nterview sche INTERVIEW 1
|
|
|
- Madison Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GLoSS GloSS nterview sche INTERVIEW 1 PAGE GLoSS 1 INTERVIEW 1 GloSS INTERVIEW PAGE 1
2
3 task 1 action: Place 8 counters of the same colour on the table. Say: How many counters are there? 0 Student cannot count 8 objects 1 Correctly counts the 8 objects decision: If 1 is circled in Task 1, CONTINUE the interview. If 0 is circled, rate the student at 0 and STOP the interview. task 2 Say: Please hold out your hands for me. action: Place 3 counters in the student s hand. Say: Here are 3 counters. action: Place 6 counters in their other hand. Say: Here are another 6 counters. action: Close the student s hands to encourage imaging. Say: How many counters have you got altogether? action: 1 Cannot solve the addition problem ( 1) Allow the student to open their hands if they find imaging difficult. 2 3 Physically counts all the objects from 1 on materials ( 2) Correctly counts all the items from 1 by imaging ( 3) 4 Counts on e.g., 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 or 7, 8, 9 Knows decision: If either 2 3 or 4 are circled in Task 2, CONTINUE the interview. If 1 is circled, STOP the interview. If in any doubt, CONTINUE the interview.
4 Interview 1 Task = Interview 1 Task =
5 task 3 action: Place 9 counters under a card then place 7 under another card. Say: Here are 9 counters, and here are 7 counters. How many counters are there altogether? IntervIew 1 TASk = 3 Cannot solve the problem (After removing the cards 1) Counts all objects from 1 on materials ( 2) e.g., 1, 2, 3,, 16 Counts all objects from 1 by imaging ( 3) e.g., 1, 2, 3,, 16 4 Counts on ( 4) e.g., 10, 11, 12,, 15, 16 or 8, 9, 10,, 15, 16 Early 5 Uses a part-whole strategy e.g., - Making to ten e.g., = 10; = 16 - Doubling with compensation e.g., = 14; = 16 or = 16 or = 18; 18 2 = 16 - Addition fact e.g., = 16 task 4 IntervIew 1 TASk 4 There are 5 cups in each row. There are 6 rows of cups. How many cups are there altogether? Say: Say: Say: There are 5 cups in each row. There are 6 rows of cups. How many cups are there altogether? action: Sweep one row with your finger. action: Point to each row one by one. 3 Cannot solve the problem Counts all objects from 1 on materials ( 2) e.g., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,, 30 Counts all objects from 1 by imaging ( 3) e.g., 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,, 30 4 Skip counting ( 4) e.g., 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 [or 6, 12, 18, 24, 30] Early 5 Uses an additive or multiplicative strategy e.g., - Repeat addition e.g., = 30 or = 10; = 15; ; = 30 - Multiplication strategies e.g., 4 5 = 20; = 30 - Multiplication fact e.g., 6 5 = 30
6 Interview 1 Task 4 There are 5 cups in each row. There are 6 rows of cups. How many cups are there altogether? Interview 1 Task 5 You have 20 jellybeans. Each quarter of the cake should have the same number of jellybeans on it. How many jellybeans go on each quarter of the cake?
7 task 5 action: Provide 20 counters (jellybeans). Allow the student access to these counters if necessary. Say: You have 20 jellybeans. Each quarter of the cake should have the same number of jellybeans on it. How many jellybeans go on each quarter of the cake? Note: Say fourth instead of quarter if this is more familiar to your student. IntervIew 1 TASk 5 You have 20 jellybeans. Each quarter of the cake should have the same number of jellybeans on it. How many jellybeans go on each quarter of the cake? 2 4 Cannot solve the problem Equally shares the beans, on materials or by imaging ( 2 4) Early 5 Uses an additive or multiplicative strategy e.g., - Additive partitioning e.g., = 20; (5 + 5) + (5 + 5) = 20 - Multiplication strategy e.g., 5 2 = 10; 10 2 = 20 - Multiplication or division fact e.g., 5 4 = 20 or 20 4 = 5 decision: If any E5 are circled in Tasks 3, 4 or 5, or if the 4s are circled in both Task 3 and Task 4, CONTINUE the interview. Otherwise STOP the interview. If in any doubt, CONTINUE the interview. task 6 Say: Tamati had 57 model dinosaurs. He gives 25 to his cousin Alice. How many does he have left? IntervIew 1 TASk 6 Tamati had 57 model dinosaurs. He gives 25 to his cousin Alice. How many does he have left? Early 5 5 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Counting on or Counting back ( 4) e.g., 26, 27,, 57 or 56, 55,, 25 Skip counting in tens and ones ( 4) e.g., [57] 47, 37, 36, 35, 34, 33, 32 Repeat addition in tens and ones ( E5) e.g., = 47; = 37; 37 5 = 32 or = 35; = 45; = 55; = 57; = 32 Mix of counting and part-whole strategies ( E5) e.g., = 30; = 40; = 50; 51, 52,, 56, 57 Uses a part-whole strategy e.g., - Doubling e.g., = 50; = 57; = 32 - Place value partitioning e.g., (50 20) + (7 5) = 32 - Subtracting in parts e.g., = 37; 37 5 = 32 - Making to ten e.g., 57 7 = 50; = 30; = 32
8 Interview 1 Task 6 Tamati had 57 model dinosaurs. He gives 25 to his cousin Alice. How many does he have left? Interview 1 Task 7 Malcolm has 24 pegs. He uses 2 pegs to hang out each piece of clothing. How many pieces of clothing can he hang out?
9 task 7 Say: Malcolm has 24 pegs. He uses 2 pegs to hang out each piece of clothing. How many pieces of clothing can he hang out? IntervIew 1 TASk 7 Malcolm has 24 pegs. He uses 2 pegs to hang out each piece of clothing. How many pieces of clothing can he hang out? Early 5 5 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Skip counting ( 4) e.g., 2, 4, 6,, 24 Repeated addition ( E5) e.g., = 24 Uses an additive or multiplicative strategy e.g., - Doubling additively e.g., = 4; = 8; = 24; = 12 - Derive from multiplication facts e.g., 10 2 = 20; 2 2 = 4; = 12 - Multiplication or division facts e.g., 12 2 = 24 or 24 2 = 12 task 8 Say: Alex and his friends ate 12 slices of pizza. Each slice was one-quarter of a pizza. How many pizzas did they eat? Note: Say fourth instead of quarter if this is more familiar to your student. IntervIew 1 TASk 8 Alex and his friends ate 12 slices of pizza. Each slice was one-quarter ( 1) of a pizza. 4 How many pizzas did they eat? Early 5 5 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Counting strategy ( E5) e.g., , 4,, (one whole), 5 4,..., 11 4, 12 (three wholes) Uses a proportional approach e.g., - Addition strategies e.g., 4 pieces is 1 pizza; = 12 so the answer is 3 - Rate strategies e.g., 4 quarters is 1 pizza, 8 quarters is 2, 12 quarters is 3 - Multiplication facts e.g., 4 3 = 12 or 12 4 = 3 decision: If any 5 are circled in Tasks 6, 7 or 8, CONTINUE the interview. If only E5 are circled, STOP the interview. If in any doubt, CONTINUE the interview.
10 Interview 1 Task 8 Alex and his friends ate 12 slices of pizza. 1 Each slice was one-quarter ( 4 ) of a pizza. How many pizzas did they eat? Interview 1 Task 9 Jodie had some pens. She was given another 26 pens and she now has 86 altogether. How many pens did she have in the beginning?
