Measurements of the Level of Surgical Expertise Using Flight Path Analysis from da Vinci Robotic Surgical System
|
|
|
- Gary Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Measurements of the Level of Surgical Expertise Using Flight Path Analysis from da Vinci Robotic Surgical System Lawton Verner 1, Dmitry Oleynikov, MD 1, Stephen Holtmann 1, Hani Haider, Ph D 1, Leonid Zhukov, Ph D 2 1 University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE 2 California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA doleynik@unmc.edu URL: Abstract. Laparoscopic surgical procedures require precise hand and eye coordination based on a 2-dimensional representation of 3-dimensional space. Currently, no metric exists to guide the educational process while surgeons are still on the learning curve. In this paper, we propose to identify and qualify the patterns of movements recorded from the da Vinci robotic surgical system (Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale CA) that are most consistent with mastery and can define levels of proficiency. We have recorded velocities and positions of complex movements made by both novice and expert surgeons using da Vinci system and performed geometric and statistical analysis of the data. 1. Background Surgical skill is difficult to learn and ultimate competency is even more difficult to define and measure. To accurately assess a physician s technical skills, an objective analysis method must be established. Current methods of assessing surgical skill include subjective testing procedures which require an expert in the field to judge the aptitude of a lesser experienced surgeon [1,7]. The Minimally Invasive Surgical Trainer; Virtual Reality (MIST VR) represents the first attempt to quantify movements by a surgeon and therefore draw conclusions concerning the skill level. Gallagher et al. demonstrated that experts performed better and therefore could be distinguished form novice surgeons [4]. This, however, was done in a virtual reality trainer and cannot be easily adapted to clinical practice. To obtain practical assessment of surgical skill, direct procedures must be analyzed to ensure proficiency when immersed in a real surgical environment. Rosen et al. have developed instrumented graspers which allow for the measurement of forces and torques during actual clinical procedure. By using Hidden Markov Modeling, analysis these signatures can be stratified into expert or novice performances [5, 9-12]. We have applied these principles to the human telerobotic interface to determine if entire movements could be classified into expert or beginner patterns. The da Vinci robotic surgical system allows the surgeons to perform
2 surgical procedures without mechanical link. We have measured the output of these signals of this system to objectively determine what characteristics are associated with surgical expertise. The procedure tested was adapted from standard surgical assessment methods [2,3]. 2. Methods With coordination from Intuitive Surgical, makers of the da Vinci robotic surgical system, a commercial, telemanipulating, computer assisted, FDA approved, surgical device (Figure 1), an interface was developed between the da Vinci system and an external computer. With this interface, real-time telemanipulator data can be extracted from the surgical system. This data includes elapsed time, position, orientation, grip (7 total degrees of freedom) and corresponding linear and angular velocity information of the surgical tools and hand manipulations. The tool and surgeon manipulator data are logged at 11 samples per second (for each signal) by the external computer. Figure 1. da Vinci robotic surgical system Novice and expert surgical operators were logged performing the task of lifting a bead, placing it on a peg, and then returning the surgical tool to its origin using only one hand (Figure 2). The procedure was repeated five times using the operator s dominate hand. Two right-handed expert and four right-handed novice operator data logs were obtained. The procedure was then repeated using the non-dominate hand. The data was statistically analyzed with Student t-test and analysis of variance (ANOVA) tests. Significant differences in handedness of individual surgeons and differences in the elapsed time it to ok to perform the task between experts and novices were determined.
3 Figure 2. The task performed 3. Results Comparison of the 3 dimensional trajectories demonstrates a visual disparity between expert and novice operators. Analysis of grip position over time (Figure 3) illustrates the difference between the novice (dashed line) and expert (solid line) grip patterns. Not only is it apparent that the novice required more total time, but spent much longer in transition states (constant grip values). Figure 4 illustrates the difference in the 3 dimensional positioning of the tool. The novice (darker line, square data points) trajectory shows excess movement, a more erratic flight path, and slower movements when compared to the expert (lighter line, X data points). The slower movements are evident by the data points (stars), which are sampled at a constant 11 hertz, being closer together during the major movement portions of the test. Figure 3. Grip position
4 Figure 4. 3-D movements Analysis of elapsed time illustrates an increase in procedural time for novices as expected (p<0.05). Novices, but not experts, had a statistically significant difference in time between their right and left hands (Table 1). Experts were on average 15% faster with the right hand, and over 50% faster with the left compared to novices (Table 1). Velocity analysis showed statistically significant difference in novice but not expert flight path (p<0.05 in 5/7 velocity variables). Statistical analysis of variance in flight path data showed significant difference between novices and experts (Table 1). Although the difference in data could be seen in both right and left hand flight path the left hand difference was more dramatic (4/7 right vs 6/7 left velocity variables differed significantly). TABLE 1: Analytical Results Flight Path Mean Velocities: Novice Expert P value X-axis (m/s) Y-axis (m/s) Z-axis (m/s) NS Rotational (rad/s) Pivot (major) (rad/s) Pivot (minor) (rad/s) Jaw position (rad/s) Time: Average Time Left Average Time Right Inter-group P value NS
5 4. Conclusions Complex tasks in three-dimensional space could be analyzed with flight path calculations and level of expertise determined by objective measures. Level of expertise was demonstrated by shorter times to complete the task as well as in the pattern of positions and velocities of the operator. The effect of handedness diminished with the level of expertise. It can be hypothesize that if performing a simple task such as placement of a bead illustrates a statistic disparity between expert and novice operators, it can easy delineate skill level if a more difficult task were completed. Similar findings were shown by Rosen et al. when forces and torques were studied at the tissue tool interaction [5, 9-12]. Although the raw data was voluminous, offline analysis allowed specification of patterns of movement that could be applied to the entire data set. We were able to compare the entire data set using statistical manipulation with expert performance as the bench mark. The limitation of this approach lies in the need to compare against an individual s performance rather that an ideal path analysis. That is to say that the novice could only hope to be as good as the expert rather than seek perfection due to the lack of a perfection benchmark. The goal of any metric of surgical skill must seek objective gold standards that are not biased by human operators. Such a benchmark would be far more enduring. The ability to analyze telemetry from a robotic surgery system such as the da Vinci provides detailed procedural reconstruction which can lead to benchmarking expert and novice kinematics of surgical procedures. Future work will need to be performed to better define objective analysis of surgical skill. 