ACTUATED HYBRID MIRROR TECHNOLOGY LARGE OPTICS WORKING GROUP (LOWG)
|
|
|
- Jeremy Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ACTUATED HYBRID MIRROR TECHNOLOGY LARGE OPTICS WORKING GROUP (LOWG) From: Howard A. MacEwen ManTech SRS Technologies, Inc. Chantilly, VA I INTRODUCTION Developments over the past five to ten years have led to the successful demonstration of the technologies needed for Actuated Hybrid Mirrors (AHMs), providing a new option to conventional glass primary mirror assemblies (PMAs) for space telescopes 1. In its current form, as illustrated in Figure 1, the AHM consists of the following elements: A rib-stiffened silicon carbide (SiC) substrate, cast to near net shape and generated to the required optical figure. A metallic nanolaminate facesheet deposited on a precision mandrel and adhesively bonded to the surface of the substrate to provide the optical finish of the mirror. Surface parallel actuators (SPAs) embedded in the substrate ribs and used to actively control the final figure of the mirror. A sensing system (typically, but not necessarily, a wavefront sensor) to determine the real time figure of the mirror and provide the control inputs needed by the actuation system. Figure 1: Actuated Hybrid Mirror Concept 1 Although AHMs have been developed for space applications purposes, they should also be considered for ground telescopes. 1
2 Because of the need for a precision deposition mandrel 2 for production of the nanolaminate facesheet, this technology is generally most suited to two classes of applications, both of which require the fabrication of multiple mirrors or mirror segments that have identical (or nearly identical) prescriptions: Very large space telescope PMAs that must be formed through the deployment of multiple segments due to launch vehicle size limitations. Examples of telescope concepts that could benefit from this capability include the Single Aperture Far Infrared (SAFIR) telescope and the Advanced Technology Large-Aperture Space Telescope (ATLAST) Architectures that consist of a number of smaller telescopes (i.e., within the volumetric capability of an existing launch vehicle) that can employ nearly identical monolithic PMAs for multiple different science applications or that are proliferated for survey or time sensitive applications. For example, AHM technology could enable fabrication of multiple telescopes for an external occulter exoplanet detection system, increasing the efficiency of both exoplanet detection and general astronomical observations, as well as serving as the basis for a Joint Dark Energy Mission (JDEM). These two cases do not exhaust the utility range of the AHM, however. Because it enables both rapid mirror replication once program tooling is in place as well as real time control of mirror figures in operating systems, AHM technology can also provide economic benefits, including: An ability to relax manufacturing constraints on space telescope primary mirrors since they can be controlled to the higher precision required for a mission once placed into operation. A manufacturing capability to rapidly produce duplicate PMAs to rapidly respond to changing circumstances, such as: o Replacement for a lost or failed vehicle. o Supplement an initially small architecture with additional vehicles, either in accordance with a planned strategy or to realize unexpected opportunities. o Enable flight demonstrations that can, upon success, be expanded into a more extensive operational architecture Of course, as with any technology, the AHM has its own set of limitations. These include: Although the initial impetus for the development of the AHM was to produce lightweight mirrors, the technology of conventional passive mirrors (particularly in glass) has also advanced, and the two technologies are currently quite competitive, both being able to achieve areal densities in the same approximate range (10 15 kg/m 2 ). 2 Necessarily convex for a primary mirror, and therefore generally more difficult and costly to fabricate (and measure) than a single conventional passive primary mirror. 2
3 The AHM requires the added complexity of a sensing and control system. 3 Space qualification of the technology and mirror system. AHM technology will require significant development before it can be considered for cryogenic applications, specifically due to the critical role played by the adhesive bond between the nanolaminate facesheet and the SiC substrate. II CURRENT STATE OF THE ART The AHM was first developed early in the current century by a merger of two technologies: the actuated Integrated Meniscus Mirror (1) and magnetron sputtering of thick, metallic nanolaminate optical facesheets (2). This development occurred through collaboration between Lawrence Livermore National Laboratories (the nanolaminates), and Xinetics, Inc., a private corporation (the meniscus mirrors), and is graphically illustrated in Figure 2. Figure 2. Demonstration of the AHM Concept Over the past several years, these Actuated Hybrid Mirrors have evolved through a range of sizes, establishing the ability to scale their manufacture up to the 1.5 meter diameter class. In addition, the infrastructure that has been assembled will enable further scale-up to mirrors with dimensions greater than 2 meters as the need arises. AHMs have been fabricated as flat, spherical, and aspherical (both on- and off-axis) mirrors and mirror segments. The substrate employed has been reaction bonded silicon carbide fabricated by what is now Northrop Grumman Xinetics (NGX) in Devens, Massachusetts, although other substrate materials have been considered (see below). The nanolaminate facesheets have been deposited with alternating layers of zirconium and zirconiumcopper (Zr/ZrCu) by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Livermore, California 4. Actuation is accomplished using standard NGX lead magnesium niobate (PMN) electrostrictive actuators, and adhesion is provided by an NGX proprietary epoxy. 3 Note that these sensing and control systems are included in the areal density claimed for the AHM in the preceding sub-paragraph. 4 For production purposes, the capability to deposit these nanolaminates has recently been installed at NGX as well. 3
4 Next Steps. The Naval Postgraduate School (NPS) will soon install a large AHM for further experimentation (e.g., for wavefront sensing and control systems). In addition to this technology testbed, the most important next step to enabling future applications of AHM technology is to demonstrate fabrication at carefully judged larger scales up to the full capacity of the existing infrastructure. Following the conservative methodology of earlier AHM programs, this should include mirrors fabricated in on-axis and off-axis, spherical and aspherical configurations. To this end, designs have been already been developed for mirrors at apertures up to 1.5 meters, and some tooling has been acquired to enable near term fabrication. In addition, the materials and processes required for manufacture of AHMs are currently passing through a rigorous space qualification process to ensure that their survival and operational capabilities in all phases of spaceflight have been demonstrated to the level required. III AHM TECHNOLOGY PROJECTIONS Finally, several technology development programs are being conducted to refine and enhance the foundational AHM technologies, extending and simplifying their applications to future operational programs. These include the development of different materials for AHM components, enhanced actuation, better sensing and control technologies, and more flexible manufacturing techniques. The following paragraphs provide examples of each of these development areas. 