Glass Membrane Mirrors beyond NGST
|
|
|
- Cleopatra Ball
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Glass Membrane Mirrors beyond NGST J.H. Burge, J. R. P. Angel, B. Cuerden, N. J Woolf Steward Observatory, University of Arizona Much of the technology and hardware are in place for manufacturing the primary mirror for the Next Generation Space Telescope as a glass membrane with active rigid support. We are now pursuing advances in this technology, beyond NGST, to provide mirrors that are lighter and less expensive. The evolution of the technology, going to thinner facesheets, more optimized structures, and lighter actuators, can extend the concept to mirrors with 5 kg/m 2 areal density, approximately 3 times more lightweight than for NGST. The concept We have developed a type of mirror that achieves high quality and low mass using a glass membrane as the optical surface, coupled to a stiff, lightweight support structure through an array of actuators. The optical quality of the system is maintained by an active system that uses periodic adjustment of the actuators based on wavefront measurements (as shown in Fig. 1). The actuators themselves are simple fine pitch screws that are driven in small steps using electromagnets. The backing structure, optimized for stiffness and mass, is made from thin sheets of carbon fiber reinforced plastic. Any instability of the backing structure will be compensated with the actuators. Glass is used for the membranes because it is extremely stable, can be made in large, highly homogenous pieces, and it takes an excellent polish. Ideal shape Structure deforms, taking membrane with it Actuators are driven to compensate Figure 1. The mirror shape is maintained by making adjustments with actuators, based on wavefront measurements. Implementation for NGST The need for increasingly lightweight mirrors in space has led to an evolution of glass technologies. The Hubble Space Telescope used a primary mirror that achieved 180 kg/m 2 using a honeycomb construction. Further evolution of this method has made smaller mirrors as light as 30 kg/m 2. Also, large glass shells 2 cm thick (40 kg/m 2 ) have been developed for flyable laser
2 projectors such as LAMP. These mirrors were stiff enough to allow support by traditional actuators that control the force applied to the glass. For the still lighter mirrors, thinner glass shells are sufficiently flexible that the traditional flotation (force actuated) support is no longer desirable. However, as we have demonstrated, glass membranes as thin as 2 mm can be made into high quality mirrors, provided they are attached rigidly to a stiff back-up structure. This structure need not be stable to optical tolerance, provided the actuators can be adjusted to compensate for thermal or other deformations. The advantage of making a mirror in this way is that the attributes of a smooth, polishable surface and a rigid lightweight structure are separated. The choice of materials and structural designs for each can be separately optimized, and a great reduction in density obtained. We first demonstrated this concept with a 52-cm mirror with a 2-mm thick Zerodur and 36 actuators. This mirror system weighed 20 kg/m 2 in total, including the glass membrane, actuators and carbon fiber composite support. We are currently making a 2-m NGST Mirror System Demonstrator (NMSD) that weighs only 12 kg/m 2. Further refinement of the NMSD design can achieve optical quality performance with a mass density of only 5 kg/m 2. Figure 2. University of Arizona 2-m NGST Mirror System Demonstrator The design and analysis of the 2-m NMSD form the basis for the 5 kg/m 2 design. This mirror, shown in Fig. 2, uses a borosilicate glass membrane (optimal for operation at 35 K), supported by 166 screw type actuators. The support structure was made by Composite Optics, Inc using laminate sheets of M55J carbon fiber/cyanate ester. To manufacture glass membranes, we start with a relatively thick substrate, block it down, and thin and polish the membrane while it is blocked, as shown in Fig. 3. This allows us to work the optical surface of the membrane while it is rigidly supported, so we can use all of our
3 polishing methods and equipment. The blocking is done using pitch to allow a low-stress bond. We perform the blocking by supporting the proto-membrane in a blocking oven, heat the system to about 100 C and slowly settle the membrane into the molten pitch. The final part is deblocked by reversing this operation, with the membrane attached to a support fixture. The performance expectations for the 2-m NMSD are high. Using the actuators to implement closed loop control of the mirror surface, we expect diffraction limited performance, even for visible wavelengths. Figure 4 shows the Strehl ratio calculated from a detailed model of the 2-m surface Exact calculation from simulated mirror data Strehl ratio Calculated from 27 nm rms surface using standard approximation 0.2 Figure 3. Membrane is carved out of a thicker glass substrate while held to a rigid blocking body with pitch wavelength in um Figure 4. Strehl ratio calculated from simulated figure for the 2-m NMSD. The next step beyond NGST So far, our detailed mirror designs and optimizations have been based on NGST requirements, which are 15 kg/m 2 mass density, diffraction limited at 1 µm wavelengths, 35 K operating temperature, and launch in Since the current 12 kg/m 2 already exceeds NGST requirements, we have made no effort to decrease this for NGST. It is imperative that NGST adopt a design and move forward aggressively to meet their schedule requirements. However, future missions could benefit from further refinement of this mirror design. For this reason, we have studied the next step that we can make to decrease the mass of our mirrors. We believe that a flyable 5 kg/m 2 mirror can be made using existing technologies. Our strategy for taking this next step builds on the experience from the 2-m, 12 kg/m 2 mirror. We assume the same basic design, including actuator spacing, but we reduce the mass by making the following changes: 1. Decrease facesheet thickness from 2 to 1 mm 2. Reduce mass of glass attachment hardware by half 3. Reduce actuator mass significantly to 7 gm/actuator. (Electronics and cabling have not been reduced.) 4. Use highly optimized backing structure with mass ~ 1 kg/m 2
4 These steps, summarized in Table 1, were not made arbitrarily and we have good reason for believing that we can achieve such mass reduction. In most cases, we have already demonstrated improvement beyond that needed for the 5 kg/m 2 mirror. Our design assumes a glass facesheet 1 mm thick. This is a modest change over the 2 mm thick membranes for the NMSD. However, we have already manufactured glass membranes as thin as 0.4 mm thick for high performance deformable mirrors. We have not made detailed designs for the hardware that is used to connect the actuators to the glass, but we can expect this to be at least 2 times lighter because it supports half the mass for the thinner membrane. For the baseline design, we assume actuators of 7 grams. To verify the ability to make actuators this light, we built one and verified that it can make steps as small as 5 nm. This actuator and its much larger NMSD cousin are shown in Figure 5. These actuators, invented at the University of Arizona, use an impact driven nut to make small advancements of a fine pitch screw. By modifying the pulse width used for the impact, different step sizes can be made, as shown in Figure 6. For the 5 kg/m 2 mirror, the weight of the drive electronics and cabling are assumed to be the same as those for the NMSD. 7 Gram Actuator Step Size 7 grams 43 grams Figure 5. Miniature actuators invented and built at the University of Arizona. Step Size, nm Nominal Preload Increased Preload Relative Pulse Width (Approx.) Figure 6. Measured step size for the 7 gram actuator. We budget the support structure to have mass density of 1.1 kg/m 2. This is consistent with the state of the art for composite structures used as microwave reflectors. Composite Optics, Inc. has fabricated 1-m class structures with 0.56 kg/m 2 density, shown in Fig. 7. There is no doubt that the backing structure for our mirror can be made at 1.1 kg/m 2. The only open issue is the optimization, which depends critically on application and mounting requirements.
