(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
|
|
|
- Hilary Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1 JOLY et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 20, 2017 (54) SHIELDING ATTENUATION (30) Foreign Application Priority Data MEASUREMENT Oct. 16, 2015 (FR) (71) Applicant: Commissariat a L'Energie Atomique et aux Energies Alternatives, Paris Publication Classification (FR) (51) Int. Cl. H04B 7/ O1 (72) Inventors: Jean-Christophe JOLY, Gramat (FR): ( ) Sylvain JONNIAU, Sainghin En (52) is: C. H04B 17/318 ( ) Melantois (FR); Matthieu WERQUIN, ' ' '" Sainghin En Melantois (FR); Nicolas (57) ABSTRACT VELLAS, Sainghin En Melantois (FR): Christophe GAQUIERE, Sainghin En A system for measuring the attenuation of electromagnetic Melantois (FR); Benjamin CHOTEAU, shielding of an infrastructure as a function of the frequency, Sainghin En Melantois (FR) including a transmitter of a white noise signal with a constant power over a frequency band between a minimum (73) Assignee: Commissariat a L'Energie Atomique frequency and a maximum frequency, a signal receiver, the et aux Energies Alternatives, Paris (FR) transmitter and the receiver being capable of sending a signal and receiving a signal across the infrastructure, the receiver including a filter module capable of applying slid ing filter on the received signal between the minimum (21) Appl. No.: 15/292,640 frequency and the maximum frequency, and a double Syn chronous detection module capable of double synchronous (22) Filed: Oct. 13, 2016 detection on a signal output by the filter module. 11
2 Patent Application Publication Apr. 20, Sheet 1 of 3 US 2017/ A1
3 Patent Application Publication Apr. 20, Sheet 2 of 3 US 2017/ A1 SE Frmin Fmax frequency FIG 3 SR -O- FO Fmax frequency FIG. 4
4 Patent Application Publication Apr. 20, Sheet 3 of 3 US 2017/ A1 Transmission power in kw Fhigh Flow time FIG. 5 Transmission power in kw RHref RB ref time F.G. 6a Transmission power in kw RH RB time F.G. 6b
5 US 2017/ A1 Apr. 20, 2017 SHIELDING ATTENUATION MEASUREMENT TECHNICAL FIELD This invention relates to the measurement of the attenuation of electromagnetic shielding of an infrastructure as a function of the frequency. STATE OF PRIOR ART 0002 Conventionally, the attenuation of electromagnetic shielding of an infrastructure, also called the shielding efficiency or faradisation, is measured using the principle of double weighing. This is done using a measurement device comprising a signal transmitter and a signal receiver, that is used as follows A first reference or calibration measurement is made with the transmitter and the receiver positioned at a predetermined distance in the absence of an infrastructure. The transmitter transmits a signal with a known transmission power and this signal is received by the receiver A second measurement is made, firstly positioning the transmitter and the receiver on opposite sides of the infrastructure for which the shielding attenuation is to be determined. The transmitter and the receiver are positioned at the same distance and at the same orientation and the signal is transmitted with the same transmission power as for the first measurement. The receiver receives this signal The shielding attenuation is the ratio between the first and the second received powers The attenuation measurement is made as a function of the frequency, typically from the order of 1 khz to about 10 GHz. Therefore the shielding attenuation is given as a function of the frequency: for example, a power factor 5 (namely 10 logo.5-7 db) at 1 GHz. This implies that the transmission frequency and reception frequency are syn chronised A first solution for synchronising the transmitter and the receiver is to make measurements at discrete fre quencies. In this case, a measurement is only valid at a given frequency and the measurement steps have to be repeated for each frequency A second way of synchronising is to make a connection between the transmitter and the receiver. This liaison can be set up using a wire conductor or an optic fibre, but this requires the presence of a passageway through the infrastructure, for example such as an opening, a honeycomb structure or a wave guide. Furthermore, passing a wire conductor without repairing the shielding would distort the measurement because the wire conductor would be per ceived as a faradisation defect The connection between the transmitter and the receiver can also be made by radio waves, possibly in the measurement band. This is only possible if the infrastructure shielding attenuation is relatively limited, such that the radio wave can transit through the infrastructure Furthermore, the electromagnetic environment of the infrastructure to be characterised is likely to be noisy. GSM, wifi or radar waves, for example, can form ambient electromagnetic pollution. This electromagnetic pollution could be interpreted as being a faradisation defect of the infrastructure. Thus, the measured shielding attenuation would be wrong at the frequencies of the electromagnetic pollution Electromagnetic pollution can be taken into account with known measuring instruments by making an ambient background noise measurement before starting the calibration. A noise power is thus determined. It is sub tracted from power measurements made afterwards during the attenuation calibration However, this calculation assumes that electromag netic pollution remains constant in time. The calculated attenuation will then be distorted if the electromagnetic pollution is intermittent and if it varies between or during measurements. PRESENTATION OF THE INVENTION 0013 The invention aims to solve problems with prior art by providing a system for measuring the attenuation of electromagnetic shielding of an infrastructure as a function of the frequency, characterised in that it comprises: A signal transmitter that is a white noise with a constant power over a frequency band between a minimum frequency and a maximum frequency, A signal receiver, the transmitter and the receiver being capable of sending a signal and receiving a signal across the infrastructure, the receiver comprising: 0016 A filter module capable of applying a sliding filter on the received signal (SR) between the minimum frequency and the maximum frequency, and A double synchronous detection module capable of double synchronous detection on a signal output by the filter module With the invention, the shielding attenuation mea Surement is made more easily and quickly then with prior art In particular, the measurement is made for a fre quency chosen in a frequency range, without it being nec essary to repeat signal transmission and reception opera tions According to one preferred characteristic: The transmitter is capable of transmitting a signal that is chopped white noise comprising two alternating power levels, and The receiver is capable of determining the differ ence between received powers corresponding to two power levels of the transmitted signal Thus, the contribution of ambient noise can be cancelled. The shielding attenuation measurement according to this invention is independent of the electromagnetic environment According to one preferred characteristic, the receiver also comprises a module for determination of the shielding attenuation as a function of the results obtained by the double synchronous detection module determined fol lowing signal transmission and reception in the absence of the infrastructure and then on each side of the infrastructure This invention also relates to a receiver for a system for measurement of the attenuation of electromag netic shielding of an infrastructure as a function of the frequency, 0026 characterised it that it is capable of receiving a signal transmitted by a transmitter of a white noise signal with constant power over a frequency band between a minimum frequency and a maximum fre quency, the transmitter and the receiver being capable of transmitting and receiving a signal on opposite sides of the infrastructure,
