Reliability and Validity of EndoTower, a Virtual Reality Trainer for Angled Endoscope Navigation
|
|
|
- Lee Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 2002 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds) IOS Press, 2002 Reliability and Validity of EndoTower, a Virtual Reality Trainer for Angled Endoscope Navigation Randy S. HALUCK MD FACS 1, Anthony G. GALLAGHER PhD 2,3, Richard M. SATAVA MD FACS 2, Roger WEBSTER PhD 4, Thomas L. BASS MD 1, Cynthia A. MILLER BS 1 1 Department of Surgery, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA Department of Surgery, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT School of Psychology, The Queen s University of Belfast, Belfast BT7 1NN, NI 4 Department of Computer Science, Millersville University of Pennsylvania School of Science and Mathematics, Millersville, PA Abstract. We hypothesized that a simulator designed to train surgical novices angled laparoscopic navigation would show an improvement in subjects performance, a high test re-test reliability and high internal validity as measured by standardized coefficient alpha. It was also predicted that simulator performance would be strongly related to objectively assess perceptual and visuospatial ability. EndoTower has good face validity in that it mimics precisely the performance of an angled laparoscope and previous studies suggest construct validity. In this study, EndoTower is shown to be a trainer intended for laparoscopic skill than can test for inherent perceptual and visuospatial ability. 1. Background/Problem: The Penn State EndoTower (EndoTower) is a PC based simulator/trainer that utilizes the Virtual Laparoscopic Interface (VLI, Immersion Corp., San Jose, CA). An additional hardware component attached to the VLI device represents an angled laparoscope structure and function. It is designed to provide instruction and practice in the skills necessary for camera/laparoscope navigation for minimally invasive surgery [1]. All surgical procedures require some degree of visual navigation within an operative field. Laparoscopy presents additional challenges as visual and spatial cues are altered. Most commercially available angled laparoscopic camera and lens systems must be independently rotated, or not rotated by the user in order to achieve the desired angle of view while maintaining correct right-side-up orientation. This camera and angled rigid lens system is used in many different operations covering a number of surgical specialties. The function, orientation, and correct manipulation of an angled laparoscopic lens in combination with an independently rotating camera system is not necessarily intuitive. As the surgeon performs the actual operation, the duty of camera navigation falls to the assistant, often a less-experienced team member. Robotic assisted camera navigation also requires that the surgeon have a fluid understanding of the workings of the optical system. Several studies suggest that an inherent trait, visuospatial ability, correlate with a higher level of surgical skill [2-4]. Visuospatial abilities relate to the ability to mentally
2 represent three-dimensional situation using key landmarks, and to have a clear mental picture of their relationship in space [5]. While other studies do not support this conclusion [6], it is apparent that some degree of visuospatial ability is required for surgical performance, Surgeons using video assistance need to form visual impressions of threedimensional structures, organs and instruments, from a two-dimensional television monitor. While this is often described as loss of binocularity [7], it is simpler and more accurate to call it pictorial perception. So-called primary cues binocular disparity and convergence, accommodation, and motion parallax are present in abundance. The difficulty is that the primary cues and other cues related to lighting and texture yield a conclusion that is inimical to surgery. The conclusion specified is that the structures in view form a single surface, virtually flat and usually vertical. The surgeon has to set aside that conclusion in order to register the information carried by subtler pictorial cues and to reconstruct the structure that they specify despite the incompleteness of the information provided. Individuals differ in this ability and such differences could clearly contribute to performance differences for pictorially guided laparoscopic surgery. Although EndoTower was designed to provide instruction in angled laparoscope navigation, we hypothesized that it would also serve as a testing platform to reliably assess visuospatial and perceptual ability. A simulation tool that is able to reliably assess these abilities, identifying levels of inherent ability in surgeons, while increasing skill acquisition may have additional value for surgical education. 2. Methods: The task for the EndoTower testing session entailed identifying randomly placed arrows in the virtual "EndoTower". The EndoTower is a three-dimensional (3D) block tower with cylindrical holes within its various arms (Figure 1). The EndoTower provides a relatively complex three-dimensional structure for exploration with the virtual angled lens. In the simulator, 3D arrows of varying colors and directional orientation are randomly placed around the tower and inside the cylindrical cut-outs. Arrows were chosen as the targets so that participants would be required to maintain right-side-up orientation in order to be able to properly identify them. Arrows could have one of four colors and six directional orientations giving 24 possible combinations. Six arrows were randomly placed on and within the virtual EndoTower as part of the software program (Figure 2). To operate the simulator, the subject held one of the VLI laparoscopic tools, modified to simulate the angled lens laparoscope. Rotation of this mock camera and lens rotated the horizon and angle of view from the longitudinal axis of the virtual laparoscope, respectively. The virtual world mimics the real world as the user's viewpoint is placed at the tip of the laparoscopic tool. Due to the 3D nature of the EndoTower and the cylindrical cutouts, identifying all the arrows entailed manipulating the laparoscope to many different and challenging orientations and positions. Once a target arrow was found and identified, the student selected the matching arrow from a list using the foot-pedal function of the VLI. Any collision with the EndoTower caused the view to become fuzzy and blurry with 'red out', simulating touching the laparoscope to an organ and smudging the lens with blood. The learner was required to withdraw the virtual laparoscope and await a cleaning mode, thus penalizing the user s score in terms of time efficiency and also scoring an error. EndoTower mechanism recorded the amount of time to correctly identify the color and orientation of each arrow and the number of arrows.
3 Figure 1: The three dimensional EndoTower Figure 2: A randomly placed arrow within the virtual EndoTower
4 A time limit of four minutes was selected to complete the task of correctly identifying all six arrows. Computerized scoring was determined by the time to find all six of the target arrows plus the number of red-out errors multiplied by a factor of 10. If at the end of the four minute time limit, all of the arrows were not identified, the number of arrows not found was multiplied by 30 and added to the score. Therefore, a lower score indicated a better performance. Twenty-five laparoscopic novices completed three trials on EndoTower. None of the subjects had ever used EndoTower or manipulated a rigid laparoscopic lens. All subjects received a brief and standardized instruction session on the goals and function of EndoTower. One testing was accomplished and the computer-generated score was recorded. All subjects also completed the Pictorial Surface Orientation (PicSOr) test battery, a perceptual task that assesses the ability to reconstruct 3-D from 2-D perceptual cues [8]. They also completed three tests that assess fundamental visuospatial abilities, Card Rotation (CR), Cube Comparison (CC), and Map Plan (MP) [9]. Gallagher et al have reported that these tests are reliably associated with laparoscopic performance [10, 11]. The study was approved by the institutional review board with informed consent obtained from all participants. 3. Results: The mean EndoTower scores were, trial 1 = 337 ± 50, trial 2 = 324 ± 73 and trial ± 71. Subjects performance improved consistently across the three trials. Analysis of variance for repeated measures showed that there was a statistically significant difference between the trials (F(2, 24) = 13.05, p < ). Differences between the different trials were compared for significance with Scheffe Post Hoc F-Tests. Although there was an improvement in scores between trial 1 and trial 2 this improvement was not statistically significant. The improvement in scores between trial 1 and 3 was statistically significant (Scheffe F = 12.62, p < ) as were the differences between trials 2 and 3 (Scheffe F = 6.87, p < 0.01). A statistically significant within subject effect was also observed. The within subject effect means that some subjects EndoTower scores were statistically different from the mean EndoTower score (F(2, 24) = 5.05, p < ). The test re-test reliability of EndoTower was calculated using Pearson s Product Moment Correlation Coefficient. The observed correlation coefficient was r = 0.8 (F(1, 23) = 33.82, p < ) and r 2 = 0.6. To determine the internal validity or consistency of EndoTower as a measurement device Standardize Coefficient Alpha was calculated and was observed to be = 0.88 (F(2, 24) = , p < ). The correlations between EndoTower performance and PicSOr, CR, CC and MP were r=0.591, r=0.296, r=0.354 and r=0.392 respectively. However, when any single visuospatial test was combined with the PicSOr perceptual test in a multiple regression model the correlations increased dramatically. The results for the different regression models showed that for, PicSOr and CR, r=0.658, r 2 =0.43 (F(2,37)=14.2; p< ); PicSOr and CC, r=0.701, r 2 =0.49 (F(2,37)=17.89; p< ); and PicSOr and MP, r=0.708, r 2 =0.50 (F(2,37)=118.6; p< ).
