Continuity of the Norm of a Composition Operator
|
|
|
- Willis Casey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Integr. equ. oper. theory 45 (003) X/ $ /0 c 003 Birkhäuser Verlag Basel/Switzerl Integral Equations Operator Theory Continuity of the Norm of a Composition Operator David B. Pokorny Jonathan E. Shapiro Abstract. We explore the continuity of the map which, given an analytic selfmap of the disk, takes as its value the norm of the associated composition operator on the Hardy space H. We also examine the continuity the functions which assign to a self-map of the disk the Hilbert-Schmidt norm or the essential norm of the associated composition operator show these to be discontinuous. Additionally, we characterize when the norm of a composition operator is minimal. Mathematics Subject Classification (000). Primary 47-A30. Keywords. composition operator, norm.. Introduction Let D denote the unit disc of the complex plane ϕ be a holomorphic function on D with ϕ(d) D. The equation C ϕ f = f ϕ defines a composition operator on the Hardy Space H. For any such ϕ, C ϕ is a bounded operator (see [4, pg. 7]). It is known that if ϕ n ϕ weakly in H then C ϕn C ϕ weakly. If ϕ n ϕ in H then C ϕn C ϕ pointwise or strongly. These results others are found in [7]. It is also known that ϕ n ϕ in some sense does not in general imply that C ϕ C ϕn 0. However, we show that in several cases, it does imply that C ϕn C ϕ. Let ASM(D) be the set of all analytic self-maps of the disk, considered as a subset of H or H. We will denote this set ASM(D) or ASM(D) respectively, when we wish to make a distinction. Recall that the H norm is given by ϕ = We would like to thank Joel Shapiro for his helpful comments during the preparation of this work. This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No
2 35 Pokorny Shapiro IEOT sup z < ϕ(z), the H norm is given by π ϕ = ϕ(e iθ ) dθ 0 π. Let N : ASM(D) R be given by N(ϕ) = C ϕ. We will use N : ASM(D) R N : ASM(D) R to distinguish the topologies on the domain (N N N ). Stated in a different way, we are asking: For which functions ϕ ASM(D) is N or N continuous? In addition to questions of the convergence of C ϕn to C ϕ, we will consider similar questions with the operator norm replaced with either the essential norm e or the Hilbert-Schmidt norm HS. Recall that T e is the distance from T to the subspace of compact operators in the operator norm topology T HS = Te n n= where {e n } is a complete orthonormal basis. We will also often suppress the subscript write f = f for the H norm of an analytic function in D. In Section 5, we show that the well known lower bound for the norm of a composition operator C ϕ, equation (3.), is attained (when ϕ(0) 0) only when ϕ is a constant function. This appears here as Theorem 4. Chris Hammond, in [6], has recently obtained this same theorem with a different proof.. Hilbert-Schmidt Operators Let ASM(D) HS denote the set of analytic self-maps of D that induce Hilbert- Schmidt composition operators, give this set the H norm. Suppose that ϕ n ϕ are all in ASM(D) HS. Does it then follow that C ϕ n HS C ϕ HS?In general, the answer is no, as the example below demonstrates. Let [ ϕ(z) = + ( ) ] / z +z [ ( n ϕ n (z) = n+ ) / + ( n n+ z +z ) / ] where the real part of z / is always positive. We approach the Hilbert-Schmidt norms of composition operators by using the formulas (as in [4, Sec. 3.3]) C ϕ,c ψ HS = π 0 ϕ(e iθ )ψ(e iθ ) dθ π
3 Vol. 45 (003) Continuity of the Norm 353 π C ϕ dθ HS = 0 ϕ(e iθ ) π. To prove that C ϕ is Hilbert-Schmidt, we will show by direct computation that the integral π dθ 0 ϕ(e iθ ) π is finite. Since ϕ(e iθ )=ϕ(e iθ ) this will show that C ϕ HS is finite. First note that for 0 <θ<π, e iθ tan(θ/) =, +eiθ i if we set t = tan(θ/), so thus ϕ(e iθ )= + t i = + t i t ϕ(e iθ ) = + t + t ϕ(e iθ ) = =+ + t+t It can be shown using basic calculus that the integral π 0 ( + t + t. ) dθ tan(θ/) + tan(θ/) π converges. Each of the maps ϕ n has an angular derivative at because each ϕ n is in fact analytic in a disc centered at. Thus none of the C ϕn are compact thus none have finite Hilbert-Schmidt norm. n For each n, choose n+ <r n < such that C rnϕ n HS >n. Note that each r n ϕ n induces a Hilbert-Schmidt operator. Now C rnϕ n HS while r n ϕ n ϕ in H. What about ϕ such that ϕ <? Is the map N HS (ϕ) = ϕ HS continuous at such points? Suppose that ϕ < ϕ n ϕ in ASM(D) HS. There exists an r< such that for sufficiently large n, ϕ n <r.thus C ϕn C ϕ HS = C ϕ HS + C ϕn HS C ϕ,c ϕn HS C ϕn,c ϕ HS π π = 0 ϕ n + π 0 ϕ π 0 ϕ n ϕ 0 ϕ n ϕ. This in turn gives π C ϕn C ϕ ϕ(ϕ ϕ n ) π HS = 0 ( ϕ )( ϕ n ϕ) + ϕ n (ϕ n ϕ) 0 ( ϕ n )( ϕ n ϕ)
4 354 Pokorny Shapiro IEOT π ( r ) ϕ n ϕ 0 0 as n. It now follows that C ϕn HS C ϕ HS. We thus have the following Theorem. N HS is continuous at all ϕ with ϕ <. Does this theorem hold if we replace the norm on the space ASM(D) HS with the H norm? No: Let η(z) = ( ) / + i( z ) α p (z) = p z (p D). pz Then η(z) maps D to the upper half-disk (with i mapping to 0) α p is the automorphism of the disk that sends 0 to p. For any p D, C η αp HS = because η α p (z) = on a set of positive measure (an arc of the upper halfcircle in a neighborhood of i). For each n, letη n = η α i( n ). Then, as n gets large, η n maps the unit circle (at least all of it away from some neighborhood of i) to arbitrarily small segments on the real line centered at 0, so η n 0as n n. Choose r n such that n+ <r n < C rnη n HS >n.wenowhave C rnη n HS r n η n 0inH as n. Remark: It is easy to check that if ϕ ASM(D) satisfies C ϕ HS = then C rϕ HS is unbounded for r (0, ). 3. Continuity of the norm We now address the first question raised in the introduction. Is N or N continuous? As the H topology is stronger than H topology, a map ϕ at which N is continuous is a map at which N is continuous. Theorem. The map N ( thus N ) is continuous at ϕ if either ϕ(0) = 0 or ϕ is an inner map. The map N is continuous at ϕ which satisfy ϕ(d) rd for some r<. Proof. The following estimate for the norm of a composition operator is well-known (for instance in [4, Cor. 3.7]): C ϕ + ϕ(0) (3.) ϕ(0) ϕ(0) Furthermore, it is noted in [8] that the upper bound is attained if ϕ is inner. If ϕ(0) = 0, then C ϕ =ϕ n (0) 0, so the bounds given above force lim n C ϕn =.LetT L(H ) be a bounded linear operator. Define T (m) =