5. References [1] Darzi A, Smith S, Taffinder N (1999) Assessing operative skill. Br Med J 318:887 [2] Rosser JC, Rosser LE, Savalgi RS (1998) Objective evaluation of laparoscopic surgical skill program for residents and senior surgeons. Arch Surg 133: [3] Rosser JC, Rosser LE, Savalgi RS (1997) Skill Acquisition and Assessment for Laparoscopic Surgery. Arch Surg 132: [4] Gallagher AG, Ritchie K, McClure N, McGuigan J (2001) Objective psychomotor assessment of senior, junior and novice laparoscopists with virtual reality. World J Surg 25: [5] Rosen J, Solazzo M, Brown JD, Oleynikov D, Hannaford B, Sinanan MN (2001) Objective laparoscopic skills assessments of surgical residence using Hidden Markov Models based on haptic information and tool/tissue interactions. Medicine Meets Virtual Reality Abstract. [6] Hannaford B, Trujillo J, Sinanan M, et al. (1998) Computerized endoscopic surgical grasper. Stud Health Technol Inform 50: [7] Darzi A, Smith S, Taffinder N (1999) Assessing operative skill. Br Med J 318:887 [8] V. Falk, D. Mintz, J. Grunenfelder, J. I. Fann, T. A. Burdon (2001) Influence of three-dimensional vision on surgical telemanipulator performance. Surg Endosc 15: [9] Rosen J, Hannaford B, Richards CG, Sinanan MN (2001) Markov modeling of minimally invasive surgery based on tool/tissue interaction and force/torque signatures for evaluating surgical skills. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 48:
6 [10] Rosen J, Richards C, Hannaford B, Sinanan MN (2000) Hidden Markov models of minimally invasive surgery. Stud Health Technol Inform 70: [11] Rosen J, Hannaford B, MacFarlane MP, Sinanan MN (1999) Force controlled and teleoperated endoscopic grasper for minimally invasive surgery experimental performance evaluation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 46: [12] Rosen J, MacFarlane M, Richards C, et al. (1999) Surgeon- tool force/torque signatures evaluation of surgical skills in minimally invasive surgery. Stud Health Inform
Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Robot-Assisted Surgical Motions
 Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Robot-Assisted Surgical Motions Henry C. Lin 1, Izhak Shafran 2, Todd E. Murphy, Allison M. Okamura, David D. Yuh, and Gregory D. Hager 1 1 Department of Computer
Automatic Detection and Segmentation of Robot-Assisted Surgical Motions Henry C. Lin 1, Izhak Shafran 2, Todd E. Murphy, Allison M. Okamura, David D. Yuh, and Gregory D. Hager 1 1 Department of Computer
Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures - Evaluation of Surgical Skills in Minimally Invasive Surgery
 # J. Rosen et al. Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures - Evaluation of Surgical Skills in Minimally Invasive Surgery Jacob Rosen +, Ph.D., Mark MacFarlane *, M.D.,
# J. Rosen et al. Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures Surgeon-Tool Force/Torque Signatures - Evaluation of Surgical Skills in Minimally Invasive Surgery Jacob Rosen +, Ph.D., Mark MacFarlane *, M.D.,
Optimization of a Vector Quantization Codebook for Objective Evaluation of Surgical Skill
 Optimization of a Vector Quantization Codebook for Objective Evaluation of Surgical Skill Timothy M. KOWALEWSKI BS (1), Jacob ROSEN Ph.D. (1,2), Lily CHANG, MD (2), Mika N. SINANAN MD Ph.D. (2,1), Blake
Optimization of a Vector Quantization Codebook for Objective Evaluation of Surgical Skill Timothy M. KOWALEWSKI BS (1), Jacob ROSEN Ph.D. (1,2), Lily CHANG, MD (2), Mika N. SINANAN MD Ph.D. (2,1), Blake
Reliability and Validity of EndoTower, a Virtual Reality Trainer for Angled Endoscope Navigation
 Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 2002 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds) IOS Press, 2002 Reliability and Validity of EndoTower, a Virtual Reality Trainer for Angled Endoscope Navigation Randy S. HALUCK MD FACS 1,
Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 2002 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds) IOS Press, 2002 Reliability and Validity of EndoTower, a Virtual Reality Trainer for Angled Endoscope Navigation Randy S. HALUCK MD FACS 1,
A Virtual Reality Training Program for Improvement of Robotic Surgical Skills
 A Virtual Reality Training Program for Improvement of Robotic Surgical Skills *M. MUKHERJEE 1, K.-C. SIU 1 4, I. H. SUH 1,2 4, A. KLUTMAN 2, D. OLEYNIKOV2. 4, and N. STERGIOU 1,3 4 1 Nebraska Biomechanics
A Virtual Reality Training Program for Improvement of Robotic Surgical Skills *M. MUKHERJEE 1, K.-C. SIU 1 4, I. H. SUH 1,2 4, A. KLUTMAN 2, D. OLEYNIKOV2. 4, and N. STERGIOU 1,3 4 1 Nebraska Biomechanics
Effects of Geared Motor Characteristics on Tactile Perception of Tissue Stiffness
 Effects of Geared Motor Characteristics on Tactile Perception of Tissue Stiffness Jeff Longnion +, Jacob Rosen+, PhD, Mika Sinanan++, MD, PhD, Blake Hannaford+, PhD, ++ Department of Electrical Engineering,
Effects of Geared Motor Characteristics on Tactile Perception of Tissue Stiffness Jeff Longnion +, Jacob Rosen+, PhD, Mika Sinanan++, MD, PhD, Blake Hannaford+, PhD, ++ Department of Electrical Engineering,
Wearable Haptic Feedback Actuators for Training in Robotic Surgery
 Wearable Haptic Feedback Actuators for Training in Robotic Surgery NSF Summer Undergraduate Fellowship in Sensor Technologies Joshua Fernandez (Mechanical Eng.) University of Maryland Baltimore County
Wearable Haptic Feedback Actuators for Training in Robotic Surgery NSF Summer Undergraduate Fellowship in Sensor Technologies Joshua Fernandez (Mechanical Eng.) University of Maryland Baltimore County
A Virtual Reality Surgical Trainer for Navigation in Laparoscopic Surgery
 Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 2001 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds) IOS Press, 2001 A Virtual Reality Surgical Trainer for Navigation in Laparoscopic Surgery Randy S. Haluck M.D. 1, Roger W. Webster Ph.D. 2,
Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 2001 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds) IOS Press, 2001 A Virtual Reality Surgical Trainer for Navigation in Laparoscopic Surgery Randy S. Haluck M.D. 1, Roger W. Webster Ph.D. 2,
A NEW CLASS OF ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES IN MEDICAL TRAINING BASED ON COMBINING CLASSIFIERS
 A NEW CLASS OF ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES IN MEDICAL TRAINING BASED ON COMBINING CLASSIFIERS Ronei Marcos de Moraes 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 Abstract Researches on training assessment for simulators
A NEW CLASS OF ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES IN MEDICAL TRAINING BASED ON COMBINING CLASSIFIERS Ronei Marcos de Moraes 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 Abstract Researches on training assessment for simulators
Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery
 Young Group 5 1 Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery Paper Review Jessie Young Group 5: Haptic Interface for Surgical Manipulator System March 12, 2012 Paper Selection: A. M. Okamura.
Young Group 5 1 Methods for Haptic Feedback in Teleoperated Robotic Surgery Paper Review Jessie Young Group 5: Haptic Interface for Surgical Manipulator System March 12, 2012 Paper Selection: A. M. Okamura.
