(12) United States Patent
|
|
|
- Garey Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US B2 (12) United States Patent Yahagi et al. (54) HIGH-FREQUENCY TREATMENT INSTRUMENT (75) Inventors: Naohisa Yahagi, Tokyo (JP); Yuta Muyari, Tokyo (JP); Tsutomu Nakamura, Tokyo (JP); Chika Miyajima, Tokyo (JP): Tsutomu Okada, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: OLYMPUSMEDICAL SYSTEMS CORP., Tokyo (JP) (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 1753 days. (21) Appl. No.: 11/810,372 (22) Filed: Jun. 5, 2007 (65) Prior Publication Data US 2007/ A1 Dec. 6, 2007 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Jun. 5, 2006 (JP)... P (51) Int. Cl. A61B 18/14 ( ) A61B 7/32O5 ( ) A61B 7/221 ( ) (Continued) (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61B 18/1402 ( ); A61 B 17/32056 ( ); A61B 2017/22 12 ( ); A61B 2018/141 ( ); A61B 18/1492 ( ); A61B 2017/00269 ( ); A61B 2018/00214 ( ); A61B 2018/00898 ( ); A61B 2018/1407 ( ); A61B 2018/144 ( ); A61B 2018/1475 ( ) (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... A61B 2018/1405; A61B 2018/1407; A61B 2018/141; A61B 2018/144: A61B (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 19, /1475; A61B 2017/00358: A61B 2017/2212: A61B 2017/2217: A61B 17/32056; A61B 17/221; A61B 2017/00269; A61B 2018/20 USPC /45 47, 49, 113 See application file for complete search history. (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 3,805,791 A * 4, 1974 Seuberth et al /47 3,955,578 A * 5, 1976 Chamness et al /47 (Continued) FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS JP S , 1978 JP S , 1987 (Continued) OTHER PUBLICATIONS Japanese Official Action datedmar. 9, 2010 together with an English language translation. (Continued) Primary Examiner Jaymi Della (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Scully, Scott, Murphy & Presser, P.C. (57) ABSTRACT A high-frequency treatment instrument having a sheath; an elongated extension member; a narrow portion provided on an inner Surface of the sheath; and a pressing member which allows the elongated extension member to advance and retract only in a part of the sheath. The elongated extension member is advanced to form a first treatment electrode extending along a central axial line of the sheath and the elongated extension member is further advanced to form a second treatment electrode which intersects with the central axial line of the sheath. 2 Claims, 18 Drawing Sheets
2 Page 2 (51) Int. Cl. FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS A61B 7/OO ( ) A61B 18/00 ( ) JP HO , 1993 JP HO , 1996 (56) References Cited JP JP T 2000 T 2000 U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS JP , 2004 JP /2005 4,181,131 A 1/1980 Ogiu WO WO97/ , ,202,338 A * 5/1980 Bitrolf /47 WO WO99, , ,643,187 A 2, 1987 Okada /47 4,718,419 1, 1988 Okada 5.437,665 A 8/1995 Munro OTHER PUBLICATIONS 6,015,415. A * 1/2000 Avellanet ,113 6,221,039 B1* 4/2001 Durgin et al /22 Japanese Office Action dated Nov. 16, ,395,001 B1 5, 2002 Ellman et al. Chinese Office Action dated Nov. 16, R ck 858 Ellis et al ,28 Official Action mailed Feb. 15, 2011 from the Japan Patent Office in s B2 * 7, 2010 S. 606,113 counterpart Japanese Patent Application No , together A1 1/2004 Xiao et al. with a partial English language translation. 2004/ A1 9, 2004 Okada 2006, OO64113 A1 3, 2006 Nakao * cited by examiner
3 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 1 of 18 Cld c cy d se d S?KWIE)
4 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 2 of 18
5 U.S. Patent
6 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 4 of 18
7 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 5 of 18 F.G. 5 into 1 S X FIG. 6
8 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 6 of 18 FIG 7 FIG. 8
9 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 7 of 18 6 " OIH
10 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 8 of 18 FIG 10 31B 33 31A N-32
11 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 9 of 18 FG 11 A 30 31A N 35 31B 32 FG 11B 30 / 31A - FIG 11 C 35 N 31B 32
12 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 10 of 18 FIG. 12A FIG. 12B 41A I)fé: -ÉZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ)
13 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 11 of 18 FIG. 13A 2 41A 42 - er SS, N NXN 35 FIG. 13B 4. A 2 NSN 2CNN elev 35 ZZZZZZZYZZYZZAZZZ N ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
14 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 12 of 18 FIG. 14A ZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ 9 t-y 41B 42 FIG. 14B 35 sz SNNNN, aw-mm -Y-L-as-s- ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ
15 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 13 of 18 FIG. 15A FIG. 15B N 52B 53 52A 55A 55A
16 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 14 of 18
17 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 15 of 18 [YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\S\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Ý ÑÑ???YNNYÈ?Š??SYYYYYYYYYYYYYS? LI 'OIH
18 U.S. Patent 8 "OIH May 19, 2015 ege\svig) Sheet 16 of 18 (~)~~~~); ~~~~~ ; )»}~$?9
19 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 17 of 18
20 U.S. Patent May 19, 2015 Sheet 18 of ZZZZZZZZZ...'. 4\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ SZZZZ. 7 ZZZZZZZZ Ray Nrryryessyrinxvyyyyyyyyyyyyy ya2A2 CASACACAYA 76B
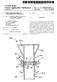
21 1. HIGH-FREQUENCY TREATMENT INSTRUMENT BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to a high-frequency treatment instrument. Priority is claimed on Japanese Patent Application No , filed on Jun. 5, 2006, the content of which is incorporated herein by reference. 2. Description of the Related Art As a treatment method of removing a biological tissue Such as a mucous membrane by the use of an endoscope, in order to remove the pathological lesion portion generated on a Surface of an alimentary canal, an endoscopic Submucosal dissection (ESD) method of cutting out a normal mucous membrane around a pathological lesion portion and then dis secting a submucosal layer and remove the pathological lesion portion, for example, is known. Various treatment instruments are used for such kind of dissecting treatment. For example, a high-frequency treat ment instrument having a knife portion as a treatment elec trode at a distal end of a rod-shaped electrode portion housed in a sheath is known (for example, see Japanese Unexamined Patent Application, First Publication No. H ). By the use of the high-frequency treatment instrument described in Japanese Unexamined Patent Application, First Publication No. H , it is possible to dissect the Submucosal layer by allowing high-frequency current to flow in the knife portion to cut out a mucous membrane contacting the knife portion. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION In a first aspect of the high-frequency treatment instrument of the present invention, there is provided a high-frequency treatment instrument for performing a high-frequency treat ment on a target tissue, the high-frequency treatment instru ment includes: a sheath; a pair of arm portions which is disposed in the sheath so as to freely extend and retract, is in a closed State in the sheath, and is opened in a direction away from a center axial line of the sheath when it protrudes from a distal end of the sheath; and a linear treatment electrode which is connected to distal end sides of the pair of arm portions and which is stretched between the arm portions when the pair of arm portions is opened. In a second aspect of the high-frequency treatment instru ment of the present invention, at least a part of the treatment electrode may be stretched in a bent state when the pair of arm portions is opened. In a third aspect of the high-frequency treatment instru ment of the present invention, at least one of the pair of arm portions is formed in a tube shape, and the treatment electrode is relatively fixed to the other of the pair of arm portions and is disposed to extend and retract in the one of the pair of arm portions. In a fourth aspect of the high-frequency treatment instru ment of the present invention, the high-frequency treatment instrument further includes an elongated extension member disposed to extend in the sheath so as to freely extend and retract in which the sheath communicates with the one of the pair of arm portions and one end of the treatment electrode is connected to the elongated extension member. In a fifth aspect of the high-frequency treatment instrument of the present invention, there is provided a high-frequency treatment instrument including: an elongated extension mem ber having an axial core; a pair of arm portions which is disposed at a distal end of the elongated extension member and which can be opened and closed relative to the axial core; and a linear treatment electrode which is connected to distal ends of the pair of arm portions, which is folded when the pair ofarm portions is closed, and which is stretched between the arm portions when the pair of arm portions is opened. In a sixth aspect of the high-frequency treatment instru ment of the present invention, there is provided a high-fre quency treatment instrument which further includes a sheath through which the pair of arm portions is inserted to freely extend and retract and the distal end sides of the pair of arm portions is urged to move away from the axial core Such that a distance therebetween becomes larger than the outer diam eter of the sheath. In a seventh aspect of the high-frequency treatment instru ment of the present invention, there is provided a high-fre quency treatment instrument including: a sheath; and an elon gated extension member which is disposed in the sheath so as to freely extend and retract and which has a first linear portion disposed along the sheath, a first bent portion formed at a distal end of the first linear portion, a second linear portion extending from the first bent portion, and a second bent por tion formed halfway along the second linear portion. In an eighth aspect of the high-frequency treatment instru ment of the present invention, there is provided a high-fre quency treatment instrument, when the first linear portion and the second linear portion are made to extend toward the distal end direction of the sheath and thus the first bent portion and the second bent portion are made to protrude from the sheath, a treatment electrode intersecting with a center axial line of the sheath is formed between the first bent portion and the second bent portion. In a ninth aspect of the high-frequency treatment instru ment of the present invention, there is provided a high-fre quency treatment instrument in which a control portion for controlling a protruding amount of the first linear portion and the second linear portion from the distal end of the sheath is disposed in the first linear portion and the second linear por tion which are closer to a proximal end side than the second bent portion. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a sectional view of substantial part illustrating a high-frequency treatment instrument according to a first embodiment of the invention. FIG. 2A is a cross-sectional view taken along line A-A of FIG 1. FIG. 2B is a cross-sectional view taken along line B-B of FIG 1. FIG.3 is a sectional view of substantial part illustrating the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the first embodiment of the invention. FIG. 4 is a sectional view illustrating an operating portion of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the first embodiment of the invention. FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a usage example of the high-frequency treatment instrument accord ing to the first embodiment of the invention. FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a usage example of the high-frequency treatment instrument accord ing to the first embodiment of the invention. FIG. 7 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a usage example of the high-frequency treatment instrument accord ing to the first embodiment of the invention.
