Folding Activity 1. Colored paper Tape or glue stick
|
|
|
- Miranda Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Folding Activity 1 We ll do this first activity as a class, and I will model the steps with the document camera. Part 1 You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie Colored paper Tape or glue stick As you do the following, be careful not to smudge your work. For any step that includes the use of a Sharpie, wait about 30 seconds after marking before you do any folding. 1. With a ruler and a pencil, draw a straight line across the bottom of your wax paper, about a ruler s width above the bottom of an edge. 2. Fold the paper in half so that one end of the line you drew lands on top of the other end, and crease it in that position. 3. Using a pencil, draw a point on this crease no more than 3 cm above the line (try and use a different value for each member in your group). 4. Fold the paper so that one end of the line (not the crease) lands on the point. 5. Crease the paper along this fold. 6. Slide the line along just a little bit so that a different place on the line is over the point. 7. Crease again. 8. Keep sliding and folding the paper so that different places along the line land on the point. The closer together your creases are, the more refined your shape will be. 9. Keep doing this until you reach the other end of the line. 10. Unfold your wax paper. Do you see a definitive shape? 11. Carefully darken the outline of your shape with a Sharpie. You ve just drawn a parabola! 12. Label the point F, and label the line directrix. 13. Tape or glue the edges of your patty paper to a piece of colored paper. 14. Write The Parabola and your name at the top of the colored paper. This point is called the focus.
2 Folding Activity 2 Part 2 You ll need: Patty paper Protractor Sharpie Your colored paper Tape or glue stick 1. With a ruler and a pencil, trace the straight line and the point you made on your parabola layer. 2. Fold the paper so that the point lands somewhere on the line, but only once. Make sure your directrix lands on top of your focus. It should not be at either extreme end of the line or too near the middle. Aim to fold it about! or! of the way across the line from either!! end. Try to arrange it so that everyone in your group has their fold in a different place. 3. With your paper still folded, set a protractor down on your paper so that the 90 mark lines up with the directrix, and move it along the paper until its edge lines up with the focus F. 4. Using a pencil, draw a line segment on the back of your paper from the folded edge to the focus. Don t draw beyond the focus or the directrix. 5. Leave your paper folded, and flip it over. 6. Trace the line segment you drew in step 3 (you should still use a straightedge), on the other side of the back of the folded paper. 7. Unfold your paper, and draw a point where the two new line segments meet. 8. Label the new point T. This is called the point of tangency. 9. Draw a point where your perpendicular line meets the directrix. 10. Label this point D. 11. Using a Sharpie and a ruler, trace over the line segments FT and TD. 12. With the directrix and the focus F carefully aligned, tape or glue this copy only on one edge over the parabola on your colored paper.
3 Discovering the Parabola Parts 1 and 2 Name When you have finished making and labeling your Parabolas, answer the following questions. Each person should fill in their own answers, and your answers should match your individual parabola where appropriate, but work together to compare answers on your different parabolas before answering: a) Using your two-layer wax paper parabola, what do you observe about the distances between the points F and T and the points T and D? b) How could you explain your answer to part a) to someone who is not in this class? c) Compare your results from part a) to your other group members results. Answer for your group: Do all your answers have the same values? How are they the same or different (What are the values?) Do all your answers have any of the same properties? How are they the same or different (What are the properties that are the same?)
4 d) Compare your parabola to those of your group members, and compare your answers to parts a) through c) to your group members answers. Use what you learn to decide as a group what the definition of a parabola is. Answer for your group:
5 Folding Activity 3 Part 3 You ll need: Patty paper Protractor Sharpie Your colored paper Tape or glue stick 1. With a ruler and a pencil, trace the straight line and the point you made on your parabola layer. 2. Using a protractor, draw a line segment in pencil that goes from the focus to the directrix at 90 to the directrix. 3. Draw a line segment in pencil that goes through the focus at 90 to the line you drew in step Lay this copy on top of your finished parabola and carefully align the focus and the directrix, but don t tape it down yet. 5. Draw a point on the top layer where your vertical pencil line meets the parabola. 6. Label this point V. 7. Draw points on the parabola where your horizontal line meets the parabola. If your pencil line is not long enough, use a straightedge to extend it before you draw your points. Remember that this line should be at 90 to the line that goes from F to V. 8. Label these points A! and A!. 9. Darken the line segment from A! to A! with a Sharpie, but do not draw beyond the parabola. 10. Darken the line segment from F to V with a Sharpie, but do not draw beyond the parabola. 11. Measure the distance from V to F in cm and make a note of your measurement in the right column. 12. Measure the distance from A! to A! in cm and make a note of your measurement in the right column. 13. With the directrix and the focus F carefully aligned, tape or glue this copy only on one edge over the two previous layers on your colored paper. 11. VF = cm 12. A! A! = cm
6 Discovering the Parabola Part 3 Name When you have finished making your third layer, answer the following questions. Each person should fill in their own answers, and your answers should match your individual parabola where appropriate, but work together to compare answers on your different parabolas before answering: e) If the point V on your parabola were on the origin ((0,0) on a graph), what would be the coordinates of the following points? Use the measurements you wrote down in steps 11 and 12 on the previous page. F? A!? A!? f) Using what you know about graphing lines, your group s definition of a parabola, your answer from part a) and your measurements from steps 11 and 12 in part 3, find the equation of the line that is the directrix of your parabola from part 3. V (0,0) F(, ) A! (, ) A! (, ) g) What do you observe about the measurements of A! A! and FV? Note: the segment A! A! is called the latus rectum. h) Is this observation consistent across your team? (Do you all get approximately the same result from this comparison with potentially different measurements for your parabolas?) Answer for your group:
7 i) Using the coordinates of either point A! or A!, find the generalized formula (equation) for your parabola, and write it in the form y = ax!. Note that you are stull assuming that your parabola is sitting so that its vertex is at the point (0,0). j) Solve the equation in part i) for x! and divide the coefficient of the right hand side by 4, so that your equation looks like this: x! = 4cy Your final answer should have a 4 in it, as above, but your value for c may be different from those of your other group members. k) Compare your results to those of your group members. Each person should look at their answer to part j), and then look back at their answers to parts g) and h). Could you have written the equations for your parabolas without first having to write it as you did in part i)? l) Use your answers to these questions to decide as a group what the parabola looks like which has the equation x! = 20y. Accurately describe its features (vertex, latus rectum, directrix, focus) or draw a labeled sketch. Answer for your group: Answer for your group:
8 Folding Activity 4 Part 4 You ll need: Cartesian grid (see back page of this packet) Patty paper (1 piece) pencil 1. Label the axes of a Cartesian grid with values from 10 to 10 in both the x and y directions. x y 2. Lay a piece of wax paper over the grid. -4 2! 3. On the wax paper, not on the graph paper plot these points,à -2! and connect them to form the graph of a parabola: 0 0! 2! Determine the equation of this parabola in the form y = ax! 5. Determine the equation of the same parabola in the form x! = 4cy You did this for a different parabola in Discovering the Parabola Part 3, question j) 6. Hold out your left hand so that you re looking at the back of it, like this: Now rotate your hand so that you re looking at the palm, like this: 7. Pick up the wax paper, and with the same type of motion, flip and rotate it, and set it down on the same set of axes so that the parabola hugs the x-axis instead of the yaxis. 8. What is the relationship that this parabola has with the one you had before you flipped? The rotated parabola is the of the original one. 9. Find the equation of the rotated parabola in the same form as you did in question How are these two equations the same? How are they different? 11. Find the coordinates of the focus of this parabola. 12. Find the equation of its directrix
9 Discovering the Parabola Part 4 Name 13. Now that you know something about parabolas whose vertices are at the origin (the point (0,0)), discuss the following in your group to determine what the equation of a parabola would be if it were centered at a different point. m) If the equation of a parabola is x! = 4cy, what would the equation be of the parabola where c = 3? Answers for your group: n) What would the equation be of the same parabola if it were shifted over so that instead of having its center at the point (0,0), its center was at the point (1, 4)? Write this equation so that the shift in the x direction is on the same side of the equation as the variable x, and the shift in the y direction is on the same side of the equation as the variable y. o) Graph this parabola on one of the grids at the back of this packet, and label all of its features, including: i) Vertex ii) Coordinates of vertex iii) Equation of directrix iv) Latus rectum v) Coordinates of both endpoints of the latus rectum vi) Coordinates of the focus p) Using algebra, write the equation of this parabola in polynomial form (ax! + bx + cy + k = 0).
10 q) Rewrite the equation in the form y! 6y 8x 7 = 0 x h! = 4c y k or y k! = 4c x h. Now that it s in this form, how does this equation for a parabola compare to the one in question n)? What has changed in the equation? How do you think this will manifest in the graph of this parabola? r) On another grid at the back of this packet, graph the parabola from part q). Add this page to your Conics portfolio
11
12
Folding Activity 3. Compass Colored paper Tape or glue stick
 Folding Activity 3 Part 1 You re not done until everyone in your group is done! If you finish before someone else, help them finish before starting on the next part. You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie
Folding Activity 3 Part 1 You re not done until everyone in your group is done! If you finish before someone else, help them finish before starting on the next part. You ll need: Patty paper Ruler Sharpie
2.3: The Human Cannonball
 2.3: The Human Cannonball Parabola Equations and Graphs As a human cannonball Rosa is shot from a special cannon. She is launched into the air by a spring. Rosa lands in a horizontal net 150 ft. from the
2.3: The Human Cannonball Parabola Equations and Graphs As a human cannonball Rosa is shot from a special cannon. She is launched into the air by a spring. Rosa lands in a horizontal net 150 ft. from the
UNIT 1 SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS Lesson 2: Constructing Lines, Segments, and Angles Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: using a compass understanding the geometry terms line, segment, ray, and angle Introduction Two basic instruments used in geometry
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: using a compass understanding the geometry terms line, segment, ray, and angle Introduction Two basic instruments used in geometry
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Pre-Calc Conics
 Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160 Pre-Calc Conics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 160 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections
Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160 Pre-Calc Conics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 160 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections
Pre-Calc. Slide 1 / 160. Slide 2 / 160. Slide 3 / 160. Conics Table of Contents. Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas
 Slide 1 / 160 Pre-Calc Slide 2 / 160 Conics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 160 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections
Slide 1 / 160 Pre-Calc Slide 2 / 160 Conics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 160 Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections
This early Greek study was largely concerned with the geometric properties of conics.
 4.3. Conics Objectives Recognize the four basic conics: circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. Recognize, graph, and write equations of parabolas (vertex at origin). Recognize, graph, and write equations
4.3. Conics Objectives Recognize the four basic conics: circle, ellipse, parabola, and hyperbola. Recognize, graph, and write equations of parabolas (vertex at origin). Recognize, graph, and write equations
Learn to use translations, reflections, and rotations to transform geometric shapes.
