A COMPACT EMAT RECEIVER FOR ULTRASONIC TESTING AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES* L. R. Burns, G. A. Alers, and D. T. MacLauchlan
|
|
|
- Nigel Dorsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A COMPACT EMAT RECEIVER FOR ULTRASONIC TESTING AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES* L. R. Burns, G. A. Alers, and D. T. MacLauchlan Magnasonics, Inc. 215 Sierra Drive, SE Albuquerque, New Mexico INTRODUCTION For the past several years, the AISI and several national laboratories have cooperated on a program to develop ultrasonic transducers that can be used in steel mills at the highest temperatures encountered during the processing of the solid metal {I}. To date, pulsed laser light focused on the surface appears to make a satisfactory generator or transmitter for ultrasonic pulses while the EMAT or Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer appears to hold the greatest promise for the receiver {2}. Both of these essentially noncontact devices can be made to withstand the very hot environmnent and they are not very sensitive to the quality of the surface. This paper describes the most recent developments in the design of an EMAT receiver to be used in conjunction with a pulsed laser for the measurement of the transit time of ultrasonic waves through a thick strand of steel as it emerges from a continuous casting furnace. The final device was tested at Battelle Northwest Laboratories by Boyd and Sperline and their results are described in another paper at this conference. DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS Ultrasonic Design An EMAT or electromagnetic acoustic transducer {3} can detect the vibrations caused by an ultrasonic wave across an air gap by using an electromagnetic induction mechanism. The device itself consists of a coil of wire held close to the surface and a source of magnetic field to flood the region around the coil with magnetic flux. By choosing the direction of the magnetic field, the transducer can be made sensitive to either longitudinal or shear type waves. Theoretical predictions of the efficiency show that the air gap between the sensor coil and the work piece must be kept as small as possible and the magnetic field at the surface of the piece must be made as large as possible. Since it is well 1677
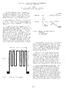
2 known that shear waves are highly attenuated in very hot steel {4}, longitudinal waves must be used for the present case so the magnetic field must be parallel to the surface. An operating frequency near I MHz appears to be high enough to retain adequate precision in the measurement of the arrival time of the acoustic pulse yet it is low enough to allow penetration of up to 10 inches of large grain size material {2}. Magnet Design Out of all of these acoustic requirements, the magnet to supply the EMAT's magnetic field is the most demanding because it must be actively cooled and should be made compact enough to be scanned over the surface of large billets. Common practice is to use a DC electromagnet equipped with pointed pole pieces to concentrate the magnetic flux to the region directly under the sensor coil. Although magnetic fields greater than I Tesla can be generated this way, the approach leads to small sensor coils and massive support structures that restrict the applicability of the EMAT concept. Permanent magnets made out of the most modern alloys such as neodymium-iron-boron can be housed in water cooled jackets to make a very compact probe but the available magnetic fields drop to the range of 0.3 to 0.4 Tesla and the sensitivity therefore decreases by a factor of ten. A third magnet design based on what might be characterized as a "brute force" technique arises when one utilizes the magnetic field close to a conductor carrying a very large current. It is well known that this field increases as the distance between the field point and the conductor approaches zero. In fact, classical formulae predict that I Tesla can be observed at the surface of a 2 mm diameter wire carrying 5000 amperes. Such a current is easily obtained for a short period of time by discharging a capacitor bank" through the wire. It, therefore, seems practical to design a sensitive EMAT receiver using the configuration shown in Figure I. Here, the magnetizing coil consists of several turns of heavy wire inside a water cooled box that not only removes the heat produced by the current pulse but also carries away the radiant heat from the steel. The pickup coil is placed directly under the magnetizing coil as indicated in the figure so that all the essential parts can be kept very close together and close to the work piece. Since the pancake geometry of the magnetizing coil is very simple, a calculation of the tangential component of the magnetic field under such a coil was made as a function of radial distance from the central hole in the coil and with the air gap as a parameter. -Even for a modest number of turns (20) and only a small current (500 amperes), fields greater than I Tesla were predicted for an air gap of one mm. To test the concept experimentally, a coil of 50 turns of lib-inch wide copper tape was wound with an I.D. of 1/4 inch and an O.D. of 1.6 inches. A simple gaussmeter was used to measure the field distribution around this coil and it was found that only 2BO amperes were needed to generate a tangential field of 0.3 Tesla directly under the face of the coil. Thermal Design The flat layered structure of magnet and pickup coil shown in Figure I lent itself nicely to a calculation of the heat flow and temperature distribution that might be expected when the EMAT was in close contact to a steel billet at 25000F (13600 C). For the calculation, thin layers of common insulating materials were considered at the interfaces between the key elements of the structure. It was assumed that a ceramic crucible material such as Mullite could be used at the front face of the EMAT and 1678
3 Figure I. Schematic diagram of the magnetizing coil, heat exchanger and sensor coil for a compact EMAT. that thin layers of the alumina used as electronic circuit substrates could separate the copper conductors in the magnetizing and pickup coils. A metal can made from 60-mil thick titanium and filled with flowing water was assumed to extract the heat flowing from the steel through the structure. The calculations showed that all of the temperatures within the sandwich were well within the capability limits of the materials involved even though the front surface was at F (13600 C). An EMAT probe that was actually constructed is shown in cross section in Figure 2. Here the magnetizing coil was placed in the flowing water on the inside of an alumina crucible whose bottom had been ground to a thickness of about 0.5 mm. The top of this crucible was closed by a stainless steel lid which held two stainless steel tubes for delivering and removing cooling water. It also had two holes through which the wires for the magnet coil passed. On the outside of this heat exchanger crucible, the EMAT sensor coil was attached with a high temperature cement and protected from the hot steel by a second alumina crucible with a thin bottom. Wires to and from the sensor coil were run up the side of the heat exchanger through the gap between the crucibles. At the top of the heat exchanger, these wires joined the leads to the magnetizing coil and ran out to the electronic circuits following the cold water inlet tube so that they could be kept cool. Since a considerable amount of heat load on the structure arose from the radiant energy eminating from the hot steel, the sides of the probe were insulated by Marenite rings held in place by a stainless steel tube that also acted as a handle for the total structure. Figure 3 shows a photograph of the completed probe disassembled to show the heat exchanger section next to the handle. A spring assembly in the handle pushed the front face of the probe lightly against the hot steel during operation. Experimental tests using this structure showed that it could withstand contact with objects at even higher temperatures than the design 1679
