CREATIVE CONNECTIONS ART AND MATHS PROJECT WORKBOOK THIS BOOK BELONGS TO: ... CLASS / YEAR GROUP: ...
|
|
|
- Bethanie Chloe Phillips
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CREATIVE CONNECTIONS ART AND MATHS PROJECT WORKBOOK THIS BOOK BELONGS TO:... CLASS / YEAR GROUP:...
2 INTRODUCTION This workbook has been created in order to identify the clear and fascinating connections between The Courtauld s Islamic metalwork and Italian Maiolica ceramic collections and mathematics. The various mathematical activities in this workbook use designs from The Courtauld Collection to introduce and explain important mathematical principles. The activities can be used in conjunction with the Art and Maths in the Courtauld learning resource or as stand-alone activities used to supplement existing lesson plans. Teachers can access all elements needed to run the project including the Art and Maths in the Courtauld Collection learning resource, lesson plans and this student workbook via our website or by ing the Learning Department. education@courtauld.ac.uk Telephone: Website: Francesca Herrick, Courtauld Alumni and Gallery Learning Educator, who has worked with the Collection for almost a decade wrote and edited this workbook. IMAGES Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity 1: Dish, Italy (Venice?), about , Bronze with silver inlay, 45.9cm 3 & 16: Metalwork bag, Mosul, Iraq, Early 14th century, Brass with gold and silver inlay, 13.5x 19.2x 15.2x 22cm 3: Moulded dish or crespina with Cupid holding a basket of fruit, Circ 1540, Tin-glazed earthenware, 21cm 4: Workshop of Giorgio Andreoli, Dish with ornamental letter, about 1525, Lustred earthenware, 23cm 5: Moulded dish or crespina with Cupid holding a basket of fruit, 16th century, Lustred earthenware, 21cm 5: Lustred dish or piatto da pompa with one of the Magi, 16th century, Lustred earthenware, 41cm 6: Moulded lustred dish or tondino with rays and bosses, 16th century, Lustred earthenware 6: Dragon-spouted drug jar, Italy (Castelli), about 1520, Lustred earthenware, 25.3cm 7: Dish or tondino with a female martyr inscribed S.L., probably for St Lucretia, 16th century, Lustred earthenware, 23cm 11: Lustred ewer with scale and leaf design, 16th century, Lustred earthenware, 18.3cm 12: Lustred dishes or piatto da pompa with one of the Magi, 16th century, Lustred earthenware, 41cm 13 & 14: School of Islamic Geometry : Photograph credits Stephanie Christodoulou & Francesca Herrick Typeset: JWD
3 ACTIVITY 1: ANGLES Knowing how to measure angles and understanding the properties of certain shapes are important skills for making patterns. This bowl was produced in Italy in the 1500s where inlaid metalwork from Egypt and Syria was often traded. The craftsperson who made it was inspired by the rich decoration of Islamic metalwork. Parts of the design are highlighted out in silver. Two lines of symmetry have been drawn on top of this design to create four equally sized sectors of a circle. These are known as quadrants. What is the value in degrees of each angle marked with a small square?... How many degrees are there in a circle in total?... Don t forget to add the degrees sign Another way to divide the plate is into 6 equally sized sectors of identical pattern. Each angle measures 60. How many angles are in a semi-circle?... What do we call an angle smaller than 90?... What do we call an angle larger than 90?... 1
4 ACTIVITY 2: PLATE TEMPLATE Now see if you can divide the circle below into six equal angles and segments using a protractor and ruler. The centre of the circle is marked with a dot and one line has already been added. Decorate your plate with curvy shapes and flowing plant-like forms. 2
5 ACTIVITY 3: CIRCLES AND HEXAGONS Your tutor will explain how it is possible to divide a circle into 6 parts using just a compass and ruler. You can try this back at school. Draw a circle and place the compass point anywhere on the circumference. Keeping the compass open by the same length as the circle s radius, draw an arc and then use this as the starting point for drawing the next arc. Continue until you have drawn 6 arcs. Draw a circle and place your compass point anywhere on the circumference. Draw another circle of the same size. Use the two points of intersection to draw two more circles. Continue in this way until you have a flower shape. Choose which lines to go over in order to make the six-petal design picked out in gold on the Courtauld Bag. Use a coloured pencil of your choice. There are some bigger pictures of the bag on the next page. Now see how many hexagons you can make from the same group of intersecting circles. 3
6 THE COURTAULD BAG 4
7 ACTIVITY 4: SYMMETRY Symmetry can often be found in the designs produced by Islamic metalworkers and Renaissance ceramicists. It helped them to bring qualities of balance, order and unity to their creations. A design has a line of symmetry if the two halves it divides are exact reflections of each other. One line of symmetry has already been drawn on this dish made by Giorgio Andreoli in around How many more lines are there in total? (use a mirror to test your answers). Name the shapes below and add all of the lines of symmetry you can find for them
8 ACTIVITY 5: DIVISION & SYMMETRY Make an octagon by folding along its lines of symmetry. The tutor will give you a circle of paper. Carefully fold this in half to make a semi-circle (180 ). Fold this in half to make a quadrant (90 ). Fold this in half to make an octant (45 ) Open the circle back up and use a ruler and pencil to join the points where the fold lines meet the circumference. Keep your octagon and decorate it with patterns from The Courtauld Gallery Create a plate border: Draw the mirror image of this plate design in the opposite space. You can either do this by eye or by tracing and flipping over the original design. 6
9 ACTIVITY 6: ROTATION How many times has this motif been rotated to create the border? Use a ruler to mark each rotation as the spoke of a wheel. Two rotations are already marked. The slice-like portions of the circle are called sectors. The spotted cat design below has been taken from a Majolica pharmacy jar. How should the spotted cat look in the last rectangle when it has been rotated 270 (3 x 90 ) anti-clockwise? 7
10 ACTIVITY 7: DESCRIBING FEATURES OF CIRCLES Let s find out how much we have learnt about circles. Label the following features of a circle: Radius Diameter Circumference Arc Tangent (clue: from the Latin word tangere, to touch ) Segment (clue: think of a segment of orange)
