NIGHT VISION GOGGLES NVG COMPONENTS AND GOGGLE OPERATION
|
|
|
- Jocelyn Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NVG COMPONENTS AND GOGGLE OPERATION Image intensifier (I²) assembly An electro-optical device that detects and amplifies light to produce a visual image. The components include: Objective lens - Photons enter the monocular assembly through the objective lens (an optical element that gathers light, and can be focused for the distance of an object). The objective lens contains a "minus-blue" coating which filters out light from the aircraft instrument panel. The image is inverted due to the shape of the objective lens, and then projected onto the photocathode. The photocathode releases electrons proportional to the amount of incoming photons. The electrons are accelerated by an electrical field in the direction of the phosphor screen. Microchannel Plate- This electricallycharged plate consists of millions of microchannels which are coated with an emissive material on the inside of the channel walls. The microchannels are cut at approximately five to eight degrees, to ensure that the incoming electrons strike the channel walls. Upon con-tact, the primary electrons cause the release of electrons from the emissive material which, in turn, strike the walls and release additional electrons. This amplification of electrons exit the microchannel plate in the same pattern that the original electrons entered. Phosphors Screen- A very thin layer of phosphor is applied to the input of the fiber optic inverter & emits light when struck by electrons. The electrons strike the phosphor screen causing the phosphor to glow, creating a visible image. Fiber Optic Inverter-The image is then reinverted (upright) by the fiberoptic inverter where the image is displayed. Eyepiece Lens-The image is focused to the individual eye by the eyepiece lens.
2 F E E S NIGHT VISION GOGGLES OPERATIONAL DEFECTS These defects relate to the reliability of the image intensifier and are an indication of instability. If identified, they are an immediate cause for rejecting the ANVIS. When a defect has been identified, record the specific nature of the problem on the maintenance forms and return the ANVIS to the NVG maintainer for repair. Do not fly with an ANVIS that has an identified operational defect. Return the ANVIS to the NVG maintainer. Flashing, Flickering, or Intermittent Operation - The image may appear to flicker or flash. This can occur in either one or both monoculars and is most commonly seen when adjusting the eyespan knob(s). If there is more than one flicker, check for loose wires, loose battery cap, or weak batteries. Indicate the rate of flashing or flickering on the maintenance forms. Edge Glow Emission Points Shading Edge Glow - Edge glow is a bright area (sometimes sparkling) in the outer portion of the viewing area. Edge glow is sometimes caused by an emission point (or series of emission points) just outside the field of view or by a defective phosphor screen that permits light feedback to the photocathode. To check for edge glow, block out all light by cupping a hand over the objective lens. If the image monocular assembly is displaying edge glow, the bright area will remain visible. Emission Points - A steady or fluctuating pinpoint of bright light in the image area and does not go away when all light is blocked from the objective lens of that monocular. The position of an emission point within the image area does not move. Make sure any emission point is not simply a point light source in the viewed scene. Place a cupped hand over the lens to block out all light. If the bright spot remains, return the ANVIS to the maintainer to be checked for tolerances. Shading - Each monocular should present a full circle. If shading is present, a full circular image will not be seen. Shading is indicative of a dying photocathode caused by a defective vacuum seal of the image intensifier. Shading is very dark and images cannot be seen through it. Shading always begins on the edge and migrates inward eventually across the entire image. Shading is a high contrast area with a distinct line of demarcation. Do not confuse shading with variations in output brightness. NOTE: Make sure the shading is not the result of improper tilt, eye-span adjustment, or vertical adjustment.
3 COSMETIC BLEMISHES These are usually the result of manufacturing imperfections that do not affect image intensifier reliability, and are not normally a cause for rejecting the ANVIS. However, some types of blemishes can get worse over time. Cosmetic blemishes are not a cause for rejection unless they become severe enough to interfere with the ability to perform the mission. When a blemish is cause for rejection, record the specific nature of the problem on the maintenance forms, identify the position of the blemish by using the clock method and approximate distance from the center (e.g., 5 o'clock toward the outside, 2:30 near the center, or 1:00 midway), and return the ANVIS to the NVG maintainer for repair. Bright Spots Bright Spots - These are signal-induced blemishes in the image area, caused by a flaw in the film on the MCP. A bright spot is a small, non-uniform, bright area that may flicker or appear constant. Cup your hand over the lens to block out all light. If the bright spot remains it is considered and emission point and an operational defect. Bright spots go away when the light is blocked out. Black Spots - These are cosmetic blemishes in the image intensifier or dirt or debris between the lenses. Black Spots Chicken Wire - An irregular pattern of dark lines throughout the image area, or in parts of the image area. Under the worst case condition, these lines will form hexagonal or square-wave shaped lines. Chicken Wire
4 Fixed-Pattern Noise Fixed-Pattern Noise (Honeycomb) - This is usually a cosmetic blemish characterized by a faint hexagonal pattern throughout the viewing area that most often occurs at high-light levels or when viewing very bright lights. The pattern can be seen in every image intensifier if the light level is high enough. Output Brightness Variation - This condition is evidenced by areas of varying brightness in or across the image area. The lower contrasts do not exhibit distinct lines of demarcation nor do they degrade image quality. Do not confuse output brightness with shading. Image Disparity - This condition may exist when there is a difference in brightness between the two image-intensifier assemblies within the same binocular.
