International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 32
|
|
|
- William Fox
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 32 Instrumentation of the Data Acquisition System for the MonRAt Telescope M. A. Leigui de Oliveira a,*, V. P. Luzio a, A. F. Barbosa b,**, H. P. Lima Jr b,v. A. Ferraz b, A. B. Vilar c, M. S. A. B. Leão d a Universidade Federal do ABC (UFABC), Santo André, Brazil b Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas (CBPF), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil c Instituto Federal de Educação, Ciência e Tecnologia (IFRJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil d Faculdade Independente do Nordeste (FAINOR), Vitória da Conquista, Brazil Abstract-- MonRAt is a telescope designed to detect photons generated in the atmosphere by ultra-high energy cosmic ray particles. It is composed of a parabolic mirror focusing light onto a 64-pixel multianode photomultiplier tube. Ultraviolet-passing filters are positioned in front of the photocathode to select photons within the wavelength range of 300 to 400 nm. The data acquisition system consists of a front-end, a set of preamplifiers and FPGA-based boards able to record trigger times and waveforms from each channel. MonRAt is being designed to detect air fluorescence radiation under different atmospheric and geomagnetic conditions. Also planned are Cherenkov radiation measurements as well as atmospheric monitoring in the lidar mode. Index Term-- Cosmic rays, atmospheric fluorescence, data acquisition system. 1. INTRODUCTION Cosmic rays studies through measurements of atmospheric nitrogen fluorescence light have long been shown to be successful and, nowadays, experiments like HiRes [1], the Pierre Auger Observatory [2] and Telescope Array[3] employ this technique to detect cosmic ray showers with energies exceeding ev. The detection is performed by measuring the amount of near-ultraviolet light generated by de-excitation of nitrogen molecules, after their excitations or ionizations due to air shower charged particles. For ultra-high energy showers, the huge number of charged particles near the shower axis is responsible for the light generation with enough intensity to be detected by photomultipliers placed kilometers away from the emission point. The absolute fluorescence yield is known for some electron energies, air pressures and temperatures [4], [5], [6], [7], but further and more precise results are needed, since their extrapolation is the main sources of systematic errors in the reconstruction of showers using fluorescence telescopes [8], [9]. For a given atmospheric height h, the number of fluorescence photons N γ is proportional to number of electrons N e and the Fluorescence Yield (FY), which, in turn, depends on energy deposit by electrons in the air at, air pressure P, air temperature T and the emitted radiation wavelength λ: N ( ) ( ) de h Ne h FY,, P( h), T( h) (1) dx 2. THE APPARATUS MonRAt 1 [10] is a compact telescope designed to detect fluorescence photons in the atmosphere. We use a 64-pixel MultiAnode PhotoMultiplier Tube (MAPMT) from Hamamatsu [11] (model H7546B) as the photosensitive component (see figure 1). The MAPMT is placed at the focus of a parabolic mirror mounted in a Newtonian setup. Therefore, the data acquisition system consists of the integration of several channels with preamplifiers, discriminators and digitizers. The digitizers are FPGA-based boards, able to record waveforms (ADCs) and time stamps (TDCs) from each channel and send this information through a USB interface to the computer running the data acquisition software. * Corresponding author: leigui@ufabc.edu.br ** Deceased. 1 For the abbreviation of Atmospheric Radiation Monitor, in Portuguese.
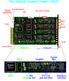
2 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 33 In figure 2, we show a diagram representing the main components of the MonRAt experiment [12] [13]. The signals from the MAPMT are initially collected by a front-end interface that reads 65 analog signals: 64 anodes plus the twelfth dynode which integrates them all. These signals are sent to a stage with a double function: amplification (about 10 times in amplitude for each anode signal) and pulse formatting (TTL for all the signals). The signals are then sent to 4 boxes housing 4 DPMs (Data Processing Modules) boards each, able to handle 4 channels each (totaling 64 analog inputs). The analog inputs are sampled by 12 bit ADCs and through the trigger inputs they give the start condition for all TDC channels (by the twelfth dynode) and the stop condition for each TDC channel (by the anodes). Part of the electronics has been purchased and part has been developed in our laboratories, in the next sections we will discuss these components in detail MAPMT front-end board and the divider boards The front-end board to collect and condition the MAPMT signals was manufactured by Vertilon Corporation [14]. The board (model SIB164A) provides electrical and mechanical connectivity between the MAPMT and the signal processing electronics of the experiment. The MAPMT is connected through a 76 pin socket in the lower side of the front-end board, giving inputs for the high voltage and outputs for the 64 anodes, the twelfth dynode signal and a common ground. In figure 3, one can see the two sides of the board with its main components and connections, according to the following legend: 1- high voltage input; 2- preamplifier output; 3- interface connector J1 (model SBC090P); 4- interface connector J2 (model SBC090P); 5- trigger indicator LED; 6- last (12th) dynode signal; 7- external input; 8- high voltage area; 9- socket to the H7546B MAPMT; 10- MAPMT
3 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 34 high voltage input. The signals from the anodes are routed to 2 connectors (J1 and J2), located on the backside of the board, that allows us to conveniently mount the system with the photocathode facing the optical arrangement and take the cables from the other side. We purchased the front-end board (model SIB164A), 2 flat cables (model CNN020) with 32 channels each and 2 extra connectors (model SBC090P) to build 2 divider boards. The divider boards are designed to attach the cables and divide their signals in groups of 4 each (see figure 4). The output signals from the divider boards are then sent to another 8 boards in order to be amplified and formatted, as described in the next section Preamplifiers and discriminators The signals coming from the MAPMT must be preamplified, since they have low amplitude and short duration (~30 ns). Thus, circuits with low noise, broadband and performing the functions of integrator, amplifier and filter are required. The active element is the operational amplifier OPA657 (see upper part of figure 5 for the preamplifier circuit). The time constant of the second stage ( = R shape C shape ) sets the rising and falling times for the signals which must be compatible to the sampling times of ~10 ns of the analog to digital converter. Moreover, R shape and C shape form a low-pass filter that influences the bandwidth of the preamplifier.
4 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 35 The discriminator produces digital TTL pulses when the input signal has a higher amplitude than a threshold. For this project we used a fast analog comparator (propagation time of 7 ns), model AD8561 from Analog Devices (see lower part of figure 5 for the discriminator circuit). The input voltage (V in_disc ) is compared to a constant threshold voltage (V th ), adjusted by the potentiometer R2. If V in_disc is greater than V th, the comparator is left enabled (~3.5 V), otherwise it remains at 0 V. A digital output signal compatible with the TTL standard is then produced. A high precision stable voltage reference (2.5 V) is provided for the potentiometers. This is generated by the integrated circuit REF43GS. The comparator is configured with hysteresis by adding feedback to the noninverting input through the resistor R3. The addition of hysteresis to the comparator offers advantages in noisy environments, where is not desirable for the output signal to switch between states when the input signal is near threshold. The MonRAt detector uses a set of 64 preamplifiers and discriminators, housed in 8 boards of 8 channels each, as shown in figure 6. Subsequently, the signals are sent to the DPMs Data processing module The Data Processing Module (DPM), shown in figure 7, is the main circuit of the acquisition of MonRAt. It is based on a logic Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)
5 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 36 device and is responsible for the digital signal processing and communication with the computer via a USB port. Each module has 2 ADCs (2 channels each, totaling 4 analog input channels), 8 channels of time-to-digital conversions, the FPGA device, 24 channels of digital input/output pins and a bus interface for communication with a DB-25 connector. A USB board interface module enables communication with the computer via the communication bus of one DPM, positioned in the top of the box and called master. This master board also controls the communication of the other 3 DPMs in the box, through the DB-25 connector, and sends their data to the USB board. The USB interface uses a commercial chip transceiver (FT232BL).The analog inputs at each DPM board are 50 Ω LEMO connectors supporting high frequency signals. Each module contains two analog-to-digital converters with a resolution of 2 channels of 12 bits and a sampling rate of 60 MSs -1. Amplitude measurements of analog signals are made within the dynamic range of 2 Vpp, with theoretical resolution of 2/2 12 V ~ 0.5 mv. The first stage of each channel scanning is an amplifier circuit that has a single-ended input signal and differential output. In the converter, the analog signal is sampled and digitized continuously, operating in free running mode. The resulting digital word from conversion remains available in synchronism with a clock signal of 60 MHz, generated by the FPGA. The data of the first channel are synchronized with the rising edge of the clock, while data from the second channel are synchronized with the falling edge. This feature permits the synchronous transfer of the converted data to the FPGA which controls the flow of data acquisition and stores it in internal FIFO (First-In First-Out) memories. Following the diagram shown in figure 8, the data available in the internal memory can be transferred by the USB bus communication through the control performed by the logic FPGA circuits.