5 Vol. 45 (003) Continuity of the Norm 355 TK m where K m is the orthogonal projection of H onto the subspace spanned by {,z,z,...,z m }. Then T (n) T () + T (z) + + T (z m ), so if ϕ n ϕ in H ( thus in H ), one obtains C ϕn C ϕ (n) ϕ n ϕ + ϕ n ϕ + + ϕ m n ϕ m. Since ϕ k n ϕ k ϕ n ϕ ϕ k n + + ϕ k k ϕ n ϕ, we have C ϕn C ϕ (m) m ϕ n ϕ.thusϕ C ϕ (m) is a continuous map on ASM(D) for all m. As lim m C ϕ (m) = C ϕ is an increasing limit for all ϕ ASM(D), N (ϕ) is lower semi-continuous for all ϕ. In other words, if ϕ is given ε>0then there exists δ>0such that ϕ ψ δ implies C ψ C ϕ ε. Note that if ϕ n ϕ in H then ϕ n (0) ϕ(0). This can be seen using properties of subharmonic functions (see [5, Th..6.4]). For each n, g n (z) =ϕ n (z) ϕ(z) is a bounded analytic function in D g n is subharmonic so π g n = lim r 0 If, on the other h, ϕ is inner, then lim n C ϕ n lim n g n (re iθ ) dθ π g n(0). + ϕ n (0) ϕn (0) = + ϕ(0) ϕ(0) = C ϕ. Since N (ϕ) is lower semi-continuous, this gives lim C ϕ n n = C ϕ. Suppose now that ϕ n ϕ in H ϕ(d) rd for some r<. In this case, there exists an r < such that ϕ n (z) <r for sufficiently large n. We have already shown, while proving Theorem, that we can conclude that C ϕn C ϕ HS 0, so C ϕn C ϕ 0 hence C ϕn C ϕ. This theorem shows that, in several cases, C ϕn C ϕ when ϕ n ϕ in H. In general, it is not true that C ϕ C ϕn 0. It is well known that C ϕ C ϕn can stay large, even when ϕ n ϕ in H. As a simple example, consider the functions ϕ n (z) =e i π n z ϕ(z) =z. Here (C ϕ C ϕn )(z n ) = z n (e i π n z) n = z n + z n =, so C ϕn C ϕ for all n. 4. The essential norm Let ϕ n (z) =( n )z ϕ(z) =z. Since ϕ n = n <, each C ϕ n is compact hence C ϕn e = 0 for all n (see [9] for details). Using the formula for the essential norm given in [0], we have C ϕ e = lim sup w N ϕ (w)/( log w ) = (here N ϕ is the Nevanlinna counting function). Thus the map ϕ C ϕ e is not continuous everywhere on ASM(D). In fact we have the following
6 356 Pokorny Shapiro IEOT Theorem 3. If the map ϕ C ϕ e on ASM(D) is continuous at ϕ, then C ϕ is a compact operator. Proof. Suppose that C ϕ is not a compact operator. Let ϕ n = n n+ ϕ.wehave C ϕn e = 0 for all n, but C ϕ e > 0. The converse of this theorem remains open. For reference, define the maps N,e on ASM(D) N,e on ASM(D) by N,e (ϕ) =N,e (ϕ) = C ϕ e. 5. Composition operators of minimal norm Consider the upper lower bounds for the norm of a composition operator on H that appear in equation (3.). It is known precisely when C ϕ achieves this upper bound (see [8]). Namely, if ϕ(0) = 0, then C ϕ =,ifϕ(0) 0 then C ϕ = + ϕ(0) ϕ(0) if only if ϕ is inner. Suppose that ϕ is now a constant function. A straightforward calculation shows that C ϕ = ϕ(0). Does this equation characterize the constant analytic self-maps of D? The answer is yes: Theorem 4. Suppose that ϕ is an analytic self-map of D, ϕ(0) 0,ϕ is not constant. Then C ϕ > ϕ(0). Proof. Let ϕ(0) = a without loss of generality assume that a is real positive. Since non-constant analytic maps are open, there is a real b>asuch that ϕ(z) =b for some z D. Letx>0 observe that Cϕ(K 0 + xk z ) C ϕ K 0 + xk z where K t (w) = is the reproducing kernel at t D. Wehave tw C ϕ(k 0 + xk z ) K 0 + xk z = a + x ab + x b +x + x z ( +x a = a ab + x a b +x + x z Now notice that since b > a > 0, we have a ab >. If x satisfies 0 < x < ( ( z a ) ab ), then x a < x z ab x, ).
7 Vol. 45 (003) Continuity of the Norm 357 so We thus have +x + x a a < +x + x z ab b < a a +x ab + x b. +x + x z a < C ϕ(k 0 + xk z ) K 0 + xk z C ϕ. 6. Conclusion We have examined the continuity of several types of norms on composition operators with respect the symbols of those composition operators. We have proved that the map N is lower semi-continuous, indeed, continuous at all ϕ which either map 0 to 0, or are inner, N is continuous at all ϕ which map D into rd for some r<. K To our knowledge, other functions such as N L (ϕ) =sup ϕ(w) w D K w C N L3 (ϕ) =sup ϕk w w D K w have not yet been investigated in terms of continuity. (The L notation follows [].) The continuity of these maps could possibly have some relationship with that of N, since, for ϕ in a large subset of ASM(D), we have K ϕ(w) C ϕ =sup w D K w =sup C ϕ K w w D K w. This is not true for all ϕ in ASM(D), as was shown in [] discussed further in [] [3]. We conclude with the following conjecture: Conjecture. The map N (ϕ) is a continuous function on ASM(D). This would in turn demonstrate the continuity of N. We also ask if N,e N,e are continuous at ϕ if only if C ϕ is a compact operator. References [] M. Appell, P. Bourdon, J. Thrall, Norms of composition operators on Hardy spaces, Experimental Math. 5 (996), -7. [] P. Avramidou F. Jafari, On norms of composition operators on Hardy spaces, Contemp. Math. 3 (999), [3] P. Bourdon D. Retsek, Reproducing kernels norms of composition operators, Acta Sci. Math. (Szeged) 67 (00),
8 358 Pokorny Shapiro IEOT [4] C. C. Cowen B. D. MacCluer, Composition Operators on Spaces of Analytic Functions, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 996. [5] P. Duren, Theory of H p Spaces, Academic Press, New York, 970. [6] C. Hammond, On the norm of a composition operator with linear fractional symbol, preprint. [7] H. J. Schwartz, Composition operators on H p, Thesis, Univ. of Toledo, 969. [8] J. H. Shapiro, What do composition operators know about inner functions?, Monatsh. Math. 30(000), [9] J. H. Shapiro, Composition Operators Classical Function Theory, Springer- Verlag, New York, 993. [0] J. H. Shapiro, The essential norm of a composition operator, Ann. of Math. () 5(987), David B. Pokorny Mathematics Department, University of California, Berkeley, CA davebrok@soda.csua.berkeley.edu URL: Jonathan E. Shapiro Mathematics Department, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, CA jshapiro@calpoly.edu URL: Submitted: January 3, 00 Revised: March, 00 To access this journal online:
TOPOLOGY, LIMITS OF COMPLEX NUMBERS. Contents 1. Topology and limits of complex numbers 1
 TOPOLOGY, LIMITS OF COMPLEX NUMBERS Contents 1. Topology and limits of complex numbers 1 1. Topology and limits of complex numbers Since we will be doing calculus on complex numbers, not only do we need
TOPOLOGY, LIMITS OF COMPLEX NUMBERS Contents 1. Topology and limits of complex numbers 1 1. Topology and limits of complex numbers Since we will be doing calculus on complex numbers, not only do we need
Functions of several variables
 Chapter 6 Functions of several variables 6.1 Limits and continuity Definition 6.1 (Euclidean distance). Given two points P (x 1, y 1 ) and Q(x, y ) on the plane, we define their distance by the formula
Chapter 6 Functions of several variables 6.1 Limits and continuity Definition 6.1 (Euclidean distance). Given two points P (x 1, y 1 ) and Q(x, y ) on the plane, we define their distance by the formula
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET 5. Section 9.1
 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET 5 Section 9.1 Exercise 2. Recall that for (a, m) = 1 we have ord m a divides φ(m). a) We have φ(11) = 10 thus ord 11 3 {1, 2, 5, 10}. We check 3 1 3 (mod 11), 3 2 9 (mod 11), 3
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEM SET 5 Section 9.1 Exercise 2. Recall that for (a, m) = 1 we have ord m a divides φ(m). a) We have φ(11) = 10 thus ord 11 3 {1, 2, 5, 10}. We check 3 1 3 (mod 11), 3 2 9 (mod 11), 3
Solutions to the problems from Written assignment 2 Math 222 Winter 2015
 Solutions to the problems from Written assignment 2 Math 222 Winter 2015 1. Determine if the following limits exist, and if a limit exists, find its value. x2 y (a) The limit of f(x, y) = x 4 as (x, y)
Solutions to the problems from Written assignment 2 Math 222 Winter 2015 1. Determine if the following limits exist, and if a limit exists, find its value. x2 y (a) The limit of f(x, y) = x 4 as (x, y)
