olli Luukkonen, Joni Vehmas, and Sergei A. Tretyakov. 2008. Impedance matched microwave lens. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, volume 7, pages 187 191. 2008 IEEE Reprinted
Pekka Alitalo, Olli Luukkonen, Joni Vehmas, and Sergei A. Tretyakov. 2008. Impedance matched microwave lens. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, volume 7, pages 187 191. 2008 IEEE Reprinted
Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research
 International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 2, March 2016 Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research Bowen Li and Yongsheng Dai Abstract
International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering, Vol. 6, No. 2, March 2016 Subminiature Multi-stage Band-Pass Filter Based on LTCC Technology Research Bowen Li and Yongsheng Dai Abstract
By choosing to view this document, you agree to all provisions of the copyright laws protecting it.
 Pekka Alitalo, Frédéric Bongard, Juan Mosig, and Sergei Tretyakov. 2009. Transmission line lens antenna with embedded source. In: Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Antennas and Propagation
Pekka Alitalo, Frédéric Bongard, Juan Mosig, and Sergei Tretyakov. 2009. Transmission line lens antenna with embedded source. In: Proceedings of the 3rd European Conference on Antennas and Propagation
HARMONIC-SUPPRESSED MINIATURIZED-ELEMENT FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACES WITH HIGHER-ORDER BANDPASS RESPONSES. Seyed Mohamad Amin Momeni Hasan Abadi
 HARMONIC-SUPPRESSED MINIATURIZED-ELEMENT FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACES WITH HIGHER-ORDER BANDPASS RESPONSES by Seyed Mohamad Amin Momeni Hasan Abadi A masters project report submitted in partial fulfillment
HARMONIC-SUPPRESSED MINIATURIZED-ELEMENT FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACES WITH HIGHER-ORDER BANDPASS RESPONSES by Seyed Mohamad Amin Momeni Hasan Abadi A masters project report submitted in partial fulfillment
BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 235 247, 2011 BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS B. Zhou, H. Li, X. Y. Zou, and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 120, 235 247, 2011 BROADBAND AND HIGH-GAIN PLANAR VIVALDI AN- TENNAS BASED ON INHOMOGENEOUS ANISOTROPIC ZERO-INDEX METAMATERIALS B. Zhou, H. Li, X. Y. Zou, and
Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 47 52, 2018 Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application Gobinda Sen * and Santanu Das Abstract A frequency tunable multi-layer
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 47 52, 2018 Frequency Tunable Low-Cost Microwave Absorber for EMI/EMC Application Gobinda Sen * and Santanu Das Abstract A frequency tunable multi-layer
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 A full-parameter unidirectional metamaterial cloak for microwaves Bilinear Transformations Figure 1 Graphical depiction of the bilinear transformation and derived material parameters. (a) The transformation
A full-parameter unidirectional metamaterial cloak for microwaves Bilinear Transformations Figure 1 Graphical depiction of the bilinear transformation and derived material parameters. (a) The transformation
A MINIATURIZED UWB BPF BASED ON NOVEL SCRLH TRANSMISSION LINE STRUCTURE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 19, 67 73, 2010 A MINIATURIZED UWB BPF BASED ON NOVEL SCRLH TRANSMISSION LINE STRUCTURE J.-K. Wang and Y.-J. Zhao College of Information Science and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 19, 67 73, 2010 A MINIATURIZED UWB BPF BASED ON NOVEL SCRLH TRANSMISSION LINE STRUCTURE J.-K. Wang and Y.-J. Zhao College of Information Science and
A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 62, 131 137, 2016 A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation Ayed R. AlAjmi and Mohammad A. Saed * Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 62, 131 137, 2016 A Pin-Loaded Microstrip Patch Antenna with the Ability to Suppress Surface Wave Excitation Ayed R. AlAjmi and Mohammad A. Saed * Abstract
Accurate Models for Spiral Resonators
 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Accurate Models for Spiral Resonators Ellstein, D.; Wang, B.; Teo, K.H. TR1-89 October 1 Abstract Analytically-based circuit models for two
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Accurate Models for Spiral Resonators Ellstein, D.; Wang, B.; Teo, K.H. TR1-89 October 1 Abstract Analytically-based circuit models for two
METAMATERIAL BASED NOVEL DUAL BAND ANTENNA
 METAMATERIAL BASED NOVEL DUAL BAND ANTENNA Er.Maninder Singh 1, Er.Ravinder Kumar 2, Er.Neeraj Kumar Sharma 3 1, 2 & 3 Assistant Professor at Department of ECE, Saint Soldier Institute of Engineering &
METAMATERIAL BASED NOVEL DUAL BAND ANTENNA Er.Maninder Singh 1, Er.Ravinder Kumar 2, Er.Neeraj Kumar Sharma 3 1, 2 & 3 Assistant Professor at Department of ECE, Saint Soldier Institute of Engineering &
Study of Microstrip Antenna Behavior with Metamaterial Substrate of SRR Type Combined with TW
 Study of Microstrip Antenna Behavior with Metamaterial Substrate of SRR Type Combined with TW JOSÉ LUCAS DA SILVA 1, HUMBERTO CÉSAR CHAVES FERNANDES, HUMBERTO DIONÍSIO DE ANDRADE 3 1, Department of Electrical
Study of Microstrip Antenna Behavior with Metamaterial Substrate of SRR Type Combined with TW JOSÉ LUCAS DA SILVA 1, HUMBERTO CÉSAR CHAVES FERNANDES, HUMBERTO DIONÍSIO DE ANDRADE 3 1, Department of Electrical