6 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 37 The DPM has a single time-integrated digital converter, TDC F1 circuit, manufactured by Acam. The F1 has 8 channels with resolution of ~120 ps per channel and 16 bit precision, which can measure time intervals between 5 ns and 7.8 μs. The resolution is adjustable by internal configuration and is calibrated by a crystal oscillator through a PLL (Phase Locked Loop) circuit. There is only a single signal common to all stop channels. Once the signal is detected, the TDC begins the process of measurement of time and waits for the stop signals. The converted output value is placed on the digital bus, identifying the respective conversion channel. All these bus signals are connected to the FPGA, where the synthesized logic circuits are responsible for receiving the converted data and sending them to the computer via the USB port. Besides the main components mentioned above, on the board there is a device for configuration of the FPGA with JTAG (Joint Test Action Group), which stores the synthesized logic. Moreover, there are other active and passive electronic components, which are essential for the functioning of all other devices. For use in MonRAt we grouped 4 boxes with 4 DPMs each, totaling 64 input channels. In addition to the analog inputs, the DPM has a digital input, which activates the process of data acquisition at the analog channels in their positive transition. The set of DPMs has a single power input shared by every board with a supply voltage of +6 V and maximum current of 2.8 A. There is also another input for feeding the cooling fan, with a voltage of +12 V and maximum current of 0.15 A. 3. SOFTWARE The data acquisition software was developed using the platform ROOT [15] developed at CERN and widely used by the high energy physics community for tasks such as data analysis, as well as the construction and development of graphic applications and the library of functions for the USB transceiver.
7 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 38 The program is written in C++, under Linux operating system, and is object-oriented. The software has the main objectives of running data acquisitions, provide visualizations of the signals and output files for offline analyses. It was modeled and implemented with a structure of packages, which assembles a group of 12 classes that provides the functionality of each part of the application. The class diagram is shown in figure 9. Most relationships between classes are associations, with only one inheritance relationship between the DPM and DPMMonRAt classes, and one single dependency relationship between DPM and ftd2xx classes. The graphic interface of the software was built from several objects belonging to the ROOT framework. Figure 10 shows the acquisition program running, taking data from a DPM board. The program features 4 visualization areas for graphics (one for each input in this given DPM) and options for writing outputs into files. These options are user selectable via checkboxes located in the upper left side and the right side. The recording options, on the right side, include the types of files that will be generated (waveforms or tables), the nomenclature (or the initial path of the files) and the DPM box data source. The content of these areas, i.e. the analog or TDC channel, can be selected by combo boxes located on the left upper side. Event counters for each device are shown on screen and a status bar displays the conditions of the connections and messages to the user. The components of the user interface feature information and instructions that are displayed when the mouse overlaps the component. To connect a device function it is required to press the Con respective button and then press the Run button. Afterwards, the class starts pthread responsible for the device, which, in turn, executes the acquisition routine and processes the data. These routines monitor the buffer data from the USB port: when this buffer has reached a minimum amount of data, they are read and processed for validation by reading headers. After the validation, the acquisition of the event is held, otherwise it is discarded. 4. THE SINGLE PHOTOELECTRON AND THE GAIN OF INDIVIDUAL PIXELS In order to test the MonRAt system, we performed the measurement of the gain of each channel of the MAPMT, using the single photoelectron procedure. In this procedure, we impinge the minimal amount of light (~ 1 photon) on each MAPMT pixel with a blue LED, both placed in a dark room (see figure 11), and read the resulting ADC signals, after preamplification and conversion in the DPMs. In this method, the probability of converting the photon into a single photoelectron inside the tube is maximized. Thus, obtaining the spectrum of signals of multiplied electrons in the anodes, one can measure the gain of each MAPMT channels. A power supply provides three channels for the preamplifiers (±8 V and ground), and two for the DPMs (±6 V), while a high voltage source (C4900 from Hamamatsu) feeds the MAPMT with 950 V. A pulse generator provided signals to turn on the LED synchronized with TTL pulses to trigger the data acquisition in the DPMs.
8 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No:05 39 In the left side of figure 12, we can see the single photon spectrum for a selected channel and, on the right side, the histogram of gains for all the channels. We estimate an 6 average gain of , in accordance with the manufacturer of the photomultiplier[11]. 5. THE LIGHT SPOT AND TRANSIT TEST Another test to the MonRAt system was to use the same blue LED as light source in the dark room, aligned near the optical axis and positioned 2.5 m away from a small spherical mirror (15 cm of diameter). The spot size formed at the MAPMT photocathode can be seen at the upper part of figure 13(a) for an amount of light much bigger than used. Actually, this test has been performed near the single photon regime, such that this light would be impossible to be seen by naked eye. Then, the data acquisition system (MAPMT, front-end, preamplifiers and DPMs) for the 16 central pixels was turned on and the signals read through the MonRAt software. In the lower part of figure 13(a), we plot the histogram of signals: there is one central pixel with counts well above the others (showing the most illuminated pixel) and a small aberration upon two neighbors. However, the MonRAt system was able to collect this small amount of light, which gives us confidence that the experiment can detect fluorescence photons under the desired conditions: moonless and clear night skies. A second test was to progressively displace the LED by some centimeters to simulate a cosmic ray shower track developing in the MAPMT field of view. The result for this acquisition is given in figure 13(b). 6. CONCLUSIONS We have presented the design of the MonRAt detector electronics and software, measurements of individual channels gains, and its expected performance under simulated conditions. MonRAt is designed for the detection of atmospheric fluorescence radiation generated by cosmic ray 17.5 showers of energies greater than 10 ev. The detector construction has been finished and the assemblies of the mechanical and optical structures are under way. We soon will be able to measure real events, pioneering detecting the fluorescence radiation in Brazil.