5 Tri-axial IRAD Reflectors Triaxial Reflector 1.0m Aperture 440 grams (0.56 kg/m 2 ) 3.0 mil rms F/D = 3.0 Figure 7. Lightweight reflectors built by COI demonstrate the technology for the backing structure. This mirror weighs 0.56 kg/m 2 including the mesh reflector surface. In summary, we feel that all of the technologies are in place to build a mirror that matches the performance of our 2-m NMSD mirror, but with mass of 5 kg/m 2. Table 1. Mass summary for 2-m NMSD currently being built and the proposed 5 kg/m 2 mirror. NMSD under construction (kg/m 2 ) Next generation mirror (kg/m 2 ) Glass membrane Actuators, electronics, and cabling Load spreaders Attachments to membrane Launch restraint hardware Carbon fiber support structure Total mass per square meter Total mass for an 8-m mirror 623 kg 250 kg
6 Beyond the next step The mirror described here achieves 5 kg/m 2 by applying existing technology to a fairly mature mirror design. This represents a natural evolution of today s advanced technology to serve the needs of tomorrow. But what about the day after tomorrow? It seems likely that this technology can be further refined for mass reductions by another factor of two or three. It is not clear, however, that further mass reductions make sense. The mirrors are made to be lightweight so they can be launched using moderately priced rockets and shrouds. At some point, the critical parameter for launch becomes volume, not mass. For example, a 30-m aperture could be made from 4-m segments, which fit inside existing launch vehicles. This mirror would require 60 of these segments, weighing 3500 kg. A single rocket could take the mass without difficulty, but this stack of segments is likely to be 10 meters tall, nearly filling the available volume. Conclusion We present a concept for lightweight mirrors that is evolutionary, not revolutionary. However, the advantages of this mirror must be considered: This mirror requires no new advances in materials or other technologies. We could build and fly one of these mirrors in as little as one year. Fabrication technologies and facilities exist to implement this design NOW for mirrors up to 8 meters across.
Lightweight mirror technology using a thin facesheet with active rigid support
 Lightweight mirror technology using a thin facesheet with active rigid support J. H. Burge, J. R. P. Angel, B. Cuerden, H. M. Martin, S. M. Miller, D. G. Sandler ABSTRACT The next generation of space telescopes
Lightweight mirror technology using a thin facesheet with active rigid support J. H. Burge, J. R. P. Angel, B. Cuerden, H. M. Martin, S. M. Miller, D. G. Sandler ABSTRACT The next generation of space telescopes
Ultralightweight active mirror technology at the University of Arizona
 Ultralightweight active mirror technology at the University of Arizona J. H. Burge, D. Baiocchia, B. Cuerden' aoptical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ bsteward Observatory, University
Ultralightweight active mirror technology at the University of Arizona J. H. Burge, D. Baiocchia, B. Cuerden' aoptical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ bsteward Observatory, University
Design and Manufacture of 8.4 m Primary Mirror Segments and Supports for the GMT
 Design and Manufacture of 8.4 m Primary Mirror Segments and Supports for the GMT Introduction The primary mirror for the Giant Magellan telescope is made up an 8.4 meter symmetric central segment surrounded
Design and Manufacture of 8.4 m Primary Mirror Segments and Supports for the GMT Introduction The primary mirror for the Giant Magellan telescope is made up an 8.4 meter symmetric central segment surrounded
Large Aperture Telescope Technology: a design for an active lightweight multi-segmented fold-out space mirror
 Large Aperture Telescope Technology: a design for an active lightweight multi-segmented fold-out space mirror Presenter: Samantha Thompson, University College London UK LATT Team Martin Whalley Ruben Edeson
Large Aperture Telescope Technology: a design for an active lightweight multi-segmented fold-out space mirror Presenter: Samantha Thompson, University College London UK LATT Team Martin Whalley Ruben Edeson
Ultra-Flat Tip-Tilt-Piston MEMS Deformable Mirror
 Ultra-Flat Tip-Tilt-Piston MEMS Deformable Mirror Mirror Technology Days June 16 th, 2009 Jason Stewart Steven Cornelissen Paul Bierden Boston Micromachines Corp. Thomas Bifano Boston University Mirror
Ultra-Flat Tip-Tilt-Piston MEMS Deformable Mirror Mirror Technology Days June 16 th, 2009 Jason Stewart Steven Cornelissen Paul Bierden Boston Micromachines Corp. Thomas Bifano Boston University Mirror
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes
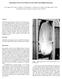 Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
FABRICATION OF MIRROR SEGMENTS for the GSMT
 FABRICATION OF MIRROR SEGMENTS for the GSMT Segment Fabrication Workshop May 30, 2002 The USA Decadal Review In May 2000, the US astronomy decadal review committee recommended the construction of a 30-meter
FABRICATION OF MIRROR SEGMENTS for the GSMT Segment Fabrication Workshop May 30, 2002 The USA Decadal Review In May 2000, the US astronomy decadal review committee recommended the construction of a 30-meter
ACTUATED HYBRID MIRROR TECHNOLOGY LARGE OPTICS WORKING GROUP (LOWG)
 ACTUATED HYBRID MIRROR TECHNOLOGY LARGE OPTICS WORKING GROUP (LOWG) From: Howard A. MacEwen ManTech SRS Technologies, Inc. Chantilly, VA 20151 I INTRODUCTION Developments over the past five to ten years
ACTUATED HYBRID MIRROR TECHNOLOGY LARGE OPTICS WORKING GROUP (LOWG) From: Howard A. MacEwen ManTech SRS Technologies, Inc. Chantilly, VA 20151 I INTRODUCTION Developments over the past five to ten years
Adaptive Optics for ELTs with Low-Cost and Lightweight Segmented Deformable Mirrors
 1st AO4ELT conference, 06006 (20) DOI:.51/ao4elt/2006006 Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 20 Adaptive Optics for ELTs with Low-Cost and Lightweight Segmented Deformable Mirrors Gonçalo
1st AO4ELT conference, 06006 (20) DOI:.51/ao4elt/2006006 Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 20 Adaptive Optics for ELTs with Low-Cost and Lightweight Segmented Deformable Mirrors Gonçalo
The 20/20 telescope: Concept for a 30 m GSMT
 The : Concept for a 30 m GSMT Roger Angel, Warren Davison, Keith Hege, Phil Hinz, Buddy Martin, Steve Miller, Jose Sasian & Neville Woolf University of Arizona 1 The : combining the best of filled aperture
The : Concept for a 30 m GSMT Roger Angel, Warren Davison, Keith Hege, Phil Hinz, Buddy Martin, Steve Miller, Jose Sasian & Neville Woolf University of Arizona 1 The : combining the best of filled aperture
System Architecting: Defining Optical and Mechanical Tolerances from an Error Budget
 System Architecting: Defining Optical and Mechanical Tolerances from an Error Budget Julia Zugby OPTI-521: Introductory Optomechanical Engineering, Fall 2016 Overview This tutorial provides a general overview
System Architecting: Defining Optical and Mechanical Tolerances from an Error Budget Julia Zugby OPTI-521: Introductory Optomechanical Engineering, Fall 2016 Overview This tutorial provides a general overview
AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%.