INDUCTIVE TRI-BAND DOUBLE ELEMENT FSS FOR SPACE APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 18, 87 101, 2011 INDUCTIVE TRI-BAND DOUBLE ELEMENT FSS FOR SPACE APPLICATIONS D. Ramaccia and A. Toscano Department of Applied Electronics University of Rome
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 18, 87 101, 2011 INDUCTIVE TRI-BAND DOUBLE ELEMENT FSS FOR SPACE APPLICATIONS D. Ramaccia and A. Toscano Department of Applied Electronics University of Rome
Design and analysis of T shaped broad band micro strip patch antenna for Ku band application
 International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 5, Issue 2 (February 2016), PP.44-49 Design and analysis of T shaped broad band micro
International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES) ISSN (Online) 2319-183X, (Print) 2319-1821 Volume 5, Issue 2 (February 2016), PP.44-49 Design and analysis of T shaped broad band micro
Bandwidth Enhancement of Microstrip Patch Antenna Using Metamaterials
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 8, Issue 4 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 05-10 Bandwidth Enhancement of Microstrip Patch Antenna
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 8, Issue 4 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 05-10 Bandwidth Enhancement of Microstrip Patch Antenna
Two-dimensional beam steering array using planar eight-element composite right/left-handed leaky-wave antennas
 RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 43,, doi:10.1029/2007rs003800, 2008 Two-dimensional beam steering array using planar eight-element composite right/left-handed leaky-wave antennas Atsushi Sanada 1 Received 4 December
RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 43,, doi:10.1029/2007rs003800, 2008 Two-dimensional beam steering array using planar eight-element composite right/left-handed leaky-wave antennas Atsushi Sanada 1 Received 4 December
An MNG-TL Loop Antenna for UHF Near-Field RFID Applications
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 52, 79 85, 215 An MNG-TL Loop Antenna for UHF Near-Field RFID Applications Hu Liu *, Ying Liu, Ming Wei, and Shuxi Gong Abstract A loop antenna is designed
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 52, 79 85, 215 An MNG-TL Loop Antenna for UHF Near-Field RFID Applications Hu Liu *, Ying Liu, Ming Wei, and Shuxi Gong Abstract A loop antenna is designed
Double Negative Left-Handed Metamaterials for Miniaturization of Rectangular Microstrip Antenna
 J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 2010, 2, 347-351 doi:10.4236/jemaa.2010.26044 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 347 Double Negative Left-Handed Metamaterials for
J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 2010, 2, 347-351 doi:10.4236/jemaa.2010.26044 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 347 Double Negative Left-Handed Metamaterials for
Study on Transmission Characteristic of Split-ring Resonator Defected Ground Structure
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 2, NO. 6, 26 71 Study on Transmission Characteristic of Split-ring Resonator Defected Ground Structure Bian Wu, Bin Li, Tao Su, and Chang-Hong Liang National Key Laboratory of Antennas
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 2, NO. 6, 26 71 Study on Transmission Characteristic of Split-ring Resonator Defected Ground Structure Bian Wu, Bin Li, Tao Su, and Chang-Hong Liang National Key Laboratory of Antennas
The Shaped Coverage Area Antenna for Indoor WLAN Access Points
 The Shaped Coverage Area Antenna for Indoor WLAN Access Points A.BUMRUNGSUK and P. KRACHODNOK School of Telecommunication Engineering, Institute of Engineering Suranaree University of Technology 111 University
The Shaped Coverage Area Antenna for Indoor WLAN Access Points A.BUMRUNGSUK and P. KRACHODNOK School of Telecommunication Engineering, Institute of Engineering Suranaree University of Technology 111 University
A VARACTOR-TUNABLE HIGH IMPEDANCE SURFACE FOR ACTIVE METAMATERIAL ABSORBER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 43, 247 254, 2013 A VARACTOR-TUNABLE HIGH IMPEDANCE SURFACE FOR ACTIVE METAMATERIAL ABSORBER Bao-Qin Lin *, Shao-Hong Zhao, Qiu-Rong Zheng, Meng Zhu, Fan Li,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 43, 247 254, 2013 A VARACTOR-TUNABLE HIGH IMPEDANCE SURFACE FOR ACTIVE METAMATERIAL ABSORBER Bao-Qin Lin *, Shao-Hong Zhao, Qiu-Rong Zheng, Meng Zhu, Fan Li,
Non Invasive Electromagnetic Quality Control System
 ECNDT 2006 - Tu.4.6.2 Non Invasive Electromagnetic Quality Control System Jérôme DREAN, Luc DUCHESNE, SATIMO, Courtaboeuf, France Per NOREN, SATIMO, Gothenburg (Sweden) Abstract. The quality control of
ECNDT 2006 - Tu.4.6.2 Non Invasive Electromagnetic Quality Control System Jérôme DREAN, Luc DUCHESNE, SATIMO, Courtaboeuf, France Per NOREN, SATIMO, Gothenburg (Sweden) Abstract. The quality control of
Estimation of the Loss in the ECH Transmission Lines for ITER
 Estimation of the Loss in the ECH Transmission Lines for ITER S. T. Han, M. A. Shapiro, J. R. Sirigiri, D. Tax, R. J. Temkin and P. P. Woskov MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center, MIT Building NW16-186,
Estimation of the Loss in the ECH Transmission Lines for ITER S. T. Han, M. A. Shapiro, J. R. Sirigiri, D. Tax, R. J. Temkin and P. P. Woskov MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center, MIT Building NW16-186,
PAPER Wide-Band Coaxial-to-Coplanar Transition
