Section 3.5 Graphing Techniques: Transformations
|
|
|
- Dina Wood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Addition Shifts Subtraction Inside Horizontal Outside Vertical Left Right Up Down (Add inside) (Subtract inside) (Add Outside) (Subtract Outside) Transformation Multiplication Compressions Stretches Inside Horizontal Outside Vertical Compressions Stretches Compressions Stretches (Negative Outside) Opposite About x-axis (Replace by ) Reflections About y-axis (Replace by ) (Negative Inside) Horizontal and Vertical Shifts If is a positive real number, then A function is the graph of shifted horizontally left units. A function is the graph of shifted horizontally right units. A function is the graph of shifted vertically up units. A function is the graph of shifted vertically down units. Horizontal Shifts Vertical Shifts Cheon-Sig Lee Page 1
2 Stretches and Compressions A function is the graph of compressed vertically if. A function is the graph of stretched vertically if. A function is the graph of compressed horizontally if. A function is the graph of stretched horizontally if., 1, 0 1, 0 1, 1 Vertical Compressions/Stretches, 1, 0 1, 1, 0 1 Horizontal Compressions/Stretches Reflection A function is the graph of the reflected about the x-axis. A function is the graph of the reflected about the y-axis. Reflection about x-axis Reflection about y-axis Cheon-Sig Lee Page 2
3 Increasing and Decreasing For in an open interval, A function is increasing if. A function is decreasing if. Local Maxima and Minima A function has a local maximum,, at if for all x in an open interval and. A function has a local minimum,, at if for all x in an open interval and. Exercises 1. (Solution 1) Reflection about x-axis Shift up 1 unit (Solution 2) Reflection about x-axis Shift left 2 units 2 2 Cheon-Sig Lee Page 3
4 3. (Solution 3) Reflection about x-axis Reflection about y-axis (Solution 4) 1 is the graph of shifted left 1 unit. Thus, 1 is the graph of shifted left 1 unit. For using a graphing calculator, the window is better to be fixed; 12, 12, 2 by 12, 12, 2 for this problem. The domain is 1, because the graph starts at 1. The Range is 0, because the minimum for is (Solution 5) Vertical Stretch 5 Window: 3, 11, 1 by 1, 12, 1 Cheon-Sig Lee Page 4
5 Section 3.5 Graphing Technique es: Transformations 6. (Solution 6.a) Adjust the window; 4, 4,,1 by 12, 12, 2 (Solution 6.b) (Solution 6.c) 2nd TRACE Cheon-Sig Lee Page 5
6 Section 3.5 Graphing Technique es: Transformations (c) Continued (Solution 6.c) Continued 2nd TRACE (Solution 6.e) x-intercept 2 is the graph of shifted left 2 units, so does x-intercept. Because x-intercept of was 3, 0, 3, the x-intercepts of 2 is 3 2, 0 2,3 2,, 3..73, 10.39, , (Solution 6.e) Minimum/ Maximum, Because 2 is the graph of shifted left, x-values are shifted left 2 units but Minima remain the same. Because 2 is the graph of shifted left, x-values are shifted left 2 units but Maxima remain the same. Cheon-Sig Lee Page 6
7 (6.e) Continued 3.73, 10.39, , 10.39, (Solution 6.e) Increasing/ Decreasing Intervals that is increasing are 4, and, 4. Because 2 is shifted left 2 units, intervals that 2 is increasing are also shifted left 2 units. Thus, 6, 3.73 and 0.27, 2. Intervals that is decreasing is,. Because 2 is shifted left 2 units, intervals that 2 is increasing is also shifted left 2 units, Thus, 3.73, , 31.17, 10.39, 31.17, (Solution 6.f) x-intercepts/ Minimum/ Maximum 3 is the graph of stretched vertically by a factor of 3. Because the graph is stretched vertically, x-intercepts remain the same and the maxima and minima are stretched vertically by a factor of 3. Minimum:, 10.39, , Maximum:, 10.39, , Cheon-Sig Lee Page 7
8 (6.f) Continued 3 (Solution 6.f) Increasing/ Decreasing Because 3 is stretched vertically, x-values remain the same. Thus, intervals that 3 is increasing are same as those of and intervals that 3 is increasing are also same as those of. (Solution 6.g ) 3 is the graph of reflected about y-axis. Because reflected about y-axis, x-intercepts of is opposite of x-intercepts in., 10.39, , 10.39, Because is reflected about y-axis, x-values of are opposite to x-values in. Intervals that is decreasing are intervals that is increasing and intervals that is increasing are intervals that is increasing. Cheon-Sig Lee Page 8
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 A Periodic Function and Its Period Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions A nonconstant function f is said to be periodic if there is a number p > 0 such that f(x + p) = f(x) for all x in
A Periodic Function and Its Period Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions A nonconstant function f is said to be periodic if there is a number p > 0 such that f(x + p) = f(x) for all x in
Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions
 Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions In this section, we will examine transformations of the sine and cosine function and learn how to read various properties from the equation. Transformed
Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions In this section, we will examine transformations of the sine and cosine function and learn how to read various properties from the equation. Transformed
Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function
 Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function Sunday, October 07, 2012 11:23 AM Multiple Choice [ /10] Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. For the function y = sin x,
Chapter #2 test sinusoidal function Sunday, October 07, 2012 11:23 AM Multiple Choice [ /10] Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. For the function y = sin x,
5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions.notebook. Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs
 Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions and Graphs 1 Chapter 5 5.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Pages 222 237 Complete the following table using your calculator. Round answers to the nearest tenth. 2
Sect 4.5 Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function
 71 Sect 4. Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function Objective #0: Solving Inequalities using a graph Use the graph to the right to find the following: Ex. 1 a) Find the intervals where f(x) > 0. b) Find
71 Sect 4. Inequalities Involving Quadratic Function Objective #0: Solving Inequalities using a graph Use the graph to the right to find the following: Ex. 1 a) Find the intervals where f(x) > 0. b) Find
Section 8.4 Equations of Sinusoidal Functions soln.notebook. May 17, Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions.
 Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions Stop Sine 1 In this section, we will examine transformations of the sine and cosine function and learn how to read various properties from the equation.
Section 8.4: The Equations of Sinusoidal Functions Stop Sine 1 In this section, we will examine transformations of the sine and cosine function and learn how to read various properties from the equation.
6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions. The smallest number p with the above property is called the period of the function.
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
Math 160 www.timetodare.com Periods of trigonometric functions Definition A function y f ( t) f ( t p) f ( t) 6.4 & 6.5 Graphing Trigonometric Functions = is periodic if there is a positive number p such
E. Slope-Intercept Form and Direct Variation (pp )
 and Direct Variation (pp. 32 35) For any two points, there is one and only one line that contains both points. This fact can help you graph a linear equation. Many times, it will be convenient to use the
and Direct Variation (pp. 32 35) For any two points, there is one and only one line that contains both points. This fact can help you graph a linear equation. Many times, it will be convenient to use the
Math 1023 College Algebra Worksheet 1 Name: Prof. Paul Bailey September 22, 2004
 Math 1023 College Algebra Worksheet 1 Name: Prof. Paul Bailey September 22, 2004 Every vertical line can be expressed by a unique equation of the form x = c, where c is a constant. Such lines have undefined
Math 1023 College Algebra Worksheet 1 Name: Prof. Paul Bailey September 22, 2004 Every vertical line can be expressed by a unique equation of the form x = c, where c is a constant. Such lines have undefined
Graph of the Sine Function
 1 of 6 8/6/2004 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE Periodic Functions Graph of the Sine Function Graph of the Cosine Function Graphing Techniques, Amplitude, and Period
1 of 6 8/6/2004 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE 6.3 GRAPHS OF THE SINE AND COSINE Periodic Functions Graph of the Sine Function Graph of the Cosine Function Graphing Techniques, Amplitude, and Period
Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing. 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane
 Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane Rectangular Coordinate System Quadrant II (-,+) y-axis Quadrant
Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane Rectangular Coordinate System Quadrant II (-,+) y-axis Quadrant
Section 7.6 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
4 Section 7. Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the sine and cosine function. The input values will be the angle in radians so we will be using x is
5.1N Key Features of Rational Functions
 5.1N Key Features of Rational Functions A. Vocabulary Review Domain: Range: x-intercept: y-intercept: Increasing: Decreasing: Constant: Positive: Negative: Maximum: Minimum: Symmetry: End Behavior/Limits:
5.1N Key Features of Rational Functions A. Vocabulary Review Domain: Range: x-intercept: y-intercept: Increasing: Decreasing: Constant: Positive: Negative: Maximum: Minimum: Symmetry: End Behavior/Limits:
Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions
 Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the other four trigonometric functions. We will start by examining the tangent
Section 7.7 Graphs of the Tangent, Cotangent, Cosecant, and Secant Functions In this section, we will look at the graphs of the other four trigonometric functions. We will start by examining the tangent
2.3 BUILDING THE PERFECT SQUARE
 16 2.3 BUILDING THE PERFECT SQUARE A Develop Understanding Task Quadratic)Quilts Optimahasaquiltshopwhereshesellsmanycolorfulquiltblocksforpeoplewhowant tomaketheirownquilts.shehasquiltdesignsthataremadesothattheycanbesized
16 2.3 BUILDING THE PERFECT SQUARE A Develop Understanding Task Quadratic)Quilts Optimahasaquiltshopwhereshesellsmanycolorfulquiltblocksforpeoplewhowant tomaketheirownquilts.shehasquiltdesignsthataremadesothattheycanbesized
THE DOMAIN AND RANGE OF A FUNCTION Basically, all functions do is convert inputs into outputs.
 THE DOMAIN AND RANGE OF A FUNCTION Basically, all functions do is convert inputs into outputs. Exercise #1: Consider the function y = f (x) shown on the graph below. (a) Evaluate each of the following:
THE DOMAIN AND RANGE OF A FUNCTION Basically, all functions do is convert inputs into outputs. Exercise #1: Consider the function y = f (x) shown on the graph below. (a) Evaluate each of the following:
LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES What You Should Learn Use slope to graph linear equations in two " variables. Find the slope of a line given two points on the line. Write linear equations in two variables.
LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES What You Should Learn Use slope to graph linear equations in two " variables. Find the slope of a line given two points on the line. Write linear equations in two variables.