11 task 9 Say: Jodie had some pens. She was given another 26 pens and she now has 86 altogether. How many pens did she have in the beginning? IntervIew 1 TASk 9 Jodie had some pens. She was given another 26 pens and she now has 86 altogether. How many pens did she have in the beginning? 5 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Skip counting in tens ( 4) e.g., [26] 36, 46, 56, 66, 76, 86 Repeat addition in tens ( E5) e.g., = 86 Early 6 Uses a part-whole strategy e.g., - Place value partitioning e.g., (80 20) + (6 6) = = 60 - Addition in parts (with reversibility) e.g., = 86 or = 60 task 10 Say: Zac has 8 packs of drink. Each pack has 6 cans. How many cans is that altogether? IntervIew 1 TASk 10 Zac has 8 packs of drink. Each pack has 6 cans. How many cans is that altogether? 5 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Uses an additive strategy e.g., - Skip counting ( 4) e.g., 6, 12, 18, 24,, 48 [or 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48] - Repeated addition ( E5) e.g., [or ] - Doubling additively ( 5) e.g., = 12; = 24; = 48 Early 6 Uses a multiplicative strategy e.g., - Derives from multiplication facts e.g., 8 5 = 40; = 48 - Multiplication facts e.g., 8 6 = 48
12 Interview 1 Task 10 Zac has 8 packs of drink. Each pack has 6 cans. How many cans is that altogether? Interview 1 Task 11 Ruka picks 6 boxes of raspberries in 18 minutes. How long does Ruka take to pick 3 boxes?
13 task 11 IntervIew 1 TASk 11 Ruka picks 6 boxes of raspberries in 18 minutes. Say: Ruka picks 6 boxes of raspberries in 18 minutes. How long does Ruka take to pick 3 boxes? How long does Ruka take to pick 3 boxes? 5 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Early 6 Uses additive strategies only ( 5) e.g., = 18 so 3 minutes per box; = 9 Uses a mix of additive and multiplicative strategies e.g., 3 6 = 18 so 3 minutes per box; = 9 Uses multiplicative strategies e.g., 3 6 = 18 so 3 minutes per box; 3 3 = 9 Proportional approach e.g., 3 1 Equate fraction of boxes to fraction of time e.g., = ; of 18 = decision: If any E6 are circled in Tasks 9, 10 or 11, CONTINUE the interview. If only 5 are circled, STOP the interview. If in any doubt, CONTINUE the interview. task 12 Say: Tana got an ipod with some songs on it. He downloaded another 148 songs and he now has 176 songs in total. How many songs were on his ipod when he first got it? IntervIew 1 TASk 12 Tana got an ipod with some songs on it. He downloaded another 148 songs and he now has 176 songs in total. How many songs were on his ipod when he first got it? Early 6 6 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Mix of counting and part-whole strategies ( E5) e.g., [148] 158, 168; = 170; = 176; Attempts part-whole strategy with error ( 5) e.g., = 26; 26 2 = 24 (compensates in the wrong direction) Uses a part-whole strategy e.g., - Place value partitioning e.g., ( ) + (70 40) + (6 8) = 30 2 = 28 - Adding on in parts e.g., = 168; = 176; = 28 or = 156; = 148; = 28 - Rounding and compensation e.g., = 176; 30 2 = 28 - Making to tens and compensation e.g., = 150; = 170; = 176; = 28
14 Interview 1 Task 12 Tana got an ipod with some songs on it. He downloaded another 148 songs and he now has 176 songs in total. How many songs were on his ipod when he first got it? Interview 1 Task 13 There are 40 small squares in the chocolate block. How many rows are hidden under the wrapping?
15 task 13 IntervIew 1 TASk 13 There are 40 small squares in the chocolate block. Say: There are 40 small squares in the chocolate block. How many rows are hidden under the wrapping? If the student does not understand that the question is asking for the number of rows, explain this to them. How many rows are hidden under the wrapping? Early 6 6 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Uses an additive strategy ( 5) e.g., - Doubling additively e.g., = 8; = 16; = 32; = 8 Uses a multiplicative strategy e.g., - Derived from basic fact e.g., 10 4 = 40 so 8 4 = 32 so the answer is 8 or 10 4 = 40 so there are 10 2 = 8 - Multiplication facts e.g., 40 8 = 32 and 32 4 = 8 (or 8 4 = 32) task 14 IntervIew 1 TASk 14 Hanni uses 32 carrots to fill 4 bags. Say: Hanni uses 32 carrots to fill 4 bags. How many carrots does he need to fill 12 bags? How many carrots does he need to fill 12 bags? Early 6 6 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Uses an additive strategy ( 5) e.g., - Doubling additively e.g., = 64; = 96 Uses a multiplicative strategy - Unitising e.g., 8 carrots per bag because 4 8 = 32; 12 8 = 96 - Using ratios e.g., Three times as many bags because 3 4 = 12; 3 32 = 96 decision: If any 6 are circled in Tasks 12, 13 or 14, CONTINUE the interview. If only E6 are circled, STOP the interview. If in any doubt, CONTINUE the interview.
16 Interview 1 Task 14 Hanni uses 32 carrots to fill 4 bags. How many carrots does he need to fill 12 bags? Interview 1 Task 15 Kathie ran 4.3 kilometres on the first day. She ran 5.15 kilometres on the second day. How far did Kathie run altogether?
17 task 15 Say: Kathie ran 4.3 kilometres on the first day. She ran 5.15 kilometres on the second day. How far did Kathie run altogether? IntervIew 1 TASk 15 Kathie ran 4.3 kilometres on the first day. She ran 5.15 kilometres on the second day. How far did Kathie run altogether? 6 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Misunderstands decimal place value ( 6) e.g., - Ignores the decimal points e.g., = Treats numbers after the decimal as whole numbers e.g., = 9.18 [often said nine point eighteen ] Early 7 Uses part-whole strategies with decimal place value understanding e.g., - Place value partitioning e.g., (4 + 5) + ( ) = Adding on in parts e.g., = 9.3; = 9.45 or = 9.4; = 9.45 task 16 Say: There are 33 boxes. Each box holds 12 bottles of lemonade. How many bottles are there altogether? IntervIew 1 TASk 16 There are 33 boxes. Each box holds 12 bottles of lemonade. How many bottles are there altogether? 6 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Uses a mix of multiplicative and additive strategies ( 6) e.g., = 36; = 360; = 396 or = 360; = 396 Early 7 Uses a multiplicative strategy e.g., - Partitioning e.g., = 330; 33 2 = 66; = 396 or = 300; 3 10 = 30; 30 2 = 60; 3 2 = 6; = Derived from basic facts e.g., 3 12 = 36 and = 360; = Triples and thirds e.g., = 4 99; = 400; = 396
18 Interview 1 Task 16 There are 33 boxes. Each box holds 12 bottles of lemonade. How many bottles are there altogether? Interview 1 Task 17 There are 20 children who go to a country school. Three-fifths ( 5 3 ) of them travel to school by bus. How many children is that?
19 task 17 Say: There are 20 children who go to a country school. Three-fifths of them travel to school by bus. How many children is that? IntervIew 1 TASk 17 There are 20 children who go to a country school. Three-fifths ( 3) of them travel to school by bus. 5 How many children is that? 6 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Uses additive strategies ( 5) e.g., 1 3 of 20 is 4 because = 20; of 20 = = 12 Early Uses multiplicative strategies e.g., 1 of 20 is 4 because 5 4 = 20 or 20 5 = then multiplies (or adds) to get, i.e., 3 4 = 12 [or = 12] 5 decision: If any E7 are circled in Tasks 15, 16 or 17, CONTINUE the interview. If only 6 are circled, STOP the interview. If in any doubt, CONTINUE the interview. task 18 Say: In 1912 the world record time for the 100 metre sprint was 10.6 seconds. It is now 9.69 seconds. By how much has the record changed? IntervIew 1 TASk 18 In 1912 the world record time for the 100 metre sprint was 10.6 seconds. It is now 9.69 seconds. By how much has the record changed? Early 7 7 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Misinterprets decimal place value ( 6) e.g., - Treats numbers after the decimal as whole numbers e.g., (10 9) + ( ) = = 0.37 Attempts part-whole strategy with error ( 6) e.g., ( ) = 0.09; = 1.09 (compensates in the wrong direction) Uses part-whole strategies e.g., - Place value partitioning e.g., (10 9) + ( ) = = Making to ones e.g., = 10; = 10.6; = Takes off a tidy number and compensates e.g., = 9.6; = 9.69; = Takes off to get a tidy number and compensates e.g., = 1.0; = 0.91
20 Interview 1 Task 18 In 1912 the world record time for the 100 metre sprint was 10.6 seconds. It is now 9.69 seconds. By how much has the record changed? Interview 1 Task 19 Bas needs to buy 114 cans of soft drink. How many 6-packs should he get?