22 3 FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram illustrating a usage example of the high-frequency treatment instrument accord ing to the first embodiment of the invention. FIG. 9 is a sectional view illustrating a high-frequency treatment instrument according to a second embodiment of 5 the invention. FIG. 10 is a plan view illustrating a high-frequency treat ment instrument according to a third embodiment of the invention. FIG. 11A is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating a closed State of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the third embodiment of the invention. FIG. 11B is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating a state in the way of opening or closing of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the third embodiment of the invention. FIG. 11C is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating an opened State of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the third embodiment of the invention. FIG. 12A is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating an opened state of a high-frequency treatment instrument according to a fourth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 12B is a partially-sectional side view illustrating an opened state of a high-frequency treatment instrument according to a fourth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 13A is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating a closed State of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the fourth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 13B is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating a state in the way of opening or closing of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the fourth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 13C is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating an opened State of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the fourth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 14A is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating a closed State of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the fourth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 14B is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating a state in the way of opening or closing the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the fourth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 15A is a partially-sectional plan view illustrating a closed State of a high-frequency treatment instrument accord ing to a fifth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 15B is a partially-sectional plan view of substantial part illustrating an opened State of a high-frequency treatment instrument according to a fifth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 16A is a sectional view illustrating a high-frequency treatment instrument according to a sixth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 16B is a cross-sectional view taken along line D-D of FIG.16A. FIG. 17 is a sectional view illustrating a closed state of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the sixth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 18 is a sectional view illustrating a state in the way of opening or closing of the high-frequency treatment instru- 60 ment according to the sixth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 19 is a sectional view illustrating an opened state of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the sixth embodiment of the invention. FIG. 20 is an enlarged sectional view illustrating a modi- 65 fied example of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the first embodiment of the invention FIG. 21 is an enlarged sectional view illustrating a modi fied example of the high-frequency treatment instrument according to the first embodiment of the invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION A first embodiment of the invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 8. A high-frequency treatment instrument 1 according to the first embodiment of the invention is a high-frequency treat ment instrument for performing a high-frequency treatment on a pathological lesion portion (target tissue) not shown and includes an elongated flexible sheath 2, a pair of arm portions 3A and 3B which is disposed in the sheath 2 so as to freely extend and retract, which is in a closed state in the sheath 2, and which is stretched in a direction moving away from a center axial line C of the sheath 2 when it protrudes from the distal end of the sheath 2, a linear treatment electrode 5 which is connected to the distal end sides of the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B and which is stretched between the arm portions 3A and 3B when the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B are opened, an operating wire (elongated extension member) 6 which is disposed to be extended in the sheath 2 so as to freely extend and retract and the distal end of which is connected to the treatment electrode 5, and an operating portion 7 to which the proximal ends of the sheath 2 and the operating wire 6 are connected and which operates the operating wire 6 to extend and retract relative to the sheath 2, as shown in FIGS. 1 to 4. The sheath 2 has such an outer diameter that it can be inserted through a treatment instrument channel of an endo Scope not shown. The pair of arm portions 3A and 3B is both formed in a tube shape and is communicated with the sheath 2. At least in the vicinity of the distal end of the sheath 2, the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B is flexibly provided to be curved relative to the sheath 2. Insertion holes 8A and 8B through which the treatment electrode 5 can be inserted are formed in the distal end sides of the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B in the loca tions opposing each other when the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B are closed. The distal ends of the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B are sealed with sealing members 10. The proximal end side of one of the pair of arm portions 3A extends to the vicinity of the distal end of the operating wire 6. The treatment electrode 5 is formed in a wire shape, is inserted through one of the pair of arm portions 3A so as to extend and retract, protrudes from the insertion hole 8A, and is inserted through the other of the pair of arm portions 3B from the insertion hole 8B of the other of the pair of arm portions 3B. The distal end of the treatment electrode 5 is fixed in a folded-back state to a position where the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B is connected to the sheath 2. Accordingly, the treatment electrode 5 is disposed to freely extend and retract in one of the pair of arm portions 3A and is relatively fixed in the other of the pair of arm portions 3B. In the treatment electrode 5 located in the insertion hole 8A of one of the pair of arm portions 3A when the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B are opened at a predetermined opening angle, a bent portion 11 which engages the insertion hole 8A so as to control the extend and retract movement of the treat ment electrode 5 is formed. The operating portion 7 includes an operating portion body 13 connected to the proximal end of the sheath 2 and a slider 15 to which the proximal end of the operating wire 6 is connected and which can freely slide relative to the operating portion body 13. In the slider 15, an electrode terminal 16 which is electrically connected to the operating wire 6 and
23 5 which is connected to a connection cable extending from a high-frequency power source not shown is disposed. Next, operations of the high-frequency treatment instru ment 1 will be described with reference to a procedure of removing a pathological lesion portion X generated on the Surface of an alimentary canal by dissecting a Submucosal layer W by the high-frequency treatment instrument 1 accord ing to this embodiment. First, as shown in FIG. 5, an injection needle 17 is intro duced into a body cavity through a treatment instrument channel of an endoscope not shown and a physiologic saline solution is locally injected into the submucosal layer W in the vicinity of the pathological lesion portion X to be removed, thereby distending the pathologicallesion portionxas shown in FIG. 6. Before performing the local injection, it is prefer able that a dye be applied around the pathological lesion portion X to clarify the boundary of the pathological lesion portion X, and then a mucous membrane S is marked at a plurality of positions Surrounding the circumference of the pathological lesion portion X by the use of an existing high frequency knife 18. Next, the existing high-frequency knife 18 is inserted through the treatment instrument channel and is brought into contact with a part of the mucous membrane S in the vicinity of the pathological lesion portion X as shown in FIG. 7, and a hole H which is a starting point of the entire peripheral cut-out is formed by Supplying high-frequency current thereto. By operating both the endoscope and the high-frequency knife, the mucous membrane around the pathological lesion portion X is cut out to expose the submucosal layer W. Subsequently, the high-frequency knife is pulled out of the channel and the high-frequency treatment instrument 1 is inserted into the channel. Then, with the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B protruding from the distal end of the channel, the slider 15 of the high-frequency treatment instrument 1 is made to extend relative to the operating portion body 13. At this time, the operating wire 6 extends toward the distal end direction of the sheath 2 relative to the sheath 2. Here, since the distal end of the treatment electrode 5 is fixed to the vicinity of the distal end of the sheath 2, the treatment electrode 5 is pushed in a compressing direction and one of the pair of arm portions 3A and the other of the pair ofarm portions 3B are separated from each other as a reaction thereto, thereby opening the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B. Then, the bent portion 11 formed in the treatment electrode 5 engages the insertion hole 8A of the one of the pair of arm portions 3A, whereby the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B are opened at a predetermined opening angle. At this time, a straight line portion 5A substantially perpendicular to the center axial line C of the sheath 2, that is, the extend and retract direction of the operating wire 6 is formed in the treatment electrode 5. Depending on the size of the pathologi cal lesion portion X, the operating wire 6 may be operated to extend and retract to adjust the opening angle of the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B. High-frequency current is made to flow while the straight line portion 5A is brought into contact with the submucosal layer W. and the sheath 2 of the high-frequency treatment instrument 1 is made to extend relative to the channel while observing with the endoscope which is in fixed state. In this way, as shown in FIG. 8, the submucosal layer W is cut out to remove the pathological lesion portion X by the Straight line portion 5A. According to the high-frequency treatment instrument 1, when the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B is made to protrude from the distal end of the sheath 2 and is thus opened, the treatment electrode 5 can be stretched in a direction intersect ing with the center axial line C of the sheath 2 at the distal end sides of the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B. Accordingly, when the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B is operated to extend