4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 What You Will Learn Determine the slope of a line through two points Write linear equations in slope-intercept
4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 What You Will Learn Determine the slope of a line through two points Write linear equations in slope-intercept
Math 1330 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5.1 and 5.2.
 Math 0 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5. and 5.. Work the following problems and choose the correct answer. The problems that refer to the Textbook may be found at www.casa.uh.edu in
Math 0 Precalculus Electronic Homework (EHW 6) Sections 5. and 5.. Work the following problems and choose the correct answer. The problems that refer to the Textbook may be found at www.casa.uh.edu in
Algebra and Trig. I. The graph of
 Algebra and Trig. I 4.5 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions The graph of The graph of. The trigonometric functions can be graphed in a rectangular coordinate system by plotting points whose coordinates
Algebra and Trig. I 4.5 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions The graph of The graph of. The trigonometric functions can be graphed in a rectangular coordinate system by plotting points whose coordinates
Section 2.3 Task List
 Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We know from previously studying the periodicity of the trigonometric functions that the sine and cosine functions repeat themselves after 2 radians.
Section 5.2 Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions We know from previously studying the periodicity of the trigonometric functions that the sine and cosine functions repeat themselves after 2 radians.
How to Graph Trigonometric Functions
 How to Graph Trigonometric Functions This handout includes instructions for graphing processes of basic, amplitude shifts, horizontal shifts, and vertical shifts of trigonometric functions. The Unit Circle
How to Graph Trigonometric Functions This handout includes instructions for graphing processes of basic, amplitude shifts, horizontal shifts, and vertical shifts of trigonometric functions. The Unit Circle
You analyzed graphs of functions. (Lesson 1-5)
 You analyzed graphs of functions. (Lesson 1-5) LEQ: How do we graph transformations of the sine and cosine functions & use sinusoidal functions to solve problems? sinusoid amplitude frequency phase shift
You analyzed graphs of functions. (Lesson 1-5) LEQ: How do we graph transformations of the sine and cosine functions & use sinusoidal functions to solve problems? sinusoid amplitude frequency phase shift
Lesson 15: The Slope of a Non Vertical Line
 Classwork Opening Exercise Example Graph A Graph B a. Which graph is steeper? b. Write directions that explain how to move from one point on the graph to the other for each of Graph A and Graph B. c. Write
Classwork Opening Exercise Example Graph A Graph B a. Which graph is steeper? b. Write directions that explain how to move from one point on the graph to the other for each of Graph A and Graph B. c. Write
Warm-Up. Complete the second homework worksheet (the one you didn t do yesterday). Please begin working on FBF010 and FBF011.
 Warm-Up Complete the second homework worksheet (the one you didn t do yesterday). Please begin working on FBF010 and FBF011. You have 20 minutes at the beginning of class to work on these three tasks.
Warm-Up Complete the second homework worksheet (the one you didn t do yesterday). Please begin working on FBF010 and FBF011. You have 20 minutes at the beginning of class to work on these three tasks.
Chapter 2: Functions and Graphs Lesson Index & Summary
 Section 1: Relations and Graphs Cartesian coordinates Screen 2 Coordinate plane Screen 2 Domain of relation Screen 3 Graph of a relation Screen 3 Linear equation Screen 6 Ordered pairs Screen 1 Origin
Section 1: Relations and Graphs Cartesian coordinates Screen 2 Coordinate plane Screen 2 Domain of relation Screen 3 Graph of a relation Screen 3 Linear equation Screen 6 Ordered pairs Screen 1 Origin
4-4 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions
 Describe how the graphs of f (x) and g(x) are related. Then find the amplitude of g(x), and sketch two periods of both functions on the same coordinate axes. 1. f (x) = sin x; g(x) = sin x The graph of
Describe how the graphs of f (x) and g(x) are related. Then find the amplitude of g(x), and sketch two periods of both functions on the same coordinate axes. 1. f (x) = sin x; g(x) = sin x The graph of
Graphing Exponential Functions
 Graphing Eponential Functions What is an Eponential Function? Eponential functions are one of the most important functions in mathematics. Eponential functions have many scientific applications, such as
Graphing Eponential Functions What is an Eponential Function? Eponential functions are one of the most important functions in mathematics. Eponential functions have many scientific applications, such as
A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
 The Slope of a Line (2.2) Find the slope of a line given two points on the line (Objective #1) A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
The Slope of a Line (2.2) Find the slope of a line given two points on the line (Objective #1) A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation)
 SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation) Factor the following quadratic expressions: x 2 + 11x + 30 x 2 10x 24 x 2 8x + 15 Standard Form Quadratic Equation (x + 5)(x + 6) (x 12)(x + 2) (x 5)(x
SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation) Factor the following quadratic expressions: x 2 + 11x + 30 x 2 10x 24 x 2 8x + 15 Standard Form Quadratic Equation (x + 5)(x + 6) (x 12)(x + 2) (x 5)(x
2.4 Translating Sine and Cosine Functions
 www.ck1.org Chapter. Graphing Trigonometric Functions.4 Translating Sine and Cosine Functions Learning Objectives Translate sine and cosine functions vertically and horizontally. Identify the vertical
www.ck1.org Chapter. Graphing Trigonometric Functions.4 Translating Sine and Cosine Functions Learning Objectives Translate sine and cosine functions vertically and horizontally. Identify the vertical
Students use absolute value to determine distance between integers on the coordinate plane in order to find side lengths of polygons.