4 STAINLESS STEEL LID WATER IN WATER OUT STAINLESS STEEL TUBE HANDLE EXCHANGER CRUCIBLE Figure 2. MAGNETIZING COIL OUTER CRUCIBLE ADHESIVE Cross sectional diagram of a water cooled EMAT probe used as an ultrasonic receiver on hot steel. Figure 3. Photograph of a high temperature EMAT probe assemled from ceramic crucibles. 1680
5 criteria used to establish the theoretical thermal gradients. This fortuitous circumstance occurred because in actual practice there was a thin air gap between the steel and the front face of the probe that introduced a very large thermal resistance and caused a very large temperature drop at the interface that separated the steel from the front face of the probe. Thus. the heat flow estimates used to calculate the operating temperatures of the parts of the probe were actually very conservative and choices of materials to be used in the construction of future generations of the device will be much easier. Electronic Design In order to exploit the high magnetic fields available to the pancake coil design. it was necessary to design a high current pulser circuit able to deliver a few thousand amperes to the magnet coil in a few hundred microseconds. This was accomplished by using a circuit based on the use of a commercial ser that could withstand high voltages and high currents while still being able to respond in microsecond time intervals. This circuit also provided an adjustable trigger signal that allowed the pulsed magnet to be synchronized with the laser pulse to guarantee that the magnetic field would be at its maximum value when the acoustic pulse reached the EMAT. Equally important to the operation of the system was a circuit to prevent the pulsed magnetic field from inducing voltages in the sensor coil that would completely saturate the preamplifier when it should be available for amplifying the small acoustic signals. This was accomplished by inserting a high pass filter at the input of the preamplifier to allow only the high frequency ultrasonic signals to enter the amplifier and to block the low frequency magnetic pulse from this path. Since the ultrasonic signals were near I MHz and the magnetic pulse was centered near a frequency of a few khz. this filter did not have to be of a very special design. Operating Results The EMAT described above was tested on a sample of stainless steel 10-inches thick as it sat in a tube furnace at a temperature of 500 degrees centigrade (842 degrees Fahrenheit). Figure 4 shows the results in the form of two graphs as a function of time after triggering the pulsed magnet. The bottom graph plots the magnet current and shows that it reached a maximum value of 1400 amperes 30 microseconds after being triggered. Separate calibration measurements made at room temperature with an integrating fluxmeter indicated that the magnetic field associated with this maximum current was approximately eight kilogauss at the position of the steel surface. The top graph shows the output of the preamplifier connected to the sensor coil located between the magnetizing coil and the surface of the steel. Large, electromagnetic noise gignals were observed both early and late in the time sequence when the time rate of change of the magnetic field was at its maximum and when there were switching transients in the timing circuits. The acoustic signal was recognized because it arrived at the correct time for a compressional acoustic wave produced by the laser impulse. Its rapid time variation and well defined leading edge make it quite suitable for deducing accurate transit times for ultrasonic waves in hot steel. More complete discussions of the results that have been obtained with this pulsed electromagnet, water cooled EMAT can be found in the paper by Boyd and Sperline elsewhere in this volume. 1681
6 ,...J...: z l!l H U) U H z 0 U) f-',...j II..1.., T I r. I I ( F) Q) '" Q) NOISE ULTRASONIC NOISE 0- S SIGNALS...: 1500 "",--- '-- ' ". f-' / '-. Z w 500 / '-,. tlg tlg 0 U f-' W Z l!l I ' , o TIME (Microseconds) Figure 4. Ultrasonic signals generated by a pulsed laser in hot steel as detected by an EMAT receiver whose magnetic field was produced by the pulsed current waveform at the bottom of the figure.... OJ... '" 3 0 > w 0 :=> f-'......l l...: z l!l... V) MHz NOISE LEVEL 0.04 Figure TEMPERATURE (deg. F) Variation of the ultrasonic echo amplitude from the back surface of a 3-1/2-inch thick aluminum slab as a function of temperature. 1682
7 A second use of this compact. high temperature EMAT could be for the detection of the so-called alligatoring that develops during the hot rolling of aluminum plate. As a cast billet is rolled into plate. the upper and lower surfaces deform more extensively than the center so that the corners extend outward to form a deep indentation that resembles the open mouth of an alligator. Continued rolling can leave a central discontinuity near the ends of the plate and this must be removed by shearing off of material in order to prevent it from being incorporated into the final products. Needless to say. it is very important to shear off only what is absolutely necessary and ultrasonic testing should be able to locate the exact extent of the crack if a transducer could be made to survive the temperatures involved. Feasibility tests with the EMAT described above indicate that it can easily meet these environmental requirements. Figure 5 shows some results obtained with the EMAT acting both as a transmitter and receiver on a 3-1/2-inch thick slab of aluminum alloy heated to near its melting point of 9500 F (5100 C). Plotted is the longitudinal wave signal amplitude as it was reflected from the back face of the slab as a function of temperature. Since these data were obtained without any coupling fluid and with the probe simply resting on the slab. it is clear that the transducer sy-stem has enough sensitivity to overcome the attenuation of the sound as the melting temperature is approached and that an echo from a discontinuity within the slab could easily be detected. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT *Supported by Contract B-Q2202-A-N from Battelle Pacific Northwest Laboratories. REFERENCES 1. R. Mehrabian and H. N. G. Wadley. "Needs for Process Control in Advanced Processing of Materials." Rev. of Prog. in QNDE, vol. 4, D. O. Thompson and D. E. Chimenti. Eds Plenum Press G. A. Alers and H. N. G. Wadley. "A Pulsed Laser/EMAT Approach to Ultrasonic Needs for Steel Processing." Rev. of Prog. in QNDE. vol. 6A. p D. O. Thompson and D. E. Chimenti, Eds Plenum Press R. Bruce Thompson. "Noncontact Transducers," Proc. of 1977 Ultrasonics Symposium. IEEE Cat. No. 77CHI264-1SU. p. 74 (1977). 4. E. P. Papadakis. et al., J. Acous. Soc. Am., vol. 52. p. 855 (1972). 1683
THE ANALYSIS OF ADHESIVE BONDS USING ELECfROMAGNETIC
 THE ANALYSIS OF ADHESIVE BONDS USING ELECfROMAGNETIC ACOUSTIC TRANSDUCERS S.Dixon, C.Edwards, S.B.Palmer Dept of Physics University of Warwick Coventry CV 4 7 AL INTRODUCfION EMATs have been used in ultrasonic
THE ANALYSIS OF ADHESIVE BONDS USING ELECfROMAGNETIC ACOUSTIC TRANSDUCERS S.Dixon, C.Edwards, S.B.Palmer Dept of Physics University of Warwick Coventry CV 4 7 AL INTRODUCfION EMATs have been used in ultrasonic
G. A. Alers and D. T. MacLauchlan
 HIGH FREQUENCY, ANGLE BEAM EMATS FOR WELD INSPECTION G. A. Alers and D. T. MacLauchlan Magnasonics, Inc. Albuquerque, New Mexico INTRODUCTION Accompanying the requirements for higher quality welds in structural
HIGH FREQUENCY, ANGLE BEAM EMATS FOR WELD INSPECTION G. A. Alers and D. T. MacLauchlan Magnasonics, Inc. Albuquerque, New Mexico INTRODUCTION Accompanying the requirements for higher quality welds in structural
