What is a Lane? serial link lane parallel link
|
|
|
- Austen Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PCI Express This lecture is based on the Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, which is a standard for computer expansion cards. More specifically, this is a standard for the communication link by which a PCIe device communicates with the CPU. According to Wikipedia, PCIe 3.0 (August 2007) is the latest standard. The PCIe standard is an outgrowth of the original PCI standard, but is not compatible with PCI at the hardware level. The PCIe standard is based on a new protocol for electrical signaling. This protocol is built on the concept of a lane, which we must define. Here are some capacity quotes from Wikipedia Per Lane 16 Lane Slot Version MB/s 4 GB/s Version MB/s 8 GB/s Version 3 1 GB/s 16 GB/s
2 What is a Lane? A lane is pair of point to point serial links. It is a full duplex link, able to communicate in two directions simultaneously. Each of the serial links in the pair handles one of the two directions. By definition, a serial link transmits one bit at a time. By extension, a lane may transmit two bits at any one time, one bit in each direction. One may view a parallel link, transmitting multiple bits in one direction at any given time, as a collection of serial links. The only difference is that a parallel link must provide for synchronization of the bits sent by the individual links.
3 Data Transmission Codes The PCIe standard is byte oriented, in that it should be viewed logically as a full duplex byte stream. What is actually transmitted? The association of bits (transmitted or received) with bytes is handled at the Data Link layer. Suppose a byte is to be transmitted serially. The conversion from byte data to bit oriented data for serial transmission is done by a shift register. The register takes in eight bits at a time and shifts out one bit at a time. The bits, as shifted out, are still represented in standard logic levels. The serial transmit unit takes the standard logic levels as input, and converts them to voltage levels appropriate for serial transmission.
4 Three Possible Transmission Codes The serial transmit unit sends data by asserting a voltage on the serial link. On simple method would be as follows. To transmit a logic 1, assert +5 volts on the transmission line. To transmit a logic 0, assert 0 volts on the transmission line. This simple method has so many difficulties in practice that it cannot be used. Two of the most obvious are transmission of power and lack of data framing. Standard methods for link management use codes that avoid these problems. Two of the more common methods used are NRZ and NRZI. Non Return to Zero coding transmits by asserting the following voltages: For a logic 1, it asserts a positive voltage ( volts) on the link. For a logic 0, it asserts a negative voltage ( 3.0 to 5.0 volts). Non Return to Zero Invert is a modification of NRZ, using the same voltage levels.
5 The Problem of Noise One problem with these serial links is that they function as antennas. They will pick up any stray electromagnetic radiation if in the radio range. In other words, the signal received at the destination might not be what was actually transmitted. It might be the original signal, corrupted by noise. The solution to the problem of noise is based on the observation that two links placed in close proximity will receive noise signals that are almost identical. To make use of this observation, we use differential transmitters to send the signals and differential receivers to reconstruct the signals.
6 Differential Transmitters and Receivers In differential transmission, rather than asserting a voltage on a single output line, the transmitter asserts two voltages: +V/2 and V/2. A +6 volt signal would be asserted as two: +3 volts and 3 volts. A 8 volt signal would be asserted as two: 4 volts and +4 volts. Here is a standard diagram of a differential transmitter. The standard differential receiver is an analog subtractor.
7 For a 6 volt transmitted signal, we have A = 3, B = 3; A B = 3 ( 3) = 6.
8 Noise in a Differential Link We now assume that the lines used to transmit the differential signals are physically close together, so that each line is subject to the same noise signal. Here the received signal is the difference of the two voltages input to the differential receiver. The value received is V/2 ( V/2) = V, the desired value.
9 Ground Offsets in Standard Links All voltages are measured relative to a standard value, called ground. Here is the complete version of the simple circuit that we want to implement. Basically, there is an assumed second connection between the two devices. This second connection fixes the zero level for the voltage. There is no necessity for the two devices to have the same ground. Suppose that the ground for the receiver is offset from the ground of the transmitter.
10 The signal sent out as +V(t) will be received as V(t) V O.
11 Ground Offsets in Differential Links Here again, the subtractor in the differential receiver handles this problem. The signal originates as a given voltage, which can be positive, negative, or 0. The signal is transmitted as the pair (+V/2, V/2). Due to the ground offset for the receiver, the signal is taken in as (+V/2 V O, V/2 V O ). The signal is interpreted as (+V/2 V O ) ( V/2 V O ) = +V/2 V O + V/2 + V O = V. The differential link will correct for both ground offset and line noise at the same time.
12 References 1. Wikipedia 2. Wikipedia 3. Web Site 4. Wikipedia
EECE494: Computer Bus and SoC Interfacing. Serial Communication: RS-232. Dr. Charles Kim Electrical and Computer Engineering Howard University
 EECE494: Computer Bus and SoC Interfacing Serial Communication: RS-232 Dr. Charles Kim Electrical and Computer Engineering Howard University Spring 2014 1 Many types of wires/pins in the communication
EECE494: Computer Bus and SoC Interfacing Serial Communication: RS-232 Dr. Charles Kim Electrical and Computer Engineering Howard University Spring 2014 1 Many types of wires/pins in the communication
Data Communications Computer Eng. 3 rd class course Lecturer : Hamid Mousa
 University Of Technology Control & Systems Dept. Computer Eng. Lecture No. 1 Lecturer: Hamid Mousa Data Communications Computer Eng. 3 rd class course Lecturer : Hamid Mousa Course Reference Data Communications
University Of Technology Control & Systems Dept. Computer Eng. Lecture No. 1 Lecturer: Hamid Mousa Data Communications Computer Eng. 3 rd class course Lecturer : Hamid Mousa Course Reference Data Communications
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT.1302 *
 Rec. ITU-R BT.1302 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT.1302 * Interfaces for digital component video signals in 525-line and 625-line television systems operating at the 4:2:2 level of Recommendation ITU-R BT.601
Rec. ITU-R BT.1302 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT.1302 * Interfaces for digital component video signals in 525-line and 625-line television systems operating at the 4:2:2 level of Recommendation ITU-R BT.601
EECS 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Encoding and Framing. Questions
 EECS 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Encoding and Framing Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720-1776
EECS 122: Introduction to Computer Networks Encoding and Framing Computer Science Division Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Berkeley, CA 94720-1776
Module 3: Physical Layer
 Module 3: Physical Layer Dr. Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 Phone: 601-979-3661 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu 1 Topics 3.1 Signal Levels: Baud
Module 3: Physical Layer Dr. Associate Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 Phone: 601-979-3661 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu 1 Topics 3.1 Signal Levels: Baud
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT *
 Rec. ITU-R BT.656-4 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT.656-4 * Interfaces for digital component video signals in 525-line and 625-line television systems operating at the 4:2:2 level of Recommendation ITU-R BT.601
Rec. ITU-R BT.656-4 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT.656-4 * Interfaces for digital component video signals in 525-line and 625-line television systems operating at the 4:2:2 level of Recommendation ITU-R BT.601
Hello and welcome to today s lecture. In the last couple of lectures we have discussed about various transmission media.