21 task 19 IntervIew 1 TASk 19 Bas needs to buy 114 cans of soft drink. Say: Bas needs to buy 114 cans of soft drink. How many 6-packs should he get? How many 6-packs should he get? Early 7 7 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Uses a mix of multiplicative and additive strategies ( 6) e.g., 6 10 = 60; = 120; = 114; = 19 Uses a multiplicative strategy e.g., - Basic facts with adjustment e.g., 10 6 = 60; 20 6 = 120; = 114; = 19 - Halving then basic facts with adjustment e.g., = 57 3; 60 3 = 20; 20 1 = 19 - Nice (compatible) numbers e.g., = 20; = 114; 20 1 = 19 task 20 IntervIew 1 TASk 20 Three boys share two pizzas equally. Say: Three boys share two pizzas equally. Eight girls share six pizzas equally. Who gets more pizza, one of the boys or one of the girls? Eight girls share six pizzas equally. Who gets more pizza, one of the boys or one of the girls? Early 7 7 decision: Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Uses proportional approach e.g., - Uses equivalent fractions to get unit rate 2 8 e.g., 2 3 = = 3 12 of a pizza and 6 8 = 6 = = 9 12 of a pizza, 9 12 > 8 so girls get more each Uses equivalent ratios e.g., 2:3 = 6:9 so 9 boys would share 6 pizza and they get a lesser share than 8 girls sharing 6 pizza. - Rate argument e.g., 3 times as much pizza for the girls but fewer than 3 times as many girls. Partial solution e.g., 2 3 = 2 of a pizza, 6 8 = = 4 3 of a pizza, and 4 3 > 2 3 [Ask: How do you know 3 > 2? Rate as 7 if they can explain why.] 4 3 If any 7 are circled in Tasks 18, 19 or 20, CONTINUE the interview. If only E7 are circled, STOP the interview If in any doubt, CONTINUE the interview.
22 Interview 1 Task 20 Three boys share two pizzas equally. Eight girls share six pizzas equally. Who gets more pizza, one of the boys or one of the girls? Interview 1 Task 21 The hairdresser has 4.5 litres of dye left. Each tint uses litres of dye. How many tints can the hairdresser do?
23 task 21 Say: The hairdresser has 4.5 litres of dye left. Each tint uses litres of dye. How many tints can the hairdresser do? IntervIew 1 TASk 21 The hairdresser has 4.5 litres of dye left. Each tint uses litres of dye. How many tints can the hairdresser do? 7 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Early 8 Uses multiplicative strategies e.g., - Successive doubling e.g., = 0.75; = 1.5; = 4.5; = 12 - Multiplication facts and compensation e.g., = 10; = 0.750; = 2; = 12 or = 3.75; = 0.75; = Turns decimals into fractions e.g., = 8; 4.5 = 4 2 ; 4 2 = 36 8 ; = 12 task 22 Say: Jacinda gets 32 of her 40 shots in. What percentage of her shots does she get in? IntervIew 1 TASk 22 Jacinda gets 32 of her 40 shots in. What percentage of her shots does she get in? 7 Cannot solve the problem or Uses an earlier numeracy stage Estimation strategies ( 7) e.g., Half of 40 is 20 (that s 50%) and 30 shots is three-quarters (that s 75%) so it is more than three-quarters. Early 8 Uses multiplicative strategies e.g., is 100; is 80; 80 out of 100 = 80% 32 Uses equivalent fractions e.g., 40 = 8 10 = = 80% Stop the interview
24 Interview 1 Task 22 Jacinda gets 32 of her 40 shots in. What percentage of her shots does she get in?
E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP E CA AC EA AA AM AP
 1 The role of this book. School wide assessment resource instructions. Contents page Pg3 Pg3 E CA AC EA AA AM AP I am learning my addition and subtraction facts to five. Pg4, 5 I am learning my doubles
1 The role of this book. School wide assessment resource instructions. Contents page Pg3 Pg3 E CA AC EA AA AM AP I am learning my addition and subtraction facts to five. Pg4, 5 I am learning my doubles
These tests contain questions ranging from Level 2 to Level 4. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to
 These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test and ten seconds to answer questions.
These tests contain questions ranging from Level to Level. They get progressively more difficult. Children should have five seconds to answer questions in each test and ten seconds to answer questions.
4 One ticket costs What will four tickets cost? 17.50
 TOP TEN Set X TEST 1 1 Multiply 6.08 by one thousand. 2 Write one quarter as a decimal. 3 35% of a number is 42. What is 70% of the number? 4 One ticket costs 17.50. What will four tickets cost? 17.50
TOP TEN Set X TEST 1 1 Multiply 6.08 by one thousand. 2 Write one quarter as a decimal. 3 35% of a number is 42. What is 70% of the number? 4 One ticket costs 17.50. What will four tickets cost? 17.50
Multiplication and Division
 F Student Book Name Series F Contents Topic Mental multiplication strategies (p. - 0) doubling strategy multiply by 0s, 00s and 000s split strategy compensation strategy factors and multiples Date completed
F Student Book Name Series F Contents Topic Mental multiplication strategies (p. - 0) doubling strategy multiply by 0s, 00s and 000s split strategy compensation strategy factors and multiples Date completed
Compare fractions. Introduction. Additional materials Numeracy Level 1
 Additional materials Numeracy Level Introduction You may see fractions in newspapers, on adverts and sale signs, or used with weights and measures. You need to be able to read and understand them, and
Additional materials Numeracy Level Introduction You may see fractions in newspapers, on adverts and sale signs, or used with weights and measures. You need to be able to read and understand them, and
Properties of Numbers
 Properties of Numbers 1. Write the number twelve thousand and forty-eight in figures. 2. Round two hundred and thirty-five to the nearest ten. 3. Which of these numbers is not a multiple of eight? Fifty-four,
Properties of Numbers 1. Write the number twelve thousand and forty-eight in figures. 2. Round two hundred and thirty-five to the nearest ten. 3. Which of these numbers is not a multiple of eight? Fifty-four,
Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths. Mark schemes
 Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths Mark schemes Introduction This booklet contains the mark schemes for the higher tiers tests (Tests A and B) and the lower tier test (Test C). The
Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths Mark schemes Introduction This booklet contains the mark schemes for the higher tiers tests (Tests A and B) and the lower tier test (Test C). The
Year 6 Spring 1 Maths Activity Mat 5
 Year Spring Maths Activity Mat Section It is less than 000. All the digits are even. The hundreds digit is half the tens digit. The ones digit is half way between the tens and hundreds digits. Section
Year Spring Maths Activity Mat Section It is less than 000. All the digits are even. The hundreds digit is half the tens digit. The ones digit is half way between the tens and hundreds digits. Section
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy
 The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
Fractions & Decimals Student Clinical Interview
 Fractions & Decimals Student Clinical Interview Fractions Learning Pathway Curricular Connection QUESTION/PROMPT/VISUAL Anticipated Response Notes Unit Fractions Unit A Use proportional reasoning to make
Fractions & Decimals Student Clinical Interview Fractions Learning Pathway Curricular Connection QUESTION/PROMPT/VISUAL Anticipated Response Notes Unit Fractions Unit A Use proportional reasoning to make
Time. On the first day of Christmas. Memory. Notation
 Hour Minute Second Duration Period Notation 24 hour OR 12 hour clock (am or pm or 12 midnight or 12 noon) On the first day of Time 1 year = 52 weeks = 365 days 1 week = 7 days 1 day = 24 hours 1 hour =
Hour Minute Second Duration Period Notation 24 hour OR 12 hour clock (am or pm or 12 midnight or 12 noon) On the first day of Time 1 year = 52 weeks = 365 days 1 week = 7 days 1 day = 24 hours 1 hour =
Building Concepts: Fractions and Unit Squares
 Lesson Overview This TI-Nspire lesson, essentially a dynamic geoboard, is intended to extend the concept of fraction to unit squares, where the unit fraction b is a portion of the area of a unit square.
