Tolerancing Primer. Marshall R. Scott. University of Arizona. December 17, 2015
|
|
|
- Cecily Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
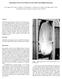
1 Tolerancing Primer Marshall R. Scott University of Arizona December 17, Introduction The goal of the engineer is to design a system that meets a set of requirements while minimizing cost and complexity, knowing full well that once the thing is built everything will be wrong. Take, for instance, the lens shown in Fig. 1. In optical design software, each of the lens elements are chosen to have particular focal lengths and refractive indices, with very particular positions all set to some arbitrary level of precision. However, the actual lenses cannot be placed with absolute precision and accuracy, and so the real-world lens will not be as designed. Each lens will be shifted by some small amount from the optimal position and will be tilted with respect to the optical axis which will compromise the performance. To make matters worse, the focal length, diameter, and thickness of each lens 1
2 Figure 1: Cutaway of a Canon EF600mm F4L IS II USM lens. Photo by Morio[1]. will not be as designed, and the index of refraction will be wrong as well. The key, then, to designing a system is to carefully control how wrong each of these parameters may be. The naive engineer may simply constrain tolerances to be very tight, but this can be difficult for the machinist, and generally results in a very expensive system. He or she may include in the assembly procedures a tedious and intricate alignment process where the position of each element is carefully measured and aligned by hand, but again the added complexity will increase the required labor, and increase the cost. In general, a well-designed system has balanced cost with performance, utilizing the simplest design that still meets the requirements, and finding this optimum requires tolerance analysis. In this paper, I outline the very basics of the tolerancing process. First, a quantitative figure of merit (FOM) is chosen the reflects the performance requirements of the system. Then, a list is made of each parameter that could impact the performance. The effect of each of these parameters is calculated or simulated, and the system performance is modeled assuming loose Tolerancing Primer 2
3 tolerances. The tolerances on each parameter are tightened or loosened as required, and if necessary the design or requirements are modified. The process is iterated until the optimum design is found. While the examples here will be optomechanical in nature, the principles may be applied to any system where uncertainties in components affect overall performance of an assembled system. An amplifying circuit for a photodiode is a good example. Such a system will have uncertainties associated with the values of resistors and capacitors and other components that will make the overall performance of the circuit uncertain. The concepts are the same. 2 Figure of Merit The first step in the tolerancing process is to define the FOM, Φ, a number that reflects the performance of a system. For an imaging system, this could be the RMS spot size or MTF. In a fiber optic system, this could be the coupling efficiency between two fibers. In mechanics it may be the drift in position of a part, and in electronics it could be the gain or bandwidth of a circuit. The choice is limited by imagination, but should be simple, and should reflect the requirements of the system. Tolerancing Primer 3
4 3 Parameters Next, a list is made of all the things in the system that could go wrong. In an imaging system, this could be the focal length, diameter, thickness, or index of refraction of each lens element, or the positioning and tilt. In electronics, this could be the values of each capacitor and resistor. Other parameters could be related to the environment, like temperature, which can change the focal length of lenses, dimensions of mechanics, and values of electronic components. The FOM will be a function of this set of parameters {x i }, Φ( x) = f ( x). (1) 4 Statistics Since the values of the parameters cannot be known exactly, each one will have some uncertainty, x i, and this will propagate to an uncertainty in the FOM, Φ i. Then as long as the set of parameters are independent from one another, the overall uncertainty in the FOM can be calculated by taking the root-sum-square (RSS) of the set of { Φ i }, Φ = Φ ( Φ 1) 2 + ( Φ 2 ) 2 +, (2) where Φ 0 is the residual uncertainty in the FOM, the value when there is no uncertainty in the parameters {x i } (due to diffraction, for instance, the RMS spot Tolerancing Primer 4
5 size of an imaging system will never be zero). The central limit theorem states that under certain conditions, the sum of many random variables follows a Gaussian distribution the bell curve regardless of how the individual parameters are distributed. This is not always strictly true, but it is usually a very good approximation for the purposes of tolerancing. If we assume that the Φ i values are 2σ values a sometimes pessimistic assumption then the Φ in Eq. 2 will be the 2σ uncertainty in the overall system performance. This means that we can expect that 95% of systems built will fall within ± Φ of our designed FOM. Similarly we could ±1σ values which would would include 68% of builds, or ±3σ values which would include 99.7% of the builds. Typically 2σ values are used. As an example, consider 3 3 mm spacers, each with a thickness tolerance of ±0.1mm. We would like to put these together to get a 9 mm spacer. Clearly, an uncertainty of x in one of the spacers will result in an uncertainty in the total thickness Φ i of the same amount. Using equation 2, Φ = x 2 + x 2 + x 2 = 3 x. (3) Thus, the total uncertainty in the thickness of the combined spacers is about 1.7 times the tolerance on each spacer. In general, when N uncertainties of about the same value x are added in RSS, the resulting uncertainty is N x. Another important consequence of Equation 2 is that big terms tend to dominate the sum since they are first squared. For example, if two uncertainties of value 1 and 10 are added, then the root sum square is The uncertainty of 1 Tolerancing Primer 5
6 has increased the total uncertainty by only half a percent. 5 Sensitivities In order to efficiently tolerance a system, we need to calculate the relationship between the tolerance on each parameter, x i, and its effect on the merit function, Φ i. This is easiest when we make the assumption that figure of merit is linear with respect to each parameter. This is typically a good approximation as tolerances in the parameters are small, though it is good practice to verify that the parameter is sufficiently linear over the expected tolerance range of each parameter. If that is the case, then the sensitivity for a parameter x i is given by the partial derivative of the merit function with respect to the value of the parameter, Φ/ x i. Then the effect on the merit function can be calculated using Φ i Φ x i x i. (4) If we know the equation, then it is straight forward to apply Eq. 4 to find the sensitivity, but for more complex systems like a photographic lens, this can be difficult. Instead, we can use a model from a simulation program such as Zemax to do the calculation. Programs like these usually have a tolerance feature that can be very useful, but it important to really understand what is going on, or it may give wrong or misinterpreted results. The sensitivity for a given parameter may be estimated by perturbing it by some small amount, and then recording the effect Tolerancing Primer 6