 Data Communication Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No # 7 Transmission of Digital Signal-I Hello and welcome to today s lecture.
Data Communication Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No # 7 Transmission of Digital Signal-I Hello and welcome to today s lecture.
Encoding and Framing
 Encoding and Framing EECS 489 Computer Networks http://www.eecs.umich.edu/~zmao/eecs489 Z. Morley Mao Tuesday Nov 2, 2004 Acknowledgement: Some slides taken from Kurose&Ross and Katz&Stoica 1 Questions
Encoding and Framing EECS 489 Computer Networks http://www.eecs.umich.edu/~zmao/eecs489 Z. Morley Mao Tuesday Nov 2, 2004 Acknowledgement: Some slides taken from Kurose&Ross and Katz&Stoica 1 Questions
Encoding and Framing. Questions. Signals: Analog vs. Digital. Signals: Periodic vs. Aperiodic. Attenuation. Data vs. Signal
 Questions Encoding and Framing Why are some links faster than others? What limits the amount of information we can send on a link? How can we increase the capacity of a link? EECS 489 Computer Networks
Questions Encoding and Framing Why are some links faster than others? What limits the amount of information we can send on a link? How can we increase the capacity of a link? EECS 489 Computer Networks
CS601-Data Communication Latest Solved Mcqs from Midterm Papers
 CS601-Data Communication Latest Solved Mcqs from Midterm Papers May 07,2011 Lectures 1-22 Moaaz Siddiq Latest Mcqs MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Effective
CS601-Data Communication Latest Solved Mcqs from Midterm Papers May 07,2011 Lectures 1-22 Moaaz Siddiq Latest Mcqs MIDTERM EXAMINATION Spring 2010 Question No: 1 ( Marks: 1 ) - Please choose one Effective
CSCI-1680 Physical Layer Rodrigo Fonseca
 CSCI-1680 Physical Layer Rodrigo Fonseca Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazières, Phil Levis, John Janno< Administrivia Signup for Snowcast milestone Make sure you signed up Make sure you are on
CSCI-1680 Physical Layer Rodrigo Fonseca Based partly on lecture notes by David Mazières, Phil Levis, John Janno< Administrivia Signup for Snowcast milestone Make sure you signed up Make sure you are on
Lecture-8 Transmission of Signals
 Lecture-8 Transmission of Signals The signals are transmitted as electromagnetic waveforms. As the signal may be analog or digital, there four case of signal transmission. Analog data Analog Signal:- The
Lecture-8 Transmission of Signals The signals are transmitted as electromagnetic waveforms. As the signal may be analog or digital, there four case of signal transmission. Analog data Analog Signal:- The
2.0 Discussion: 2.1 Approach:
 2.0 Discussion: 2.1 Approach: The design for a Power Monitor and Data Logging System is comprised of two major components: the Power Meter and the Data Logger. The Power Meter is the package that plugs
2.0 Discussion: 2.1 Approach: The design for a Power Monitor and Data Logging System is comprised of two major components: the Power Meter and the Data Logger. The Power Meter is the package that plugs
In this lecture, we will look at how different electronic modules communicate with each other. We will consider the following topics:
 In this lecture, we will look at how different electronic modules communicate with each other. We will consider the following topics: Links between Digital and Analogue Serial vs Parallel links Flow control
In this lecture, we will look at how different electronic modules communicate with each other. We will consider the following topics: Links between Digital and Analogue Serial vs Parallel links Flow control
Datacommunication I. Layers of the OSI-model. Lecture 3. signal encoding, error detection/correction
 Datacommunication I Lecture 3 signal encoding, error detection/correction Layers of the OSI-model repetition 1 The OSI-model and its networking devices repetition The OSI-model and its networking devices
Datacommunication I Lecture 3 signal encoding, error detection/correction Layers of the OSI-model repetition 1 The OSI-model and its networking devices repetition The OSI-model and its networking devices
6. has units of bits/second. a. Throughput b. Propagation speed c. Propagation time d. (b)or(c)
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Information Technology Department First Semester 1436/1437 IT224: Networks 1 Sheet# 10 (chapter 3-4-5) Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Before
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Information Technology Department First Semester 1436/1437 IT224: Networks 1 Sheet# 10 (chapter 3-4-5) Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Before
Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection
 Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection Aim: overview of existing methods and techniques Terms used: -Data entities conveying meaning (of information) -Signals data
Lecture 3 Concepts for the Data Communications and Computer Interconnection Aim: overview of existing methods and techniques Terms used: -Data entities conveying meaning (of information) -Signals data
9.4. Synchronization:
 9.4. Synchronization: It is the process of timing the serial transmission to properly identify the data being sent. There are two most common modes: Synchronous transmission: Synchronous transmission relies
9.4. Synchronization: It is the process of timing the serial transmission to properly identify the data being sent. There are two most common modes: Synchronous transmission: Synchronous transmission relies
BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security, BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering. Cohorts: BCNS/17A/FT & BEE/16B/FT
 BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security, BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering Cohorts: BCNS/17A/FT & BEE/16B/FT Examinations for 2016-2017 Semester 2 & 2017 Semester 1 Resit Examinations for BEE/12/FT
BSc (Hons) Computer Science with Network Security, BEng (Hons) Electronic Engineering Cohorts: BCNS/17A/FT & BEE/16B/FT Examinations for 2016-2017 Semester 2 & 2017 Semester 1 Resit Examinations for BEE/12/FT
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering Dept
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering Dept COE 342 Data and Computer Communications Term 021 Dr. Ashraf S. Hasan Mahmoud Rm 22-144 Ext. 1724 Email: ashraf@ccse.kfupm.edu.sa
