TPA mW MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
|
|
|
- Shona Hill
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 350 mw at V DD = 5 V, BTL 250 mw at V DD = 5 V, 250 mw at V DD = 3.3 V, BTL 75 mw at V DD = 3.3 V, Shutdown Control I DD = 7 µa at 3.3 V I DD = 60 µa at 5 V BTL to Mode Control Integrated Depop Circuitry Thermal and Short-Circuit Protection Surface Mount Packaging SOIC PowerPAD MSOP description The TPA3 is a bridge-tied load (BTL) or single-ended () audio power amplifier developed especially for low-voltage applications where internal speakers and external earphone operation are required. Operating with a 3.3-V supply, the TPA3 can deliver 250-mW of SHUTDOWN BYPASS /BTL IN D OR DGN PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) continuous power into a BTL 8-Ω load at less than % THD+N throughout voice band frequencies. Although this device is characterized out to 20 khz, its operation was optimized for narrower band applications such as cellular communications. The BTL configuration eliminates the need for external coupling capacitors on the output in most applications, which is particularly important for small battery-powered equipment. A unique feature of the TPA3 is that it allows the amplifier to switch from BTL to on the fly when an earphone drive is required. This eliminates complicated mechanical switching or auxiliary devices just to drive the external load. This device features a shutdown mode for power-sensitive applications with special depop circuitry to virtually eliminate speaker noise when exiting shutdown mode and during power cycling. The TPA3 is available in an 8-pin SOIC surface-mount package and the surface-mount PowerPAD MSOP, which reduces board space by 50% and height by 40% V O GND V DD V O + Audio Input RI RF 4 IN VDD/2 VDD VO+ 6 5 CC CS CI 2 BYPASS + CBF From System Control From HP Jack 3 SHUTDOWN /BTL Bias Control + VO 8 GND mw Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet. PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments. PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters. Copyright , Texas Instruments Incorporated POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
2 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 TERMINAL NAME TA SMALL OUTLINE (D) AVAILABLE OPTIONS PACKAGED DEVICES MSOP (DGN) MSOP Symbolization 40 C to 85 C TPA3D TPA3DGN AAB The D and DGN packages are available taped and reeled. To order a taped and reeled part, add the suffix R to the part number (e.g., TPA3DR). NO. I/O BYPASS 2 I GND 7 GND is the ground connection. IN 4 I IN is the audio input terminal. Terminal Functions DESCRIPTION BYPASS is the tap to the voltage divider for internal mid-supply bias. This terminal should be connected to a 0.-µF to -µf capacitor when used as an audio amplifier. /BTL 3 I When /BTL is held low, the TPA3 is in BTL mode. When /BTL is held high, the TPA3 is in mode. SHUTDOWN I SHUTDOWN places the entire device in shutdown mode when held high (IDD = 60 µa, ). VDD 6 VDD is the supply voltage terminal. VO+ 5 O VO+ is the positive output for BTL and modes. VO 8 O VO is the negative output in BTL mode and a high-impedance output in mode. absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) Supply voltage, V DD V Input voltage, V I V to V DD +0.3 V Continuous total power dissipation internally limited (see Dissipation Rating Table) Operating free-air temperature range, T A (see Table 3) C to 85 C Operating junction temperature range, T J C to 50 C Storage temperature range, T stg C to 50 C Lead temperature,6 mm (/6 inch) from case for 0 seconds C Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. DISSIPATION RATING TABLE PACKAGE TA 25 C DERATING FACTOR TA = 70 C TA = 85 C D 725 mw 5.8 mw/ C 464 mw 377 mw DGN 2.4 W 7. mw/ C.37 W. W Please see the Texas Instruments document, PowerPAD Thermally Enhanced Package Application Report (literature number SLMA002), for more information on the PowerPAD package. The thermal data was measured on a PCB layout based on the information in the section entitled Texas Instruments Recommended Board for PowerPAD on page 33 of the before mentioned document. 2 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3 TPA3 recommended operating conditions SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 MIN MAX UNIT Supply voltage, VDD V SHUTDOWN 0.9 VDD Á High-level voltage, VIH Á V /BTL 0.9 VDD Á SHUTDOWN 0. VDD Á Low-level voltage, VIL ÁÁ /BTL 0. VDD V ÁÁ Operating free-air temperature, TA (see Table 3) 40 Á 85 electrical characteristics at specified free-air temperature, V DD = 3.3 V, T A = 25 C (unless otherwise noted) PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT SHUTDOWN = 0 V, /BTL = 0 V, Output offset voltage (measured differentially), Á 5 20 mv RF = 0 kω ÁÁ BTL mode 85 ÁÁ Power supply rejection ratio VDD = 32Vto34V V Á modeáá 83 ÁÁ db SHUTDOWN = 0 V, Á ÁÁ BTL mode /BTL = 0.33 V, RF = 0 kω Supply current (see Figure 6) ÁÁ SHUTDOWN = 0 V, mode /BTL = 2.97 V, RF = 0 kω ma Supply current, shutdown mode SHUTDOWN = VDD, /BTL = 0 V, (see Figure 7) RF = 0 kω 50 µa VOO ÁÁ PSRR ÁÁ IDD ÁÁ IDD(SD) 7 Á SHUTDOWN,, VI = VDD IIH High-level input current Á /BTL,, VI = VDD µa SHUTDOWN,, VI = 0 V Á Á IIL Low-level input current /BTL,, VI = 0 V C µa operating characteristics, V DD = 3.3 V, T A = 25 C, R L = 8 Ω PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT Á ÁÁ ÁÁ THD = 0.5%, BTL mode, See Figure ÁÁ Á PO Output power, see Note ÁÁ THD = 0.5%, mode 0 ÁÁ mw Total harmonic distortion plus ÁÁ THD + N PO = 250 mw, f = 20 Hz to 4 khz,áá AV = 2 V/V, noise ÁÁ See Figure 2.3% Á BOM Maximum output power bandwidth ÁÁ AV = 2 V/V, THD = 3%, ÁÁ See Figure 2 ÁÁ 0 ÁÁ khz B Unity-gain bandwidth Open loop, See Figure 36.4 MHz Á Á Á f = khz, CB = µf, BTL mode, Á See Figure 5 7 Á Á Supply ripple rejection ratio ÁÁ f = khz, CB = µf, ÁÁ mode, Á See Figure 3 86 db Noise output voltage ÁÁ AV = V/V, CB = 0. µf, ÁÁ RL = 32 Ω, ÁÁ 5ÁÁ µv(rms) Vn BTL, See Figure 42 NOTE : Output power is measured at the output terminals of the device at f = khz. POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
4 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 electrical characteristics at specified free-air temperature, V DD = 5 V, T A = 25 C (unless otherwise noted) PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT Á SHUTDOWN = 0 V, /BTL = 0 V, VOO Output offset voltage (measured differentially) ÁÁ, RF = 0 kω 5 20 mv Á BTL mode 49Vto5V ÁÁ 78 ÁÁ PSRR Power supply rejection ratio VDD = V db mode 76 Á SHUTDOWN = 0 V, ÁÁ BTL mode /BTL = 0.5 V, RF = 0 kω Á IDD Supply current (see Figure 6) SHUTDOWN = 0 V, Á mode /BTL = 4.5 V, RF = 0Ω Á ma Supply current, shutdown mode SHUTDOWN = VDD, /BTL = 0 V, IDD(SD) µa (see Figure 7) RF = 0 kω, ÁÁ SHUTDOWN, VDD = 5.5 V, VI = VDD Á IIH High-level input current /BTL, VDD = 5.5 V, VI = VDD µa ÁÁ SHUTDOWN, VDD = 5.5 V, VI = 0 V Á Á IIL Low-level input current /BTL, VDD = 5.5 V, VI = 0 V Á µa operating characteristics, V DD = 5 V, T A = 25 C, R L = 8 Ω PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT ÁÁ THD = 0.5%, BTL mode, ÁÁ See Figure 8 ÁÁ Output power, see Note 2 mw ÁÁ THD = 0.5%, mode Total harmonic distortion plus ÁÁ PO = 350 mw, f = 20 Hz to 4 khz, ÁÁ AV = 2 V/V, ÁÁ noise ÁÁ See Figure 6 Á ÁÁ Maximum output power bandwidth AV = 2 V/V, THD = 2%, See Figure 6 khz Á 700 ÁÁ PO Á 300 ÁÁ Á THD + NÁ % ÁÁ Á Á BOM 0 ÁÁ Á B Unity-gain bandwidth ÁÁ Open loop, See Figure 37.4 ÁÁ MHz Á Á Á ÁÁ f = khz, CB = µf, ÁÁ BTL mode, ÁÁ See Figure 5 65 Supply ripple rejection ratio db f = khz, Á CB = µf, mode, ÁÁ ÁÁ 75 ÁÁ See Figure 4 ÁÁ Vn Noise output voltage AV = V/V, CB = 0. µf, ÁÁ RL = 32 Ω, ÁÁ BTL, See Figure 43 Á 5 µv(rms) NOTE 2: Output power is measured at the output terminals of the device at f = khz. 4 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
5 TPA3 PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 Audio Input RI RF 4 IN VDD/2 VDD VO+ 6 5 CS µf VDD CI 2 BYPASS + CB 0. µf VO 8 3 SHUTDOWN /BTL Bias Control + GND 7 Figure. BTL Mode Test Circuit Audio Input RI RF 4 IN VDD/2 VDD VO+ 6 5 CS µf VDD CI CB 0. µf 2 BYPASS + CC 330 µf RL = 32 Ω VO 8 VDD 3 SHUTDOWN /BTL Bias Control + GND 7 Figure 2. Mode Test Circuit POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
6 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS Table of Graphs FIGURE Supply voltage rejection ratio Frequency 3, 4, 5 IDD Supply current Supply voltage 6, 7 PO Output power THD +N Total harmonic distortion plus noise Supply voltage 8, 9 Load resistance 0, Frequency Output power 2, 3, 6, 7, 20, 2, 24, 25, 28, 29, 32, 33 4, 5, 8, 9, 22, 23, 26, 27, 30, 3, 34, 35 Open loop gain and phase Frequency 36, 37 Closed loop gain and phase Frequency 38, 39, 40, 4 Vn Output noise voltage Frequency 42, 43 PD Power dissipation Output power 44, 45, 46, 47 Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio db SUPPLY VOLTAGE REJECTION RATIO CB = µf CB = 0. µf BYPASS = /2 VDD Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio db SUPPLY VOLTAGE REJECTION RATIO CB = µf CB = 0. µf BYPASS = /2 VDD k 0 k 20 k k 0 k 20 k Figure 3 Figure 4 6 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7 TPA3 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio db SUPPLY VOLTAGE REJECTION RATIO CB = µf BTL I DD Supply Current ma SHUTDOWN = 0 V RF = 0 kω SUPPLY CURRENT SUPPLY VOLTAGE /BTL = 0. VDD /BTL = 0.9 VDD k Figure 5 0 k 20 k VDD Supply Voltage V Figure 6 I DD(SD) Supply Current µ A SUPPLY CURRENT (SHUTDOWN) SUPPLY VOLTAGE SHUTDOWN = VDD /BTL = 0 V RF = 0 kω VDD Supply Voltage V 5.5 Figure 7 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
8 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS THD+N % BTL SUPPLY VOLTAGE THD+N % SUPPLY VOLTAGE Output Power mw O P RL = 32 Ω Output Power mw O P RL = 32 Ω VDD Supply Voltage V Figure VDD Supply Voltage V Figure LOAD RESISTANCE THD+N = % BTL LOAD RESISTANCE THD+N = % Output Power mw O P P O Output Power mw RL Load Resistance Ω Figure RL Load Resistance Ω Figure POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9 TPA3 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY PO = 250 mw BTL AV = 0 V/V AV = 20 V/V AV = 2 V/V k 0k 20k 0 0. AV = 2 V/V BTL PO = 50 mw PO = 25 mw PO = 250 mw k 0k 20k Figure 2 Figure f = khz AV = 2 V/V BTL PO Output Power W 0 0. f = 0 khz f = 20 khz f = khz f = 20 Hz AV = 2 V/V BTL PO Output Power W Figure 4 Figure 5 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
10 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS 0 0. PO = 350 mw BTL AV = 0 V/V AV = 20 V/V AV = 2 V/V k 0k 20k 0 0. AV = 2 V/V BTL PO = 350 mw PO = 50 mw PO = 75 mw k 0k 20k Figure 6 Figure f = khz AV = 2 V/V BTL PO Output Power W 0 0. f = 20 Hz f = 20 khz f = 0 khz f = khz AV = 2 V/V BTL PO Output Power W Figure 8 Figure 9 0 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
11 TPA3 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY PO = 30 mw RL = 32 Ω AV = V/V Figure 20 AV = 5 V/V AV = 0 V/V k 0k 20k RL = 32 Ω AV = V/V PO = 30 mw PO = 5 mw k 0k Figure 2 PO = 0 mw 20k 0 0. f = khz RL = 32 Ω AV = V/V PO Output Power W 0 f = 20 khz f = 0 khz 0. f = khz f = 20 Hz RL = 32 Ω AV = V/V PO Output Power W Figure 22 Figure 23 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
12 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS PO = 60 mw RL = 32 Ω AV = 5 V/V AV = 0 V/V AV = V/V k 0k Figure 24 20k RL = 32 Ω AV = V/V PO = 30 mw PO = 60 mw k 0k Figure 25 PO = 5 mw 20k 0 0. f = khz RL = 32 Ω AV = V/V PO Output Power W 0 0. f = 20 khz f = 0 khz f = khz f = 20 Hz RL = 32 Ω AV = V/V PO Output Power W Figure 26 Figure 27 2 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
13 TPA3 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY PO = 0. mw RL = 0 kω AV = V/V AV = 2 V/V AV = 5 V/V k 0k 20k 0. RL = 0 kω AV = V/V PO = 0.05 mw k 0 k PO = 0.3 mw PO = 0. mw 20 k Figure 28 Figure f = khz RL = 0 kω AV = V/V PO Output Power µw Figure RL = 0 kω AV = V/V f = 20 Hz f = 20 khz PO Output Power µw Figure 3 f = khz f = 0 khz POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
14 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS 0. PO = 0.3 mw RL = 0 kω AV = V/V AV = 2 V/V AV = 5 V/V k 0k 20k 0. RL = 0 kω AV = V/V k 0k PO = 0.3 mw PO = 0.2 mw PO = 0. mw 20k Figure 32 Figure f = khz RL = 0 kω AV = V/V PO Output Power µw Figure RL = 0 kω AV = V/V f = 20 Hz PO Output Power µw Figure 35 f = 0 khz f = 20 khz f = khz POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
15 TPA3 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY OPEN-LOOP GAIN AND PHA Gain Phase RL = Open BTL Open-Loop Gain db Phase f Frequency khz Figure OPEN-LOOP GAIN AND PHA Gain Phase RL = Open BTL Open-Loop Gain db Phase f Frequency khz Figure 37 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
16 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS CLOD-LOOP GAIN AND PHA Phase Closed-Loop Gain db PO = 0.25 W CI = µf BTL Gain Figure 38 Phase CLOD-LOOP GAIN AND PHA Phase Closed-Loop Gain db PO = 0.35 W CI = µf BTL Gain Figure 39 Phase 6 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
17 TPA3 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 Closed-Loop Gain db Closed-Loop Gain db CLOD-LOOP GAIN AND PHA RL = 32 Ω AV = 2 V/V PO = 30 mw CI = µf CC =470 µf Phase Gain Figure 40 CLOD-LOOP GAIN AND PHA RL = 32 Ω AV = 2 V/V PO = 60 mw CI = µf CC =470 µf Phase Gain Figure Phase Phase POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