7 on the merit function. Then the sensitivity may be calculated using Φ Φ (5) x i x i When the residual merit function Φ 0 is much smaller than the perturbed merit function, then it may be ignored and Φ Φ(x i + x i ). If it not small, and it is correlated with with the perturbed parameter, then Φ = Φ(x i + x i ) Φ 0. In the more common case where Φ 0 is independent of the perturbed parameter, then the net effect on the merit function is the RSS, Φ(x i + x i ) = Φ ( Φ i) 2, which can be inverted to find Φ = Φ(x i + x i ) 2 Φ 2 0. Fig. 3 shows how Excel can be used to calculate sensitivity of the doublet shown in Fig. 2. The tilt of the first lens is changed in 1 mrad steps, and the figure of merit is computed for each. The results may be plotted to verify linearity, and the slope of the line is the sensitivity. In some cases, a model may not be available and an experiment is required to find the sensitivity. The procedure works the same way, except parameters are perturbed in a real system. 6 The tolerance table When the parameters and sensitivities have been calculated, the tolerance table, Table 1 may be constructed in a spreadsheet such as Excel. Loose initial tolerances should be chosen using rules of thumb and knowledge of the fabrication process. Tolerancing Primer 7
8 Figure 2: A simple doublet requiring tolerance analysis. Figure 3: Excel is used to quickly calculate sensitivities and verify linearity. Tolerancing Primer 8
9 Table 1: The tolerance table Parameter Tolerance Sensitivity Effect on merit function x 1 x 1 Φ/ x 1 = x 1 Φ/ x 1 x 2 x 2 Φ/ x 2 = x 2 Φ/ x 2 x 3 x 3 Φ/ x 3 = x 3 Φ/ x 3. RSS... =sqrt(sumsq( )) Sensitivies are loaded in the third column, and the effect on the merit function is automatically computed in the fourth column, and finally the root-sum-square is calclulated. The tolerances may now easily be adjusted until the RSS meets the required specification. Tolerances whose effect on the merit function is high compared to the others should be tightened, and those whose effect is small should be loosened. A well tolerenced system will exhibit similar effects on the merit function from each parameter. An Excel assembly tolerance table for the doublet lens in Fig. 2 is shown in Fig. 4. In this case a compensator was used the position of the detector was allowed to be adjusted to compensate for focusing errors. When compensators are used, they must be accounted for when calculating the sensitivities. Therefore, when each parameter was perturbed, the focus position was adjusted to simulate the focus adjustment. Then the resolution of the adjustment appears in the tolerance table, in this case as Detector Axial Position. The RSS shows that performance of the system is better than 1/20λ rms which meets the requirement. The tolerances are reasonable, and the values of the effect on merit function are all close in value. Tolerancing Primer 9
10 Figure 4: Tolerance table for assembly of a simple doublet (Fig Conclusion Tolerancing is a complex, yet essential, skill in engineering that becomes easier with practice. It allows us to predict how a system will perform when it is actually built, and allows us to minimize the cost of the design. The principles listed herein are very basic. Each field, and each application, will pose its own challenges. Sources for further reading are listed below. References [1] File:canon ef600mmm f4l is ii usm cutaway 2012 cp+.jpg. https: //commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:canon_ef600mmm_f4l_is_ii_ USM_cutaway_2012_CP%2B.jpg. Accessed: December 14, [2] Jim Burge. Tolerancing optical systems, opti521 lecture notes, Tolerancing Primer 10
11 [3] Warren J Smith. Fundamentals of establishing an optical tolerance budget. In 1985 Los Angeles Technical Symposium, pages International Society for Optics and Photonics, [4] Robert H Ginsberg. Outline of tolerancing (from performance specification to toleranced drawings). Optical Engineering, 20(2): , [5] Richard N Youngworth and Bryan D Stone. Cost-based tolerancing of optical systems. Applied optics, 39(25): , [6] Richard N Youngworth. Twenty-first century optical tolerancing: a look at the past and improvements for the future. In Contract Proceedings 2006, pages International Society for Optics and Photonics, [7] Jessica DeGroote Nelson, Richard N Youngworth, and David M Aikens. The cost of tolerancing. In SPIE Optical Engineering+ Applications, pages 74330E 74330E. International Society for Optics and Photonics, [8] Simon Magarill. Optomechanical sensitivity and tolerancing. In SPIE s International Symposium on Optical Science, Engineering, and Instrumentation, pages International Society for Optics and Photonics, [9] JH Burge. An easy way to relate optical element motion to system pointing stability. In SPIE Optics+ Photonics, pages 62880I 62880I. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Tolerancing Primer 11
Tolerancing in Zemax. Lecture 4
 Tolerancing in Zemax Lecture 4 Objectives: Lecture 4 At the end of this lecture you should: 1. Understand the reason for tolerancing and its relation to typical manufacturing errors 2. Be able to perform
Tolerancing in Zemax Lecture 4 Objectives: Lecture 4 At the end of this lecture you should: 1. Understand the reason for tolerancing and its relation to typical manufacturing errors 2. Be able to perform
Tolerancing in Zemax
 Tolerancing in Zemax Rachel Haynes Opti 521 Tutorial December 10, 2007 Introduction Being able to design a good optical system is important as an optical engineer, but equally as important is being able
Tolerancing in Zemax Rachel Haynes Opti 521 Tutorial December 10, 2007 Introduction Being able to design a good optical system is important as an optical engineer, but equally as important is being able
System Architecting: Defining Optical and Mechanical Tolerances from an Error Budget
 System Architecting: Defining Optical and Mechanical Tolerances from an Error Budget Julia Zugby OPTI-521: Introductory Optomechanical Engineering, Fall 2016 Overview This tutorial provides a general overview
System Architecting: Defining Optical and Mechanical Tolerances from an Error Budget Julia Zugby OPTI-521: Introductory Optomechanical Engineering, Fall 2016 Overview This tutorial provides a general overview
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Measurement of low-order aberrations with an autostigmatic microscope
 PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Measurement of low-order aberrations with an autostigmatic microscope William P. Kuhn Measurement of low-order aberrations with
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Measurement of low-order aberrations with an autostigmatic microscope William P. Kuhn Measurement of low-order aberrations with