 Learn to use translations, reflections, and rotations to transform geometric shapes. Insert Lesson Title Here Vocabulary transformation translation rotation reflection line of reflection A rigid transformation
Learn to use translations, reflections, and rotations to transform geometric shapes. Insert Lesson Title Here Vocabulary transformation translation rotation reflection line of reflection A rigid transformation
Angles and. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
Student Exploration: Quadratics in Factored Form
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Quadratics in Factored Form Vocabulary: factored form of a quadratic function, linear factor, parabola, polynomial, quadratic function, root of an equation, vertex of a
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Quadratics in Factored Form Vocabulary: factored form of a quadratic function, linear factor, parabola, polynomial, quadratic function, root of an equation, vertex of a
The Folded Rectangle Construction
 The Folded Rectangle Construction Name(s): With nothing more than a sheet of paper and a single point on the page, you can create a parabola. No rulers and no measuring required! Constructing a Physical
The Folded Rectangle Construction Name(s): With nothing more than a sheet of paper and a single point on the page, you can create a parabola. No rulers and no measuring required! Constructing a Physical
4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 What You Will Learn Determine the slope of a line through two points Write linear equations in slope-intercept
4.4 Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 1 What You Will Learn Determine the slope of a line through two points Write linear equations in slope-intercept
Pre Calc. Conics.
 1 Pre Calc Conics 2015 03 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections Parabolas Circles Ellipses Hyperbolas
1 Pre Calc Conics 2015 03 24 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and Distance Formulas Intro to Conic Sections Parabolas Circles Ellipses Hyperbolas
The Geometric Definitions for Circles and Ellipses
 18 Conic Sections Concepts: The Origin of Conic Sections Equations and Graphs of Circles and Ellipses The Geometric Definitions for Circles and Ellipses (Sections 10.1-10.3) A conic section or conic is
18 Conic Sections Concepts: The Origin of Conic Sections Equations and Graphs of Circles and Ellipses The Geometric Definitions for Circles and Ellipses (Sections 10.1-10.3) A conic section or conic is
1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Homework 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw. c.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Homework 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw. c.
We are going to begin a study of beadwork. You will be able to create beadwork on the computer using the culturally situated design tools.
 Bead Loom Questions We are going to begin a study of beadwork. You will be able to create beadwork on the computer using the culturally situated design tools. Read the first page and then click on continue
Bead Loom Questions We are going to begin a study of beadwork. You will be able to create beadwork on the computer using the culturally situated design tools. Read the first page and then click on continue
Graphs of linear equations will be perfectly straight lines. Why would we say that A and B are not both zero?
 College algebra Linear Functions : Definition, Horizontal and Vertical Lines, Slope, Rate of Change, Slopeintercept Form, Point-slope Form, Parallel and Perpendicular Lines, Linear Regression (sections.3
College algebra Linear Functions : Definition, Horizontal and Vertical Lines, Slope, Rate of Change, Slopeintercept Form, Point-slope Form, Parallel and Perpendicular Lines, Linear Regression (sections.3
A A B B C C D D. NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation
 NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation Name # For this investigation, you will work with a partner. You and your partner should take turns practicing the rotations with the stencil. You and your partner
NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation Name # For this investigation, you will work with a partner. You and your partner should take turns practicing the rotations with the stencil. You and your partner
You identified, analyzed, and graphed quadratic functions. (Lesson 1 5) Analyze and graph equations of parabolas. Write equations of parabolas.
 You identified, analyzed, and graphed quadratic functions. (Lesson 1 5) Analyze and graph equations of parabolas. Write equations of parabolas. conic section degenerate conic locus parabola focus directrix
You identified, analyzed, and graphed quadratic functions. (Lesson 1 5) Analyze and graph equations of parabolas. Write equations of parabolas. conic section degenerate conic locus parabola focus directrix
(3,4) focus. y=1 directrix
 Math 153 10.5: Conic Sections Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas Parabolas: Definition: A parabola is the set of all points in a plane such that its distance from a fixed point F (called the focus) is equal
Math 153 10.5: Conic Sections Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas Parabolas: Definition: A parabola is the set of all points in a plane such that its distance from a fixed point F (called the focus) is equal
HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934)
 HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934) Presented by Shelley Kriegler President, Center for Mathematics and Teaching shelley@mathandteaching.org Fall 2014 8.F.1 8.G.1a
HANDS-ON TRANSFORMATIONS: RIGID MOTIONS AND CONGRUENCE (Poll Code 39934) Presented by Shelley Kriegler President, Center for Mathematics and Teaching shelley@mathandteaching.org Fall 2014 8.F.1 8.G.1a
Cartesian Coordinate System. Student Instruction S-23
 QuickView Design a 6 x 6 grid based on the Cartesian coordinates. Roll two dice to determine the coordinate points on the grid for a specific quadrant. Use the T-Bot II to place a foam block onto the rolled
QuickView Design a 6 x 6 grid based on the Cartesian coordinates. Roll two dice to determine the coordinate points on the grid for a specific quadrant. Use the T-Bot II to place a foam block onto the rolled
Table of Contents Problem Solving with the Coordinate Plane
 GRADE 5 UNIT 6 Table of Contents Problem Solving with the Coordinate Plane Lessons Topic 1: Coordinate Systems 1-6 Lesson 1: Construct a coordinate system on a line. Lesson 2: Construct a coordinate system
GRADE 5 UNIT 6 Table of Contents Problem Solving with the Coordinate Plane Lessons Topic 1: Coordinate Systems 1-6 Lesson 1: Construct a coordinate system on a line. Lesson 2: Construct a coordinate system
Unit 4, Activity 1, Vocabulary Self-Awareness
 Unit 4, Activity 1, Vocabulary Self-Awareness Word/Phrase + Definition/Rule Example rigid (rigid motion) non-rigid (non-rigid motion) orientation isometry reflection line of reflection translation rotation
Unit 4, Activity 1, Vocabulary Self-Awareness Word/Phrase + Definition/Rule Example rigid (rigid motion) non-rigid (non-rigid motion) orientation isometry reflection line of reflection translation rotation
The Ellipse. PF 1 + PF 2 = constant. Minor Axis. Major Axis. Focus 1 Focus 2. Point 3.4.2
 Minor Axis The Ellipse An ellipse is the locus of all points in a plane such that the sum of the distances from two given points in the plane, the foci, is constant. Focus 1 Focus 2 Major Axis Point PF
Minor Axis The Ellipse An ellipse is the locus of all points in a plane such that the sum of the distances from two given points in the plane, the foci, is constant. Focus 1 Focus 2 Major Axis Point PF
Chapter 4: The Ellipse
 Chapter 4: The Ellipse SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 4: The Ellipse Lecture 1: Introduction to Ellipse Lecture 13: Converting
Chapter 4: The Ellipse SSMth1: Precalculus Science and Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Mr. Migo M. Mendoza Chapter 4: The Ellipse Lecture 1: Introduction to Ellipse Lecture 13: Converting
Problem Solving with the Coordinate Plane
 Grade 5 Module 6 Problem Solving with the Coordinate Plane OVERVIEW In this 40-day module, students develop a coordinate system for the first quadrant of the coordinate plane and use it to solve problems.