Medical Robotics. Part II: SURGICAL ROBOTICS
 5 Medical Robotics Part II: SURGICAL ROBOTICS In the last decade, surgery and robotics have reached a maturity that has allowed them to be safely assimilated to create a new kind of operating room. This
5 Medical Robotics Part II: SURGICAL ROBOTICS In the last decade, surgery and robotics have reached a maturity that has allowed them to be safely assimilated to create a new kind of operating room. This
Evaluation of Haptic Virtual Fixtures in Psychomotor Skill Development for Robotic Surgical Training
 Department of Electronics, Information and Bioengineering Neuroengineering and medical robotics Lab Evaluation of Haptic Virtual Fixtures in Psychomotor Skill Development for Robotic Surgical Training
Department of Electronics, Information and Bioengineering Neuroengineering and medical robotics Lab Evaluation of Haptic Virtual Fixtures in Psychomotor Skill Development for Robotic Surgical Training
Virtual Reality Based Training to resolve Visio-motor Conflicts in Surgical Environments
 HAVE 2008 IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual Environments and their Applications Ottawa Canada, 18-19 October 2008 Virtual Reality Based Training to resolve Visio-motor Conflicts in Surgical
HAVE 2008 IEEE International Workshop on Haptic Audio Visual Environments and their Applications Ottawa Canada, 18-19 October 2008 Virtual Reality Based Training to resolve Visio-motor Conflicts in Surgical
da Vinci Skills Simulator
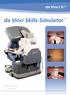 da Vinci Skills Simulator Introducing Simulation for the da Vinci Surgical System Skills Practice in an Immersive Virtual Environment Portable. Practical. Powerful. The da Vinci Skills Simulator contains
da Vinci Skills Simulator Introducing Simulation for the da Vinci Surgical System Skills Practice in an Immersive Virtual Environment Portable. Practical. Powerful. The da Vinci Skills Simulator contains
Surgical robot simulation with BBZ console
 Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Surgical robot simulation with BBZ console Francesco Bovo 1, Giacomo De Rossi 2, Francesco Visentin 2,3 1 BBZ srl, Verona, Italy; 2 Department of Computer Science, Università
Review Article on Thoracic Surgery Surgical robot simulation with BBZ console Francesco Bovo 1, Giacomo De Rossi 2, Francesco Visentin 2,3 1 BBZ srl, Verona, Italy; 2 Department of Computer Science, Università
LS-DYNA Simulation of in vivo Surgical Robot Mobility
 9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (2) LS-DYNA Simulation of in vivo Surgical Robot Mobility Mark Rentschler and John D. Reid Department of Mechanical Engineering University
9 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference Simulation Technology (2) LS-DYNA Simulation of in vivo Surgical Robot Mobility Mark Rentschler and John D. Reid Department of Mechanical Engineering University
Gaussian Naive Bayes for Online Training Assessment in Virtual Reality-Based Simulators
 Mathware & Soft Computing 16 (2009), 123-132 Gaussian Naive Bayes for Online Training Assessment in Virtual Reality-Based Simulators Ronei Marcos de Moraes, 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 1 Department
Mathware & Soft Computing 16 (2009), 123-132 Gaussian Naive Bayes for Online Training Assessment in Virtual Reality-Based Simulators Ronei Marcos de Moraes, 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 1 Department
Simulating Haptic Feedback of Abdomen Organs on Laparoscopic Surgery Tools
 Simulating Haptic Feedback of Abdomen Organs on Laparoscopic Surgery Tools Shirani M. Kannangara1*, Eranga Fernando1, Sumudu K. Kumarage2, Nuwan D. Nanayakkara1 1 Department 2 Department of Electronic
Simulating Haptic Feedback of Abdomen Organs on Laparoscopic Surgery Tools Shirani M. Kannangara1*, Eranga Fernando1, Sumudu K. Kumarage2, Nuwan D. Nanayakkara1 1 Department 2 Department of Electronic
Cutaneous Feedback of Fingertip Deformation and Vibration for Palpation in Robotic Surgery
 Cutaneous Feedback of Fingertip Deformation and Vibration for Palpation in Robotic Surgery Claudio Pacchierotti Domenico Prattichizzo Katherine J. Kuchenbecker Motivation Despite its expected clinical
Cutaneous Feedback of Fingertip Deformation and Vibration for Palpation in Robotic Surgery Claudio Pacchierotti Domenico Prattichizzo Katherine J. Kuchenbecker Motivation Despite its expected clinical
ANOTHER APPROACH FOR FUZZY NAIVE BAYES APPLIED ON ONLINE TRAINING ASSESSMENT IN VIRTUAL REALITY SIMULATORS
 ANOTHER APPROACH FOR FUZZY NAIVE BAYES APPLIED ON ONLINE TRAINING ASSESSMENT IN VIRTUAL REALITY SIMULATORS Ronei Marcos de Moraes 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 Abstract Training systems based on virtual
ANOTHER APPROACH FOR FUZZY NAIVE BAYES APPLIED ON ONLINE TRAINING ASSESSMENT IN VIRTUAL REALITY SIMULATORS Ronei Marcos de Moraes 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 Abstract Training systems based on virtual
Haptic Virtual Fixtures for Robot-Assisted Manipulation
 Haptic Virtual Fixtures for Robot-Assisted Manipulation Jake J. Abbott, Panadda Marayong, and Allison M. Okamura Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Johns Hopkins University {jake.abbott, pmarayong,
Haptic Virtual Fixtures for Robot-Assisted Manipulation Jake J. Abbott, Panadda Marayong, and Allison M. Okamura Department of Mechanical Engineering, The Johns Hopkins University {jake.abbott, pmarayong,
Differences in Fitts Law Task Performance Based on Environment Scaling
 Differences in Fitts Law Task Performance Based on Environment Scaling Gregory S. Lee and Bhavani Thuraisingham Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas 800 West Campbell Road Richardson,
Differences in Fitts Law Task Performance Based on Environment Scaling Gregory S. Lee and Bhavani Thuraisingham Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Dallas 800 West Campbell Road Richardson,
Cooperative Robotic Assistant for Laparoscopic Surgery: CoBRASurge
 The 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 11-15, 2009 St. Louis, USA Cooperative Robotic Assistant for Laparoscopic Surgery: CoBRASurge Xiaoli Zhang, Amy Lehman,
The 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 11-15, 2009 St. Louis, USA Cooperative Robotic Assistant for Laparoscopic Surgery: CoBRASurge Xiaoli Zhang, Amy Lehman,
Consistency of Performance of Robot Assisted Surgical Tasks in Virtual Reality
 Consistency of Performance of Robot Assisted Surgical Tasks in Virtual Reality I H SUH 12 4 *K.-C SIUJ. 4 M i'
Consistency of Performance of Robot Assisted Surgical Tasks in Virtual Reality I H SUH 12 4 *K.-C SIUJ. 4 M i'
Computer Assisted Medical Interventions
 Outline Computer Assisted Medical Interventions Force control, collaborative manipulation and telemanipulation Bernard BAYLE Joint course University of Strasbourg, University of Houston, Telecom Paris
Outline Computer Assisted Medical Interventions Force control, collaborative manipulation and telemanipulation Bernard BAYLE Joint course University of Strasbourg, University of Houston, Telecom Paris
Using Simulation to Design Control Strategies for Robotic No-Scar Surgery
 Using Simulation to Design Control Strategies for Robotic No-Scar Surgery Antonio DE DONNO 1, Florent NAGEOTTE, Philippe ZANNE, Laurent GOFFIN and Michel de MATHELIN LSIIT, University of Strasbourg/CNRS,
Using Simulation to Design Control Strategies for Robotic No-Scar Surgery Antonio DE DONNO 1, Florent NAGEOTTE, Philippe ZANNE, Laurent GOFFIN and Michel de MATHELIN LSIIT, University of Strasbourg/CNRS,
ASSESSMENT BASED ON NAIVE BAYES FOR TRAINING BASED ON VIRTUAL REALITY
 ASSESSMENT BASED ON NAIVE BAYES FOR TRAINING BASED ON VIRTUAL REALITY Ronei Marcos de Moraes1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 Abstract Nowadays several areas present training systems based on virtual reality.