A tutorial for designing. fundamental imaging systems
 A tutorial for designing fundamental imaging systems OPTI 521 College of Optical Science University of Arizona November 2009 Abstract This tutorial shows what to do when we design opto-mechanical system
A tutorial for designing fundamental imaging systems OPTI 521 College of Optical Science University of Arizona November 2009 Abstract This tutorial shows what to do when we design opto-mechanical system
CHAPTER 36 TOLERANCING TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER 36 TOLERANCING TECHNIQUES Robert R. Shannon Optical Sciences Center Uni ersity of Arizona Tucson, Arizona 3 6. 1 GLOSSARY a relative tolerance error BK7, SF2 types of optical glass C to F spectral
CHAPTER 36 TOLERANCING TECHNIQUES Robert R. Shannon Optical Sciences Center Uni ersity of Arizona Tucson, Arizona 3 6. 1 GLOSSARY a relative tolerance error BK7, SF2 types of optical glass C to F spectral
CODE V Tolerancing: A Key to Product Cost Reduction
 CODE V Tolerancing: A Key to Product Cost Reduction A critical step in the design of an optical system destined to be manufactured is to define a fabrication and assembly tolerance budget and to accurately
CODE V Tolerancing: A Key to Product Cost Reduction A critical step in the design of an optical system destined to be manufactured is to define a fabrication and assembly tolerance budget and to accurately
Using Stock Optics. ECE 5616 Curtis
 Using Stock Optics What shape to use X & Y parameters Please use achromatics Please use camera lens Please use 4F imaging systems Others things Data link Stock Optics Some comments Advantages Time and
Using Stock Optics What shape to use X & Y parameters Please use achromatics Please use camera lens Please use 4F imaging systems Others things Data link Stock Optics Some comments Advantages Time and
ABSTRACT. Keywords: Computer-aided alignment, Misalignments, Zernike polynomials, Sensitivity matrix 1. INTRODUCTION
 Computer-Aided Alignment for High Precision Lens LI Lian, FU XinGuo, MA TianMeng, WANG Bin The institute of optical and electronics, the Chinese Academy of Science, Chengdu 6129, China ABSTRACT Computer-Aided
Computer-Aided Alignment for High Precision Lens LI Lian, FU XinGuo, MA TianMeng, WANG Bin The institute of optical and electronics, the Chinese Academy of Science, Chengdu 6129, China ABSTRACT Computer-Aided
The Cost of Tolerancing
 The Cost of Tolerancing Jessica DeGroote Nelson, a Richard N. Youngworth, b David M. Aikens c a Optimax Systems Inc., 6367 Dean Parkway, Ontario, NY 14519 USA b Light Capture Inc., 1006 15 th St., Riviera
The Cost of Tolerancing Jessica DeGroote Nelson, a Richard N. Youngworth, b David M. Aikens c a Optimax Systems Inc., 6367 Dean Parkway, Ontario, NY 14519 USA b Light Capture Inc., 1006 15 th St., Riviera
Tutorial: Thermal Modeling in Zemax
 Tutorial: Thermal Modeling in Zemax Heidi Warriner, Opti 521, 10-31-2010 Contents Introduction...2 Design Parameters...2 Analytical Approach...3 Zemax Approach...5 Acrylic Lens and Tube at 20 C...5 Acrylic
Tutorial: Thermal Modeling in Zemax Heidi Warriner, Opti 521, 10-31-2010 Contents Introduction...2 Design Parameters...2 Analytical Approach...3 Zemax Approach...5 Acrylic Lens and Tube at 20 C...5 Acrylic
Performance Factors. Technical Assistance. Fundamental Optics
 Performance Factors After paraxial formulas have been used to select values for component focal length(s) and diameter(s), the final step is to select actual lenses. As in any engineering problem, this
Performance Factors After paraxial formulas have been used to select values for component focal length(s) and diameter(s), the final step is to select actual lenses. As in any engineering problem, this
OPTI 521 OPTOMECHANICAL DESIGN. Tutorial: Overview of the Optical and Optomechanical Design Process. Professor: Jim Burge
 OPTI 521 OPTOMECHANICAL DESIGN Tutorial: Overview of the Optical and Optomechanical Design Process Professor: Jim Burge Sara Landau Date: December 14, 2007 1 I. Introduction A wise mentor told me as I
OPTI 521 OPTOMECHANICAL DESIGN Tutorial: Overview of the Optical and Optomechanical Design Process Professor: Jim Burge Sara Landau Date: December 14, 2007 1 I. Introduction A wise mentor told me as I
MRO Delay Line. Performance of Beam Compressor for Agilent Laser Head INT-406-VEN The Cambridge Delay Line Team. rev 0.
 MRO Delay Line Performance of Beam Compressor for Agilent Laser Head INT-406-VEN-0123 The Cambridge Delay Line Team rev 0.45 1 April 2011 Cavendish Laboratory Madingley Road Cambridge CB3 0HE UK Change
MRO Delay Line Performance of Beam Compressor for Agilent Laser Head INT-406-VEN-0123 The Cambridge Delay Line Team rev 0.45 1 April 2011 Cavendish Laboratory Madingley Road Cambridge CB3 0HE UK Change
AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%.
 Application Note AN004: Fiber Coupling Improvement Introduction AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%. Industrial lasers used for cutting, welding, drilling,
Application Note AN004: Fiber Coupling Improvement Introduction AgilOptics mirrors increase coupling efficiency into a 4 µm diameter fiber by 750%. Industrial lasers used for cutting, welding, drilling,
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus
 Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
EVLA Memo 105. Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope
 EVLA Memo 105 Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope Steven Durand, James Jackson, and Keith Morris National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 1003 Lopezville Road, Socorro, NM, USA 87801 ABSTRACT The
EVLA Memo 105 Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope Steven Durand, James Jackson, and Keith Morris National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 1003 Lopezville Road, Socorro, NM, USA 87801 ABSTRACT The
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II
 PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet Thin Lenses 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to be able to measure the focal length of a converging lens.
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet Thin Lenses 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to be able to measure the focal length of a converging lens.
Laboratory 1: Uncertainty Analysis
 University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH101 / LeClair May 26, 2014 Laboratory 1: Uncertainty Analysis Hypothesis: A statistical analysis including both mean and standard deviation can
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH101 / LeClair May 26, 2014 Laboratory 1: Uncertainty Analysis Hypothesis: A statistical analysis including both mean and standard deviation can
Physics 2310 Lab #5: Thin Lenses and Concave Mirrors Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming)
 Physics 2310 Lab #5: Thin Lenses and Concave Mirrors Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce students to some of the properties of thin lenses and mirrors.
Physics 2310 Lab #5: Thin Lenses and Concave Mirrors Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce students to some of the properties of thin lenses and mirrors.
