Points, Lines, & Slopes (Oh My!)
|
|
|
- Shannon Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 About the Lesson In this activity students will explore the relationship among coordinates of points and locations on the coordinate plane, the relationships of lines with their equations, slopes and y-intercepts, and lastly, the slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines. As a result, students will: Graph an equation of the form y = mx + b and determine properties such as slope and y-intercept. Graph an equation of the form y = mx + b and describe how m and b change as the graph of the line is rotated and translated. Understand that the coordinates of a line are the solution set to the equation of the line. Show that lines with equal slope are parallel. Graph lines whose slopes are negative reciprocals. Deduce that the slopes of perpendicular lines are negative reciprocals. Vocabulary parallel perpendicular reciprocal slope Teacher Preparation and Notes This activity can review coordinates and then go on to introduce or review the relationships of points, lines, slopes, and equations. The graph could also be divided into different zones by graphing f(x) = x and f(x) = x and having students generalize the slope for each of these zones. After graphing lines and looking at relationships, another point could be placed on the plane and students could look at the coordinates of the point with respect to the line. This could be used to introduce inequalities. Tech Tips: This activity includes screen captures taken from the TI-84 Plus C Silver Edition. It is also appropriate for use with the TI- 84 Plus family with the latest TI- 84 Plus operating system (2.55MP) featuring MathPrint TM functionality. Slight variations to these directions given within may be required if using other calculator models. Access free tutorials at calculators/pd/us/online- Learning/Tutorials Any required calculator files can be distributed to students via handheld-to-handheld transfer. Compatible Devices: TI-84 Plus Family Software Application: Cabri Jr. Associated Materials: PointsLinesSlopes_Student.pdf PointsLinesSlopes_Student.doc PARALLEL.8xv PERPENDI.8xv 2014 Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 education.ti.com
2 Tech Tip: Before beginning the activity, the files PARALLEL.8xv and PERPENDI.8xv need to be transferred to the students calculators via handheld-to-handheld transfer or transferred from the computer to the calculator via TI-Connect. Three focus questions define this activity. (Some discussion should follow the posing of these questions): 1. What are the relationships of the coordinates of points with various locations in the Cartesian plane? 2. What is the relationship of a line with its slope, equation, and y-intercept? 3. What is the relationship between the slopes of parallel or perpendicular lines? Problem 1 Coordinates of Points Have students open the Cabri TM Jr application by pressing A. Open a new file (! for ) and make sure the axes are displayed (press % for º and select Hide/Show > Axes). Note, to undo press F1 > Undo. Students should place a point, R, on the x-axis and a point, S, on the y-axis. Use F2 > Point > Point On. Press F5 > Alpha-Num and e to label the points. When finished with a tool press C. Have students display the coordinates of the points. Use F5 > Coord & Eq and move the cursor to a point until the point is flashing. Press e to select that point, then have students move the cursor to where they want the coordinate to remain and press e again. To grab a point that is flashing, press a. To let go of a point press C. This works as Escape. 1. Explain what is common to all points on the x-axis. Answer: For any x-value, the y-value is zero. 2. Explain what is common to all points on the y-axis. Answer: For all y-values, the x-value is zero Texas Instruments Incorporated 2 education.ti.com
3 Have students delete points R and S by moving the cursor to that location and pressing d. Place two points, P and Q, in the top right quadrant. Drag the points around into different quadrants. Complete the sentences by writing positive or negative. 3. A point is in Quadrant 1 (top right) when its x-coordinate is positive and its y-coordinate is positive. 4. A point is in Quadrant 2 (top left) when its x-coordinate is negative and its y-coordinate is positive. 5. A point is in Quadrant 3 (bottom left) when its x-coordinate is negative and its y-coordinate is negative. 6. A point is in Quadrant 4 (bottom right) when its x-coordinate is positive and its y-coordinate is negative. Teacher Tip: Students should now be able to make sense of exactly what the coordinates should be in different quadrants as well as on each axis. Give students the coordinates of a point and ask which quadrant it is in and visa versa. This simple activity is good for students to develop their technology skills and establish sign patterns for the four quadrants. Have students use the Perpendicular tool (# > Perp.) to construct perpendicular lines through point P to each axis. After the perpendicular lines are in place, direct students to construct segments from point P to each axis (@ > Segment) and then hide the excess perpendicular lines using the Hide/Show tool. To select the intersection point of the perpendicular line and the axis using the Segment tool, students should select both lines so that they flash. They students should press e. Now have students measure the length of each segment using the D. & Length tool from Appearance > Measure menu. Drag point P and have students conjecture about the distances and the coordinates. 7. What is this relationship between the coordinates of point P and the distances to each axis? Answer: The distance from P to each x-axis is the absolute value of the y-coordinate. The distance from P to each y-axis is the absolute value of the x-coordinate Texas Instruments Incorporated 3 education.ti.com
4 Problem 2 Lines, Equations, and Slopes Delete or hide the segments and measurements. Ask students to visualize a line between points P and Q and conjecture as to whether the slope is positive or negative, small or large, etc. Then use F2 to draw a line connecting P and Q. They will use the Line tool from the Creation menu. Next, using tools from the F5 Appearance menu to display the equation and slope of the line. As they find the slope (% > Measure > Slope) and equation (% > Coord. & Eq.) of the line they can label the slope measurement as shown to the right by choosing the Alph-Num tool and typing SLOPE: in the appropriate place. If this is a student s first introduction to slope, encourage students to discover the relationship of the displayed points and the slope. They should discover the slope of a line connecting two points is the change in the y-values of the points divided by the change in the x- values of the points. Have students place a point on the line and then drag the point along the line. They should note the coordinates of several points along the line. 8. Place a point on the line. Drag the point along the line and record several coordinates of points. How do the coordinates relate to the equation of the line? Answer: Coordinates will vary. Each ordered pair is a solution to the equation of the line. Have students look for relationships between the slope and equation as they change the line by grabbing and dragging point P as well as grabbing and dragging the line itself. Press + as you hover over a value to display more digits. Students should attend to precision and understand that discrepancies may be due to the number of digits shown throughout this activity. 9. When dragging the line by a point, what is the relationship between the points and the slope? Answer: The slope is the change in the y-values divided by the change in the x-values 10. When dragging the line by a point, what is the relationship of the slope and the equation? Answer: The slope changes. The coefficient in front of the variable x changes Texas Instruments Incorporated 4 education.ti.com
