Receiver Design for Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) Imaging
|
|
|
- Collin Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction Receiver Design for Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) Imaging Millimeter Wave Systems, LLC Passive Millimeter Wave (PMMW) sensors are used for remote sensing and security applications. They rely on radiometric receivers to sense very small power differences. The performance of radiometric receivers should be characterized in different ways than communications and radar receivers. In communications we typically think in terms of carrier-to-noise ratio (CNR) or signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) relating a generated signal to noise floor. In a PMMW system, the signal sources are random white noise resulting from black body radiation from objects in a scene. The power emitted by an object is proportional to its temperature on a Kelvin scale (relative to absolute zero) and contrast is achieved in a PMMW image by spatial correlation of temperature differences within the scene. All objects radiate black body radiation and PMMW systems are sensitive enough to measure the minute noise power differences between objects. Objects in the scene will partially reflect the surroundings so the noise power perceived is a weighted average of the object s temperature and the surroundings. The weighting factor is known the object s emissivity, ε, and the observed temperature can be expressed as, = +(1 ) At millimeter wave frequencies, most clothing is relatively transparent while the human body is a good absorber (or emitter). Security sensors exploit both these attributes. Many concealed objects, even if they rise to body temperature, tend to reflect the temperature of the surroundings making them detectable. Contrast can be enhanced in these systems by lowering the temperature of the surroundings. For example, outdoor millimeter wave images will have contrasting bands at the tops of objects as a result of the reflection of the cold sky. These images are often shown in reverse contrast resulting in bright areas. The millimeter wave frequency band ( GHz) is considered the most desirable band for personal security screening. Above the millimeter wave band clothing becomes less transparent and below, the resolution, which is limited by aperture (antenna/lens) diffraction, is insufficient or the size of the aperture becomes impractical. Other applications include all-weather imaging. PMMW cameras can see through environmental conditions that would obscure visual or IR cameras making it a desirable complimentary technology. Typical radiometer receiver block diagrams are shown below: (a) Direct Detection Receiver
2 (b) Heterodyne Receiver In both cases power is detected using a detector; typically a square-law detector diode. (a) is a direct detection receiver and (b) shows a heterodyne receiver. For the direct detection receiver, only gain is needed before the detector to overcome the detection limit (NEP) of the detector. The sensitivity of the detector is not critical, however lower NEP requires less RF gain and this is desirable. The heterodyne receiver does not require any gain on the RF end. Heterodyning makes higher frequency operation easier to achieve since mixers are more readily available than amplifiers above W-band. The LO frequency can be multiplied using diode multipliers or though harmonic mixing, or both. Heterodyning is somewhat less common, at least through W-band, with the availability of COTS low noise amplifier MMICs which are readily available and have significant bandwidth (10s of GHz). In both cases the post detection circuit is the same and the detected output is integrated over time to produce the radiometric output. The Noise Equivalent Delta-T (NEDT) is the temperature difference equivalent to the RMS noise level of the system and is given by the Radiometer Equation: where B is the pre-detection bandwidth, Tsys is the system noise temperature and τ is the integration time. It is interesting to note that one can increase B or τ to make an NEDT as small as desired. For imaging, at least a few times the NEDT level is needed to create contrast. The dwell time per pixel is usually limited; particularly if the application is at video rate. Achieving video rate, even for a modest number of pixels, requires a wide bandwidth and low noise temperature. Multi-element receiver arrays are used to overcome sensitivity and bandwidth limitations. Due to the cost and complexity of having a receiver for each pixel, these systems usually have some combination of multiple elements and scanning (e.g. a scanning mirror). Furthermore, practical limitations on minimum element spacing can be overcome with scanning to fill in between elements. In the radiometer equation T sys is the system noise temperature and includes the antenna temperature = +
3 Noise temperature is for the receiver is easily relatable to the noise figure by, or in db, ( )= ( 1) ( )= (10 1) Reception Bandwidth More precisely, the system bandwidth, B, in the radiometer equation is referred to as the radiometer Reception Bandwidth, and is defined as: () = () where G(f) is the gain of the system at frequency, f. Reception bandwidth is not the same as the -3dB bandwidth although it is often approximated that way. Over wide bandwidths the gain response versus frequency of the system can vary significantly and this can result in significant reduction in reception bandwidth (and therefore system performance). Integrator Integration of the output power over the integration time is performed by the integrator. The detector voltage is assumed to be proportional to power (square law): = () () The simplest integrator is an R-C low pass filter with an integration time constant, τ, approximately equal to R*C. R-C integrators have memory wherein some of the energy from one pixel position will bleed into the next pixel. This is typically mitigated by using a time constant that is much shorter than the dwell time per pixel and then summing multiple Nyquist-sampled measurements to form a single observable. = Other integrator schemes include using a V-to-F converter with a counter, and charging a capacitor through a current source proportional to the detector output. Receiver Budget Example Consider a 400 pixel single receiver system operating at 15 Hz. The maximum dwell time per pixel is 1/15*1/400 = 167 microseconds. With a reception bandwidth of 10 GHz, we have:
4 The result is an NEDT of 0.2 K (or C). Note that the noise power over that bandwidth is -74dBm. With 50dB of RF gain, we d have -24dBm into the detector which is more than adequate for a typical GaAs Schottky diode detector, yet is still in its linear (square law) range. Some MMIC LNAs can have an output compression point as low as -24dBm, so it is important to consider this. The P1dB of the receiver should be 10dB or more below the RMS noise level. A medium power amplifier could be used as a second stage, if needed, without substantively affecting the noise temperature which is set by the first MMIC. System Stability Bandwidth MHz Integration time (tau) ms Tsys 300 K ktb dbm RMS Out (dv/v) NEdT 0.2 K There are two main contributors to system instability: 1) Additive noise and 2) thermal drift. These effects can dominate over the radiometric uncertainty in milliseconds. Low frequency additive noise (ΔG/G) as a result of RF amplification (RF, IF and/or LO) typically has a characteristically 1/f dependence. The noise figure of a HEMT amplifier, for example, can have a 1dB noise figure at 1 GHz and over 15dB at 1 Hz due to 1/f noise. Most commercially available millimeter wave amplifiers are GaAs phemt and will exhibit significant 1/f. Bipolar transistors have comparatively better 1/f performance (Weinreb and Schleeh 2014). Thermal drift is typically dominated by the detector, but can also be caused by temperature induced gain fluctuations in the amplifiers. Comparison to a reference using a switch can be used to track out drift errors as in the example of a Dicke radiometer shown below: The NEDT of the Dicke radiometer is twice that of a total power radiometer: 2 Solid state switches at millimeter wave frequencies can significantly degrade the receiver noise temperature. Quasi-optical means (e.g. - chopper) can also be used to avoid switch loss. Dicke switching is not always necessary for imaging so long as the radiometer is relatively stable over the timescale of a video frame and the image is auto-scaled. The situation becomes significantly more complicated when
5 there are multiple pixels since each pixel can drift independently of each other and it may be necessary to perform two-point calibration to normalize their outputs. Stability Characterization The sources of instability are difficult to measure directly because they are small compared to the random fluctuations of the measurement over short periods of time. An excellent method for characterizing radiometer stability is Allan Variance (G. Rau et al 1984). This analysis method, named after David M. Allan, was originally used for characterizing time standards. The Allan variance of the radiometer output for a given integration time, τ 0, is ( )= ( ) 2( 1) for N samples, each with an integration time, τ 0. The Allan variance has the same value as the conventional variance for Gaussian noise. The Allan variance can be calculated for integration times that are a multiples of τ 0 by aggregating adjacent samples to effectively form samples of 2τ 0, 3τ 0,, using the same data set. When plotted on a log-log scale, the theoretical σ A is a straight line with a negative slope tracking the radiometer equation, whereas 1/f shows up as a positive slope. The ability of the Allan variance to make these distinctions makes it a powerful diagnostic tool. Other sources of drift can also be revealed using the Allan variance technique. Conclusions In general the PMMW receiver design needs to match the application. Stability factors can quickly dominate system performance and managing these factors in the design is at least as important as noise temperature. Dicke switching can be an effective way to mitigate drifts including 1/f over longer integration times. Generally Bipolar amplifiers (HBT) have better 1/f performance than FET amplifiers (HEMT). Maximizing the reception bandwidth is critical to achieving good system performance. Receiver and detector flatness are critical parameters in achieving wide reception bandwidth. Allan Variance is an excellent tool for analyzing the stability and sources of drift. Because it acts on the regular data output of system, and no additional measurement equipment is required.
6 References: S. Weinreb and J. Schleeh, Multiplicative and Additive Low-Frequency Noise in Microwave Transistors, IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, VOL. 62, NO. 1, Jan G. Rau, R. Schieder, B. Vohwinkel, Characterization and Measurement of Radiometer Stability, Proc. 14th European Microwave Conf., Sept , 1984, pp About Millimeter Wave Systems, LLC Millimeter Wave Systems, LLC is a supplier of custom specialized millimeter wave hardware including sub-systems, modules and antennas. Our facilities are located in Amherst, Massachusetts. MWS is a U.S. small business.
A Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements Using Two Hot Noise Sources
 A Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements Using Two Hot Noise Sources Vince Rodriguez and Charles Osborne MI Technologies: Suwanee, 30024 GA, USA vrodriguez@mitechnologies.com Abstract P Gain over
A Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements Using Two Hot Noise Sources Vince Rodriguez and Charles Osborne MI Technologies: Suwanee, 30024 GA, USA vrodriguez@mitechnologies.com Abstract P Gain over
TECH BRIEF Addressing Phase Noise Challenges in Radar and Communication Systems
 Addressing Phase Noise Challenges in Radar and Communication Systems Phase noise is rapidly becoming the most critical factor addressed in sophisticated radar and communication systems. This is because
Addressing Phase Noise Challenges in Radar and Communication Systems Phase noise is rapidly becoming the most critical factor addressed in sophisticated radar and communication systems. This is because
MMA RECEIVERS: HFET AMPLIFIERS
 MMA Project Book, Chapter 5 Section 4 MMA RECEIVERS: HFET AMPLIFIERS Marian Pospieszalski Ed Wollack John Webber Last revised 1999-04-09 Revision History: 1998-09-28: Added chapter number to section numbers.
MMA Project Book, Chapter 5 Section 4 MMA RECEIVERS: HFET AMPLIFIERS Marian Pospieszalski Ed Wollack John Webber Last revised 1999-04-09 Revision History: 1998-09-28: Added chapter number to section numbers.
AGRON / E E / MTEOR 518 Laboratory
 AGRON / E E / MTEOR 518 Laboratory Brian Hornbuckle, Nolan Jessen, and John Basart April 5, 2018 1 Objectives In this laboratory you will: 1. identify the main components of a ground based microwave radiometer
AGRON / E E / MTEOR 518 Laboratory Brian Hornbuckle, Nolan Jessen, and John Basart April 5, 2018 1 Objectives In this laboratory you will: 1. identify the main components of a ground based microwave radiometer
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM Method for measurements of radio noise
 Rec. ITU-R SM.1753 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1753 Method for measurements of radio noise (Question ITU-R 1/45) (2006) Scope For radio noise measurements there is a need to have a uniform, frequency-independent
Rec. ITU-R SM.1753 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1753 Method for measurements of radio noise (Question ITU-R 1/45) (2006) Scope For radio noise measurements there is a need to have a uniform, frequency-independent
Signal Flow & Radiometer Equation. Aletha de Witt AVN-Newton Fund/DARA 2018 Observational & Technical Training HartRAO
 Signal Flow & Radiometer Equation Aletha de Witt AVN-Newton Fund/DARA 2018 Observational & Technical Training HartRAO Understanding Radio Waves The meaning of radio waves How radio waves are created -
Signal Flow & Radiometer Equation Aletha de Witt AVN-Newton Fund/DARA 2018 Observational & Technical Training HartRAO Understanding Radio Waves The meaning of radio waves How radio waves are created -
A Reduced Uncertainty Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements in an Anechoic Chamber
 A Reduced Uncertainty Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements in an Anechoic Chamber Vince Rodriguez and Charles Osborne MI Technologies Suwanee, GA, USA vrodriguez@mitechnologies.com Abstract P
A Reduced Uncertainty Method for Gain over Temperature Measurements in an Anechoic Chamber Vince Rodriguez and Charles Osborne MI Technologies Suwanee, GA, USA vrodriguez@mitechnologies.com Abstract P
Low frequency noise measurements in direct detection radiometers