Measure Preserving Isomorphisms
 Gen. Math. Notes, Vol. 29, No., July 205, pp.-5 ISSN 229-784; Copyright c ICSRS Publication, 205 www.i-csrs.org Available free online at http://www.geman.in Measure Preserving Isomorphisms M. Gheytaran
Gen. Math. Notes, Vol. 29, No., July 205, pp.-5 ISSN 229-784; Copyright c ICSRS Publication, 205 www.i-csrs.org Available free online at http://www.geman.in Measure Preserving Isomorphisms M. Gheytaran
Strongly nonlinear elliptic problem without growth condition
 2002-Fez conference on Partial Differential Equations, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conference 09, 2002, pp 41 47. http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu
2002-Fez conference on Partial Differential Equations, Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Conference 09, 2002, pp 41 47. http://ejde.math.swt.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.swt.edu
International Journal of Mathematical Archive-5(6), 2014, Available online through ISSN
 International Journal of Mathematical Archive-5(6), 2014, 119-124 Available online through www.ijma.info ISSN 2229 5046 CLOSURE OPERATORS ON COMPLETE ALMOST DISTRIBUTIVE LATTICES-I G. C. Rao Department
International Journal of Mathematical Archive-5(6), 2014, 119-124 Available online through www.ijma.info ISSN 2229 5046 CLOSURE OPERATORS ON COMPLETE ALMOST DISTRIBUTIVE LATTICES-I G. C. Rao Department
KY FAN S INEQUALITIES FOR VECTOR-VALUED MULTIFUNCTIONS IN TOPOLOGICAL ORDERED SPACES
 Fixed Point They, 15(2014), No. 1, 253-264 http://www.math.ubbcluj.ro/ nodeacj/sfptcj.html KY FAN S INEQUALITIES FOR VECTOR-VALUED MULTIFUNCTIONS IN TOPOLOGICAL ORDERED SPACES NGUYEN THE VINH AND PHAM
Fixed Point They, 15(2014), No. 1, 253-264 http://www.math.ubbcluj.ro/ nodeacj/sfptcj.html KY FAN S INEQUALITIES FOR VECTOR-VALUED MULTIFUNCTIONS IN TOPOLOGICAL ORDERED SPACES NGUYEN THE VINH AND PHAM
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.cv] 12 Dec 2005
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.cv] 12 Dec 2005 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.cv] 12 Dec 2005](/thumbs/94/119258602.jpg) arxiv:math/0512241v1 [math.cv] 12 Dec 2005 The pluri-fine topology is locally connected Said El Marzguioui and Jan Wiegerinck November 1, 2018 Abstract We prove that the pluri-fine topology on any open
arxiv:math/0512241v1 [math.cv] 12 Dec 2005 The pluri-fine topology is locally connected Said El Marzguioui and Jan Wiegerinck November 1, 2018 Abstract We prove that the pluri-fine topology on any open
Definitions and claims functions of several variables
 Definitions and claims functions of several variables In the Euclidian space I n of all real n-dimensional vectors x = (x 1, x,..., x n ) the following are defined: x + y = (x 1 + y 1, x + y,..., x n +
Definitions and claims functions of several variables In the Euclidian space I n of all real n-dimensional vectors x = (x 1, x,..., x n ) the following are defined: x + y = (x 1 + y 1, x + y,..., x n +
Assignment 2. Due: Monday Oct. 15, :59pm
 Introduction To Discrete Math Due: Monday Oct. 15, 2012. 11:59pm Assignment 2 Instructor: Mohamed Omar Math 6a For all problems on assignments, you are allowed to use the textbook, class notes, and other
Introduction To Discrete Math Due: Monday Oct. 15, 2012. 11:59pm Assignment 2 Instructor: Mohamed Omar Math 6a For all problems on assignments, you are allowed to use the textbook, class notes, and other
PD-SETS FOR CODES RELATED TO FLAG-TRANSITIVE SYMMETRIC DESIGNS. Communicated by Behruz Tayfeh Rezaie. 1. Introduction
 Transactions on Combinatorics ISSN (print): 2251-8657, ISSN (on-line): 2251-8665 Vol. 7 No. 1 (2018), pp. 37-50. c 2018 University of Isfahan www.combinatorics.ir www.ui.ac.ir PD-SETS FOR CODES RELATED
Transactions on Combinatorics ISSN (print): 2251-8657, ISSN (on-line): 2251-8665 Vol. 7 No. 1 (2018), pp. 37-50. c 2018 University of Isfahan www.combinatorics.ir www.ui.ac.ir PD-SETS FOR CODES RELATED
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Homework 1. Table 1: 11.1:8 t x y
 MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2 Homework Section., pg. 692: 8, 24, 43. Section.2, pg. 72:, 2 (no graph required), 32, 4. Section.3, pg. 73: 4, 2, 54, 8. Section.4, pg. 79: 6, 35, 46. Solutions.:
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2 Homework Section., pg. 692: 8, 24, 43. Section.2, pg. 72:, 2 (no graph required), 32, 4. Section.3, pg. 73: 4, 2, 54, 8. Section.4, pg. 79: 6, 35, 46. Solutions.:
NUMBER THEORY AMIN WITNO
 NUMBER THEORY AMIN WITNO.. w w w. w i t n o. c o m Number Theory Outlines and Problem Sets Amin Witno Preface These notes are mere outlines for the course Math 313 given at Philadelphia
NUMBER THEORY AMIN WITNO.. w w w. w i t n o. c o m Number Theory Outlines and Problem Sets Amin Witno Preface These notes are mere outlines for the course Math 313 given at Philadelphia
Review guide for midterm 2 in Math 233 March 30, 2009
 Review guide for midterm 2 in Math 2 March, 29 Midterm 2 covers material that begins approximately with the definition of partial derivatives in Chapter 4. and ends approximately with methods for calculating
Review guide for midterm 2 in Math 2 March, 29 Midterm 2 covers material that begins approximately with the definition of partial derivatives in Chapter 4. and ends approximately with methods for calculating
RESTRICTED PERMUTATIONS AND POLYGONS. Ghassan Firro and Toufik Mansour Department of Mathematics, University of Haifa, Haifa, Israel
 RESTRICTED PERMUTATIONS AND POLYGONS Ghassan Firro and Toufik Mansour Department of Mathematics, University of Haifa, 905 Haifa, Israel {gferro,toufik}@mathhaifaacil abstract Several authors have examined
RESTRICTED PERMUTATIONS AND POLYGONS Ghassan Firro and Toufik Mansour Department of Mathematics, University of Haifa, 905 Haifa, Israel {gferro,toufik}@mathhaifaacil abstract Several authors have examined
University of California, Berkeley Department of Mathematics 5 th November, 2012, 12:10-12:55 pm MATH 53 - Test #2
 University of California, Berkeley epartment of Mathematics 5 th November, 212, 12:1-12:55 pm MATH 53 - Test #2 Last Name: First Name: Student Number: iscussion Section: Name of GSI: Record your answers
University of California, Berkeley epartment of Mathematics 5 th November, 212, 12:1-12:55 pm MATH 53 - Test #2 Last Name: First Name: Student Number: iscussion Section: Name of GSI: Record your answers
Gauss and AGM. Burton Rosenberg. January 30, 2004
 Gauss and AGM Burton Rosenberg January 3, 24 Introduction derivation of equation. what has it to do w/ the lemniscate agm properties of I elliptic integrals The Elliptic Integral of the First Kind Define
Gauss and AGM Burton Rosenberg January 3, 24 Introduction derivation of equation. what has it to do w/ the lemniscate agm properties of I elliptic integrals The Elliptic Integral of the First Kind Define
[f(t)] 2 + [g(t)] 2 + [h(t)] 2 dt. [f(u)] 2 + [g(u)] 2 + [h(u)] 2 du. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus implies that s(t) is differentiable and