5 11. To the right is a graph with two points labeled. Consider the line through these points. Then, consider the graph of the equation y = ½ x + 2. Show you work and explain how the two lines compare. Especially consider the slope and y-intercepts. Answer: The slope of the graph is (1 ( 3))/(3 1) = 4/2 = 2. This is a larger slope than the equation which has a slope of ½. The graph is much steeper than the equation. The y-intercept of the equation is positive 2, whereas the y-intercept of the graph is a negative number. From the equation of the graph, y + 3 = 2(x 1) or y = 2x 5, it can be seen the y-intercept is 5. Problem 3 Slopes of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Open the Cabri TM Jr. file PARALLEL. Drag the lines by points P and Q and examine the slopes. 12. What can you say about the slopes of two parallel lines? Answer: The slopes of the two parallel lines are equal. Students are given two parallel lines, their equations, and their slopes. (This construction is done for them. Alternatively, students can construct the parallel lines, show the slopes, and explore.) Open the Cabri TM Jr. file PERPENDI. Again, have students drag the lines to investigate the relationship between the slopes. 13. What can you say about the slopes of two perpendicular lines? Answer: Students will observe that when one slope is positive, the other slope is negative. They may need to continue exploring to discover that the slopes of the perpendicular lines are the opposite reciprocals of each other. Another way to look at the relationship of the slopes is to find the product of the two slopes. Have students select % > Calculate. Next, they should position the cursor over the first slope, and press e. Students should then press * to specify the operation and move the cursor to the second slope and press e again. This will yield the product of the two slopes have students drag it to a convenient location on the screen. Now, change the lines by grabbing and dragging point P. 14. What do you observe about the product of the slopes? Answer: The product is always -1. The slope of perpendicular lines is the opposite reciprocal of each other Texas Instruments Incorporated 5 education.ti.com
6 Extensions As stated in the teacher preparation notes, there are many extensions to this activity depending on the level of the student. This activity can easily be manipulated to lead students into a deeper study of slopes, slopes of parallel lines and slope of perpendicular lines. Either with a student TI-84 Plus C or the TI-SmartView TI-84 Plus C, turn on Background Image2 from the Format Graphs screen, ` # and view that graph with a decimal window. Press # ZDecimal. Ask students for coordinates along a line. For example, (-3, 0) and (2, -2). They can use the point slope formula to write an equation of the line. 2 0 y 0 ( x ( 3)) 2 ( 3) 2 y ( x 3) y x 5 5 Then, have them graph a line parallel to that equation Texas Instruments Incorporated 6 education.ti.com
TIalgebra.com Algebra 1
 Perpendicular Slopes ID: 8973 Time required 45 minutes Topic: Linear Functions Graph lines whose slopes are negative reciprocals and measure the angles to verify they are perpendicular. Activity Overview
Perpendicular Slopes ID: 8973 Time required 45 minutes Topic: Linear Functions Graph lines whose slopes are negative reciprocals and measure the angles to verify they are perpendicular. Activity Overview
Polar Conics TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED. Math Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator System
 Math Objectives Students will understand that the equations for conics can be expressed in polar form. Students will be able to describe the relationship between eccentricity and the type of conic section.
Math Objectives Students will understand that the equations for conics can be expressed in polar form. Students will be able to describe the relationship between eccentricity and the type of conic section.
Products of Linear Functions
 Math Objectives Students will understand relationships between the horizontal intercepts of two linear functions and the horizontal intercepts of the quadratic function resulting from their product. Students
Math Objectives Students will understand relationships between the horizontal intercepts of two linear functions and the horizontal intercepts of the quadratic function resulting from their product. Students
Slope as Rate TEACHER NOTES
 Math Objectives Students will be able to interpret the slope of a line as the rate of change of the y-coordinate per unit increase in the x-coordinate as one moves from left to right along the line. Students
Math Objectives Students will be able to interpret the slope of a line as the rate of change of the y-coordinate per unit increase in the x-coordinate as one moves from left to right along the line. Students
Investigating the Sine Function
 Grade level: 9-12 Investigating the Sine Function by Marco A. Gonzalez Activity overview In this activity, students will use their Nspire handhelds to discover the different attributes of the graph of
Grade level: 9-12 Investigating the Sine Function by Marco A. Gonzalez Activity overview In this activity, students will use their Nspire handhelds to discover the different attributes of the graph of
Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing. 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane
 Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane Rectangular Coordinate System Quadrant II (-,+) y-axis Quadrant
Chapter 9 Linear equations/graphing 1) Be able to graph points on coordinate plane 2) Determine the quadrant for a point on coordinate plane Rectangular Coordinate System Quadrant II (-,+) y-axis Quadrant
Chapter 2: Functions and Graphs Lesson Index & Summary
 Section 1: Relations and Graphs Cartesian coordinates Screen 2 Coordinate plane Screen 2 Domain of relation Screen 3 Graph of a relation Screen 3 Linear equation Screen 6 Ordered pairs Screen 1 Origin
Section 1: Relations and Graphs Cartesian coordinates Screen 2 Coordinate plane Screen 2 Domain of relation Screen 3 Graph of a relation Screen 3 Linear equation Screen 6 Ordered pairs Screen 1 Origin
CHAPTER 3. Parallel & Perpendicular lines
 CHAPTER 3 Parallel & Perpendicular lines 3.1- Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Parallel Lines: two lines are parallel if they do not intersect and are coplaner Skew lines: Two lines are skew if they
CHAPTER 3 Parallel & Perpendicular lines 3.1- Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Parallel Lines: two lines are parallel if they do not intersect and are coplaner Skew lines: Two lines are skew if they
y-intercept remains constant?