6 US 2017/ A1 Apr. 20, and characterised in that it comprises A filter module capable of applying a sliding filter on the received signal between the minimum frequency and the maximum frequency, and A double synchronous detection module capable of double synchronous detection on a signal output by the filter module According to one preferred characteristic, the receiver also comprises a module for determination of the shielding attenuation as a function of the results obtained by the double synchronous detection module determined fol lowing signal transmission and reception in the absence of the infrastructure and then on each side of the infrastructure The invention also relates to a method for measur ing the attenuation of electromagnetic shielding of an infra structure as a function of the frequency, characterised in that it comprises the following steps: 0032 Transmission of a white noise signal with a con stant power over a frequency band between a minimum frequency and a maximum frequency, 0033 Reception of a signal, the signal transmission and reception taking place on opposite sides of the infrastruc ture, 0034 Application of a sliding filter on the received signal between the minimum frequency and the maximum fre Cuency, 0035 Synchronous double detection on a signal output by the filter module According to one preferred characteristic, the method for measuring the attenuation of electromagnetic shielding of an infrastructure also comprises preliminary steps for the transmission and reception of a signal in the absence of the infrastructure, applying a sliding filter on the received signal and double synchronous detection on a signal output by the filter module According to one preferred characteristic, the method for measuring the attenuation of electromagnetic shielding of an infrastructure also comprises a step to determine the shielding attenuation as a function of the results obtained by the sliding filter and double synchronous detection steps made following signal transmission and reception in the absence of the infrastructure and then on each side of the infrastructure The receiver and the method have advantages similar to those mentioned above In one particular embodiment, the sliding filter and double synchronous detection steps in the method according to the invention are implemented by the instructions in a computer program Consequently, the invention also relates to a com puter program stored on a data medium, this program possibly being installed on a computer, this program includ ing instructions adapted to implementation of the sliding filter and double synchronous detection steps in a method like that described above This program can use any programming language and may be in the form of source code, object code or a code intermediate between source code and object code, such as a partially compiled form, or in any other desirable form The invention also relates to a data medium that can be read by a computer, containing computer program instructions adapted to implementation of the steps in a method like that described above The data medium may be any entity or device on which the program can be stored. For example, the medium may include a storage means such as a ROM, for example a CD ROM or a microelectronic circuit ROM, or a magnetic recording device Such as for example a diskette or a hard disk. 0044) The data medium may also be a transmissible medium Such as an electrical or optical signal that can be routed on an electrical or optical cable, by radio or by other means. In particular, the program according to the invention can be downloaded on an Internet type network Alternately, the data medium can be an integrated circuit in which the program is included, the circuit being adapted to run or to be used for running the method according to the invention. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS Other characteristics and advantages will become clear after reading the following description of a preferred embodiment given as a non-limitative example, described with reference to the figures in which: 0047 FIG. 1 represents a system for measuring the shielding attenuation according to one embodiment of this invention, 0048 FIG. 2 represents a method for measuring the shielding attenuation according to one embodiment of this invention, 0049 FIG. 3 represents a signal transmitted by the sys tem for measuring the shielding attenuation according to one embodiment of this invention, 0050 FIG. 4 represents a sliding filter performed on a signal received by the system for measuring the shielding attenuation according to one embodiment of this invention, 0051 FIG. 5 represents a signal transmitted by the sys tem for measuring the shielding attenuation according to one embodiment of this invention, FIGS. 6a and 6b represent signals received by the system for measuring the shielding attenuation, according to one embodiment of this invention, DETAILED PRESENTATION OF PARTICULAR EMBODIMENTS 0053 According to one preferred embodiment shown on FIG. 1, a system for measuring the shielding attenuation comprises a signal transmitter 10 connected to a transmis sion antenna 11. The transmitter 10 is capable of transmit ting a signal that is described below The shielding attenuation measurement system also comprises a receiver 12 connected to a reception antenna The transmission and reception antennas may be of any type, for example: 0056 Directional or omnidirectional, 0057 Wide band or narrow band, Linear or circular polarisation, 0059 Electronic or mechanical directional control, 0060 Wire, aperture or planar, with progressive or stationary waves The receiver 12 is capable of receiving a signal received by the reception antenna 13. The receiver 12 comprises a filter module 121, a double synchronous detec tion module 122 and a measurement processing module 123
7 US 2017/ A1 Apr. 20, 2017 to determine the attenuation of a shielding. Processing done by the different modules is described below The shielding attenuation measurement system may be battery powered. 0063) Note that the description only includes elements of the shielding attenuation measurement system that are useful for understanding the invention The shielding attenuation measurement system is used according to the double weighing principle. A first measurement, called the reference measurement, is made when the transmission antenna 11 and the reception antenna 13 are put into place in the absence of a structure for which the shielding attenuation is to be determined, at a determined distance and orientation. The transmission antenna and the reception antenna are then placed on each side of the structure for which the shielding attenuation is to be deter mined, at the same determined distance and orientation. A second measurement is made The signals transmitted for the two measurements have the same power The shielding attenuation is the ratio of the powers received during the two measurement operations. The attenuation measurement is made as a function of the frequency, typically of the order of 1 khz to about 10 GHz FIG. 1 illustrates the configuration for making the second measurement in the case in which the structure is a wall 20 of a room in a building. The wall 20 comprises a door 21, the corners of which form potential shielding defects. The antennas 11 and 13 are thus located on each side of the wall FIG. 2 represents the operation of the system for measuring the shielding attenuation according to one embodiment of the invention. This operation is represented in the form of a flowchart comprising steps E1 to E Step E1 is the transmission of a signal SE by the transmitter