Grade 5 Module 6 Problem Solving with the Coordinate Plane OVERVIEW In this 40-day module, students develop a coordinate system for the first quadrant of the coordinate plane and use it to solve problems.
1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Problem Set 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Problem Set 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: and. b. Use a straightedge to draw.
Pre-Calc. Midpoint and Distance Formula. Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160. Slide 4 / 160. Slide 3 / 160. Slide 5 / 160. Slide 6 / 160.
 Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160 Pre-alc onics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 160 Slide 4 / 160 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas Intro to
Slide 1 / 160 Slide 2 / 160 Pre-alc onics 2015-03-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 160 Slide 4 / 160 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Review of Midpoint and istance Formulas Intro to
G 1 3 G13 BREAKING A STICK #1. Capsule Lesson Summary
 G13 BREAKING A STICK #1 G 1 3 Capsule Lesson Summary Given two line segments, construct as many essentially different triangles as possible with each side the same length as one of the line segments. Discover
G13 BREAKING A STICK #1 G 1 3 Capsule Lesson Summary Given two line segments, construct as many essentially different triangles as possible with each side the same length as one of the line segments. Discover
7.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing
 Math 2201 Date: 7.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing In Mathematics 1201, students factored difference of squares, perfect square trinomials and polynomials of the form x 2 + bx + c and ax 2 + bx
Math 2201 Date: 7.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing In Mathematics 1201, students factored difference of squares, perfect square trinomials and polynomials of the form x 2 + bx + c and ax 2 + bx
Hyperbolas Graphs, Equations, and Key Characteristics of Hyperbolas Forms of Hyperbolas p. 583
 C H A P T ER Hyperbolas Flashlights concentrate beams of light by bouncing the rays from a light source off a reflector. The cross-section of a reflector can be described as hyperbola with the light source
C H A P T ER Hyperbolas Flashlights concentrate beams of light by bouncing the rays from a light source off a reflector. The cross-section of a reflector can be described as hyperbola with the light source
PART I: Emmett s teacher asked him to analyze the table of values of a quadratic function to find key features. The table of values is shown below:
 Math (L-3a) Learning Targets: I can find the vertex from intercept solutions calculated by quadratic formula. PART I: Emmett s teacher asked him to analyze the table of values of a quadratic function to
Math (L-3a) Learning Targets: I can find the vertex from intercept solutions calculated by quadratic formula. PART I: Emmett s teacher asked him to analyze the table of values of a quadratic function to
Constructing Perpendicular and Parallel Lines. Adapted from Walch Education
 Constructing Perpendicular and Adapted from Walch Education Perpendicular Lines and Bisectors Perpendicular lines are two lines that intersect at a right angle (90 ). A perpendicular line can be constructed
Constructing Perpendicular and Adapted from Walch Education Perpendicular Lines and Bisectors Perpendicular lines are two lines that intersect at a right angle (90 ). A perpendicular line can be constructed
Unit 6 Task 2: The Focus is the Foci: ELLIPSES
 Unit 6 Task 2: The Focus is the Foci: ELLIPSES Name: Date: Period: Ellipses and their Foci The first type of quadratic relation we want to discuss is an ellipse. In terms of its conic definition, you can
Unit 6 Task 2: The Focus is the Foci: ELLIPSES Name: Date: Period: Ellipses and their Foci The first type of quadratic relation we want to discuss is an ellipse. In terms of its conic definition, you can
CONSTRUCTION #1: Segment Copy
 CONSTRUCTION #1: Segment Copy Objective: Given a line segment, construct a line segment congruent to the given one. Procedure: After doing this Your work should look like this Start with a line segment
CONSTRUCTION #1: Segment Copy Objective: Given a line segment, construct a line segment congruent to the given one. Procedure: After doing this Your work should look like this Start with a line segment
Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review
 Name: Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review Vocabulary Equation: a math sentence that contains Linear: makes a straight line (no Variables: quantities represented by (often x and y) Function: equations can
Name: Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review Vocabulary Equation: a math sentence that contains Linear: makes a straight line (no Variables: quantities represented by (often x and y) Function: equations can
Math Labs. Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates. Procedure
 Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
Math Labs Activity 1: Rectangles and Rectangular Prisms Using Coordinates Problem Statement Use the Cartesian coordinate system to draw rectangle ABCD. Use an x-y-z coordinate system to draw a rectangular
VOCABULARY WORDS. quadratic equation root(s) of an equation zero(s) of a function extraneous root quadratic formula discriminant
 VOCABULARY WORDS quadratic equation root(s) of an equation zero(s) of a function extraneous root quadratic formula discriminant 1. Each water fountain jet creates a parabolic stream of water. You can represent
VOCABULARY WORDS quadratic equation root(s) of an equation zero(s) of a function extraneous root quadratic formula discriminant 1. Each water fountain jet creates a parabolic stream of water. You can represent
Patterns and Graphing Year 10
 Patterns and Graphing Year 10 While students may be shown various different types of patterns in the classroom, they will be tested on simple ones, with each term of the pattern an equal difference from
Patterns and Graphing Year 10 While students may be shown various different types of patterns in the classroom, they will be tested on simple ones, with each term of the pattern an equal difference from
Objective: Use the addition of adjacent angle measures to solve problems using a symbol for the unknown angle measure.