 Low frequency noise measurements in direct detection radiometers E. Artal, B. Aja, J. Cagigas, J.L. Cano, L. de la Fuente, A. Pérez, E. Villa Universidad de Cantabria, Santander (Spain) Receiver Gain Stability
Low frequency noise measurements in direct detection radiometers E. Artal, B. Aja, J. Cagigas, J.L. Cano, L. de la Fuente, A. Pérez, E. Villa Universidad de Cantabria, Santander (Spain) Receiver Gain Stability
The Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation B. Winstein, U of Chicago
 The Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation B. Winstein, U of Chicago Lecture #1 Lecture #2 What is it? How its anisotropies are generated? What Physics does it reveal? How it is measured. Lecture #3 Main
The Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation B. Winstein, U of Chicago Lecture #1 Lecture #2 What is it? How its anisotropies are generated? What Physics does it reveal? How it is measured. Lecture #3 Main
More Radio Astronomy
 More Radio Astronomy Radio Telescopes - Basic Design A radio telescope is composed of: - a radio reflector (the dish) - an antenna referred to as the feed on to which the radiation is focused - a radio
More Radio Astronomy Radio Telescopes - Basic Design A radio telescope is composed of: - a radio reflector (the dish) - an antenna referred to as the feed on to which the radiation is focused - a radio
Advanced bridge instrument for the measurement of the phase noise and of the short-term frequency stability of ultra-stable quartz resonators
 Advanced bridge instrument for the measurement of the phase noise and of the short-term frequency stability of ultra-stable quartz resonators F. Sthal, X. Vacheret, S. Galliou P. Salzenstein, E. Rubiola
Advanced bridge instrument for the measurement of the phase noise and of the short-term frequency stability of ultra-stable quartz resonators F. Sthal, X. Vacheret, S. Galliou P. Salzenstein, E. Rubiola
GPS receivers built for various
 GNSS Solutions: Measuring GNSS Signal Strength angelo joseph GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions
GNSS Solutions: Measuring GNSS Signal Strength angelo joseph GNSS Solutions is a regular column featuring questions and answers about technical aspects of GNSS. Readers are invited to send their questions
Noise generators. Spatial Combining of Multiple Microwave Noise Radiators NOISE ARRAY. This article reports on. experiments to increase the
 From April 2008 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2008 Summit Technical Media LLC Spatial Combining of Multiple Microwave Noise Radiators By Jiri Polivka Spacek Labs Inc. Noise generators This article
From April 2008 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2008 Summit Technical Media LLC Spatial Combining of Multiple Microwave Noise Radiators By Jiri Polivka Spacek Labs Inc. Noise generators This article
EVLA System Commissioning Results
 EVLA System Commissioning Results EVLA Advisory Committee Meeting, March 19-20, 2009 Rick Perley EVLA Project Scientist t 1 Project Requirements EVLA Project Book, Chapter 2, contains the EVLA Project
EVLA System Commissioning Results EVLA Advisory Committee Meeting, March 19-20, 2009 Rick Perley EVLA Project Scientist t 1 Project Requirements EVLA Project Book, Chapter 2, contains the EVLA Project
AM Noise in Drivers for Frequency Multiplied Local Oscillators
 15th International Symposium on Space Terahert, Technology AM Noise in Drivers for Frequency Multiplied Local Oscillators Neal Erickson Astronomy Dept. University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 USA
15th International Symposium on Space Terahert, Technology AM Noise in Drivers for Frequency Multiplied Local Oscillators Neal Erickson Astronomy Dept. University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 USA
THEORY OF MEASUREMENTS
 THEORY OF MEASUREMENTS Brian Mason Fifth NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy Arecibo, PR July 2009 OUTLINE Antenna-Sky Coupling Noise the Radiometer Equation Minimum Tsys Performance measures
THEORY OF MEASUREMENTS Brian Mason Fifth NAIC-NRAO School on Single-Dish Radio Astronomy Arecibo, PR July 2009 OUTLINE Antenna-Sky Coupling Noise the Radiometer Equation Minimum Tsys Performance measures
Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING. Radar Signal Processing Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti. Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti
 Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING Signal Reception Receiver Bandwidth Pulse Shape Power Relation Beam Width Pulse Repetition Frequency Antenna Gain Radar Cross Section of Target. Signal-to-noise ratio Receiver
Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING Signal Reception Receiver Bandwidth Pulse Shape Power Relation Beam Width Pulse Repetition Frequency Antenna Gain Radar Cross Section of Target. Signal-to-noise ratio Receiver
To print higher-resolution math symbols, click the Hi-Res Fonts for Printing button on the jsmath control panel.
 To print higher-resolution math symbols, click the Hi-Res Fonts for Printing button on the jsmath control panel. Radiometers Natural radio emission from the cosmic microwave background, discrete astronomical
To print higher-resolution math symbols, click the Hi-Res Fonts for Printing button on the jsmath control panel. Radiometers Natural radio emission from the cosmic microwave background, discrete astronomical
Sources classification
 Sources classification Radiometry relates to the measurement of the energy radiated by one or more sources in any region of the electromagnetic spectrum. As an antenna, a source, whose largest dimension
Sources classification Radiometry relates to the measurement of the energy radiated by one or more sources in any region of the electromagnetic spectrum. As an antenna, a source, whose largest dimension
Stability Measurements of a NbN HEB Receiver at THz Frequencies
 Stability Measurements of a NbN HEB Receiver at THz Frequencies T. Berg, S. Cherednichenko, V. Drakinskiy, H. Merkel, E. Kollberg Department of Microtechnology and Nanoscience, Chalmers University of Technology
Stability Measurements of a NbN HEB Receiver at THz Frequencies T. Berg, S. Cherednichenko, V. Drakinskiy, H. Merkel, E. Kollberg Department of Microtechnology and Nanoscience, Chalmers University of Technology
IN propagation path between the satellite and
 Journal of Advances in Computer Engineering and Technology, 1(2) 215 Typical Ka band Satellite Beacon Receiver Design for Propagation Experimentation Reza Bahri 1, Hossein Yarmohammadi 2, Mohammadreza
Journal of Advances in Computer Engineering and Technology, 1(2) 215 Typical Ka band Satellite Beacon Receiver Design for Propagation Experimentation Reza Bahri 1, Hossein Yarmohammadi 2, Mohammadreza
note application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise by David Owen
 application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System
 Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
Long-term stability of an SiGe HBTbased active cold load
 Long-term stability of an SiGe HBTbased active cold load Emilie Leynia de la Jarrige 1, eleyniad@laasfr LEscotte 1, EGonneau 2, JMGoutoule 3 1 CNRS ; LAAS ; Université de Toulouse, 7 avenue du colonel
Long-term stability of an SiGe HBTbased active cold load Emilie Leynia de la Jarrige 1, eleyniad@laasfr LEscotte 1, EGonneau 2, JMGoutoule 3 1 CNRS ; LAAS ; Université de Toulouse, 7 avenue du colonel