9 International Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences IJBAS-IJENS Vol:14 No: ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The financial supports for this work were given by the Brazilian foundations CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) and FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo). The authors are thankful to our colleagues at UFABC and CBPF for the facilities used in the development of this work. REFERENCES [1] T. Abu-Zayyad et al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth.in Phys. Res., 2000, A450:253. [2] J. Abraham et al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth.in Phys., 2004, A523: 50. [3] M. Fukushima, Prog. Theo. Phys. Suppl., 2003, 151: 206. [4] K. Kakimoto et al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth.in Phys. Res., 1996, A372:527. [5] M. Nagano et al., Astropart. Phys., 2003, 20: 293; 2004, Astropart. Phys.,22: 235. [6] J. W. Beltz et al., Astropart. Phys., 2006, 25: 129. [7] P. Collin et al., astroph/ [8] V. de Souza, G. Medina-Tanco and J. A. Ortiz, Astropart. Phys., 2006,25: 84. [9] B. Keilheuer et al., Astropart. Phys., 2006, 25: 256. [10] M. A. Leigui de Oliveira et al., The MonRAt telescope for atmospheric radiation, Proc. of the 33rd ICRC (2013), Rio de Janeiro CR-IN, ID=1082;Proc. of the 32nd ICRC (2011), Beijing, Session HE.3.6, ID=1041; Atmospheric Radiation Monitor, Proc. of the 31st ICRC (2009), Lódz, Session HE.2.4, ID=0097. [11] [12] V. A. Ferraz, Sistema multicanal para aquisição de dados em um experimento de fluorescência atmosférica, Master Thesis, CBPF (2012), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. [13] A. B. Vilar, Instrumentação para observação de fluorescência de raios cósmicos com fotomultiplicadora multianódica, Master Thesis, CBPF(2009), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. [14] [15]
Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project
 Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 012-2009 (Draft) Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project H. P. Lima Jr, A. F. Barbosa, R. G. Gama Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas - CBPF L. F. G. Gonzalez
Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 012-2009 (Draft) Data Acquisition System for the Angra Project H. P. Lima Jr, A. F. Barbosa, R. G. Gama Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas - CBPF L. F. G. Gonzalez
Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs
 Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 1-27 (Draft) Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs A. F. Barbosa Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Fsicas - CBPF, e-mail:
Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 1-27 (Draft) Preliminary simulation study of the front-end electronics for the central detector PMTs A. F. Barbosa Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Fsicas - CBPF, e-mail:
Water Cerenkov muon detector near the Angra-II reactor core: the hardware.
 Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 007-2009 (Draft) Water Cerenkov muon detector near the Angra-II reactor core: the hardware. A. F. Barbosa, R. Machado, A. Vilar, A. Schiappacassa, R. G. Gama, L. M. de
Angra Neutrino Project AngraNote 007-2009 (Draft) Water Cerenkov muon detector near the Angra-II reactor core: the hardware. A. F. Barbosa, R. Machado, A. Vilar, A. Schiappacassa, R. G. Gama, L. M. de
Development of a 256-channel Time-of-flight Electronics System For Neutron Beam Profiling
 JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. 14, NO. 8, AUGUST 2015 1 Development of a 256-channel Time-of-flight Electronics System For Neutron Beam Profiling Haolei Chen, Changqing Feng, Jiadong Hu, Laifu Luo,
JOURNAL OF L A TEX CLASS FILES, VOL. 14, NO. 8, AUGUST 2015 1 Development of a 256-channel Time-of-flight Electronics System For Neutron Beam Profiling Haolei Chen, Changqing Feng, Jiadong Hu, Laifu Luo,
Positron Emission Tomography
 Positron Emission Tomography UBC Physics & Astronomy / PHYS 409 1 Introduction Positron emission tomography (PET) is a non-invasive way to produce the functional 1 image of a patient. It works by injecting
Positron Emission Tomography UBC Physics & Astronomy / PHYS 409 1 Introduction Positron emission tomography (PET) is a non-invasive way to produce the functional 1 image of a patient. It works by injecting
A NOVEL FPGA-BASED DIGITAL APPROACH TO NEUTRON/ -RAY PULSE ACQUISITION AND DISCRIMINATION IN SCINTILLATORS
 10th ICALEPCS Int. Conf. on Accelerator & Large Expt. Physics Control Systems. Geneva, 10-14 Oct 2005, PO2.041-4 (2005) A NOVEL FPGA-BASED DIGITAL APPROACH TO NEUTRON/ -RAY PULSE ACQUISITION AND DISCRIMINATION
10th ICALEPCS Int. Conf. on Accelerator & Large Expt. Physics Control Systems. Geneva, 10-14 Oct 2005, PO2.041-4 (2005) A NOVEL FPGA-BASED DIGITAL APPROACH TO NEUTRON/ -RAY PULSE ACQUISITION AND DISCRIMINATION
Development of an atmospheric Cherenkov era for the CANGAROO-III experiment
 The Universe Viewed in Gamma-Rays 1 imaging cam- Development of an atmospheric Cherenkov era for the CANGAROO-III experiment S. Kabuki, K. Tsuchiya, K. Okumura, R. Enomoto, T. Uchida, and H. Tsunoo Institute
The Universe Viewed in Gamma-Rays 1 imaging cam- Development of an atmospheric Cherenkov era for the CANGAROO-III experiment S. Kabuki, K. Tsuchiya, K. Okumura, R. Enomoto, T. Uchida, and H. Tsunoo Institute
Multianode Photo Multiplier Tubes as Photo Detectors for Ring Imaging Cherenkov Detectors
 Multianode Photo Multiplier Tubes as Photo Detectors for Ring Imaging Cherenkov Detectors F. Muheim a edin]department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Edinburgh Mayfield Road, Edinburgh EH9 3JZ,
Multianode Photo Multiplier Tubes as Photo Detectors for Ring Imaging Cherenkov Detectors F. Muheim a edin]department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Edinburgh Mayfield Road, Edinburgh EH9 3JZ,
PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response
 DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response (response time) 5) Stability 6) Cost 7) convenience Photoelectric
DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response (response time) 5) Stability 6) Cost 7) convenience Photoelectric
Digital coincidence acquisition applied to portable β liquid scintillation counting device
 Nuclear Science and Techniques 24 (2013) 030401 Digital coincidence acquisition applied to portable β liquid scintillation counting device REN Zhongguo 1,2 HU Bitao 1 ZHAO Zhiping 2 LI Dongcang 1,* 1 School
Nuclear Science and Techniques 24 (2013) 030401 Digital coincidence acquisition applied to portable β liquid scintillation counting device REN Zhongguo 1,2 HU Bitao 1 ZHAO Zhiping 2 LI Dongcang 1,* 1 School
CHAPTER 8 PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBE MODULES
 CHAPTER 8 PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBE MODULES This chapter describes the structure, usage, and characteristics of photomultiplier tube () modules. These modules consist of a photomultiplier tube, a voltage-divider
CHAPTER 8 PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBE MODULES This chapter describes the structure, usage, and characteristics of photomultiplier tube () modules. These modules consist of a photomultiplier tube, a voltage-divider
The HPD DETECTOR. Michele Giunta. VLVnT Workshop "Technical Aspects of a Very Large Volume Neutrino Telescope in the Mediterranean Sea"
 The HPD DETECTOR VLVnT Workshop "Technical Aspects of a Very Large Volume Neutrino Telescope in the Mediterranean Sea" In this presentation: The HPD working principles The HPD production CLUE Experiment
The HPD DETECTOR VLVnT Workshop "Technical Aspects of a Very Large Volume Neutrino Telescope in the Mediterranean Sea" In this presentation: The HPD working principles The HPD production CLUE Experiment
Homework Set 3.5 Sensitive optoelectronic detectors: seeing single photons
 Homework Set 3.5 Sensitive optoelectronic detectors: seeing single photons Due by 12:00 noon (in class) on Tuesday, Nov. 7, 2006. This is another hybrid lab/homework; please see Section 3.4 for what you
Homework Set 3.5 Sensitive optoelectronic detectors: seeing single photons Due by 12:00 noon (in class) on Tuesday, Nov. 7, 2006. This is another hybrid lab/homework; please see Section 3.4 for what you