 1. The graph of a line that contains the points ( 1, 5) and (4, 5) is shown below. Which best represents this line if the slope is doubled and the y-intercept remains constant? F) G) H) J) 2. The graph
1. The graph of a line that contains the points ( 1, 5) and (4, 5) is shown below. Which best represents this line if the slope is doubled and the y-intercept remains constant? F) G) H) J) 2. The graph
Algebra/Geometry. Slope/Triangle Area Exploration
 Slope/Triangle Area Exploration ID: 9863 Time required 60 90 minutes Topics: Linear Functions, Triangle Area, Rational Functions Graph lines in slope-intercept form Find the coordinate of the x- and y-intercepts
Slope/Triangle Area Exploration ID: 9863 Time required 60 90 minutes Topics: Linear Functions, Triangle Area, Rational Functions Graph lines in slope-intercept form Find the coordinate of the x- and y-intercepts
Exploring Triangles. Exploring Triangles. Overview. Concepts Understanding area of triangles Relationships of lengths of midsegments
 Exploring Triangles Concepts Understanding area of triangles Relationships of lengths of midsegments of triangles Justifying parallel lines Materials TI-Nspire TI N-spire document Exploring Triangles Overview
Exploring Triangles Concepts Understanding area of triangles Relationships of lengths of midsegments of triangles Justifying parallel lines Materials TI-Nspire TI N-spire document Exploring Triangles Overview
Math Labs. Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates. Procedure
 Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Algebra/Geometry. Slope/Triangle Area Exploration
 Slope/Triangle Area Exploration ID: Time required 60 minutes Topics: Linear Functions, Triangle Area, Rational Functions Graph lines in slope-intercept form Find the coordinate of the x- and y-intercepts
Slope/Triangle Area Exploration ID: Time required 60 minutes Topics: Linear Functions, Triangle Area, Rational Functions Graph lines in slope-intercept form Find the coordinate of the x- and y-intercepts
Visualizing Equations TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED
 Math Objectives Students will describe what it means to solve a linear equation. Students will recognize how to maintain the equality between two expressions when adding or taking away tiles Vocabulary
Math Objectives Students will describe what it means to solve a linear equation. Students will recognize how to maintain the equality between two expressions when adding or taking away tiles Vocabulary
The Picture Tells the Linear Story
 The Picture Tells the Linear Story Students investigate the relationship between constants and coefficients in a linear equation and the resulting slopes and y-intercepts on the graphs. This activity also
The Picture Tells the Linear Story Students investigate the relationship between constants and coefficients in a linear equation and the resulting slopes and y-intercepts on the graphs. This activity also
constant EXAMPLE #4:
 Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Outcome 7 Review. *Recall that -1 (-5) means
 Outcome 7 Review Level 2 Determine the slope of a line that passes through A(3, -5) and B(-2, -1). Step 1: Remember that ordered pairs are in the form (x, y). Label the points so you can substitute into
Outcome 7 Review Level 2 Determine the slope of a line that passes through A(3, -5) and B(-2, -1). Step 1: Remember that ordered pairs are in the form (x, y). Label the points so you can substitute into
Perfect Shuffles TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED. Math Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator System
 Math Objectives Students will create a piecewise linear function to model a method for shuffling a deck of cards. Students will apply composite functions to represent two or more shuffles of a deck. Students
Math Objectives Students will create a piecewise linear function to model a method for shuffling a deck of cards. Students will apply composite functions to represent two or more shuffles of a deck. Students
Outcome 9 Review Foundations and Pre-Calculus 10
 Outcome 9 Review Foundations and Pre-Calculus 10 Level 2 Example: Writing an equation in slope intercept form Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + b m = slope b = y-intercept Ex : Write the equation of a line
Outcome 9 Review Foundations and Pre-Calculus 10 Level 2 Example: Writing an equation in slope intercept form Slope-Intercept Form: y = mx + b m = slope b = y-intercept Ex : Write the equation of a line
Solids Washers /G. TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED. Math Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator System
 Math Objectives Students will be able to visualize the solid generated by revolving the region bounded between two function graphs and the vertical lines x = a and x = b about the x-axis. Students will
Math Objectives Students will be able to visualize the solid generated by revolving the region bounded between two function graphs and the vertical lines x = a and x = b about the x-axis. Students will
Block: Date: Name: REVIEW Linear Equations. 7.What is the equation of the line that passes through the point (5, -3) and has a slope of -3?
 Name: REVIEW Linear Equations 1. What is the slope of the line y = -2x + 3? 2. Write the equation in slope-intercept form. Block: Date: 7.What is the equation of the line that passes through the point
Name: REVIEW Linear Equations 1. What is the slope of the line y = -2x + 3? 2. Write the equation in slope-intercept form. Block: Date: 7.What is the equation of the line that passes through the point
Slopes of of Parallel and and Perpendicular Lines Lines Holt Algebra 1
 5-8 Slopes of of Parallel and and Lines Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Bell Quiz 5-8 Find the reciprocal. 1. 2 2. 1 pt 1 pt 1 pt 3. 2 pts 2 pts 2 pts Find the slope of the line that passes through
5-8 Slopes of of Parallel and and Lines Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Bell Quiz 5-8 Find the reciprocal. 1. 2 2. 1 pt 1 pt 1 pt 3. 2 pts 2 pts 2 pts Find the slope of the line that passes through
ACT Coordinate Geometry Review
 ACT Coordinate Geometry Review Here is a brief review of the coordinate geometry concepts tested on the ACT. Note: there is no review of how to graph an equation on this worksheet. Questions testing this
ACT Coordinate Geometry Review Here is a brief review of the coordinate geometry concepts tested on the ACT. Note: there is no review of how to graph an equation on this worksheet. Questions testing this
SE Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - TI
 SE Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - TI CK12 Editor Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other
SE Parallel and Perpendicular Lines - TI CK12 Editor Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other
Topic: Right Triangles & Trigonometric Ratios Calculate the trigonometric ratios for , and triangles.