Understanding Noise Figure
 Understanding Noise Figure Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul One of the most frequently discussed forms of noise is known as Thermal Noise. Thermal noise is a random fluctuation in
Understanding Noise Figure Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul One of the most frequently discussed forms of noise is known as Thermal Noise. Thermal noise is a random fluctuation in
Guide to observation planning with GREAT
 Guide to observation planning with GREAT G. Sandell GREAT is a heterodyne receiver designed to observe spectral lines in the THz region with high spectral resolution and sensitivity. Heterodyne receivers
Guide to observation planning with GREAT G. Sandell GREAT is a heterodyne receiver designed to observe spectral lines in the THz region with high spectral resolution and sensitivity. Heterodyne receivers
Understanding the performance of atmospheric free-space laser communications systems using coherent detection
 !"#$%&'()*+&, Understanding the performance of atmospheric free-space laser communications systems using coherent detection Aniceto Belmonte Technical University of Catalonia, Department of Signal Theory
!"#$%&'()*+&, Understanding the performance of atmospheric free-space laser communications systems using coherent detection Aniceto Belmonte Technical University of Catalonia, Department of Signal Theory
EVLA Memo 105. Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope
 EVLA Memo 105 Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope Steven Durand, James Jackson, and Keith Morris National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 1003 Lopezville Road, Socorro, NM, USA 87801 ABSTRACT The
EVLA Memo 105 Phase coherence of the EVLA radio telescope Steven Durand, James Jackson, and Keith Morris National Radio Astronomy Observatory, 1003 Lopezville Road, Socorro, NM, USA 87801 ABSTRACT The
Coherent Receivers Principles Downconversion
 Coherent Receivers Principles Downconversion Heterodyne receivers mix signals of different frequency; if two such signals are added together, they beat against each other. The resulting signal contains
Coherent Receivers Principles Downconversion Heterodyne receivers mix signals of different frequency; if two such signals are added together, they beat against each other. The resulting signal contains
Design of a 212 GHz LO Source Used in the Terahertz Radiometer Front-End
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 66, 65 70, 2017 Design of a 212 GHz LO Source Used in the Terahertz Radiometer Front-End Jin Meng *, De Hai Zhang, Chang Hong Jiang, Xin Zhao, and Xiao
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 66, 65 70, 2017 Design of a 212 GHz LO Source Used in the Terahertz Radiometer Front-End Jin Meng *, De Hai Zhang, Chang Hong Jiang, Xin Zhao, and Xiao
SHF Communication Technologies AG. Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23D Berlin Germany. Phone Fax
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23D 12277 Berlin Germany Phone +49 30 772051-0 Fax ++49 30 7531078 E-Mail: sales@shf.de Web: http://www.shf.de Datasheet SHF 100 BPP Broadband
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23D 12277 Berlin Germany Phone +49 30 772051-0 Fax ++49 30 7531078 E-Mail: sales@shf.de Web: http://www.shf.de Datasheet SHF 100 BPP Broadband
Solution: NF=6 db, B=2.1 GHz, SNR min =7dB T=290 k, P in,1db = 10.5 dbm
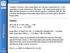 Consider a receiver with a noise figure of 6 db and a bandwidth of 2.1 GHz operating at room temperature. The input 1-dB compression point is 10.5 dbm and the detector at receiver output requires a minimum
Consider a receiver with a noise figure of 6 db and a bandwidth of 2.1 GHz operating at room temperature. The input 1-dB compression point is 10.5 dbm and the detector at receiver output requires a minimum
325 to 500 GHz Vector Network Analyzer System
 325 to 500 GHz Vector Network Analyzer System By Chuck Oleson, Tony Denning and Yuenie Lau OML, Inc. Abstract - This paper describes a novel and compact WR-02.2 millimeter wave frequency extension transmission/reflection
325 to 500 GHz Vector Network Analyzer System By Chuck Oleson, Tony Denning and Yuenie Lau OML, Inc. Abstract - This paper describes a novel and compact WR-02.2 millimeter wave frequency extension transmission/reflection
Amplifier Characterization in the millimeter wave range. Tera Hertz : New opportunities for industry 3-5 February 2015
 Amplifier Characterization in the millimeter wave range Tera Hertz : New opportunities for industry 3-5 February 2015 Millimeter Wave Converter Family ZVA-Z500 ZVA-Z325 Y Band (WR02) ZVA-Z220 J Band (WR03)
Amplifier Characterization in the millimeter wave range Tera Hertz : New opportunities for industry 3-5 February 2015 Millimeter Wave Converter Family ZVA-Z500 ZVA-Z325 Y Band (WR02) ZVA-Z220 J Band (WR03)
Symmetry in the Ka-band Correlation Receiver s Input Circuit and Spectral Baseline Structure NRAO GBT Memo 248 June 7, 2007
 Symmetry in the Ka-band Correlation Receiver s Input Circuit and Spectral Baseline Structure NRAO GBT Memo 248 June 7, 2007 A. Harris a,b, S. Zonak a, G. Watts c a University of Maryland; b Visiting Scientist,
Symmetry in the Ka-band Correlation Receiver s Input Circuit and Spectral Baseline Structure NRAO GBT Memo 248 June 7, 2007 A. Harris a,b, S. Zonak a, G. Watts c a University of Maryland; b Visiting Scientist,
The WVR at Effelsberg. Thomas Krichbaum
 The WVR at Effelsberg Alan Roy Ute Teuber Helge Rottmann Thomas Krichbaum Reinhard Keller Dave Graham Walter Alef The Scanning 18-26 GHz WVR for Effelsberg ν = 18.5 GHz to 26.0 GHz Δν = 900 MHz Channels
The WVR at Effelsberg Alan Roy Ute Teuber Helge Rottmann Thomas Krichbaum Reinhard Keller Dave Graham Walter Alef The Scanning 18-26 GHz WVR for Effelsberg ν = 18.5 GHz to 26.0 GHz Δν = 900 MHz Channels
THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN
 THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN Mark Hunter * Abstract This paper is intended to give an overview of the design of radio transceivers to the engineer new to the field. It is shown how the requirements
THE BASICS OF RADIO SYSTEM DESIGN Mark Hunter * Abstract This paper is intended to give an overview of the design of radio transceivers to the engineer new to the field. It is shown how the requirements
A DISCUSSION ON QAM SNARE SENSITIVITY
 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY A DISCUSSION ON QAM SNARE SENSITIVITY HOW PROCESSING GAIN DELIVERS BEST SENSITIVITY IN THE CATEGORY 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 / WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM ADVANCED
ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY A DISCUSSION ON QAM SNARE SENSITIVITY HOW PROCESSING GAIN DELIVERS BEST SENSITIVITY IN THE CATEGORY 185 AINSLEY DRIVE SYRACUSE, NY 13210 800.448.1655 / WWW.ARCOMDIGITAL.COM ADVANCED
Application Note 1293
 A omparison of Various Bipolar Transistor Biasing ircuits Application Note 1293 Introduction The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is quite often used as a low noise amplifier in cellular, PS, and pager
A omparison of Various Bipolar Transistor Biasing ircuits Application Note 1293 Introduction The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is quite often used as a low noise amplifier in cellular, PS, and pager
Introduction to Radio Astronomy!