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION OF ULTRASONIC WAVES: EMAT, EMUS, EMAR G. Alers EMAT Consulting, San Luis Obispo, CA
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION OF ULTRASONIC WAVES: EMAT, EMUS, EMAR G. Alers EMAT Consulting, San Luis Obispo, CA Electromagnetic induction of ultrasonic waves is restricted to conducting materials like eddy
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION OF ULTRASONIC WAVES: EMAT, EMUS, EMAR G. Alers EMAT Consulting, San Luis Obispo, CA Electromagnetic induction of ultrasonic waves is restricted to conducting materials like eddy
RECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN THE APPLICATION OF EMATS TO NDE
 RECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN THE APPLICATION OF EMATS TO NDE D. MacLauchlan, S. Clark, B. Cox, T. Doyle, B. Grimmett, J. Hancock, K. Hour, C. Rutherford BWXT Services, Non Destructive Evaluation and Inspection
RECENT ADVANCEMENTS IN THE APPLICATION OF EMATS TO NDE D. MacLauchlan, S. Clark, B. Cox, T. Doyle, B. Grimmett, J. Hancock, K. Hour, C. Rutherford BWXT Services, Non Destructive Evaluation and Inspection
ULTRASONIC GUIDED WAVES FOR AGING WIRE INSULATION ASSESSMENT
 ULTRASONIC GUIDED WAVES FOR AGING WIRE INSULATION ASSESSMENT Robert F. Anastasi 1 and Eric I. Madaras 2 1 U.S. Army Research Laboratory, Vehicle Technology Directorate, AMSRL-VT-S, Nondestructive Evaluation
ULTRASONIC GUIDED WAVES FOR AGING WIRE INSULATION ASSESSMENT Robert F. Anastasi 1 and Eric I. Madaras 2 1 U.S. Army Research Laboratory, Vehicle Technology Directorate, AMSRL-VT-S, Nondestructive Evaluation
FATIGUE CRACK CHARACTERIZATION IN CONDUCTING SHEETS BY NON
 FATIGUE CRACK CHARACTERIZATION IN CONDUCTING SHEETS BY NON CONTACT STIMULATION OF RESONANT MODES Buzz Wincheski, J.P. Fulton, and R. Todhunter Analytical Services and Materials 107 Research Drive Hampton,
FATIGUE CRACK CHARACTERIZATION IN CONDUCTING SHEETS BY NON CONTACT STIMULATION OF RESONANT MODES Buzz Wincheski, J.P. Fulton, and R. Todhunter Analytical Services and Materials 107 Research Drive Hampton,
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
THE USE OF MAGNETOSTRICTIVE EMAT TRANSDUCERS ON OXIDE SCALED BOILER TUBES
 THE USE OF MAGNETOSTRICTIVE EMAT TRANSDUCERS ON OXIDE SCALED BOILER TUBES K. Lee, T. Nelligan Panametrics-NDT, A business of R/D Tech Instruments, Inc., Waltham, Massachusetts, USA Abstract: The utilization
THE USE OF MAGNETOSTRICTIVE EMAT TRANSDUCERS ON OXIDE SCALED BOILER TUBES K. Lee, T. Nelligan Panametrics-NDT, A business of R/D Tech Instruments, Inc., Waltham, Massachusetts, USA Abstract: The utilization
EVOLUTION OF THE CRYOGENIC EDDY CURRENT MICROPROBE
 EVOLUTION OF THE CRYOGENIC EDDY CURRENT MICROPROBE J.L. Fisher, S.N. Rowland, J.S. Stolte, and Keith S. Pickens Southwest Research Institute 6220 Culebra Road San Antonio, TX 78228-0510 INTRODUCTION In
EVOLUTION OF THE CRYOGENIC EDDY CURRENT MICROPROBE J.L. Fisher, S.N. Rowland, J.S. Stolte, and Keith S. Pickens Southwest Research Institute 6220 Culebra Road San Antonio, TX 78228-0510 INTRODUCTION In
NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION OF CLOSED CRACKS USING AN ULTRASONIC TRANSIT TIMING METHOD J. Takatsubo 1, H. Tsuda 1, B. Wang 1
 NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION OF CLOSED CRACKS USING AN ULTRASONIC TRANSIT TIMING METHOD J. Takatsubo 1, H. Tsuda 1, B. Wang 1 1 National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Tsukuba, Japan
NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION OF CLOSED CRACKS USING AN ULTRASONIC TRANSIT TIMING METHOD J. Takatsubo 1, H. Tsuda 1, B. Wang 1 1 National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Tsukuba, Japan
DETECTION OF CORROSION IN BOTTOM PLATES OF GAS AND OIL TANKS USING GUIDED ULTRASONIC WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC ULTRASONIC (EMAT) TRANSDUCERS
 DETECTION OF CORROSION IN BOTTOM PLATES OF GAS AND OIL TANKS USING GUIDED ULTRASONIC WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC ULTRASONIC (EMAT) TRANSDUCERS A Presentation prepared for the Jahrestagung der Deutsche Gesellschaft
DETECTION OF CORROSION IN BOTTOM PLATES OF GAS AND OIL TANKS USING GUIDED ULTRASONIC WAVES AND ELECTROMAGNETIC ULTRASONIC (EMAT) TRANSDUCERS A Presentation prepared for the Jahrestagung der Deutsche Gesellschaft
Testing Critical Medical Tubing Using High Frequency Eddy Current Coils
 Testing Critical Medical Tubing Using High Frequency Eddy Current Coils Troy M Libby Magnetic Analysis Corporation, Mt. Vernon, NY, USA Phone: (914) 699-9450, Fax: (914) 699-9837; e-mail: info@mac-ndt.com
Testing Critical Medical Tubing Using High Frequency Eddy Current Coils Troy M Libby Magnetic Analysis Corporation, Mt. Vernon, NY, USA Phone: (914) 699-9450, Fax: (914) 699-9837; e-mail: info@mac-ndt.com
EMAT Application on Incoloy furnace Tubing Ramamohan Reddy M (ASNT Level III UT, PCN Level III UT,PAUT&TOFD)
 EMAT Application on Incoloy furnace Tubing By Ramamohan Reddy M (ASNT Level III UT, PCN Level III UT,PAUT&TOFD) Outlines 1. Introduction EMAT 2. EMAT- Ultrasound waves 3. EMAT-Surface waves 4. EMAT-Guided
EMAT Application on Incoloy furnace Tubing By Ramamohan Reddy M (ASNT Level III UT, PCN Level III UT,PAUT&TOFD) Outlines 1. Introduction EMAT 2. EMAT- Ultrasound waves 3. EMAT-Surface waves 4. EMAT-Guided
Maximizing the Fatigue Crack Response in Surface Eddy Current Inspections of Aircraft Structures
 Maximizing the Fatigue Crack Response in Surface Eddy Current Inspections of Aircraft Structures Catalin Mandache *1, Theodoros Theodoulidis 2 1 Structures, Materials and Manufacturing Laboratory, National
Maximizing the Fatigue Crack Response in Surface Eddy Current Inspections of Aircraft Structures Catalin Mandache *1, Theodoros Theodoulidis 2 1 Structures, Materials and Manufacturing Laboratory, National
Application of Ultrasonic Guided Waves for Characterization of Defects in Pipeline of Nuclear Power Plants. Younho Cho
 Application of Ultrasonic Guided Waves for Characterization of Defects in Pipeline of Nuclear Power Plants Younho Cho School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Korea ABSTRACT State-of-art
Application of Ultrasonic Guided Waves for Characterization of Defects in Pipeline of Nuclear Power Plants Younho Cho School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Korea ABSTRACT State-of-art
MultiScan MS Tube Inspection System. Multi-technology System Eddy Current Magnetic Flux Leakage Remote Field IRIS Ultrasound
 MultiScan MS 5800 Tube Inspection System Multi-technology System Eddy Current Magnetic Flux Leakage Remote Field IRIS Ultrasound 920-107 MultiScan MS 5800 E Tube Inspection with Eddy Current Condensers
MultiScan MS 5800 Tube Inspection System Multi-technology System Eddy Current Magnetic Flux Leakage Remote Field IRIS Ultrasound 920-107 MultiScan MS 5800 E Tube Inspection with Eddy Current Condensers
MultiScan MS Tube Inspection System. Multi-technology System Eddy Current Magnetic Flux Leakage Remote Field IRIS Ultrasound
 MultiScan MS 5800 Tube Inspection System 920-107 Multi-technology System Eddy Current Magnetic Flux Leakage Remote Field IRIS Ultrasound MultiScan MS 5800 E Tube Inspection with Eddy Current Condensers
MultiScan MS 5800 Tube Inspection System 920-107 Multi-technology System Eddy Current Magnetic Flux Leakage Remote Field IRIS Ultrasound MultiScan MS 5800 E Tube Inspection with Eddy Current Condensers
Application of Ultrasonic Guided Wave to Heat Exchanger Tubes Inspection
 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Application of Ultrasonic Guided Wave to Heat Exchanger Tubes Inspection Ik-Keun PARK 1,a, Yong-Kwon KIM 2,b, Sae-Jun PARK
17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China Application of Ultrasonic Guided Wave to Heat Exchanger Tubes Inspection Ik-Keun PARK 1,a, Yong-Kwon KIM 2,b, Sae-Jun PARK