 Application Note AN004: Fiber Coupling Improvement Introduction AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%. Industrial lasers used for cutting, welding, drilling,
Application Note AN004: Fiber Coupling Improvement Introduction AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%. Industrial lasers used for cutting, welding, drilling,
Development of a Deformable Mirror for High-Power Lasers
 Development of a Deformable Mirror for High-Power Lasers Dr. Justin Mansell and Robert Praus MZA Associates Corporation Mirror Technology Days August 1, 2007 1 Outline Introduction & Project Goal Deformable
Development of a Deformable Mirror for High-Power Lasers Dr. Justin Mansell and Robert Praus MZA Associates Corporation Mirror Technology Days August 1, 2007 1 Outline Introduction & Project Goal Deformable
from ground adaptive secondaries to a space active primary Xompero, M., Briguglio, R., Lisi, F., Arcidiacono, C., Riccardi, A.
 LATT: Large Aperture Telescope Technology from ground adaptive secondaries to a space active primary Xompero, M., Briguglio, R., Lisi, F., Arcidiacono, C., Riccardi, A. The LATT Team CGS S.p.A.: coordinator
LATT: Large Aperture Telescope Technology from ground adaptive secondaries to a space active primary Xompero, M., Briguglio, R., Lisi, F., Arcidiacono, C., Riccardi, A. The LATT Team CGS S.p.A.: coordinator
"Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements
 "Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements by Dr. Frank Melsheimer DFM Engineering, Inc. 1035 Delaware Avenue Longmont, Colorado 80501 phone 303-678-8143 fax 303-772-9411 www.dfmengineering.com Table
"Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements by Dr. Frank Melsheimer DFM Engineering, Inc. 1035 Delaware Avenue Longmont, Colorado 80501 phone 303-678-8143 fax 303-772-9411 www.dfmengineering.com Table
Stretched Membrane with Electrostatic Curvature (SMEC) Mirrors: A new technology for large lightweight space telescopes
 Stretched Membrane with Electrostatic Curvature (SMEC) Mirrors: A new technology for large lightweight space telescopes Simona Errico a, Roger Angel b, Brian Stamper a, James Burge a, Tom Connors b a Optical
Stretched Membrane with Electrostatic Curvature (SMEC) Mirrors: A new technology for large lightweight space telescopes Simona Errico a, Roger Angel b, Brian Stamper a, James Burge a, Tom Connors b a Optical
Manufacturing Process of the Hubble Space Telescope s Primary Mirror
 Kirkwood 1 Manufacturing Process of the Hubble Space Telescope s Primary Mirror Chase Kirkwood EME 050 Winter 2017 03/11/2017 Kirkwood 2 Abstract- The primary mirror of the Hubble Space Telescope was a
Kirkwood 1 Manufacturing Process of the Hubble Space Telescope s Primary Mirror Chase Kirkwood EME 050 Winter 2017 03/11/2017 Kirkwood 2 Abstract- The primary mirror of the Hubble Space Telescope was a
POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS
 POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS Leonid Beresnev1, Mikhail Vorontsov1,2 and Peter Wangsness3 1) US Army Research Laboratory, 2800 Powder Mill Road, Adelphi Maryland 20783, lberesnev@arl.army.mil,
POCKET DEFORMABLE MIRROR FOR ADAPTIVE OPTICS APPLICATIONS Leonid Beresnev1, Mikhail Vorontsov1,2 and Peter Wangsness3 1) US Army Research Laboratory, 2800 Powder Mill Road, Adelphi Maryland 20783, lberesnev@arl.army.mil,
Advanced UVOIR Mirror Technology Development for Very Large Space Telescopes. H. Philip Stahl
 Advanced UVOIR Mirror Technology Development for Very Large Space Telescopes H. Philip Stahl Objective Define and initiate a long-term program to mature six inter-linked critical technologies for future
Advanced UVOIR Mirror Technology Development for Very Large Space Telescopes H. Philip Stahl Objective Define and initiate a long-term program to mature six inter-linked critical technologies for future
Testing an off-axis parabola with a CGH and a spherical mirror as null lens
 Testing an off-axis parabola with a CGH and a spherical mirror as null lens Chunyu Zhao a, Rene Zehnder a, James H. Burge a, Hubert M. Martin a,b a College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona 1630
Testing an off-axis parabola with a CGH and a spherical mirror as null lens Chunyu Zhao a, Rene Zehnder a, James H. Burge a, Hubert M. Martin a,b a College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona 1630
Segmented deformable mirrors for Ground layer Adaptive Optics
 Segmented deformable mirrors for Ground layer Adaptive Optics Edward Kibblewhite, University of Chicago Adaptive Photonics LLC Ground Layer AO Shack Hartmann Images of 5 guide stars in Steward Observatory
Segmented deformable mirrors for Ground layer Adaptive Optics Edward Kibblewhite, University of Chicago Adaptive Photonics LLC Ground Layer AO Shack Hartmann Images of 5 guide stars in Steward Observatory
A JWST Derivative Design for the Next Large Aperture UV/Optical Telescope
 A JWST Derivative Design for the Next Large Aperture UV/Optical Telescope W. B. Whiddon Next Large Aperture Optical/UV Telescope Workshop 11 April 2003 Strategy JWST is the nation's investment in large
A JWST Derivative Design for the Next Large Aperture UV/Optical Telescope W. B. Whiddon Next Large Aperture Optical/UV Telescope Workshop 11 April 2003 Strategy JWST is the nation's investment in large
Integrated Micro Machines Inc.