ASSESSMENT BASED ON NAIVE BAYES FOR TRAINING BASED ON VIRTUAL REALITY Ronei Marcos de Moraes1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 Abstract Nowadays several areas present training systems based on virtual reality.
Teleoperation with Sensor/Actuator Asymmetry: Task Performance with Partial Force Feedback
 Teleoperation with Sensor/Actuator Asymmetry: Task Performance with Partial Force Wagahta Semere, Masaya Kitagawa and Allison M. Okamura Department of Mechanical Engineering The Johns Hopkins University
Teleoperation with Sensor/Actuator Asymmetry: Task Performance with Partial Force Wagahta Semere, Masaya Kitagawa and Allison M. Okamura Department of Mechanical Engineering The Johns Hopkins University
Medical robotics and Image Guided Therapy (IGT) Bogdan M. Maris, PhD Temporary Assistant Professor
 Medical robotics and Image Guided Therapy (IGT) Bogdan M. Maris, PhD Temporary Assistant Professor E-mail bogdan.maris@univr.it Medical Robotics History, current and future applications Robots are Accurate
Medical robotics and Image Guided Therapy (IGT) Bogdan M. Maris, PhD Temporary Assistant Professor E-mail bogdan.maris@univr.it Medical Robotics History, current and future applications Robots are Accurate
Da Vinci Tool Torque Mapping over 50,000 Grasps and its Implications on Grip Force Estimation Accuracy
 Da Vinci Tool Torque Mapping over 50,000 Grasps and its Implications on Grip Force Estimation Accuracy Nathan J. Kong, Trevor K. Stephens, and Timothy M. Kowalewski Abstract Despite the increasing use
Da Vinci Tool Torque Mapping over 50,000 Grasps and its Implications on Grip Force Estimation Accuracy Nathan J. Kong, Trevor K. Stephens, and Timothy M. Kowalewski Abstract Despite the increasing use
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine
 Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 52 (2011) 115 121 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Artificial Intelligence in Medicine jou rn al h om epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aiim Intelligent dental
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 52 (2011) 115 121 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Artificial Intelligence in Medicine jou rn al h om epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aiim Intelligent dental
Towards Objective Surgical Skill Evaluation with Hidden. Markov Model-based Motion Recognition. Todd Edward Murphy
 Towards Objective Surgical Skill Evaluation with Hidden Markov Model-based Motion Recognition by Todd Edward Murphy An essay submitted to The Johns Hopkins University in conformity with the requirements
Towards Objective Surgical Skill Evaluation with Hidden Markov Model-based Motion Recognition by Todd Edward Murphy An essay submitted to The Johns Hopkins University in conformity with the requirements
A Framework for Analysis of Surgeon Arm Posture Variability in Robot-Assisted Surgery
 A Framework for Analysis of Surgeon Arm Posture Variability in Robot-Assisted Surgery Ilana Nisky, Michael H. Hsieh, and Allison M. Okamura Abstract Teleoperated robot-assisted surgery (RAS) provides surgeons
A Framework for Analysis of Surgeon Arm Posture Variability in Robot-Assisted Surgery Ilana Nisky, Michael H. Hsieh, and Allison M. Okamura Abstract Teleoperated robot-assisted surgery (RAS) provides surgeons
An Inexpensive Experimental Setup for Teaching The Concepts of Da Vinci Surgical Robot
 An Inexpensive Experimental Setup for Teaching The Concepts of Da Vinci Surgical Robot S.Vignesh kishan kumar 1, G. Anitha 2 1 M.TECH Biomedical Engineering, SRM University, Chennai 2 Assistant Professor,
An Inexpensive Experimental Setup for Teaching The Concepts of Da Vinci Surgical Robot S.Vignesh kishan kumar 1, G. Anitha 2 1 M.TECH Biomedical Engineering, SRM University, Chennai 2 Assistant Professor,
Robots in the Field of Medicine
 Robots in the Field of Medicine Austin Gillis and Peter Demirdjian Malden Catholic High School 1 Pioneers Robots in the Field of Medicine The use of robots in medicine is where it is today because of four
Robots in the Field of Medicine Austin Gillis and Peter Demirdjian Malden Catholic High School 1 Pioneers Robots in the Field of Medicine The use of robots in medicine is where it is today because of four
Haptic Feedback in Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery
 Haptic Feedback in Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery Dr. Warren Grundfest Professor Bioengineering, Electrical Engineering & Surgery UCLA, Los Angeles, California Acknowledgment This Presentation & Research
Haptic Feedback in Laparoscopic and Robotic Surgery Dr. Warren Grundfest Professor Bioengineering, Electrical Engineering & Surgery UCLA, Los Angeles, California Acknowledgment This Presentation & Research
Wireless Master-Slave Embedded Controller for a Teleoperated Anthropomorphic Robotic Arm with Gripping Force Sensing
 Wireless Master-Slave Embedded Controller for a Teleoperated Anthropomorphic Robotic Arm with Gripping Force Sensing Presented by: Benjamin B. Rhoades ECGR 6185 Adv. Embedded Systems January 16 th 2013
Wireless Master-Slave Embedded Controller for a Teleoperated Anthropomorphic Robotic Arm with Gripping Force Sensing Presented by: Benjamin B. Rhoades ECGR 6185 Adv. Embedded Systems January 16 th 2013
Towards robotic heart surgery: Introduction of autonomous procedures into an experimental surgical telemanipulator system
 74 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Towards robotic heart surgery: Introduction of autonomous procedures into an experimental surgical telemanipulator system R Bauernschmitt*, E U Schirmbeck*, A Knoll, H Mayer, I Nagy,
74 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Towards robotic heart surgery: Introduction of autonomous procedures into an experimental surgical telemanipulator system R Bauernschmitt*, E U Schirmbeck*, A Knoll, H Mayer, I Nagy,
The capability of haptic feedback as additional sensory quality for robotic heart surgery
 Research Article The capability of haptic feedback as additional sensory quality for robotic heart surgery Eva U. Schirmbeck 1*, Constanze Haßelbeck 1, Hermann Mayer 1,2, Alois Knoll 2, Franziska K. B.
Research Article The capability of haptic feedback as additional sensory quality for robotic heart surgery Eva U. Schirmbeck 1*, Constanze Haßelbeck 1, Hermann Mayer 1,2, Alois Knoll 2, Franziska K. B.