CHAPTER 6 FABRICATION OF PROTOTYPE: PERFORMANCE RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
 80 CHAPTER 6 FABRICATION OF PROTOTYPE: PERFORMANCE RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTION The proposed permanent magnet brushless dc motor has quadruplex winding redundancy armature stator assembly,
80 CHAPTER 6 FABRICATION OF PROTOTYPE: PERFORMANCE RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS 6.1 INTRODUCTION The proposed permanent magnet brushless dc motor has quadruplex winding redundancy armature stator assembly,
EFFECT OF SURFACE COATINGS ON GENERATION OF LASER BASED ULTRASOUND
 EFFECT OF SURFACE COATINGS ON GENERATION OF LASER BASED ULTRASOUND V.V. Shah, K. Balasubramaniam and J.P. Singh+ Department of Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics +Diagnostic Instrumentation and Analysis
EFFECT OF SURFACE COATINGS ON GENERATION OF LASER BASED ULTRASOUND V.V. Shah, K. Balasubramaniam and J.P. Singh+ Department of Aerospace Engineering and Mechanics +Diagnostic Instrumentation and Analysis
TYPE SE and TSE, SILICON CARBIDE SPIRAL HEATING ELEMENTS
 TYPE SE and TSE, SILICON CARBIDE SPIRAL HEATING ELEMENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION The spiral Starbars are made of special high-density reaction-bonded silicon carbide. A spiral slot in the hot zone reduces
TYPE SE and TSE, SILICON CARBIDE SPIRAL HEATING ELEMENTS GENERAL DESCRIPTION The spiral Starbars are made of special high-density reaction-bonded silicon carbide. A spiral slot in the hot zone reduces
Modelling of Pulsed Eddy Current Testing of wall thinning of carbon steel pipes through insulation and cladding
 Modelling of Pulsed Eddy Current Testing of wall thinning of carbon steel pipes through insulation and cladding S Majidnia a,b, J Rudlin a, R. Nilavalan b a TWI Ltd, Granta Park Cambridge, b Brunel University
Modelling of Pulsed Eddy Current Testing of wall thinning of carbon steel pipes through insulation and cladding S Majidnia a,b, J Rudlin a, R. Nilavalan b a TWI Ltd, Granta Park Cambridge, b Brunel University
DAMAGE DETECTION IN PLATE STRUCTURES USING SPARSE ULTRASONIC TRANSDUCER ARRAYS AND ACOUSTIC WAVEFIELD IMAGING
 DAMAGE DETECTION IN PLATE STRUCTURES USING SPARSE ULTRASONIC TRANSDUCER ARRAYS AND ACOUSTIC WAVEFIELD IMAGING T. E. Michaels 1,,J.E.Michaels 1,B.Mi 1 and M. Ruzzene 1 School of Electrical and Computer
DAMAGE DETECTION IN PLATE STRUCTURES USING SPARSE ULTRASONIC TRANSDUCER ARRAYS AND ACOUSTIC WAVEFIELD IMAGING T. E. Michaels 1,,J.E.Michaels 1,B.Mi 1 and M. Ruzzene 1 School of Electrical and Computer
Generation Laser Scanning Method for Visualizing Ultrasonic Waves Propagating on a 3-D Object
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Generation Laser Scanning Method for Visualizing Ultrasonic Waves Propagating on
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Generation Laser Scanning Method for Visualizing Ultrasonic Waves Propagating on
HIGH ENERGY RATE FORMING PROCESSES
 HIGH ENERGY RATE FORMING PROCESSES In these forming processes large amount of energy is applied for a very short interval of time. Many metals tend to deform more readily under extra fast application of
HIGH ENERGY RATE FORMING PROCESSES In these forming processes large amount of energy is applied for a very short interval of time. Many metals tend to deform more readily under extra fast application of
Implementation of electromagnetic acoustic resonance in pipe inspection
 E-Journal of Advanced Maintenance Vol.5-1(2013) 25-33 Implementation of electromagnetic acoustic resonance in pipe inspection Ryoichi URAYAMA 1 Toshiyuki TAKAGI 1,*, Tetsuya UCHIMOTO 1, Shigeru KANEMOTO
E-Journal of Advanced Maintenance Vol.5-1(2013) 25-33 Implementation of electromagnetic acoustic resonance in pipe inspection Ryoichi URAYAMA 1 Toshiyuki TAKAGI 1,*, Tetsuya UCHIMOTO 1, Shigeru KANEMOTO
MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One
 MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One 1 MAIN COMPONENTS Magnet Gradient Coils RF Coils Host Computer / Electronic Support System Operator Console and Display Systems 2 3 4 5 Magnet Components 6 The magnet The
MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One 1 MAIN COMPONENTS Magnet Gradient Coils RF Coils Host Computer / Electronic Support System Operator Console and Display Systems 2 3 4 5 Magnet Components 6 The magnet The
ULTRASONIC SIGNAL CHARACTERIZATIONS OF FLAT-BOTTOM HOLES IN
 ULTRASONIC SIGNAL CHARACTERIZATIONS OF FLAT-BOTTOM HOLES IN TITANIUM ALLOYS: EXPERIMENT AND THEORY INTRODUCTION Chien-Ping Chiou 1, Frank J. Margetan 1 and R. Bruce Thompson2 1 FAA Center for Aviation
ULTRASONIC SIGNAL CHARACTERIZATIONS OF FLAT-BOTTOM HOLES IN TITANIUM ALLOYS: EXPERIMENT AND THEORY INTRODUCTION Chien-Ping Chiou 1, Frank J. Margetan 1 and R. Bruce Thompson2 1 FAA Center for Aviation
A NON-CONTACT LASER-EMAT SYSTEM FOR CRACK AND HOLE
 A NON-CONTACT LASER-EMAT SYSTEM FOR CRACK AND HOLE DETECTON N METAL PLATES NTRODUCTON S. Dixon, C. Edwards and S. B. Palmer Department of Physics University of Warwick Coventry CV 4 7 AL United Kingdom
A NON-CONTACT LASER-EMAT SYSTEM FOR CRACK AND HOLE DETECTON N METAL PLATES NTRODUCTON S. Dixon, C. Edwards and S. B. Palmer Department of Physics University of Warwick Coventry CV 4 7 AL United Kingdom
DEVELOPMENT OF MEASUREMENT SYSTEM USING OPTICAL FIBER AE SENSORS FOR ACTUAL PIPING
 DEVELOPMENT OF MEASUREMENT SYSTEM USING OPTICAL FIBER AE SENSORS FOR ACTUAL PIPING SATOSHI NISHINOIRI, PORNTHEP CHIVAVIBUL, HIROYUKI FUKUTOMI and TAKASHI OGATA Materials Science Research Laboratory, Central
DEVELOPMENT OF MEASUREMENT SYSTEM USING OPTICAL FIBER AE SENSORS FOR ACTUAL PIPING SATOSHI NISHINOIRI, PORNTHEP CHIVAVIBUL, HIROYUKI FUKUTOMI and TAKASHI OGATA Materials Science Research Laboratory, Central
Developments in Ultrasonic Guided Wave Inspection
 Developments in Ultrasonic Guided Wave Inspection Wireless Structural Health Monitoring Technology for Heat Exchanger Shells using Magnetostrictive Sensor Technology N. Muthu, EPRI, USA; G. Light, Southwest
Developments in Ultrasonic Guided Wave Inspection Wireless Structural Health Monitoring Technology for Heat Exchanger Shells using Magnetostrictive Sensor Technology N. Muthu, EPRI, USA; G. Light, Southwest
Corrosion Steel Inspection under Steel Plate Using Pulsed Eddy Current Testing
 4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2012 - Poster 4 Corrosion Steel Inspection under Steel Plate Using Pulsed Eddy Current Testing D.M. SUH *, K.S. JANG **, J.E. JANG **, D.H. LEE ** * Raynar
4th International Symposium on NDT in Aerospace 2012 - Poster 4 Corrosion Steel Inspection under Steel Plate Using Pulsed Eddy Current Testing D.M. SUH *, K.S. JANG **, J.E. JANG **, D.H. LEE ** * Raynar
THE DECI REPORT. H. L. Dunegan. August, 2000 AN ALTERNATIVE TO PENCIL LEAD BREAKS FOR SIMULATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNAL SOURCES.
 THE DECI REPORT H. L. Dunegan August, 2000 AN ALTERNATIVE TO PENCIL LEAD BREAKS FOR SIMULATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNAL SOURCES. INTRODUCTION Over 25 years ago Nelson Hsu while working with Cliff Bailey
THE DECI REPORT H. L. Dunegan August, 2000 AN ALTERNATIVE TO PENCIL LEAD BREAKS FOR SIMULATION OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION SIGNAL SOURCES. INTRODUCTION Over 25 years ago Nelson Hsu while working with Cliff Bailey
STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC
 STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION D. F ei, X. R. Zhang, C. M. Gan, and S. Y. Zhang Lab of Modern Acoustics and Institute of Acoustics Nanjing University, Nanjing,
STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION D. F ei, X. R. Zhang, C. M. Gan, and S. Y. Zhang Lab of Modern Acoustics and Institute of Acoustics Nanjing University, Nanjing,
Introduction. Inductors in AC Circuits.