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Computer Engineering Dept COE 342 Data and Computer Communications Term 021 Dr. Ashraf S. Hasan Mahmoud Rm 22-144 Ext. 1724 Email: ashraf@ccse.kfupm.edu.sa
CS601 Data Communication Solved Objective For Midterm Exam Preparation
 CS601 Data Communication Solved Objective For Midterm Exam Preparation Question No: 1 Effective network mean that the network has fast delivery, timeliness and high bandwidth duplex transmission accurate
CS601 Data Communication Solved Objective For Midterm Exam Preparation Question No: 1 Effective network mean that the network has fast delivery, timeliness and high bandwidth duplex transmission accurate
CHAPTER 10: DIGITAL INSTRUMENTATION PRINCIPLES
 I. Why digital? CHAPTER 10: DIGITAL INSTRUMENTATION PRINCIPLES Almost all the transducers we have considered so far have had an analog output, that is, the output is a different form from the input but
I. Why digital? CHAPTER 10: DIGITAL INSTRUMENTATION PRINCIPLES Almost all the transducers we have considered so far have had an analog output, that is, the output is a different form from the input but
Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Data and Signals
 Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Data and Signals TRUE/FALSE 1. The terms data and signal mean the same thing. F PTS: 1 REF: 30 2. By convention, the minimum and maximum values of analog data and signals are
Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Data and Signals TRUE/FALSE 1. The terms data and signal mean the same thing. F PTS: 1 REF: 30 2. By convention, the minimum and maximum values of analog data and signals are
Source Coding and Pre-emphasis for Double-Edged Pulse width Modulation Serial Communication
 Source Coding and Pre-emphasis for Double-Edged Pulse width Modulation Serial Communication Abstract: Double-edged pulse width modulation (DPWM) is less sensitive to frequency-dependent losses in electrical
Source Coding and Pre-emphasis for Double-Edged Pulse width Modulation Serial Communication Abstract: Double-edged pulse width modulation (DPWM) is less sensitive to frequency-dependent losses in electrical
Castle Creations, INC.
 Castle Link Live Communication Protocol Castle Creations, INC. 6-Feb-2012 Version 2.0 Subject to change at any time without notice or warning. Castle Link Live Communication Protocol - Page 1 1) Standard
Castle Link Live Communication Protocol Castle Creations, INC. 6-Feb-2012 Version 2.0 Subject to change at any time without notice or warning. Castle Link Live Communication Protocol - Page 1 1) Standard
Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks))
 Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks)) Lesson 5... SIGNAL ENCODING TECHNIQUES Abstract Both analog and digital information can be encoded as either analog or digital signals. The particular encoding
Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks)) Lesson 5... SIGNAL ENCODING TECHNIQUES Abstract Both analog and digital information can be encoded as either analog or digital signals. The particular encoding
Week 2 Lecture 1. Introduction to Communication Networks. Review: Analog and digital communications
 Week 2 Lecture 1 Introduction to Communication Networks Review: Analog and digital communications Topic: Internet Trend, Protocol, Transmission Principle Digital Communications is the foundation of Internet
Week 2 Lecture 1 Introduction to Communication Networks Review: Analog and digital communications Topic: Internet Trend, Protocol, Transmission Principle Digital Communications is the foundation of Internet
Electrical signal types
 Electrical signal types With BogusBus, our signals were very simple and straightforward: each signal wire (1 through 5) carried a single bit of digital data, 0 Volts representing "off" and 24 Volts DC
Electrical signal types With BogusBus, our signals were very simple and straightforward: each signal wire (1 through 5) carried a single bit of digital data, 0 Volts representing "off" and 24 Volts DC
Published by: PIONEER RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT GROUP ( 1
 Biomimetic Based Interactive Master Slave Robots T.Anushalalitha 1, Anupa.N 2, Jahnavi.B 3, Keerthana.K 4, Shridevi.S.C 5 Dept. of Telecommunication, BMSCE Bangalore, India. Abstract The system involves
Biomimetic Based Interactive Master Slave Robots T.Anushalalitha 1, Anupa.N 2, Jahnavi.B 3, Keerthana.K 4, Shridevi.S.C 5 Dept. of Telecommunication, BMSCE Bangalore, India. Abstract The system involves
Applications. Operating Modes. Description. Part Number Description Package. Many to one. One to one Broadcast One to many
 RXQ2 - XXX GFSK MULTICHANNEL RADIO TRANSCEIVER Intelligent modem Transceiver Data Rates to 100 kbps Selectable Narrowband Channels Crystal controlled design Supply Voltage 3.3V Serial Data Interface with
RXQ2 - XXX GFSK MULTICHANNEL RADIO TRANSCEIVER Intelligent modem Transceiver Data Rates to 100 kbps Selectable Narrowband Channels Crystal controlled design Supply Voltage 3.3V Serial Data Interface with
Data transmission - Transmission modes
 Data transmission - Transmission modes Transmission modes A given transmission on a communications channel between two machines can occur in several different ways. The transmission is characterised by:
Data transmission - Transmission modes Transmission modes A given transmission on a communications channel between two machines can occur in several different ways. The transmission is characterised by:
Basic Communications Theory Chapter 2
 TEMPEST Engineering and Hardware Design Dr. Bruce C. Gabrielson, NCE 1998 Basic Communications Theory Chapter 2 Communicating Information Communications occurs when information is transmitted or sent between
TEMPEST Engineering and Hardware Design Dr. Bruce C. Gabrielson, NCE 1998 Basic Communications Theory Chapter 2 Communicating Information Communications occurs when information is transmitted or sent between
SEN366 Computer Networks
 SEN366 Computer Networks Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (5 th Week) 5. Signal Encoding Techniques 5.Outline An overview of the basic methods of encoding digital data into a digital signal An overview of
SEN366 Computer Networks Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (5 th Week) 5. Signal Encoding Techniques 5.Outline An overview of the basic methods of encoding digital data into a digital signal An overview of
The wireless alternative to expensive cabling...