18 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS V(rms) Output Noise Voltage µ 00 0 OUTPUT NOI VOLTAGE BW = 22 Hz to 22 khz RL = 32 Ω CB =0. µf AV = V/V VO BTL VO+ V n V(rms) Output Noise Voltage µ 00 0 OUTPUT NOI VOLTAGE BW = 22 Hz to 22 khz RL = 32 Ω CB =0. µf AV = V/V VO BTL VO+ V n k 0 k 20 k k 0 k 20 k Figure 42 Figure POWER DISSIPATION 80 POWER DISSIPATION P D Power Dissipation mw PO Output Power mw Figure 44 BTL P D Power Dissipation mw RL = 32 Ω PO Output Power mw Figure 45 8 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
19 TPA3 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY POWER DISSIPATION 80 POWER DISSIPATION P D Power Dissipation mw PO Output Power mw Figure 46 BTL P D Power Dissipation mw RL = 32 Ω PO Output Power mw Figure 47 bridge-tied load versus single-ended mode APPLICATION INFORMATION Figure 48 shows a linear audio power amplifier (APA) in a BTL configuration. The TPA3 BTL amplifier consists of two linear amplifiers driving both ends of the load. There are several potential benefits to this differential drive configuration but initially consider power to the load. The differential drive to the speaker means that as one side is slewing up, the other side is slewing down, and vice versa. This in effect doubles the voltage swing on the load as compared to a ground referenced load. Plugging 2 V O(PP) into the power equation, where voltage is squared, yields 4 the output power from the same supply rail and load impedance (see equation ). V (rms) Power V O(PP) V (rms) R L () POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
20 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 APPLICATION INFORMATION bridge-tied load versus single-ended mode (continued) VDD VO(PP) VDD RL 2x VO(PP) VO(PP) Figure 48. Bridge-Tied Load Configuration In typical portable handheld equipment, a sound channel operating at 3.3 V and using bridging raises the power into an 8-Ω speaker from a single-ended (, ground reference) limit of 62.5 mw to 250 mw. In terms of sound power that is a 6-dB improvement, which is loudness that can be heard. In addition to increased power there are frequency response concerns. Consider the single-supply configuration shown in Figure 49. A coupling capacitor is required to block the dc offset voltage from reaching the load. These capacitors can be quite large (approximately 33 µf to 000 µf), tend to be expensive, heavy, and occupy valuable PCB area. These capacitors also have the additional drawback of limiting low-frequency performance of the system. This frequency limiting effect is due to the high-pass filter network created with the speaker impedance and the coupling capacitance and is calculated with equation 2. f c 2 R L C C (2) For example, a 68-µF capacitor with an 8-Ω speaker would attenuate low frequencies below 293 Hz. The BTL configuration cancels the dc offsets, which eliminates the need for the blocking capacitors. Low-frequency performance is then limited only by the input network and speaker response. Cost and PCB space are also minimized by eliminating the bulky coupling capacitor. 20 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
21 TPA3 APPLICATION INFORMATION SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 bridge-tied load versus single-ended mode (continued) VDD VO(PP) 3 db CC RL VO(PP) Figure 49. Single-Ended Configuration and Frequency Response Increasing power to the load does carry a penalty of increased internal power dissipation. The increased dissipation is understandable, considering that the BTL configuration produces 4 the output power of the configuration. Internal dissipation versus output power is discussed further in the thermal considerations section. BTL amplifier efficiency Linear amplifiers are notoriously inefficient. The primary cause of these inefficiencies is voltage drop across the output stage transistors. There are two components of the internal voltage drop. One is the headroom or dc voltage drop that varies inversely to output power. The second component is due to the sinewave nature of the output. The total voltage drop can be calculated by subtracting the RMS value of the output voltage from V DD. The internal voltage drop multiplied by the RMS value of the supply current, I DD rms, determines the internal power dissipation of the amplifier. An easy-to-use equation to calculate efficiency starts out as being equal to the ratio of power from the power supply to the power delivered to the load. To accurately calculate the RMS values of power in the load and in the amplifier, the current and voltage waveform shapes must first be understood (see Figure 50). fc VO IDD V(LRMS) IDD(RMS) Figure 50. Voltage and Current Waveforms for BTL Amplifiers POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
22 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 BTL amplifier efficiency (continued) APPLICATION INFORMATION Although the voltages and currents for and BTL are sinusoidal in the load, currents from the supply are very different between and BTL configurations. In an application the current waveform is a half-wave rectified shape whereas, in BTL it is a full-wave rectified waveform. This means RMS conversion factors are different. Keep in mind that for most of the waveform, both the push and pull transistors are not on at the same time, which supports the fact that each amplifier in the BTL device only draws current from the supply for half the waveform. The following equations are the basis for calculating amplifier efficiency. Efficiency P L P SUP (3) where P L V L rms2 R L V L rms V P 2 V 2 p 2R L P SUP V DD I DD rms V DD 2V P R L I DD rms 2V P R L Efficiency of a BTL Configuration V P 2V DD P L R L 2 2 2V DD (4) Table employs equation 4 to calculate efficiencies for three different output power levels. The efficiency of the amplifier is quite low for lower power levels and rises sharply as power to the load is increased resulting in a nearly flat internal power dissipation over the normal operating range. The internal dissipation at full output power is less than in the half power range. Calculating the efficiency for a specific system is the key to proper power supply design. Table. Efficiency Vs Output Power in 3.3-V 8-Ω BTL Systems (W) EFFICIENCY (%) PEAK-TO-PEAK VOLTAGE (V) INTERNAL DISSIPATION (W) High-peak voltage values cause the THD to increase. A final point to remember about linear amplifiers (either or BTL) is how to manipulate the terms in the efficiency equation to utmost advantage when possible. In equation 4, V DD is in the denominator. This indicates that as V DD goes down, efficiency goes up. 22 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
23 TPA3 APPLICATION INFORMATION SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 application schematic Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of a typical handheld audio application circuit, configured for a gain of 0 V/V. CF 5 pf Audio Input RF 50 kω RI 0 kω 4 IN VDD/2 VDD VO+ 6 5 CC 330 µf CS µf VDD CI 0.47 µf CB 2.2 µf 2 BYPASS + kω VO 8 From System Control 3 SHUTDOWN /BTL Bias Control + GND 7 0. µf VDD 00 kω 00 kω Figure 5. TPA3 Application Circuit The following sections discuss the selection of the components used in Figure 5. component selection gain setting resistors, R F and R I The gain for each audio input of the TPA3 is set by resistors R F and R I according to equation 5 for BTL mode. BTL Gain A V 2 R F (5) R I BTL mode operation brings about the factor 2 in the gain equation due to the inverting amplifier mirroring the voltage swing across the load. Given that the TPA3 is a MOS amplifier, the input impedance is very high, consequently input leakage currents are not generally a concern, although noise in the circuit increases as the value of R F increases. In addition, a certain range of R F values is required for proper start-up operation of the amplifier. Taken together it is recommended that the effective impedance seen by the inverting node of the amplifier be set between 5 kω and 20 kω. The effective impedance is calculated in equation 6. Effective Impedance R F R I R F R I (6) POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
24 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 component selection (continued) APPLICATION INFORMATION As an example consider an input resistance of 0 kω and a feedback resistor of 50 kω. The BTL gain of the amplifier would be 0 V/V and the effective impedance at the inverting terminal would be 8.3 kω, which is well within the recommended range. For high performance applications, metal film resistors are recommended because they tend to have lower noise levels than carbon resistors. For values of R F above 50 kω the amplifier tends to become unstable due to a pole formed from R F and the inherent input capacitance of the MOS input structure. For this reason, a small compensation capacitor, C F, of approximately 5 pf should be placed in parallel with R F when R F is greater than 50 kω. This, in effect, creates a low pass filter network with the cutoff frequency defined in equation 7. 3 db f c(lowpass) 2 R F C F (7) For example, if R F is 00 kω and C F is 5 pf then f c is 38 khz, which is well outside the audio range. input capacitor, C I In the typical application an input capacitor, C I, is required to allow the amplifier to bias the input signal to the proper dc level for optimum operation. In this case, C I and R I form a high-pass filter with the corner frequency determined in equation 8. fc 3 db f c(highpass) 2 R I C I (8) The value of C I is important to consider as it directly affects the bass (low frequency) performance of the circuit. Consider the example where R I is 0 kω and the specification calls for a flat bass response down to 40 Hz. Equation 8 is reconfigured as equation 9. fc C I 2 R I f c (9) 24 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
25 TPA3 APPLICATION INFORMATION SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 component selection (continued) In this example, C I is 0.40 µf, so one would likely choose a value in the range of 0.47 µf to µf. A further consideration for this capacitor is the leakage path from the input source through the input network (R I, C I ) and the feedback resistor (R F ) to the load. This leakage current creates a dc offset voltage at the input to the amplifier that reduces useful headroom, especially in high gain applications. For this reason a low-leakage tantalum or ceramic capacitor is the best choice. When polarized capacitors are used, the positive side of the capacitor should face the amplifier input in most applications as the dc level there is held at V DD /2, which is likely higher than the source dc level. It is important to confirm the capacitor polarity in the application. power supply decoupling, C S The TPA3 is a high-performance CMOS audio amplifier that requires adequate power supply decoupling to ensure the output total harmonic distortion (THD) is as low as possible. Power supply decoupling also prevents oscillations for long lead lengths between the amplifier and the speaker. The optimum decoupling is achieved by using two capacitors of different types that target different types of noise on the power supply leads. For higher frequency transients, spikes, or digital hash on the line, a good low equivalent-series-resistance (ESR) ceramic capacitor, typically 0. µf placed as close as possible to the device V DD lead, works best. For filtering lower-frequency noise signals, a larger aluminum electrolytic capacitor of 0 µf or greater placed near the audio power amplifier is recommended. midrail bypass capacitor, C B The midrail bypass capacitor, C B, is the most critical capacitor and serves several important functions. During start-up or recovery from shutdown mode, C B determines the rate at which the amplifier starts up. The second function is to reduce noise produced by the power supply caused by coupling into the output drive signal. This noise is from the midrail generation circuit internal to the amplifier, which appears as degraded PSRR and THD + N. The capacitor is fed from a 250-kΩ source inside the amplifier. To keep the start-up pop as low as possible, the relationship shown in equation 0 should be maintained, which insures the input capacitor is fully charged before the bypass capacitor is fuly charged and the amplifier starts up. 0 CB 250 kω RF R I CI As an example, consider a circuit where C B is 2.2 µf, C I is 0.47 µf, R F is 50 kω and R I is 0 kω. Inserting these values into the equation 0 we get: which satisfies the rule. Bypass capacitor, C B, values of 0. µf to 2.2 µf ceramic or tantalum low-esr capacitors are recommended for the best THD and noise performance. single-ended operation In mode (see Figure 5), the load is driven from the primary amplifier output (V O +, terminal 5). In mode the gain is set by the R F and R I resistors and is shown in equation. Since the inverting amplifier is not used to mirror the voltage swing on the load, the factor of 2, from equation 5, is not included. Gain A V R F () R I (0) POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