Lesson Overview This TI-Nspire lesson, essentially a dynamic geoboard, is intended to extend the concept of fraction to unit squares, where the unit fraction b is a portion of the area of a unit square.
MATH NUMBER SENSE 3 Performance Objective Task Analysis Benchmarks/Assessment Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers.
 Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers. 1. Count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. Count to 10,000 Which numbers are whole numbers? Whole number 0, 15.3, 4/5, 8, 25 1/2 Count
Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers. 1. Count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. Count to 10,000 Which numbers are whole numbers? Whole number 0, 15.3, 4/5, 8, 25 1/2 Count
6. TYPES OF FRACTIONS
 . TYPES OF FRACTIONS - Parts of a whole - Complementary fractions - Measuring fractions - Fractions and percentages - Parts of a group - A fraction of what? 0 - Improper fractions - Equivalent fractions
. TYPES OF FRACTIONS - Parts of a whole - Complementary fractions - Measuring fractions - Fractions and percentages - Parts of a group - A fraction of what? 0 - Improper fractions - Equivalent fractions
Incoming Advanced Grade 7
 Name Date Incoming Advanced Grade 7 Tell whether the two fractions form a proportion. 1. 3 16, 4 20 2. 5 30, 7 42 3. 4 6, 18 27 4. Use the ratio table to find the unit rate in dollars per ounce. Order
Name Date Incoming Advanced Grade 7 Tell whether the two fractions form a proportion. 1. 3 16, 4 20 2. 5 30, 7 42 3. 4 6, 18 27 4. Use the ratio table to find the unit rate in dollars per ounce. Order
Counting Stick: Infants: First and Second Class: Third and Fourth Class: Fifth and Sixth Class
 Counting Stick: What is it? A 1-metre long stick divided into ten sections, each 10 cms long. What can it be used for and with what classes? The stick can be used for a variety of number activities and
Counting Stick: What is it? A 1-metre long stick divided into ten sections, each 10 cms long. What can it be used for and with what classes? The stick can be used for a variety of number activities and
Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40
 8th September Convert 90 millimetres into centimetres Convert 2 centimetres into millimetres Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40 A printer prints 6 pages
8th September Convert 90 millimetres into centimetres Convert 2 centimetres into millimetres Write down all the factors of 15 Write down all the multiples of 6 between 20 and 40 A printer prints 6 pages
Improper Fractions. An Improper Fraction has a top number larger than (or equal to) the bottom number.
 Improper Fractions (seven-fourths or seven-quarters) 7 4 An Improper Fraction has a top number larger than (or equal to) the bottom number. It is "top-heavy" More Examples 3 7 16 15 99 2 3 15 15 5 See
Improper Fractions (seven-fourths or seven-quarters) 7 4 An Improper Fraction has a top number larger than (or equal to) the bottom number. It is "top-heavy" More Examples 3 7 16 15 99 2 3 15 15 5 See
b) 12 - = 6 d) 9 - = 3 e) 11 - = 8 f) 10 - = 7
 Level 7 Card 1 a) Using the number chart count by 2s from 10 to 30. Use counters for these equations: b) + 2 = 6 c) 2 + 6 = d) 2 + = 6 e) 12 = + 6 f) + 5 = 8 g) 9 = + 4 h) 7 + = 11 Level 7 Card 2 a) Using
Level 7 Card 1 a) Using the number chart count by 2s from 10 to 30. Use counters for these equations: b) + 2 = 6 c) 2 + 6 = d) 2 + = 6 e) 12 = + 6 f) + 5 = 8 g) 9 = + 4 h) 7 + = 11 Level 7 Card 2 a) Using
Section A Sharing Amounts in a Given Ratio Grade D / C
 Name: Teacher Assessment Section A Sharing Amounts in a Given Grade D / C 1. Divide 60 in the ratio 1:5 Answer. and 2. Divide 438 in the ratio 5:1............ 3. A packet contains 24 fibre-tipped pens.
Name: Teacher Assessment Section A Sharing Amounts in a Given Grade D / C 1. Divide 60 in the ratio 1:5 Answer. and 2. Divide 438 in the ratio 5:1............ 3. A packet contains 24 fibre-tipped pens.
Paper B Numeracy Paper 11+ Candidate Number... This is a multiple-choice test. Please fill in the details on the multiple-choice answer sheet.
 Paper B. 2015 Numeracy Paper 11+ Name... Candidate Number... Seat Number... This is a multiple-choice test. Please fill in the details on the multiple-choice answer sheet. This numeracy paper contains
Paper B. 2015 Numeracy Paper 11+ Name... Candidate Number... Seat Number... This is a multiple-choice test. Please fill in the details on the multiple-choice answer sheet. This numeracy paper contains
Foundation Stage. Using and applying mathematics. Framework review. Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems
 Foundation Stage Using and applying mathematics Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Look at the apples. Are there more green apples or more red apples? How can you
Foundation Stage Using and applying mathematics Use developing mathematical ideas and methods to solve practical problems Look at the apples. Are there more green apples or more red apples? How can you
Adding and Subtracting Fractions Part 1: The same sized slice
 Adding and Subtracting Fractions Part : The same sized slice Exercise What to do We are learning to add simple fractions Each of these fraction problems can be shown with fraction symbols. Use fraction
Adding and Subtracting Fractions Part : The same sized slice Exercise What to do We are learning to add simple fractions Each of these fraction problems can be shown with fraction symbols. Use fraction
Place Value, Fractions & Decimals
 Cabarrus 3-5 Workshop February 28, 2017 Concord, NC Greg Tang s Place Value, Fractions & Decimals www.gregtang.com 1 gregtang@gregtang.com copyright www.gregtang.com Gregory Tang Number Nicknames Focus
Cabarrus 3-5 Workshop February 28, 2017 Concord, NC Greg Tang s Place Value, Fractions & Decimals www.gregtang.com 1 gregtang@gregtang.com copyright www.gregtang.com Gregory Tang Number Nicknames Focus
TIMSS 2011 released items: Mathematics
 TIMSS 2011 released items: Mathematics The items shown in this document are real items that were administered to Fourth class pupils who took part in TIMSS in 2011. Each item is shown in the format that
TIMSS 2011 released items: Mathematics The items shown in this document are real items that were administered to Fourth class pupils who took part in TIMSS in 2011. Each item is shown in the format that
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT
 Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Divide and Conquer Division Strategies
 Lucky Dip? Divide and Conquer Division Strategies We are learning to practise divisibility rules. 15 18 400 99 108 87 300 35 63 90 70 64 200 45 24 12 93 125 75 AC EA AA AM AP Exercise 1 Find the numbers
Lucky Dip? Divide and Conquer Division Strategies We are learning to practise divisibility rules. 15 18 400 99 108 87 300 35 63 90 70 64 200 45 24 12 93 125 75 AC EA AA AM AP Exercise 1 Find the numbers
Year 9 mathematics: holiday revision. 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four?
 DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
DAY 1 ANSWERS Mental questions 1 Multiply seven by seven. 49 2 How many nines are there in fifty-four? 54 9 = 6 6 3 What number should you add to negative three to get the answer five? -3 0 5 8 4 Add two
Year 6 Spring Term Week 10 to 11 Number: Ratio
 1 Using ratio language Ratio and fractions Introducing the ratio symbol Calculating ratio Using scale factors Calculating scale factors Ratio and proportion problems Solve problems involving the relative
1 Using ratio language Ratio and fractions Introducing the ratio symbol Calculating ratio Using scale factors Calculating scale factors Ratio and proportion problems Solve problems involving the relative
Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack:
 Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack: Below is a guide with example questions to use with students preparing for NAPLAN for three weeks prior to the test. By this stage students are expected to have spent a
Grade 3 NAPLAN preparation pack: Below is a guide with example questions to use with students preparing for NAPLAN for three weeks prior to the test. By this stage students are expected to have spent a
[WORD PROBLEMS] Advanced Word Problems for Key Stage Two children.