 Integrated Micro Machines Inc. Segmented Galvanometer-Driven Deformable Mirrors Keith O Hara The segmented mirror array developed for an optical cross connect Requirements for the cross-connect Requirements
Integrated Micro Machines Inc. Segmented Galvanometer-Driven Deformable Mirrors Keith O Hara The segmented mirror array developed for an optical cross connect Requirements for the cross-connect Requirements
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Optics Quality Assessment for Lightweight Deployable Optics
 Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Optics Quality Assessment for Lightweight Deployable Optics Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Ty Martinez 1, Sergio R. Restaino 1, Freddie Santiago 1, Christopher C. Wilcox
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) Optics Quality Assessment for Lightweight Deployable Optics Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Ty Martinez 1, Sergio R. Restaino 1, Freddie Santiago 1, Christopher C. Wilcox
Technology Days GSFC Optics Technologies. Dr. Petar Arsenovic
 Technology Days 2011 GSFC Optics Technologies Dr. Petar Arsenovic Optics Capabilities Optical Design and Analysis Opto-mechanical Design and Fabrication Materials and Thin Films Component Development and
Technology Days 2011 GSFC Optics Technologies Dr. Petar Arsenovic Optics Capabilities Optical Design and Analysis Opto-mechanical Design and Fabrication Materials and Thin Films Component Development and
Design parameters Summary
 634 Entrance pupil diameter 100-m Entrance pupil location Primary mirror Exit pupil location On M6 Focal ratio 6.03 Plate scale 2.924 mm / arc second (on-axis) Total field of view 10 arc minutes (unvignetted)
634 Entrance pupil diameter 100-m Entrance pupil location Primary mirror Exit pupil location On M6 Focal ratio 6.03 Plate scale 2.924 mm / arc second (on-axis) Total field of view 10 arc minutes (unvignetted)
Manufacture of 8.4 m off-axis segments: a 1/5 scale demonstration
 Manufacture of 8.4 m off-axis segments: a 1/5 scale demonstration H. M. Martin a, J. H. Burge a,b, B. Cuerden a, S. M. Miller a, B. Smith a, C. Zhao b a Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson,
Manufacture of 8.4 m off-axis segments: a 1/5 scale demonstration H. M. Martin a, J. H. Burge a,b, B. Cuerden a, S. M. Miller a, B. Smith a, C. Zhao b a Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson,
Steve O Dell
 Optics requirements for the Generation-X x-ray telescope Steve O Dell NASA Marshall Space Flight Center 2008.10.09-11 Authors Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) Roger Brissenden, Dan Schwartz,
Optics requirements for the Generation-X x-ray telescope Steve O Dell NASA Marshall Space Flight Center 2008.10.09-11 Authors Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) Roger Brissenden, Dan Schwartz,
MODULAR ADAPTIVE OPTICS TESTBED FOR THE NPOI
 MODULAR ADAPTIVE OPTICS TESTBED FOR THE NPOI Jonathan R. Andrews, Ty Martinez, Christopher C. Wilcox, Sergio R. Restaino Naval Research Laboratory, Remote Sensing Division, Code 7216, 4555 Overlook Ave
MODULAR ADAPTIVE OPTICS TESTBED FOR THE NPOI Jonathan R. Andrews, Ty Martinez, Christopher C. Wilcox, Sergio R. Restaino Naval Research Laboratory, Remote Sensing Division, Code 7216, 4555 Overlook Ave
Optics for the 20/20 telescope
 Optics for the 20/20 telescope H. M. Martin a, J. R. P. Angel a, J. H. Burge a,b, S. M. Miller a, J. M. Sasian b and P. A. Strittmatter a a Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
Optics for the 20/20 telescope H. M. Martin a, J. R. P. Angel a, J. H. Burge a,b, S. M. Miller a, J. M. Sasian b and P. A. Strittmatter a a Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
Design, Fabrication, and Validation of an Ultra-Lightweight Membrane Mirror
 Design, Fabrication, and Validation of an Ultra-Lightweight Membrane Mirror Surya Chodimella, James D. Moore, Brian G. Patrick SRS Technologies, Huntsville AL, USA 35806 Brett deblonk, Dan K. Marker Air
Design, Fabrication, and Validation of an Ultra-Lightweight Membrane Mirror Surya Chodimella, James D. Moore, Brian G. Patrick SRS Technologies, Huntsville AL, USA 35806 Brett deblonk, Dan K. Marker Air
BMC s heritage deformable mirror technology that uses hysteresis free electrostatic
 Optical Modulator Technical Whitepaper MEMS Optical Modulator Technology Overview The BMC MEMS Optical Modulator, shown in Figure 1, was designed for use in free space optical communication systems. The
Optical Modulator Technical Whitepaper MEMS Optical Modulator Technology Overview The BMC MEMS Optical Modulator, shown in Figure 1, was designed for use in free space optical communication systems. The
3M Custom Formed Reflectors Design Guide Considerations
 3M Custom Formed Reflectors Design Guide Considerations 3M Custom Formed Reflectors increase the optical efficiency of a light fixture by using precise reflection optics to raise the lumen output. Each
3M Custom Formed Reflectors Design Guide Considerations 3M Custom Formed Reflectors increase the optical efficiency of a light fixture by using precise reflection optics to raise the lumen output. Each
A Scalable Deployable High Gain Reflectarray Antenna - DaHGR
 A Scalable Deployable High Gain Reflectarray Antenna - DaHGR Presented by: P. Keith Kelly, PhD MMA Design LLC 1 MMA Overview Facilities in Boulder County Colorado 10,000 SF facility Cleanroom / Flight
A Scalable Deployable High Gain Reflectarray Antenna - DaHGR Presented by: P. Keith Kelly, PhD MMA Design LLC 1 MMA Overview Facilities in Boulder County Colorado 10,000 SF facility Cleanroom / Flight
Micro Precision Apertures
 National Aperture, Inc. Micro Precision Apertures Product Guide Precision apertures, targets and patterns, including round, slit, square, etc., for universal and high power applications National Aperture,
National Aperture, Inc. Micro Precision Apertures Product Guide Precision apertures, targets and patterns, including round, slit, square, etc., for universal and high power applications National Aperture,
Panel 2: Observatories
 NRC Workshop on NASA Instruments, Observatories, & Sensor Systems Technology National Academies Beckman Center, Irvine, CA 3/29/2011 Panel 2: Observatories Tony Hull L-3 Integrated Optical Systems Tinsley,
NRC Workshop on NASA Instruments, Observatories, & Sensor Systems Technology National Academies Beckman Center, Irvine, CA 3/29/2011 Panel 2: Observatories Tony Hull L-3 Integrated Optical Systems Tinsley,
Practical Applications of Laser Technology for Semiconductor Electronics
 Practical Applications of Laser Technology for Semiconductor Electronics MOPA Single Pass Nanosecond Laser Applications for Semiconductor / Solar / MEMS & General Manufacturing Mark Brodsky US Application
Practical Applications of Laser Technology for Semiconductor Electronics MOPA Single Pass Nanosecond Laser Applications for Semiconductor / Solar / MEMS & General Manufacturing Mark Brodsky US Application
Starshade Technology Development Status
 Starshade Technology Development Status Dr. Nick Siegler NASA Exoplanets Exploration Program Chief Technologist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Dr. John Ziemer NASA Exoplanets
Starshade Technology Development Status Dr. Nick Siegler NASA Exoplanets Exploration Program Chief Technologist Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Dr. John Ziemer NASA Exoplanets
Mirrors. Plano and Spherical. Mirrors. Published on II-VI Infrared
 Page 1 of 13 Published on II-VI Infrared Plano and Spherical or total reflectors are used in laser cavities as rear reflectors and fold mirrors, and externally as beam benders in beam delivery systems.
Page 1 of 13 Published on II-VI Infrared Plano and Spherical or total reflectors are used in laser cavities as rear reflectors and fold mirrors, and externally as beam benders in beam delivery systems.