11 ACTIVITY 8: TESSELATION This describes when we cover a surface with a repeated pattern of flat shapes so that there are no overlaps or gaps. It is rare that shapes will fit perfectly together. In fact this only happens in three situations (illustrated below). This is called regular tessellation. In most cases we will need to use two or more shapes to cover a surface without any gaps. What do the above shapes have in common? (Clue: it may help to measure the sides). DESIGNS WITH A TRIANGULAR GRID See if you can continue the patterns. Each side of a triangle measures 1.5cm. 9
12 ACTIVITY 9: TRIANGLES POLYGONS are shapes made up of straight sides. Equilateral triangles are regular polygons. Can you label the other main types of triangles? These are irregular polygons because not all of their sides are of equal length Measure and label the angles in each corner for all three triangles. They should all add up to the same total of degrees. What is this number?... AREAS OF TRIANGLES AND PARALLELOGRAMS Measure the Perimeter of the triangle P = a + b + c Measure the Area of the triangle to the nearest 2 decimal places (you may use a calculator) A = ½ base x height Measure the Perimeter of the parallelogram P = 2a + 2b Measure the Area of the parallelogram to the nearest 2 decimal places (you may use a calculator) A = base x height If you feel unsure about working with decimal places, see if you can still learn the formula for the area of a triangle and the formula for the area of a parallelogram. 10
13 ACTIVITY 10: MAKING STARS The same shapes and patterns appear in Islamic design in different counties. Ideas may have been shared through craftspeople travelling and through objects being traded. It is also possible that designers were simply experimenting with the same tools and construction lines so came up with identical patterns by themselves. Some of the earliest geometric motifs to be used in Islamic design were 6 and 8-pointed stars. A 6-pointed star is easy to make. Draw 6 equally spaced arcs on the circumference of the empty circle (look back at Activity Sheet 3 you will need to measure the radius of the circle). Join up every other point to make the star. How many equilateral triangles have you drawn? Go to page 14 if you get stuck and need a little help. Turn over to practise using a compass. An 8-pointed star can be made by drawing two squares inside a circle. See if you can join up the correct points on the construction lines below to create your own 8-pointed star. 11
14 TIPS FOR USING A COMPASS When the two arms of the compass are placed together, the metal point and the tip of the pencil should just touch. Tighten the holder for the pencil so that it does not slip. It is easier if you use a pencil that is shorter than the compass itself. When drawing your circle or arc, only hold the plastic top of the compass. Do not touch any other part of the compass/ pencil or your radius may change in length. 12
15 PRACTICE PAGE 13
16 ACTIVITY 10 (with construction points) A 6-pointed star is easy to make. Join up the correct points to make the star. How many equilateral triangles have you drawn? An 8-pointed star can be made by drawing two squares inside a circle. See if you can join up the correct points on the construction lines below to create your own 8-pointed star. 14
17 ACTIVITY 11: DESIGNS WITH A SQUARE GRID Scale or petal-like designs appear on all sorts of Majolica objects. Here are instructions to make similar designs using a square grid and circles. Measure the height of a square on the grid below and open your compass by the same amount. The first design is made of full circles and the second design is made from half circles. See if you can continue the patterns. Customise the patterns below by colouring each one in a choice of two colours. 15
18 ACTIVITY 12: PERIMETER AND AREA OF QUADRILATERALS A QUADRILATERAL is a polygon with four sides. The square floor tiles in the plate designs below are regular quadrilaterals because all sides are equal and all angles inside are right angles. Shapes that have four sides, which are not all equal, and angles that are not all right angles, are called irregular quadrilaterals. In the Renaissance era, wealthy Italian people would often have floor tiles in their homes and palaces made of Majolica. They would have to tread very carefully! If the side of one of the tiles in real life measures 20cm what is the perimeter of the tile? 20cm 20cm... What is the area of one tile (don t forget to use the correct units)?... Imagine you are a Renaissance potter. How many tiles would you need to make by hand for a square floor which covers an area of 4m²? Show your workings. What would be the perimeter of this room in cm? Show your workings
19 ACTIVITY 13: MAKING CONTINUOUS PATTERN WITH STARS Here are the instructions to make a design that can be repeated and put together to make an infinite surface pattern. It is another version of the 8-pointed star. STAGE 1 Begin by making a square 21 x 21cm (the width of a sheet of A4 paper). To find the centre point, fold/ draw diagonal lines between opposite corners. Fold/ draw a vertical line and a horizontal line through the centre point. Place the compass point on the centre and draw a circle with a radius of 10.5cm. STAGES 2 & 3 Draw the construction lines shown above using the points of intersection that are highlighted with coloured circles STAGE 4 & 5 Go over the construction lines that you want to use in a coloured pencil FINALLY Lay a sheet of transparent acetate on top and trace your design using a ruler and coloured marker pen. Place your acetate sheet next to your classmates designs and see what happens. You might like to display them altogether on a window. 17
20 ACTIVITY 14: MAKING AN ISLAMIC TILE DESIGN Here are the instructions to make an Islamic tile design with semi-regular tessellation. STAGE 1 Create a square grid and constructions lines. Your teacher will give you a large square sheet of paper. Carefully fold this in half to make a rectangle. Fold this in half to make a small square. Open the paper back up and go over the fold lines with a ruler and pencil. Your square should be divided into four equally sized squares (labelled 1 4). Draw diagonal lines between the corners of each squares as you did for Activity Sheet 10. Add vertical and horizontal lines through the centre points where the diagonals meet. Measure the distance marked r on the diagram below and open your compass by this amount. Place your compass point in the centre of each square and draw a circle. 18
21 STAGE 2: Draw an 8-pointed star inside each circle on your grid STAGE 3: Go over the star s outer construction lines in a coloured pencil STAGE 4: You should have created four star shapes and one cross shape in the middle. These will be the templates for making your tiles. Roll out a small amount of clay out so that it is 8mm thick (use a ruler to check) on top of a star or the cross. Cut out the shape in clay using a plastic knife. Cut out one star and one cross to begin with. STAGE 5: You can decorate your tiles by carving a design into them, adding clay decorations or impressing patterns into them. 19