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part I. BASIC ELEMENTS AND METHODS FOR CHARACTERIZATION OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS
 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part I. BASIC ELEMENTS AND METHODS FOR CHARACTERIZATION OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS Equipment and accessories: an optical bench with a scale, an incandescent lamp, matte, a set of
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Practical 1. Part I. BASIC ELEMENTS AND METHODS FOR CHARACTERIZATION OF OPTICAL SYSTEMS Equipment and accessories: an optical bench with a scale, an incandescent lamp, matte, a set of
Adaptive Optics for LIGO
 Adaptive Optics for LIGO Justin Mansell Ginzton Laboratory LIGO-G990022-39-M Motivation Wavefront Sensor Outline Characterization Enhancements Modeling Projections Adaptive Optics Results Effects of Thermal
Adaptive Optics for LIGO Justin Mansell Ginzton Laboratory LIGO-G990022-39-M Motivation Wavefront Sensor Outline Characterization Enhancements Modeling Projections Adaptive Optics Results Effects of Thermal
Lecture 7: Op,cal Design. Christoph U. Keller
 Lecture 7: Op,cal Design Christoph U. Keller Overview 1. Introduc5on 2. Requirements Defini5on 3. Op5cal Design Principles 4. Ray- Tracing and Design Analysis 5. Op5miza5on: Merit Func5on 6. Tolerance
Lecture 7: Op,cal Design Christoph U. Keller Overview 1. Introduc5on 2. Requirements Defini5on 3. Op5cal Design Principles 4. Ray- Tracing and Design Analysis 5. Op5miza5on: Merit Func5on 6. Tolerance
For rotationally symmetric optical
 : Maintaining Uniform Temperature Fluctuations John Tejada, Janos Technology, Inc. An optical system is athermalized if its critical performance parameters (such as MTF, BFL, EFL, etc.,) do not change
: Maintaining Uniform Temperature Fluctuations John Tejada, Janos Technology, Inc. An optical system is athermalized if its critical performance parameters (such as MTF, BFL, EFL, etc.,) do not change
Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing
 Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing Dr. Jim Burge Associate Professor Optical Sciences and Astronomy University of Arizona jburge@optics.arizona.edu 520-621-8182 Computer Generated Holograms
Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing Dr. Jim Burge Associate Professor Optical Sciences and Astronomy University of Arizona jburge@optics.arizona.edu 520-621-8182 Computer Generated Holograms
Correlation of mid-spatial features to image performance in aspheric mirrors
 Correlation of mid-spatial features to image performance in aspheric mirrors Flemming Tinker, Kai Xin Aperture Optical Sciences Inc., 27 Parson Ln. Unit G, Durham, CT 06422 ABSTRACT Modern techniques in
Correlation of mid-spatial features to image performance in aspheric mirrors Flemming Tinker, Kai Xin Aperture Optical Sciences Inc., 27 Parson Ln. Unit G, Durham, CT 06422 ABSTRACT Modern techniques in
Post PDR Optical Design Study. Robert Barkhouser JHU/IDG January 6, 2014
 ARCTIC Post PDR Optical Design Study Robert Barkhouser JHU/IDG January 6, 2014 1 APO 3.5 m Telescope Model From Joe H. as part of f8v240 imager model. dl Note (1) curved focal surface and (2) limiting
ARCTIC Post PDR Optical Design Study Robert Barkhouser JHU/IDG January 6, 2014 1 APO 3.5 m Telescope Model From Joe H. as part of f8v240 imager model. dl Note (1) curved focal surface and (2) limiting
Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr.
 Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr. Introduction Chapter 4 of Opto-Mechanical Systems Design by Paul R. Yoder, Jr. is an introduction
Technical Report Synopsis: Chapter 4: Mounting Individual Lenses Opto-Mechanical System Design Paul R. Yoder, Jr. Introduction Chapter 4 of Opto-Mechanical Systems Design by Paul R. Yoder, Jr. is an introduction
2.2 Wavefront Sensor Design. Lauren H. Schatz, Oli Durney, Jared Males
 Page: 1 of 8 Lauren H. Schatz, Oli Durney, Jared Males 1 Pyramid Wavefront Sensor Overview The MagAO-X system uses a pyramid wavefront sensor (PWFS) for high order wavefront sensing. The wavefront sensor
Page: 1 of 8 Lauren H. Schatz, Oli Durney, Jared Males 1 Pyramid Wavefront Sensor Overview The MagAO-X system uses a pyramid wavefront sensor (PWFS) for high order wavefront sensing. The wavefront sensor
Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1
 Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1 Short answer 1.) Sketch a pechan prism. Name a possible application of this prism., write the mirror matrix for this prism (or any other common
Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1 Short answer 1.) Sketch a pechan prism. Name a possible application of this prism., write the mirror matrix for this prism (or any other common
Tolerancing microlenses using ZEMAX
 Tolerancing microlenses using ZEMAX Andrew Stockham, John G. Smith MEMS Optical *, Inc., 05 Import Circle, Huntsville, AL, USA 35806 ABSTRACT This paper demonstrates a new tolerancing technique that allows
Tolerancing microlenses using ZEMAX Andrew Stockham, John G. Smith MEMS Optical *, Inc., 05 Import Circle, Huntsville, AL, USA 35806 ABSTRACT This paper demonstrates a new tolerancing technique that allows
Optical System Design
 Phys 531 Lecture 12 14 October 2004 Optical System Design Last time: Surveyed examples of optical systems Today, discuss system design Lens design = course of its own (not taught by me!) Try to give some
Phys 531 Lecture 12 14 October 2004 Optical System Design Last time: Surveyed examples of optical systems Today, discuss system design Lens design = course of its own (not taught by me!) Try to give some
Receiver Design for Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) Imaging
 Introduction Receiver Design for Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) Imaging Millimeter Wave Systems, LLC Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) sensors are used for remote sensing and security applications. They rely