Precision Micro-Aperture Catalog
 National Aperture, Inc. Precision Micro-Aperture Catalog Version 2012 PLEASE CONTACT: Data Optics, Inc. Distributor for National Aperture, Inc. Phone: (734) 483-8228 (800) 321-9026 Fax: (734) 483-9879
National Aperture, Inc. Precision Micro-Aperture Catalog Version 2012 PLEASE CONTACT: Data Optics, Inc. Distributor for National Aperture, Inc. Phone: (734) 483-8228 (800) 321-9026 Fax: (734) 483-9879
Vladimir Vassiliev UCLA
 Vladimir Vassiliev UCLA Reduce cost of FP instrumentation (small plate scale) Improve imaging quality (angular resolution) Minimize isochronous distortion (energy threshold, +) Increase FoV (sky survey,
Vladimir Vassiliev UCLA Reduce cost of FP instrumentation (small plate scale) Improve imaging quality (angular resolution) Minimize isochronous distortion (energy threshold, +) Increase FoV (sky survey,
Agilent 10705A Single Beam Interferometer and Agilent 10704A Retroreflector
 7B Agilent 10705A Single Beam Interferometer and Agilent 10704A Retroreflector Description Description The Agilent 10705A Single Beam Interferometer (shown in Figure 7B-1) is intended for use in low-mass
7B Agilent 10705A Single Beam Interferometer and Agilent 10704A Retroreflector Description Description The Agilent 10705A Single Beam Interferometer (shown in Figure 7B-1) is intended for use in low-mass
The Challenge. SPOT Vegetation. miniaturization. Proba Vegetation. Technology assessment:
 The Challenge Spot-5 lifetime expires in 2012. The next French satellite, Pleiades, is solely dedicated to HiRes. The Belgian Federal Science Policy Office (BELSPO) declared their interest to develop an
The Challenge Spot-5 lifetime expires in 2012. The next French satellite, Pleiades, is solely dedicated to HiRes. The Belgian Federal Science Policy Office (BELSPO) declared their interest to develop an
ESCC2006 European Supply Chain Convention
 ESCC2006 European Supply Chain Convention PCB Paper 20 Laser Technology for cutting FPC s and PCB s Mark Hüske, Innovation Manager, LPKF Laser & Electronics AG, Germany Laser Technology for cutting FPCs
ESCC2006 European Supply Chain Convention PCB Paper 20 Laser Technology for cutting FPC s and PCB s Mark Hüske, Innovation Manager, LPKF Laser & Electronics AG, Germany Laser Technology for cutting FPCs
Refractive index homogeneity TWE effect on large aperture optical systems
 Refractive index homogeneity TWE effect on large aperture optical systems M. Stout*, B. Neff II-VI Optical Systems 36570 Briggs Road., Murrieta, CA 92563 ABSTRACT Sapphire windows are routinely being used
Refractive index homogeneity TWE effect on large aperture optical systems M. Stout*, B. Neff II-VI Optical Systems 36570 Briggs Road., Murrieta, CA 92563 ABSTRACT Sapphire windows are routinely being used
62xxH Series Galvanometer Scanners
 Product Highlights Our popular xxh Series of closed loop, galvanometer-based scanners is consistently the industry s leading solution for high-performance laser beam steering. Each motor combines our moving
Product Highlights Our popular xxh Series of closed loop, galvanometer-based scanners is consistently the industry s leading solution for high-performance laser beam steering. Each motor combines our moving
Selective Soldering for Interconnection Technology Used in Enterprise Communication Apparatuses
 Selective Soldering for Interconnection Technology Used in Enterprise Communication Apparatuses Mark Woolley, Wesley Brown, and Dr. Jae Choi Avaya Inc. 1300 W 120 th Avenue Westminster, CO 80234 Abstract:
Selective Soldering for Interconnection Technology Used in Enterprise Communication Apparatuses Mark Woolley, Wesley Brown, and Dr. Jae Choi Avaya Inc. 1300 W 120 th Avenue Westminster, CO 80234 Abstract:
Figure 1 : Topologies of a capacitive switch The actuation voltage can be expressed as the following :
 ABSTRACT This paper outlines the issues related to RF MEMS packaging and low actuation voltage. An original approach is presented concerning the modeling of capacitive contacts using multiphysics simulation
ABSTRACT This paper outlines the issues related to RF MEMS packaging and low actuation voltage. An original approach is presented concerning the modeling of capacitive contacts using multiphysics simulation
Vixar High Power Array Technology
 Vixar High Power Array Technology I. Introduction VCSELs arrays emitting power ranging from 50mW to 10W have emerged as an important technology for applications within the consumer, industrial, automotive
Vixar High Power Array Technology I. Introduction VCSELs arrays emitting power ranging from 50mW to 10W have emerged as an important technology for applications within the consumer, industrial, automotive
Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr.
 Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr. Introduction Chapter 4 of Opto-Mechanical Systems Design by Paul R. Yoder, Jr. is an introduction
Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr. Introduction Chapter 4 of Opto-Mechanical Systems Design by Paul R. Yoder, Jr. is an introduction
Fabrication and testing of large free-form surfaces Jim H. Burge
 Fabrication and testing of large free-form surfaces Jim H. Burge College of Optical Sciences + Steward Observatory University of Arizona Tucson, AZ 85721 Introduction A tutorial on Fabrication and testing
Fabrication and testing of large free-form surfaces Jim H. Burge College of Optical Sciences + Steward Observatory University of Arizona Tucson, AZ 85721 Introduction A tutorial on Fabrication and testing
Difrotec Product & Services. Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions
 Difrotec Product & Services Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions Content 1. Overview 2. Interferometer D7 3. Benefits 4. Measurements 5. Specifications 6. Applications 7. Cases
Difrotec Product & Services Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions Content 1. Overview 2. Interferometer D7 3. Benefits 4. Measurements 5. Specifications 6. Applications 7. Cases
Non-adaptive Wavefront Control
 OWL Phase A Review - Garching - 2 nd to 4 th Nov 2005 Non-adaptive Wavefront Control (Presented by L. Noethe) 1 Specific problems in ELTs and OWL Concentrate on problems which are specific for ELTs and,
OWL Phase A Review - Garching - 2 nd to 4 th Nov 2005 Non-adaptive Wavefront Control (Presented by L. Noethe) 1 Specific problems in ELTs and OWL Concentrate on problems which are specific for ELTs and,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
The Core Optics. Input Mirror T ~ 3% T ~ 3% Signal Recycling Photodetector
 The Core Optics End Mirror Power Recycling Mirror Input Mirror T ~ 3% T ~ 3% End Mirror T ~ 10 ppm Laser Nd:Yag 6 W 100 W 12 kw 20 m 4000 m Signal Recycling Photodetector Mirror (dark fringe) Fold mirrors
The Core Optics End Mirror Power Recycling Mirror Input Mirror T ~ 3% T ~ 3% End Mirror T ~ 10 ppm Laser Nd:Yag 6 W 100 W 12 kw 20 m 4000 m Signal Recycling Photodetector Mirror (dark fringe) Fold mirrors
ADALAM Sensor based adaptive laser micromachining using ultrashort pulse lasers for zero-failure manufacturing D2.2. Ger Folkersma (Demcon)
 D2.2 Automatic adjustable reference path system Document Coordinator: Contributors: Dissemination: Keywords: Ger Folkersma (Demcon) Ger Folkersma, Kevin Voss, Marvin Klein (Demcon) Public Reference path,
D2.2 Automatic adjustable reference path system Document Coordinator: Contributors: Dissemination: Keywords: Ger Folkersma (Demcon) Ger Folkersma, Kevin Voss, Marvin Klein (Demcon) Public Reference path,
THICK-FILM LASER TRIMMING PRINCIPLES, TECHNIQUES
 Electrocomponent Science and Technology, 1981, Vol. 9, pp. 9-14 0305,3091/81/0901-0009 $06.50/0 (C) 1981 Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Inc. Printed in Great Britain THICK-FILM LASER TRIMMING PRINCIPLES,
Electrocomponent Science and Technology, 1981, Vol. 9, pp. 9-14 0305,3091/81/0901-0009 $06.50/0 (C) 1981 Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Inc. Printed in Great Britain THICK-FILM LASER TRIMMING PRINCIPLES,
Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing
 Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing Dr. Jim Burge Associate Professor Optical Sciences and Astronomy University of Arizona jburge@optics.arizona.edu 520-621-8182 Computer Generated Holograms
Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing Dr. Jim Burge Associate Professor Optical Sciences and Astronomy University of Arizona jburge@optics.arizona.edu 520-621-8182 Computer Generated Holograms
Copyright 2006 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers.