![[WORD PROBLEMS] Advanced Word Problems for Key Stage Two children. [WORD PROBLEMS] Advanced Word Problems for Key Stage Two children.](/thumbs/86/94440268.jpg) Levels 5 & 6 Advanced Word Problems for Key Stage Two children. Q1. 427 children visit a castle. They go in groups of 15. One group has less than 15. Every group of children has one adult with them. How
Levels 5 & 6 Advanced Word Problems for Key Stage Two children. Q1. 427 children visit a castle. They go in groups of 15. One group has less than 15. Every group of children has one adult with them. How
Task Possible response & comments Level Student:
 Aspect 2 Early Arithmetic Strategies Task 1 I had 8 cards and I was given another 7. How many do I have now? EAS Task 2 I have 17 grapes. I ate some and now I have 11 left. How many did I eat? Note: Teacher
Aspect 2 Early Arithmetic Strategies Task 1 I had 8 cards and I was given another 7. How many do I have now? EAS Task 2 I have 17 grapes. I ate some and now I have 11 left. How many did I eat? Note: Teacher
Answer Key Lesson 10: Add Fractions
 nswer Key Lesson 0: dd Fractions Student uide dd Fractions (S pp. 99) Questions.. ossible response:.. Use fraction circle pieces to model the problem.. Is Kathy s estimate correct Explain your reasoning.
nswer Key Lesson 0: dd Fractions Student uide dd Fractions (S pp. 99) Questions.. ossible response:.. Use fraction circle pieces to model the problem.. Is Kathy s estimate correct Explain your reasoning.
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM 1: 2012 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM
 ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM : 0 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM : 0 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM COUNT FORWARDS AND BACKWARDS IN DECIMALS TO AT LEAST DECIMAL PLACES.. C. C.
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM : 0 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM GRADE 6 MATHEMATICS TERM : 0 EXEMPLAR MEMORANDUM COUNT FORWARDS AND BACKWARDS IN DECIMALS TO AT LEAST DECIMAL PLACES.. C. C.
We are packing 22 balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) 3 balls in each box b) 5 balls in each box
 1 We are packing balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) balls in each box b) balls in each box E.g: E.g: Write each as a multiplication and addition, then as a division. = 7
1 We are packing balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) balls in each box b) balls in each box E.g: E.g: Write each as a multiplication and addition, then as a division. = 7
Important Words in Mathematics
 1 P a g e Important Words in Mathematics... 2 Numbers... 3 Number Words... 4 EVEN OR ODD... 5 PLACE VALUE... 6 PLACE VALUE... 7 VALUE... 8 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 9 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 10
1 P a g e Important Words in Mathematics... 2 Numbers... 3 Number Words... 4 EVEN OR ODD... 5 PLACE VALUE... 6 PLACE VALUE... 7 VALUE... 8 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 9 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 10
1 x 12 = 12 2 x 6 = 12 4 x 3 = 12 3 x 4 = 12 2 x 6 = 12
 Juice Problem You will need a ten shape and 2 shape, s, s, 6 s, fraction cards A shop sells packs of juices. orange, mango, pineapple. These are equal proportions. Show the fraction that is orange. Find
Juice Problem You will need a ten shape and 2 shape, s, s, 6 s, fraction cards A shop sells packs of juices. orange, mango, pineapple. These are equal proportions. Show the fraction that is orange. Find
Thank you for Downloading
 Thank you for Downloading Get More FREE resources at You ve Got This Math YOU MAY Print as many copies as you would like for your OWN personal use Save this file on YOUR computer Share on a blog, facebook
Thank you for Downloading Get More FREE resources at You ve Got This Math YOU MAY Print as many copies as you would like for your OWN personal use Save this file on YOUR computer Share on a blog, facebook
Name Date Class. Total (A) Total (B) Total (C) Test Total (A+B+C) R (0-9) I y (10-19) I G (20-25) Maths Basic Skills Week 1
 rk bo k,let t r a h Maths Basic Skills Week 1 Name Date Class. 1. What are the next two numbers? 11. Six times a number is forty two. 21. In a sale, there is twenty-five per -19' -15' -11'... '... What
rk bo k,let t r a h Maths Basic Skills Week 1 Name Date Class. 1. What are the next two numbers? 11. Six times a number is forty two. 21. In a sale, there is twenty-five per -19' -15' -11'... '... What
Oaktree School Assessment MATHS: NUMBER P4
 MATHS: NUMBER P4 I can collect objects I can pick up and put down objects I can hold one object I can see that all the objects have gone I can help to count I can help to match things up one to one (ie.
MATHS: NUMBER P4 I can collect objects I can pick up and put down objects I can hold one object I can see that all the objects have gone I can help to count I can help to match things up one to one (ie.
St Anselm s College Maths Sample Paper 2
 St Anselm s College Maths Sample Paper 2 45 mins No Calculator Allowed 1 1) The speed of light is 186,000 miles per second. Write the speed of light in words. 2) The speed of light is more accurately given
St Anselm s College Maths Sample Paper 2 45 mins No Calculator Allowed 1 1) The speed of light is 186,000 miles per second. Write the speed of light in words. 2) The speed of light is more accurately given
Chuckra 11+ Maths Test 4
 Chuckra 11+ Maths Test 4 1 The table below shows how many bottles were collected in a bottle bank during one week. How many green bottles were put in the bottle bank? 2 6 55 Between 5 and 6 Between 50
Chuckra 11+ Maths Test 4 1 The table below shows how many bottles were collected in a bottle bank during one week. How many green bottles were put in the bottle bank? 2 6 55 Between 5 and 6 Between 50
Mathematics Paper 1 (Non-Calculator)
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Mathematics Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Specimen Papers Set 1 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Candidate Number Foundation
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) Centre Number Mathematics Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Specimen Papers Set 1 Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Candidate Number Foundation
Smiley Face Math Grade 2, Worksheet I
 Section 2 Smiley Face Math Grade 2, Worksheet I Name 1. Complete the two patterns. 448, 458, 468,,, 498,, 518 285, 385, 485, 585,,,,,1085 2. Jackson ate a cookie at 1:00. He ate another cookie every 2½
Section 2 Smiley Face Math Grade 2, Worksheet I Name 1. Complete the two patterns. 448, 458, 468,,, 498,, 518 285, 385, 485, 585,,,,,1085 2. Jackson ate a cookie at 1:00. He ate another cookie every 2½
Maths SATs practice paper 2: reasoning
 Maths SATs paper 2: reasoning First name... Middle name... Last name... Date of birth Day... Month... Year... School name... www.teachitprimary.co.uk 208 320 Page of 8 Instructions You must not use a calculator
Maths SATs paper 2: reasoning First name... Middle name... Last name... Date of birth Day... Month... Year... School name... www.teachitprimary.co.uk 208 320 Page of 8 Instructions You must not use a calculator
1 /4. (One-Half) (One-Quarter) (Three-Eighths)
 LESSON 4: Fractions: A fraction is a part of a whole. Slice a pizza, and you will have fractions: 1 /2 1 /4 3 /8 (One-Half) (One-Quarter) (Three-Eighths) The top number tells how many slices you have and
LESSON 4: Fractions: A fraction is a part of a whole. Slice a pizza, and you will have fractions: 1 /2 1 /4 3 /8 (One-Half) (One-Quarter) (Three-Eighths) The top number tells how many slices you have and
We are packing 22 balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) 3 balls in each box b) 5 balls in each box
 MEP Book We are packing balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) balls in each box b) balls in each box Write each as a multiplication and addition, then as a division. = + = +
MEP Book We are packing balls into boxes. Show how many boxes we will need if we pack: a) balls in each box b) balls in each box Write each as a multiplication and addition, then as a division. = + = +
Topic. Easter Intervention. If you have any questions, feel free to
 Easter Intervention Foundation Questions Topic Angles Transformations Multiples, Factors, Primes Indices Algebra Area and Perimeter Factions, Decimals and Percentages Ratio Equations Probability Averages
Easter Intervention Foundation Questions Topic Angles Transformations Multiples, Factors, Primes Indices Algebra Area and Perimeter Factions, Decimals and Percentages Ratio Equations Probability Averages
11+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION Mathematics