FIG.3 represents the signal SE transmitted by the transmitter 10 as a function of the frequency. The transmit ted signal SE is a white noise signal with a constant power over a frequency band between a minimum frequency F, and a maximum frequency F The next step E2 is the reception of a signal SR by the receiver The next step E3 is a sliding filter applied to the received signal SR FIG. 4 represents the sliding filter applied to the signal SR received by the receiver 12. The signal SR is within the frequency band between frequencies F, and Fina A sliding filter is applied between frequencies F, and F. The sliding filter has a predetermined width LF around a frequency Fo that varies from F to F The next step E4 is determination of the received power at a given frequency within the frequency band of the transmitted signal SE. The received power is expressed in Watts. It is memorised in a memory (not shown) internal to the receiver or associated with the receiver As described above, a reference measurement is made when the transmission antenna and the reception antenna are put into place in the absence of the structure for which the shielding attenuation is to be determined, at a determined distance and orientation. Therefore steps E1 to E4 are performed for this first measurement. The memorised power is then a received reference power PR. It should be noted that this power depends on the distance between the transmission antenna and the reference antenna, the orien tation of the antennas and the power of the transmitted signal. Therefore, provided that these parameters are respec tively the same for several different shielding attenuation determinations, the same received reference power can be used later for these different shielding attenuation determi nations The transmission antenna and the reception antenna are then placed on each side of the structure for which the shielding attenuation is to be determined, at the same determined distance and orientation. A second mea Surement is made from the same transmission signal SE. Therefore steps E1 to E4 are performed for this second measurement. The result of step E4 is then a received signal power PR for a given frequency within the frequency band of the transmitted signal SE Step E5 determines the shielding attenuation for one or more frequencies in the frequency band between the frequencies F, and F The shielding attenuation is determined for a given frequency F. It is equal to the ratio between the power of the reference signal PR, and the power of the received signal PR during the second measurement, at the given frequency F. Note that the powers are expressed in Watts. Step E5 is described in detail below Any variations in the environmental noise between the two measurements are taken into account as follows. I0081 FIG. 5 represents the signal SE transmitted by the transmitter 10, as a function of time. The transmitted signal SE is a chopped white noise in the form of square wave with a cyclic ratio equal to /2. The cyclic ratio may be different. I0082. The transmitted power is alternatively in a high state E, corresponding to a transmission time and a low state E, in which the transmitted power is null, corre sponding to the transmission being cut off. I0083 FIGS. 6a and 6b represent the signal SR received by the receiver 12 as a function of time, during the reference measurement and during the second measurement respec tively In both cases, for the reference measurement and the second measurement, the received signal SR is also chopped in the form of square wave with a cyclic ratio equal to /2. The received power is alternatively in a high state corresponding to a transmission time and a low state in which the received power is low but not null, corresponding to the transmission being cut off. The power received in the low state corresponds to environmental noise and the power received in the high state corresponds to the sum of white noise received from the transmitter and environmental noise After the reference measurement, the difference between the power received in the high state RH, and the power received in the low state RB, is calculated, to cancel the contribution of ambient noise. I0086 Similarly, after the second measurement, the dif ference between the power received in the high state RH and the power received in the low state RB is calculated, once again to cancel the contribution of ambient noise. I0087. The module 122 uses double synchronous detec tion to measure the difference in power received between Successive phases with and without transmission, without knowing the instant of the phase change controlled by the transmitter 10. This avoids the influence of a possible phase
8 US 2017/ A1 Apr. 20, 2017 shift Acp between the received signal SR at the modulation frequency Fm and a demodulation signal The processing done on the signal V, output from the sliding filter 121 is considered. The signal V is applied to the input of the double synchronous detection module 122. The quantity AV is representative of the difference in received powers (RH-RB) corresponding to the emission of white noise with cyclic ratio / Compared with classical synchronous detection, the module 122 makes a first demodulation at the modula tion frequency Fm and a second demodulation at frequency (Fm+1/2). The quantities: 0.5 'AV' cos(ap) and 0.5'AV'cos(A(p+L/2)=0.5. AV sin(ap) are thus deter mined. These quantities are then squared and Summated. The module 122 then outputs the quantity (0.5AV) (cos' (A?p)+sin (A?p)). This quantity is equal to (0.5-AV). I0090 Thus, the output signal obtained is (0.5. AV). The output signal is independent of a possible phase shift between the modulation signal used for transmission and the demodulation signal used for reception This quantity is an image of AV in which AV is representative of the difference in received powers (RH RB) corresponding to the emission of white noise with cyclic ratio 96 at the modulation frequency Fm The shielding attenuation is determined for a given frequency F, by the module 123. It is equal to the ratio of the difference calculated for the reference measurement and the difference calculated for the second measurement: (RH,- RB)/(RH-RB). Note again that all powers are expressed herein in Watts Processing done on the signal received by the receiver 12 can be repeated for all frequencies within the frequency band varying from F to F The range of the measurement system is increased by the use of an automatic gain control so as to work at constant power at the input to the detection diode. 1. A system for measuring the attenuation of electromag netic shielding of an infrastructure as a function of the frequency, comprising: a transmitter of a white noise signal with a constant power over a frequency band between a minimum frequency and a maximum frequency; and a receiver of a signal, the transmitter and the receiver being capable of sending a signal and receiving a signal across the infrastructure, the receiver comprising: a filter module configured to apply a sliding filter on the received signal between the minimum frequency and the maximum frequency, and a double synchronous detection module configured to double synchronous detect on a signal output by the filter module. 2. The system for measuring the attenuation of electro magnetic shielding of an infrastructure according to claim 1, wherein: the transmitter is configured to transmit a signal that is chopped white noise comprising two alternating power levels, the receiver is capable of determining is configured to determine the difference between received powers cor responding to two power levels of the transmitted signal. 