 2030 PAPER Wide-Band Coaxial-to-Coplanar Transition Toshihisa KAMEI a),yozoutsumi, Members, NguyenQUOCDINH, and Nguyen THANH, Student Members SUMMARY Targeting the transition from a coaxial wave guide
2030 PAPER Wide-Band Coaxial-to-Coplanar Transition Toshihisa KAMEI a),yozoutsumi, Members, NguyenQUOCDINH, and Nguyen THANH, Student Members SUMMARY Targeting the transition from a coaxial wave guide
Keywords: Array antenna; Metamaterial structure; Microstrip antenna; Split ring resonator
 International Journal of Technology (2016) 4: 683-690 ISSN 2086-9614 IJTech 2016 LEFT-HANDED METAMATERIAL (LHM) STRUCTURE STACKED ON A TWO- ELEMENT MICROSTRIP ANTENNA ARRAY Fitri Yuli Zulkifli 1*, Nugroho
International Journal of Technology (2016) 4: 683-690 ISSN 2086-9614 IJTech 2016 LEFT-HANDED METAMATERIAL (LHM) STRUCTURE STACKED ON A TWO- ELEMENT MICROSTRIP ANTENNA ARRAY Fitri Yuli Zulkifli 1*, Nugroho
Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity
 263 Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity Victor Dmitriev and Marcelo N. Kawakatsu Department of Electrical Engineering, Federal
263 Microwave switchable frequency selective surface with high quality factor resonance and low polarization sensitivity Victor Dmitriev and Marcelo N. Kawakatsu Department of Electrical Engineering, Federal
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 62, 17 22, 2016 A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency Ning Liu 1, *, Xian-Jun Sheng 2, and Jing-Jing Fan
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 62, 17 22, 2016 A Compact Miniaturized Frequency Selective Surface with Stable Resonant Frequency Ning Liu 1, *, Xian-Jun Sheng 2, and Jing-Jing Fan
Research Article Miniaturized Circularly Polarized Microstrip RFID Antenna Using Fractal Metamaterial
 Antennas and Propagation Volume 3, Article ID 7357, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/3/7357 Research Article Miniaturized Circularly Polarized Microstrip RFID Antenna Using Fractal Metamaterial Guo Liu, Liang
Antennas and Propagation Volume 3, Article ID 7357, pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/3/7357 Research Article Miniaturized Circularly Polarized Microstrip RFID Antenna Using Fractal Metamaterial Guo Liu, Liang
DESIGN AND MODELING OF PLANAR LENS ANTENNA ELEMENT IN X-BAND APPLICATIONS
 VOL. 1, NO 19, OCTOBER, 215 ISSN 1819-668 26-215 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. DESIGN AND MODELING OF PLANAR LENS ANTENNA ELEMENT IN X-BAND APPLICATIONS Abdisamad A. Awaleh,
VOL. 1, NO 19, OCTOBER, 215 ISSN 1819-668 26-215 Asian Research Publishing Network (ARPN). All rights reserved. DESIGN AND MODELING OF PLANAR LENS ANTENNA ELEMENT IN X-BAND APPLICATIONS Abdisamad A. Awaleh,
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 28 Sep 2005](/thumbs/91/105523130.jpg) Near-field enhancement and imaging in double cylindrical polariton-resonant structures: Enlarging perfect lens Pekka Alitalo, Stanislav Maslovski, and Sergei Tretyakov arxiv:physics/0509232v1 [physics.optics]
Near-field enhancement and imaging in double cylindrical polariton-resonant structures: Enlarging perfect lens Pekka Alitalo, Stanislav Maslovski, and Sergei Tretyakov arxiv:physics/0509232v1 [physics.optics]
Planar Transmission Line Technologies
 Planar Transmission Line Technologies CMB Polarization Technology Workshop NIST/Boulder Edward J. Wollack Observational Cosmology Laboratory NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, Maryland Overview
Planar Transmission Line Technologies CMB Polarization Technology Workshop NIST/Boulder Edward J. Wollack Observational Cosmology Laboratory NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, Maryland Overview
Chapter 3 Broadside Twin Elements 3.1 Introduction
 Chapter 3 Broadside Twin Elements 3. Introduction The focus of this chapter is on the use of planar, electrically thick grounded substrates for printed antennas. A serious problem with these substrates
Chapter 3 Broadside Twin Elements 3. Introduction The focus of this chapter is on the use of planar, electrically thick grounded substrates for printed antennas. A serious problem with these substrates
A PARAMETRIC STUDY OF TEXTILE ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC CONDUCTOR WITH WIRE DIPOLE AT 2.45GHZ AND 5.8GHZ
 A PARAMETRIC STUDY OF TEXTILE ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC CONDUCTOR WITH WIRE DIPOLE AT 2.45GHZ AND 5.8GHZ Kamilia Kamardin 1, Mohamad Kamal A. Rahim 2, Noor Asmawati Samsuri 2, Mohd Ezwan Jalil 2, Siti Sophiayati
A PARAMETRIC STUDY OF TEXTILE ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC CONDUCTOR WITH WIRE DIPOLE AT 2.45GHZ AND 5.8GHZ Kamilia Kamardin 1, Mohamad Kamal A. Rahim 2, Noor Asmawati Samsuri 2, Mohd Ezwan Jalil 2, Siti Sophiayati
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
A MINIATURIZED LOWPASS/BANDPASS FILTER US- ING DOUBLE ARROW HEAD DEFECTED GROUND STRUCTURE WITH CENTERED ETCHED ELLIPSE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 24, 99 107, 2011 A MINIATURIZED LOWPASS/BANDPASS FILTER US- ING DOUBLE ARROW HEAD DEFECTED GROUND STRUCTURE WITH CENTERED ETCHED ELLIPSE M. H. Al Sharkawy
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 24, 99 107, 2011 A MINIATURIZED LOWPASS/BANDPASS FILTER US- ING DOUBLE ARROW HEAD DEFECTED GROUND STRUCTURE WITH CENTERED ETCHED ELLIPSE M. H. Al Sharkawy
Today I would like to present a short introduction to microstrip cross-coupled filter design. I will be using Sonnet em to analyze my planar circuit.
