The Scientific Status of New Security Studies: A Critical Search for Epistemic Identity of Homeland and Civil Security Research
|
|
|
- Daniella Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13 The Scientific Status of New Security Studies: A Critical Search for Epistemic Identity of Homeland and Civil Security Research rachel suissa Introduction This chapter puts the contributions to this volume into perspective, focusing on the status of homeland and civil security as a field of research. It argues that the epistemic identity of this field can be provided by the overarching academic discipline of new security studies. The conceptual radical shifts from security as defense and war studies, military, grand strategy, and geopolitics to comprehensive new security studies, 1 including homeland and civil security, require an epistemological inquiry (i.e., a study of the nature and grounds of the knowledge in the field) to help evaluate their scientific status. An evaluation of the scientific status of a research program and its theoretical core assumptions should be differentiated from the epistemology of the evolution of the discipline to which the research program relates. New security studies and their novelty are defined by the following four pillars, 2 each of which have been addressed by chapters in this book: New security concepts hybrid threats (see Chapter 1), human security, civilizational security, comprehensive approach, resilience (see Chapter 4 and also Chapter 12), etc.; New security subjects biopolitics of security, financial security, security as ethics (see Chapter 10), etc.;
2 232 Cross-disciplinary Perspectives on Homeland and Civil Security New security objects environmental security, food security, cybersecurity, health and pandemic security, border security (see Chapter 2), etc.; and New security practices migration and insecurity, security technologies (see Chapter 7), commercial security practices, including management of industrial accidents (see Chapter 3), professional security practices such as leadership (see Chapter 9), intelligence (see Chapters 5 and 6), risk management (see Chapter 8), etc., as well as academic teaching practices (see Chapter 11). Thus, new security studies are being discussed mainly through their ontological entities, with valuable contributions to the state of the art, though sometimes at the risk of confusing security ontology (what the nature of security is) with questions of its epistemology (how we can gain knowledge about security). Any inquiry into the scientific status of new security studies as an overarching discipline for scientific inquiry into homeland and civil security should acknowledge that security belongs to hermeneutics, which is the study of society rather than of nature or built environment. In our field, this is probably best exemplified by securitization theory, which assumes that security issues do not appear and dissolve because the threat environment changes, but because dominant discourses transform. 3 The securitization of the European Union s external border and the creation of FRONTEX, for example (see Chapters 2 and 12), have been interpreted in this sense. 4 Further, when pursuing the evolution of a discipline or field, its conceptualization in ontological terms is crucial. This involves both theoretical and practical reasons. However, if the aspect of practicality that dominates security as a branch of knowledge is the reason for inquiring on its scientific status, its ontological entities might be used mistakenly to identify science as equal to practice. This is of special relevance when referring to new security studies as an overarching frame of reference for homeland and civil security research, which itself is multidisciplinary. Therefore, the chapter will first discuss distinctions made in the evolution of security studies elaborating ontological entities. A discussion of new security studies in the context of classical and anti-classical epistemology will follow in order to determine its place in different epistemic contours. The evaluation of the scientific status of this branch will be carried out through the examination of different demarcation criteria, as discussed in the study and philosophy of science and to be addressed below.
3 Beyond One Discipline The Scientific Status of New Security Studies 233 Questioning the scientific status of a discipline cannot be detached from the epistemic culture its branch of knowledge belongs to. When raising this question in new security studies, the relevant concept of epistemic culture is associated with relativism, constructivism, and securitization. 5 Security is no longer limited to the traditional policies and military tools of the nation-state, and is no longer considered dependent primarily on geopolitics and military strength. Security has expanded into a broad, comprehensive field that encompasses social, economic, environmental, and ethical models of analysis and tools of action. This comprehensiveness exposes the security-cultural epistemic relativism to intersubjective levels when different entities differ in the ontological concept of security and the balance between models of tools and actions. It increases the relevance of different approaches to constructivist analysis of how security threats, policies, and strategies emerge within the securitization of everyday life across borders. There is no reason to suspect that homeland and civil security as a specific subject matter and field of study should be exempt from those implications of the postmodern condition. Issues acquire a security status and become securitized as a result of an intersubjective process involving a particular discursive and political force that, once established, enables policy makers to immediately adopt whatever means they deem appropriate to curb the threat. 6 Informed by Popper s critical approach to historicism, 7 new security studies need to explore the linkage between the ontology of disciplines, the scientific methods they use, and their political implications. Following Popper s demarcation criterion between science and pseudoscience, new security studies will only be a science if they are open to be disproven, or falsified, by the facts. As the following example from homeland security shows, this is not a theoretical construct but of direct practical relevance. In order to protect against potential terrorist threats, it may be legitimate to take preventive measures when there is a valid threat, yet insufficient evidence of an impending terrorist attack. This must be distinguished from taking measures against an alleged terrorist threat that may be a theoretical possibility, but for which there is no valid evidence present. Therefore, decision-makers in homeland security must be able to distinguish between scientific and pseudoscientific claims. Security acquires a particular discursive and political force as it becomes concept related to action securitizing (or de-securitizing) something rather to an objective (or subjective) condition. 8 This consensual assumption risks being accused of using epistemology as a normative political force to criticize security
4 234 Cross-disciplinary Perspectives on Homeland and Civil Security governance and the political management security problems. New security studies however entail much more than securitization studies. They as well reach beyond critical analysis of riskification, that is, how risk assessment is politically and socially managed rather than being threat-based, directly addressing causes of harm. 9 Rather, in broad terms, new security studies can be considered holistic: Within a particular research program, they are subjective, objective, and discursive; use different methods; address different levels and units of analysis; as well as use multi-method and multi-level analysis. New security studies are also crossdisciplinary in that perspectives from a variety of disciplines are actively involved. For example, security can be viewed through economics as a perceived threat, like extreme energy-price volatility, global imbalances and currency volatility, infrastructure fragility, and regulatory failures. It can also be viewed in relation to national security and national power. In addition, new security studies have multidisciplinary characteristics because they involve people from different disciplines working on the same security topics to address them comprehensively, each contributing their specific disciplinary knowledge to the common effort. 10 This is particularly relevant in homeland security practice and civil security research, which both are based on an all-hazards approach. Using the study of vulnerability as an example, the following Table 13.1 illustrates a holistic view on this topic by summarizing different relevant disciplinary perspectives and the practical recommendations that follow for vulnerability-reducing measures: Table Vulnerability in Multidisciplinary Perspective. Discipline View(s) of Vulnerability Recommendation(s) Geography Meteorology Engineering Anthropology Vulnerability is determined by the use of hazard-prone areas Vulnerability is due to a lack of advanced warning of severe weather Vulnerability occurs when structures and infrastructure cannot withstand the forces of hazards Vulnerability emanates from constraining values, attitudes, and practices Land-use planning that takes into account hazards to reduce risk Acquisition, creation, and effective use of warning systems Design and construction of buildings and infrastructure that promotes disaster resistance Alter attitudes to discourage risk-taking practices and susceptibility
5 The Scientific Status of New Security Studies 235 Discipline View(s) of Vulnerability Recommendation(s) Economics Sociology Psychology Epidemiology Environmental Science Political Science Public Administration Law Vulnerability is related to poverty and results in an inability to prevent, prepare for, or recover from a disaster Vulnerability is a product of inaccurate assumptions about disaster behavior and is related to race, gender, age, disability, etc. Vulnerability is a function of overlooking or minimizing risk and not being able to cope emotionally with stress and/ or loss Vulnerability is susceptibility to disease or injury and is related to malnutrition and other health factors Vulnerability is proneness to environmental degradation, which may change weather patterns and produce longterm disasters Vulnerability is produced by the political structure and incorrect decision making Vulnerability results from misguided laws, the failure to implement policies effectively, and an inability to enforce regulations Vulnerability results from negligence, which is a failure to act as reason or legal statutes dictate Improve the distribution of wealth and purchase insurance to minimize losses and promote resilience Understand behavioral patterns in disasters and pay attention to needs of special populations Help people to recognize risk and provide crisis counseling to enable resilience Improve provision of public health/emergency medical care before, during, and after disasters Conserve natural resources, protect green space areas, and ensure that debris management is performed in an environmentally conscious manner Alter structure of political system and educate politicians and legislators about disasters Strengthen response and recovery capabilities through preparedness measures, improved policy implementation and increased code enforcement Understand the law, alter statutes, and ensure compliance to widely accepted ethical practices in emergency management
6 236 Cross-disciplinary Perspectives on Homeland and Civil Security Discipline View(s) of Vulnerability Recommendation(s) Journalism Emergency Management Homeland Security Vulnerability is a result of insufficient public awareness about hazards and how to respond to disasters Vulnerability is the lack of capacity to perform important functions before and after disaster strikes (e.g., evacuation, search and rescue, public information, etc.) Vulnerability is due to cultural misunderstandings, permeable borders and fragile infrastructure, and weak disaster management institutions Dispel myths about disasters, foster increased media capabilities, and educate the public about hazards Foster public awareness about disasters and build capacities through hazard and vulnerability analyses, resource acquisition, planning, training, and exercises Correct domestic and foreign policy mistakes, enhance counterterrorism measures, protect borders and infrastructure, and improve WMD capabilities Source: David A. McEntire, The Importance of Multi- and Interdisciplinary Research on Disasters and for Emergency Management, FEMA Emergency Management Institute, last accessed May 3, 2015, 15, Introduction.doc In an ideal stage of evolution, new security studies would be interdisciplinary, integrating knowledge and methods from different disciplines by synthesizing approaches: for instance, integrating political science in homeland security decision-making thought, processes, and institutions (see Chapter 11); or integrating computer sciences and information management in cybersecurity strategy and cyber preparedness. That way, new security studies could become an overarching academic discipline for homeland and civil security research. New Security Studies between Classical and Anti-Classical Epistemology Classical epistemology that is concerned with the pursuit of truth with rationality or epistemic justification cannot serve the security researcher. This approach relates to an individual engaging in cognitive activity to arrive at a true belief and to avoid false belief. However, security studies cannot be described as a branch of an epistemology in its individualistic guise restricted to truth or justification.