Introduction Receiver Design for Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) Imaging Millimeter Wave Systems, LLC Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) sensors are used for remote sensing and security applications. They rely
Chapter 3. Introduction to Zemax. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Zemax
 Chapter 3 Introduction to Zemax 3.1 Introduction Ray tracing is practical only for paraxial analysis. Computing aberrations and diffraction effects are time consuming. Optical Designers need some popular
Chapter 3 Introduction to Zemax 3.1 Introduction Ray tracing is practical only for paraxial analysis. Computing aberrations and diffraction effects are time consuming. Optical Designers need some popular
Vibration-compensated interferometer for measuring cryogenic mirrors
 Vibration-compensated interferometer for measuring cryogenic mirrors Chunyu Zhao and James H. Burge Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, 1630 E. University Blvd, Tucson, AZ 85721 Abstract An
Vibration-compensated interferometer for measuring cryogenic mirrors Chunyu Zhao and James H. Burge Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, 1630 E. University Blvd, Tucson, AZ 85721 Abstract An
Section 8. Objectives
 8-1 Section 8 Objectives Objectives Simple and Petval Objectives are lens element combinations used to image (usually) distant objects. To classify the objective, separated groups of lens elements are
8-1 Section 8 Objectives Objectives Simple and Petval Objectives are lens element combinations used to image (usually) distant objects. To classify the objective, separated groups of lens elements are
Optical Design with Zemax
 Optical Design with Zemax Lecture : Correction II 3--9 Herbert Gross Summer term www.iap.uni-jena.de Correction II Preliminary time schedule 6.. Introduction Introduction, Zemax interface, menues, file
Optical Design with Zemax Lecture : Correction II 3--9 Herbert Gross Summer term www.iap.uni-jena.de Correction II Preliminary time schedule 6.. Introduction Introduction, Zemax interface, menues, file
Optical Design with Zemax for PhD
 Optical Design with Zemax for PhD Lecture 7: Optimization II 26--2 Herbert Gross Winter term 25 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed content.. Introduction 2 2.2. Basic Zemax
Optical Design with Zemax for PhD Lecture 7: Optimization II 26--2 Herbert Gross Winter term 25 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed content.. Introduction 2 2.2. Basic Zemax
Wavefront sensing by an aperiodic diffractive microlens array
 Wavefront sensing by an aperiodic diffractive microlens array Lars Seifert a, Thomas Ruppel, Tobias Haist, and Wolfgang Osten a Institut für Technische Optik, Universität Stuttgart, Pfaffenwaldring 9,
Wavefront sensing by an aperiodic diffractive microlens array Lars Seifert a, Thomas Ruppel, Tobias Haist, and Wolfgang Osten a Institut für Technische Optik, Universität Stuttgart, Pfaffenwaldring 9,
Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design)
 Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Wavefront Sensing In Other Disciplines. 15 February 2003 Jerry Nelson, UCSC Wavefront Congress
 Wavefront Sensing In Other Disciplines 15 February 2003 Jerry Nelson, UCSC Wavefront Congress QuickTime and a Photo - JPEG decompressor are needed to see this picture. 15feb03 Nelson wavefront sensing
Wavefront Sensing In Other Disciplines 15 February 2003 Jerry Nelson, UCSC Wavefront Congress QuickTime and a Photo - JPEG decompressor are needed to see this picture. 15feb03 Nelson wavefront sensing
Sequential Ray Tracing. Lecture 2
 Sequential Ray Tracing Lecture 2 Sequential Ray Tracing Rays are traced through a pre-defined sequence of surfaces while travelling from the object surface to the image surface. Rays hit each surface once
Sequential Ray Tracing Lecture 2 Sequential Ray Tracing Rays are traced through a pre-defined sequence of surfaces while travelling from the object surface to the image surface. Rays hit each surface once
Homework Set 3.5 Sensitive optoelectronic detectors: seeing single photons
 Homework Set 3.5 Sensitive optoelectronic detectors: seeing single photons Due by 12:00 noon (in class) on Tuesday, Nov. 7, 2006. This is another hybrid lab/homework; please see Section 3.4 for what you
Homework Set 3.5 Sensitive optoelectronic detectors: seeing single photons Due by 12:00 noon (in class) on Tuesday, Nov. 7, 2006. This is another hybrid lab/homework; please see Section 3.4 for what you
Technical Synopsis and Discussion of:
 OPTI-521, Fall 2008 E.D. Fasse, Page 1 Technical Synopsis and Discussion of: Optical Alignment of a Pupil Imaging Spectrometer by Stephen Horchem and Richard Kohrman Proc. of SPIE Vol. 1167, Precision
OPTI-521, Fall 2008 E.D. Fasse, Page 1 Technical Synopsis and Discussion of: Optical Alignment of a Pupil Imaging Spectrometer by Stephen Horchem and Richard Kohrman Proc. of SPIE Vol. 1167, Precision
Accuracy Estimation of Microwave Holography from Planar Near-Field Measurements
 Accuracy Estimation of Microwave Holography from Planar Near-Field Measurements Christopher A. Rose Microwave Instrumentation Technologies River Green Parkway, Suite Duluth, GA 9 Abstract Microwave holography
Accuracy Estimation of Microwave Holography from Planar Near-Field Measurements Christopher A. Rose Microwave Instrumentation Technologies River Green Parkway, Suite Duluth, GA 9 Abstract Microwave holography
Physics 2310 Lab #6: Multiple Thin Lenses Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming)
 Physics 2310 Lab #6: Multiple Thin Lenses Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to investigate the properties of multiple thin lenses. The primary goals are to understand
Physics 2310 Lab #6: Multiple Thin Lenses Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to investigate the properties of multiple thin lenses. The primary goals are to understand
NRZ Bandwidth (-3db HF Cutoff vs SNR) How Much Bandwidth is Enough?