5 Binocular Variations. There are two models of binoculars. apple AN/AVS-6(V)1. the fore-&-aft slide assembly is centered on the PAS. apple AN/AVS-6(V)2. the fore-&-aft slide is offset on the PAS. apple Both Models. Larger eyepieces to provide 25mm of eye relief instead of 15mm, & the PAS has two eyes-pan knobs to enable independent eye-span adjustments. Power Packs. Power pack attaches to the back of the helmet & contains the system power switch. On some dual-battery packs, there is a new circuit card inside that will make the low-battery indicator blink. apple G1 / G2 produce a steady lowbattery indicator. apple G3 / P/N contain the blinking circuitry. Low-Battery Indicator: The ANVIS incorporates a red LED at the base of the mount that comes on when active battery voltage drops to Vdc. Environmental Data. Operating Temp.-32 C to +52 C Illumination Required...starlight to moonlight Electrical Data. Using AA Alkaline Batteries. Cell Life Until low-battery indicator turns on 100F Hours 70F Hours 0F 5-10 Hours -22F 1-3 Hours Mechanical Data. apple Breakaway Force: 10G-15G apple Counterweight: 0 to 22 ounces. apple Binocular Weight o 15mm 19.4 ounces o 25mm 20.8 ounces Optical Data. apple Obj Focus Range.. 11 (±1 ) to or >180 apple Eyepiece Focus Ring...± 2 to 6 diopters apple Magnification...Unity (1:1) apple Acuity..Based on type(20/40 typ.) apple Astigmatism.Doesn t correct for it apple Field-of-View...40 vs. 200 deg unaided. apple Amplification Light apple green- Monochromatic...Color ANVIS Performance by Type. Types 1 & Name (V)1 (V)1 (V)1A (V)3 (V)3 Resolution Lp/mm Noise ratio 16:1 17:1 21:1 26:1 28:1 Max Halo mm High Light (acuity) /40 /33 /28 /25 /23 Low Light (acuity) /120 /105 /85 /70 /62
6 WARNING Limitations The equipment requires some ambient light (moonlight, starlight, or artificial light, etc.) to operate. The level of performance depends on the level of light Ambient light may be reduced by such factors as passing cloud cover & objects that produce shadows. The equipment is less effective viewing into shadows & other darkened areas. The equipment is less effective through rain, fog, sleet, snow, smoke, & other reflective material. Adjust speed & altitude to prevent over-flying the field-of-view when conditions of possible reduction or loss of vision exist. Exercise extreme caution when flying over low-contrast terrain such as snow-covered territory, sandy desert environments, large bodies of water, grassy hills. Under ambient starlight conditions, low-contrast environments degrade visibility, thereby disguising or masking changes in terrain. This is especially true under low light conditions. Exercise extreme caution when flying from high ambient light conditions to low ambient light conditions. Under low light condition, the goggles lose some resolution that they have under highlight conditions. Flying from highlight to low light conditions quickly reduces the sharpness & definition of terrain images. Some goggles may experience a measurable loss of performance at temperatures above 100F (38 C). This is caused by ambient heat beginning to increase thermonic emissions of the photocathode. If this begins to occur, it will appear as though you are looking through eyeglasses that are starting to fog or develop a slight haze. The equipment has a field-of-view limited to 40 deg, which requires appropriate continuous side-to-side head movements. If eyeglasses are worn, the upper rims of the eyeglasses can obscure the low-battery indicator & reduce the field-of-view. Do not attach the lanyard to the flight helmet. Attaching the lanyard to the flight helmet may cause head & neck injuries in a survivable accident. The only authorized way of attaching the lanyard to the flight helmet is with the use of fastener tape, hook, & fastener tape, pile.
7 WARNING Electrical/Battery Do not carry batteries in pockets containing metal objects such as coins, keys, etc. Metal objects can cause batteries to short circuit & become very hot. Batteries may explode On the original type of power pack, make sure the batteries are not expired. If a dead battery is in the compartment opposite the one being used to power the goggles, the low battery indicator will not come on when the voltage of the active battery drops to 2.4 Vdc & may result in system failure. Inspect Batteries before use. To insure uninterrupted operation of the ANVIS in the event you lose aircraft power, make sure you have appropriate batteries in the battery compartment & place the ON-OFF-ON switch on the power pack in the ON position. WARNING Toxic material The image-intensifiers phosphor screen in each monocular contains toxic material if it breaks. Don t inhale, ingest, suck-on, or stick into open wounds. Wash off skin if you contact it. If you inhale/swallow, drink a lot of water, induce vomiting, & call the coroner. WARNING General Warnings Some external lighting below 625 nanometers wavelength (blue-green lighting) cannot be viewed through the ANVIS because of the minus-blue coating on the inside of the objective lenses. All crewmembers with access to a set of flight controls must wear the same type of night vision goggles (NVG s), for example, both pilots wearing ANVIS goggles. Aircraft lighting that may not be compatible or acceptable with ANVIS will interfere with ANVIS performance, such as glare on the aircraft windscreen.
