1. (2 point deduction for failure to complete this problem!)
|
|
|
- Calvin Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Instructor: Section: ENGR Exam 1 October 11, 2016 Allowed Materials: F.E. approved calculator(s) see syllabus; pencils and/or pens. ExamForm 11. Honor Statement: On my honor, I promise that I have not received any unauthorized assistance on this exam (I didn t look at another student s paper, I didn t view any unauthorized written materials, I didn t talk or listen to another student, I didn't use an unauthorized calculator, I didn't use any electronic device, any visual or auditory signals, or any other techniques of exchanging information with others.) I have maintained the highest standards of academic integrity while completing this exam. Signed: 1. (2 point deduction for failure to complete this problem!) Write in all of the indicated information in the boxes of your response form. Darken the appropriate circles to encode the corresponding information. Write your name on this exam and sign the Honor Statement. Notes: If your last name is too long, just write the first 10 letters. "F.I." and "M.I." are your first and middle initials, respectively Your "Username" is the first part of your LATech address For "Section" use the guide provided to the right Your "Exam Form" is printed on the upper right corner of this page. Indicate "ENGR" as the "Program" Bubble: For Course Section: 91 H01 - Harbour MW 12-1:50 92 H02 - Long TR 12-1:50 93 H03 - Cronk MW 2-3:50 94 H04 - Scoggin MW 4-5:50 95 H05 - Reeves TR10-11:50 96 H06 - Easley MW10-11: Bhattarai MW10-11: Scoggin MW 2-3: Cronk TR 2-3: Scoggin MW 8-9: Hartmann TR 4-5: Corbett TR 12-1: Pathak MW 12-1: Cronk MW 4-5:50 Choices "I properly completed all required items in problem 1, so I will not lose these points" "I did not properly complete problem 1 because I am fine with losing these points." 2. (3 points) Electrons migrate from to in a path due to atom oscillation. Choices "shortage, supply, scattered" "shortage, supply, straight" "supply, shortage, scattered" "shortage, supply, straight" "positive, negative, scatered" "supply, shortage, straight" "positive, negative, scattered" 3. (3 points) Resistance can be described as: Choices "The push that causes the electrons to start flowing" "A material that is designed only to conduct under certain conditions" "The rate at which charged particles pass a distance per unit of time" "The frictional opposition encountered by electrons as they attempt to pass through a material" "The work done per Coulomb of charge passing through a point" "The potential difference of charged particles in a closed circuit"
2 2 4. (3 points) Given the image of the circuit on the Arduino, identify all of the correct symbolic representation(s). "i and iv" "i, iv, and v" "ii, iv, and vii" "i only" Choices "iv and v" "ii and vii" "i, ii, iv, and vii" "ii only" i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. 5. (3 points) Given the two circuits provided, the LED in circuit A will than the LED in circuit B because the resistor in A Choices "Burn out faster; is smaller" "Be less bright; has less resistance and more current passes through to the LED" "Have no difference in brightness; does not affect the brightness of an LED" "Not enough information is given about the circuit to know." "Be less bright; has less resistance and less current passes through to the LED" "Be brighter; has less resistance and less current passes through to the LED" "Be brighter; has less resistance and more current passes through to the LED" "Burn out slower; is smaller" Note: the ; in the answer choices denotes the start of content for the second blank
3 3 6. (3 points) Identify all of the complete circuits as shown on the breadboard images below: Assume the positive (+) column on the breadboard is plugged into +5V and the negative column (-) on the breadboard is plugged into ground. A "complete circuit" is one that will allow a flow of current from the positive column to the negative column of the breadboard. i. ii. Choices "ii, iii, and iv" "i, ii, and iv" "ii only" "i and iii" "i and ii" "i only" "iii only" "i, iii, and iv" iii. iv. 7. (3 points) The below command will: pinmode(13, OUTPUT) Choices "Set pin 13 to maintain 5V" "Cause the LED to blink" "Print in the serial monitor what the voltage of pin 13 is" "Prepare pin 13 for inputs of voltage" "Prepare pin 13 for outputs of voltage" "Prepare the input from the output of pin 13" "Prepare pin 13 for a delayed output" "Prepare pin 13 for outputs of current"
4 4 8. (3 points) The ln in the below cammand will: Serial.println(x); Choices "initializes the serial monitor" "takes the natural log of x" "prints the value of x continuously on the same line" "ln serves no purpose" "prints the value of x upside down" "prints the value of x and then moves to a new line" "sets the baud rate for the serial monitor" "prints the letters ln to the srial monitor" 9. (3 points) Given the code of the for loop, the number of mes the command is executed is equal to: for (int x=0; x <= 300; x++) { println(x); } Choices "298" "301" "299" "297" "304" "306" "not enough information" "300" 10. (3 points) The substance that cleans the surface of a part being soldered and allows the solder to flow and stick is called: Choices "Soldering Iron" "Solder" "Heat Shrink" "Nibbling" "Flux" "Tinning" "Solvent" "Wax"
5 5 11. (3 points) If a switch does not allow electricity to flow through a set of contacts only when it is mechanically actuated, then those contacts are wired to be: Choices "Single throw" "Normal Flow" "Double throw" "Abnormally open" "Abnormally closed" "Normally closed" "Normally open" "Normally Entered" 12. (5 points) Given the value of R2 shown below. The current leaving the source is closest to: R2 220 Ω Choices A 13. (5 points) Given the value of the source voltage shown below, the voltage drop at the 1000Ω resistor is closest to: SourceVoltage 5 V Choices V
6 6 14. (5 points) (5 points) Given the value of R3 shown below, the equivalent resistance of the circuit is closest to: R3 70 Ω Choices Ω 15. (5 points) The equivalent resistance of the resistor network shown below is closest to: R 1 40 Ω R 2 20 Ω R 3 50 Ω Choices Ω
7 7 16. (5 points) For the circuit below, if the current labeled I 2 2A and I 3 5A total power supplied by the battery is closest to: R 1 7 Ω R 2 5 Ω R 3 2 Ω, the Choices W 17. (5 points) Given the value of the voltage source Vin below, the voltage drop across the 50 Ω resistor is closest to: Vin 5 V Choices V "I" "J" 0.816
8 8 18. (5 points) For the circuit shown below, the power dissipated across the 110 Ω resistor is represented as P 110. The value of the unknown resistor, Rx, is closest to: P W Choices "I" "J" Ω 19. (5 points) Consider point A in the circuit below. When power is connected, electrons will flow past this point and through the resistors. If electrons over a time 5.5s then the voltage drop across the 1,000 Ω resistor is closest to: Choices "I" "J" V