 Introduction to Radio Astronomy! Sources of radio emission! Radio telescopes - collecting the radiation! Processing the radio signal! Radio telescope characteristics! Observing radio sources Sources of
Introduction to Radio Astronomy! Sources of radio emission! Radio telescopes - collecting the radiation! Processing the radio signal! Radio telescope characteristics! Observing radio sources Sources of
Characteristics of InP HEMT Harmonic Optoelectronic Mixers and Their Application to 60GHz Radio-on-Fiber Systems
 . TU6D-1 Characteristics of Harmonic Optoelectronic Mixers and Their Application to 6GHz Radio-on-Fiber Systems Chang-Soon Choi 1, Hyo-Soon Kang 1, Dae-Hyun Kim 2, Kwang-Seok Seo 2 and Woo-Young Choi 1
. TU6D-1 Characteristics of Harmonic Optoelectronic Mixers and Their Application to 6GHz Radio-on-Fiber Systems Chang-Soon Choi 1, Hyo-Soon Kang 1, Dae-Hyun Kim 2, Kwang-Seok Seo 2 and Woo-Young Choi 1
Rethinking The Role Of phemt Cascode Amplifiers In RF Design
 Guest Column February 10, 2014 Rethinking The Role Of phemt Cascode Amplifiers In RF Design By Alan Ake, Skyworks Solutions, Inc. I consider myself fortunate that, as a fresh-out-of-school EE, I was able
Guest Column February 10, 2014 Rethinking The Role Of phemt Cascode Amplifiers In RF Design By Alan Ake, Skyworks Solutions, Inc. I consider myself fortunate that, as a fresh-out-of-school EE, I was able
LOW COST PHASED ARRAY ANTENNA TRANSCEIVER FOR WPAN APPLICATIONS
 LOW COST PHASED ARRAY ANTENNA TRANSCEIVER FOR WPAN APPLICATIONS Introduction WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network) transceivers are being designed to operate in the 60 GHz frequency band and will mainly
LOW COST PHASED ARRAY ANTENNA TRANSCEIVER FOR WPAN APPLICATIONS Introduction WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network) transceivers are being designed to operate in the 60 GHz frequency band and will mainly
Clock Measurements Using the BI220 Time Interval Analyzer/Counter and Stable32
 Clock Measurements Using the BI220 Time Interval Analyzer/Counter and Stable32 W.J. Riley Hamilton Technical Services Beaufort SC 29907 USA Introduction This paper describes methods for making clock frequency
Clock Measurements Using the BI220 Time Interval Analyzer/Counter and Stable32 W.J. Riley Hamilton Technical Services Beaufort SC 29907 USA Introduction This paper describes methods for making clock frequency
A Low Noise GHz Amplifier
 A Low Noise 3.4-4.6 GHz Amplifier C. Risacher*, M. Dahlgren*, V. Belitsky* * GARD, Radio & Space Science Department with Onsala Space Observatory, Microtechnology Centre at Chalmers (MC2), Chalmers University
A Low Noise 3.4-4.6 GHz Amplifier C. Risacher*, M. Dahlgren*, V. Belitsky* * GARD, Radio & Space Science Department with Onsala Space Observatory, Microtechnology Centre at Chalmers (MC2), Chalmers University
Introduction to ixblue RF drivers and amplifiers for optical modulators
 Introduction to ixblue RF drivers and amplifiers for optical modulators Introduction : ixblue designs, produces and commercializes optical modulators intended for a variety of applications including :
Introduction to ixblue RF drivers and amplifiers for optical modulators Introduction : ixblue designs, produces and commercializes optical modulators intended for a variety of applications including :
MICROWAVE RADIO SYSTEMS GAIN. PENTel.Com Engr. Josephine Bagay, Ece faculty
 MICROWAVE RADIO SYSTEMS GAIN PENTel.Com Engr. Josephine Bagay, Ece faculty SYSTEM GAIN G s is the difference between the nominal output power of a transmitter (P t ) and the minimum input power to a receiver
MICROWAVE RADIO SYSTEMS GAIN PENTel.Com Engr. Josephine Bagay, Ece faculty SYSTEM GAIN G s is the difference between the nominal output power of a transmitter (P t ) and the minimum input power to a receiver
Sub-Millimeter RF Receiver. Sub-Millimeter 19Receiver. balanced using Polarization Vectors. Intrel Service Company
 Sub-Millimeter RF Receiver balanced using Polarization Vectors Intrel Service Company iscmail@intrel.com Sub-Millimeter Week of RF 19Receiver August 2012 Copyright Intrel Service Company 2012 Some Rights
Sub-Millimeter RF Receiver balanced using Polarization Vectors Intrel Service Company iscmail@intrel.com Sub-Millimeter Week of RF 19Receiver August 2012 Copyright Intrel Service Company 2012 Some Rights
Receiver Design. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21
 Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
APPLICATION NOTE 3942 Optimize the Buffer Amplifier/ADC Connection
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Communications Circuits > APP 3942 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > High-Speed Interconnect > APP 3942
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Communications Circuits > APP 3942 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > High-Speed Interconnect > APP 3942
Estimation of cross coupling of receiver noise between the EoR fat-dipole antennas
 Estimation of cross coupling of receiver noise between the EoR fat-dipole antennas Due to the proximity of the fat dipoles in the EoR receiver configuration, the receiver noise of individual antennas may
Estimation of cross coupling of receiver noise between the EoR fat-dipole antennas Due to the proximity of the fat dipoles in the EoR receiver configuration, the receiver noise of individual antennas may
Microwave Power Amplifiers for Broadband Applications
 Microwave Power Amplifiers for Broadband Applications White Paper by Leonard Dickstein, Marketing Manager A mplifiers are one of the most basic electrical elements in any electronic system. Broadband microwave
Microwave Power Amplifiers for Broadband Applications White Paper by Leonard Dickstein, Marketing Manager A mplifiers are one of the most basic electrical elements in any electronic system. Broadband microwave
Module 10 : Receiver Noise and Bit Error Ratio
 Module 10 : Receiver Noise and Bit Error Ratio Lecture : Receiver Noise and Bit Error Ratio Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Receiver Noise and Bit Error Ratio Shot Noise Thermal
Module 10 : Receiver Noise and Bit Error Ratio Lecture : Receiver Noise and Bit Error Ratio Objectives In this lecture you will learn the following Receiver Noise and Bit Error Ratio Shot Noise Thermal
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY
 Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
Dual-band LNA Design for Wireless LAN Applications. 2.4 GHz LNA 5 GHz LNA Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
 Dual-band LNA Design for Wireless LAN Applications White Paper By: Zulfa Hasan-Abrar, Yut H. Chow Introduction Highly integrated, cost-effective RF circuitry is becoming more and more essential to the
Dual-band LNA Design for Wireless LAN Applications White Paper By: Zulfa Hasan-Abrar, Yut H. Chow Introduction Highly integrated, cost-effective RF circuitry is becoming more and more essential to the
Microwave-Radiometer
 Microwave-Radiometer Figure 1: History of cosmic background radiation measurements. Left: microwave instruments, right: background radiation as seen by the corresponding instrument. Picture: NASA/WMAP
Microwave-Radiometer Figure 1: History of cosmic background radiation measurements. Left: microwave instruments, right: background radiation as seen by the corresponding instrument. Picture: NASA/WMAP
The Design of E-band MMIC Amplifiers
 The Design of E-band MMIC Amplifiers Liam Devlin, Stuart Glynn, Graham Pearson, Andy Dearn * Plextek Ltd, London Road, Great Chesterford, Essex, CB10 1NY, UK; (lmd@plextek.co.uk) Abstract The worldwide
The Design of E-band MMIC Amplifiers Liam Devlin, Stuart Glynn, Graham Pearson, Andy Dearn * Plextek Ltd, London Road, Great Chesterford, Essex, CB10 1NY, UK; (lmd@plextek.co.uk) Abstract The worldwide
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers
 ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper
 Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses
 564 Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses Hidemi Tsuchida National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology 1-1-1 Umezono, Tsukuba, 305-8568 JAPAN Tel: 81-29-861-5342;
564 Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses Hidemi Tsuchida National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology 1-1-1 Umezono, Tsukuba, 305-8568 JAPAN Tel: 81-29-861-5342;
Photons and solid state detection
 Photons and solid state detection Photons represent discrete packets ( quanta ) of optical energy Energy is hc/! (h: Planck s constant, c: speed of light,! : wavelength) For solid state detection, photons
Photons and solid state detection Photons represent discrete packets ( quanta ) of optical energy Energy is hc/! (h: Planck s constant, c: speed of light,! : wavelength) For solid state detection, photons
Noise Figure Definitions and Measurements What is this all about?...
 Noise Figure Definitions and Measurements What is this all about?... Bertrand Zauhar, ve2zaz@rac.ca November 2011 1 Today's Program on Noise Figure What is RF noise, how to quantify it, What is Noise Factor
Noise Figure Definitions and Measurements What is this all about?... Bertrand Zauhar, ve2zaz@rac.ca November 2011 1 Today's Program on Noise Figure What is RF noise, how to quantify it, What is Noise Factor
Keysight Technologies Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range. Application Note
 Keysight Technologies Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note 02 Keysight Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note 1. Introduction
Keysight Technologies Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note 02 Keysight Optimizing RF and Microwave Spectrum Analyzer Dynamic Range Application Note 1. Introduction
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters
 High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
Modulated Multimode Mixing Illumination for the Elimination of Speckle and Target Orientation Requirements in Active Imaging
 Modulated Multimode Mixing Illumination for the Elimination of Speckle and Target Orientation Requirements in Active Imaging Mark A. Patrick Jennifer A. Holt Frank C. De Lucia Physics Department, Ohio
Modulated Multimode Mixing Illumination for the Elimination of Speckle and Target Orientation Requirements in Active Imaging Mark A. Patrick Jennifer A. Holt Frank C. De Lucia Physics Department, Ohio
Technical Note. HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements
 Technical Note HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements Joe Kelly, Ph.D. Verigy 1/13 Abstract In the last few years, low-noise amplifiers (LNA) have become integrated into receiver devices that bring signals
Technical Note HVM Receiver Noise Figure Measurements Joe Kelly, Ph.D. Verigy 1/13 Abstract In the last few years, low-noise amplifiers (LNA) have become integrated into receiver devices that bring signals
Microwave Radiometry Laboratory Experiment
 Microwave Radiometry Laboratory Experiment JEFFREY D. DUDA Iowa State University Department of Geologic and Atmospheric Sciences ABSTRACT A laboratory experiment involving the use of a microwave radiometer
Microwave Radiometry Laboratory Experiment JEFFREY D. DUDA Iowa State University Department of Geologic and Atmospheric Sciences ABSTRACT A laboratory experiment involving the use of a microwave radiometer
Optical Communications
 Optical Communications Telecommunication Engineering School of Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2005-2006 Lecture #4, May 9 2006 Receivers OVERVIEW Photodetector types: Photodiodes
Optical Communications Telecommunication Engineering School of Engineering University of Rome La Sapienza Rome, Italy 2005-2006 Lecture #4, May 9 2006 Receivers OVERVIEW Photodetector types: Photodiodes
Residual Phase Noise Measurement Extracts DUT Noise from External Noise Sources By David Brandon and John Cavey
 Residual Phase Noise easurement xtracts DUT Noise from xternal Noise Sources By David Brandon [david.brandon@analog.com and John Cavey [john.cavey@analog.com Residual phase noise measurement cancels the
Residual Phase Noise easurement xtracts DUT Noise from xternal Noise Sources By David Brandon [david.brandon@analog.com and John Cavey [john.cavey@analog.com Residual phase noise measurement cancels the
SHF Communication Technologies AG
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23D 12277 Berlin Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.de Web: http://www.shf.de Datasheet SHF 806 E SHF
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23D 12277 Berlin Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.de Web: http://www.shf.de Datasheet SHF 806 E SHF