Analysis of Suture Manipulation Forces for Teleoperation with Force Feedback
 Analysis of Suture Manipulation Forces for Teleoperation with Force Feedback Masaya Kitagawa 1, Allison M. Okamura 1, Brian T. Bethea 2, Vincent L. Gott 2, and William A. Baumgartner 2 1 Johns Hopkins
Analysis of Suture Manipulation Forces for Teleoperation with Force Feedback Masaya Kitagawa 1, Allison M. Okamura 1, Brian T. Bethea 2, Vincent L. Gott 2, and William A. Baumgartner 2 1 Johns Hopkins
Haptic control in a virtual environment
 Haptic control in a virtual environment Gerard de Ruig (0555781) Lourens Visscher (0554498) Lydia van Well (0566644) September 10, 2010 Introduction With modern technological advancements it is entirely
Haptic control in a virtual environment Gerard de Ruig (0555781) Lourens Visscher (0554498) Lydia van Well (0566644) September 10, 2010 Introduction With modern technological advancements it is entirely
Simendo laparoscopy. product information
 Simendo laparoscopy product information Simendo laparoscopy The Simendo laparoscopy simulator is designed for all laparoscopic specialties, such as general surgery, gynaecology en urology. The simulator
Simendo laparoscopy product information Simendo laparoscopy The Simendo laparoscopy simulator is designed for all laparoscopic specialties, such as general surgery, gynaecology en urology. The simulator
Application of Force Feedback in Robot Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery
 Application of Force Feedback in Robot Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery István Nagy, Hermann Mayer, and Alois Knoll Technische Universität München, 85748 Garching, Germany, {nagy mayerh knoll}@in.tum.de,
Application of Force Feedback in Robot Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery István Nagy, Hermann Mayer, and Alois Knoll Technische Universität München, 85748 Garching, Germany, {nagy mayerh knoll}@in.tum.de,
Image Guided Robotic Assisted Surgical Training System using LabVIEW and CompactRIO
 Image Guided Robotic Assisted Surgical Training System using LabVIEW and CompactRIO Weimin Huang 1, Tao Yang 1, Liang Jing Yang 2, Chee Kong Chui 2, Jimmy Liu 1, Jiayin Zhou 1, Jing Zhang 1, Yi Su 3, Stephen
Image Guided Robotic Assisted Surgical Training System using LabVIEW and CompactRIO Weimin Huang 1, Tao Yang 1, Liang Jing Yang 2, Chee Kong Chui 2, Jimmy Liu 1, Jiayin Zhou 1, Jing Zhang 1, Yi Su 3, Stephen
Face, content and construct validation of the first virtual reality laparoscopic nephrectomy simulator
 29 THE AUTHORS. JOURNAL COMPILATION 29 BJU INTERNATIONAL Original Articles BREWIN ET AL. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Face, content and construct validation of the first virtual reality laparoscopic nephrectomy
29 THE AUTHORS. JOURNAL COMPILATION 29 BJU INTERNATIONAL Original Articles BREWIN ET AL. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Face, content and construct validation of the first virtual reality laparoscopic nephrectomy
Evaluation of robotically controlled advanced endoscopic instruments
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2013; 9: 240 246. Published online 23 April 2013 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).1496
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL ROBOTICS AND COMPUTER ASSISTED SURGERY Int J Med Robotics Comput Assist Surg 2013; 9: 240 246. Published online 23 April 2013 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).1496
Can technological solutions support user experience, learning, and operation outcome in robotic surgery?
 VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND LTD Can technological solutions support user experience, learning, and operation outcome in robotic surgery? ERF2016 Session Image Guided Robotic Surgery and Interventions
VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND LTD Can technological solutions support user experience, learning, and operation outcome in robotic surgery? ERF2016 Session Image Guided Robotic Surgery and Interventions
Performance Issues in Collaborative Haptic Training
 27 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Roma, Italy, 1-14 April 27 FrA4.4 Performance Issues in Collaborative Haptic Training Behzad Khademian and Keyvan Hashtrudi-Zaad Abstract This
27 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Roma, Italy, 1-14 April 27 FrA4.4 Performance Issues in Collaborative Haptic Training Behzad Khademian and Keyvan Hashtrudi-Zaad Abstract This
Telemanipulation and Telestration for Microsurgery Summary
 Telemanipulation and Telestration for Microsurgery Summary Microsurgery presents an array of problems. For instance, current methodologies of Eye Surgery requires freehand manipulation of delicate structures
Telemanipulation and Telestration for Microsurgery Summary Microsurgery presents an array of problems. For instance, current methodologies of Eye Surgery requires freehand manipulation of delicate structures
Chapter 2 Introduction to Haptics 2.1 Definition of Haptics
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Haptics 2.1 Definition of Haptics The word haptic originates from the Greek verb hapto to touch and therefore refers to the ability to touch and manipulate objects. The haptic
Chapter 2 Introduction to Haptics 2.1 Definition of Haptics The word haptic originates from the Greek verb hapto to touch and therefore refers to the ability to touch and manipulate objects. The haptic
Enhancing Fundamental Robot-Assisted Surgical Proficiency by Using a Portable Virtual Simulator
 University of Nebraska at Omaha DigitalCommons@UNO Journal Articles Department of Biomechanics 4-2013 Enhancing Fundamental Robot-Assisted Surgical Proficiency by Using a Portable Virtual Simulator Jung
University of Nebraska at Omaha DigitalCommons@UNO Journal Articles Department of Biomechanics 4-2013 Enhancing Fundamental Robot-Assisted Surgical Proficiency by Using a Portable Virtual Simulator Jung
A Tactile Magnification Instrument for Minimally Invasive Surgery
 A Tactile Magnification Instrument for Minimally Invasive Surgery Hsin-Yun Yao 1, Vincent Hayward 1, and Randy E. Ellis 2 1 Center for Intelligent Machines, McGill University, Montréal, Canada, {hyyao,hayward}@cim.mcgill.ca
A Tactile Magnification Instrument for Minimally Invasive Surgery Hsin-Yun Yao 1, Vincent Hayward 1, and Randy E. Ellis 2 1 Center for Intelligent Machines, McGill University, Montréal, Canada, {hyyao,hayward}@cim.mcgill.ca
A Modular 2-DOF Force-Sensing Instrument for Laparoscopic Surgery
 A Modular 2-DOF Force-Sensing Instrument for Laparoscopic Surgery Srinivas K. Prasad 1,3, Masaya Kitagawa 1, Gregory S. Fischer 1, Jason Zand 2, Mark A. Talamini 2, Russell H. Taylor 1, and Allison M.
A Modular 2-DOF Force-Sensing Instrument for Laparoscopic Surgery Srinivas K. Prasad 1,3, Masaya Kitagawa 1, Gregory S. Fischer 1, Jason Zand 2, Mark A. Talamini 2, Russell H. Taylor 1, and Allison M.
Virtual and Augmented Reality techniques embedded and based on a Operative Microscope. Training for Neurosurgery.
 Virtual and Augmented Reality techniques embedded and based on a Operative Microscope. Training for Neurosurgery. 1 M. Aschke 1, M.Ciucci 1,J.Raczkowsky 1, R.Wirtz 2, H. Wörn 1 1 IPR, Institute for Process
Virtual and Augmented Reality techniques embedded and based on a Operative Microscope. Training for Neurosurgery. 1 M. Aschke 1, M.Ciucci 1,J.Raczkowsky 1, R.Wirtz 2, H. Wörn 1 1 IPR, Institute for Process
RENDERING MEDICAL INTERVENTIONS VIRTUAL AND ROBOT
 RENDERING MEDICAL INTERVENTIONS VIRTUAL AND ROBOT Lavinia Ioana Săbăilă Doina Mortoiu Theoharis Babanatsas Aurel Vlaicu Arad University, e-mail: lavyy_99@yahoo.com Aurel Vlaicu Arad University, e mail:
RENDERING MEDICAL INTERVENTIONS VIRTUAL AND ROBOT Lavinia Ioana Săbăilă Doina Mortoiu Theoharis Babanatsas Aurel Vlaicu Arad University, e-mail: lavyy_99@yahoo.com Aurel Vlaicu Arad University, e mail:
Title: Effects of robotic manipulators on movements of novices and surgeons.