and retract relative to the sheath 2 with the treatment electrode 5 stretched, it is possible to increase the contact area between the treatment electrode 5 and the target tissue such as the pathological lesion portion X or the like compared to the conventional technique. Accordingly, it is possible to perform treatments on the target tissue by directly operating the treat ment electrode 5, thereby facilitating the procedure. The pair of arm portions 3A and 3B can be opened and closed by allowing the treatment electrode 5 to extend and retract relative to the sheath 2 via the operating wire 6. When the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B is closed, the treatment electrode 5 can be housed in the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B. Next, a second embodiment of the invention will be described with reference to FIG. 9. The same elements as the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals and descriptions thereof will be omitted. The second embodiment is different from the first embodi ment, in that a part of a treatment electrode 21 of a high frequency treatment instrument 20 according to the second embodiment is stretched in a bent state when a pair of arm portions 3A and 3B is opened. In the treatment electrode 21, a bent portion 22 is disposed in a portion corresponding to the straight line portion 5A of the treatment electrode 5 according to the first embodiment. The bent portion 22 is formed to face the distal end of the sheath 2 in a state that the treatment electrode 21 is stretched. That is, since a first straight line portion 23A and a second straight line portion 23B are formed with the bent portion 22 interposed therebetween, the treatment electrode 21 is stretched in a Substantially M shape including the portions disposed in the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B. According to the high-frequency treatment instrument 20, since a target tissue not shown can be interposed in the bent portion 22, it is possible to bring the treatment electrode 21 into stable contact with the target tissue. Next, a third embodiment of the invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 10 and 11. The same elements as the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals and descriptions thereof will be omitted. The third embodiment is different from the first embodi ment, in that a pair of arm portions 31A and 31B of a high frequency treatment instrument 30 according to the third embodiment freely extends and retracts in a coil sheath (sheath)32 and is disposed at a distal end of an operating wire (not shown) having an axial core via a link mechanism (not shown) having an axis 33 so as to be opened and closed relative to the axial core, and a treatment electrode 35 is connected to both distal ends of the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B, is folded when the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B is closed, and is stretched between the arm portions 31A and 31B when the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B is opened. Operations of the high-frequency treatment instrument 30 will be described. As shown in FIG. 11A, when the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B is made to protrude from a treatment instrument channel not shown in a state that the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B is closed and the treatment electrode 35 is folded between the pair of arms 31A and 31B, and is then opened, an operating wire not shown is made to extend toward the distal end side relative to the coil sheath 32.
24 7 At this time, the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B moves away from the axial core of the operating wire 32 via the link mechanism not shown and thus is opened. In this case, as shown in FIG. 11B, both ends of the treatment electrode 35 moves away from each other along with the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B and thus the treatment electrode 35 is gradually stretched. Then, when the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B is opened at a predetermined opening angle, as shown in FIG. 11C, the treatment electrode 35 is stretched between the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B. When a cut-out operation is finished and the operating wire is made to retract toward the proximal end side of the coil sheath 32 to close the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B, as shown in FIG. 11A, the treatment electrode 35 is housed in a state where it is interposed again between the pair of arm portions 31A and 31B. According to the high-frequency treatment instrument 30, the same advantages as the first embodiment can be obtained. Next, a fourth embodiment of the invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 12 to 14. The same elements as the above-mentioned embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals and descriptions thereof will be omitted. The fourth embodiment is different from the third embodi ment, in that distal end sides of a pair of arm portions 41A and 41B of a high-frequency treatment instrument 40 according to the fourth embodiment are urged to move away from the axial core of an operating wire 42 such that the distance therebetween becomes larger than the outer diameter of the sheath 2, as shown in FIG. 12. The pair of arm portions 41A and 41B is formed in a plate shape and the proximal ends thereof are directly fixed and connected to the distal end of the operating wire 42 by, for example, a brazing method or a laser welding method. The pair of arm portions 41A and 41B is curved outwardly in the diameter direction of the sheath 2 gradually from the proxi mal ends to the distal ends. Next, operations of the high-frequency treatment instru ment 40 according to this embodiment will be described. First, as shown in FIG. 13A, in a state where the pair of arm portions 41A and 41B is closed and housed in the sheath 2, the treatment electrode 35 is folded and housed in the sheath 2. When the pair of arm portions 41A and 41B is opened, the operating wire 42 is made to extend toward the distal end sides relative to the sheath 2. At this time, as shown in FIG. 13B, as the distal end sides of the pair of arm portions 41A and 41B protrude from the sheath 2, the control by the sheath 2 is released and thus the distal end sides of the pair of arm portions 41A and 41B starts opening. Then, both ends of the treatment electrode 35 are drawn in the opposite directions and thus the treatment electrode 35 is gradually stretched. When the entire pair of arm portions 41A and 41B pro trudes from the distal end of the sheath 2, as shown in FIG. 13C, the pair of arm portions 41A and 41B are opened at a predetermined opening angle and the treatment electrode 35 is accordingly stretched between the pair of arm portions 41A and 41B. Depening on the stretched state of the treatment electrode 35, as shown in FIG. 14A, the treatment electrode 35 may be folded closer to the distal end side than the pair of arm portions 41A and 41B and may be housed in the sheath 2. In this case, as shown in FIG.14B, the treatment electrode 35 is stretched from the distal end sides of the pair of arm por tions 41A and 41B to the proximal end sides thereof. According to the high-frequency treatment instrument 40, the treatment electrode 35 can be housed in the sheath 2 along with the pair of arm portions 41A and 41B Next, a fifth embodiment of the invention will be described with reference to FIG. 15. The same elements as the above-mentioned embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals and descriptions thereof will be omitted. The fifth embodiment is different from the fourth embodi ment, in that a short tube portion 53 through which a pair of arm portions 52A and 52B can be inserted is connected to a distal end of an operating wire 51 of a high-frequency treat ment instrument 50 according to the fifth embodiment and is disposed along the outside of the sheath 55. The short tube portion 53 has an outer diameter substan tially equal to the outer diameter of the sheath 55. The length of the short tube portion 53 is adjusted so that the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B is opened at a predetermined opening angle when the short tube portion is made to move from the distal ends of the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B to a connection position to the sheath 55. The distal ends of the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B are bent outward so as to control the separation of the short tube portion 53. The proximal ends of the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B are connected to a connection portion 55A disposed at the distal end of a sheath 55. Next, operations of the high-frequency treatment instru ment 50 according to this embodiment will be described. First, as shown in FIG. 15A, in a state where the short tube portion 53 is moved to the distal ends of the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B, the treatment electrode 35 is folded between the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B. When the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B is opened, the operating wire 51 is made to retract toward the proximal end side relative to the sheath 55. At this time, the short tube portion 53 moves relative to the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B, the distal end sides of the pair of arm portions 52A and 52B protrude from the short tube portion 53 as shown in FIG. 15B, and thus the control by the short tube portion 53 is released, thereby starting opening of the distal ends of the pair ofarm portion 52A and 52B. Then, both ends of the treatment electrode 35 are drawn in the opposite directions and the treatment electrode 35 is gradually stretched. According to the high-frequency treatment instrument 50. similarly to the fourth embodiment, the same advantages can be obtained by operating the operating wire 51 to extend and retract relative to the sheath 55. Next, a sixth embodiment of the invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 16 to 19. The same elements as the above-mentioned embodiments are denoted by the same reference numerals and descriptions thereof will be omitted. The sixth embodiment is different from the first embodi ment, in that a high-frequency treatment instrument 60 according to this embodiment does not include the pair of arm portions 3A and 3B as in the first embodiment but an operat ing wire 61 includes a first linear portion 61A disposed along a sheath 62, a first bent portion 61B formed at the distal end of the first linear portion 61A, a second linear portion 61C extending from the first bent portion 61B, and a second bent portion 61D formed halfway along the second linear portion 61C, as shown in FIG. 16. The operating wire 61 is usually housed in the sheath 62 in a state where it is folded back at the second bent portion 6 ID and the distal end of the second linear portion 61C is disposed to extend halfway along the first linear portion 61A. When the first linear portion 61A and the second linear portion 61C are made to extend toward the distalend direction of the sheath 62 and the first bent portion 61B and the second bent portion 61D are made to protrude from the sheath 62, a treatment electrode