1. New Materials. With few exceptions, AHMs fabricated to date have all been based upon substrates cast from silicon carbide, a material with a low but non-zero coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) that complicates mirror design and thermal control. For this reason (and potentially to expedite low-cost fabrication of AHMs while further reducing their areal densities), development of AHMs utilizing Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP) 5 substrates is now underway (and accounts for the few exceptions noted in the preceding sentence). Pathfinder mirrors with 45 cm diameters have been fabricated, and the future direction of this program will depend upon the success in fabricating an optical quality CFRP AHM with an aperture of 75 cm. This part of the program is scheduled to be completed in the late summer to early autumn of Enhanced Actuation. In the simplest version of an AHM, the only actuators are those embedded in the vertical ribs on the back of the substrate. These actuators impart a moment to the ribs, thus altering the curvature of the mirror at relatively low spatial frequencies. This low frequency correction induces surface errors at higher spatial frequencies that (depending upon their magnitudes) limit the ability to control the low frequency surface figure. To counter this effect, smaller actuators are being developed to be embedded in intimate contact with the back side of the substrate facesheet (i.e., in the triangular spaces between the ribs, visible in Figure 2 above). These actuators (currently designated as Compound Actuators), which can be either Surface Parallel Actuators (SPAs) or Surface Normal Actuators (SNAs), being smaller than the SPAs in the ribs proper, can be used to control higher frequency surface errors. The effectiveness and 5 More specifically, Graphite Epoxy (GrEp) composites. 4
5 range of applicability of Compound Actuators is currently the subject of simulation and experimental development programs scheduled to extend at least into the winter of Flexible Manufacturing. Experience with AHMs has established quite firmly that one of the most difficult elements (perhaps the most challenging element) of an AHM program is fabrication of the mandrel to be used for nanolaminate deposition. The mandrel must be convex, larger than the mirror (or segment) to be fabricated, precisely characterized, and must possess a surface finish of higher quality than that required of the final mirror itself. These facts imply that fabrication of the mandrel (including metrology) is the basic long lead item of an AHM program, and will generally be more costly and demanding than conventional fabrication of a single glass mirror to the same specifications as required of the AHM. From this results the statement in the Introduction to the effect that AHM technology is generally applicable only to programs that require multiple mirrors or segments built to nearly identical prescriptions. It has been noted that this issue could be alleviated to some degree by at least two technical advances currently under development: An inexpensive, flexible metrology system for the accurate and repeatable characterization of convex optical surfaces. A four point stitching profilometry 6 technology has been developed by Bauer Associates of Natick, Massachusetts, and a program is currently underway to validate this technology and determine its limits of applicability (e.g., precision, maximum radius of curvature and size of the test item, etc.). Direct application of the foundational actuated mirror 7 technology to fabrication of the mandrel itself. That is, using the same technology as employed to fabricate and actuate the SiC substrates for AHMs, it may be possible to fabricate a convex mandrel to a general prescription, polish it to the required optical quality, and then actuate it to any of a number of prescriptions required for deposition of a family of AHM nanolaminate facesheets. While such a mandrel would face more serious difficulties than those faced by a mirror substrate (the mandrel must rotate at high speed, endure high and variable temperatures in a deposition chamber, etc.), the potential payoff is sufficient to support a current investigation expected to yield a general indication of the concept s basic feasibility by the autumn of IV CONCLUSION The Actuated Hybrid Mirror architecture offers a potential for a new approach to the design, development, and manufacture of space telescopes, both large and small. Combined with imaginative deployment technologies, it may enable the construction and launch of very large space telescopes with multiple segment primary mirrors. In addition, it can also enable space telescope architectures that consist of a series of smaller, single monolithic segment telescopes, none capable of the scientific productivity of 6 Which is applicable to concave as well as convex surfaces. 7 Not the complete AHM technology, since no nanolaminate facesheet would be incorporated. 5
6 Observatories such as Hubble, Spitzer, or the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), but which as a whole could contribute a capability to survey broad regions of space, monitor time dependent phenomena, and react to unexpected events providing vital new insights into astronomy (and, quite possibly, new questions). 6
7 REFERENCES (1) Ealey, Mark A., Large Optics in the 21 st Century: A Transition from Discrete Manufacturing to Highly Integrated Techniques, Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Aerospace Conference (Big Sky, Montana), IEEE, March (2) Barbee, Troy W., Jr., Nano-Laminates: A New Class of Materials for Aerospace Applications, Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Aerospace Conference (Big Sky, Montana), IEEE, March
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Optics Quality Assessment for Lightweight Deployable Optics
 Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Optics Quality Assessment for Lightweight Deployable Optics Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Ty Martinez 1, Sergio R. Restaino 1, Freddie Santiago 1, Christopher C. Wilcox
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Optics Quality Assessment for Lightweight Deployable Optics Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Ty Martinez 1, Sergio R. Restaino 1, Freddie Santiago 1, Christopher C. Wilcox
Glass Membrane Mirrors beyond NGST
 Glass Membrane Mirrors beyond NGST J.H. Burge, J. R. P. Angel, B. Cuerden, N. J Woolf Steward Observatory, University of Arizona Much of the technology and hardware are in place for manufacturing the primary
Glass Membrane Mirrors beyond NGST J.H. Burge, J. R. P. Angel, B. Cuerden, N. J Woolf Steward Observatory, University of Arizona Much of the technology and hardware are in place for manufacturing the primary
FABRICATION OF MIRROR SEGMENTS for the GSMT
 FABRICATION OF MIRROR SEGMENTS for the GSMT Segment Fabrication Workshop May 30, 2002 The USA Decadal Review In May 2000, the US astronomy decadal review committee recommended the construction of a 30-meter
FABRICATION OF MIRROR SEGMENTS for the GSMT Segment Fabrication Workshop May 30, 2002 The USA Decadal Review In May 2000, the US astronomy decadal review committee recommended the construction of a 30-meter
Design and Manufacture of 8.4 m Primary Mirror Segments and Supports for the GMT
 Design and Manufacture of 8.4 m Primary Mirror Segments and Supports for the GMT Introduction The primary mirror for the Giant Magellan telescope is made up an 8.4 meter symmetric central segment surrounded