22 OPTIONAL TEMPLATE FOR ACTIVITY 13 Teacher instructions: This template can be photocopied and doubled in size to create a square 21 x 21cm (the same width as the A4 acetate) 20
23 OPTIONAL TEMPLATE FOR ACTIVITY 14 Teacher instructions: Photocopy and enlarge on an A3 sheet of paper to the desired size. 21
24 ACTIVITY 15: AREA AND VOLUME (ADVANCED LEVEL) Name the 3D shapes: How much clay do we need for our tiles?... Volume is the amount of space an object takes up. The volume of shape a is found by multiplying the area of the square cross section (length x breadth) by the height (h). V = l x b x h Measure one side of the squares you made for Activity 14 (this tells you the length and breadth for the formula above). Our tiles should be 8mm (0.8cm) high/ thick.. These four corner pieces make a cross What is the volume of clay in total needed in mm³ to make one star shaped tile and one cross shaped tile? (you may use a calculator)... What is the volume of clay needed in cm³? (you may use a calculator)... 22
25 ACTIVITY 16: AREA AND VOLUME NET DESIGN Decorate and cut out your own version of the Courtauld Bag. Or, you could ask your teacher to photocopy and enlarge the net design. 23
26 LEARNING RESOURCE CREATIVE CONNECTIONS ART AND MATHS PROJECT WORKBOOK First Edition Learning resources are free to teachers and other education and learning professionals. To be used for education purposes only. Any redistribution or reproduction of any materials herein is strictly prohibited. Stephanie Christodoulou Programme Manager - Gallery Learning Courtauld Institute of Art Somerset House, Strand LONDON, WC2R 0RN education@courtauld.ac.uk All details correct at time of going to production
Basic Mathematics Review 5232
 Basic Mathematics Review 5232 Symmetry A geometric figure has a line of symmetry if you can draw a line so that if you fold your paper along the line the two sides of the figure coincide. In other words,
Basic Mathematics Review 5232 Symmetry A geometric figure has a line of symmetry if you can draw a line so that if you fold your paper along the line the two sides of the figure coincide. In other words,
You need to be really accurate at this before trying the next task. Keep practicing until you can draw a perfect regular hexagon.
 Starter 1: On plain paper practice constructing equilateral triangles using a ruler and a pair of compasses. Use a base of length 7cm. Measure all the sides and all the angles to check they are all the
Starter 1: On plain paper practice constructing equilateral triangles using a ruler and a pair of compasses. Use a base of length 7cm. Measure all the sides and all the angles to check they are all the
2. Here are some triangles. (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is. right-angled, ... (ii) isosceles. ... (2)
 Topic 8 Shapes 2. Here are some triangles. A B C D F E G (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is (i) right-angled,... (ii) isosceles.... (2) Two of the triangles are congruent. (b) Write down
Topic 8 Shapes 2. Here are some triangles. A B C D F E G (a) Write down the letter of the triangle that is (i) right-angled,... (ii) isosceles.... (2) Two of the triangles are congruent. (b) Write down
Unit 5 Shape and space
 Unit 5 Shape and space Five daily lessons Year 4 Summer term Unit Objectives Year 4 Sketch the reflection of a simple shape in a mirror line parallel to Page 106 one side (all sides parallel or perpendicular
Unit 5 Shape and space Five daily lessons Year 4 Summer term Unit Objectives Year 4 Sketch the reflection of a simple shape in a mirror line parallel to Page 106 one side (all sides parallel or perpendicular
SHAPE level 2 questions. 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. 1 mark. International School of Madrid 1
 SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
SHAPE level 2 questions 1. Match each shape to its name. One is done for you. International School of Madrid 1 2. Write each word in the correct box. faces edges vertices 3. Here is half of a symmetrical
Grades 3-5. Robert Smith. Author
 Editors Polly Hoffman Gisela Lee Editorial Manager Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Cover Artist Jessica Orlando Grades 3-5 Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Creative Director
Editors Polly Hoffman Gisela Lee Editorial Manager Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Cover Artist Jessica Orlando Grades 3-5 Art Coordinator Kevin Barnes Creative Director
Drawing Daisy Wheel Angles and Triangles
 Drawing Daisy Wheel Angles and Triangles Laurie Smith Laurie Smith is an independent early-building design researcher, specialising in geometrical design systems. Because geometry was part of the medieval
Drawing Daisy Wheel Angles and Triangles Laurie Smith Laurie Smith is an independent early-building design researcher, specialising in geometrical design systems. Because geometry was part of the medieval
Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers
 LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
Refer to Blackboard for Activities and/or Resources
 Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions. For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8
 Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
Standards of Learning Guided Practice Suggestions For use with the Mathematics Tools Practice in TestNav TM 8 Table of Contents Change Log... 2 Introduction to TestNav TM 8: MC/TEI Document... 3 Guided
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important
 Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
Many artists use geometric concepts in their work. Think about what you have learned in geometry. How do these examples of First Nations art and architecture show geometry ideas? What You ll Learn Identify
The Arabesque of Paul Barchilon
 The Arabesque of Paul Barchilon by Annie Chrietzberg Paul Barchilon s work is covered with complex and precisely laid out pattern. If you delve into his mind, you ll find that there is a structure and
The Arabesque of Paul Barchilon by Annie Chrietzberg Paul Barchilon s work is covered with complex and precisely laid out pattern. If you delve into his mind, you ll find that there is a structure and
Developing geometric thinking. A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9
 Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Developing geometric thinking A developmental series of classroom activities for Gr. 1-9 Developing geometric thinking ii Contents Van Hiele: Developing Geometric Thinking... 1 Sorting objects using Geostacks...