26 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 single-ended operation (continued) APPLICATION INFORMATION The output coupling capacitor required in single-supply mode also places additional constraints on the selection of other components in the amplifier circuit. The rules described earlier still hold with the addition of the following relationship: 0 CB 250 kω RF R I CI R L C C As an example, consider a circuit where C B is µf, C I is 0.47 µf, C C is 330 µf, R F is 50 kωr L is 32 Ω, and R I is 0 kω. Inserting these values into the equation 2 we get: which satisfies the rule. output coupling capacitor, C C In the typical single-supply configuration, an output coupling capacitor (C C ) is required to block the dc bias at the output of the amplifier, thus preventing dc currents in the load. As with the input coupling capacitor, the output coupling capacitor and impedance of the load form a high-pass filter governed by equation 3. (2) 3 db f c(high pass) 2 R L C C (3) The main disadvantage, from a performance standpoint, is that the typically small load impedances drive the low-frequency corner higher degrading the bass response. Large values of C C are required to pass low frequencies into the load. Consider the example where a C C of 330 µf is chosen and loads vary from 8 Ω, 32 Ω, to 47 kω. Table 2 summarizes the frequency response characteristics of each configuration. Table 2. Common Load Impedances Low Frequency Output Characteristics in Mode RL CC LOWEST 8 Ω 330 µf 60 Hz 32 Ω 330 µf 5 Hz 47,000 Ω 330 µf 0.0 Hz As Table 2 indicates an 8-Ω load is adequate, earphone response is good, and drive into line level inputs (a home stereo for example) is exceptional. fc 26 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
27 TPA3 APPLICATION INFORMATION SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 /BTL operation The ability of the TPA3 to easily switch between BTL and modes is one of its most important cost saving features. This feature eliminates the requirement for an additional earphone amplifier in applications where internal speakers are driven in BTL mode but external earphone or speaker must be accommodated. Internal to the TPA3, two separate amplifiers drive V O + and V O. The /BTL input (terminal 3) controls the operation of the follower amplifier that drives V O (terminal 8). When /BTL is held low, the amplifier is on and the TPA3 is in the BTL mode. When /BTL is held high, the V O amplifier is in a high output impedance state, which configures the TPA3 as an driver from V O + (terminal 5). I DD is reduced by approximately one-half in mode. Control of the /BTL input can be from a logic-level TTL source or, more typically, from a resistor divider network as shown in Figure IN VO+ 5 CC 330 µf 2 BYPASS + kω VO 8 3 SHUTDOWN /BTL Bias Control + GND 7 0. µf VDD 00 kω 00 kω Figure 52. TPA3 Resistor Divider Network Circuit Using a readily available /8-in. (3,5 mm) mono earphone jack, the control switch is closed when no plug is inserted. When closed the 00-kΩ/-kΩ divider pulls the /BTL input low. When a plug is inserted, the -kω resistor is disconnected and the /BTL input is pulled high. When the input goes high, the V O amplifier is shutdown causing the BTL speaker to mute (virtually open-circuits the speaker). The V O + amplifier then drives through the output capacitor (C C ) into the earphone jack. using low-esr capacitors Low-ESR capacitors are recommended throughout this application. A real (as opposed to ideal) capacitor can be modeled simply as a resistor in series with an ideal capacitor. The voltage drop across this resistor minimizes the beneficial effects of the capacitor in the circuit. The lower the equivalent value of this resistance the more the real capacitor behaves like an ideal capacitor. POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
28 TPA3 SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY V versus 3.3-V operation APPLICATION INFORMATION The TPA3 operates over a supply range of 2.5 V to 5.5 V. This data sheet provides full specifications for 5-V and 3.3-V operation, as these are considered to be the two most common standard voltages. There are no special considerations for 3.3-V versus 5-V operation with respect to supply bypassing, gain setting, or stability. The most important consideration is that of output power. Each amplifier in TPA3 can produce a maximum voltage swing of V DD V. This means, for 3.3-V operation, clipping starts to occur when V O(PP) = 2.3 V as opposed to V O(PP) = 4 V at 5 V. The reduced voltage swing subsequently reduces maximum output power into an 8-Ω load before distortion becomes significant. Operation from 3.3-V supplies, as can be shown from the efficiency formula in equation 4, consumes approximately two-thirds the supply power for a given output-power level of operation from 5-V supplies. headroom and thermal considerations Linear power amplifiers dissipate a significant amount of heat in the package under normal operating conditions. A typical music CD requires 2 db to 5 db of dynamic headroom to pass the loudest portions without distortion as compared with the average power output. From the TPA3 data sheet, one can see that when the TPA3 is operating from a 5-V supply into a 8-Ω speaker that 350 mw peaks are available. Converting watts to db: P db 0Log P W P ref 0Log 350 mw W 4.6 db Subtracting the headroom restriction to obtain the average listening level without distortion yields: 4.6 db 5 db 9.6 db (5 db headroom) 4.6 db 2 db 6.6 db (2 db headroom) 4.6 db 9dB 3.6 db (9 db headroom) 4.6 db 6dB 0.6 db (6 db headroom) 4.6 db 3dB 7.6 db (3 db headroom) Converting db back into watts: P W 0 PdB 0 P ref mw (5 db headroom) 22 mw (2 db headroom) 44 mw (9 db headroom) 88 mw (6 db headroom) 75 mw (3 db headroom) 28 POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
29 TPA3 APPLICATION INFORMATION headroom and thermal considerations (continued) SLOS207C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 2003 This is valuable information to consider when attempting to estimate the heat dissipation requirements for the amplifier system. Comparing the absolute worst case, which is 350 mw of continuous power output with 0 db of headroom, against 2 db and 5 db applications drastically affects maximum ambient temperature ratings for the system. Using the power dissipation curves for a 5-V, 8-Ω system, the internal dissipation in the TPA3 and maximum ambient temperatures is shown in Table 3. Table 3. TPA3 Power Rating, 5-V, 8-Ω, BTL POWER MAXIMUM AMBIENT PEAK AVERAGE OUTPUT DISSIPATION TEMPERATURE (mw) POWER (mw) 0 CFM SOIC 0 CFM DGN mw C 4 C mw (3 db) C 20 C mw (6 db) C 25 C mw (9 db) C 25 C mw (2 db) C 25 C 350 mw (5 db) 80 9 C 25 C Table 3 shows that the TPA3 can be used to its full 350-mW rating without any heat sinking in still air up to 46 C. POST OFFICE BOX DALLAS, TEXAS
30 PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM 24-Jan-203 PACKAGING INFORMATION Orderable Device Status () Package Type Package Drawing Pins Package Qty Eco Plan TPA3D ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) TPA3DG4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 75 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) TPA3DGN ACTIVE MSOP- PowerPAD TPA3DGNG4 ACTIVE MSOP- PowerPAD TPA3DGNR ACTIVE MSOP- PowerPAD TPA3DGNRG4 ACTIVE MSOP- PowerPAD DGN 8 80 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) DGN 8 80 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) DGN Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) DGN Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) TPA3DR ACTIVE SOIC D Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) TPA3DRG4 ACTIVE SOIC D Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) (2) Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp (3) Op Temp ( C) Top-Side Markings (4) CU NIPDAU Level--260C-UNLIM 3 CU NIPDAU Level--260C-UNLIM 3 CU NIPDAU Level--260C-UNLIM AAB CU NIPDAU Level--260C-UNLIM AAB CU NIPDAU Level--260C-UNLIM AAB CU NIPDAU Level--260C-UNLIM AAB CU NIPDAU Level--260C-UNLIM 3 CU NIPDAU Level--260C-UNLIM 3 Samples () The marketing status values are defined as follows: ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs. LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect. NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in a new design. PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available. OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device. (2) Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check for the latest availability information and additional product content details. TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined. Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes. Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either ) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS compatible) as defined above. Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.% by weight in homogeneous material) (3) MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder temperature. Addendum-Page
31 PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM 24-Jan-203 (4) Only one of markings shown within the brackets will appear on the physical device. Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited information may not be available for release. In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI to Customer on an annual basis. Addendum-Page 2
32 PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION 3-Aug-207 TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION *All dimensions are nominal Device TPA3DGNR Package Type MSOP- Power PAD Package Drawing Pins SPQ Reel Diameter (mm) Reel Width W (mm) A0 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P (mm) W (mm) Pin Quadrant DGN Q TPA3DR SOIC D Q Pack Materials-Page
33 PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION 3-Aug-207 *All dimensions are nominal Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm) TPA3DGNR MSOP-PowerPAD DGN TPA3DR SOIC D Pack Materials-Page 2
34
35
36
37
38
39 IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) reserves the right to make corrections, enhancements, improvements and other changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. TI s published terms of sale for semiconductor products ( apply to the sale of packaged integrated circuit products that TI has qualified and released to market. Additional terms may apply to the use or sale of other types of TI products and services. Reproduction of significant portions of TI information in TI data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. TI is not responsible or liable for such reproduced documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional restrictions. Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements. Buyers and others who are developing systems that incorporate TI products (collectively, Designers ) understand and agree that Designers remain responsible for using their independent analysis, evaluation and judgment in designing their applications and that Designers have full and exclusive responsibility to assure the safety of Designers' applications and compliance of their applications (and of all TI products used in or for Designers applications) with all applicable regulations, laws and other applicable requirements. Designer represents that, with respect to their applications, Designer has all the necessary expertise to create and implement safeguards that () anticipate dangerous consequences of failures, (2) monitor failures and their consequences, and (3) lessen the likelihood of failures that might cause harm and take appropriate actions. Designer agrees that prior to using or distributing any applications that include TI products, Designer will thoroughly test such applications and the functionality of such TI products as used in such applications. TI s provision of technical, application or other design advice, quality characterization, reliability data or other services or information, including, but not limited to, reference designs and materials relating to evaluation modules, (collectively, TI Resources ) are intended to assist designers who are developing applications that incorporate TI products; by downloading, accessing or using TI Resources in any way, Designer (individually or, if Designer is acting on behalf of a company, Designer s company) agrees to use any particular TI Resource solely for this purpose and subject to the terms of this Notice. TI s provision of TI Resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI s applicable published warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products, and no additional obligations or liabilities arise from TI providing such TI Resources. TI reserves the right to make corrections, enhancements, improvements and other changes to its TI Resources. TI has not conducted any testing other than that specifically described in the published documentation for a particular TI Resource. Designer is authorized to use, copy and modify any individual TI Resource only in connection with the development of applications that include the TI product(s) identified in such TI Resource. NO OTHER LICEN, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWI TO ANY OTHER TI INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT, AND NO LICEN TO ANY TECHNOLOGY OR INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT OF TI OR ANY THIRD PARTY IS GRANTED HEREIN, including but not limited to any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information regarding or referencing third-party products or services does not constitute a license to use such products or services, or a warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of TI Resources may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI. TI RESOURCES ARE PROVIDED AS IS AND WITH ALL FAULTS. TI DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES OR REPRENTATIONS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, REGARDING RESOURCES OR U THEREOF, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ACCURACY OR COMPLETENESS, TITLE, ANY EPIDEMIC FAILURE WARRANTY AND ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPO, AND NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS. TI SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR AND SHALL NOT DEFEND OR INDEMNIFY DESIGNER AGAINST ANY CLAIM, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY INFRINGEMENT CLAIM THAT RELATES TO OR IS BAD ON ANY COMBINATION OF PRODUCTS EVEN IF DESCRIBED IN TI RESOURCES OR OTHERWI. IN NO EVENT SHALL TI BE LIABLE FOR ANY ACTUAL, DIRECT, SPECIAL, COLLATERAL, INDIRECT, PUNITIVE, INCIDENTAL, CONQUENTIAL OR EXEMPLARY DAMAGES IN CONNECTION WITH OR ARISING OUT OF TI RESOURCES OR U THEREOF, AND REGARDLESS OF WHETHER TI HAS BEEN ADVID OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. Unless TI has explicitly designated an individual product as meeting the requirements of a particular industry standard (e.g., ISO/TS 6949 and ISO 26262), TI is not responsible for any failure to meet such industry standard requirements. Where TI specifically promotes products as facilitating functional safety or as compliant with industry functional safety standards, such products are intended to help enable customers to design and create their own applications that meet applicable functional safety standards and requirements. Using products in an application does not by itself establish any safety features in the application. Designers must ensure compliance with safety-related requirements and standards applicable to their applications. Designer may not use any TI products in life-critical medical equipment unless authorized officers of the parties have executed a special contract specifically governing such use. Life-critical medical equipment is medical equipment where failure of such equipment would cause serious bodily injury or death (e.g., life support, pacemakers, defibrillators, heart pumps, neurostimulators, and implantables). Such equipment includes, without limitation, all medical devices identified by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as Class III devices and equivalent classifications outside the U.S. TI may expressly designate certain products as completing a particular qualification (e.g., Q00, Military Grade, or Enhanced Product). Designers agree that it has the necessary expertise to select the product with the appropriate qualification designation for their applications and that proper product selection is at Designers own risk. Designers are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such selection. Designer will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages, costs, losses, and/or liabilities arising out of Designer s noncompliance with the terms and provisions of this Notice. Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box , Dallas, Texas Copyright 207, Texas Instruments Incorporated
TPA mW MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA30 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 350 mw at V DD = 5 V, BTL 250 mw at V DD = 3.3 V, BTL Ultra-Low Quiescent Current
TPA30 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 350 mw at V DD = 5 V, BTL 250 mw at V DD = 3.3 V, BTL Ultra-Low Quiescent Current
TPA6110A2 150-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA6A2 5-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS34 DECEMBER 2 5 mw Stereo Output PC Power Supply Compatible Fully Specified for 3.3 V and 5 V Operation Operation to 2.5 V Pop Reduction Circuitry Internal
TPA6A2 5-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS34 DECEMBER 2 5 mw Stereo Output PC Power Supply Compatible Fully Specified for 3.3 V and 5 V Operation Operation to 2.5 V Pop Reduction Circuitry Internal
150-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA22 5-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS2E AUGUST 998 REVISED JUNE 4 FEATURES DESCRIPTION 5-mW Stereo Output The TPA22 is a stereo audio power amplifier packaged PC Power Supply Compatible in either
TPA22 5-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS2E AUGUST 998 REVISED JUNE 4 FEATURES DESCRIPTION 5-mW Stereo Output The TPA22 is a stereo audio power amplifier packaged PC Power Supply Compatible in either
TPA W MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER WITH HEADPHONE DRIVE
 Ideal for Notebook Computers, PDAs, and Other Small Portable Audio Devices 1 W Into 8-Ω From 5-V Supply 0.3 W Into 8-Ω From 3-V Supply Stereo Head Phone Drive Mono (BTL) Signal Created by Summing Left
Ideal for Notebook Computers, PDAs, and Other Small Portable Audio Devices 1 W Into 8-Ω From 5-V Supply 0.3 W Into 8-Ω From 3-V Supply Stereo Head Phone Drive Mono (BTL) Signal Created by Summing Left
TPA mW LOW-VOLTAGE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA3 SLOS27A JANUARY 998 REVID OCTOBER 998 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 35 mw at V DD = 5 V, 25 mw at V DD = 5 V, 25
TPA3 SLOS27A JANUARY 998 REVID OCTOBER 998 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 35 mw at V DD = 5 V, 25 mw at V DD = 5 V, 25
description SHUTDOWN GND BYPASS IN+ D OR DGN PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) MicroStar Junior (GQS) Package (TOP VIEW) (A2) (A3) (A4) (A5) (E2) SHUTDOWN (E3) GND
 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Power Supply Rejection at 27 Hz 84 db at V DD = 5 V 8 db at V DD = 3.3 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 700 mw at V DD
Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Power Supply Rejection at 27 Hz 84 db at V DD = 5 V 8 db at V DD = 3.3 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 700 mw at V DD
TPA mW MONO LOW-VOLTAGE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 700 mw at V DD = 5 V, 250 mw at V DD = 3.3 V, Integrated Depop Circuitry Thermal and Short-Circuit
Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 700 mw at V DD = 5 V, 250 mw at V DD = 3.3 V, Integrated Depop Circuitry Thermal and Short-Circuit
1-W MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
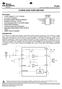 -W MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER TPA486 SLOS63C SEPTEMBER 996 REVISED JUNE 4 FEATURES -W BTL Output (5 V,. % THD+N) 3.3-V and 5-V Operation No Output Coupling Capacitors Required Shutdown Control (I DD =.6
-W MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER TPA486 SLOS63C SEPTEMBER 996 REVISED JUNE 4 FEATURES -W BTL Output (5 V,. % THD+N) 3.3-V and 5-V Operation No Output Coupling Capacitors Required Shutdown Control (I DD =.6
50-mW ULTRALOW VOLTAGE STEREO HEADPHONE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA600A2D SLOS269B JUNE 2000 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2004 50-mW ULTRALOW VOLTAGE STEREO HEADPHONE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER FEATURES 50-mW Stereo Output Low Supply Current... 0.75 ma Low Shutdown Current... 50 na
TPA600A2D SLOS269B JUNE 2000 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2004 50-mW ULTRALOW VOLTAGE STEREO HEADPHONE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER FEATURES 50-mW Stereo Output Low Supply Current... 0.75 ma Low Shutdown Current... 50 na
TPA mW MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA3 SLOS27C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 23 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 35 mw at V DD = 5 V, BTL 25 mw at V DD = 5 V, 25
TPA3 SLOS27C JANUARY 998 REVID MAY 23 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 35 mw at V DD = 5 V, BTL 25 mw at V DD = 5 V, 25
description/ordering information
 µ SLVS060K JUNE 1976 REVISED APRIL 2005 3-Terminal Regulators Output Current Up To 500 ma No External Components High Power-Dissipation Capability Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting Output Transistor
µ SLVS060K JUNE 1976 REVISED APRIL 2005 3-Terminal Regulators Output Current Up To 500 ma No External Components High Power-Dissipation Capability Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting Output Transistor
TPA mW MONO LOW-VOLTAGE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
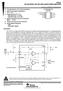 TPA70 SLOS229D NOVEMBER998 REVISED MAY 2003 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 700 mw at V DD = 5 V, 250 mw at V DD = 3.3
TPA70 SLOS229D NOVEMBER998 REVISED MAY 2003 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power for R L = 8 Ω 700 mw at V DD = 5 V, 250 mw at V DD = 3.3
350-mW MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
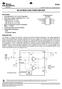 TPA30 350-mW MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS208E JANUARY 998 REVISED JUNE 2004 FEATURES Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V - 5.5 V Output Power for 350 mw
TPA30 350-mW MONO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS208E JANUARY 998 REVISED JUNE 2004 FEATURES Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V - 5.5 V Output Power for 350 mw
LF411 JFET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 LF411 JFET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Low Input Bias Current, 50 pa Typ Low Input Noise Current, 0.01 pa/ Hz Typ Low Supply Current, 2 ma Typ High Input impedance, 10 12 Ω Typ Low Total Harmonic Distortion
LF411 JFET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Low Input Bias Current, 50 pa Typ Low Input Noise Current, 0.01 pa/ Hz Typ Low Supply Current, 2 ma Typ High Input impedance, 10 12 Ω Typ Low Total Harmonic Distortion
ua9637ac DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER
 ua9637ac DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-422-B and EIA/TIA-423-B and ITU Recommendations V.10 and V.11 Operates From Single 5-V Power Supply
ua9637ac DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-422-B and EIA/TIA-423-B and ITU Recommendations V.10 and V.11 Operates From Single 5-V Power Supply
SN75150 DUAL LINE DRIVER
 SN75150 DUAL LINE DRIVER Meets or Exceeds the Requirement of TIA/EIA-232-F and ITU Recommendation V.28 Withstands Sustained Output Short Circuit to Any Low-Impedance Voltage Between 25 V and 25 V 2-µs
SN75150 DUAL LINE DRIVER Meets or Exceeds the Requirement of TIA/EIA-232-F and ITU Recommendation V.28 Withstands Sustained Output Short Circuit to Any Low-Impedance Voltage Between 25 V and 25 V 2-µs
700-mW MONO LOW-VOLTAGE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA72 SLOS23E NOVEMBER 998 REVISED JUNE 2004 700-mW MONO LOW-VOLTAGE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER FEATURES DESCRIPTION Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation The TPA72 is a bridge-tied load () audio power
TPA72 SLOS23E NOVEMBER 998 REVISED JUNE 2004 700-mW MONO LOW-VOLTAGE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER FEATURES DESCRIPTION Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation The TPA72 is a bridge-tied load () audio power
AVAILABLE OPTIONS PACKAGE VIOmax SMALL OUTLINE. PLASTIC DIP at 25 C (D) (P) 0 C to 70 C 5 mv LM306D LM306P
 SLCS8A OCTOBER 979 REVISED OCTOBER 99 Fast Response Times Improved Gain and Accuracy Fanout to Series 5/7 TTL Loads Strobe Capability Short-Circuit and Surge Protection Designed to Be Interchangeable With
SLCS8A OCTOBER 979 REVISED OCTOBER 99 Fast Response Times Improved Gain and Accuracy Fanout to Series 5/7 TTL Loads Strobe Capability Short-Circuit and Surge Protection Designed to Be Interchangeable With
TL4581 DUAL LOW-NOISE HIGH-DRIVE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 TL4581 DUAL LOW-NOISE HIGH-DRIVE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER SLVS457A JANUARY 2003 REVISED MARCH 2003 Equivalent Input Noise Voltage 5 nv/ Hz Typ at 1 khz Unity-Gain Bandwidth... 10 MHz Typ High Slew Rate...9
TL4581 DUAL LOW-NOISE HIGH-DRIVE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER SLVS457A JANUARY 2003 REVISED MARCH 2003 Equivalent Input Noise Voltage 5 nv/ Hz Typ at 1 khz Unity-Gain Bandwidth... 10 MHz Typ High Slew Rate...9
LM2900, LM3900 QUADRUPLE NORTON OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 LM29, LM39 QUADRUPLE NORTON OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS SLOS59 JULY 1979 REVISED SEPTEMBER 199 Wide Range of Supply Voltages, Single or Dual Supplies Wide Bandwidth Large Output Voltage Swing Output Short-Circuit
LM29, LM39 QUADRUPLE NORTON OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS SLOS59 JULY 1979 REVISED SEPTEMBER 199 Wide Range of Supply Voltages, Single or Dual Supplies Wide Bandwidth Large Output Voltage Swing Output Short-Circuit
AVAILABLE OPTIONS PACKAGE SMALL OUTLINE (D) The D package is available taped and reeled. Add the suffix R to the device type (i.e., LT1030CDR).