7 The Scientific Status of New Security Studies 237 In homeland and civil security research that rests on the vision of providing scientific knowledge to improve the creation of security as a public good and its delivery to the whole community of citizens, social epistemology the study of the social dimensions of knowledge or information is an important framework for security knowledge to be evaluated. New security studies thus belong to the branch of social epistemology that studies the evolution of security knowledge within social contexts and practices, such as securitization. Social epistemology does not have a long history of systematic use. However, Plato, in his dialogue Charmides, can be seen as one who made a brief foray into the social dimensions of knowledge or rational belief. Plato posed the question of how a layperson can determine whether someone who purports to be an expert in an area really is one. The seventeenth and eighteenth century British philosophers John Locke, David Hume, and Thomas Reid used the term testimony, asking, When should cognitive agents rely on the opinions and reports of others? and What must a listener know about a speaker to be entitled to trust his assertions? Locke s intellectual self-reliance doubted giving authority to the opinions of others. Hume took reliance on factual statements of others for granted only when there are adequate reasons for thinking that these sources are reliable. Hume s empiricism was grounded on personal observations that establish the veracity of human testimony. Reid, by contrast, related to our natural attitude of trusting others as reasonable even if little is known about their reliability. 11 These epistemological positions are all practically relevant when describing the communicative profile of security knowledge. Threat detection and threat perception involve intersubjective relationship between experts/authorities/testimony and laypersons/listeners. Threat detectors differ in threat perceptions. Their audience might either doubt their assessment due to their intellectual self-reliance, might reject/accept the empirical observations that support their assessment, or even trust without proof. Security knowledge also seems to fit into a different tradition, which focuses on aspects of knowledge that are social in a sociological or political sense. Karl Marx s theory of ideology could well be considered a type of social epistemology in which ideology is a set of beliefs, a worldview, or a form of consciousness that in some respects is false or delusive. These beliefs and their delusiveness derive from the social situation and interests of the believers. 12 In contrast, many approaches have focused on security as constituting something that needs to be secured: the nation, the state, the homeland, the infrastructure, etc. almost to the extent of necessitating the conclusion that none of those would even exist if they did not need to be secured.
8 238 Cross-disciplinary Perspectives on Homeland and Civil Security The critical theory of the Frankfurt School proclaimed, [c]ritical theory aims at emancipation and enlightenment by making agents aware of hidden coercion in their environment, enabling them to determine where their true interests lie. 13 Jürgen Habermas, one of their exponents, introduced the concept of ideal speech situation, a hypothetical situation of absolutely uncoerced and unlimited discussion between completely free and equal human agents, and described this speech situation as a transcendental criterion of truth. Though this notion of perfect cognitive symmetry is a valid epistemic standard, it cannot be applied to security knowledge, or to the assessment of its scientific quality. While critical thinking is important in all fields of security studies, based on its own set of research methods, 14 the generic properties of security knowledge cannot be reduced to the universal standard posited by critical theory, judging all knowledge on the basis of symmetry of power between speaker and listener. The reason for this is that security is about leadership (see Chapter 9) and involves differences in professional power and expertise reflected in the social epistemology of knowledge. Again, the argument is not that there is no place for critical thinking when it comes to security, but that the absence of the ideal speech situation does not preclude security knowledge being able to be formulated as scientific knowledge. New security studies therefore have an anti-classical, social epistemology that rejects the classical concerns of epistemology with truth, justification, and rationality and seeks to understand a selected community s norms of rationality. It also rejects the notion that this discipline of knowledge has universal or objective norms of rationality, or criteria of truth, that it could appropriately invoke. Security studies are neither context-free nor do they establish norms of rationality without cultural roots and limitations. At the same time, the epistemic effort of new security studies cannot be isolated from disciplines in which rationality is a natural objective norm. For instance, analyzing security threats that stem from environmental disciplines might involve molecular biology, genetics, chemistry, etc., that do evoke rationality as a legitimate objective norm. Another example is the theorizing process in cybersecurity that integrates different technology disciplines to various problematic fields of security. Homeland and civil security research cannot be detached from its transdisciplinary profile, and the question of the scientific status of a research program in security studies, in this case, is the scientific status of a transdisciplinary set of knowledge. A crucial challenge for new security studies as a transdisciplinary research process relates to the complexity of the problems it seeks to understand: the diversity of life; scientific perceptions of problems it takes into account; the link to abstract and case-specific knowledge; and the development of knowledge and
9 The Scientific Status of New Security Studies 239 practices that promote what is perceived to be the common good. 15 In this process, engaging research and collaboration between disciplines are the means of meeting all these requirements. Thus, if the evaluation of scientific status were to be made according to the demarcation between science and pseudo-science, through informal logic and rational argumentation, this challenge could possibly be overcome. Due to the practical implications of the transdisciplinary study of security, the demarcation criterion is important for decision support and we need to distinguish its scientific knowledge from its look-alikes. Because of the high relevance of security in today s societies, the need for demarcation is not only important for the validity of the social epistemology of security research, but also of high practical relevance. However, although the demarcation criterion could be applied to evaluate the scientific status of a research program in security studies on the grounds of practical benefits one may gain, such an approach is opposed to Popper s demarcation based on empirical falsification. According to Popper, a theory or in a broader sense the validity of knowledge in the empirical sciences can never generally be proven, but it can only be falsified on a case-by-case basis, meaning that it can and should be scrutinized using specific experiments. Falsifying a theory that has reached its transformation to practical applications could add to the challenge of evaluating a transdisciplinary research program for homeland and civil security and its underlying assumptions. Therefore, a careful analysis of the status of new security studies through the demarcation criterion is necessary. New security studies cannot be reduced to a single branch of knowledge, due to their comprehensive and transdisciplinary profile, and its proximity to practice and co-evolution with real-world security policies and programs raises the question of its scientific status. This needs clarification. The English word science is primarily used for the natural sciences and other fields of research that are considered similar to them. Hence, political economy and sociology are considered sciences, whereas studies of literature and history are not. The corresponding German word Wissenschaft covers all academic specializations, including the humanities, and has the advantage of more adequately delimiting the type of systematic knowledge that is in dispute in the conflict between science and pseudo-science. New security studies, like the natural sciences, social sciences, and the humanities, are part of the same human endeavor, namely, systematic and critical investigation aimed at acquiring the best possible understanding of the workings of nature, people, and human society. The disciplines that form this community of knowledge are increasingly interdependent. Integrative disciplines such as evolutionary biology, biochemistry,
10 240 Cross-disciplinary Perspectives on Homeland and Civil Security ecology, the neurosciences, and game theory play a role in conceptualizing new security studies today and thus contribute to linking previously unconnected disciplines. 16 These interconnections have brought the sciences and the humanities closer to each other. Evolutionary biology theory, for instance, has been considered as evolutionary thinking in global challenges in the areas of food security, emerging diseases, and resilience. Biochemistry contributes to this challenge, to the industrial manufacture of strategic weapons and even to relevant ethical dilemmas of the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention (BWC) and the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC). Improving the latter cannot be done without biologists, chemists, and researchers from a variety of other disciplines whose work helps assess dual-use implications, including researchers from the humanities. The question remains of what demarcation criteria should be applied to assess the scientific status of new security studies. Should they be evaluated through a research program, an epistemic field, or cognitive discipline (i.e., a group of people with common knowledge aims and practices), a theory, a practice, or a scientific inquiry? The answer is that new security studies cannot be reduced to any one of these levels, as argued in the following. The Scientific Status of New Security Studies under Alternative Demarcation Criteria Although focused on international and strategic security rather than homeland and civil security, the new edition of Barry Buzan s book People, States, and Fear: An Agenda for International Security Studies in the Post-Cold War Era (2009) provides a model for our discipline as well, since it offers constructivist and ethical reflections that no longer reduce security as such to positivist and rationalist epistemologies. 17 New security studies as an overarching academic discipline for the analysis of homeland and civil security in fact follow a constructivist and interpretive epistemology, with new quality criteria for its knowledge, such as being plausible; meeting social needs; underpinning values; helping to build and maintain communities; etc. in addition to the traditional, rational(ist) criteria of validity, reliability, and objectivity. Based on this, the following four demarcation criteria are proposed to determine the scientific status of new security studies: falsificationism; puzzle solving; scientific progress; and multi-criteria approaches. Falsificationism was introduced by Popper, who rejected, as mentioned above, verifiability as a criterion for a theory or hypothesis to be scientific, rather than pseudo-scientific or metaphysical. To be ranked as scientific, a theory should be