 Today I would like to present a short introduction to microstrip cross-coupled filter design. I will be using Sonnet em to analyze my planar circuit. And I will be using our optimizer, EQR_OPT_MWO, in
Today I would like to present a short introduction to microstrip cross-coupled filter design. I will be using Sonnet em to analyze my planar circuit. And I will be using our optimizer, EQR_OPT_MWO, in
Omnidirectional planar Antennas for PCS-Band Applications using Fiberglass Substrates.
 18th International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Computers Omnidirectional planar Antennas for PCS-Band Applications using Fiberglass Substrates. Humberto Lobato-Morales 1, Alonso Corona-Chavez
18th International Conference on Electronics, Communications and Computers Omnidirectional planar Antennas for PCS-Band Applications using Fiberglass Substrates. Humberto Lobato-Morales 1, Alonso Corona-Chavez
METAMATERIAL INSPIRED PATCH ANTENNA WITH L-SHAPE SLOT LOADED GROUND PLANE FOR DUAL BAND (WIMAX/WLAN) APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 31, 35 43, 2012 METAMATERIAL INSPIRED PATCH ANTENNA WITH L-SHAPE SLOT LOADED GROUND PLANE FOR DUAL BAND (WIMAX/WLAN) APPLICATIONS J. Malik and M. V.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 31, 35 43, 2012 METAMATERIAL INSPIRED PATCH ANTENNA WITH L-SHAPE SLOT LOADED GROUND PLANE FOR DUAL BAND (WIMAX/WLAN) APPLICATIONS J. Malik and M. V.
A New Hyperthermia Scheme with a Cylindrical LHM Lens
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect APCBEE Procedia 7 (3 ) 3 36 ICBET 3: May 9-, 3, Copenhagen, Denmark A New Hyperthermia Scheme with a Cylindrical LHM Lens Yonghui Tao and Gang Wang
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect APCBEE Procedia 7 (3 ) 3 36 ICBET 3: May 9-, 3, Copenhagen, Denmark A New Hyperthermia Scheme with a Cylindrical LHM Lens Yonghui Tao and Gang Wang
Impedance Modeling for a Unit Cell of the Square Loop Frequency Selective Surface at 2.4 GHz
 Impedance Modeling for a Unit Cell of the Square Loop Frequency Selective Surface at 2.4 GHz M.Z.A. Abd. Aziz #1, M. Md. Shukor #2, B. H. Ahmad #3, M. F. Johar #4, M. F. Abd. Malek* 5 #Center for Telecommunication
Impedance Modeling for a Unit Cell of the Square Loop Frequency Selective Surface at 2.4 GHz M.Z.A. Abd. Aziz #1, M. Md. Shukor #2, B. H. Ahmad #3, M. F. Johar #4, M. F. Abd. Malek* 5 #Center for Telecommunication
Design and Matching of a 60-GHz Printed Antenna
 Application Example Design and Matching of a 60-GHz Printed Antenna Using NI AWR Software and AWR Connected for Optenni Figure 1: Patch antenna performance. Impedance matching of high-frequency components
Application Example Design and Matching of a 60-GHz Printed Antenna Using NI AWR Software and AWR Connected for Optenni Figure 1: Patch antenna performance. Impedance matching of high-frequency components
Efficient Electromagnetic Analysis of Spiral Inductor Patterned Ground Shields
 Efficient Electromagnetic Analysis of Spiral Inductor Patterned Ground Shields James C. Rautio, James D. Merrill, and Michael J. Kobasa Sonnet Software, North Syracuse, NY, 13212, USA Abstract Patterned
Efficient Electromagnetic Analysis of Spiral Inductor Patterned Ground Shields James C. Rautio, James D. Merrill, and Michael J. Kobasa Sonnet Software, North Syracuse, NY, 13212, USA Abstract Patterned
Experimental verification of backward-wave radiation from a negative refractive index metamaterial
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 10 15 NOVEMBER 2002 Experimental verification of backward-wave radiation from a negative refractive index metamaterial Anthony Grbic and George V. Eleftheriades
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 92, NUMBER 10 15 NOVEMBER 2002 Experimental verification of backward-wave radiation from a negative refractive index metamaterial Anthony Grbic and George V. Eleftheriades
Metamaterial Inspired CPW Fed Compact Low-Pass Filter
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 57, 173 180, 2015 Metamaterial Inspired CPW Fed Compact Low-Pass Filter BasilJ.Paul 1, *, Shanta Mridula 1,BinuPaul 1, and Pezholil Mohanan 2 Abstract A metamaterial
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 57, 173 180, 2015 Metamaterial Inspired CPW Fed Compact Low-Pass Filter BasilJ.Paul 1, *, Shanta Mridula 1,BinuPaul 1, and Pezholil Mohanan 2 Abstract A metamaterial
Performance Factors. Technical Assistance. Fundamental Optics
 Performance Factors After paraxial formulas have been used to select values for component focal length(s) and diameter(s), the final step is to select actual lenses. As in any engineering problem, this
Performance Factors After paraxial formulas have been used to select values for component focal length(s) and diameter(s), the final step is to select actual lenses. As in any engineering problem, this
STUDY OF ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC MATERIAL FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS
 International Journal of Advances in Materials Science and Engineering (IJAMSE) Vol., No.,July 3 STUDY OF ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC MATERIAL FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS H. Benosman, N.Boukli Hacene Department
International Journal of Advances in Materials Science and Engineering (IJAMSE) Vol., No.,July 3 STUDY OF ARTIFICIAL MAGNETIC MATERIAL FOR MICROWAVE APPLICATIONS H. Benosman, N.Boukli Hacene Department
THE PROBLEM of electromagnetic interference between
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY, VOL. 50, NO. 2, MAY 2008 399 Estimation of Current Distribution on Multilayer Printed Circuit Board by Near-Field Measurement Qiang Chen, Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY, VOL. 50, NO. 2, MAY 2008 399 Estimation of Current Distribution on Multilayer Printed Circuit Board by Near-Field Measurement Qiang Chen, Member, IEEE,
Design of Low-Index Metamaterial Lens Used for Wideband Circular Polarization Antenna