5 4. Discussion / Conclusions: A number of factors cumulate in the successful performance of an operation. Spencer suggested that probably about 75% of the important events in an operation are related to making decisions, and about 25% to dexterity [12]. Although this may be true, an operation is the result of manipulation of tissues ultimately requiring technical performance and skill. At this point in time, the acquisition of operative technical skill is poorly understood, both from the standpoint of the ingredients or abilities that serve as the basis for skill and which individuals might posses those ingredients. A test that replicates tasks for which surgical skill is required, yet can assess inherent abilities, may help to further the understanding of skill acquisition. One factor that will affect operative performance is practice. The human brain has a limited capacity to attend to different sources and amounts of information. This means that the surgeon can only attend to a given amount of information at any given time. The more familiar the surgeon is with information, or the more frequently they have come in contact with it, the less attentional processing resources that information will require. The opposite is also true. This is important in surgery because attentional resources that are used on behaviors such as instrument navigation are not available for the most important aspect of surgery, i.e., surgical performance. We believe that simple but fundamental aspects of video assisted surgery such as camera navigation should be largely learned in the laboratory so that residents can hone their skills in the operating room rather than acquire them from basics. One of the primary functions of a simulator, virtual reality or otherwise, is to improve performance. Another function of a virtual reality simulator is to provide objective assessment of performance, however, assessment cannot be accepted at face value. Satava [13] has suggested that if a virtual reality system purports to assess performance, validation metrics associated with that claim must be reported. In this paper we have reported that EndoTower has good face validity in that it mimics precisely the performance of an angled laparoscope. Interestingly, EndoTower also appears to be able to discriminate those individuals who have difficulty performing the task as indicated by the significant probability value for between subjects ANOVA results. It also has been demonstrated to have high test re-test reliability and a high alpha coefficient. In this study, we have also taken the validation a stage further. Visuospatial ability and perceptual ability have been hypothesized and reported to be correlated with laparoscopic performance [10, 11]. These hypotheses appear sensible but need further experimental validation. In this study these abilities were found to be strongly related to EndoTower performance, particularly when included in a multiple regression model. In fact, simple regression models accounted for 43 50% of the variance. This is an important point because multimodal behaviors (e.g., perceptual, cognitive and psychomotor) required for complex real-world performance, such as surgery are unlikely to be explained by a simple correlation model, more likely a multiple regression model or ideally a Structural Equation Model. Intuitively, it would seem that an ability to mentally reconstruct 3D from 2D cues and manipulate complex 3D structures and environments would be fundamental to performing operative manipulations. However, there is disagreement in the surgical literature regarding their ability to predict surgical skill. The study reported here shows that objectively assessed perceptual and visuospatial abilities predict angled scope navigation performance. This lends support to the hypothesis that these abilities are related to laparoscopic surgical performance. Furthermore, EndoTower assessment of these abilities has greater face validity for the assessment of a surgical skill, i.e., the test is
6 simulated angled scope navigation. However, further validation work on this issue is required. Virtual reality simulation has moved from is it pretty to does it work and where is the evidence to sophisticated metrics about performance parameters. Satava [13] has suggested that all virtual reality simulators must meet these fundamental criterion markers to be considered as a scientifically validated simulator. EndoTower has gone some way to meet these criteria however one of the major challenges for virtual reality remains, Does training in the virtual environment transfer to the OR? This work is currently underway in our laboratories and we are optimistic about the outcome. 5. Acknowledgements: This project was funded in part by the Penn State Eberly Virtual Hospital Project and one of the authors (AGG) was supported by the Fulbright Distinguished Scholar program. 6. References: 1. Haluck RS, Webster R, Melkonian M, Mohler B, Dise M, LeFever A: A virtual reality surgical training module for instruction in angled laparoscopic lens navigation. Stud Health Technol Inform 2001;81: Schueneman AL, Pickleman J, Hesslein MA et al: Neuropsychological predictors of operative skill among general surgery residents. Surgery 1984;96: Gibbons RD, Baker RJ, Skinner DB: Field articulation testing: A predictor of technical skills in surgical residents. J Surg Res 1986;41: Risucci D, Tortolani A, Horowitz M: Neuropsychological assessment of general surgery interns. Focus Surg Edu 1991;10: DesCoteaux JG, Leclere H: Learning surgical technical skills. CJS 1995;38: Francis NK, Hanna GB, Cresswell AB, Carer FJ, Cuschieri A. The performance of master surgeons on standard aptitude testing. Am J Surg 2001;182: Reinhardt-Rutland AH and Gallagher AG. Visual depth perception in Minimally Invasive Surgery. In SA Robertson (Ed) Contemporary Ergonomics;1996: Cowie R. Measurement and modeling of perceived slant in surfaces represented by freely viewed line drawings. Perception 1998;27: Ekstrom RB, French JW, Harman HH, Dermen D. Manual Kit for Factor Referenced Cognitive Tests Princeton New Jersey: Educational Testing Service. 10. Gallagher AG, Crothers I, Satava RM. Comprehensive objective assessment of fundamental skills for laparoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc 2001; In Press. 11. Gallagher AG, Cowie R, Crothers I, Jordan JA, McGlade K, McGuigan J, McClure N. PicSOr: An objective test of perceptual skill that predicts laparoscopic performance in three separate studies. Surg Endosc 2001; In Press. 12. Spencer FC. Observations on the teaching of operative technique. Bull Am Coll Surg 1983;3: Satava, RM. The need for metrics in surgical education. (1999) Surg Endosc; 13:
A Virtual Reality Surgical Trainer for Navigation in Laparoscopic Surgery
 Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 2001 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds) IOS Press, 2001 A Virtual Reality Surgical Trainer for Navigation in Laparoscopic Surgery Randy S. Haluck M.D. 1, Roger W. Webster Ph.D. 2,
Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 2001 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds) IOS Press, 2001 A Virtual Reality Surgical Trainer for Navigation in Laparoscopic Surgery Randy S. Haluck M.D. 1, Roger W. Webster Ph.D. 2,
Measurements of the Level of Surgical Expertise Using Flight Path Analysis from da Vinci Robotic Surgical System
 Measurements of the Level of Surgical Expertise Using Flight Path Analysis from da Vinci Robotic Surgical System Lawton Verner 1, Dmitry Oleynikov, MD 1, Stephen Holtmann 1, Hani Haider, Ph D 1, Leonid
Measurements of the Level of Surgical Expertise Using Flight Path Analysis from da Vinci Robotic Surgical System Lawton Verner 1, Dmitry Oleynikov, MD 1, Stephen Holtmann 1, Hani Haider, Ph D 1, Leonid
Surgical robot simulation with BBZ console
 Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Surgical robot simulation with BBZ console Francesco Bovo 1, Giacomo De Rossi 2, Francesco Visentin 2,3 1 BBZ srl, Verona, Italy; 2 Department of Computer Science, Università
Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Surgical robot simulation with BBZ console Francesco Bovo 1, Giacomo De Rossi 2, Francesco Visentin 2,3 1 BBZ srl, Verona, Italy; 2 Department of Computer Science, Università
Perceptual-motor coordination in an endoscopic surgery simulation