8 TYPES OF VISION DISTANCE ESTIMATION AND MONOCULAR CUES P M S G R A M LAV KITO FLL TYPES/DEFINITION PHOTOPIC- Daylight, NVG, or High Light vision. Uses Cone vision. Colors are visible. MESOPIC- Used at Dusk and Dawn. Uses both Cone and Rod cells for visibility. SCOTOPIC- Night or Low Light Vision. Uses Rod cells located in the parafovea. Requires use of scanning and off-center viewing to avoid the night blind spot (5 12 degrees) due to concentration of Cones in the central fovea. Colors are not visible. GEOMETRIC PERSPECTIVE- Object shapes effect perception of distance. LINEAR PERSPECTIVE- Parallel lines converge over long distance. APPARENT FORESHORTENING- Objects appear elliptical when viewed from various heights and distance. VERTICAL POSITION- Objects that appear higher on the horizon are further away. RETINAL IMAGE SIZE- Brains use of an images size to determine distance. KNOWN SIZE OF OBJECTS- Brain uses the known size of an object to determine distance. INCREASING/DECREASING SIZE- Objects increase in size as you get closer and decrease as you move away. TERRESTRIAL ASSOCIATION- Using an object with a known size to determine the distance of another. OVERLAPPING CONTOURS- The overlapped object is further away. AERIAL PERSPECTIVE- Using the clarity of an object/objects to determine distance. FADING OF COLORS AND SHAPES- Objects tend to fade as distance increases. LOSS OF DETAIL- Far objects are not as detailed. LIGHTS AND SHADOWS- Light sources cause objects to cast shadows even if they are not seen. MOTION PARALLAX Near objects move by the visual field fast while far objects move slowly or tend to stay still. Same visual cue used to determine ground speed during an approach (brisk walk).
Thermal Imaging. Version 1.1
 AMERICAN TECHNOLOGIES NETWORK CORP. Night Vision Digital Night Vision Important Export Restrictions! Commodities, products, technologies and services contained in this manual are subject to one or more
AMERICAN TECHNOLOGIES NETWORK CORP. Night Vision Digital Night Vision Important Export Restrictions! Commodities, products, technologies and services contained in this manual are subject to one or more
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of. Light. Warmth. Light is life. Sun as a deity (god) If sun would turn off the life on earth would extinct
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
HUMAN PERFORMANCE DEFINITION
 VIRGINIA FLIGHT SCHOOL SAFETY ARTICLES NO 01/12/07 HUMAN PERFORMANCE DEFINITION Human Performance can be described as the recognising and understanding of the Physiological effects of flying on the human
VIRGINIA FLIGHT SCHOOL SAFETY ARTICLES NO 01/12/07 HUMAN PERFORMANCE DEFINITION Human Performance can be described as the recognising and understanding of the Physiological effects of flying on the human
[NIGHT VISION TECHNOLOGY] SEMINAR REPORT
![[NIGHT VISION TECHNOLOGY] SEMINAR REPORT [NIGHT VISION TECHNOLOGY] SEMINAR REPORT](/thumbs/87/96501259.jpg) 20 th JANUARY 2010 Night Vision Technology Introduction Night vision technology, by definition, literally allows one to see in the dark. Originally developed for military use. Federal and state agencies
20 th JANUARY 2010 Night Vision Technology Introduction Night vision technology, by definition, literally allows one to see in the dark. Originally developed for military use. Federal and state agencies
1-YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY
 1-YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY The igen NV20/20 is warranted against defects in materials and workmanship under normal use for one year from the date of purchase to the original owner. Damage due to neglect,
1-YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY The igen NV20/20 is warranted against defects in materials and workmanship under normal use for one year from the date of purchase to the original owner. Damage due to neglect,
LUNOX Monocular Night Vision Device OPERATOR MANUAL
 ACTinBlack LUNOX Monocular Night Vision Device OPERATOR MANUAL Inside Cover OPERATOR MANUAL LUNOX Monocular Night Vision Device ACTinWhite S.à r.l. Rue de l Industrie, L-3895 Foetz, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
ACTinBlack LUNOX Monocular Night Vision Device OPERATOR MANUAL Inside Cover OPERATOR MANUAL LUNOX Monocular Night Vision Device ACTinWhite S.à r.l. Rue de l Industrie, L-3895 Foetz, Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh
 Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Human Senses : Vision week 11 Dr. Belal Gharaibeh 1 Body senses Seeing Hearing Smelling Tasting Touching Posture of body limbs (Kinesthetic) Motion (Vestibular ) 2 Kinesthetic Perception of stimuli relating
Basics of Light Microscopy and Metallography
 ENGR45: Introduction to Materials Spring 2012 Laboratory 8 Basics of Light Microscopy and Metallography In this exercise you will: gain familiarity with the proper use of a research-grade light microscope