9 9 20. (5 points) Suppose the net number of electrons that leave the negative side of a voltage source is e electrons. For the voltage and resistance values given below, the length of time this circuit is in operation is closest to: V1 6.1 V R 33Ω Choices "I" "J" s 21. (5 points) Suppose the net number of electrons that leave the negative side of a voltage source is e electrons and the circuit has been in operation for t 2.5 hr. For the voltage source value given below, the value of the resistor R is closest to V V Choices kω "I" "J" 17.64
10 (5 points) For the given resistor values, find the power provided by Voltage Source. V 1 5V R 1 13 Ω R 2 9 Ω R 3 14 Ω Choices W 23. (5 points) Two multimeters are used to analyze a circuit. Multimeter M1 measures X Amps and Multimeter M2 measures Y Volts. For the values of X and Y shown below, the value of resistor R2 should be closest to: X 0.5 A Y 38.4 V Choices "I" "J" Ω
11 (5 points) Given the power absorbed by R 8, what is the current flowing through R 3? Hint: No Source Voltage is Given. P 8 32 W R 1 R 2 R 3 R 4 R 5 11 Ω R 6 32 Ω 10 Ω R 7 12 Ω 29 Ω R 8 25 Ω 75 Ω R 9 52 Ω 132 Ω R Ω Choices ma
12 (5 points) You are charged with making boxes from scrap pieces of flat cardboard. All your boxes must have a width shown in the figure below. The length and height of the box, however, may vary depending on the available piece of cardboard. You want to make a chart in Excel that will calculate the surface area of the various box sizes so that, for a given piece of cardboard, you can quickly tell if you are able to make a particular box size. What formula in cell C5 should you use to be able to click and drag to fill the rest of the table shown below? Surface_Area = 2WL 2H L 2W H Choices "=2*($D$1*C:$+$B:*C:$+$D$1*$B:)" "=2*($D$1*$B5+C$4*$B5+$D$1*C$4)" "=2*(D1$$*C4$+B5$*C4$+D1$$*B5$)" "=2*($D$1*C$5+$B4*C$5+$D$1*$B4)" "=2*(D$$1*C$4+B$5*C$4+D$$1*B$5)" "=2*($$D1*$C4+$B5*$C4+$$D1*$B5)" "=2*$D$1*$C4+2*B$5*$C4+2*$D$1*B$5" "=2*($1$D*4$C+$5B*4$C+$1$D*$5B)"
13 (5 points) Dr. Harbour's pet alligator Lig has trouble staying warm during the frigid Ruston winter, so Dr. Harbour has decided to build a special alligator house with heating elements built into the structure, as shown. The resistance of each heating element is listed near the figure. A wire is routed from Dr. Harbour's house to Lig's house to supply power. Unfortunately, once the power has been turned on, Dr. Harbour's multimeter indicates a reduced voltage actually being applied to the gator house. He realizes this reduction is because the supply wire is so long that its resistance cannot be assumed zero as is usually assumed with wires. Considering the long wire between the power supply and Lig's house to function as a single resistor, the long wire's resistance is closest to: V meter R 1 R V R 3 21 Ω R 6 30 Ω R 9 15 Ω 15 Ω R 4 42 Ω R 7 5 Ω R 10 3 Ω 42 Ω R 5 20 Ω R 8 10 Ω Choices "I" "J" Ω
14 14 While you are waiting to begin your test: Please write and bubble your name and initials on your response sheet Please write and bubble your LATech username (e.g. abc567) on your response sheet Please write and bubble your section number on your response sheet using the guide shown here Please write and bubble your ExamForm number. This is your ExamForm: ExamForm 11 Notes: If your last name is too long, just write the first 10 letters. "F.I." and "M.I." are your first and middle initials, respectively Your "Username" is the first part of your LATech address For "Section" use the guide provided to the right Indicate "ENGR" as the "Program" Bubble: For Course Section: 91 H01 - Harbour MW 12-1:50 92 H02 - Long TR 12-1:50 93 H03 - Cronk MW 2-3:50 94 H04 - Scoggin MW 4-5:50 95 H05 - Reeves TR10-11:50 96 H06 - Easley MW10-11: Bhattarai MW10-11: Scoggin MW 2-3: Cronk TR 2-3: Scoggin MW 8-9: Hartmann TR 4-5: Corbett TR 12-1: Pathak MW 12-1: Cronk MW 4-5:50 Also Note: Mobile phones or other electronic devices (other than FE-approved calculators and plain timepieces) are not allowed on this exam. If you have non-approved devices (including smartwatches), please deposit them at the front of the room for the duration of the exam. Don't forget to retrieve them when you prepare to depart. Please deposit any bags you might have brought in the front of the room for the duration of the exam. There is a reference sheet given below. If you need additional scratch paper, please ask your proctor. Turn in any scratch paper with your exam, even if unused. If you have questions during the exam, please remain in your seat and raise your hand. A proctor will come to you. Please use a restroom now if you need it so as to minimize potential disruptions during the exam. Reference Information:
15 15 ExamForm _ENGR120_E1 October 10, 2017 ind 1 Key "J"
Lab 2: Blinkie Lab. Objectives. Materials. Theory
 Lab 2: Blinkie Lab Objectives This lab introduces the Arduino Uno as students will need to use the Arduino to control their final robot. Students will build a basic circuit on their prototyping board and
Lab 2: Blinkie Lab Objectives This lab introduces the Arduino Uno as students will need to use the Arduino to control their final robot. Students will build a basic circuit on their prototyping board and
Exam Practice Problems (3 Point Questions)
 Exam Practice Problems (3 Point Questions) Below are practice problems for the three point questions found on the exam. These questions come from past exams as well additional questions created by faculty.
Exam Practice Problems (3 Point Questions) Below are practice problems for the three point questions found on the exam. These questions come from past exams as well additional questions created by faculty.
Lab 2.4 Arduinos, Resistors, and Circuits
 Lab 2.4 Arduinos, Resistors, and Circuits Objectives: Investigate resistors in series and parallel and Kirchoff s Law through hands-on learning Get experience using an Arduino hat you need: Arduino Kit:
Lab 2.4 Arduinos, Resistors, and Circuits Objectives: Investigate resistors in series and parallel and Kirchoff s Law through hands-on learning Get experience using an Arduino hat you need: Arduino Kit:
Objective of the lesson
 Arduino Lesson 5 1 Objective of the lesson Learn how to program an Arduino in S4A All of you will: Add an LED to an Arduino and get it to come on and blink Most of you will: Add an LED to an Arduino and
Arduino Lesson 5 1 Objective of the lesson Learn how to program an Arduino in S4A All of you will: Add an LED to an Arduino and get it to come on and blink Most of you will: Add an LED to an Arduino and
Lab #1 Help Document. This lab will be completed in room 335 CTB. You will need to partner up for this lab in groups of two.