![[f(t)] 2 + [g(t)] 2 + [h(t)] 2 dt. [f(u)] 2 + [g(u)] 2 + [h(u)] 2 du. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus implies that s(t) is differentiable and [f(t)] 2 + [g(t)] 2 + [h(t)] 2 dt. [f(u)] 2 + [g(u)] 2 + [h(u)] 2 du. The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus implies that s(t) is differentiable and](/thumbs/92/108353356.jpg) Midterm 2 review Math 265 Fall 2007 13.3. Arc Length and Curvature. Assume that the curve C is described by the vector-valued function r(r) = f(t), g(t), h(t), and that C is traversed exactly once as t
Midterm 2 review Math 265 Fall 2007 13.3. Arc Length and Curvature. Assume that the curve C is described by the vector-valued function r(r) = f(t), g(t), h(t), and that C is traversed exactly once as t
On uniquely k-determined permutations
 On uniquely k-determined permutations Sergey Avgustinovich and Sergey Kitaev 16th March 2007 Abstract Motivated by a new point of view to study occurrences of consecutive patterns in permutations, we introduce
On uniquely k-determined permutations Sergey Avgustinovich and Sergey Kitaev 16th March 2007 Abstract Motivated by a new point of view to study occurrences of consecutive patterns in permutations, we introduce
Lecture 3 - Regression
 Lecture 3 - Regression Instructor: Prof Ganesh Ramakrishnan July 25, 2016 1 / 30 The Simplest ML Problem: Least Square Regression Curve Fitting: Motivation Error measurement Minimizing Error Method of
Lecture 3 - Regression Instructor: Prof Ganesh Ramakrishnan July 25, 2016 1 / 30 The Simplest ML Problem: Least Square Regression Curve Fitting: Motivation Error measurement Minimizing Error Method of
An Erdős-Lovász-Spencer Theorem for permutations and its. testing
 An Erdős-Lovász-Spencer Theorem for permutations and its consequences for parameter testing Carlos Hoppen (UFRGS, Porto Alegre, Brazil) This is joint work with Roman Glebov (ETH Zürich, Switzerland) Tereza
An Erdős-Lovász-Spencer Theorem for permutations and its consequences for parameter testing Carlos Hoppen (UFRGS, Porto Alegre, Brazil) This is joint work with Roman Glebov (ETH Zürich, Switzerland) Tereza
11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values Just like functions of a single variable, functions of several variables can have local and global extrema,
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 11.7 Maximum and Minimum Values Just like functions of a single variable, functions of several variables can have local and global extrema,
Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion Notes
 Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion Notes The Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion (often abbreviated PIE is the following general formula used for finding the cardinality of a union of finite sets. Theorem 0.1.
Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion Notes The Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion (often abbreviated PIE is the following general formula used for finding the cardinality of a union of finite sets. Theorem 0.1.
Zhanjiang , People s Republic of China
 Math. Comp. 78(2009), no. 267, 1853 1866. COVERS OF THE INTEGERS WITH ODD MODULI AND THEIR APPLICATIONS TO THE FORMS x m 2 n AND x 2 F 3n /2 Ke-Jian Wu 1 and Zhi-Wei Sun 2, 1 Department of Mathematics,
Math. Comp. 78(2009), no. 267, 1853 1866. COVERS OF THE INTEGERS WITH ODD MODULI AND THEIR APPLICATIONS TO THE FORMS x m 2 n AND x 2 F 3n /2 Ke-Jian Wu 1 and Zhi-Wei Sun 2, 1 Department of Mathematics,
Wilson s Theorem and Fermat s Theorem
 Wilson s Theorem and Fermat s Theorem 7-27-2006 Wilson s theorem says that p is prime if and only if (p 1)! = 1 (mod p). Fermat s theorem says that if p is prime and p a, then a p 1 = 1 (mod p). Wilson
Wilson s Theorem and Fermat s Theorem 7-27-2006 Wilson s theorem says that p is prime if and only if (p 1)! = 1 (mod p). Fermat s theorem says that if p is prime and p a, then a p 1 = 1 (mod p). Wilson
Cardinality of Accumulation Points of Infinite Sets
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 11, 2016, no. 11, 539-546 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2016.6224 Cardinality of Accumulation Points of Infinite Sets A. Kalapodi CTI
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 11, 2016, no. 11, 539-546 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/imf.2016.6224 Cardinality of Accumulation Points of Infinite Sets A. Kalapodi CTI
Congruences Modulo Small Powers of 2 and 3 for Partitions into Odd Designated Summands
 1 3 47 6 3 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 0 (017), Article 17.4.3 Congruences Modulo Small Powers of 3 for Partitions into Odd Designated Summs B. Hemanthkumar Department of Mathematics M. S. Ramaiah
1 3 47 6 3 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 0 (017), Article 17.4.3 Congruences Modulo Small Powers of 3 for Partitions into Odd Designated Summs B. Hemanthkumar Department of Mathematics M. S. Ramaiah
ON THE EQUATION a x x (mod b) Jam Germain
 ON THE EQUATION a (mod b) Jam Germain Abstract. Recently Jimenez and Yebra [3] constructed, for any given a and b, solutions to the title equation. Moreover they showed how these can be lifted to higher
ON THE EQUATION a (mod b) Jam Germain Abstract. Recently Jimenez and Yebra [3] constructed, for any given a and b, solutions to the title equation. Moreover they showed how these can be lifted to higher
Generic Attacks on Feistel Schemes
 Generic Attacks on Feistel Schemes Jacques Patarin 1, 1 CP8 Crypto Lab, SchlumbergerSema, 36-38 rue de la Princesse, BP 45, 78430 Louveciennes Cedex, France PRiSM, University of Versailles, 45 av. des
Generic Attacks on Feistel Schemes Jacques Patarin 1, 1 CP8 Crypto Lab, SchlumbergerSema, 36-38 rue de la Princesse, BP 45, 78430 Louveciennes Cedex, France PRiSM, University of Versailles, 45 av. des
11.2 LIMITS AND CONTINUITY
 11. LIMITS AND CONTINUITY INTRODUCTION: Consider functions of one variable y = f(x). If you are told that f(x) is continuous at x = a, explain what the graph looks like near x = a. Formal definition of
11. LIMITS AND CONTINUITY INTRODUCTION: Consider functions of one variable y = f(x). If you are told that f(x) is continuous at x = a, explain what the graph looks like near x = a. Formal definition of
Permutations with short monotone subsequences
 Permutations with short monotone subsequences Dan Romik Abstract We consider permutations of 1, 2,..., n 2 whose longest monotone subsequence is of length n and are therefore extremal for the Erdős-Szekeres
Permutations with short monotone subsequences Dan Romik Abstract We consider permutations of 1, 2,..., n 2 whose longest monotone subsequence is of length n and are therefore extremal for the Erdős-Szekeres
Finite homomorphism-homogeneous permutations via edge colourings of chains
 Finite homomorphism-homogeneous permutations via edge colourings of chains Igor Dolinka dockie@dmi.uns.ac.rs Department of Mathematics and Informatics, University of Novi Sad First of all there is Blue.
Finite homomorphism-homogeneous permutations via edge colourings of chains Igor Dolinka dockie@dmi.uns.ac.rs Department of Mathematics and Informatics, University of Novi Sad First of all there is Blue.