 11+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION Mathematics SPECIMIN PAPER Instructions Time allowed: 60 minutes Use black ink or ball-point pen. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided there may be
11+ ENTRANCE EXAMINATION Mathematics SPECIMIN PAPER Instructions Time allowed: 60 minutes Use black ink or ball-point pen. Answer all questions. Answer the questions in the spaces provided there may be
Patterns in Multiplication and Division
 UNIT 3 1 STUDENT BOOK LESSO N Patterns in Multiplication and Division Quick Review Here are some strategies to help you multiply and divide. Skip count up or down from a known fact to multiply. To find
UNIT 3 1 STUDENT BOOK LESSO N Patterns in Multiplication and Division Quick Review Here are some strategies to help you multiply and divide. Skip count up or down from a known fact to multiply. To find
Graphs and Probability
 Name: Chapter Date: Practice 1 Making and Interpreting Double Bar Graphs Complete. Use the data in the graph. The double bar graph shows the number of boys and girls in two classes, 5A and 5B. Students
Name: Chapter Date: Practice 1 Making and Interpreting Double Bar Graphs Complete. Use the data in the graph. The double bar graph shows the number of boys and girls in two classes, 5A and 5B. Students
THE SULTAN S SCHOOL HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME
 HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME Your child has taken home a letter which explains the main things that your child has or will be learning in maths. Have a look through this letter so you can get
HELPING YOUR CHILD WITH MATHS AT HOME Your child has taken home a letter which explains the main things that your child has or will be learning in maths. Have a look through this letter so you can get
Question 7. Question 8. Question 9. Question 10. Question 11. Question 12
 Do not turn the page until you are told to do so Answers should be marked on the answer sheet using a pencil Only give one answer to each question If you become stuck on a question go on to the next and
Do not turn the page until you are told to do so Answers should be marked on the answer sheet using a pencil Only give one answer to each question If you become stuck on a question go on to the next and
Chapter 2: Numeration Systems
 Chapter 2: Numeration Systems 8. In base ten, 215.687 is exactly ones, exactly tens, exactly hundreds, and exactly thousands; also, 3421 is exactly tenths and exactly hundredths. In base ten, 215.687 is
Chapter 2: Numeration Systems 8. In base ten, 215.687 is exactly ones, exactly tens, exactly hundreds, and exactly thousands; also, 3421 is exactly tenths and exactly hundredths. In base ten, 215.687 is
Scaffolded Math Practice. Daily Morning Work: 1 Quarter. 3 Grade. 45 Days
 Scaffolded Math Practice Daily Morning Work: st 1 Quarter rd 3 Grade 45 Days Table of Contents Using this Product Pages 3 5 Weekly Skills Practiced Pages 6 10 Morning Work Pages Pages 11 56 Grading Rubric
Scaffolded Math Practice Daily Morning Work: st 1 Quarter rd 3 Grade 45 Days Table of Contents Using this Product Pages 3 5 Weekly Skills Practiced Pages 6 10 Morning Work Pages Pages 11 56 Grading Rubric
A fraction (from Latin: fractus, "broken") represents a part of a whole.
 Math 4. Class work. Fractions. A fraction (from Latin: fractus, "broken") represents a part of a whole. Look at the picture on the right: the whole chocolate bar is divided into equal pieces: (whole chocolate
Math 4. Class work. Fractions. A fraction (from Latin: fractus, "broken") represents a part of a whole. Look at the picture on the right: the whole chocolate bar is divided into equal pieces: (whole chocolate
Dumfries and Galloway Council. Added Value Revision pack. Name... Suzanne Stoppard. National 4
 Dumfries and Galloway Council Added Value Revision pack Name... Suzanne Stoppard National 4 Self Assessment Summary- Part one Non Calculator Assessment standard Traffic Lights Pupils Signature Parents
Dumfries and Galloway Council Added Value Revision pack Name... Suzanne Stoppard National 4 Self Assessment Summary- Part one Non Calculator Assessment standard Traffic Lights Pupils Signature Parents
CEM 11+ Preparation Series Maths Booklet 25
 BM6.25 CEM 11+ Preparation Series Maths Booklet 25 Name: Date started: Try to work neatly Ask for help if you get stuck Show how you got your answers Section A Section B Section C WM65.7: Investigating
BM6.25 CEM 11+ Preparation Series Maths Booklet 25 Name: Date started: Try to work neatly Ask for help if you get stuck Show how you got your answers Section A Section B Section C WM65.7: Investigating
Number and Operations Fractions
 Number and Operations Fractions Standards Entry Points Access Skills 3 Page 59 Pages 60 61 Pages 60 62 4 Pages 63 64 Page 65 67 5 Pages 68 69 Page 70 72 MATHEMATICS 58 CONTENT AREA Mathematics DOMAIN Number
Number and Operations Fractions Standards Entry Points Access Skills 3 Page 59 Pages 60 61 Pages 60 62 4 Pages 63 64 Page 65 67 5 Pages 68 69 Page 70 72 MATHEMATICS 58 CONTENT AREA Mathematics DOMAIN Number
Act it Out or Use Objects
 Act it Out or Use Objects Class Counting A class contained 32 students. The students were standing in a circle and began to count round the room starting from one, with each student saying one number.
Act it Out or Use Objects Class Counting A class contained 32 students. The students were standing in a circle and began to count round the room starting from one, with each student saying one number.
Chuckra 11+ Maths Test 1
 Chuckra 11+ Maths Test 1 1 The table below shows how many people own each type of pet. How many people own pet cats? 4 50 150 300 2000 2 There are 310 tourists on a plane for London. Of these, 185 people
Chuckra 11+ Maths Test 1 1 The table below shows how many people own each type of pet. How many people own pet cats? 4 50 150 300 2000 2 There are 310 tourists on a plane for London. Of these, 185 people
We are herbivores. We eat plants and twigs. We are the largest dinosaurs.
 1 The Link of mathematics is designed to help children develop their mathematical skills. Each Link or page has four practice exercises with short and varied activities to consolidate learning and increase
1 The Link of mathematics is designed to help children develop their mathematical skills. Each Link or page has four practice exercises with short and varied activities to consolidate learning and increase
Entrance Examination Maths Practice Paper ? 17
 Page1. 1. I bought pencils. I was given 2p change from 1. How much did each pencil cost? 2. ionne has a note, a 0 pence piece, three 2 pence pieces and two 1 pence pieces. How much money does she have?
Page1. 1. I bought pencils. I was given 2p change from 1. How much did each pencil cost? 2. ionne has a note, a 0 pence piece, three 2 pence pieces and two 1 pence pieces. How much money does she have?
3. The answer key. Download the answer key and make as many copies as you need.
 A. You will need: 1. A blank response form with the title Mathematica, identical (except for the title) to the ones which are used for the Contests. Download this form and make as many copies as you need,
A. You will need: 1. A blank response form with the title Mathematica, identical (except for the title) to the ones which are used for the Contests. Download this form and make as many copies as you need,
Question Bank for grade 6. Numbers
 Question Bank for grade 6 Q1. a) List the factors of 24 b) List the prime factors of 18 c) Write 24 as a product of its prime factors. d) List three multiples of 24 Q2.Complete the table below: Check the
Question Bank for grade 6 Q1. a) List the factors of 24 b) List the prime factors of 18 c) Write 24 as a product of its prime factors. d) List three multiples of 24 Q2.Complete the table below: Check the
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 04
 Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 4m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations, to
Factors and Multiples. Chapter NUMBER. Big Idea. Learning Goals. Essential Question. Important Words
 NUMBER Factors and Multiples Chapter 4 Big Idea Understanding multiples and factors helps me describe and solve realworld problems. Learning Goals I can determine factors and multiples of numbers less
NUMBER Factors and Multiples Chapter 4 Big Idea Understanding multiples and factors helps me describe and solve realworld problems. Learning Goals I can determine factors and multiples of numbers less
UNIT 5: RATIO, PROPORTION, AND PERCENT WEEK 20: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 5: RATIO, PROPORTION, AND PERCENT WEEK 20: Student Packet 20.1 Solving Proportions 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. Use rates and proportions to solve problems.