 Surg Endosc (1999) 13: 127 132 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 1999 Perceptual-motor coordination in an endoscopic surgery simulation J. G. Holden, 1, * J. M. Flach, 1 Y. Donchin 2 1 Psychology Department,
Surg Endosc (1999) 13: 127 132 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 1999 Perceptual-motor coordination in an endoscopic surgery simulation J. G. Holden, 1, * J. M. Flach, 1 Y. Donchin 2 1 Psychology Department,
Simendo laparoscopy. product information
 Simendo laparoscopy product information Simendo laparoscopy The Simendo laparoscopy simulator is designed for all laparoscopic specialties, such as general surgery, gynaecology en urology. The simulator
Simendo laparoscopy product information Simendo laparoscopy The Simendo laparoscopy simulator is designed for all laparoscopic specialties, such as general surgery, gynaecology en urology. The simulator
Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning
 Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
Perceived Depth is Enhanced with Parallax Scanning March 1, 1999 Dennis Proffitt & Tom Banton Department of Psychology University of Virginia Perceived depth is enhanced with parallax scanning Background
Evaluation of Haptic Virtual Fixtures in Psychomotor Skill Development for Robotic Surgical Training
 Department of Electronics, Information and Bioengineering Neuroengineering and medical robotics Lab Evaluation of Haptic Virtual Fixtures in Psychomotor Skill Development for Robotic Surgical Training
Department of Electronics, Information and Bioengineering Neuroengineering and medical robotics Lab Evaluation of Haptic Virtual Fixtures in Psychomotor Skill Development for Robotic Surgical Training
Virtual Reality Based Training to resolve Visio-motor Conflicts in Surgical Environments
 HAVE 2008 IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual Environments and their Applications Ottawa Canada, 18-19 October 2008 Virtual Reality Based Training to resolve Visio-motor Conflicts in Surgical
HAVE 2008 IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual Environments and their Applications Ottawa Canada, 18-19 October 2008 Virtual Reality Based Training to resolve Visio-motor Conflicts in Surgical
Medical robotics and Image Guided Therapy (IGT) Bogdan M. Maris, PhD Temporary Assistant Professor
 Medical robotics and Image Guided Therapy (IGT) Bogdan M. Maris, PhD Temporary Assistant Professor E-mail bogdan.maris@univr.it Medical Robotics History, current and future applications Robots are Accurate
Medical robotics and Image Guided Therapy (IGT) Bogdan M. Maris, PhD Temporary Assistant Professor E-mail bogdan.maris@univr.it Medical Robotics History, current and future applications Robots are Accurate
MECHANICAL DESIGN LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS BASED ON VIRTUAL REALITY TECHNOLOGIES
 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ENGINEERING AND PRODUCT DESIGN EDUCATION 4 & 5 SEPTEMBER 2008, UNIVERSITAT POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA, BARCELONA, SPAIN MECHANICAL DESIGN LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS BASED ON VIRTUAL
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ENGINEERING AND PRODUCT DESIGN EDUCATION 4 & 5 SEPTEMBER 2008, UNIVERSITAT POLITECNICA DE CATALUNYA, BARCELONA, SPAIN MECHANICAL DESIGN LEARNING ENVIRONMENTS BASED ON VIRTUAL
IAC-08-B3.6. Investigating the Effects of Frame Disparity on the Performance of Telerobotic Tasks
 IAC-8-B3.6 Investigating the Effects of Frame Disparity on the Performance of Telerobotic Tasks Adrian Collins*, Zakiya Tomlinson, Charles Oman, Andrew Liu, Alan Natapoff Man Vehicle Laboratory Department
IAC-8-B3.6 Investigating the Effects of Frame Disparity on the Performance of Telerobotic Tasks Adrian Collins*, Zakiya Tomlinson, Charles Oman, Andrew Liu, Alan Natapoff Man Vehicle Laboratory Department
Differences in Fitts Law Task Performance Based on Environment Scaling
 Differences in Fitts Law Task Performance Based on Environment Scaling Gregory S. Lee and Bhavani Thuraisingham Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas 800 West Campbell Road Richardson,
Differences in Fitts Law Task Performance Based on Environment Scaling Gregory S. Lee and Bhavani Thuraisingham Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas 800 West Campbell Road Richardson,
Effects of Geared Motor Characteristics on Tactile Perception of Tissue Stiffness
 Effects of Geared Motor Characteristics on Tactile Perception of Tissue Stiffness Jeff Longnion +, Jacob Rosen+, PhD, Mika Sinanan++, MD, PhD, Blake Hannaford+, PhD, ++ Department of Electrical Engineering,
Effects of Geared Motor Characteristics on Tactile Perception of Tissue Stiffness Jeff Longnion +, Jacob Rosen+, PhD, Mika Sinanan++, MD, PhD, Blake Hannaford+, PhD, ++ Department of Electrical Engineering,
Haptic Abilities of Freshman Engineers as Measured by the Haptic Visual Discrimination Test
 a u t u m n 2 0 0 3 Haptic Abilities of Freshman Engineers as Measured by the Haptic Visual Discrimination Test Nancy E. Study Virginia State University Abstract The Haptic Visual Discrimination Test (HVDT)
a u t u m n 2 0 0 3 Haptic Abilities of Freshman Engineers as Measured by the Haptic Visual Discrimination Test Nancy E. Study Virginia State University Abstract The Haptic Visual Discrimination Test (HVDT)
Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery
 Young Group 5 1 Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery Paper Review Jessie Young Group 5: Haptic Interface for Surgical Manipulator System March 12, 2012 Paper Selection: A. M. Okamura.
Young Group 5 1 Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery Paper Review Jessie Young Group 5: Haptic Interface for Surgical Manipulator System March 12, 2012 Paper Selection: A. M. Okamura.
AGING AND STEERING CONTROL UNDER REDUCED VISIBILITY CONDITIONS. Wichita State University, Wichita, Kansas, USA
 AGING AND STEERING CONTROL UNDER REDUCED VISIBILITY CONDITIONS Bobby Nguyen 1, Yan Zhuo 2, & Rui Ni 1 1 Wichita State University, Wichita, Kansas, USA 2 Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
AGING AND STEERING CONTROL UNDER REDUCED VISIBILITY CONDITIONS Bobby Nguyen 1, Yan Zhuo 2, & Rui Ni 1 1 Wichita State University, Wichita, Kansas, USA 2 Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Using Simulation to Design Control Strategies for Robotic No-Scar Surgery
 Using Simulation to Design Control Strategies for Robotic No-Scar Surgery Antonio DE DONNO 1, Florent NAGEOTTE, Philippe ZANNE, Laurent GOFFIN and Michel de MATHELIN LSIIT, University of Strasbourg/CNRS,
Using Simulation to Design Control Strategies for Robotic No-Scar Surgery Antonio DE DONNO 1, Florent NAGEOTTE, Philippe ZANNE, Laurent GOFFIN and Michel de MATHELIN LSIIT, University of Strasbourg/CNRS,
NAVIGATIONAL CONTROL EFFECT ON REPRESENTING VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS
 NAVIGATIONAL CONTROL EFFECT ON REPRESENTING VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS Xianjun Sam Zheng, George W. McConkie, and Benjamin Schaeffer Beckman Institute, University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign This present
NAVIGATIONAL CONTROL EFFECT ON REPRESENTING VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENTS Xianjun Sam Zheng, George W. McConkie, and Benjamin Schaeffer Beckman Institute, University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign This present
Chapter 2 Influence of Binocular Disparity in Depth Perception Mechanisms in Virtual Environments
 Chapter 2 Influence of Binocular Disparity in Depth Perception Mechanisms in Virtual Environments Matthieu Poyade, Arcadio Reyes-Lecuona, and Raquel Viciana-Abad Abstract In this chapter, an experimental
Chapter 2 Influence of Binocular Disparity in Depth Perception Mechanisms in Virtual Environments Matthieu Poyade, Arcadio Reyes-Lecuona, and Raquel Viciana-Abad Abstract In this chapter, an experimental
The Representational Effect in Complex Systems: A Distributed Representation Approach
 1 The Representational Effect in Complex Systems: A Distributed Representation Approach Johnny Chuah (chuah.5@osu.edu) The Ohio State University 204 Lazenby Hall, 1827 Neil Avenue, Columbus, OH 43210,
1 The Representational Effect in Complex Systems: A Distributed Representation Approach Johnny Chuah (chuah.5@osu.edu) The Ohio State University 204 Lazenby Hall, 1827 Neil Avenue, Columbus, OH 43210,
Module 2. Lecture-1. Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation.