Trigonometry. David R. Wilkins
 Trigonometry David R. Wilkins 1. Trigonometry 1. Trigonometry 1.1. Trigonometric Functions There are six standard trigonometric functions. They are the sine function (sin), the cosine function (cos), the
Trigonometry David R. Wilkins 1. Trigonometry 1. Trigonometry 1.1. Trigonometric Functions There are six standard trigonometric functions. They are the sine function (sin), the cosine function (cos), the
Dedekind Sums with Arguments Near Euler s Number e
 1 47 6 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 1 (01), Article 1..8 Dedeind Sums with Arguments Near Euler s Number e Kurt Girstmair Institut für Mathemati Universität Innsbruc Technierstr. 1/7 A-600 Innsbruc
1 47 6 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 1 (01), Article 1..8 Dedeind Sums with Arguments Near Euler s Number e Kurt Girstmair Institut für Mathemati Universität Innsbruc Technierstr. 1/7 A-600 Innsbruc
Univalence Conditions for a New Family of Integral Operators
 Filomat 30:5 (2016, 1243 1251 DOI 10.2298/FIL1605243O Published by Faculty of Sciences Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Univalence Conditions for a New
Filomat 30:5 (2016, 1243 1251 DOI 10.2298/FIL1605243O Published by Faculty of Sciences Mathematics, University of Niš, Serbia Available at: http://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filomat Univalence Conditions for a New
Math236 Discrete Maths with Applications
 Math236 Discrete Maths with Applications P. Ittmann UKZN, Pietermaritzburg Semester 1, 2012 Ittmann (UKZN PMB) Math236 2012 1 / 43 The Multiplication Principle Theorem Let S be a set of k-tuples (s 1,
Math236 Discrete Maths with Applications P. Ittmann UKZN, Pietermaritzburg Semester 1, 2012 Ittmann (UKZN PMB) Math236 2012 1 / 43 The Multiplication Principle Theorem Let S be a set of k-tuples (s 1,
Ramanujan-type Congruences for Overpartitions Modulo 5. Nankai University, Tianjin , P. R. China
 Ramanujan-type Congruences for Overpartitions Modulo 5 William Y.C. Chen a,b, Lisa H. Sun a,, Rong-Hua Wang a and Li Zhang a a Center for Combinatorics, LPMC-TJKLC Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, P.
Ramanujan-type Congruences for Overpartitions Modulo 5 William Y.C. Chen a,b, Lisa H. Sun a,, Rong-Hua Wang a and Li Zhang a a Center for Combinatorics, LPMC-TJKLC Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, P.
arxiv: v3 [math.co] 4 Dec 2018 MICHAEL CORY
![arxiv: v3 [math.co] 4 Dec 2018 MICHAEL CORY arxiv: v3 [math.co] 4 Dec 2018 MICHAEL CORY](/thumbs/95/123049633.jpg) CYCLIC PERMUTATIONS AVOIDING PAIRS OF PATTERNS OF LENGTH THREE arxiv:1805.05196v3 [math.co] 4 Dec 2018 MIKLÓS BÓNA MICHAEL CORY Abstract. We enumerate cyclic permutations avoiding two patterns of length
CYCLIC PERMUTATIONS AVOIDING PAIRS OF PATTERNS OF LENGTH THREE arxiv:1805.05196v3 [math.co] 4 Dec 2018 MIKLÓS BÓNA MICHAEL CORY Abstract. We enumerate cyclic permutations avoiding two patterns of length
Exam 2 Summary. 1. The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputes of the function and the range is the set of all outputs.
 Exam 2 Summary Disclaimer: The exam 2 covers lectures 9-15, inclusive. This is mostly about limits, continuity and differentiation of functions of 2 and 3 variables, and some applications. The complete
Exam 2 Summary Disclaimer: The exam 2 covers lectures 9-15, inclusive. This is mostly about limits, continuity and differentiation of functions of 2 and 3 variables, and some applications. The complete
2.1 Partial Derivatives
 .1 Partial Derivatives.1.1 Functions of several variables Up until now, we have only met functions of single variables. From now on we will meet functions such as z = f(x, y) and w = f(x, y, z), which
.1 Partial Derivatives.1.1 Functions of several variables Up until now, we have only met functions of single variables. From now on we will meet functions such as z = f(x, y) and w = f(x, y, z), which
MATH 12 CLASS 9 NOTES, OCT Contents 1. Tangent planes 1 2. Definition of differentiability 3 3. Differentials 4
 MATH 2 CLASS 9 NOTES, OCT 0 20 Contents. Tangent planes 2. Definition of differentiability 3 3. Differentials 4. Tangent planes Recall that the derivative of a single variable function can be interpreted
MATH 2 CLASS 9 NOTES, OCT 0 20 Contents. Tangent planes 2. Definition of differentiability 3 3. Differentials 4. Tangent planes Recall that the derivative of a single variable function can be interpreted
PRIMES IN SHIFTED SUMS OF LUCAS SEQUENCES. Lenny Jones Department of Mathematics, Shippensburg University, Shippensburg, Pennsylvania
 #A52 INTEGERS 17 (2017) PRIMES IN SHIFTED SUMS OF LUCAS SEQUENCES Lenny Jones Department of Mathematics, Shippensburg University, Shippensburg, Pennsylvania lkjone@ship.edu Lawrence Somer Department of
#A52 INTEGERS 17 (2017) PRIMES IN SHIFTED SUMS OF LUCAS SEQUENCES Lenny Jones Department of Mathematics, Shippensburg University, Shippensburg, Pennsylvania lkjone@ship.edu Lawrence Somer Department of
14.2 Limits and Continuity
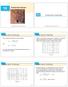 14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
The Cauchy Criterion
 The Cauchy Criterion MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Cauchy Sequences Definition A sequence X = (x n ) of real numbers is a Cauchy sequence if it satisfies
The Cauchy Criterion MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Cauchy Sequences Definition A sequence X = (x n ) of real numbers is a Cauchy sequence if it satisfies
Ky Fan minimax inequalities for set-valued mappings
 RESEARCH Ky Fan minimax inequalities for set-valued mappings Yu Zhang 1* and Sheng-Jie Li 1,2 Open Access * Correspondence: zhangyu198606@sina.com 1 College of Mathematics and Statistics, Chongqing University,
RESEARCH Ky Fan minimax inequalities for set-valued mappings Yu Zhang 1* and Sheng-Jie Li 1,2 Open Access * Correspondence: zhangyu198606@sina.com 1 College of Mathematics and Statistics, Chongqing University,
Non-overlapping permutation patterns
 PU. M. A. Vol. 22 (2011), No.2, pp. 99 105 Non-overlapping permutation patterns Miklós Bóna Department of Mathematics University of Florida 358 Little Hall, PO Box 118105 Gainesville, FL 326118105 (USA)
PU. M. A. Vol. 22 (2011), No.2, pp. 99 105 Non-overlapping permutation patterns Miklós Bóna Department of Mathematics University of Florida 358 Little Hall, PO Box 118105 Gainesville, FL 326118105 (USA)
A Signal Space Theory of Interferences Cancellation Systems
 A Signal Space Theory of Interferences Cancellation Systems Osamu Ichiyoshi Human Network for Better 21 Century E-mail: osamu-ichiyoshi@muf.biglobe.ne.jp Abstract Interferences among signals from different
A Signal Space Theory of Interferences Cancellation Systems Osamu Ichiyoshi Human Network for Better 21 Century E-mail: osamu-ichiyoshi@muf.biglobe.ne.jp Abstract Interferences among signals from different
Monotone Sequences & Cauchy Sequences Philippe B. Laval
 Monotone Sequences & Cauchy Sequences Philippe B. Laval Monotone Sequences & Cauchy Sequences 2 1 Monotone Sequences and Cauchy Sequences 1.1 Monotone Sequences The techniques we have studied so far require
Monotone Sequences & Cauchy Sequences Philippe B. Laval Monotone Sequences & Cauchy Sequences 2 1 Monotone Sequences and Cauchy Sequences 1.1 Monotone Sequences The techniques we have studied so far require
Dyck paths, standard Young tableaux, and pattern avoiding permutations
 PU. M. A. Vol. 21 (2010), No.2, pp. 265 284 Dyck paths, standard Young tableaux, and pattern avoiding permutations Hilmar Haukur Gudmundsson The Mathematics Institute Reykjavik University Iceland e-mail:
PU. M. A. Vol. 21 (2010), No.2, pp. 265 284 Dyck paths, standard Young tableaux, and pattern avoiding permutations Hilmar Haukur Gudmundsson The Mathematics Institute Reykjavik University Iceland e-mail:
Minimal generating sets of Weierstrass semigroups of certain m-tuples on the norm-trace function field
 Minimal generating sets of Weierstrass semigroups of certain m-tuples on the norm-trace function field Gretchen L. Matthews and Justin D. Peachey Abstract. The norm-trace function field is a generalization
Minimal generating sets of Weierstrass semigroups of certain m-tuples on the norm-trace function field Gretchen L. Matthews and Justin D. Peachey Abstract. The norm-trace function field is a generalization
On repdigits as product of consecutive Fibonacci numbers 1