11 The Scientific Status of New Security Studies 241 falsifiable and must be capable of conflicting with possible or conceivable observations. However, a theory of security is almost impossible to refute or falsify. New security studies have become a diverse branch of knowledge in which a weak and limited theory can never really be thrown away. Once verified under limited conditions, it will typically become part of the established set of knowledge and assumptions and be followed by researchers. It may even resist logical and practical falsification, as arguably security policy may as well. This also applies to Thomas Kuhn s criterion of puzzle solving. 18 Kuhn divided the process of doing science into normal science and extraordinary science. In normal science, the scientist s activity consists of solving puzzles rather than testing fundamental theories. In puzzle solving, current theory is accepted, and the puzzle is defined in its terms. Kuhn s own demarcation criterion is the capability of puzzle solving, which he sees as an essential characteristic of normal science. However, since Kuhn s view develops into paradigm shifts in which a jettisoned paradigm is atrophied when no longer useful for solving puzzles, it becomes similar to Popper s falsificationism. The only difference is in the volume of the research scope. Popper refers to the scope of a theory, while Kuhn refers to the scope of a paradigm. Since both can be invalid as different demarcation criteria, they cannot be used to demark new security studies as a scientific or pseudo-scientific branch of knowledge. A good example is the development of the different generations of dominant paradigms in security studies, such as the post-behaviorist and constructivist approaches that followed the behaviorist one. Behaviorism is still relevant to new security studies, not as a dominant paradigm but as one adapted alongside other paradigms. In homeland security and emergency management for example, assumptions on response to perceived threat (such as evacuation behavior) as well as models for societal resilience still rest on behaviorist reasoning. The criteria based on scientific progress follow Imre Lakatos, who rejects Popper s demarcation criterion that focuses on the theory level and expands it to become sophisticated (methodological) falsificationism. 19 Instead of applying it to an isolated hypothesis or theory, he refers to this criterion as a whole research program that is characterized by a series of theories successively replacing each other. In his view, new security studies can be considered as a scientific branch if its progress is in new theories that make surprising predictions that are confirmed. In contrast, they would be considered a degenerating research program if characterized by theories being fabricated only in order to accommodate known facts: Progress in science is only possible if a research program satisfies the minimum requirement that each new theory that is developed in the program has a larger
12 242 Cross-disciplinary Perspectives on Homeland and Civil Security empirical content than its predecessor. If a research program does not satisfy this requirement, then it is pseudo-scientific. 20 According to Lakatos demarcation criterion, new security studies in general, and homeland and civil security research in particular, are scientific epistemic fields. They are far from being described as a degenerating research program. Since they possess the requirement of being adequately integrated into other sciences and are incorporated into the existing network of established sciences, they are fully in line with the criteria of a progressive research program. Lakatos s demarcation criterion can be used to identify new security studies, including homeland and civil security research, as a science when combined with the following criteria to rule out pseudo-science or pseudo-scientific practice. According to Mario Bunge, pseudo-science may be diagnosed using the following criteria: 21 Belief in authority: It is contended that some person or persons have a special ability to determine what is true or false. Others have to accept their judgments. Unrepeatable experiments: Reliance is put on experiments [or quasi-experiments and case studies] that cannot be repeated by others with the same outcome. Handpicked examples: Handpicked examples are used although they are not representative of the general category that the investigation refers to. Unwillingness to test: A theory is not tested although it is possible to test it. Disregard of refuting information: Observations or experiments that conflict with a theory are neglected. Built-in subterfuge: The testing of a theory is so arranged that the theory can only be confirmed, never disconfirmed, by the outcome. Explanations are abandoned without replacement: Tenable explanations are given up without being replaced, so that the new theory leaves much more unexplained than the previous one. 22 Our research enterprise mainly is co-evolving with the mission space of the realworld homeland security enterprise, to which it seeks to offer problem solving as well as critical thinking related to policies and strategies aiming at averting harm from societies. It thus can be identified as: a scientific field that progresses through new assumptions and theories that can be confirmed by current reality, but that might not be repeated by others; might be resistant to more thorough testing as long as they seem to work in reality, with practical value; and might neglect
13 The Scientific Status of New Security Studies 243 conflicting observations and stick to theories and assumptions that can only be confirmed, but not refuted (or falsified). While the grant-driven and end-user needs-based evolution of security research may be seen to add to these risks of making new security studies a pseudo-science, the strong focus of security research on tangible results and consortia that are multidisciplinary by design and involve industrial research and development (see Chapter 12) certainly adds to the scientific status of the field. While on a good way, we as a community of scholars need to maintain the momentum in our effort to avail homeland and civil security research a valid epistemic identity within a field of new security studies that is consolidating its scientific status. At the same time, we need to bear in mind that while there is a set of features that are characteristic of science, every part of science will have some of these features, but not any part of science can be expected to have them all. 23 Conclusion The contributions to this volume have demonstrated how cross-disciplinary perspectives including practical accounts of single cases and threat environments, as well as comparative studies of homeland security policies can collude to foster the common goal of advancing a common epistemic field and share practices of scientific inquiry (see Part I of this book, Chapters 1 4). This chapter has discussed how the scientific status of the evolving field can be evaluated according to several demarcation criteria as they derive from major results of the study of science. The recent emphasis of transversal aspects of the field and of critical thinking (see Part III of this book, Chapters 9 10), including a critical perspective on the inquiries own limitations and risks (e.g., ethical issues as addressed in Chapter 10), roots homeland and civil security research still stronger within the overarching discipline of new security studies. To further forge its epistemic identity supported by forward-looking programming (as addressed in Part IV of this book, Chapters 11 12), and maintain its scientific status and its utility (i.e., to remain practically relevant), homeland and civil security research will need to maintain multi- and cross-disciplinary approaches (as exemplified in Part II of this book, Chapters 5 8) to vulnerability assessment, to resilience enhancement, and to many other objectives, both scientific and practical. It will also need to remain open to reviewing the epistemology of the homeland and civil security field of research as well as that of the evolving real-world mission space, such as
14 244 Cross-disciplinary Perspectives on Homeland and Civil Security the main assumptions about the threats that constitute the homeland security enterprise and the civil security model. Notes This chapter has been supported by the Haifa Center for German and European Studies, University of Haifa. 1. J. Peter Burgess, ed., The Routledge Handbook of New Security Studies (Milton Park: Routledge, 2010). 2. Ibid., own examples added. 3. Constructivism and the Copenhagen School s theory of securitization are particularly relevant here. A seminal source is Thierry Balzacq et al., Forum: What Kind of Theory If Any Is Securitization? International Relations, first published on October 21, 2014 as doi: / , early/2014/10/27/ full.pdf+html; see also Thierry Balzacq, ed., Securitization Theory: How Security Problems Emerge and Dissolve (London and New York: Routledge, 2011). 4. Andrew W. Neal, Securitizing and Risk at the EU Border: The Origins of FRONTEX, Journal of Common Market Studies 47 (2009). 5. See Mike Bourne, Understanding Security (Houndmills, Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, 2014), chapter 3: Critical Approaches and New Frameworks, Barry Buzan, People, States & Fear: The National Security Problem in International Relations (Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 1983); Barry Buzan and Lene Hansen, The Evolution of International Security (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2009); Balzacq, Securitization Theory; Balzacq et al., Forum: What Kind of Theory if Any Is Securitization? 7. Karl Popper, The Open Society and Its Enemies (London: Routledge, 1945). 8. Balzacq, Securitization Theory. 9. Olaf Corry, Securitisation and Riskification : Second Order Security and the Politics of Climate Change, Millennium: Journal of International Studies 40 (2011). 10. David A. McEntire: The Importance of Multi- and Interdisciplinary Research on Disasters and for Emergency Management, in Disciplines, Disasters and Emergency Management: The Convergence and Divergence of Concepts, Issues and Trends from the Research Literature, ed. David A. McEntire (Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas, 2007), 6 [also available in an e-book version: Emmitsburg, MD: FEMA Emergency Management Institute, book]
15 The Scientific Status of New Security Studies Alvin Goldman, Social Epistemology, in Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, ed. Edward N. Zalta, last published August 18, 2006, chapter 1, edu/entries/epistemology-social 12. Ibid. 13. Ibid. 14. See Mark B. Salter and Can E. Mutlu, eds., Research Methods in Critical Security Studies: An Introduction (New York and London: Routledge, 2013); Laura J. Shepherd, ed., Critical Approaches to Security: An Introduction to Theories and Methods (New York and London: Routledge, 2013). 15. Gabriela Wuelser, Christian Pohl, and Gabriela Hirsch Hadorn, Structuring Complexity for Tailoring Research Contributions to Sustainable Development: A Framework, Sustainability Science 7 (2011). 16. See CEUSS Center for European Security Studies, Sigmund Freud University Vienna, Roadmap Proposal for the Development of a Trans-disciplinary Security Research Paradigm, deliverable 8.3, EU security research project FOCUS (Foresight Security Scenarios Mapping Research to a Comprehensive Approach to Exogenous EU Roles), March 2013, 63ec147d-c599-4d61-b2c7-be3d4590d3ea 17. Barry Buzan, People, States & Fear: The National Security Problem in International Relations (Boulder, CO: Rienner, 2009). 18. See Thomas Kuhn, The Structure of Scientific Revolutions (Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 1962). 19. See Imre Lakatos and Alan Musgrave, eds., Criticism and the Growth of Knowledge (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1965). 20. Sven Ove Hansson, Science and Pseudo-Science, in Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, ed. Edward N. Zalta, last published February 10, 2014, chapter 4.4, stanford.edu/entries/pseudo-science, Mario Bunge, Diagnosing Pseudoscience, in Philosophy in Crisis. The Need for Reconstruction, by Mario Bunge (Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books, 2001). 22. Hansson, Science and Pseudo-Science, chapter Cf. ibid.