 Student Outcomes Students use absolute value to determine distance between integers on the coordinate plane in order to find side lengths of polygons. Lesson Notes Students build on their work in Module
Student Outcomes Students use absolute value to determine distance between integers on the coordinate plane in order to find side lengths of polygons. Lesson Notes Students build on their work in Module
the input values of a function. These are the angle values for trig functions
 SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
SESSION 8: TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS KEY CONCEPTS: Graphs of Trigonometric Functions y = sin θ y = cos θ y = tan θ Properties of Graphs Shape Intercepts Domain and Range Minimum and maximum values Period
Graphs of sin x and cos x
 Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Graphs of sin x and cos x One cycle of the graph of sin x, for values of x between 0 and 60, is given below. 1 0 90 180 270 60 1 It is this same shape that one gets between 60 and below). 720 and between
Lesson 7 Slope-Intercept Formula
 Lesson 7 Slope-Intercept Formula Terms Two new words that describe what we've been doing in graphing lines are slope and intercept. The slope is referred to as "m" (a mountain has slope and starts with
Lesson 7 Slope-Intercept Formula Terms Two new words that describe what we've been doing in graphing lines are slope and intercept. The slope is referred to as "m" (a mountain has slope and starts with
Name Date Class Period. What happens to ordered pairs when a rule is applied to the coordinates?
 Name Date Class Period Activity B Extension 4.1 Modeling Transformations MATERIALS small white boards or paper markers masking tape yarn QUESTION What happens to ordered pairs when a rule is applied to
Name Date Class Period Activity B Extension 4.1 Modeling Transformations MATERIALS small white boards or paper markers masking tape yarn QUESTION What happens to ordered pairs when a rule is applied to
MA Lesson 16 Sections 2.3 and 2.4
 MA 1500 Lesson 16 Sections.3 and.4 I Piecewise Functions & Evaluating such Functions A cab driver charges $4 a ride for a ride less than 5 miles. He charges $4 plus $0.50 a mile for a ride greater than
MA 1500 Lesson 16 Sections.3 and.4 I Piecewise Functions & Evaluating such Functions A cab driver charges $4 a ride for a ride less than 5 miles. He charges $4 plus $0.50 a mile for a ride greater than
2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations
 2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations Algebra III Mr. Niedert Algebra III 2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations Mr. Niedert 1 / 11 Forms of a Line Slope-Intercept Form The slope-intercept form of a linear
2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations Algebra III Mr. Niedert Algebra III 2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations Mr. Niedert 1 / 11 Forms of a Line Slope-Intercept Form The slope-intercept form of a linear
Then finding the slope, we can just use the same method that we have done the other ones we get the slope 4 1
 169 Graphing Equations with Slope Okay, now that you know how to graph a line by getting some points, and you know how to find the slope between two points, you should be able to find the slope of a line
169 Graphing Equations with Slope Okay, now that you know how to graph a line by getting some points, and you know how to find the slope between two points, you should be able to find the slope of a line
Graphing - Slope-Intercept Form
 2.3 Graphing - Slope-Intercept Form Objective: Give the equation of a line with a known slope and y-intercept. When graphing a line we found one method we could use is to make a table of values. However,
2.3 Graphing - Slope-Intercept Form Objective: Give the equation of a line with a known slope and y-intercept. When graphing a line we found one method we could use is to make a table of values. However,
Activity Overview This activity takes the concept of derivative and applies it to various maximum and minimum problems.