 Lab #1 Help Document This help document will be structured as a walk-through of the lab. We will include instructions about how to write the report throughout this help document. This lab will be completed
Lab #1 Help Document This help document will be structured as a walk-through of the lab. We will include instructions about how to write the report throughout this help document. This lab will be completed
1 V = IR P = IV R eq. 1 R i. = R i. = R eq. V = Energy Q. I = Q t
 Chapters 34 & 35: Electric Circuits NAME: Text: Chapter 34 Chapter 35 Think and Explain: 1-3, 6-8, 10 Think and Explain: 1-10 Think and Solve: 1-6 Think and Solve: 1-4 Vocabulary: Ohm s Law, resistance,
Chapters 34 & 35: Electric Circuits NAME: Text: Chapter 34 Chapter 35 Think and Explain: 1-3, 6-8, 10 Think and Explain: 1-10 Think and Solve: 1-6 Think and Solve: 1-4 Vocabulary: Ohm s Law, resistance,
Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control
 CS281: Computer Systems Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control The main purpose of this lab is to build a servo motor control circuit. As with prior labs, there will be some exploratory sections designed
CS281: Computer Systems Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control The main purpose of this lab is to build a servo motor control circuit. As with prior labs, there will be some exploratory sections designed
ENGR 1181 Lab 3: Circuits
 ENGR 1181 Lab 3: Circuits - - Lab Procedure - Report Guidelines 2 Overview of Circuits Lab: The Circuits Lab introduces basic concepts of electric circuits such as series and parallel circuit, used in
ENGR 1181 Lab 3: Circuits - - Lab Procedure - Report Guidelines 2 Overview of Circuits Lab: The Circuits Lab introduces basic concepts of electric circuits such as series and parallel circuit, used in
Activity Electrical Circuits Simulation
 Activity 1.2.3 Electrical Circuits Simulation Introduction Since the late 1800s, engineers have designed systems to utilize electrical energy due to its ability to be converted, stored, transmitted, and
Activity 1.2.3 Electrical Circuits Simulation Introduction Since the late 1800s, engineers have designed systems to utilize electrical energy due to its ability to be converted, stored, transmitted, and
The answer is R= 471 ohms. So we can use a 470 ohm or the next higher one, a 560 ohm.
 Introducing Resistors & LED s P a g e 1 Resistors are used to adjust the voltage and current in a circuit. The higher the resistance value, the more electrons it blocks. Thus, higher resistance will lower
Introducing Resistors & LED s P a g e 1 Resistors are used to adjust the voltage and current in a circuit. The higher the resistance value, the more electrons it blocks. Thus, higher resistance will lower
Direct Current Circuits
 PC1143 Physics III Direct Current Circuits 1 Objectives Apply Kirchhoff s rules to several circuits, solve for the currents in the circuits and compare the theoretical values predicted by Kirchhoff s rule
PC1143 Physics III Direct Current Circuits 1 Objectives Apply Kirchhoff s rules to several circuits, solve for the currents in the circuits and compare the theoretical values predicted by Kirchhoff s rule
Give one or two examples of electrical devices that you have personally noticed getting warm when they are turned on.
 Resistors We begin by learning how to read the values of resistors and to measure the values using a digital multimeter (DMM). Resistors are the most common and simplest electrical component. In an electrical
Resistors We begin by learning how to read the values of resistors and to measure the values using a digital multimeter (DMM). Resistors are the most common and simplest electrical component. In an electrical
Experiment 3. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 3 Ohm s Law 3.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 3 Ohm s Law 3.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 2. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Ohm's Law and DC Circuits
 Physics Lab II Ohm s Law Name: Partner: Partner: Partner: Ohm's Law and DC Circuits EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Circuits Experiment Board Two Dcell Batteries Wire leads Multimeter 100, 330, 560, 1k, 10k, 100k, 220k
Physics Lab II Ohm s Law Name: Partner: Partner: Partner: Ohm's Law and DC Circuits EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Circuits Experiment Board Two Dcell Batteries Wire leads Multimeter 100, 330, 560, 1k, 10k, 100k, 220k
Resistance Measurements (Measure all of your resistors, since even those that are labeled the same can be at least a little different)
 Resistors We begin by learning how to read the values of resistors and to measure the values using a digital multimeter (DMM). Resistors are the most common and simplest electrical component. In an electrical
Resistors We begin by learning how to read the values of resistors and to measure the values using a digital multimeter (DMM). Resistors are the most common and simplest electrical component. In an electrical
EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs Introduction to Arduino
 EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs 10-11 Introduction to Arduino In this lab we will introduce the idea of using a microcontroller as a tool for controlling
EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs 10-11 Introduction to Arduino In this lab we will introduce the idea of using a microcontroller as a tool for controlling
Syllabus OP49 Test electrical conduction in a variety of materials, and classify each material as a conductor or insulator
 Physics: 14. Current Electricity Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OP49 Test electrical conduction in a variety of materials,
Physics: 14. Current Electricity Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OP49 Test electrical conduction in a variety of materials,
Blink. EE 285 Arduino 1
 Blink At the end of the previous lecture slides, we loaded and ran the blink program. When the program is running, the built-in LED blinks on and off on for one second and off for one second. It is very
Blink At the end of the previous lecture slides, we loaded and ran the blink program. When the program is running, the built-in LED blinks on and off on for one second and off for one second. It is very
Final Reg Current and Circuits Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Final Reg Current and Circuits Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) How much energy does a 100-W light bulb use in 8.0 hours? 1)
Final Reg Current and Circuits Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) How much energy does a 100-W light bulb use in 8.0 hours? 1)
n = V1 n = V2 110 = So the output current will be times the input current = = 123 Amp (ANS)
 Unit 4 Physics 016 14. Transformers and transmission Page 1 of 6 Checkpoints Chapter 14 and transmission. Question 556 Transformers This is a step down transformer, because the output voltage is less than
Unit 4 Physics 016 14. Transformers and transmission Page 1 of 6 Checkpoints Chapter 14 and transmission. Question 556 Transformers This is a step down transformer, because the output voltage is less than
Electronics Merit Badge Class 4. 12/30/2010 Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 1
 Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 12/30/2010 Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 1 Soldering Safety Note: A Soldering Iron gets hotter than 374 F. Do not touch the soldering iron s metal parts or you will receive
Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 12/30/2010 Electronics Merit Badge Class 4 1 Soldering Safety Note: A Soldering Iron gets hotter than 374 F. Do not touch the soldering iron s metal parts or you will receive
HANDS-ON LAB INSTRUCTION SHEETS MODULE
 HANDS-ON LAB INSTRUCTION SHEETS MODULE 1 MEASURING RESISTANCE AND VOLTAGE NOTES: 1) Each student will be assigned to a unique Lab Equipment number MS01-MS30 which will match to a Tool Kit and a Radio Shack
HANDS-ON LAB INSTRUCTION SHEETS MODULE 1 MEASURING RESISTANCE AND VOLTAGE NOTES: 1) Each student will be assigned to a unique Lab Equipment number MS01-MS30 which will match to a Tool Kit and a Radio Shack
Introduction to the Op-Amp
 Purpose: ENGR 210/EEAP 240 Lab 5 Introduction to the Op-Amp To become familiar with the operational amplifier (OP AMP), and gain experience using this device in electric circuits. Equipment Required: HP
Purpose: ENGR 210/EEAP 240 Lab 5 Introduction to the Op-Amp To become familiar with the operational amplifier (OP AMP), and gain experience using this device in electric circuits. Equipment Required: HP
EE Laboratory 2 - Nodal Analysis and Thévenin Equivalents
 Page 1 215 Nodal Analysis and Thévenin quivalents Authors D. Wilson, R.D. hristie, W.R. Lynes, K.F. öhringer, M. Ostendorf Objectives At the end of this lab, you will be able to: onstruct, analyze and
Page 1 215 Nodal Analysis and Thévenin quivalents Authors D. Wilson, R.D. hristie, W.R. Lynes, K.F. öhringer, M. Ostendorf Objectives At the end of this lab, you will be able to: onstruct, analyze and
Lab 3: Digital Multimeter and Voltage Generator
 Lab 3: Digital Multimeter and Voltage Generator Lab Goals: Learn how to use your mydaq as a Digital Multimeter (DMM) Learn how to output a signal to a specified output port on the mydaq and verify its
Lab 3: Digital Multimeter and Voltage Generator Lab Goals: Learn how to use your mydaq as a Digital Multimeter (DMM) Learn how to output a signal to a specified output port on the mydaq and verify its
Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink
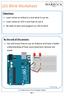 Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink By the end of this session: You will know how to use an Arduino
Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink By the end of this session: You will know how to use an Arduino
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 2 BASIC CIRCUIT ELEMENTS OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the student with
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 2 BASIC CIRCUIT ELEMENTS OBJECTIVES The purpose of this experiment is to familiarize the student with
Voltage, Current and Resistance
 Voltage, Current and Resistance Foundations in Engineering WV Curriculum, 2002 Foundations in Engineering Content Standards and Objectives 2436.8.3 Explain the relationship between current, voltage, and
Voltage, Current and Resistance Foundations in Engineering WV Curriculum, 2002 Foundations in Engineering Content Standards and Objectives 2436.8.3 Explain the relationship between current, voltage, and
EE Laboratory 2 - Nodal Analysis and Thévenin Equivalents *** Due in recitation on the week of May 5-9, 2008 *** Authors
 Page 1 215 Nodal Analysis and Thévenin quivalents *** Due in recitation on the week of May 59, 2008 *** Authors D. Wilson, R.D. hristie, W.R. Lynes, K.F. öhringer, M. Ostendorf Objectives At the end of
Page 1 215 Nodal Analysis and Thévenin quivalents *** Due in recitation on the week of May 59, 2008 *** Authors D. Wilson, R.D. hristie, W.R. Lynes, K.F. öhringer, M. Ostendorf Objectives At the end of
MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 1 - Laboratory tools
 MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 1 - Laboratory tools University of California, Irvine Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Goals To learn how to use the oscilloscope, function generator,
MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 1 - Laboratory tools University of California, Irvine Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Goals To learn how to use the oscilloscope, function generator,
Bluetooth Based IOT through Arduino
 1 Bluetooth Based IOT through Arduino G V V Sharma Fig. 1: Breadboard 1 Measuring the resistance Problem 1. Connect the 5V pin of the Arduino to an extreme pin of the Breadboard shown in Fig. 1. Let this
1 Bluetooth Based IOT through Arduino G V V Sharma Fig. 1: Breadboard 1 Measuring the resistance Problem 1. Connect the 5V pin of the Arduino to an extreme pin of the Breadboard shown in Fig. 1. Let this
STEADY HAND GAME WITH LATCHING LED
 ESSENTIAL INFORMATION BUILD INSTRUCTIONS CHECKING YOUR PCB & FAULT-FINDING MECHANICAL DETAILS HOW THE KIT WORKS TEST YOUR HAND-EYE COORDINATION WITH THIS STEADY HAND GAME WITH LATCHING LED Version 2.0
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION BUILD INSTRUCTIONS CHECKING YOUR PCB & FAULT-FINDING MECHANICAL DETAILS HOW THE KIT WORKS TEST YOUR HAND-EYE COORDINATION WITH THIS STEADY HAND GAME WITH LATCHING LED Version 2.0
Activity Electrical Circuits Simulation
 Activity 1.2.3 Electrical Circuits Simulation Introduction Since the late 1800s, engineers have designed systems to utilize electrical energy due to its ability to be converted, stored, transmitted, and
Activity 1.2.3 Electrical Circuits Simulation Introduction Since the late 1800s, engineers have designed systems to utilize electrical energy due to its ability to be converted, stored, transmitted, and
Series and parallel resistances
 Series and parallel resistances Objectives Calculate the equivalent resistance for resistors connected in both series and parallel combinations. Construct series and parallel circuits of lamps (resistors).
Series and parallel resistances Objectives Calculate the equivalent resistance for resistors connected in both series and parallel combinations. Construct series and parallel circuits of lamps (resistors).
Resistors & Circuits. Module 4.0 Current & Voltage. Module. Current & Voltage in Resistor Networks
 Module 4 www.learnabout-electronics.org Resistors & Circuits Module 4.0 Current & Voltage What you ll learn in Module 4.0 After studying this section, you should be able to: Describe the distribution of
Module 4 www.learnabout-electronics.org Resistors & Circuits Module 4.0 Current & Voltage What you ll learn in Module 4.0 After studying this section, you should be able to: Describe the distribution of
Unit 6 ~ Learning Guide Name:
 Unit 6 ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have
Unit 6 ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, complete the following notes as you work through the related lessons. Show ALL work as is explained in the lessons. You are required to have
Unit 3.C Electrical Theory, Circuits Essential Fundamentals of Electrical Theory, Circuits
 Unit 3.C Electrical Theory, Circuits Essential Fundamentals of Electrical Theory, Circuits Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 3.C Hwk. Pts.: / 36 Unit 3.C Lab Pts.: / 50 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees?