 Copyright 2006 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in SPIE Proceedings, Volume 6304 and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or
Copyright 2006 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in SPIE Proceedings, Volume 6304 and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or
RESTEO REFLECTOR SYNERGY BETWEEN TELECOM AND EARTH OBSERVATION
 European Space Agency ESA-ESTEC ITT: AO 1-6282/09/NL/AF ESA Contract N. 4000101324/10/NL/AF RESTEO REFLECTOR SYNERGY BETWEEN TELECOM AND EARTH OBSERVATION Executive Summary March 2012 Page 1 of 10 LIST
European Space Agency ESA-ESTEC ITT: AO 1-6282/09/NL/AF ESA Contract N. 4000101324/10/NL/AF RESTEO REFLECTOR SYNERGY BETWEEN TELECOM AND EARTH OBSERVATION Executive Summary March 2012 Page 1 of 10 LIST
Payload Configuration, Integration and Testing of the Deformable Mirror Demonstration Mission (DeMi) CubeSat
 SSC18-VIII-05 Payload Configuration, Integration and Testing of the Deformable Mirror Demonstration Mission (DeMi) CubeSat Jennifer Gubner Wellesley College, Massachusetts Institute of Technology 21 Wellesley
SSC18-VIII-05 Payload Configuration, Integration and Testing of the Deformable Mirror Demonstration Mission (DeMi) CubeSat Jennifer Gubner Wellesley College, Massachusetts Institute of Technology 21 Wellesley
Lockheed Martin 2016 LOCKHEED MARTIN CORPORATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 Lockheed Martin 1 Helping the Future Arrive 2 Our People 115,000 Employees 60,000 Scientists & Engineers 500+ U.S. Facilities Operating in 70 Countries 3 Lockheed Martin 100+ Years of Accelerating Tomorrow
Lockheed Martin 1 Helping the Future Arrive 2 Our People 115,000 Employees 60,000 Scientists & Engineers 500+ U.S. Facilities Operating in 70 Countries 3 Lockheed Martin 100+ Years of Accelerating Tomorrow
NIRCam optical calibration sources
 NIRCam optical calibration sources Stephen F. Somerstein, Glen D. Truong Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, D/ABDS, B/201 3251 Hanover St., Palo Alto, CA 94304-1187 ABSTRACT The Near Infrared
NIRCam optical calibration sources Stephen F. Somerstein, Glen D. Truong Lockheed Martin Advanced Technology Center, D/ABDS, B/201 3251 Hanover St., Palo Alto, CA 94304-1187 ABSTRACT The Near Infrared
Agilent 10774A Short Range Straightness Optics and Agilent 10775A Long Range Straightness Optics
 7Y Agilent 10774A Short Range Straightness Optics and Agilent 10775A Long Range Straightness Optics Introduction Introduction Straightness measures displacement perpendicular to the axis of intended motion
7Y Agilent 10774A Short Range Straightness Optics and Agilent 10775A Long Range Straightness Optics Introduction Introduction Straightness measures displacement perpendicular to the axis of intended motion
New Optics for Astronomical Polarimetry
 New Optics for Astronomical Polarimetry Located in Colorado USA Topics Components for polarization control and polarimetry Organic materials Liquid crystals Birefringent polymers Microstructures Metrology
New Optics for Astronomical Polarimetry Located in Colorado USA Topics Components for polarization control and polarimetry Organic materials Liquid crystals Birefringent polymers Microstructures Metrology
Exercise 8: Interference and diffraction
 Physics 223 Name: Exercise 8: Interference and diffraction 1. In a two-slit Young s interference experiment, the aperture (the mask with the two slits) to screen distance is 2.0 m, and a red light of wavelength
Physics 223 Name: Exercise 8: Interference and diffraction 1. In a two-slit Young s interference experiment, the aperture (the mask with the two slits) to screen distance is 2.0 m, and a red light of wavelength
USER MANUAL VarioS-Microscanner-Demonstrators
 FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTE FOR PHOTONIC MICROSYSTEMS IPMS USER MANUAL VarioS-Microscanner-Demonstrators last revision : 2014-11-14 [Fb046.08] USER MANUAL.doc Introduction Thank you for purchasing a VarioS-microscanner-demonstrator
FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTE FOR PHOTONIC MICROSYSTEMS IPMS USER MANUAL VarioS-Microscanner-Demonstrators last revision : 2014-11-14 [Fb046.08] USER MANUAL.doc Introduction Thank you for purchasing a VarioS-microscanner-demonstrator
Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror Contract No. NNX09CF40P (SBIR ) (MSFC)
 Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror Contract No. NNX09CF40P (SBIR 2008-1) (MSFC) Mirror Technology SBIR/STTR Workshop June 16 th to 18 th, 2009 Hilton Albuquerque, Albuquerque, NM John M. Casstevens
Low Cost Very Large Diamond Turned Metal Mirror Contract No. NNX09CF40P (SBIR 2008-1) (MSFC) Mirror Technology SBIR/STTR Workshop June 16 th to 18 th, 2009 Hilton Albuquerque, Albuquerque, NM John M. Casstevens
PHYS 202 OUTLINE FOR PART III LIGHT & OPTICS
 PHYS 202 OUTLINE FOR PART III LIGHT & OPTICS Electromagnetic Waves A. Electromagnetic waves S-23,24 1. speed of waves = 1/( o o ) ½ = 3 x 10 8 m/s = c 2. waves and frequency: the spectrum (a) radio red
PHYS 202 OUTLINE FOR PART III LIGHT & OPTICS Electromagnetic Waves A. Electromagnetic waves S-23,24 1. speed of waves = 1/( o o ) ½ = 3 x 10 8 m/s = c 2. waves and frequency: the spectrum (a) radio red
Adaptive optics for laser-based manufacturing processes
 Adaptive optics for laser-based manufacturing processes Rainer Beck 1, Jon Parry 1, Rhys Carrington 1,William MacPherson 1, Andrew Waddie 1, Derryck Reid 1, Nick Weston 2, Jon Shephard 1, Duncan Hand 1
Adaptive optics for laser-based manufacturing processes Rainer Beck 1, Jon Parry 1, Rhys Carrington 1,William MacPherson 1, Andrew Waddie 1, Derryck Reid 1, Nick Weston 2, Jon Shephard 1, Duncan Hand 1
Inflatably Deployed Membrane Waveguide Array Antenna for Space
 Inflatably Deployed Membrane Waveguide Array Antenna for Space David Lichodziejewski * L Garde, Inc. Dr. Robin Cravey NASA LaRC Glenn Hopkins Georgia Technical Research Institute Abstract As an alternative
Inflatably Deployed Membrane Waveguide Array Antenna for Space David Lichodziejewski * L Garde, Inc. Dr. Robin Cravey NASA LaRC Glenn Hopkins Georgia Technical Research Institute Abstract As an alternative
Manufacture of a 1.7 m prototype of the GMT primary mirror segments
 Manufacture of a 1.7 m prototype of the GMT primary mirror segments H. M. Martin a, J. H. Burge a,b, S. M. Miller a, B. K. Smith a, R. Zehnder b, C. Zhao b a Steward Observatory, University of Arizona,
Manufacture of a 1.7 m prototype of the GMT primary mirror segments H. M. Martin a, J. H. Burge a,b, S. M. Miller a, B. K. Smith a, R. Zehnder b, C. Zhao b a Steward Observatory, University of Arizona,
Large Submillimeter Atacama Telescope. A Strawman Concept
 Large Submillimeter Atacama Telescope A Strawman Concept T.A. Sebring, G. Cortes, C. Henderson The Real Process Define Science Goals Derive Telescope Reqts Flow-Down Subsystem Reqts Develop Concepts An
Large Submillimeter Atacama Telescope A Strawman Concept T.A. Sebring, G. Cortes, C. Henderson The Real Process Define Science Goals Derive Telescope Reqts Flow-Down Subsystem Reqts Develop Concepts An
Alternative to Germanium Gaining Momentum for IR Optics
 Alternative to Germanium Gaining Momentum for IR Optics Chalcogenides are fast becoming the material of choice, thanks to advances in system modeling tools and metrology techniques, combined with the efficiencies
Alternative to Germanium Gaining Momentum for IR Optics Chalcogenides are fast becoming the material of choice, thanks to advances in system modeling tools and metrology techniques, combined with the efficiencies
Adaptive Optics for LIGO
 Adaptive Optics for LIGO Justin Mansell Ginzton Laboratory LIGO-G990022-39-M Motivation Wavefront Sensor Outline Characterization Enhancements Modeling Projections Adaptive Optics Results Effects of Thermal
Adaptive Optics for LIGO Justin Mansell Ginzton Laboratory LIGO-G990022-39-M Motivation Wavefront Sensor Outline Characterization Enhancements Modeling Projections Adaptive Optics Results Effects of Thermal
Lawrence Livermore National. Laboratory. Large Aperture Fresnel Telescopes. R. A. Hyde. July 16, 1998 UCRL-ID
 UCRL-ID-131320 Large Aperture Fresnel Telescopes R. A. Hyde July 16, 1998 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory This is an informal report intended primarily for internal or limited external distribution.