 Rend. Istit. Mat. Univ. Trieste Volume 44 (2012), 33 37 On repdigits as product of consecutive Fibonacci numbers 1 Diego Marques and Alain Togbé Abstract. Let (F n ) n 0 be the Fibonacci sequence. In 2000,
Rend. Istit. Mat. Univ. Trieste Volume 44 (2012), 33 37 On repdigits as product of consecutive Fibonacci numbers 1 Diego Marques and Alain Togbé Abstract. Let (F n ) n 0 be the Fibonacci sequence. In 2000,
ON COMMUTATION PROPERTIES OF THE COMPOSITION RELATION OF CONVERGENT AND DIVERGENT PERMUTATIONS (PART I)
 t m Mathematical Publications DOI: 10.2478/tmmp-2014-0002 Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 58 (2014), 13 22 ON COMMUTATION PROPERTIES OF THE COMPOSITION RELATION OF CONVERGENT AND DIVERGENT PERMUTATIONS (PART I)
t m Mathematical Publications DOI: 10.2478/tmmp-2014-0002 Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 58 (2014), 13 22 ON COMMUTATION PROPERTIES OF THE COMPOSITION RELATION OF CONVERGENT AND DIVERGENT PERMUTATIONS (PART I)
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) Operation Principles
 Afriyie Abraham Kwabena Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) Operation Principles Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachlor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis June 0 Abstract
Afriyie Abraham Kwabena Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) Operation Principles Helsinki Metropolia University of Applied Sciences Bachlor of Engineering Information Technology Thesis June 0 Abstract
Introduction to Computational Manifolds and Applications
 IMPA - Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil Introduction to Computational Manifolds and Applications Part - Constructions Prof. Marcelo Ferreira Siqueira mfsiqueira@dimap.ufrn.br
IMPA - Instituto de Matemática Pura e Aplicada, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil Introduction to Computational Manifolds and Applications Part - Constructions Prof. Marcelo Ferreira Siqueira mfsiqueira@dimap.ufrn.br
18 Completeness and Compactness of First-Order Tableaux
 CS 486: Applied Logic Lecture 18, March 27, 2003 18 Completeness and Compactness of First-Order Tableaux 18.1 Completeness Proving the completeness of a first-order calculus gives us Gödel s famous completeness
CS 486: Applied Logic Lecture 18, March 27, 2003 18 Completeness and Compactness of First-Order Tableaux 18.1 Completeness Proving the completeness of a first-order calculus gives us Gödel s famous completeness
An Aperiodic Tiling from a Dynamical System: An Exposition of An Example of Culik and Kari. S. Eigen J. Navarro V. Prasad
 An Aperiodic Tiling from a Dynamical System: An Exposition of An Example of Culik and Kari S. Eigen J. Navarro V. Prasad These tiles can tile the plane But only Aperiodically Example A (Culik-Kari) Dynamical
An Aperiodic Tiling from a Dynamical System: An Exposition of An Example of Culik and Kari S. Eigen J. Navarro V. Prasad These tiles can tile the plane But only Aperiodically Example A (Culik-Kari) Dynamical
Chapter 1. Probability
 Chapter 1. Probability 1.1 Basic Concepts Scientific method a. For a given problem, we define measures that explains the problem well. b. Data is collected with observation and the measures are calculated.
Chapter 1. Probability 1.1 Basic Concepts Scientific method a. For a given problem, we define measures that explains the problem well. b. Data is collected with observation and the measures are calculated.
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS WORKING PAPER SERIES. Stable Networks and Convex Payoffs. Robert P. Gilles Virginia Tech University
 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS WORKING PAPER SERIES Stable Networks and Convex Payoffs Robert P. Gilles Virginia Tech University Sudipta Sarangi Louisiana State University Working Paper 2005-13 http://www.bus.lsu.edu/economics/papers/pap05_13.pdf
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS WORKING PAPER SERIES Stable Networks and Convex Payoffs Robert P. Gilles Virginia Tech University Sudipta Sarangi Louisiana State University Working Paper 2005-13 http://www.bus.lsu.edu/economics/papers/pap05_13.pdf
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 5c: Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques
 Antennas and Propagation : Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques Introduction Time-domain Signal Processing Fourier spectral analysis Identify important frequency-content of signal
Antennas and Propagation : Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques Introduction Time-domain Signal Processing Fourier spectral analysis Identify important frequency-content of signal
Differentiable functions (Sec. 14.4)
 Math 20C Multivariable Calculus Lecture 3 Differentiable functions (Sec. 4.4) Review: Partial derivatives. Slide Partial derivatives and continuity. Equation of the tangent plane. Differentiable functions.
Math 20C Multivariable Calculus Lecture 3 Differentiable functions (Sec. 4.4) Review: Partial derivatives. Slide Partial derivatives and continuity. Equation of the tangent plane. Differentiable functions.
Pattern Avoidance in Unimodal and V-unimodal Permutations
 Pattern Avoidance in Unimodal and V-unimodal Permutations Dido Salazar-Torres May 16, 2009 Abstract A characterization of unimodal, [321]-avoiding permutations and an enumeration shall be given.there is
Pattern Avoidance in Unimodal and V-unimodal Permutations Dido Salazar-Torres May 16, 2009 Abstract A characterization of unimodal, [321]-avoiding permutations and an enumeration shall be given.there is
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 30 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 30 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 30 Nov 2017](/thumbs/95/126343447.jpg) A NOTE ON 3-FREE PERMUTATIONS arxiv:1712.00105v1 [math.co] 30 Nov 2017 Bill Correll, Jr. MDA Information Systems LLC, Ann Arbor, MI, USA william.correll@mdaus.com Randy W. Ho Garmin International, Chandler,
A NOTE ON 3-FREE PERMUTATIONS arxiv:1712.00105v1 [math.co] 30 Nov 2017 Bill Correll, Jr. MDA Information Systems LLC, Ann Arbor, MI, USA william.correll@mdaus.com Randy W. Ho Garmin International, Chandler,
A STUDY OF EULERIAN NUMBERS FOR PERMUTATIONS IN THE ALTERNATING GROUP
 INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 6 (2006), #A31 A STUDY OF EULERIAN NUMBERS FOR PERMUTATIONS IN THE ALTERNATING GROUP Shinji Tanimoto Department of Mathematics, Kochi Joshi University
INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 6 (2006), #A31 A STUDY OF EULERIAN NUMBERS FOR PERMUTATIONS IN THE ALTERNATING GROUP Shinji Tanimoto Department of Mathematics, Kochi Joshi University
5 Symmetric and alternating groups
 MTHM024/MTH714U Group Theory Notes 5 Autumn 2011 5 Symmetric and alternating groups In this section we examine the alternating groups A n (which are simple for n 5), prove that A 5 is the unique simple
MTHM024/MTH714U Group Theory Notes 5 Autumn 2011 5 Symmetric and alternating groups In this section we examine the alternating groups A n (which are simple for n 5), prove that A 5 is the unique simple
10.1 Curves defined by parametric equations
 Outline Section 1: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 1.1 Curves defined by parametric equations 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves 1.3 Polar Coordinates 1.4 Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
Outline Section 1: Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates 1.1 Curves defined by parametric equations 1.2 Calculus with Parametric Curves 1.3 Polar Coordinates 1.4 Areas and Lengths in Polar Coordinates
Fast Sorting and Pattern-Avoiding Permutations
 Fast Sorting and Pattern-Avoiding Permutations David Arthur Stanford University darthur@cs.stanford.edu Abstract We say a permutation π avoids a pattern σ if no length σ subsequence of π is ordered in
Fast Sorting and Pattern-Avoiding Permutations David Arthur Stanford University darthur@cs.stanford.edu Abstract We say a permutation π avoids a pattern σ if no length σ subsequence of π is ordered in
Degree project NUMBER OF PERIODIC POINTS OF CONGRUENTIAL MONOMIAL DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS
 Degree project NUMBER OF PERIODIC POINTS OF CONGRUENTIAL MONOMIAL DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS Author: MD.HASIRUL ISLAM NAZIR BASHIR Supervisor: MARCUS NILSSON Date: 2012-06-15 Subject: Mathematics and Modeling Level:
Degree project NUMBER OF PERIODIC POINTS OF CONGRUENTIAL MONOMIAL DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS Author: MD.HASIRUL ISLAM NAZIR BASHIR Supervisor: MARCUS NILSSON Date: 2012-06-15 Subject: Mathematics and Modeling Level:
Solutions for the Practice Questions
 Solutions for the Practice Questions Question 1. Find all solutions to the congruence 13x 12 (mod 35). Also, answer the following questions about the solutions to the above congruence. Are there solutions
Solutions for the Practice Questions Question 1. Find all solutions to the congruence 13x 12 (mod 35). Also, answer the following questions about the solutions to the above congruence. Are there solutions
Restricted Permutations Related to Fibonacci Numbers and k-generalized Fibonacci Numbers
 Restricted Permutations Related to Fibonacci Numbers and k-generalized Fibonacci Numbers arxiv:math/0109219v1 [math.co] 27 Sep 2001 Eric S. Egge Department of Mathematics Gettysburg College 300 North Washington
Restricted Permutations Related to Fibonacci Numbers and k-generalized Fibonacci Numbers arxiv:math/0109219v1 [math.co] 27 Sep 2001 Eric S. Egge Department of Mathematics Gettysburg College 300 North Washington
November 20, 2005 PERFECT COMPACTA AND BASIS PROBLEMS IN TOPOLOGY
 November 20, 2005 PERFECT COMPACTA AND BASIS PROBLEMS IN TOPOLOGY GARY GRUENHAGE AND JUSTIN TATCH MOORE An interesting example of a compact Hausdorff space that is often presented in beginning courses
November 20, 2005 PERFECT COMPACTA AND BASIS PROBLEMS IN TOPOLOGY GARY GRUENHAGE AND JUSTIN TATCH MOORE An interesting example of a compact Hausdorff space that is often presented in beginning courses
Barycentric and trilinear coordinates of some remarkable points of a hyperbolic triangle
 Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 582013), No. 4, 451 457 Barycentric and trilinear coordinates of some remarkable points of a hyperbolic triangle Andrei Neag To the memory of Professor Mircea-Eugen Craioveanu
Stud. Univ. Babeş-Bolyai Math. 582013), No. 4, 451 457 Barycentric and trilinear coordinates of some remarkable points of a hyperbolic triangle Andrei Neag To the memory of Professor Mircea-Eugen Craioveanu
Math 127: Equivalence Relations
 Math 127: Equivalence Relations Mary Radcliffe 1 Equivalence Relations Relations can take many forms in mathematics. In these notes, we focus especially on equivalence relations, but there are many other
Math 127: Equivalence Relations Mary Radcliffe 1 Equivalence Relations Relations can take many forms in mathematics. In these notes, we focus especially on equivalence relations, but there are many other
Combinatorial Aspects of Flashcard Games
 Combinatorial Aspects of Flashcard Games The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Lewis, Joel
Combinatorial Aspects of Flashcard Games The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Lewis, Joel
Teacher s Notes. Problem of the Month: Courtney s Collection
 Teacher s Notes Problem of the Month: Courtney s Collection Overview: In the Problem of the Month, Courtney s Collection, students use number theory, number operations, organized lists and counting methods
Teacher s Notes Problem of the Month: Courtney s Collection Overview: In the Problem of the Month, Courtney s Collection, students use number theory, number operations, organized lists and counting methods
MATH 2420 Discrete Mathematics Lecture notes
 MATH 2420 Discrete Mathematics Lecture notes Series and Sequences Objectives: Introduction. Find the explicit formula for a sequence. 2. Be able to do calculations involving factorial, summation and product
MATH 2420 Discrete Mathematics Lecture notes Series and Sequences Objectives: Introduction. Find the explicit formula for a sequence. 2. Be able to do calculations involving factorial, summation and product
BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 2006 Senior Preliminary Round Problems & Solutions
 BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 006 Senior Preliminary Round Problems & Solutions 1. Exactly 57.4574% of the people replied yes when asked if they used BLEU-OUT face cream. The fewest
BRITISH COLUMBIA SECONDARY SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST, 006 Senior Preliminary Round Problems & Solutions 1. Exactly 57.4574% of the people replied yes when asked if they used BLEU-OUT face cream. The fewest
The Compensating Polar Planimeter
 The Compensating Polar Planimeter Description of a polar planimeter Standard operation The neutral circle How a compensating polar planimeter compensates Show and tell: actual planimeters References (Far
The Compensating Polar Planimeter Description of a polar planimeter Standard operation The neutral circle How a compensating polar planimeter compensates Show and tell: actual planimeters References (Far
Exam 2 Review Sheet. r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t)
 Exam 2 Review Sheet Joseph Breen Particle Motion Recall that a parametric curve given by: r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) can be interpreted as the position of a particle. Then the derivative represents the particle
Exam 2 Review Sheet Joseph Breen Particle Motion Recall that a parametric curve given by: r(t) = x(t), y(t), z(t) can be interpreted as the position of a particle. Then the derivative represents the particle
Exercise 1. Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ.
 1 Radian Measures Exercise 1 Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ. 1. Suppose I know the radian measure of the
1 Radian Measures Exercise 1 Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ. 1. Suppose I know the radian measure of the
UNIVERSALITY IN SUBSTITUTION-CLOSED PERMUTATION CLASSES. with Frédérique Bassino, Mathilde Bouvel, Valentin Féray, Lucas Gerin and Mickaël Maazoun
 UNIVERSALITY IN SUBSTITUTION-CLOSED PERMUTATION CLASSES ADELINE PIERROT with Frédérique Bassino, Mathilde Bouvel, Valentin Féray, Lucas Gerin and Mickaël Maazoun The aim of this work is to study the asymptotic
UNIVERSALITY IN SUBSTITUTION-CLOSED PERMUTATION CLASSES ADELINE PIERROT with Frédérique Bassino, Mathilde Bouvel, Valentin Féray, Lucas Gerin and Mickaël Maazoun The aim of this work is to study the asymptotic
Enumeration of Two Particular Sets of Minimal Permutations
 3 47 6 3 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 8 (05), Article 5.0. Enumeration of Two Particular Sets of Minimal Permutations Stefano Bilotta, Elisabetta Grazzini, and Elisa Pergola Dipartimento di Matematica
3 47 6 3 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 8 (05), Article 5.0. Enumeration of Two Particular Sets of Minimal Permutations Stefano Bilotta, Elisabetta Grazzini, and Elisa Pergola Dipartimento di Matematica
SYMMETRIES OF FIBONACCI POINTS, MOD m
 PATRICK FLANAGAN, MARC S. RENAULT, AND JOSH UPDIKE Abstract. Given a modulus m, we examine the set of all points (F i,f i+) Z m where F is the usual Fibonacci sequence. We graph the set in the fundamental
PATRICK FLANAGAN, MARC S. RENAULT, AND JOSH UPDIKE Abstract. Given a modulus m, we examine the set of all points (F i,f i+) Z m where F is the usual Fibonacci sequence. We graph the set in the fundamental
A combinatorial proof for the enumeration of alternating permutations with given peak set
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 57 (2013), Pages 293 300 A combinatorial proof for the enumeration of alternating permutations with given peak set Alina F.Y. Zhao School of Mathematical Sciences
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 57 (2013), Pages 293 300 A combinatorial proof for the enumeration of alternating permutations with given peak set Alina F.Y. Zhao School of Mathematical Sciences
A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES
 Last update: Nov. 6, 2015. A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
Last update: Nov. 6, 2015. A CONJECTURE ON UNIT FRACTIONS INVOLVING PRIMES Zhi-Wei Sun Department of Mathematics, Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, People s Republic of China zwsun@nju.edu.cn http://math.nju.edu.cn/
Chapter 1. The alternating groups. 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Permutations
 Chapter 1 The alternating groups 1.1 Introduction The most familiar of the finite (non-abelian) simple groups are the alternating groups A n, which are subgroups of index 2 in the symmetric groups S n.