 The wireless alternative to expensive cabling... ELPRO 905U Wireless Solutions for Process Applications New Products... New Solutions The ELPRO 905U range of telemetry modules provide remote monitoring
The wireless alternative to expensive cabling... ELPRO 905U Wireless Solutions for Process Applications New Products... New Solutions The ELPRO 905U range of telemetry modules provide remote monitoring
Serial Communications RS232, RS485, RS422
 Technical Brief AN236 Technical Brief AN236Rev A Serial Communications RS232, RS485, RS422 By John Sonnenberg S u m m a r y Electronic communications is all about interlinking circuits (processors or other
Technical Brief AN236 Technical Brief AN236Rev A Serial Communications RS232, RS485, RS422 By John Sonnenberg S u m m a r y Electronic communications is all about interlinking circuits (processors or other
2. By convention, the minimum and maximum values of analog data and signals are presented as voltages.
 Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Data and Signals Data Communications and Computer Networks A Business Users Approach 8th Edition White TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/data-communications-computer-networksbusiness-users-approach-8th-edition-white-test-bank/
Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Data and Signals Data Communications and Computer Networks A Business Users Approach 8th Edition White TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/data-communications-computer-networksbusiness-users-approach-8th-edition-white-test-bank/
Stensat Transmitter Module
 Stensat Transmitter Module Stensat Group LLC Introduction The Stensat Transmitter Module is an RF subsystem designed for applications where a low-cost low-power radio link is required. The Transmitter
Stensat Transmitter Module Stensat Group LLC Introduction The Stensat Transmitter Module is an RF subsystem designed for applications where a low-cost low-power radio link is required. The Transmitter
Unit 1 Session - 3 TTL Parameters
 Objectives Understanding various TTL Parameters Floating Inputs Worst-Case Input Voltages & Output Voltages Profiles and Windows Compatibility Sourcing and Sinking Noise Immunity Standard Loading and Loading
Objectives Understanding various TTL Parameters Floating Inputs Worst-Case Input Voltages & Output Voltages Profiles and Windows Compatibility Sourcing and Sinking Noise Immunity Standard Loading and Loading
USING RS-232 to RS-485 CONVERTERS (With RS-232, RS-422 and RS-485 devices)
 ICS DataCom Application Note USING RS- to RS- CONVERTERS (With RS-, RS- and RS- devices) INTRODUCTION Table RS-/RS- Logic Levels This application note provides information about using ICSDataCom's RS-
ICS DataCom Application Note USING RS- to RS- CONVERTERS (With RS-, RS- and RS- devices) INTRODUCTION Table RS-/RS- Logic Levels This application note provides information about using ICSDataCom's RS-
2. Cyclone IV Reset Control and Power Down
 May 2013 CYIV-52002-1.3 2. Cyclone IV Reset Control and Power Down CYIV-52002-1.3 Cyclone IV GX devices offer multiple reset signals to control transceiver channels independently. The ALTGX Transceiver
May 2013 CYIV-52002-1.3 2. Cyclone IV Reset Control and Power Down CYIV-52002-1.3 Cyclone IV GX devices offer multiple reset signals to control transceiver channels independently. The ALTGX Transceiver
10Gbps 1550nm 80KM SFP+ Optical Transceiver
 10Gbps 1550nm 80KM SFP+ Optical Transceiver Model: JFSP5592-3LCD80 Size (mm): 58.4*13.9*12.6 Features Hot pluggable 1550nm cooled EML, APD Receiver Up to 80km on 9/125um SMF SFP+ MSA package with duplex
10Gbps 1550nm 80KM SFP+ Optical Transceiver Model: JFSP5592-3LCD80 Size (mm): 58.4*13.9*12.6 Features Hot pluggable 1550nm cooled EML, APD Receiver Up to 80km on 9/125um SMF SFP+ MSA package with duplex
CDR in Mercury Devices
 CDR in Mercury Devices February 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 130 Introduction Preliminary Information High-speed serial data transmission allows designers to transmit highbandwidth data using differential,
CDR in Mercury Devices February 2001, ver. 1.0 Application Note 130 Introduction Preliminary Information High-speed serial data transmission allows designers to transmit highbandwidth data using differential,
Design and Implementation of Universal Serial Bus Transceiver with Verilog
 TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol.12, No.6, June 2014, pp. 4589 ~ 4595 DOI: 10.11591/telkomnika.v12i6.5441 4589 Design and Implementation of Universal Serial Bus Transceiver with
TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol.12, No.6, June 2014, pp. 4589 ~ 4595 DOI: 10.11591/telkomnika.v12i6.5441 4589 Design and Implementation of Universal Serial Bus Transceiver with
Ș.l. dr. ing. Lucian-Florentin Bărbulescu
 Ș.l. dr. ing. Lucian-Florentin Bărbulescu 1 Data: entities that convey meaning within a computer system Signals: are the electric or electromagnetic impulses used to encode and transmit data Characteristics
Ș.l. dr. ing. Lucian-Florentin Bărbulescu 1 Data: entities that convey meaning within a computer system Signals: are the electric or electromagnetic impulses used to encode and transmit data Characteristics
HT2012. HART Modem FSK 1200 bps. Features. Description. Datasheet HT January 2016
 HT2012 HART Modem FSK 1200 bps. Description The HT2012 is a CMOS modem designed for HART field instruments and associated interfaces. This component require some external active and passive elements to
HT2012 HART Modem FSK 1200 bps. Description The HT2012 is a CMOS modem designed for HART field instruments and associated interfaces. This component require some external active and passive elements to
Lecture 3: Modulation & Clock Recovery. CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage
 Lecture 3: Modulation & Clock Recovery CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage Lecture 3 Overview Signaling constraints Shannon s Law Nyquist Limit Encoding schemes Clock recovery Manchester, NRZ, NRZI,
Lecture 3: Modulation & Clock Recovery CSE 123: Computer Networks Stefan Savage Lecture 3 Overview Signaling constraints Shannon s Law Nyquist Limit Encoding schemes Clock recovery Manchester, NRZ, NRZI,
Lecture 23: Media Access Control. CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren
 Lecture 23: Media Access Control CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Overview Finish encoding schemes Manchester, 4B/5B, etc. Methods to share physical media: multiple access Fixed partitioning
Lecture 23: Media Access Control CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Overview Finish encoding schemes Manchester, 4B/5B, etc. Methods to share physical media: multiple access Fixed partitioning
RC-WIFI CONTROLLER USER MANUAL
 RC-WIFI CONTROLLER USER MANUAL In the rapidly growing Internet of Things (IoT), applications from personal electronics to industrial machines and sensors are getting wirelessly connected to the Internet.