Unit 3.C Electrical Theory, Circuits Essential Fundamentals of Electrical Theory, Circuits Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 3.C Hwk. Pts.: / 36 Unit 3.C Lab Pts.: / 50 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees?
EE1020 Diodes and Resistors in Electrical Circuits Spring 2018
 PURPOSE The purpose of this project is for you to become familiar with some of the language, parts, and tools used in electrical engineering. You will also be introduced to some simple rule and laws. MATERIALS
PURPOSE The purpose of this project is for you to become familiar with some of the language, parts, and tools used in electrical engineering. You will also be introduced to some simple rule and laws. MATERIALS
Simple Circuits Experiment
 Physics 8.02T 1 Fall 2001 Simple Circuits Experiment Introduction Our world is filled with devices that contain electrical circuits in which various voltage sources cause currents to flow. We use radios,
Physics 8.02T 1 Fall 2001 Simple Circuits Experiment Introduction Our world is filled with devices that contain electrical circuits in which various voltage sources cause currents to flow. We use radios,
The USELESS BOX. Procedure:
 The USELESS BOX The useless box is exactly what it implies. A project that is pretty much Useless and is made for pure entertainment. You are going to go through the process of building this project from
The USELESS BOX The useless box is exactly what it implies. A project that is pretty much Useless and is made for pure entertainment. You are going to go through the process of building this project from
ECE2210 Final given: Fall 12
 ECE Final given: Fall (5 pts) a) Find and draw the Thévenin equivalent of the circuit shown The load resistor is R L b) Find and draw the Norton equivalent of the same circuit c) Find the load current
ECE Final given: Fall (5 pts) a) Find and draw the Thévenin equivalent of the circuit shown The load resistor is R L b) Find and draw the Norton equivalent of the same circuit c) Find the load current
Computational Crafting with Arduino. Christopher Michaud Marist School ECEP Programs, Georgia Tech
 Computational Crafting with Arduino Christopher Michaud Marist School ECEP Programs, Georgia Tech Introduction What do you want to learn and do today? Goals with Arduino / Computational Crafting Purpose
Computational Crafting with Arduino Christopher Michaud Marist School ECEP Programs, Georgia Tech Introduction What do you want to learn and do today? Goals with Arduino / Computational Crafting Purpose
HANDS-ON ACTIVITY 4 BUILDING SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS BACKGROUND WIRING DIRECTIONS
 ACTIVITY 4 BUILDING SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS BACKGROUND Make sure you read the background in Activity 3 before doing this activity. WIRING DIRECTIONS Materials per group of two: one or two D-cells
ACTIVITY 4 BUILDING SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS BACKGROUND Make sure you read the background in Activity 3 before doing this activity. WIRING DIRECTIONS Materials per group of two: one or two D-cells
South Pasadena A.P. Physics Chapter Electric Current & DC Circuits Date / / Period Electricity Practice Test
 South Pasadena A.P. Physics Name Chapter 18-19 Electric Current & DC Circuits Date / / Period 1 2 3 4 Electricity Practice Test Electric Current I = Q/t 1. A charge of 30 Coulombs passes through a 24-ohm
South Pasadena A.P. Physics Name Chapter 18-19 Electric Current & DC Circuits Date / / Period 1 2 3 4 Electricity Practice Test Electric Current I = Q/t 1. A charge of 30 Coulombs passes through a 24-ohm
Voltage Dividers a learn.sparkfun.com tutorial
 Voltage Dividers a learn.sparkfun.com tutorial Available online at: http://sfe.io/t44 Contents Introduction Ideal Voltage Divider Applications Extra Credit: Proof Resources and Going Further Introduction
Voltage Dividers a learn.sparkfun.com tutorial Available online at: http://sfe.io/t44 Contents Introduction Ideal Voltage Divider Applications Extra Credit: Proof Resources and Going Further Introduction
Experiment 1: Circuits Experiment Board
 01205892C AC/DC Electronics Laboratory Experiment 1: Circuits Experiment Board EQUIPMENT NEEDED: AC/DC Electronics Lab Board: Wire Leads Dcell Battery Graph Paper Purpose The purpose of this lab is to
01205892C AC/DC Electronics Laboratory Experiment 1: Circuits Experiment Board EQUIPMENT NEEDED: AC/DC Electronics Lab Board: Wire Leads Dcell Battery Graph Paper Purpose The purpose of this lab is to
Introduction to the Laboratory
 Memorial University of Newfoundland Department of Physics and Physical Oceanography Physics 2055 Laboratory Introduction to the Laboratory The purpose of this lab is to introduce you to some of the equipment
Memorial University of Newfoundland Department of Physics and Physical Oceanography Physics 2055 Laboratory Introduction to the Laboratory The purpose of this lab is to introduce you to some of the equipment
Current, resistance, and Ohm s law
 Current, resistance, and Ohm s law Apparatus DC voltage source set of alligator clips 2 pairs of red and black banana clips 3 round bulb 2 bulb sockets 2 battery holders or 1 two-battery holder 2 1.5V
Current, resistance, and Ohm s law Apparatus DC voltage source set of alligator clips 2 pairs of red and black banana clips 3 round bulb 2 bulb sockets 2 battery holders or 1 two-battery holder 2 1.5V
LED + Servo 2 devices, 1 Arduino
 LED + Servo 2 devices, 1 Arduino Learn to connect and write code to control both a Servo and an LED at the same time. Many students who come through the lab ask if they can use both an LED and a Servo
LED + Servo 2 devices, 1 Arduino Learn to connect and write code to control both a Servo and an LED at the same time. Many students who come through the lab ask if they can use both an LED and a Servo
INA169 Breakout Board Hookup Guide
 Page 1 of 10 INA169 Breakout Board Hookup Guide CONTRIBUTORS: SHAWNHYMEL Introduction Have a project where you want to measure the current draw? Need to carefully monitor low current through an LED? The
Page 1 of 10 INA169 Breakout Board Hookup Guide CONTRIBUTORS: SHAWNHYMEL Introduction Have a project where you want to measure the current draw? Need to carefully monitor low current through an LED? The
Industrial Electricity
 Industrial Electricity Name DUE //7 or //7 (Your next lab day) Prelab: efer to the tables on Page 5. Show work neatly and completely on separate paper for any entry labeled calculated. You do not need
Industrial Electricity Name DUE //7 or //7 (Your next lab day) Prelab: efer to the tables on Page 5. Show work neatly and completely on separate paper for any entry labeled calculated. You do not need
Using Voltage Dividers to Design a Photo-Sensitive LED Circuit. ( Doug Oliver & Jackie Kane. May be reproduced for non-profit classroom use.