FACULTY SENATE ACTION TRANSMITTAL FORM TO THE CHANCELLOR
 - DATE: TO: CHANCELLOR'S OFFICE FACULTY SENATE ACTION TRANSMITTAL FORM TO THE CHANCELLOR JUN 03 2011 June 3, 2011 Chancellor Sorensen FROM: Ned Weckmueller, Faculty Senate Chair UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN
- DATE: TO: CHANCELLOR'S OFFICE FACULTY SENATE ACTION TRANSMITTAL FORM TO THE CHANCELLOR JUN 03 2011 June 3, 2011 Chancellor Sorensen FROM: Ned Weckmueller, Faculty Senate Chair UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN
Belgian Position Paper
 The "INTERNATIONAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION and the "FEDERAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION of the Interministerial Conference of Science Policy of Belgium Belgian Position Paper Belgian position and recommendations
The "INTERNATIONAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION and the "FEDERAL CO-OPERATION" COMMISSION of the Interministerial Conference of Science Policy of Belgium Belgian Position Paper Belgian position and recommendations
Foresight Security Scenarios for Prepared Response to the Unplanned: Results from an EU Security Research Project and its Transatlantic Dimension
 Foresight Security Scenarios for Prepared Response to the Unplanned: Results from an EU Security Research Project and its Transatlantic Dimension National Homeland Security Conference 2014, Philadelphia,
Foresight Security Scenarios for Prepared Response to the Unplanned: Results from an EU Security Research Project and its Transatlantic Dimension National Homeland Security Conference 2014, Philadelphia,
Concept of Periodic Synthesis Report
 Concept of Periodic Synthesis Report There is no lack of scientific knowledge, but it is fragmented and not easily accessible to policy makers and practitioners. The Sendai Science and Technology Roadmap
Concept of Periodic Synthesis Report There is no lack of scientific knowledge, but it is fragmented and not easily accessible to policy makers and practitioners. The Sendai Science and Technology Roadmap
Course Unit Outline 2017/18
 Title: Course Unit Outline 2017/18 Knowledge Production and Justification in Business and Management Studies (Epistemology) BMAN 80031 Credit Rating: 15 Level: (UG 1/2/3 or PG) PG Delivery: (semester 1,
Title: Course Unit Outline 2017/18 Knowledge Production and Justification in Business and Management Studies (Epistemology) BMAN 80031 Credit Rating: 15 Level: (UG 1/2/3 or PG) PG Delivery: (semester 1,
CONTEMPORARY THEORY AND ANALYSIS OF SECURITY (JPM569)
 CONTEMPORARY THEORY AND ANALYSIS OF SECURITY (JPM569) Course description WS 2014/2015 (4 ECTS) Thursday 12:30-14:00 (J4020) Lecturers: Dagmar Rychnovská (rychnovska@fsv.cuni.cz), Jakub Záhora (zahora.jakub@gmail.com)
CONTEMPORARY THEORY AND ANALYSIS OF SECURITY (JPM569) Course description WS 2014/2015 (4 ECTS) Thursday 12:30-14:00 (J4020) Lecturers: Dagmar Rychnovská (rychnovska@fsv.cuni.cz), Jakub Záhora (zahora.jakub@gmail.com)
Learning Goals and Related Course Outcomes Applied To 14 Core Requirements
 Learning Goals and Related Course Outcomes Applied To 14 Core Requirements Fundamentals (Normally to be taken during the first year of college study) 1. Towson Seminar (3 credit hours) Applicable Learning
Learning Goals and Related Course Outcomes Applied To 14 Core Requirements Fundamentals (Normally to be taken during the first year of college study) 1. Towson Seminar (3 credit hours) Applicable Learning
Edgewood College General Education Curriculum Goals
 (Approved by Faculty Association February 5, 008; Amended by Faculty Association on April 7, Sept. 1, Oct. 6, 009) COR In the Dominican tradition, relationship is at the heart of study, reflection, and
(Approved by Faculty Association February 5, 008; Amended by Faculty Association on April 7, Sept. 1, Oct. 6, 009) COR In the Dominican tradition, relationship is at the heart of study, reflection, and
Written response to the public consultation on the European Commission Green Paper: From
 EABIS THE ACADEMY OF BUSINESS IN SOCIETY POSITION PAPER: THE EUROPEAN UNION S COMMON STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR FUTURE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION FUNDING Written response to the public consultation on the European
EABIS THE ACADEMY OF BUSINESS IN SOCIETY POSITION PAPER: THE EUROPEAN UNION S COMMON STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR FUTURE RESEARCH AND INNOVATION FUNDING Written response to the public consultation on the European
Principles of Sociology
 Principles of Sociology DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS ATHENS UNIVERSITY OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS [Academic year 2017/18, FALL SEMESTER] Lecturer: Dimitris Lallas Contact information: lallasd@aueb.gr lallasdimitris@gmail.com
Principles of Sociology DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS ATHENS UNIVERSITY OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS [Academic year 2017/18, FALL SEMESTER] Lecturer: Dimitris Lallas Contact information: lallasd@aueb.gr lallasdimitris@gmail.com
CRITERIA FOR AREAS OF GENERAL EDUCATION. The areas of general education for the degree Associate in Arts are:
 CRITERIA FOR AREAS OF GENERAL EDUCATION The areas of general education for the degree Associate in Arts are: Language and Rationality English Composition Writing and Critical Thinking Communications and
CRITERIA FOR AREAS OF GENERAL EDUCATION The areas of general education for the degree Associate in Arts are: Language and Rationality English Composition Writing and Critical Thinking Communications and
Interoperable systems that are trusted and secure
 Government managers have critical needs for models and tools to shape, manage, and evaluate 21st century services. These needs present research opportunties for both information and social scientists,
Government managers have critical needs for models and tools to shape, manage, and evaluate 21st century services. These needs present research opportunties for both information and social scientists,
Common Core Structure Final Recommendation to the Chancellor City University of New York Pathways Task Force December 1, 2011
 Common Core Structure Final Recommendation to the Chancellor City University of New York Pathways Task Force December 1, 2011 Preamble General education at the City University of New York (CUNY) should
Common Core Structure Final Recommendation to the Chancellor City University of New York Pathways Task Force December 1, 2011 Preamble General education at the City University of New York (CUNY) should
Counterfeit, Falsified and Substandard Medicines
 Meeting Summary Counterfeit, Falsified and Substandard Medicines Charles Clift Senior Research Consultant, Centre on Global Health Security December 2010 The views expressed in this document are the sole
Meeting Summary Counterfeit, Falsified and Substandard Medicines Charles Clift Senior Research Consultant, Centre on Global Health Security December 2010 The views expressed in this document are the sole
Sustainability-Related Learning Outcomes Department/ Program
 College -Related Learning Outcomes Department/ Program City and Metropolitan City and Metropolitan, Culture, Culture, Culture Learning Objective Related to Degree(s) PROGRAM PURPOSE: The undergraduate
College -Related Learning Outcomes Department/ Program City and Metropolitan City and Metropolitan, Culture, Culture, Culture Learning Objective Related to Degree(s) PROGRAM PURPOSE: The undergraduate
Revised East Carolina University General Education Program
 Faculty Senate Resolution #17-45 Approved by the Faculty Senate: April 18, 2017 Approved by the Chancellor: May 22, 2017 Revised East Carolina University General Education Program Replace the current policy,
Faculty Senate Resolution #17-45 Approved by the Faculty Senate: April 18, 2017 Approved by the Chancellor: May 22, 2017 Revised East Carolina University General Education Program Replace the current policy,
Aesthetics Change Communication Communities. Connections Creativity Culture Development. Form Global interactions Identity Logic
 MYP Key Concepts The MYP identifies 16 key concepts to be explored across the curriculum. These key concepts, shown in the table below represent understandings that reach beyond the eighth MYP subject
MYP Key Concepts The MYP identifies 16 key concepts to be explored across the curriculum. These key concepts, shown in the table below represent understandings that reach beyond the eighth MYP subject
Information Sociology
 Information Sociology Educational Objectives: 1. To nurture qualified experts in the information society; 2. To widen a sociological global perspective;. To foster community leaders based on Christianity.