 TI-Nspire Activity: Derivatives: Applied Maxima and Minima By: Tony Duncan Activity Overview This activity takes the concept of derivative and applies it to various maximum and minimum problems. Concepts
TI-Nspire Activity: Derivatives: Applied Maxima and Minima By: Tony Duncan Activity Overview This activity takes the concept of derivative and applies it to various maximum and minimum problems. Concepts
Amplitude, Reflection, and Period
 SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
Creating a foldable for Equations of Lines
 Creating a foldable for Equations of Lines Equations of Lines Slope Direct Variation Slope-Intercept Form Standard Form Point-Slope Form Equation w/ slope & 1 point Equation w/ 2 points Horizontal & Vertical
Creating a foldable for Equations of Lines Equations of Lines Slope Direct Variation Slope-Intercept Form Standard Form Point-Slope Form Equation w/ slope & 1 point Equation w/ 2 points Horizontal & Vertical
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
5.3 Trigonometric Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Graphs of Sine and Cosine Graphs of Transformations of Sine and Cosine Using Graphing Devices to Graph Trigonometric
Prolegomena. Chapter Using Interval Notation 1
 Chapter 1 Prolegomena 1.1 Using Interval Notation 1 Interval notation is another method for writing domain and range. In set builder notation braces (curly parentheses {} ) and variables are used to express
Chapter 1 Prolegomena 1.1 Using Interval Notation 1 Interval notation is another method for writing domain and range. In set builder notation braces (curly parentheses {} ) and variables are used to express
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 14A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 14-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary periodic function cycle period amplitude frequency
14A Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 14-1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 14-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary periodic function cycle period amplitude frequency
Section 2-4: Writing Linear Equations, Including Concepts of Parallel & Perpendicular Lines + Graphing Practice
 Section 2-4: Writing Linear Equations, Including Concepts of Parallel & Perpendicular Lines + Graphing Practice Name Date CP If an equation is linear, then there are three formats typically used to express
Section 2-4: Writing Linear Equations, Including Concepts of Parallel & Perpendicular Lines + Graphing Practice Name Date CP If an equation is linear, then there are three formats typically used to express
MHF4U - Unit 6 Test. Multiple Choice - Answer on SCANTRON Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MHF4U - Unit 6 Test Multiple Choice - Answer on SCANTRON Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question 1 The function has the point (10, 1) on its graph Find the coordinates
MHF4U - Unit 6 Test Multiple Choice - Answer on SCANTRON Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question 1 The function has the point (10, 1) on its graph Find the coordinates
constant EXAMPLE #4:
 Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Algebra 1 Chapter 3 Practice Test
 Algebra 1 Chapter 3 Practice Test 1. Which of the following represent functions? a. All b. I and II c. I and III d. II and III I. Input Output II. Input Output III. Input Output 4 0 2 8-2 0 5 0 4 6 1 1
Algebra 1 Chapter 3 Practice Test 1. Which of the following represent functions? a. All b. I and II c. I and III d. II and III I. Input Output II. Input Output III. Input Output 4 0 2 8-2 0 5 0 4 6 1 1
Solving Equations and Graphing
 Solving Equations and Graphing Question 1: How do you solve a linear equation? Answer 1: 1. Remove any parentheses or other grouping symbols (if necessary). 2. If the equation contains a fraction, multiply
Solving Equations and Graphing Question 1: How do you solve a linear equation? Answer 1: 1. Remove any parentheses or other grouping symbols (if necessary). 2. If the equation contains a fraction, multiply
Block: Date: Name: REVIEW Linear Equations. 7.What is the equation of the line that passes through the point (5, -3) and has a slope of -3?
 Name: REVIEW Linear Equations 1. What is the slope of the line y = -2x + 3? 2. Write the equation in slope-intercept form. Block: Date: 7.What is the equation of the line that passes through the point
Name: REVIEW Linear Equations 1. What is the slope of the line y = -2x + 3? 2. Write the equation in slope-intercept form. Block: Date: 7.What is the equation of the line that passes through the point
Lesson 10 Practice Problems
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Skills Practice 1. Determine the slope of the line between each of the following pairs of points. Show all steps, and reduce your answer to lowest terms. a. (4, 5) and ( 2, 3) b.
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Skills Practice 1. Determine the slope of the line between each of the following pairs of points. Show all steps, and reduce your answer to lowest terms. a. (4, 5) and ( 2, 3) b.
A Visual Display. A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. Communicating with Graphs
 A Visual Display A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. A Visual Display The horizontal axis, or the x-axis, measures time. Time is the independent
A Visual Display A graph is a visual display of information or data. This is a graph that shows a girl walking her dog. A Visual Display The horizontal axis, or the x-axis, measures time. Time is the independent
Oscilloscope and Function Generators
 MEHRAN UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, JAMSHORO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC WORKSHOP # 02 Oscilloscope and Function Generators Roll. No: Checked by: Date: Grade: Object: To
MEHRAN UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, JAMSHORO DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING ELECTRONIC WORKSHOP # 02 Oscilloscope and Function Generators Roll. No: Checked by: Date: Grade: Object: To
Lesson 10. Unit 2. Reading Maps. Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane
 Lesson Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane Reading Maps In the middle ages a system was developed to find the location of specific places on the Earth s surface. The system is a grid that covers the
Lesson Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane Reading Maps In the middle ages a system was developed to find the location of specific places on the Earth s surface. The system is a grid that covers the
Trigonometric Equations
 Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
Chapter Three Trigonometric Equations Solving Simple Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Solving Complicated Trigonometric Equations Algebraically Graphs of Sine and Cosine Functions Solving Trigonometric
Rev Name Date. Most equations taught in algebra classes can and should be solved using algebra to get exact solutions.
 Name Date TI-84+ GC 3 Solving Equations Using x-intercept of Difference LHS RHS = (Method ) Objectives: Review: set an equation equal to, equation of horizontal line, x-axis, x-intercept, zero Understand
Name Date TI-84+ GC 3 Solving Equations Using x-intercept of Difference LHS RHS = (Method ) Objectives: Review: set an equation equal to, equation of horizontal line, x-axis, x-intercept, zero Understand
M.I. Transformations of Functions
 M.I. Transformations of Functions Do Now: A parabola with equation y = (x 3) 2 + 8 is translated. The image of the parabola after the translation has an equation of y = (x + 5) 2 4. Describe the movement.
M.I. Transformations of Functions Do Now: A parabola with equation y = (x 3) 2 + 8 is translated. The image of the parabola after the translation has an equation of y = (x + 5) 2 4. Describe the movement.