25 63 substantially perpendicularly intersecting with a center axial line C of the sheath 62 is formed between the first bent portion 61B and the second bent portion 61D. Pressing members 66A and 66B between which a tube shaped diameter-enlarged portion (control portion) 65 con trolling a protruding amount of the first linear portion 61A and the second linear portion 61C from the distal end of the sheath 62 are disposed halfway along the first linear portion 61A and at the distal end of the second linear portion 61C. The outer diameters of the pressing members 66A and 66B are larger than the inner diameter of the diameter-enlarged por tion 65. The sheath 62 includes an outer sheath 62A and an inner sheath 62B which the inner side of the outer sheath 62A covers. A narrow tube portion 67 which allows the pressing members 66A and 66B to pass therethrough but controlling the movement of the diameter-enlarged portion 65 toward the distal end side of the sheath 62 is disposed halfway along the inner sheath 62B. A cover 68, distal end of which having a curved surface, is disposed at the distal end of the inner sheath 62B. A cap 69 is disposed at the distal end of the outer sheath 62A. An operating portion 70 includes a rod-shaped operating portion body 71 a distal end of which is connected to the proximal end of the sheath 62 and a slider 72 connected to the proximal end of the operating wire 61, as shown in FIG. 19. The slider 72 is covered onto the operating portion body 71 so as to freely slide and is connected such that the inner sheath 62B and the operating wire 61 are rotatable relative to the outer sheath 62A. An electrode terminal 16 is disposed in the slider 72. Next, operations of the high-frequency treatment instru ment 60 according to this embodiment will be described. When the treatment electrode 63 is to be formed, as shown in FIG. 17, the distal end side of the high-frequency treatment instrument 60 is made to protrude from a treatment instru ment channel not shown in a state where the entire operating wire 61 is housed in the sheath 62, the slider 72 is pushed out relative to the operating portion body 71, and thus the oper ating wire 61 is made to extend relative to the sheath 62. At this time, as shown in FIG. 16A, the first linear portion 61A and the second linear portion 61C move together toward the distal end of the sheath 62. As shown in FIG. 18, when the second bent portion 61D protrudes from the distal end of the sheath 62 by a predeter mined length, the diameter-enlarged portion 65 comes in contact with the narrow tube portion 67. Accordingly, the second linear portion 61C is fixed to the sheath 62. On the other hand, the pressing member 66A passes through the narrow tube portion 67. Accordingly, the first bent portion 61B is more bent just after the moment that the first bent portion 61B has protruded from the sheath 62, and the second linear portion 61C between the first bent portion 61B and the second bent portion 61D rotates as the second bent portion 61D being the center of rotation to a direction which is sub stantially perpendicular to the center axial line C of the sheath 62. In this way, as shown in FIG. 19, the treatment electrode 63 is formed between the first bent portion 61B and the second bent portion 61D. When a cut-out angle is to be changed, the operating portion 70 is made to rotate relative to the outer sheath 62A, thereby changing the direction of the treatment electrode 63 relative to a pathological lesion portion not shown. According to the high-frequency treatment instrument 60, the same advantages as the first embodiment can be obtained As shown in FIG. 18, in the state where the diameter enlarged portion 65 and the narrow tube portion 67 come in contact with each other, the first linear portion 61A and the second linear portion 61C remain to be substantially parallel to the sheath 62 and extend from the sheath 62, with the second bent portion 61D as a distal end thereof. Accordingly, by Supplying high-frequency current to the treatment elec trode 63, it is possible to obtain the same operations and advantages as the existing high-frequency knife. The technical scope of the invention is not limited to the above-mentioned embodiments, but various modifications may be made therein without departing from the gist of the invention. For example, in the first embodiment, not only the one of the pair of arm portions 3A but also the other of the pair of arm portions 3B is formed in a tube shape, but the other of the pair ofarm portions 3B may not beformed in a tube shape as long as one end of the treatment electrode is fixed to the other of the pair of arm portions 3B. Although the shape of the distal ends of the pair of arm portions have a chamfered shape in which the distal ends are cut out as shown in FIG.1, distalends of a pair of arm portions 75A and 75B may be chamfered to form a single circular curvature in a closed state as shown in FIG. 20. Alternatively, each distal end of a pair of arm portions 76A and 76B may be chamfered to form a circular curvature as shown in FIG. 21. According to the first aspect of the invention, when the pair ofarm portions is made to protrude from the distal end of the sheath and is thus opened, the treatment electrode can be stretched in a direction intersecting with the center axial line of the sheath at the distal end sides of the pair of arm portions. Accordingly, when the pair of arms are operated to extend and retract relative to the sheath with the treatment electrode stretched, it is possible to increase a contact area between the treatment electrode and the target tissue compared to the conventional techniques. According to the second aspect of the invention, it is pos sible to interpose the target tissue in the bent portion and thus it is possible to bring the treatment electrode into stable con tact with the target tissue. According to the third aspect of the invention, by allowing the treatment electrode to extend and retract relative to the one of the pair of arm portions, it is possible to open and close the pair of arm portions by means of an axial tension generated in the treatment electrode. At this time, it is possible to house the treatment electrode in at least one of the pair of arm portions with the pair of arm portions closed. According to the fourth aspect of the invention, by operat ing the elongated extension member so as to extend and retract relative to the sheath, it is possible to allow the treat ment electrode to extend and retract relative to the one of the pair of arm portions. According to the fifth aspect of the invention, when the pair of arm portions is opened, the treatment electrode can be stretched in a direction intersecting with an axial core of the elongated extension member at the distal end sides of the pair ofarm portions. Accordingly, when the pair of arm portions is operated to extend and retract with the treatment electrode stretched, it is possible to increase the contact area between the treatment electrode and the target tissue compared to the conventional techniques. According to the sixth aspect of the invention, it is possible to open and close the pair of arm portions by allowing the pair of arm portions to extend and retract relative to the sheath. According to the seventh aspect of the invention, when the first linear portion of the elongated extension member is made to move in a direction protruding from the distal end of the
26 11 sheath, it is possible to open the proximal end side of the second linear portion relative to the first linear portion using the first bent portion as an opening and closing center and to allow the second linear portion to intersect with the center axial line of the sheath. 5 According to the eighth aspect of the invention, since the treatment electrode is disposed in a position intersecting with the center axial line of the sheath, it is possible to increase the contact area between the treatment electrode and the target tissue compared to the conventional techniques. 10 According to the ninth aspect of the invention, it is possible to adjust the protruding amount of the first linear portion and the second linear portion from the sheath by the use of the control portion. According to the invention, it is possible to facilitate a 15 procedure by enabling a treatment on a target tissue without performing a curving operation of an endoscope. While preferred embodiments of the invention have been described and illustrated above, it should be understood that these are exemplary of the invention and are not to be con sidered as limiting. Additions, omissions, Substitutions, and other modifications can be made without departing from the spirit or scope of the present invention. Accordingly, the invention is not to be considered as being limited by the foregoing description, and is only limited by the scope of the appended claims. What is claimed is: 1. A high-frequency treatment instrument comprising: a sheath; an elongated extension member which is disposed in the sheath so as to freely extend and retract, the elongated extension member including: a first linear portion disposed along the sheath, the first linear portion having a proximal end at a proximal side of the sheath and a distalendata distal side of the sheath, a first bent portion formed at the distal end of the first linear portion, a third linear portion extending from the first bent por tion toward a distal end of the sheath, the third linear portion having a proximal end at the proximal side of the sheath and a distal end at the distal end of the sheath, a second bent portion formed at the distalend of the third linear portion, and a second linear portion extending from the second bent portion, the second linear portion having a distal end at the proximal side of the sheath and a proximal end at the distal side of the sheath, and a narrow portion provided on an inner Surface of the sheath, 50 wherein a pressing member is provided on the second linear portion, wherein the pressing member allows the dis tal end of the second linear portion to advance and retract only in a part of the sheath, wherein the part of 55 the sheath is located proximal to the narrow portion, when the second bent portion is protruded from the sheath while the first bent portion is inside of the sheath, a portion of the elongated extension member which protrudes from the sheath becomes a first treat- 60 ment electrode which extends along a centeraxial line of the sheath, and when the elongated extension member is advanced after the first treatment electrode is formed, the first bent portion protrudes from the sheath while advancement 65 of the pressing member and the second linear member is Suppressed by the narrow portion, and a part of the first treatment electrode between the first bent portion and the second bent portion becomes a second treat ment electrode which intersects with the center axial line of the sheath, wherein the high-frequency treatment instrument further comprises: a control portion, which controls a protruding amount of the third linear portion and the second linear portion from the distal end of the sheath by directly contacting the narrow portion, is disposed at a position that is closer to a proximal end of the sheath than the second bent portion, wherein the control portion is configured to be moved by movement of the first linear portion and the second linear portion toward a distal opening of the sheath until the control portion is moved into direct contact with the narrow portion. 2. A treatment instrument comprising: a sheath having a distal end and a proximal end, wherein the sheath is comprised of a sheath inner wall defining a sheath inner space extending along a lon gitudinal axis between the distal end and the proximal end, wherein the sheath inner space opens to a sheath distal opening at the distal end of the sheath, and wherein the sheath inner wall comprises an intermediate portion, a distal portion arranged distally of the inter mediate portion along the longitudinal axis, and a proximal portion arranged proximally of the interme diate portion along the longitudinal axis; a control tube configured to be guided by the proximal portion of the sheath inner wall to move along the lon gitudinal axis and to abut against the intermediate por tion of the sheath inner wall; and an operation wire comprising, in order between a first end of the operation wire and a second end of the operation wire: a first linear portion, a first bent portion, a second linear portion, a second bent portion, and a third linear portion; and a pressing member fixed to the third linear portion of the operation wire, wherein the pressing member is configured to be arranged in the sheath inner space at a position proxi mal to the control tube along the longitudinal axis and to abut against the control tube, wherein the sheath, the control tube, the operation wire and the pressing member are configured to be arranged in a first configuration, a second configuration and a third configuration, wherein in the first configuration, the second bent portion of the operation wire is arranged within the sheath inner space at a more distal position along the longitudinal axis than the second linear portion and the third linear portion, wherein in the second configuration: the control tube is guided by the proximal portion of the sheath inner wall to abut against the intermediate por tion of the sheath inner wall to limit movement of the control tube in a distal direction along the longitudinal axis, and the pressing member abuts against the control tube to limit movement of the third linear portion of the operation wire in the distal direction along the longi tudinal axis such that the second bent portion of the operation wire is exposed through the sheath distal