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 68, 93 98, 2017 Design of Low-Index Metamaterial Lens Used for Wideband Circular Polarization Antenna Yong Wang and Yanlin Zou * Abstract A novel low-index
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 68, 93 98, 2017 Design of Low-Index Metamaterial Lens Used for Wideband Circular Polarization Antenna Yong Wang and Yanlin Zou * Abstract A novel low-index
IMAGE FORMATION. Light source properties. Sensor characteristics Surface. Surface reflectance properties. Optics
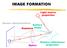 IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
IMAGE FORMATION Light source properties Sensor characteristics Surface Exposure shape Optics Surface reflectance properties ANALOG IMAGES An image can be understood as a 2D light intensity function f(x,y)
Mutual Coupling between Two Patches using Ideal High Impedance Surface
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 4, Number 3 (2011), pp. 287-293 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Mutual Coupling
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. ISSN 0974-2166 Volume 4, Number 3 (2011), pp. 287-293 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Mutual Coupling
ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 14, 113 121, 21 ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS J. Bai, S. Shi, and D. W. Prather
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 14, 113 121, 21 ANALYSIS OF EPSILON-NEAR-ZERO METAMATE- RIAL SUPER-TUNNELING USING CASCADED ULTRA- NARROW WAVEGUIDE CHANNELS J. Bai, S. Shi, and D. W. Prather
Design, Simulation and Fabrication of an Optimized Microstrip Antenna with Metamaterial Superstrate Using Particle Swarm Optimization
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 36, 101 108, 2014 Design, Simulation and Fabrication of an Optimized Microstrip Antenna with Metamaterial Superstrate Using Particle Swarm Optimization Nooshin
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 36, 101 108, 2014 Design, Simulation and Fabrication of an Optimized Microstrip Antenna with Metamaterial Superstrate Using Particle Swarm Optimization Nooshin
A NOVEL MICROSTRIP GRID ARRAY ANTENNA WITH BOTH HIGH-GAIN AND WIDEBAND PROPER- TIES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 34, 215 226, 2013 A NOVEL MICROSTRIP GRID ARRAY ANTENNA WITH BOTH HIGH-GAIN AND WIDEBAND PROPER- TIES P. Feng, X. Chen *, X.-Y. Ren, C.-J. Liu, and K.-M. Huang
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 34, 215 226, 2013 A NOVEL MICROSTRIP GRID ARRAY ANTENNA WITH BOTH HIGH-GAIN AND WIDEBAND PROPER- TIES P. Feng, X. Chen *, X.-Y. Ren, C.-J. Liu, and K.-M. Huang
MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS
 MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS M. Hawley 1, S. Farhat 1, B. Shanker 2, L. Kempel 2 1 Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Michigan State University;
MAGNETO-DIELECTRIC COMPOSITES WITH FREQUENCY SELECTIVE SURFACE LAYERS M. Hawley 1, S. Farhat 1, B. Shanker 2, L. Kempel 2 1 Dept. of Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Michigan State University;
Multiband Microstrip Patch Antenna for Wireless Applications Using Metamaterial
 Multiband Microstrip Patch Antenna for Wireless Applications Using Metamaterial Shalina Garg, Ratish Kumar Abstract A U-slot microstrip patch antenna loaded with metamaterial substrate is presented. The
Multiband Microstrip Patch Antenna for Wireless Applications Using Metamaterial Shalina Garg, Ratish Kumar Abstract A U-slot microstrip patch antenna loaded with metamaterial substrate is presented. The
Waveguides. Metal Waveguides. Dielectric Waveguides
 Waveguides Waveguides, like transmission lines, are structures used to guide electromagnetic waves from point to point. However, the fundamental characteristics of waveguide and transmission line waves
Waveguides Waveguides, like transmission lines, are structures used to guide electromagnetic waves from point to point. However, the fundamental characteristics of waveguide and transmission line waves
Design of Frequency Selective Band Stop Shield Using Analytical Method
 7 Design of Frequency Selective Band Stop Shield Using Analytical Method Mahmoud Fallah, Alireza Ghayekhloo, Ali Abdolali 3-3 Department of Electrical Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology
7 Design of Frequency Selective Band Stop Shield Using Analytical Method Mahmoud Fallah, Alireza Ghayekhloo, Ali Abdolali 3-3 Department of Electrical Engineering, Iran University of Science and Technology
Miniaturization of Branch-Line Coupler Using Composite Right/Left-Handed Transmission Lines with Novel Meander-shaped-slots CSSRR
 66 H. Y. ZENG, G. M. WANG, ET AL., MINIATURIZATION OF BRANCH-LINE COUPLER USING CRLH-TL WITH NOVEL MSSS CSSRR Miniaturization of Branch-Line Coupler Using Composite Right/Left-Handed Transmission Lines
66 H. Y. ZENG, G. M. WANG, ET AL., MINIATURIZATION OF BRANCH-LINE COUPLER USING CRLH-TL WITH NOVEL MSSS CSSRR Miniaturization of Branch-Line Coupler Using Composite Right/Left-Handed Transmission Lines
arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 6 Feb 2008
![arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 6 Feb 2008 arxiv: v1 [physics.optics] 6 Feb 2008](/thumbs/91/105523139.jpg) Impedance-matched microwave lens Pekka Alitalo, Olli Luukkonen, Joni Vehmas, Sergei A. Tretyakov Department of Radio Science and Engineering SMARAD Center of Excellence arxiv:0802.0782v1 [physics.optics]
Impedance-matched microwave lens Pekka Alitalo, Olli Luukkonen, Joni Vehmas, Sergei A. Tretyakov Department of Radio Science and Engineering SMARAD Center of Excellence arxiv:0802.0782v1 [physics.optics]
Enhanced Couplings in Broadband Planar Filters with Defected Ground Structures
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 199 212 Enhanced Couplings in Broadband Planar Filters with Defected Ground Structures N. MILITARU 1, M.G. BANCIU 2, G.