Sec Geometry - Constructions
 Sec 2.2 - Geometry - Constructions Name: 1. [COPY SEGMENT] Construct a segment with an endpoint of C and congruent to the segment AB. A B C **Using a ruler measure the two lengths to make sure they have
Sec 2.2 - Geometry - Constructions Name: 1. [COPY SEGMENT] Construct a segment with an endpoint of C and congruent to the segment AB. A B C **Using a ruler measure the two lengths to make sure they have
Geometry 2001 part 1
 Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
Geometry 2001 part 1 1. Point is the center of a circle with a radius of 20 inches. square is drawn with two vertices on the circle and a side containing. What is the area of the square in square inches?
MODULE FRAMEWORK AND ASSESSMENT SHEET
 MODULE FRAMEWORK AND ASSESSMENT SHEET LEARNING OUTCOMES (LOS) ASSESSMENT STANDARDS (ASS) FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT ASs Pages and (mark out of 4) LOs (ave. out of 4) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT Tasks or tests Ave for
MODULE FRAMEWORK AND ASSESSMENT SHEET LEARNING OUTCOMES (LOS) ASSESSMENT STANDARDS (ASS) FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT ASs Pages and (mark out of 4) LOs (ave. out of 4) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT Tasks or tests Ave for
AREA See the Math Notes box in Lesson for more information about area.
 AREA..1.. After measuring various angles, students look at measurement in more familiar situations, those of length and area on a flat surface. Students develop methods and formulas for calculating the
AREA..1.. After measuring various angles, students look at measurement in more familiar situations, those of length and area on a flat surface. Students develop methods and formulas for calculating the
Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet
 Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet Dear students, The problems in this packet will give you a chance to practice geometry-related skills from Grades 6 and 7. Do your best to complete each problem so that
Honors Geometry Summer Math Packet Dear students, The problems in this packet will give you a chance to practice geometry-related skills from Grades 6 and 7. Do your best to complete each problem so that
UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA
 UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will define basic geometric shapes and use definitions to categorize geometric figures. Then we will use the ideas of measuring length and area
UNIT 10 PERIMETER AND AREA INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will define basic geometric shapes and use definitions to categorize geometric figures. Then we will use the ideas of measuring length and area
Mathematical Construction
 Mathematical Construction Full illustrated instructions for the two bisectors: Perpendicular bisector Angle bisector Full illustrated instructions for the three triangles: ASA SAS SSS Note: These documents
Mathematical Construction Full illustrated instructions for the two bisectors: Perpendicular bisector Angle bisector Full illustrated instructions for the three triangles: ASA SAS SSS Note: These documents
The Magic Circle Basic Lesson. Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation
 The Magic Circle Basic Lesson Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation The Tools Needed Compass Straightedge Pencil Paper (not graph paper, 8.5 x 11 is fine) Your Brain (the most important tool!)
The Magic Circle Basic Lesson Developed by The Alexandria Seaport Foundation The Tools Needed Compass Straightedge Pencil Paper (not graph paper, 8.5 x 11 is fine) Your Brain (the most important tool!)
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII. Mathematics Laboratory
 LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
LIST OF HANDS-ON ACTIVITIES IN MATHEMATICS FOR CLASSES III TO VIII Mathematics Laboratory The concept of Mathematics Laboratory has been introduced by the Board in its affiliated schools with the objective
UNIT PLAN. Grade Level: Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles
 UNIT PLAN Subject: Geometry Grade Level: 10-12 Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles Big Idea/Theme: The understanding of properties of circles, the lines that intersect them, and the use of their special segments
UNIT PLAN Subject: Geometry Grade Level: 10-12 Unit #: 7 Unit Name: Circles Big Idea/Theme: The understanding of properties of circles, the lines that intersect them, and the use of their special segments
Course: Math Grade: 7. Unit Plan: Geometry. Length of Unit:
 Course: Math Grade: 7 Unit Plan: Geometry Length of Unit: Enduring Understanding(s): Geometry is found in the visual world in two and three dimension. We use geometry daily in problem solving. Essential
Course: Math Grade: 7 Unit Plan: Geometry Length of Unit: Enduring Understanding(s): Geometry is found in the visual world in two and three dimension. We use geometry daily in problem solving. Essential
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2004 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open your booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures. Grade 9 Mathematics
 Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
Worksheet 10 Memorandum: Construction of Geometric Figures Grade 9 Mathematics For each of the answers below, we give the steps to complete the task given. We ve used the following resources if you would
First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed
 Mathematics First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Mathematics First Practice Test 1 Levels 5-7 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You will need:
Copying a Line Segment
 Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Copying a Line Segment Steps 1 4 below show you how to copy a line segment. Step 1 You are given line segment AB to copy. A B Step 2 Draw a line segment that is longer than line segment AB. Label one of
Key Stage 3 Mathematics. Common entrance revision
 Key Stage 3 Mathematics Key Facts Common entrance revision Number and Algebra Solve the equation x³ + x = 20 Using trial and improvement and give your answer to the nearest tenth Guess Check Too Big/Too
Key Stage 3 Mathematics Key Facts Common entrance revision Number and Algebra Solve the equation x³ + x = 20 Using trial and improvement and give your answer to the nearest tenth Guess Check Too Big/Too
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry
 Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines. Look at each group of lines. Tick the parallel lines.
 Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines Parallel lines are always the same distance away from each other at any point and can never meet. They can be any length and go in any direction. Look
Lines and angles parallel and perpendicular lines Parallel lines are always the same distance away from each other at any point and can never meet. They can be any length and go in any direction. Look
Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 Practice Paper Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Foundation Tier Paper Reference 5MM1F/01
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 Practice Paper Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Foundation Tier Paper Reference 5MM1F/01
How to Design a Geometric Stained Glass Lamp Shade
 This technique requires no calculation tables, math, or angle computation. Instead you can use paper & pencil with basic tech drawing skills to design any size or shape spherical lamp with any number of
This technique requires no calculation tables, math, or angle computation. Instead you can use paper & pencil with basic tech drawing skills to design any size or shape spherical lamp with any number of
Unit 4: Geometric Construction (Chapter4: Geometry For Modeling and Design)
 Unit 4: Geometric Construction (Chapter4: Geometry For Modeling and Design) DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Instructor: Jimmy Nhan OBJECTIVES 1. Identify and specify basic geometric elements and primitive
Unit 4: Geometric Construction (Chapter4: Geometry For Modeling and Design) DFTG-1305 Technical Drafting Instructor: Jimmy Nhan OBJECTIVES 1. Identify and specify basic geometric elements and primitive
Angles and. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
Name Date Class Practice A. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see.
 Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Practice A Geometric Patterns Identify a possible pattern. Use the pattern to draw the next figure. 5. Look around your classroom. Describe a geometric pattern you see. 6. Use squares to create a geometric
Angle Measure and Plane Figures
 Grade 4 Module 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures OVERVIEW This module introduces points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles, as well as the relationships between them. Students construct, recognize,
Grade 4 Module 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures OVERVIEW This module introduces points, lines, line segments, rays, and angles, as well as the relationships between them. Students construct, recognize,
Paper 1. Calculator not allowed. Mathematics test. First name. Last name. School. Remember KEY STAGE 3 TIER 4 6
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2008 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Ma KEY STAGE 3 Mathematics test TIER 4 6 Paper 1 Calculator not allowed First name Last name School 2008 Remember The test is 1 hour long. You must not use a calculator for any question in this test. You
Mathematics 43601F. Geometry. In the style of General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier. Past Paper Questions by Topic TOTAL
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials In the style of General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials In the style of General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier Pages 2 3 4 5 Mark
Constructing and Classifying Designs of al-andalus
 ISAMA The International Society of the Arts, Mathematics, and Architecture Constructing and Classifying Designs of al-andalus BRIDGES Mathematical Connections in Art, Music, and Science B. Lynn Bodner
ISAMA The International Society of the Arts, Mathematics, and Architecture Constructing and Classifying Designs of al-andalus BRIDGES Mathematical Connections in Art, Music, and Science B. Lynn Bodner
Geometry. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
U N I T Geometry Building Castles Learning Goals describe, name, and sort prisms construct prisms from their nets construct models of prisms identify, create, and sort symmetrical and non-symmetrical shapes
DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY CONSTRUCTION PROJECT
 Name Period DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY CONSTRUCTION PROJECT Materials needed: Objective: Standards: 8 pieces of unlined white computer paper (8.5 in. by 11in.), compass, ruler, protractor, pencil, and markers/colored
Name Period DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY CONSTRUCTION PROJECT Materials needed: Objective: Standards: 8 pieces of unlined white computer paper (8.5 in. by 11in.), compass, ruler, protractor, pencil, and markers/colored
Downloaded from
 Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT
 INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
INTERMEDIATE LEVEL MEASUREMENT TABLE OF CONTENTS Format & Background Information...3-6 Learning Experience 1- Getting Started...6-7 Learning Experience 2 - Cube and Rectangular Prisms...8 Learning Experience
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes
 18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
Measuring and Drawing Angles and Triangles
 NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
NME DTE Measuring and Drawing ngles and Triangles Measuring an angle 30 arm origin base line 0 180 0 If the arms are too short to reach the protractor scale, lengthen them. Step 1: lace the origin of the
Maths Makes Sense. 3 Medium-term plan
 Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Maths Makes Sense 3 Medium-term plan 2 Maths Makes Sense 3 Block 1 End-of-block objectives Arithmetic 1 Respond to I will act the Real Story, you write the Maths Story (including the answer), for addition
Activity: Islamic Mosaics
 Activity: Islamic Mosaics Materials Printed template(s) Compass or bull s eye Straight edge Colour pencils Skills Motor Drawing a circle with a compass Tracing a straight line Affective/metacognitive Persevering
Activity: Islamic Mosaics Materials Printed template(s) Compass or bull s eye Straight edge Colour pencils Skills Motor Drawing a circle with a compass Tracing a straight line Affective/metacognitive Persevering
1. Convert 60 mi per hour into km per sec. 2. Convert 3000 square inches into square yards.
 ACT Practice Name Geo Unit 3 Review Hour Date Topics: Unit Conversions Length and Area Compound shapes Removing Area Area and Perimeter with radicals Isosceles and Equilateral triangles Pythagorean Theorem
ACT Practice Name Geo Unit 3 Review Hour Date Topics: Unit Conversions Length and Area Compound shapes Removing Area Area and Perimeter with radicals Isosceles and Equilateral triangles Pythagorean Theorem
S1/2 Checklist S1/2 Checklist. Whole Numbers. No. Skill Done CfE Code(s) 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting
 Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
Whole Numbers 1 Know that a whole number is a normal counting MNU 0-0a number such as 0, 1,, 3, 4, Count past 10 MNU 0-03a 3 Know why place value is important MNU 1-0a 4 Know that approximating means to
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
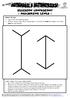 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme
 Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme Every student is assigned to a Stage, based on their academic year and assessed study level. Stage 2 students are approximately 8 to 10 years old. The sheets
Workshops: The heart of the MagiKats Programme Every student is assigned to a Stage, based on their academic year and assessed study level. Stage 2 students are approximately 8 to 10 years old. The sheets
Activities. for building. geometric connections. MCTM Conference Cheryl Tucker
 Activities for building geometric connections (handout) MCTM Conference 2013 Cheryl Tucker Minneapolis Public Schools Tucker.cherylj@gmail.com (Many materials are from Geometry Connections, CPM, used with
Activities for building geometric connections (handout) MCTM Conference 2013 Cheryl Tucker Minneapolis Public Schools Tucker.cherylj@gmail.com (Many materials are from Geometry Connections, CPM, used with
Teacher Lesson Pack Lines and Angles. Suitable for Gr. 6-9
 Teacher Lesson Pack Lines and Angles Suitable for Gr. 6-9 1 2 Sir Cumference and the Great Knight of Angleland By: Cindy Neuschwander, Charlsebridge Publishing, ISBN: 1570911525 Read the book to the students.