 LT1030C QUADRUPLE LOW-POWER LINE DRIVER Low Supply Voltage... ±5 V to ±15 V Supply Current...500 µa Typical Zero Supply Current When Shut Down Outputs Can Be Driven ±30 V Output Open When Off (3-State)
LT1030C QUADRUPLE LOW-POWER LINE DRIVER Low Supply Voltage... ±5 V to ±15 V Supply Current...500 µa Typical Zero Supply Current When Shut Down Outputs Can Be Driven ±30 V Output Open When Off (3-State)
150-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA6A2 5-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS34A DECEMBER 2 REVISED SEPTEMBER 24 FEATURES 5 mw Stereo Output PC Power Supply Compatible Fully Specified for 3.3 V and 5 V Operation Operation to 2.5 V Pop
TPA6A2 5-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS34A DECEMBER 2 REVISED SEPTEMBER 24 FEATURES 5 mw Stereo Output PC Power Supply Compatible Fully Specified for 3.3 V and 5 V Operation Operation to 2.5 V Pop
1 to 4 Configurable Clock Buffer for 3D Displays
 1 S3 GND S4 4 5 6 CLKIN 3 CLKOUT3 S1 2 Top View CLKOUT4 S2 1 7 8 9 OE 12 11 10 CLKOUT1 VDD CLKOUT2 CDC1104 SCAS921 SEPTEMBER 2011 1 to 4 Configurable Clock Buffer for 3D Displays Check for Samples: CDC1104
1 S3 GND S4 4 5 6 CLKIN 3 CLKOUT3 S1 2 Top View CLKOUT4 S2 1 7 8 9 OE 12 11 10 CLKOUT1 VDD CLKOUT2 CDC1104 SCAS921 SEPTEMBER 2011 1 to 4 Configurable Clock Buffer for 3D Displays Check for Samples: CDC1104
SN75157 DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER
 SN75157 DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-422-B and EIA/TIA-423-B and ITU Recommendation V.1 and V.11 Operates From Single 5-V Power Supply Wide
SN75157 DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-422-B and EIA/TIA-423-B and ITU Recommendation V.1 and V.11 Operates From Single 5-V Power Supply Wide
Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS083B Revised March 2003
 Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS083B Revised March 2003 The CD4536B types are supplied in 16-lead hermetic dual-in-line ceramic packages (F3A suffix), 16-lead dual-in-line plastic packages
Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS083B Revised March 2003 The CD4536B types are supplied in 16-lead hermetic dual-in-line ceramic packages (F3A suffix), 16-lead dual-in-line plastic packages
SN75471 THRU SN75473 DUAL PERIPHERAL DRIVERS
 SN747 THRU SN747 DUAL PERIPHERAL DRIVERS SLRS024 DECEMBER 976 REVISED MAY 990 PERIPHERAL DRIVERS FOR HIGH-VOLTAGE HIGH-CURRENT DRIVER APPLICATIONS Characterized for Use to 00 ma High-Voltage Outputs No
SN747 THRU SN747 DUAL PERIPHERAL DRIVERS SLRS024 DECEMBER 976 REVISED MAY 990 PERIPHERAL DRIVERS FOR HIGH-VOLTAGE HIGH-CURRENT DRIVER APPLICATIONS Characterized for Use to 00 ma High-Voltage Outputs No
SN74LV04A-Q1 HEX INVERTER
 SN74LV04A-Q1 HEX INVERTER Qualified for Automotive Applications ESD Protection Exceeds 2000 V Per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015; Exceeds 200 V Using Machine Model (C = 200 pf, R = 0) 2-V to 5.5-V Operation
SN74LV04A-Q1 HEX INVERTER Qualified for Automotive Applications ESD Protection Exceeds 2000 V Per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015; Exceeds 200 V Using Machine Model (C = 200 pf, R = 0) 2-V to 5.5-V Operation
150-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA6A2 5-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS33B DECEMBER 2 REVISED JUNE 24 FEATURES DESCRIPTION 5-mW Stereo Output The TPA6A2 is a stereo audio power amplifier PC Power Supply Compatible packaged in either
TPA6A2 5-mW STEREO AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER SLOS33B DECEMBER 2 REVISED JUNE 24 FEATURES DESCRIPTION 5-mW Stereo Output The TPA6A2 is a stereo audio power amplifier PC Power Supply Compatible packaged in either
SN74CBT3861DWR 10-BIT FET BUS SWITCH. description. logic diagram (positive logic)
 SN74CBT3861 10-BIT FET BUS SWITCH SCDS061D APRIL 1998 REVISED OCTOBER 2000 5-Ω Switch Connection Between Two Ports TTL-Compatible Input Levels Latch-Up Performance Exceeds 250 ma Per JESD 17 description
SN74CBT3861 10-BIT FET BUS SWITCH SCDS061D APRIL 1998 REVISED OCTOBER 2000 5-Ω Switch Connection Between Two Ports TTL-Compatible Input Levels Latch-Up Performance Exceeds 250 ma Per JESD 17 description
description/ordering information
 3-Terminal Regulators Output Current Up To 100 ma No External Components Required Internal Thermal-Overload Protection Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting Direct Replacement for Industry-Standard MC79L00
3-Terminal Regulators Output Current Up To 100 ma No External Components Required Internal Thermal-Overload Protection Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting Direct Replacement for Industry-Standard MC79L00
TPA mW MONO LOW-VOLTAGE AUDIO POWER AMPLIFIER
 TPA7 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power 7 mw at V DD = 5 V,, R L = 8 Ω 85 mw at V DD = 5 V,, R L = 32 Ω 25 mw at V DD = 3.3 V,, R L = 8
TPA7 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power 7 mw at V DD = 5 V,, R L = 8 Ω 85 mw at V DD = 5 V,, R L = 32 Ω 25 mw at V DD = 3.3 V,, R L = 8
SN75158 DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE DRIVER
 SN7558 DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE DRIVER Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI EIA/TIA-422-B and ITU Recommendation V. Single 5-V Supply Balanced-Line Operation TTL Compatible High Output Impedance in
SN7558 DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE DRIVER Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI EIA/TIA-422-B and ITU Recommendation V. Single 5-V Supply Balanced-Line Operation TTL Compatible High Output Impedance in
LP324, LP2902 ULTRA-LOW-POWER QUADRUPLE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 www.ti.com FEATURES Low Supply Current... 85 µa Typ Low Offset Voltage... 2 mv Typ Low Input Bias Current... 2 na Typ Input Common Mode to GND Wide Supply Voltage... 3 V < V CC < 32 V Pin Compatible With
www.ti.com FEATURES Low Supply Current... 85 µa Typ Low Offset Voltage... 2 mv Typ Low Input Bias Current... 2 na Typ Input Common Mode to GND Wide Supply Voltage... 3 V < V CC < 32 V Pin Compatible With
CD74HC4017-Q1 HIGH-SPEED CMOS LOGIC DECADE COUNTER/DIVIDER WITH 10 DECODED OUTPUTS
 Qualified for Automotive Applications Fully Static Operation Buffered Inputs Common Reset Positive Edge Clocking Typical f MAX = 60 MHz at = 5 V, = 5 pf, T A = 25 C Fanout (Over Temperature Range) Standard
Qualified for Automotive Applications Fully Static Operation Buffered Inputs Common Reset Positive Edge Clocking Typical f MAX = 60 MHz at = 5 V, = 5 pf, T A = 25 C Fanout (Over Temperature Range) Standard
74ACT11244 OCTAL BUFFER/LINE DRIVER WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
 3-State Outputs Drive Bus Lines or Buffer Memory Address Registers Inputs Are TTL-Voltage Compatible Flow-Through Architecture Optimizes PCB Layout Center-Pin V CC and GND Configurations to Minimize High-Speed
3-State Outputs Drive Bus Lines or Buffer Memory Address Registers Inputs Are TTL-Voltage Compatible Flow-Through Architecture Optimizes PCB Layout Center-Pin V CC and GND Configurations to Minimize High-Speed
Block Diagram 2
 2.5-W Stereo Audio Power Amplifier with Advanced DC Volume Control DESCRIPTOIN The EUA6021A is a stereo audio power amplifier that drives 2.5 W/channel of continuous RMS power into a 4-Ω load. Advanced
2.5-W Stereo Audio Power Amplifier with Advanced DC Volume Control DESCRIPTOIN The EUA6021A is a stereo audio power amplifier that drives 2.5 W/channel of continuous RMS power into a 4-Ω load. Advanced
GENERAL-PURPOSE LOW-VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 1 LMV331-Q1 SINGLE, LMV393-Q1 DUAL SLOS468D MAY 2005 REVISED AUGUST 2011 GENERAL-PURPOSE LOW-VOLTAGE COMPARATORS Check for Samples: LMV331-Q1 SINGLE, LMV393-Q1 DUAL 1FEATURES Qualified for Automotive Applications
1 LMV331-Q1 SINGLE, LMV393-Q1 DUAL SLOS468D MAY 2005 REVISED AUGUST 2011 GENERAL-PURPOSE LOW-VOLTAGE COMPARATORS Check for Samples: LMV331-Q1 SINGLE, LMV393-Q1 DUAL 1FEATURES Qualified for Automotive Applications
3.3 V Dual LVTTL to DIfferential LVPECL Translator
 1 SN65LVELT22 www.ti.com... SLLS928 DECEMBER 2008 3.3 V Dual LVTTL to DIfferential LVPECL Translator 1FEATURES 450 ps (typ) Propagation Delay Operating Range: V CC 3.0 V to 3.8 with GND = 0 V
1 SN65LVELT22 www.ti.com... SLLS928 DECEMBER 2008 3.3 V Dual LVTTL to DIfferential LVPECL Translator 1FEATURES 450 ps (typ) Propagation Delay Operating Range: V CC 3.0 V to 3.8 with GND = 0 V
5-V Dual Differential PECL Buffer-to-TTL Translator
 1 1FEATURES Dual 5-V Differential PECL-to-TTL Buffer 24-mA TTL Ouputs Operating Range PECL V CC = 4.75 V to 5.25 V with GND = 0 V Support for Clock Frequencies of 250 MHz (TYP) 3.5-ns Typical Propagation
1 1FEATURES Dual 5-V Differential PECL-to-TTL Buffer 24-mA TTL Ouputs Operating Range PECL V CC = 4.75 V to 5.25 V with GND = 0 V Support for Clock Frequencies of 250 MHz (TYP) 3.5-ns Typical Propagation
description logic diagram (positive logic) logic symbol
 SDAS074B APRIL 1982 REVISED JANUARY 1995 AS1004A Offer High Capacitive-Drive Capability Driver Version of ALS04B and AS04 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic Chip Carriers
SDAS074B APRIL 1982 REVISED JANUARY 1995 AS1004A Offer High Capacitive-Drive Capability Driver Version of ALS04B and AS04 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic Chip Carriers
RC4136, RM4136, RV4136 QUAD GENERAL-PURPOSE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 The RM4136 and RV4136 are obsolete and are no longer supplied. Continuous Short-Circuit Protection Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption
The RM4136 and RV4136 are obsolete and are no longer supplied. Continuous Short-Circuit Protection Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption
PRECISION VOLTAGE REGULATORS
 PRECISION LTAGE REGULATORS 150-mA Load Current Without External Power Transistor Adjustable Current-Limiting Capability Input Voltages up to 40 V Output Adjustable From 2 V to 37 V Direct Replacement for
PRECISION LTAGE REGULATORS 150-mA Load Current Without External Power Transistor Adjustable Current-Limiting Capability Input Voltages up to 40 V Output Adjustable From 2 V to 37 V Direct Replacement for
A733C...D, N, OR NS PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) ORDERING INFORMATION
 The A733M is obsolete and no longer supplied. 200-MHz Bandwidth 250-kΩ Input Resistance SLFS027B NOVEMBER 1970 REVISED MAY 2004 Selectable Nominal Amplification of 10, 100, or 400 No Frequency Compensation
The A733M is obsolete and no longer supplied. 200-MHz Bandwidth 250-kΩ Input Resistance SLFS027B NOVEMBER 1970 REVISED MAY 2004 Selectable Nominal Amplification of 10, 100, or 400 No Frequency Compensation
description FILT_CAP SHUTDOWN V DD BYPASS RIN LO/MO LIN GND ST/MN RO/MO+ DGQ PACKAGE (TOP VIEW)
 Ideal for Notebook Computers, PDAs, and Other Small Portable Audio Devices 2 W Into 4 Ω From 5-V Supply 0.6 W Into 4 Ω From 3-V Supply Stereo Head Phone Drive Mono (BTL) Signal Created by Summing Left
Ideal for Notebook Computers, PDAs, and Other Small Portable Audio Devices 2 W Into 4 Ω From 5-V Supply 0.6 W Into 4 Ω From 3-V Supply Stereo Head Phone Drive Mono (BTL) Signal Created by Summing Left
High-Side, Bidirectional CURRENT SHUNT MONITOR
 High-Side, Bidirectional CURRENT SHUNT MONITOR SBOS193D MARCH 2001 REVISED JANUARY 200 FEATURES COMPLETE BIDIRECTIONAL CURRENT MEASUREMENT CIRCUIT WIDE SUPPLY RANGE: 2.7V to 0V SUPPLY-INDEPENDENT COMMON-MODE
High-Side, Bidirectional CURRENT SHUNT MONITOR SBOS193D MARCH 2001 REVISED JANUARY 200 FEATURES COMPLETE BIDIRECTIONAL CURRENT MEASUREMENT CIRCUIT WIDE SUPPLY RANGE: 2.7V to 0V SUPPLY-INDEPENDENT COMMON-MODE
SN75124 TRIPLE LINE RECEIVER
 SN75124 TRIPLE LINE RECEIER Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of IBM System 360 Input/Output Interface Specification Operates From Single 5- Supply TTL Compatible Built-In Input Threshold Hysteresis High
SN75124 TRIPLE LINE RECEIER Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of IBM System 360 Input/Output Interface Specification Operates From Single 5- Supply TTL Compatible Built-In Input Threshold Hysteresis High
Dual Voltage Detector with Adjustable Hysteresis
 TPS3806J20 Dual Voltage Detector with Adjustable Hysteresis SLVS393A JULY 2001 REVISED NOVEMBER 2004 FEATURES DESCRIPTION Dual Voltage Detector With Adjustable The TPS3806 integrates two independent voltage
TPS3806J20 Dual Voltage Detector with Adjustable Hysteresis SLVS393A JULY 2001 REVISED NOVEMBER 2004 FEATURES DESCRIPTION Dual Voltage Detector With Adjustable The TPS3806 integrates two independent voltage
5-V PECL-to-TTL Translator
 1 SN65ELT21 www.ti.com... SLLS923 JUNE 2009 5-V PECL-to-TTL Translator 1FEATURES 3ns (TYP) Propagation Delay Operating Range: V CC = 4.2 V to 5.7 V with GND = 0 V 24-mA TTL Output Deterministic Output
1 SN65ELT21 www.ti.com... SLLS923 JUNE 2009 5-V PECL-to-TTL Translator 1FEATURES 3ns (TYP) Propagation Delay Operating Range: V CC = 4.2 V to 5.7 V with GND = 0 V 24-mA TTL Output Deterministic Output
AVAILABLE OPTIONS CERAMIC DIP (J) 6 mv ua747cd ua747cn. 5 mv ua747mj ua747mw ua747mfk
 SLOS9A D971, FEBRUARY 1971 REVISED OCTOBER 199 No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption Short-Circuit Protection Offset-Voltage Null Capability Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage
SLOS9A D971, FEBRUARY 1971 REVISED OCTOBER 199 No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption Short-Circuit Protection Offset-Voltage Null Capability Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage
MC3486 QUADRUPLE DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
 Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-422-B and EIA/TIA-423-B and ITU Recommendations V.10 and V.11 3-State, TTL-Compatible s Fast Transition Times Operates From Single 5-V Supply
Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-422-B and EIA/TIA-423-B and ITU Recommendations V.10 and V.11 3-State, TTL-Compatible s Fast Transition Times Operates From Single 5-V Supply
Precision Gain = 10 DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
 Precision Gain = 0 DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER SBOSA AUGUST 987 REVISED OCTOBER 00 FEATURES ACCURATE GAIN: ±0.0% max HIGH COMMON-MODE REJECTION: 8dB min NONLINEARITY: 0.00% max EASY TO USE PLASTIC 8-PIN DIP,
Precision Gain = 0 DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER SBOSA AUGUST 987 REVISED OCTOBER 00 FEATURES ACCURATE GAIN: ±0.0% max HIGH COMMON-MODE REJECTION: 8dB min NONLINEARITY: 0.00% max EASY TO USE PLASTIC 8-PIN DIP,
SN54ALS139, SN74ALS139 DUAL 2-LINE TO 4-LINE DECODERS/DEMULTIPLEXERS
 SN54ALS9, SN74ALS9 DUAL 2-LINE TO 4-LINE DECODERS/DEMULTIPLEXERS Designed Specifically for High-Speed Memory Decoders and Data Transmission Systems Incorporate Two Enable Inputs to Simplify Cascading and/or
SN54ALS9, SN74ALS9 DUAL 2-LINE TO 4-LINE DECODERS/DEMULTIPLEXERS Designed Specifically for High-Speed Memory Decoders and Data Transmission Systems Incorporate Two Enable Inputs to Simplify Cascading and/or
AM26C31-EP QUADRUPLE DIFFERENTIAL LINE DRIVER
 1 1FEATURES Controlled Baseline One Assembly One Test Site One Fabrication Site Extended Temperature Performance of 55 C to 125 C Enhanced Diminishing Manufacturing Sources (DMS) Support Enhanced Product-Change
1 1FEATURES Controlled Baseline One Assembly One Test Site One Fabrication Site Extended Temperature Performance of 55 C to 125 C Enhanced Diminishing Manufacturing Sources (DMS) Support Enhanced Product-Change
description BTL to SE Mode Control Integrated Depop Circuitry Thermal and Short-Circuit Protection Surface-Mount Packaging SOIC PowerPAD MSOP
 Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power 7 mw at V DD = 5 V, BTL, R L = 8 Ω 85 mw at V DD = 5 V,, R L = 32 Ω 25 mw at V DD = 3.3 V, BTL, R L
Fully Specified for 3.3-V and 5-V Operation Wide Power Supply Compatibility 2.5 V 5.5 V Output Power 7 mw at V DD = 5 V, BTL, R L = 8 Ω 85 mw at V DD = 5 V,, R L = 32 Ω 25 mw at V DD = 3.3 V, BTL, R L
CD74AC251, CD74ACT251
 Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS246 August 1998 CD74AC251, CD74ACT251 8-Input Multiplexer, Three-State Features Buffered Inputs Typical Propagation Delay - 6ns at V CC = 5V, T A = 25
Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS246 August 1998 CD74AC251, CD74ACT251 8-Input Multiplexer, Three-State Features Buffered Inputs Typical Propagation Delay - 6ns at V CC = 5V, T A = 25
TL780 SERIES POSITIVE-VOLTAGE REGULATORS
 FEATURES TL780 SERIES POSITIVE-VOLTAGE REGULATORS SLVS055M APRIL 1981 REVISED OCTOBER 2006 ±1% Output Tolerance at 25 C Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting ±2% Output Tolerance Over Full Operating
FEATURES TL780 SERIES POSITIVE-VOLTAGE REGULATORS SLVS055M APRIL 1981 REVISED OCTOBER 2006 ±1% Output Tolerance at 25 C Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting ±2% Output Tolerance Over Full Operating
description block diagram
 Fast Transient Response 10-mA to 3-A Load Current Short Circuit Protection Maximum Dropout of 450-mV at 3-A Load Current Separate Bias and VIN Pins Available in Adjustable or Fixed-Output Voltages 5-Pin
Fast Transient Response 10-mA to 3-A Load Current Short Circuit Protection Maximum Dropout of 450-mV at 3-A Load Current Separate Bias and VIN Pins Available in Adjustable or Fixed-Output Voltages 5-Pin
description/ordering information
 µ SLVS060K JUNE 1976 REVISED APRIL 2005 3-Terminal Regulators Output Current Up To 500 ma No External Components High Power-Dissipation Capability Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting Output Transistor
µ SLVS060K JUNE 1976 REVISED APRIL 2005 3-Terminal Regulators Output Current Up To 500 ma No External Components High Power-Dissipation Capability Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting Output Transistor
SN74LVC2G32-EP DUAL 2-INPUT POSITIVE-OR GATE
 www.ti.com SN74LVC2G32-EP DUAL 2-INPUT POSITIVE-OR GATE SCES543A FEBRUARY 2004 REVISED AUGUST 2006 FEATURES Controlled Baseline Typical V OHV (Output V OH Undershoot) >2 V at V CC = 3.3 V, T A = 25 C One
www.ti.com SN74LVC2G32-EP DUAL 2-INPUT POSITIVE-OR GATE SCES543A FEBRUARY 2004 REVISED AUGUST 2006 FEATURES Controlled Baseline Typical V OHV (Output V OH Undershoot) >2 V at V CC = 3.3 V, T A = 25 C One
Supports Partial-Power Down Mode 4.5-V to 5.5-V V Operation. (Output Ground Bounce) <0.8 V at V ESD Protection Exceeds JESD 22
 www.ti.com FEATURES SN74LV138AT 3-LINE TO 8-LINE DECODER/DEMULTIPLEXER SCLS691 AUGUST 2005 Inputs Are TTL-Voltage Compatible I off Supports Partial-Power Down Mode 4.5-V to 5.5-V V Operation CC Operation
www.ti.com FEATURES SN74LV138AT 3-LINE TO 8-LINE DECODER/DEMULTIPLEXER SCLS691 AUGUST 2005 Inputs Are TTL-Voltage Compatible I off Supports Partial-Power Down Mode 4.5-V to 5.5-V V Operation CC Operation
description/ordering information
 SLVS053D FEBRUARY 1988 REVISED NOVEMBER 2003 Complete PWM Power-Control Function Totem-Pole Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Parallel or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry
SLVS053D FEBRUARY 1988 REVISED NOVEMBER 2003 Complete PWM Power-Control Function Totem-Pole Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Parallel or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry
ORDERING INFORMATION ORDERABLE PART NUMBER SN74CBTS3306PWR
 5-Ω Switch Connection Between Two Ports TTL-Compatible Input Levels description/ordering information The SN74CBTS3306 features independent line switches with Schottky diodes on the I/Os to clamp undershoot.