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 199 212 Enhanced Couplings in Broadband Planar Filters with Defected Ground Structures N. MILITARU 1, M.G. BANCIU 2, G.
Chalmers Publication Library
 Chalmers Publication Library Numerical studies of bandwidth of parallel-plate cut-off realised by a bed of nails, corrugations and mushroom-type electromagnetic bandgap for use in gap waveguides This document
Chalmers Publication Library Numerical studies of bandwidth of parallel-plate cut-off realised by a bed of nails, corrugations and mushroom-type electromagnetic bandgap for use in gap waveguides This document
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Microwave Metamaterial Antennas and Other Applications
 Forum for Electromagnetic Research Methods and Application Technologies (FERMAT) Microwave Metamaterial Antennas and Other Applications Tie Jun Cui and Hui Feng Ma State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves
Forum for Electromagnetic Research Methods and Application Technologies (FERMAT) Microwave Metamaterial Antennas and Other Applications Tie Jun Cui and Hui Feng Ma State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves
Reflectarray Antennas
 Reflectarray Antennas International Journal of Computer Applications (0975 8887) Kshitij Lele P.G. Student, Department of EXTC DJ Sanghvi College of Engineering Ami A. Desai P.G. Student Department of
Reflectarray Antennas International Journal of Computer Applications (0975 8887) Kshitij Lele P.G. Student, Department of EXTC DJ Sanghvi College of Engineering Ami A. Desai P.G. Student Department of
SMALL SEMI-CIRCLE-LIKE SLOT ANTENNA FOR ULTRA-WIDEBAND APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 13, 149 158, 2010 SMALL SEMI-CIRCLE-LIKE SLOT ANTENNA FOR ULTRA-WIDEBAND APPLICATIONS F. Amini and M. N. Azarmanesh Microelectronics Research Laboratory Urmia
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 13, 149 158, 2010 SMALL SEMI-CIRCLE-LIKE SLOT ANTENNA FOR ULTRA-WIDEBAND APPLICATIONS F. Amini and M. N. Azarmanesh Microelectronics Research Laboratory Urmia
Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays
 Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays Mr. F. Benikhlef 1 and Mr. N. Boukli-Hacen 2 1 Research Scholar, telecommunication,
Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays Mr. F. Benikhlef 1 and Mr. N. Boukli-Hacen 2 1 Research Scholar, telecommunication,
WIRELESS power transfer through coupled antennas
 3442 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 58, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2010 Fundamental Aspects of Near-Field Coupling Small Antennas for Wireless Power Transfer Jaechun Lee, Member, IEEE, and Sangwook
3442 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 58, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2010 Fundamental Aspects of Near-Field Coupling Small Antennas for Wireless Power Transfer Jaechun Lee, Member, IEEE, and Sangwook
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF DUAL BAND HIGH DIRECTIVITY EBG RESONATOR ANTENNA USING SQUARE LOOP FSS AS SUPERSTRATE LAYER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 70, 1 20, 2007 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF DUAL BAND HIGH DIRECTIVITY EBG RESONATOR ANTENNA USING SQUARE LOOP FSS AS SUPERSTRATE LAYER A. Pirhadi Department of Electrical
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 70, 1 20, 2007 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF DUAL BAND HIGH DIRECTIVITY EBG RESONATOR ANTENNA USING SQUARE LOOP FSS AS SUPERSTRATE LAYER A. Pirhadi Department of Electrical
NOVEL PLANAR MULTIMODE BANDPASS FILTERS WITH RADIAL-LINE STUBS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, 33 42, 2010 NOVEL PLANAR MULTIMODE BANDPASS FILTERS WITH RADIAL-LINE STUBS L. Zhang, Z.-Y. Yu, and S.-G. Mo Institute of Applied Physics University of Electronic
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 101, 33 42, 2010 NOVEL PLANAR MULTIMODE BANDPASS FILTERS WITH RADIAL-LINE STUBS L. Zhang, Z.-Y. Yu, and S.-G. Mo Institute of Applied Physics University of Electronic
Broadband and High Efficiency Single-Layer Reflectarray Using Circular Ring Attached Two Sets of Phase-Delay Lines
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 66, 193 202, 2018 Broadband and High Efficiency Single-Layer Reflectarray Using Circular Ring Attached Two Sets of Phase-Delay Lines Fei Xue 1, *, Hongjian
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 66, 193 202, 2018 Broadband and High Efficiency Single-Layer Reflectarray Using Circular Ring Attached Two Sets of Phase-Delay Lines Fei Xue 1, *, Hongjian
Mathematical Model for Progressive Phase Distribution of Ku-band Reflectarray Antennas
 Mathematical Model for Progressive Phase Distribution of Ku-band Reflectarray Antennas M. Y. Ismail, M. Inam, A.. M. Zain, N. Misran Abstract Progressive phase distribution is an important consideration