Design and Manufacture of 8.4 m Primary Mirror Segments and Supports for the GMT Introduction The primary mirror for the Giant Magellan telescope is made up an 8.4 meter symmetric central segment surrounded
Technology Days GSFC Optics Technologies. Dr. Petar Arsenovic
 Technology Days 2011 GSFC Optics Technologies Dr. Petar Arsenovic Optics Capabilities Optical Design and Analysis Opto-mechanical Design and Fabrication Materials and Thin Films Component Development and
Technology Days 2011 GSFC Optics Technologies Dr. Petar Arsenovic Optics Capabilities Optical Design and Analysis Opto-mechanical Design and Fabrication Materials and Thin Films Component Development and
Large Aperture Telescope Technology: a design for an active lightweight multi-segmented fold-out space mirror
 Large Aperture Telescope Technology: a design for an active lightweight multi-segmented fold-out space mirror Presenter: Samantha Thompson, University College London UK LATT Team Martin Whalley Ruben Edeson
Large Aperture Telescope Technology: a design for an active lightweight multi-segmented fold-out space mirror Presenter: Samantha Thompson, University College London UK LATT Team Martin Whalley Ruben Edeson
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Adaptive X-ray Optics Development at AOA-Xinetics Charles F. Lillie* a, Jeffrey L. Cavaco b, Audrey D. Brooks b, Kevin Ezzo b, David D. Pearson c, John A. Wellman d a Lillie Consulting LLC, 6202 Vista
Adaptive X-ray Optics Development at AOA-Xinetics Charles F. Lillie* a, Jeffrey L. Cavaco b, Audrey D. Brooks b, Kevin Ezzo b, David D. Pearson c, John A. Wellman d a Lillie Consulting LLC, 6202 Vista
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes
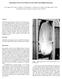 Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
Lightweight mirror technology using a thin facesheet with active rigid support
 Lightweight mirror technology using a thin facesheet with active rigid support J. H. Burge, J. R. P. Angel, B. Cuerden, H. M. Martin, S. M. Miller, D. G. Sandler ABSTRACT The next generation of space telescopes
Lightweight mirror technology using a thin facesheet with active rigid support J. H. Burge, J. R. P. Angel, B. Cuerden, H. M. Martin, S. M. Miller, D. G. Sandler ABSTRACT The next generation of space telescopes
Manufacturing Process of the Hubble Space Telescope s Primary Mirror
 Kirkwood 1 Manufacturing Process of the Hubble Space Telescope s Primary Mirror Chase Kirkwood EME 050 Winter 2017 03/11/2017 Kirkwood 2 Abstract- The primary mirror of the Hubble Space Telescope was a
Kirkwood 1 Manufacturing Process of the Hubble Space Telescope s Primary Mirror Chase Kirkwood EME 050 Winter 2017 03/11/2017 Kirkwood 2 Abstract- The primary mirror of the Hubble Space Telescope was a
Shape Adaptive Grinding of CVD Silicon Carbide on Graphite. for X-Ray Mirror Molding Dies
 Shape Adaptive Grinding of CVD Silicon Carbide on Graphite for X-Ray Mirror Molding Dies Yoshiharu Namba, Anthony Beaucamp Richard Freeman (Zeeko Ltd.) Producing X-ray imaging telescopes is a very expensive
Shape Adaptive Grinding of CVD Silicon Carbide on Graphite for X-Ray Mirror Molding Dies Yoshiharu Namba, Anthony Beaucamp Richard Freeman (Zeeko Ltd.) Producing X-ray imaging telescopes is a very expensive
POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS
 POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS Leonid Beresnev1, Mikhail Vorontsov1,2 and Peter Wangsness3 1) US Army Research Laboratory, 2800 Powder Mill Road, Adelphi Maryland 20783, lberesnev@arl.army.mil,
POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS Leonid Beresnev1, Mikhail Vorontsov1,2 and Peter Wangsness3 1) US Army Research Laboratory, 2800 Powder Mill Road, Adelphi Maryland 20783, lberesnev@arl.army.mil,
Design parameters Summary
 634 Entrance pupil diameter 100-m Entrance pupil location Primary mirror Exit pupil location On M6 Focal ratio 6.03 Plate scale 2.924 mm / arc second (on-axis) Total field of view 10 arc minutes (unvignetted)
634 Entrance pupil diameter 100-m Entrance pupil location Primary mirror Exit pupil location On M6 Focal ratio 6.03 Plate scale 2.924 mm / arc second (on-axis) Total field of view 10 arc minutes (unvignetted)
Bend Sensor Technology Mechanical Application Design Guide
 Bend Sensor Technology Mechanical Application Design Guide Copyright 2015 Flexpoint Sensor Systems Page 1 of 10 www.flexpoint.com Contents Bend Sensor Description. 3 How the Bend Sensor Potentiometer Works.
Bend Sensor Technology Mechanical Application Design Guide Copyright 2015 Flexpoint Sensor Systems Page 1 of 10 www.flexpoint.com Contents Bend Sensor Description. 3 How the Bend Sensor Potentiometer Works.
Vladimir Vassiliev UCLA
 Vladimir Vassiliev UCLA Reduce cost of FP instrumentation (small plate scale) Improve imaging quality (angular resolution) Minimize isochronous distortion (energy threshold, +) Increase FoV (sky survey,
Vladimir Vassiliev UCLA Reduce cost of FP instrumentation (small plate scale) Improve imaging quality (angular resolution) Minimize isochronous distortion (energy threshold, +) Increase FoV (sky survey,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Advanced UVOIR Mirror Technology Development for Very Large Space Telescopes. H. Philip Stahl
 Advanced UVOIR Mirror Technology Development for Very Large Space Telescopes H. Philip Stahl Objective Define and initiate a long-term program to mature six inter-linked critical technologies for future
Advanced UVOIR Mirror Technology Development for Very Large Space Telescopes H. Philip Stahl Objective Define and initiate a long-term program to mature six inter-linked critical technologies for future
SBIR S2.05 Development
 SBIR S2.05 Development GSFC Optics Branch Technologies Dr. Petar Arsenovic Topic: S2: Advanced Telescope Systems Subtopic: S2.05: Optics Manufacturing and Metrology for Telescope Optical Surfaces Solicitation
SBIR S2.05 Development GSFC Optics Branch Technologies Dr. Petar Arsenovic Topic: S2: Advanced Telescope Systems Subtopic: S2.05: Optics Manufacturing and Metrology for Telescope Optical Surfaces Solicitation
Design of the cryo-optical test of the Planck reflectors
 Design of the cryo-optical test of the Planck reflectors S. Roose, A. Cucchiaro & D. de Chambure* Centre Spatial de Liège, Avenue du Pré-Aily, B-4031 Angleur-Liège, Belgium *ESTEC, Planck project, Keplerlaan
Design of the cryo-optical test of the Planck reflectors S. Roose, A. Cucchiaro & D. de Chambure* Centre Spatial de Liège, Avenue du Pré-Aily, B-4031 Angleur-Liège, Belgium *ESTEC, Planck project, Keplerlaan
TMT Segment Polishing Principles
 TMT Segment Polishing Principles Eric Williams a, Jerry Nelson b, and Larry Stepp a a TMT Observatory Corporation, Pasadena, CA 91107 b University of California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 95064 April 3,
TMT Segment Polishing Principles Eric Williams a, Jerry Nelson b, and Larry Stepp a a TMT Observatory Corporation, Pasadena, CA 91107 b University of California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 95064 April 3,
Aspheric Lenses. Contact us for a Stock or Custom Quote Today! Edmund Optics BROCHURE
 Edmund Optics BROCHURE Aspheric Lenses products & capabilities Contact us for a Stock or Custom Quote Today! USA: +1-856-547-3488 EUROPE: +44 (0) 1904 788600 ASIA: +65 6273 6644 JAPAN: +81-3-3944-6210
Edmund Optics BROCHURE Aspheric Lenses products & capabilities Contact us for a Stock or Custom Quote Today! USA: +1-856-547-3488 EUROPE: +44 (0) 1904 788600 ASIA: +65 6273 6644 JAPAN: +81-3-3944-6210