RC-WIFI CONTROLLER USER MANUAL In the rapidly growing Internet of Things (IoT), applications from personal electronics to industrial machines and sensors are getting wirelessly connected to the Internet.
Lecture 3: Modulation & Clock Recovery. CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren
 Lecture 3: Modulation & Clock Recovery CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Lecture 3 Overview Signaling constraints Shannon s Law Nyquist Limit Encoding schemes Clock recovery Manchester, NRZ, NRZI,
Lecture 3: Modulation & Clock Recovery CSE 123: Computer Networks Alex C. Snoeren Lecture 3 Overview Signaling constraints Shannon s Law Nyquist Limit Encoding schemes Clock recovery Manchester, NRZ, NRZI,
Lecture LTE (4G) -Technologies used in 4G and 5G. Spread Spectrum Communications
 COMM 907: Spread Spectrum Communications Lecture 10 - LTE (4G) -Technologies used in 4G and 5G The Need for LTE Long Term Evolution (LTE) With the growth of mobile data and mobile users, it becomes essential
COMM 907: Spread Spectrum Communications Lecture 10 - LTE (4G) -Technologies used in 4G and 5G The Need for LTE Long Term Evolution (LTE) With the growth of mobile data and mobile users, it becomes essential
Lecture 5 Transmission. Physical and Datalink Layers: 3 Lectures
 Lecture 5 Transmission Peter Steenkiste School of Computer Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Spring 2004 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441
Lecture 5 Transmission Peter Steenkiste School of Computer Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Spring 2004 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/15-441
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University
 Name...ID... Section...Seat No... Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Midterm Examination: Semester 1/2009 Course Title Instructor : ITS323 Introduction to Data Communications
Name...ID... Section...Seat No... Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Midterm Examination: Semester 1/2009 Course Title Instructor : ITS323 Introduction to Data Communications
10G CWDM SFP+ 40km ER Transceiver Hot Pluggable, Duplex LC, +3.3V, 1470~1610nm CWDM EML, DDMI PSFP10-1C41SF-XX
 DATASHEET DESCRIPTION: CWDM SFP+ ER transceiver is a very compact 10Gb/s optical transceiver module for serial optical communication applications, supporting data-rate of 10.3125Gbps (10GBASE-ER) or 9.953Gbps
DATASHEET DESCRIPTION: CWDM SFP+ ER transceiver is a very compact 10Gb/s optical transceiver module for serial optical communication applications, supporting data-rate of 10.3125Gbps (10GBASE-ER) or 9.953Gbps
GSM Interceptor Fast and reliable interception of GSM traffic
 GSM Interceptor Fast and reliable interception of GSM traffic Maximum accuracy, sensitivity and flexibility Total indefectibility Support for all frequency bands User-friendly operation Wide range of antennas
GSM Interceptor Fast and reliable interception of GSM traffic Maximum accuracy, sensitivity and flexibility Total indefectibility Support for all frequency bands User-friendly operation Wide range of antennas
Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Cyclone IV GX Devices
 Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Cyclone IV GX Devices AN-609-2013.03.05 Application Note Cyclone IV GX transceivers support the dynamic reconfiguration feature which provides a solution that allows
Implementing Dynamic Reconfiguration in Cyclone IV GX Devices AN-609-2013.03.05 Application Note Cyclone IV GX transceivers support the dynamic reconfiguration feature which provides a solution that allows
Data and Computer Communications. Chapter 3 Data Transmission
 Data and Computer Communications Chapter 3 Data Transmission Data Transmission quality of the signal being transmitted The successful transmission of data depends on two factors: characteristics of the
Data and Computer Communications Chapter 3 Data Transmission Data Transmission quality of the signal being transmitted The successful transmission of data depends on two factors: characteristics of the
10G SFP+ CWDM 20km Transceiver Hot Pluggable, Duplex LC, +3.3V, 1270~1350nm CWDM DFB, DDMI PSFP-2C41SF-XX
 DATASHEET DESCRIPTION: transceiver is a very compact 10Gb/s optical transceiver module for serial optical communication applications, supporting data-rate of 10.3125Gbps (10GBASE-LR) or 9.953Gbps (10GBASE-LW),
DATASHEET DESCRIPTION: transceiver is a very compact 10Gb/s optical transceiver module for serial optical communication applications, supporting data-rate of 10.3125Gbps (10GBASE-LR) or 9.953Gbps (10GBASE-LW),
Interface converter RS-232 / RS-485 TECHNICAL GUIDE. Review date: 9 Jun 2010 TECHNOTRADE LTD
 Interface converter RS-232 / TECHNICAL GUIDE Review date: 9 Jun 2010 TECHNOTRADE LTD This document is the property of TECHNOTRADE LTD It is not to be used or duplicated without written permission of the
Interface converter RS-232 / TECHNICAL GUIDE Review date: 9 Jun 2010 TECHNOTRADE LTD This document is the property of TECHNOTRADE LTD It is not to be used or duplicated without written permission of the
Digital to Digital Encoding
 MODULATION AND ENCODING Data must be transformed into signals to send them from one place to another Conversion Schemes Digital-to-Digital Analog-to-Digital Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Analog Digital to
MODULATION AND ENCODING Data must be transformed into signals to send them from one place to another Conversion Schemes Digital-to-Digital Analog-to-Digital Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Analog Digital to
2. Transceiver Basics for Arria V Devices
 2. Transceiver Basics for Arria V Devices November 2011 AV-54002-1.1 AV-54002-1.1 This chapter contains basic technical details pertaining to specific features in the Arria V device transceivers. This
2. Transceiver Basics for Arria V Devices November 2011 AV-54002-1.1 AV-54002-1.1 This chapter contains basic technical details pertaining to specific features in the Arria V device transceivers. This
905U Wireless. New Products... New Solutions. The wireless alternative to expensive cabling... Simple but Reliable. Easy to Use
 Wireless New Products... New Solutions The range of telemetry modules provide remote monitoring and control by radio or twisted-pair wire, over short or long distances. Transducer signals connected at
Wireless New Products... New Solutions The range of telemetry modules provide remote monitoring and control by radio or twisted-pair wire, over short or long distances. Transducer signals connected at