Information Sociology Educational Objectives: 1. To nurture qualified experts in the information society; 2. To widen a sociological global perspective;. To foster community leaders based on Christianity.
ADDENDUM 1. Changes Related to the Bachelor of Science in Intelligence Degree:
 ADDENDUM 1 CE UNIVERSITY 2017 2018 CATALOG ADDENDUM 1 National Intelligence University (NIU) produced this Catalog Addendum to supplement the NIU Catalog and Defense Intelligence Agency publications. You
ADDENDUM 1 CE UNIVERSITY 2017 2018 CATALOG ADDENDUM 1 National Intelligence University (NIU) produced this Catalog Addendum to supplement the NIU Catalog and Defense Intelligence Agency publications. You
Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science
 United States Geological Survey. 2002. "Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science." Unpublished paper, 4 April. Posted to the Science, Environment, and Development Group web site, 19 March 2004
United States Geological Survey. 2002. "Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science." Unpublished paper, 4 April. Posted to the Science, Environment, and Development Group web site, 19 March 2004
1 Name of Course Module: History and Philosophy of Science-2. 2 Course Code: 3 Name(s) of academic staff: Prof. C. K. Raju
 1 Name of Course Module: History and Philosophy of Science-2 2 Course Code: 3 Name(s) of academic staff: Prof. C. K. Raju 4 Rationale for the inclusion of the course/module in the programme: 1. Part 1
1 Name of Course Module: History and Philosophy of Science-2 2 Course Code: 3 Name(s) of academic staff: Prof. C. K. Raju 4 Rationale for the inclusion of the course/module in the programme: 1. Part 1
Academic Vocabulary Test 1:
 Academic Vocabulary Test 1: How Well Do You Know the 1st Half of the AWL? Take this academic vocabulary test to see how well you have learned the vocabulary from the Academic Word List that has been practiced
Academic Vocabulary Test 1: How Well Do You Know the 1st Half of the AWL? Take this academic vocabulary test to see how well you have learned the vocabulary from the Academic Word List that has been practiced
Descriptions of cross-curricular topics
 Appendix 14 of Regulation No 2 of the Government of the Republic of 6 January 2011 National Curriculum for Upper Secondary Schools Last amendment 29 August 2014 Descriptions of cross-curricular topics
Appendix 14 of Regulation No 2 of the Government of the Republic of 6 January 2011 National Curriculum for Upper Secondary Schools Last amendment 29 August 2014 Descriptions of cross-curricular topics
GUIDE TO SPEAKING POINTS:
 GUIDE TO SPEAKING POINTS: The following presentation includes a set of speaking points that directly follow the text in the slide. The deck and speaking points can be used in two ways. As a learning tool
GUIDE TO SPEAKING POINTS: The following presentation includes a set of speaking points that directly follow the text in the slide. The deck and speaking points can be used in two ways. As a learning tool
Grades 5 to 8 Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy
 Grades 5 to 8 Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy 5 8 Science Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy The Five Foundations To develop scientifically
Grades 5 to 8 Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy 5 8 Science Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy The Five Foundations To develop scientifically
S&T roadmap and implementation strategy: Perspective from the DRR process
 S&T roadmap and implementation strategy: Perspective from the DRR process Brussels, 29 th November 2018 Annisa Triyanti Young scientists representative, UNISDR Science and Technology Advisory Group (STAG)
S&T roadmap and implementation strategy: Perspective from the DRR process Brussels, 29 th November 2018 Annisa Triyanti Young scientists representative, UNISDR Science and Technology Advisory Group (STAG)
Correlation Guide. Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text
 Presented by the Center for Civic Education, The National Conference of State Legislatures, and The State Bar of Wisconsin Correlation Guide For Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text Jack
Presented by the Center for Civic Education, The National Conference of State Legislatures, and The State Bar of Wisconsin Correlation Guide For Wisconsin s Model Academic Standards Level II Text Jack
Report on Emerging and Interdisciplinary Research Fields. - Solving Social Issues and Expanding the Frontiers of Science and Technology -
 Report on Emerging and Interdisciplinary - Solving Social Issues and Expanding the Frontiers of Science and Technology - February 2009 Report on Emerging and Interdisciplinary i EXECUTIVE SUMMARY It is
Report on Emerging and Interdisciplinary - Solving Social Issues and Expanding the Frontiers of Science and Technology - February 2009 Report on Emerging and Interdisciplinary i EXECUTIVE SUMMARY It is
Tuning-CALOHEE Assessment Frameworks for the Subject Area of CIVIL ENGINEERING The Tuning-CALOHEE Assessment Frameworks for Civil Engineering offers
 Tuning-CALOHEE Assessment Frameworks for the Subject Area of CIVIL ENGINEERING The Tuning-CALOHEE Assessment Frameworks for Civil Engineering offers an important and novel tool for understanding, defining
Tuning-CALOHEE Assessment Frameworks for the Subject Area of CIVIL ENGINEERING The Tuning-CALOHEE Assessment Frameworks for Civil Engineering offers an important and novel tool for understanding, defining
Introduction to Foresight
 Introduction to Foresight Prepared for the project INNOVATIVE FORESIGHT PLANNING FOR BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT INTERREG IVb North Sea Programme By NIBR - Norwegian Institute for Urban and Regional Research
Introduction to Foresight Prepared for the project INNOVATIVE FORESIGHT PLANNING FOR BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT INTERREG IVb North Sea Programme By NIBR - Norwegian Institute for Urban and Regional Research
Refining foresight approaches to crisis, inertia and transition
 Refining foresight approaches to crisis, inertia and transition 25-27 April 2017 Aalto University, Espoo, Finland Jennifer Cassingena Harper, Malta Council for Science and Technology This presentation
Refining foresight approaches to crisis, inertia and transition 25-27 April 2017 Aalto University, Espoo, Finland Jennifer Cassingena Harper, Malta Council for Science and Technology This presentation
Towards a Magna Carta for Data
 Towards a Magna Carta for Data Expert Opinion Piece: Engineering and Computer Science Committee February 2017 Expert Opinion Piece: Engineering and Computer Science Committee Context Big Data is a frontier
Towards a Magna Carta for Data Expert Opinion Piece: Engineering and Computer Science Committee February 2017 Expert Opinion Piece: Engineering and Computer Science Committee Context Big Data is a frontier
Scenario Development Process
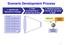 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Correlations to NATIONAL SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS
 Correlations to NATIONAL SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS This chart indicates which of the activities in this guide teach or reinforce the National Council for the Social Studies standards for middle grades and
Correlations to NATIONAL SOCIAL STUDIES STANDARDS This chart indicates which of the activities in this guide teach or reinforce the National Council for the Social Studies standards for middle grades and
Role of Knowledge Economics as a Driving Force in Global World
 American International Journal of Research in Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-3734, ISSN (Online): 2328-3696, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3688 AIJRHASS
American International Journal of Research in Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences Available online at http://www.iasir.net ISSN (Print): 2328-3734, ISSN (Online): 2328-3696, ISSN (CD-ROM): 2328-3688 AIJRHASS
Colombia s Social Innovation Policy 1 July 15 th -2014
 Colombia s Social Innovation Policy 1 July 15 th -2014 I. Introduction: The background of Social Innovation Policy Traditionally innovation policy has been understood within a framework of defining tools
Colombia s Social Innovation Policy 1 July 15 th -2014 I. Introduction: The background of Social Innovation Policy Traditionally innovation policy has been understood within a framework of defining tools
Inter and Transdisciplinarity in Social Sciences. Approaches and lessons learned
 Inter and Transdisciplinarity in Social Sciences Approaches and lessons learned Symposium on Sustainability Science, 19 December 2016 Overview 1. The ISSC: short intro 2. ID and TD research 3. ISSC s initiatives:
Inter and Transdisciplinarity in Social Sciences Approaches and lessons learned Symposium on Sustainability Science, 19 December 2016 Overview 1. The ISSC: short intro 2. ID and TD research 3. ISSC s initiatives:
Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May
 Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May 9-11 2016 David Ludlow University of the West of England, Bristol Workshop Aims Key question addressed - how do we advance towards a smart
Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May 9-11 2016 David Ludlow University of the West of England, Bristol Workshop Aims Key question addressed - how do we advance towards a smart
MANITOBA FOUNDATIONS FOR SCIENTIFIC LITERACY
 Senior 1 Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy MANITOBA FOUNDATIONS FOR SCIENTIFIC LITERACY The Five Foundations To develop scientifically literate students, Manitoba science curricula are built
Senior 1 Manitoba Foundations for Scientific Literacy MANITOBA FOUNDATIONS FOR SCIENTIFIC LITERACY The Five Foundations To develop scientifically literate students, Manitoba science curricula are built
Smart Management for Smart Cities. How to induce strategy building and implementation
 Smart Management for Smart Cities How to induce strategy building and implementation Why a smart city strategy? Today cities evolve faster than ever before and allthough each city has a unique setting,
Smart Management for Smart Cities How to induce strategy building and implementation Why a smart city strategy? Today cities evolve faster than ever before and allthough each city has a unique setting,
European Commission. 6 th Framework Programme Anticipating scientific and technological needs NEST. New and Emerging Science and Technology
 European Commission 6 th Framework Programme Anticipating scientific and technological needs NEST New and Emerging Science and Technology REFERENCE DOCUMENT ON Synthetic Biology 2004/5-NEST-PATHFINDER
European Commission 6 th Framework Programme Anticipating scientific and technological needs NEST New and Emerging Science and Technology REFERENCE DOCUMENT ON Synthetic Biology 2004/5-NEST-PATHFINDER
Lumeng Jia. Northeastern University
 Philosophy Study, August 2017, Vol. 7, No. 8, 430-436 doi: 10.17265/2159-5313/2017.08.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Techno-ethics Embedment: A New Trend in Technology Assessment Lumeng Jia Northeastern University
Philosophy Study, August 2017, Vol. 7, No. 8, 430-436 doi: 10.17265/2159-5313/2017.08.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING Techno-ethics Embedment: A New Trend in Technology Assessment Lumeng Jia Northeastern University
Preface: A Study in Science, Technology, and Society (STS)
 Preface: A Study in Science, Technology, and Society (STS) Aims and Major Themes I have written this book to help you to systematically explore Ambient Intelligence (AmI) and the Internet of Things (IoT)
Preface: A Study in Science, Technology, and Society (STS) Aims and Major Themes I have written this book to help you to systematically explore Ambient Intelligence (AmI) and the Internet of Things (IoT)
High School Social Studies Grades 9 12
 Standard 1: Time, Continuity and Change Learners understand patterns of change and continuity, relationships between people and events through time, and various interpretations of these relationships.