Stretched Membrane with Electrostatic Curvature (SMEC) Mirrors: A new technology for large lightweight space telescopes
 Stretched Membrane with Electrostatic Curvature (SMEC) Mirrors: A new technology for large lightweight space telescopes Simona Errico a, Roger Angel b, Brian Stamper a, James Burge a, Tom Connors b a Optical
Stretched Membrane with Electrostatic Curvature (SMEC) Mirrors: A new technology for large lightweight space telescopes Simona Errico a, Roger Angel b, Brian Stamper a, James Burge a, Tom Connors b a Optical
MODULAR ADAPTIVE OPTICS TESTBED FOR THE NPOI
 MODULAR ADAPTIVE OPTICS TESTBED FOR THE NPOI Jonathan R. Andrews, Ty Martinez, Christopher C. Wilcox, Sergio R. Restaino Naval Research Laboratory, Remote Sensing Division, Code 7216, 4555 Overlook Ave
MODULAR ADAPTIVE OPTICS TESTBED FOR THE NPOI Jonathan R. Andrews, Ty Martinez, Christopher C. Wilcox, Sergio R. Restaino Naval Research Laboratory, Remote Sensing Division, Code 7216, 4555 Overlook Ave
Ultra-Flat Tip-Tilt-Piston MEMS Deformable Mirror
 Ultra-Flat Tip-Tilt-Piston MEMS Deformable Mirror Mirror Technology Days June 16 th, 2009 Jason Stewart Steven Cornelissen Paul Bierden Boston Micromachines Corp. Thomas Bifano Boston University Mirror
Ultra-Flat Tip-Tilt-Piston MEMS Deformable Mirror Mirror Technology Days June 16 th, 2009 Jason Stewart Steven Cornelissen Paul Bierden Boston Micromachines Corp. Thomas Bifano Boston University Mirror
Panel 2: Observatories
 NRC Workshop on NASA Instruments, Observatories, & Sensor Systems Technology National Academies Beckman Center, Irvine, CA 3/29/2011 Panel 2: Observatories Tony Hull L-3 Integrated Optical Systems Tinsley,
NRC Workshop on NASA Instruments, Observatories, & Sensor Systems Technology National Academies Beckman Center, Irvine, CA 3/29/2011 Panel 2: Observatories Tony Hull L-3 Integrated Optical Systems Tinsley,
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics
 Chapter 34 Geometric Optics Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals of Chapter 34 To see how plane and curved mirrors form images To learn how lenses form images To understand how a simple image system works Reflection
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals of Chapter 34 To see how plane and curved mirrors form images To learn how lenses form images To understand how a simple image system works Reflection
Steve O Dell
 Optics requirements for the Generation-X x-ray telescope Steve O Dell NASA Marshall Space Flight Center 2008.10.09-11 Authors Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) Roger Brissenden, Dan Schwartz,
Optics requirements for the Generation-X x-ray telescope Steve O Dell NASA Marshall Space Flight Center 2008.10.09-11 Authors Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) Roger Brissenden, Dan Schwartz,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
Testing an off-axis parabola with a CGH and a spherical mirror as null lens
 Testing an off-axis parabola with a CGH and a spherical mirror as null lens Chunyu Zhao a, Rene Zehnder a, James H. Burge a, Hubert M. Martin a,b a College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona 1630
Testing an off-axis parabola with a CGH and a spherical mirror as null lens Chunyu Zhao a, Rene Zehnder a, James H. Burge a, Hubert M. Martin a,b a College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona 1630
Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted
 Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted Ulrike Fuchs (Ph.D.), Sven R. Kiontke asphericon GmbH Stockholmer Str. 9 07743 Jena, Germany Tel: +49-3641-3100500 Introduction Everyday work in an optics
Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted Ulrike Fuchs (Ph.D.), Sven R. Kiontke asphericon GmbH Stockholmer Str. 9 07743 Jena, Germany Tel: +49-3641-3100500 Introduction Everyday work in an optics
Starshade Technology Development Status
 Starshade Technology Development Status Dr. Nick Siegler NASA Exoplanets Exploration Program Chief Technologist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Dr. John Ziemer NASA Exoplanets
Starshade Technology Development Status Dr. Nick Siegler NASA Exoplanets Exploration Program Chief Technologist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Dr. John Ziemer NASA Exoplanets
CONFORMAL OGIVE ALON DOME FABRICATION
 16 September 2004 TECHNOLOGY DEMONSTRATION BRIEF CONFORMAL OGIVE ALON DOME FABRICATION Keywords: Conformal, freeform, optics, ogive, ALON, domes, near-net-shape castings, infrared transmitting ceramics
16 September 2004 TECHNOLOGY DEMONSTRATION BRIEF CONFORMAL OGIVE ALON DOME FABRICATION Keywords: Conformal, freeform, optics, ogive, ALON, domes, near-net-shape castings, infrared transmitting ceramics
NIRCam optical calibration sources
 NIRCam optical calibration sources Stephen F. Somerstein, Glen D. Truong Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, D/ABDS, B/201 3251 Hanover St., Palo Alto, CA 94304-1187 ABSTRACT The Near Infrared
NIRCam optical calibration sources Stephen F. Somerstein, Glen D. Truong Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, D/ABDS, B/201 3251 Hanover St., Palo Alto, CA 94304-1187 ABSTRACT The Near Infrared
12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes
 330 Chapter 12 12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes Similar to the JWST, the next-generation large-aperture space telescope for optical and UV astronomy has a segmented
330 Chapter 12 12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes Similar to the JWST, the next-generation large-aperture space telescope for optical and UV astronomy has a segmented
NIRCAM PUPIL IMAGING LENS MECHANISM AND OPTICAL DESIGN
 NIRCAM PUPIL IMAGING LENS MECHANISM AND OPTICAL DESIGN Charles S. Clark and Thomas Jamieson Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center ABSTRACT The Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) instrument for NASA s James
NIRCAM PUPIL IMAGING LENS MECHANISM AND OPTICAL DESIGN Charles S. Clark and Thomas Jamieson Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center ABSTRACT The Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) instrument for NASA s James
Optical Telescope Design Study Results
 Optical Telescope Design Study Results 10 th International LISA Symposium Jeff Livas 20 May 2014 See also poster #19: Shannon Sankar UF and GSFC Telescope Design for a Space-based Gravitational-wave Mission
Optical Telescope Design Study Results 10 th International LISA Symposium Jeff Livas 20 May 2014 See also poster #19: Shannon Sankar UF and GSFC Telescope Design for a Space-based Gravitational-wave Mission
A 1-metre Ni coated CFRP demonstrator for large deformable mirrors
 1st AO4ELT conference, 06007 (2010) DOI:10.1051/ao4elt/201006007 Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2010 A 1-metre Ni coated CFRP demonstrator for large deformable mirrors Samantha J. Thompson
1st AO4ELT conference, 06007 (2010) DOI:10.1051/ao4elt/201006007 Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2010 A 1-metre Ni coated CFRP demonstrator for large deformable mirrors Samantha J. Thompson
COS NCM2 Mirror Substrate Specification
 Date: Document Number: Revision: Contract No.: NAS5-98043 CDRL No.: N/A Prepared By: E. Wilkinson 2-18-99 E. Wilkinson, COS Instrument Scientist, CU/CASA Date Reviewed By: R. Cahill 2-18-99 R. Cahill,
Date: Document Number: Revision: Contract No.: NAS5-98043 CDRL No.: N/A Prepared By: E. Wilkinson 2-18-99 E. Wilkinson, COS Instrument Scientist, CU/CASA Date Reviewed By: R. Cahill 2-18-99 R. Cahill,
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