UCRL-ID-131320 Large Aperture Fresnel Telescopes R. A. Hyde July 16, 1998 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory This is an informal report intended primarily for internal or limited external distribution.
The Renishaw Additive Manufacturing formula
 Renishaw Investor Day 2018 The Renishaw Additive Manufacturing formula Clive Martell Head of Global Additive Manufacturing What is Renishaw additive manufacturing? Renishaw and additive manufacturing Additive
Renishaw Investor Day 2018 The Renishaw Additive Manufacturing formula Clive Martell Head of Global Additive Manufacturing What is Renishaw additive manufacturing? Renishaw and additive manufacturing Additive
Figure 7 Dynamic range expansion of Shack- Hartmann sensor using a spatial-light modulator
 Figure 4 Advantage of having smaller focal spot on CCD with super-fine pixels: Larger focal point compromises the sensitivity, spatial resolution, and accuracy. Figure 1 Typical microlens array for Shack-Hartmann
Figure 4 Advantage of having smaller focal spot on CCD with super-fine pixels: Larger focal point compromises the sensitivity, spatial resolution, and accuracy. Figure 1 Typical microlens array for Shack-Hartmann
Advances in stacked-die packaging
 pg.10-15-carson-art 16/6/03 4:12 pm Page 1 The stacking of die within IC packages, primarily Chip Scale Packages (CSP) Ball Grid Arrays (BGAs) has evolved rapidly over the last few years. The now standard
pg.10-15-carson-art 16/6/03 4:12 pm Page 1 The stacking of die within IC packages, primarily Chip Scale Packages (CSP) Ball Grid Arrays (BGAs) has evolved rapidly over the last few years. The now standard
Deformable MEMS Micromirror Array for Wavelength and Angle Insensitive Retro-Reflecting Modulators Trevor K. Chan & Joseph E. Ford
 Photonics Systems Integration Lab UCSD Jacobs School of Engineering Deformable MEMS Micromirror Array for Wavelength and Angle Insensitive Retro-Reflecting Modulators Trevor K. Chan & Joseph E. Ford PHOTONIC
Photonics Systems Integration Lab UCSD Jacobs School of Engineering Deformable MEMS Micromirror Array for Wavelength and Angle Insensitive Retro-Reflecting Modulators Trevor K. Chan & Joseph E. Ford PHOTONIC
Progress in manufacturing the first 8.4 m off-axis segment for the Giant Magellan Telescope
 Progress in manufacturing the first 8.4 m off-axis segment for the Giant Magellan Telescope H. M. Martin a, J. H. Burge a,b, B. Cuerden a, W. B. Davison a, J. S. Kingsley a, W. C. Kittrell a, R. D. Lutz
Progress in manufacturing the first 8.4 m off-axis segment for the Giant Magellan Telescope H. M. Martin a, J. H. Burge a,b, B. Cuerden a, W. B. Davison a, J. S. Kingsley a, W. C. Kittrell a, R. D. Lutz
Sintec Optronics Technology Pte Ltd 10 Bukit Batok Crescent #07-02 The Spire Singapore Tel: Fax:
 Sintec Optronics Technology Pte Ltd 10 Bukit Batok Crescent #07-02 The Spire Singapore 658079 Tel: +65 63167112 Fax: +65 63167113 High-power Nd:YAG Self-floating Laser Cutting Head We supply the laser
Sintec Optronics Technology Pte Ltd 10 Bukit Batok Crescent #07-02 The Spire Singapore 658079 Tel: +65 63167112 Fax: +65 63167113 High-power Nd:YAG Self-floating Laser Cutting Head We supply the laser
Production of 8.4 m segments for the Giant Magellan Telescope
 Production of 8.4 m segments for the Giant Magellan Telescope H. M. Martin a, R. G. Allen a, J. H. Burge a,b, D. W. Kim b, J. S. Kingsley a, K. Law a, R. D. Lutz a, P. A. Strittmatter a, P. Su b, M. T.
Production of 8.4 m segments for the Giant Magellan Telescope H. M. Martin a, R. G. Allen a, J. H. Burge a,b, D. W. Kim b, J. S. Kingsley a, K. Law a, R. D. Lutz a, P. A. Strittmatter a, P. Su b, M. T.