Name Period Date UNIT 5: RATIO, PROPORTION, AND PERCENT WEEK 20: Student Packet 20.1 Solving Proportions 1 Add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers. Use rates and proportions to solve problems.
Reigate Grammar School. 11+ Entrance Examination January 2012 MATHEMATICS
 Reigate Grammar School + Entrance Examination January 0 MATHEMATICS Time allowed: 45 minutes NAME Work through the paper carefully You do not have to finish everything Do not spend too much time on any
Reigate Grammar School + Entrance Examination January 0 MATHEMATICS Time allowed: 45 minutes NAME Work through the paper carefully You do not have to finish everything Do not spend too much time on any
SAMPLE BOOKLET Published July 2015
 National curriculum tests Key stage 1 Mathematics Paper 2: reasoning First name Middle name Last name SAMPLE BOOKLET Published July 2015 This sample test indicates how the national curriculum will be assessed
National curriculum tests Key stage 1 Mathematics Paper 2: reasoning First name Middle name Last name SAMPLE BOOKLET Published July 2015 This sample test indicates how the national curriculum will be assessed
0:45. year. Use 2B or HB pencil only. Time available for students to complete test: 45 minutes
 national assessment program literacy and numeracy NUMERACY year 3 2009 0:45 Time available for students to complete test: 45 minutes Use 2B or HB pencil only Curriculum Corporation, on behalf of the Ministerial
national assessment program literacy and numeracy NUMERACY year 3 2009 0:45 Time available for students to complete test: 45 minutes Use 2B or HB pencil only Curriculum Corporation, on behalf of the Ministerial
Equivalent Fractions
 Grade 6 Ch 4 Notes Equivalent Fractions Have you ever noticed that not everyone describes the same things in the same way. For instance, a mother might say her baby is twelve months old. The father might
Grade 6 Ch 4 Notes Equivalent Fractions Have you ever noticed that not everyone describes the same things in the same way. For instance, a mother might say her baby is twelve months old. The father might
Easy problems. E2 Calculate A -1 B 0 C 1 D 2 E 5 E3 Calculate A 8 B 9 C 10 D 12 E 24
 Easy problems E1 How many tadpoles are there in this picture? A 1B 3 C 6 D 12 E cannot tell E2 Calculate 1-1 + 1-1 + 1 A -1 B 0 C 1 D 2 E 5 E3 Calculate 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 A 8 B 9 C 10 D 12 E 24 E4 1 + 11 +
Easy problems E1 How many tadpoles are there in this picture? A 1B 3 C 6 D 12 E cannot tell E2 Calculate 1-1 + 1-1 + 1 A -1 B 0 C 1 D 2 E 5 E3 Calculate 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 A 8 B 9 C 10 D 12 E 24 E4 1 + 11 +
You Try: 1 of the free throws and Kevin. Riley and Jasper were working on their science fair project. Riley completed and
 1 Jason made made of the free throws and Kevin of the free throws. What fraction of the free throws did they make altogether? Area Model 1 You Try: Riley and Jasper were working on their science fair project.
1 Jason made made of the free throws and Kevin of the free throws. What fraction of the free throws did they make altogether? Area Model 1 You Try: Riley and Jasper were working on their science fair project.
Number Addition and subtraction
 Number Addition and subtraction This activity can be adapted for many of the addition and subtraction objectives by varying the questions used 1 Slide 1 (per class); number fan (per child); two different
Number Addition and subtraction This activity can be adapted for many of the addition and subtraction objectives by varying the questions used 1 Slide 1 (per class); number fan (per child); two different
We can see from columns 1 and 2 that: [Bottom number 12 = Top number] OR. [Top number 12 = Bottom number] [132] [6] 11 [10]
![We can see from columns 1 and 2 that: [Bottom number 12 = Top number] OR. [Top number 12 = Bottom number] [132] [6] 11 [10] We can see from columns 1 and 2 that: [Bottom number 12 = Top number] OR. [Top number 12 = Bottom number] [132] [6] 11 [10]](/thumbs/87/96232432.jpg) Q1-3. To complete the table, pick a column where you have been given both the top and the bottom numbers. Work out the relationship between the top and the bottom number. Apply the same rule to all columns.
Q1-3. To complete the table, pick a column where you have been given both the top and the bottom numbers. Work out the relationship between the top and the bottom number. Apply the same rule to all columns.
OCR Statistics 1. Probability. Section 2: Permutations and combinations. Factorials
 OCR Statistics Probability Section 2: Permutations and combinations Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Factorials Permutations Combinations Factorials An important aspect of life is
OCR Statistics Probability Section 2: Permutations and combinations Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Factorials Permutations Combinations Factorials An important aspect of life is
5th Grade. Divisibility Rules. Slide 1 / 239 Slide 2 / 239. Slide 3 / 239. Slide 4 / 239. Slide 6 / 239. Slide 5 / 239. Division. Division Unit Topics
 Slide 1 / 239 Slide 2 / 239 5th Grade Division 2015-11-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 239 Slide 4 / 239 Division Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Divisibility Rules Patterns in Multiplication
Slide 1 / 239 Slide 2 / 239 5th Grade Division 2015-11-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 239 Slide 4 / 239 Division Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Divisibility Rules Patterns in Multiplication
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests
 Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests 1 Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Year 5 Mental Arithmetic Tests 1 Equipment Required Printed question and answer sheet for the reader Printed blank answer page for child Stopwatch or timer Pencil No other equipment is required to complete
Hillhead High School. Fractions. What you need to know. S.O Grady 1
 Fractions What you need to know S.O Grady What is a fraction? A fraction is a part of a whole (). Fractions consist of two numbers, a numerator and a denominator. Top number How many parts we have Bottom
Fractions What you need to know S.O Grady What is a fraction? A fraction is a part of a whole (). Fractions consist of two numbers, a numerator and a denominator. Top number How many parts we have Bottom
Mathematics Workshop. For Parents of 3 & 4
 Mathematics Workshop For Parents of 3 & 4 Objectives Participants will be able to: Learn how to help your child solve P3 & P4 Math problem sums using the Polya s problem solving approach. Learn how to
Mathematics Workshop For Parents of 3 & 4 Objectives Participants will be able to: Learn how to help your child solve P3 & P4 Math problem sums using the Polya s problem solving approach. Learn how to
Fourth Grade Quarter 3 Unit 5: Fraction Equivalence, Ordering, and Operations Part 2, Topics D-H Approximately 25 days Begin around January 4 th
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Fourth Grade Quarter 3 Unit 5: Fraction Equivalence, Ordering, and Operations Part 2, Topics D-H Approximately 25 days Begin around January 4 th In
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Fourth Grade Quarter 3 Unit 5: Fraction Equivalence, Ordering, and Operations Part 2, Topics D-H Approximately 25 days Begin around January 4 th In
Mathematics Grade 2. grade 2 17
 Mathematics Grade 2 In Grade 2, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) extending understanding of base-ten notation; (2) building fluency with addition and subtraction; (3) using standard
Mathematics Grade 2 In Grade 2, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) extending understanding of base-ten notation; (2) building fluency with addition and subtraction; (3) using standard
Essentials. Week by. Week. Investigations. Let s Write Write a story about. Seeing Math $ $ $ $ What Do You Think? Patterns, Patterns, Patterns
 Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 21 Let s Write Write a story about 1 2 Seeing Math What Do You Think? Suppose you hit the target with three darts. How could you score 15? Is there more
Week by Week MATHEMATICS Essentials Grade 2 WEEK 21 Let s Write Write a story about 1 2 Seeing Math What Do You Think? Suppose you hit the target with three darts. How could you score 15? Is there more
Numbers. Counting. Key Point. Key Point. Understand what a number is Count from 0 20 in numbers and words Count to 100
 Number - Number and Place Value Numbers and Counting Understand what a number is Count from 0 20 in numbers and words Count to 100 Numbers A number is a symbol used to count how many there are of something.