 Module 2 Lecture-1 Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation. Initially let us take the reference of Gestalt law in order to have an understanding of the basic
Module 2 Lecture-1 Understanding basic principles of perception including depth and its representation. Initially let us take the reference of Gestalt law in order to have an understanding of the basic
Perception. What We Will Cover in This Section. Perception. How we interpret the information our senses receive. Overview Perception
 Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
Perception 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 1 What We Will Cover in This Section Overview Perception Visual perception. Organizing principles. 10/3/2002 Perception.ppt 2 Perception How we interpret the information
da Vinci Skills Simulator
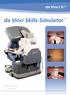 da Vinci Skills Simulator Introducing Simulation for the da Vinci Surgical System Skills Practice in an Immersive Virtual Environment Portable. Practical. Powerful. The da Vinci Skills Simulator contains
da Vinci Skills Simulator Introducing Simulation for the da Vinci Surgical System Skills Practice in an Immersive Virtual Environment Portable. Practical. Powerful. The da Vinci Skills Simulator contains
VR based HCI Techniques & Application. November 29, 2002
 VR based HCI Techniques & Application November 29, 2002 stefan.seipel@hci.uu.se What is Virtual Reality? Coates (1992): Virtual Reality is electronic simulations of environments experienced via head mounted
VR based HCI Techniques & Application November 29, 2002 stefan.seipel@hci.uu.se What is Virtual Reality? Coates (1992): Virtual Reality is electronic simulations of environments experienced via head mounted
Minimally invasive surgical skills evaluation in the field of otolaryngology
 Minimally invasive surgical skills evaluation in the field of otolaryngology Alejandro Cuevas 1, Daniel Lorias 1, Arturo Minor 1, Jose A. Gutierrez 2, Rigoberto Martinez 3 1 CINVESTAV-IPN, México D.F.,
Minimally invasive surgical skills evaluation in the field of otolaryngology Alejandro Cuevas 1, Daniel Lorias 1, Arturo Minor 1, Jose A. Gutierrez 2, Rigoberto Martinez 3 1 CINVESTAV-IPN, México D.F.,
A Virtual Reality Training Program for Improvement of Robotic Surgical Skills
 A Virtual Reality Training Program for Improvement of Robotic Surgical Skills *M. MUKHERJEE 1, K.-C. SIU 1 4, I. H. SUH 1,2 4, A. KLUTMAN 2, D. OLEYNIKOV2. 4, and N. STERGIOU 1,3 4 1 Nebraska Biomechanics
A Virtual Reality Training Program for Improvement of Robotic Surgical Skills *M. MUKHERJEE 1, K.-C. SIU 1 4, I. H. SUH 1,2 4, A. KLUTMAN 2, D. OLEYNIKOV2. 4, and N. STERGIOU 1,3 4 1 Nebraska Biomechanics
EYE MOVEMENT STRATEGIES IN NAVIGATIONAL TASKS Austin Ducworth, Melissa Falzetta, Lindsay Hyma, Katie Kimble & James Michalak Group 1
 EYE MOVEMENT STRATEGIES IN NAVIGATIONAL TASKS Austin Ducworth, Melissa Falzetta, Lindsay Hyma, Katie Kimble & James Michalak Group 1 Abstract Navigation is an essential part of many military and civilian
EYE MOVEMENT STRATEGIES IN NAVIGATIONAL TASKS Austin Ducworth, Melissa Falzetta, Lindsay Hyma, Katie Kimble & James Michalak Group 1 Abstract Navigation is an essential part of many military and civilian
Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Robot-Assisted Surgical Motions
 Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Robot-Assisted Surgical Motions Henry C. Lin 1, Izhak Shafran 2, Todd E. Murphy, Allison M. Okamura, David D. Yuh, and Gregory D. Hager 1 1 Department of Computer
Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Robot-Assisted Surgical Motions Henry C. Lin 1, Izhak Shafran 2, Todd E. Murphy, Allison M. Okamura, David D. Yuh, and Gregory D. Hager 1 1 Department of Computer
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Introduction to Psychology Prof. Braj Bhushan Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 10 Perception Role of Culture in Perception Till now we have
Quantitative Comparison of Interaction with Shutter Glasses and Autostereoscopic Displays
 Quantitative Comparison of Interaction with Shutter Glasses and Autostereoscopic Displays Z.Y. Alpaslan, S.-C. Yeh, A.A. Rizzo, and A.A. Sawchuk University of Southern California, Integrated Media Systems
Quantitative Comparison of Interaction with Shutter Glasses and Autostereoscopic Displays Z.Y. Alpaslan, S.-C. Yeh, A.A. Rizzo, and A.A. Sawchuk University of Southern California, Integrated Media Systems
3D Modelling Is Not For WIMPs Part II: Stylus/Mouse Clicks
 3D Modelling Is Not For WIMPs Part II: Stylus/Mouse Clicks David Gauldie 1, Mark Wright 2, Ann Marie Shillito 3 1,3 Edinburgh College of Art 79 Grassmarket, Edinburgh EH1 2HJ d.gauldie@eca.ac.uk, a.m.shillito@eca.ac.uk
3D Modelling Is Not For WIMPs Part II: Stylus/Mouse Clicks David Gauldie 1, Mark Wright 2, Ann Marie Shillito 3 1,3 Edinburgh College of Art 79 Grassmarket, Edinburgh EH1 2HJ d.gauldie@eca.ac.uk, a.m.shillito@eca.ac.uk
Studying the Effects of Stereo, Head Tracking, and Field of Regard on a Small- Scale Spatial Judgment Task
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS, MANUSCRIPT ID 1 Studying the Effects of Stereo, Head Tracking, and Field of Regard on a Small- Scale Spatial Judgment Task Eric D. Ragan, Regis
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VISUALIZATION AND COMPUTER GRAPHICS, MANUSCRIPT ID 1 Studying the Effects of Stereo, Head Tracking, and Field of Regard on a Small- Scale Spatial Judgment Task Eric D. Ragan, Regis
Do Stereo Display Deficiencies Affect 3D Pointing?