Standard 1: Time, Continuity and Change Learners understand patterns of change and continuity, relationships between people and events through time, and various interpretations of these relationships.
Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History
 Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History 1. Identification Name of programme Scope of programme Level Programme code Master Programme in Economic History 60/120 ECTS Master level Decision
Programme Curriculum for Master Programme in Economic History 1. Identification Name of programme Scope of programme Level Programme code Master Programme in Economic History 60/120 ECTS Master level Decision
Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical Thinking Skills
 AP World History 2015-2016 Nacogdoches High School Nacogdoches Independent School District Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical
AP World History 2015-2016 Nacogdoches High School Nacogdoches Independent School District Goals of the AP World History Course Historical Periodization Course Themes Course Schedule (Periods) Historical
Global learning outcomes Philosophy
 Global learning outcomes Philosophy Global Engagement Students will gain an appreciation of the interconnectedness and interdependence of the human experience on a global scale. This includes, for example,
Global learning outcomes Philosophy Global Engagement Students will gain an appreciation of the interconnectedness and interdependence of the human experience on a global scale. This includes, for example,
Effective Societal engagement in Horizon 2020
 Effective Societal engagement in Horizon 2020 A Contribution to the EC Workshop 'Fostering innovative dialogue between researchers and stakeholders to meet future challenges' Land, Soil, Desertification,
Effective Societal engagement in Horizon 2020 A Contribution to the EC Workshop 'Fostering innovative dialogue between researchers and stakeholders to meet future challenges' Land, Soil, Desertification,
A Research and Innovation Agenda for a global Europe: Priorities and Opportunities for the 9 th Framework Programme
 A Research and Innovation Agenda for a global Europe: Priorities and Opportunities for the 9 th Framework Programme A Position Paper by the Young European Research Universities Network About YERUN The
A Research and Innovation Agenda for a global Europe: Priorities and Opportunities for the 9 th Framework Programme A Position Paper by the Young European Research Universities Network About YERUN The
SOCIAL STUDIES 10-1: Perspectives on Globalization
 SOCIAL STUDIES 10-1: Perspectives on Globalization Overview Students will explore multiple perspectives on the origins of globalization and the local, national and international impacts of globalization
SOCIAL STUDIES 10-1: Perspectives on Globalization Overview Students will explore multiple perspectives on the origins of globalization and the local, national and international impacts of globalization
ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF SUSTAINABLE ENGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT. Summary of Allenby s ESEM Principles.
 ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF SUSTAINABLE ENGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT Summary of Allenby s ESEM Principles Tom Roberts SSEBE-CESEM-2013-WPS-002 Working Paper Series May 20, 2011 Summary
ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF SUSTAINABLE ENGINEERING AND THE BUILT ENVIRONMENT Summary of Allenby s ESEM Principles Tom Roberts SSEBE-CESEM-2013-WPS-002 Working Paper Series May 20, 2011 Summary
TECHNOLOGY, ARTS AND MEDIA (TAM) CERTIFICATE PROPOSAL. November 6, 1999
 TECHNOLOGY, ARTS AND MEDIA (TAM) CERTIFICATE PROPOSAL November 6, 1999 ABSTRACT A new age of networked information and communication is bringing together three elements -- the content of business, media,
TECHNOLOGY, ARTS AND MEDIA (TAM) CERTIFICATE PROPOSAL November 6, 1999 ABSTRACT A new age of networked information and communication is bringing together three elements -- the content of business, media,
GUIDELINES SOCIAL SCIENCES AND HUMANITIES RESEARCH MATTERS. ON HOW TO SUCCESSFULLY DESIGN, AND IMPLEMENT, MISSION-ORIENTED RESEARCH PROGRAMMES
 SOCIAL SCIENCES AND HUMANITIES RESEARCH MATTERS. GUIDELINES ON HOW TO SUCCESSFULLY DESIGN, AND IMPLEMENT, MISSION-ORIENTED RESEARCH PROGRAMMES to impact from SSH research 2 INSOCIAL SCIENCES AND HUMANITIES
SOCIAL SCIENCES AND HUMANITIES RESEARCH MATTERS. GUIDELINES ON HOW TO SUCCESSFULLY DESIGN, AND IMPLEMENT, MISSION-ORIENTED RESEARCH PROGRAMMES to impact from SSH research 2 INSOCIAL SCIENCES AND HUMANITIES
Two Perspectives on Logic
 LOGIC IN PLAY Two Perspectives on Logic World description: tracing the structure of reality. Structured social activity: conversation, argumentation,...!!! Compatible and Interacting Views Process Product
LOGIC IN PLAY Two Perspectives on Logic World description: tracing the structure of reality. Structured social activity: conversation, argumentation,...!!! Compatible and Interacting Views Process Product
Table of Contents. Two Cultures of Ecology...0 RESPONSES TO THIS ARTICLE...3
 Table of Contents Two Cultures of Ecology...0 RESPONSES TO THIS ARTICLE...3 Two Cultures of Ecology C.S. (Buzz) Holling University of Florida This editorial was written two years ago and appeared on the
Table of Contents Two Cultures of Ecology...0 RESPONSES TO THIS ARTICLE...3 Two Cultures of Ecology C.S. (Buzz) Holling University of Florida This editorial was written two years ago and appeared on the
OXNARD COLLEGE ACADEMIC SENATE
 OXNARD COLLEGE ACADEMIC SENATE Our College Mission Oxnard College is a learning-centered institution that embraces academic excellence by providing multiple pathways to student success. MEETING AGENDA
OXNARD COLLEGE ACADEMIC SENATE Our College Mission Oxnard College is a learning-centered institution that embraces academic excellence by providing multiple pathways to student success. MEETING AGENDA
Introduction to the Special Section. Character and Citizenship: Towards an Emerging Strong Program? Andrea M. Maccarini *
 . Character and Citizenship: Towards an Emerging Strong Program? Andrea M. Maccarini * Author information * Department of Political Science, Law and International Studies, University of Padova, Italy.
. Character and Citizenship: Towards an Emerging Strong Program? Andrea M. Maccarini * Author information * Department of Political Science, Law and International Studies, University of Padova, Italy.
6/14/2017. Engineering Future Cities The Value of Extreme Scenario Methodologies
 Engineering Future Cities The Value of Extreme Scenario Methodologies Resilience Through Innovation Critical Local Transport and Utility Infrastructure Professor Chris Rogers University of Birmingham 12
Engineering Future Cities The Value of Extreme Scenario Methodologies Resilience Through Innovation Critical Local Transport and Utility Infrastructure Professor Chris Rogers University of Birmingham 12
Program Level Learning Outcomes for the Department of International Studies Page 1
 Page 1 INTERNATIONAL STUDIES Honours Major, International Relations By the end of the Honours International Relations program, a successful student will be able to: I. Depth and Breadth of Knowledge A.
Page 1 INTERNATIONAL STUDIES Honours Major, International Relations By the end of the Honours International Relations program, a successful student will be able to: I. Depth and Breadth of Knowledge A.