ENGR45: Introduction to Materials Spring 2012 Laboratory 8 Basics of Light Microscopy and Metallography In this exercise you will: gain familiarity with the proper use of a research-grade light microscope
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
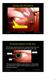 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Electroluminescent Lighting Applications
 Electroluminescent Lighting Applications By Chesley S. Pieroway Major, USAF PRAM Program Office Aeronauical Systems Division Wright-Patterson AFB OH 45433 Presented to illuminating Engineering Society
Electroluminescent Lighting Applications By Chesley S. Pieroway Major, USAF PRAM Program Office Aeronauical Systems Division Wright-Patterson AFB OH 45433 Presented to illuminating Engineering Society
U.S. ARMY AVIATION CENTER. Aviation Medicine
 SUBCOURSE EDITION AV0593 6 U.S. ARMY AVIATION CENTER Aviation Medicine THIS SUBCOURSE HAS BEEN REVIEWED FOR OPERATIONS SECURITY CONSIDERATIONS. UNITED STATES ARMY CORRESPONDENCE COURSE AVIATION SUBCOURSE
SUBCOURSE EDITION AV0593 6 U.S. ARMY AVIATION CENTER Aviation Medicine THIS SUBCOURSE HAS BEEN REVIEWED FOR OPERATIONS SECURITY CONSIDERATIONS. UNITED STATES ARMY CORRESPONDENCE COURSE AVIATION SUBCOURSE
Chapter 20 Human Vision
 Chapter 20 GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Characterize the physical parameters that are significant in human vision. Visual
Chapter 20 GOALS When you have mastered the contents of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Characterize the physical parameters that are significant in human vision. Visual
Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness )
 Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness ) Monochromat - person who needs only one wavelength to match any color Dichromat - person who needs only two wavelengths to match any color Anomalous trichromat - needs
Color Deficiency ( Color Blindness ) Monochromat - person who needs only one wavelength to match any color Dichromat - person who needs only two wavelengths to match any color Anomalous trichromat - needs
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Voyager. u s e r ` s g u i d e AMERICAN TECHNOLOGIES NETWORK CORP.
 Voyager u s e r ` s g u i d e AMERICAN TECHNOLOGIES NETWORK CORP. Lens assembly Infrared (IR) illuminator Power button Ocular lens assembly Battery housing Smart sensor Control panel box + adjustment button
Voyager u s e r ` s g u i d e AMERICAN TECHNOLOGIES NETWORK CORP. Lens assembly Infrared (IR) illuminator Power button Ocular lens assembly Battery housing Smart sensor Control panel box + adjustment button
Vision is a pilot s most important sense to obtain reference information during
 Vision is a pilot s most important sense to obtain reference information during flight. Most pilots are familiar with the optical aspects of the eye. Before we start flying, we know whether we have normal
Vision is a pilot s most important sense to obtain reference information during flight. Most pilots are familiar with the optical aspects of the eye. Before we start flying, we know whether we have normal
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Getting light to imager. Capturing Images. Depth and Distance. Ideal Imaging. CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes
 CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes Last time: what is an image idea of image-based (raster representation) Today: image capture/acquisition, focus cameras and eyes displays and intensities Corrected
CS559 Lecture 2 Lights, Cameras, Eyes Last time: what is an image idea of image-based (raster representation) Today: image capture/acquisition, focus cameras and eyes displays and intensities Corrected
Refraction of Light. Refraction of Light
 1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
The Eye and Vision. Activities: Linda Shore, Ed.D. Exploratorium Teacher Institute Exploratorium, all rights reserved
 The Eye and Vision By Linda S. Shore, Ed.D. Director,, San Francisco, California, United States lindas@exploratorium.edu Activities: Film Can Eyeglasses a pinhole can help you see better Vessels using
The Eye and Vision By Linda S. Shore, Ed.D. Director,, San Francisco, California, United States lindas@exploratorium.edu Activities: Film Can Eyeglasses a pinhole can help you see better Vessels using
3x Magnification. Digital Zoom to 6x. CAUTION: Do not point Infrared Emitter directly into eye at close range.
 MxGenPRO MANUAL-English.qx_MxGenPRO Manual-English 12/16/14 9:24 AM Page 3 Instruction Manual 3x Magnification. Digital Zoom to 6x. CAUTION: Do not point Infrared Emitter directly into eye at close range.
MxGenPRO MANUAL-English.qx_MxGenPRO Manual-English 12/16/14 9:24 AM Page 3 Instruction Manual 3x Magnification. Digital Zoom to 6x. CAUTION: Do not point Infrared Emitter directly into eye at close range.