 Using Voltage Dividers to Design a Photo-Sensitive LED Circuit ( 2009 - Doug Oliver & Jackie Kane. May be reproduced for non-profit classroom use.) Purpose: After completing the module students will: 1.
Using Voltage Dividers to Design a Photo-Sensitive LED Circuit ( 2009 - Doug Oliver & Jackie Kane. May be reproduced for non-profit classroom use.) Purpose: After completing the module students will: 1.
For this exercise, you will need a partner, an Arduino kit (in the plastic tub), and a laptop with the Arduino programming environment.
 Physics 222 Name: Exercise 6: Mr. Blinky This exercise is designed to help you wire a simple circuit based on the Arduino microprocessor, which is a particular brand of microprocessor that also includes
Physics 222 Name: Exercise 6: Mr. Blinky This exercise is designed to help you wire a simple circuit based on the Arduino microprocessor, which is a particular brand of microprocessor that also includes
Congratulations on your purchase of the SparkFun Arduino ProtoShield Kit!
 Congratulations on your purchase of the SparkFun Arduino ProtoShield Kit! Well, now what? The focus of this guide is to aid you in turning that box of parts in front of you into a fully functional prototyping
Congratulations on your purchase of the SparkFun Arduino ProtoShield Kit! Well, now what? The focus of this guide is to aid you in turning that box of parts in front of you into a fully functional prototyping
Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
18-3 Circuit Analogies, and Kirchoff s Rules
 18-3 Circuit Analogies, and Kirchoff s Rules Analogies can help us to understand circuits, because an analogous system helps us build a model of the system we are interested in. For instance, there are
18-3 Circuit Analogies, and Kirchoff s Rules Analogies can help us to understand circuits, because an analogous system helps us build a model of the system we are interested in. For instance, there are
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT PROBLEMS 12 AUGUST 2014
 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT PROBLEMS 12 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Discuss the application of Ohm s Law Explain the series and parallel connection of resistors Discuss the effect of internal
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT PROBLEMS 12 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Discuss the application of Ohm s Law Explain the series and parallel connection of resistors Discuss the effect of internal
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016
 ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Patrick Nicholson Aric Lu Kaeini Ekong 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Intro 3 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Patrick Nicholson Aric Lu Kaeini Ekong 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Intro 3 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits
Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's
 2240 Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's Abstract-You will construct and test two LED power-indicator circuits for your breadboard in preparation for building the Electromyogram circuit in Lab
2240 Laboratory Project 1a: Power-Indicator LED's Abstract-You will construct and test two LED power-indicator circuits for your breadboard in preparation for building the Electromyogram circuit in Lab
Electric Circuits. Physics 6 th Six Weeks
 Electric Circuits Physics 6 th Six Weeks Electric Circuits (a review) A circuit is a path through which electricity can flow Electric Circuits always contain 3 things: a voltage source, a conductor (usually
Electric Circuits Physics 6 th Six Weeks Electric Circuits (a review) A circuit is a path through which electricity can flow Electric Circuits always contain 3 things: a voltage source, a conductor (usually
Circuits: Light-Up Creatures Teacher version
 Circuits: Light-Up Creatures Teacher version In this lab you will explore current, voltage and resistance and their relationships as given by the Ohm s law. You will also explore of how resistance can
Circuits: Light-Up Creatures Teacher version In this lab you will explore current, voltage and resistance and their relationships as given by the Ohm s law. You will also explore of how resistance can
DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW
 July 15, 2008 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law 1 Name Date Partners DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action
July 15, 2008 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law 1 Name Date Partners DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action
Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response
 ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Circuits
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 27 Circuits Combination of resistors Potential differences Single loop circuits Kirchhoff laws Multiloop circuits RC circuits General 1. Figure 1 shows two resistors
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 27 Circuits Combination of resistors Potential differences Single loop circuits Kirchhoff laws Multiloop circuits RC circuits General 1. Figure 1 shows two resistors
DIODE / TRANSISTOR TESTER KIT
 DIODE / TRANSISTOR TESTER KIT MODEL DT-100K 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176 Phone 781-665-1400 Toll Free 1-800-517-8431 Visit us at www.testequipmentdepot.com Assembly and Instruction Manual Elenco
DIODE / TRANSISTOR TESTER KIT MODEL DT-100K 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176 Phone 781-665-1400 Toll Free 1-800-517-8431 Visit us at www.testequipmentdepot.com Assembly and Instruction Manual Elenco
Pre-Lab for Batteries and Bulbs
 Pre-Lab for Batteries and Bulbs Complex circuits composed of resistors can be simplified by using the concept of equivalent resistors. For example if resistors R 1, R 2, and R 3 are connected in series,
Pre-Lab for Batteries and Bulbs Complex circuits composed of resistors can be simplified by using the concept of equivalent resistors. For example if resistors R 1, R 2, and R 3 are connected in series,
Lab. I Electrical Measurements, Serial and Parallel Circuits
 Name (last, first) ECE 2100 ID Lab. I Electrical Measurements, Serial and Parallel Circuits Pre-Lab Important note: this is the pre-lab of Lab I. You can type in the answers, or print out and write in
Name (last, first) ECE 2100 ID Lab. I Electrical Measurements, Serial and Parallel Circuits Pre-Lab Important note: this is the pre-lab of Lab I. You can type in the answers, or print out and write in
LED ROBOT BLINKER KIT
 LED ROBOT BLINKER KIT MODEL K-17 Assembly and Instruction Manual Elenco Electronics, Inc. Copyright 1989, 1998 Elenco Electronics, Inc. Revised 2001 REV-J 753217 PARTS LIST If any parts are missing or
LED ROBOT BLINKER KIT MODEL K-17 Assembly and Instruction Manual Elenco Electronics, Inc. Copyright 1989, 1998 Elenco Electronics, Inc. Revised 2001 REV-J 753217 PARTS LIST If any parts are missing or
Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall DC techniques, dividers, and bridges
 Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall 2002 DC techniques, dividers, and bridges Purpose You will gain a familiarity with the circuit board and work with a variety of DC techniques, including voltage dividers,
Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall 2002 DC techniques, dividers, and bridges Purpose You will gain a familiarity with the circuit board and work with a variety of DC techniques, including voltage dividers,
Experiment #5 Series and Parallel Resistor Circuits
 Experiment #5 Series and Parallel Resistor Circuits Objective: You will become familiar with the MB Board and learn how to build simple DC circuits. This will introduce you to series and parallel circuits
Experiment #5 Series and Parallel Resistor Circuits Objective: You will become familiar with the MB Board and learn how to build simple DC circuits. This will introduce you to series and parallel circuits
Resistance and Ohm s law
 Resistance and Ohm s law Objectives Characterize materials as conductors or insulators based on their electrical properties. State and apply Ohm s law to calculate current, voltage or resistance in an
Resistance and Ohm s law Objectives Characterize materials as conductors or insulators based on their electrical properties. State and apply Ohm s law to calculate current, voltage or resistance in an
Lightbulbs and Dimmer Switches: DC Circuits
 Introduction It is truly amazing how much we rely on electricity, and especially on devices operated off of DC current. Your PDA, cell phone, laptop computer and calculator are all examples of DC electronics.