Draft Recommendation concerning the Protection and Promotion of Museums, their Diversity and their Role in Society
 1 Draft Recommendation concerning the Protection and Promotion of Museums, their Diversity and their Role in Society Preamble The General Conference, Considering that museums share some of the fundamental
1 Draft Recommendation concerning the Protection and Promotion of Museums, their Diversity and their Role in Society Preamble The General Conference, Considering that museums share some of the fundamental
Design as a phronetic approach to policy making
 Design as a phronetic approach to policy making This position paper is an expansion on a talk given at the Faultlines Design Research Conference in June 2015. Dr. Simon O Rafferty Design Factors Research
Design as a phronetic approach to policy making This position paper is an expansion on a talk given at the Faultlines Design Research Conference in June 2015. Dr. Simon O Rafferty Design Factors Research
CHAPTER 8 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND DESIGN
 CHAPTER 8 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND DESIGN 8.1 Introduction This chapter gives a brief overview of the field of research methodology. It contains a review of a variety of research perspectives and approaches
CHAPTER 8 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND DESIGN 8.1 Introduction This chapter gives a brief overview of the field of research methodology. It contains a review of a variety of research perspectives and approaches
The Research Project Portfolio of the Humanistic Management Center
 The Research Project Portfolio of the Humanistic Our Pipeline of Research Projects Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Myths and Misunderstandings in the CR Debate Humanistic Case Studies The Makings of Humanistic Corporate
The Research Project Portfolio of the Humanistic Our Pipeline of Research Projects Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Myths and Misunderstandings in the CR Debate Humanistic Case Studies The Makings of Humanistic Corporate
SOCIAL CHALLENGES IN TECHNICAL DECISION-MAKING: LESSONS FROM SOCIAL CONTROVERSIES CONCERNING GM CROPS. Tomiko Yamaguchi
 SOCIAL CHALLENGES IN TECHNICAL DECISION-MAKING: LESSONS FROM SOCIAL CONTROVERSIES CONCERNING GM CROPS Tomiko Yamaguchi International Christian University 3-10-2 Osawa, Mitaka-shi, Tokyo 181-8585 JAPAN
SOCIAL CHALLENGES IN TECHNICAL DECISION-MAKING: LESSONS FROM SOCIAL CONTROVERSIES CONCERNING GM CROPS Tomiko Yamaguchi International Christian University 3-10-2 Osawa, Mitaka-shi, Tokyo 181-8585 JAPAN
STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK Updated August 2017
 STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK Updated August 2017 STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK The UC Davis Library is the academic hub of the University of California, Davis, and is ranked among the top academic research libraries in North
STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK Updated August 2017 STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK The UC Davis Library is the academic hub of the University of California, Davis, and is ranked among the top academic research libraries in North
UNIVERSIDAD ANAHUAC UNIVERSITY AUTHORIZED NAME INTERNATIONAL DOCTORATE OF TOURISM LEVEL AND NAME OF THE CURRICULAR PLAN
 UNIVERSIDAD ANAHUAC UNIVERSITY AUTHORIZED NAME INTERNATIONAL DOCTORATE OF TOURISM LEVEL AND NAME OF THE CURRICULAR PLAN VALIDITY Master s Degree in any area of knowledge, preferably in tourism, entertainment
UNIVERSIDAD ANAHUAC UNIVERSITY AUTHORIZED NAME INTERNATIONAL DOCTORATE OF TOURISM LEVEL AND NAME OF THE CURRICULAR PLAN VALIDITY Master s Degree in any area of knowledge, preferably in tourism, entertainment
17.181/ SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy
 17.181/17.182 SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy Department of Political Science Fall 2016 Professor N. Choucri 1 ` 17.181/17.182 Week 1 Introduction-Leftover Item 1. INTRODUCTION Background Early
17.181/17.182 SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy Department of Political Science Fall 2016 Professor N. Choucri 1 ` 17.181/17.182 Week 1 Introduction-Leftover Item 1. INTRODUCTION Background Early
Social Innovation and new pathways to social changefirst insights from the global mapping
 Social Innovation and new pathways to social changefirst insights from the global mapping Social Innovation2015: Pathways to Social change Vienna, November 18-19, 2015 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Howaldt/Antonius
Social Innovation and new pathways to social changefirst insights from the global mapping Social Innovation2015: Pathways to Social change Vienna, November 18-19, 2015 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Howaldt/Antonius
University of Massachusetts Amherst Libraries. Digital Preservation Policy, Version 1.3
 University of Massachusetts Amherst Libraries Digital Preservation Policy, Version 1.3 Purpose: The University of Massachusetts Amherst Libraries Digital Preservation Policy establishes a framework to
University of Massachusetts Amherst Libraries Digital Preservation Policy, Version 1.3 Purpose: The University of Massachusetts Amherst Libraries Digital Preservation Policy establishes a framework to
HOMELAND SECURITY & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT (HSEM)
 Homeland Security & Emergency Management (HSEM) 1 HOMELAND SECURITY & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT (HSEM) HSEM 501 CRITICAL ISSUES IN This course reintroduces the homeland security professional to the wicked problems
Homeland Security & Emergency Management (HSEM) 1 HOMELAND SECURITY & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT (HSEM) HSEM 501 CRITICAL ISSUES IN This course reintroduces the homeland security professional to the wicked problems
POSITION PAPER. GREEN PAPER From Challenges to Opportunities: Towards a Common Strategic Framework for EU Research and Innovation funding
 POSITION PAPER GREEN PAPER From Challenges to Opportunities: Towards a Common Strategic Framework for EU Research and Innovation funding Preamble CNR- National Research Council of Italy shares the vision
POSITION PAPER GREEN PAPER From Challenges to Opportunities: Towards a Common Strategic Framework for EU Research and Innovation funding Preamble CNR- National Research Council of Italy shares the vision
Impediments to designing and developing for accessibility, accommodation and high quality interaction
 Impediments to designing and developing for accessibility, accommodation and high quality interaction D. Akoumianakis and C. Stephanidis Institute of Computer Science Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas
Impediments to designing and developing for accessibility, accommodation and high quality interaction D. Akoumianakis and C. Stephanidis Institute of Computer Science Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved
 Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
National approach to artificial intelligence
 National approach to artificial intelligence Illustrations: Itziar Castany Ramirez Production: Ministry of Enterprise and Innovation Article no: N2018.36 Contents National approach to artificial intelligence
National approach to artificial intelligence Illustrations: Itziar Castany Ramirez Production: Ministry of Enterprise and Innovation Article no: N2018.36 Contents National approach to artificial intelligence
Almost by definition, issues of risk are both complex and complicated.
 E d itorial COMPLEXITY, RISK AND EMERGENCE: ELEMENTS OF A MANAGEMENT DILEMMA Risk Management (2006) 8, 221 226. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.rm.8250024 Introduction Almost by definition, issues of risk are both
E d itorial COMPLEXITY, RISK AND EMERGENCE: ELEMENTS OF A MANAGEMENT DILEMMA Risk Management (2006) 8, 221 226. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.rm.8250024 Introduction Almost by definition, issues of risk are both
Assessment of DU s Natural Science General Education Curriculum: Student Understanding of Evolution Dean Saitta Department of Anthropology
 Assessment of DU s Natural Science General Education Curriculum: Student Understanding of Evolution 2009 Dean Saitta Department of Anthropology A simple, standardized test of student understanding of concepts
Assessment of DU s Natural Science General Education Curriculum: Student Understanding of Evolution 2009 Dean Saitta Department of Anthropology A simple, standardized test of student understanding of concepts
ISSN (print) ISSN (online) INTELEKTINĖ EKONOMIKA INTELLECTUAL ECONOMICS 2011, Vol. 5, No. 4(12), p
 ISSN 1822-8011 (print) ISSN 1822-8038 (online) INTELEKTINĖ EKONOMIKA INTELLECTUAL ECONOMICS 2011, Vol. 5, No. 4(12), p. 644 648 The Quality of Life of the Lithuanian Population 1 Review Professor Ona Gražina
ISSN 1822-8011 (print) ISSN 1822-8038 (online) INTELEKTINĖ EKONOMIKA INTELLECTUAL ECONOMICS 2011, Vol. 5, No. 4(12), p. 644 648 The Quality of Life of the Lithuanian Population 1 Review Professor Ona Gražina
BHX Oil spill! Design Portfolio Assessment Rubric
 BHX 2017-2018- Oil spill! Design Portfolio Assessment Rubric https://response.restoration.noaa.gov/about/media/how-do-oil-spills-out-sea-typically-get-cleaned.htm l https://www.seeker.com/animal-clean-up-after-oil-spill-a-lengthy-process-1765097115.html
BHX 2017-2018- Oil spill! Design Portfolio Assessment Rubric https://response.restoration.noaa.gov/about/media/how-do-oil-spills-out-sea-typically-get-cleaned.htm l https://www.seeker.com/animal-clean-up-after-oil-spill-a-lengthy-process-1765097115.html
Section 3 The Desired Human Resource System
 Section 3 The Desired Human Resource System 1 Reform of the Human Resource System People are the main actors in promoting science, technology and innovation. One of the most important pillars To strongly
Section 3 The Desired Human Resource System 1 Reform of the Human Resource System People are the main actors in promoting science, technology and innovation. One of the most important pillars To strongly