The SiC hardware of the Sentinel-2 Multi Spectral Instrument
 The SiC hardware of the Sentinel-2 Multi Spectral Instrument ICSO 6c Telescopes and Large Optics Oral Session N 028 Michel BOUGOIN and Jérôme LAVENAC BOOSTEC michel.bougoin@mersen.com jerome.lavenac@mersen.com
The SiC hardware of the Sentinel-2 Multi Spectral Instrument ICSO 6c Telescopes and Large Optics Oral Session N 028 Michel BOUGOIN and Jérôme LAVENAC BOOSTEC michel.bougoin@mersen.com jerome.lavenac@mersen.com
Gran Telescopio Canarias optics manufacture : Final Report
 Gran Telescopio Canarias optics manufacture : Final Report Roland GEYL, Marc CAYREL, Michel TARREAU SAGEM Aerospace & Defence - REOSC High Performance Optics Avenue de la Tour Maury - 91280 Saint Pierre
Gran Telescopio Canarias optics manufacture : Final Report Roland GEYL, Marc CAYREL, Michel TARREAU SAGEM Aerospace & Defence - REOSC High Performance Optics Avenue de la Tour Maury - 91280 Saint Pierre
Ultralightweight active mirror technology at the University of Arizona
 Ultralightweight active mirror technology at the University of Arizona J. H. Burge, D. Baiocchia, B. Cuerden' aoptical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ bsteward Observatory, University
Ultralightweight active mirror technology at the University of Arizona J. H. Burge, D. Baiocchia, B. Cuerden' aoptical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ bsteward Observatory, University
Classical Optical Solutions
 Petzval Lens Enter Petzval, a Hungarian mathematician. To pursue a prize being offered for the development of a wide-field fast lens system he enlisted Hungarian army members seeing a distraction from
Petzval Lens Enter Petzval, a Hungarian mathematician. To pursue a prize being offered for the development of a wide-field fast lens system he enlisted Hungarian army members seeing a distraction from
Large Submillimeter Atacama Telescope. A Strawman Concept
 Large Submillimeter Atacama Telescope A Strawman Concept T.A. Sebring, G. Cortes, C. Henderson The Real Process Define Science Goals Derive Telescope Reqts Flow-Down Subsystem Reqts Develop Concepts An
Large Submillimeter Atacama Telescope A Strawman Concept T.A. Sebring, G. Cortes, C. Henderson The Real Process Define Science Goals Derive Telescope Reqts Flow-Down Subsystem Reqts Develop Concepts An
The Optics of Mirrors
 Use with Text Pages 558 563 The Optics of Mirrors Use the terms in the list below to fill in the blanks in the paragraphs about mirrors. reversed smooth eyes concave focal smaller reflect behind ray convex
Use with Text Pages 558 563 The Optics of Mirrors Use the terms in the list below to fill in the blanks in the paragraphs about mirrors. reversed smooth eyes concave focal smaller reflect behind ray convex
Manufacture and Performance of a Z-interconnect HDI Circuit Card Abstract Introduction
 Manufacture and Performance of a Z-interconnect HDI Circuit Card Michael Rowlands, Rabindra Das, John Lauffer, Voya Markovich EI (Endicott Interconnect Technologies) 1093 Clark Street, Endicott, NY 13760
Manufacture and Performance of a Z-interconnect HDI Circuit Card Michael Rowlands, Rabindra Das, John Lauffer, Voya Markovich EI (Endicott Interconnect Technologies) 1093 Clark Street, Endicott, NY 13760
Bend Sensor Technology Mechanical Application Design Guide Mechanical Application Design Guide
 Bend Sensor Technology Mechanical Application Design Guide Mechanical Application Design Guide www.flexpoint.com Copyright 2015 Flexpoint Sensor Systems Page 1 of 10 2 Bend Sensor Technology Mechanical
Bend Sensor Technology Mechanical Application Design Guide Mechanical Application Design Guide www.flexpoint.com Copyright 2015 Flexpoint Sensor Systems Page 1 of 10 2 Bend Sensor Technology Mechanical
The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces
 The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces James T. McCann OFC - Diamond Turning Division 69T Island Street, Keene New Hampshire
The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces James T. McCann OFC - Diamond Turning Division 69T Island Street, Keene New Hampshire
A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor
 TECHNOLOGY by Charles Taylor, Darryl Barlett, Eric Chason, and Jerry Floro A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor The Multi-beam Optical Sensor (MOS) was developed jointly by k-space Associates (Ann Arbor,
TECHNOLOGY by Charles Taylor, Darryl Barlett, Eric Chason, and Jerry Floro A Laser-Based Thin-Film Growth Monitor The Multi-beam Optical Sensor (MOS) was developed jointly by k-space Associates (Ann Arbor,
Design, Fabrication, and Validation of an Ultra-Lightweight Membrane Mirror
 Design, Fabrication, and Validation of an Ultra-Lightweight Membrane Mirror Surya Chodimella, James D. Moore, Brian G. Patrick SRS Technologies, Huntsville AL, USA 35806 Brett deblonk, Dan K. Marker Air
Design, Fabrication, and Validation of an Ultra-Lightweight Membrane Mirror Surya Chodimella, James D. Moore, Brian G. Patrick SRS Technologies, Huntsville AL, USA 35806 Brett deblonk, Dan K. Marker Air
Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror Contract No. NNX09CF40P (SBIR ) (MSFC)
 Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror Contract No. NNX09CF40P (SBIR 2008-1) (MSFC) Mirror Technology SBIR/STTR Workshop June 16 th to 18 th, 2009 Hilton Albuquerque, Albuquerque, NM John M. Casstevens
Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror Contract No. NNX09CF40P (SBIR 2008-1) (MSFC) Mirror Technology SBIR/STTR Workshop June 16 th to 18 th, 2009 Hilton Albuquerque, Albuquerque, NM John M. Casstevens
PART 3: LENS FORM AND ANALYSIS PRACTICE TEST
 PART 3: LENS FORM AND ANALYSIS PRACTICE TEST 1. 2. To determine the power of a thin lens in air, it is necessary to consider: a. front curve and index of refraction b. back curve and index of refraction
PART 3: LENS FORM AND ANALYSIS PRACTICE TEST 1. 2. To determine the power of a thin lens in air, it is necessary to consider: a. front curve and index of refraction b. back curve and index of refraction
COS FUV Grating Substrate Specification
 COS FUV Grating Substrate Specification Date: Document Number: Revision: Contract No.: NAS5-98043 CDRL No.: N/A Prepared By: Reviewed By: Approved By: Approved By: Approved By: E. Wilkinson, COS Instrument
COS FUV Grating Substrate Specification Date: Document Number: Revision: Contract No.: NAS5-98043 CDRL No.: N/A Prepared By: Reviewed By: Approved By: Approved By: Approved By: E. Wilkinson, COS Instrument
Next generation IR imaging component requirements
 Next generation IR imaging component requirements Dr Andy Wood VP Technology Optical Systems November 2017 0 2013 Excelitas Technologies E N G A G E. E N A B L E. E X C E L. 0 Some background Optical design
Next generation IR imaging component requirements Dr Andy Wood VP Technology Optical Systems November 2017 0 2013 Excelitas Technologies E N G A G E. E N A B L E. E X C E L. 0 Some background Optical design
High Resolution SSA Imaging using Carbon Fiber Telescopes
 High Resolution SSA Imaging using Carbon Fiber Telescopes Ryan Swindle Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL/RDSM), thomas.swindle@us.af.mil Douglas Hope Hart Scientific Consulting International, dhope@hartsci.com
High Resolution SSA Imaging using Carbon Fiber Telescopes Ryan Swindle Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL/RDSM), thomas.swindle@us.af.mil Douglas Hope Hart Scientific Consulting International, dhope@hartsci.com
Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror! Mirror Technology SBIR/STTR Workshop June 20 th to 23 rd, 2011 Greenbelt Marriott, Greenbelt, Md.
 Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror! Contract No. NNX10CB49C (SBIR 08-2 S2.04-9926) (MSFC)! Mirror Technology SBIR/STTR Workshop June 20 th to 23 rd, 2011 Greenbelt Marriott, Greenbelt, Md.
Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror! Contract No. NNX10CB49C (SBIR 08-2 S2.04-9926) (MSFC)! Mirror Technology SBIR/STTR Workshop June 20 th to 23 rd, 2011 Greenbelt Marriott, Greenbelt, Md.
Optics Practice. Version #: 0. Name: Date: 07/01/2010
 Optics Practice Date: 07/01/2010 Version #: 0 Name: 1. Which of the following diagrams show a real image? a) b) c) d) e) i, ii, iii, and iv i and ii i and iv ii and iv ii, iii and iv 2. A real image is
Optics Practice Date: 07/01/2010 Version #: 0 Name: 1. Which of the following diagrams show a real image? a) b) c) d) e) i, ii, iii, and iv i and ii i and iv ii and iv ii, iii and iv 2. A real image is
The 20/20 telescope: Concept for a 30 m GSMT
 The : Concept for a 30 m GSMT Roger Angel, Warren Davison, Keith Hege, Phil Hinz, Buddy Martin, Steve Miller, Jose Sasian & Neville Woolf University of Arizona 1 The : combining the best of filled aperture
The : Concept for a 30 m GSMT Roger Angel, Warren Davison, Keith Hege, Phil Hinz, Buddy Martin, Steve Miller, Jose Sasian & Neville Woolf University of Arizona 1 The : combining the best of filled aperture
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL THESIS
 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS OPTICAL CORRECTION OF SPACE-BASED TELESCOPES USING A DEFORMABLE MIRROR SYSTEM by Mark C. Mueller December 2016 Co-Advisors: Brij Agrawal Jae Jun Kim
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA THESIS OPTICAL CORRECTION OF SPACE-BASED TELESCOPES USING A DEFORMABLE MIRROR SYSTEM by Mark C. Mueller December 2016 Co-Advisors: Brij Agrawal Jae Jun Kim
Optical design of Dark Matter Telescope: improving manufacturability of telescope
 Optical design of Dark Matter Telescope: improving manufacturability of telescope Lynn G. Seppala November 5, 2001 The attached slides contain some talking point that could be useful during discussions
Optical design of Dark Matter Telescope: improving manufacturability of telescope Lynn G. Seppala November 5, 2001 The attached slides contain some talking point that could be useful during discussions
Joint Milli-Arcsecond Pathfinder Survey (JMAPS): Overview and Application to NWO Mission
 Joint Milli-Arcsecond Pathfinder Survey (JMAPS): Overview and Application to NWO Mission B.DorlandandR.Dudik USNavalObservatory 11March2009 1 MissionOverview TheJointMilli ArcsecondPathfinderSurvey(JMAPS)missionisaDepartmentof
Joint Milli-Arcsecond Pathfinder Survey (JMAPS): Overview and Application to NWO Mission B.DorlandandR.Dudik USNavalObservatory 11March2009 1 MissionOverview TheJointMilli ArcsecondPathfinderSurvey(JMAPS)missionisaDepartmentof
"Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements
 "Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements by Dr. Frank Melsheimer DFM Engineering, Inc. 1035 Delaware Avenue Longmont, Colorado 80501 phone 303-678-8143 fax 303-772-9411 www.dfmengineering.com Table
"Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements by Dr. Frank Melsheimer DFM Engineering, Inc. 1035 Delaware Avenue Longmont, Colorado 80501 phone 303-678-8143 fax 303-772-9411 www.dfmengineering.com Table
1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter
 8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
A PORTABLE RUBIDIUM FOUNTAIN 1
 A PORTABLE RUBIDIUM FOUNTAIN 1 P. D. Kunz Time and Frequency Division National Institute of Standards and Technology 325 Broadway, Boulder, CO 80305 kunzp@nist.gov T. P. Heavner (heavner@nist.gov) and
A PORTABLE RUBIDIUM FOUNTAIN 1 P. D. Kunz Time and Frequency Division National Institute of Standards and Technology 325 Broadway, Boulder, CO 80305 kunzp@nist.gov T. P. Heavner (heavner@nist.gov) and
Difrotec Product & Services. Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions
 Difrotec Product & Services Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions Content 1. Overview 2. Interferometer D7 3. Benefits 4. Measurements 5. Specifications 6. Applications 7. Cases
Difrotec Product & Services Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions Content 1. Overview 2. Interferometer D7 3. Benefits 4. Measurements 5. Specifications 6. Applications 7. Cases
NIRCam Instrument Optics
 NIRCam Instrument Optics Lynn W. Huff Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center 3251 Hanover Street, Palo Alto, CA 94304 ABSTRACT The Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) for NASA s James Webb Space Telescope
NIRCam Instrument Optics Lynn W. Huff Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center 3251 Hanover Street, Palo Alto, CA 94304 ABSTRACT The Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) for NASA s James Webb Space Telescope
Department of Astronomy, Graduate School of Science, the University of Tokyo, Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo , Japan;
 Verification of the controllability of refractive index by subwavelength structure fabricated by photolithography: toward single-material mid- and far-infrared multilayer filters Hironobu Makitsubo* a,b,
Verification of the controllability of refractive index by subwavelength structure fabricated by photolithography: toward single-material mid- and far-infrared multilayer filters Hironobu Makitsubo* a,b,
Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication
 UCRL-JC- 134763 PREPRINT Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication for G. E. Sommargren D. W. Phillion E. W. Campbell This paper was prepared for submittal to the 9th International Conference
UCRL-JC- 134763 PREPRINT Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication for G. E. Sommargren D. W. Phillion E. W. Campbell This paper was prepared for submittal to the 9th International Conference
PART 3: LENS FORM AND ANALYSIS PRACTICE TEST - KEY
 PART 3: LENS FORM AND ANALYSIS PRACTICE TEST - KEY d 1. c 2. To determine the power of a thin lens in air, it is necessary to consider: a. front curve and index of refraction b. back curve and index of
PART 3: LENS FORM AND ANALYSIS PRACTICE TEST - KEY d 1. c 2. To determine the power of a thin lens in air, it is necessary to consider: a. front curve and index of refraction b. back curve and index of
Vertex Detector Mechanics
 Vertex Detector Mechanics Bill Cooper Fermilab (Layer 5) (Layer 1) VXD Introduction The overall approach to mechanical support and cooling has been developed in conjunction with SiD. The support structures
Vertex Detector Mechanics Bill Cooper Fermilab (Layer 5) (Layer 1) VXD Introduction The overall approach to mechanical support and cooling has been developed in conjunction with SiD. The support structures
Silicon Meta-Shell Optics for AXIS: High-Resolution, Light-Weight, and Low-Cost