 Lesson 10 Objective: Use the addition of adjacent angle measures to solve problems using a Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time
Lesson 10 Objective: Use the addition of adjacent angle measures to solve problems using a Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time
Name: Class: Date: Around the Web
 Around the Web Directions: Plot the coordinate points in order. Connect the points with a straight line using a straightedge or a ruler. Draw the lines as you plot each point. (0, 15) (3, 13) (7, 11) (10,
Around the Web Directions: Plot the coordinate points in order. Connect the points with a straight line using a straightedge or a ruler. Draw the lines as you plot each point. (0, 15) (3, 13) (7, 11) (10,
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Discussion 8 Solution Thursday, February 10th. Consider the function f(x, y) := y 2 x 2.
 Discussion 8 Solution Thursday, February 10th. 1. Consider the function f(x, y) := y 2 x 2. (a) This function is a mapping from R n to R m. Determine the values of n and m. The value of n is 2 corresponding
Discussion 8 Solution Thursday, February 10th. 1. Consider the function f(x, y) := y 2 x 2. (a) This function is a mapping from R n to R m. Determine the values of n and m. The value of n is 2 corresponding
SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation)
 SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation) Factor the following quadratic expressions: x 2 + 11x + 30 x 2 10x 24 x 2 8x + 15 Standard Form Quadratic Equation (x + 5)(x + 6) (x 12)(x + 2) (x 5)(x
SM3 Lesson 2-3 (Intercept Form Quadratic Equation) Factor the following quadratic expressions: x 2 + 11x + 30 x 2 10x 24 x 2 8x + 15 Standard Form Quadratic Equation (x + 5)(x + 6) (x 12)(x + 2) (x 5)(x
Extra Practice 1. Name Date. Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines. 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d)
 Master 8.24 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d) 2. Look at the diagram below. Find as many pairs of parallel line segments as you
Master 8.24 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 8.1: Parallel Lines 1. Which line segments are parallel? How do you know? a) b) c) d) 2. Look at the diagram below. Find as many pairs of parallel line segments as you
6. True or false? Shapes that have no right angles also have no perpendicular segments. Draw some figures to help explain your thinking.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 3 Homework 4 4 5. Use your right angle template as a guide and mark each right angle in the following figure with a small square. (Note that a right angle
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 3 Homework 4 4 5. Use your right angle template as a guide and mark each right angle in the following figure with a small square. (Note that a right angle
Algebraic Analysis of Huzita s Origami
 1 / 19 Algebraic Analysis of Huzita s Origami Origami Operations and their Extensions Fadoua Ghourabi, Asem Kasem, Cezary Kaliszyk University of Tsukuba, Japan. Yarmouk Private University, Syria University
1 / 19 Algebraic Analysis of Huzita s Origami Origami Operations and their Extensions Fadoua Ghourabi, Asem Kasem, Cezary Kaliszyk University of Tsukuba, Japan. Yarmouk Private University, Syria University
ACT Coordinate Geometry Review
 ACT Coordinate Geometry Review Here is a brief review of the coordinate geometry concepts tested on the ACT. Note: there is no review of how to graph an equation on this worksheet. Questions testing this
ACT Coordinate Geometry Review Here is a brief review of the coordinate geometry concepts tested on the ACT. Note: there is no review of how to graph an equation on this worksheet. Questions testing this
Principles of Technology DUE one week from your lab day. Lab 2: Measuring Forces
 Lab 2: Measuring Forces Principles of Technology DUE one week from your lab day Lab Objectives When you ve finished this lab, you should be able to do the following: Measure forces by using appropriate
Lab 2: Measuring Forces Principles of Technology DUE one week from your lab day Lab Objectives When you ve finished this lab, you should be able to do the following: Measure forces by using appropriate
Conic and Quadric Surface Lab page 4. NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Department of Mathematics Fall 03 Conic Sections and Quadratic Surface Lab
 Conic and Quadric Surface Lab page 4 NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Department of Mathematics Fall 03 Conic Sections and Quadratic Surface Lab Goals By the end of this lab you should: 1.) Be familar with the
Conic and Quadric Surface Lab page 4 NORTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY Department of Mathematics Fall 03 Conic Sections and Quadratic Surface Lab Goals By the end of this lab you should: 1.) Be familar with the
Lesson 10. Unit 2. Reading Maps. Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane
 Lesson Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane Reading Maps In the middle ages a system was developed to find the location of specific places on the Earth s surface. The system is a grid that covers the
Lesson Graphing Points on the Coordinate Plane Reading Maps In the middle ages a system was developed to find the location of specific places on the Earth s surface. The system is a grid that covers the
Wing. Gently bend the top of the wing over. With the paper removed, it should produce a nice curve.
 Fuselage Remove the paper in the four areas shown. Basically, from the trailing edge of the canard forward in the three nose segments and on the rear bottom of the fuse. Normal B fold for the sides but
Fuselage Remove the paper in the four areas shown. Basically, from the trailing edge of the canard forward in the three nose segments and on the rear bottom of the fuse. Normal B fold for the sides but
2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations
 2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations Algebra III Mr. Niedert Algebra III 2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations Mr. Niedert 1 / 11 Forms of a Line Slope-Intercept Form The slope-intercept form of a linear
2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations Algebra III Mr. Niedert Algebra III 2.3 Quick Graphs of Linear Equations Mr. Niedert 1 / 11 Forms of a Line Slope-Intercept Form The slope-intercept form of a linear
Section 1.3. Slope formula: If the coordinates of two points on the line are known then we can use the slope formula to find the slope of the line.