27 13 opening sheath and the first bent portion of the opera tion wire is maintained within the sheath inner space, and wherein in the third configuration: the control tube remains abutted against the intermediate 5 portion of the sheath inner wall to limit movement of the control tube in the distal direction along the lon gitudinal axis, the pressing member remains abutted against the control tube to limit movement of the third linear portion of 10 the operation wire in the distal direction along the longitudinal axis such that the second bent portion of the operation wire remains exposed through the sheath distal opening and the first linear portion of the operation wire is moved in 15 the distal direction along the longitudinal axis Such that the first bent portion and the second linear portion are exposed through the sheath distal opening. k k k k k 14
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
III IIII. United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. application of welds thereto for attaching the hub member to
 United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. 54) EARTH SCREW ANCHOR ASSEMBLY HAVING ENHANCED PENETRATING CAPABILITY (75) Inventors: Daniel V. Hamilton; Robert M. Hoyt, both of Centralia; Patricia J. Halferty,
United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. 54) EARTH SCREW ANCHOR ASSEMBLY HAVING ENHANCED PENETRATING CAPABILITY (75) Inventors: Daniel V. Hamilton; Robert M. Hoyt, both of Centralia; Patricia J. Halferty,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Ogawa 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 30, 1990 54 ENDOSCOPICTREATING TOOL 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Mototsugu Ogawa, Hachioji, Japan Olympus Optical Co., Ltd., Tokyo,
United States Patent (19) Ogawa 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 30, 1990 54 ENDOSCOPICTREATING TOOL 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Mototsugu Ogawa, Hachioji, Japan Olympus Optical Co., Ltd., Tokyo,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7325359B2 (12) United States Patent Vetter (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 5, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) PROJECTION WINDOW OPERATOR Inventor: Gregory J. Vetter,
USOO7325359B2 (12) United States Patent Vetter (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 5, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) (56) PROJECTION WINDOW OPERATOR Inventor: Gregory J. Vetter,
(12) United States Patent
 US00795.5254B2 (12) United States Patent Hanke (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 2011 (54) MEDICAL VIDEOSCOPE WITH A PIVOTABLY ADJUSTABLE END PART (75) Inventor: Harald Hanke, Hamburg (DE)
US00795.5254B2 (12) United States Patent Hanke (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 2011 (54) MEDICAL VIDEOSCOPE WITH A PIVOTABLY ADJUSTABLE END PART (75) Inventor: Harald Hanke, Hamburg (DE)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,665 B2
 USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
Y 6a W SES. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States. Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov.
 (19) United States US 2005O2521.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 17, 2005 (54) STEELTRUSS FASTENERS FOR MULTI-POSITIONAL INSTALLATION (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O2521.52A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Belinda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 17, 2005 (54) STEELTRUSS FASTENERS FOR MULTI-POSITIONAL INSTALLATION (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,068,465 B2
 USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
United States Patent (19) Lin
 United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO867761 OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,677,610 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2014 (54) CRIMPING TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Jen Kai Liu, New Taipei (TW) U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO867761 OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,677,610 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2014 (54) CRIMPING TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Jen Kai Liu, New Taipei (TW) U.S.
Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, (73 Assignee: Molex Incorporated, Lisle, Ill. 57) ABSTRACT
 United States Patent (19) 11 US005577318A Patent Number: Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 1996 54 ELECTRICAL TERMINAL APPLICATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WEMPROVED TRACK ADJUSTMENT 2643514 8/1990
United States Patent (19) 11 US005577318A Patent Number: Smith et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 1996 54 ELECTRICAL TERMINAL APPLICATOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WEMPROVED TRACK ADJUSTMENT 2643514 8/1990
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
/ 7. 2 LOWER CASE. (12) United States Patent US 6,856,819 B2. Feb. 15, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 5 PARASITIC ELEMENT
 (12) United States Patent toh USOO6856819B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005 (54) PORTABLE WIRELESS UNIT (75) Inventor: Ryoh Itoh, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: NEC Corporation, Tokyo (JP)
(12) United States Patent toh USOO6856819B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005 (54) PORTABLE WIRELESS UNIT (75) Inventor: Ryoh Itoh, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: NEC Corporation, Tokyo (JP)
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) United States Patent
 US009136507B2 (12) United States Patent Lee et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,136,507 B2 Sep. 15, 2015 (54) CAN AND LITHIUMSECONDARY BATTERY USING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Sang-Woo Lee,
US009136507B2 (12) United States Patent Lee et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,136,507 B2 Sep. 15, 2015 (54) CAN AND LITHIUMSECONDARY BATTERY USING THE SAME (75) Inventors: Sang-Woo Lee,
IIH. United States Patent (19) Chen. (11) Patent Number: 5,318,090 (45. Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 1994
 United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2
 USOO8926262B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2 Tanahashi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) CMCTURBINE STATOR BLADE USPC... 415/9, 200, 209.3, 209.4, 210.1, 211.2,
USOO8926262B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2 Tanahashi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) CMCTURBINE STATOR BLADE USPC... 415/9, 200, 209.3, 209.4, 210.1, 211.2,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1
 USOO6729834B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1 McKinley (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) WAFER MANIPULATING AND CENTERING 5,788,453 A * 8/1998 Donde et al.... 414/751 APPARATUS
USOO6729834B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1 McKinley (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) WAFER MANIPULATING AND CENTERING 5,788,453 A * 8/1998 Donde et al.... 414/751 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,880,737 B2
 USOO6880737B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bauer (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) CELL PHONE HOLSTER SUBSIDIARY 5,217,294 A 6/1993 Liston STRAP AND HOLDER 5,503,316 A 4/1996 Stewart
USOO6880737B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bauer (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) CELL PHONE HOLSTER SUBSIDIARY 5,217,294 A 6/1993 Liston STRAP AND HOLDER 5,503,316 A 4/1996 Stewart
United States Patent (19) Breslow
 United States Patent (19) Breslow (54. SHELVING ASSEMBLY 75 Inventor: David S. Breslow, Chicago, Ill. 73 Assignee: RTC Industries, Inc., Chicago, Ill. (21) Appl. No.: 325,395 22 Filed: Mar. 20, 1989 5ll
United States Patent (19) Breslow (54. SHELVING ASSEMBLY 75 Inventor: David S. Breslow, Chicago, Ill. 73 Assignee: RTC Industries, Inc., Chicago, Ill. (21) Appl. No.: 325,395 22 Filed: Mar. 20, 1989 5ll
III IIII III. United States Patent (19) Cheng. 11) Patent Number: 5,529,288 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 1996
 United States Patent (19) Cheng 54 STRUCTURE OF A HANDRAIL FOR A STARCASE 76 Inventor: Lin Cheng-I, P.O. Box 82-144, Taipei, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 284,223 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51 Int. Cl.... E04F 11/18
United States Patent (19) Cheng 54 STRUCTURE OF A HANDRAIL FOR A STARCASE 76 Inventor: Lin Cheng-I, P.O. Box 82-144, Taipei, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 284,223 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51 Int. Cl.... E04F 11/18
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,857,696 B1. Merah et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 14, 2014
 United States Patent US008857696B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,857,696 B1 Merah et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 14, 2014 (54) METHOD AND TOOL FOR FRICTION STIR 7.954,691 B2 * 6/2011 Roos et al.... 228,112.1
United States Patent US008857696B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,857,696 B1 Merah et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 14, 2014 (54) METHOD AND TOOL FOR FRICTION STIR 7.954,691 B2 * 6/2011 Roos et al.... 228,112.1
Appl. No.: 619,775 Filed: Nov. 29, 1990 Int. Cl... E21B 4/02 U.S. Cl /907. 1; 175/ /95, 97, 282,303,
 United States Patent (19) Justman et al. (54) (75) (73) 21 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) BEARING STRUCTURE FOR DOWNHOLE MOTORS Inventors: Dan B. Justman, Houston; George A. Cross, Kingwood, both of Tex. Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Justman et al. (54) (75) (73) 21 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) BEARING STRUCTURE FOR DOWNHOLE MOTORS Inventors: Dan B. Justman, Houston; George A. Cross, Kingwood, both of Tex. Assignee:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2
 US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al.