 Silicon Meta-Shell Optics for AXIS: High-Resolution, Light-Weight, and Low-Cost William W. Zhang NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Next Generation X-ray Optics (NGXO) Team K.D. Allgood 1, M.P. Biskach 1,
Silicon Meta-Shell Optics for AXIS: High-Resolution, Light-Weight, and Low-Cost William W. Zhang NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Next Generation X-ray Optics (NGXO) Team K.D. Allgood 1, M.P. Biskach 1,
Design of a Piezoelectric-based Structural Health Monitoring System for Damage Detection in Composite Materials
 Design of a Piezoelectric-based Structural Health Monitoring System for Damage Detection in Composite Materials Seth S. Kessler S. Mark Spearing Technology Laboratory for Advanced Composites Department
Design of a Piezoelectric-based Structural Health Monitoring System for Damage Detection in Composite Materials Seth S. Kessler S. Mark Spearing Technology Laboratory for Advanced Composites Department
OWL OPTICAL DESIGN, ACTIVE OPTICS AND ERROR BUDGET
 OWL OPTICAL DESIGN, ACTIVE OPTICS AND ERROR BUDGET P. Dierickx, B. Delabre, L. Noethe European Southern Observatory Abstract We explore solutions for the optical design of the OWL 100-m telescope, and
OWL OPTICAL DESIGN, ACTIVE OPTICS AND ERROR BUDGET P. Dierickx, B. Delabre, L. Noethe European Southern Observatory Abstract We explore solutions for the optical design of the OWL 100-m telescope, and
Breakout Session 3: Mirror Update. 2007/4/ /22 Peter M. Stefan LCLS Facility Advisory Committee (FAC) Meeting
 Breakout Session 3: Mirror Update 2007/4/16-17 1/22 Peter M. Stefan LCLS Facility Advisory Committee (FAC) Meeting stefan@slac.stanford.edu Breakout Session 3: Mirror Update Overall Offset Mirror System
Breakout Session 3: Mirror Update 2007/4/16-17 1/22 Peter M. Stefan LCLS Facility Advisory Committee (FAC) Meeting stefan@slac.stanford.edu Breakout Session 3: Mirror Update Overall Offset Mirror System
Lamb Wave Ultrasonic Stylus
 Lamb Wave Ultrasonic Stylus 0.1 Motivation Stylus as an input tool is used with touchscreen-enabled devices, such as Tablet PCs, to accurately navigate interface elements, send messages, etc. They are,
Lamb Wave Ultrasonic Stylus 0.1 Motivation Stylus as an input tool is used with touchscreen-enabled devices, such as Tablet PCs, to accurately navigate interface elements, send messages, etc. They are,
19. Ray Optics. S. G. Rajeev. April 2, 2009
 9. Ray Optics S. G. Rajeev April 2, 2009 When the wave length is small light travels along straightlines called rays. Ray optics (also called geometrical optics) is the study of this light in this situation.
9. Ray Optics S. G. Rajeev April 2, 2009 When the wave length is small light travels along straightlines called rays. Ray optics (also called geometrical optics) is the study of this light in this situation.
Manufacturing, testing and alignment of Sentinel-2 MSI telescope mirrors
 Manufacturing, testing and alignment of Sentinel-2 MSI telescope mirrors P. Gloesener, F. Wolfs, F. Lemagne, C. Flebus AMOS Angleur, Belgium pierre.gloesener@amos.be P. Gloesener, F. Wolfs, F. Lemagne,
Manufacturing, testing and alignment of Sentinel-2 MSI telescope mirrors P. Gloesener, F. Wolfs, F. Lemagne, C. Flebus AMOS Angleur, Belgium pierre.gloesener@amos.be P. Gloesener, F. Wolfs, F. Lemagne,
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part I. BASIC ELEMENTS AND METHODS FOR CHARACTERIZATION OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS
 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part I. BASIC ELEMENTS AND METHODS FOR CHARACTERIZATION OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS Equipment and accessories: an optical bench with a scale, an incandescent lamp, matte, a set of
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part I. BASIC ELEMENTS AND METHODS FOR CHARACTERIZATION OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS Equipment and accessories: an optical bench with a scale, an incandescent lamp, matte, a set of
The Ultra-Precision Polishing of Large Aperture Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbide Mirror
 American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (2): 45-50, 2010 ISSN 1949-0216 2010 Science Publications The Ultra-Precision Polishing of Large Aperture Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbide Mirror Yong Shu, Yifan Dai,
American Journal of Nanotechnology 1 (2): 45-50, 2010 ISSN 1949-0216 2010 Science Publications The Ultra-Precision Polishing of Large Aperture Reaction Bonded Silicon Carbide Mirror Yong Shu, Yifan Dai,
from ground adaptive secondaries to a space active primary Xompero, M., Briguglio, R., Lisi, F., Arcidiacono, C., Riccardi, A.
 LATT: Large Aperture Telescope Technology from ground adaptive secondaries to a space active primary Xompero, M., Briguglio, R., Lisi, F., Arcidiacono, C., Riccardi, A. The LATT Team CGS S.p.A.: coordinator
LATT: Large Aperture Telescope Technology from ground adaptive secondaries to a space active primary Xompero, M., Briguglio, R., Lisi, F., Arcidiacono, C., Riccardi, A. The LATT Team CGS S.p.A.: coordinator
UNCLASSIFIED R-1 ITEM NOMENCLATURE FY 2013 OCO
 Exhibit R-2, RDT&E Budget Item Justification: PB 2013 Air Force DATE: February 2012 BA 3: Advanced Development (ATD) COST ($ in Millions) Program Element 75.103 74.009 64.557-64.557 61.690 67.075 54.973
Exhibit R-2, RDT&E Budget Item Justification: PB 2013 Air Force DATE: February 2012 BA 3: Advanced Development (ATD) COST ($ in Millions) Program Element 75.103 74.009 64.557-64.557 61.690 67.075 54.973
Achieving milli-arcsecond residual astrometric error for the JMAPS mission
 Achieving milli-arcsecond residual astrometric error for the JMAPS mission Gregory S. Hennessy a,benjaminf.lane b, Dan Veilette a, and Christopher Dieck a a US Naval Observatory, 3450 Mass Ave. NW, Washington
Achieving milli-arcsecond residual astrometric error for the JMAPS mission Gregory S. Hennessy a,benjaminf.lane b, Dan Veilette a, and Christopher Dieck a a US Naval Observatory, 3450 Mass Ave. NW, Washington
On machine Measurement for Precision Corrective polishing of Aspheres and Freeform Surfaces
 On machine Measurement for Precision Corrective polishing of Aspheres and Freeform Surfaces David Walker, Christopher King University College London Zeeko Ltd & Zeeko Research Ltd Based at the OpTIC Technium,
On machine Measurement for Precision Corrective polishing of Aspheres and Freeform Surfaces David Walker, Christopher King University College London Zeeko Ltd & Zeeko Research Ltd Based at the OpTIC Technium,
Tip-Tilt Correction for Astronomical Telescopes using Adaptive Control. Jim Watson
 UCRL-JC-128432 PREPRINT Tip-Tilt Correction for Astronomical Telescopes using Adaptive Control Jim Watson This paper was prepared for submittal to the Wescon - Integrated Circuit Expo 1997 Santa Clara,