 Title: Effects of robotic manipulators on movements of novices and surgeons. Running head: Effects of robotic manipulators. Authors: Ilana Nisky, PhD a, Allison M. Okamura, PhD a, Michael H. Hsieh, MD,
Title: Effects of robotic manipulators on movements of novices and surgeons. Running head: Effects of robotic manipulators. Authors: Ilana Nisky, PhD a, Allison M. Okamura, PhD a, Michael H. Hsieh, MD,
INDIRECT FEEDBACK OF HAPTIC INFORMATION FOR ROBOT-ASSISTED TELEMANIPULATION. by Masaya Kitagawa. Baltimore, Maryland September, 2003
 INDIRECT FEEDBACK OF HAPTIC INFORMATION FOR ROBOT-ASSISTED TELEMANIPULATION by Masaya Kitagawa A thesis submitted to the Johns Hopkins University in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master
INDIRECT FEEDBACK OF HAPTIC INFORMATION FOR ROBOT-ASSISTED TELEMANIPULATION by Masaya Kitagawa A thesis submitted to the Johns Hopkins University in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master
A NEW APPROACH FOR ONLINE TRAINING ASSESSMENT FOR BONE MARROW HARVEST WHEN PATIENTS HAVE BONES DETERIORATED BY DISEASE
 A NEW APPROACH FOR ONLINE TRAINING ASSESSMENT FOR BONE MARROW HARVEST WHEN PATIENTS HAVE BONES DETERIORATED BY DISEASE Ronei Marcos de Moraes 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 Abstract Training systems based
A NEW APPROACH FOR ONLINE TRAINING ASSESSMENT FOR BONE MARROW HARVEST WHEN PATIENTS HAVE BONES DETERIORATED BY DISEASE Ronei Marcos de Moraes 1, Liliane dos Santos Machado 2 Abstract Training systems based
Needle Path Planning for Autonomous Robotic Surgical Suturing
 Needle Path Planning for Autonomous Robotic Surgical Suturing Russell C. Jackson and M. Cenk Çavuşoğlu Abstract This paper develops a path plan for suture needles used with solid tissue volumes in endoscopic
Needle Path Planning for Autonomous Robotic Surgical Suturing Russell C. Jackson and M. Cenk Çavuşoğlu Abstract This paper develops a path plan for suture needles used with solid tissue volumes in endoscopic
Medical Robotics LBR Med
 Medical Robotics LBR Med EN KUKA, a proven robotics partner. Discerning users around the world value KUKA as a reliable partner. KUKA has branches in over 30 countries, and for over 40 years, we have been
Medical Robotics LBR Med EN KUKA, a proven robotics partner. Discerning users around the world value KUKA as a reliable partner. KUKA has branches in over 30 countries, and for over 40 years, we have been
Design and Implementation of a Haptic Device for Training in Urological Operations
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION, VOL. 19, NO. 5, OCTOBER 2003 801 Design and Implementation of a Haptic Device for Training in Urological Operations Kostas Vlachos, Evangelos Papadopoulos,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION, VOL. 19, NO. 5, OCTOBER 2003 801 Design and Implementation of a Haptic Device for Training in Urological Operations Kostas Vlachos, Evangelos Papadopoulos,
Force Feedback Benefit Depends on Experience in Multiple Degree of Freedom Robotic Surgery Task Abstract
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS, VOL. 23, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2007 1235 Short Papers Force Feedback Benefit Depends on Experience in Multiple Degree of Freedom Robotic Surgery Task Christopher R. Wagner and
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ROBOTICS, VOL. 23, NO. 6, DECEMBER 2007 1235 Short Papers Force Feedback Benefit Depends on Experience in Multiple Degree of Freedom Robotic Surgery Task Christopher R. Wagner and
Shape Memory Alloy Actuator Controller Design for Tactile Displays
 34th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control New Orleans, Dec. 3-5, 995 Shape Memory Alloy Actuator Controller Design for Tactile Displays Robert D. Howe, Dimitrios A. Kontarinis, and William J. Peine
34th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control New Orleans, Dec. 3-5, 995 Shape Memory Alloy Actuator Controller Design for Tactile Displays Robert D. Howe, Dimitrios A. Kontarinis, and William J. Peine
Advanced Augmented Reality Telestration Techniques With Applications In Laparoscopic And Robotic Surgery
 Wayne State University Wayne State University Dissertations 1-1-2013 Advanced Augmented Reality Telestration Techniques With Applications In Laparoscopic And Robotic Surgery Stephen Dworzecki Wayne State
Wayne State University Wayne State University Dissertations 1-1-2013 Advanced Augmented Reality Telestration Techniques With Applications In Laparoscopic And Robotic Surgery Stephen Dworzecki Wayne State
Medtronic Payer Solutions
 Medtronic Payer Solutions Delivering Cost-Savings Opportunities through Minimally Invasive Surgery In today s business environment, managing employee overhead and healthcare benefit costs necessitate that
Medtronic Payer Solutions Delivering Cost-Savings Opportunities through Minimally Invasive Surgery In today s business environment, managing employee overhead and healthcare benefit costs necessitate that
Play Me Back: A Unified Training Platform for Robotic and Laparoscopic Surgery
 Play Me Back: A Unified Training Platform for Robotic and Laparoscopic Surgery Alaa Eldin Abdelaal Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada, V6T
Play Me Back: A Unified Training Platform for Robotic and Laparoscopic Surgery Alaa Eldin Abdelaal Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada, V6T
AC : MEDICAL ROBOTICS LABORATORY FOR BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERS
 AC 2008-1272: MEDICAL ROBOTICS LABORATORY FOR BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERS Shahin Sirouspour, McMaster University http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/~sirouspour/ Mahyar Fotoohi, Quanser Inc Pawel Malysz, McMaster University
AC 2008-1272: MEDICAL ROBOTICS LABORATORY FOR BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERS Shahin Sirouspour, McMaster University http://www.ece.mcmaster.ca/~sirouspour/ Mahyar Fotoohi, Quanser Inc Pawel Malysz, McMaster University
Robots for Medicine and Personal Assistance. Guest lecturer: Ron Alterovitz
 Robots for Medicine and Personal Assistance Guest lecturer: Ron Alterovitz Growth of Robotics Industry Worldwide $70 $56 Market Size (Billions) $42 $28 $14 $0 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 Source:
Robots for Medicine and Personal Assistance Guest lecturer: Ron Alterovitz Growth of Robotics Industry Worldwide $70 $56 Market Size (Billions) $42 $28 $14 $0 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 Source:
TRENDS IN SURGICAL ROBOTICS
 TRENDS IN SURGICAL ROBOTICS HANNES BLEULER, MOHAMED BOURI, LAURA SANTOS-CARRERAS, SIMON GALLO, ALI SENGÜL, GIULIO ROGNINI, REYMOND CLAVEL * Abstract. Surgical Robotics today is essentially about two families
TRENDS IN SURGICAL ROBOTICS HANNES BLEULER, MOHAMED BOURI, LAURA SANTOS-CARRERAS, SIMON GALLO, ALI SENGÜL, GIULIO ROGNINI, REYMOND CLAVEL * Abstract. Surgical Robotics today is essentially about two families
VIRTUAL REALITY Introduction. Emil M. Petriu SITE, University of Ottawa
 VIRTUAL REALITY Introduction Emil M. Petriu SITE, University of Ottawa Natural and Virtual Reality Virtual Reality Interactive Virtual Reality Virtualized Reality Augmented Reality HUMAN PERCEPTION OF
VIRTUAL REALITY Introduction Emil M. Petriu SITE, University of Ottawa Natural and Virtual Reality Virtual Reality Interactive Virtual Reality Virtualized Reality Augmented Reality HUMAN PERCEPTION OF