User Guide. SIB Channel MAPMT Interface Board Hamamatsu H7546 series
 SIB164-1018 64 Channel MAPMT Interface Board Hamamatsu H7546 series Disclaimer Vertilon Corporation has made every attempt to ensure that the information in this document is accurate and complete. Vertilon
SIB164-1018 64 Channel MAPMT Interface Board Hamamatsu H7546 series Disclaimer Vertilon Corporation has made every attempt to ensure that the information in this document is accurate and complete. Vertilon
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 Atomic and Nuclear Physics Nuclear physics -spectroscopy LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Detecting radiation with a scintillation counter Objects of the experiments Studying the scintillator pulses with an oscilloscope
Atomic and Nuclear Physics Nuclear physics -spectroscopy LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Detecting radiation with a scintillation counter Objects of the experiments Studying the scintillator pulses with an oscilloscope
Photon Counters SR430 5 ns multichannel scaler/averager
 Photon Counters SR430 5 ns multichannel scaler/averager SR430 Multichannel Scaler/Averager 5 ns to 10 ms bin width Count rates up to 100 MHz 1k to 32k bins per record Built-in discriminator No interchannel
Photon Counters SR430 5 ns multichannel scaler/averager SR430 Multichannel Scaler/Averager 5 ns to 10 ms bin width Count rates up to 100 MHz 1k to 32k bins per record Built-in discriminator No interchannel
Overview 256 channel Silicon Photomultiplier large area using matrix readout system The SensL Matrix detector () is the largest area, highest channel
 技股份有限公司 wwwrteo 公司 wwwrteo.com Page 1 Overview 256 channel Silicon Photomultiplier large area using matrix readout system The SensL Matrix detector () is the largest area, highest channel count, Silicon
技股份有限公司 wwwrteo 公司 wwwrteo.com Page 1 Overview 256 channel Silicon Photomultiplier large area using matrix readout system The SensL Matrix detector () is the largest area, highest channel count, Silicon
The influence of noise on radio signals from cosmic rays
 The influence of noise on radio signals from cosmic rays Bachelor Thesis in Physics & Astronomy Katharina Holland Supervisor: Dr. Charles Timmermans Institute for Mathematics, Astrophysics and Particle
The influence of noise on radio signals from cosmic rays Bachelor Thesis in Physics & Astronomy Katharina Holland Supervisor: Dr. Charles Timmermans Institute for Mathematics, Astrophysics and Particle
Digital trigger system for the RED-100 detector based on the unit in VME standard
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Digital trigger system for the RED-100 detector based on the unit in VME standard To cite this article: D Yu Akimov et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Digital trigger system for the RED-100 detector based on the unit in VME standard To cite this article: D Yu Akimov et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
PoS(ICRC2017)449. First results from the AugerPrime engineering array
 First results from the AugerPrime engineering array a for the Pierre Auger Collaboration b a Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay, INP-CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, 9106 Orsay
First results from the AugerPrime engineering array a for the Pierre Auger Collaboration b a Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay, INP-CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, 9106 Orsay
Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector
 Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector Dmitri Kotchetkov University of Hawaii at Manoa for Belle II itop Detector Group March 3, 2017 Barrel Particle Identification
Electronic Readout System for Belle II Imaging Time of Propagation Detector Dmitri Kotchetkov University of Hawaii at Manoa for Belle II itop Detector Group March 3, 2017 Barrel Particle Identification
UV Light Shower Simulator for Fluorescence and Cerenkov Radiation Studies
 UV Light Shower Simulator for Fluorescence and Cerenkov Radiation Studies P. Gorodetzky, J. Dolbeau, T. Patzak, J. Waisbard, C. Boutonnet To cite this version: P. Gorodetzky, J. Dolbeau, T. Patzak, J.
UV Light Shower Simulator for Fluorescence and Cerenkov Radiation Studies P. Gorodetzky, J. Dolbeau, T. Patzak, J. Waisbard, C. Boutonnet To cite this version: P. Gorodetzky, J. Dolbeau, T. Patzak, J.
MAROC: Multi-Anode ReadOut Chip for MaPMTs
 Author manuscript, published in "2006 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference, and 15th International Room 2006 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Temperature Record Semiconductor
Author manuscript, published in "2006 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Medical Imaging Conference, and 15th International Room 2006 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Temperature Record Semiconductor
A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 2 journal of August 2005 physics pp. 273 283 A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator S K GUPTA a, Y HAYASHI b, A JAIN a, S KARTHIKEYAN
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 2 journal of August 2005 physics pp. 273 283 A high-performance, low-cost, leading edge discriminator S K GUPTA a, Y HAYASHI b, A JAIN a, S KARTHIKEYAN
LHCb Preshower(PS) and Scintillating Pad Detector (SPD): commissioning, calibration, and monitoring
 LHCb Preshower(PS) and Scintillating Pad Detector (SPD): commissioning, calibration, and monitoring Eduardo Picatoste Olloqui on behalf of the LHCb Collaboration Universitat de Barcelona, Facultat de Física,
LHCb Preshower(PS) and Scintillating Pad Detector (SPD): commissioning, calibration, and monitoring Eduardo Picatoste Olloqui on behalf of the LHCb Collaboration Universitat de Barcelona, Facultat de Física,
Pixel hybrid photon detectors
 Pixel hybrid photon detectors for the LHCb-RICH system Ken Wyllie On behalf of the LHCb-RICH group CERN, Geneva, Switzerland 1 Outline of the talk Introduction The LHCb detector The RICH 2 counter Overall
Pixel hybrid photon detectors for the LHCb-RICH system Ken Wyllie On behalf of the LHCb-RICH group CERN, Geneva, Switzerland 1 Outline of the talk Introduction The LHCb detector The RICH 2 counter Overall
Implementation of A Nanosecond Time-resolved APD Detector System for NRS Experiment in HEPS-TF
 Implementation of A Nanosecond Time-resolved APD Detector System for NRS Experiment in HEPS-TF LI Zhen-jie a ; MA Yi-chao c ; LI Qiu-ju a ; LIU Peng a ; CHANG Jin-fan b ; ZHOU Yang-fan a * a Beijing Synchrotron
Implementation of A Nanosecond Time-resolved APD Detector System for NRS Experiment in HEPS-TF LI Zhen-jie a ; MA Yi-chao c ; LI Qiu-ju a ; LIU Peng a ; CHANG Jin-fan b ; ZHOU Yang-fan a * a Beijing Synchrotron
arxiv:hep-ex/ v1 19 Apr 2002
 STUDY OF THE AVALANCHE TO STREAMER TRANSITION IN GLASS RPC EXCITED BY UV LIGHT. arxiv:hep-ex/0204026v1 19 Apr 2002 Ammosov V., Gapienko V.,Kulemzin A., Semak A.,Sviridov Yu.,Zaets V. Institute for High
STUDY OF THE AVALANCHE TO STREAMER TRANSITION IN GLASS RPC EXCITED BY UV LIGHT. arxiv:hep-ex/0204026v1 19 Apr 2002 Ammosov V., Gapienko V.,Kulemzin A., Semak A.,Sviridov Yu.,Zaets V. Institute for High
Monitoring DC anode current of a grounded-cathode photomultiplier tube
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 435 (1999) 484}489 Monitoring DC anode current of a grounded-cathode photomultiplier tube S. Argirò, D.V. Camin*, M. Destro, C.K. GueH rard Dipartimento
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 435 (1999) 484}489 Monitoring DC anode current of a grounded-cathode photomultiplier tube S. Argirò, D.V. Camin*, M. Destro, C.K. GueH rard Dipartimento
Results on the LED Pulser System for the Hall A DVCS Experiment
 Results on the LED Pulser System for the Hall A DVCS Experiment Fernando J. Barbosa, Pierre Bertin Jefferson Lab 28 February 2003 System Description The LED Pulser System Diagram is shown in figure 1.
Results on the LED Pulser System for the Hall A DVCS Experiment Fernando J. Barbosa, Pierre Bertin Jefferson Lab 28 February 2003 System Description The LED Pulser System Diagram is shown in figure 1.
Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan
 1, Hiroaki Aihara, Masako Iwasaki University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan E-mail: chojyuro@gmail.com Manobu Tanaka Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator
1, Hiroaki Aihara, Masako Iwasaki University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan E-mail: chojyuro@gmail.com Manobu Tanaka Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator
Tutors Dominik Dannheim, Thibault Frisson (CERN, Geneva, Switzerland)
 Danube School on Instrumentation in Elementary Particle & Nuclear Physics University of Novi Sad, Serbia, September 8 th 13 th, 2014 Lab Experiment: Characterization of Silicon Photomultipliers Dominik
Danube School on Instrumentation in Elementary Particle & Nuclear Physics University of Novi Sad, Serbia, September 8 th 13 th, 2014 Lab Experiment: Characterization of Silicon Photomultipliers Dominik
CHAPTER 11 HPD (Hybrid Photo-Detector)
 CHAPTER 11 HPD (Hybrid Photo-Detector) HPD (Hybrid Photo-Detector) is a completely new photomultiplier tube that incorporates a semiconductor element in an evacuated electron tube. In HPD operation, photoelectrons
CHAPTER 11 HPD (Hybrid Photo-Detector) HPD (Hybrid Photo-Detector) is a completely new photomultiplier tube that incorporates a semiconductor element in an evacuated electron tube. In HPD operation, photoelectrons
HF Upgrade Studies: Characterization of Photo-Multiplier Tubes
 HF Upgrade Studies: Characterization of Photo-Multiplier Tubes 1. Introduction Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are very sensitive light detectors which are commonly used in high energy physics experiments.
HF Upgrade Studies: Characterization of Photo-Multiplier Tubes 1. Introduction Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are very sensitive light detectors which are commonly used in high energy physics experiments.
Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer
 Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer The scientific field of Mass Spectrometry (MS) has been under constant research and development for over a hundred years, ever since scientists discovered that
Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer The scientific field of Mass Spectrometry (MS) has been under constant research and development for over a hundred years, ever since scientists discovered that
Detectors for microscopy - CCDs, APDs and PMTs. Antonia Göhler. Nov 2014
 Detectors for microscopy - CCDs, APDs and PMTs Antonia Göhler Nov 2014 Detectors/Sensors in general are devices that detect events or changes in quantities (intensities) and provide a corresponding output,
Detectors for microscopy - CCDs, APDs and PMTs Antonia Göhler Nov 2014 Detectors/Sensors in general are devices that detect events or changes in quantities (intensities) and provide a corresponding output,
Testing the Electronics for the MicroBooNE Light Collection System
 Testing the Electronics for the MicroBooNE Light Collection System Kathleen V. Tatem Nevis Labs, Columbia University & Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory August 3, 2012 Abstract This paper discusses
Testing the Electronics for the MicroBooNE Light Collection System Kathleen V. Tatem Nevis Labs, Columbia University & Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory August 3, 2012 Abstract This paper discusses
Multi-channel front-end board for SiPM readout
 Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION Multi-channel front-end board for SiPM readout arxiv:1606.02290v1 [physics.ins-det] 7 Jun 2016 M. Auger, A. Ereditato, D. Goeldi, I. Kreslo, D. Lorca, M.
Preprint typeset in JINST style - HYPER VERSION Multi-channel front-end board for SiPM readout arxiv:1606.02290v1 [physics.ins-det] 7 Jun 2016 M. Auger, A. Ereditato, D. Goeldi, I. Kreslo, D. Lorca, M.
astro-ph/ Nov 1996
 Analog Optical Transmission of Fast Photomultiplier Pulses Over Distances of 2 km A. Karle, T. Mikolajski, S. Cichos, S. Hundertmark, D. Pandel, C. Spiering, O. Streicher, T. Thon, C. Wiebusch, R. Wischnewski
Analog Optical Transmission of Fast Photomultiplier Pulses Over Distances of 2 km A. Karle, T. Mikolajski, S. Cichos, S. Hundertmark, D. Pandel, C. Spiering, O. Streicher, T. Thon, C. Wiebusch, R. Wischnewski
Scintillation Counters
 PHY311/312 Detectors for Nuclear and Particle Physics Dr. C.N. Booth Scintillation Counters Unlike many other particle detectors, which exploit the ionisation produced by the passage of a charged particle,
PHY311/312 Detectors for Nuclear and Particle Physics Dr. C.N. Booth Scintillation Counters Unlike many other particle detectors, which exploit the ionisation produced by the passage of a charged particle,
The Analog Signal Processing System for the Auger Fluorescence Detector Prototype
 444 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 48, NO. 3, JUNE 2001 The Analog Signal Processing System for the Auger Fluorescence Detector Prototype S. Argirò, D. V. Camin, P. Cattaneo, M. Cuautle, M.
444 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 48, NO. 3, JUNE 2001 The Analog Signal Processing System for the Auger Fluorescence Detector Prototype S. Argirò, D. V. Camin, P. Cattaneo, M. Cuautle, M.
CAEN. Electronic Instrumentation. CAEN Silicon Photomultiplier Kit
 CAEN Tools for Discovery Electronic Instrumentation CAEN Silicon Photomultiplier Kit CAEN realized a modular development kit dedicated to Silicon Photomultipliers, representing the state-of-the art in
CAEN Tools for Discovery Electronic Instrumentation CAEN Silicon Photomultiplier Kit CAEN realized a modular development kit dedicated to Silicon Photomultipliers, representing the state-of-the art in
Portable compact cold atoms clock topology
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Portable compact cold atoms clock topology To cite this article: R D Pechoneri et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 733 012049 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Portable compact cold atoms clock topology To cite this article: R D Pechoneri et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 733 012049 View the article online
PH2510 Nuclear Physics Laboratory Use of Scintillation Counters (NP5)
 Physics Department Royal Holloway University of London PH2510 Nuclear Physics Laboratory Use of Scintillation Counters (NP5) 1. Introduction 1.1 Object of the Experiment The object of this experiment is
Physics Department Royal Holloway University of London PH2510 Nuclear Physics Laboratory Use of Scintillation Counters (NP5) 1. Introduction 1.1 Object of the Experiment The object of this experiment is
Development of a spectrometry system Using lock-in amplification technique
 VNU. JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, Mathematics - Physics, T.xXI, n 0 2, 2005 Development of a spectrometry system Using lock-in amplification technique Department of Physics, College of Science, VNU Abstract. Raman
VNU. JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, Mathematics - Physics, T.xXI, n 0 2, 2005 Development of a spectrometry system Using lock-in amplification technique Department of Physics, College of Science, VNU Abstract. Raman
CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES
 CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES The current multiplication mechanism offered by dynodes makes photomultiplier tubes ideal for low-light-level measurement. As explained earlier, there
CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES The current multiplication mechanism offered by dynodes makes photomultiplier tubes ideal for low-light-level measurement. As explained earlier, there
NIM INDEX. Attenuators. ADCs (Peak Sensing) Discriminators. Translators Analog Pulse Processors Amplifiers (Fast) Amplifiers (Spectroscopy)
 NIM The NIM-Nuclear Instrumentation Module standard is a very popular form factor widely used in experimental Particle and Nuclear Physics setups. Defined the first time by the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission
NIM The NIM-Nuclear Instrumentation Module standard is a very popular form factor widely used in experimental Particle and Nuclear Physics setups. Defined the first time by the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission
Development and Application of 500MSPS Digitizer for High Resolution Ultrasonic Measurements
 Indian Society for Non-Destructive Testing Hyderabad Chapter Proc. National Seminar on Non-Destructive Evaluation Dec. 7-9, 2006, Hyderabad Development and Application of 500MSPS Digitizer for High Resolution
Indian Society for Non-Destructive Testing Hyderabad Chapter Proc. National Seminar on Non-Destructive Evaluation Dec. 7-9, 2006, Hyderabad Development and Application of 500MSPS Digitizer for High Resolution
SHM-180 Eight Channel Sample & Hold Module
 Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2003 Printer HP 4500 PS High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.becker-hickl.com email: info@becker-hickl.com SHM-180 Eight
Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2003 Printer HP 4500 PS High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.becker-hickl.com email: info@becker-hickl.com SHM-180 Eight
Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1]
![Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1] Traditional analog QDC chain and Digital Pulse Processing [1]](/thumbs/75/72878980.jpg) Giuliano Mini Viareggio April 22, 2010 Introduction The aim of this paper is to compare the energy resolution of two gamma ray spectroscopy setups based on two different acquisition chains; the first chain
Giuliano Mini Viareggio April 22, 2010 Introduction The aim of this paper is to compare the energy resolution of two gamma ray spectroscopy setups based on two different acquisition chains; the first chain
PMT tests at UMD. Vlasios Vasileiou Version st May 2006
 PMT tests at UMD Vlasios Vasileiou Version 1.0 1st May 2006 Abstract This memo describes the tests performed on three Milagro PMTs in UMD. Initially, pulse-height distributions of the PMT signals were
PMT tests at UMD Vlasios Vasileiou Version 1.0 1st May 2006 Abstract This memo describes the tests performed on three Milagro PMTs in UMD. Initially, pulse-height distributions of the PMT signals were
Gamma Ray Spectroscopy with NaI(Tl) and HPGe Detectors
 Nuclear Physics #1 Gamma Ray Spectroscopy with NaI(Tl) and HPGe Detectors Introduction: In this experiment you will use both scintillation and semiconductor detectors to study γ- ray energy spectra. The
Nuclear Physics #1 Gamma Ray Spectroscopy with NaI(Tl) and HPGe Detectors Introduction: In this experiment you will use both scintillation and semiconductor detectors to study γ- ray energy spectra. The
A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors
 A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors L.L.Jones a, P.Seller a, I.Lazarus b, P.Coleman-Smith b a STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, OX11 0QX, UK b STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, UK
A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors L.L.Jones a, P.Seller a, I.Lazarus b, P.Coleman-Smith b a STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, OX11 0QX, UK b STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, UK
The Light Amplifier Concept
 The Light Amplifier Concept Daniel Ferenc 1 Eckart Lorenz 1,2 Daniel Kranich 1 Alvin Laille 1 (1) Physics Department, University of California Davis (2) Max Planck Institute, Munich Work supported partly
The Light Amplifier Concept Daniel Ferenc 1 Eckart Lorenz 1,2 Daniel Kranich 1 Alvin Laille 1 (1) Physics Department, University of California Davis (2) Max Planck Institute, Munich Work supported partly
InGaAs SPAD BIOMEDICAL APPLICATION INDUSTRIAL APPLICATION ASTRONOMY APPLICATION QUANTUM APPLICATION
 InGaAs SPAD The InGaAs Single-Photon Counter is based on InGaAs/InP SPAD for the detection of Near-Infrared single photons up to 1700 nm. The module includes a pulse generator for gating the detector,
InGaAs SPAD The InGaAs Single-Photon Counter is based on InGaAs/InP SPAD for the detection of Near-Infrared single photons up to 1700 nm. The module includes a pulse generator for gating the detector,
ADQ214. Datasheet. Features. Introduction. Applications. Software support. ADQ Development Kit. Ordering information
 ADQ214 is a dual channel high speed digitizer. The ADQ214 has outstanding dynamic performance from a combination of high bandwidth and high dynamic range, which enables demanding measurements such as RF/IF
ADQ214 is a dual channel high speed digitizer. The ADQ214 has outstanding dynamic performance from a combination of high bandwidth and high dynamic range, which enables demanding measurements such as RF/IF
arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 17 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 17 Oct 2015 arxiv: v2 [physics.ins-det] 17 Oct 2015](/thumbs/90/102879181.jpg) arxiv:55.9v2 [physics.ins-det] 7 Oct 25 Performance of VUV-sensitive MPPC for Liquid Argon Scintillation Light T.Igarashi, S.Naka, M.Tanaka, T.Washimi, K.Yorita Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan E-mail:
arxiv:55.9v2 [physics.ins-det] 7 Oct 25 Performance of VUV-sensitive MPPC for Liquid Argon Scintillation Light T.Igarashi, S.Naka, M.Tanaka, T.Washimi, K.Yorita Waseda University, Tokyo, Japan E-mail:
Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO
 Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO Abstract The ALICE Time of Flight Detector system comprises about 176.000 channels and covers an area of more than 100 m 2. The timing resolution
Study of the ALICE Time of Flight Readout System - AFRO Abstract The ALICE Time of Flight Detector system comprises about 176.000 channels and covers an area of more than 100 m 2. The timing resolution
Measurement of the FD camera light collection efficiency and uniformity
 GAP - 2000-010 Roma, 1 March 2000 Measurement of the FD camera light collection efficiency and uniformity P. Facal San Luis Sezione INFN di Roma II, Roma, Italy and Universidad de Santiago de Compostela,
GAP - 2000-010 Roma, 1 March 2000 Measurement of the FD camera light collection efficiency and uniformity P. Facal San Luis Sezione INFN di Roma II, Roma, Italy and Universidad de Santiago de Compostela,
ADQ108. Datasheet. Features. Introduction. Applications. Software support. ADQ Development Kit. Ordering information
 ADQ18 is a single channel high speed digitizer in the ADQ V6 Digitizer family. The ADQ18 has an outstanding combination of dynamic range and unique bandwidth, which enables demanding measurements such
ADQ18 is a single channel high speed digitizer in the ADQ V6 Digitizer family. The ADQ18 has an outstanding combination of dynamic range and unique bandwidth, which enables demanding measurements such
ORTEC. Research Applications. Pulse-Height, Charge, or Energy Spectroscopy. Detectors. Processing Electronics
 ORTEC Spectroscopy systems for ORTEC instrumentation produce pulse height distributions of gamma ray or alpha energies. MAESTRO-32 (model A65-B32) is the software included with most spectroscopy systems
ORTEC Spectroscopy systems for ORTEC instrumentation produce pulse height distributions of gamma ray or alpha energies. MAESTRO-32 (model A65-B32) is the software included with most spectroscopy systems
Pierre Auger Observatory Overview of the Acquisition Systems
 Pierre Auger Observatory Overview of the Acquisition Systems Cyril Lachaud for the Auger Collaboration LPCC/CDF 11 place Marcelin Berthelot 75231 Paris Cedex 05 (FRANCE) Phone: (+33)1 44 27 15 20 Fax:
Pierre Auger Observatory Overview of the Acquisition Systems Cyril Lachaud for the Auger Collaboration LPCC/CDF 11 place Marcelin Berthelot 75231 Paris Cedex 05 (FRANCE) Phone: (+33)1 44 27 15 20 Fax:
Characterisation of SiPM Index :
 Characterisation of SiPM --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Index : 1. Basics of SiPM* 2. SiPM module 3. Working principle 4. Experimental setup