 Module 3 AC Theory What you ll learn in Module 3. Section 3.1 Electromagnetic Induction. Magnetic Fields around Conductors. The Solenoid. Section 3.2 Inductance & Back e.m.f. The Unit of Inductance. Factors
Module 3 AC Theory What you ll learn in Module 3. Section 3.1 Electromagnetic Induction. Magnetic Fields around Conductors. The Solenoid. Section 3.2 Inductance & Back e.m.f. The Unit of Inductance. Factors
Standard Practice for Ultrasonic Examinations Using Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer (EMAT) Techniques 1
 Designation: E 1816 96 Standard Practice for Ultrasonic Examinations Using Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer (EMAT) Techniques 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 1816; the number
Designation: E 1816 96 Standard Practice for Ultrasonic Examinations Using Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer (EMAT) Techniques 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 1816; the number
Fastener Hole Crack Detection Using Adjustable Slide Probes
 Fastener Hole Crack Detection Using Adjustable Slide Probes General The guidelines for the adjustable sliding probes are similar to the fixed types, therefore much of the information that is given here
Fastener Hole Crack Detection Using Adjustable Slide Probes General The guidelines for the adjustable sliding probes are similar to the fixed types, therefore much of the information that is given here
Testing of the Toroidal Field Model Coil (TFMC)
 1 CT/P 14 Testing of the Toroidal Field Model Coil (TFMC) E. Salpietro on behalf of the ITER-TFMC Team EFDA-CSU, Garching,, Germany ettore.salpietro@tech.efda.org Abstract The paper shortly describes the
1 CT/P 14 Testing of the Toroidal Field Model Coil (TFMC) E. Salpietro on behalf of the ITER-TFMC Team EFDA-CSU, Garching,, Germany ettore.salpietro@tech.efda.org Abstract The paper shortly describes the
A SHEAR WAVE TRANSDUCER ARRAY FOR REAL-TIME IMAGING. R.L. Baer and G.S. Kino. Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
 A SHEAR WAVE TRANSDUCER ARRAY FOR REAL-TIME IMAGING R.L. Baer and G.S. Kino Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 INTRODUCTION In this paper we describe a contacting shear
A SHEAR WAVE TRANSDUCER ARRAY FOR REAL-TIME IMAGING R.L. Baer and G.S. Kino Edward L. Ginzton Laboratory Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 INTRODUCTION In this paper we describe a contacting shear
Particulate Control O&M Training. APC/PCUG Conference July 12-16, 2009 The Woodlands, TX
 Particulate Control O&M Training APC/PCUG Conference July 12-16, 2009 The Woodlands, TX WPCA Particulate Training Seminar July 11, 2009 ESP Power Supply Choices Slide No 1 Precipitator Power Supplies Conventional
Particulate Control O&M Training APC/PCUG Conference July 12-16, 2009 The Woodlands, TX WPCA Particulate Training Seminar July 11, 2009 ESP Power Supply Choices Slide No 1 Precipitator Power Supplies Conventional
THE UNDER HUNG VOICE COIL MOTOR ASSEMBLY REVISITED IN THE LARGE SIGNAL DOMAIN BY STEVE MOWRY
 THE UNDER HUNG VOICE COIL MOTOR ASSEMBLY REVISITED IN THE LARGE SIGNAL DOMAIN BY STEVE MOWRY The under hung voice coil can be defined as a voice coil being shorter in wind height than the magnetic gap
THE UNDER HUNG VOICE COIL MOTOR ASSEMBLY REVISITED IN THE LARGE SIGNAL DOMAIN BY STEVE MOWRY The under hung voice coil can be defined as a voice coil being shorter in wind height than the magnetic gap
EDDY CURRENT INSPECTION FOR DEEP CRACK DETECTION AROUND FASTENER HOLES IN AIRPLANE MULTI-LAYERED STRUCTURES
 EDDY CURRENT INSPECTION FOR DEEP CRACK DETECTION AROUND FASTENER HOLES IN AIRPLANE MULTI-LAYERED STRUCTURES Teodor Dogaru Albany Instruments Inc., Charlotte, NC tdogaru@hotmail.com Stuart T. Smith Center
EDDY CURRENT INSPECTION FOR DEEP CRACK DETECTION AROUND FASTENER HOLES IN AIRPLANE MULTI-LAYERED STRUCTURES Teodor Dogaru Albany Instruments Inc., Charlotte, NC tdogaru@hotmail.com Stuart T. Smith Center
Aging Wire Insulation Assessment by Phase Spectrum Examination of Ultrasonic Guided Waves 1
 Aging Wire Insulation Assessment by Phase Spectrum Examination of Ultrasonic Guided Waves 1 Robert F. Anastasi 1 and Eric I. Madaras 2 1 U.S. Army Research Laboratory, Vehicle Technology Directorate, AMSRL-VT-S,
Aging Wire Insulation Assessment by Phase Spectrum Examination of Ultrasonic Guided Waves 1 Robert F. Anastasi 1 and Eric I. Madaras 2 1 U.S. Army Research Laboratory, Vehicle Technology Directorate, AMSRL-VT-S,
Conduit measured transfer impedance and shielding effectiveness (typically achieved in the RS103 and CS114 tests)
 Conduit measured transfer impedance and shielding effectiveness (typically achieved in the RS3 and CS4 tests) D. A. Weston K. McDougall conduitse.doc 5-2-27 The data and information contained within this
Conduit measured transfer impedance and shielding effectiveness (typically achieved in the RS3 and CS4 tests) D. A. Weston K. McDougall conduitse.doc 5-2-27 The data and information contained within this
Reactor and inductor are names used interchangeably for this circuit device.
 Recommended Design Criteria for Air-Cooled Reactor for Line and Track Circuits Revised 2015 (7 Pages) A. Purpose This Manual Part recommends design criteria for an air-cooled reactor for line and track
Recommended Design Criteria for Air-Cooled Reactor for Line and Track Circuits Revised 2015 (7 Pages) A. Purpose This Manual Part recommends design criteria for an air-cooled reactor for line and track
So in MAF process use of controllable magnetic field to direct the brush to adapt the contour of the workpiece surface to be finished and nature of
 Advanced Machining Processes Dr. Manas Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 02 Lecture - 06 Magnetic Abrasive Finishing Welcome to the course on advance
Advanced Machining Processes Dr. Manas Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 02 Lecture - 06 Magnetic Abrasive Finishing Welcome to the course on advance
TECHNICAL BACKGROUND ON MsS
 TECHNICAL BACKGROUND ON MsS Sensor Principle Guided wave generation Based on the magnetostrictive (or Joule) effect Guided wave detection Based on the inverse-magnetostrictive (or Villari) effect The magnetostrictive
TECHNICAL BACKGROUND ON MsS Sensor Principle Guided wave generation Based on the magnetostrictive (or Joule) effect Guided wave detection Based on the inverse-magnetostrictive (or Villari) effect The magnetostrictive
USE OF GUIDED WAVES FOR DETECTION OF INTERIOR FLAWS IN LAYERED
 USE OF GUIDED WAVES FOR DETECTION OF INTERIOR FLAWS IN LAYERED MATERIALS Gordon G. Krauss Julie Chen Paul E. Barbone Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering Boston University Boston, MA 02215
USE OF GUIDED WAVES FOR DETECTION OF INTERIOR FLAWS IN LAYERED MATERIALS Gordon G. Krauss Julie Chen Paul E. Barbone Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering Boston University Boston, MA 02215
DEEP FLAW DETECTION WITH GIANT MAGNETORESISTIVE (GMR) BASED SELF-NULLING PROBE
 DEEP FLAW DETECTION WITH GIANT MAGNETORESISTIVE (GMR) BASED SELF-NULLING PROBE Buzz Wincheski and Min Namkung NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA 23681 INTRODUCTION The use of giant magnetoresistive
DEEP FLAW DETECTION WITH GIANT MAGNETORESISTIVE (GMR) BASED SELF-NULLING PROBE Buzz Wincheski and Min Namkung NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA 23681 INTRODUCTION The use of giant magnetoresistive
Electromagnetic Can Crusher Victoria Meadows and Matthew Kundrock Advisor: Dr. Gore. Introduction
 Electromagnetic Can Crusher Victoria Meadows and Matthew Kundrock Advisor: Dr. Gore Introduction Our Capstone Project was to build an Electromagnetic Can Crusher, a device that will crush an aluminum can
Electromagnetic Can Crusher Victoria Meadows and Matthew Kundrock Advisor: Dr. Gore Introduction Our Capstone Project was to build an Electromagnetic Can Crusher, a device that will crush an aluminum can
RECENT ADVANCES AND IMPLEMENTATIONS OF FLEXIBLE EDDY. RJ. Filkins, J.P. Fulton, T.e. Patton, and J.D. Young
 RECENT ADVANCES AND IMPLEMENTATIONS OF FLEXIBLE EDDY CURRENT PROBE TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION RJ. Filkins, J.P. Fulton, T.e. Patton, and J.D. Young General Electric Corporate Research and Development P.O.
RECENT ADVANCES AND IMPLEMENTATIONS OF FLEXIBLE EDDY CURRENT PROBE TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION RJ. Filkins, J.P. Fulton, T.e. Patton, and J.D. Young General Electric Corporate Research and Development P.O.
Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses
 Chapter - 6 Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses 6.1 Introduction principle of peaking circuit In certain applications like high power microwaves (HPM), pulsed laser drivers, etc., very fast rise times
Chapter - 6 Generation of Sub-nanosecond Pulses 6.1 Introduction principle of peaking circuit In certain applications like high power microwaves (HPM), pulsed laser drivers, etc., very fast rise times
AUTOMATED EDDY CURRENT DETECTION OF FLAWS IN SHOT-PEENED
 AUTOMATED EDDY CURRENT DETECTION OF FLAWS IN SHOT-PEENED TITANIUM MATERIALS INTRODUCTION Ray T. Ko and Stephen J. Pipenberg Automated Inspection Systems Systems Research Laboratories, Inc. 2800 Indian
AUTOMATED EDDY CURRENT DETECTION OF FLAWS IN SHOT-PEENED TITANIUM MATERIALS INTRODUCTION Ray T. Ko and Stephen J. Pipenberg Automated Inspection Systems Systems Research Laboratories, Inc. 2800 Indian
DETECTION OF SUB LAYER FATIGUE CRACKS UNDER AIRFRAME RIVETS
 DETECTION OF SUB LAYER FATIGUE CRACKS UNDER AIRFRAME RIVETS Buzz Wincheski and Min Namkung NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA 23681 INTRODUCTION The Rotating Self-Nulling Probe System developed as
DETECTION OF SUB LAYER FATIGUE CRACKS UNDER AIRFRAME RIVETS Buzz Wincheski and Min Namkung NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA 23681 INTRODUCTION The Rotating Self-Nulling Probe System developed as
BASICS ULTRASONIC TESTING METHOD. -Dr.Oruganti Prabhakar Proprietor-OP-TECH
 BASICS ULTRASONIC TESTING METHOD -Dr.Oruganti Prabhakar Proprietor-OP-TECH INTRODUCTION Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is done by first generating high frequency acoustic waves at the outer surface of the component
BASICS ULTRASONIC TESTING METHOD -Dr.Oruganti Prabhakar Proprietor-OP-TECH INTRODUCTION Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is done by first generating high frequency acoustic waves at the outer surface of the component
A New Lamb-Wave Based NDT System for Detection and Identification of Defects in Composites
 SINCE2013 Singapore International NDT Conference & Exhibition 2013, 19-20 July 2013 A New Lamb-Wave Based NDT System for Detection and Identification of Defects in Composites Wei LIN, Lay Siong GOH, B.
SINCE2013 Singapore International NDT Conference & Exhibition 2013, 19-20 July 2013 A New Lamb-Wave Based NDT System for Detection and Identification of Defects in Composites Wei LIN, Lay Siong GOH, B.
New Multi-Technology In-Line Inspection Tool For The Quantitative Wall Thickness Measurement Of Gas Pipelines
 New Multi-Technology In-Line Inspection Tool For The Quantitative Wall Thickness Measurement Of Gas Pipelines A. Barbian 1, M. Beller 1, F. Niese 2, N. Thielager 1, H. Willems 1 1 NDT Systems & Services
New Multi-Technology In-Line Inspection Tool For The Quantitative Wall Thickness Measurement Of Gas Pipelines A. Barbian 1, M. Beller 1, F. Niese 2, N. Thielager 1, H. Willems 1 1 NDT Systems & Services
Air Coupled Ultrasonic Inspection of Steel Rubber Interface
 Air Coupled Ultrasonic Inspection of Steel Rubber Interface More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=15204 Bikash Ghose 1, a, Krishnan Balasubramaniam 2, b 1 High Energy Materials Research Laboratory,
Air Coupled Ultrasonic Inspection of Steel Rubber Interface More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=15204 Bikash Ghose 1, a, Krishnan Balasubramaniam 2, b 1 High Energy Materials Research Laboratory,
Nondestructive Testing (CALIBRATION)
 NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (CALIBRATION) HPI Nondestructive Testing (CALIBRATION) Hybrid Petroleum institute His allies at all times Calibration of Nondestructive Testing Devices (PND's) INTRODUCTION Nondestructive
NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (CALIBRATION) HPI Nondestructive Testing (CALIBRATION) Hybrid Petroleum institute His allies at all times Calibration of Nondestructive Testing Devices (PND's) INTRODUCTION Nondestructive
In-line eddy current testing of wire rod
 In-line eddy current testing of wire rod By Dr. Thomas Knöll Dr. Thomas Knöll is Managing Director of, Ismaning, Germany. This article appeared in Millennium Steel Journal 2004 and has been reprinted with
In-line eddy current testing of wire rod By Dr. Thomas Knöll Dr. Thomas Knöll is Managing Director of, Ismaning, Germany. This article appeared in Millennium Steel Journal 2004 and has been reprinted with
An instrument for detecting corrosion in anchorage zones of bridge cables using guided waves
 18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa An instrument for detecting corrosion in anchorage zones of bridge cables using guided waves Jiang XU, Xinjun WU,
18th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 16-20 April 2012, Durban, South Africa An instrument for detecting corrosion in anchorage zones of bridge cables using guided waves Jiang XU, Xinjun WU,
In service application of EMAT in Boiler Water Wall Tubes and High Temperature Components
 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18662 In service application of EMAT in Boiler Water Wall Tubes and High Temperature Components R Dhanasekaran 1, Lopez Borja 2, Mukesh Arora 1 1 NDTS
More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=18662 In service application of EMAT in Boiler Water Wall Tubes and High Temperature Components R Dhanasekaran 1, Lopez Borja 2, Mukesh Arora 1 1 NDTS
ULTRASONIC TESTING OF BARS AND BILLETS
 ULTRASONIC TESTING OF BARS AND BILLETS Ultrasonic testing (UT) of bars and billets is a pressing problem to be solved by the metallurgical industry. Manual testing of the above mentioned products is practically
ULTRASONIC TESTING OF BARS AND BILLETS Ultrasonic testing (UT) of bars and billets is a pressing problem to be solved by the metallurgical industry. Manual testing of the above mentioned products is practically
Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007
 19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 LARGE CAPACITY ULTRASONIC COMPLEX VIBRATION SOURCES USING MULTIPLE TRANSDUCERS INTEGRATED USING A CIRCULAR VIBRATION DISK PACS: 43.55.Cs
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 LARGE CAPACITY ULTRASONIC COMPLEX VIBRATION SOURCES USING MULTIPLE TRANSDUCERS INTEGRATED USING A CIRCULAR VIBRATION DISK PACS: 43.55.Cs
Target Temperature Effect on Eddy-Current Displacement Sensing
 Target Temperature Effect on Eddy-Current Displacement Sensing Darko Vyroubal Karlovac University of Applied Sciences Karlovac, Croatia, darko.vyroubal@vuka.hr Igor Lacković Faculty of Electrical Engineering
Target Temperature Effect on Eddy-Current Displacement Sensing Darko Vyroubal Karlovac University of Applied Sciences Karlovac, Croatia, darko.vyroubal@vuka.hr Igor Lacković Faculty of Electrical Engineering
Development of Magnetostriction Based Ultrasonic Transducer. For In-situ High Temperature Inspection
 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=21116 Development of Magnetostriction Based Ultrasonic Transducer For In-situ High Temperature Inspection Antony Jacob Ashish 1, Prabhu Rajagopal 1,
More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=21116 Development of Magnetostriction Based Ultrasonic Transducer For In-situ High Temperature Inspection Antony Jacob Ashish 1, Prabhu Rajagopal 1,
NONLINEAR C-SCAN ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPE AND ITS APPLICATION TO CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFUSION- BONDED INTERFACES OF DIFFERENT METALS
 NONLINEAR C-SCAN ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPE AND ITS APPLICATION TO CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFUSION- BONDED INTERFACES OF DIFFERENT METALS K. Kawashima 1, M. Murase 1, Y. Ohara 1, R. Yamada 2, H. Horio 2, T. Miya