Teacher Lesson Pack Lines and Angles Suitable for Gr. 6-9 1 2 Sir Cumference and the Great Knight of Angleland By: Cindy Neuschwander, Charlsebridge Publishing, ISBN: 1570911525 Read the book to the students.
STRAND H: Angle Geometry
 Mathematics SKE, Strand H UNIT H3 onstructions and Loci: Text STRND H: ngle Geometry H3 onstructions and Loci Text ontents Section H3.1 Drawing and Symmetry H3.2 onstructing Triangles and ther Shapes H3.3
Mathematics SKE, Strand H UNIT H3 onstructions and Loci: Text STRND H: ngle Geometry H3 onstructions and Loci Text ontents Section H3.1 Drawing and Symmetry H3.2 onstructing Triangles and ther Shapes H3.3
Year 4 Homework Activities
 Year 4 Homework Activities Teacher Guidance The Inspire Maths Home Activities provide opportunities for children to explore maths further outside the classroom. The engaging Home Activities help you to
Year 4 Homework Activities Teacher Guidance The Inspire Maths Home Activities provide opportunities for children to explore maths further outside the classroom. The engaging Home Activities help you to
5.2. Drawing the Nets of Prisms and Cylinders. LEARN ABOUT the Math. How can Nikita and Misa draw nets of the models? Reflecting
 5.2 Drawing the Nets of Prisms and Cylinders YOU WILL NEED 1 cm Grid Paper scissors transparent tape a compass Draw nets of prisms and cylinders. LEARN ABOUT the Math service building Nikita is building
5.2 Drawing the Nets of Prisms and Cylinders YOU WILL NEED 1 cm Grid Paper scissors transparent tape a compass Draw nets of prisms and cylinders. LEARN ABOUT the Math service building Nikita is building
Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Perimeter and Area
 Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Perimeter and Area Objective: Students will be able to: Distinguish between area and perimeter. Calculate the perimeter of a polygon whose side lengths are given or can be determined.
Lesson 3 Pre-Visit Perimeter and Area Objective: Students will be able to: Distinguish between area and perimeter. Calculate the perimeter of a polygon whose side lengths are given or can be determined.
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2011 KCATM Contest
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2011 KCATM Contest GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 4 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 15 minutes You may use calculators
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2011 KCATM Contest GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 4 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 15 minutes You may use calculators
1. If one side of a regular hexagon is 2 inches, what is the perimeter of the hexagon?
 Geometry Grade 4 1. If one side of a regular hexagon is 2 inches, what is the perimeter of the hexagon? 2. If your room is twelve feet wide and twenty feet long, what is the perimeter of your room? 3.
Geometry Grade 4 1. If one side of a regular hexagon is 2 inches, what is the perimeter of the hexagon? 2. If your room is twelve feet wide and twenty feet long, what is the perimeter of your room? 3.
1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
 Joint Beginning and Intermediate Engineering Graphics 2 nd Week 1st Meeting Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: Geometric Construction 1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
Joint Beginning and Intermediate Engineering Graphics 2 nd Week 1st Meeting Lecture Notes Instructor: Edward N. Locke Topic: Geometric Construction 1 st Subject: 2D Geometric Shape Construction and Division
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD. We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential
 Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Kenmore-Town of Tonawanda UFSD We educate, prepare, and inspire all students to achieve their highest potential Grade 2 Module 8 Parent Handbook The materials contained within this packet have been taken
Shape, space and measures 4
 Shape, space and measures 4 contents There are three lessons in this unit, Shape, space and measures 4. S4.1 Rotation and rotation symmetry 3 S4.2 Reflection and line symmetry 6 S4.3 Problem solving 9
Shape, space and measures 4 contents There are three lessons in this unit, Shape, space and measures 4. S4.1 Rotation and rotation symmetry 3 S4.2 Reflection and line symmetry 6 S4.3 Problem solving 9
Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern
 Published on Sew4Home Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern Editor: Liz Johnson Thursday, 25 August 2016 1:00 The circle is, in my humble opinion, the Queen of the geometric shapes. Don't get me
Published on Sew4Home Make and Measure a Circle Without a Pattern Editor: Liz Johnson Thursday, 25 August 2016 1:00 The circle is, in my humble opinion, the Queen of the geometric shapes. Don't get me
Challenges from Ancient Greece
 Challenges from ncient Greece Mathematical goals Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods. Use congruent triangles to justify geometric constructions. Common Core State Standards
Challenges from ncient Greece Mathematical goals Make formal geometric constructions with a variety of tools and methods. Use congruent triangles to justify geometric constructions. Common Core State Standards
Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles. Angle Bisector. Perpendicular Bisector
 Lessons and Activities GEOMETRY Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles Angle Bisector Perpendicular Bisector 1 Lessons and Activities POLYGONS are PLANE SHAPES (figures) with at least 3 STRAIGHT sides and
Lessons and Activities GEOMETRY Elementary Geometric Drawings Angles Angle Bisector Perpendicular Bisector 1 Lessons and Activities POLYGONS are PLANE SHAPES (figures) with at least 3 STRAIGHT sides and
MATHEMATICS TEST. Paper 1 calculator not allowed LEVEL 6 TESTS ANSWER BOOKLET. First name. Middle name. Last name. Date of birth Day Month Year
 2012 LEVEL 6 TESTS ANSWER BOOKLET Ma MATHEMATICS TEST LEVEL 6 TESTS Paper 1 calculator not allowed First name Middle name Last name Date of birth Day Month Year Please circle one Boy Girl Year group School
2012 LEVEL 6 TESTS ANSWER BOOKLET Ma MATHEMATICS TEST LEVEL 6 TESTS Paper 1 calculator not allowed First name Middle name Last name Date of birth Day Month Year Please circle one Boy Girl Year group School
PENNSYLVANIA. List properties, classify, draw, and identify geometric figures in two dimensions.