 MATH 11009: Linear Functions Section 1.3 Linear Function: A linear function is a function that can be written in the form f(x) = ax + b or y = ax + b where a and b are constants. The graph of a linear
MATH 11009: Linear Functions Section 1.3 Linear Function: A linear function is a function that can be written in the form f(x) = ax + b or y = ax + b where a and b are constants. The graph of a linear
Appendix C: Graphing. How do I plot data and uncertainties? Another technique that makes data analysis easier is to record all your data in a table.
 Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Chapter 9. Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry. 9.1 The Ellipse. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Graph ellipses centered at the origin. Write equations of ellipses in standard
Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.1 The Ellipse Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Graph ellipses centered at the origin. Write equations of ellipses in standard
Engineering Graphics, Class 5 Geometric Construction. Mohammad I. Kilani. Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan
 Engineering Graphics, Class 5 Geometric Construction Mohammad I. Kilani Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan Conic Sections A cone is generated by a straight line moving in contact with
Engineering Graphics, Class 5 Geometric Construction Mohammad I. Kilani Mechanical Engineering Department University of Jordan Conic Sections A cone is generated by a straight line moving in contact with
2.3 BUILDING THE PERFECT SQUARE
 16 2.3 BUILDING THE PERFECT SQUARE A Develop Understanding Task Quadratic)Quilts Optimahasaquiltshopwhereshesellsmanycolorfulquiltblocksforpeoplewhowant tomaketheirownquilts.shehasquiltdesignsthataremadesothattheycanbesized
16 2.3 BUILDING THE PERFECT SQUARE A Develop Understanding Task Quadratic)Quilts Optimahasaquiltshopwhereshesellsmanycolorfulquiltblocksforpeoplewhowant tomaketheirownquilts.shehasquiltdesignsthataremadesothattheycanbesized
10 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS
 0 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS We now expand our discussion of the single-variable equation to the linear equation in two variables, x and y. Some examples of linear equations are x+ y = 0, y = 3 x, x= 4,
0 GRAPHING LINEAR EQUATIONS We now expand our discussion of the single-variable equation to the linear equation in two variables, x and y. Some examples of linear equations are x+ y = 0, y = 3 x, x= 4,
*Unit 1 Constructions and Transformations
 *Unit 1 Constructions and Transformations Content Area: Mathematics Course(s): Geometry CP, Geometry Honors Time Period: September Length: 10 blocks Status: Published Transfer Skills Previous coursework:
*Unit 1 Constructions and Transformations Content Area: Mathematics Course(s): Geometry CP, Geometry Honors Time Period: September Length: 10 blocks Status: Published Transfer Skills Previous coursework:
Objective: Investigate patterns in vertical and horizontal lines, and. interpret points on the plane as distances from the axes.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 5 6 Lesson 6 Objective: Investigate patterns in vertical and horizontal lines, and Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 5 6 Lesson 6 Objective: Investigate patterns in vertical and horizontal lines, and Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
 1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Strand Measurement and Geometry Overall Expectations MGV.02: solve problems involving the measurements of two-dimensional shapes and the volumes of three-dimensional figures;
1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Strand Measurement and Geometry Overall Expectations MGV.02: solve problems involving the measurements of two-dimensional shapes and the volumes of three-dimensional figures;
UNIT I PLANE CURVES AND FREE HAND SKETCHING CONIC SECTIONS
 UNIT I PLANE CURVES AND FREE HAND SKETCHING CONIC SECTIONS Definition: The sections obtained by the intersection of a right circular cone by a cutting plane in different positions are called conic sections
UNIT I PLANE CURVES AND FREE HAND SKETCHING CONIC SECTIONS Definition: The sections obtained by the intersection of a right circular cone by a cutting plane in different positions are called conic sections
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
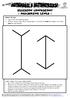 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
6.1 Slope of a Line Name: Date: Goal: Determine the slope of a line segment and a line.
 6.1 Slope of a Line Name: Date: Goal: Determine the slope of a line segment and a line. Toolkit: - Rate of change - Simplifying fractions Main Ideas: Definitions Rise: the vertical distance between two
6.1 Slope of a Line Name: Date: Goal: Determine the slope of a line segment and a line. Toolkit: - Rate of change - Simplifying fractions Main Ideas: Definitions Rise: the vertical distance between two
Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 4 Lesson 6 Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 6 4 Lesson 6 Objective: Use varied protractors to distinguish angle measure from length Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept
Graphs. This tutorial will cover the curves of graphs that you are likely to encounter in physics and chemistry.