Mathematical Model for Progressive Phase Distribution of Ku-band Reflectarray Antennas M. Y. Ismail, M. Inam, A.. M. Zain, N. Misran Abstract Progressive phase distribution is an important consideration
GPS Patch Antenna Loaded with Fractal EBG Structure Using Organic Magnetic Substrate
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 58, 23 28, 2016 GPS Patch Antenna Loaded with Fractal EBG Structure Using Organic Magnetic Substrate Encheng Wang * and Qiuping Liu Abstract In this
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 58, 23 28, 2016 GPS Patch Antenna Loaded with Fractal EBG Structure Using Organic Magnetic Substrate Encheng Wang * and Qiuping Liu Abstract In this
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 4: Antenna Types
 Antennas and Propagation : Antenna Types 4.4 Aperture Antennas High microwave frequencies Thin wires and dielectrics cause loss Coaxial lines: may have 10dB per meter Waveguides often used instead Aperture
Antennas and Propagation : Antenna Types 4.4 Aperture Antennas High microwave frequencies Thin wires and dielectrics cause loss Coaxial lines: may have 10dB per meter Waveguides often used instead Aperture
RF Board Design for Next Generation Wireless Systems
 RF Board Design for Next Generation Wireless Systems Page 1 Introduction Purpose: Provide basic background on emerging WiMax standard Introduce a new tool for Genesys that will aide in the design and verification
RF Board Design for Next Generation Wireless Systems Page 1 Introduction Purpose: Provide basic background on emerging WiMax standard Introduce a new tool for Genesys that will aide in the design and verification
Application of Metamaterials for the Microwave Antenna Realisations*
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 9, No. 1, February 01, 1-7 UDK: 61.396.67:66.017 DOI: 10.98/SJEE101001A Application of Metamaterials for the Microwave Antenna Realisations* Tatjana Asenov
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 9, No. 1, February 01, 1-7 UDK: 61.396.67:66.017 DOI: 10.98/SJEE101001A Application of Metamaterials for the Microwave Antenna Realisations* Tatjana Asenov
Proximity fed gap-coupled half E-shaped microstrip antenna array
 Sādhanā Vol. 40, Part 1, February 2015, pp. 75 87. c Indian Academy of Sciences Proximity fed gap-coupled half E-shaped microstrip antenna array AMIT A DESHMUKH 1, and K P RAY 2 1 Department of Electronics
Sādhanā Vol. 40, Part 1, February 2015, pp. 75 87. c Indian Academy of Sciences Proximity fed gap-coupled half E-shaped microstrip antenna array AMIT A DESHMUKH 1, and K P RAY 2 1 Department of Electronics
Design Fundamentals by A. Ciccomancini Scogna, PhD Suppression of Simultaneous Switching Noise in Power and Ground Plane Pairs
 Design Fundamentals by A. Ciccomancini Scogna, PhD Suppression of Simultaneous Switching Noise in Power and Ground Plane Pairs Photographer: Janpietruszka Agency: Dreamstime.com 36 Conformity JUNE 2007
Design Fundamentals by A. Ciccomancini Scogna, PhD Suppression of Simultaneous Switching Noise in Power and Ground Plane Pairs Photographer: Janpietruszka Agency: Dreamstime.com 36 Conformity JUNE 2007
Design, Trade-Off and Advantages of a Reconfigurable Dual Reflector for Ku Band Applications
 Design, Trade-Off and Advantages of a Reconfigurable Dual Reflector for Ku Band Applications Cecilia Cappellin, Knud Pontoppidan TICRA Læderstræde 34 1201 Copenhagen Denmark Email:cc@ticra.com, kp@ticra.com
Design, Trade-Off and Advantages of a Reconfigurable Dual Reflector for Ku Band Applications Cecilia Cappellin, Knud Pontoppidan TICRA Læderstræde 34 1201 Copenhagen Denmark Email:cc@ticra.com, kp@ticra.com
Broadband and Gain Enhanced Bowtie Antenna with AMC Ground
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 61, 25 30, 2016 Broadband and Gain Enhanced Bowtie Antenna with AMC Ground Xue-Yan Song *, Chuang Yang, Tian-Ling Zhang, Ze-Hong Yan, and Rui-Na Lian
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 61, 25 30, 2016 Broadband and Gain Enhanced Bowtie Antenna with AMC Ground Xue-Yan Song *, Chuang Yang, Tian-Ling Zhang, Ze-Hong Yan, and Rui-Na Lian
A COMPACT MULTIBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA FOR WLAN/WIMAX APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 23, 147 155, 2011 A COMPACT MULTIBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA FOR WLAN/WIMAX APPLICATIONS Z.-N. Song, Y. Ding, and K. Huang National Key Laboratory of Antennas
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 23, 147 155, 2011 A COMPACT MULTIBAND MONOPOLE ANTENNA FOR WLAN/WIMAX APPLICATIONS Z.-N. Song, Y. Ding, and K. Huang National Key Laboratory of Antennas
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 12, , 2010
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 12, 23 213, 21 MICROSTRIP ARRAY ANTENNA WITH NEW 2D-EECTROMAGNETIC BAND GAP STRUCTURE SHAPES TO REDUCE HARMONICS AND MUTUA COUPING D. N. Elsheakh and M. F.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 12, 23 213, 21 MICROSTRIP ARRAY ANTENNA WITH NEW 2D-EECTROMAGNETIC BAND GAP STRUCTURE SHAPES TO REDUCE HARMONICS AND MUTUA COUPING D. N. Elsheakh and M. F.