 Do Stereo Display Deficiencies Affect 3D Pointing? Mayra Donaji Barrera Machuca SIAT, Simon Fraser University Vancouver, CANADA mbarrera@sfu.ca Wolfgang Stuerzlinger SIAT, Simon Fraser University Vancouver,
Do Stereo Display Deficiencies Affect 3D Pointing? Mayra Donaji Barrera Machuca SIAT, Simon Fraser University Vancouver, CANADA mbarrera@sfu.ca Wolfgang Stuerzlinger SIAT, Simon Fraser University Vancouver,
Psychophysics of night vision device halo
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 Psychophysics of night vision device halo Robert S Allison
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2009 Psychophysics of night vision device halo Robert S Allison
Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures - Evaluation of Surgical Skills in Minimally Invasive Surgery
 # J. Rosen et al. Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures - Evaluation of Surgical Skills in Minimally Invasive Surgery Jacob Rosen +, Ph.D., Mark MacFarlane *, M.D.,
# J. Rosen et al. Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures - Evaluation of Surgical Skills in Minimally Invasive Surgery Jacob Rosen +, Ph.D., Mark MacFarlane *, M.D.,
Development and Validation of Virtual Driving Simulator for the Spinal Injury Patient
 CYBERPSYCHOLOGY & BEHAVIOR Volume 5, Number 2, 2002 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Development and Validation of Virtual Driving Simulator for the Spinal Injury Patient JEONG H. KU, M.S., 1 DONG P. JANG, Ph.D.,
CYBERPSYCHOLOGY & BEHAVIOR Volume 5, Number 2, 2002 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Development and Validation of Virtual Driving Simulator for the Spinal Injury Patient JEONG H. KU, M.S., 1 DONG P. JANG, Ph.D.,
VIRTUAL REALITY FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION APPLICATIONS
 VIRTUAL REALITY FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION APPLICATIONS Jaejoon Kim, S. Mandayam, S. Udpa, W. Lord, and L. Udpa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 500
VIRTUAL REALITY FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION APPLICATIONS Jaejoon Kim, S. Mandayam, S. Udpa, W. Lord, and L. Udpa Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 500
Depth Perception in Virtual Reality: Distance Estimations in Peri- and Extrapersonal Space ABSTRACT
 CYBERPSYCHOLOGY & BEHAVIOR Volume 11, Number 1, 2008 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/cpb.2007.9935 Depth Perception in Virtual Reality: Distance Estimations in Peri- and Extrapersonal Space Dr. C.
CYBERPSYCHOLOGY & BEHAVIOR Volume 11, Number 1, 2008 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/cpb.2007.9935 Depth Perception in Virtual Reality: Distance Estimations in Peri- and Extrapersonal Space Dr. C.
New Method for Evaluating Light Source Color Rendition (IES TM-30-15)
 New Method for Evaluating Light Source Color Rendition (IES TM-30-15) IES México XVII Seminario de Iluminación May 18, 2016 Kevin W. Houser, PhD, PE, FIES Professor of Architectural Engineering The Pennsylvania
New Method for Evaluating Light Source Color Rendition (IES TM-30-15) IES México XVII Seminario de Iluminación May 18, 2016 Kevin W. Houser, PhD, PE, FIES Professor of Architectural Engineering The Pennsylvania
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Sensation and Perception Chapter Module 9 Perception Perception While sensation is the process by
A Study of Perceptual Performance in Haptic Virtual Environments
 Paper: Rb18-4-2617; 2006/5/22 A Study of Perceptual Performance in Haptic Virtual Marcia K. O Malley, and Gina Upperman Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science, Rice University 6100 Main Street, MEMS
Paper: Rb18-4-2617; 2006/5/22 A Study of Perceptual Performance in Haptic Virtual Marcia K. O Malley, and Gina Upperman Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science, Rice University 6100 Main Street, MEMS
Head-Movement Evaluation for First-Person Games
 Head-Movement Evaluation for First-Person Games Paulo G. de Barros Computer Science Department Worcester Polytechnic Institute 100 Institute Road. Worcester, MA 01609 USA pgb@wpi.edu Robert W. Lindeman
Head-Movement Evaluation for First-Person Games Paulo G. de Barros Computer Science Department Worcester Polytechnic Institute 100 Institute Road. Worcester, MA 01609 USA pgb@wpi.edu Robert W. Lindeman
AUGMENTED REALITY IN VOLUMETRIC MEDICAL IMAGING USING STEREOSCOPIC 3D DISPLAY
 AUGMENTED REALITY IN VOLUMETRIC MEDICAL IMAGING USING STEREOSCOPIC 3D DISPLAY Sang-Moo Park 1 and Jong-Hyo Kim 1, 2 1 Biomedical Radiation Science, Graduate School of Convergence Science Technology, Seoul
AUGMENTED REALITY IN VOLUMETRIC MEDICAL IMAGING USING STEREOSCOPIC 3D DISPLAY Sang-Moo Park 1 and Jong-Hyo Kim 1, 2 1 Biomedical Radiation Science, Graduate School of Convergence Science Technology, Seoul
Advanced Augmented Reality Telestration Techniques With Applications In Laparoscopic And Robotic Surgery
 Wayne State University Wayne State University Dissertations 1-1-2013 Advanced Augmented Reality Telestration Techniques With Applications In Laparoscopic And Robotic Surgery Stephen Dworzecki Wayne State
Wayne State University Wayne State University Dissertations 1-1-2013 Advanced Augmented Reality Telestration Techniques With Applications In Laparoscopic And Robotic Surgery Stephen Dworzecki Wayne State
Ravikiran Joseph Singapogu, Ph.D.
 Ravikiran Joseph Singapogu, Ph.D. Contact Information Research Interests 520 Rhodes Engineering Research Center 864-650-4144 Clemson, SC 29634 joseph@clemson.edu Virtual and Augmented Reality Medical Simulators
Ravikiran Joseph Singapogu, Ph.D. Contact Information Research Interests 520 Rhodes Engineering Research Center 864-650-4144 Clemson, SC 29634 joseph@clemson.edu Virtual and Augmented Reality Medical Simulators
Chapter 1 Virtual World Fundamentals
 Chapter 1 Virtual World Fundamentals 1.0 What Is A Virtual World? {Definition} Virtual: to exist in effect, though not in actual fact. You are probably familiar with arcade games such as pinball and target
Chapter 1 Virtual World Fundamentals 1.0 What Is A Virtual World? {Definition} Virtual: to exist in effect, though not in actual fact. You are probably familiar with arcade games such as pinball and target
the dimensionality of the world Travelling through Space and Time Learning Outcomes Johannes M. Zanker
 Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Travelling through Space and Time Johannes M. Zanker http://www.pc.rhul.ac.uk/staff/j.zanker/ps1061/l4/ps1061_4.htm 05/02/2015 PS1061 Sensation & Perception #4 JMZ 1 Learning Outcomes at the end of this
Application of 3D Terrain Representation System for Highway Landscape Design
 Application of 3D Terrain Representation System for Highway Landscape Design Koji Makanae Miyagi University, Japan Nashwan Dawood Teesside University, UK Abstract In recent years, mixed or/and augmented
Application of 3D Terrain Representation System for Highway Landscape Design Koji Makanae Miyagi University, Japan Nashwan Dawood Teesside University, UK Abstract In recent years, mixed or/and augmented
Vision. Definition. Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes
 Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
Vision Vision Definition Sensing of objects by the light reflected off the objects into our eyes Only occurs when there is the interaction of the eyes and the brain (Perception) What is light? Visible
THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION. Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K.
 THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K. Simpson The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute Ann
THE RELATIVE IMPORTANCE OF PICTORIAL AND NONPICTORIAL DISTANCE CUES FOR DRIVER VISION Michael J. Flannagan Michael Sivak Julie K. Simpson The University of Michigan Transportation Research Institute Ann
Exploring 3D in Flash
 1 Exploring 3D in Flash We live in a three-dimensional world. Objects and spaces have width, height, and depth. Various specialized immersive technologies such as special helmets, gloves, and 3D monitors
1 Exploring 3D in Flash We live in a three-dimensional world. Objects and spaces have width, height, and depth. Various specialized immersive technologies such as special helmets, gloves, and 3D monitors
NeuroSim - The Prototype of a Neurosurgical Training Simulator
 NeuroSim - The Prototype of a Neurosurgical Training Simulator Florian BEIER a,1,stephandiederich a,kirstenschmieder b and Reinhard MÄNNER a,c a Institute for Computational Medicine, University of Heidelberg
NeuroSim - The Prototype of a Neurosurgical Training Simulator Florian BEIER a,1,stephandiederich a,kirstenschmieder b and Reinhard MÄNNER a,c a Institute for Computational Medicine, University of Heidelberg
Perception of Haptic Force Magnitude during Hand Movements
 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 2008 Perception of Haptic Force Magnitude during Hand Movements Xing-Dong Yang, Walter F. Bischof, and Pierre
2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 2008 Perception of Haptic Force Magnitude during Hand Movements Xing-Dong Yang, Walter F. Bischof, and Pierre
Gaussian Naive Bayes for Online Training Assessment in Virtual Reality-Based Simulators
 Mathware & Soft Computing 16 (2009), 123-132 Gaussian Naive Bayes for Online Training Assessment in Virtual Reality-Based Simulators Ronei Marcos de Moraes, 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 1 Department
Mathware & Soft Computing 16 (2009), 123-132 Gaussian Naive Bayes for Online Training Assessment in Virtual Reality-Based Simulators Ronei Marcos de Moraes, 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 1 Department
Evaluation of an Enhanced Human-Robot Interface
 Evaluation of an Enhanced Human-Robot Carlotta A. Johnson Julie A. Adams Kazuhiko Kawamura Center for Intelligent Systems Center for Intelligent Systems Center for Intelligent Systems Vanderbilt University
Evaluation of an Enhanced Human-Robot Carlotta A. Johnson Julie A. Adams Kazuhiko Kawamura Center for Intelligent Systems Center for Intelligent Systems Center for Intelligent Systems Vanderbilt University
Eye Gaze Patterns Differentiate Novice and Experts in a Virtual Laparoscopic Surgery Training Environment
 Gaze Patterns Differentiate Novice and Experts in a Virtual Laparoscopic Surgery Training Environment Benjamin Law School of Computing Science Alan J. Lomax School of Kinesiology M. Stella Atkins School
Gaze Patterns Differentiate Novice and Experts in a Virtual Laparoscopic Surgery Training Environment Benjamin Law School of Computing Science Alan J. Lomax School of Kinesiology M. Stella Atkins School
Multisensory Virtual Environment for Supporting Blind Persons' Acquisition of Spatial Cognitive Mapping a Case Study
 Multisensory Virtual Environment for Supporting Blind Persons' Acquisition of Spatial Cognitive Mapping a Case Study Orly Lahav & David Mioduser Tel Aviv University, School of Education Ramat-Aviv, Tel-Aviv,
Multisensory Virtual Environment for Supporting Blind Persons' Acquisition of Spatial Cognitive Mapping a Case Study Orly Lahav & David Mioduser Tel Aviv University, School of Education Ramat-Aviv, Tel-Aviv,
Scholarly Article Review. The Potential of Using Virtual Reality Technology in Physical Activity Settings. Aaron Krieger.
 Scholarly Article Review The Potential of Using Virtual Reality Technology in Physical Activity Settings Aaron Krieger October 22, 2015 The Potential of Using Virtual Reality Technology in Physical Activity
Scholarly Article Review The Potential of Using Virtual Reality Technology in Physical Activity Settings Aaron Krieger October 22, 2015 The Potential of Using Virtual Reality Technology in Physical Activity
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Overview
 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experience data, which is manipulated
Integrating PhysX and OpenHaptics: Efficient Force Feedback Generation Using Physics Engine and Haptic Devices
 This is the Pre-Published Version. Integrating PhysX and Opens: Efficient Force Feedback Generation Using Physics Engine and Devices 1 Leon Sze-Ho Chan 1, Kup-Sze Choi 1 School of Nursing, Hong Kong Polytechnic
This is the Pre-Published Version. Integrating PhysX and Opens: Efficient Force Feedback Generation Using Physics Engine and Devices 1 Leon Sze-Ho Chan 1, Kup-Sze Choi 1 School of Nursing, Hong Kong Polytechnic
Introduction to HCI. CS4HC3 / SE4HC3/ SE6DO3 Fall Instructor: Kevin Browne
 Introduction to HCI CS4HC3 / SE4HC3/ SE6DO3 Fall 2011 Instructor: Kevin Browne brownek@mcmaster.ca Slide content is based heavily on Chapter 1 of the textbook: Designing the User Interface: Strategies
Introduction to HCI CS4HC3 / SE4HC3/ SE6DO3 Fall 2011 Instructor: Kevin Browne brownek@mcmaster.ca Slide content is based heavily on Chapter 1 of the textbook: Designing the User Interface: Strategies
Robots in the Field of Medicine
 Robots in the Field of Medicine Austin Gillis and Peter Demirdjian Malden Catholic High School 1 Pioneers Robots in the Field of Medicine The use of robots in medicine is where it is today because of four
Robots in the Field of Medicine Austin Gillis and Peter Demirdjian Malden Catholic High School 1 Pioneers Robots in the Field of Medicine The use of robots in medicine is where it is today because of four
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL OVERVIEW 1
 OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
OVERVIEW 1 In normal experience, our eyes are constantly in motion, roving over and around objects and through ever-changing environments. Through this constant scanning, we build up experiential data,
Geographic information systems and virtual reality Ivan Trenchev, Leonid Kirilov
 Geographic information systems and virtual reality Ivan Trenchev, Leonid Kirilov Abstract. In this paper, we present the development of three-dimensional geographic information systems (GISs) and demonstrate
Geographic information systems and virtual reality Ivan Trenchev, Leonid Kirilov Abstract. In this paper, we present the development of three-dimensional geographic information systems (GISs) and demonstrate
Role of virtual simulation in surgical training
 Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Role of virtual simulation in surgical training Davide Zerbato 1, Diego Dall Alba 2 1 BBZ srl, Verona, Italy; 2 Department of Computer Science, University of Verona,
Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Role of virtual simulation in surgical training Davide Zerbato 1, Diego Dall Alba 2 1 BBZ srl, Verona, Italy; 2 Department of Computer Science, University of Verona,
Right Angle Screwdriver
 Right Angle Screwdriver October 12, 2009 Team: Scott Carpenter - Team Leader Chuck Donaldson - Communicator Nate Retzlaff - BWIG John McGuire - BSAC Client: Ashish Mahajan, MD Resident Plastic and Reconstructive
Right Angle Screwdriver October 12, 2009 Team: Scott Carpenter - Team Leader Chuck Donaldson - Communicator Nate Retzlaff - BWIG John McGuire - BSAC Client: Ashish Mahajan, MD Resident Plastic and Reconstructive
Distributed Vision System: A Perceptual Information Infrastructure for Robot Navigation
 Distributed Vision System: A Perceptual Information Infrastructure for Robot Navigation Hiroshi Ishiguro Department of Information Science, Kyoto University Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-01, Japan E-mail: ishiguro@kuis.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Distributed Vision System: A Perceptual Information Infrastructure for Robot Navigation Hiroshi Ishiguro Department of Information Science, Kyoto University Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-01, Japan E-mail: ishiguro@kuis.kyoto-u.ac.jp