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
ATN PS28 NIGHT VISION CLIP-ON
 ATN PS28 NIGHT VISION CLIP-ON ATN PS28 OPERATOR S MANUAL (REV. 2, MAY, 2014) operator s manual Important Export Restrictions! Commodities, products, technologies and services contained in this manual are
ATN PS28 NIGHT VISION CLIP-ON ATN PS28 OPERATOR S MANUAL (REV. 2, MAY, 2014) operator s manual Important Export Restrictions! Commodities, products, technologies and services contained in this manual are
Spotting Scopes INSTRUCTION MANUAL. Lit. #: /10-10
 Spotting Scopes INSTRUCTION MANUAL Lit. #: 98-2307/10-10 Have a look at your boot soles... If they re worn thin by miles of trail, the Trophy XLT series is your spotting scope. It s built to withstand
Spotting Scopes INSTRUCTION MANUAL Lit. #: 98-2307/10-10 Have a look at your boot soles... If they re worn thin by miles of trail, the Trophy XLT series is your spotting scope. It s built to withstand
Reading. 1. Visual perception. Outline. Forming an image. Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, sections
 Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
Reading Optional: Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Brian Wandell. Foundations of Vision. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1995. Research papers:
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL CORONAFINDER UV VIEWER
 A Division of www.syntronics.net OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL CORONAFINDER UV VIEWER SYNTRONICS, LLC 3500 Shannon Park Drive Fredericksburg, VA 22408 USA Telephone and fax: (540) 374-1000 E-mail: nightvision@syntronics.net
A Division of www.syntronics.net OPERATING AND MAINTENANCE MANUAL CORONAFINDER UV VIEWER SYNTRONICS, LLC 3500 Shannon Park Drive Fredericksburg, VA 22408 USA Telephone and fax: (540) 374-1000 E-mail: nightvision@syntronics.net
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Fall 2016 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Reading. Optics, cont d. Lenses. d d f. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015
 Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Vision and Color Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2015 1 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY
 OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY The pupil as a first line of defence against excessive light. DEMONSTRATION 1. PUPIL SHAPE; SIZE CHANGE Make a triangular shape with the
OPTICAL DEMONSTRATIONS ENTOPTIC PHENOMENA, VISION AND EYE ANATOMY The pupil as a first line of defence against excessive light. DEMONSTRATION 1. PUPIL SHAPE; SIZE CHANGE Make a triangular shape with the
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
12.1. Human Perception of Light. Perceiving Light
 12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
12.1 Human Perception of Light Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Focussing of light in your eye is accomplished by the cornea, the lens, and the fluids contained in your eye. Light
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception. Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation
 Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Unit IV: Sensation & Perception Module 19 Vision Organization & Interpretation Visual Organization 19-1 Perceptual Organization 19-1 How do we form meaningful perceptions from sensory information? A group
Vision and Color. Reading. The lensmaker s formula. Lenses. Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn Good resources:
 Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Reading Good resources: Vision and Color Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2017 Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Wandell. Foundations
Components of the Microscope
 Swift M3 Microscope The Swift M3 is a versatile microscope designed for both microscopic (high magnification, small field of view) and macroscopic (low magnification, large field of view) applications.
Swift M3 Microscope The Swift M3 is a versatile microscope designed for both microscopic (high magnification, small field of view) and macroscopic (low magnification, large field of view) applications.
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation
 IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
IV: Visual Organization and Interpretation Describe Gestalt psychologists understanding of perceptual organization, and explain how figure-ground and grouping principles contribute to our perceptions Explain
Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain
 Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Sensation Detection of external stimuli Response to the stimuli Transmission of the response to the brain Perception Processing, organizing and interpreting sensory signals Internal representation of the
Chapter 29/30. Wave Fronts and Rays. Refraction of Sound. Dispersion in a Prism. Index of Refraction. Refraction and Lenses
 Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Sensation. Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes
 Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Sensation Our sensory and perceptual processes work together to help us sort out complext processes Sensation Bottom-Up Processing analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Application Note 1030
 LED Displays and Indicators for Night Vision Imaging System Lighting Application Note 1030 Contents Introduction 1 The Concept of Night Vision Imaging 2 Night Vision Goggles 2 GEN II Night Vision Goggles.
LED Displays and Indicators for Night Vision Imaging System Lighting Application Note 1030 Contents Introduction 1 The Concept of Night Vision Imaging 2 Night Vision Goggles 2 GEN II Night Vision Goggles.
RHEINMETALL ARABIA SIMULATION AND TRAINING
 RHEINMETALL ARABIA SIMULATION AND TRAINING Flying with Night Vision Goggles The Desire for realistic Flight Training SATCE 2015, Jeddah RAST 2015 Presentation Agenda 1. Motivation 2. Technical Background
RHEINMETALL ARABIA SIMULATION AND TRAINING Flying with Night Vision Goggles The Desire for realistic Flight Training SATCE 2015, Jeddah RAST 2015 Presentation Agenda 1. Motivation 2. Technical Background
AH Auto-Darkening Welding Helmet User Manual. Made in China
 AH7-220-0000 Auto-Darkening Welding Helmet User Manual Made in China 2016 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AH7-220-0000 Auto-Darkening Welding Helmet 2016 WARNING Please read all instructions before using the
AH7-220-0000 Auto-Darkening Welding Helmet User Manual Made in China 2016 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS AH7-220-0000 Auto-Darkening Welding Helmet 2016 WARNING Please read all instructions before using the
INTELLIGENT SOLUTIONS FOR ENHANCING THE COMBAT CAPABILITY IN URBAN ENVIRONMENT
 INTELLIGENT SOLUTIONS FOR ENHANCING THE COMBAT CAPABILITY IN URBAN ENVIRONMENT prof. ing. Emil CREŢU, PhD Titu Maiorescu University ing. Marius TIŢA, PhD Departamentul pentru Armamente ing. Niculae GUZULESCU
INTELLIGENT SOLUTIONS FOR ENHANCING THE COMBAT CAPABILITY IN URBAN ENVIRONMENT prof. ing. Emil CREŢU, PhD Titu Maiorescu University ing. Marius TIŢA, PhD Departamentul pentru Armamente ing. Niculae GUZULESCU
The eye, displays and visual effects
 The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
The eye, displays and visual effects Week 2 IAT 814 Lyn Bartram Visible light and surfaces Perception is about understanding patterns of light. Visible light constitutes a very small part of the electromagnetic
Why is blue tinted backlight better?