Gilbert Cell Multiplier Measurements from GHz II: Sample of Eight Multipliers
 Gilbert Cell Multiplier Measurements from 2-18.5 GHz II: Sample of Eight Multipliers A.I. Harris 26 February 2002, 7 June 2002 1 Overview and summary This note summarizes a set of measurements of eight
Gilbert Cell Multiplier Measurements from 2-18.5 GHz II: Sample of Eight Multipliers A.I. Harris 26 February 2002, 7 June 2002 1 Overview and summary This note summarizes a set of measurements of eight
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator
 Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
LINEAR MICROWAVE FIBER OPTIC LINK SYSTEM DESIGN
 LINEAR MICROWAVE FIBER OPTIC LINK SYSTEM DESIGN John A. MacDonald and Allen Katz Linear Photonics, LLC Nami Lane, Suite 7C, Hamilton, NJ 869 69-584-5747 macdonald@linphotonics.com LINEAR PHOTONICS, LLC
LINEAR MICROWAVE FIBER OPTIC LINK SYSTEM DESIGN John A. MacDonald and Allen Katz Linear Photonics, LLC Nami Lane, Suite 7C, Hamilton, NJ 869 69-584-5747 macdonald@linphotonics.com LINEAR PHOTONICS, LLC
The Friis Transmission Formula
 The Friis Transmission Formula If we assume that the antennas are aligned for maximum transmission and reception, then in free space, P RX = G TXA e P TX 4πr 2 where A e is the receiving aperture of the
The Friis Transmission Formula If we assume that the antennas are aligned for maximum transmission and reception, then in free space, P RX = G TXA e P TX 4πr 2 where A e is the receiving aperture of the
Varactor-Tuned Oscillators. Technical Data. VTO-8000 Series
 Varactor-Tuned Oscillators Technical Data VTO-8000 Series Features 600 MHz to 10.5 GHz Coverage Fast Tuning +7 to +13 dbm Output Power ± 1.5 db Output Flatness Hermetic Thin-film Construction Description
Varactor-Tuned Oscillators Technical Data VTO-8000 Series Features 600 MHz to 10.5 GHz Coverage Fast Tuning +7 to +13 dbm Output Power ± 1.5 db Output Flatness Hermetic Thin-film Construction Description
NEWTON TRAINING (2018):
 NEWTON TRAINING (2018): RADIOMETER, SQUARE LAW DETECTOR and Noise Diodes Basics and HartRAO implementations. Keith Jones Basic Radiometer A device for measuring the radiant flux (power) of Electromagnetic
NEWTON TRAINING (2018): RADIOMETER, SQUARE LAW DETECTOR and Noise Diodes Basics and HartRAO implementations. Keith Jones Basic Radiometer A device for measuring the radiant flux (power) of Electromagnetic
ECE Lecture 32
 ECE 5010 - Lecture 32 1 Microwave Radiometry 2 Properties of a Radiometer 3 Radiometric Calibration and Uncertainty 4 Types of Radiometer Measurements Levis, Johnson, Teixeira (ESL/OSU) Radiowave Propagation
ECE 5010 - Lecture 32 1 Microwave Radiometry 2 Properties of a Radiometer 3 Radiometric Calibration and Uncertainty 4 Types of Radiometer Measurements Levis, Johnson, Teixeira (ESL/OSU) Radiowave Propagation
NOISE INTERNAL NOISE. Thermal Noise
 NOISE INTERNAL NOISE......1 Thermal Noise......1 Shot Noise......2 Frequency dependent noise......3 THERMAL NOISE......3 Resistors in series......3 Resistors in parallel......4 Power Spectral Density......4
NOISE INTERNAL NOISE......1 Thermal Noise......1 Shot Noise......2 Frequency dependent noise......3 THERMAL NOISE......3 Resistors in series......3 Resistors in parallel......4 Power Spectral Density......4
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
LWIR NUC Using an Uncooled Microbolometer Camera
 LWIR NUC Using an Uncooled Microbolometer Camera Joe LaVeigne a, Greg Franks a, Kevin Sparkman a, Marcus Prewarski a, Brian Nehring a, Steve McHugh a a Santa Barbara Infrared, Inc., 30 S. Calle Cesar Chavez,
LWIR NUC Using an Uncooled Microbolometer Camera Joe LaVeigne a, Greg Franks a, Kevin Sparkman a, Marcus Prewarski a, Brian Nehring a, Steve McHugh a a Santa Barbara Infrared, Inc., 30 S. Calle Cesar Chavez,
Application Note 5057
 A 1 MHz to MHz Low Noise Feedback Amplifier using ATF-4143 Application Note 7 Introduction In the last few years the leading technology in the area of low noise amplifier design has been gallium arsenide
A 1 MHz to MHz Low Noise Feedback Amplifier using ATF-4143 Application Note 7 Introduction In the last few years the leading technology in the area of low noise amplifier design has been gallium arsenide
Receiver Performance and Comparison of Incoherent (bolometer) and Coherent (receiver) detection
 At ev gap /h the photons have sufficient energy to break the Cooper pairs and the SIS performance degrades. Receiver Performance and Comparison of Incoherent (bolometer) and Coherent (receiver) detection
At ev gap /h the photons have sufficient energy to break the Cooper pairs and the SIS performance degrades. Receiver Performance and Comparison of Incoherent (bolometer) and Coherent (receiver) detection
RF, Microwave & Wireless. All rights reserved
 RF, Microwave & Wireless All rights reserved 1 Non-Linearity Phenomenon All rights reserved 2 Physical causes of nonlinearity Operation under finite power-supply voltages Essential non-linear characteristics
RF, Microwave & Wireless All rights reserved 1 Non-Linearity Phenomenon All rights reserved 2 Physical causes of nonlinearity Operation under finite power-supply voltages Essential non-linear characteristics
Heterodyne Sweeping Radiometer
 46 Robezu str. LV-1004 Riga, Latvia Fax: +371-7-065102 Mm-wave Division in St. Petersburg, Russia Fax: +7-812- 326-10-60 Tel: +7-812-326-59-24 E-mail: ivanovph@nnz.ru Heterodyne Sweeping Radiometer Operation
46 Robezu str. LV-1004 Riga, Latvia Fax: +371-7-065102 Mm-wave Division in St. Petersburg, Russia Fax: +7-812- 326-10-60 Tel: +7-812-326-59-24 E-mail: ivanovph@nnz.ru Heterodyne Sweeping Radiometer Operation
Forest Fire Detection by Low-Cost 13GHz Radiometer
 Forest Fire Detection by Low-Cost 13GHz Radiometer F. Alimenti, S. Bonafoni, G. Tasselli, S. Leone, L. Roselli, K. Solbach, P. Basili 1 Summary Introduction Principle of operation Sensor architecture Radiometer
Forest Fire Detection by Low-Cost 13GHz Radiometer F. Alimenti, S. Bonafoni, G. Tasselli, S. Leone, L. Roselli, K. Solbach, P. Basili 1 Summary Introduction Principle of operation Sensor architecture Radiometer
A 330 GHz active terahertz imaging system for hidden objects detection
 Invited Paper A 330 GHz active terahertz imaging system for hidden objects detection C. C. Qi *, G. S. Wu, Q. Ding, and Y. D. Zhang China Communication Technology Co., Ltd., Baotian Road No. 1, Building