3. The system for measuring the attenuation of electro magnetic shielding of an infrastructure according to claim 1, wherein the receiver comprises a determination module configured to determine the shielding attenuation as a func tion of the results output by the double synchronous detec tion module determined following signal transmission and reception in the absence of the infrastructure and then on each side of the infrastructure. 4. A receiver for a system for measurement of the attenu ation of electromagnetic shielding of an infrastructure as a function of the frequency, comprising: circuitry configured to receive a signal transmitted by a transmitter of a white noise signal with constant power over a frequency band between a minimum frequency and a maximum frequency, the transmitter and the receiver being configured to transmit and receive a signal on opposite sides of the infrastructure; a filter module configured to apply a sliding filter on the received signal between the minimum frequency and the maximum frequency; and a double synchronous detection module configured to double synchronous detect on a signal output by the filter module. 5. The receiver according to claim 4, comprising a deter mination module configured to determine the shielding attenuation as a function of the results output by the double synchronous detection module determined following signal transmission and reception in the absence of the infrastruc ture and then on each side of the infrastructure. 6. A method for measuring the attenuation of electromag netic shielding of an infrastructure as a function of the frequency, comprising the following steps: transmitting a white noise signal with a constant power over a frequency band between a minimum frequency and a maximum frequency; receiving a signal, the signal transmission and reception taking place on opposite sides of the infrastructure; performing sliding filtering on the received signal between the minimum frequency and the maximum frequency; and performing synchronous double detection on a signal output by the filtering. 7. The method for measuring the attenuation of electro magnetic shielding of an infrastructure according to claim 6. further comprising preliminary steps of the transmitting and receiving of a signal in the absence of the infrastructure, and applying the sliding filter on the received signal and double synchronous detection on a signal output by the sliding filter step. 8. The method for measuring the attenuation of electro magnetic shielding of an infrastructure according to claim 7. further comprising a step of determining the shielding attenuation as a function of the results of the sliding filter and double synchronous detection steps performed follow ing signal transmission and reception in the absence of the infrastructure and then on each side of the infrastructure. 9. (canceled) 10. A non-transitory storage medium that can be read by a computer, in which a computer program is stored contain ing instructions for execution of the sliding filter and double synchronous detection steps in the method according to claim 6.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0139394A1 LEE et al. US 2014O139394A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ULTRA-WIDEBAND ANTENNA
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0139394A1 LEE et al. US 2014O139394A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ULTRA-WIDEBAND ANTENNA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O190276A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0190276A1 Taguchi (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR CCD SENSOR CONTROL, (30) Foreign Application
US 2005O190276A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0190276A1 Taguchi (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR CCD SENSOR CONTROL, (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7043221B2 (12) United States Patent Jovenin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 13, 2001
USOO7043221B2 (12) United States Patent Jovenin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 13, 2001
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701.24860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/012.4860 A1 SHH et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) OPTICAL TRANSMITTER AND METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. THEREOF
(19) United States US 201701.24860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/012.4860 A1 SHH et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) OPTICAL TRANSMITTER AND METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. THEREOF
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
USOO7123644B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) PEAK CANCELLATION APPARATUS OF BASE STATION TRANSMISSION UNIT (75) Inventors: Won-Hyoung Park,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0193375 A1 Lee US 2006O193375A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) TRANSCEIVER FOR ZIGBEE AND BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0193375 A1 Lee US 2006O193375A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 31, 2006 (54) TRANSCEIVER FOR ZIGBEE AND BLUETOOTH COMMUNICATIONS (76)
United States Patent (19) PeSola et al.
 United States Patent (19) PeSola et al. 54) ARRANGEMENT FORTRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING RADIO FREQUENCY SIGNAL AT TWO FREQUENCY BANDS 75 Inventors: Mikko Pesola, Marynummi; Kari T. Lehtinen, Salo, both of
United States Patent (19) PeSola et al. 54) ARRANGEMENT FORTRANSMITTING AND RECEIVING RADIO FREQUENCY SIGNAL AT TWO FREQUENCY BANDS 75 Inventors: Mikko Pesola, Marynummi; Kari T. Lehtinen, Salo, both of
(12) United States Patent
 USOO965 1411 B2 (12) United States Patent Yamaguchi et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,651.411 B2 May 16, 2017 (54) ELECTROMAGNETIC FLOWMETER AND SELF-DAGNOSING METHOD OF EXCITING CIRCUIT
USOO965 1411 B2 (12) United States Patent Yamaguchi et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,651.411 B2 May 16, 2017 (54) ELECTROMAGNETIC FLOWMETER AND SELF-DAGNOSING METHOD OF EXCITING CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 201400 12573A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0012573 A1 Hung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) SIGNAL PROCESSINGAPPARATUS HAVING
(19) United States US 201400 12573A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0012573 A1 Hung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) SIGNAL PROCESSINGAPPARATUS HAVING
Transmitting the map definition and the series of Overlays to
 (19) United States US 20100100325A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0100325 A1 LOVell et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) SITE MAP INTERFACE FORVEHICULAR APPLICATION (75)
(19) United States US 20100100325A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0100325 A1 LOVell et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 22, 2010 (54) SITE MAP INTERFACE FORVEHICULAR APPLICATION (75)
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,850,085 B2. Claessen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2010
 United States Patent US007850085B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,850,085 B2 Claessen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2010 (54) BARCODE SCANNER WITH MIRROR 2002/010O805 A1 8, 2002 Detwiler ANTENNA 2007/0063045
United States Patent US007850085B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,850,085 B2 Claessen (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 2010 (54) BARCODE SCANNER WITH MIRROR 2002/010O805 A1 8, 2002 Detwiler ANTENNA 2007/0063045
the sy (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 29, 2015 slope Zero-CIOSSing
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0028830 A1 CHEN US 2015 0028830A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) CURRENTMODE BUCK CONVERTER AND ELECTRONIC