 Why is blue tinted backlight better? L. Paget a,*, A. Scott b, R. Bräuer a, W. Kupper a, G. Scott b a Siemens Display Technologies, Marketing and Sales, Karlsruhe, Germany b Siemens Display Technologies,
Why is blue tinted backlight better? L. Paget a,*, A. Scott b, R. Bräuer a, W. Kupper a, G. Scott b a Siemens Display Technologies, Marketing and Sales, Karlsruhe, Germany b Siemens Display Technologies,
II.C. Visual Scanning and Collision Avoidance
 References: FAA-H-8083-3; FAA-8083-3-25; AC 90-48; AIM Objectives Key Elements Elements Schedule Equipment IP s Actions SP s Actions Completion Standards The student should develop knowledge of the elements
References: FAA-H-8083-3; FAA-8083-3-25; AC 90-48; AIM Objectives Key Elements Elements Schedule Equipment IP s Actions SP s Actions Completion Standards The student should develop knowledge of the elements
User Manual. Digital Compound Binocular LED Microscope. MicroscopeNet.com
 User Manual Digital Compound Binocular LED Microscope Model MD82ES10 MicroscopeNet.com Table of Contents i. Caution... 1 ii. Care and Maintenance... 2 1. Components Illustration... 3 2. Installation...
User Manual Digital Compound Binocular LED Microscope Model MD82ES10 MicroscopeNet.com Table of Contents i. Caution... 1 ii. Care and Maintenance... 2 1. Components Illustration... 3 2. Installation...
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ. Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. Topics
 Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Physiology of Vision The Eye as a Sense Organ Rodolfo T. Rafael,M.D. www.clinicacayanga.dailyhealthupdates.com 1 Topics Perception of Light Perception of Color Visual Fields Perception of Movements of
Image Formation and Capture
 Figure credits: B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, A. Theuwissen, and J. Malik Image Formation and Capture COS 429: Computer Vision Image Formation and Capture Real world Optics Sensor Devices
Figure credits: B. Curless, E. Hecht, W.J. Smith, B.K.P. Horn, A. Theuwissen, and J. Malik Image Formation and Capture COS 429: Computer Vision Image Formation and Capture Real world Optics Sensor Devices
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
11/25/2009 CHAPTER THREE INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION (CONT D) THE AERIAL CAMERA: LENS PHOTOGRAPHIC SENSORS
 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER THREE IC SENSORS Photography means to write with light Today s meaning is often expanded to include radiation just outside the visible spectrum, i. e. ultraviolet and near infrared
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER THREE IC SENSORS Photography means to write with light Today s meaning is often expanded to include radiation just outside the visible spectrum, i. e. ultraviolet and near infrared
Reading. Lenses, cont d. Lenses. Vision and color. d d f. Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp
 Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Vision and color Wandell. Foundations of Vision. 1 2 Lenses The human
Reading Good resources: Glassner, Principles of Digital Image Synthesis, pp. 5-32. Palmer, Vision Science: Photons to Phenomenology. Vision and color Wandell. Foundations of Vision. 1 2 Lenses The human
CompM4 and CompM4s User manual
 CompM4 and CompM4s User manual 1 PRESENTATION Aimpoint red dot sights are designed for the two eyes open method of sighting, which greatly enhances situational awareness and target acquisition speed. Thanks
CompM4 and CompM4s User manual 1 PRESENTATION Aimpoint red dot sights are designed for the two eyes open method of sighting, which greatly enhances situational awareness and target acquisition speed. Thanks
Micro T-1 User manual
 Micro T-1 User manual 1 PRESENTATION Aimpoint red dot sights are designed for the two eyes open method which greatly enhances situational awareness and target acquisition. Thanks to the optical design
Micro T-1 User manual 1 PRESENTATION Aimpoint red dot sights are designed for the two eyes open method which greatly enhances situational awareness and target acquisition. Thanks to the optical design
Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms
 CHAPTER 16 14 SECTION Sound and Light Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens to light when it passes from one medium to another? How
CHAPTER 16 14 SECTION Sound and Light Refraction, Lenses, and Prisms KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What happens to light when it passes from one medium to another? How
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision. Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic
 Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I
 DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I 4 Topics to Cover Light and EM Spectrum Visual Perception Structure Of Human Eyes Image Formation on the Eye Brightness Adaptation and
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING LECTURE # 4 DIGITAL IMAGE FUNDAMENTALS-I 4 Topics to Cover Light and EM Spectrum Visual Perception Structure Of Human Eyes Image Formation on the Eye Brightness Adaptation and
Lecture 26. PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision. Finalities. Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm. Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134
 PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 26 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Finalities Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm ESS 079 (this room) Lecture 26 PHY 112 Lecture 1 Introductory Chapters Chapters
PHY 112: Light, Color and Vision Lecture 26 Prof. Clark McGrew Physics D 134 Finalities Final: Thursday May 19, 2:15 to 4:45 pm ESS 079 (this room) Lecture 26 PHY 112 Lecture 1 Introductory Chapters Chapters
Inspiration strikes. VS-210 FLASH. User s Manual
 Inspiration strikes. VS-210 FLASH User s Manual Copyright 2015 Gradus Group. Bolt and other names of Bolt products are trademarks of Gradus Group. Other product and corporate names mentioned herein are
Inspiration strikes. VS-210 FLASH User s Manual Copyright 2015 Gradus Group. Bolt and other names of Bolt products are trademarks of Gradus Group. Other product and corporate names mentioned herein are
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Overview
 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
NIGHT VISION VIEWER & STILL CAMERA OWNER S MANUAL
 NIGHT VISION VIEWER & STILL CAMERA OWNER S MANUAL 2 CAUTION: Do not point Infrared Emitter directly into eye at close range. Keep out of reach of children. The infrared emitter emits a BRIGHT, although
NIGHT VISION VIEWER & STILL CAMERA OWNER S MANUAL 2 CAUTION: Do not point Infrared Emitter directly into eye at close range. Keep out of reach of children. The infrared emitter emits a BRIGHT, although
Human Vision. Human Vision - Perception
 1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
1 Human Vision SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 2 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses SPATIAL ORIENTATION IN FLIGHT 3 Limitations of the Senses Visual Sense Nonvisual Senses Sluggish source
Howie's Laser Collimator Instructions:
 Howie's Laser Collimator Instructions: WARNING: AVOID DIRECT OR MIRROR REFLECTED EYE EXPOSURE TO LASER BEAM The laser collimator is a tool that enables precise adjustment of the alignment of telescope
Howie's Laser Collimator Instructions: WARNING: AVOID DIRECT OR MIRROR REFLECTED EYE EXPOSURE TO LASER BEAM The laser collimator is a tool that enables precise adjustment of the alignment of telescope
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL OVERVIEW 1
 OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Physics of the Eye *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42482 1 Physics of the Eye * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain the image formation by
OpenStax-CNX module: m42482 1 Physics of the Eye * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain the image formation by
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
Chapter 25. Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume
 Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume Refraction can change the perception of depth and volume because the apparent path of light does not equal the actual path of light. 1 Underwater Vision Atmospheric
Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume Refraction can change the perception of depth and volume because the apparent path of light does not equal the actual path of light. 1 Underwater Vision Atmospheric
CGT 511 Perception. Facts. Facts. Facts. When perceiving visual information
 CGT 511 Perception Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Facts When perceiving visual information light is the most important factor light is mostly reflected or scattered
CGT 511 Perception Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Facts When perceiving visual information light is the most important factor light is mostly reflected or scattered
SFR 406 Spring 2015 Lecture 7 Notes Film Types and Filters
 SFR 406 Spring 2015 Lecture 7 Notes Film Types and Filters 1. Film Resolution Introduction Resolution relates to the smallest size features that can be detected on the film. The resolving power is a related
SFR 406 Spring 2015 Lecture 7 Notes Film Types and Filters 1. Film Resolution Introduction Resolution relates to the smallest size features that can be detected on the film. The resolving power is a related
P20 Zoom Flash Zoom Flash P20 P20 Zoomblitz Flash con zoom P20 Flash externo P20 Flash Zoom P20
 P20 Zoom Flash Zoom Flash P20 P20 Zoomblitz Flash con zoom P20 Flash externo P20 Flash Zoom P20 User s Guide Guide d'utilisation Benutzerhandbuch Manuale per l'utente Guía del usuario Guia do usuário 4J6021
P20 Zoom Flash Zoom Flash P20 P20 Zoomblitz Flash con zoom P20 Flash externo P20 Flash Zoom P20 User s Guide Guide d'utilisation Benutzerhandbuch Manuale per l'utente Guía del usuario Guia do usuário 4J6021
Further reading. 1. Visual perception. Restricting the light. Forming an image. Angel, section 1.4
 Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Contours, Saliency & Tone Mapping. Donald P. Greenberg Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Lecture 21 November 3, 2016
 Contours, Saliency & Tone Mapping Donald P. Greenberg Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Lecture 21 November 3, 2016 Foveal Resolution Resolution Limit for Reading at 18" The triangle subtended by a
Contours, Saliency & Tone Mapping Donald P. Greenberg Visual Imaging in the Electronic Age Lecture 21 November 3, 2016 Foveal Resolution Resolution Limit for Reading at 18" The triangle subtended by a
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1)
 Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Spatial Vision: Primary Visual Cortex (Chapter 3, part 1) Lecture 6 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Eye growth regulation KL Schmid, CF Wildsoet
Chapter 4 PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University
 Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception PSY 100 Dr. Rick Grieve Western Kentucky University Copyright 1999 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Sensation and Perception Sensation The process of stimulating the
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See
 Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
Beau Lotto: Optical Illusions Show How We See What is the background of the presenter, what do they do? How does this talk relate to psychology? What topics does it address? Be specific. Describe in great
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
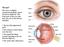 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Performance Characterization Of A Simultaneous Positive and Negative Ion Detector For Mass Spectrometry Applications
 Performance Characterization Of A Simultaneous Positive and Negative Ion Detector For Mass Spectrometry Applications Bruce Laprade and Raymond Cochran Introduction Microchannel Plates (Figures 1) are parallel
Performance Characterization Of A Simultaneous Positive and Negative Ion Detector For Mass Spectrometry Applications Bruce Laprade and Raymond Cochran Introduction Microchannel Plates (Figures 1) are parallel
VIZ REFLECTIVES NORTH AMERICA 2016 FULL LINE CATALOG
 VIZ REFLECTIVES NORTH AMERICA 2016 FULL LINE CATALOG TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 A202 Surveyor 3 Featuring: 3 Levels of Protection Alpha Work Wear is the only High Visibility clothing range that incorporates
VIZ REFLECTIVES NORTH AMERICA 2016 FULL LINE CATALOG TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 1 A202 Surveyor 3 Featuring: 3 Levels of Protection Alpha Work Wear is the only High Visibility clothing range that incorporates
HOW WE LL PROCEED. I ll put up a statement. You guess the answer Yes no True-false. You Focus the Lensometer Using the Target Circles.
 HOW WE LL PROCEED I ll put up a statement Lensometers Don t Read Power Ed De Gennaro Midlothian, Virginia OPTICAL MYTHS, HALF TRUTHS AND FALSEHOODS You guess the answer Yes no True-false True! HOW A LENSOMETER
HOW WE LL PROCEED I ll put up a statement Lensometers Don t Read Power Ed De Gennaro Midlothian, Virginia OPTICAL MYTHS, HALF TRUTHS AND FALSEHOODS You guess the answer Yes no True-false True! HOW A LENSOMETER
Table of Contents DSM II. Lenses and Mirrors (Grades 5 6) Place your order by calling us toll-free
 DSM II Lenses and Mirrors (Grades 5 6) Table of Contents Actual page size: 8.5" x 11" Philosophy and Structure Overview 1 Overview Chart 2 Materials List 3 Schedule of Activities 4 Preparing for the Activities
DSM II Lenses and Mirrors (Grades 5 6) Table of Contents Actual page size: 8.5" x 11" Philosophy and Structure Overview 1 Overview Chart 2 Materials List 3 Schedule of Activities 4 Preparing for the Activities
Reflection! Reflection and Virtual Image!
 1/30/14 Reflection - wave hits non-absorptive surface surface of a smooth water pool - incident vs. reflected wave law of reflection - concept for all electromagnetic waves - wave theory: reflected back
1/30/14 Reflection - wave hits non-absorptive surface surface of a smooth water pool - incident vs. reflected wave law of reflection - concept for all electromagnetic waves - wave theory: reflected back
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Micro T-2 User manual
 Micro T-2 User manual 1 PRESENTATION Aimpoint red dot sights are designed for the two eyes open method which greatly enhances situational awareness and target acquisition. Thanks to the optical design
Micro T-2 User manual 1 PRESENTATION Aimpoint red dot sights are designed for the two eyes open method which greatly enhances situational awareness and target acquisition. Thanks to the optical design
Match the microscope structures given in the left column with the statements in the right column that identify or describe them.
 49 Prelab for Name Match the microscope structures given in the left column with the statements in the right column that identify or describe them. Key: a. coarse adjustment knob f. turret or nosepiece
49 Prelab for Name Match the microscope structures given in the left column with the statements in the right column that identify or describe them. Key: a. coarse adjustment knob f. turret or nosepiece
DTIC. R university of Dayton Research Institu e LET. 9 i IIll(llI!lIII! AD-A ,.; B Mesa, AZ
 AL/HR-TR-1 993-0111 AD-A271 079 4,.; R M T S NIGHT VISION GOGGLE MODEL F4949 PREFLIGHT ADJUSTMENT/ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES Joseph C. Antonio DTIC ELECTE R university of Dayton Research Institu e LET 300 College
AL/HR-TR-1 993-0111 AD-A271 079 4,.; R M T S NIGHT VISION GOGGLE MODEL F4949 PREFLIGHT ADJUSTMENT/ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES Joseph C. Antonio DTIC ELECTE R university of Dayton Research Institu e LET 300 College
Photography (cont d)
 Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 24 th, 2017 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor TA Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 2 Aug 24 th, 2017 Slides from Dr. Shishir K Shah, Rajesh Rao and Frank (Qingzhong) Liu 1 Instructor TA Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Pranav Mantini