 NRZ Bandwidth (-3db HF Cutoff vs SNR) How Much Bandwidth is Enough? Introduction 02XXX-WTP-001-A March 28, 2003 A number of customer-initiated questions have arisen over the determination of the optimum
NRZ Bandwidth (-3db HF Cutoff vs SNR) How Much Bandwidth is Enough? Introduction 02XXX-WTP-001-A March 28, 2003 A number of customer-initiated questions have arisen over the determination of the optimum
12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes
 330 Chapter 12 12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes Similar to the JWST, the next-generation large-aperture space telescope for optical and UV astronomy has a segmented
330 Chapter 12 12.4 Alignment and Manufacturing Tolerances for Segmented Telescopes Similar to the JWST, the next-generation large-aperture space telescope for optical and UV astronomy has a segmented
Lens Design I Seminar 1
 Xiang Lu, Ralf Hambach Friedrich Schiller University Jena Institute of Applied Physics Albert-Einstein-Str 15 07745 Jena Lens Design I Seminar 1 Warm-Up (20min) Setup a single, symmetric, biconvex lens
Xiang Lu, Ralf Hambach Friedrich Schiller University Jena Institute of Applied Physics Albert-Einstein-Str 15 07745 Jena Lens Design I Seminar 1 Warm-Up (20min) Setup a single, symmetric, biconvex lens
Tolerance analysis of lenses with high zoom ratio
 Tolerance analysis of lenses with high zoom ratio Chir-Weei Chang, a, Gung-Hsuan Ho a, Chy-Lin Wang a, Wei-Chung Chao a, John D. Griffith b a Opto-Electronics & Systems Laboratories/Industrial Technology
Tolerance analysis of lenses with high zoom ratio Chir-Weei Chang, a, Gung-Hsuan Ho a, Chy-Lin Wang a, Wei-Chung Chao a, John D. Griffith b a Opto-Electronics & Systems Laboratories/Industrial Technology
Basic Optics System OS-8515C
 40 50 30 60 20 70 10 80 0 90 80 10 20 70 T 30 60 40 50 50 40 60 30 70 20 80 90 90 80 BASIC OPTICS RAY TABLE 10 0 10 70 20 60 50 40 30 Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-09900B
40 50 30 60 20 70 10 80 0 90 80 10 20 70 T 30 60 40 50 50 40 60 30 70 20 80 90 90 80 BASIC OPTICS RAY TABLE 10 0 10 70 20 60 50 40 30 Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-09900B
Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted
 Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted Ulrike Fuchs (Ph.D.), Sven R. Kiontke asphericon GmbH Stockholmer Str. 9 07743 Jena, Germany Tel: +49-3641-3100500 Introduction Everyday work in an optics
Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted Ulrike Fuchs (Ph.D.), Sven R. Kiontke asphericon GmbH Stockholmer Str. 9 07743 Jena, Germany Tel: +49-3641-3100500 Introduction Everyday work in an optics
P202/219 Laboratory IUPUI Physics Department THIN LENSES
 THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
THIN LENSES OBJECTIVE To verify the thin lens equation, m = h i /h o = d i /d o. d o d i f, and the magnification equations THEORY In the above equations, d o is the distance between the object and the
Industrial quality control HASO for ensuring the quality of NIR optical components
 Industrial quality control HASO for ensuring the quality of NIR optical components In the sector of industrial detection, the ability to massproduce reliable, high-quality optical components is synonymous
Industrial quality control HASO for ensuring the quality of NIR optical components In the sector of industrial detection, the ability to massproduce reliable, high-quality optical components is synonymous
Datum reference frame Position and shape tolerances Tolerance analysis
 Datum reference frame Position and shape tolerances Tolerance analysis Šimon Kovář Datum reference frame Datum reference frames are typically for 3D. A typical datum reference frame is made up of three
Datum reference frame Position and shape tolerances Tolerance analysis Šimon Kovář Datum reference frame Datum reference frames are typically for 3D. A typical datum reference frame is made up of three
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings
 A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
The 34th International Physics Olympiad
 The 34th International Physics Olympiad Taipei, Taiwan Experimental Competition Wednesday, August 6, 2003 Time Available : 5 hours Please Read This First: 1. Use only the pen provided. 2. Use only the
The 34th International Physics Olympiad Taipei, Taiwan Experimental Competition Wednesday, August 6, 2003 Time Available : 5 hours Please Read This First: 1. Use only the pen provided. 2. Use only the
ENSC 470/894 Lab 3 Version 6.0 (Nov. 19, 2015)
 ENSC 470/894 Lab 3 Version 6.0 (Nov. 19, 2015) Purpose The purpose of the lab is (i) To measure the spot size and profile of the He-Ne laser beam and a laser pointer laser beam. (ii) To create a beam expander
ENSC 470/894 Lab 3 Version 6.0 (Nov. 19, 2015) Purpose The purpose of the lab is (i) To measure the spot size and profile of the He-Ne laser beam and a laser pointer laser beam. (ii) To create a beam expander
Optical Design & Analysis Paul Martini
 Optical Design & Analysis Paul Martini July 6 th, 2004 PM 1 Outline Optical Design Filters and Grisms Pupils Throughput Estimate Ghost Analysis Tolerance Analysis Critical Areas Task List PM 2 Requirements
Optical Design & Analysis Paul Martini July 6 th, 2004 PM 1 Outline Optical Design Filters and Grisms Pupils Throughput Estimate Ghost Analysis Tolerance Analysis Critical Areas Task List PM 2 Requirements
A Prototype Wire Position Monitoring System
 LCLS-TN-05-27 A Prototype Wire Position Monitoring System Wei Wang and Zachary Wolf Metrology Department, SLAC 1. INTRODUCTION ¹ The Wire Position Monitoring System (WPM) will track changes in the transverse
LCLS-TN-05-27 A Prototype Wire Position Monitoring System Wei Wang and Zachary Wolf Metrology Department, SLAC 1. INTRODUCTION ¹ The Wire Position Monitoring System (WPM) will track changes in the transverse
Exposure schedule for multiplexing holograms in photopolymer films
 Exposure schedule for multiplexing holograms in photopolymer films Allen Pu, MEMBER SPIE Kevin Curtis,* MEMBER SPIE Demetri Psaltis, MEMBER SPIE California Institute of Technology 136-93 Caltech Pasadena,
Exposure schedule for multiplexing holograms in photopolymer films Allen Pu, MEMBER SPIE Kevin Curtis,* MEMBER SPIE Demetri Psaltis, MEMBER SPIE California Institute of Technology 136-93 Caltech Pasadena,
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Practical Guide to Specifying Optical Components
 Practical Guide to Specifying Optical Components OPTI 521 Introduction to Opto-Mechanical Engineering Fall 2012 December 10, 2012 Brian Parris Introduction This paper is intended to serve as a practical
Practical Guide to Specifying Optical Components OPTI 521 Introduction to Opto-Mechanical Engineering Fall 2012 December 10, 2012 Brian Parris Introduction This paper is intended to serve as a practical
WJM Technologies excellence in material joining
 Girish P. Kelkar, Ph.D. (562) 743-7576 girish@welding-consultant.com www.welding-consultant.com Laser Focus Spot Size Control Interaction of a laser beam with any material is a function of energy density,
Girish P. Kelkar, Ph.D. (562) 743-7576 girish@welding-consultant.com www.welding-consultant.com Laser Focus Spot Size Control Interaction of a laser beam with any material is a function of energy density,
Tangents. The f-stops here. Shedding some light on the f-number. by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann
 Tangents Shedding some light on the f-number The f-stops here by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann The f-number has peen around for nearly a century now, and it is certainly one of the fundamental
Tangents Shedding some light on the f-number The f-stops here by Marcus R. Hatch and David E. Stoltzmann The f-number has peen around for nearly a century now, and it is certainly one of the fundamental
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 24. Optical Receivers-
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 24 Optical Receivers- Receiver Sensitivity Degradation Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K.