 Investigating Special Triangles ID: 7896 Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students will investigate the properties of an isosceles triangle. Then students will construct a 30-60
Investigating Special Triangles ID: 7896 Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students will investigate the properties of an isosceles triangle. Then students will construct a 30-60
Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem
 Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem Lesson 11 Mathematics Objectives Students will analyze relationships to develop the Pythagorean Theorem. Students will find missing sides in right triangles using the
Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem Lesson 11 Mathematics Objectives Students will analyze relationships to develop the Pythagorean Theorem. Students will find missing sides in right triangles using the
4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 What You Will Learn Determine the slope of a line through two points Write linear equations in slope-intercept
4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 What You Will Learn Determine the slope of a line through two points Write linear equations in slope-intercept
Review for Mastery. Identifying Linear Functions
 Identifying Linear Functions You can determine if a function is linear by its graph, ordered pairs, or equation. Identify whether the graph represents a linear function. Step 1: Determine whether the graph
Identifying Linear Functions You can determine if a function is linear by its graph, ordered pairs, or equation. Identify whether the graph represents a linear function. Step 1: Determine whether the graph
Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review
 Name: Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review Vocabulary Equation: a math sentence that contains Linear: makes a straight line (no Variables: quantities represented by (often x and y) Function: equations can
Name: Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review Vocabulary Equation: a math sentence that contains Linear: makes a straight line (no Variables: quantities represented by (often x and y) Function: equations can
Getting Started with. Math & Science Learning Technology
 Getting Started with Math & Science Learning Technology Important notice regarding book materials Texas Instruments makes no warranty, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to any implied
Getting Started with Math & Science Learning Technology Important notice regarding book materials Texas Instruments makes no warranty, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to any implied
Wondering About Waves
 Science Objectives Students will explore and compare the properties of standing waves and an electromagnetic wave. Students will observe different resonant frequencies of a standing wave on a spring. Vocabulary
Science Objectives Students will explore and compare the properties of standing waves and an electromagnetic wave. Students will observe different resonant frequencies of a standing wave on a spring. Vocabulary
E. Slope-Intercept Form and Direct Variation (pp )
 and Direct Variation (pp. 32 35) For any two points, there is one and only one line that contains both points. This fact can help you graph a linear equation. Many times, it will be convenient to use the
and Direct Variation (pp. 32 35) For any two points, there is one and only one line that contains both points. This fact can help you graph a linear equation. Many times, it will be convenient to use the
Look Alikes Purpose: Objective: TExES Mathematics 4-8 Competencies. TEKS Mathematics Objectives. Terms. Materials. Transparencies.
 Look Alikes Purpose: Participants will investigate ways to construct congruent triangles given three measurements (sides and/or angles) and validate the SSS, SAS, and ASA congruence postulates using technology.
Look Alikes Purpose: Participants will investigate ways to construct congruent triangles given three measurements (sides and/or angles) and validate the SSS, SAS, and ASA congruence postulates using technology.
Warm-Up. Complete the second homework worksheet (the one you didn t do yesterday). Please begin working on FBF010 and FBF011.
 Warm-Up Complete the second homework worksheet (the one you didn t do yesterday). Please begin working on FBF010 and FBF011. You have 20 minutes at the beginning of class to work on these three tasks.
Warm-Up Complete the second homework worksheet (the one you didn t do yesterday). Please begin working on FBF010 and FBF011. You have 20 minutes at the beginning of class to work on these three tasks.
Visualizing Integers TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED. Math Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator System
 Math Objectives Students will identify expressions that balance an equation. Students will find values that satisfy integer equalities. Students will recognize and use the additive inverse property. Students
Math Objectives Students will identify expressions that balance an equation. Students will find values that satisfy integer equalities. Students will recognize and use the additive inverse property. Students
About Cabri JR. Press APPS Chose Cabri JR Press any bu8on to con:nue
 5.5 Parallelograms About Cabri JR Press APPS Chose Cabri JR Press any bu8on to con:nue Tips for Cabri Jr Menus are on F 1, F 2, F 3, F 4, and F 5 You must have the arrow to drag. Press when you are poin:ng
5.5 Parallelograms About Cabri JR Press APPS Chose Cabri JR Press any bu8on to con:nue Tips for Cabri Jr Menus are on F 1, F 2, F 3, F 4, and F 5 You must have the arrow to drag. Press when you are poin:ng
Trigonometric Transformations TEACHER NOTES MATH NSPIRED
 Math Objectives Students will determine the type of function modeled by the height of a capsule on the London Eye observation wheel. Students will translate observational information to use as the parameters
Math Objectives Students will determine the type of function modeled by the height of a capsule on the London Eye observation wheel. Students will translate observational information to use as the parameters
Find the equation of a line given its slope and y-intercept. (Problem Set exercises 1 6 are similar.)
 Directions Each problem below is similar to the example with the same number in your textbook. After reading through an example in your textbook, or watching one of the videos of that example on MathTV,
Directions Each problem below is similar to the example with the same number in your textbook. After reading through an example in your textbook, or watching one of the videos of that example on MathTV,
Algebra. Teacher s Guide
 Algebra Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management..................................................
Algebra Teacher s Guide WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Teacher.......................................................... vi Classroom Management..................................................
LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES What You Should Learn Use slope to graph linear equations in two " variables. Find the slope of a line given two points on the line. Write linear equations in two variables.
LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES What You Should Learn Use slope to graph linear equations in two " variables. Find the slope of a line given two points on the line. Write linear equations in two variables.
TEACHER NOTES MIDDLE GRADES SCIENCE NSPIRED
 Science Objectives Students will explore an animation of particle flow in a battery. Students will vary the electron flow in a DC circuit with a battery of varying voltages and one, two, and three resistors.
Science Objectives Students will explore an animation of particle flow in a battery. Students will vary the electron flow in a DC circuit with a battery of varying voltages and one, two, and three resistors.