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0028830 A1 CHEN US 2015 0028830A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) CURRENTMODE BUCK CONVERTER AND ELECTRONIC
United States Patent (19) Nonami
 United States Patent (19) Nonami 54 RADIO COMMUNICATION APPARATUS WITH STORED CODING/DECODING PROCEDURES 75 Inventor: Takayuki Nonami, Hyogo, Japan 73 Assignee: Mitsubishi Denki Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo,
United States Patent (19) Nonami 54 RADIO COMMUNICATION APPARATUS WITH STORED CODING/DECODING PROCEDURES 75 Inventor: Takayuki Nonami, Hyogo, Japan 73 Assignee: Mitsubishi Denki Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,438,377 B1
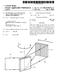
 USOO6438377B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Savolainen (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 : (54) HANDOVER IN A MOBILE 5,276,906 A 1/1994 Felix... 455/438 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM 5,303.289 A 4/1994
USOO6438377B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Savolainen (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 : (54) HANDOVER IN A MOBILE 5,276,906 A 1/1994 Felix... 455/438 COMMUNICATION SYSTEM 5,303.289 A 4/1994
Elastomeric Ferrite Ring
 (19) United States US 2011 0022336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0022336A1 Coates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SENSING PRESSURE USING AN
(19) United States US 2011 0022336A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0022336A1 Coates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2011 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR SENSING PRESSURE USING AN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 20040070460A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0070460 A1 Norton (43) Pub. Date: (54) MICROWAVE OSCILLATOR Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Philip
US 20040070460A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0070460 A1 Norton (43) Pub. Date: (54) MICROWAVE OSCILLATOR Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Philip
United States Patent (19) Levine
 United States Patent (19) Levine 54 FM TRANSMITTER WITH FREQUENCY RAMP PHASE AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION MEANS 75 Inventor: Arnold M. Levine, Chatsworth, Calif. 73 Assignee: International Telephone and Telegraph
United States Patent (19) Levine 54 FM TRANSMITTER WITH FREQUENCY RAMP PHASE AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION MEANS 75 Inventor: Arnold M. Levine, Chatsworth, Calif. 73 Assignee: International Telephone and Telegraph
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. Goeke (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2014
 US 201401 11188A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0111188 A1 Goeke (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2014 (54) ACTIVE SHUNTAMMETER APPARATUS (52) U.S. Cl. AND METHOD
US 201401 11188A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0111188 A1 Goeke (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 24, 2014 (54) ACTIVE SHUNTAMMETER APPARATUS (52) U.S. Cl. AND METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication
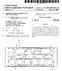 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Ryken et al. US 2003.0076261A1 (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0076261 A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIPURPOSE MICROSTRIPANTENNA FOR USE ON MISSILE (76) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Ryken et al. US 2003.0076261A1 (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0076261 A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) MULTIPURPOSE MICROSTRIPANTENNA FOR USE ON MISSILE (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
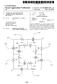
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kiiski USOO6356604B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2002 (54) RECEIVING METHOD, AND RECEIVER (75) Inventor: Matti Kiiski, Oulunsalo (FI) (73) Assignee: Nokia Telecommunications
(12) United States Patent Kiiski USOO6356604B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2002 (54) RECEIVING METHOD, AND RECEIVER (75) Inventor: Matti Kiiski, Oulunsalo (FI) (73) Assignee: Nokia Telecommunications
(12) United States Patent
 USOO69997.47B2 (12) United States Patent Su (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2006 (54) PASSIVE HARMONIC SWITCH MIXER (75) Inventor: Tung-Ming Su, Kao-Hsiung Hsien (TW) (73) Assignee: Realtek
USOO69997.47B2 (12) United States Patent Su (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 14, 2006 (54) PASSIVE HARMONIC SWITCH MIXER (75) Inventor: Tung-Ming Su, Kao-Hsiung Hsien (TW) (73) Assignee: Realtek
Soffen 52 U.S.C /99; 375/102; 375/11; 370/6, 455/295; 455/ /1992 Japan. 18 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets
 United States Patent (19) Mizoguchi 54 CROSS POLARIZATION INTERFERENCE CANCELLER 75 Inventor: Shoichi Mizoguchi, Tokyo, Japan 73) Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 980,662 (22 Filed: Nov.
United States Patent (19) Mizoguchi 54 CROSS POLARIZATION INTERFERENCE CANCELLER 75 Inventor: Shoichi Mizoguchi, Tokyo, Japan 73) Assignee: NEC Corporation, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 980,662 (22 Filed: Nov.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014.0035783A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0035783 A1 Contarino et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 6, 2014 (54) MULTI-BEAMANTENNA ARRAY FOR (52) U.S. Cl. PROTECTING
(19) United States US 2014.0035783A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0035783 A1 Contarino et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 6, 2014 (54) MULTI-BEAMANTENNA ARRAY FOR (52) U.S. Cl. PROTECTING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
(12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010O2O8236A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0208236A1 Damink et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE POSITION OF AN OBJECT
(19) United States US 2010O2O8236A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0208236A1 Damink et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) METHOD FOR DETERMINING THE POSITION OF AN OBJECT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150318920A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0318920 A1 Johnston (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) DISTRIBUTEDACOUSTICSENSING USING (52) U.S. Cl. LOWPULSE
(19) United States US 20150318920A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0318920 A1 Johnston (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) DISTRIBUTEDACOUSTICSENSING USING (52) U.S. Cl. LOWPULSE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0167538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0167538 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2016 (54) METHOD AND CHARGING SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016.0167538A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0167538 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2016 (54) METHOD AND CHARGING SYSTEM FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
title (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: May 9, 2013 Azadet et al.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0114762 A1 Azadet et al. US 2013 O114762A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 9, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) RECURSIVE DIGITAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0114762 A1 Azadet et al. US 2013 O114762A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 9, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) RECURSIVE DIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1. (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 2, 2000 (JP)...