ECT-215 Homework #1 Solution Set Chapter 14 Problems 1-29
 Scoring: 1 point per problem, 29 points total. ECT-215 Homework #1 Solution Set Chapter 14 Problems 1-29 1. For the system of figure 14-1, give the binary code output that will result for each of the following
Scoring: 1 point per problem, 29 points total. ECT-215 Homework #1 Solution Set Chapter 14 Problems 1-29 1. For the system of figure 14-1, give the binary code output that will result for each of the following
RF Based Pick and Place Robot
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 12, Issue 3, Ver. I (May.-Jun. 2017), PP 34-38 www.iosrjournals.org RF Based Pick and Place
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 12, Issue 3, Ver. I (May.-Jun. 2017), PP 34-38 www.iosrjournals.org RF Based Pick and Place
Complete Software Defined RFID System Using GNU Radio
 Complete Defined RFID System Using GNU Radio Aurélien Briand, Bruno B. Albert, and Edmar C. Gurjão, Member, IEEE, Abstract In this paper we describe a complete Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system,
Complete Defined RFID System Using GNU Radio Aurélien Briand, Bruno B. Albert, and Edmar C. Gurjão, Member, IEEE, Abstract In this paper we describe a complete Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system,
Project Name Here CSEE 4840 Project Design Document. Thomas Chau Ben Sack Peter Tsonev
 Project Name Here CSEE 4840 Project Design Document Thomas Chau tc2165@columbia.edu Ben Sack bs2535@columbia.edu Peter Tsonev pvt2101@columbia.edu Table of contents: Introduction Page 3 Block Diagram Page
Project Name Here CSEE 4840 Project Design Document Thomas Chau tc2165@columbia.edu Ben Sack bs2535@columbia.edu Peter Tsonev pvt2101@columbia.edu Table of contents: Introduction Page 3 Block Diagram Page
Inter-Device Synchronous Control Technology for IoT Systems Using Wireless LAN Modules
 Inter-Device Synchronous Control Technology for IoT Systems Using Wireless LAN Modules TOHZAKA Yuji SAKAMOTO Takafumi DOI Yusuke Accompanying the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), interconnections
Inter-Device Synchronous Control Technology for IoT Systems Using Wireless LAN Modules TOHZAKA Yuji SAKAMOTO Takafumi DOI Yusuke Accompanying the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), interconnections
Lecture 5 Transmission
 Lecture 5 Transmission David Andersen Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Spring 2005 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~srini/15-441/s05 1 Physical and Datalink Layers: 3
Lecture 5 Transmission David Andersen Department of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University 15-441 Networking, Spring 2005 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~srini/15-441/s05 1 Physical and Datalink Layers: 3
The Sampling Theorem:
 The Sampling Theorem: Aim: Experimental verification of the sampling theorem; sampling and message reconstruction (interpolation). Experimental Procedure: Taking Samples: In the first part of the experiment
The Sampling Theorem: Aim: Experimental verification of the sampling theorem; sampling and message reconstruction (interpolation). Experimental Procedure: Taking Samples: In the first part of the experiment
RF and Microwave Test and Design Roadshow Cape Town & Midrand
 RF and Microwave Test and Design Roadshow Cape Town & Midrand Advanced PXI Technologies Signal Recording, FPGA s, and Synchronization Philip Ehlers Outline Introduction to the PXI Architecture PXI Data
RF and Microwave Test and Design Roadshow Cape Town & Midrand Advanced PXI Technologies Signal Recording, FPGA s, and Synchronization Philip Ehlers Outline Introduction to the PXI Architecture PXI Data
2014, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 459
 Volume 4, Issue 9, September 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Verilog Implementation
Volume 4, Issue 9, September 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Verilog Implementation
RS-232 Electrical Specifications and a Typical Connection
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Interface Circuits > APP 723 Keywords: RS-232, rs232, RS-422, rs422, RS-485, rs485, RS-232 port powered, RS-232 to RS-485 conversion, daisy chain,
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Interface Circuits > APP 723 Keywords: RS-232, rs232, RS-422, rs422, RS-485, rs485, RS-232 port powered, RS-232 to RS-485 conversion, daisy chain,
HY448 Sample Problems
 HY448 Sample Problems 10 November 2014 These sample problems include the material in the lectures and the guided lab exercises. 1 Part 1 1.1 Combining logarithmic quantities A carrier signal with power
HY448 Sample Problems 10 November 2014 These sample problems include the material in the lectures and the guided lab exercises. 1 Part 1 1.1 Combining logarithmic quantities A carrier signal with power
Serial Input/Output. Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo
 Serial Input/Output Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Serial communication Concepts Standards USART in AVR Lecture overview 2 Why Serial I/O? Problems with Parallel I/O: Needs a wire for
Serial Input/Output Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Serial communication Concepts Standards USART in AVR Lecture overview 2 Why Serial I/O? Problems with Parallel I/O: Needs a wire for
2. HardCopy IV GX Dynamic Reconfiguration
 March 2012 HIV53002-2.1 2. HardCopy IV GX Dynamic Reconfiguration HIV53002-2.1 HardCopy IV GX transceivers allow you to dynamically reconfigure different portions of the transceivers without powering down
March 2012 HIV53002-2.1 2. HardCopy IV GX Dynamic Reconfiguration HIV53002-2.1 HardCopy IV GX transceivers allow you to dynamically reconfigure different portions of the transceivers without powering down
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT.1362 * Interfaces for digital component video signals in 525- and 625-line progressive scan television systems
 Rec. ITU-R BT.6 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT.6 * Interfaces for digital component video signals in 55- and 65-line progressive scan television systems (Question ITU-R 4/6) (998) The ITU Radiocommunication Assembly,
Rec. ITU-R BT.6 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BT.6 * Interfaces for digital component video signals in 55- and 65-line progressive scan television systems (Question ITU-R 4/6) (998) The ITU Radiocommunication Assembly,
NETWORK. TE = Terminal Equipment (DTE - Data Terminal Equipment) NT = Network - Terminating Equipment (DCE - Data Circuit - Terminating Equipment)