 Know: Understand: Do: CC.2.3.4.A.1 -- Draw lines and angles and identify these in two-dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 -- Classify twodimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3
Know: Understand: Do: CC.2.3.4.A.1 -- Draw lines and angles and identify these in two-dimensional figures. CC.2.3.4.A.2 -- Classify twodimensional figures by properties of their lines and angles. CC.2.3.4.A.3
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines
 Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Problem of the Month: Between the Lines Overview: In the Problem of the Month Between the Lines, students use polygons to solve problems involving area. The mathematical topics that underlie this POM are
Find the area and perimeter of any enlargement of the original rug above. Your work must include the following:
 7-1.Your friend Alonzo owns a rug manufacturing company, which is famous for its unique designs. Each rug design has an original size as well as enlargements that are exactly the same shape. Find the area
7-1.Your friend Alonzo owns a rug manufacturing company, which is famous for its unique designs. Each rug design has an original size as well as enlargements that are exactly the same shape. Find the area
Sketching Fundamentals
 Sketching Fundamentals Learning Outcome When you complete this module you will be able to: Make basic engineering sketches of plant equipment. Learning Objectives Here is what you will be able to do when
Sketching Fundamentals Learning Outcome When you complete this module you will be able to: Make basic engineering sketches of plant equipment. Learning Objectives Here is what you will be able to do when
How to Draw with a Grid
 Level: Beginner Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level: 8.3 Flesch-Kincaid Reading Ease: 67.5-6 Pages and 12 Illustrations How to Draw with a Grid Exploring the grid method to draw accurate outline drawings This resource
Level: Beginner Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level: 8.3 Flesch-Kincaid Reading Ease: 67.5-6 Pages and 12 Illustrations How to Draw with a Grid Exploring the grid method to draw accurate outline drawings This resource
What You ll Learn. Why It s Important. You see geometric figures all around you.
 You see geometric figures all around you. Look at these pictures. Identify a figure. What would you need to know to find the area of that figure? What would you need to know to find the perimeter of the
You see geometric figures all around you. Look at these pictures. Identify a figure. What would you need to know to find the area of that figure? What would you need to know to find the perimeter of the
1. Geometry/Measurement Grade 9 Angles, Lines & Line Segments G/M-1e
 1. Geometry/Measurement Grade 9 Angles, Lines & Line Segments G/M-1e small rectangle or square of colored paper mira Geometry Set cardboard strips Your friend call you over the telephone and says, How
1. Geometry/Measurement Grade 9 Angles, Lines & Line Segments G/M-1e small rectangle or square of colored paper mira Geometry Set cardboard strips Your friend call you over the telephone and says, How
40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016
 THE CALGARY MATHEMATICAL ASSOCIATION 40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016 NAME: PLEASE PRINT (First name Last name) GENDER: SCHOOL: GRADE: (9,8,7,...) You have 90 minutes for the examination.
THE CALGARY MATHEMATICAL ASSOCIATION 40 th JUNIOR HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST MAY 4, 2016 NAME: PLEASE PRINT (First name Last name) GENDER: SCHOOL: GRADE: (9,8,7,...) You have 90 minutes for the examination.
Session 1 What Is Geometry?
 Key Terms for This Session Session 1 What Is Geometry? New in This Session altitude angle bisector concurrent line line segment median midline perpendicular bisector plane point ray Introduction In this
Key Terms for This Session Session 1 What Is Geometry? New in This Session altitude angle bisector concurrent line line segment median midline perpendicular bisector plane point ray Introduction In this
Geometry. Practice Pack
 Geometry Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Lines and Angles Practice 1.1 What Is Geometry?........................ 1 Practice 1.2 What Is Geometry?........................ 2 Practice
Geometry Practice Pack WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents Unit 1: Lines and Angles Practice 1.1 What Is Geometry?........................ 1 Practice 1.2 What Is Geometry?........................ 2 Practice
2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core
 2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core Name: Note to the Student: In middle school, you worked with a variety of geometric measures, such as: length, area, volume, angle, surface
2016 Summer Break Packet for Students Entering Geometry Common Core Name: Note to the Student: In middle school, you worked with a variety of geometric measures, such as: length, area, volume, angle, surface
Finishes Size: 95" x 95" 2000, 2015, RJR Fabrics. All rights reserved. r
 Finishes Size: 9" x 9" 000, 0, RJR Fabrics. All rights reserved. r0.06- New Moon features a mariner s compass block alternated with a traditional pineapple block. Set side-by-side and with carefully shaded
Finishes Size: 9" x 9" 000, 0, RJR Fabrics. All rights reserved. r0.06- New Moon features a mariner s compass block alternated with a traditional pineapple block. Set side-by-side and with carefully shaded
Instructions to Candidates
 Gozo College Boys Secondary School Victoria - Gozo, Malta Half Yearly Examination 2012 2013 Form 2 Mathematics - Level 7-8 Non-Calculator Paper Time: 30 mins Name: Class: Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total
Gozo College Boys Secondary School Victoria - Gozo, Malta Half Yearly Examination 2012 2013 Form 2 Mathematics - Level 7-8 Non-Calculator Paper Time: 30 mins Name: Class: Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total
The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships.
 The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships. Notes 3and textbook 3.01 Use the coordinate system to describe the location and relative position of points and draw figures in
The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships. Notes 3and textbook 3.01 Use the coordinate system to describe the location and relative position of points and draw figures in
ORIGAMI BOXES Using Paper Folding to Teach Geometry
 W 409 ORIGAMI BOXES Using Paper Folding to Teach Geometry James Swart, Extension Graduate Assistant, 4-H Youth Development MANAGEMENT OF APHIDS AND BYD IN TENNESSEE WHEAT 1 Tennessee 4-H Youth Development
W 409 ORIGAMI BOXES Using Paper Folding to Teach Geometry James Swart, Extension Graduate Assistant, 4-H Youth Development MANAGEMENT OF APHIDS AND BYD IN TENNESSEE WHEAT 1 Tennessee 4-H Youth Development
Missing Sequence. You have 10 minutes to complete this test. Select the square that comes next in the sequence.