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 24 Optical Receivers- Receiver Sensitivity Degradation Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K.
Using molded chalcogenide glass technology to reduce cost in a compact wide-angle thermal imaging lens
 Using molded chalcogenide glass technology to reduce cost in a compact wide-angle thermal imaging lens George Curatu a, Brent Binkley a, David Tinch a, and Costin Curatu b a LightPath Technologies, 2603
Using molded chalcogenide glass technology to reduce cost in a compact wide-angle thermal imaging lens George Curatu a, Brent Binkley a, David Tinch a, and Costin Curatu b a LightPath Technologies, 2603
Null Hartmann test for the fabrication of large aspheric surfaces
 Null Hartmann test for the fabrication of large aspheric surfaces Ho-Soon Yang, Yun-Woo Lee, Jae-Bong Song, and In-Won Lee Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science, P.O. Box 102, Yuseong, Daejon
Null Hartmann test for the fabrication of large aspheric surfaces Ho-Soon Yang, Yun-Woo Lee, Jae-Bong Song, and In-Won Lee Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science, P.O. Box 102, Yuseong, Daejon
Design of the Wide-view Collimator Based on ZEMAX
 www.ccsenet.org/cis Computer and Information Science Vol. 4, No. 5; September 2011 Design of the Wide-view Collimator Based on ZEMAX Xuemei Bai (Corresponding author) Institute of Electronic and Information
www.ccsenet.org/cis Computer and Information Science Vol. 4, No. 5; September 2011 Design of the Wide-view Collimator Based on ZEMAX Xuemei Bai (Corresponding author) Institute of Electronic and Information
Mechanical Tolerancing Results For the SALT/PFIS Collimator and Camera. January 24, 2003 J. Alan Schier
 Mechanical Tolerancing Results For the SALT/PFIS Collimator and Camera January 24, 2003 J. Alan Schier This report contains the tolerance information needed to produce a mechanical design for the SALT/PFIS
Mechanical Tolerancing Results For the SALT/PFIS Collimator and Camera January 24, 2003 J. Alan Schier This report contains the tolerance information needed to produce a mechanical design for the SALT/PFIS
The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces
 The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces James T. McCann OFC - Diamond Turning Division 69T Island Street, Keene New Hampshire
The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces James T. McCann OFC - Diamond Turning Division 69T Island Street, Keene New Hampshire
Properties of Structured Light
 Properties of Structured Light Gaussian Beams Structured light sources using lasers as the illumination source are governed by theories of Gaussian beams. Unlike incoherent sources, coherent laser sources
Properties of Structured Light Gaussian Beams Structured light sources using lasers as the illumination source are governed by theories of Gaussian beams. Unlike incoherent sources, coherent laser sources
Tutorial Zemax 9: Physical optical modelling I
 Tutorial Zemax 9: Physical optical modelling I 2012-11-04 9 Physical optical modelling I 1 9.1 Gaussian Beams... 1 9.2 Physical Beam Propagation... 3 9.3 Polarization... 7 9.4 Polarization II... 11 9 Physical
Tutorial Zemax 9: Physical optical modelling I 2012-11-04 9 Physical optical modelling I 1 9.1 Gaussian Beams... 1 9.2 Physical Beam Propagation... 3 9.3 Polarization... 7 9.4 Polarization II... 11 9 Physical
Warren J. Smith Chief Scientist, Consultant Rockwell Collins Optronics Carlsbad, California
 Modern Optical Engineering The Design of Optical Systems Warren J. Smith Chief Scientist, Consultant Rockwell Collins Optronics Carlsbad, California Fourth Edition Me Graw Hill New York Chicago San Francisco
Modern Optical Engineering The Design of Optical Systems Warren J. Smith Chief Scientist, Consultant Rockwell Collins Optronics Carlsbad, California Fourth Edition Me Graw Hill New York Chicago San Francisco
0.0 An Optics Primer. ,/r. e.=e. 0.1 Geometrical Optics \,, { \ \t 0;'. / (0.1)
 0.0 An Optics Primer The field of optics is a fascinating area of study. In many areas of science and engineering, the understanding of the concepts and effects in that field can be difficult because the
0.0 An Optics Primer The field of optics is a fascinating area of study. In many areas of science and engineering, the understanding of the concepts and effects in that field can be difficult because the
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes
 Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT
 CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
Optimisation. Lecture 3
 Optimisation Lecture 3 Objectives: Lecture 3 At the end of this lecture you should: 1. Understand the use of Petzval curvature to balance lens components 2. Know how different aberrations depend on field
Optimisation Lecture 3 Objectives: Lecture 3 At the end of this lecture you should: 1. Understand the use of Petzval curvature to balance lens components 2. Know how different aberrations depend on field
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014
 PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014 Laboratory #1 Week of January 13 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp.150-170 of Optics by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
PH 481/581 Physical Optics Winter 2014 Laboratory #1 Week of January 13 Read: Handout (Introduction & Projects #2 & 3 from Newport Project in Optics Workbook), pp.150-170 of Optics by Hecht Do: 1. Experiment
PHYS 1020 LAB 7: LENSES AND OPTICS. Pre-Lab
 PHYS 1020 LAB 7: LENSES AND OPTICS Note: Print and complete the separate pre-lab assignment BEFORE the lab. Hand it in at the start of the lab. Pre-Lab Start by reading the entire prelab and lab write-up.
PHYS 1020 LAB 7: LENSES AND OPTICS Note: Print and complete the separate pre-lab assignment BEFORE the lab. Hand it in at the start of the lab. Pre-Lab Start by reading the entire prelab and lab write-up.
FIBER105.TIF OUTLINE DIMENSIONS in inches (mm) .176 (4.47).165 (4.19) .500 MIN (12.7) FIBER203.DIM. Pinout 1. Capacitor 2. VÙÙ 3.