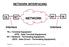 NETWORK INTERFACING TE NT NETWORK NT TE Interface Interface TE = Terminal Equipment (DTE - Data Terminal Equipment) NT = Network - Terminating Equipment (DCE - Data Circuit - Terminating Equipment) Interface
NETWORK INTERFACING TE NT NETWORK NT TE Interface Interface TE = Terminal Equipment (DTE - Data Terminal Equipment) NT = Network - Terminating Equipment (DCE - Data Circuit - Terminating Equipment) Interface
Wireless Infrared Data Communications Using the IRM3XXX Family of IrDA Compatible Infrared Transceivers. Appnote 68
 Wireless Infrared Data Communications Using the IRMXXX Family of IrDA Compatible Infrared Transceivers Appnote 68 Introduction Data interchange, computer to computer and computer to peripherals, requires
Wireless Infrared Data Communications Using the IRMXXX Family of IrDA Compatible Infrared Transceivers Appnote 68 Introduction Data interchange, computer to computer and computer to peripherals, requires
The wireless alternative to expensive cabling...
 The wireless alternative to expensive cabling... ELPRO 105U ISO 9001 Certified New Products... New Solutions The ELPRO 105 range of telemetry modules provide remote monitoring and control by radio or twisted-pair
The wireless alternative to expensive cabling... ELPRO 105U ISO 9001 Certified New Products... New Solutions The ELPRO 105 range of telemetry modules provide remote monitoring and control by radio or twisted-pair
DMR Rx Test Solution. Signal Analyzer MS2830A. Reference Specifications
 Product Introduction DMR Rx Test Solution Signal Analyzer MS2830A Reference Specifications ETSI EN 300 113 Version 2.1.1 (2016-08) / Technical characteristics of the receiver ETSI TS 102 361-1 Version
Product Introduction DMR Rx Test Solution Signal Analyzer MS2830A Reference Specifications ETSI EN 300 113 Version 2.1.1 (2016-08) / Technical characteristics of the receiver ETSI TS 102 361-1 Version
USB Multifunction Arbitrary Waveform Generator AWG2300. User Guide
 USB Multifunction Arbitrary Waveform Generator AWG2300 User Guide Contents Safety information... 3 About this guide... 4 AWG2300 specifications... 5 Chapter 1. Product introduction 1 1. Package contents......
USB Multifunction Arbitrary Waveform Generator AWG2300 User Guide Contents Safety information... 3 About this guide... 4 AWG2300 specifications... 5 Chapter 1. Product introduction 1 1. Package contents......
Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1
 Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 3-6 PERFORMANCE One important issue in networking
Chapter 6 Bandwidth Utilization: Multiplexing and Spreading 6.1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 3-6 PERFORMANCE One important issue in networking
SMARTALPHA RF TRANSCEIVER
 SMARTALPHA RF TRANSCEIVER Intelligent RF Modem Module RF Data Rates to 19200bps Up to 300 metres Range Programmable to 433, 868, or 915MHz Selectable Narrowband RF Channels Crystal Controlled RF Design
SMARTALPHA RF TRANSCEIVER Intelligent RF Modem Module RF Data Rates to 19200bps Up to 300 metres Range Programmable to 433, 868, or 915MHz Selectable Narrowband RF Channels Crystal Controlled RF Design
Data Communication (CS601)
 Data Communication (CS601) MOST LATEST (2012) PAPERS For MID Term (ZUBAIR AKBAR KHAN) Page 1 Q. Suppose a famous Telecomm company AT&T is using AMI encoding standard for its digital telephone services,
Data Communication (CS601) MOST LATEST (2012) PAPERS For MID Term (ZUBAIR AKBAR KHAN) Page 1 Q. Suppose a famous Telecomm company AT&T is using AMI encoding standard for its digital telephone services,
F i n i s a r. Product Specification. CWDM Pluggable SFP Transceiver FWLF15197Dxx APPLICATIONS
 Product Specification CWDM Pluggable SFP Transceiver FWLF15197Dxx PRODUCT FEATURES Up to 1.25 Gb/s bi-directional data links Hot-pluggable SFP footprint Built-in digital diagnostic functions Uncooled DFB
Product Specification CWDM Pluggable SFP Transceiver FWLF15197Dxx PRODUCT FEATURES Up to 1.25 Gb/s bi-directional data links Hot-pluggable SFP footprint Built-in digital diagnostic functions Uncooled DFB
Tracking, Telemetry and Command
 Tracking, Telemetry and Command Jyh-Ching Juang ( 莊智清 ) Department of Electrical Engineering National Cheng Kung University juang@mail.ncku.edu.tw April, 2006 1 Purpose Given that the students have acquired
Tracking, Telemetry and Command Jyh-Ching Juang ( 莊智清 ) Department of Electrical Engineering National Cheng Kung University juang@mail.ncku.edu.tw April, 2006 1 Purpose Given that the students have acquired
Introduction to Telecommunications and Computer Engineering Unit 3: Communications Systems & Signals
 Introduction to Telecommunications and Computer Engineering Unit 3: Communications Systems & Signals Syedur Rahman Lecturer, CSE Department North South University syedur.rahman@wolfson.oxon.org Acknowledgements
Introduction to Telecommunications and Computer Engineering Unit 3: Communications Systems & Signals Syedur Rahman Lecturer, CSE Department North South University syedur.rahman@wolfson.oxon.org Acknowledgements
Computer Facilities and Network Management BUS3150 Assignment 1
 Computer Facilities and Network Management BUS3150 Assignment 1 Due date: Friday 1st September 2006 (Week 7) This Assignment has 6 questions, and you should complete answers for all 6. The Assignment contributes
Computer Facilities and Network Management BUS3150 Assignment 1 Due date: Friday 1st September 2006 (Week 7) This Assignment has 6 questions, and you should complete answers for all 6. The Assignment contributes
The "FISH" Quad Hand Sensor
 The "FISH" Quad Hand Sensor Physics and Media Group MIT Media Laboratory 20 Ames Street E15-022 Cambridge, Mass 02139-4307 (617) 253-2383 phm@media.mit.edu ** U S E R S G U I D E ********* TABLE OF CONTENTS
The "FISH" Quad Hand Sensor Physics and Media Group MIT Media Laboratory 20 Ames Street E15-022 Cambridge, Mass 02139-4307 (617) 253-2383 phm@media.mit.edu ** U S E R S G U I D E ********* TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 2. Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication ( )
 CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.3 Modulation Techniques Reasons for Choosing Encoding Techniques Digital data,
CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.3 Modulation Techniques Reasons for Choosing Encoding Techniques Digital data,
ROM/UDF CPU I/O I/O I/O RAM
 DATA BUSSES INTRODUCTION The avionics systems on aircraft frequently contain general purpose computer components which perform certain processing functions, then relay this information to other systems.