 (19) United States US 200200152O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0015202 A1 Michishita et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2002 (54) WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXING OPTICAL TRANSMISSION
(19) United States US 200200152O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0015202 A1 Michishita et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2002 (54) WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXING OPTICAL TRANSMISSION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Kohayakawa 54) OCULAR LENS MEASURINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventor: Yoshimi Kohayakawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 544,486 (22 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Kohayakawa 54) OCULAR LENS MEASURINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventor: Yoshimi Kohayakawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 544,486 (22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 2015O145528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0145528A1 YEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) PASSIVE INTERMODULATION Publication Classification
US 2015O145528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0145528A1 YEO et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 28, 2015 (54) PASSIVE INTERMODULATION Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003O185410A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0185410 A1 June et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2003 (54) ORTHOGONAL CIRCULAR MICROPHONE ARRAY SYSTEM AND METHOD
(19) United States US 2003O185410A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0185410 A1 June et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 2, 2003 (54) ORTHOGONAL CIRCULAR MICROPHONE ARRAY SYSTEM AND METHOD
(12) United States Patent
 US009355808B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) NECTION LOCKED MAGNETRON MCROWAVE GENERATOR WITH RECYCLE OF SPURIOUS ENERGY Applicant: Sichuan
US009355808B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) NECTION LOCKED MAGNETRON MCROWAVE GENERATOR WITH RECYCLE OF SPURIOUS ENERGY Applicant: Sichuan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. Li (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016
 (19) United States US 2016031 6375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0316375 A1 Li (43) Pub. Date: (54) NETWORK CONTROLLER, STATION, AND H04B 7/06 (2006.01) METHOD FORESTABLISHING
(19) United States US 2016031 6375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0316375 A1 Li (43) Pub. Date: (54) NETWORK CONTROLLER, STATION, AND H04B 7/06 (2006.01) METHOD FORESTABLISHING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040070347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0070347 A1 Nishida et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2004 (54) PLASMAGENERATING APPARATUS USING MICROWAVE (76)
(19) United States US 20040070347A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0070347 A1 Nishida et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 15, 2004 (54) PLASMAGENERATING APPARATUS USING MICROWAVE (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,227,109 B2
 US007227109B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,227,109 B2 Eke (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007 (54) MICROWAVE OVENS (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Kenneth Ian Eke, Franklin, TN (US)
US007227109B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,227,109 B2 Eke (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 5, 2007 (54) MICROWAVE OVENS (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Kenneth Ian Eke, Franklin, TN (US)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0054723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0054723 A1 NISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) ROBOT CONTROLLER OF ROBOT USED (52) U.S. Cl. WITH MACHINE TOOL, AND
(19) United States US 2016.0054723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0054723 A1 NISH (43) Pub. Date: (54) ROBOT CONTROLLER OF ROBOT USED (52) U.S. Cl. WITH MACHINE TOOL, AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) McKinney et al. (11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 1990 54 CHANNEL FREQUENCY GENERATOR FOR USE WITH A MULTI-FREQUENCY OUTP GENERATOR - (75) Inventors: Larry S. McKinney,
United States Patent (19) McKinney et al. (11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: Oct. 23, 1990 54 CHANNEL FREQUENCY GENERATOR FOR USE WITH A MULTI-FREQUENCY OUTP GENERATOR - (75) Inventors: Larry S. McKinney,
(71) Applicant: :VINKELMANN (UK) LTD., West (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20140342673A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0342673 A1 Edmans (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 20, 2014 (54) METHODS OF AND SYSTEMS FOR (52) US. Cl. LOGGING AND/OR
US 20140342673A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. N0.: US 2014/0342673 A1 Edmans (43) Pub. Date: NOV. 20, 2014 (54) METHODS OF AND SYSTEMS FOR (52) US. Cl. LOGGING AND/OR
REPEATER I. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. REPEATER is. A v. (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20140370888A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0370888 A1 Kunimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, LOCATION REGISTRATION METHOD, REPEATER,
(19) United States US 20140370888A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0370888 A1 Kunimoto (43) Pub. Date: (54) RADIO COMMUNICATION SYSTEM, LOCATION REGISTRATION METHOD, REPEATER,
United States Patent (19) Minowa
 United States Patent (19) Minowa 54 ANALOG DISPLAY ELECTRONIC STOPWATCH (75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Yoshiki Minowa, Suwa, Japan Kubushiki Kaisha Suwa Seikosha, Tokyo, Japan 21) Appl. No.: 30,963 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Minowa 54 ANALOG DISPLAY ELECTRONIC STOPWATCH (75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Yoshiki Minowa, Suwa, Japan Kubushiki Kaisha Suwa Seikosha, Tokyo, Japan 21) Appl. No.: 30,963 22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,639,203 B2
 USOO7639203B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7,639,203 B2 HaO (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 29, 2009 (54) SPIRAL COIL LOADED SHORT WIRE (52) U.S. Cl.... 343/895; 343/719; 343/745 ANTENNA (58)
USOO7639203B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7,639,203 B2 HaO (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 29, 2009 (54) SPIRAL COIL LOADED SHORT WIRE (52) U.S. Cl.... 343/895; 343/719; 343/745 ANTENNA (58)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030095174A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0095174A1 Terasaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2003 (54) PRINTER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20030095174A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0095174A1 Terasaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2003 (54) PRINTER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070109547A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0109547 A1 Jungwirth (43) Pub. Date: (54) SCANNING, SELF-REFERENCING (22) Filed: Nov. 15, 2005 INTERFEROMETER
US 20070109547A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0109547 A1 Jungwirth (43) Pub. Date: (54) SCANNING, SELF-REFERENCING (22) Filed: Nov. 15, 2005 INTERFEROMETER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007.0024399A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0024399 A1 Martin Antolin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 1, 2007 (54) FILTERS AND ANTENNAS FOR MICROWAVES AND
(19) United States US 2007.0024399A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0024399 A1 Martin Antolin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 1, 2007 (54) FILTERS AND ANTENNAS FOR MICROWAVES AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
FDD Uplink 2 TDD 2 VFDD Downlink
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0094409 A1 Li et al. US 2013 0094409A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING CARRIER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0094409 A1 Li et al. US 2013 0094409A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR OBTAINING CARRIER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030042949A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0042949 A1 Si (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2003 (54) CURRENT-STEERING CHARGE PUMP Related U.S. Application Data
US 20030042949A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0042949 A1 Si (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 6, 2003 (54) CURRENT-STEERING CHARGE PUMP Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
\ POWER l United States Patent (19) Moreira 4,994,811. Feb. 19, 1991 (ALUATING. 11) Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Moreira 11) Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 54 SENSITIVITY TIME CONTROL DEVICE 75) Inventor: Joao Moreira, Landsberg, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Deutsche Forschungsanstalt
United States Patent (19) Moreira 11) Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: 54 SENSITIVITY TIME CONTROL DEVICE 75) Inventor: Joao Moreira, Landsberg, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Deutsche Forschungsanstalt
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. ROZen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 6, 2006
 (19) United States US 20060072253A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0072253 A1 ROZen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 6, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR HIGH (57) ABSTRACT SPEED
(19) United States US 20060072253A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0072253 A1 ROZen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 6, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR HIGH (57) ABSTRACT SPEED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,555,242 Saitou 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 1996
 IIII USOO5555242A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Saitou 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 1996 54 SUBSTATION APPARATUS FOR SATELLITE 5,216,427 6/1993 Yan et al.... 370/85.2 COMMUNICATIONS 5,257,257
IIII USOO5555242A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Saitou 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 1996 54 SUBSTATION APPARATUS FOR SATELLITE 5,216,427 6/1993 Yan et al.... 370/85.2 COMMUNICATIONS 5,257,257
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. KO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 28, 2010
 (19) United States US 20100271151A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0271151 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 28, 2010 (54) COMPACT RC NOTCH FILTER FOR (21) Appl. No.: 12/430,785 QUADRATURE
(19) United States US 20100271151A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0271151 A1 KO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 28, 2010 (54) COMPACT RC NOTCH FILTER FOR (21) Appl. No.: 12/430,785 QUADRATURE
Foreign Application Priority Data
 US 20140298879A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0298879 A1 JARVI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2014 (54) CRIMPING MACHINE SYSTEM (52) US. Cl. ' CPC.....