 Missing Sequence Select the square that comes next in the sequence. 1. 2. 3. Similarities 4. 5. 6. Analogies 7. 8. ` 9. Odd one out 10. 11. 12. Complete the grid 13. 14. 15. Answers 1. A- The pattern along
Missing Sequence Select the square that comes next in the sequence. 1. 2. 3. Similarities 4. 5. 6. Analogies 7. 8. ` 9. Odd one out 10. 11. 12. Complete the grid 13. 14. 15. Answers 1. A- The pattern along
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7064186759* MATHEMATICS 0580/32 Paper 3 (Core) February/March 2017 Candidates answer on the Question
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7064186759* MATHEMATICS 0580/32 Paper 3 (Core) February/March 2017 Candidates answer on the Question
DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY HONORS CONSTRUCTION PROJECT
 Name Period DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY HONORS CONSTRUCTION PROJECT Materials needed: Objective: Standards: 8 pieces of unlined white computer / copy paper (8.5 in. by 11in.), compass, ruler, protractor, pencil,
Name Period DIRECTIONS FOR GEOMETRY HONORS CONSTRUCTION PROJECT Materials needed: Objective: Standards: 8 pieces of unlined white computer / copy paper (8.5 in. by 11in.), compass, ruler, protractor, pencil,
A A B B C C D D. NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation
 NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation Name # For this investigation, you will work with a partner. You and your partner should take turns practicing the rotations with the stencil. You and your partner
NC Math 2: Transformations Investigation Name # For this investigation, you will work with a partner. You and your partner should take turns practicing the rotations with the stencil. You and your partner
Euclid s Muse MATERIALS VOCABULARY. area perimeter triangle quadrilateral rectangle line point plane. TIME: 40 minutes
 Euclid s Muse In this activity, participants match geometry terms to definitions and definitions to words. MATERIALS Transparency: Euclid s Muse Directions Transparency/Page: Euclid s Muse Transparency/Page:
Euclid s Muse In this activity, participants match geometry terms to definitions and definitions to words. MATERIALS Transparency: Euclid s Muse Directions Transparency/Page: Euclid s Muse Transparency/Page:
Teacher / Parent Guide for the use of Tantrix tiles with children of all ages
 Teacher / Parent Guide for the use of Tantrix tiles with children of all ages TANTRIX is a registered trademark. Teacher / Parent Guide 2010 Tantrix UK Ltd This guide may be photocopied for non-commercial
Teacher / Parent Guide for the use of Tantrix tiles with children of all ages TANTRIX is a registered trademark. Teacher / Parent Guide 2010 Tantrix UK Ltd This guide may be photocopied for non-commercial
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
University of Houston High School Mathematics Contest Geometry Exam Spring 2016
 University of Houston High School Mathematics ontest Geometry Exam Spring 016 nswer the following. Note that diagrams may not be drawn to scale. 1. In the figure below, E, =, = 4 and E = 0. Find the length
University of Houston High School Mathematics ontest Geometry Exam Spring 016 nswer the following. Note that diagrams may not be drawn to scale. 1. In the figure below, E, =, = 4 and E = 0. Find the length
SPIRE MATHS Stimulating, Practical, Interesting, Relevant, Enjoyable Maths For All
 Imaginings in shape and space TYPE: Main OBJECTIVE(S): DESCRIPTION: OVERVIEW: EQUIPMENT: Begin to identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; solve geometrical
Imaginings in shape and space TYPE: Main OBJECTIVE(S): DESCRIPTION: OVERVIEW: EQUIPMENT: Begin to identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; solve geometrical
Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator) Wednesday 6 March 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Write your name here Surname Other names Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Mathematics B Unit 3: Number, Algebra, Geometry 2 (Calculator) Wednesday 6 March 2013 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning. Progressive Mathematics Initiative
 Slide 1 / 126 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
Slide 1 / 126 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Mathematics Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students
CTB/McGraw-Hill. Math Quarter 2: Week 5: Mixed Review Test ID:
 Page 1 of 35 Developed and published by CTB/McGraw-Hill LLC, a subsidiary of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 20 Ryan Ranch Road, Monterey, California 93940-5703. All rights reserved. Only authorized customers
Page 1 of 35 Developed and published by CTB/McGraw-Hill LLC, a subsidiary of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 20 Ryan Ranch Road, Monterey, California 93940-5703. All rights reserved. Only authorized customers
How to Draw a Rose Flower
 How to Draw a Rose Flower Easy Fast Have you ever wanted to be able to draw a beautiful rose? This easy step-by-step drawing tutorial outlines the steps necessary to draw a cartoon style rose, complete
How to Draw a Rose Flower Easy Fast Have you ever wanted to be able to draw a beautiful rose? This easy step-by-step drawing tutorial outlines the steps necessary to draw a cartoon style rose, complete
Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem
 UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot)
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot) Unit 2 Geometry and Algebra Monday 11 November 2013
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Methods in Mathematics (Linked Pair Pilot) Unit 2 Geometry and Algebra Monday 11 November 2013
Solutions to Exercise problems
 Brief Overview on Projections of Planes: Solutions to Exercise problems By now, all of us must be aware that a plane is any D figure having an enclosed surface area. In our subject point of view, any closed
Brief Overview on Projections of Planes: Solutions to Exercise problems By now, all of us must be aware that a plane is any D figure having an enclosed surface area. In our subject point of view, any closed
Paper 2. Mathematics test. Calculator allowed. First name. Last name. School. Pupil number KEY STAGE TIER
 Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2001 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open the booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Ma KEY STAGE 3 TIER 6 8 2001 Mathematics test Paper 2 Calculator allowed Please read this page, but do not open the booklet until your teacher tells you to start. Write your name and the name of your school
Methods in Mathematics
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Monday 10 November
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Candidate Number Methods in Mathematics Unit 1: Methods 1 For Approved Pilot Centres ONLY Foundation Tier Monday 10 November