Introduction It is truly amazing how much we rely on electricity, and especially on devices operated off of DC current. Your PDA, cell phone, laptop computer and calculator are all examples of DC electronics.
1. The coulomb is a unit of. A. charge B. voltage C. energy D. capacitance E. current. 2. The following is not true about voltage:
 BioE 1310 - Review 1 - DC 1/16/2017 Instructions: On the Answer Sheet, enter your 2-digit ID number (with a leading 0 if needed) in the boxes of the ID section. Fill in the corresponding numbered circles.
BioE 1310 - Review 1 - DC 1/16/2017 Instructions: On the Answer Sheet, enter your 2-digit ID number (with a leading 0 if needed) in the boxes of the ID section. Fill in the corresponding numbered circles.
Chapter 2: Electricity
 Chapter 2: Electricity Lesson 2.1 Static Electricity 1 e.g. a polythene rod Lesson 2.3 Electric current 1 I = Q / t = 80 / 16 = 5 A 2 t = Q / I = 96 / 6 = 16 s 1b e.g. a metal wire 2 If static charge begins
Chapter 2: Electricity Lesson 2.1 Static Electricity 1 e.g. a polythene rod Lesson 2.3 Electric current 1 I = Q / t = 80 / 16 = 5 A 2 t = Q / I = 96 / 6 = 16 s 1b e.g. a metal wire 2 If static charge begins
// Parts of a Multimeter
 Using a Multimeter // Parts of a Multimeter Often you will have to use a multimeter for troubleshooting a circuit, testing components, materials or the occasional worksheet. This section will cover how
Using a Multimeter // Parts of a Multimeter Often you will have to use a multimeter for troubleshooting a circuit, testing components, materials or the occasional worksheet. This section will cover how
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting AC to DC
 EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 6 Diodes: Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Converting C to DC The process of converting a sinusoidal C voltage to a
Electric Circuit Experiments
 Electric Circuit Experiments 1. Using the resistor on the 5-resistor block, vary the potential difference across it in approximately equal increments for eight different values (i.e. use one to eight D-
Electric Circuit Experiments 1. Using the resistor on the 5-resistor block, vary the potential difference across it in approximately equal increments for eight different values (i.e. use one to eight D-
Sensor Calibration Lab
 Sensor Calibration Lab The lab is organized with an introductory background on calibration and the LED speed sensors. This is followed by three sections describing the three calibration techniques which
Sensor Calibration Lab The lab is organized with an introductory background on calibration and the LED speed sensors. This is followed by three sections describing the three calibration techniques which
RESISTANCE & OHM S LAW (PART I
 RESISTANCE & OHM S LAW (PART I and II) Objectives: To understand the relationship between potential and current in a resistor and to verify Ohm s Law. To understand the relationship between potential and
RESISTANCE & OHM S LAW (PART I and II) Objectives: To understand the relationship between potential and current in a resistor and to verify Ohm s Law. To understand the relationship between potential and
Chapters 34: Ohm s Law
 Text: Chapter 34 Think and Explain: 1-3, 6-8, 10 Think and Solve: 1-6 Chapters 34: Ohm s Law Vocabulary: Ohm s Law, resistance, resistivity, superconductor, current, amps, volts, ohms, kw-h, AC, DC Equations:
Text: Chapter 34 Think and Explain: 1-3, 6-8, 10 Think and Solve: 1-6 Chapters 34: Ohm s Law Vocabulary: Ohm s Law, resistance, resistivity, superconductor, current, amps, volts, ohms, kw-h, AC, DC Equations:
Pacific Antenna Easy TR Switch
 Pacific Antenna Easy TR Switch Kit Description The Easy TR Switch is an RF sensing circuit with a double pole double throw relay that can be used to automatically switch an antenna between a separate receiver
Pacific Antenna Easy TR Switch Kit Description The Easy TR Switch is an RF sensing circuit with a double pole double throw relay that can be used to automatically switch an antenna between a separate receiver
Oregon State University Lab Session #1 (Week 3)
 Oregon State University Lab Session #1 (Week 3) ENGR 201 Electrical Fundamentals I Equipment and Resistance Winter 2016 EXPERIMENTAL LAB #1 INTRO TO EQUIPMENT & OHM S LAW This set of laboratory experiments
Oregon State University Lab Session #1 (Week 3) ENGR 201 Electrical Fundamentals I Equipment and Resistance Winter 2016 EXPERIMENTAL LAB #1 INTRO TO EQUIPMENT & OHM S LAW This set of laboratory experiments
Breadboard Primer. Experience. Objective. No previous electronics experience is required.
 Breadboard Primer Experience No previous electronics experience is required. Figure 1: Breadboard drawing made using an open-source tool from fritzing.org Objective A solderless breadboard (or protoboard)
Breadboard Primer Experience No previous electronics experience is required. Figure 1: Breadboard drawing made using an open-source tool from fritzing.org Objective A solderless breadboard (or protoboard)
Series and Parallel Circuits Basics 1
 1 Name: Symbols for diagrams Directions: 1. Log on to your computer 2. Go to the following website: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/-construction-kit-dc Click the button that says Play with sims
1 Name: Symbols for diagrams Directions: 1. Log on to your computer 2. Go to the following website: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/-construction-kit-dc Click the button that says Play with sims
ABC V1.0 ASSEMBLY IMPORTANT!