UNIT FOUR COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH 421A 23 HOURS
 UNIT FOUR COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH 421A 23 HOURS 71 UNIT 4: Coordinate Geometry Previous Knowledge With the implementation of APEF Mathematics at the Intermediate level, students should be able to: - Grade
UNIT FOUR COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH 421A 23 HOURS 71 UNIT 4: Coordinate Geometry Previous Knowledge With the implementation of APEF Mathematics at the Intermediate level, students should be able to: - Grade
 Page 1 of 1-7 Equations Teks Focus TEKS (2)(B) Derive and use the distance, slope, and midpoint formulas to verify geometric relationships, including congruence of segments and parallelism or perpendicularity
Page 1 of 1-7 Equations Teks Focus TEKS (2)(B) Derive and use the distance, slope, and midpoint formulas to verify geometric relationships, including congruence of segments and parallelism or perpendicularity
Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines
 Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines Two lines are if they are coplanar and do not intersect. Skew lines. Two
Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines Two lines are if they are coplanar and do not intersect. Skew lines. Two
Student Exploration: Quadratics in Factored Form
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Quadratics in Factored Form Vocabulary: factored form of a quadratic function, linear factor, parabola, polynomial, quadratic function, root of an equation, vertex of a
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Quadratics in Factored Form Vocabulary: factored form of a quadratic function, linear factor, parabola, polynomial, quadratic function, root of an equation, vertex of a
4.4 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular
 www.ck12.org Chapter 4. Determining Linear Equations 4.4 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Learning Objectives Determine whether lines are parallel or perpendicular. Write equations of perpendicular
www.ck12.org Chapter 4. Determining Linear Equations 4.4 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Learning Objectives Determine whether lines are parallel or perpendicular. Write equations of perpendicular
Section 2.3 Task List
 Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Unit 1 Introduction to Precalculus Linear Equations in Two Variables (Unit 1.3)
 Unit 1 Introduction to Precalculus Linear Equations in Two Variables (Unit 1.3) William (Bill) Finch Mathematics Department Denton High School Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Find
Unit 1 Introduction to Precalculus Linear Equations in Two Variables (Unit 1.3) William (Bill) Finch Mathematics Department Denton High School Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Find
Educator s Guide to Graphing y = mx + b
 Educator s Guide to Graphing y = mx + b Overview: Using an ipad and Sketchpad Explorer, students will graph a linear equation using the y intercept and slope. Grades and Subject Areas: High School Algebra
Educator s Guide to Graphing y = mx + b Overview: Using an ipad and Sketchpad Explorer, students will graph a linear equation using the y intercept and slope. Grades and Subject Areas: High School Algebra
Lesson 7A Slope-Intercept Formula
 Lesson 7A Slope-Intercept Formula Terms Two new words that describe what we've been doing in graphing lines are slope and intercept. The slope is referred to as "m" (a mountain has slope and starts with
Lesson 7A Slope-Intercept Formula Terms Two new words that describe what we've been doing in graphing lines are slope and intercept. The slope is referred to as "m" (a mountain has slope and starts with
Math 1023 College Algebra Worksheet 1 Name: Prof. Paul Bailey September 22, 2004
 Math 1023 College Algebra Worksheet 1 Name: Prof. Paul Bailey September 22, 2004 Every vertical line can be expressed by a unique equation of the form x = c, where c is a constant. Such lines have undefined
Math 1023 College Algebra Worksheet 1 Name: Prof. Paul Bailey September 22, 2004 Every vertical line can be expressed by a unique equation of the form x = c, where c is a constant. Such lines have undefined
8.2 Slippery Slopes. A Solidify Understanding Task
 7 8.2 Slippery Slopes A Solidify Understanding Task CC BY https://flic.kr/p/kfus4x While working on Is It Right? in the previous module you looked at several examples that lead to the conclusion that the
7 8.2 Slippery Slopes A Solidify Understanding Task CC BY https://flic.kr/p/kfus4x While working on Is It Right? in the previous module you looked at several examples that lead to the conclusion that the
5 Day Unit Plan. Algebra/Grade 9. JenniferJohnston
 5 Day Unit Plan Algebra/Grade 9 JenniferJohnston Geometer s Sketchpad Graph Explorer Algebra I TI-83 Plus Topics in Algebra Application Transform Application Overall Objectives Students will use a variety
5 Day Unit Plan Algebra/Grade 9 JenniferJohnston Geometer s Sketchpad Graph Explorer Algebra I TI-83 Plus Topics in Algebra Application Transform Application Overall Objectives Students will use a variety
3.4 and 4.3 Explain Graphing and Writing Linear Equations in Standard Form - Notes
 3.4 and 4.3 Explain Graphing and Writing Linear Equations in Standard Form - Notes Essential Question: How can you describe the graph of the equation Ax + By = C? How can you write the equation of a line
3.4 and 4.3 Explain Graphing and Writing Linear Equations in Standard Form - Notes Essential Question: How can you describe the graph of the equation Ax + By = C? How can you write the equation of a line
Building Concepts: Connecting Ratios and Scaling
 Lesson Overview In this TI-Nspire lesson, students investigate ratios and scale factors. Scale factors are ratios that can be used to make a figure smaller or larger, depending on whether the scale factor
Lesson Overview In this TI-Nspire lesson, students investigate ratios and scale factors. Scale factors are ratios that can be used to make a figure smaller or larger, depending on whether the scale factor
SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation)
 SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation) Factor the following quadratic expressions: x 2 + 11x + 30 x 2 10x 24 x 2 8x + 15 Standard Form Quadratic Equation (x + 5)(x + 6) (x 12)(x + 2) (x 5)(x
SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation) Factor the following quadratic expressions: x 2 + 11x + 30 x 2 10x 24 x 2 8x + 15 Standard Form Quadratic Equation (x + 5)(x + 6) (x 12)(x + 2) (x 5)(x
Building 3-D Initials with a Vanishing Point
 Grade level: 9-12 Building 3-D Initials with a Vanishing Point Tallahassee Activity overview Students will use a vanishing point for a one point perspective drawing of the initial of their choice. Concepts
Grade level: 9-12 Building 3-D Initials with a Vanishing Point Tallahassee Activity overview Students will use a vanishing point for a one point perspective drawing of the initial of their choice. Concepts
In Lesson 2.5 you were introduced to linear functions. Slope-intercept form is the most common equation
 GRAPHING USING SLOPE-INTERCEPT FORM LESSON 3.1 In Lesson 2.5 you were introduced to linear functions. Slope-intercept form is the most common equation used to represent a linear function. It is called
GRAPHING USING SLOPE-INTERCEPT FORM LESSON 3.1 In Lesson 2.5 you were introduced to linear functions. Slope-intercept form is the most common equation used to represent a linear function. It is called
1.7 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
 Section 1.7 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 11 Eplaining the Concepts 17. Name the five forms of equations of lines given in this section. 18. What tpe of line has one -intercept, but no -intercept? 19.