NONLINEAR C-SCAN ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPE AND ITS APPLICATION TO CHARACTERIZATION OF DIFFUSION- BONDED INTERFACES OF DIFFERENT METALS K. Kawashima 1, M. Murase 1, Y. Ohara 1, R. Yamada 2, H. Horio 2, T. Miya
Acoustic Transducer*
 Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, 29[4], pp. 400~407 (April 1992). SUMMARY REPORT Development of Ultrasonic Testing Equipment Incorporating Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer* Michio SATO, Hideharu
Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, 29[4], pp. 400~407 (April 1992). SUMMARY REPORT Development of Ultrasonic Testing Equipment Incorporating Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer* Michio SATO, Hideharu
SonaFlex. Set of Portable Multifunctional Equipment for Non-contact Ultrasonic Examination of Materials
 SonaFlex Set of Portable Multifunctional Equipment for Non-contact Ultrasonic Examination of Materials General Overview of the Testing Equipment SonaFlex is a unique intelligent ultrasonic testing system
SonaFlex Set of Portable Multifunctional Equipment for Non-contact Ultrasonic Examination of Materials General Overview of the Testing Equipment SonaFlex is a unique intelligent ultrasonic testing system
1393 DISPLACEMENT SENSORS
 1393 DISPLACEMENT SENSORS INTRODUCTION While regular sensors detect the existence of objects, displacement sensors detect the amount of displacement when objects move from one position to another. Detecting
1393 DISPLACEMENT SENSORS INTRODUCTION While regular sensors detect the existence of objects, displacement sensors detect the amount of displacement when objects move from one position to another. Detecting
A NEW APPROACH FOR THE ANALYSIS OF IMPACT-ECHO DATA
 A NEW APPROACH FOR THE ANALYSIS OF IMPACT-ECHO DATA John S. Popovics and Joseph L. Rose Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA 16802 INTRODUCTION
A NEW APPROACH FOR THE ANALYSIS OF IMPACT-ECHO DATA John S. Popovics and Joseph L. Rose Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA 16802 INTRODUCTION
2.3 PF System. WU Weiyue PF5 PF PF1
 2.3 PF System WU Weiyue 2.3.1 Introduction The poloidal field (PF) system consists of fourteen superconducting coils, including 6 pieces of central selenoid coils, 4 pieces of divertor coils and 4 pieces
2.3 PF System WU Weiyue 2.3.1 Introduction The poloidal field (PF) system consists of fourteen superconducting coils, including 6 pieces of central selenoid coils, 4 pieces of divertor coils and 4 pieces
Instruction Manual Veritest
 Instruction Manual Veritest 4.2-1 - The Veritest 4.2 is a simple eddy current test instrument. It is designed for the detection of flaws in tubular and wire product for in-line applications where end suppression
Instruction Manual Veritest 4.2-1 - The Veritest 4.2 is a simple eddy current test instrument. It is designed for the detection of flaws in tubular and wire product for in-line applications where end suppression
Induction heating of internal
 OPTIMAL DESIGN OF INTERNAL INDUCTION COILS The induction heating of internal surfaces is more complicated than heating external ones. The three main types of internal induction coils each has its advantages
OPTIMAL DESIGN OF INTERNAL INDUCTION COILS The induction heating of internal surfaces is more complicated than heating external ones. The three main types of internal induction coils each has its advantages
FGJTCFWP"KPUVKVWVG"QH"VGEJPQNQI[" FGRCTVOGPV"QH"GNGEVTKECN"GPIKPGGTKPI" VGG"246"JKIJ"XQNVCIG"GPIKPGGTKPI
 FGJTFWP"KPUKWG"QH"GEJPQNQI[" FGRTOGP"QH"GNGETKEN"GPIKPGGTKPI" GG"46"JKIJ"XQNIG"GPIKPGGTKPI Resonant Transformers: The fig. (b) shows the equivalent circuit of a high voltage testing transformer (shown
FGJTFWP"KPUKWG"QH"GEJPQNQI[" FGRTOGP"QH"GNGETKEN"GPIKPGGTKPI" GG"46"JKIJ"XQNIG"GPIKPGGTKPI Resonant Transformers: The fig. (b) shows the equivalent circuit of a high voltage testing transformer (shown
Line Frequency Transformer
 Line Frequency Transformer For frequencies of 50/60 Hz, specify a Frequency Transformer. Line Line Frequency Transformers are customized to meet customer requirements, and are available in various ratings.
Line Frequency Transformer For frequencies of 50/60 Hz, specify a Frequency Transformer. Line Line Frequency Transformers are customized to meet customer requirements, and are available in various ratings.
CAPACITIVE FOR WINDING ELECTRIC MOTORS, TRANSFORMERS AND ELECTRO-MAGNETS
 CAPACITIVE FOR WINDING ELECTRIC MOTORS, TRANSFORMERS AND ELECTRO-MAGNETS The invention relates to a capacitive coil of copper wire that can be used for all electromagnetic energy converters and their inductive
CAPACITIVE FOR WINDING ELECTRIC MOTORS, TRANSFORMERS AND ELECTRO-MAGNETS The invention relates to a capacitive coil of copper wire that can be used for all electromagnetic energy converters and their inductive
Objectives Demonstrate new sensing techniques to improve performance of CA refrigeration systems.
 FINAL REPORT Project Title: PI: Organization: Co-PI(s): and Affiliation(s) Sensors for CA Refrigeration Systems Jeff Griffin Battelle Northwest Doubl Kold, Stemilt Growers Objectives Demonstrate new sensing
FINAL REPORT Project Title: PI: Organization: Co-PI(s): and Affiliation(s) Sensors for CA Refrigeration Systems Jeff Griffin Battelle Northwest Doubl Kold, Stemilt Growers Objectives Demonstrate new sensing
Use of inductive heating for superconducting magnet protection*
 PSFC/JA-11-26 Use of inductive heating for superconducting magnet protection* L. Bromberg, J. V. Minervini, J.H. Schultz, T. Antaya and L. Myatt** MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center November 4, 2011
PSFC/JA-11-26 Use of inductive heating for superconducting magnet protection* L. Bromberg, J. V. Minervini, J.H. Schultz, T. Antaya and L. Myatt** MIT Plasma Science and Fusion Center November 4, 2011
Standard Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Turbine and Generator Steel Rotor Forgings 1
 Designation: Standard Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Turbine and Generator Steel Rotor Forgings 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 418/A 418M; the number immediately following
Designation: Standard Practice for Ultrasonic Examination of Turbine and Generator Steel Rotor Forgings 1 This standard is issued under the fixed designation A 418/A 418M; the number immediately following
DEVELOPMENT OF VERY LOW FREQUENCY SELF-NULLING PROBE FOR INSPECTION OF THICK LAYERED ALUMINUM STRUCTURES
 DEVELOPMENT OF VERY LOW FREQUENCY SELF-NULLING PROBE FOR INSPECTION OF THICK LAYERED ALUMINUM STRUCTURES Buzz Wincheski and Min Namkung NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA 23681 INTRODUCTION Nondestructive
DEVELOPMENT OF VERY LOW FREQUENCY SELF-NULLING PROBE FOR INSPECTION OF THICK LAYERED ALUMINUM STRUCTURES Buzz Wincheski and Min Namkung NASA Langley Research Center Hampton, VA 23681 INTRODUCTION Nondestructive
Design and Construction of a150kv/300a/1µs Blumlein Pulser
 Design and Construction of a150kv/300a/1µs Blumlein Pulser J.O. ROSSI, M. UEDA and J.J. BARROSO Associated Plasma Laboratory National Institute for Space Research Av. dos Astronautas 1758, São José dos
Design and Construction of a150kv/300a/1µs Blumlein Pulser J.O. ROSSI, M. UEDA and J.J. BARROSO Associated Plasma Laboratory National Institute for Space Research Av. dos Astronautas 1758, São José dos
CRACK SIZING USING A NEURAL NETWORK CLASSIFIER TRAINED WITH DATA OBTAINED FROM FINI1E ELEMENT MODELS
 CRACK SIZING USING A NEURAL NETWORK CLASSIFIER TRAINED WITH DATA OBTAINED FROM FINI1E ELEMENT MODELS Kornelija Zgonc, Jan D. Achenbach and Yung-Chung Lee Center for Quality Engineering and Failure Prevention
CRACK SIZING USING A NEURAL NETWORK CLASSIFIER TRAINED WITH DATA OBTAINED FROM FINI1E ELEMENT MODELS Kornelija Zgonc, Jan D. Achenbach and Yung-Chung Lee Center for Quality Engineering and Failure Prevention
G. Hughes Department of Mechanical Engineering University College London Torrington Place London, WClE 7JE, United Kingdom