UCRL-JC-128432 PREPRINT Tip-Tilt Correction for Astronomical Telescopes using Adaptive Control Jim Watson This paper was prepared for submittal to the Wescon - Integrated Circuit Expo 1997 Santa Clara,
Application Bulletin 240
 Application Bulletin 240 Design Consideration CUSTOM CAPABILITIES Standard PC board fabrication flexibility allows for various component orientations, mounting features, and interconnect schemes. The starting
Application Bulletin 240 Design Consideration CUSTOM CAPABILITIES Standard PC board fabrication flexibility allows for various component orientations, mounting features, and interconnect schemes. The starting
Development of a Deformable Mirror for High-Power Lasers
 Development of a Deformable Mirror for High-Power Lasers Dr. Justin Mansell and Robert Praus MZA Associates Corporation Mirror Technology Days August 1, 2007 1 Outline Introduction & Project Goal Deformable
Development of a Deformable Mirror for High-Power Lasers Dr. Justin Mansell and Robert Praus MZA Associates Corporation Mirror Technology Days August 1, 2007 1 Outline Introduction & Project Goal Deformable
nanovea.com PROFILOMETERS 3D Non Contact Metrology
 PROFILOMETERS 3D Non Contact Metrology nanovea.com PROFILOMETER INTRO Nanovea 3D Non-Contact Profilometers are designed with leading edge optical pens using superior white light axial chromatism. Nano
PROFILOMETERS 3D Non Contact Metrology nanovea.com PROFILOMETER INTRO Nanovea 3D Non-Contact Profilometers are designed with leading edge optical pens using superior white light axial chromatism. Nano
Design of null lenses for testing of elliptical surfaces
 Design of null lenses for testing of elliptical surfaces Yeon Soo Kim, Byoung Yoon Kim, and Yun Woo Lee Null lenses are designed for testing the oblate elliptical surface that is the third mirror of the
Design of null lenses for testing of elliptical surfaces Yeon Soo Kim, Byoung Yoon Kim, and Yun Woo Lee Null lenses are designed for testing the oblate elliptical surface that is the third mirror of the
In their earliest form, bandpass filters
 Bandpass Filters Past and Present Bandpass filters are passive optical devices that control the flow of light. They can be used either to isolate certain wavelengths or colors, or to control the wavelengths
Bandpass Filters Past and Present Bandpass filters are passive optical devices that control the flow of light. They can be used either to isolate certain wavelengths or colors, or to control the wavelengths
Adaptive Optics for. High Peak Power Lasers
 Adaptive Optics for High Peak Power Lasers Chris Hooker Central Laser Facility STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Chilton, Oxfordshire OX11 0QX U.K. What does High-Power Laser mean nowadays? Distinguish
Adaptive Optics for High Peak Power Lasers Chris Hooker Central Laser Facility STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory Chilton, Oxfordshire OX11 0QX U.K. What does High-Power Laser mean nowadays? Distinguish
For rotationally symmetric optical
 : Maintaining Uniform Temperature Fluctuations John Tejada, Janos Technology, Inc. An optical system is athermalized if its critical performance parameters (such as MTF, BFL, EFL, etc.,) do not change
: Maintaining Uniform Temperature Fluctuations John Tejada, Janos Technology, Inc. An optical system is athermalized if its critical performance parameters (such as MTF, BFL, EFL, etc.,) do not change
Visible Improvements to Non-Visible Imaging Systems: Improving Efficiency with Precision Molded Chalcogenide Glass Components
 Visible Improvements to Non-Visible Imaging Systems: Improving Efficiency with Precision Molded Chalcogenide Glass Components Infrared (IR) imaging systems are seeing increasing demand for surveillance,
Visible Improvements to Non-Visible Imaging Systems: Improving Efficiency with Precision Molded Chalcogenide Glass Components Infrared (IR) imaging systems are seeing increasing demand for surveillance,
DESIGN OF A FABRY-PEROT OPEN RESONATOR AT RADIO FREQUENCIES FOR AN MgB2 TESTING PLATFORM
 DESIGN OF A FABRY-PEROT OPEN RESONATOR AT RADIO FREQUENCIES FOR AN MgB2 TESTING PLATFORM Lauren Perez, Florida International University, FL 33193, U.S.A. Supervisors: Ali Nassiri and Bob Kustom, Argonne
DESIGN OF A FABRY-PEROT OPEN RESONATOR AT RADIO FREQUENCIES FOR AN MgB2 TESTING PLATFORM Lauren Perez, Florida International University, FL 33193, U.S.A. Supervisors: Ali Nassiri and Bob Kustom, Argonne
ASSEMBLY AND SERVICING OF SPACE TELESCOPES
 ASSEMBLY AND SERVICING OF SPACE TELESCOPES NASA MIRROR TECH DAYS 2017 HAWTHORNE, CALIFORNIA 16 NOVEMBER 2017 REVIRESCO LLC howard.macewen@hmacewen.com 1 The Astrophysics Advisory Council (APAC) also recognizes
ASSEMBLY AND SERVICING OF SPACE TELESCOPES NASA MIRROR TECH DAYS 2017 HAWTHORNE, CALIFORNIA 16 NOVEMBER 2017 REVIRESCO LLC howard.macewen@hmacewen.com 1 The Astrophysics Advisory Council (APAC) also recognizes
Shape correction of thin mirrors in a reconfigurable modular space telescope
 Shape correction of thin mirrors in a reconfigurable modular space telescope Keith Patterson, Sergio Pellegrino and James Breckinridge Graduate Aerospace Laboratories, California Institute of Technology,
Shape correction of thin mirrors in a reconfigurable modular space telescope Keith Patterson, Sergio Pellegrino and James Breckinridge Graduate Aerospace Laboratories, California Institute of Technology,
Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN
 Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN A typical astronomical instrument must maintain about one cubic meter at a pressure of
Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN A typical astronomical instrument must maintain about one cubic meter at a pressure of
A JWST Derivative Design for the Next Large Aperture UV/Optical Telescope
 A JWST Derivative Design for the Next Large Aperture UV/Optical Telescope W. B. Whiddon Next Large Aperture Optical/UV Telescope Workshop 11 April 2003 Strategy JWST is the nation's investment in large
A JWST Derivative Design for the Next Large Aperture UV/Optical Telescope W. B. Whiddon Next Large Aperture Optical/UV Telescope Workshop 11 April 2003 Strategy JWST is the nation's investment in large
Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices
 644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
Using molded chalcogenide glass technology to reduce cost in a compact wide-angle thermal imaging lens
 Using molded chalcogenide glass technology to reduce cost in a compact wide-angle thermal imaging lens George Curatu a, Brent Binkley a, David Tinch a, and Costin Curatu b a LightPath Technologies, 2603
Using molded chalcogenide glass technology to reduce cost in a compact wide-angle thermal imaging lens George Curatu a, Brent Binkley a, David Tinch a, and Costin Curatu b a LightPath Technologies, 2603