Number - Number and Place Value Numbers and Counting Understand what a number is Count from 0 20 in numbers and words Count to 100 Numbers A number is a symbol used to count how many there are of something.
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS Time allowed: 1 hour and 15 minutes
 ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2018 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 15 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and write your answers
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS 2018 MATHEMATICS FIRST FORM Time allowed: 1 hour and 15 minutes Answer ALL questions. Show all necessary working on the question paper in the spaces provided and write your answers
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Rising 6 th Grade Summer Interactive Math Practice
 Rising 6 th Grade Summer Interactive Math Practice Rising Sixth Grade Summer Math Packet I. Place Value Write each number in word form, in expanded form, expanded notation, name the place of the underlined
Rising 6 th Grade Summer Interactive Math Practice Rising Sixth Grade Summer Math Packet I. Place Value Write each number in word form, in expanded form, expanded notation, name the place of the underlined
2008 Cedar Ridge Test Solutions
 2008 Cedar Ridge Test Solutions 1) The value of 1.4 + 0.03 + 0.009 + 7 is Step 1: Line up all of the decimals in the equation: 1.4 0.03 0.009 + 7 8.439 2) Solve: 4 + 2 x 3 4 2 + 3 = Answer: 8.439 Order
2008 Cedar Ridge Test Solutions 1) The value of 1.4 + 0.03 + 0.009 + 7 is Step 1: Line up all of the decimals in the equation: 1.4 0.03 0.009 + 7 8.439 2) Solve: 4 + 2 x 3 4 2 + 3 = Answer: 8.439 Order
Helping your child with Maths at the end of Reception and in Year 1
 Shape activity At home, or when you are out, look at the surface of shapes. Ask your child what shape is this plate, this mirror, the bath mat, the tea towel, the window, the door, the red traffic light,
Shape activity At home, or when you are out, look at the surface of shapes. Ask your child what shape is this plate, this mirror, the bath mat, the tea towel, the window, the door, the red traffic light,
a) 1/2 b) 3/7 c) 5/8 d) 4/10 e) 5/15 f) 2/4 a) two-fifths b) three-eighths c) one-tenth d) two-thirds a) 6/7 b) 7/10 c) 5/50 d) ½ e) 8/15 f) 3/4
 MATH M010 Unit 2, Answers Section 2.1 Page 72 Practice 1 a) 1/2 b) 3/7 c) 5/8 d) 4/10 e) 5/15 f) 2/4 Page 73 Practice 2 a) two-fifths b) three-eighths c) one-tenth d) two-thirds e) four-ninths f) one quarter
MATH M010 Unit 2, Answers Section 2.1 Page 72 Practice 1 a) 1/2 b) 3/7 c) 5/8 d) 4/10 e) 5/15 f) 2/4 Page 73 Practice 2 a) two-fifths b) three-eighths c) one-tenth d) two-thirds e) four-ninths f) one quarter
Fractions( ½(,(Halves( (((((((( 1/3(,(Thirds( (((((((( ¼(,(Fourths( (((((((( ( ( (Primary(Partners.((
 Fractions( ½(,(Halves( (((((((( 1/3(,(Thirds( (((((((( ¼(,(Fourths( (((((((( (Primary(Partners.(( ( ( Tips on how to use these word problems 1. Determine the math readiness of the students in terms of
Fractions( ½(,(Halves( (((((((( 1/3(,(Thirds( (((((((( ¼(,(Fourths( (((((((( (Primary(Partners.(( ( ( Tips on how to use these word problems 1. Determine the math readiness of the students in terms of
Odd one out. Odd one out
 SAMPLE Odd one out Odd one out NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE Spot the difference Spot the difference The same different NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it
SAMPLE Odd one out Odd one out NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE Spot the difference Spot the difference The same different NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it
1. What percentage of the hundredths grids below are shaded in?
 Math Review Fractions, Ratio and Percent (Units 6 & 7) 1. What percentage of the hundredths grids below are shaded in? 45% 75% 5% 2. Write one part-to-whole and one part-to-part ratio for the following
Math Review Fractions, Ratio and Percent (Units 6 & 7) 1. What percentage of the hundredths grids below are shaded in? 45% 75% 5% 2. Write one part-to-whole and one part-to-part ratio for the following
These are skills that we have covered within our math outcomes this year
 Patterns & Relationships Whole Number Multiplication & Division Fractions, Decimals, and Percents Measurement, Data, and Geometry Word Problem Analysis These are skills that we have covered within our
Patterns & Relationships Whole Number Multiplication & Division Fractions, Decimals, and Percents Measurement, Data, and Geometry Word Problem Analysis These are skills that we have covered within our
You must have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser. Tracing paper may be used.
 Write your name here Surname Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Thursday 26 May 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Other names Candidate Number Foundation Tier
Write your name here Surname Pearson Edexcel GCSE Centre Number Mathematics A Paper 1 (Non-Calculator) Thursday 26 May 2016 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Other names Candidate Number Foundation Tier
Year 6 Maths Assessment Guidance - NUMBER Meeting expectations 3 Working Within Year 6 4 Secure within Year 6
 6.1.a.1 Calculate intervals across zero (^) 6.1.a.2 Consolidate counting forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number to 1 000 000 (+) 6.1.a.3 Consolidate counting in multiples of
6.1.a.1 Calculate intervals across zero (^) 6.1.a.2 Consolidate counting forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number to 1 000 000 (+) 6.1.a.3 Consolidate counting in multiples of
2. Write the products for these. SAMPLE 4 6 = = = 4 3 = 8 3 = 3. Use a doubling strategy to complete this table. Step Ahead 6.
 . Introducing the Eights Multiplication Facts. Write the products for these. Look at this array. What do you see? What strategy can you use to figure out the product? = = Look at the next array. What do
. Introducing the Eights Multiplication Facts. Write the products for these. Look at this array. What do you see? What strategy can you use to figure out the product? = = Look at the next array. What do
A collection of 9-1 Maths GCSE Sample and Specimen questions from AQA, OCR, Pearson-Edexcel and WJEC Eduqas. Name: Total Marks:
 Ratio Sharing (F) A collection of 9-1 Maths GCSE Sample and Specimen questions from AQA, OCR, Pearson-Edexcel and WJEC Eduqas. Name: Total Marks: 1. Write 40 : 2000 as a ratio in its simplest form....
Ratio Sharing (F) A collection of 9-1 Maths GCSE Sample and Specimen questions from AQA, OCR, Pearson-Edexcel and WJEC Eduqas. Name: Total Marks: 1. Write 40 : 2000 as a ratio in its simplest form....
2 parts of the circle are shaded is called the numerator. the circle is divided into 7 equal parts
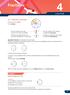 Fractions CHAPTER. Fractions revision of this circle is shaded. is a fraction. The top number shows that The top number of the fraction parts of the circle are shaded is called the numerator The bottom
Fractions CHAPTER. Fractions revision of this circle is shaded. is a fraction. The top number shows that The top number of the fraction parts of the circle are shaded is called the numerator The bottom
Weekly Math Magic- Set 1
 Weekly Math Magic- Set 1 Weekly Math Magic consists of nine weeks of mathematics printables designed to introduce, practice and review essential skills. Each week is presented in the exact same format
Weekly Math Magic- Set 1 Weekly Math Magic consists of nine weeks of mathematics printables designed to introduce, practice and review essential skills. Each week is presented in the exact same format