Math 154 :: Elementary Algebra
 Math :: Elementary Algebra Section. Section. Section. Section. Section. Math :: Elementary Algebra Section. The Rectangular (Cartesian) Coordinate System. The variable x usually represents the independent
Math :: Elementary Algebra Section. Section. Section. Section. Section. Math :: Elementary Algebra Section. The Rectangular (Cartesian) Coordinate System. The variable x usually represents the independent
b = 7 The y-intercept is 7.
 State the x- and y-intercepts of each equation. Then use the intercepts to graph the equation. 1. y = 2x + 7 To find the x-intercept, substitute 0 for y and solve for x. y = 2x + 7 0 = 2x + 7 7 = 2x 3.5
State the x- and y-intercepts of each equation. Then use the intercepts to graph the equation. 1. y = 2x + 7 To find the x-intercept, substitute 0 for y and solve for x. y = 2x + 7 0 = 2x + 7 7 = 2x 3.5
1.7 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
 Section 1.7 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 11 Eplaining the Concepts 17. Name the five forms of equations of lines given in this section. 18. What tpe of line has one -intercept, but no -intercept? 19.
Section 1.7 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 11 Eplaining the Concepts 17. Name the five forms of equations of lines given in this section. 18. What tpe of line has one -intercept, but no -intercept? 19.
Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions
 HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 5 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions This is a BASIC CALCULATORS ONLY unit. (2) Periodic Functions (3) Graph of the Sine Function (4) Graph of the Cosine Function
HARTFIELD PRECALCULUS UNIT 5 NOTES PAGE 1 Unit 5 Graphing Trigonmetric Functions This is a BASIC CALCULATORS ONLY unit. (2) Periodic Functions (3) Graph of the Sine Function (4) Graph of the Cosine Function
 http://www.math.utah.edu/~palais/sine.html http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/trig/index.html http://www.analyzemath.com/function/periodic.html http://math.usask.ca/maclean/sincosslider/sincosslider.html http://www.analyzemath.com/unitcircle/unitcircle.html
http://www.math.utah.edu/~palais/sine.html http://www.ies.co.jp/math/java/trig/index.html http://www.analyzemath.com/function/periodic.html http://math.usask.ca/maclean/sincosslider/sincosslider.html http://www.analyzemath.com/unitcircle/unitcircle.html
Section 3.5. Equations of Lines
 Section 3.5 Equations of Lines Learning objectives Use slope-intercept form to write an equation of a line Use slope-intercept form to graph a linear equation Use the point-slope form to find an equation
Section 3.5 Equations of Lines Learning objectives Use slope-intercept form to write an equation of a line Use slope-intercept form to graph a linear equation Use the point-slope form to find an equation
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions
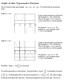 Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Graphs of other Trigonometric Functions Now we will look at other types of graphs: secant. tan x, cot x, csc x, sec x. We will start with the cosecant and y csc x In order to draw this graph we will first
Lesson 8.3: The Graphs of Sinusoidal Functions, page 536
 . The graph of sin x repeats itself after it passes through 360 or π. 3. e.g. The graph is symmetrical along the x-axis, with the axis of symmetry being at 90 and 70, respectively. The graph is rotationally
. The graph of sin x repeats itself after it passes through 360 or π. 3. e.g. The graph is symmetrical along the x-axis, with the axis of symmetry being at 90 and 70, respectively. The graph is rotationally
Mathematics Success Grade 6
 T428 Mathematics Success Grade 6 [OBJECTIVE] The students will plot ordered pairs containing rational values to identify vertical and horizontal lengths between two points in order to solve real-world
T428 Mathematics Success Grade 6 [OBJECTIVE] The students will plot ordered pairs containing rational values to identify vertical and horizontal lengths between two points in order to solve real-world
Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review
 Name: Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review Vocabulary Equation: a math sentence that contains Linear: makes a straight line (no Variables: quantities represented by (often x and y) Function: equations can
Name: Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review Vocabulary Equation: a math sentence that contains Linear: makes a straight line (no Variables: quantities represented by (often x and y) Function: equations can
Use the Point-Slope Form to Write the Equation of a Line
 Math 90 8.3 "Writing Equations of Lines" Objectives: * Use the point-slope form to write the equation of a line. * Use the slope-intercept form to write the equation of a line. * Use slope as an aid when
Math 90 8.3 "Writing Equations of Lines" Objectives: * Use the point-slope form to write the equation of a line. * Use the slope-intercept form to write the equation of a line. * Use slope as an aid when
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions
 Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
Chapter 6: Periodic Functions In the previous chapter, the trigonometric functions were introduced as ratios of sides of a right triangle, and related to points on a circle. We noticed how the x and y
y-intercept remains constant?
 1. The graph of a line that contains the points ( 1, 5) and (4, 5) is shown below. Which best represents this line if the slope is doubled and the y-intercept remains constant? F) G) H) J) 2. The graph
1. The graph of a line that contains the points ( 1, 5) and (4, 5) is shown below. Which best represents this line if the slope is doubled and the y-intercept remains constant? F) G) H) J) 2. The graph
Section 1.3. Slope formula: If the coordinates of two points on the line are known then we can use the slope formula to find the slope of the line.