 LEAKY RAYLEIGH WAVE INSPECTION UNDER SURFACE LAYERS G. Hughes Department of Mechanical Engineering University College London Torrington Place London, WClE 7JE, United Kingdom L.J. Bond Department of Mechanical
LEAKY RAYLEIGH WAVE INSPECTION UNDER SURFACE LAYERS G. Hughes Department of Mechanical Engineering University College London Torrington Place London, WClE 7JE, United Kingdom L.J. Bond Department of Mechanical
Multi Level Temperature Measurement Using a single 90 bend waveguide
 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=21199 Multi Level Temperature Measurement Using a single 90 bend waveguide Nishanth R 1a, Lingadurai K 1, Suresh Periyannan a and Krishnan Balasubramaniam
More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=21199 Multi Level Temperature Measurement Using a single 90 bend waveguide Nishanth R 1a, Lingadurai K 1, Suresh Periyannan a and Krishnan Balasubramaniam
MULTI-CHANNEL ULTRASONIC FLAW DETECTOR ОКО-22М-UT THE BEST INDUSTRIAL OEM SOLUTION FOR IN-LINE AND IN-SERVICE SYSTEMS
 MULTI-CHANNEL ULTRASONIC FLAW DETECTOR ОКО-22М-UT THE BEST INDUSTRIAL OEM SOLUTION FOR IN-LINE AND IN-SERVICE SYSTEMS www.ndt.com.ua PURPOSE OKO-22M-UT PRO WIRELESS INTERFACE WI-FI The ОКО-22М-UT ultrasonic
MULTI-CHANNEL ULTRASONIC FLAW DETECTOR ОКО-22М-UT THE BEST INDUSTRIAL OEM SOLUTION FOR IN-LINE AND IN-SERVICE SYSTEMS www.ndt.com.ua PURPOSE OKO-22M-UT PRO WIRELESS INTERFACE WI-FI The ОКО-22М-UT ultrasonic
In-Line EMAT Ultrasonic Weld Inspection for ERW Tube Mill Using Guided Ultrasonic Waves
 In-Line EMAT Ultrasonic Weld Inspection for ERW Tube Mill Using Guided Ultrasonic Waves Jeffrey S. Monks Innerspec Technologies, Inc. 4004 Murray Place Lynchburg, VA 24501 Phone- 434-948-1306 Fax-434-948-1313
In-Line EMAT Ultrasonic Weld Inspection for ERW Tube Mill Using Guided Ultrasonic Waves Jeffrey S. Monks Innerspec Technologies, Inc. 4004 Murray Place Lynchburg, VA 24501 Phone- 434-948-1306 Fax-434-948-1313
CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC SURFACE WAVE TRANSDUCERS
 CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC SURFACE WAVE TRANSDUCERS T. J. MORAN Air Force Materials Laboratory (AFML/LLP) Wright-Patterson AF8, Ohio 45433 Tom Szabo mentioned during his presentation
CHARACTERISTICS AND APPLICATIONS OF ELECTROMAGNETIC SURFACE WAVE TRANSDUCERS T. J. MORAN Air Force Materials Laboratory (AFML/LLP) Wright-Patterson AF8, Ohio 45433 Tom Szabo mentioned during his presentation
NONDISTRUCTIVE TESTING INSTRUMENT OF DISHED Nb SHEETS FOR SRF CAVITIES BASED ON SQUID TECHNOLOGY
 NONDISTRUCTIVE TESTING INSTRUMENT OF DISHED Nb SHEETS FOR SRF CAVITIES BASED ON SQUID TECHNOLOGY Q.-S. Shu, J. Susta, G. F. Cheng, I. Phipps, AMAC International Inc., Newport News, VA 23606 R. Selim, J.
NONDISTRUCTIVE TESTING INSTRUMENT OF DISHED Nb SHEETS FOR SRF CAVITIES BASED ON SQUID TECHNOLOGY Q.-S. Shu, J. Susta, G. F. Cheng, I. Phipps, AMAC International Inc., Newport News, VA 23606 R. Selim, J.
Laboratory no. 3 FLUORESCENT LAMPS FITTINGS
 Laboratory no. 3 FLUORESCENT LAMPS FITTINGS 3.1 General information The fluorescent lamps powered at industrial frequency voltage act as nonlinear resistors, non-inertial, with a dynamic symmetric volt-ampere
Laboratory no. 3 FLUORESCENT LAMPS FITTINGS 3.1 General information The fluorescent lamps powered at industrial frequency voltage act as nonlinear resistors, non-inertial, with a dynamic symmetric volt-ampere
Application of Guided Wave Technology to Tube Inspection
 ECNDT 2006 - Th.3.1.5 Application of Guided Wave Technology to Tube Inspection T. VOGT, D. ALLEYNE, B. PAVLAKOVIC, Guided Ultrasonics Limited, Nottingham, United Kingdom 1. Introduction Abstract. The inspection
ECNDT 2006 - Th.3.1.5 Application of Guided Wave Technology to Tube Inspection T. VOGT, D. ALLEYNE, B. PAVLAKOVIC, Guided Ultrasonics Limited, Nottingham, United Kingdom 1. Introduction Abstract. The inspection
STUDY ON IDENTIFICATION OF FAULT ON OUTER RACE OF ROLLER BEARING USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION
 STUDY ON IDENTIFICATION OF FAULT ON OUTER RACE OF ROLLER BEARING USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION Avinash V. Patil and Dr. Bimlesh Kumar 2 Faculty of Mechanical Engg.Dept., S.S.G.B.C.O.E.&T.,Bhusawal,Maharashtra,India
STUDY ON IDENTIFICATION OF FAULT ON OUTER RACE OF ROLLER BEARING USING ACOUSTIC EMISSION Avinash V. Patil and Dr. Bimlesh Kumar 2 Faculty of Mechanical Engg.Dept., S.S.G.B.C.O.E.&T.,Bhusawal,Maharashtra,India
Detecting 1 st and 2 nd Layer Simulated Cracks in Aircraft Wing Spanwise Splice Standards Using Remote-Field Eddy Current Technique
 Detecting 1 st and Layer imulated Cracks in Aircraft Wing panwise plice tandards Using Remote-Field Eddy Current Technique Yushi un, Tianhe Ouyang Innovative Materials Testing Technologies, Inc. 251 N.
Detecting 1 st and Layer imulated Cracks in Aircraft Wing panwise plice tandards Using Remote-Field Eddy Current Technique Yushi un, Tianhe Ouyang Innovative Materials Testing Technologies, Inc. 251 N.
High-Precision Internal Diameter Measurements Using Eddy Current Arrays
 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China High-Precision Internal Diameter Measurements Using Eddy Current Arrays Benoit LEPAGE 1, Dave KATZ 2,Simon LABBE 1, 1 Olympus
17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, 25-28 Oct 2008, Shanghai, China High-Precision Internal Diameter Measurements Using Eddy Current Arrays Benoit LEPAGE 1, Dave KATZ 2,Simon LABBE 1, 1 Olympus
Electromagnetic Eddy Current Sensors for Evaluation of Sea-Cure and 2205 Duplex Condenser Tubing
 6th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring - We.3.B.2 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=14151 Electromagnetic Eddy Current Sensors for Evaluation of Sea-Cure and 2205 Duplex
6th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring - We.3.B.2 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=14151 Electromagnetic Eddy Current Sensors for Evaluation of Sea-Cure and 2205 Duplex
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD. Non-destructive testing Ultrasonic thickness measurement
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 16809 First edition 2012-11-15 Non-destructive testing Ultrasonic thickness measurement Essais non destructifs Mesurage de l'épaisseur par ultrasons Reference number ISO 2012
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 16809 First edition 2012-11-15 Non-destructive testing Ultrasonic thickness measurement Essais non destructifs Mesurage de l'épaisseur par ultrasons Reference number ISO 2012
Design of Differential Protection Scheme Using Rogowski Coil
 2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X National Conference on Advances in Engineering and Applied Science (NCAEAS) 16 th February 2017 In association with International
2017 IJSRST Volume 3 Issue 2 Print ISSN: 2395-6011 Online ISSN: 2395-602X National Conference on Advances in Engineering and Applied Science (NCAEAS) 16 th February 2017 In association with International
LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES
 LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES USING GAS-COUPLED LASER ACOUSTIC DETECTION INTRODUCTION Yuqiao Yang, James N. Caron, and James B. Mehl Department of Physics and Astronomy University
LASER GENERATION AND DETECTION OF SURFACE ACOUSTIC WAVES USING GAS-COUPLED LASER ACOUSTIC DETECTION INTRODUCTION Yuqiao Yang, James N. Caron, and James B. Mehl Department of Physics and Astronomy University
Final Publishable Summary
 Final Publishable Summary Task Manager: Dr. Piotr Klimczyk Project Coordinator: Mr. Stefan Siebert Dr. Brockhaus Messtechnik GmbH & Co. KG Gustav-Adolf-Str. 4 D-58507 Lüdenscheid +49 (0)2351 3644-0 +49
Final Publishable Summary Task Manager: Dr. Piotr Klimczyk Project Coordinator: Mr. Stefan Siebert Dr. Brockhaus Messtechnik GmbH & Co. KG Gustav-Adolf-Str. 4 D-58507 Lüdenscheid +49 (0)2351 3644-0 +49