DATA BUSSES INTRODUCTION The avionics systems on aircraft frequently contain general purpose computer components which perform certain processing functions, then relay this information to other systems.
SFP 3.125Gb/s 1310nm 20KM SFP Transceiver
 SFP 3.125Gb/s 1310nm 20KM SFP Transceiver PRODUCT FEATURES Up to 3.125Gb/s data links with DDM DFB laser transmitter and PIN photo-detector. Up to 20km on 9/125µm SMF Hot-pluggable SFP footprint Duplex
SFP 3.125Gb/s 1310nm 20KM SFP Transceiver PRODUCT FEATURES Up to 3.125Gb/s data links with DDM DFB laser transmitter and PIN photo-detector. Up to 20km on 9/125µm SMF Hot-pluggable SFP footprint Duplex
RS-232 to Current Loop Converters
 CL1060/1090xxx 703 5856 RS-232 to Current Loop Converters DB25F to DB25M Product Code CL1060A-M DB25M to DB25F Product Code CL1060A-F DB25M to Terminal Block Product Code CL1090A-M DB25F to Terminal Block
CL1060/1090xxx 703 5856 RS-232 to Current Loop Converters DB25F to DB25M Product Code CL1060A-M DB25M to DB25F Product Code CL1060A-F DB25M to Terminal Block Product Code CL1090A-M DB25F to Terminal Block
Modulating control valve
 Modulating control valve Automatic modulating valve Automatic modulating valve Diaphragm Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Air filter regulator gauge = AIRSET BALL VALVE GLOBE
Modulating control valve Automatic modulating valve Automatic modulating valve Diaphragm Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Air filter regulator gauge = AIRSET BALL VALVE GLOBE
U S E R S M A N U A L
 U S E R S M A N U A L C2104001 BCM 43224 WiFi Card Contents SECTION ONE: INTRODUCTION... 3 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 SCOPE... 3 1.2 FUNCTION... 3 1 2 PRODUCT SPECIFICATION... 4 2.1 HARDWARE SPECIFICATION...
U S E R S M A N U A L C2104001 BCM 43224 WiFi Card Contents SECTION ONE: INTRODUCTION... 3 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 SCOPE... 3 1.2 FUNCTION... 3 1 2 PRODUCT SPECIFICATION... 4 2.1 HARDWARE SPECIFICATION...
Superior Radar Imagery, Target Detection and Tracking SIGMA S6 RADAR PROCESSOR
 Superior Radar Imagery, Target Detection and Tracking SIGMA S6 S TA N D A R D F E AT U R E S SIGMA S6 Airport Surface Movement Radar Conventional Radar Image of Sigma S6 Ice Navigator Image of Radar Inputs
Superior Radar Imagery, Target Detection and Tracking SIGMA S6 S TA N D A R D F E AT U R E S SIGMA S6 Airport Surface Movement Radar Conventional Radar Image of Sigma S6 Ice Navigator Image of Radar Inputs
CSE 461: Bits and Bandwidth. Next Topic
 CSE 461: Bits and Bandwidth Next Topic Focus: How do we send a message across a wire? The physical / link layers: 1. Different kinds of media 2. Encoding bits, messages 3. Model of a link Application Presentation
CSE 461: Bits and Bandwidth Next Topic Focus: How do we send a message across a wire? The physical / link layers: 1. Different kinds of media 2. Encoding bits, messages 3. Model of a link Application Presentation
The figures and the logic used for the MATLAB are given below.
 MATLAB FIGURES & PROGRAM LOGIC: Transmitter: The figures and the logic used for the MATLAB are given below. Binary Data Sequence: For our project we assume that we have the digital binary data stream.
MATLAB FIGURES & PROGRAM LOGIC: Transmitter: The figures and the logic used for the MATLAB are given below. Binary Data Sequence: For our project we assume that we have the digital binary data stream.
1300nm Fast Ethernet Transceiverin1x9SC Duplex Package
 1300nm Fast Ethernet Transceiverin1x9SC Duplex Package OPF5102 Technical Data Features 1310nm LED Data Rate: 155Mbps, NRZ Single +3.3V Power Supply PECL Differential Electrical Interface Industry Standard
1300nm Fast Ethernet Transceiverin1x9SC Duplex Package OPF5102 Technical Data Features 1310nm LED Data Rate: 155Mbps, NRZ Single +3.3V Power Supply PECL Differential Electrical Interface Industry Standard
Physical Layer. Networked Systems (H) Lecture 3
 Physical Layer Networked Systems (H) Lecture 3 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/
Physical Layer Networked Systems (H) Lecture 3 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nd/4.0/
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