Open-loop performance of a high dynamic range reflective wavefront sensor
 Open-loop performance of a high dynamic range reflective wavefront sensor Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Scott W. Teare 2, Sergio R. Restaino 1, David Wick 3, Christopher C. Wilcox 1, Ty Martinez 1 Abstract: Sandia
Open-loop performance of a high dynamic range reflective wavefront sensor Jonathan R. Andrews 1, Scott W. Teare 2, Sergio R. Restaino 1, David Wick 3, Christopher C. Wilcox 1, Ty Martinez 1 Abstract: Sandia
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Optical Telescope Design Study Results
 Optical Telescope Design Study Results 10 th International LISA Symposium Jeff Livas 20 May 2014 See also poster #19: Shannon Sankar UF and GSFC Telescope Design for a Space-based Gravitational-wave Mission
Optical Telescope Design Study Results 10 th International LISA Symposium Jeff Livas 20 May 2014 See also poster #19: Shannon Sankar UF and GSFC Telescope Design for a Space-based Gravitational-wave Mission
A BASIC EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF CAST FILM EXTRUSION PROCESS FOR FABRICATION OF PLASTIC MICROLENS ARRAY DEVICE
 A BASIC EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF CAST FILM EXTRUSION PROCESS FOR FABRICATION OF PLASTIC MICROLENS ARRAY DEVICE Chih-Yuan Chang and Yi-Min Hsieh and Xuan-Hao Hsu Department of Mold and Die Engineering, National
A BASIC EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF CAST FILM EXTRUSION PROCESS FOR FABRICATION OF PLASTIC MICROLENS ARRAY DEVICE Chih-Yuan Chang and Yi-Min Hsieh and Xuan-Hao Hsu Department of Mold and Die Engineering, National
Physics 11. Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2
 Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
End Capped High Power Assemblies
 Fiberguide s end capped fiber optic assemblies allow the user to achieve higher coupled power into a fiber core by reducing the power density at the air/ silica interface, commonly the point of laser damage.
Fiberguide s end capped fiber optic assemblies allow the user to achieve higher coupled power into a fiber core by reducing the power density at the air/ silica interface, commonly the point of laser damage.
Module 10 : Improvement of rock mass responses. Content
 IMPROVEMENT OF ROCK MASS RESPONSES Content 10.1 INTRODUCTION 10.2 ROCK REINFORCEMENT Rock bolts, dowels and anchors 10.3 ROCK BOLTING MECHANICS Suspension theory Beam building theory Keying theory 10.4
IMPROVEMENT OF ROCK MASS RESPONSES Content 10.1 INTRODUCTION 10.2 ROCK REINFORCEMENT Rock bolts, dowels and anchors 10.3 ROCK BOLTING MECHANICS Suspension theory Beam building theory Keying theory 10.4
SOLDER PASTE STENCIL MANUFACTURING METHODS AND THEIR IMPACT ON PRECISION AND ACCURACY
 SOLDER PASTE STENCIL MANUFACTURING METHODS AND THEIR IMPACT ON PRECISION AND ACCURACY Ahne Oosterhof Oosterhof Consulting Hillsboro, OR, USA ahne@oosterhof.com Stephan Schmidt LPKF Laser & Electronics
SOLDER PASTE STENCIL MANUFACTURING METHODS AND THEIR IMPACT ON PRECISION AND ACCURACY Ahne Oosterhof Oosterhof Consulting Hillsboro, OR, USA ahne@oosterhof.com Stephan Schmidt LPKF Laser & Electronics
Fast Optical Form Measurements of Rough Cylindrical and Conical Surfaces in Diesel Fuel Injection Components
 Fast Optical Form Measurements of Rough Cylindrical and Conical Surfaces in Diesel Fuel Injection Components Thomas J. Dunn, Robert Michaels, Simon Lee, Mark Tronolone, and Andrew Kulawiec; Corning Tropel
Fast Optical Form Measurements of Rough Cylindrical and Conical Surfaces in Diesel Fuel Injection Components Thomas J. Dunn, Robert Michaels, Simon Lee, Mark Tronolone, and Andrew Kulawiec; Corning Tropel
Proposed Adaptive Optics system for Vainu Bappu Telescope
 Proposed Adaptive Optics system for Vainu Bappu Telescope Essential requirements of an adaptive optics system Adaptive Optics is a real time wave front error measurement and correction system The essential
Proposed Adaptive Optics system for Vainu Bappu Telescope Essential requirements of an adaptive optics system Adaptive Optics is a real time wave front error measurement and correction system The essential
Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS. Unit-03
 Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS Unit-03 INTRODUCTION FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS ABOUT OPTICAL FIBRE Multimode Fibres Multimode Step Index Fibres Multimode Graded Index Fibres INTRODUCTION In communication systems, there
Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS Unit-03 INTRODUCTION FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS ABOUT OPTICAL FIBRE Multimode Fibres Multimode Step Index Fibres Multimode Graded Index Fibres INTRODUCTION In communication systems, there
A 1-metre Ni coated CFRP demonstrator for large deformable mirrors
 1st AO4ELT conference, 06007 (2010) DOI:10.1051/ao4elt/201006007 Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2010 A 1-metre Ni coated CFRP demonstrator for large deformable mirrors Samantha J. Thompson
1st AO4ELT conference, 06007 (2010) DOI:10.1051/ao4elt/201006007 Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2010 A 1-metre Ni coated CFRP demonstrator for large deformable mirrors Samantha J. Thompson
12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes
 330 Chapter 12 12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes Similar to the JWST, the next-generation large-aperture space telescope for optical and UV astronomy has a segmented
330 Chapter 12 12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes Similar to the JWST, the next-generation large-aperture space telescope for optical and UV astronomy has a segmented
High Performance Thin Film Optical Coatings Technical Reference Document 09/13. Coatings Capabilities. Heat Control - Hot Mirror Filters
 Heat Control - Hot Mirror Filters A hot mirror is in essence a thin film coating applied to substrates in an effort to reflect infra-red radiation either as a means to harness the reflected wavelengths
Heat Control - Hot Mirror Filters A hot mirror is in essence a thin film coating applied to substrates in an effort to reflect infra-red radiation either as a means to harness the reflected wavelengths
High-speed wavefront control using MEMS micromirrors T. G. Bifano and J. B. Stewart, Boston University [ ] Introduction
![High-speed wavefront control using MEMS micromirrors T. G. Bifano and J. B. Stewart, Boston University [ ] Introduction High-speed wavefront control using MEMS micromirrors T. G. Bifano and J. B. Stewart, Boston University [ ] Introduction](/thumbs/72/66548311.jpg) High-speed wavefront control using MEMS micromirrors T. G. Bifano and J. B. Stewart, Boston University [5895-27] Introduction Various deformable mirrors for high-speed wavefront control have been demonstrated
High-speed wavefront control using MEMS micromirrors T. G. Bifano and J. B. Stewart, Boston University [5895-27] Introduction Various deformable mirrors for high-speed wavefront control have been demonstrated
Tenerife, Canary Islands, Spain International Conference on Space Optics 7-10 October 2014
 A DEPLOYABLE TELESCOPE FOR SUB-METER RESOLUTIONS FROM MICROSATELLITE PLATFORMS D. Dolkens and J. M. Kuiper Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Kluyverweg 1, 2629 HS Delft dd@spaceoptics.eu
A DEPLOYABLE TELESCOPE FOR SUB-METER RESOLUTIONS FROM MICROSATELLITE PLATFORMS D. Dolkens and J. M. Kuiper Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands Kluyverweg 1, 2629 HS Delft dd@spaceoptics.eu
AIAA/USU Small Satellite Conference 2007 Paper No. SSC07-VIII-2
 Digital Imaging Space Camera (DISC) Design & Testing Mitch Whiteley Andrew Shumway, Presenter Quinn Young Robert Burt Jim Peterson Jed Hancock James Peterson AIAA/USU Small Satellite Conference 2007 Paper
Digital Imaging Space Camera (DISC) Design & Testing Mitch Whiteley Andrew Shumway, Presenter Quinn Young Robert Burt Jim Peterson Jed Hancock James Peterson AIAA/USU Small Satellite Conference 2007 Paper