Characterisation of SiPM --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Index : 1. Basics of SiPM* 2. SiPM module 3. Working principle 4. Experimental setup
GAMMA-GAMMA CORRELATION Latest Revision: August 21, 2007
 C1-1 GAMMA-GAMMA CORRELATION Latest Revision: August 21, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: decay event? What is the angular correlation between two gamma rays emitted by a single INTRODUCTION & THEORY:
C1-1 GAMMA-GAMMA CORRELATION Latest Revision: August 21, 2007 QUESTION TO BE INVESTIGATED: decay event? What is the angular correlation between two gamma rays emitted by a single INTRODUCTION & THEORY:
CHAPTER 3 BASIC OPERATING METHODS OF PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC OPERATING METHODS OF PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES This section provides the first-time photomultiplier tube users with general information on how to choose the ideal photomultiplier tube (often
CHAPTER 3 BASIC OPERATING METHODS OF PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES This section provides the first-time photomultiplier tube users with general information on how to choose the ideal photomultiplier tube (often
PX4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
 PX4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) What is the PX4? The PX4 is a component in the complete signal processing chain of a nuclear instrumentation system. It replaces many different components in a traditional
PX4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) What is the PX4? The PX4 is a component in the complete signal processing chain of a nuclear instrumentation system. It replaces many different components in a traditional
CAMAC products. CAEN Short Form Catalog Function Model Description Page
 products Function Model Description Page Controller C111C Ethernet Crate Controller 44 Discriminator C808 16 Channel Constant Fraction Discriminator 44 Discriminator C894 16 Channel Leading Edge Discriminator
products Function Model Description Page Controller C111C Ethernet Crate Controller 44 Discriminator C808 16 Channel Constant Fraction Discriminator 44 Discriminator C894 16 Channel Leading Edge Discriminator
Gentec-EO USA. T-RAD-USB Users Manual. T-Rad-USB Operating Instructions /15/2010 Page 1 of 24
 Gentec-EO USA T-RAD-USB Users Manual Gentec-EO USA 5825 Jean Road Center Lake Oswego, Oregon, 97035 503-697-1870 voice 503-697-0633 fax 121-201795 11/15/2010 Page 1 of 24 System Overview Welcome to the
Gentec-EO USA T-RAD-USB Users Manual Gentec-EO USA 5825 Jean Road Center Lake Oswego, Oregon, 97035 503-697-1870 voice 503-697-0633 fax 121-201795 11/15/2010 Page 1 of 24 System Overview Welcome to the
Physics Experiment N -17. Lifetime of Cosmic Ray Muons with On-Line Data Acquisition on a Computer
 Introduction Physics 410-510 Experiment N -17 Lifetime of Cosmic Ray Muons with On-Line Data Acquisition on a Computer The experiment is designed to teach the techniques of particle detection using scintillation
Introduction Physics 410-510 Experiment N -17 Lifetime of Cosmic Ray Muons with On-Line Data Acquisition on a Computer The experiment is designed to teach the techniques of particle detection using scintillation
Use of a Hybrid Photo Detector (HPD) in the MAGIC micro power LIDAR system
 Use of a Hybrid Photo Detector (HPD) in the MAGIC micro power LIDAR system Christian Fruck cfruck@ph.tum.de Max-Planck-Institut für Physik LIGHT 11 - Ringberg 03.11.2011 1 / 18 Overview MAGIC uses the
Use of a Hybrid Photo Detector (HPD) in the MAGIC micro power LIDAR system Christian Fruck cfruck@ph.tum.de Max-Planck-Institut für Physik LIGHT 11 - Ringberg 03.11.2011 1 / 18 Overview MAGIC uses the
The Pierre Auger Observatory
 The Pierre Auger Observatory Hunting the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays II EAS Detection at the Pierre Auger Observatory March 07 E.Menichetti - Villa Gualino, March 2007 1 EAS The Movie March 07 E.Menichetti
The Pierre Auger Observatory Hunting the Highest Energy Cosmic Rays II EAS Detection at the Pierre Auger Observatory March 07 E.Menichetti - Villa Gualino, March 2007 1 EAS The Movie March 07 E.Menichetti
Performance of 8-stage Multianode Photomultipliers
 Performance of 8-stage Multianode Photomultipliers Introduction requirements by LHCb MaPMT characteristics System integration Test beam and Lab results Conclusions MaPMT Beetle1.2 9 th Topical Seminar
Performance of 8-stage Multianode Photomultipliers Introduction requirements by LHCb MaPMT characteristics System integration Test beam and Lab results Conclusions MaPMT Beetle1.2 9 th Topical Seminar
InGaAs SPAD freerunning
 InGaAs SPAD freerunning The InGaAs Single-Photon Counter is based on a InGaAs/InP SPAD for the detection of near-infrared single photons up to 1700 nm. The module includes a front-end circuit for fast
InGaAs SPAD freerunning The InGaAs Single-Photon Counter is based on a InGaAs/InP SPAD for the detection of near-infrared single photons up to 1700 nm. The module includes a front-end circuit for fast
Lecture 12 OPTICAL DETECTORS
 Lecture 12 OPTICL DETECTOS (eference: Optical Electronics in Modern Communications,. Yariv, Oxford, 1977, Ch. 11.) Photomultiplier Tube (PMT) Highly sensitive detector for light from near infrared ultraviolet
Lecture 12 OPTICL DETECTOS (eference: Optical Electronics in Modern Communications,. Yariv, Oxford, 1977, Ch. 11.) Photomultiplier Tube (PMT) Highly sensitive detector for light from near infrared ultraviolet
Uniformity and Crosstalk in MultiAnode Photomultiplier Tubes
 Uniformity and Crosstalk in MultiAnode Photomultiplier Tubes A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Science degree in Physics from the College of William
Uniformity and Crosstalk in MultiAnode Photomultiplier Tubes A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Bachelor of Science degree in Physics from the College of William
Silicon Photomultiplier
 Silicon Photomultiplier Operation, Performance & Possible Applications Slawomir Piatek Technical Consultant, Hamamatsu Corp. Introduction Very high intrinsic gain together with minimal excess noise make
Silicon Photomultiplier Operation, Performance & Possible Applications Slawomir Piatek Technical Consultant, Hamamatsu Corp. Introduction Very high intrinsic gain together with minimal excess noise make
NIM. ADCs (Peak Sensing) Analog Pulse Processors Amplifiers (Fast) Amplifiers (Spectroscopy) Attenuators Coincidence/Logic/Trigger Units
 The NIM-Nuclear Instrumentation Module standard is a very popular form factor widely used in experimental Particle and Nuclear Physics setups. Defined the first time by the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission
The NIM-Nuclear Instrumentation Module standard is a very popular form factor widely used in experimental Particle and Nuclear Physics setups. Defined the first time by the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission
Models 296 and 295 combine sophisticated
 Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) Models 296 and 295 50 MS/s Synthesized Multichannel Arbitrary Waveform Generators Up to 4 Independent Channels 10 Standard
Established 1981 Advanced Test Equipment Rentals www.atecorp.com 800-404-ATEC (2832) Models 296 and 295 50 MS/s Synthesized Multichannel Arbitrary Waveform Generators Up to 4 Independent Channels 10 Standard
5. Scintillation counters
 5. Scintillation counters to detect radiation by means of scintillation is among oldest methods of particle detection historical example: particle impinging on ZnS screen -> emission of light flash principle
5. Scintillation counters to detect radiation by means of scintillation is among oldest methods of particle detection historical example: particle impinging on ZnS screen -> emission of light flash principle
Silicon Photomultiplier Evaluation Kit. Quick Start Guide. Eval Kit SiPM. KETEK GmbH. Hofer Str Munich Germany.