Maneuverability Evaluation of a Surgical Robot for Single-Port Surgery
 International Journal of Pharma Medicine and Biological Sciences Vol. 5, No. 1, January 2016 Maneuverability Evaluation of a Surgical Robot for Single-Port Surgery Katsuaki Oiwa, Shotaro Maeda, and Chiharu
International Journal of Pharma Medicine and Biological Sciences Vol. 5, No. 1, January 2016 Maneuverability Evaluation of a Surgical Robot for Single-Port Surgery Katsuaki Oiwa, Shotaro Maeda, and Chiharu
Immersive Simulation in Instructional Design Studios
 Blucher Design Proceedings Dezembro de 2014, Volume 1, Número 8 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/evento/sigradi2014 Immersive Simulation in Instructional Design Studios Antonieta Angulo Ball State University,
Blucher Design Proceedings Dezembro de 2014, Volume 1, Número 8 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/evento/sigradi2014 Immersive Simulation in Instructional Design Studios Antonieta Angulo Ball State University,
Università di Roma La Sapienza. Medical Robotics. A Teleoperation System for Research in MIRS. Marilena Vendittelli
 Università di Roma La Sapienza Medical Robotics A Teleoperation System for Research in MIRS Marilena Vendittelli the DLR teleoperation system slave three versatile robots MIRO light-weight: weight < 10
Università di Roma La Sapienza Medical Robotics A Teleoperation System for Research in MIRS Marilena Vendittelli the DLR teleoperation system slave three versatile robots MIRO light-weight: weight < 10
Open surgery SIMULATION
 Open surgery SIMULATION ossimtech.com A note from the President and Co-Founder, Mr. André Blain Medical education and surgical training are going through exciting changes these days. Fast-paced innovation
Open surgery SIMULATION ossimtech.com A note from the President and Co-Founder, Mr. André Blain Medical education and surgical training are going through exciting changes these days. Fast-paced innovation
Haptic Camera Manipulation: Extending the Camera In Hand Metaphor
 Haptic Camera Manipulation: Extending the Camera In Hand Metaphor Joan De Boeck, Karin Coninx Expertise Center for Digital Media Limburgs Universitair Centrum Wetenschapspark 2, B-3590 Diepenbeek, Belgium
Haptic Camera Manipulation: Extending the Camera In Hand Metaphor Joan De Boeck, Karin Coninx Expertise Center for Digital Media Limburgs Universitair Centrum Wetenschapspark 2, B-3590 Diepenbeek, Belgium
Small Occupancy Robotic Mechanisms for Endoscopic Surgery
 Small Occupancy Robotic Mechanisms for Endoscopic Surgery Yuki Kobayashi, Shingo Chiyoda, Kouichi Watabe, Masafumi Okada, and Yoshihiko Nakamura Department of Mechano-Informatics, The University of Tokyo,
Small Occupancy Robotic Mechanisms for Endoscopic Surgery Yuki Kobayashi, Shingo Chiyoda, Kouichi Watabe, Masafumi Okada, and Yoshihiko Nakamura Department of Mechano-Informatics, The University of Tokyo,
Job Description. Commitment: Must be available to work full-time hours, M-F for weeks beginning Summer of 2018.
 Research Intern Director of Research We are seeking a summer intern to support the team to develop prototype 3D sensing systems based on state-of-the-art sensing technologies along with computer vision
Research Intern Director of Research We are seeking a summer intern to support the team to develop prototype 3D sensing systems based on state-of-the-art sensing technologies along with computer vision
Bibliography. Conclusion
 the almost identical time measured in the real and the virtual execution, and the fact that the real execution with indirect vision to be slower than the manipulation on the simulated environment. The
the almost identical time measured in the real and the virtual execution, and the fact that the real execution with indirect vision to be slower than the manipulation on the simulated environment. The
Seeing virtual while acting real: visual display and strategy effects on the time and precision of eye-hand coordination
 1 Seeing virtual while acting real: visual display and strategy effects on the time and precision of eye-hand coordination Anil U. Batmaz 1, Michel de Mathelin 1, Birgitta Dresp-Langley 1 1 ICube Laboratory,
1 Seeing virtual while acting real: visual display and strategy effects on the time and precision of eye-hand coordination Anil U. Batmaz 1, Michel de Mathelin 1, Birgitta Dresp-Langley 1 1 ICube Laboratory,
Suture Training Device with Computer Vision Based Information Acquisition
 Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 12-2016 Suture Training Device with Computer Vision Based Information Acquisition Anand Jagannathan Clemson University Follow this and additional works
Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 12-2016 Suture Training Device with Computer Vision Based Information Acquisition Anand Jagannathan Clemson University Follow this and additional works
Robotics, telepresence and minimal access surgery - A short and selective history
 Robotics, telepresence and minimal access surgery - A short and selective history Luke Hares, Technology Director, Cambridge Medical Robotics P-306v2.0 Overview o Disclaimer! o Highlights of robotics and
Robotics, telepresence and minimal access surgery - A short and selective history Luke Hares, Technology Director, Cambridge Medical Robotics P-306v2.0 Overview o Disclaimer! o Highlights of robotics and
Augmented Reality to Localize Individual Organ in Surgical Procedure
 Tutorial Healthc Inform Res. 2018 October;24(4):394-401. https://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2018.24.4.394 pissn 2093-3681 eissn 2093-369X Augmented Reality to Localize Individual Organ in Surgical Procedure Dongheon
Tutorial Healthc Inform Res. 2018 October;24(4):394-401. https://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2018.24.4.394 pissn 2093-3681 eissn 2093-369X Augmented Reality to Localize Individual Organ in Surgical Procedure Dongheon
An experimental study about the effect of interactions among functional factors in performance of telemanipulation systems
 Control Engineering Practice 15 (2007) 29 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/conengprac An experimental study about the effect of interactions among functional factors in performance of telemanipulation systems
Control Engineering Practice 15 (2007) 29 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/conengprac An experimental study about the effect of interactions among functional factors in performance of telemanipulation systems
INTRODUCING THE VIRTUAL REALITY FLIGHT SIMULATOR FOR SURGEONS
 INTRODUCING THE VIRTUAL REALITY FLIGHT SIMULATOR FOR SURGEONS SAFE REPEATABLE MEASUREABLE SCALABLE PROVEN SCALABLE, LOW COST, VIRTUAL REALITY SURGICAL SIMULATION The benefits of surgical simulation are
INTRODUCING THE VIRTUAL REALITY FLIGHT SIMULATOR FOR SURGEONS SAFE REPEATABLE MEASUREABLE SCALABLE PROVEN SCALABLE, LOW COST, VIRTUAL REALITY SURGICAL SIMULATION The benefits of surgical simulation are
The Virtual Haptic Back (VHB): a Virtual Reality Simulation of the Human Back for Palpatory Diagnostic Training
 Paper Offer #: 5DHM- The Virtual Haptic Back (VHB): a Virtual Reality Simulation of the Human Back for Palpatory Diagnostic Training John N. Howell Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuromusculoskeletal
Paper Offer #: 5DHM- The Virtual Haptic Back (VHB): a Virtual Reality Simulation of the Human Back for Palpatory Diagnostic Training John N. Howell Interdisciplinary Institute for Neuromusculoskeletal