Invited Paper A 330 GHz active terahertz imaging system for hidden objects detection C. C. Qi *, G. S. Wu, Q. Ding, and Y. D. Zhang China Communication Technology Co., Ltd., Baotian Road No. 1, Building
Noise by the Numbers
 Noise by the Numbers 1 What can I do with noise? The two primary applications for white noise are signal jamming/impairment and reference level comparison. Signal jamming/impairment is further divided
Noise by the Numbers 1 What can I do with noise? The two primary applications for white noise are signal jamming/impairment and reference level comparison. Signal jamming/impairment is further divided
1 of 7 12/20/ :04 PM
 1 of 7 12/20/2007 11:04 PM Trusted Resource for the Working RF Engineer [ C o m p o n e n t s ] Build An E-pHEMT Low-Noise Amplifier Although often associated with power amplifiers, E-pHEMT devices are
1 of 7 12/20/2007 11:04 PM Trusted Resource for the Working RF Engineer [ C o m p o n e n t s ] Build An E-pHEMT Low-Noise Amplifier Although often associated with power amplifiers, E-pHEMT devices are
Agilent Fundamentals of RF and Microwave Noise Figure Measurements
 Agilent Fundamentals of RF and Microwave Noise Figure Measurements Application Note 57-1 2 Table of Contents 1. What is Noise Figure?.....................................4 Introduction.................................................4
Agilent Fundamentals of RF and Microwave Noise Figure Measurements Application Note 57-1 2 Table of Contents 1. What is Noise Figure?.....................................4 Introduction.................................................4
A NEW GENERATION PROGRAMMABLE PHASE/AMPLITUDE MEASUREMENT RECEIVER
 GENERAL A NEW GENERATION PROGRAMMABLE PHASE/AMPLITUDE MEASUREMENT RECEIVER by Charles H. Currie Scientific-Atlanta, Inc. 3845 Pleasantdale Road Atlanta, Georgia 30340 A new generation programmable, phase-amplitude
GENERAL A NEW GENERATION PROGRAMMABLE PHASE/AMPLITUDE MEASUREMENT RECEIVER by Charles H. Currie Scientific-Atlanta, Inc. 3845 Pleasantdale Road Atlanta, Georgia 30340 A new generation programmable, phase-amplitude
6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang. General Outline
 6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang General Outline We will build a superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver circuit that will have a bandwidth of the entire AM spectrum, and whose
6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang General Outline We will build a superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver circuit that will have a bandwidth of the entire AM spectrum, and whose
Optical Delay Line Application Note
 1 Optical Delay Line Application Note 1.1 General Optical delay lines system (ODL), incorporates a high performance lasers such as DFBs, optical modulators for high operation frequencies, photodiodes,
1 Optical Delay Line Application Note 1.1 General Optical delay lines system (ODL), incorporates a high performance lasers such as DFBs, optical modulators for high operation frequencies, photodiodes,
NTT DOCOMO Technical Journal. RoF Equipment Developed for Coverage in Small Areas where Received Power is Low. 1. Introduction
 RoF Indoor Coverage MIMO System RoF Equipment Developed for Coverage in Small Areas where Received Power is Low We have developed an RoF to provide cellular services in areas where received power is low,
RoF Indoor Coverage MIMO System RoF Equipment Developed for Coverage in Small Areas where Received Power is Low We have developed an RoF to provide cellular services in areas where received power is low,
RF Fundamental Concepts and Performance Parameters
 RF Fundamental Concepts and erformance arameters CCE 50 RF and Microwave System Design Dr. Owen Casha B. Eng. (Hons.) h.d. 09/0/0 Overview Introduction Nonlinearity and Time Variance System Noise Thermal
RF Fundamental Concepts and erformance arameters CCE 50 RF and Microwave System Design Dr. Owen Casha B. Eng. (Hons.) h.d. 09/0/0 Overview Introduction Nonlinearity and Time Variance System Noise Thermal
NASTER System Definition Proposal
 Remote Sensing Team NASTER System Definition Proposal All rights reserved. - 7/14/03 Page 1 Overview Review and comment the mid-ir requirements Presentation of ABB s current platform technology Proposed
Remote Sensing Team NASTER System Definition Proposal All rights reserved. - 7/14/03 Page 1 Overview Review and comment the mid-ir requirements Presentation of ABB s current platform technology Proposed
Fundamentals Of Commercial Doppler Systems
 Fundamentals Of Commercial Doppler Systems Speed, Motion and Distance Measurements I. Introduction MDT manufactures a large variety of microwave oscillators, transceivers, and other components for the
Fundamentals Of Commercial Doppler Systems Speed, Motion and Distance Measurements I. Introduction MDT manufactures a large variety of microwave oscillators, transceivers, and other components for the
Optical generation of frequency stable mm-wave radiation using diode laser pumped Nd:YAG lasers
 Optical generation of frequency stable mm-wave radiation using diode laser pumped Nd:YAG lasers T. Day and R. A. Marsland New Focus Inc. 340 Pioneer Way Mountain View CA 94041 (415) 961-2108 R. L. Byer
Optical generation of frequency stable mm-wave radiation using diode laser pumped Nd:YAG lasers T. Day and R. A. Marsland New Focus Inc. 340 Pioneer Way Mountain View CA 94041 (415) 961-2108 R. L. Byer
ATF-531P8 900 MHz High Linearity Amplifier. Application Note 1372
 ATF-531P8 9 MHz High Linearity Amplifier Application Note 1372 Introduction This application note describes the design and construction of a single stage 85 MHz to 9 MHz High Linearity Amplifier using
ATF-531P8 9 MHz High Linearity Amplifier Application Note 1372 Introduction This application note describes the design and construction of a single stage 85 MHz to 9 MHz High Linearity Amplifier using
Notes on Optical Amplifiers
 Notes on Optical Amplifiers Optical amplifiers typically use energy transitions such as those in atomic media or electron/hole recombination in semiconductors. In optical amplifiers that use semiconductor
Notes on Optical Amplifiers Optical amplifiers typically use energy transitions such as those in atomic media or electron/hole recombination in semiconductors. In optical amplifiers that use semiconductor