 MATH 11009: Linear Functions Section 1.3 Linear Function: A linear function is a function that can be written in the form f(x) = ax + b or y = ax + b where a and b are constants. The graph of a linear
MATH 11009: Linear Functions Section 1.3 Linear Function: A linear function is a function that can be written in the form f(x) = ax + b or y = ax + b where a and b are constants. The graph of a linear
2009 A-level Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved
 2 This book is under copyright to A-level Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents radians 3 sine, cosine & tangent 7 cosecant, secant & cotangent
2 This book is under copyright to A-level Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents radians 3 sine, cosine & tangent 7 cosecant, secant & cotangent
P202/219 Laboratory IUPUI Physics Department THIN LENSES
 THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
Determine the intercepts of the line and ellipse below: Definition: An intercept is a point of a graph on an axis. Line: x intercept(s)
 Topic 1 1 Intercepts and Lines Definition: An intercept is a point of a graph on an axis. For an equation Involving ordered pairs (x, y): x intercepts (a, 0) y intercepts (0, b) where a and b are real
Topic 1 1 Intercepts and Lines Definition: An intercept is a point of a graph on an axis. For an equation Involving ordered pairs (x, y): x intercepts (a, 0) y intercepts (0, b) where a and b are real
2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work that explains how you obtained your answer or you must explain how you obtained your answer.
 Math 50, Spring 2006 Test 2 PRINT your name on the back of the test. Circle your class: MW @ 11 TTh @ 2:30 Directions 1. Time limit: 50 minutes. 2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work
Math 50, Spring 2006 Test 2 PRINT your name on the back of the test. Circle your class: MW @ 11 TTh @ 2:30 Directions 1. Time limit: 50 minutes. 2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work
1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle
 Pre- Calculus Mathematics 12 5.1 Trigonometric Functions Goal: 1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle Measuring Angles: Angles in Standard
Pre- Calculus Mathematics 12 5.1 Trigonometric Functions Goal: 1. Measure angle in degrees and radians 2. Find coterminal angles 3. Determine the arc length of a circle Measuring Angles: Angles in Standard
Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions
 Math 150 c Lynch 1 of 6 Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions Definition. Let a be any positive number not equal to 1. The logarithm of x to the base a is y if and only if a y = x. The number y is denoted
Math 150 c Lynch 1 of 6 Section 7.2 Logarithmic Functions Definition. Let a be any positive number not equal to 1. The logarithm of x to the base a is y if and only if a y = x. The number y is denoted
Graphing Lines with a Table
 Graphing Lines with a Table Select (or use pre-selected) values for x Substitute those x values in the equation and solve for y Graph the x and y values as ordered pairs Connect points with a line Graph
Graphing Lines with a Table Select (or use pre-selected) values for x Substitute those x values in the equation and solve for y Graph the x and y values as ordered pairs Connect points with a line Graph
MthSc 103 Test #1 Spring 2011 Version A JIT , 1.8, , , , 8.1, 11.1 ANSWER KEY AND CUID: GRADING GUIDELINES
 Student s Printed Name: ANSWER KEY AND CUID: GRADING GUIDELINES Instructor: Section # : You are not permitted to use a calculator on any portion of this test. You are not allowed to use any textbook, notes,
Student s Printed Name: ANSWER KEY AND CUID: GRADING GUIDELINES Instructor: Section # : You are not permitted to use a calculator on any portion of this test. You are not allowed to use any textbook, notes,
The Sine Function. Precalculus: Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 Concepts: Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Sinusoids, Terminology (amplitude, period, phase shift, frequency). The Sine Function Domain: x R Range: y [ 1, 1] Continuity: continuous for all x Increasing-decreasing
Concepts: Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Sinusoids, Terminology (amplitude, period, phase shift, frequency). The Sine Function Domain: x R Range: y [ 1, 1] Continuity: continuous for all x Increasing-decreasing
Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.
 MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
MAT 115 Spring 2015 Practice Test 3 (longer than the actual test will be) Part I: No Calculators. Show work. 1. Solve the following inequalities. Give solutions in interval notation. (Expect 1 or 2.) a.
Outline. Drawing the Graph. 1 Homework Review. 2 Introduction. 3 Histograms. 4 Histograms on the TI Assignment
 Lecture 14 Section 4.4.4 on Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 18, 2009 Outline 1 on 2 3 4 on 5 6 Even-numbered on Exercise 4.25, p. 249. The following is a list of homework scores for two students: Student
Lecture 14 Section 4.4.4 on Hampden-Sydney College Fri, Sep 18, 2009 Outline 1 on 2 3 4 on 5 6 Even-numbered on Exercise 4.25, p. 249. The following is a list of homework scores for two students: Student
4.4 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular
 www.ck12.org Chapter 4. Determining Linear Equations 4.4 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Learning Objectives Determine whether lines are parallel or perpendicular. Write equations of perpendicular
www.ck12.org Chapter 4. Determining Linear Equations 4.4 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Learning Objectives Determine whether lines are parallel or perpendicular. Write equations of perpendicular
Math Labs. Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates. Procedure
 Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Unit 10: The Equation of a Linear Function
 Section 10.1: The Equation of a Linear Function Section 10.2: Writing Linear Equations in Slope-Intercept Form Section 10.3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Section 10.4: Applications Slope-Intercept
Section 10.1: The Equation of a Linear Function Section 10.2: Writing Linear Equations in Slope-Intercept Form Section 10.3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Section 10.4: Applications Slope-Intercept
Use smooth curves to complete the graph between and beyond the vertical asymptotes.