 United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al. 11 Patent Number: (4) Date of Patent: 4,21,042 Jun. 4, 198 4 THREADED CONNECTION 7) Inventors: Jan W. Blackburn, Kingwood; Burl E. Baron, Houston, both of Tex.
United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al. 11 Patent Number: (4) Date of Patent: 4,21,042 Jun. 4, 198 4 THREADED CONNECTION 7) Inventors: Jan W. Blackburn, Kingwood; Burl E. Baron, Houston, both of Tex.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,650,825 B1
 USOO7650825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 2010 (54) CASE TRIMMER AND CHAMFER TOOL 4.325,282 A 4, 1982 Schaenzer... 86,24 4.385,546 A 5/1983 Lee...
USOO7650825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 2010 (54) CASE TRIMMER AND CHAMFER TOOL 4.325,282 A 4, 1982 Schaenzer... 86,24 4.385,546 A 5/1983 Lee...
(51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 ( ) B21D 41/00 ( ) B62D 1/20 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 56 5A_T (11) EP 3 115 635 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16177975.6 (51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 (2006.01) B21D
(19) TEPZZ 56 5A_T (11) EP 3 115 635 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 11.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/02 (21) Application number: 16177975.6 (51) Int Cl.: F16D 1/08 (2006.01) B21D
Oct. 25, ,280,665. Filed April 8, ATToRNEYs H. BLOCK. 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK TWEEZERS
 Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H. BLOCK 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATToRNEYs Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H, BLOCK 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 ZZZZZZ Taseo (7 INVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATTORNEYS United
Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H. BLOCK 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATToRNEYs Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H, BLOCK 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 ZZZZZZ Taseo (7 INVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATTORNEYS United
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9206864B2 (12) United States Patent Krusinski et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.206,864 B2 Dec. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) TORQUE CONVERTERLUG
USOO9206864B2 (12) United States Patent Krusinski et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.206,864 B2 Dec. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) TORQUE CONVERTERLUG
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1
 US008769908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1 Santini (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2014 (54) MODULAR BUILDING PANEL 4,813,193 A 3, 1989 Altizer.............. (76) Inventor: Patrick
US008769908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1 Santini (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2014 (54) MODULAR BUILDING PANEL 4,813,193 A 3, 1989 Altizer.............. (76) Inventor: Patrick
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.276,333 B1
 USOO9276333B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.276,333 B1 W (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) TERMINAL BLOCK WITH IMPROVED 8,647,158 B2 * 2/2014 Kawabata... HO1R 9/2608 RAILENGAGING
USOO9276333B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.276,333 B1 W (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) TERMINAL BLOCK WITH IMPROVED 8,647,158 B2 * 2/2014 Kawabata... HO1R 9/2608 RAILENGAGING
TSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS??ºzzz-->
 US007591574B2 (12) United States Patent Eschbach (54) OPTICAL ELEMENT FORVARIABLE MESSAGE SIGNS (75) Inventor: Bernd Eschbach, Karlsruhe (DE) (73) Assignee: Dambach-Werke GmbH, Kuppenheim (DE) (*) Notice:
US007591574B2 (12) United States Patent Eschbach (54) OPTICAL ELEMENT FORVARIABLE MESSAGE SIGNS (75) Inventor: Bernd Eschbach, Karlsruhe (DE) (73) Assignee: Dambach-Werke GmbH, Kuppenheim (DE) (*) Notice:
United States Patent 19 Perets
 United States Patent 19 Perets USOO5623875A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,623,875 Apr. 29, 1997 54 MULTI-COLOR AND EASY TO ASSEMBLE AUTOMATIC RUBBER STAMP 76 Inventor: Mishel Perets, clo M. Perets
United States Patent 19 Perets USOO5623875A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,623,875 Apr. 29, 1997 54 MULTI-COLOR AND EASY TO ASSEMBLE AUTOMATIC RUBBER STAMP 76 Inventor: Mishel Perets, clo M. Perets
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2
 USOO6752496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2 Conner (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 2004 (54) PLASTIC FOLDING AND TELESCOPING 5,929.966 A * 7/1999 Conner... 351/118 EYEGLASS
USOO6752496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2 Conner (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 2004 (54) PLASTIC FOLDING AND TELESCOPING 5,929.966 A * 7/1999 Conner... 351/118 EYEGLASS
United States Patent (19) Leonardis
 United States Patent (19) Leonardis 54 SUPPORT STRUCTURE FOR AMOTOR BUS 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Raffaele Leonardis, Turin, Italy Centro Ricerche Fiat S.p.A., Orbassano, Italy (21) Appl. No.: 97,606
United States Patent (19) Leonardis 54 SUPPORT STRUCTURE FOR AMOTOR BUS 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Raffaele Leonardis, Turin, Italy Centro Ricerche Fiat S.p.A., Orbassano, Italy (21) Appl. No.: 97,606
<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< 2. INVENTORS RSS SES`R`? %.2/ June 6, ,986,
 June 6, 1961 C. J. OXFORD, J.R., ETAL GUN DRILL AND THE METHOD OF PRODUCING THE SAME Filed June 15, 1959 RSS SES`R`?
June 6, 1961 C. J. OXFORD, J.R., ETAL GUN DRILL AND THE METHOD OF PRODUCING THE SAME Filed June 15, 1959 RSS SES`R`?