UC Merced Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society
 UC Merced Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society Title Examining the Connection Between Dynamic and Static Spatial Skills and Video Game Performance Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8vc391r3
UC Merced Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society Title Examining the Connection Between Dynamic and Static Spatial Skills and Video Game Performance Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8vc391r3
Evaluation of Operative Imaging Techniques in Surgical Education
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Evaluation of Operative Imaging Techniques in Surgical Education Shanu N. Kothari, MD, Timothy J. Broderick, MD, Eric J. DeMaria, MD, Ronald C. Merrell, MD ABSTRACT Background: Certain
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Evaluation of Operative Imaging Techniques in Surgical Education Shanu N. Kothari, MD, Timothy J. Broderick, MD, Eric J. DeMaria, MD, Ronald C. Merrell, MD ABSTRACT Background: Certain
Effects of Visual-Vestibular Interactions on Navigation Tasks in Virtual Environments
 Effects of Visual-Vestibular Interactions on Navigation Tasks in Virtual Environments Date of Report: September 1 st, 2016 Fellow: Heather Panic Advisors: James R. Lackner and Paul DiZio Institution: Brandeis
Effects of Visual-Vestibular Interactions on Navigation Tasks in Virtual Environments Date of Report: September 1 st, 2016 Fellow: Heather Panic Advisors: James R. Lackner and Paul DiZio Institution: Brandeis
P rcep e t p i t on n a s a s u n u c n ons n c s ious u s i nf n e f renc n e L ctur u e 4 : Recogni n t i io i n
 Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
Lecture 4: Recognition and Identification Dr. Tony Lambert Reading: UoA text, Chapter 5, Sensation and Perception (especially pp. 141-151) 151) Perception as unconscious inference Hermann von Helmholtz
GYN / US. VITOM A Unique Visualization System for Vaginal Hysterectomy in the Operating Room
 GYN 1.0 03/2016-6-US VITOM A Unique Visualization System for Vaginal Hysterectomy in the Operating Room The VITOM System for your Exoscopy in the Operating Room Dear Colleagues, When feasible, the vaginal
GYN 1.0 03/2016-6-US VITOM A Unique Visualization System for Vaginal Hysterectomy in the Operating Room The VITOM System for your Exoscopy in the Operating Room Dear Colleagues, When feasible, the vaginal
Multisensory virtual environment for supporting blind persons acquisition of spatial cognitive mapping, orientation, and mobility skills
 Multisensory virtual environment for supporting blind persons acquisition of spatial cognitive mapping, orientation, and mobility skills O Lahav and D Mioduser School of Education, Tel Aviv University,
Multisensory virtual environment for supporting blind persons acquisition of spatial cognitive mapping, orientation, and mobility skills O Lahav and D Mioduser School of Education, Tel Aviv University,
Epona Medical simulation products catalog Version 1.0
 Epona Medical simulation products catalog Version 1.0 Simulator for laparoscopic surgery Simulator for Arthroscopic surgery Simulator for infant patient critical care Simulator for vascular procedures
Epona Medical simulation products catalog Version 1.0 Simulator for laparoscopic surgery Simulator for Arthroscopic surgery Simulator for infant patient critical care Simulator for vascular procedures
virtual reality SANJAY SINGH B.TECH (EC)
 virtual reality SINGH (EC) SANJAY B.TECH What is virtual reality? A satisfactory definition may be formulated like this: "Virtual Reality is a way for humans to visualize, manipulate and interact with
virtual reality SINGH (EC) SANJAY B.TECH What is virtual reality? A satisfactory definition may be formulated like this: "Virtual Reality is a way for humans to visualize, manipulate and interact with
Evaluation of Five-finger Haptic Communication with Network Delay
 Tactile Communication Haptic Communication Network Delay Evaluation of Five-finger Haptic Communication with Network Delay To realize tactile communication, we clarify some issues regarding how delay affects
Tactile Communication Haptic Communication Network Delay Evaluation of Five-finger Haptic Communication with Network Delay To realize tactile communication, we clarify some issues regarding how delay affects
E X P E R I M E N T 12
 E X P E R I M E N T 12 Mirrors and Lenses Produced by the Physics Staff at Collin College Copyright Collin College Physics Department. All Rights Reserved. University Physics II, Exp 12: Mirrors and Lenses
E X P E R I M E N T 12 Mirrors and Lenses Produced by the Physics Staff at Collin College Copyright Collin College Physics Department. All Rights Reserved. University Physics II, Exp 12: Mirrors and Lenses
DECISION MAKING IN THE IOWA GAMBLING TASK. To appear in F. Columbus, (Ed.). The Psychology of Decision-Making. Gordon Fernie and Richard Tunney
 DECISION MAKING IN THE IOWA GAMBLING TASK To appear in F. Columbus, (Ed.). The Psychology of Decision-Making Gordon Fernie and Richard Tunney University of Nottingham Address for correspondence: School
DECISION MAKING IN THE IOWA GAMBLING TASK To appear in F. Columbus, (Ed.). The Psychology of Decision-Making Gordon Fernie and Richard Tunney University of Nottingham Address for correspondence: School
SPATIAL ABILITIES AND PERFORMANCE IN ROBOT NAVIGATION
 TCNJ JOURNAL OF STUDENT SCHOLARSHIP VOLUME XI APRIL, 2009 SPATIAL ABILITIES AND PERFORMANCE IN ROBOT NAVIGATION Author: Jessica T. Wong Faculty Sponsor: Tamra Bireta, Department of Psychology ABSTRACT
TCNJ JOURNAL OF STUDENT SCHOLARSHIP VOLUME XI APRIL, 2009 SPATIAL ABILITIES AND PERFORMANCE IN ROBOT NAVIGATION Author: Jessica T. Wong Faculty Sponsor: Tamra Bireta, Department of Psychology ABSTRACT
Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information
 Atten Percept Psychophys (2013) 75:1570 1582 DOI 10.3758/s13414-013-0488-z Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information Zheng Bian & Myron L. Braunstein
Atten Percept Psychophys (2013) 75:1570 1582 DOI 10.3758/s13414-013-0488-z Discriminating direction of motion trajectories from angular speed and background information Zheng Bian & Myron L. Braunstein
NEW YORK STATE TEACHER CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS
 NEW YORK STATE TEACHER CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS TEST DESIGN AND FRAMEWORK June 2018 Authorized for Distribution by the New York State Education Department This test design and framework document is designed
NEW YORK STATE TEACHER CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS TEST DESIGN AND FRAMEWORK June 2018 Authorized for Distribution by the New York State Education Department This test design and framework document is designed
INTRODUCING THE VIRTUAL REALITY FLIGHT SIMULATOR FOR SURGEONS
 INTRODUCING THE VIRTUAL REALITY FLIGHT SIMULATOR FOR SURGEONS SAFE REPEATABLE MEASUREABLE SCALABLE PROVEN SCALABLE, LOW COST, VIRTUAL REALITY SURGICAL SIMULATION The benefits of surgical simulation are
INTRODUCING THE VIRTUAL REALITY FLIGHT SIMULATOR FOR SURGEONS SAFE REPEATABLE MEASUREABLE SCALABLE PROVEN SCALABLE, LOW COST, VIRTUAL REALITY SURGICAL SIMULATION The benefits of surgical simulation are
Infants perception of depth from cast shadows
 Perception & Psychophysics 2006, 68 (1), 154-160 Infants perception of depth from cast shadows ALBERT YONAS University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota and CARL E. GRANRUD University of Northern Colorado,
Perception & Psychophysics 2006, 68 (1), 154-160 Infants perception of depth from cast shadows ALBERT YONAS University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota and CARL E. GRANRUD University of Northern Colorado,