 5.3 Graphs of Rational Functions Guidelines for Graphing Rational Functions 1. Find and plot the x-intercepts. (Set numerator = 0 and solve for x) 2. Find and plot the y-intercepts. (Let x = 0 and solve
5.3 Graphs of Rational Functions Guidelines for Graphing Rational Functions 1. Find and plot the x-intercepts. (Set numerator = 0 and solve for x) 2. Find and plot the y-intercepts. (Let x = 0 and solve
Lesson #2: Exponential Functions and Their Inverses
 Unit 7: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Lesson #2: Exponential Functions and Their 1. Graph 2 by making a table. x f(x) -2.25-1.5 0 1 1 2 2 4 3 8 2. Graph the inverse of by making a table. x f(x).25-2.5-1
Unit 7: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Lesson #2: Exponential Functions and Their 1. Graph 2 by making a table. x f(x) -2.25-1.5 0 1 1 2 2 4 3 8 2. Graph the inverse of by making a table. x f(x).25-2.5-1
5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions
 5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Objectives: 1. Graph the sine and cosine functions. 2. Determine the amplitude, period and phase shift of the sine and cosine functions. 3. Find equations
5.3-The Graphs of the Sine and Cosine Functions Objectives: 1. Graph the sine and cosine functions. 2. Determine the amplitude, period and phase shift of the sine and cosine functions. 3. Find equations
Sect Linear Equations in Two Variables
 99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
7.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing
 Math 2201 Date: 7.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing In Mathematics 1201, students factored difference of squares, perfect square trinomials and polynomials of the form x 2 + bx + c and ax 2 + bx
Math 2201 Date: 7.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing In Mathematics 1201, students factored difference of squares, perfect square trinomials and polynomials of the form x 2 + bx + c and ax 2 + bx
WARM UP. 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) Factor the expression x 2 2x Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing.
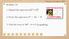 WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
WARM UP Monday, December 8, 2014 1. Expand the expression (x 2 + 3) 2 2. Factor the expression x 2 2x 8 3. Find the roots of 4x 2 x + 1 by graphing. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Objectives Distinguish between
Graphs, Linear Equations and Functions
 Graphs, Linear Equations and Functions There are several ways to graph a linear equation: Make a table of values Use slope and y-intercept Use x and y intercepts Oct 5 9:37 PM Oct 5 9:38 PM Example: Make
Graphs, Linear Equations and Functions There are several ways to graph a linear equation: Make a table of values Use slope and y-intercept Use x and y intercepts Oct 5 9:37 PM Oct 5 9:38 PM Example: Make
Chapter 7, Part 1B Equations & Functions
 Chapter 7, Part 1B Equations & Functions Fingerstache Fingerstaches cost $7 per box. Copy and complete the table to find the cost of 2, 3, and 4 boxes. Number of Boxes Multiply by 7 Cost 1 1 x 7 $7 2 3
Chapter 7, Part 1B Equations & Functions Fingerstache Fingerstaches cost $7 per box. Copy and complete the table to find the cost of 2, 3, and 4 boxes. Number of Boxes Multiply by 7 Cost 1 1 x 7 $7 2 3
Lesson 11 Practice Problems
 Lesson 11 Skills Practice 1. Determine the equation of the line between each of the following pairs of points. a. (4, 5) and (2, 3) b. ( 3, 2) and (1, 8) c. (5, 9) and (5, 2) d. (2, 1) and ( 2, 3) e. (4,
Lesson 11 Skills Practice 1. Determine the equation of the line between each of the following pairs of points. a. (4, 5) and (2, 3) b. ( 3, 2) and (1, 8) c. (5, 9) and (5, 2) d. (2, 1) and ( 2, 3) e. (4,
Section 7B Slope of a Line and Average Rates of Change
 Section 7B Slope of a Line and Average Rates of Change IBM stock had a price of $186.91 at the end of September 2014. Over the next three months the stock price rose and fell and by the end of December
Section 7B Slope of a Line and Average Rates of Change IBM stock had a price of $186.91 at the end of September 2014. Over the next three months the stock price rose and fell and by the end of December
Graphing Sine and Cosine
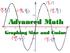 The problem with average monthly temperatures on the preview worksheet is an example of a periodic function. Periodic functions are defined on p.254 Periodic functions repeat themselves each period. The
The problem with average monthly temperatures on the preview worksheet is an example of a periodic function. Periodic functions are defined on p.254 Periodic functions repeat themselves each period. The
Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions
 Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions 7.1 Cycles and Sine Functions Data that is periodic may often be modeled by trigonometric functions. This chapter will help you use Excel to deal with periodic
Chapter 7 Repetitive Change: Cyclic Functions 7.1 Cycles and Sine Functions Data that is periodic may often be modeled by trigonometric functions. This chapter will help you use Excel to deal with periodic