United States Patent (19) Mori
 United States Patent (19) Mori 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1991 54 PAPER-CUTTING MACHINE AND METHOD OF CUTTNG PAPER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Chuzo Mori, Katsushika, Japan Carl Manufacturing
United States Patent (19) Mori 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1991 54 PAPER-CUTTING MACHINE AND METHOD OF CUTTNG PAPER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Chuzo Mori, Katsushika, Japan Carl Manufacturing
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1
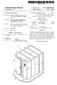 US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
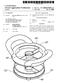 (19) United States US 20090249965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0249965 A1 Hauser (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIT REMOVER (75) Inventor: Lawrence M. Hauser, Auburn, WA (US) Correspondence
(19) United States US 20090249965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0249965 A1 Hauser (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIT REMOVER (75) Inventor: Lawrence M. Hauser, Auburn, WA (US) Correspondence
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2
 US008561977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2 Chang (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) POST-PROCESSINGAPPARATUS WITH (56) References Cited SHEET EUECTION DEVICE (75) Inventor:
US008561977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2 Chang (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) POST-PROCESSINGAPPARATUS WITH (56) References Cited SHEET EUECTION DEVICE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US009682771B2 () Patent No.: Knag et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2017 (54) CONTROLLING ROTOR BLADES OF A 5,676,334 A * /1997 Cotton... B64C 27.54 SWASHPLATELESS ROTOR 244.12.2
(12) United States Patent US009682771B2 () Patent No.: Knag et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2017 (54) CONTROLLING ROTOR BLADES OF A 5,676,334 A * /1997 Cotton... B64C 27.54 SWASHPLATELESS ROTOR 244.12.2
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,203 B1
 USOO89262O3B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,203 B1 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) WRITING INSTRUMENT GRIPPING AID AND USPC... 401/6, 88: 16/430; D19/47-49, 55 See application
USOO89262O3B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,203 B1 Chen (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) WRITING INSTRUMENT GRIPPING AID AND USPC... 401/6, 88: 16/430; D19/47-49, 55 See application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015031.6791A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0316791 A1 LACHAMBRE et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) EYEWEAR WITH INTERCHANGEABLE ORNAMENT MOUNTING SYSTEM, ORNAMENT
(19) United States US 2015031.6791A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0316791 A1 LACHAMBRE et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) EYEWEAR WITH INTERCHANGEABLE ORNAMENT MOUNTING SYSTEM, ORNAMENT
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
Oct. 19, 1971 R. F. ANDERSON E.T A. 3,613,151 HINGE CONSTRUCTION. Sed. a1sza N5 V. az-s W 7 ree-?ex Caeta' toen &
 Oct. 19, 1971 R. F. ANDERSON E.T A. 3,613,11 Filed June 27, 1969 3. Sheets-Sheet Sed a1sza N V 22 az-s W 7 ree-?ex Caeta' toen & g Oct. 19, 1971 R. F. ANDERson ET AL 3,613,11 Filed June 27, 1969 3. Sheets-Sheet
Oct. 19, 1971 R. F. ANDERSON E.T A. 3,613,11 Filed June 27, 1969 3. Sheets-Sheet Sed a1sza N V 22 az-s W 7 ree-?ex Caeta' toen & g Oct. 19, 1971 R. F. ANDERson ET AL 3,613,11 Filed June 27, 1969 3. Sheets-Sheet
United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972
![United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972](/thumbs/91/105347464.jpg) United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 54. FOLDING FNS FOR MESSELES 3,273,500 9/1966 Kongelbeck... 244/3.28 (72) Inventor: Nils-Åke Birger Svensson, Karlskoga, Primary Examiner-Verlin
United States Patent [15] 3,650,496 Svensson (45) Mar. 21, 1972 54. FOLDING FNS FOR MESSELES 3,273,500 9/1966 Kongelbeck... 244/3.28 (72) Inventor: Nils-Åke Birger Svensson, Karlskoga, Primary Examiner-Verlin
United States Patent (19) Prizzi
 United States Patent (19) Prizzi (54) TOWEL HOLDER 76 Inventor: Darin Prizzi, 8416 Mantanzas Rd., Fort Myers, Fla. 33912 (21) Appl. No.: 491,820 (22 Filed: Jun. 19, 1995 (51) Int. Cl.... A47H 13/00 (52)
United States Patent (19) Prizzi (54) TOWEL HOLDER 76 Inventor: Darin Prizzi, 8416 Mantanzas Rd., Fort Myers, Fla. 33912 (21) Appl. No.: 491,820 (22 Filed: Jun. 19, 1995 (51) Int. Cl.... A47H 13/00 (52)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1
 USOO684.8291B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1 Johnson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) PRESS BRAKE TOOL AND TOOL HOLDER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO684.8291B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1 Johnson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) PRESS BRAKE TOOL AND TOOL HOLDER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.704,201 B2
 USOO7704201B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.704,201 B2 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2010 (54) ENVELOPE-MAKING AID 3,633,800 A * 1/1972 Wallace... 223/28 4.421,500 A * 12/1983...
USOO7704201B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.704,201 B2 Johnson (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 2010 (54) ENVELOPE-MAKING AID 3,633,800 A * 1/1972 Wallace... 223/28 4.421,500 A * 12/1983...
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO900.4986B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,004,986 B2 Byers (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 2015 (54) SHARPENING TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search USPC... 451/557; 76/82, 86, 88
(12) United States Patent USOO900.4986B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,004,986 B2 Byers (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 2015 (54) SHARPENING TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search USPC... 451/557; 76/82, 86, 88
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2010/51
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 263 736 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.12.2010 Bulletin 2010/51 (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/09 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10165921.7 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 263 736 A1 (43) Date of publication: 22.12.2010 Bulletin 2010/51 (51) Int Cl.: A61M 25/09 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10165921.7 (22) Date of filing:
United States Patent (19) Shahan
 United States Patent (19) Shahan 54, HEAVY DUTY SHACKLE 75 Inventor: James B. Shahan, Tulsa, Okla. (73) Assignee: American Hoist & Derrick Company, Tulsa, Okla. (21) Appl. No.: 739,056 22 Filed: Nov. 5,
United States Patent (19) Shahan 54, HEAVY DUTY SHACKLE 75 Inventor: James B. Shahan, Tulsa, Okla. (73) Assignee: American Hoist & Derrick Company, Tulsa, Okla. (21) Appl. No.: 739,056 22 Filed: Nov. 5,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO661666OB1 (10) Patent No.: Platt (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2003 (54) MULTI-PORT SIDE-FIRE COAGULATOR 5,669,904 9/1997 Platt, Jr. et al. 5,669,907 A 9/1997 Platt, Jr. et
(12) United States Patent USOO661666OB1 (10) Patent No.: Platt (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2003 (54) MULTI-PORT SIDE-FIRE COAGULATOR 5,669,904 9/1997 Platt, Jr. et al. 5,669,907 A 9/1997 Platt, Jr. et
5 t 55O3 55 5O3. United States Patent (19) ll. 5,569,246 Oct. 29, Ojima et al. 53O O3 55O3 53O
 United States Patent (19) Ojima et al. 54 FIXING INSTRUMENT FOR SPINAL FUSION MEMBERS 75) Inventors: Satoshi Ojima, Tokyo; Shoji Uchida, Hyogo-ken, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Asahi Kogaku Kogyo Kabushiki
United States Patent (19) Ojima et al. 54 FIXING INSTRUMENT FOR SPINAL FUSION MEMBERS 75) Inventors: Satoshi Ojima, Tokyo; Shoji Uchida, Hyogo-ken, both of Japan 73) Assignee: Asahi Kogaku Kogyo Kabushiki
United States Patent (19) Van Halen
 United States Patent (19) Van Halen 11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 1987 54 MUSICAL INSTRUMENT SUPPORT 76 Inventor: Edward L. Van Halen, 1900 Ave. of Stars #1780, Los Angeles, Calif. 90067
United States Patent (19) Van Halen 11) () Patent Number: Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 1987 54 MUSICAL INSTRUMENT SUPPORT 76 Inventor: Edward L. Van Halen, 1900 Ave. of Stars #1780, Los Angeles, Calif. 90067
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,892,743 B2
 USOO6892743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,892,743 B2 Armstrong et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 17, 2005 (54) MODULAR GREENHOUSE 5,010,909 A * 4/1991 Cleveland... 135/125 5,331,725 A
USOO6892743B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,892,743 B2 Armstrong et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 17, 2005 (54) MODULAR GREENHOUSE 5,010,909 A * 4/1991 Cleveland... 135/125 5,331,725 A
Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 PEACH PITTING MACHINE INVENTOR. BY 6%au-v62. ATTORNEYS.
 Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 Filed Feb. 9, 1949 5 Sheets-Sheet INVENTOR BY 6%au-v62. ATTORNEYS. Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 Filed Feb. 9, 1949 5 Sheets-Sheet 2 /6- /2 72.2. Zsz27Z ZZZZZZZZ,
Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 Filed Feb. 9, 1949 5 Sheets-Sheet INVENTOR BY 6%au-v62. ATTORNEYS. Feb. 12, 1952 E. ALTMAN 2,585,073 Filed Feb. 9, 1949 5 Sheets-Sheet 2 /6- /2 72.2. Zsz27Z ZZZZZZZZ,
(12) United States Patent
 US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
United States Patent (19) Putman
 United States Patent (19) Putman 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 4, 1990 54. RHEOMETER DIE ASSEMBLY 76 Inventor: John B. Putman, 4.638 Commodore Dr., Stow, Ohio 44224 21 Appl. No.: 416,025 22
United States Patent (19) Putman 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 4, 1990 54. RHEOMETER DIE ASSEMBLY 76 Inventor: John B. Putman, 4.638 Commodore Dr., Stow, Ohio 44224 21 Appl. No.: 416,025 22
United States Patent (19) Morita et al.