 FEATURES Converts fiber optic input signals to TTL digital outputs Typical sensitivity 500 nw peak ( 33 dbm) Single 5 V supply requirement Edge detection circuitry gives 20 db minimum dynamic range, low
FEATURES Converts fiber optic input signals to TTL digital outputs Typical sensitivity 500 nw peak ( 33 dbm) Single 5 V supply requirement Edge detection circuitry gives 20 db minimum dynamic range, low
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Rays. Wavefronts. Aberrations. Outline
 Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Refractive index homogeneity TWE effect on large aperture optical systems
 Refractive index homogeneity TWE effect on large aperture optical systems M. Stout*, B. Neff II-VI Optical Systems 36570 Briggs Road., Murrieta, CA 92563 ABSTRACT Sapphire windows are routinely being used
Refractive index homogeneity TWE effect on large aperture optical systems M. Stout*, B. Neff II-VI Optical Systems 36570 Briggs Road., Murrieta, CA 92563 ABSTRACT Sapphire windows are routinely being used
Advanced Dimensional Management LLC
 Index for Tolerance Stackup, Tolerance Analysis and Tolerancing Manual: Plus and Minus Edition Accuracy and precision 3, 19 Ambiguity 20 ASME Y14.5M-1994 2 rule #1 2 Assembly Process 20, 28, 79-81 Assembly
Index for Tolerance Stackup, Tolerance Analysis and Tolerancing Manual: Plus and Minus Edition Accuracy and precision 3, 19 Ambiguity 20 ASME Y14.5M-1994 2 rule #1 2 Assembly Process 20, 28, 79-81 Assembly
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack To cite this article: Yuanyuan Gu et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Beam Characteristics of High Power Diode Laser Stack To cite this article: Yuanyuan Gu et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
6.098 Digital and Computational Photography Advanced Computational Photography. Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS
 6.098 Digital and Computational Photography 6.882 Advanced Computational Photography Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS Administrivia PSet 1 is out Due Thursday February 23 Digital SLR initiation? During
6.098 Digital and Computational Photography 6.882 Advanced Computational Photography Bill Freeman Frédo Durand MIT - EECS Administrivia PSet 1 is out Due Thursday February 23 Digital SLR initiation? During
Developments in Precision Asphere Manufacturing Jay Tierson, Ed Fess, Greg Mathews OptiPro Systems LLC, 6368 Dean Parkway, Ontario NY 14519
 Developments in Precision Asphere Manufacturing Jay Tierson, Ed Fess, Greg Mathews OptiPro Systems LLC, 6368 Dean Parkway, Ontario NY 14519 ABSTRACT The increased use of aspheres in today s optical systems
Developments in Precision Asphere Manufacturing Jay Tierson, Ed Fess, Greg Mathews OptiPro Systems LLC, 6368 Dean Parkway, Ontario NY 14519 ABSTRACT The increased use of aspheres in today s optical systems
REPORT ITU-R SA.2098
 Rep. ITU-R SA.2098 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2098 Mathematical gain models of large-aperture space research service earth station antennas for compatibility analysis involving a large number of distributed interference
Rep. ITU-R SA.2098 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2098 Mathematical gain models of large-aperture space research service earth station antennas for compatibility analysis involving a large number of distributed interference
"Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements
 "Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements by Dr. Frank Melsheimer DFM Engineering, Inc. 1035 Delaware Avenue Longmont, Colorado 80501 phone 303-678-8143 fax 303-772-9411 www.dfmengineering.com Table
"Internet Telescope" Performance Requirements by Dr. Frank Melsheimer DFM Engineering, Inc. 1035 Delaware Avenue Longmont, Colorado 80501 phone 303-678-8143 fax 303-772-9411 www.dfmengineering.com Table
ELEC Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW
 ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Filter Design Circularly symmetric 2-D low-pass filter Pass-band radial frequency: ω p Stop-band radial frequency: ω s 1 δ p Pass-band tolerances: δ
ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Filter Design Circularly symmetric 2-D low-pass filter Pass-band radial frequency: ω p Stop-band radial frequency: ω s 1 δ p Pass-band tolerances: δ
Optical Design with Zemax for PhD - Basics
 Optical Design with Zemax for PhD - Basics Lecture 3: Properties of optical sstems II 2013-05-30 Herbert Gross Summer term 2013 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminar Schedule No Date Subject Detailed content
Optical Design with Zemax for PhD - Basics Lecture 3: Properties of optical sstems II 2013-05-30 Herbert Gross Summer term 2013 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminar Schedule No Date Subject Detailed content
I = I 0 cos 2 θ (1.1)
 Chapter 1 Faraday Rotation Experiment objectives: Observe the Faraday Effect, the rotation of a light wave s polarization vector in a material with a magnetic field directed along the wave s direction.
Chapter 1 Faraday Rotation Experiment objectives: Observe the Faraday Effect, the rotation of a light wave s polarization vector in a material with a magnetic field directed along the wave s direction.
Lecture 8. Lecture 8. r 1
 Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
THE CCD RIDDLE REVISTED: SIGNAL VERSUS TIME LINEAR SIGNAL VERSUS VARIANCE NON-LINEAR
 THE CCD RIDDLE REVISTED: SIGNAL VERSUS TIME LINEAR SIGNAL VERSUS VARIANCE NON-LINEAR Mark Downing 1, Peter Sinclaire 1. 1 ESO, Karl Schwartzschild Strasse-2, 85748 Munich, Germany. ABSTRACT The photon
THE CCD RIDDLE REVISTED: SIGNAL VERSUS TIME LINEAR SIGNAL VERSUS VARIANCE NON-LINEAR Mark Downing 1, Peter Sinclaire 1. 1 ESO, Karl Schwartzschild Strasse-2, 85748 Munich, Germany. ABSTRACT The photon
Tolerancing. 280 Tolerancing. User-defined tolerancing
 280 Tolerancing Tolerancing User-defined tolerancing User-defined tolerancing is a term used in OSLO to describe the process of settting tolerances when optical performance is measured by a user-defined
280 Tolerancing Tolerancing User-defined tolerancing User-defined tolerancing is a term used in OSLO to describe the process of settting tolerances when optical performance is measured by a user-defined
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN
 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN Pantazis Mouroulis Associate Professor Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology John Macdonald Senior Lecturer Physics Department University of
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN Pantazis Mouroulis Associate Professor Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology John Macdonald Senior Lecturer Physics Department University of
Appendix C: Graphing. How do I plot data and uncertainties? Another technique that makes data analysis easier is to record all your data in a table.
 Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
Appendix C: Graphing One of the most powerful tools used for data presentation and analysis is the graph. Used properly, graphs are an important guide to understanding the results of an experiment. They