Section 1.7 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 11 Eplaining the Concepts 17. Name the five forms of equations of lines given in this section. 18. What tpe of line has one -intercept, but no -intercept? 19.
Actual testimonials from people that have used the survival guide:
 Algebra 1A Unit: Coordinate Plane Assignment Sheet Name: Period: # 1.) Page 206 #1 6 2.) Page 206 #10 26 all 3.) Worksheet (SIF/Standard) 4.) Worksheet (SIF/Standard) 5.) Worksheet (SIF/Standard) 6.) Worksheet
Algebra 1A Unit: Coordinate Plane Assignment Sheet Name: Period: # 1.) Page 206 #1 6 2.) Page 206 #10 26 all 3.) Worksheet (SIF/Standard) 4.) Worksheet (SIF/Standard) 5.) Worksheet (SIF/Standard) 6.) Worksheet
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane
 Did You Find a Parking Space? Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane 1.5 Learning Goals Key Term In this lesson, you will: Determine whether lines are parallel. Identify and write the
Did You Find a Parking Space? Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane 1.5 Learning Goals Key Term In this lesson, you will: Determine whether lines are parallel. Identify and write the
Section 3.5. Equations of Lines
 Section 3.5 Equations of Lines Learning objectives Use slope-intercept form to write an equation of a line Use slope-intercept form to graph a linear equation Use the point-slope form to find an equation
Section 3.5 Equations of Lines Learning objectives Use slope-intercept form to write an equation of a line Use slope-intercept form to graph a linear equation Use the point-slope form to find an equation
2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work that explains how you obtained your answer or you must explain how you obtained your answer.
 Math 50, Spring 2006 Test 2 PRINT your name on the back of the test. Circle your class: MW @ 11 TTh @ 2:30 Directions 1. Time limit: 50 minutes. 2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work
Math 50, Spring 2006 Test 2 PRINT your name on the back of the test. Circle your class: MW @ 11 TTh @ 2:30 Directions 1. Time limit: 50 minutes. 2. To receive credit on any problem, you must show work
Geometry Activity. Then enter the following numbers in L 1 and L 2 respectively. L 1 L
 Geometry Activity Introduction: In geometry we can reflect, rotate, translate, and dilate a figure. In this activity lists and statistical plots on the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition will be used to illustrate
Geometry Activity Introduction: In geometry we can reflect, rotate, translate, and dilate a figure. In this activity lists and statistical plots on the TI-83 Plus Silver Edition will be used to illustrate
Parallel Postulate. Perpendicular Postulate PARALLEL AND SKEW LINES WITH PARALLEL PLANES. Lines m and n are. Lines m and k are. Planes T and U are.
 Unit 6: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Lesson 6.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Lesson 3.1 from textbook Objectives Identify relationships between lines such as parallel and skew. Understand and
Unit 6: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines Lesson 6.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles Lesson 3.1 from textbook Objectives Identify relationships between lines such as parallel and skew. Understand and
Physics. AC Circuits ID: 9525
 AC Circuits ID: 9525 Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore a model of alternating electric current. They observe the effects of varying voltage, angular velocity,
AC Circuits ID: 9525 Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore a model of alternating electric current. They observe the effects of varying voltage, angular velocity,
Lesson 11: Linear Functions, Part 2
 Lesson 11 continues the study of linear functions. In this lesson, we look at how to write linear equations in slope-intercept and general form and applications where these may be used. We also look at
Lesson 11 continues the study of linear functions. In this lesson, we look at how to write linear equations in slope-intercept and general form and applications where these may be used. We also look at
Lenses and Light TEACHER NOTES SCIENCE NSPIRED. Science Objectives. Vocabulary. About the Lesson. TI-Nspire Navigator. Activity Materials
 Science Objectives Students will explore the direction of light rays through concave and convex lenses. Students will determine the affect the focal points have on light rays leaving a lens. Students will
Science Objectives Students will explore the direction of light rays through concave and convex lenses. Students will determine the affect the focal points have on light rays leaving a lens. Students will
Algebra I Notes Unit Seven: Writing Linear Equations
 Sllabus Objective.6 The student will be able to write the equation of a linear function given two points, a point and the slope, table of values, or a graphical representation. Slope-Intercept Form of
Sllabus Objective.6 The student will be able to write the equation of a linear function given two points, a point and the slope, table of values, or a graphical representation. Slope-Intercept Form of
Determine the intercepts of the line and ellipse below: Definition: An intercept is a point of a graph on an axis. Line: x intercept(s)
 Topic 1 1 Intercepts and Lines Definition: An intercept is a point of a graph on an axis. For an equation Involving ordered pairs (x, y): x intercepts (a, 0) y intercepts (0, b) where a and b are real
Topic 1 1 Intercepts and Lines Definition: An intercept is a point of a graph on an axis. For an equation Involving ordered pairs (x, y): x intercepts (a, 0) y intercepts (0, b) where a and b are real
Lesson 4.6 Best Fit Line
 Lesson 4.6 Best Fit Line Concept: Using & Interpreting Best Fit Lines EQs: -How do we determine a line of best fit from a scatter plot? (S.ID.6 a,c) -What does the slope and intercept tell me about the
Lesson 4.6 Best Fit Line Concept: Using & Interpreting Best Fit Lines EQs: -How do we determine a line of best fit from a scatter plot? (S.ID.6 a,c) -What does the slope and intercept tell me about the
Algebra 1B. Chapter 6: Linear Equations & Their Graphs Sections 6-1 through 6-7 & 7-5. COLYER Fall Name: Period:
 Chapter 6: Linear Equations & Their Graphs Sections 6-1 through 6-7 & 7-5 COLYER Fall 2016 Name: Period: What s the Big Idea? Analyzing Linear Equations & Inequalities What can I expect to understand when
Chapter 6: Linear Equations & Their Graphs Sections 6-1 through 6-7 & 7-5 COLYER Fall 2016 Name: Period: What s the Big Idea? Analyzing Linear Equations & Inequalities What can I expect to understand when
Contents Systems of Linear Equations and Determinants
 Contents 6. Systems of Linear Equations and Determinants 2 Example 6.9................................. 2 Example 6.10................................ 3 6.5 Determinants................................