 United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2. Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010
 US007859376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) ZIGZAGAUTOTRANSFORMER APPARATUS 7,049,921 B2 5/2006 Owen AND METHODS 7,170,268
US007859376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) ZIGZAGAUTOTRANSFORMER APPARATUS 7,049,921 B2 5/2006 Owen AND METHODS 7,170,268
IIII - HH. United States Patent 19. Nagamitsu et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,765, Date of Patent: Jun. 16, 1998
 United States Patent 19 Nagamitsu et al. 54 SPACE-SAVING WORKING EQUIPMENT (75) Inventors: Satoshi Nagamitsu, Higashiyamato; Hidemi Yaguchi, Mitsukaido; Yuji Yoshida, Yawara-mura, all of Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent 19 Nagamitsu et al. 54 SPACE-SAVING WORKING EQUIPMENT (75) Inventors: Satoshi Nagamitsu, Higashiyamato; Hidemi Yaguchi, Mitsukaido; Yuji Yoshida, Yawara-mura, all of Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent to 11 3,998,002
 United States Patent to 11 Nathanson 45 Dec. 21, 1976 54 PANEL, HOLDER FOR SMALL STRUCTURES AND TOYS 76 Inventor: Albert Nathanson, 249-26 63rd Ave., Little Neck, N.Y. 11329 22 Filed: Jan. 29, 1975 (21
United States Patent to 11 Nathanson 45 Dec. 21, 1976 54 PANEL, HOLDER FOR SMALL STRUCTURES AND TOYS 76 Inventor: Albert Nathanson, 249-26 63rd Ave., Little Neck, N.Y. 11329 22 Filed: Jan. 29, 1975 (21
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
(12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O254338A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0254338 A1 FISHER, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 20, 2011 (54) MULTI-PAWL ROUND-RECLINER MECHANISM (76)
(19) United States US 2011 O254338A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0254338 A1 FISHER, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 20, 2011 (54) MULTI-PAWL ROUND-RECLINER MECHANISM (76)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2
 USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007793.996 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.793,996 B2 Karlander (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2010 (54) CRASH BOX AND A METHOD OF (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/18703,
(12) United States Patent US007793.996 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.793,996 B2 Karlander (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2010 (54) CRASH BOX AND A METHOD OF (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/18703,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO965 1411 B2 (12) United States Patent Yamaguchi et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,651.411 B2 May 16, 2017 (54) ELECTROMAGNETIC FLOWMETER AND SELF-DAGNOSING METHOD OF EXCITING CIRCUIT
USOO965 1411 B2 (12) United States Patent Yamaguchi et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,651.411 B2 May 16, 2017 (54) ELECTROMAGNETIC FLOWMETER AND SELF-DAGNOSING METHOD OF EXCITING CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
United States Patent Fischell et al.
 United States Patent Fischell et al. 19 US006006124A 11 Patent Number: 6,006,124 (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1999 54 (75) MEANS AND METHOD FOR THE PLACEMENT OF BRAIN ELECTRODES Inventors: Robert E. Fischell,
United States Patent Fischell et al. 19 US006006124A 11 Patent Number: 6,006,124 (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1999 54 (75) MEANS AND METHOD FOR THE PLACEMENT OF BRAIN ELECTRODES Inventors: Robert E. Fischell,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
United States Patent (19) Cobb
 United States Patent (19) Cobb 54 RAM-SHEAR AND SLIP DEVICE FOR WELL PIPE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: A. Tom Cobb, Seabrook, Tex. Continental Oil Company, Ponca City, Okla. 21 Appl. No.: 671,464 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Cobb 54 RAM-SHEAR AND SLIP DEVICE FOR WELL PIPE 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: A. Tom Cobb, Seabrook, Tex. Continental Oil Company, Ponca City, Okla. 21 Appl. No.: 671,464 22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,452,105 B2. Badii et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2002
 USOO64521 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Badii et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2002 (54) COAXIAL CABLE ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,970.969 A * 7/1976 Sirel et al.... 333/12 DISCONTINUOUS OUTERJACKET
USOO64521 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Badii et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2002 (54) COAXIAL CABLE ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,970.969 A * 7/1976 Sirel et al.... 333/12 DISCONTINUOUS OUTERJACKET
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0128070 A1 Scirica et al. US 2017.0128070A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SURGICAL STAPLNG DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0128070 A1 Scirica et al. US 2017.0128070A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 11, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SURGICAL STAPLNG DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0203800 A1 Van de Geer et al. US 200802038.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SELF-COMPENSATING MECHANCAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0203800 A1 Van de Geer et al. US 200802038.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) SELF-COMPENSATING MECHANCAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0072964A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0072964 A1 Sarradon (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 21, 2013 (54) SURGICAL FORCEPS FOR PHLEBECTOMY (76) Inventor: Pierre
(19) United States US 2013 0072964A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0072964 A1 Sarradon (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 21, 2013 (54) SURGICAL FORCEPS FOR PHLEBECTOMY (76) Inventor: Pierre
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,616,442 B2
 USOO6616442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Venizelos et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2003 (54) LOW NO PREMIX BURNER APPARATUS 5,201,650 A 4/1993 Johnson... 431/9 AND METHODS 5,238,395
USOO6616442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Venizelos et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 9, 2003 (54) LOW NO PREMIX BURNER APPARATUS 5,201,650 A 4/1993 Johnson... 431/9 AND METHODS 5,238,395
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,715,221 B1. Sasaki (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004
 USOO671.51B1 (1) United States Patent (10) Patent No. US 6,715,1 B1 Sasaki (45) Date of Patent Apr. 6, 004 (54) FOOT STIMULATING SHOE INSOLE 5,860,9 A * 1/1999 Morgenstern... 36/141 (75) Inventor Manhachi
USOO671.51B1 (1) United States Patent (10) Patent No. US 6,715,1 B1 Sasaki (45) Date of Patent Apr. 6, 004 (54) FOOT STIMULATING SHOE INSOLE 5,860,9 A * 1/1999 Morgenstern... 36/141 (75) Inventor Manhachi
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0047169A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0047169 A1 Livingstone (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) DOWNHOLE MOTOR Publication Classification (71)
(19) United States US 2016.0047169A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0047169 A1 Livingstone (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 18, 2016 (54) DOWNHOLE MOTOR Publication Classification (71)
58 Field of Search /69, 70, 71, than the minor axis De of this hole (2) running perpendicu
 USO0570968.6A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,709,686 Talos et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 1998 54 BONE PLATE 5,002,544 3/1991 Klaue et al.... 606/69 5,041,113 8/1991 Biedermann et al....
USO0570968.6A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,709,686 Talos et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 1998 54 BONE PLATE 5,002,544 3/1991 Klaue et al.... 606/69 5,041,113 8/1991 Biedermann et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007025 1096A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0251096 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2007 (54) EGG BREAKING DEVICE INCORPORATING A DURABLE AND RUBBERIZED
(19) United States US 2007025 1096A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0251096 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2007 (54) EGG BREAKING DEVICE INCORPORATING A DURABLE AND RUBBERIZED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,857,315 B2
 US007857315B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,857,315 B2 Hoyt (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) MATHODOMINICS 2,748,500 A 6/1956 Cormack... 434,205 4,083,564 A * 4, 1978 Matsumoto...
US007857315B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,857,315 B2 Hoyt (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) MATHODOMINICS 2,748,500 A 6/1956 Cormack... 434,205 4,083,564 A * 4, 1978 Matsumoto...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2
 US008.937567B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2 Obata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2015 (54) DELTA-SIGMA MODULATOR, INTEGRATOR, USPC... 341/155, 143 AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
US008.937567B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2 Obata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2015 (54) DELTA-SIGMA MODULATOR, INTEGRATOR, USPC... 341/155, 143 AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
11) Patent Number: 5,323,091 Morris (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 21, STARTING SOURCE FOR ARC DISCHARGE 4,041,352 8/1977 McNeill et al...
 IIIHIIII USOO5323091A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,323,091 Morris (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 21, 1994 54 STARTING SOURCE FOR ARC DISCHARGE 4,041,352 8/1977 McNeill et al.... 315/248 LAMPS
IIIHIIII USOO5323091A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,323,091 Morris (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 21, 1994 54 STARTING SOURCE FOR ARC DISCHARGE 4,041,352 8/1977 McNeill et al.... 315/248 LAMPS
United States Patent (19) Sun
 United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Roy et al. USOO6216409 B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,216,409 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2001 (54) CLADDING PANEL FOR FLOORS, WALLS OR THE LIKE (76) Inventors: Valerie Roy, 13,
(12) United States Patent Roy et al. USOO6216409 B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,216,409 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2001 (54) CLADDING PANEL FOR FLOORS, WALLS OR THE LIKE (76) Inventors: Valerie Roy, 13,
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
United States Patent (19) Oliver
 United States Patent (19) Oliver 54 76 21 22) 51 52) 58 56 METHOD OF MANUFACTURING A GATE WALWE BODY Inventor: John P. Oliver, 37 Stillforest, Houston, Tex. 77024 Appl. No.: 300,216 Filed: Sep. 8, 1981
United States Patent (19) Oliver 54 76 21 22) 51 52) 58 56 METHOD OF MANUFACTURING A GATE WALWE BODY Inventor: John P. Oliver, 37 Stillforest, Houston, Tex. 77024 Appl. No.: 300,216 Filed: Sep. 8, 1981