5-Ω Switch Connection Between Two Ports TTL-Compatible Input Levels description/ordering information The SN74CBTS3306 features independent line switches with Schottky diodes on the I/Os to clamp undershoot.
CD54HC4015, CD74HC4015
 CD54HC4015, CD74HC4015 Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS198C November 1997 - Revised May 2003 High Speed CMOS Logic Dual 4-Stage Static Shift Register [ /Title (CD74 HC401 5) /Subject
CD54HC4015, CD74HC4015 Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS198C November 1997 - Revised May 2003 High Speed CMOS Logic Dual 4-Stage Static Shift Register [ /Title (CD74 HC401 5) /Subject
SN74LV374A-Q1 OCTAL EDGE-TRIGGERED D-TYPE FLIP-FLOP WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
 Qualified for Automotive Applications Typical V OLP (Output Ground Bounce) 2.3 V at = 3.3 V, T A = 25 C Supports Mixed-Mode Voltage
Qualified for Automotive Applications Typical V OLP (Output Ground Bounce) 2.3 V at = 3.3 V, T A = 25 C Supports Mixed-Mode Voltage
TPPM mA LOW-DROPOUT REGULATOR WITH AUXILIARY POWER MANAGEMENT AND POK
 Automatic Input Voltage Source Selection Glitch-Free Regulated Output 5-V Input Voltage Source Detector With Hysteresis 400-mA Load Current Capability With 5-V or 3.3-V Input Source Power OK Feature Based
Automatic Input Voltage Source Selection Glitch-Free Regulated Output 5-V Input Voltage Source Detector With Hysteresis 400-mA Load Current Capability With 5-V or 3.3-V Input Source Power OK Feature Based
LM317M 3-TERMINAL ADJUSTABLE REGULATOR
 FEATURES Output Voltage Range Adjustable From 1.25 V to 37 V Output Current Greater Than 5 ma Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting Thermal-Overload Protection Output Safe-Area Compensation Q Devices
FEATURES Output Voltage Range Adjustable From 1.25 V to 37 V Output Current Greater Than 5 ma Internal Short-Circuit Current Limiting Thermal-Overload Protection Output Safe-Area Compensation Q Devices
SN75207B DUAL SENSE AMPLIFIER FOR MOS MEMORIES OR DUAL HIGH-SENSITIVITY LINE RECEIVERS
 Plug-In Replacement for SN75107A and SN75107B With Improved Characteristics ± 10-mV Input Sensitivity TTL-Compatible Circuitry Standard Supply Voltages... ±5 V Differential Input Common-Mode Voltage Range
Plug-In Replacement for SN75107A and SN75107B With Improved Characteristics ± 10-mV Input Sensitivity TTL-Compatible Circuitry Standard Supply Voltages... ±5 V Differential Input Common-Mode Voltage Range
2 C Accurate Digital Temperature Sensor with SPI Interface
 TMP125 2 C Accurate Digital Temperature Sensor with SPI Interface FEATURES DIGITAL OUTPUT: SPI-Compatible Interface RELUTION: 10-Bit, 0.25 C ACCURACY: ±2.0 C (max) from 25 C to +85 C ±2.5 C (max) from
TMP125 2 C Accurate Digital Temperature Sensor with SPI Interface FEATURES DIGITAL OUTPUT: SPI-Compatible Interface RELUTION: 10-Bit, 0.25 C ACCURACY: ±2.0 C (max) from 25 C to +85 C ±2.5 C (max) from
description/ordering information
 The LP239 is obsolete and is no longer supplied. Wide Supply-Voltage Range...3 V to 30 V Ultralow Power Supply Current Drain...60 µa Typ Low Input Biasing Current...3 na Low Input Offset Current... ±0.5
The LP239 is obsolete and is no longer supplied. Wide Supply-Voltage Range...3 V to 30 V Ultralow Power Supply Current Drain...60 µa Typ Low Input Biasing Current...3 na Low Input Offset Current... ±0.5
ORDERING INFORMATION T A PACKAGE ORDERABLE PART NUMBER. SOIC D Tape and reel SN74CBTD3306DR 40 C to85 C
 5-Ω Switch Connection Between Two Ports TTL-Compatible Input Levels Designed to Be Used in Level-Shifting Applications description/ordering information The SN74CBTD3306 features two independent line switches.
5-Ω Switch Connection Between Two Ports TTL-Compatible Input Levels Designed to Be Used in Level-Shifting Applications description/ordering information The SN74CBTD3306 features two independent line switches.
CD4066B CMOS QUAD BILATERAL SWITCH
 15-V Digital or ±7.5-V Peak-to-Peak Switching 125-Ω Typical On-State Resistance for 15-V Operation Switch On-State Resistance Matched to Within 5 Ω Over 15-V Signal-Input Range On-State Resistance Flat
15-V Digital or ±7.5-V Peak-to-Peak Switching 125-Ω Typical On-State Resistance for 15-V Operation Switch On-State Resistance Matched to Within 5 Ω Over 15-V Signal-Input Range On-State Resistance Flat
ORDERING INFORMATION. SOIC DW Tape and reel SN74CBT3384ADWR
 SN74CBT3384A 10-BIT FET BUS SWITCH SCDS004L NOVEMBER 1992 REVISED JANUARY 2004 5-Ω Switch Connection Between Two Ports TTL-Compatible Input Levels description/ordering information The SN74CBT3384A provides
SN74CBT3384A 10-BIT FET BUS SWITCH SCDS004L NOVEMBER 1992 REVISED JANUARY 2004 5-Ω Switch Connection Between Two Ports TTL-Compatible Input Levels description/ordering information The SN74CBT3384A provides
OUTPUT INPUT ADJUSTMENT INPUT INPUT ADJUSTMENT INPUT
 www.ti.com FEATURES LM237, LM337 3-TERMINAL ADJUSTABLE REGULATORS SLVS047I NOVEMBER 1981 REVISED OCTOBER 2006 Output Voltage Range Adjustable From Peak Output Current Constant Over 1.2 V to 37 V Temperature
www.ti.com FEATURES LM237, LM337 3-TERMINAL ADJUSTABLE REGULATORS SLVS047I NOVEMBER 1981 REVISED OCTOBER 2006 Output Voltage Range Adjustable From Peak Output Current Constant Over 1.2 V to 37 V Temperature
4423 Typical Circuit A2 A V
 SBFS020A JANUARY 1978 REVISED JUNE 2004 FEATURES Sine and Cosine Outputs Resistor-Programmable Frequency Wide Frequency Range: 0.002Hz to 20kHz Low Distortion: 0.2% max up to 5kHz Easy Adjustments Small
SBFS020A JANUARY 1978 REVISED JUNE 2004 FEATURES Sine and Cosine Outputs Resistor-Programmable Frequency Wide Frequency Range: 0.002Hz to 20kHz Low Distortion: 0.2% max up to 5kHz Easy Adjustments Small
CD54/74AC283, CD54/74ACT283
 Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS251D August 1998 - Revised May 2000 Features Buffered Inputs Exceeds 2kV ESD Protection MIL-STD-883, Method 3015 SCR-Latchup-Resistant CMOS Process and
Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS251D August 1998 - Revised May 2000 Features Buffered Inputs Exceeds 2kV ESD Protection MIL-STD-883, Method 3015 SCR-Latchup-Resistant CMOS Process and
Precision, Gain of 0.2 Level Translation DIFFERENCE AMPLIFIER
 SBOS333B JULY 25 REVISED OCTOBER 25 Precision, Gain of.2 Level Translation DIFFERENCE AMPLIFIER FEATURES GAIN OF.2 TO INTERFACE ±1V SIGNALS TO SINGLE-SUPPLY ADCs GAIN ACCURACY: ±.24% (max) WIDE BANDWIDTH:
SBOS333B JULY 25 REVISED OCTOBER 25 Precision, Gain of.2 Level Translation DIFFERENCE AMPLIFIER FEATURES GAIN OF.2 TO INTERFACE ±1V SIGNALS TO SINGLE-SUPPLY ADCs GAIN ACCURACY: ±.24% (max) WIDE BANDWIDTH:
CD74HC4538-Q1 HIGH-SPEED CMOS LOGIC DUAL RETRIGGERABLE PRECISION MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
 Qualified for Automotive Applications Retriggerable/Resettable Capability Trigger and Reset Propagation Delays Independent of R X, C X Triggering From the Leading or Trailing Edge Q and Q Buffered Outputs
Qualified for Automotive Applications Retriggerable/Resettable Capability Trigger and Reset Propagation Delays Independent of R X, C X Triggering From the Leading or Trailing Edge Q and Q Buffered Outputs
SINGLE BUS BUFFER GATE WITH 3-STATE OUTPUT
 1 SN74LVC1G126-Q1 www.ti.com... SCES467B JULY 2003 REVISED APRIL 2008 SINGLE BUS BUFFER GATE WITH 3-STATE OUTPUT 1FEATURES Qualified for Automotive Applications ESD Protection Exceeds 2000 V Per MIL-STD-883,
1 SN74LVC1G126-Q1 www.ti.com... SCES467B JULY 2003 REVISED APRIL 2008 SINGLE BUS BUFFER GATE WITH 3-STATE OUTPUT 1FEATURES Qualified for Automotive Applications ESD Protection Exceeds 2000 V Per MIL-STD-883,
ORDERING INFORMATION. TOP-SIDE MARKING PDIP N Tube SN74S1051N SN74S1051N
 Designed to Reduce Reflection Noise Repetitive Peak Forward Current to 200 ma 12-Bit Array Structure Suited for Bus-Oriented Systems description/ordering information This Schottky barrier diode bus-termination
Designed to Reduce Reflection Noise Repetitive Peak Forward Current to 200 ma 12-Bit Array Structure Suited for Bus-Oriented Systems description/ordering information This Schottky barrier diode bus-termination
SN54ALS09, SN74ALS09 QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-AND GATES WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS
 SN54ALS09, SN74ALS09 QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-AND GATES WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS SDAS084B APRIL 1982 REVISED DECEMBER 1994 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic Chip
SN54ALS09, SN74ALS09 QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-AND GATES WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS SDAS084B APRIL 1982 REVISED DECEMBER 1994 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic Chip
SN5406, SN5416, SN7406, SN7416 HEX INVERTER BUFFERS/DRIVERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR HIGH-VOLTAGE OUTPUTS
 Convert TTL Voltage Levels to MOS Levels High Sink-Current Capability Input Clamping Diodes Simplify System Design Open-Collector Drivers for Indicator Lamps and Relays Inputs Fully Compatible With Most
Convert TTL Voltage Levels to MOS Levels High Sink-Current Capability Input Clamping Diodes Simplify System Design Open-Collector Drivers for Indicator Lamps and Relays Inputs Fully Compatible With Most
P-Channel NexFET Power MOSFET