 Graphs Graphs are made by graphing one variable which is allowed to change value and a second variable that changes in response to the first. The variable that is allowed to change is called the independent
Graphs Graphs are made by graphing one variable which is allowed to change value and a second variable that changes in response to the first. The variable that is allowed to change is called the independent
Geometer s Sketchpad Version 4
 Geometer s Sketchpad Version 4 For PC Name: Date: INVESTIGATION: The Pythagorean Theorem Directions: Use the steps below to lead you through the investigation. After each step, be sure to click in the
Geometer s Sketchpad Version 4 For PC Name: Date: INVESTIGATION: The Pythagorean Theorem Directions: Use the steps below to lead you through the investigation. After each step, be sure to click in the
Warmup 2/(20 5) Remember: p. 457 (1 7, 9) 2/15/2018
 Warmup 2/(20 5) Created by Dr. Underwood GET ROM THE SUPPLY TABLE: A ruler One piece of patty paper INSIDE YOUR DESK SHOULD BE: Graphing Sheet Marker/Eraser 1. Which axis is the x-axis and which is the
Warmup 2/(20 5) Created by Dr. Underwood GET ROM THE SUPPLY TABLE: A ruler One piece of patty paper INSIDE YOUR DESK SHOULD BE: Graphing Sheet Marker/Eraser 1. Which axis is the x-axis and which is the
GOAL Practise techniques for creating various types of geometric lines by constructing and reproducing figures. sheet of letter-sized white paper
 TECHNIQUE STUDENT BOOK Chapter 11, page 340 TOOLBOX Pages 62 67 GOAL Practise techniques for creating various types of geometric lines by constructing and reproducing figures. MATERIALS drawing board T-square
TECHNIQUE STUDENT BOOK Chapter 11, page 340 TOOLBOX Pages 62 67 GOAL Practise techniques for creating various types of geometric lines by constructing and reproducing figures. MATERIALS drawing board T-square
Contents. Congruent Triangles. Additional Practice Answers to Check Your Work. Section
 Contents Section Congruent Triangles Flip, Turn, Resize, and Slide 1 Transformed Triangles 2 Constructing Parallel Lines 5 Transformations 6 Reflections 7 Rotations 10 Summary 13 Check Your Work 14 Additional
Contents Section Congruent Triangles Flip, Turn, Resize, and Slide 1 Transformed Triangles 2 Constructing Parallel Lines 5 Transformations 6 Reflections 7 Rotations 10 Summary 13 Check Your Work 14 Additional
Section 2.3 Task List
 Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Measuring and Drawing Angles and Triangles
 NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
Graphing Techniques. Figure 1. c 2011 Advanced Instructional Systems, Inc. and the University of North Carolina 1
 Graphing Techniques The construction of graphs is a very important technique in experimental physics. Graphs provide a compact and efficient way of displaying the functional relationship between two experimental
Graphing Techniques The construction of graphs is a very important technique in experimental physics. Graphs provide a compact and efficient way of displaying the functional relationship between two experimental
Physics 2310 Lab #5: Thin Lenses and Concave Mirrors Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming)
 Physics 2310 Lab #5: Thin Lenses and Concave Mirrors Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce students to some of the properties of thin lenses and mirrors.
Physics 2310 Lab #5: Thin Lenses and Concave Mirrors Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce students to some of the properties of thin lenses and mirrors.
Algebra I Notes Unit Seven: Writing Linear Equations
 Sllabus Objective.6 The student will be able to write the equation of a linear function given two points, a point and the slope, table of values, or a graphical representation. Slope-Intercept Form of
Sllabus Objective.6 The student will be able to write the equation of a linear function given two points, a point and the slope, table of values, or a graphical representation. Slope-Intercept Form of
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane
 Did You Find a Parking Space? Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane 1.5 Learning Goals Key Term In this lesson, you will: Determine whether lines are parallel. Identify and write the
Did You Find a Parking Space? Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane 1.5 Learning Goals Key Term In this lesson, you will: Determine whether lines are parallel. Identify and write the
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines The Problems of the Month (POM) are used in a variety of ways to promote problem solving and to foster the first standard of mathematical practice from the Common
Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills
 Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills Aim: to be able to present results and draw appropriate types of graphs Must: identify mistakes in data recording Should: be
Year 10 Practical Assessment Skills Lesson 1 Results tables and Graph Skills Aim: to be able to present results and draw appropriate types of graphs Must: identify mistakes in data recording Should: be
Transformation Games
 Transformation Games These are a set of activities/games to help visualize geometric transformations (or rigid motions) movements of an object that do not change the size or shape of the object. The 3
Transformation Games These are a set of activities/games to help visualize geometric transformations (or rigid motions) movements of an object that do not change the size or shape of the object. The 3
Physics 253 Fundamental Physics Mechanic, September 9, Lab #2 Plotting with Excel: The Air Slide
 1 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 253 Fundamental Physics Mechanic, September 9, 2010 Lab #2 Plotting with Excel: The Air Slide Lab Write-up Due: Thurs., September 16, 2010 Place
1 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 253 Fundamental Physics Mechanic, September 9, 2010 Lab #2 Plotting with Excel: The Air Slide Lab Write-up Due: Thurs., September 16, 2010 Place
Algebra II B Review 3
 Algebra II B Review 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Graph the equation. Describe the graph and its lines of symmetry. 1. a. c. b. graph
Algebra II B Review 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Graph the equation. Describe the graph and its lines of symmetry. 1. a. c. b. graph
SPIRIT 2.0 Lesson: How Far Am I Traveling?
 SPIRIT 2.0 Lesson: How Far Am I Traveling? ===============================Lesson Header ============================ Lesson Title: How Far Am I Traveling? Draft Date: June 12, 2008 1st Author (Writer):
SPIRIT 2.0 Lesson: How Far Am I Traveling? ===============================Lesson Header ============================ Lesson Title: How Far Am I Traveling? Draft Date: June 12, 2008 1st Author (Writer):
MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W2B) Name: Equations of Lines Section 2.1 part 1 (Due April 13) platform. height 5 ft
 MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W2B) Name: Equations of Lines Section 2.1 part 1 (Due April 13) Learning Objectives Write the point-slope and slope-intercept forms of linear equations Write equations
MTH 103 Group Activity Problems (W2B) Name: Equations of Lines Section 2.1 part 1 (Due April 13) Learning Objectives Write the point-slope and slope-intercept forms of linear equations Write equations
Polyhedraville In need of TAPE Donations
 Polyhedraville In need of TAPE Donations You get to pick your partner Pick smart, this is a 195 point TEST grade! Don t lose your purple packet! 195 TEST POINTS Due MAY 22 Best City wins a prize Voted
Polyhedraville In need of TAPE Donations You get to pick your partner Pick smart, this is a 195 point TEST grade! Don t lose your purple packet! 195 TEST POINTS Due MAY 22 Best City wins a prize Voted
Identify and draw points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles. Recognize them in various contexts and familiar figures.