US 20140298879A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0298879 A1 JARVI et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2014 (54) CRIMPING MACHINE SYSTEM (52) US. Cl. ' CPC.....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115605 A1 Dimig et al. US 2011 0115605A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ENERGY HARVESTING SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0115605 A1 Dimig et al. US 2011 0115605A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2011 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) ENERGY HARVESTING SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060270.380A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0270380 A1 Matsushima et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.30, 2006 (54) LOW NOISE AMPLIFICATION CIRCUIT (30) Foreign
(19) United States US 20060270.380A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0270380 A1 Matsushima et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.30, 2006 (54) LOW NOISE AMPLIFICATION CIRCUIT (30) Foreign
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 OO14910A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0014910 A1 YONGE, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2011 (54) CHANNEL REUSE IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (75)
(19) United States US 2011 OO14910A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0014910 A1 YONGE, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2011 (54) CHANNEL REUSE IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O108129A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0108129 A1 Voglewede et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL FOR (21) Appl. No.: 10/012,530 DIGITAL
US 2003O108129A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0108129 A1 Voglewede et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC GAIN CONTROL FOR (21) Appl. No.: 10/012,530 DIGITAL
(10) Patent No.: US 6,295,461 B1
 (12) United States Patent Palmer et al. USOO629.5461B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep., 2001 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) MULTI-MODE RADIO FREQUENCY NETWORKSYSTEM Inventors: Brian
(12) United States Patent Palmer et al. USOO629.5461B1 (10) Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep., 2001 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) MULTI-MODE RADIO FREQUENCY NETWORKSYSTEM Inventors: Brian
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 201203281.29A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0328129 A1 Schuurmans (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) CONTROL OF AMICROPHONE Publication Classification
US 201203281.29A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0328129 A1 Schuurmans (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) CONTROL OF AMICROPHONE Publication Classification
16-?t R.S. S. Y \
 US 20170 155182A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0155182 A1 Rijssemus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2017 (54) CABLE TAP Publication Classification - - -
US 20170 155182A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0155182 A1 Rijssemus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 1, 2017 (54) CABLE TAP Publication Classification - - -
YARIABLE YEASEf 55. United States Patent (19) 4,743, INPUT OUTPUT, 54 al. Shilling et al. May 10, 1988
 United States Patent (19) Shilling et al. 11 Patent Number: (45. Date of Patent: 4,743,777 May 10, 1988 54 STARTER GENERATOR SYSTEM WITH TWO STATOR EXCITER WINDINGS (75 Inventors: William J. Shilling,
United States Patent (19) Shilling et al. 11 Patent Number: (45. Date of Patent: 4,743,777 May 10, 1988 54 STARTER GENERATOR SYSTEM WITH TWO STATOR EXCITER WINDINGS (75 Inventors: William J. Shilling,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Tang USOO647.6671B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) PING-PONG AMPLIFIER WITH AUTO ZERONG AND CHOPPING (75) Inventor: Andrew T. K. Tang, San Jose, CA (US)
(12) United States Patent Tang USOO647.6671B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 5, 2002 (54) PING-PONG AMPLIFIER WITH AUTO ZERONG AND CHOPPING (75) Inventor: Andrew T. K. Tang, San Jose, CA (US)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Kowalewski (54) RADIO FREQUENCY SWITCH EMPLOYING REED SWITCHES AND A QUARTER WAVE LINE 75) inventor: Rolf E. Kowalewski, Palatine, Ill. (73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Franklin
United States Patent (19) Kowalewski (54) RADIO FREQUENCY SWITCH EMPLOYING REED SWITCHES AND A QUARTER WAVE LINE 75) inventor: Rolf E. Kowalewski, Palatine, Ill. (73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Franklin
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1 Huang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 US 20020118726A1 19) United States 12) Patent Application Publication 10) Pub. No.: Huang et al. 43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2002 54) SYSTEM AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE FOR PROVIDING A SPREAD SPECTRUM SIGNAL 75)
US 20020118726A1 19) United States 12) Patent Application Publication 10) Pub. No.: Huang et al. 43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2002 54) SYSTEM AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE FOR PROVIDING A SPREAD SPECTRUM SIGNAL 75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070047712A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0047712 A1 Gross et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) SCALABLE, DISTRIBUTED ARCHITECTURE FOR FULLY CONNECTED
(19) United States US 20070047712A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0047712 A1 Gross et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) SCALABLE, DISTRIBUTED ARCHITECTURE FOR FULLY CONNECTED
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,116,081 B2. Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006
 United States Patent USOO7116081 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) THERMAL PROTECTION SCHEME FOR 5,497,071 A * 3/1996 Iwatani et al.... 322/28 HIGH OUTPUT VEHICLE ALTERNATOR
United States Patent USOO7116081 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) THERMAL PROTECTION SCHEME FOR 5,497,071 A * 3/1996 Iwatani et al.... 322/28 HIGH OUTPUT VEHICLE ALTERNATOR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Cheah (54) LOW COST KU BANDTRANSMITTER 75 Inventor: Jonathon Cheah, La Jolla, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hughes Aircraft Company, Los Angeles, Calif. (21) Appl. No.: 692,883 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Cheah (54) LOW COST KU BANDTRANSMITTER 75 Inventor: Jonathon Cheah, La Jolla, Calif. 73 Assignee: Hughes Aircraft Company, Los Angeles, Calif. (21) Appl. No.: 692,883 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0035840 A1 Fenton et al. US 2001 0035.840A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (63) PRECISE POSITONING SYSTEM FOR MOBILE GPS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0035840 A1 Fenton et al. US 2001 0035.840A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (63) PRECISE POSITONING SYSTEM FOR MOBILE GPS
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,477,226 Hager et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 19, 1995