Contents 6. Systems of Linear Equations and Determinants 2 Example 6.9................................. 2 Example 6.10................................ 3 6.5 Determinants................................
Sect Linear Equations in Two Variables
 99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
Absolute Value of Linear Functions
 Lesson Plan Lecture Version Absolute Value of Linear Functions Objectives: Students will: Discover how absolute value affects linear functions. Prerequisite Knowledge Students are able to: Graph linear
Lesson Plan Lecture Version Absolute Value of Linear Functions Objectives: Students will: Discover how absolute value affects linear functions. Prerequisite Knowledge Students are able to: Graph linear
Name: Date: Period: Activity 4.6.2: Point-Slope Form of an Equation. 0, 4 and moving to another point on the line using the slope.
 Name: Date: Period: Activity.6.2: Point-Slope Form of an Equation 1.) Graph the equation y x = + starting at ( ) 0, and moving to another point on the line using the slope. 2.) Now, draw another graph
Name: Date: Period: Activity.6.2: Point-Slope Form of an Equation 1.) Graph the equation y x = + starting at ( ) 0, and moving to another point on the line using the slope. 2.) Now, draw another graph
Slope-Intercept Form of a Line
 Lesson Plan Lecture Edition Slope-Intercept Form of a Line Objectives Students will: discover how slope effects the graph of a line. relate b to the y-intercept of a line. determine the equation of a line
Lesson Plan Lecture Edition Slope-Intercept Form of a Line Objectives Students will: discover how slope effects the graph of a line. relate b to the y-intercept of a line. determine the equation of a line
Investigating Intercepts
 Unit: 0 Lesson: 01 1. Can more than one line have the same slope? If more than one line has the same slope, what makes the lines different? a. Graph the following set of equations on the same set of aes.
Unit: 0 Lesson: 01 1. Can more than one line have the same slope? If more than one line has the same slope, what makes the lines different? a. Graph the following set of equations on the same set of aes.
Student Exploration: Standard Form of a Line
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Standard Form of a Line Vocabulary: slope, slope-intercept form, standard form, x-intercept, y-intercept Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1.
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Standard Form of a Line Vocabulary: slope, slope-intercept form, standard form, x-intercept, y-intercept Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1.
Mathematics of Doodles
 Mathematics of Doodles Cube Fellow: Skyler Speakman Kinser Teacher Mentor: Gina Goal: Use creative and easy to construct drawings to explain properties of lines such as slope, y-intercept, and their interactions.
Mathematics of Doodles Cube Fellow: Skyler Speakman Kinser Teacher Mentor: Gina Goal: Use creative and easy to construct drawings to explain properties of lines such as slope, y-intercept, and their interactions.
Algebra Success. LESSON 16: Graphing Lines in Standard Form. [OBJECTIVE] The student will graph lines described by equations in standard form.
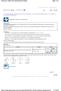
![Algebra Success. LESSON 16: Graphing Lines in Standard Form. [OBJECTIVE] The student will graph lines described by equations in standard form. Algebra Success. LESSON 16: Graphing Lines in Standard Form. [OBJECTIVE] The student will graph lines described by equations in standard form.](/thumbs/93/113878239.jpg) T328 [OBJECTIVE] The student will graph lines described by equations in standard form. [MATERIALS] Student pages S125 S133 Transparencies T336, T338, T340, T342, T344 Wall-size four-quadrant grid [ESSENTIAL
T328 [OBJECTIVE] The student will graph lines described by equations in standard form. [MATERIALS] Student pages S125 S133 Transparencies T336, T338, T340, T342, T344 Wall-size four-quadrant grid [ESSENTIAL
Analytic Geometry ةيليلحتلا ةسدنھلا
 Analytic Geometry الھندسة التحليلية نظام اإلحداثيات الديكارتي 1-1 Cartesian Coordinate System The Cartesian coordinate system, or the rectangular coordinate system, is a geometrical system that is used
Analytic Geometry الھندسة التحليلية نظام اإلحداثيات الديكارتي 1-1 Cartesian Coordinate System The Cartesian coordinate system, or the rectangular coordinate system, is a geometrical system that is used
Analytic Geometry. The x and y axes divide the Cartesian plane into four regions called quadrants.
 Analytic Geometry الھندسة التحليلية نظام اإلحداثيات الديكارتي 1-1 Cartesian Coordinate System The Cartesian coordinate system, or the rectangular coordinate system, is a geometrical system that is used
Analytic Geometry الھندسة التحليلية نظام اإلحداثيات الديكارتي 1-1 Cartesian Coordinate System The Cartesian coordinate system, or the rectangular coordinate system, is a geometrical system that is used
Ch. 6 Linear Functions Notes
 First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. 6 Linear Functions Notes 6.1 SLOPE OF A LINE Ch. 6.1 HW: p. 9 #4 1, 17,,, 8 6. SLOPES OF PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES 6 Ch. 6. HW: p. 49 # 6 odd letters, 7 0 8 6.
First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. 6 Linear Functions Notes 6.1 SLOPE OF A LINE Ch. 6.1 HW: p. 9 #4 1, 17,,, 8 6. SLOPES OF PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES 6 Ch. 6. HW: p. 49 # 6 odd letters, 7 0 8 6.
Math 152 Rodriguez Blitzer 2.5 The Point-Slope Form of the Equation of a Line
 Math 152 Rodriguez Blitzer 2.5 The Point-Slope Form of the Equation of a Line I. Point-Slope Form A. Linear equations we have seen so far: 1. standard form: Ax +By=C A, B, and C real numbers 2. slope-intercept
Math 152 Rodriguez Blitzer 2.5 The Point-Slope Form of the Equation of a Line I. Point-Slope Form A. Linear equations we have seen so far: 1. standard form: Ax +By=C A, B, and C real numbers 2. slope-intercept
t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: y = mx + b
 CH PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES INTRODUCTION I t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: mx + b SLOPE -INTERCEPT To be precise, b is not the -intercept; b is the -coordinate of the -intercept.