 KETEK GmbH Hofer Str. 3 81737 Munich Germany www.ketek.net info@ketek.net phone +49 89 673 467 70 fax +49 89 673 467 77 Silicon Photomultiplier Evaluation Kit Quick Start Guide Eval Kit Table of Contents
KETEK GmbH Hofer Str. 3 81737 Munich Germany www.ketek.net info@ketek.net phone +49 89 673 467 70 fax +49 89 673 467 77 Silicon Photomultiplier Evaluation Kit Quick Start Guide Eval Kit Table of Contents
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 614 (2010) 308 312 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 614 (2010) 308 312 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/nima
5. Scintillation counters
 5. Scintillation counters to detect radiation by means of scintillation is among oldest methods of particle detection particle impinging on ZnS screen -> emission of light flash principle of scintillation
5. Scintillation counters to detect radiation by means of scintillation is among oldest methods of particle detection particle impinging on ZnS screen -> emission of light flash principle of scintillation
Nyquist filter FIFO. Amplifier. Impedance matching. 40 MHz sampling ADC. DACs for gain and offset FPGA. clock distribution (not yet implemented)
 The Digital Gamma Finder (DGF) Firewire clock distribution (not yet implemented) DSP One of four channels Inputs Camac for 4 channels 2 cm System FPGA Digital part Analog part FIFO Amplifier Nyquist filter
The Digital Gamma Finder (DGF) Firewire clock distribution (not yet implemented) DSP One of four channels Inputs Camac for 4 channels 2 cm System FPGA Digital part Analog part FIFO Amplifier Nyquist filter
A Fast Waveform-Digitizing ASICbased DAQ for a Position & Time Sensing Large-Area Photo-Detector System
 A Fast Waveform-Digitizing ASICbased DAQ for a Position & Time Sensing Large-Area Photo-Detector System Eric Oberla on behalf of the LAPPD collaboration PHOTODET 2012 12-June-2012 Outline LAPPD overview:
A Fast Waveform-Digitizing ASICbased DAQ for a Position & Time Sensing Large-Area Photo-Detector System Eric Oberla on behalf of the LAPPD collaboration PHOTODET 2012 12-June-2012 Outline LAPPD overview:
Experiment 10. The Speed of Light c Introduction Apparatus
 Experiment 10 The Speed of Light c 10.1 Introduction In this experiment you will measure the speed of light, c. This is one of the most fundamental constants in physics, and at the same time the fastest
Experiment 10 The Speed of Light c 10.1 Introduction In this experiment you will measure the speed of light, c. This is one of the most fundamental constants in physics, and at the same time the fastest
PRELIMINARY. Specifications are at array temperature of -30 C and package ambient temperature of 23 C All values are typical
 DAPD NIR 5x5 Array+PCB 1550 Series: Discrete Amplification Photon Detector Array Including Pre-Amplifier Board The DAPDNIR 5x5 Array 1550 series takes advantage of the breakthrough Discrete Amplification
DAPD NIR 5x5 Array+PCB 1550 Series: Discrete Amplification Photon Detector Array Including Pre-Amplifier Board The DAPDNIR 5x5 Array 1550 series takes advantage of the breakthrough Discrete Amplification
DETERMINATION OF INHERENT AND ADDITIONAL FILTRATION IN ORDER TO ESTABLISH RADIATION QUALITIES ACCORDING TO IEC 61267
 2009 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2009 Rio de Janeiro,RJ, Brazil, September27 to October 2, 2009 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-03-8 DETERMINATION
2009 International Nuclear Atlantic Conference - INAC 2009 Rio de Janeiro,RJ, Brazil, September27 to October 2, 2009 ASSOCIAÇÃO BRASILEIRA DE ENERGIA NUCLEAR - ABEN ISBN: 978-85-99141-03-8 DETERMINATION
An electrical photon source
 An electrical photon source A word of explanation right at the start is required: the title of this document will not make sense to anyone familiar with even the basic principles in physics. In actual
An electrical photon source A word of explanation right at the start is required: the title of this document will not make sense to anyone familiar with even the basic principles in physics. In actual
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. For additional information about this
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a preprint version which may differ from the publisher's version. For additional information about this
PMF the front end electronic for the ALFA detector
 PMF the front end electronic for the ALFA detector P. Barrillon, S. Blin, C. Cheikali, D. Cuisy, M. Gaspard, D. Fournier, M. Heller, W. Iwanski, B. Lavigne, C. De La Taille, et al. To cite this version:
PMF the front end electronic for the ALFA detector P. Barrillon, S. Blin, C. Cheikali, D. Cuisy, M. Gaspard, D. Fournier, M. Heller, W. Iwanski, B. Lavigne, C. De La Taille, et al. To cite this version:
SPACIROC3: A Front-End Readout ASIC for JEM- EUSO cosmic ray observatory
 : A Front-End Readout ASIC for JEM- EUSO cosmic ray observatory Sylvie Blin-Bondil a1, Pierre Barrillon b, Sylvie Dagoret-Campagne b, Frederic Dulucq a, Christophe de La Taille a, Hiroko Miyamoto b, Camille
: A Front-End Readout ASIC for JEM- EUSO cosmic ray observatory Sylvie Blin-Bondil a1, Pierre Barrillon b, Sylvie Dagoret-Campagne b, Frederic Dulucq a, Christophe de La Taille a, Hiroko Miyamoto b, Camille
A large area TOF-tracker
 A large area TOF-tracker P. Assis 1,2, A. Bernardino 2, A. Blanco 2, F. Clemêncio 3, N. Carolino 2, O. Cunha 2, M. Ferreira 2, P. Fonte 2,4, L. Lopes 2, C. Loureiro 5, R. Luz 1,2, L. Mendes 2, J. Michel
A large area TOF-tracker P. Assis 1,2, A. Bernardino 2, A. Blanco 2, F. Clemêncio 3, N. Carolino 2, O. Cunha 2, M. Ferreira 2, P. Fonte 2,4, L. Lopes 2, C. Loureiro 5, R. Luz 1,2, L. Mendes 2, J. Michel
High collection efficiency MCPs for photon counting detectors
 High collection efficiency MCPs for photon counting detectors D. A. Orlov, * T. Ruardij, S. Duarte Pinto, R. Glazenborg and E. Kernen PHOTONIS Netherlands BV, Dwazziewegen 2, 9301 ZR Roden, The Netherlands
High collection efficiency MCPs for photon counting detectors D. A. Orlov, * T. Ruardij, S. Duarte Pinto, R. Glazenborg and E. Kernen PHOTONIS Netherlands BV, Dwazziewegen 2, 9301 ZR Roden, The Netherlands
Sub-nanosecond timing system design and development for LHAASO project
 Sub-nanosecond timing system design and development for LHAASO project Guanghua Gong, Qiang Du Dept. of Engineering Physics Tsinghua Univ. Beijing 13 th International Conference on Accelerator And Large
Sub-nanosecond timing system design and development for LHAASO project Guanghua Gong, Qiang Du Dept. of Engineering Physics Tsinghua Univ. Beijing 13 th International Conference on Accelerator And Large
Description of options, upgrades and accessories for the laser beam stabilization system Compact
 Description of options, upgrades and accessories for the laser beam stabilization system Compact The basic configuration of the Compact laser beam stabilization system is fully equipped for stabilization
Description of options, upgrades and accessories for the laser beam stabilization system Compact The basic configuration of the Compact laser beam stabilization system is fully equipped for stabilization
Contents. ZT530PCI & PXI Specifications. Arbitrary Waveform Generator. 16-bit, 400 MS/s, 2 Ch
 ZT530PCI & PXI Specifications Arbitrary Waveform Generator 16-bit, 400 MS/s, 2 Ch Contents Outputs... 2 Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)... 3 Internal DAC Clock... 3 Spectral Purity... 3 External DAC
ZT530PCI & PXI Specifications Arbitrary Waveform Generator 16-bit, 400 MS/s, 2 Ch Contents Outputs... 2 Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)... 3 Internal DAC Clock... 3 Spectral Purity... 3 External DAC
Picosecond Time Analyzer Applications in...
 ORTEC AN52 Picosecond Time Analyzer Applications in... LIDAR and DIAL Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Fluorescence/Phosphorescence Lifetime Spectrometry Pulse or Signal Jitter Analysis CONTENTS of this
ORTEC AN52 Picosecond Time Analyzer Applications in... LIDAR and DIAL Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Fluorescence/Phosphorescence Lifetime Spectrometry Pulse or Signal Jitter Analysis CONTENTS of this
SOAR Integral Field Spectrograph (SIFS): Call for Science Verification Proposals
 Published on SOAR (http://www.ctio.noao.edu/soar) Home > SOAR Integral Field Spectrograph (SIFS): Call for Science Verification Proposals SOAR Integral Field Spectrograph (SIFS): Call for Science Verification
Published on SOAR (http://www.ctio.noao.edu/soar) Home > SOAR Integral Field Spectrograph (SIFS): Call for Science Verification Proposals SOAR Integral Field Spectrograph (SIFS): Call for Science Verification
Final Results from the APV25 Production Wafer Testing
 Final Results from the APV Production Wafer Testing M.Raymond a, R.Bainbridge a, M.French b, G.Hall a, P. Barrillon a a Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London, UK b Rutherford Appleton Laboratory,
Final Results from the APV Production Wafer Testing M.Raymond a, R.Bainbridge a, M.French b, G.Hall a, P. Barrillon a a Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, London, UK b Rutherford Appleton Laboratory,