 III IIHIIII US005477226A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,477,226 Hager et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 19, 1995 (54) LOW COST RADAR ALTIMETER WITH 5,160,933 11/1992 Hager... 342/174 ACCURACY
III IIHIIII US005477226A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,477,226 Hager et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 19, 1995 (54) LOW COST RADAR ALTIMETER WITH 5,160,933 11/1992 Hager... 342/174 ACCURACY
IIIH. United States Patent (19) Nakamura. 5,375,336 Dec. 27, (11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: (54) GYRO-COMPASS 75 Inventor:
 United States Patent (19) Nakamura (54) GYR-CMPASS 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Takeshi Nakamura, Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Nagaokakyo, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 53,659 22 Filed: Apr. 29,
United States Patent (19) Nakamura (54) GYR-CMPASS 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Takeshi Nakamura, Nagaokakyo, Japan Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Nagaokakyo, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 53,659 22 Filed: Apr. 29,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070214484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0214484 A1 Taylor et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2007 (54) DIGITAL VIDEO BROADCAST TRANSITION METHOD AND
(19) United States US 20070214484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0214484 A1 Taylor et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2007 (54) DIGITAL VIDEO BROADCAST TRANSITION METHOD AND
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,275,104 B1
 USOO6275104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Holter (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIER WITH LOCAL 4,816,711 3/1989 Roza... 330/149 ERROR CORRECTION 5,030.925 7/1991
USOO6275104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Holter (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 14, 2001 (54) MULTISTAGE AMPLIFIER WITH LOCAL 4,816,711 3/1989 Roza... 330/149 ERROR CORRECTION 5,030.925 7/1991
United States Patent (19) Theriault
 United States Patent (19) Theriault 54 DIPLEXER FOR TELEVISION TUNING SYSTEMS 75) Inventor: Gerald E. Theriault, Hopewell, N.J. 73) Assignee: RCA Corporation, New York, N.Y. 21) Appi. No.: 294,131 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Theriault 54 DIPLEXER FOR TELEVISION TUNING SYSTEMS 75) Inventor: Gerald E. Theriault, Hopewell, N.J. 73) Assignee: RCA Corporation, New York, N.Y. 21) Appi. No.: 294,131 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130256528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0256528A1 XIAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 3, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (57) ABSTRACT DETECTING BURED
(19) United States US 20130256528A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0256528A1 XIAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 3, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (57) ABSTRACT DETECTING BURED
58 Field of Search /341,484, structed from polarization splitters in series with half-wave
 USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United S tates US 20020003503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0003503 A1 Justice (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 10, 2002 (54) TWIN COILA NTENNA (76) Inventor: Christopher M. Justice,
(19) United S tates US 20020003503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0003503 A1 Justice (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 10, 2002 (54) TWIN COILA NTENNA (76) Inventor: Christopher M. Justice,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9577348B2 (10) Patent No.: Gomme et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 2017 (54) COMBINATION ANTENNA USPC... 343/718, 702 (71) 1 dh (NL) 71) Applicant: NXP B.V., Eindhoven
(12) United States Patent USOO9577348B2 (10) Patent No.: Gomme et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 21, 2017 (54) COMBINATION ANTENNA USPC... 343/718, 702 (71) 1 dh (NL) 71) Applicant: NXP B.V., Eindhoven
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Querry et al. (54) (75) PHASE LOCKED LOOP WITH AUTOMATIC SWEEP Inventors: 73) Assignee: 21) (22 (51) (52) 58 56) Lester R. Querry, Laurel; Ajay Parikh, Gaithersburg, both of Md.
United States Patent (19) Querry et al. (54) (75) PHASE LOCKED LOOP WITH AUTOMATIC SWEEP Inventors: 73) Assignee: 21) (22 (51) (52) 58 56) Lester R. Querry, Laurel; Ajay Parikh, Gaithersburg, both of Md.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9206864B2 (12) United States Patent Krusinski et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.206,864 B2 Dec. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) TORQUE CONVERTERLUG
USOO9206864B2 (12) United States Patent Krusinski et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.206,864 B2 Dec. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) TORQUE CONVERTERLUG
( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub. No. : US 2017 / A1 ( 52 ) U. S. CI. CPC... HO2P 9 / 48 ( 2013.
 THE MAIN TEA ETA AITOA MA EI TA HA US 20170317630A1 ( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub No : US 2017 / 0317630 A1 Said et al ( 43 ) Pub Date : Nov 2, 2017 ( 54 ) PMG BASED
THE MAIN TEA ETA AITOA MA EI TA HA US 20170317630A1 ( 19 ) United States ( 12 ) Patent Application Publication ( 10 ) Pub No : US 2017 / 0317630 A1 Said et al ( 43 ) Pub Date : Nov 2, 2017 ( 54 ) PMG BASED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160255572A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0255572 A1 Kaba (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) ONBOARDAVIONIC SYSTEM FOR COMMUNICATION BETWEEN AN AIRCRAFT
(19) United States US 20160255572A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0255572 A1 Kaba (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 1, 2016 (54) ONBOARDAVIONIC SYSTEM FOR COMMUNICATION BETWEEN AN AIRCRAFT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015033O851A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0330851 A1 Belligere et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADAPTIVE WIRELESS TORQUE (52) U.S. Cl. MEASUREMENT SYSTEMAND
(19) United States US 2015033O851A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0330851 A1 Belligere et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ADAPTIVE WIRELESS TORQUE (52) U.S. Cl. MEASUREMENT SYSTEMAND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0081252 A1 Markgraf et al. US 2013 0081252A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) ARRANGEMENT FOR FIXINGA COMPONENT INSIDE OF
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0081252 A1 Markgraf et al. US 2013 0081252A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) ARRANGEMENT FOR FIXINGA COMPONENT INSIDE OF
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Honda (54 FISH FINDER CAPABLE OF DISCRIMINATING SIZES OF FISH 76) Inventor: Keisuke Honda, 37, Shingashi-cho, Toyohashi, Aichi, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 725,392 (22 Filed: Sep. 22,
United States Patent (19) Honda (54 FISH FINDER CAPABLE OF DISCRIMINATING SIZES OF FISH 76) Inventor: Keisuke Honda, 37, Shingashi-cho, Toyohashi, Aichi, Japan 21 Appl. No.: 725,392 (22 Filed: Sep. 22,