An Inexpensive Experimental Setup for Teaching The Concepts of Da Vinci Surgical Robot
 An Inexpensive Experimental Setup for Teaching The Concepts of Da Vinci Surgical Robot S.Vignesh kishan kumar 1, G. Anitha 2 1 M.TECH Biomedical Engineering, SRM University, Chennai 2 Assistant Professor,
An Inexpensive Experimental Setup for Teaching The Concepts of Da Vinci Surgical Robot S.Vignesh kishan kumar 1, G. Anitha 2 1 M.TECH Biomedical Engineering, SRM University, Chennai 2 Assistant Professor,
A TELE-INSTRUCTION SYSTEM FOR ULTRASOUND PROBE OPERATION BASED ON SHARED AR TECHNOLOGY
 A TELE-INSTRUCTION SYSTEM FOR ULTRASOUND PROBE OPERATION BASED ON SHARED AR TECHNOLOGY T. Suenaga 1, M. Nambu 1, T. Kuroda 2, O. Oshiro 2, T. Tamura 1, K. Chihara 2 1 National Institute for Longevity Sciences,
A TELE-INSTRUCTION SYSTEM FOR ULTRASOUND PROBE OPERATION BASED ON SHARED AR TECHNOLOGY T. Suenaga 1, M. Nambu 1, T. Kuroda 2, O. Oshiro 2, T. Tamura 1, K. Chihara 2 1 National Institute for Longevity Sciences,
Open surgery SIMULATION
 Open surgery SIMULATION ossimtech.com A note from the President and Co-Founder, Mr. André Blain Medical education and surgical training are going through exciting changes these days. Fast-paced innovation
Open surgery SIMULATION ossimtech.com A note from the President and Co-Founder, Mr. André Blain Medical education and surgical training are going through exciting changes these days. Fast-paced innovation
The Mona Lisa Effect: Perception of Gaze Direction in Real and Pictured Faces
 Studies in Perception and Action VII S. Rogers & J. Effken (Eds.)! 2003 Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Mona Lisa Effect: Perception of Gaze Direction in Real and Pictured Faces Sheena Rogers 1,
Studies in Perception and Action VII S. Rogers & J. Effken (Eds.)! 2003 Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Mona Lisa Effect: Perception of Gaze Direction in Real and Pictured Faces Sheena Rogers 1,
Regan Mandryk. Depth and Space Perception
 Depth and Space Perception Regan Mandryk Disclaimer Many of these slides include animated gifs or movies that may not be viewed on your computer system. They should run on the latest downloads of Quick
Depth and Space Perception Regan Mandryk Disclaimer Many of these slides include animated gifs or movies that may not be viewed on your computer system. They should run on the latest downloads of Quick
The Shape-Weight Illusion
 The Shape-Weight Illusion Mirela Kahrimanovic, Wouter M. Bergmann Tiest, and Astrid M.L. Kappers Universiteit Utrecht, Helmholtz Institute Padualaan 8, 3584 CH Utrecht, The Netherlands {m.kahrimanovic,w.m.bergmanntiest,a.m.l.kappers}@uu.nl
The Shape-Weight Illusion Mirela Kahrimanovic, Wouter M. Bergmann Tiest, and Astrid M.L. Kappers Universiteit Utrecht, Helmholtz Institute Padualaan 8, 3584 CH Utrecht, The Netherlands {m.kahrimanovic,w.m.bergmanntiest,a.m.l.kappers}@uu.nl
M M V R USUHS. Facility for Medical. Simulation and. Training NATIONAL CAPITAL AREA MEDICAL SIMULATION CENTER
 M M V R 2 0 0 4 The National Capital Area Medical Simulation Center- A Case Study MMVR 2004 Tutorial Col. Mark W. Bowyer, MD, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery Surgical Director National Capital Area
M M V R 2 0 0 4 The National Capital Area Medical Simulation Center- A Case Study MMVR 2004 Tutorial Col. Mark W. Bowyer, MD, FACS Associate Professor of Surgery Surgical Director National Capital Area
Brief summary report of novel digital capture techniques
 Brief summary report of novel digital capture techniques Paul Bourke, ivec@uwa, February 2014 The following briefly summarizes and gives examples of the various forms of novel digital photography and video
Brief summary report of novel digital capture techniques Paul Bourke, ivec@uwa, February 2014 The following briefly summarizes and gives examples of the various forms of novel digital photography and video
Composite Fractional Power Wavelets Jason M. Kinser
 Composite Fractional Power Wavelets Jason M. Kinser Inst. for Biosciences, Bioinformatics, & Biotechnology George Mason University jkinser@ib3.gmu.edu ABSTRACT Wavelets have a tremendous ability to extract
Composite Fractional Power Wavelets Jason M. Kinser Inst. for Biosciences, Bioinformatics, & Biotechnology George Mason University jkinser@ib3.gmu.edu ABSTRACT Wavelets have a tremendous ability to extract
Sensation. Perception. Perception
 Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Ch 4D depth and gestalt 1 Sensation Basic principles in perception o Absolute Threshold o Difference Threshold o Weber s Law o Sensory Adaptation Description Examples Color Perception o Trichromatic Theory
Comparison of Simulated Ovary Training Over Different Skill Levels
 Comparison of Simulated Ovary Training Over Different Skill Levels Andrew Crossan, Stephen Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12
Comparison of Simulated Ovary Training Over Different Skill Levels Andrew Crossan, Stephen Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12
Transforming Surgical Robotics. 34 th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference January 14, 2016
 1 Transforming Surgical Robotics 34 th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference January 14, 2016 Forward Looking Statements 2 This presentation includes statements relating to TransEnterix s current regulatory
1 Transforming Surgical Robotics 34 th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference January 14, 2016 Forward Looking Statements 2 This presentation includes statements relating to TransEnterix s current regulatory
Haptic control in a virtual environment
 Haptic control in a virtual environment Gerard de Ruig (0555781) Lourens Visscher (0554498) Lydia van Well (0566644) September 10, 2010 Introduction With modern technological advancements it is entirely
Haptic control in a virtual environment Gerard de Ruig (0555781) Lourens Visscher (0554498) Lydia van Well (0566644) September 10, 2010 Introduction With modern technological advancements it is entirely
Medical Robotics. Part II: SURGICAL ROBOTICS
 5 Medical Robotics Part II: SURGICAL ROBOTICS In the last decade, surgery and robotics have reached a maturity that has allowed them to be safely assimilated to create a new kind of operating room. This
5 Medical Robotics Part II: SURGICAL ROBOTICS In the last decade, surgery and robotics have reached a maturity that has allowed them to be safely assimilated to create a new kind of operating room. This
VIRTUAL ASSISTIVE ROBOTS FOR PLAY, LEARNING, AND COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT
 3-59 Corbett Hall University of Alberta Edmonton, AB T6G 2G4 Ph: (780) 492-5422 Fx: (780) 492-1696 Email: atlab@ualberta.ca VIRTUAL ASSISTIVE ROBOTS FOR PLAY, LEARNING, AND COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Mengliao
3-59 Corbett Hall University of Alberta Edmonton, AB T6G 2G4 Ph: (780) 492-5422 Fx: (780) 492-1696 Email: atlab@ualberta.ca VIRTUAL ASSISTIVE ROBOTS FOR PLAY, LEARNING, AND COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT Mengliao
Analysis of structural effects formation in fancy yarn
 Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 32, March 2007, pp. 21-26 Analysis of structural effects formation in fancy yarn Salvinija Petrulyte a Department of Textile Technology, Kaunas University
Indian Journal of Fibre & Textile Research Vol. 32, March 2007, pp. 21-26 Analysis of structural effects formation in fancy yarn Salvinija Petrulyte a Department of Textile Technology, Kaunas University
Unit 9: May/June Solid Shapes
 Approximate time: 4-5 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Students have experience studying attributes and names of flat shapes (2-dimensional). Focus of the Unit: Students will extend knowledge of
Approximate time: 4-5 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Students have experience studying attributes and names of flat shapes (2-dimensional). Focus of the Unit: Students will extend knowledge of