Chapter 1 The alternating groups 1.1 Introduction The most familiar of the finite (non-abelian) simple groups are the alternating groups A n, which are subgroups of index 2 in the symmetric groups S n.
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 8 Oct 2012
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 8 Oct 2012 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 8 Oct 2012](/thumbs/93/114153326.jpg) Flashcard games Joel Brewster Lewis and Nan Li November 9, 2018 arxiv:1210.2419v1 [math.co] 8 Oct 2012 Abstract We study a certain family of discrete dynamical processes introduced by Novikoff, Kleinberg
Flashcard games Joel Brewster Lewis and Nan Li November 9, 2018 arxiv:1210.2419v1 [math.co] 8 Oct 2012 Abstract We study a certain family of discrete dynamical processes introduced by Novikoff, Kleinberg
Shuffling with ordered cards
 Shuffling with ordered cards Steve Butler (joint work with Ron Graham) Department of Mathematics University of California Los Angeles www.math.ucla.edu/~butler Combinatorics, Groups, Algorithms and Complexity
Shuffling with ordered cards Steve Butler (joint work with Ron Graham) Department of Mathematics University of California Los Angeles www.math.ucla.edu/~butler Combinatorics, Groups, Algorithms and Complexity
Permutation Tableaux and the Dashed Permutation Pattern 32 1
 Permutation Tableaux and the Dashed Permutation Pattern William Y.C. Chen, Lewis H. Liu, Center for Combinatorics, LPMC-TJKLC Nankai University, Tianjin 7, P.R. China chen@nankai.edu.cn, lewis@cfc.nankai.edu.cn
Permutation Tableaux and the Dashed Permutation Pattern William Y.C. Chen, Lewis H. Liu, Center for Combinatorics, LPMC-TJKLC Nankai University, Tianjin 7, P.R. China chen@nankai.edu.cn, lewis@cfc.nankai.edu.cn
Analysis on the Properties of a Permutation Group
 International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics 2017; 3(1): 19-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijtam doi: 10.11648/j.ijtam.20170301.13 Analysis on the Properties of a Permutation
International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics 2017; 3(1): 19-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijtam doi: 10.11648/j.ijtam.20170301.13 Analysis on the Properties of a Permutation
Constructions of Coverings of the Integers: Exploring an Erdős Problem
 Constructions of Coverings of the Integers: Exploring an Erdős Problem Kelly Bickel, Michael Firrisa, Juan Ortiz, and Kristen Pueschel August 20, 2008 Abstract In this paper, we study necessary conditions
Constructions of Coverings of the Integers: Exploring an Erdős Problem Kelly Bickel, Michael Firrisa, Juan Ortiz, and Kristen Pueschel August 20, 2008 Abstract In this paper, we study necessary conditions
arxiv: v1 [math.gt] 21 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.gt] 21 Mar 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.gt] 21 Mar 2018](/thumbs/90/103265808.jpg) Space-Efficient Knot Mosaics for Prime Knots with Mosaic Number 6 arxiv:1803.08004v1 [math.gt] 21 Mar 2018 Aaron Heap and Douglas Knowles June 24, 2018 Abstract In 2008, Kauffman and Lomonaco introduce
Space-Efficient Knot Mosaics for Prime Knots with Mosaic Number 6 arxiv:1803.08004v1 [math.gt] 21 Mar 2018 Aaron Heap and Douglas Knowles June 24, 2018 Abstract In 2008, Kauffman and Lomonaco introduce
1.6 Congruence Modulo m
 1.6 Congruence Modulo m 47 5. Let a, b 2 N and p be a prime. Prove for all natural numbers n 1, if p n (ab) and p - a, then p n b. 6. In the proof of Theorem 1.5.6 it was stated that if n is a prime number
1.6 Congruence Modulo m 47 5. Let a, b 2 N and p be a prime. Prove for all natural numbers n 1, if p n (ab) and p - a, then p n b. 6. In the proof of Theorem 1.5.6 it was stated that if n is a prime number
The Classification of Quadratic Rook Polynomials of a Generalized Three Dimensional Board
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 3 (2017), pp. 1091-1101 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com The Classification of Quadratic Rook Polynomials
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 3 (2017), pp. 1091-1101 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com The Classification of Quadratic Rook Polynomials
The Perfect Binary One-Error-Correcting Codes of Length 15: Part I Classification
 1 The Perfect Binary One-Error-Correcting Codes of Length 15: Part I Classification Patric R. J. Östergård, Olli Pottonen Abstract arxiv:0806.2513v3 [cs.it] 30 Dec 2009 A complete classification of the
1 The Perfect Binary One-Error-Correcting Codes of Length 15: Part I Classification Patric R. J. Östergård, Olli Pottonen Abstract arxiv:0806.2513v3 [cs.it] 30 Dec 2009 A complete classification of the
Math 3560 HW Set 6. Kara. October 17, 2013
 Math 3560 HW Set 6 Kara October 17, 013 (91) Let I be the identity matrix 1 Diagonal matrices with nonzero entries on diagonal form a group I is in the set and a 1 0 0 b 1 0 0 a 1 b 1 0 0 0 a 0 0 b 0 0
Math 3560 HW Set 6 Kara October 17, 013 (91) Let I be the identity matrix 1 Diagonal matrices with nonzero entries on diagonal form a group I is in the set and a 1 0 0 b 1 0 0 a 1 b 1 0 0 0 a 0 0 b 0 0
THE ENUMERATION OF PERMUTATIONS SORTABLE BY POP STACKS IN PARALLEL
 THE ENUMERATION OF PERMUTATIONS SORTABLE BY POP STACKS IN PARALLEL REBECCA SMITH Department of Mathematics SUNY Brockport Brockport, NY 14420 VINCENT VATTER Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College
THE ENUMERATION OF PERMUTATIONS SORTABLE BY POP STACKS IN PARALLEL REBECCA SMITH Department of Mathematics SUNY Brockport Brockport, NY 14420 VINCENT VATTER Department of Mathematics Dartmouth College
Primitive Roots. Chapter Orders and Primitive Roots
 Chapter 5 Primitive Roots The name primitive root applies to a number a whose powers can be used to represent a reduced residue system modulo n. Primitive roots are therefore generators in that sense,
Chapter 5 Primitive Roots The name primitive root applies to a number a whose powers can be used to represent a reduced residue system modulo n. Primitive roots are therefore generators in that sense,
DVA325 Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation (FABER)
 DVA325 Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation (FABER) Lecture 1 - Introduction School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Mälardalen University 11 November 2014 Abu Naser Masud FABER November
DVA325 Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation (FABER) Lecture 1 - Introduction School of Innovation, Design and Engineering Mälardalen University 11 November 2014 Abu Naser Masud FABER November
Unique Sequences Containing No k-term Arithmetic Progressions
 Unique Sequences Containing No k-term Arithmetic Progressions Tanbir Ahmed Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering Concordia University, Montréal, Canada ta ahmed@cs.concordia.ca Janusz
Unique Sequences Containing No k-term Arithmetic Progressions Tanbir Ahmed Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering Concordia University, Montréal, Canada ta ahmed@cs.concordia.ca Janusz