 CSD252W5 www.ti.com SLPS269A JUNE 2 REVISED JULY 2 P-Channel NexFET Power MOSFET Check for Samples: CSD252W5 FEATURES PRODUCT SUMMARY V DS Drain to Drain Voltage 2 V Low Resistance Q g Gate Charge Total
CSD252W5 www.ti.com SLPS269A JUNE 2 REVISED JULY 2 P-Channel NexFET Power MOSFET Check for Samples: CSD252W5 FEATURES PRODUCT SUMMARY V DS Drain to Drain Voltage 2 V Low Resistance Q g Gate Charge Total
SN5406, SN5416, SN7406, SN7416 HEX INVERTER BUFFERS/DRIVERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR HIGH-VOLTAGE OUTPUTS SDLS031A DECEMBER 1983 REVISED DECEMBER 2001
 SN5406, SN5416, SN7406, SN7416 HEX INVERTER BUFFERS/DRIVERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR HIGH-VOLTAGE OUTPUTS SDLS031A DECEMBER 1983 REVISED DECEMBER 2001 Convert TTL Voltage Levels to MOS Levels High Sink-Current
SN5406, SN5416, SN7406, SN7416 HEX INVERTER BUFFERS/DRIVERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR HIGH-VOLTAGE OUTPUTS SDLS031A DECEMBER 1983 REVISED DECEMBER 2001 Convert TTL Voltage Levels to MOS Levels High Sink-Current
TS5A4594 SINGLE-CHANNEL 8- SPST ANALOG SWITCH
 www.ti.com TS5A4594 SGLE-CHANNEL 8- SPST ANALOG SWITCH Description The TS5A4594 is a single-pole single-throw (SPST) analog switch that is designed to operate from V to 5.5 V. This device can handle both
www.ti.com TS5A4594 SGLE-CHANNEL 8- SPST ANALOG SWITCH Description The TS5A4594 is a single-pole single-throw (SPST) analog switch that is designed to operate from V to 5.5 V. This device can handle both
CD54HC283, CD74HC283, CD54HCT283, CD74HCT283
 CD54HC283, CD74HC283, CD54HCT283, CD74HCT283 [ /Title (CD74 HC283, CD74 HCT28 3) /Subject (High Speed CMOS Logic 4-Bit Binary Full Adder Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS176D November
CD54HC283, CD74HC283, CD54HCT283, CD74HCT283 [ /Title (CD74 HC283, CD74 HCT28 3) /Subject (High Speed CMOS Logic 4-Bit Binary Full Adder Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS176D November
SN74LVC1G32-Q1 SINGLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-OR GATE
 FEATURES Qualified for Automotive Applications Customer-Specific Configuration Control Can Be Supported Along With Major-Change Approval Supports 5-V V CC Operation Inputs Accept Voltages to 5.5 V Low
FEATURES Qualified for Automotive Applications Customer-Specific Configuration Control Can Be Supported Along With Major-Change Approval Supports 5-V V CC Operation Inputs Accept Voltages to 5.5 V Low
description LO/MO LIN GND ST/MN RO/MO+ MONO IN SHUTDOWN V DD BYPASS RIN DGQ PACKAGE (TOP VIEW)
 Ideal for Notebook Computers, PDAs, and Other Small Portable Audio Devices 2 W Into 4 Ω From 5-V Supply 0.6 W Into 4 Ω From 3-V Supply Stereo Headphone Drive Separate Inputs for the Mono (BTL) Signal,
Ideal for Notebook Computers, PDAs, and Other Small Portable Audio Devices 2 W Into 4 Ω From 5-V Supply 0.6 W Into 4 Ω From 3-V Supply Stereo Headphone Drive Separate Inputs for the Mono (BTL) Signal,
3.3 V ECL 1:2 Fanout Buffer
 1 1FEATURES 1:2 ECL Fanout Buffer DESCRIPTION Operating Range The SN65LVEL11 is a fully differential 1:2 ECL fanout PECL V buffer. The device includes circuitry to maintain a CC = 3.0 V to 3.8 V With known
1 1FEATURES 1:2 ECL Fanout Buffer DESCRIPTION Operating Range The SN65LVEL11 is a fully differential 1:2 ECL fanout PECL V buffer. The device includes circuitry to maintain a CC = 3.0 V to 3.8 V With known
description/ordering information
 AC Types Feature 1.5-V to 5.5-V Operation and Balanced Noise Immunity at 30% of the Supply Speed of Bipolar F, AS, and S, With Significantly Reduced Power Consumption Balanced Propagation Delays ±24-mA
AC Types Feature 1.5-V to 5.5-V Operation and Balanced Noise Immunity at 30% of the Supply Speed of Bipolar F, AS, and S, With Significantly Reduced Power Consumption Balanced Propagation Delays ±24-mA
UC1842A-EP, UC1843A-EP, UC1844A-EP, UC1845A-EP CURRENT-MODE PWM CONTROLLER
 Controlled Baseline One Assembly/Test Site, One Fabrication Site Extended Temperature Performance of 55 C to 125 C Enhanced Diminishing Manufacturing Sources (DMS) Support Enhanced Product Change Notification
Controlled Baseline One Assembly/Test Site, One Fabrication Site Extended Temperature Performance of 55 C to 125 C Enhanced Diminishing Manufacturing Sources (DMS) Support Enhanced Product Change Notification
MC3303, MC3403 QUADRUPLE LOW-POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 MC3303, MC3403 QUADRUPLE LOW-POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS SLOS101C FEBRUARY 1979 REVISED FEBRUARY 2002 Wide Range of Supply Voltages, Single Supply...3 V to 36 V or Dual Supplies Class AB Output Stage
MC3303, MC3403 QUADRUPLE LOW-POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS SLOS101C FEBRUARY 1979 REVISED FEBRUARY 2002 Wide Range of Supply Voltages, Single Supply...3 V to 36 V or Dual Supplies Class AB Output Stage
CD54HC147, CD74HC147, CD74HCT147
 CD54HC147, CD74HC147, CD74HCT147 Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS149F September 1997 - Revised November 2003 High-Speed CMOS Logic 10- to 4-Line Priority Encoder [ /Title (CD74 HC147,
CD54HC147, CD74HC147, CD74HCT147 Data sheet acquired from Harris Semiconductor SCHS149F September 1997 - Revised November 2003 High-Speed CMOS Logic 10- to 4-Line Priority Encoder [ /Title (CD74 HC147,
SN74AUC1G125 SINGLE BUS BUFFER GATE WITH 3-STATE OUTPUT
 www.ti.com FEATURES SN74AUC1G125 SINGLE BUS BUFFER GATE WITH 3-STATE OUTPUT SCES382K MARCH 2002 REVISED APRIL 2007 Available in the Texas Instruments Low Power Consumption, 10-µA Max I CC NanoFree Package
www.ti.com FEATURES SN74AUC1G125 SINGLE BUS BUFFER GATE WITH 3-STATE OUTPUT SCES382K MARCH 2002 REVISED APRIL 2007 Available in the Texas Instruments Low Power Consumption, 10-µA Max I CC NanoFree Package
150-mA LOW-NOISE LDO WITH IN-RUSH CURRENT CONTROL FOR USB APPLICATION
 TPS7882, TPS78833 -ma LOW-NOISE LDO WITH IN-RUSH CURRENT CONTROL FOR USB APPLICATION SLVS382A JUNE 2 REVISED JULY 2 FEATURES -ma Low-Dropout Regulator Available in 2. V, 3.3 V Programmable Slew Rate Control
TPS7882, TPS78833 -ma LOW-NOISE LDO WITH IN-RUSH CURRENT CONTROL FOR USB APPLICATION SLVS382A JUNE 2 REVISED JULY 2 FEATURES -ma Low-Dropout Regulator Available in 2. V, 3.3 V Programmable Slew Rate Control
Dual, VARIABLE GAIN AMPLIFIER with Input Buffer
 JULY 22 REVISED NOVEMBER 23 Dual, VARIABLE GAIN AMPLIFIER with Input Buffer FEATURES GAIN RANGE: up to 43dB 3MHz BANDWIDTH LOW CROSSTALK: 65dB at Max Gain, 5MHz HIGH-SPEED VARIABLE GAIN ADJUST POWER SHUTDOWN
JULY 22 REVISED NOVEMBER 23 Dual, VARIABLE GAIN AMPLIFIER with Input Buffer FEATURES GAIN RANGE: up to 43dB 3MHz BANDWIDTH LOW CROSSTALK: 65dB at Max Gain, 5MHz HIGH-SPEED VARIABLE GAIN ADJUST POWER SHUTDOWN
description/ordering information
 Controlled Baseline One Assembly/Test Site, One Fabrication Site Extended Temperature Performance of 40 C to 105 C Enhanced Diminishing Manufacturing Sources (DMS) Support Enhanced Product-Change Notification
Controlled Baseline One Assembly/Test Site, One Fabrication Site Extended Temperature Performance of 40 C to 105 C Enhanced Diminishing Manufacturing Sources (DMS) Support Enhanced Product-Change Notification
description/ordering information
 The LM118 and LM218 are obsolete and are no longer supplied. Small Signal Bandwidth... 15 MHz Typ Slew Rate... 50 V/µs Min Bias Current... 250 na Max (LM118, LM218) Supply Voltage Range... ±5 V to ±20
The LM118 and LM218 are obsolete and are no longer supplied. Small Signal Bandwidth... 15 MHz Typ Slew Rate... 50 V/µs Min Bias Current... 250 na Max (LM118, LM218) Supply Voltage Range... ±5 V to ±20
SN54ALS38B, SN74ALS38B QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-NAND BUFFERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS
 SN54ALS38B, SN74ALS38B QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-NAND BUFFERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS SDAS196B APRIL 1982 REVISED DECEMBER 1994 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic
SN54ALS38B, SN74ALS38B QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-NAND BUFFERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS SDAS196B APRIL 1982 REVISED DECEMBER 1994 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic
Related Synchronous MOSFET Drivers DEVICE NAME ADDITIONAL FEATURES INPUTS TPS2830. Noninverted TPS2831. Inverted TPS2834. Noninverted TPS2835
 Floating Bootstrap or Ground-Reference High-Side Driver Adaptive Dead-Time Control 50-ns Max Rise/Fall Times and 00-ns Max Propagation Delay 3.3-nF Load Ideal for High-Current Single or Multiphase Power
Floating Bootstrap or Ground-Reference High-Side Driver Adaptive Dead-Time Control 50-ns Max Rise/Fall Times and 00-ns Max Propagation Delay 3.3-nF Load Ideal for High-Current Single or Multiphase Power
NOT RECOMMENDED FOR NEW DESIGNS USE CDCVF2510A AS A REPLACEMENT
 CDCVF2510 3.3-V PHASE-LOCK LOOP CLOCK DRIVER FEATURES Designed to Meet and Exceed PC133 SDRAM Registered DIMM Specification Rev. 1.1 Spread Spectrum Clock Compatible Operating Frequency 50 MHz to 175 MHz
CDCVF2510 3.3-V PHASE-LOCK LOOP CLOCK DRIVER FEATURES Designed to Meet and Exceed PC133 SDRAM Registered DIMM Specification Rev. 1.1 Spread Spectrum Clock Compatible Operating Frequency 50 MHz to 175 MHz