Software for Electron and Ion Beam Column Design. An integrated workplace for simulating and optimizing electron and ion beam columns
 OPTICS Software for Electron and Ion Beam Column Design An integrated workplace for simulating and optimizing electron and ion beam columns Base Package (OPTICS) Field computation Imaging and paraxial
OPTICS Software for Electron and Ion Beam Column Design An integrated workplace for simulating and optimizing electron and ion beam columns Base Package (OPTICS) Field computation Imaging and paraxial
Compact UWB antenna with dual band-notches for WLAN and WiMAX applications
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.10, No.17, 1 6 Compact UWB antenna with dual band-notches for WLAN and WiMAX applications Hao Liu a), Ziqiang Xu, Bo Wu, and Jiaxuan Liao Research Institute of Electronic
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.10, No.17, 1 6 Compact UWB antenna with dual band-notches for WLAN and WiMAX applications Hao Liu a), Ziqiang Xu, Bo Wu, and Jiaxuan Liao Research Institute of Electronic
Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using BST
 Integrated Ferroelectrics, 56: 1087 1095, 2003 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580390259623 Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using
Integrated Ferroelectrics, 56: 1087 1095, 2003 Copyright C Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1058-4587 print/ 1607-8489 online DOI: 10.1080/10584580390259623 Compact Distributed Phase Shifters at X-Band Using
High Gain and Wideband Stacked Patch Antenna for S-Band Applications
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 76, 97 104, 2018 High Gain and Wideband Stacked Patch Antenna for S-Band Applications Ali Khaleghi 1, 2, 3, *, Seyed S. Ahranjan 3, and Ilangko Balasingham
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 76, 97 104, 2018 High Gain and Wideband Stacked Patch Antenna for S-Band Applications Ali Khaleghi 1, 2, 3, *, Seyed S. Ahranjan 3, and Ilangko Balasingham
Radiation Analysis of Phased Antenna Arrays with Differentially Feeding Networks towards Better Directivity
 Radiation Analysis of Phased Antenna Arrays with Differentially Feeding Networks towards Better Directivity Manohar R 1, Sophiya Susan S 2 1 PG Student, Department of Telecommunication Engineering, CMR
Radiation Analysis of Phased Antenna Arrays with Differentially Feeding Networks towards Better Directivity Manohar R 1, Sophiya Susan S 2 1 PG Student, Department of Telecommunication Engineering, CMR
Antenna Gain Enhancement and Beamshaping using a Diffractive Optical Element (DOE) Lens
 Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 214 Antenna Gain Enhancement and Beamshaping using a Diffractive Optical Element (DOE) Lens Christopher Torbitt
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses Thesis/Dissertation Collections 214 Antenna Gain Enhancement and Beamshaping using a Diffractive Optical Element (DOE) Lens Christopher Torbitt
Mutual Coupling Reduction of Micro strip antenna array by using the Electromagnetic Band Gap structures
 Mutual Coupling Reduction of Micro strip antenna array by using the Electromagnetic Band Gap structures A.Rajasekhar 1, K.Vara prasad 2 1M.tech student, Dept. of electronics and communication engineering,
Mutual Coupling Reduction of Micro strip antenna array by using the Electromagnetic Band Gap structures A.Rajasekhar 1, K.Vara prasad 2 1M.tech student, Dept. of electronics and communication engineering,
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Planar Circularly Symmetric Electromagnetic Band- Gap Antennas for Low Cost High Performance Integrated Antennas
 Planar Circularly Symmetric Electromagnetic Band- Gap Antennas for Low Cost High Performance Integrated Antennas A. Neto #1, N. LLombart o1, G. Gerini #2, P.J. de Maagt *1, # TNO Defense and Security,
Planar Circularly Symmetric Electromagnetic Band- Gap Antennas for Low Cost High Performance Integrated Antennas A. Neto #1, N. LLombart o1, G. Gerini #2, P.J. de Maagt *1, # TNO Defense and Security,
MITER BEND MIRROR DESIGN FOR CORRUGATED WAVEGUIDES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol., 57 6, 9 MITER BED MIRROR DESIG FOR CORRUGATED WAVEGUIDES S. Liao Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison 45 Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol., 57 6, 9 MITER BED MIRROR DESIG FOR CORRUGATED WAVEGUIDES S. Liao Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison 45 Engineering
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES
 ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BYAENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2017 May 11(7):pages 52-56 Open Access Journal Design and Modeling of
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BYAENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2017 May 11(7):pages 52-56 Open Access Journal Design and Modeling of
Efficient Metasurface Rectenna for Electromagnetic Wireless Power Transfer and Energy Harvesting
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 161, 35 40, 2018 Efficient Metasurface Rectenna for Electromagnetic Wireless Power Transfer and Energy Harvesting Mohamed El Badawe and Omar M. Ramahi * Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 161, 35 40, 2018 Efficient Metasurface Rectenna for Electromagnetic Wireless Power Transfer and Energy Harvesting Mohamed El Badawe and Omar M. Ramahi * Abstract
Design of Substrate-Integrated Waveguide Slot Antenna with AZIM Coating
 Design of Substrate-Integrated Waveguide Slot Antenna with Coating Pomal Dhara Anantray 1, Prof. Satish Ramdasji Bhoyar 2 1 Student, Electronics and Telecommunication, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology,
Design of Substrate-Integrated Waveguide Slot Antenna with Coating Pomal Dhara Anantray 1, Prof. Satish Ramdasji Bhoyar 2 1 Student, Electronics and Telecommunication, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology,
Postwall waveguide slot array with cosecant radiation pattern and null filling for base station antennas in local multidistributed systems
 RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 2, 8009, doi:10.1029/2001rs002580, 2003 Postwall waveguide slot array with cosecant radiation pattern and null filling for base station antennas in local multidistributed systems
RADIO SCIENCE, VOL. 38, NO. 2, 8009, doi:10.1029/2001rs002580, 2003 Postwall waveguide slot array with cosecant radiation pattern and null filling for base station antennas in local multidistributed systems