 ABC V1.0 ASSEMBLY Before starting this kit, prepare the following tools: Soldering iron (15-20W will do), flush cutters, no.2 hex screwdriver or allen key and phillips screwdriver. Also briefly go through
ABC V1.0 ASSEMBLY Before starting this kit, prepare the following tools: Soldering iron (15-20W will do), flush cutters, no.2 hex screwdriver or allen key and phillips screwdriver. Also briefly go through
Electrical Measurements
 Electrical Measurements INTRODUCTION In this section, electrical measurements will be discussed. This will be done by using simple experiments that introduce a DC power supply, a multimeter, and a simplified
Electrical Measurements INTRODUCTION In this section, electrical measurements will be discussed. This will be done by using simple experiments that introduce a DC power supply, a multimeter, and a simplified
Electronics. Module Descriptor
 The Further Education and Training Awards Council (FETAC) was set up as a statutory body on 11 June 2001 by the Minister for Education and Science. Under the Qualifications (Education & Training) Act,
The Further Education and Training Awards Council (FETAC) was set up as a statutory body on 11 June 2001 by the Minister for Education and Science. Under the Qualifications (Education & Training) Act,
Lecture 4: Basic Electronics. Lecture 4 Brief Introduction to Electronics and the Arduino
 Lecture 4: Basic Electronics Lecture 4 Page: 1 Brief Introduction to Electronics and the Arduino colintan@nus.edu.sg Lecture 4: Basic Electronics Page: 2 Objectives of this Lecture By the end of today
Lecture 4: Basic Electronics Lecture 4 Page: 1 Brief Introduction to Electronics and the Arduino colintan@nus.edu.sg Lecture 4: Basic Electronics Page: 2 Objectives of this Lecture By the end of today
Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals
 Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals Introduction This experiment has two parts. Each part will have to be carried out using the Multisim Electronics Workbench software. The experiment will then
Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals Introduction This experiment has two parts. Each part will have to be carried out using the Multisim Electronics Workbench software. The experiment will then
Chapter 13. Electric Circuits
 Chapter 13 Electric Circuits Lower Potential Battery (EMF - E) - + Higher Potential Bulb (Resistor) Wires (No Change in Potential) EMF (Voltage Source) _ + Resistor Working Circuits For a circuit to work,
Chapter 13 Electric Circuits Lower Potential Battery (EMF - E) - + Higher Potential Bulb (Resistor) Wires (No Change in Potential) EMF (Voltage Source) _ + Resistor Working Circuits For a circuit to work,
Measuring Voltage, Current & Resistance Building: Resistive Networks, V and I Dividers Design and Build a Resistance Indicator
 ECE 3300 Lab 2 ECE 1250 Lab 2 Measuring Voltage, Current & Resistance Building: Resistive Networks, V and I Dividers Design and Build a Resistance Indicator Overview: In Lab 2 you will: Measure voltage
ECE 3300 Lab 2 ECE 1250 Lab 2 Measuring Voltage, Current & Resistance Building: Resistive Networks, V and I Dividers Design and Build a Resistance Indicator Overview: In Lab 2 you will: Measure voltage
Check out from stockroom:! Servo! DMM (Digital Multi-meter)
 Objectives 1 Teach the student to keep an engineering notebook. 2 Talk about lab practices, check-off, and grading. 3 Introduce the lab bench equipment. 4 Teach wiring techniques. 5 Show how voltmeters,
Objectives 1 Teach the student to keep an engineering notebook. 2 Talk about lab practices, check-off, and grading. 3 Introduce the lab bench equipment. 4 Teach wiring techniques. 5 Show how voltmeters,
Laboratory 6 Diodes and Transistors
 Laboratory 6 page 1 of 6 Laboratory 6 Diodes and Transistors Introduction In this lab, you will build and test circuits using diodes and transistors. You will use a number of different types of diodes,
Laboratory 6 page 1 of 6 Laboratory 6 Diodes and Transistors Introduction In this lab, you will build and test circuits using diodes and transistors. You will use a number of different types of diodes,
Smart Garment Design
 Smart Garment Design 5. Basic Electronics Sungmin Kim SEOUL NATIONAL UNIVERSITY Definition of Circuit A closed loop of electricity that contains a power source and a load Components Power source Something
Smart Garment Design 5. Basic Electronics Sungmin Kim SEOUL NATIONAL UNIVERSITY Definition of Circuit A closed loop of electricity that contains a power source and a load Components Power source Something
Value Location Qty Transistors 2N5485 Q1, Q2, 4 Q3, Q4 2N5087 Q5 1. Trim Pots 250k VTRIM 1. Potentiometers C500k Speed 1. Toggle Switch On/On Vibe 1
 P-90 BUILD INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for your purchase of our P-90 kit! We have completely redesigned our entire line of kits to be the most user friendly, while still maintaining their same great sound!
P-90 BUILD INSTRUCTIONS Thank you for your purchase of our P-90 kit! We have completely redesigned our entire line of kits to be the most user friendly, while still maintaining their same great sound!
V (in volts) = voltage applied to the circuit, I (in amperes) = current flowing in the circuit, R (in ohms) = resistance of the circuit.
 OHM S LW OBJECTIES: PRT : 1) Become familiar with the use of ammeters and voltmeters to measure DC voltage and current. 2) Learn to use wires and a breadboard to build circuits from a circuit diagram.
OHM S LW OBJECTIES: PRT : 1) Become familiar with the use of ammeters and voltmeters to measure DC voltage and current. 2) Learn to use wires and a breadboard to build circuits from a circuit diagram.
Unit 1 Electronics Name: Form:
 Unit 1 Electronics Name: Form: Electronics Electronics is the study of components and techniques used to be able to build circuits controlled by electricity. An electronic system uses discrete components.
Unit 1 Electronics Name: Form: Electronics Electronics is the study of components and techniques used to be able to build circuits controlled by electricity. An electronic system uses discrete components.
EEE 201 CIRCUIT THEORY I EXPERIMENT 3
 EEE 0 CIRCUIT THEORY I OLTAGE DIIDER 3. Objectives: oltage Divider in No-load Operation: Measurement of the voltage ratios on a voltage divider in no-load operation. oltage divider Formula. oltage Divider
EEE 0 CIRCUIT THEORY I OLTAGE DIIDER 3. Objectives: oltage Divider in No-load Operation: Measurement of the voltage ratios on a voltage divider in no-load operation. oltage divider Formula. oltage Divider
DuoDrive Nixie Bargraph Kit
 Assembly Instructions And User Guide Nixie Bargraph Kit - 1 - REVISION HISTORY Issue Date Reason for Issue Number 1 12 December 2017 New document - 2 - 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 About Nixie Bargraph Driver IN-9
Assembly Instructions And User Guide Nixie Bargraph Kit - 1 - REVISION HISTORY Issue Date Reason for Issue Number 1 12 December 2017 New document - 2 - 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 About Nixie Bargraph Driver IN-9