CH PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES INTRODUCTION I t s time we revisit our friend, the equation of a line: mx + b SLOPE -INTERCEPT To be precise, b is not the -intercept; b is the -coordinate of the -intercept.
Angles formed by Transversals
 Section 3-1: Parallel Lines and Transversals SOL: None Objectives: Identify the relationships between two lines or two planes Name angles formed by a pair of lines and a transversal Vocabulary: Parallel
Section 3-1: Parallel Lines and Transversals SOL: None Objectives: Identify the relationships between two lines or two planes Name angles formed by a pair of lines and a transversal Vocabulary: Parallel
Lesson 7 Slope-Intercept Formula
 Lesson 7 Slope-Intercept Formula Terms Two new words that describe what we've been doing in graphing lines are slope and intercept. The slope is referred to as "m" (a mountain has slope and starts with
Lesson 7 Slope-Intercept Formula Terms Two new words that describe what we've been doing in graphing lines are slope and intercept. The slope is referred to as "m" (a mountain has slope and starts with
A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
 The Slope of a Line (2.2) Find the slope of a line given two points on the line (Objective #1) A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
The Slope of a Line (2.2) Find the slope of a line given two points on the line (Objective #1) A slope of a line is the ratio between the change in a vertical distance (rise) to the change in a horizontal
Plotting Points in 2-dimensions. Graphing 2 variable equations. Stuff About Lines
 Plotting Points in 2-dimensions Graphing 2 variable equations Stuff About Lines Plotting Points in 2-dimensions Plotting Points: 2-dimension Setup of the Cartesian Coordinate System: Draw 2 number lines:
Plotting Points in 2-dimensions Graphing 2 variable equations Stuff About Lines Plotting Points in 2-dimensions Plotting Points: 2-dimension Setup of the Cartesian Coordinate System: Draw 2 number lines:
Section 1.3. Slope formula: If the coordinates of two points on the line are known then we can use the slope formula to find the slope of the line.
 MATH 11009: Linear Functions Section 1.3 Linear Function: A linear function is a function that can be written in the form f(x) = ax + b or y = ax + b where a and b are constants. The graph of a linear
MATH 11009: Linear Functions Section 1.3 Linear Function: A linear function is a function that can be written in the form f(x) = ax + b or y = ax + b where a and b are constants. The graph of a linear
Name: Date: Per: A# c. Trace a copy of e and place it over g. What do you observe?
 Name: Date: Per: A# In a previous course you probably learned the vocabulary and considered the relationships created by two intersecting lines. Now you will look at the vocabulary and relationships created
Name: Date: Per: A# In a previous course you probably learned the vocabulary and considered the relationships created by two intersecting lines. Now you will look at the vocabulary and relationships created
TImath.com. Geometry. Angle Relationships
 Angle Relationships ID: 8670 Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore the angle relationships that exist when two lines intersect. They begin by exploring vertical
Angle Relationships ID: 8670 Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore the angle relationships that exist when two lines intersect. They begin by exploring vertical
Review Journal 6 Assigned Work: Page 146, All questions
 MFM2P Linear Relations Checklist 1 Goals for this unit: I can explain the properties of slope and calculate its value as a rate of change. I can determine y-intercepts and slopes of given relations. I
MFM2P Linear Relations Checklist 1 Goals for this unit: I can explain the properties of slope and calculate its value as a rate of change. I can determine y-intercepts and slopes of given relations. I
10 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS
 0 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS We now expand our discussion of the single-variable equation to the linear equation in two variables, x and y. Some examples of linear equations are x+ y = 0, y = 3 x, x= 4,
0 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS We now expand our discussion of the single-variable equation to the linear equation in two variables, x and y. Some examples of linear equations are x+ y = 0, y = 3 x, x= 4,
Lesson 16: The Computation of the Slope of a Non Vertical Line
 ++ Lesson 16: The Computation of the Slope of a Non Vertical Line Student Outcomes Students use similar triangles to explain why the slope is the same between any two distinct points on a non vertical
++ Lesson 16: The Computation of the Slope of a Non Vertical Line Student Outcomes Students use similar triangles to explain why the slope is the same between any two distinct points on a non vertical
Lesson 10.1 Skills Practice
 Lesson 10.1 Skills Practice Location, Location, Location! Line Relationships Vocabulary Write the term or terms from the box that best complete each statement. intersecting lines perpendicular lines parallel
Lesson 10.1 Skills Practice Location, Location, Location! Line Relationships Vocabulary Write the term or terms from the box that best complete each statement. intersecting lines perpendicular lines parallel
In this section, we find equations for straight lines lying in a coordinate plane.
 2.4 Lines Lines In this section, we find equations for straight lines lying in a coordinate plane. The equations will depend on how the line is inclined. So, we begin by discussing the concept of slope.
2.4 Lines Lines In this section, we find equations for straight lines lying in a coordinate plane. The equations will depend on how the line is inclined. So, we begin by discussing the concept of slope.
1. Graph y = 2x 3. SOLUTION: The slope-intercept form of a line is y = mx + b, where m is the slope, and b is the y-intercept.
 1. Graph y = 2x 3. The slope-intercept form of a line is y = mx + b, where m is the slope, and b is the y-intercept. Plot the y-intercept (0, 3). The slope is. From (0, 3), move up 2 units and right 1
1. Graph y = 2x 3. The slope-intercept form of a line is y = mx + b, where m is the slope, and b is the y-intercept. Plot the y-intercept (0, 3). The slope is. From (0, 3), move up 2 units and right 1
MATH 150 Pre-Calculus
 MATH 150 Pre-Calculus Fall, 2014, WEEK 5 JoungDong Kim Week 5: 3B, 3C Chapter 3B. Graphs of Equations Draw the graph x+y = 6. Then every point on the graph satisfies the equation x+y = 6. Note. The graph
MATH 150 Pre-Calculus Fall, 2014, WEEK 5 JoungDong Kim Week 5: 3B, 3C Chapter 3B. Graphs of Equations Draw the graph x+y = 6. Then every point on the graph satisfies the equation x+y = 6. Note. The graph