 Lesson 1 Homework 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: WW and XX. b. Use a straightedge to draw WWWW. c. Draw a new point that is not
Lesson 1 Homework 4 Name Date 1. Use the following directions to draw a figure in the box to the right. a. Draw two points: WW and XX. b. Use a straightedge to draw WWWW. c. Draw a new point that is not
7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures
 Slide 1 / 53 Slide 2 / 53 7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 53 Topics Table of Contents Determining if a Triangle is Possible Click on a topic to go to that section
Slide 1 / 53 Slide 2 / 53 7th Grade Drawing Geometric Figures 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 53 Topics Table of Contents Determining if a Triangle is Possible Click on a topic to go to that section
Creating a foldable for Equations of Lines
 Creating a foldable for Equations of Lines Equations of Lines Slope Direct Variation Slope-Intercept Form Standard Form Point-Slope Form Equation w/ slope & 1 point Equation w/ 2 points Horizontal & Vertical
Creating a foldable for Equations of Lines Equations of Lines Slope Direct Variation Slope-Intercept Form Standard Form Point-Slope Form Equation w/ slope & 1 point Equation w/ 2 points Horizontal & Vertical
Chapter 2 Using Drawing Tools & Applied Geometry
 Chapter 2 Using Drawing Tools & Applied Geometry TOPICS Preparation of Tools. Using of Tools Applied Geometry PREPARATION OF TOOLS Fastening Paper to Drafting Board 1. Place the paper close to the table
Chapter 2 Using Drawing Tools & Applied Geometry TOPICS Preparation of Tools. Using of Tools Applied Geometry PREPARATION OF TOOLS Fastening Paper to Drafting Board 1. Place the paper close to the table
Line Graphs. Name: The independent variable is plotted on the x-axis. This axis will be labeled Time (days), and
 Name: Graphing Review Graphs and charts are great because they communicate information visually. For this reason graphs are often used in newspapers, magazines, and businesses around the world. Sometimes,
Name: Graphing Review Graphs and charts are great because they communicate information visually. For this reason graphs are often used in newspapers, magazines, and businesses around the world. Sometimes,
Investigating the equation of a straight line
 Task one What is the general form of a straight line equation? Open the Desmos app on your ipad If you do not have the app, then you can access Desmos by going to www.desmos.com and then click on the red
Task one What is the general form of a straight line equation? Open the Desmos app on your ipad If you do not have the app, then you can access Desmos by going to www.desmos.com and then click on the red
Fair Game Review. Chapter 4. Name Date. Find the area of the square or rectangle Find the area of the patio.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Find the area of the square or rectangle... ft cm 0 ft cm.. in. d in. d. Find the area of the patio. ft 0 ft Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Big Ideas Math Green Name
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Find the area of the square or rectangle... ft cm 0 ft cm.. in. d in. d. Find the area of the patio. ft 0 ft Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Big Ideas Math Green Name
All in the Family. b. Use your paper tracing to compare the side lengths of the parallelogram. What appears to be true? Summarize your findings below.
 The quadrilateral family is organized according to the number pairs of sides parallel in a particular quadrilateral. Given a quadrilateral, there are three distinct possibilities: both pairs of opposite
The quadrilateral family is organized according to the number pairs of sides parallel in a particular quadrilateral. Given a quadrilateral, there are three distinct possibilities: both pairs of opposite
Forced Perspective Photography Structured Inquiry
 Forced Perspective Photography Structured Inquiry Question: Can we define the relationships between objects and the camera in Forced Perspective Photography mathematically? Part 1: Locate photos 1 3 and
Forced Perspective Photography Structured Inquiry Question: Can we define the relationships between objects and the camera in Forced Perspective Photography mathematically? Part 1: Locate photos 1 3 and
S. Stirling Page 1 of 14
 3.1 Duplicating Segments and ngles [and riangles] hese notes replace pages 144 146 in the book. You can read these pages for extra clarifications. Instructions for making geometric figures: You can sketch
3.1 Duplicating Segments and ngles [and riangles] hese notes replace pages 144 146 in the book. You can read these pages for extra clarifications. Instructions for making geometric figures: You can sketch
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. Signature Paper Reference(s) 4420/03 4437/09 London Examinations IGCSE Physics 4420 Paper 3 Science (Double Award) 4437 Paper
Centre No. Paper Reference (complete below) Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. Signature Paper Reference(s) 4420/03 4437/09 London Examinations IGCSE Physics 4420 Paper 3 Science (Double Award) 4437 Paper
coordinate system: (0, 2), (0, 0), (0, 3).
 Lesson. Objectives Find the slope of a line from the graph of the line. Find the slope of a line given two points on the line. Activity The Slope of a Line A surveyor places two stakes, A and B, on the
Lesson. Objectives Find the slope of a line from the graph of the line. Find the slope of a line given two points on the line. Activity The Slope of a Line A surveyor places two stakes, A and B, on the
Volumes of Revolution
 Connecting Geometry to Advanced Placement* Mathematics A Resource and Strategy Guide Updated: 0/7/ Volumes of Revolution Objective: Students will visualize the volume of a geometric solid generated by
Connecting Geometry to Advanced Placement* Mathematics A Resource and Strategy Guide Updated: 0/7/ Volumes of Revolution Objective: Students will visualize the volume of a geometric solid generated by
Year 11 Graphing Notes
 Year 11 Graphing Notes Terminology It is very important that students understand, and always use, the correct terms. Indeed, not understanding or using the correct terms is one of the main reasons students
Year 11 Graphing Notes Terminology It is very important that students understand, and always use, the correct terms. Indeed, not understanding or using the correct terms is one of the main reasons students