Accuracy evaluation of an image overlay in an instrument guidance system for laparoscopic liver surgery
 Accuracy evaluation of an image overlay in an instrument guidance system for laparoscopic liver surgery Matteo Fusaglia 1, Daphne Wallach 1, Matthias Peterhans 1, Guido Beldi 2, Stefan Weber 1 1 Artorg
Accuracy evaluation of an image overlay in an instrument guidance system for laparoscopic liver surgery Matteo Fusaglia 1, Daphne Wallach 1, Matthias Peterhans 1, Guido Beldi 2, Stefan Weber 1 1 Artorg
A Novel Computerized Surgeon Machine Interface for Robot-Assisted Laser Phonomicrosurgery
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. A Novel Computerized Surgeon Machine Interface for Robot-Assisted Laser Phonomicrosurgery Leonardo S. Mattos,
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. A Novel Computerized Surgeon Machine Interface for Robot-Assisted Laser Phonomicrosurgery Leonardo S. Mattos,
HUMAN Robot Cooperation Techniques in Surgery
 HUMAN Robot Cooperation Techniques in Surgery Alícia Casals Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Barcelona, Spain alicia.casals@upc.edu Keywords:
HUMAN Robot Cooperation Techniques in Surgery Alícia Casals Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC), Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), Barcelona, Spain alicia.casals@upc.edu Keywords:
University of Alabama at Birmingham. ObGyn Residency. Laparoscopy Training Lab PGY 1-4. Individual Pelvic Trainer Tasks
 University of Alabama at Birmingham ObGyn Residency Laparoscopy Training Lab PGY 1-4 Individual Pelvic Trainer Tasks 2010-2011 Skill 1: Peg Board (Blue Board) Goal: Pick up various rings and move them
University of Alabama at Birmingham ObGyn Residency Laparoscopy Training Lab PGY 1-4 Individual Pelvic Trainer Tasks 2010-2011 Skill 1: Peg Board (Blue Board) Goal: Pick up various rings and move them
Transforming Surgical Robotics. 34 th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference January 14, 2016
 1 Transforming Surgical Robotics 34 th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference January 14, 2016 Forward Looking Statements 2 This presentation includes statements relating to TransEnterix s current regulatory
1 Transforming Surgical Robotics 34 th Annual J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference January 14, 2016 Forward Looking Statements 2 This presentation includes statements relating to TransEnterix s current regulatory
Modeling and Experimental Studies of a Novel 6DOF Haptic Device
 Proceedings of The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering Forum 2010 CSME FORUM 2010 June 7-9, 2010, Victoria, British Columbia, Canada Modeling and Experimental Studies of a Novel DOF Haptic Device
Proceedings of The Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering Forum 2010 CSME FORUM 2010 June 7-9, 2010, Victoria, British Columbia, Canada Modeling and Experimental Studies of a Novel DOF Haptic Device
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. X, NO. X, SEPTEMBER 201X 1
 IEEE TRNSCTIONS ON IOMEDICL ENGINEERING, VOL. X, NO. X, SEPTEMER 1X 1 Uncontrolled Manifold nalysis of rm Joint ngle Variability During Robotic Teleoperation and Freehand Movement of Surgeons and s Ilana
IEEE TRNSCTIONS ON IOMEDICL ENGINEERING, VOL. X, NO. X, SEPTEMER 1X 1 Uncontrolled Manifold nalysis of rm Joint ngle Variability During Robotic Teleoperation and Freehand Movement of Surgeons and s Ilana
Analysis and Physics of Laparoscopic Intracorporeal Square-Knot Tying
 TECHNIQUE Analysis and Physics of Laparoscopic Intracorporeal Square-Knot Tying Marelyn Medina, MD ABSTRACT Square knots are often used in open surgery to approximate tissue borders or tie off tubular
TECHNIQUE Analysis and Physics of Laparoscopic Intracorporeal Square-Knot Tying Marelyn Medina, MD ABSTRACT Square knots are often used in open surgery to approximate tissue borders or tie off tubular
CAST News UNMC CENTER FOR ADVANCED SURGICAL TECHNOLOGY
 INSIDE THIS ISSUE Parabolic Flight test Grant in Robotic Telesurgery CAST publishes a textbook Meet the 2014-2015 Fellows Open House Update: 2013-2014 Fellows Letter from the Director Learn more about
INSIDE THIS ISSUE Parabolic Flight test Grant in Robotic Telesurgery CAST publishes a textbook Meet the 2014-2015 Fellows Open House Update: 2013-2014 Fellows Letter from the Director Learn more about
Methods and mechanisms for contact feedback in a robot-assisted minimally invasive environment
 Surg Endosc (2006) 20: 1570 1579 DOI: 10.1007/s00464-005-0582-y Ó Springer Science+Business Media, Inc. 2006 Methods and mechanisms for contact feedback in a robot-assisted minimally invasive environment
Surg Endosc (2006) 20: 1570 1579 DOI: 10.1007/s00464-005-0582-y Ó Springer Science+Business Media, Inc. 2006 Methods and mechanisms for contact feedback in a robot-assisted minimally invasive environment
Eye Gaze Patterns Differentiate Novice and Experts in a Virtual Laparoscopic Surgery Training Environment
 Gaze Patterns Differentiate Novice and Experts in a Virtual Laparoscopic Surgery Training Environment Benjamin Law School of Computing Science Alan J. Lomax School of Kinesiology M. Stella Atkins School
Gaze Patterns Differentiate Novice and Experts in a Virtual Laparoscopic Surgery Training Environment Benjamin Law School of Computing Science Alan J. Lomax School of Kinesiology M. Stella Atkins School
CHAPTER 2. RELATED WORK 9 similar study, Gillespie (1996) built a one-octave force-feedback piano keyboard to convey forces derived from this model to
 Chapter 2 Related Work 2.1 Haptic Feedback in Music Controllers The enhancement of computer-based instrumentinterfaces with haptic feedback dates back to the late 1970s, when Claude Cadoz and his colleagues
Chapter 2 Related Work 2.1 Haptic Feedback in Music Controllers The enhancement of computer-based instrumentinterfaces with haptic feedback dates back to the late 1970s, when Claude Cadoz and his colleagues
Haptic Feedback in Robot Assisted Minimal Invasive Surgery
 K. Bhatia Haptic Feedback in Robot Assisted Minimal Invasive Surgery 1 / 33 MIN Faculty Department of Informatics Haptic Feedback in Robot Assisted Minimal Invasive Surgery Kavish Bhatia University of
K. Bhatia Haptic Feedback in Robot Assisted Minimal Invasive Surgery 1 / 33 MIN Faculty Department of Informatics Haptic Feedback in Robot Assisted Minimal Invasive Surgery Kavish Bhatia University of
Comparison of Simulated Ovary Training Over Different Skill Levels
 Comparison of Simulated Ovary Training Over Different Skill Levels Andrew Crossan, Stephen Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12
Comparison of Simulated Ovary Training Over Different Skill Levels Andrew Crossan, Stephen Brewster Glasgow Interactive Systems Group Department of Computing Science University of Glasgow, Glasgow, G12
Current Status and Future of Medical Virtual Reality
 2011.08.16 Medical VR Current Status and Future of Medical Virtual Reality Naoto KUME, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Kyoto University Hospital 1. History of Medical Virtual Reality Virtual reality (VR)
2011.08.16 Medical VR Current Status and Future of Medical Virtual Reality Naoto KUME, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Kyoto University Hospital 1. History of Medical Virtual Reality Virtual reality (VR)