F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business
 The Australian Curriculum Subjects Year levels F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business Foundation Year, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, Year 4, Year
The Australian Curriculum Subjects Year levels F 6/7 HASS, 7 10 History, 7 10 Geography, 7 10 Civics and Citizenship and 7 10 Economics and Business Foundation Year, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, Year 4, Year
Depth and Breadth of Knowledge
 Depth and Breadth of Knowledge 1) Identify and explain central concepts, theoretical approaches, and methodologies in cultural studies and draw upon them to critically examine and analyze contemporary
Depth and Breadth of Knowledge 1) Identify and explain central concepts, theoretical approaches, and methodologies in cultural studies and draw upon them to critically examine and analyze contemporary
the Companies and Intellectual Property Commission of South Africa (CIPC)
 organized by the Companies and Intellectual Property Commission of South Africa (CIPC) the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) the International Criminal Police Organization (INTERPOL) the
organized by the Companies and Intellectual Property Commission of South Africa (CIPC) the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) the International Criminal Police Organization (INTERPOL) the
Revolutionizing Engineering Science through Simulation May 2006
 Revolutionizing Engineering Science through Simulation May 2006 Report of the National Science Foundation Blue Ribbon Panel on Simulation-Based Engineering Science EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Simulation refers to
Revolutionizing Engineering Science through Simulation May 2006 Report of the National Science Foundation Blue Ribbon Panel on Simulation-Based Engineering Science EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Simulation refers to
#Renew2030. Boulevard A Reyers 80 B1030 Brussels Belgium
 #Renew2030 Boulevard A Reyers 80 B1030 Brussels Belgium secretariat@orgalim.eu +32 2 206 68 83 @Orgalim_EU www.orgalim.eu SHAPING A FUTURE THAT S GOOD. Orgalim is registered under the European Union Transparency
#Renew2030 Boulevard A Reyers 80 B1030 Brussels Belgium secretariat@orgalim.eu +32 2 206 68 83 @Orgalim_EU www.orgalim.eu SHAPING A FUTURE THAT S GOOD. Orgalim is registered under the European Union Transparency
Executive Summary: Understanding Risk Communication Best Practices and Theory
 Executive Summary: Understanding Risk Communication Best Practices and Theory Report to the Human Factors/Behavioral Sciences Division, Science and Technology Directorate, U.S. Department of Homeland Security
Executive Summary: Understanding Risk Communication Best Practices and Theory Report to the Human Factors/Behavioral Sciences Division, Science and Technology Directorate, U.S. Department of Homeland Security
WORKSHOP ON BASIC RESEARCH: POLICY RELEVANT DEFINITIONS AND MEASUREMENT ISSUES PAPER. Holmenkollen Park Hotel, Oslo, Norway October 2001
 WORKSHOP ON BASIC RESEARCH: POLICY RELEVANT DEFINITIONS AND MEASUREMENT ISSUES PAPER Holmenkollen Park Hotel, Oslo, Norway 29-30 October 2001 Background 1. In their conclusions to the CSTP (Committee for
WORKSHOP ON BASIC RESEARCH: POLICY RELEVANT DEFINITIONS AND MEASUREMENT ISSUES PAPER Holmenkollen Park Hotel, Oslo, Norway 29-30 October 2001 Background 1. In their conclusions to the CSTP (Committee for
Birger Hjorland 101 Neil Pollock June 2002
 Birger Hjorland 101 Neil Pollock June 2002 The Problems (1) IS has been marginalised. We draw our theories from bigger sciences. Those theories don t work. (2) A majority of so-called information scientists
Birger Hjorland 101 Neil Pollock June 2002 The Problems (1) IS has been marginalised. We draw our theories from bigger sciences. Those theories don t work. (2) A majority of so-called information scientists
Assessing the Welfare of Farm Animals
 Assessing the Welfare of Farm Animals Part 1. Part 2. Review Development and Implementation of a Unified field Index (UFI) February 2013 Drewe Ferguson 1, Ian Colditz 1, Teresa Collins 2, Lindsay Matthews
Assessing the Welfare of Farm Animals Part 1. Part 2. Review Development and Implementation of a Unified field Index (UFI) February 2013 Drewe Ferguson 1, Ian Colditz 1, Teresa Collins 2, Lindsay Matthews
Science and Technology Studies (STS)
 Science and Technology Studies (STS) Science and technology are among the most powerful forces transforming our world today. They have changed social institutions like work and the family, produced new
Science and Technology Studies (STS) Science and technology are among the most powerful forces transforming our world today. They have changed social institutions like work and the family, produced new
General Education Rubrics
 General Education Rubrics Rubrics represent guides for course designers/instructors, students, and evaluators. Course designers and instructors can use the rubrics as a basis for creating activities for
General Education Rubrics Rubrics represent guides for course designers/instructors, students, and evaluators. Course designers and instructors can use the rubrics as a basis for creating activities for
An exploration of the future Latin America and Caribbean (ALC) and European Union (UE) bi-regional cooperation in science, technology and innovation
 An exploration of the future Latin America and Caribbean (ALC) and European Union (UE) bi-regional cooperation in science, technology and innovation A resume of a foresight exercise undertaken for the
An exploration of the future Latin America and Caribbean (ALC) and European Union (UE) bi-regional cooperation in science, technology and innovation A resume of a foresight exercise undertaken for the
RecordDNA DEVELOPING AN R&D AGENDA TO SUSTAIN THE DIGITAL EVIDENCE BASE THROUGH TIME
 RecordDNA DEVELOPING AN R&D AGENDA TO SUSTAIN THE DIGITAL EVIDENCE BASE THROUGH TIME DEVELOPING AN R&D AGENDA TO SUSTAIN THE DIGITAL EVIDENCE BASE THROUGH TIME The RecordDNA international multi-disciplinary
RecordDNA DEVELOPING AN R&D AGENDA TO SUSTAIN THE DIGITAL EVIDENCE BASE THROUGH TIME DEVELOPING AN R&D AGENDA TO SUSTAIN THE DIGITAL EVIDENCE BASE THROUGH TIME The RecordDNA international multi-disciplinary
Civil Society in Greece: Shaping new digital divides? Digital divides as cultural divides Implications for closing divides
 Civil Society in Greece: Shaping new digital divides? Digital divides as cultural divides Implications for closing divides Key words: Information Society, Cultural Divides, Civil Society, Greece, EU, ICT
Civil Society in Greece: Shaping new digital divides? Digital divides as cultural divides Implications for closing divides Key words: Information Society, Cultural Divides, Civil Society, Greece, EU, ICT
g~:~: P Holdren ~\k, rjj/1~
 July 9, 2015 M-15-16 OF EXECUTIVE DEPARTMENTS AND AGENCIES FROM: g~:~: P Holdren ~\k, rjj/1~ Office of Science a~fechno!o;} ~~~icy SUBJECT: Multi-Agency Science and Technology Priorities for the FY 2017
July 9, 2015 M-15-16 OF EXECUTIVE DEPARTMENTS AND AGENCIES FROM: g~:~: P Holdren ~\k, rjj/1~ Office of Science a~fechno!o;} ~~~icy SUBJECT: Multi-Agency Science and Technology Priorities for the FY 2017
This file was downloaded from BI Open Archive, the institutional repository at BI Norwegian Business School
 This file was downloaded from BI Open Archive, the institutional repository at BI Norwegian Business School http://brage.bibsys.no/bi. It contains the accepted and peer reviewed manuscript to the article
This file was downloaded from BI Open Archive, the institutional repository at BI Norwegian Business School http://brage.bibsys.no/bi. It contains the accepted and peer reviewed manuscript to the article
Public Acceptance Considerations
 Public Acceptance Considerations Dr Craig Cormick ThinkOutsideThe Craig.Cormick@thinkoutsidethe.com.au Alternate truths Anti-science and contested Diminishing beliefs growing We are living in an era of
Public Acceptance Considerations Dr Craig Cormick ThinkOutsideThe Craig.Cormick@thinkoutsidethe.com.au Alternate truths Anti-science and contested Diminishing beliefs growing We are living in an era of
DiMe4Heritage: Design Research for Museum Digital Media
 MW2013: Museums and the Web 2013 The annual conference of Museums and the Web April 17-20, 2013 Portland, OR, USA DiMe4Heritage: Design Research for Museum Digital Media Marco Mason, USA Abstract This
MW2013: Museums and the Web 2013 The annual conference of Museums and the Web April 17-20, 2013 Portland, OR, USA DiMe4Heritage: Design Research for Museum Digital Media Marco Mason, USA Abstract This
Topic and Reading Schedule
 Technological, Social, and Sustainable Systems Topic and Reading Schedule Topic and Reading Schedule The topics of the lectures, and the chapters of the text with which it is associated, are given for
Technological, Social, and Sustainable Systems Topic and Reading Schedule Topic and Reading Schedule The topics of the lectures, and the chapters of the text with which it is associated, are given for
The Human and Organizational Part of Nuclear Safety
 The Human and Organizational Part of Nuclear Safety International Atomic Energy Agency Safety is more than the technology The root causes Organizational & cultural root causes are consistently identified
The Human and Organizational Part of Nuclear Safety International Atomic Energy Agency Safety is more than the technology The root causes Organizational & cultural root causes are consistently identified
WMD Events and Other Catastrophes
 WMD Events and Other Catastrophes 2012 Joint CBRN Conference National Defense Industrial Association March 13, 2012 Tara O Toole, M.D., M.P.H. Under Secretary for Science and Technology U.S. Department
WMD Events and Other Catastrophes 2012 Joint CBRN Conference National Defense Industrial Association March 13, 2012 Tara O Toole, M.D., M.P.H. Under Secretary for Science and Technology U.S. Department
